Low-nickel austenitic stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
A technique for austenitic stainless steel and its manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of austenitic stainless steel, can solve problems such as not being very high and reducing the stability of austenite, and achieve the effects of reducing raw material costs, improving formability, and avoiding delayed cracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
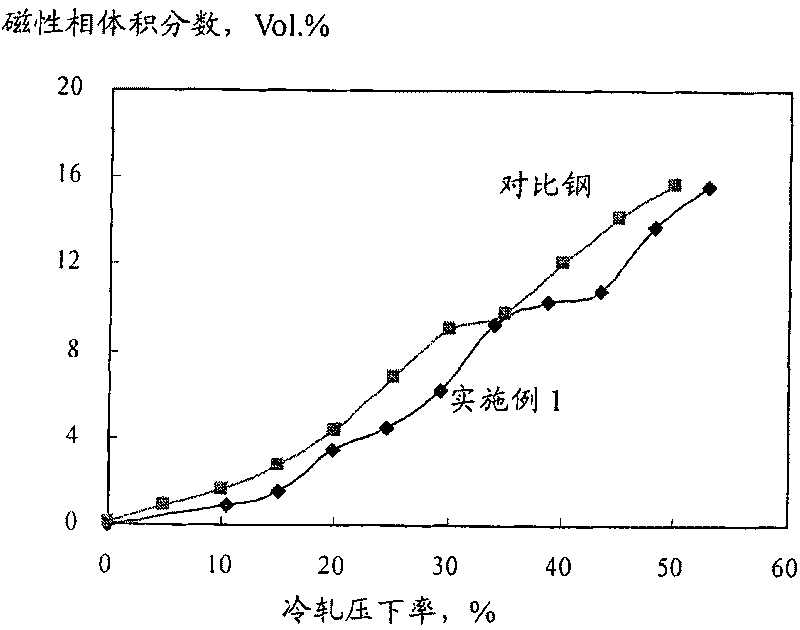
[0070] Adopt electric arc furnace and AOD two-step method to smelt stainless steel, feed Ca-Si-Ba wire and Fe-B wire before continuous casting to realize Ca treatment and B alloying treatment, continuous casting into slab, hot rolling into 3.00mm thick of hot-rolled coils. After intermediate annealing, the intermediate annealing temperature is 100-1100°C, and then the volume fraction of strain-induced martensite after annealing and at different cold rolling reductions is tested respectively. The specific results are shown in Table 4. The chemical composition of the nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel in this embodiment is shown in Table 3.
[0071]
[0072] Table 4 Comparison of strain-induced martensite volume fraction between Example 1 and 4% Ni-free austenitic stainless steel at different cold rolling reductions
[0073]
Embodiment 2
[0075] Stainless steel is smelted by electric furnace, AOD, VOD three-step method. Feed Ca-Si-Ba wire and Fe-B wire before continuous casting to realize Ca treatment and B alloying treatment, continuous casting into slab, hot rolling into 3.00mm thick hot-rolled coil. Through intermediate annealing, pickling, then carry out cold rolling, test gained nickel-saving type austenitic stainless steel cold after passing through 50% cold rolling reduction, the changing situation of the cold-rolled sheet hardness of stainless steel of the present invention, its result is as table 5 shown. The chemical composition of the nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel in this embodiment is shown in Table 3.
[0076] Table 5 Hardness comparison between Example 2 and 4% Ni-free austenitic stainless steel at different cold rolling reductions
[0077]
Embodiment 3
[0079] Stainless steel is smelted by electric arc furnace single smelting method, and continuously cast into slabs. Ca treatment and B alloying treatment are achieved by feeding Ca-Si-Ba wire and Fe-B wire before continuous casting. Then cut a slab of 200mm×200mm×100mm from the central part of the continuous casting slab, and keep it at 1000°C, 1050°C, 1100°C, 1150°C, 1200°C, and 1250°C for 30 minutes respectively, and then adopt rapid water cooling. The high-temperature structure was fixed and the content of high-temperature ferrite was tested with a ferrite meter. The results are shown in Table 6.
[0080] Table 6 High-temperature ferrite content of Example 3 after high-temperature heating
[0081] Test conditions
[0082] Test conditions
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com