Use of trehalase genes to confer nematode resistance to plants
A trehalase, transgenic plant technology, applied in plant products, genetic engineering, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as plant yield loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] Example 1: Identification of genes specifically expressed in syncytia
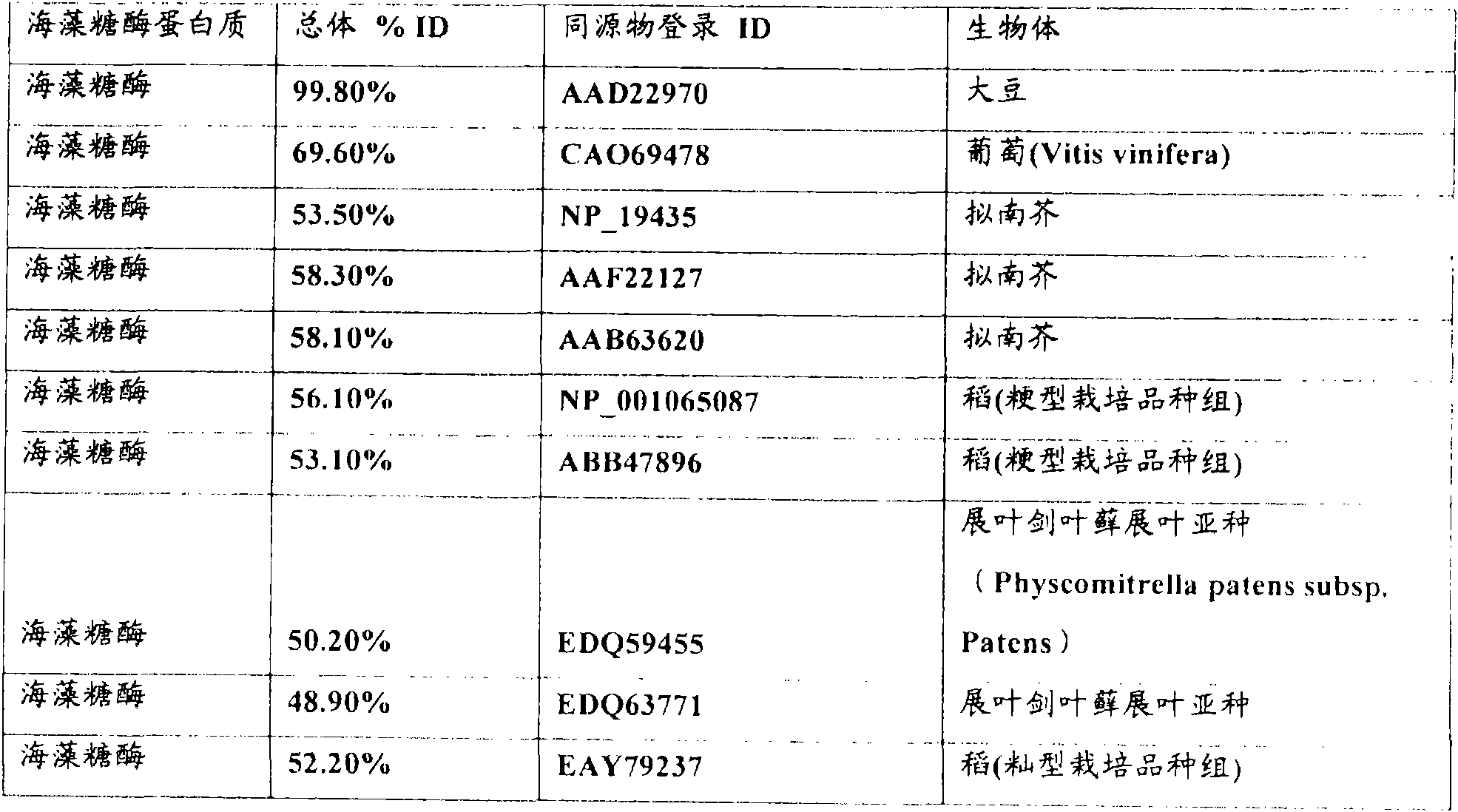
[0102] Microarray analysis of laser-ablated syncytial cells from soybean roots inoculated with second-stage larvae (J2) of the soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines) race3 led to the identification of genes specifically or differentially expressed in syncytia. One such gene (52015943) is called trehalase-like protein. Table 1 summarizes the expression data determined by cDNA microarray analysis of all three cell / tissue samples: syncytia, SCN-infected non-syncytia and untreated control root tissue. Relative levels of gene expression are expressed as normalized signal intensities (± standard deviation) as described above.
[0103] Table 1. Expression of trehalase-like genes
[0104] gene name
Syncytium #1(N)
Syncytium #2(N)
Non-syncytia
control root
52015943 *
698±259(4)
525±75(5)
122±38
126±60
[0105] (N) Number ...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Embodiment 2: Cloning of soybean trehalase gene
[0108] The GM59678499 open reading frame was amplified using a standard PCR amplification protocol. Primers used for PCR amplification of trehalase-like sequences are shown in Table 2 and were designed based on the sequence of the open reading frame of GM59678499. The primer sequence (SEQ ID NO: 14) shown in GW59678499F contains an AscI restriction site for easy cloning. The primer sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 15 contains XhoI for ease of cloning. The primer sequences shown by SEQ ID NO: 14 and SEQ ID NO: 15 (GW59678499F and GW59678499R) were used to amplify the 1674bp open reading frame from the 111th to 1784th bases of SEQ ID NO: 11 (the entire cDNA of GM59678499 sequence).
[0109] Amplified DNA PCR products were confirmed by standard agarose gel electrophoresis and DNA extracted from the gel was TOPO cloned into pCR2.1 using the TOPO TA cloning kit following the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen). The clone...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com