A transcription factor of root-knot nematode mgbtf3 and its application in disease control
A root-knot nematode, transcription factor technology, applied in application, nematicide, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problem of undiscovered effector protein of transcription factor type
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 Cloning and sequence analysis of MgBTF3 gene
[0049] Based on the secretome of M. incognita and the genome of M. graminearum, the full-length cDNA sequence of MgBTF3 was amplified from M. graminearum through homologous cloning technology ( figure 1 ). The full-length cDNA sequence of MgBTF3 contains an open reading frame of 492bp, encoding 163aa, with a size of 18kDa. Using SignalP, it was found that the MgBTF3 protein does not contain a typical secretion signal peptide at the N-terminus. Further predicting SecretomeP 2.0 software by atypical secreted protein, the results showed that BTF3 may be an atypical signal peptide secreted protein. At the same time, TMHMM 2.0 online prediction of the transmembrane domain showed that MgBTF3 did not have a transmembrane domain.
Embodiment 2
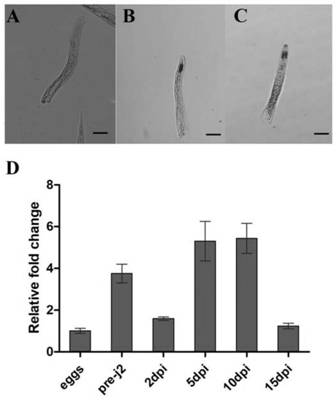
[0050] Example 2 The MgBTF3 gene is specifically expressed in the head sensory organs of nematodes, and the expression is highest at the stage of feeding site formation
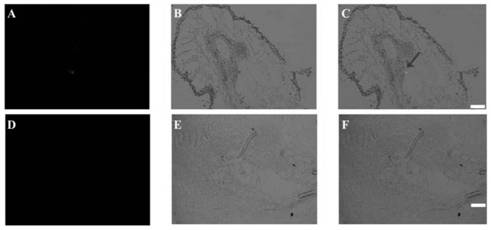
[0051] In this study, in situ hybridization was used to determine the expression position of MgBTF3 gene in Meloidogyne graminearum. The results showed that the sense strand probe of MgBTF3 had no obvious signal on the worm body (Fig. 2A). On the contrary, the antisense strand probe had obvious hybridization signal in the head sensilla of the 2nd instar larvae ( figure 2 B-2C), illustrating the site-specific expression of MgBTF3 in the head sensilla of M. graminearum.
[0052] The developmental expression of MgBTF3 gene was analyzed by real-time fluorescence quantitative qRT-PCR. In this experiment, five stages of the life cycle of root-knot nematode graminaceae were selected: eggs, 2nd instar larvae before infection (pre-J2s), 2nd instar worms in the parasitic stage (par-J2s), 3rd and 4th instar larvae (...
Embodiment 3
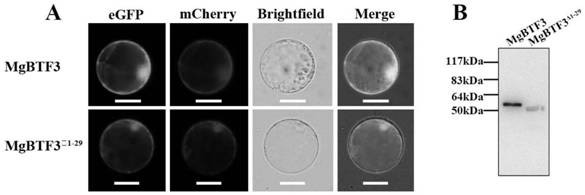
[0054] Example 3 The acquisition and specificity detection of MgBTF3 antiserum
[0055] In this study, the MgBTF3 immunogen protein ( image 3 A). The polyclonal antiserum of MgBTF3 was obtained by immunizing New Zealand white rabbits. The total protein of pre-J2s and healthy rice roots was extracted, and the specificity of MgBTF3 antiserum was verified by western blot. The results of Western blot showed that the MgBTF3 antiserum had a specific hybridization band of about 28kDa in the total protein of pre-J2s, which was 10kDa larger than the expected molecular weight of MgBTF3 protein (18kDa). In contrast, MgBTF3 antiserum showed no hybridization signal in the total protein of healthy rice roots. The comprehensive results showed that the MgBTF3 polyclonal antiserum could specifically recognize the MgBTF3 protein in nematodes, and had no non-specific signal with the total protein in rice roots. It is speculated that MgBTF3 may undergo protein modification in nematodes, lead...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com