Use of alanine racemase genes to confer nematode resistance to plants
A technology of alanine racemase and transgenic plants, applied in plant products, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as yield loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
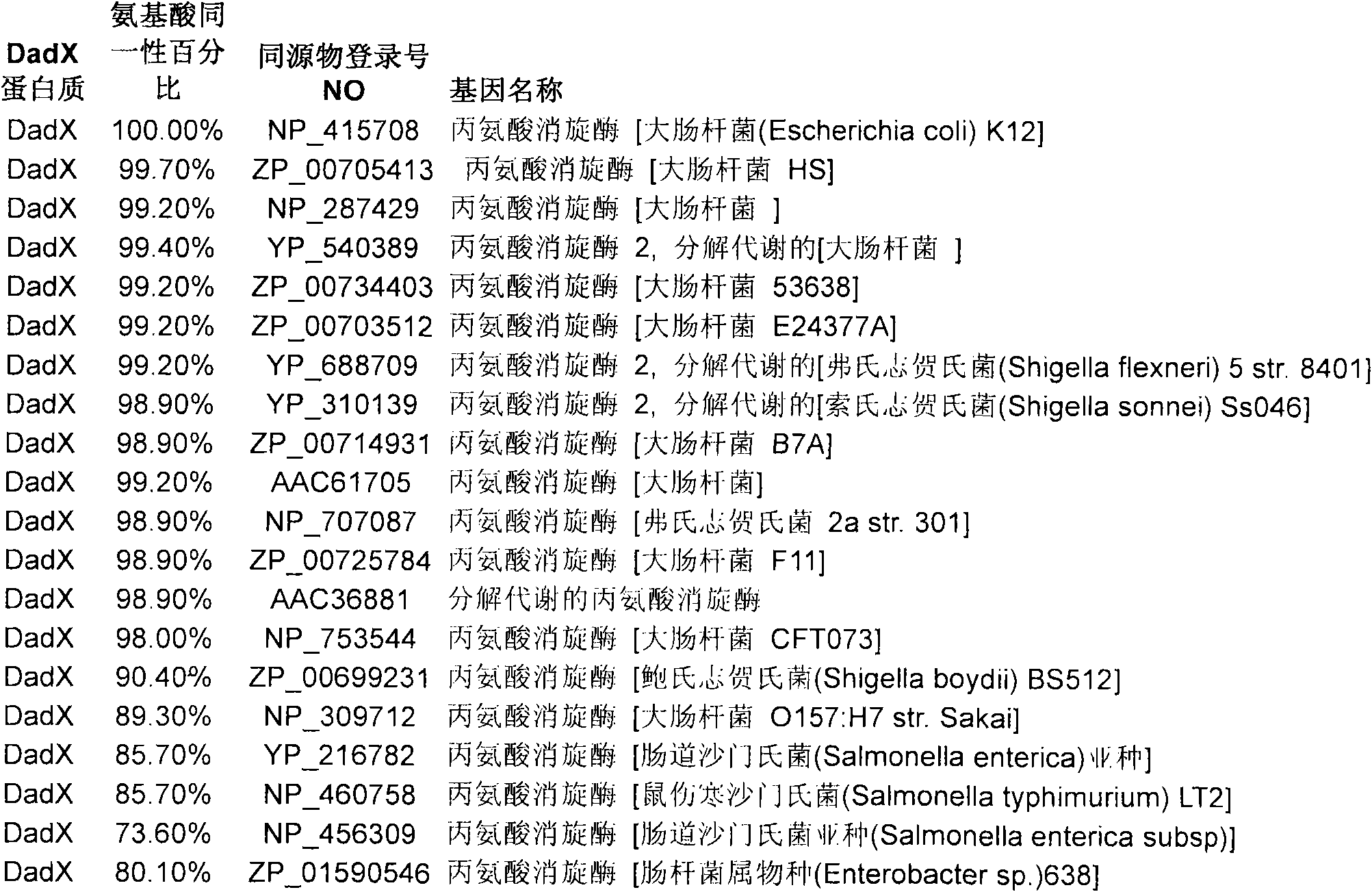
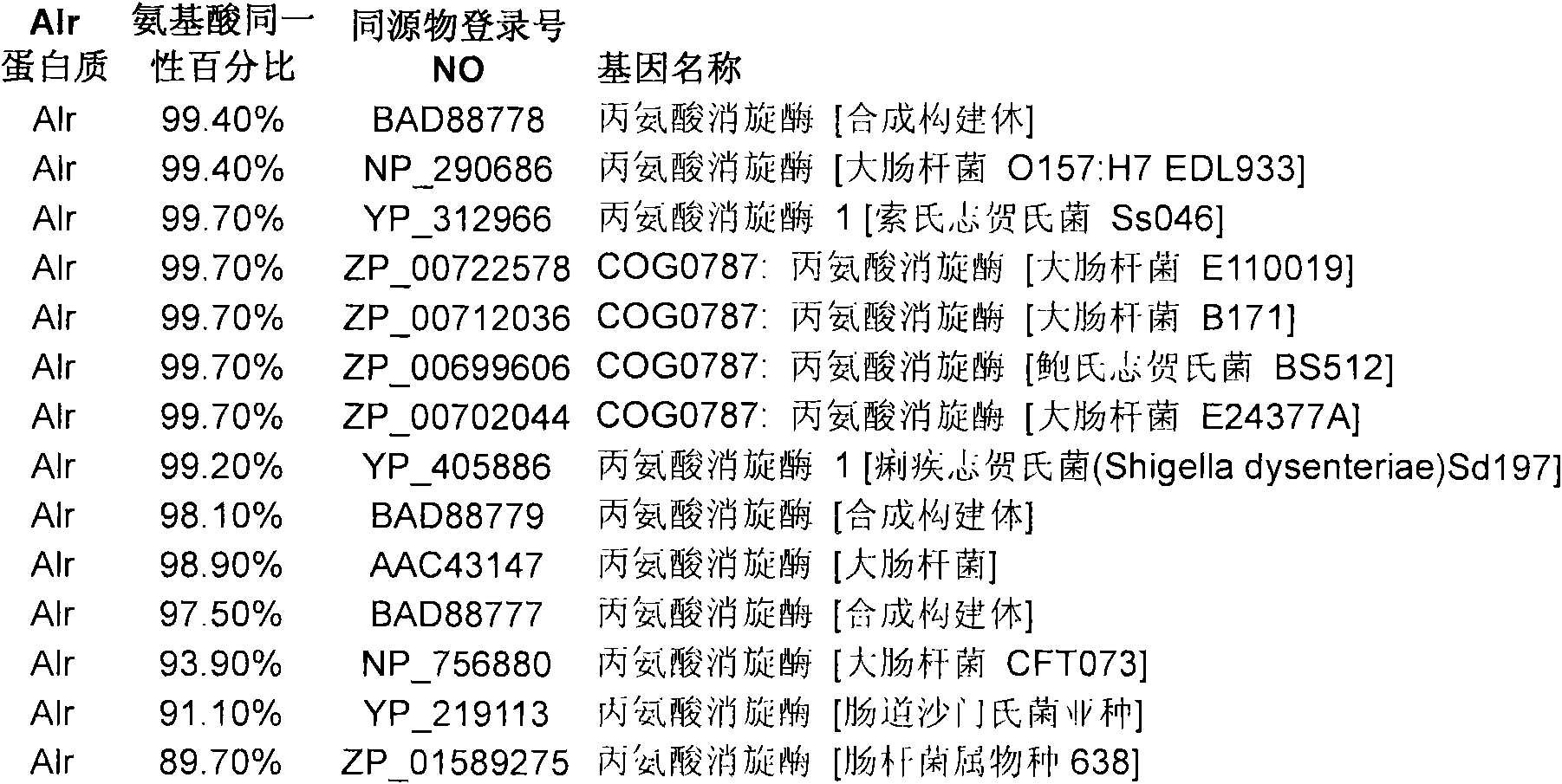
[0085] Example 1: Cloning of the gene encoding alanine racemase
[0086] Alr (SEQ ID NO: 7) and DadX (Seq ID NO: 5), two forms of alanine racemase, were cloned from E. coli genomic DNA using the PCR primers shown in Table 1 .
[0087] Table 1: Primers used to clone the gene encoding ARLNCP.
[0088] Primer
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: Vector construction for transformation and generation of transgenic roots
[0090] The PCR product generated in Example 1 was sequenced and cloned into a mass expression vector containing a syncytia-preferred (nematode-induced) promoter. Syncytium preferred promoters include soybean MTN3 SEQ ID NO: 9 (p-47116125) (USSN 60 / 899,714), Arabidopsis peroxidase POX SEQ ID NO: 10 (p-At5g05340) (USSN 60 / 876,416) and Arabidopsis TPP trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase SEQ ID NO: 11 (p-At1g35910) (USSN 60 / 874,375). Constitutive super promoters were also used. The selection marker used for transformation was a mutated acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) gene from Arabidopsis that confers resistance to the herbicide ARSENAL (imazepyr, BASF Corporation, Mount Olive, NJ). Expression of the mutant AHAS is driven by the Arabidopsis actin 2 promoter.
[0091] Table 2: Expression vectors comprising SEQ ID NO: 5 or 7
[0092] carrier
Embodiment 3
[0093] Example 3: Generation of transgenic soybean hairy-roots and nematode bioassays
[0094] Vectors RSH118, RSH120, RSH122, RSH117, RSH125, RSH127, RSH129 and RSH124 were transformed into A. rhizogenes K599 strain by electroporation. The transformed Agrobacterium strains were used to induce soybean hairy root formation using known methods. Non-transgenic hairy roots from soybean cultivars Williams 82 (SCN susceptible) and Jack (SCN resistant) were also produced by using untransformed A. rhizogenes as controls for nematode growth in the assay.
[0095] Nematode resistance was evaluated by bioassays on transgenic hairy roots transformed with the vector and non-transgenic hairy roots from Williams 82 and Jack as controls. Hairy root cultures of each line occupying at least half of the wells were inoculated with surface decontaminated second stage larvae (J2) of soybean cyst nematode (SCN) race 3. The plates were then sealed and placed back into the incubator at 25°C in the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com