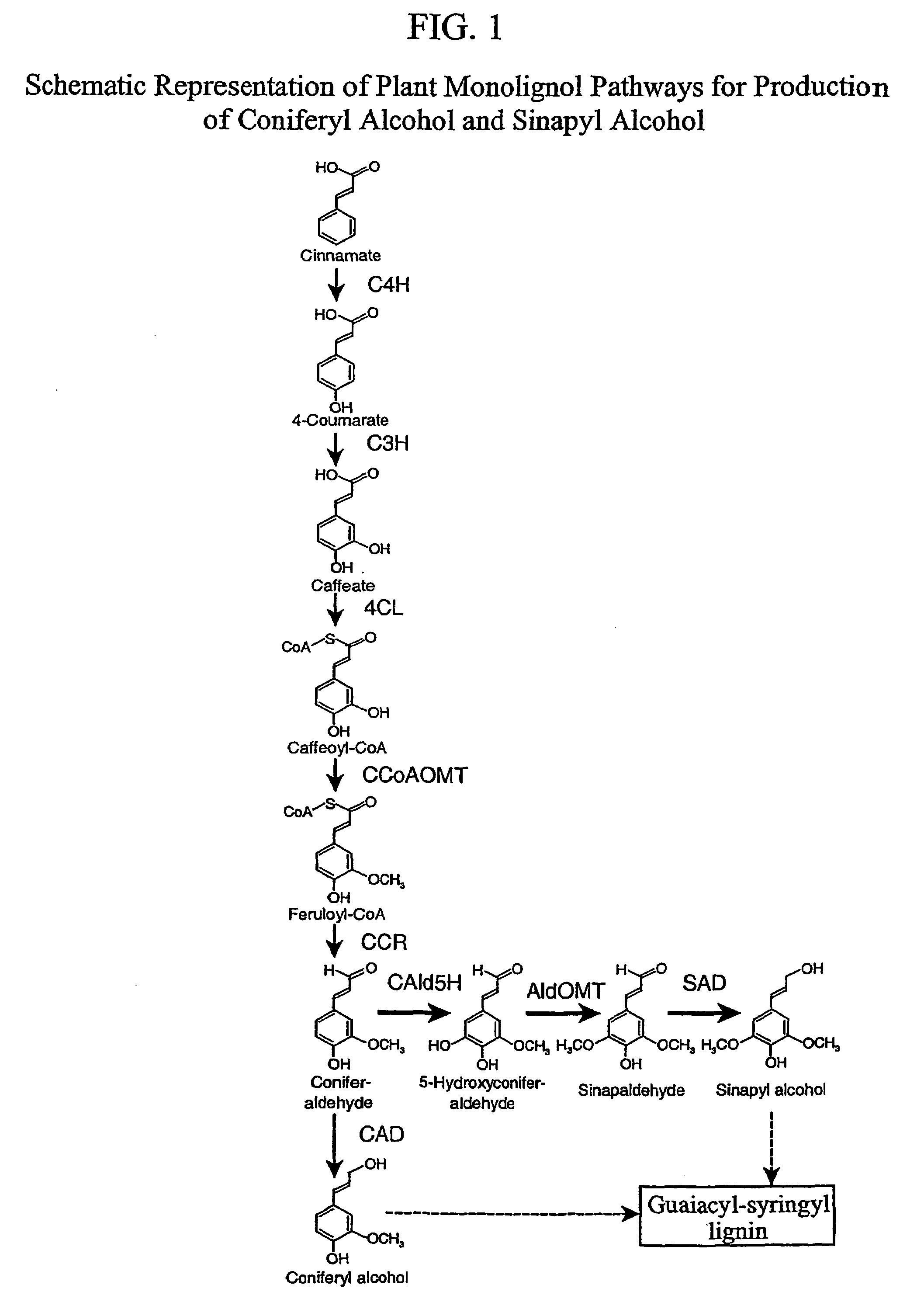Patents
Literature
36 results about "Lignin biosynthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
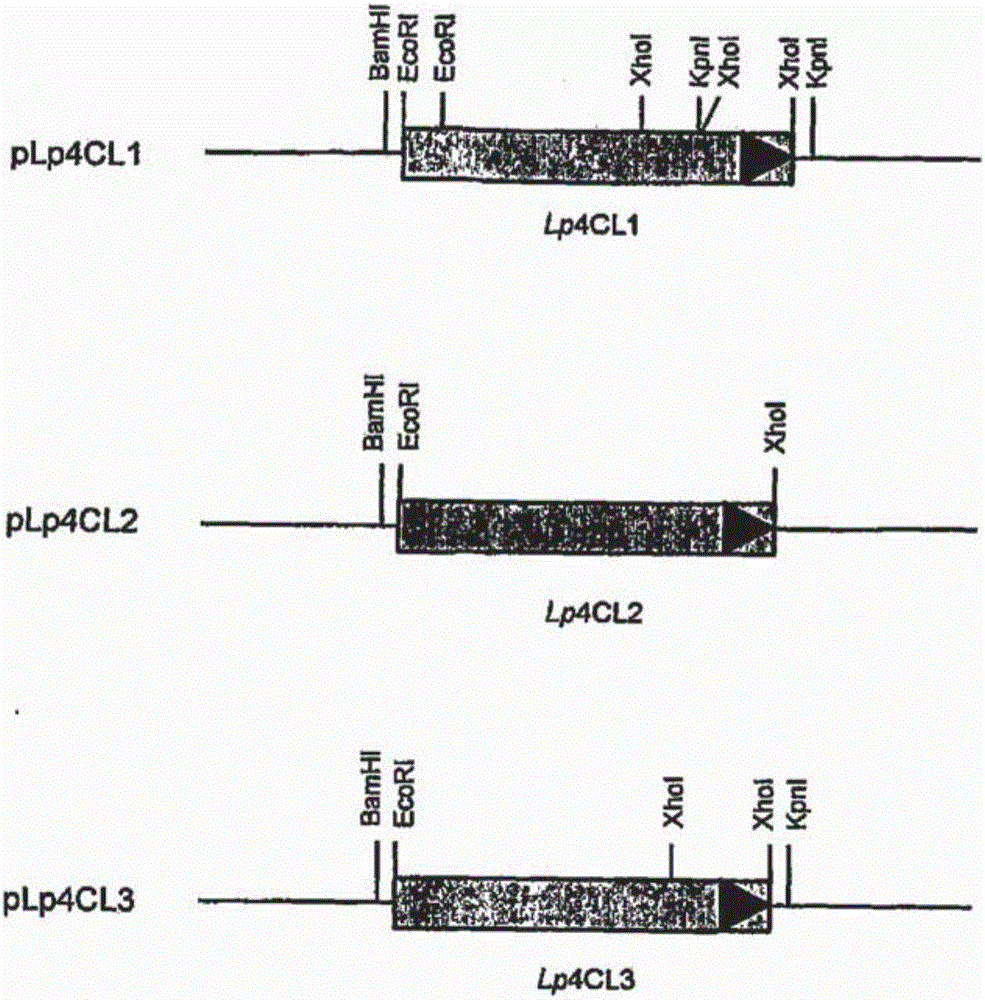
Methods and genetic constructs for modification of lignin composition of corn cobs
InactiveUS20060260011A1Reduce expressionLow lignin contentBiofuelsOther foreign material introduction processesDouble strandedLignin biosynthesis
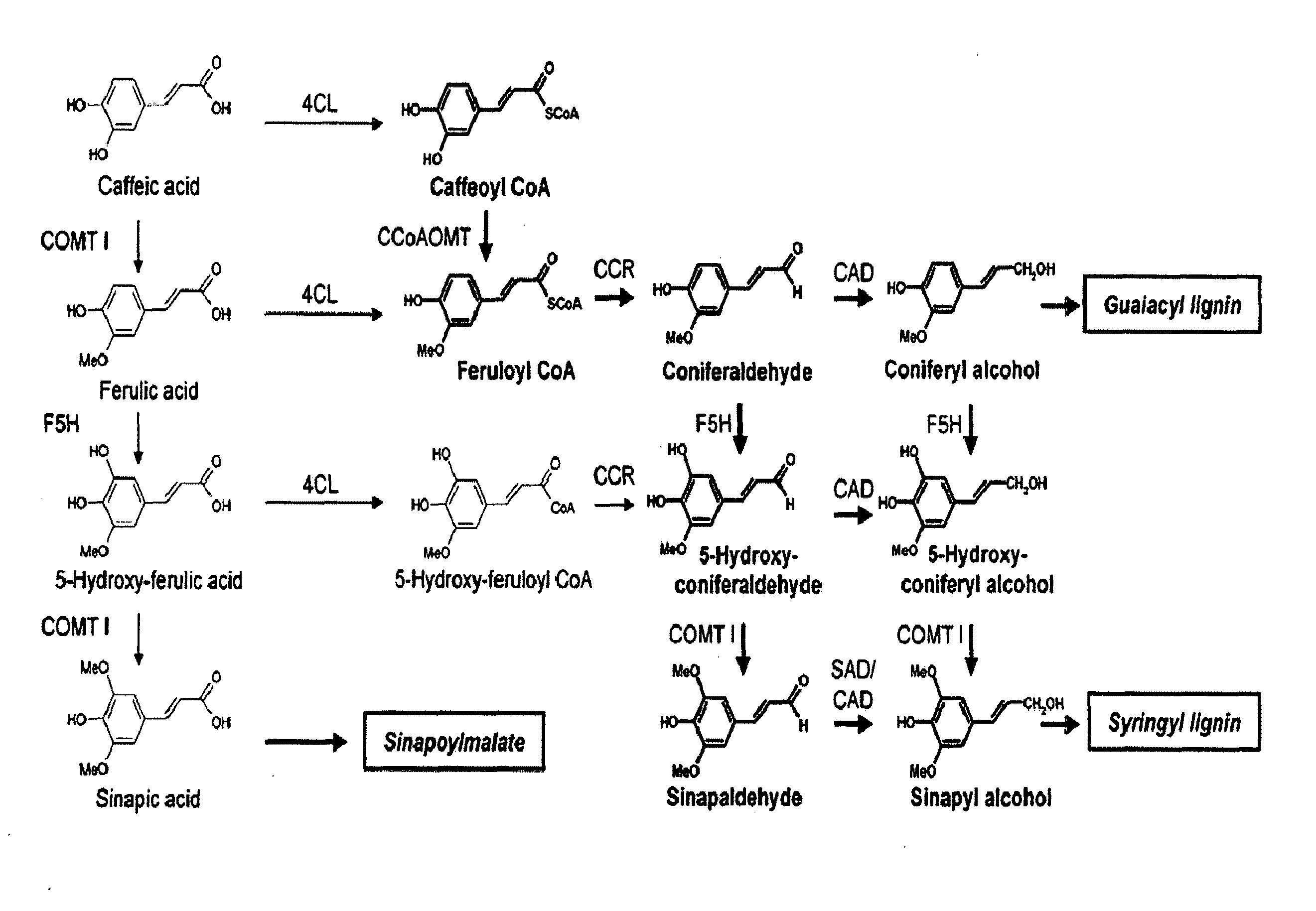
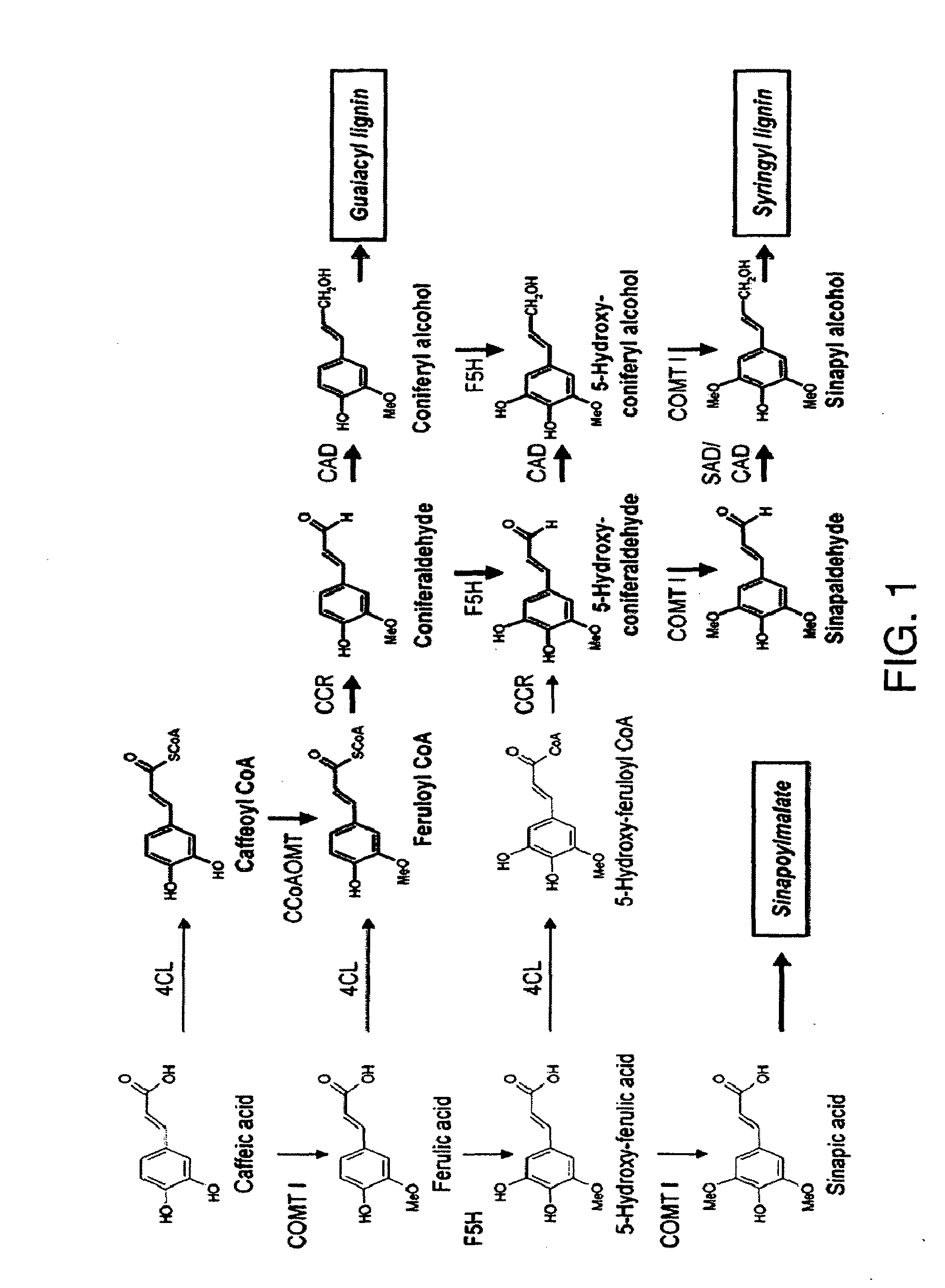
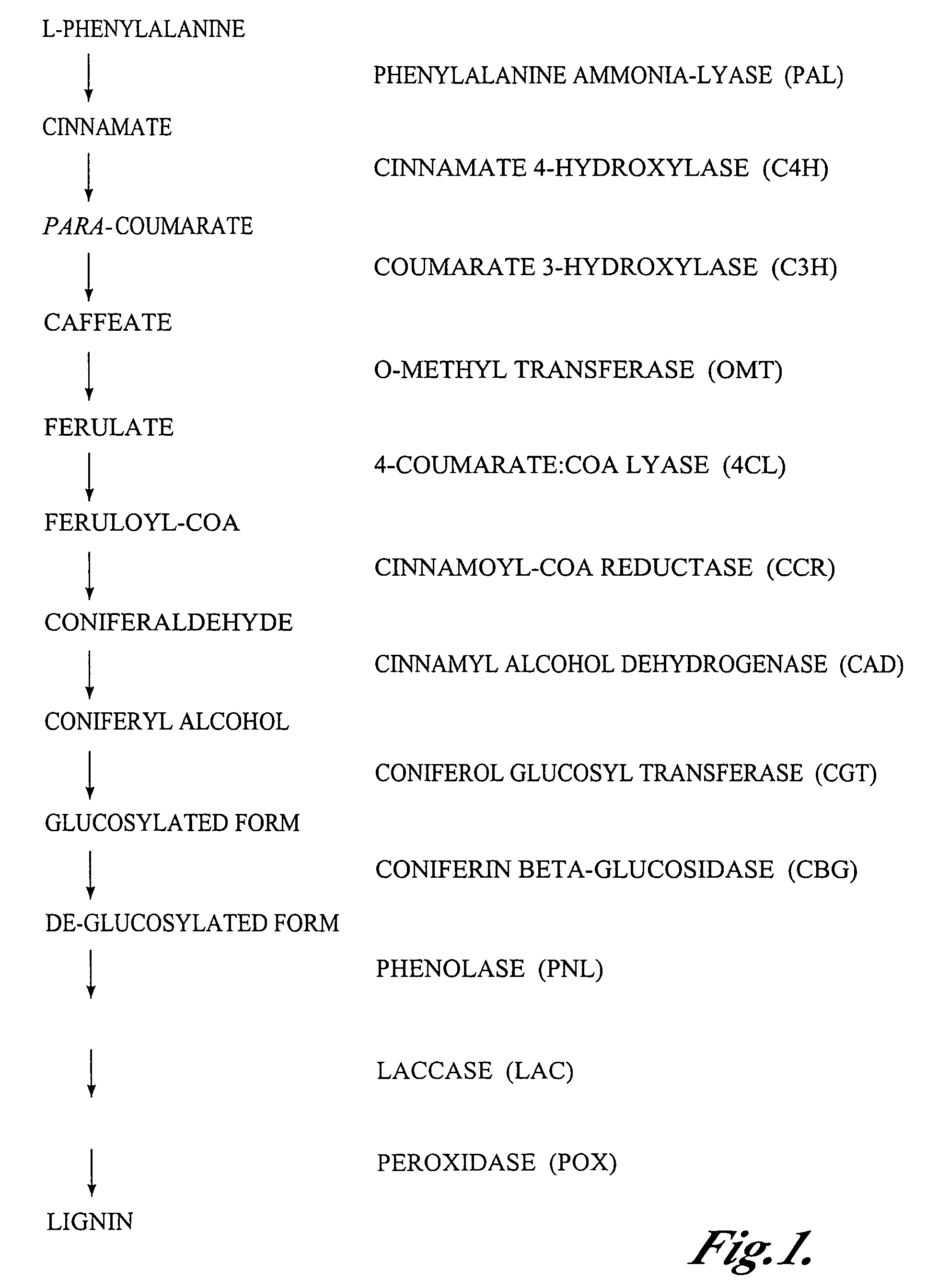
The present invention relates to methods and genetic constructs for the control of expression of enzymes involved in lignin biosynthesis in plants. The method involves the use of double-stranded RNAi to down-regulate or knock out the expression of the CAD and COMT genes. In particular embodiments the method involves the use of cob-specific or cob-preferred promoters for down-regulation of lignin biosynthesis in the cobs of corn plants.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Methods of modifying lignin biosynthesis and improving digestibility
InactiveUS20120272406A1Reduced lignin productionImprove digestibilityFungiBacteriaNucleotideLignin biosynthesis
The present invention relates to methods for increasing digestibility and / or crude protein of a plant by modifying lignin biosynthesis of the plant. The methods involve the manipulation of the expression level of genes in the lignin biosynthesis pathway by directly reducing the expression of genes using miRNA or using regulation of transcription factors. Expression cassettes for achieving such gene expression manipulation and transgenic plant cells and plants comprising the constructs and cassettes are also provided. Transcription regulating nucleotide sequences for use in the expression cassettes have also been developed as well as methods of using these sequences and cassettes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Modification of lignin biosynthesis
ActiveUS7663023B2Raise the ratioLow lignin contentClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyLignin biosynthesis
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Materials and methods for the modification of plant lignin content
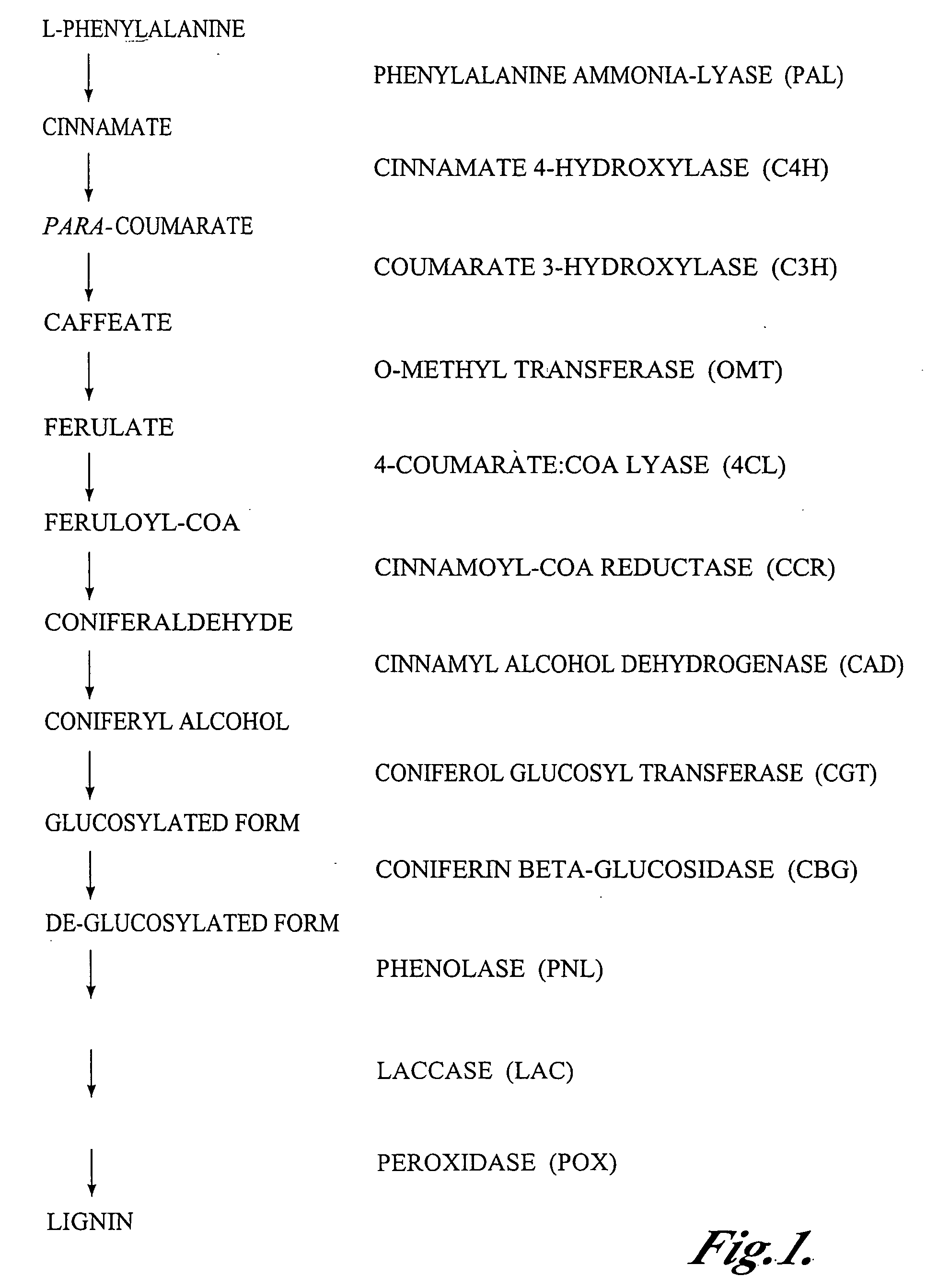
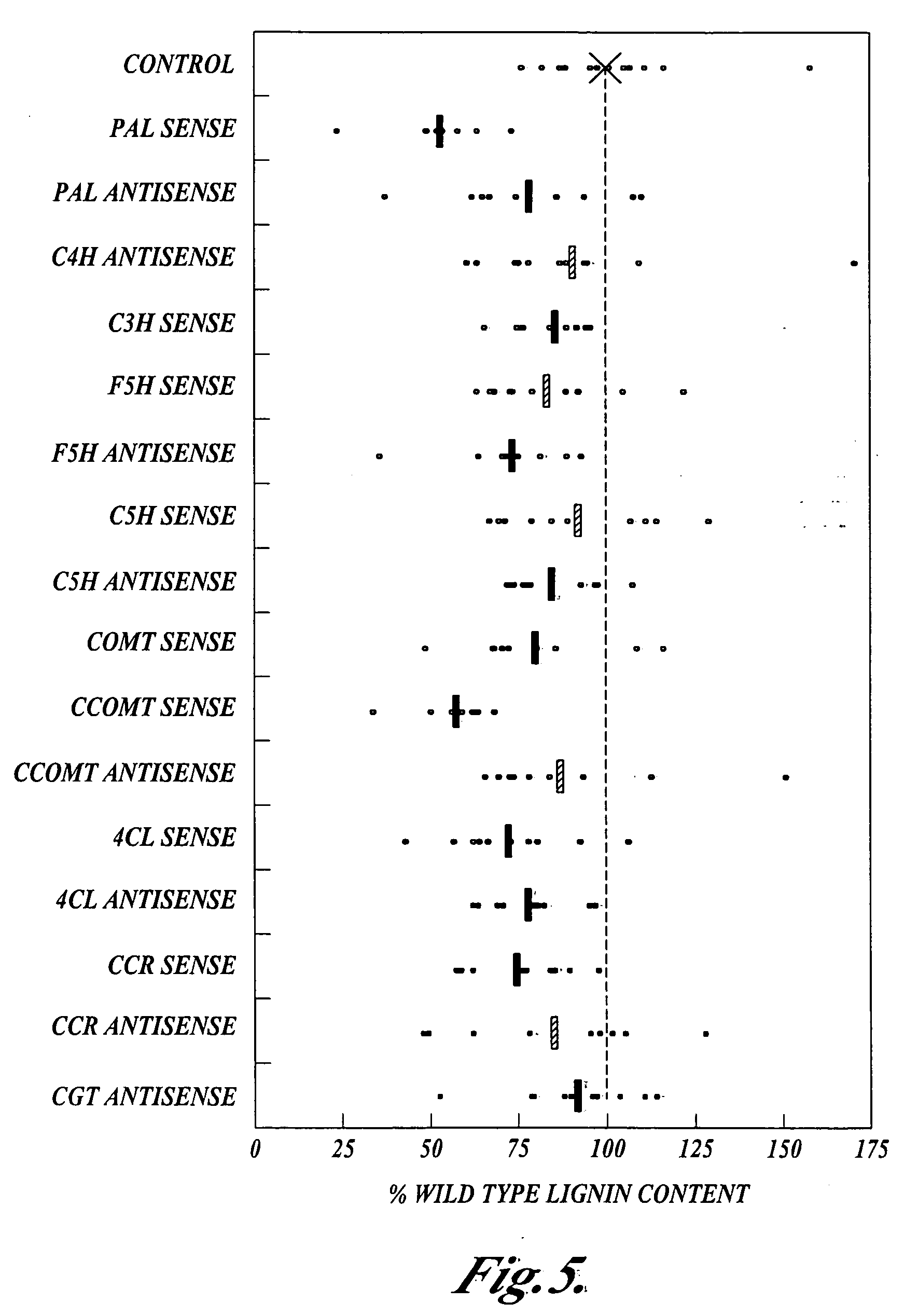
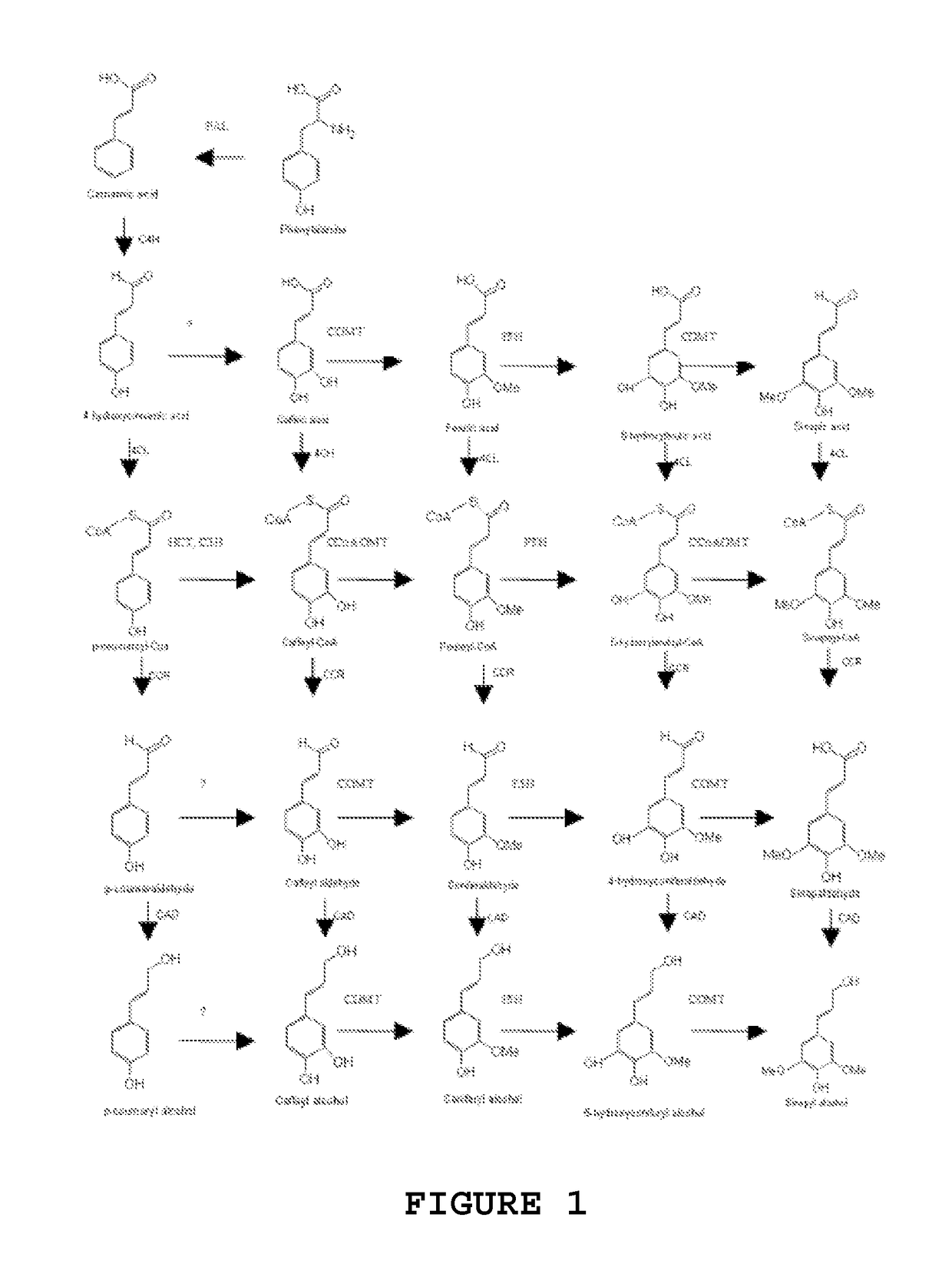
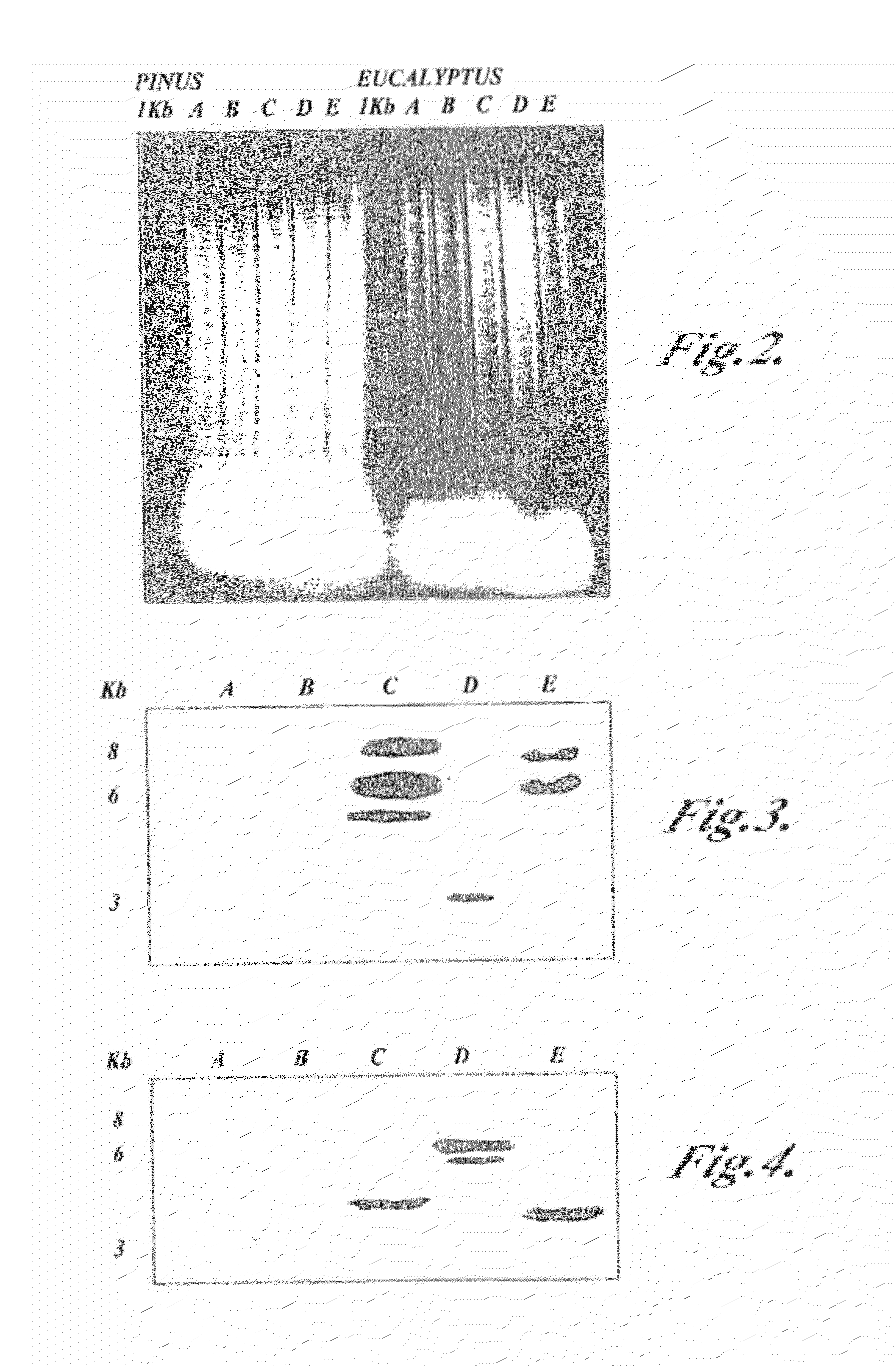
Novel isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides associated with the lignin biosynthetic pathway are provided, together with genetic constructs including such sequences. Methods for the modulation of lignin content, lignin structure and lignin composition in target organisms are also disclosed, the methods comprising incorporating one or more of the polynucleotides of the present invention into the genome of a target organism.
Owner:ARBORGEN
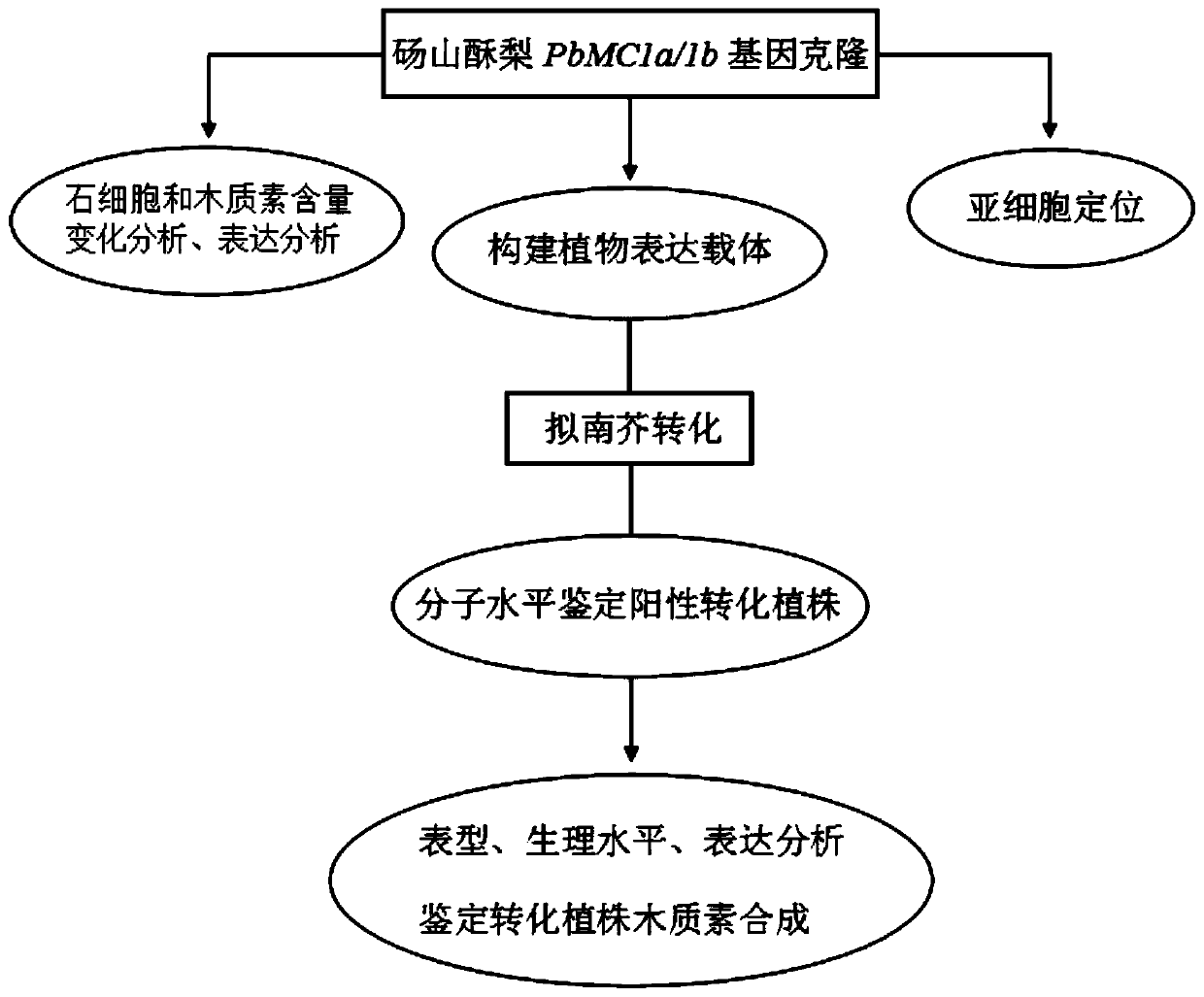
Pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a/1b and application of pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a/1b in genetic improvement of fruit quality
ActiveCN110577960AHigh expressionReduced Breeding ResearchHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyVascular bundle
The invention discloses a pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a / 1b and application of the pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a / 1b in genetic improvement of fruit quality. The PbMC1a / 1b gene is a cysteine-like protease isolated and cloned from Dangshansu pear with high lignin content, an applicant names the gene as PbMC1a / 1b, the sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the corresponding amino acid sequenceis shown as SEQ ID NO.2. A gene construction over-expression vector is introduced into arabidopsis thaliana, obtained transgenic plants are verified by a biological function, the cloned PbMC1a / 1b genecan promote the cell walls of fibers between ducts, lignocellulosic fibers and vascular bundles to be obviously thickened, lignin accumulation in stems is promoted and plant growth is inhibited, theexpression of genes related to lignin biosynthesis is increased, new genetic resources is provided for molecular design and breeding of fruit quality, and the PbMC1a / 1b gene is an important candidategene for future genetic engineering to improve fruit quality breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
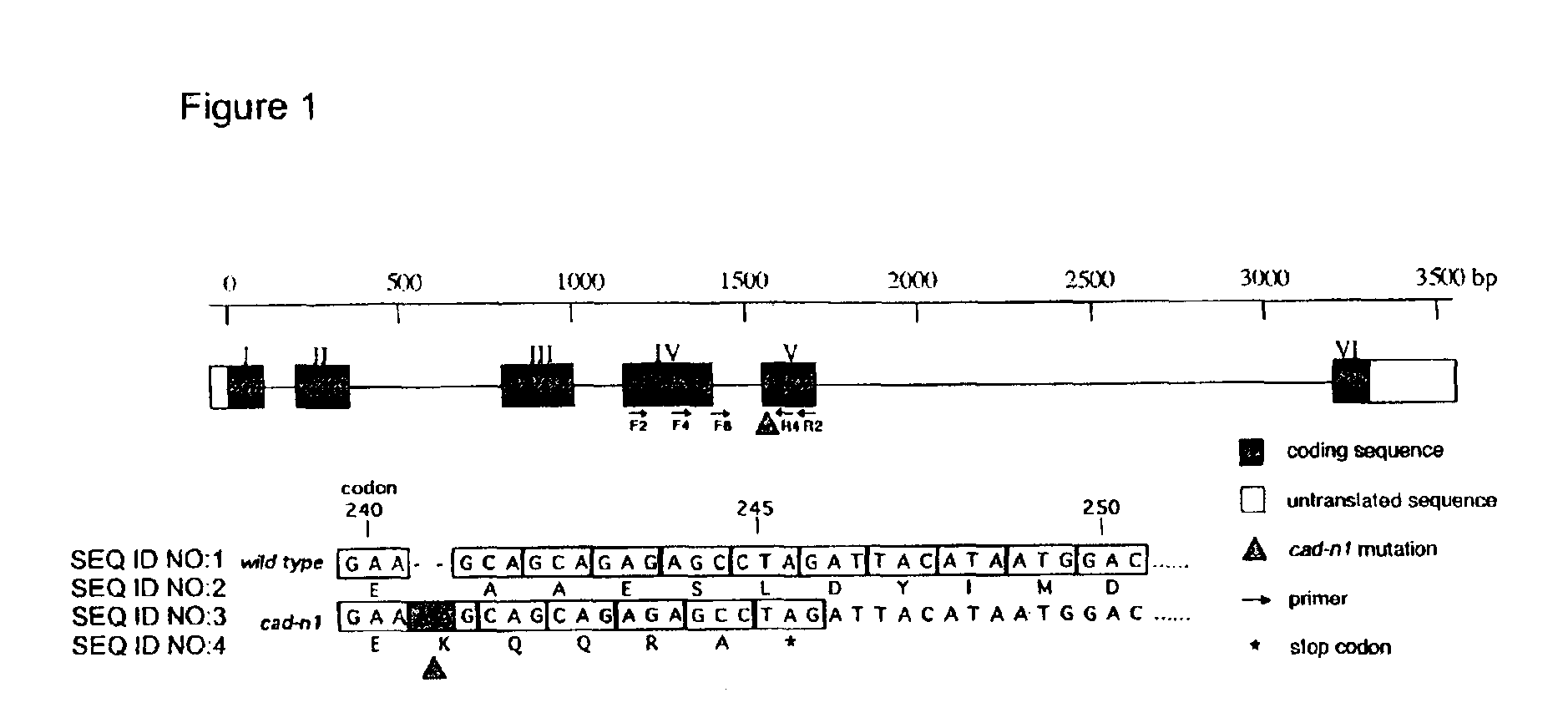
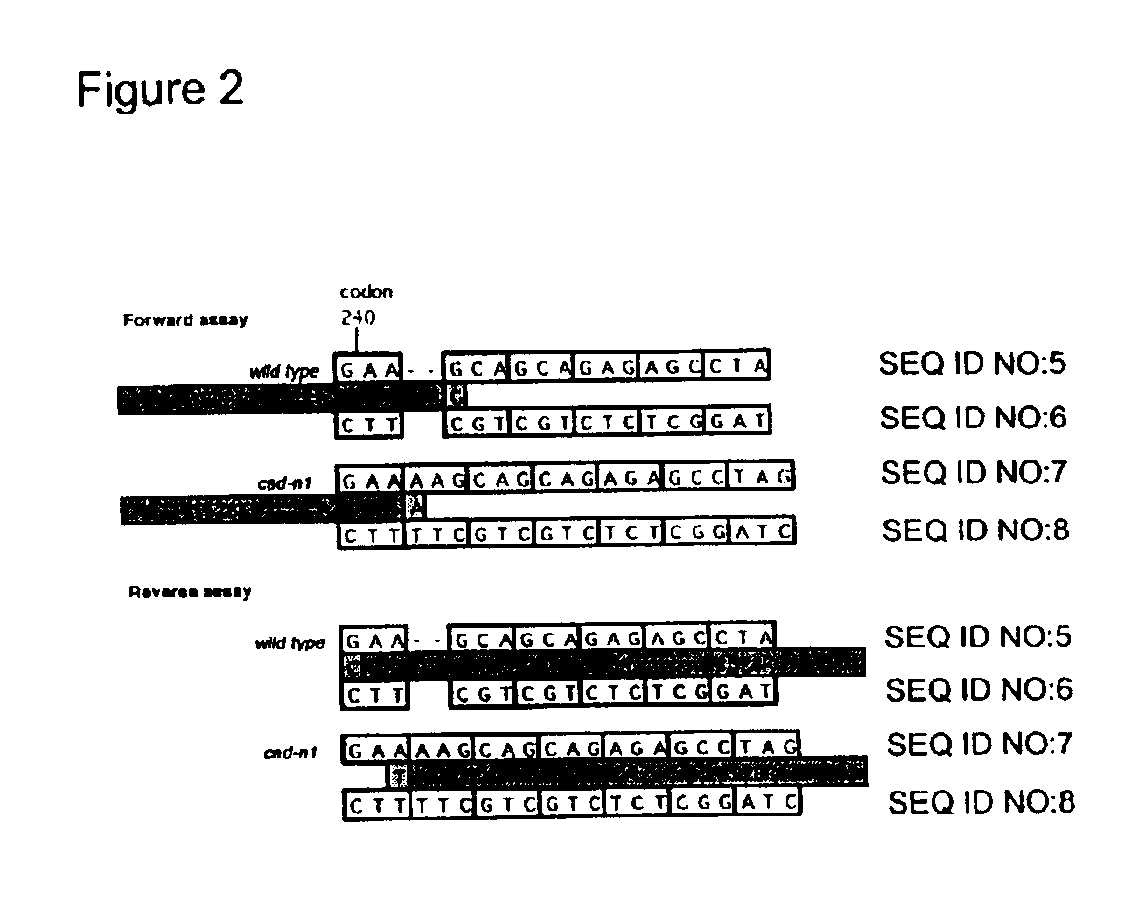
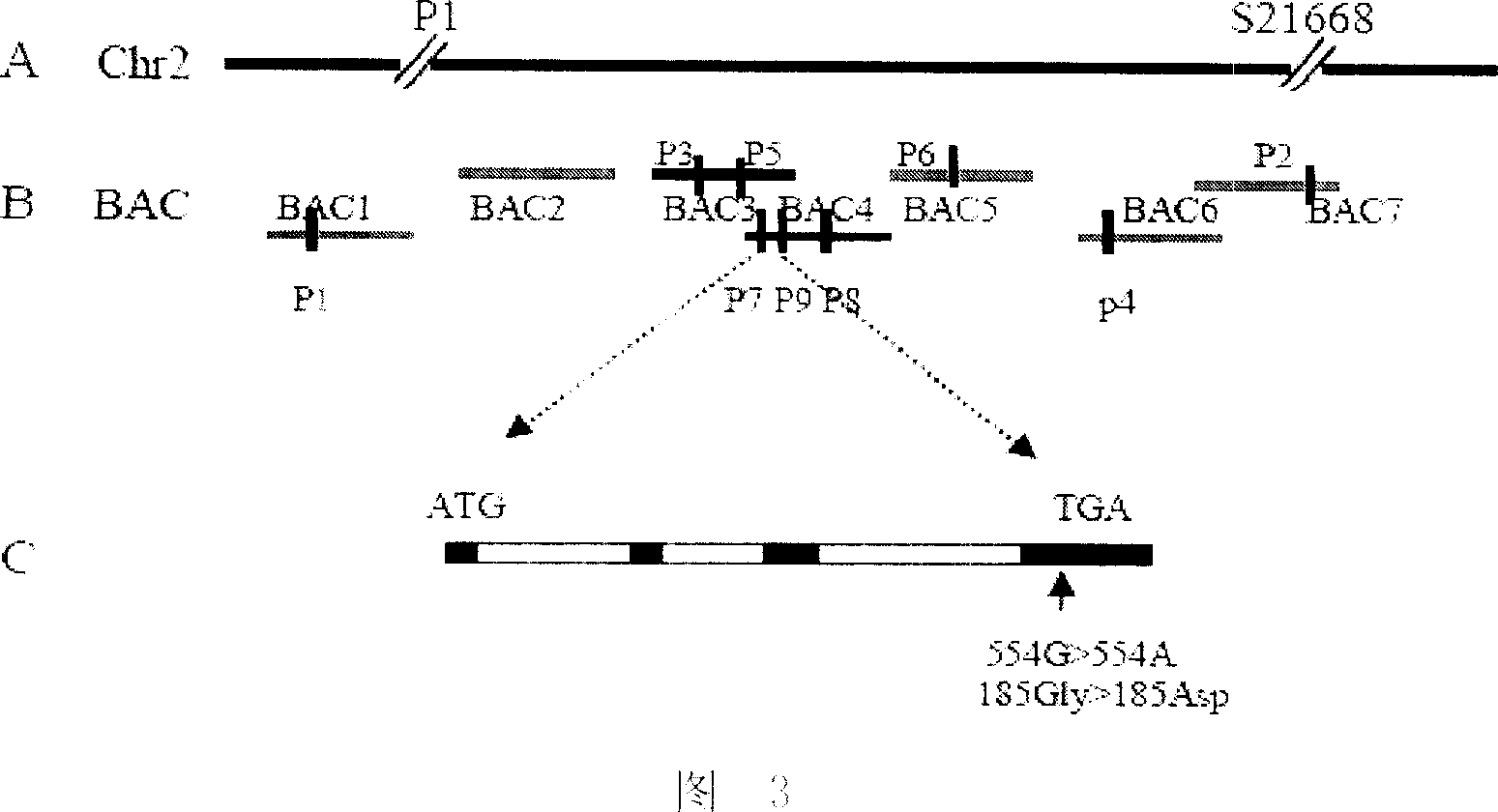
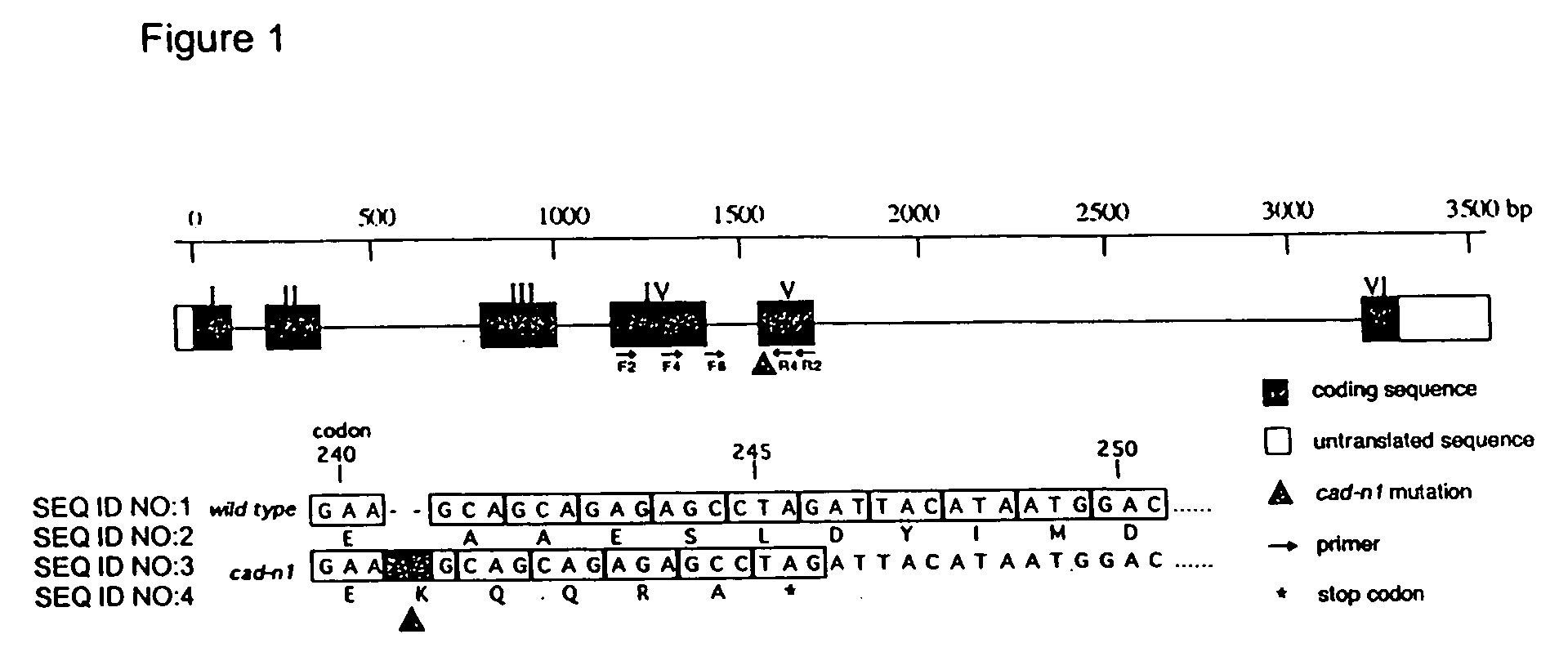
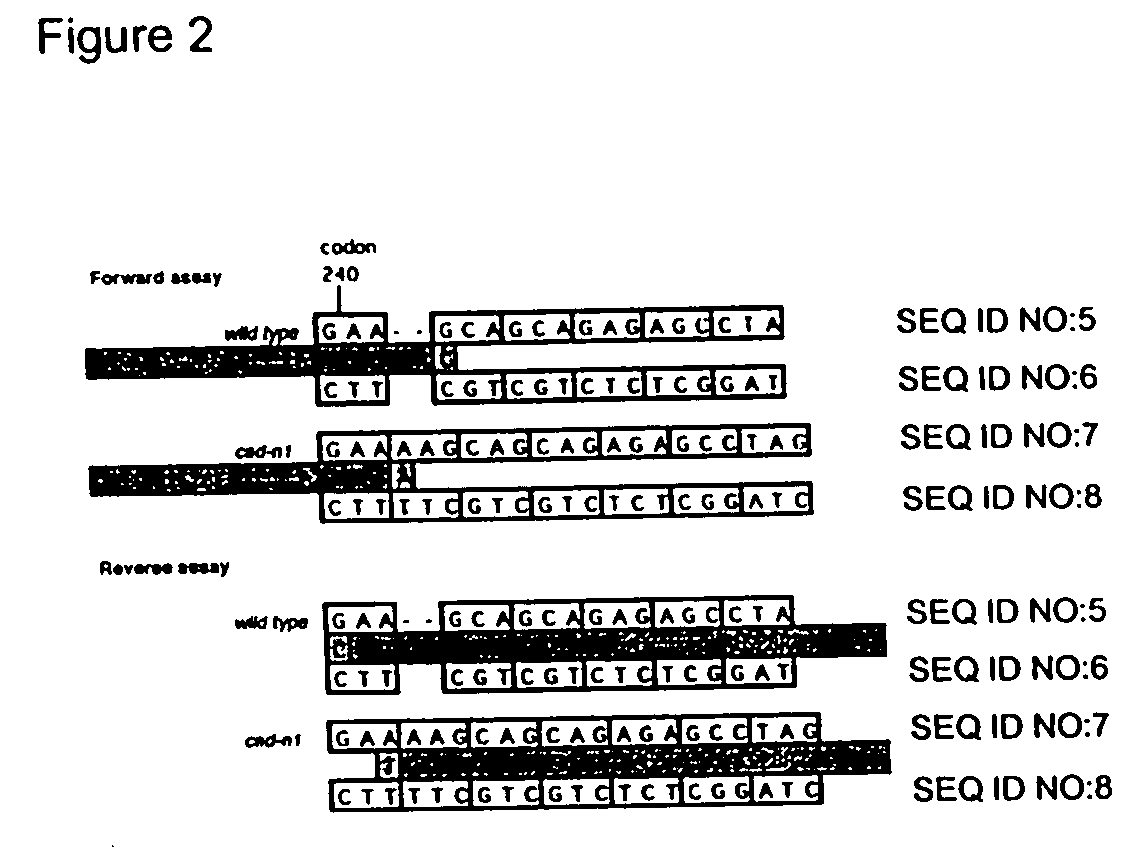
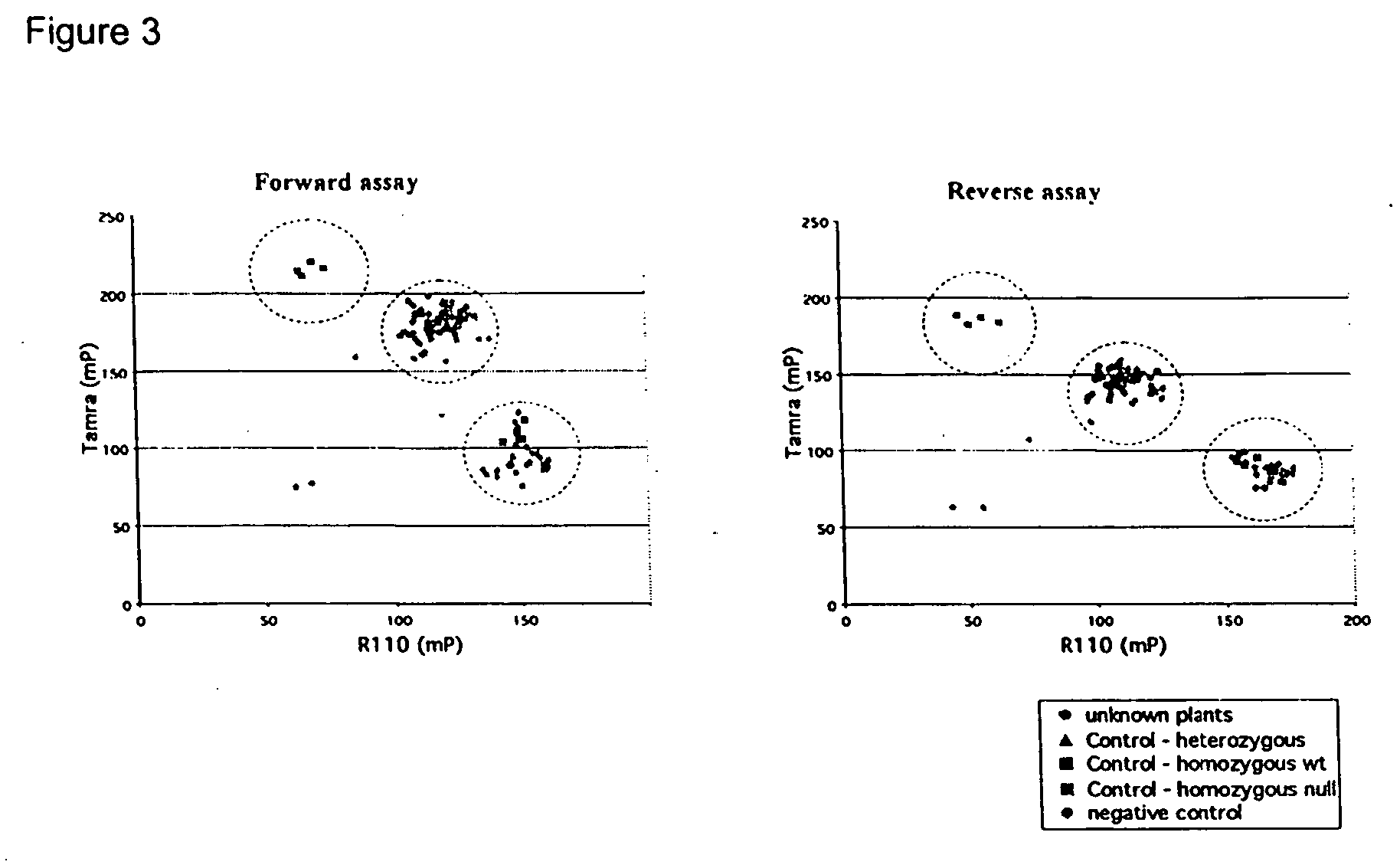
Compositions and methods for detecting a sequence mutation in the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene associated with altered lignification in loblolly pine
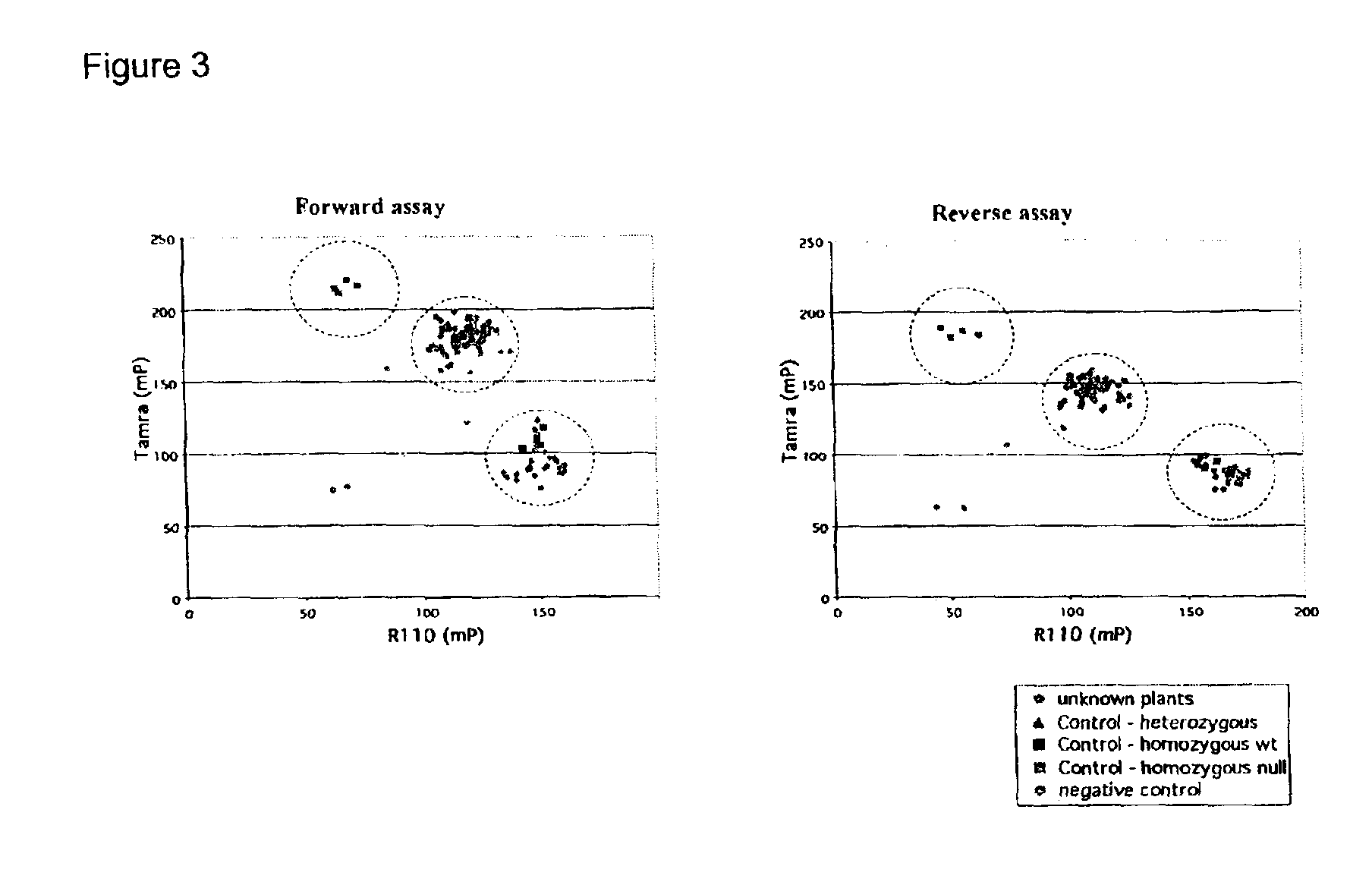
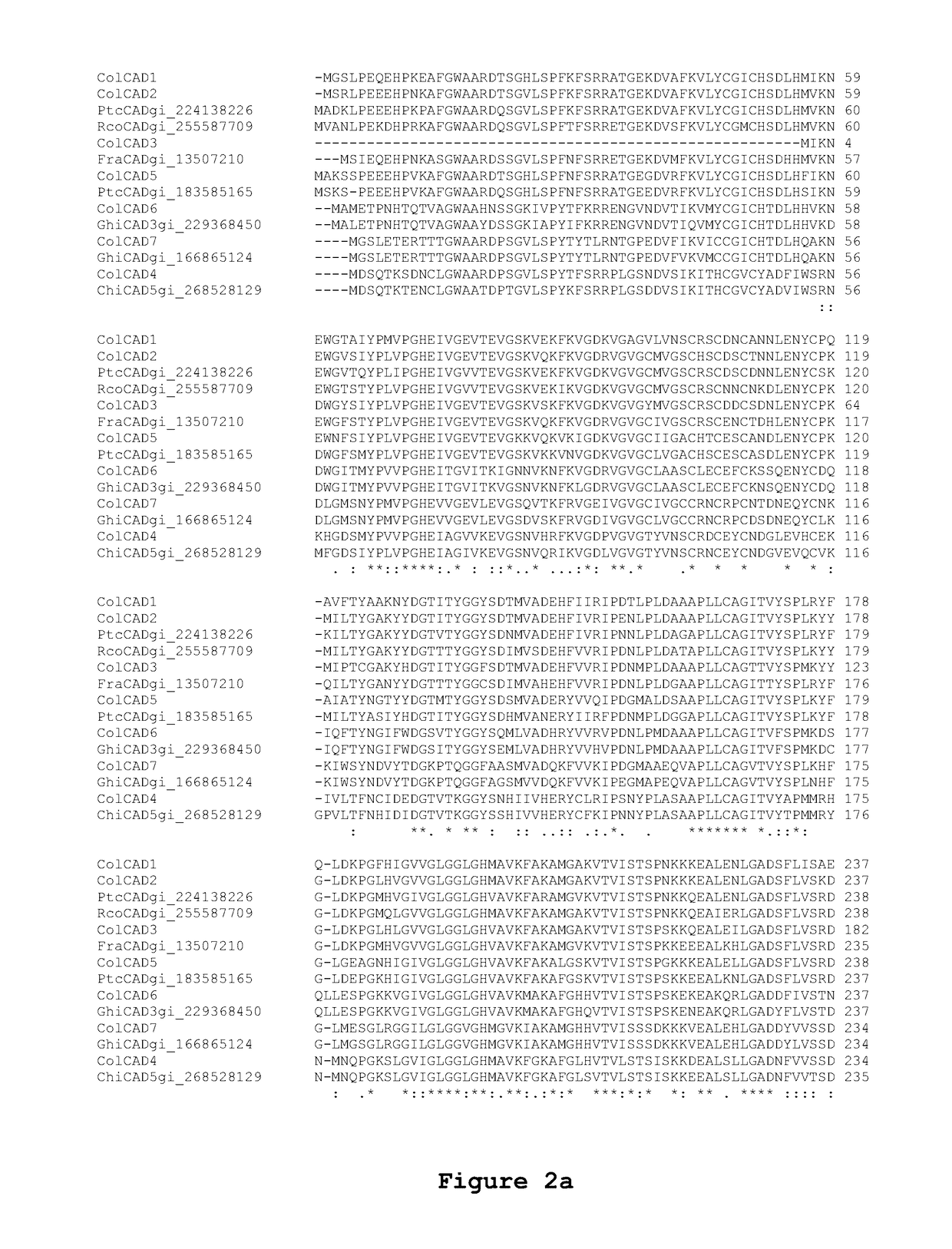
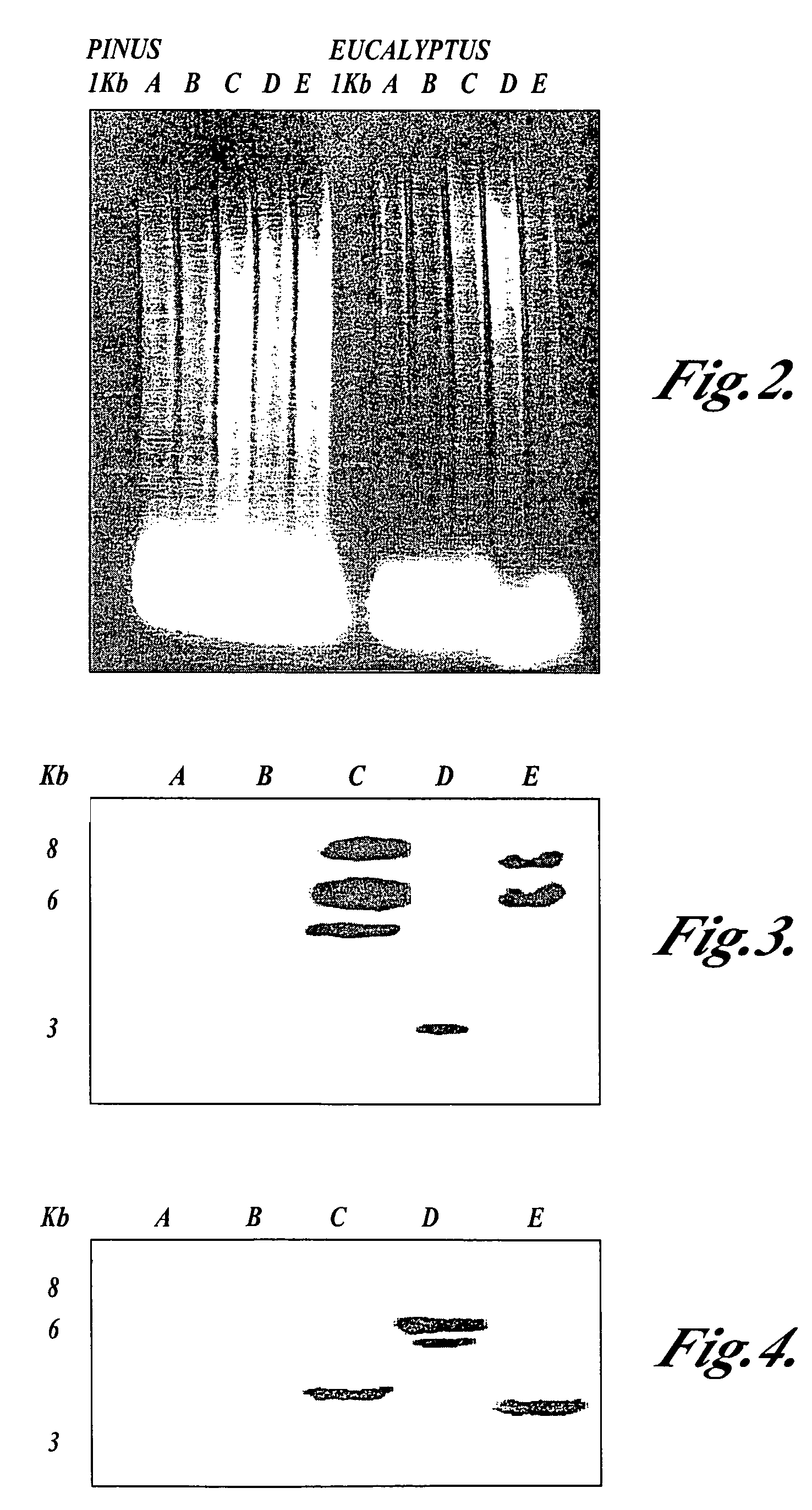
InactiveUS6921643B2Precise processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenaseLignin biosynthesis
Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) is the most important commercial tree species in the USA harvested for pulp and solid wood products. Increasing the efficiency of chemical pulping may be achieved through the manipulation of genes involved in the lignin biosynthetic pathway. A null allele of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) has been discovered in the loblolly pine clone 7-56 which displays altered lignin composition. During identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the cad gene, a two-base pair adenosine insertion located in exon five and unique to clone 7-56 was discovered. The sequence mutation causes a frame-shift predicted to result in premature termination of the protein. For routine detection of the mutation, a diagnostic assay was developed utilising Template-directed Dye-terminator Incorporation and Fluorescence Polarization detection (FP-TDI).
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Selective control of lignin biosythesis in transgenic plants
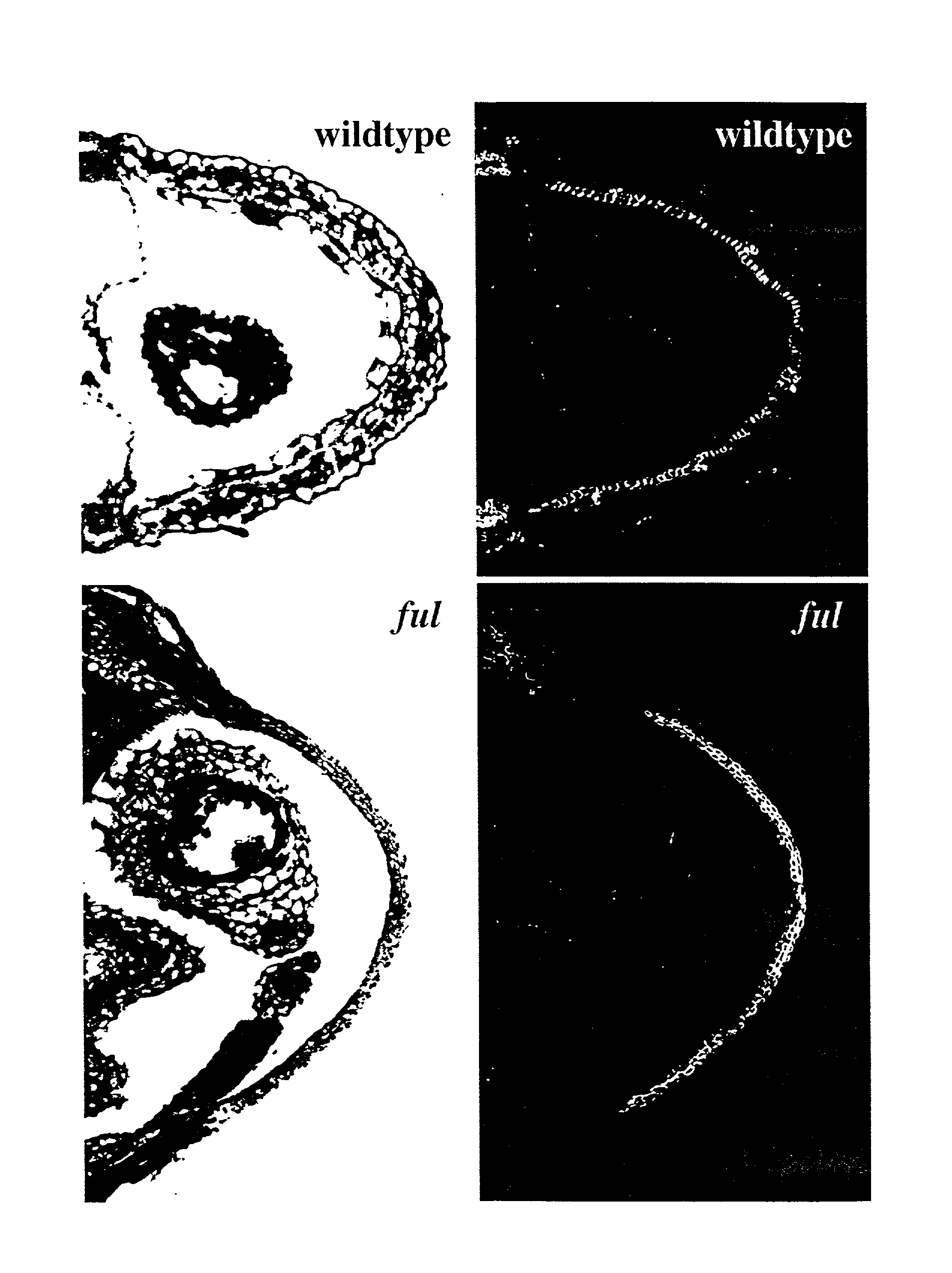
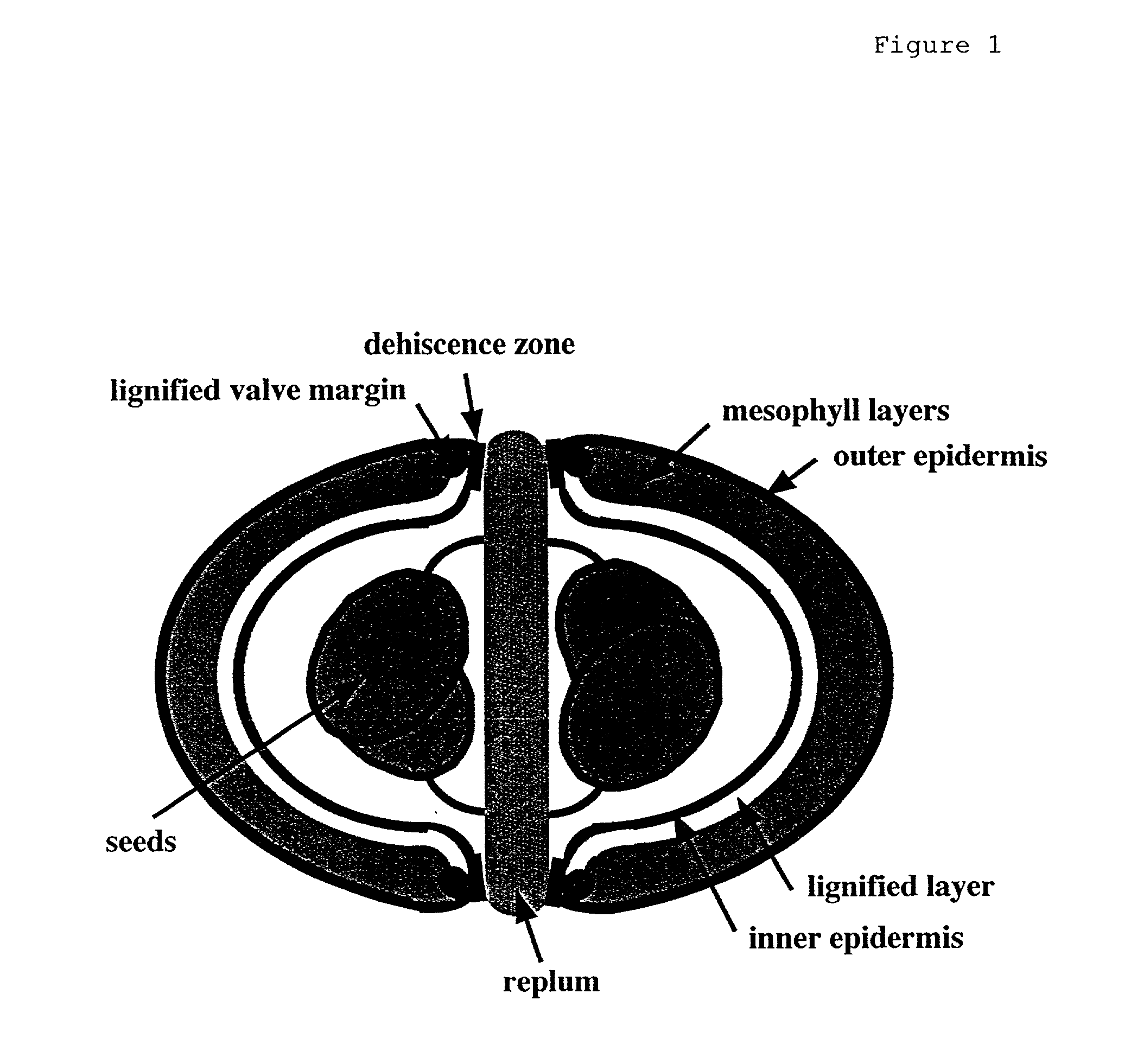
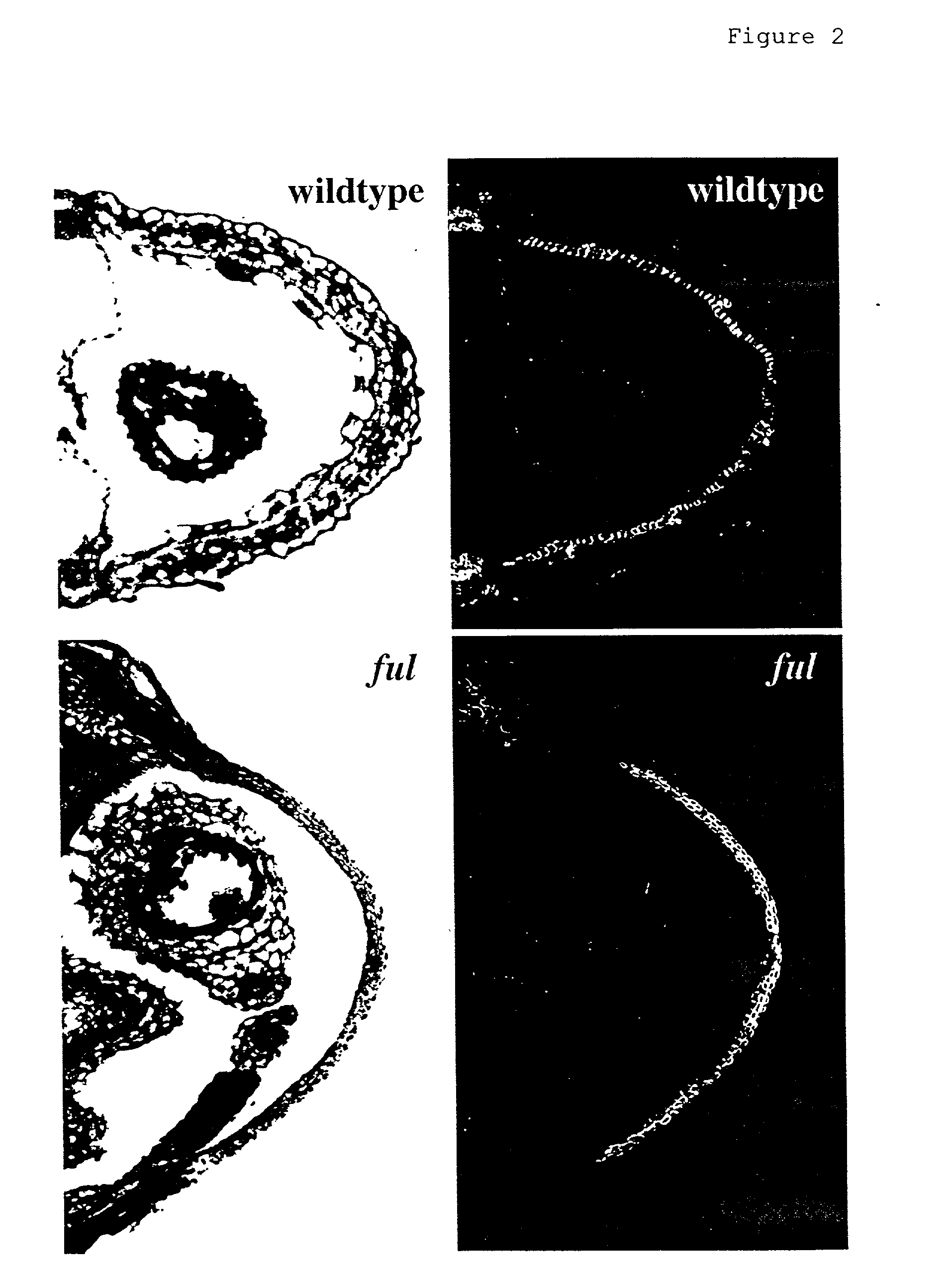
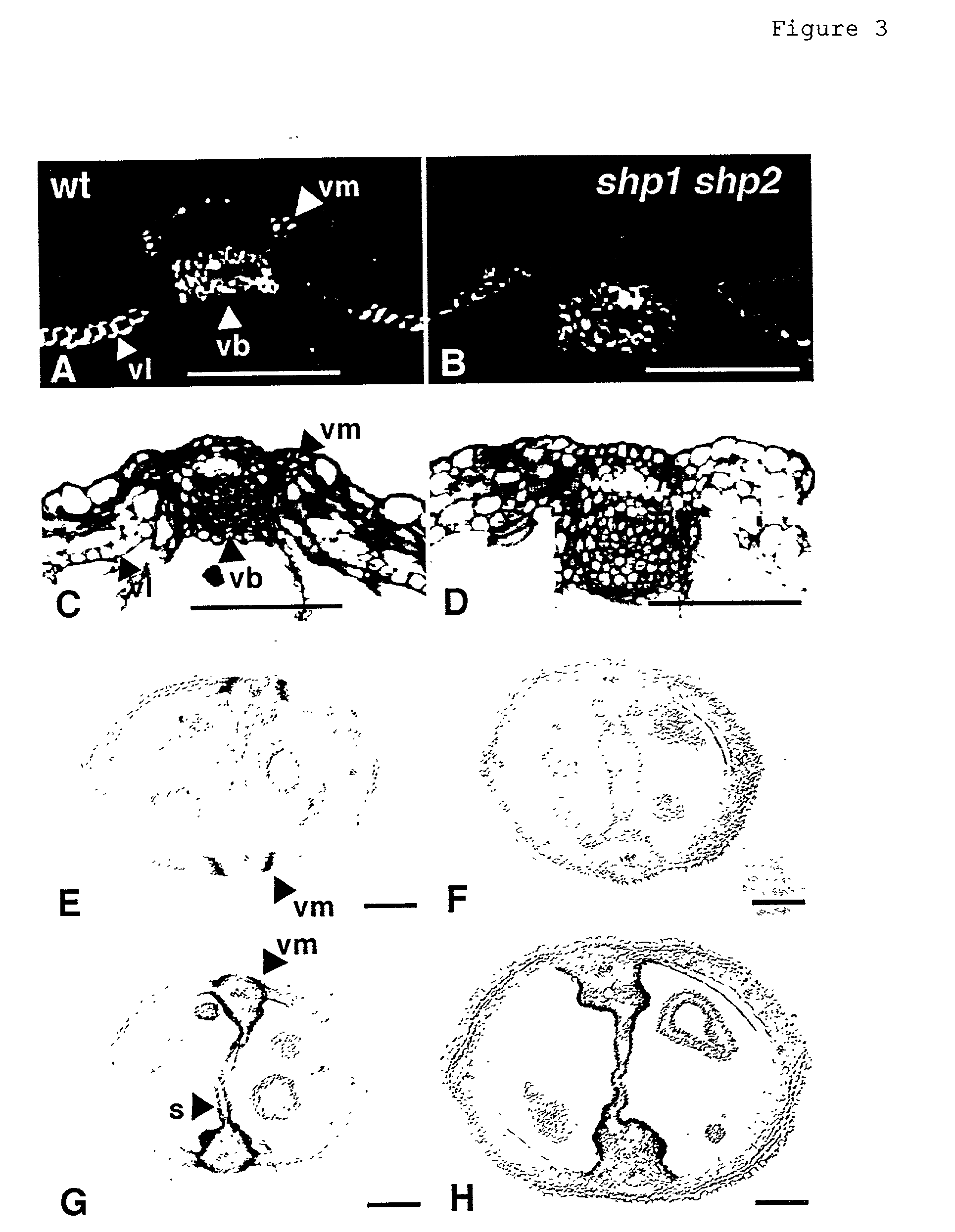
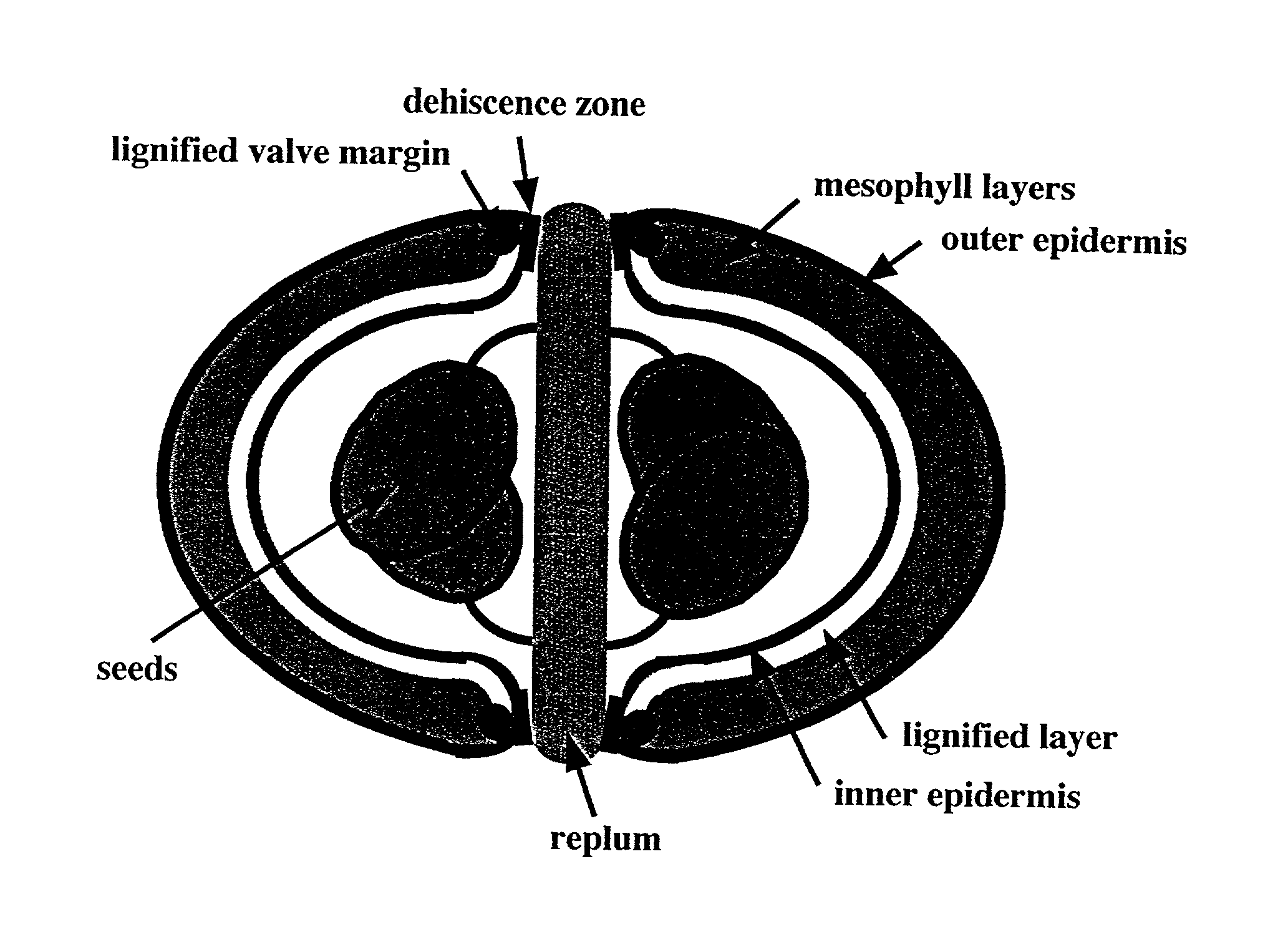
InactiveUS20030005481A1Enhancing lignificationLignification is enhancedBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesLignin biosynthesisGene product
The present invention provides methods of selectively controlling lignin biosynthesis in plants such that lignification is reduced or enhanced, as desired. The invention provides, for example, a method of reducing lignification in a vascular plant by ectopically expressing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an AGL8-like gene product in the plant, whereby lignification is reduced due to ectopic expression of the nucleic acid molecule. An AGL8-like gene product useful in the invention can have, for example, substantially the amino acid sequence of an AGL8 ortholog such as Arabidopsis AGL8 (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for enhancing cellulose and modifying lignin biosynthesis in plants
This invention relates to polynucleotide molecules encoding cellulose synthase, promoters of cellulose synthase and cellulose synthase polypeptides, methods for genetically altering cellulose and lignin biosynthesis, and methods for improving strength properties of juvenile wood and fiber in trees. The invention further relates to methods for identifying regulatory elements in a cellulose synthase promoter and transcription factors that bind to such regulatory elements, and to methods for augmenting expression of polynucleotides operably linked to a cellulose synthase promoter.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHCAL UNIV BOARD OF CONTROL +1
Methods and genetic constructs for modification of lignin composition of corn cobs
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Polynucleotides Encoding Lignin Biosynthetic Pathway Enzymes in Coffee
InactiveUS20090313728A1More productiveReduce productionBryophytesSugar derivativesLignin biosynthesisFood flavor
Polynucleotides encoding polypeptides that comprise the biosynthetic pathway for lignins in the coffee plant are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for using these polynucleotides and polypeptides for the manipulation of flavor, aroma, and other features of coffee beans, as well as the manipulation resistance to pathogen, herbivore, and insect attack in the coffee plant.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Plant cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase homologs
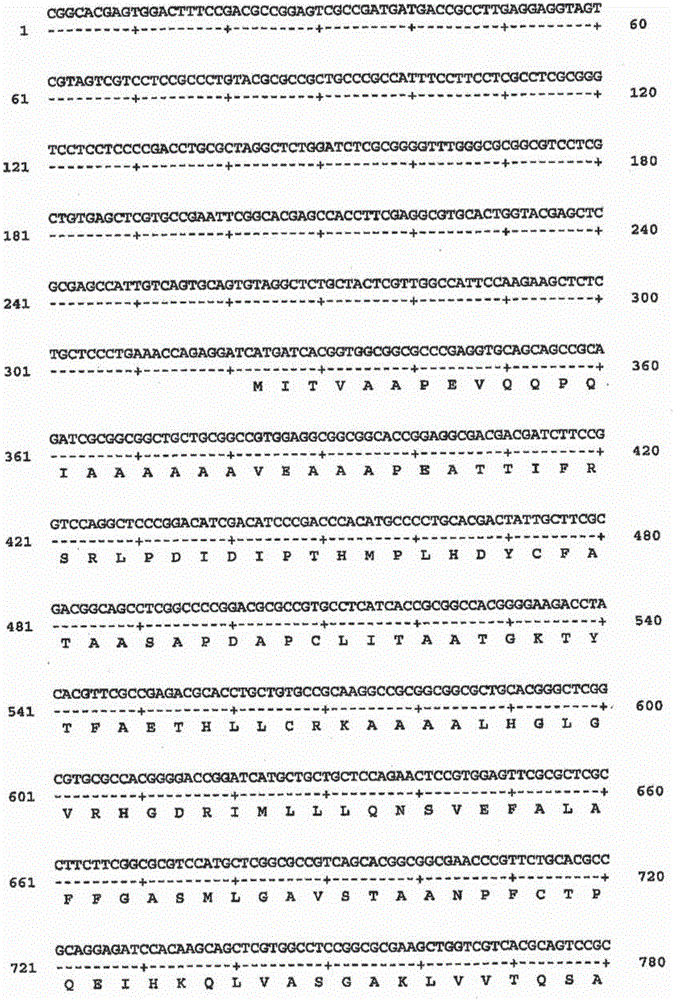
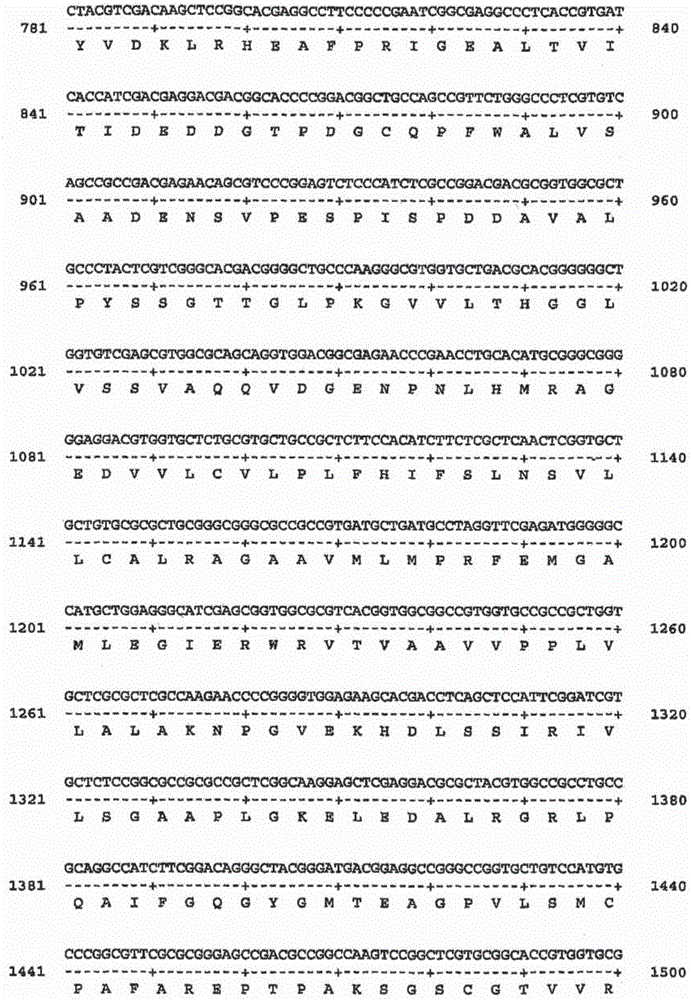
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a lignin biosynthetic enzyme. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the lignin biosynthetic enzyme, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the lignin biosynthetic enzyme in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Lignin synthesis related protein and its coding gene and uses
The invention discloses a lignin-related protein as well as its gene encoding and application. The lignin-associated protein has one of the following amino acid residues sequences: (1) SEQ ID No. : 2 in the sequence table, and (2) lignin-related protein after SEQ ID No. : 2 one or several amino acid residues replaced and / or deleted and / or added in the sequence table. The lignin-related protein gene can regulate the content and composition of rice lignin without influences on plant growth and development, and improve the values as feed and industrial raw material of paper. In addition, the lignin-related protein gene also has important theoretical value in revealing the mechanism of plant lignin biosynthesis.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
IbLEA14 gene from ipomoea batatas roots and use thereof
The invention relates to an IbLEA 14 (Ipomoea batatas Late embryogenesis abundant 14) protein related to the stress resistance of ipomoea batatas or the lignin biosynthesis. The invention further relates to a method for improving the stress resistance of plants or the lignin biosynthesis of plants through form quality conversion of recombinant vectors included in the protein genes in plant cells after the protein genes are coded and the a host cell is generated from the form quality conversion of the recombinant vectors. Further included is a method for making form quality conversing plant bodies with enhanced stress resistance or improved lignin biosynthesis by means of the recombinant vectors for form quality conversion of biological cells. The invention further relates to biologic energy obtained by the form quality conversing plant bodies provided with increased lignin biosynthesis and made by the above-mentioned method and the composition for improving the stress resistance or the lignin biosynthesis of the plant bodies having the genes.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
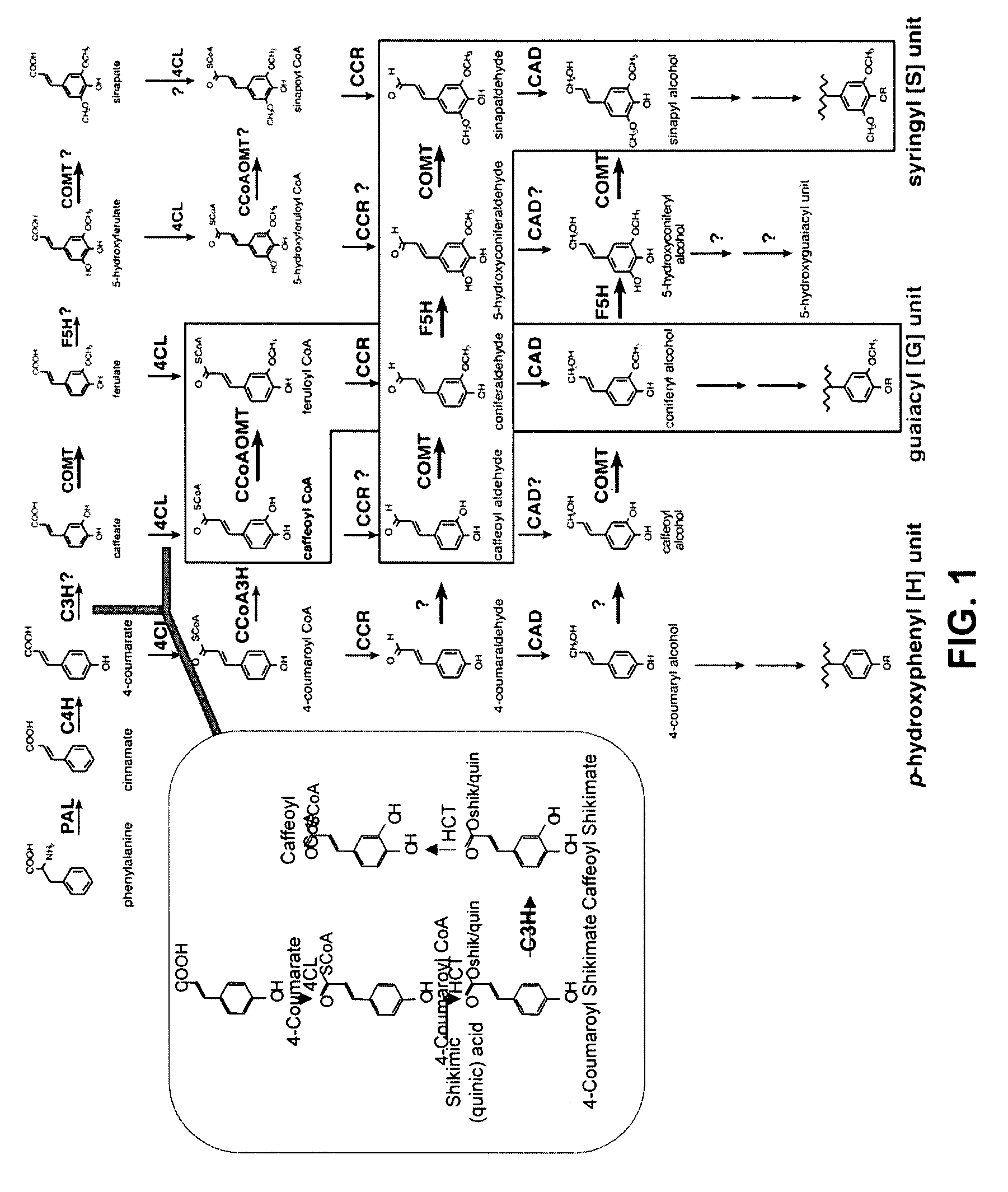
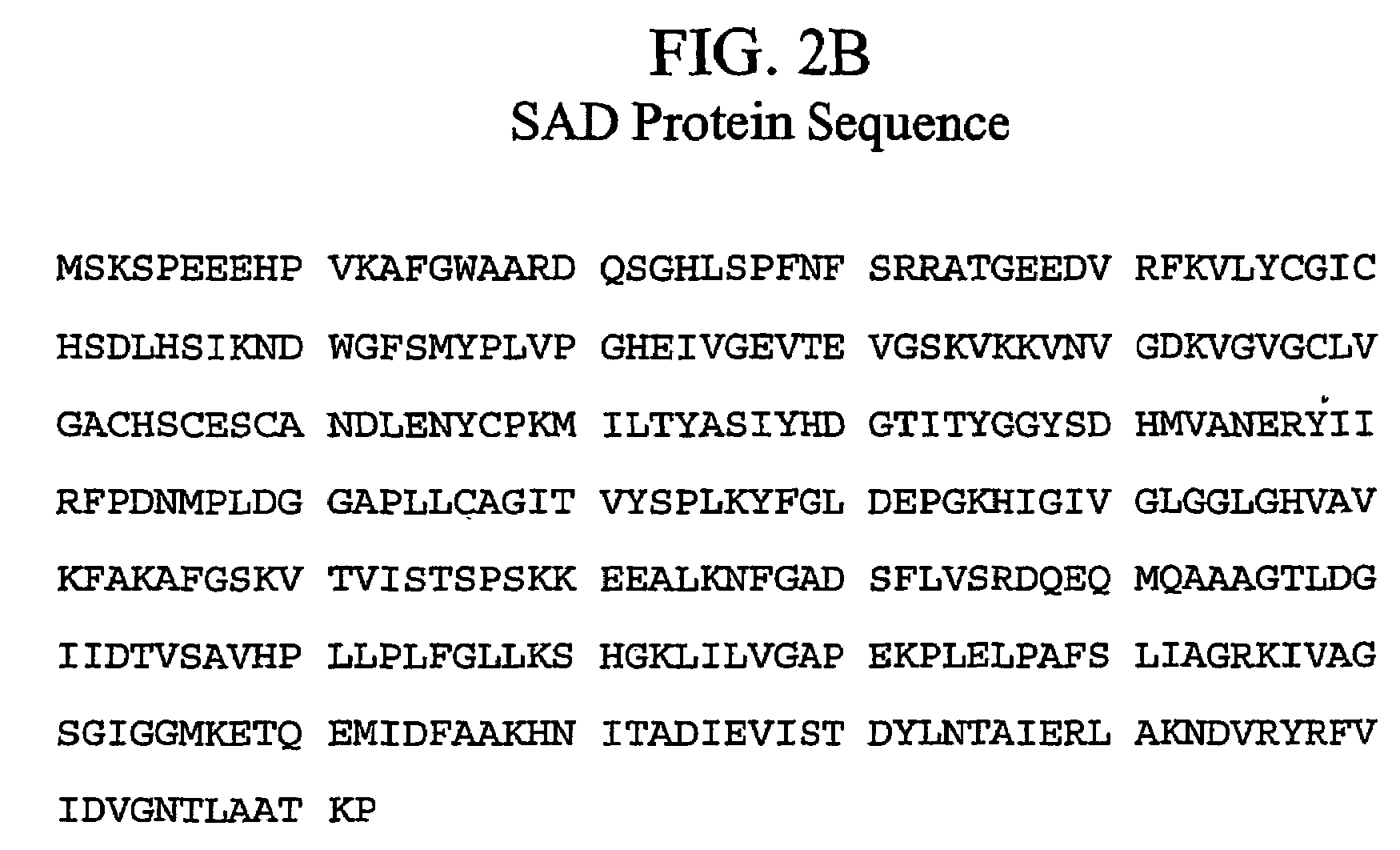
Genetic engineering of syringyl-enriched lignin in plants
InactiveUS7288696B2Increase productionReduce the amount requiredSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesLignin biosynthesisSinapyl alcohol dehydrogenase
The present invention relates to a novel DNA sequence, which encodes a previously unidentified lignin biosynthetic pathway enzyme, sinapyl alcohol dehydrogenase (SAD) that regulates the biosynthesis of syringyl lignin in plants. Also provided are methods for incorporating this novel SAD gene sequence or substantially similar sequences into a plant genome for genetic engineering of syringyl-enriched lignin in plants.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Genes encoding enzymes for lignin biosynthesis and uses thereof
The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to altering lignin biosynthesis content and / or composition of plants. The invention provides isolated nucleic acids and their encoded proteins which are involved in lignin biosynthesis. The invention further provides recombinant expression cassettes, host cells, transgenic plants, and antibody compositions.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Modification of lignin biosynthesis via sense suppression
The present invention relates to the modification of lignin biosynthesis in plants, to enzymes involved in the lignin biosynthetic pathway and nucleic acids encoding such enzymes and, more particularly, to methods of modifying lignin biosynthesis via sense suppression and to related nucleic acids and constructs.
Owner:DAIRY AUSTRALIA +1
Selective control of lignin biosynthesis in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20020129403A1Delayed lignificationSuppressed AGL and AGLOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationLignin biosynthesisGene product
The present invention provides methods of selectively controlling lignin biosynthesis in plants such that lignification is reduced or enhanced, as desired. The invention provides, for example, a method of reducing lignification in a vascular plant by ectopically expressing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an AGL8-like gene product in the plant, whereby lignification is reduced due to ectopic expression of the nucleic acid molecule. An AGL8-like gene product useful in the invention can have, for example, substantially the amino acid sequence of an AGL8 ortholog such as Arabidopsis AGL8 (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for producing transgenic plant with increased syringin production and plant produced by using the same
ActiveUS20150252338A1Effective massRaise transfer toSugar derivativesTransferasesPhenylpropanoidSyringin
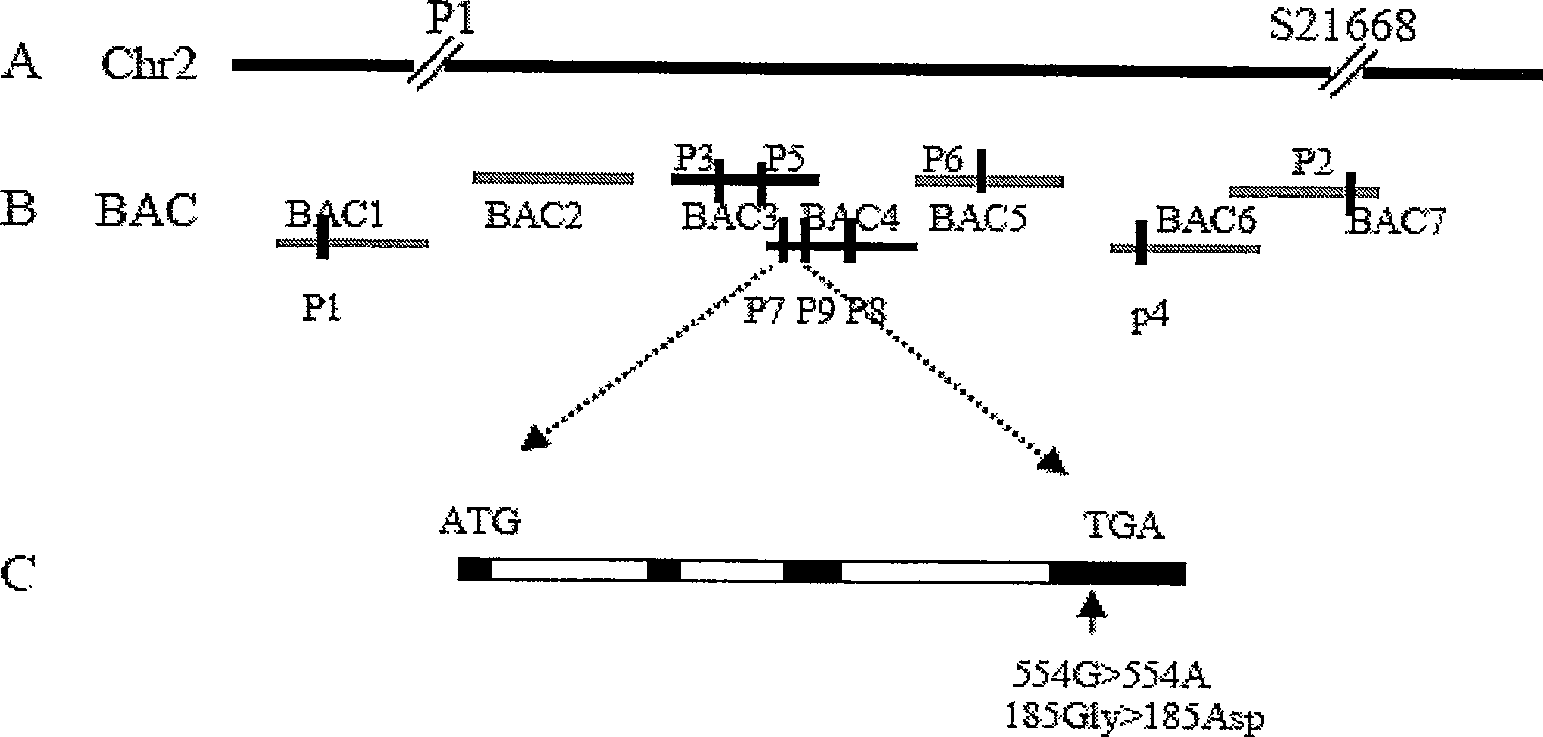
The present invention relates to recombinant glycosyl transferase UGT72E3 / 2 gene having an excellent syringin synthesis ability based on remarkable enzyme specificity for sinapyl alcohol, a method for producing a transgenic plant with increased syringin production based on a metabolic process which uses F5H and CHS genes that are involved with the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway and Myb58 gene as a transcription factor for positive regulation of the gene that is involved with lignin biosynthesis pathway, and a plant obtained by the method. According to the present invention, syringin with various pharmaceutical applications can be effectively produced in a large amount in a plant, and thus it is expected to allow the development of an industry relating to agrobiological materials that are highly valuable as foods or pharmaceuticals.
Owner:DONG A UNIV RES FOUND FOR IND ACAD COOP
Biofuel production methods and compositions
ActiveUS9309528B2Increase productionSmooth transitionSugar derivativesBiofuelsPlant tissueLignin biosynthesis
The invention provides methods for increasing the level of fermentable carbohydrates in a biofuel crop plant such as alfalfa or switchgrass, by modification of the lignin biosynthetic pathway. Also provided are plants prepared by the methods of the invention. Methods for processing plant tissue and for producing ethanol by utilizing such plants are also provided.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Materials and methods for the modification of plant lignin content
Novel isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides associated with the lignin biosynthetic pathway are provided, together with genetic constructs including such sequences. Methods for the modulation of lignin content, lignin structure and lignin composition in target organisms are also disclosed, the methods comprising incorporating one or more of the polynucleotides of the present invention into the genome of a target organism.
Owner:ARBORGEN
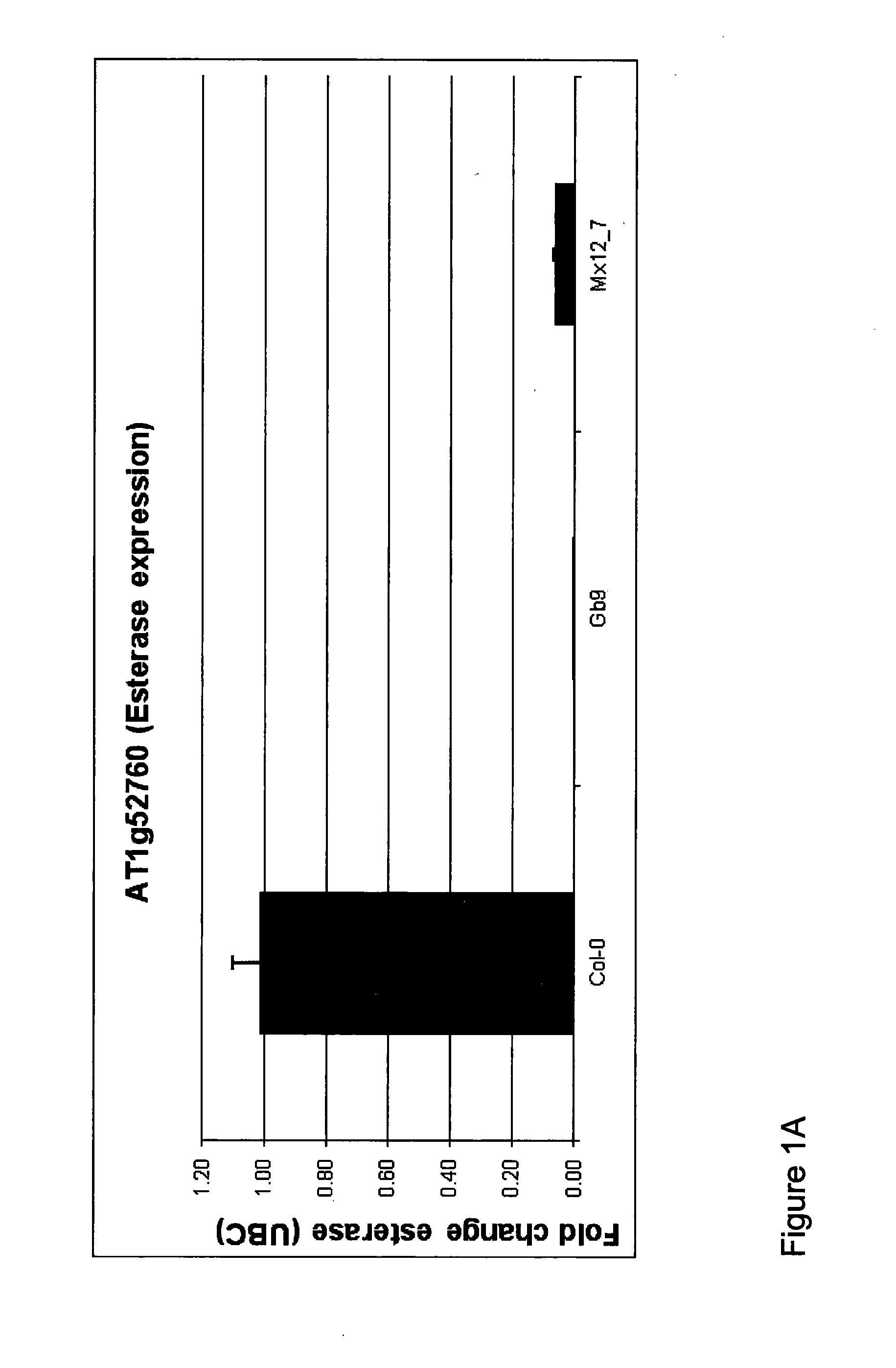
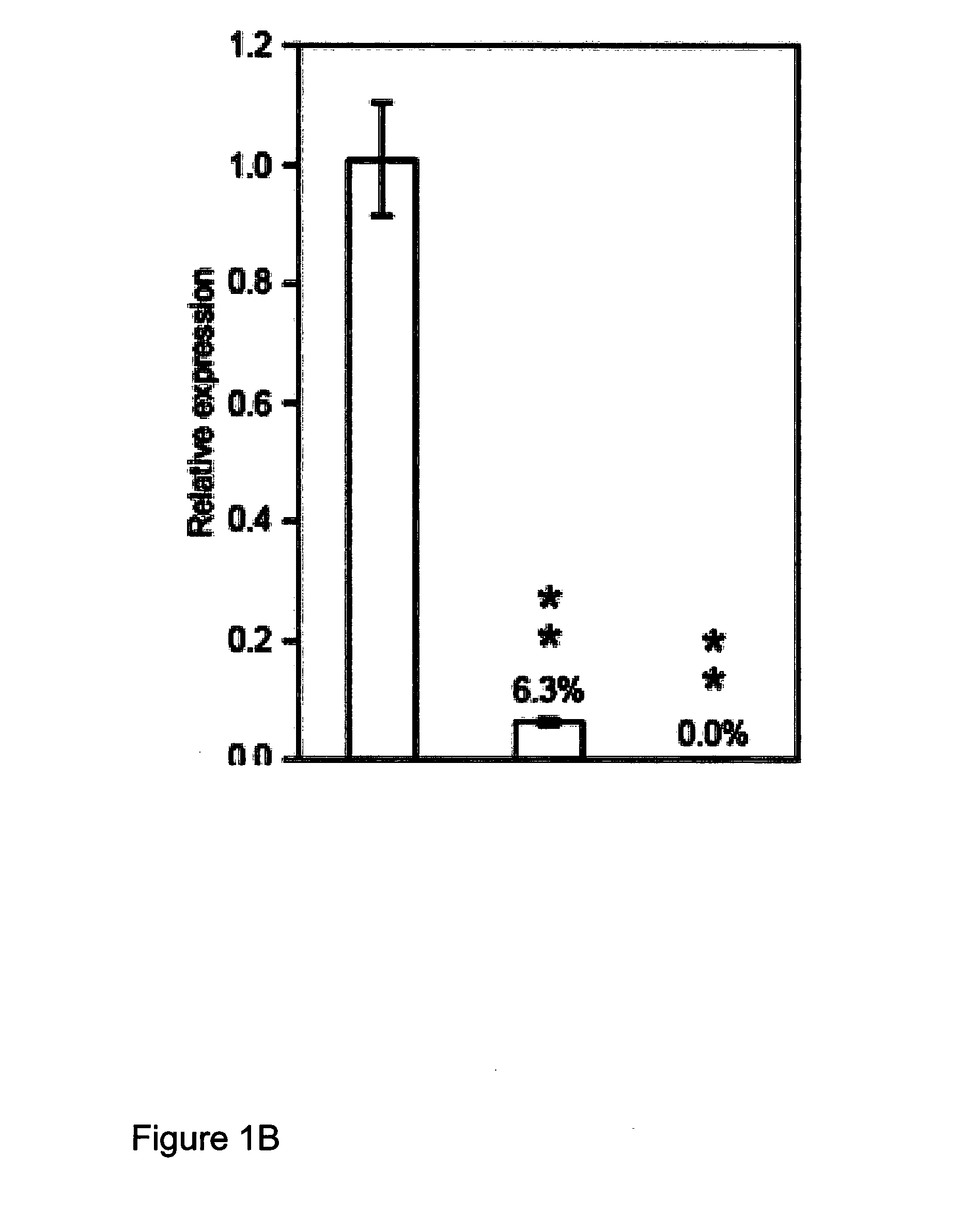
Method for modifying lignin biosynthesis in plants
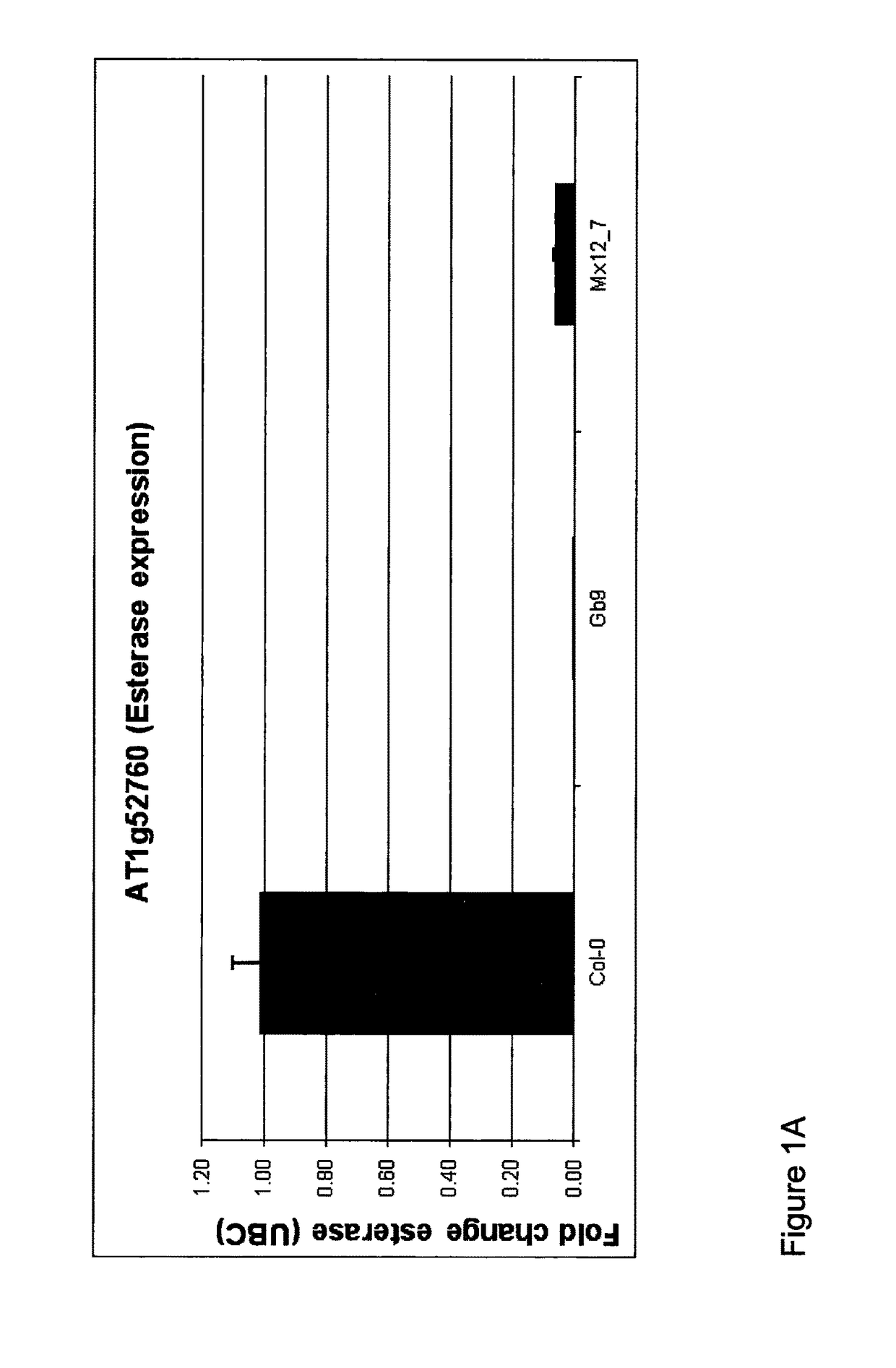
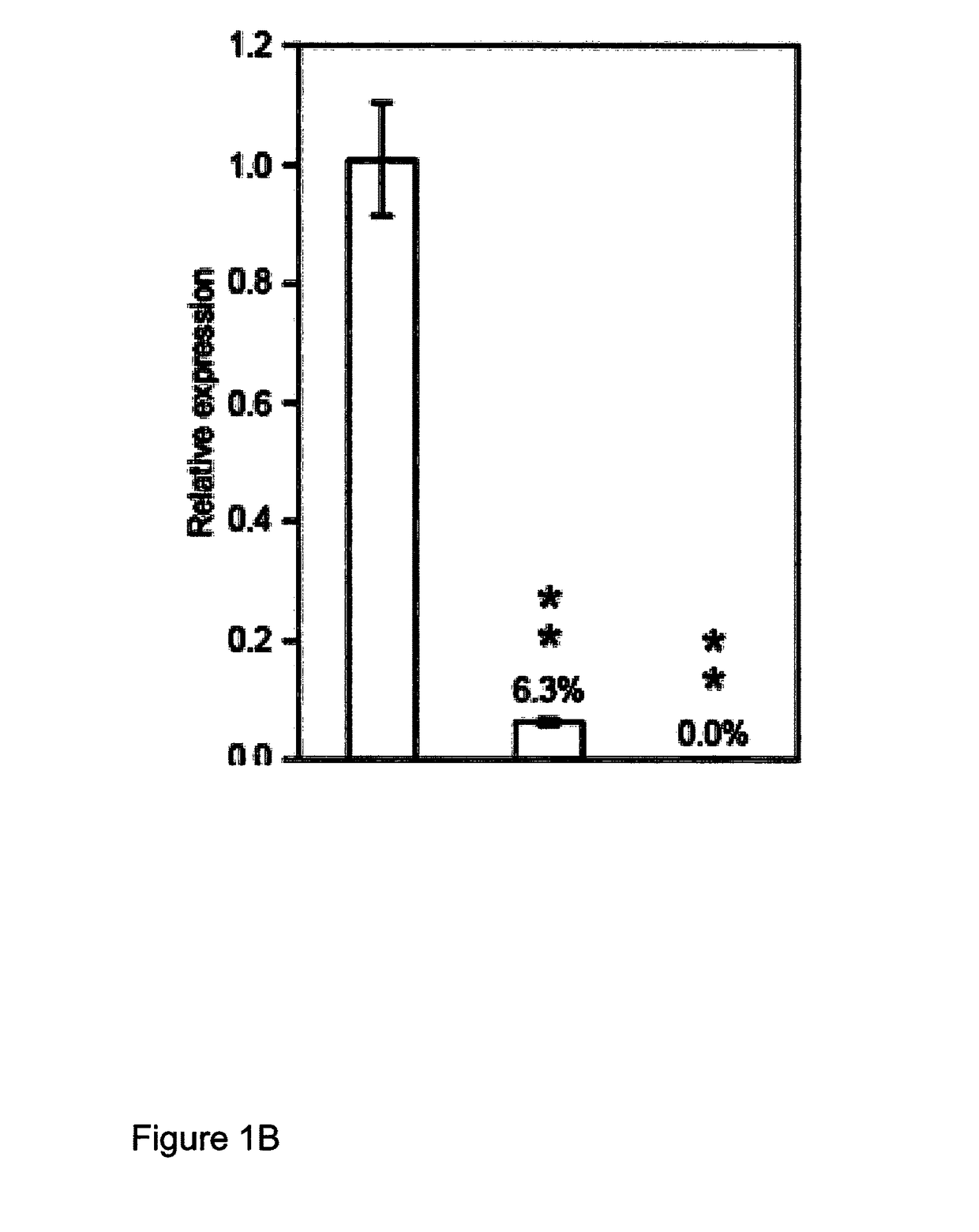
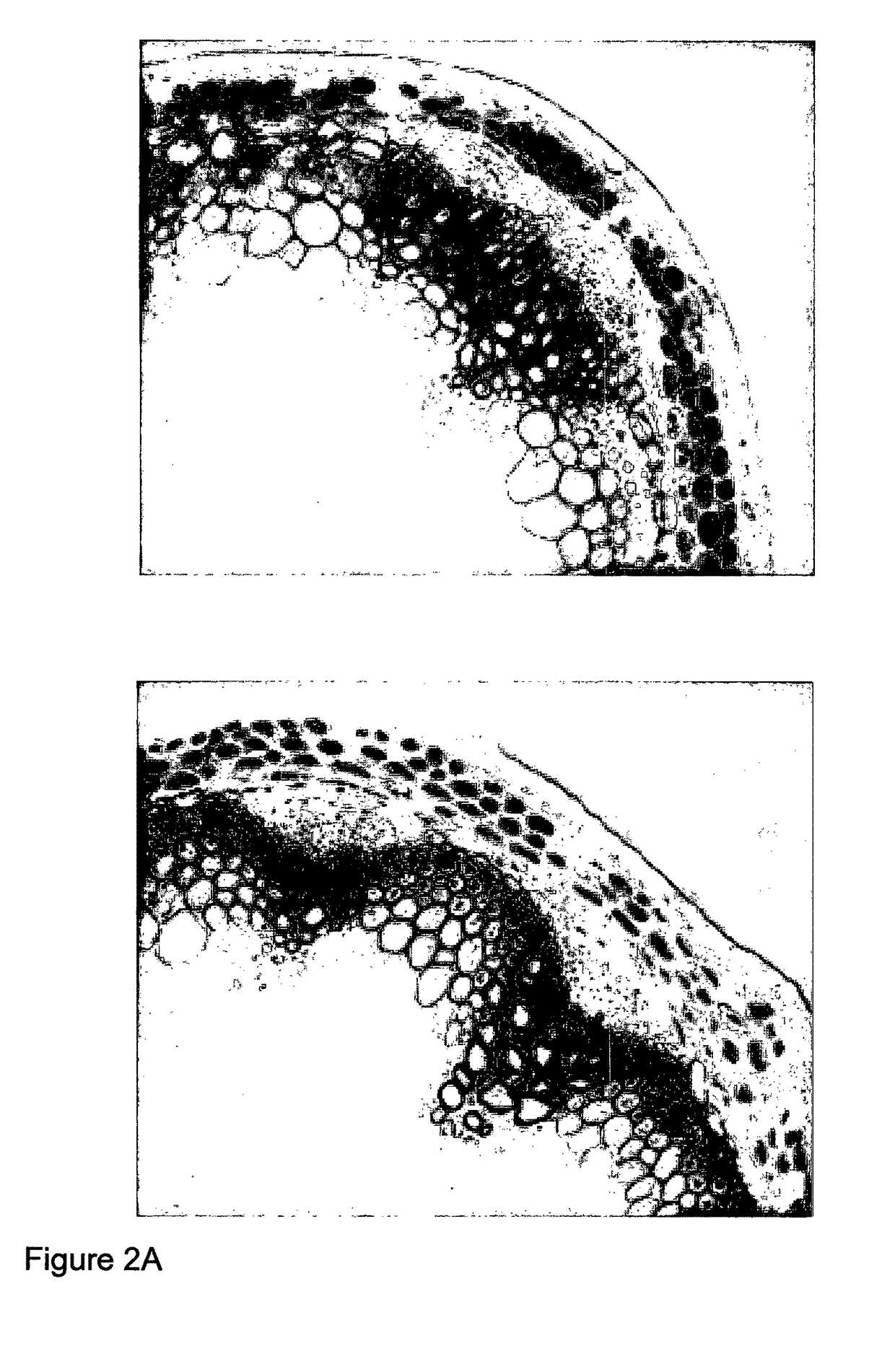
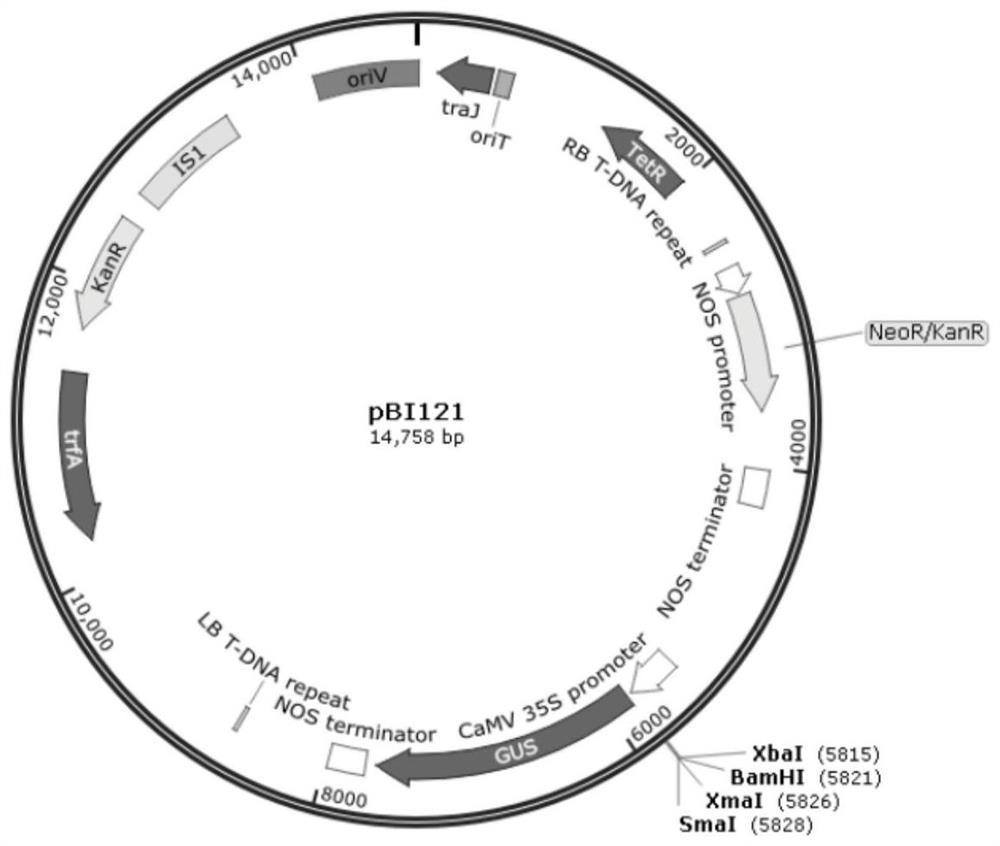
The disclosure is based on the discovery of genes which influence lignin biosynthesis. In particular, the inventors have observed that if the expression, function and / or activity of these gene(s) (or any protein products thereof) is / are modulated, the lignin content of plants can be altered. As such, this disclosure provides plants, which exhibit modulated expression of one or more lipase / esterase / thioesterase family gene(s) and which may find application in methods for producing biofuels.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DUNDEE +2
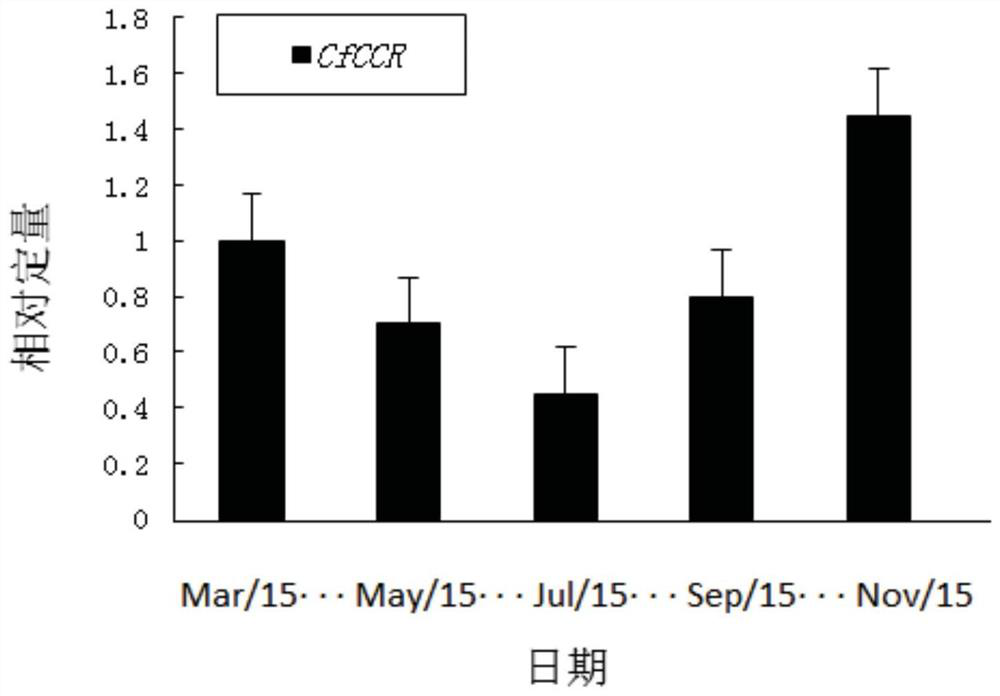
A kind of Cedar cfccr gene and its application
ActiveCN111139253BImprove stress resistanceImprove qualityBacteriaOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a cedar CfCCR gene and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of plant molecular biology and genetic engineering. The cedar lignin synthesis regulating CfCCR gene of the present invention has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of its expressed protein is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The CfCCR gene is the key rate-limiting enzyme in the specific pathway of lignin synthesis. It regulates the expression of genes related to lignin synthesis in plants by encoding proteins, and plays an important role in lignin biosynthesis and stress resistance. Tobacco transgenic for CfCCR gene had increased expression of lignin and well-developed cell wall. Therefore, the thickness of the xylem cell wall in cedar or other plant stems can be changed by expressing the CfCCR gene, thereby increasing the wood density, improving the quality and quality of the wood and the stress resistance of the plant.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for modifying lignin biosynthesis in plants
ActiveUS20150176016A1Efficient releaseAvailability of moreBryophytesHydrolasesLignin biosynthesisBiofuel
The disclosure is based on the discovery of genes which influence lignin biosynthesis. In particular, the inventors have observed that if the expression, function and / or activity of these gene(s) (or any protein products thereof) is / are modulated, the lignin content of plants can be altered. As such, this disclosure provides plants, which exhibit modulated expression of one or more lipase / esterase / thioesterase family gene(s) and which may find application in methods for producing biofuels.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DUNDEE +2
Lignin synthesis related protein and coding gene and use thereof
The invention discloses a lignin-related protein as well as its gene encoding and application. The lignin-associated protein has one of the following amino acid residues sequences: (1) SEQ ID No. : 2 in the sequence table, and (2) lignin-related protein after SEQ ID No. : 2 one or several amino acid residues replaced and / or deleted and / or added in the sequence table. The lignin-related protein gene can regulate the content and composition of rice lignin without influences on plant growth and development, and improve the values as feed and industrial raw material of paper. In addition, the lignin-related protein gene also has important theoretical value in revealing the mechanism of plant lignin biosynthesis.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Isolation and targeted suppression of lignin biosynthetic genes
InactiveUS20120180157A1BiocideOther foreign material introduction processesPlant tissueBiosynthetic genes
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for modulating lignin biosynthesis in sugarcane plants. In one embodiment, lignin biosynthesis is down-regulated. Genes and the proteins encoded thereby that can be targeted for achieving down-regulation of lignin in sugarcane include, for example, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL). In one embodiment, the 4CL gene is 4CL-M, 4CL-N, or 4CL-L. The subject invention also concerns a sugarcane plant, specific plant tissue, and plant cells having modulated (e.g., down-regulated) lignin biosynthesis. The subject invention also concerns methods for producing a sugarcane plant having modulated (e.g., decreased or down-regulated) biosynthesis of lignin.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for producing transgenic plant with increase syringin production and plant produced by using the same
ActiveUS9644191B2Effective massGood effectTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionPhenylpropanoidLignin biosynthesis
The present invention relates to recombinant glycosyl transferase UGT72E3 / 2 gene having an excellent syringin synthesis ability based on remarkable enzyme specificity for sinapyl alcohol, a method for producing a transgenic plant with increased syringin production based on a metabolic process which uses F5H and CHS genes that are involved with the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway and Myb58 gene as a transcription factor for positive regulation of the gene that is involved with lignin biosynthesis pathway, and a plant obtained by the method. According to the present invention, syringin with various pharmaceutical applications can be effectively produced in a large amount in a plant, and thus it is expected to allow the development of an industry relating to agrobiological materials that are highly valuable as foods or pharmaceuticals.
Owner:DONG A UNIV RES FOUND FOR IND ACAD COOP
Polynucleotides encoding enzymes from the jute lignin biosynthetic pathway
Disclosed are polynucleotides encoding polypeptides that comprise the biosynthetic pathway for lignin in the jute plant. The present invention relates generally to the field of plant lignin biosynthesis genes, polypeptides encoded by such genes, and the use of such polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences for controlling plant lignin production. Also disclosed are methods for using the polynucleotides and polypeptides to influence the quality and amount of fiber produced by jute.
Owner:BANGLADESH JUTE RES INST
Compositions and methods for detecting a sequence mutation in the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene associated with altered lignification in loblolly pine
InactiveUS20050235384A1Precise processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAdenosineFluorescence
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Materials and methods for the modification of plant lignin content
Novel isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides associated with the lignin biosynthetic pathway are provided, together with genetic constructs including such sequences. Methods for the modulation of lignin content, lignin structure and lignin composition in target organisms are also disclosed, the methods comprising incorporating one or more of the polynucleotides of the present invention into the genome of a target organism.
Owner:RUBICON FORESTS HLDG LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com