Methods and genetic constructs for modification of lignin composition of corn cobs
A technology of corn cobs and lignin, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve problems such as less success
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0234] Agrobacterium transformation of maize - immature embryos
[0235] Ear of Corn Preparation
[0236] Ears of corn are harvested when the immature embryos are approximately 0.5 to 1.0 mm within the center of the kernel.
[0237] Ears of corn were dehulled and sterilized in a solution of 20% Clorox and 3 drops of Tween / liter solution. Place on an orbital shaker for 20 minutes.
[0238] with sterile ddH 2 O Rinse the ear of corn 3 times.
[0239] The corn kernels are topped off in a sterile environment, the ears are placed on sterile petri dishes and the immature embryos are isolated.
[0240] Preparation of seeding solution for transformation
[0241] • In 100 mL of LP-Lsinf. medium, add 50 μl of acetosyringone (AS) stock solution (40 mg / ml stock solution / mL) so that the final concentration is 100 μM AS.
[0242] • Pipette 4ml (2.5) of the infection medium into a 10ml disposable tube.
[0243] • Prepare Eppendorf centrifuge tubes for collecting the embryos at thi...
Embodiment 2
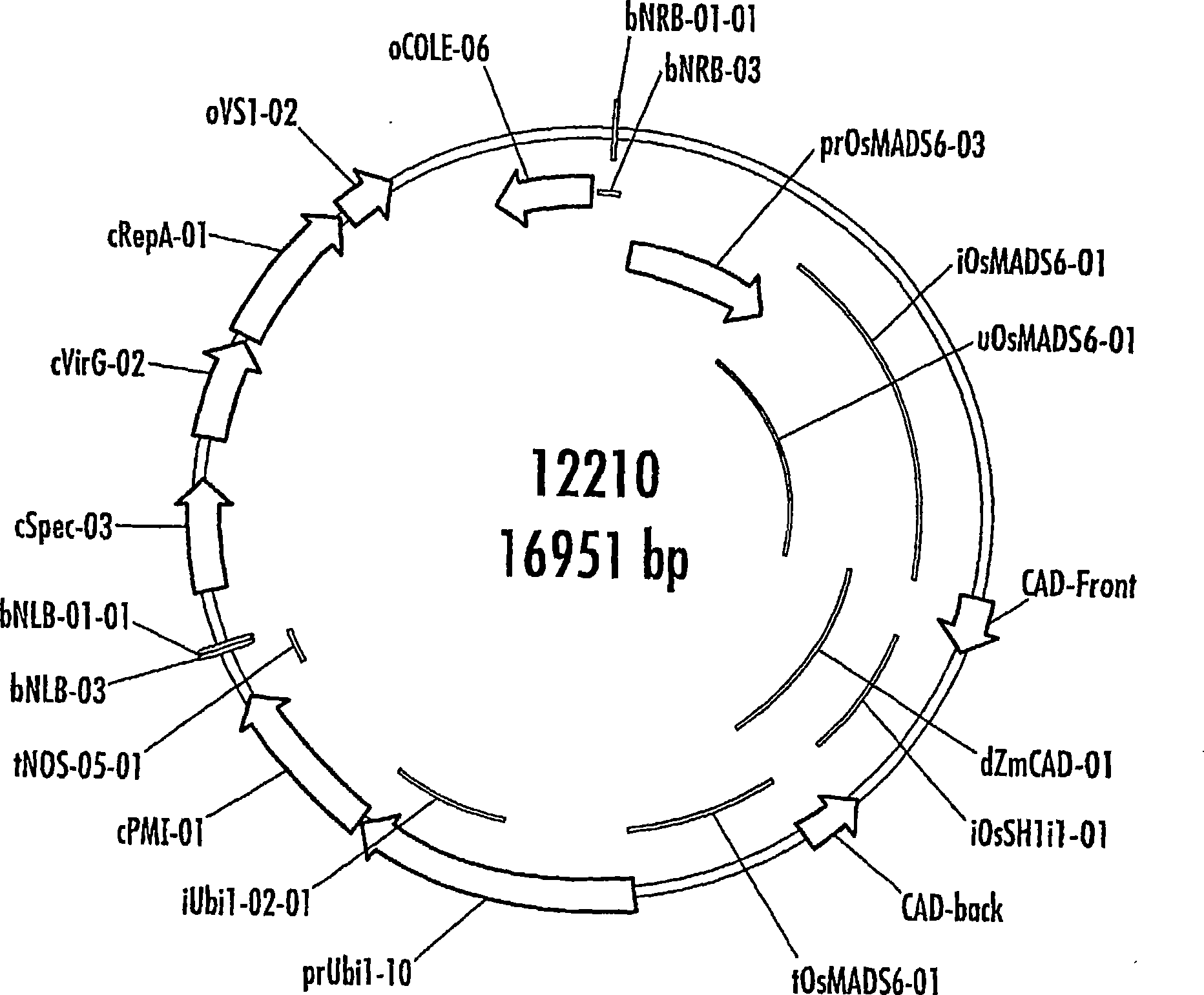
[0267] T1 CAD results select pSyn12210
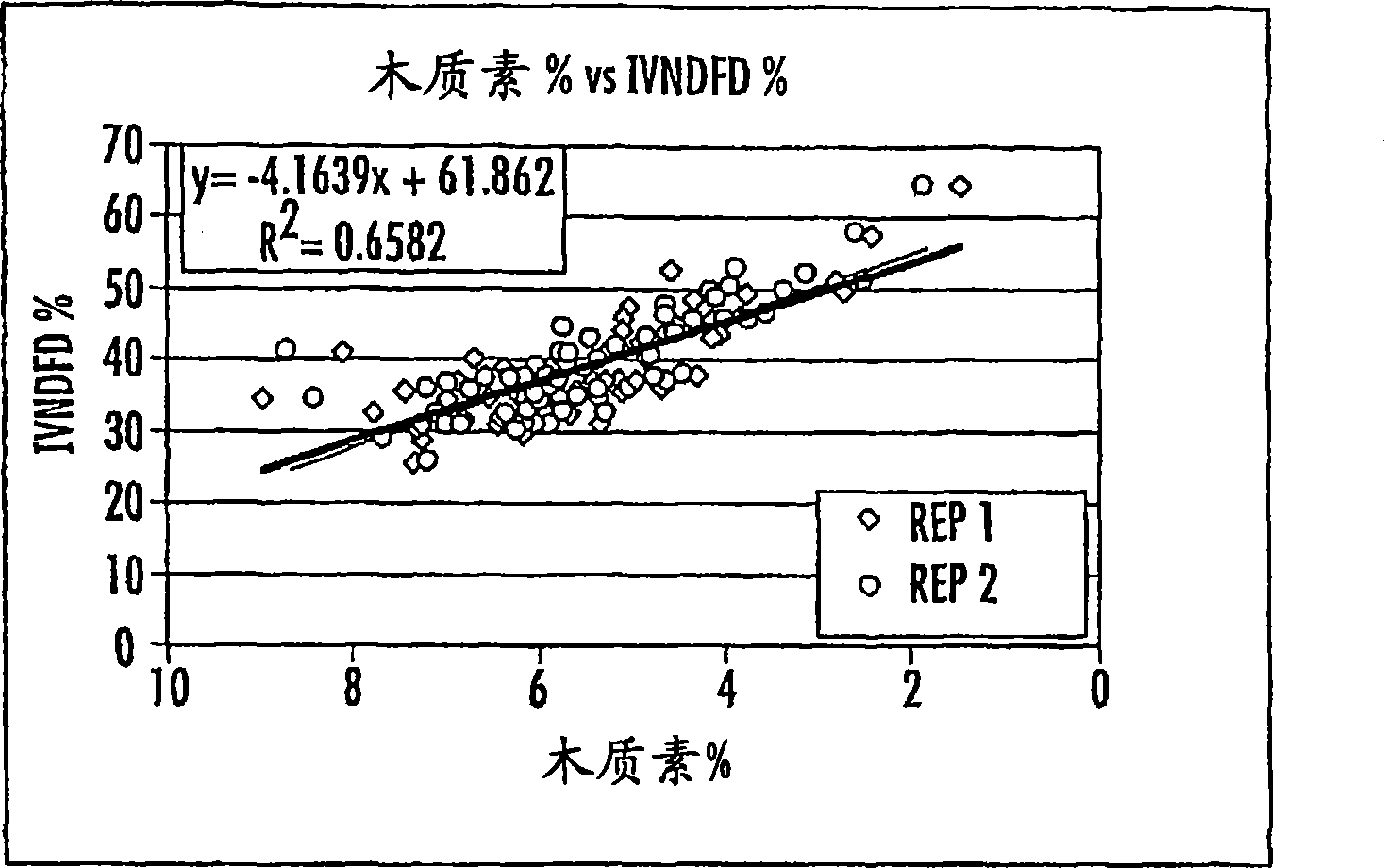
[0268] T1 cob samples from a total of 15 transgenic results (10 low-copy, 3 medium-copy and 2 high-copy) contained 65 lines (28 low-copy, 14 medium-copy, 5 high-copy and 18 Blank strain control), which were sent to MSU for NDF (fiber), ADL (lignin), and IVNDFD (in vitro NDF digestibility) analysis. Also included are 3 BM3 congeners and 2 hybrid tests. We compared the differences between individual lines of the same transgene result in the transgene result (transgene vs blank comparison), or the difference between the low copy, medium copy and high copy result with BM3 positive or negative control and hybridization test. Although some of these became the top 16 lines described below, none of them showed a sustained decrease in lignin in subsequent assays. The data are shown in Table 1, and the analysis method used is as described below.
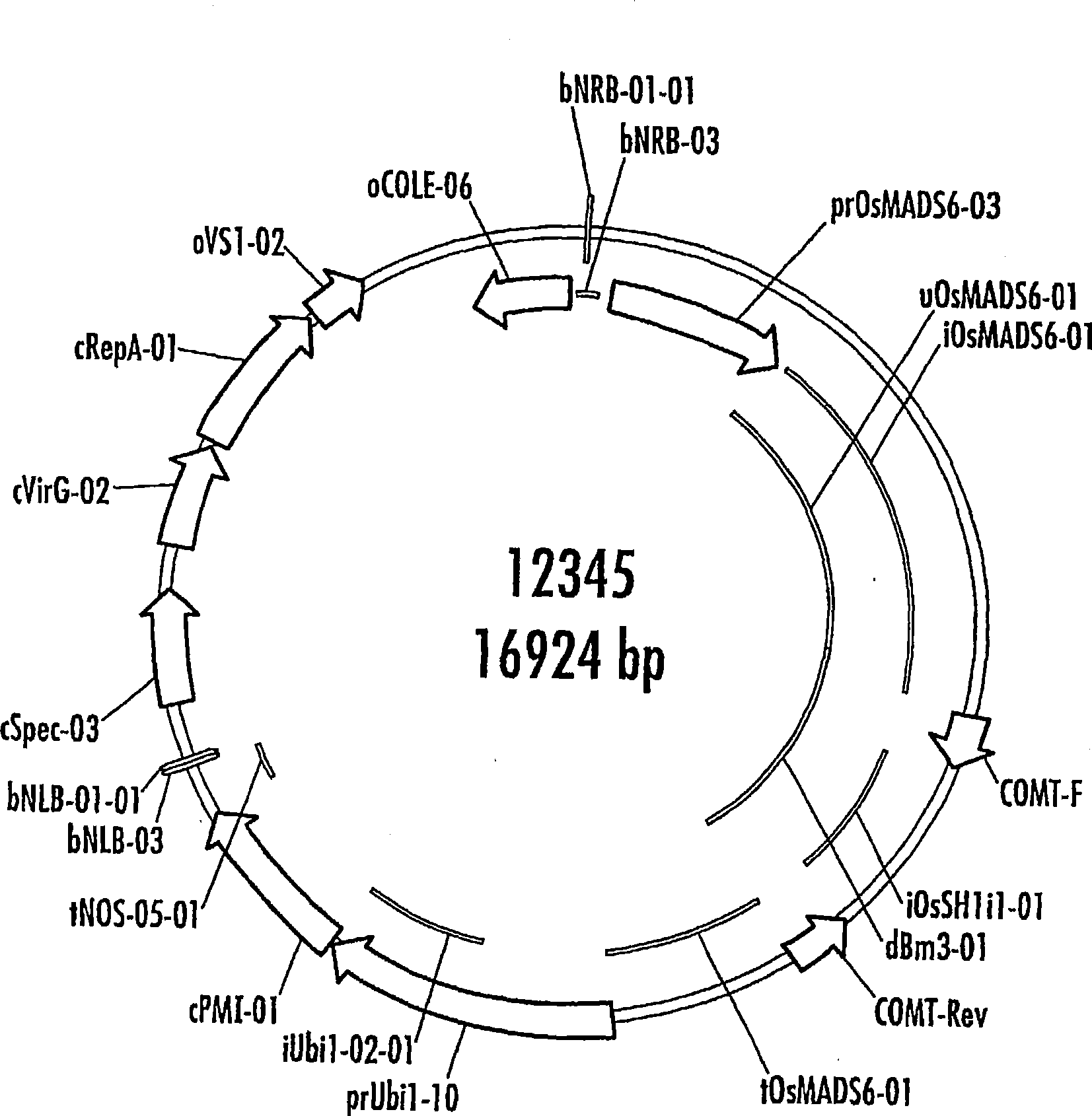
[0269] T1 COMT result selection (pSyn12345)
[0270] T1 cob analysis: A total of 41 transgen...
Embodiment 3
[0407] CAD / COMT double knockout
[0408] Co-expression of dsRNAi constructs of CAD and COMT driven by the OsMADs6 promoter can be achieved in one construct. Using the transformation procedure described in Example 1, transgenic maize bearing such a construct was produced. The sequences of the OsMADs6 promoter and the RNAi constructs are shown herein, and the assays described above were used to determine lignin content, among others. Cobs with reduced lignin content produced in this way can be used with figure 1 Those cobs produced by the plasmids of or 2 were used to the same extent and for the same purpose.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com