Engineering bacteria for over-expressing phosphoglucomutase gene and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene and construction method
A technology of phosphorylase gene and glucose phosphate, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of unclear regulation mechanism and low flocculation activity of polysaccharide flocculants, and achieves the effects of reducing cost, increasing yield and increasing yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: the construction of recombinant expression vector PHY300-pgcA-gtaB1
[0029] Design PCR primers for amplifying the pgcA gene fragment.
[0030] The upstream and downstream primers are:
[0031] Upstream primer 1: GAGGAAAATCGGTACATGAGCTGGAGAACGAG
[0032] Downstream primer 2: GACTGCTTTTTTACTTTCATTCAATTTGAAGTCGCTTTTA
[0033] Design PCR primers for amplifying the gtaB1 gene fragment.
[0034] The upstream and downstream primers are:
[0035] Upstream primer 3: TAAAAGCGACTTCAAATTGAATGAAAGTAAAAAAAGCAGTC
[0036] Downstream primer 4: CTTTTCTTCTCGAGATCATTGCCATGCTCCTT
[0037] Using Bacillus licheniformis CGMCC 2876 genomic DNA as a template, perform the following PCR program: (1) 94°C, 5min; (2) 94°C, 30s; (3) 55°C, 30s; (4) 72°C, 1min, step (2) )~(4) Repeat 35 cycles; (5) 72°C, 10min, 4°C storage.
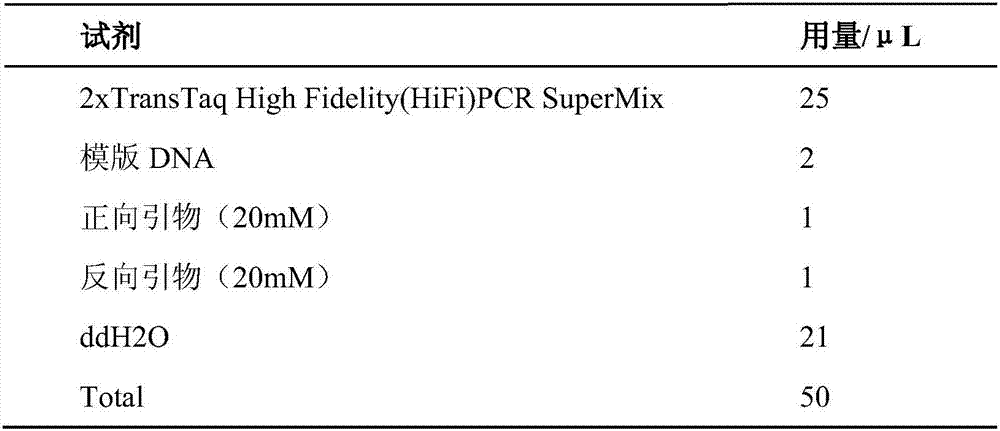
[0038] The PCR reaction system is shown in Table 1.
[0039] Table 1
[0040]
[0041] Primer 1 and primer 4 were used as upstream and downstream primer...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: the construction of bacillus licheniformis genetically engineered bacteria HN301-5
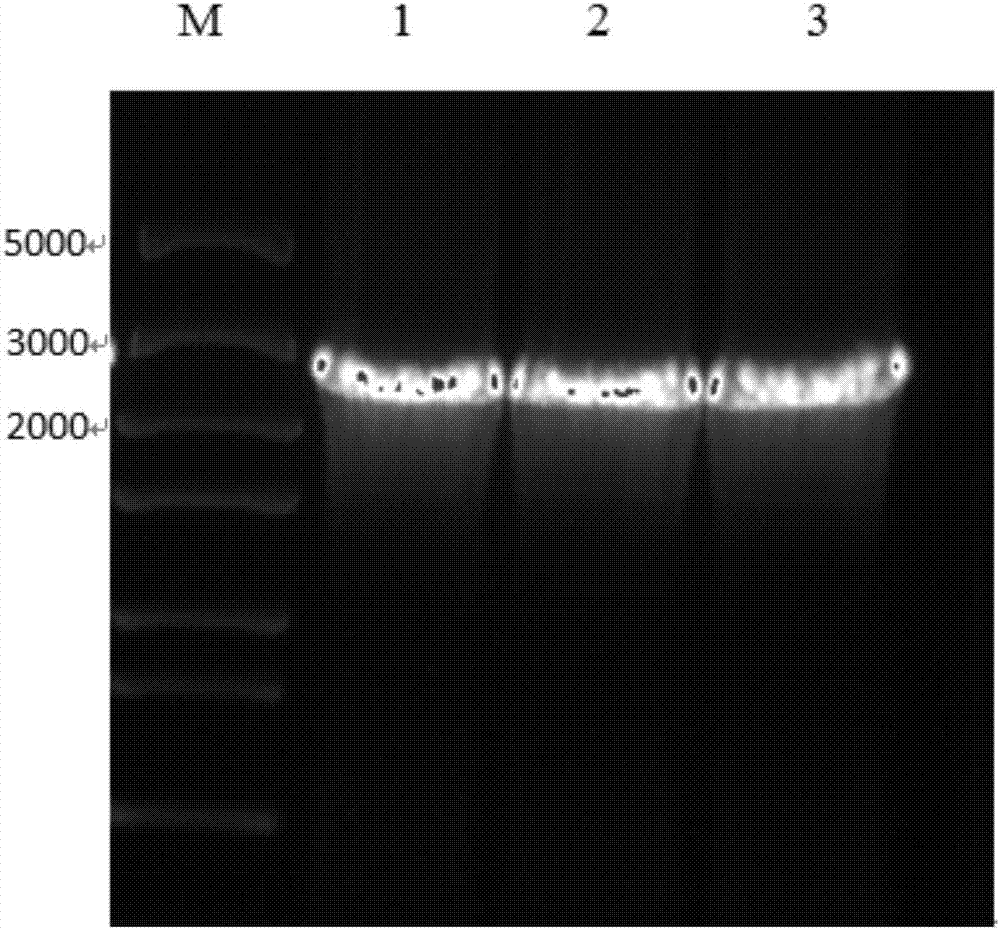
[0048] After the PHY300-pgcA-gtaB1 overexpression plasmid was extracted and concentrated, it was transformed into Bacillus licheniformis by electric shock, recovered at 37°C for 5 hours, coated with a tetracycline-resistant plate, and cultured at 37°C for 12 hours to screen transformants. After the transformant was extracted from the plasmid, it was verified by PCR (such as figure 1 ). Thus, the Bacillus licheniformis engineering strain HN301-5 overexpressing the phosphoglucomutase gene pgcA and the uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene gtaB1 was obtained.
[0049] The specific steps of electroconversion are as follows:
[0050] Preparation of Bacillus licheniformis competent:
[0051] (1) Inoculate a ring of B.licheniformis in 50mL LB medium, culture at 37°C, 200r / min overnight for 12h;
[0052] (2) Take 1 mL of the overnight culture solution and put it i...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: Utilize Bacillus licheniformis and its genetically engineered bacteria fermentation to prepare polysaccharide flocculant
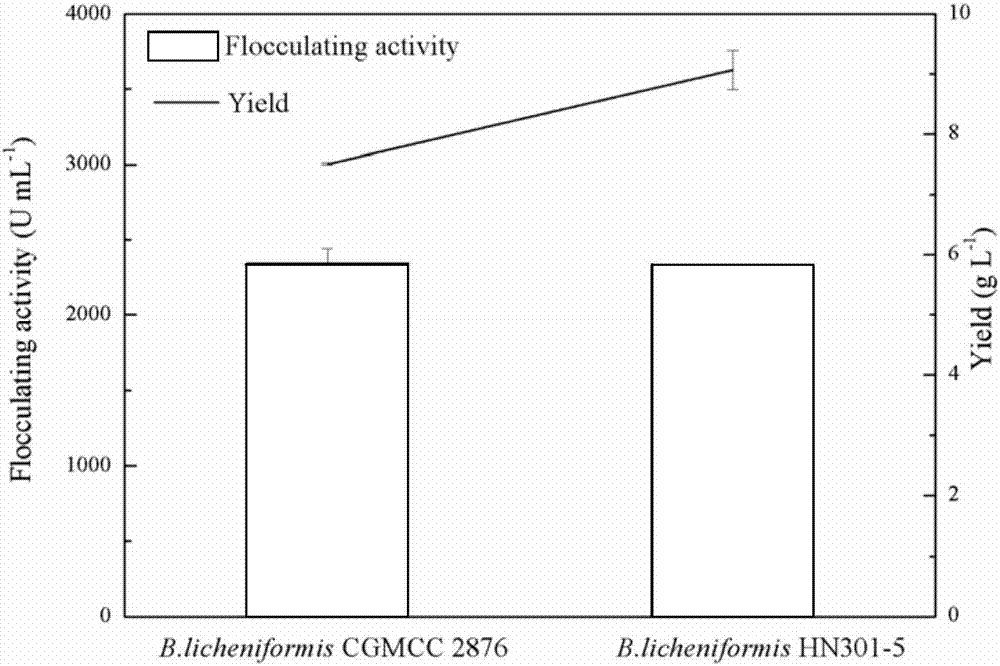
[0062] Bacillus licheniformis CGMCC 2876 starting strain and the genetically engineered bacterium described in Example 2 were inoculated in liquid seed culture medium, 37 ℃, 200r / min cultivated 16h, prepared seed culture liquid, with the inoculum size of 4% (V / V) Inoculate in the polysaccharide flocculant fermentation medium, culture at 37°C, 200r / min, and carry out the experiment of producing polysaccharide flocculant by fermentation. After 56 hours, the flocculation activity of the fermentation broth and the production of the polysaccharide flocculant (such as figure 2 ). The crude extraction yield of the polysaccharide flocculant of pgcA-gtaB1 tandem gene overexpression recombinant engineered bacteria was 9.07g / L, which was 20.77% higher than the original strain crude extraction yield of 7.51g / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com