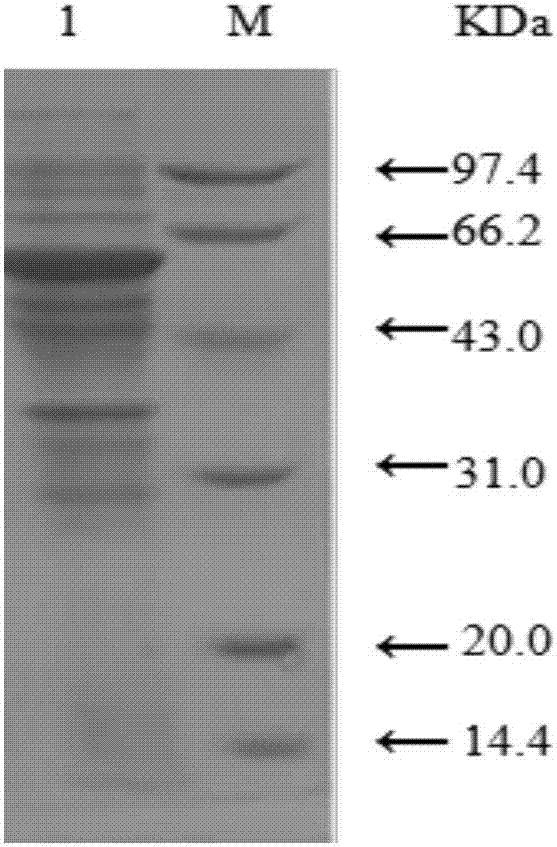
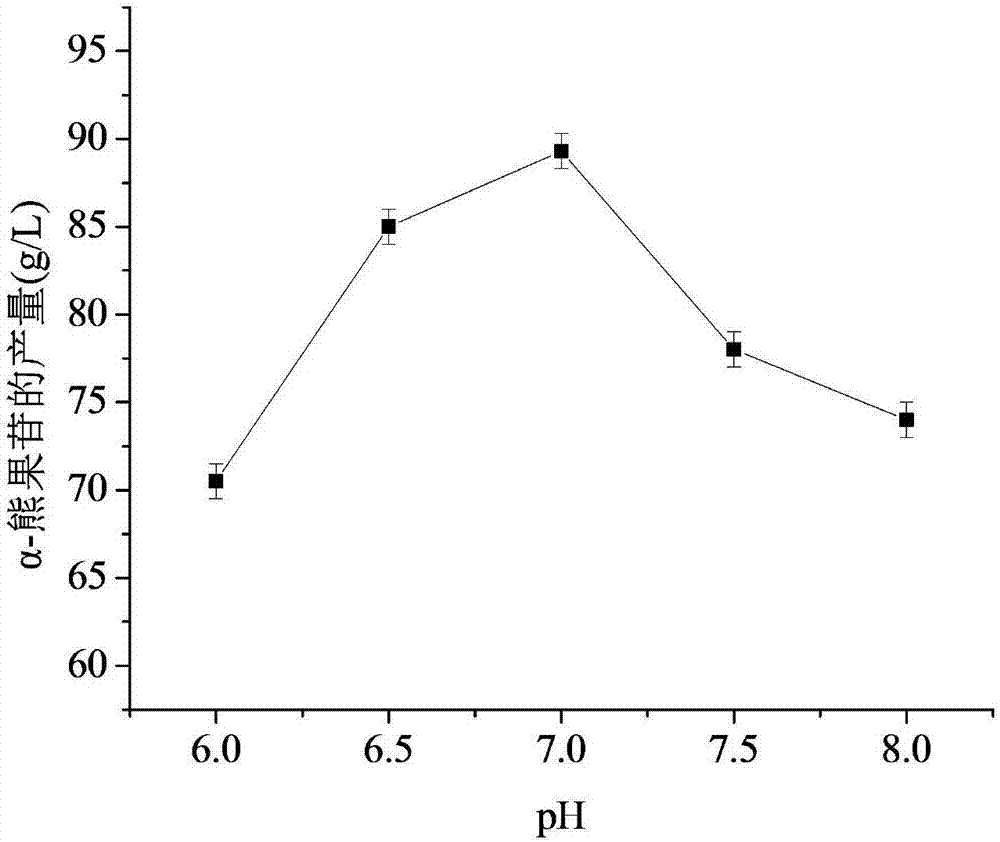
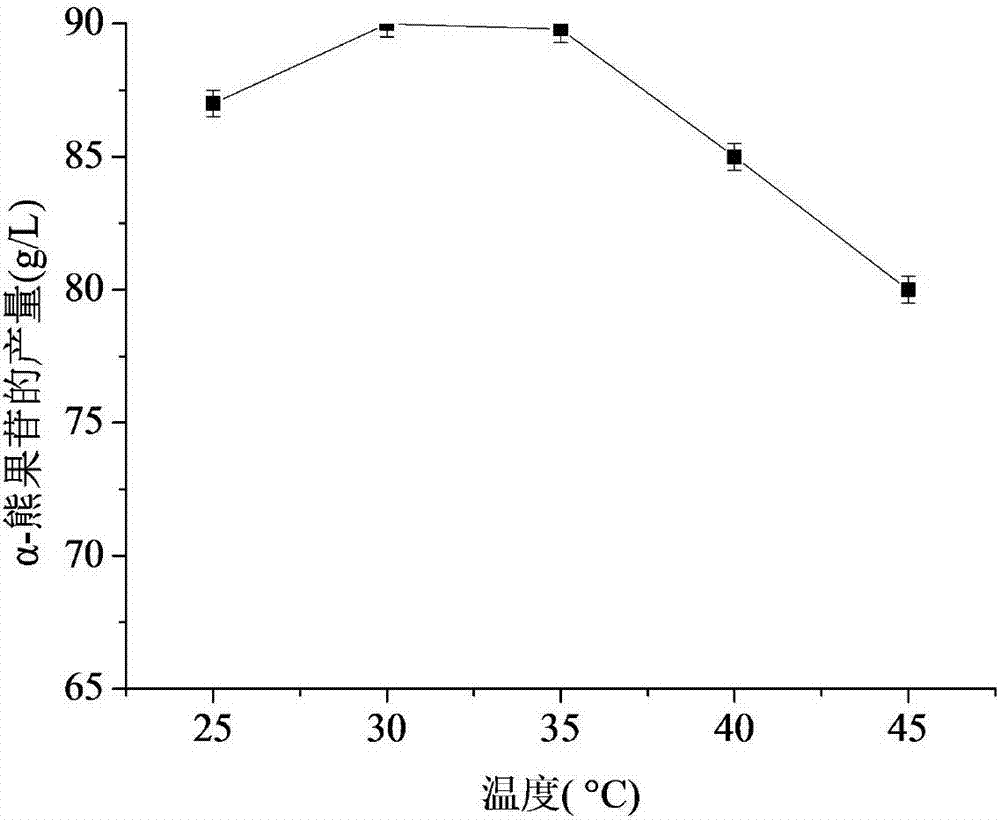
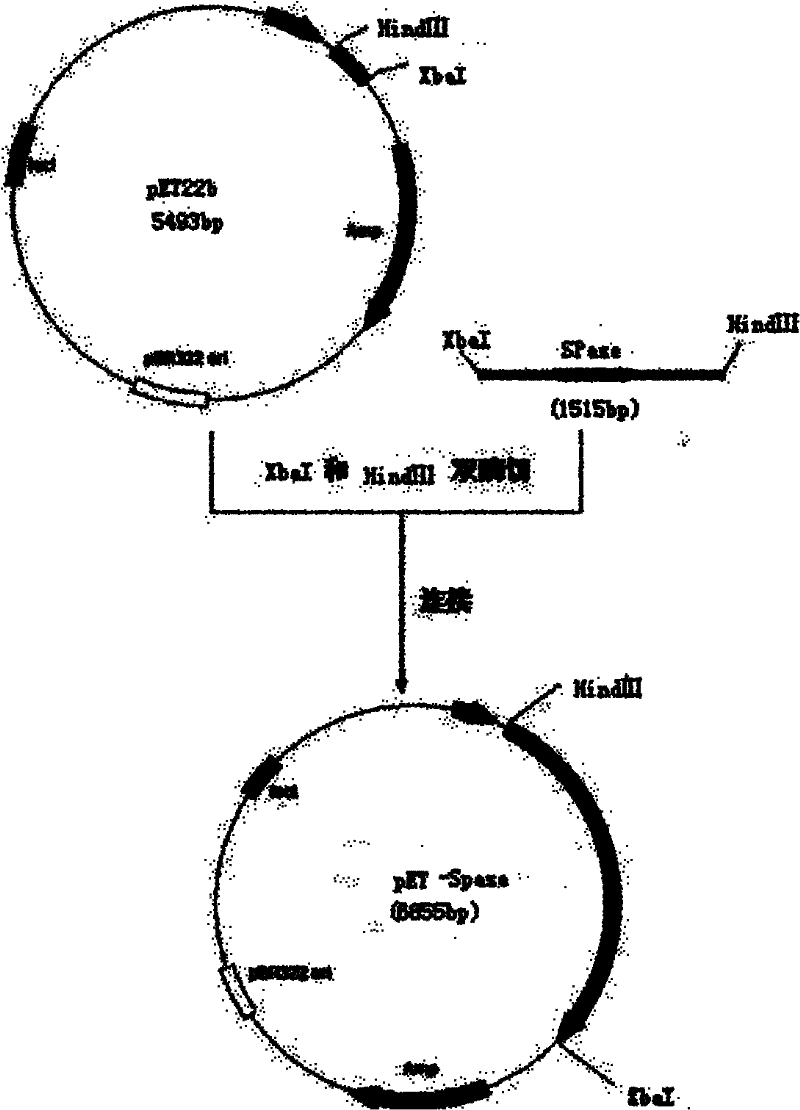
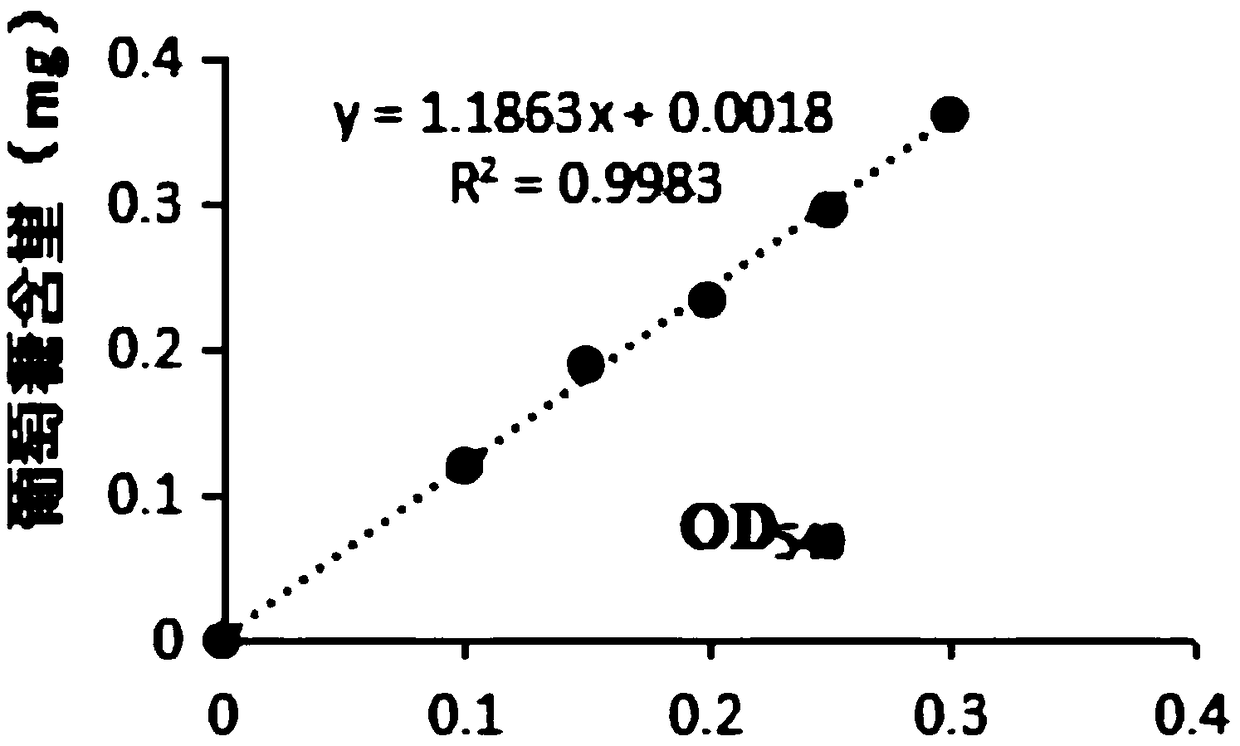
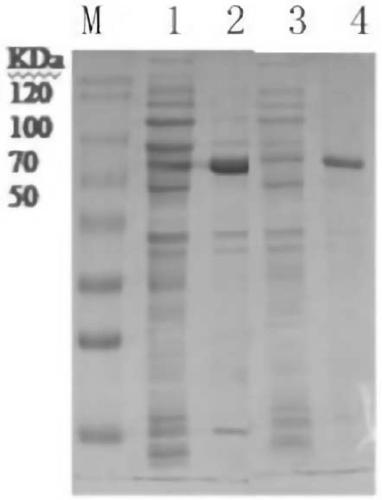
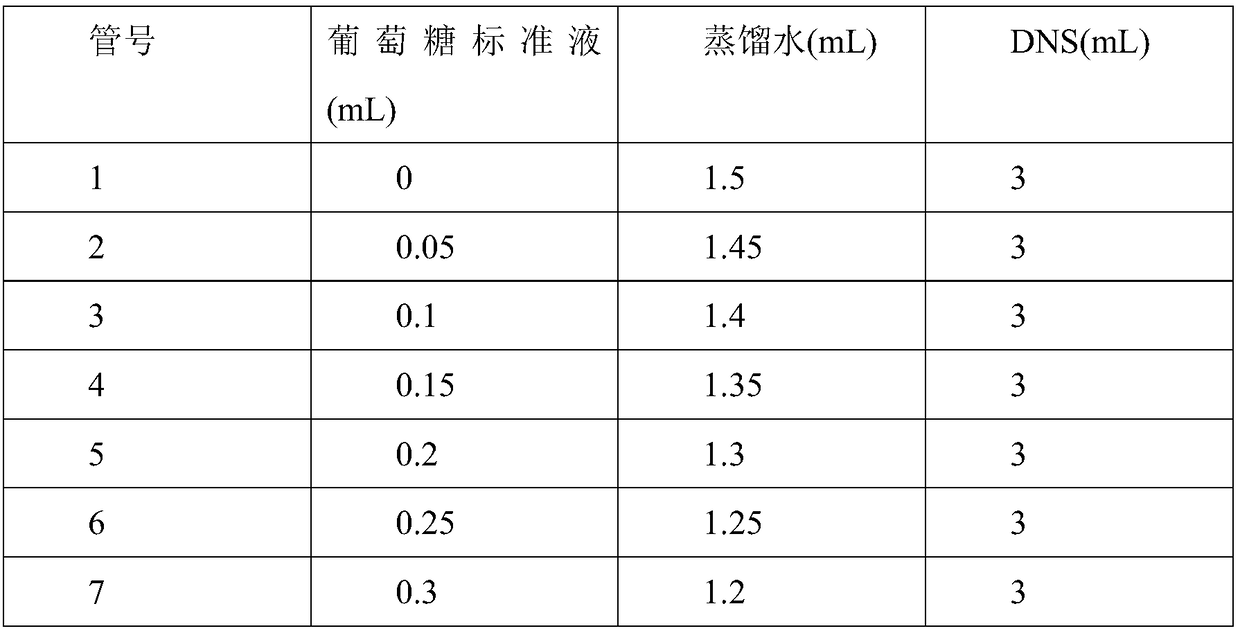
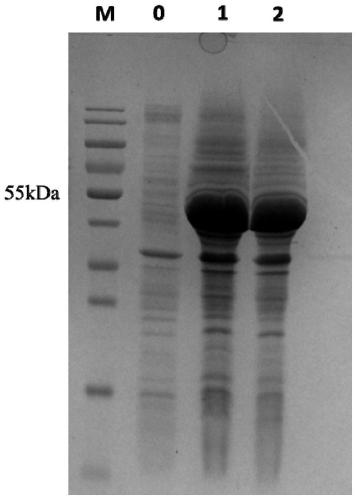
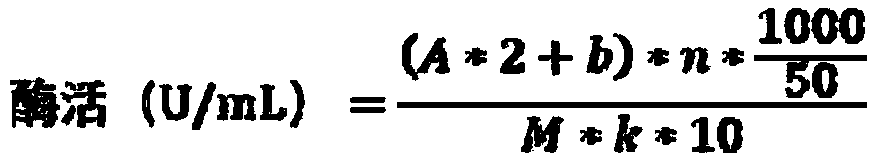Patents
Literature
103 results about "Sucrose phosphorylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
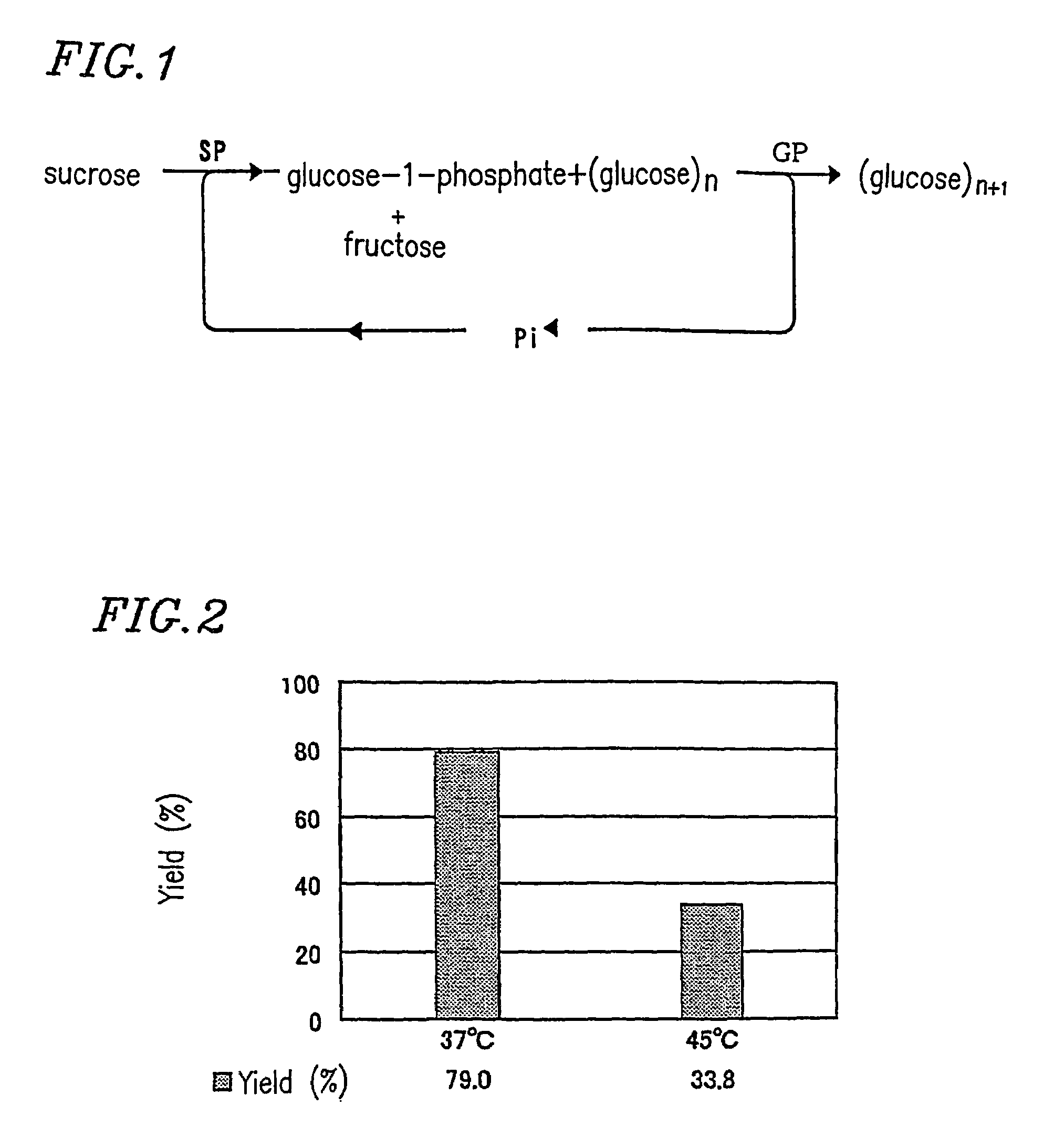
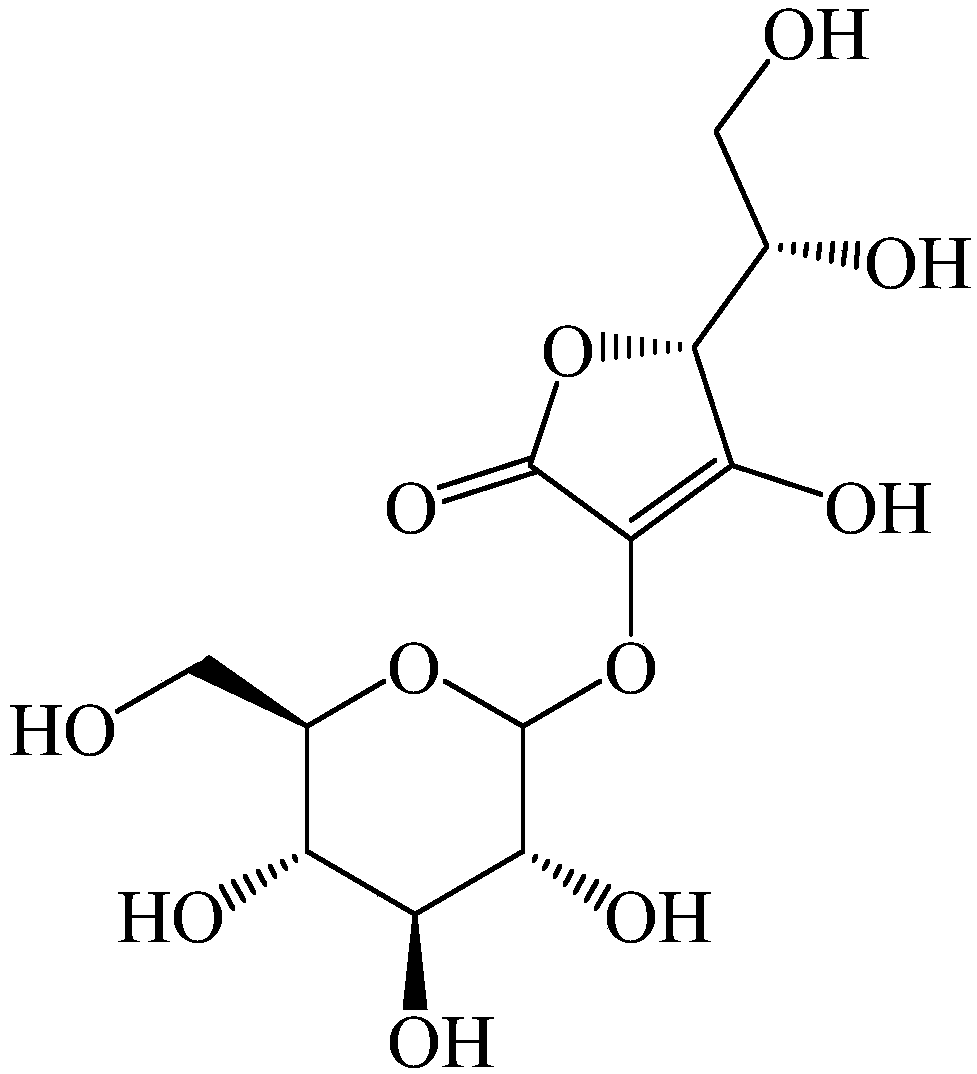
Sucrose phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.7) is an important enzyme in the metabolism of sucrose and regulation of other metabolic intermediates. Sucrose phosphorylase is in the class of hexosyltransferases. More specifically it has been placed in the retaining glycoside hydrolases family although it catalyzes a transglycosidation rather than hydrolysis. Sucrose phosphorylase catalyzes the conversion of sucrose to D-fructose and α-D-glucose-1-phosphate. It has been shown in multiple experiments that the enzyme catalyzes this conversion by a double displacement mechanism.
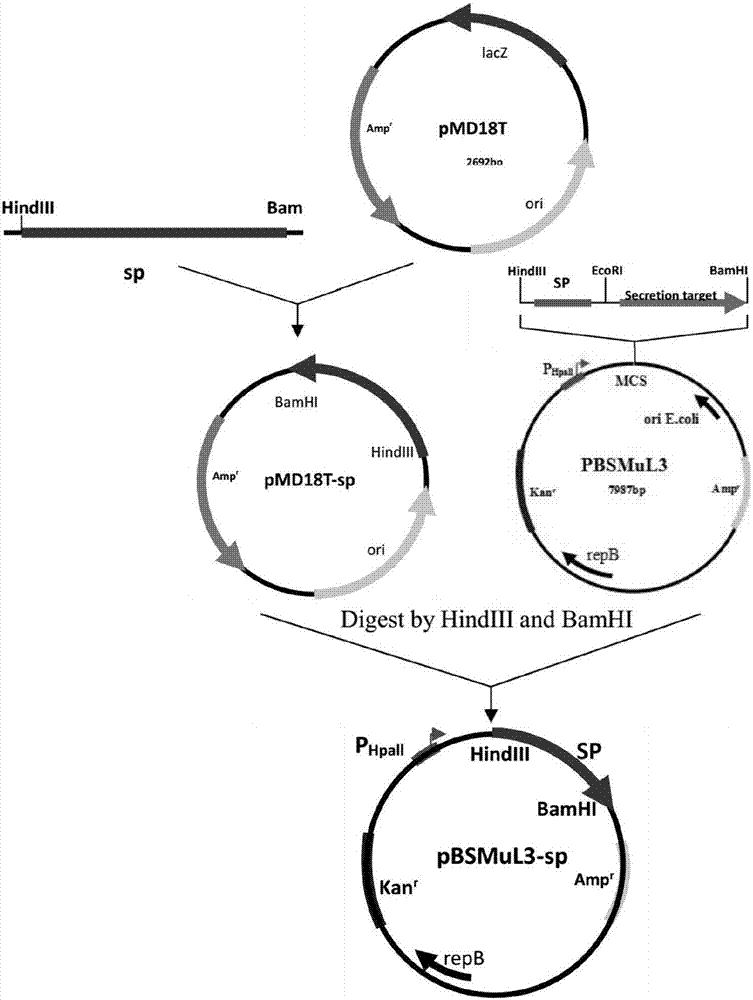
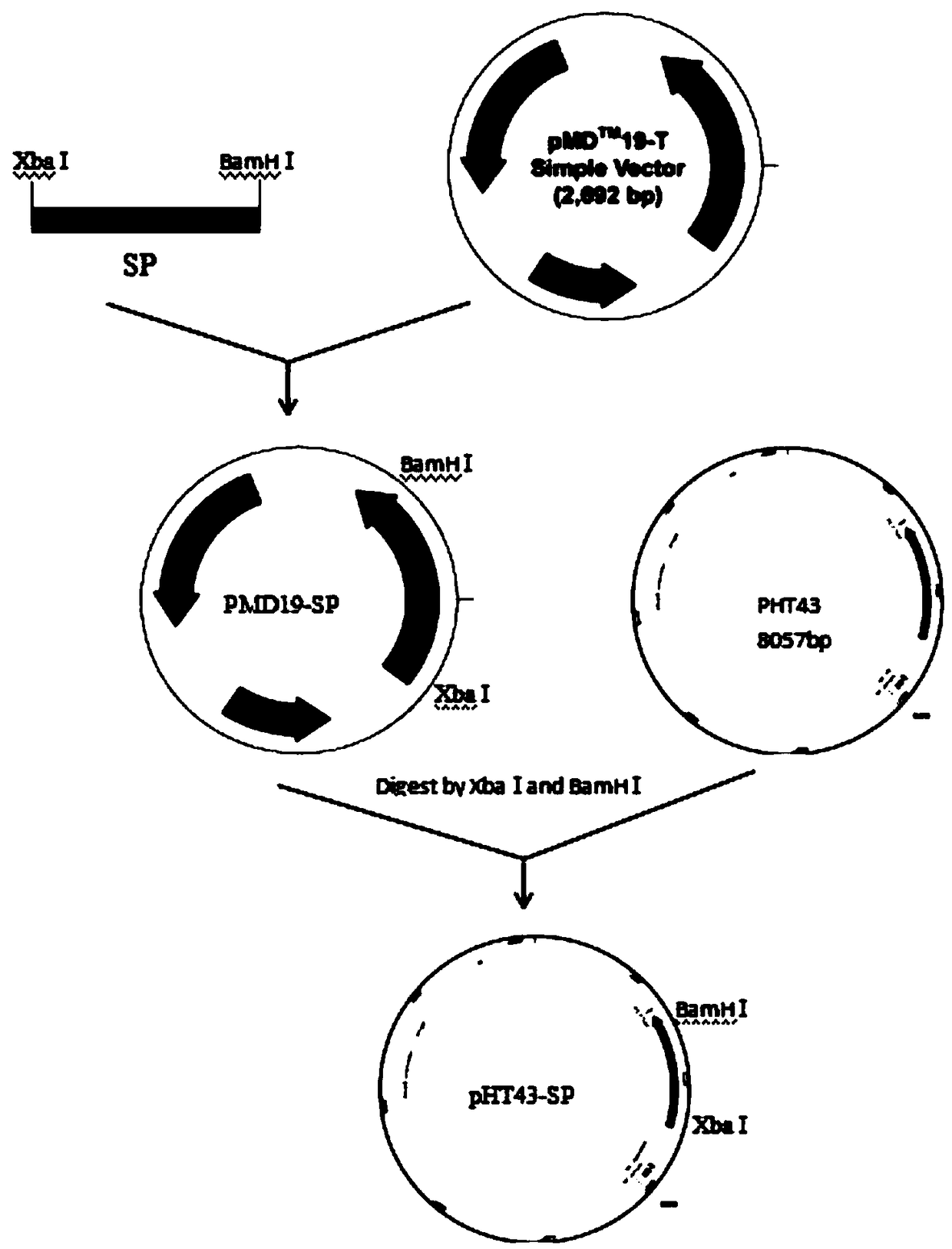
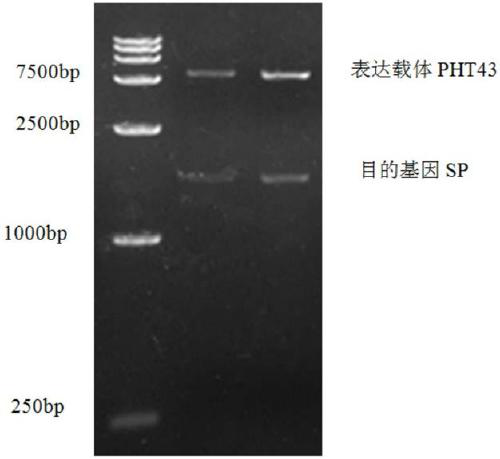
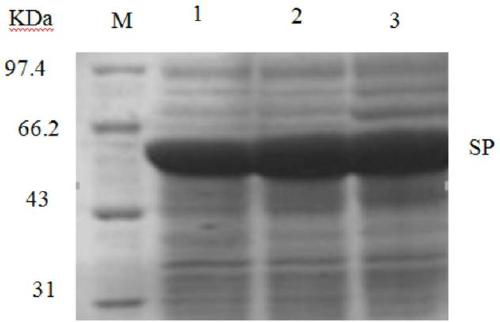
Recombinant Bacillus subtilis for expressing L.mesenteroides sourced sucrose phosphorylase
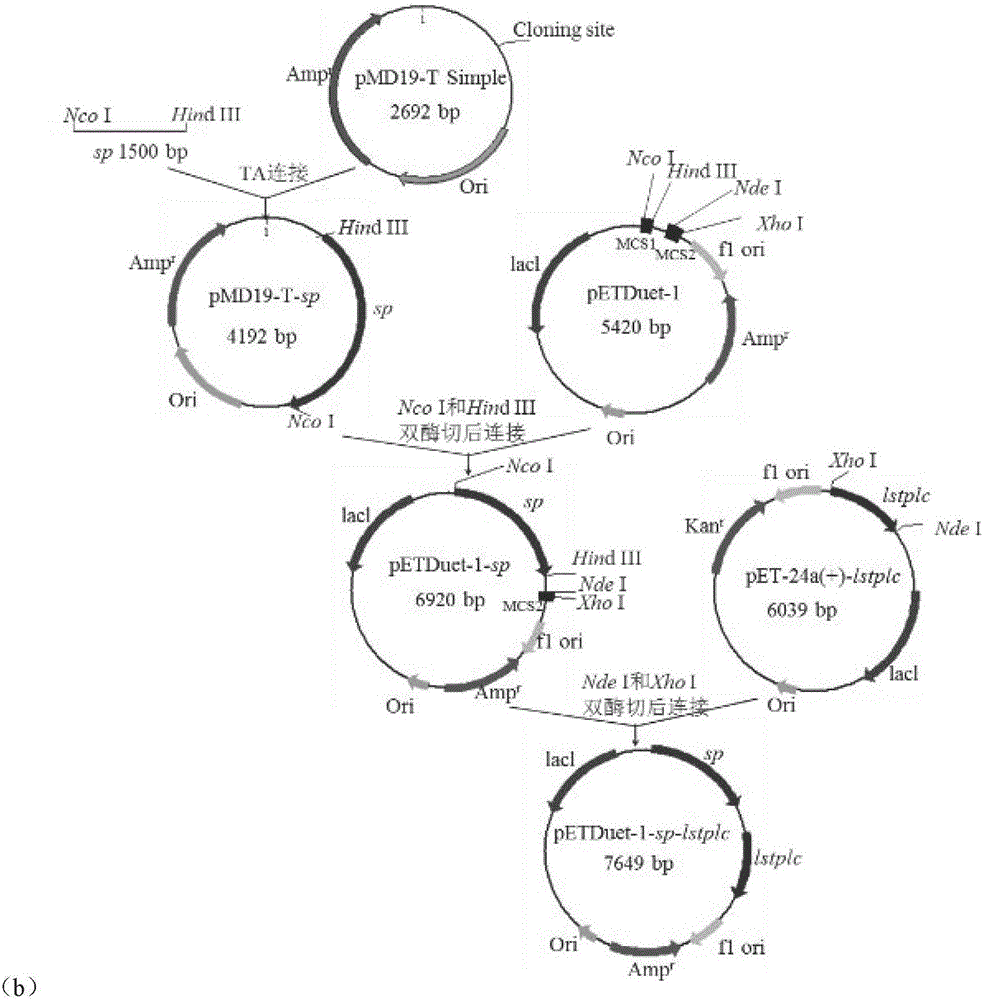
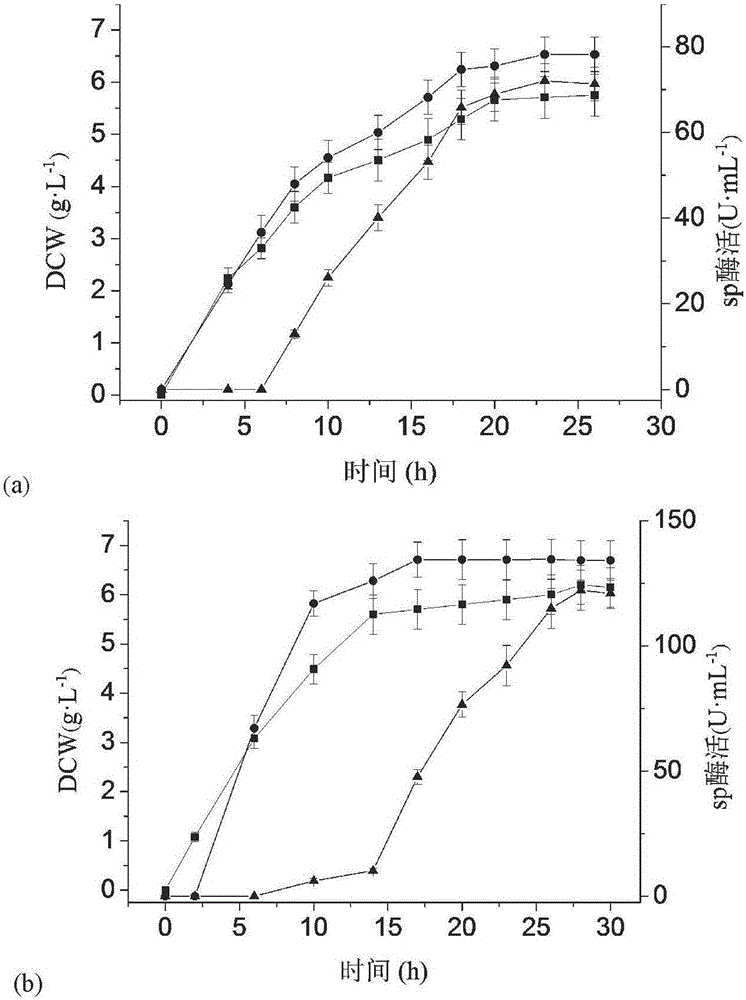
The invention discloses recombinant Bacillus subtilis for expressing L.mesenteroides sourced sucrose phosphorylase, belonging to the technical fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The recombinant Bacillus subtilis is prepared by the steps of acquiring a target gene of the L.mesenteroides sourced sucrose phosphorylase by virtue of an artificially synthesized SPase gene, a design primer and PCR, constructing a recombinant plasmid pBSMuL3-SP, and converting the recombinant plasmid pBSMuL3-SP into Bacillus subtilis (CCTCC M2016536), so as to obtain the recombinant Bacillus subtilis. The recombinant Bacillus subtilis is used as a strain for fermenting and producing SPase. The recombinant Bacillus subtilis has relatively good effect when being used for preparing alpha-arbutin. By recombining and expressing the sucrose phosphorylase by taking food-safety Bacillus subtilis as an expression host, the enzyme producing level is high, the separation and purification are convenient, the fermentation raw materials are wide in sources, and the production cost is relatively low.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Thermostable sucrose phosphorylase
InactiveUS20130029384A1TransferasesEnzyme stabilisationCross-linked enzyme aggregateSucrose phosphorylase
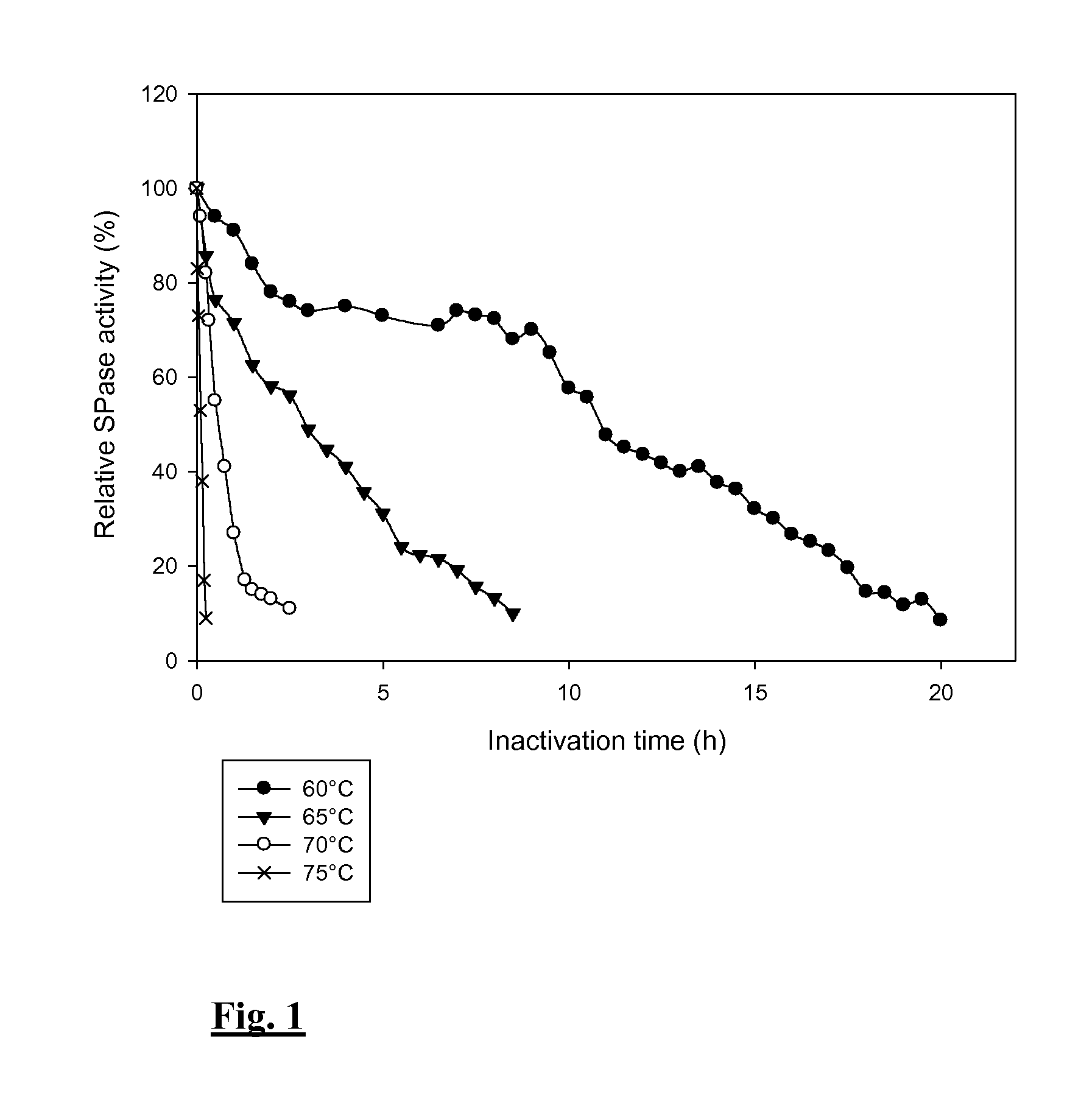
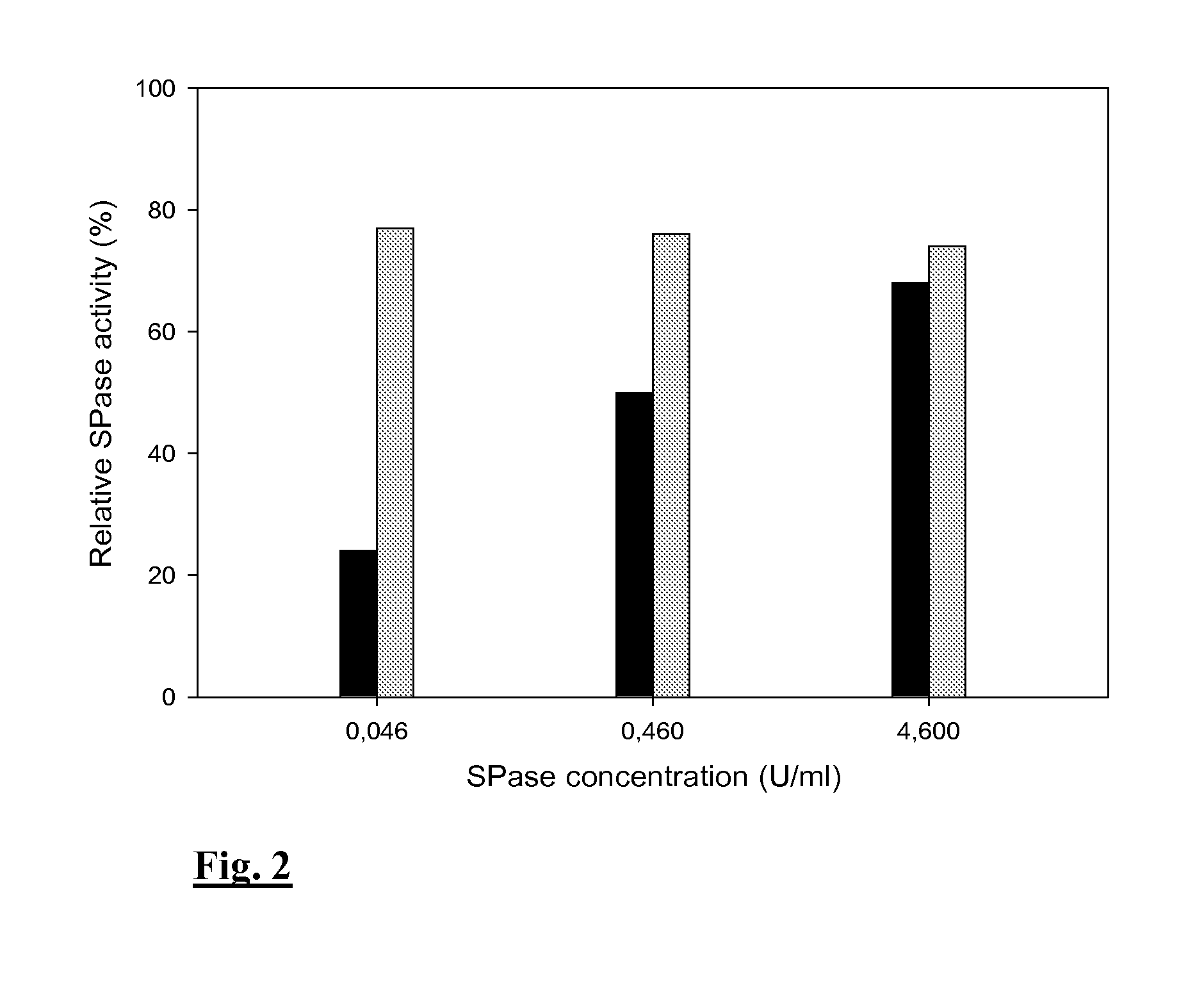
The present invention relates to a sucrose phosphorylase from Bifidobacterium adolescentis which is useful as a biocatalyst in carbohydrate conversions at high temperatures. Indeed, the biocatalysts of the present invention are enzymatically active for a time period of at least 16 h and up to 1 to 2 week(s) at a temperature of at least 60° C. The biocatalysts of the present invention are: a) immobilized on an enzyme carrier, or b) are part of a cross-linked enzyme aggregate (CLEA), and / or c) are mutated, and / or d) are enzymatically active in the continuous presence of their substrate.
Owner:UNIV GENT
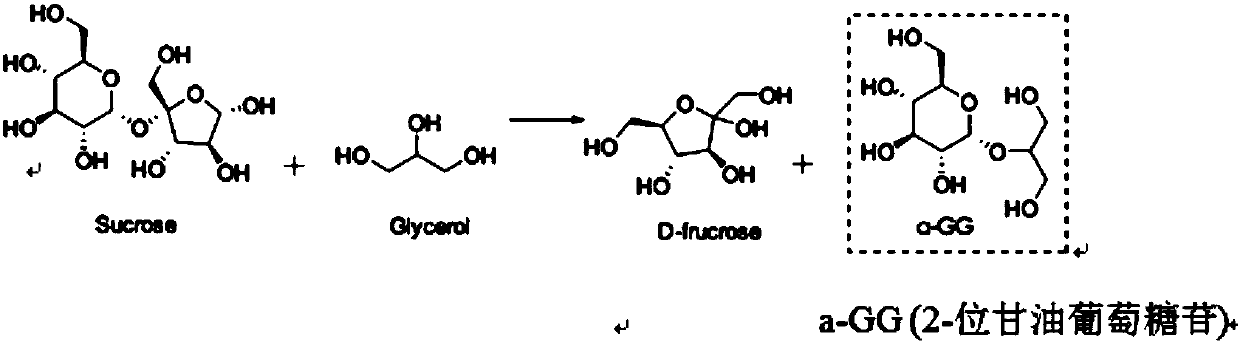
Sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof in production of glycerol glucoside
ActiveCN107858335AReduce outputStrong specificityGenetic engineeringFermentationSucrose phosphorylaseGlycerol
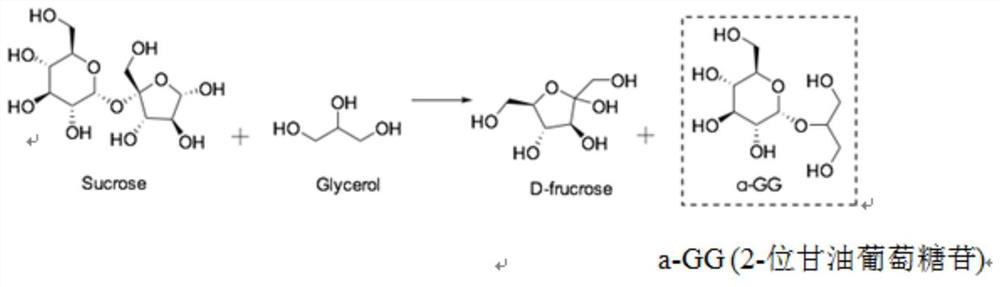
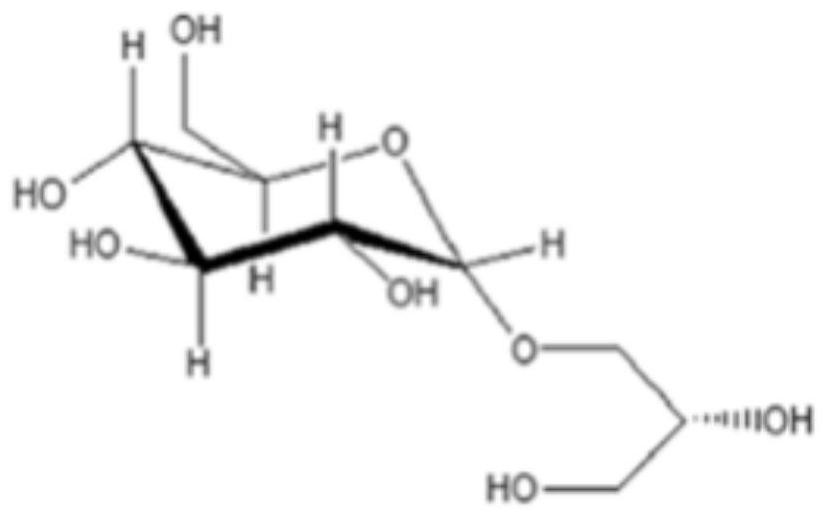
The invention aims to provide a sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof in the production of glycerol glucoside. The sucrose phosphorylase mutant which is protein is obtained by replacingthe 341st-site amino acid residue, which is leucine, of sucrose phosphorylase with other amino acid residues. The protein can be BaSP / L341W protein obtained by replacing the 341st-site amino acid residue, which is the leucine, of the sucrose phosphorylase with tryptophan. The sucrose phosphorylase mutant has the advantages that by the primer point mutation of the 341st-site amino acid residue ofthe wild sucrose phosphorylase derived from bifidobacterium adolescentis, the specificity of 2-glycerol glucoside produced by using the sucrose phosphorylase mutant, sucrose and glycerin as the raw materials, and the yield of the byproduct 1-glycerol glucoside is lowered; the sucrose phosphorylase mutant has an important application value in the field of the production of the 2-glycerol glucoside.
Owner:NANJING HUASHI NEW MATERIAL
Production method and preparation method of glucans
InactiveUS7229801B2Reduce the amount requiredIncrease temperatureSugar derivativesHydrolasesInorganic phosphateSucrose phosphorylase
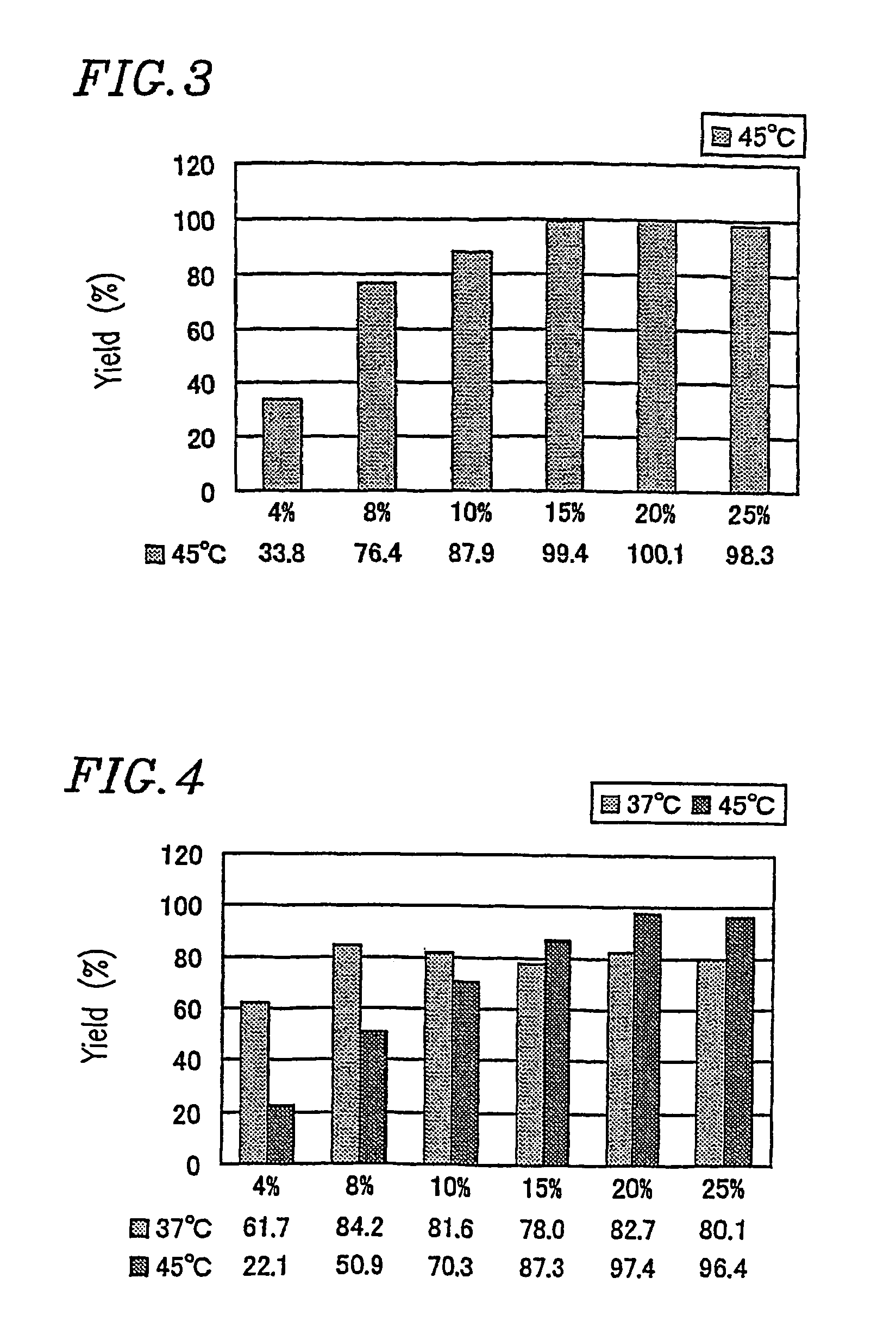
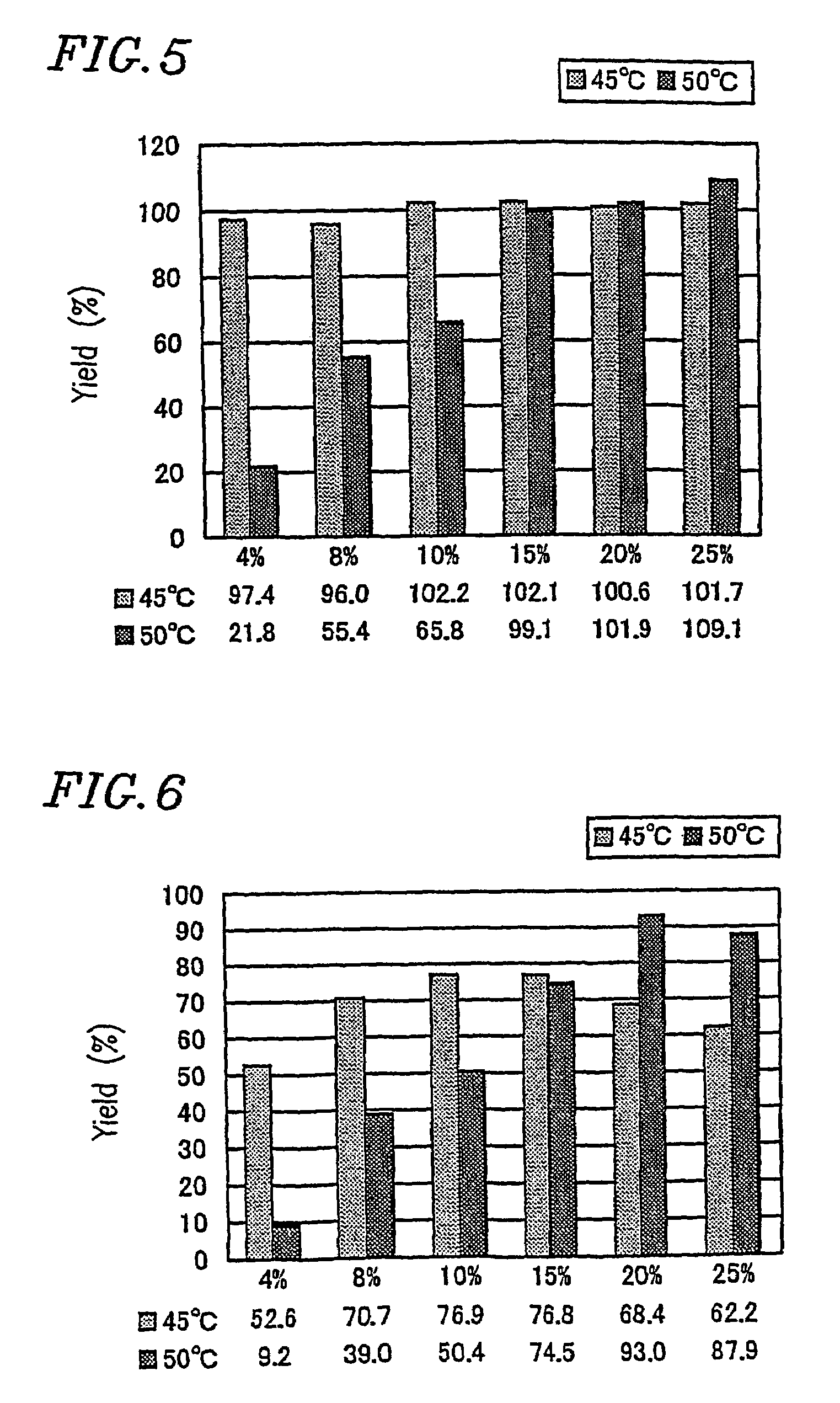
A first method for producing glucan comprises the step of allowing a reaction solution containing sucrose, a primer, inorganic phosphate or glucose-1-phosphate, sucrose phosphorylase, and glucan phosphorylase to react to produce glucans. The maximum value of the sucrose-phosphate ratio of the reaction solution from the start of the reaction to the end of the reaction is no more than about 17. A second method for producing glucan comprises the step of allowing a reaction solution containing sucrose, a primer, inorganic phosphate or glucose-1-phosphate, sucrose phosphorylase, and glucan phosphorylase to react to produce glucans. The reaction is conducted at a temperature of about 40 C to about 70 C.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein
PendingCN106754601ALarge domestic and foreign market demandImprove permeabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExtracellularProtein target
The invention discloses a method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Through co-expression phospholipase C, intracellular positioning protein is released to the outsides of cells by means of nonspecific leaking, and high-performance phospholipase C and co-expression recombinant bacteria high in target protein extracellular enzyme activity are obtained by screening. Enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular sucrose phosporylase co-expressing sucrose phosphorylase and phospholipase C is 1445.1U mL-1, and enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular trehalase co-expressing trehalase and phospholipase C is 322.3U mL-1. The method can realize extracellular expression of intracellular positioning protein, improve production efficiency and simplify post-extraction process, has wide application value in food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industry and has great demand in market at home and abroad.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing tagatose by using whole-cell catalysis
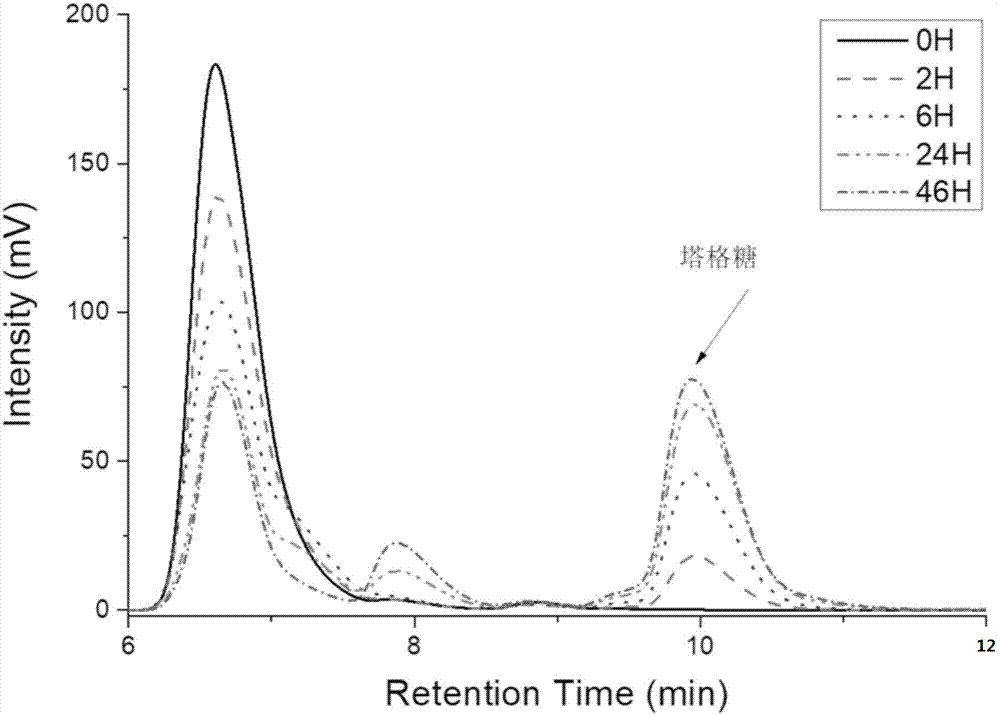
ActiveCN107988286AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliTagatose
The invention discloses a method for preparing tagatose by using whole-cell catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of transferring plasmid containing an alpha-glucan phosphorylase gene (or cellulosic polysaccharide phosphorylase and cellobiose phosphorylase genes, or a sucrose phosphorylase gene), a phosphoglucomutase gene, a glucose phosphate isomerase gene, a 6-phosphate tagatose epimerase gene, and a 6-phosphate tagatose phosphatase gene into engineered escherichia coli, so as to obtain converted bacterial strain; inducing the converted bacterial strain to produce enzyme, and permeabilizing; mixing the permeabilized bacterial strain, establishing a whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction system with starch or starch derivative (or mixture of cellulase and cellulose or cellulose derivative, or sugarcane), and performing the whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction, so as to obtain the tagatose. The method has the advantages that the tagatose is prepared by the whole-cell catalysis; the cost is low, the pollution is low, the yield rate is high, and the like; the method is suitable for preparing the tagatose in a scale way.
Owner:天工生物科技(天津)有限公司
Sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN109423485AStrong specificityReduce outputFermentationGenetic engineeringSucrose phosphorylaseArginine
The present invention discloses a sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is obtained by replacing leucine of the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of sucrose phosphorylase with other amino acid residues. The protein can be BaSP / L341D protein obtained by replacing leucine of the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of sucrose phosphorylase with aspartic acid, and can be BaSP / L341R protein obtained by replacing leucine of the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of sucrose phosphorylase with arginine. Through single-point mutation at the amino acid residue at the number 341 site of wild sucrose phosphorylase derived from Bifidobacterium adolescentis with primers, specificity for producing 2-glycosylglycerol from sucrose and glycerin is significantly improved, and the yield of 1-glycosylglycerol that is a byproduct is reduced. The sucrose phosphorylase mutant has great application value in the field of production of the 2-glycosylglycerol.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacterium for expressing sucrose phosphorylase and application of genetically engineered bacterium
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for expressing sucrose phosphorylase and application thereof, and belongs to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The genetically engineered bacterium has the advantages that a gene shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is subjected to heterologous expression in escherichia coli, recombinant escherichia coli is constructed, and is fermented to produce recombinant sucrose phosphorylase, and enzyme activity in fermented supernatant reaches 40U.mL<-1>; when the recombinant sucrose phosphorylase is used for catalyzing saccharose and hydroquinone to generate alpha-arbutin, a conversion rate can reach 91%; the industrial application potential is higher.
Owner:金韵
Escherichia coli engineering bacteria for expressing recombinant sucrose phosphorylase
InactiveCN102174454ASimplify downstream purificationStrong specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLeuconostoc mesenteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, disclosing escherichia coli engineering bacteria for expressing recombinant sucrose phosphorylase. Sucrose phosphorylase SPase genes which are derived from leuconostoc mesenteroides ATCC 12291 are introduced into escherichia coli. The invention also discloses a construction method of the escherichia coli engineering bacteria for expressing the recombinant sucrose phosphorylase and application thereof. The escherichia coli engineering bacteria for expressing the recombinant sucrose phosphorylase have the characteristics of convenience of operation, stability for expression, high efficiency, low cost, easiness of purification and the like when used for producing the SPase on a scale.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Green tea fermented tea beverage and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a green tea fermented tea beverage and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that green tea leaves are taken and smashed and are subjected to non-thermal sterilization, distilled water, saccharosephosphorylase, other complex enzymes, a carbon source,plant sourceoligopeptide, saccharomycetes and lactic acid bacteria are respectively added, a multi-process synchronized and integrated technology including low temperature digestion, enzymolysis, fermentation and the like is performed, the multi-process synchronized and integrated technology is finished after being completed, residue removal and filtration are performed to obtain green tea fermented tea juice, low temperature digestion of the tea leaves, glycosylation modification of catechin and brewing of nutrition and flavor of the fermented tea beverage are achieved at a time, the stability of the green tea fermented tea beverage is improved, the bitter taste of the product is decreased, the flavor quality of the beverage is improved, and the bioavailability of the catechin is improved. The method is simple and convenient to operate and obvious in effect and has a good popularization and application value and market prospect.
Owner:浙江圣氏生物科技有限公司
Method for improving the thermostability of sucrose phosphorylase (SP)
ActiveUS7968309B2High activityImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSucrose phosphorylaseChemistry
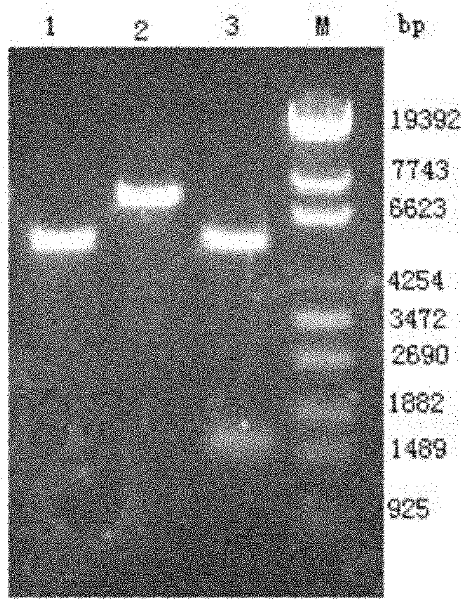
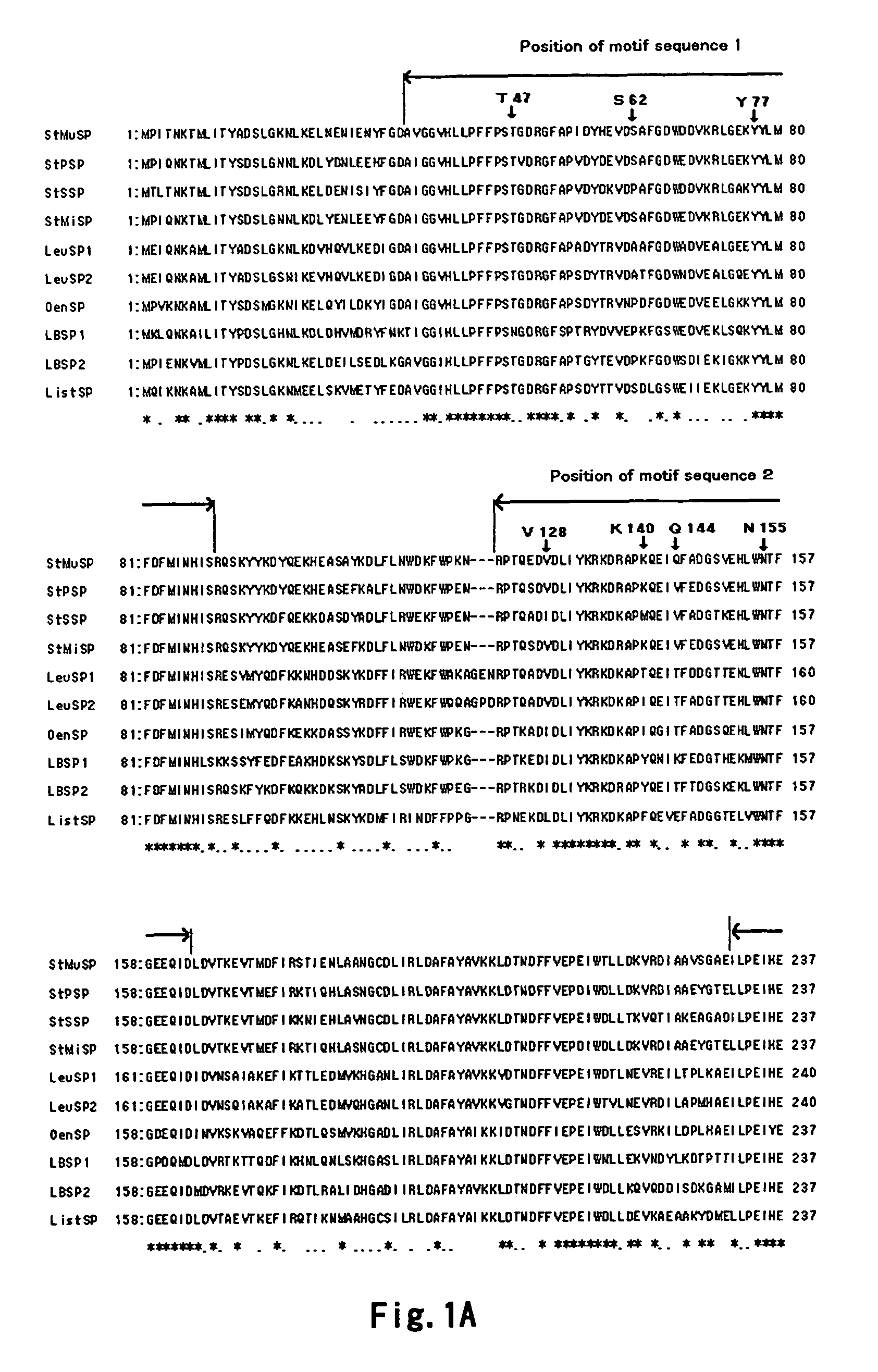
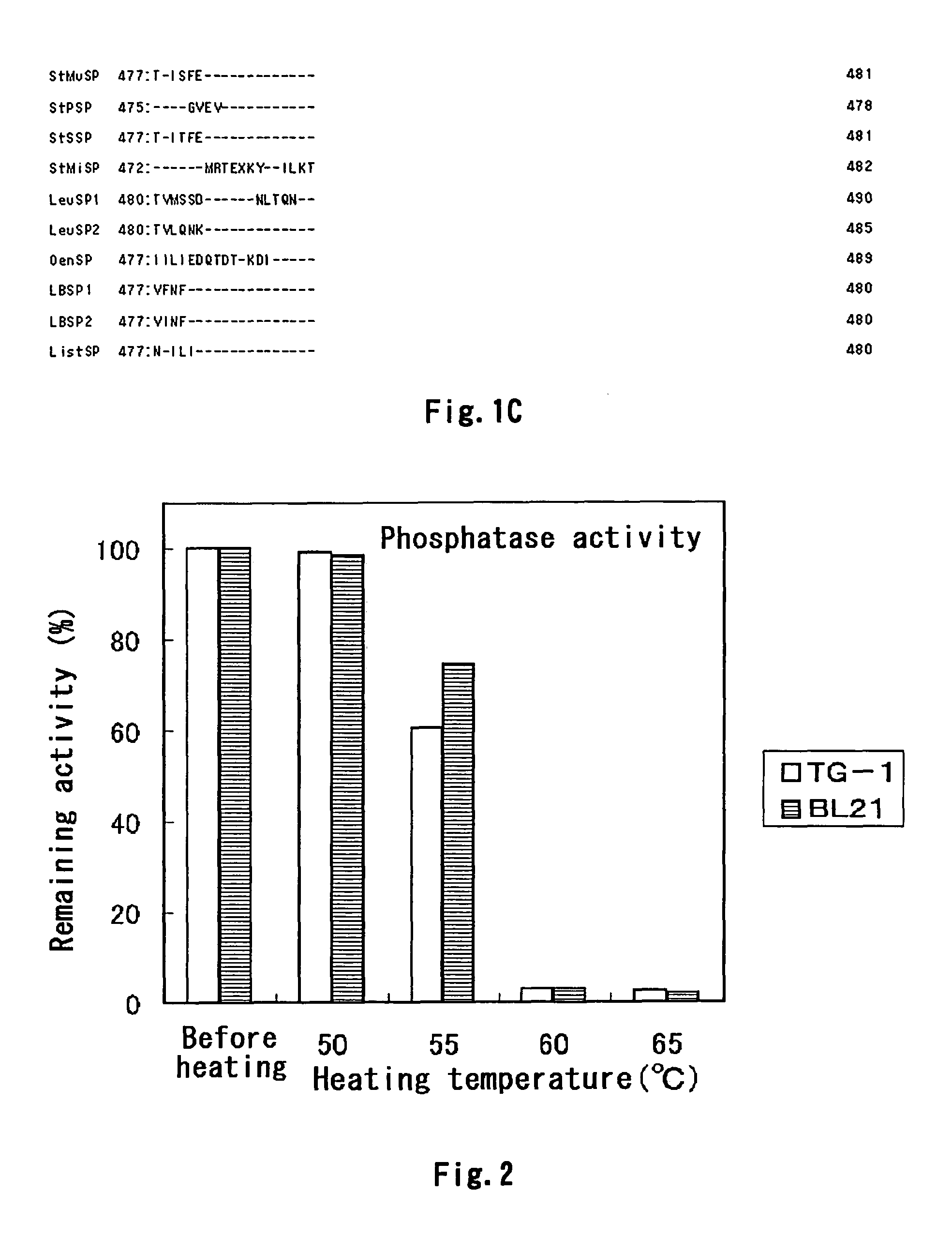
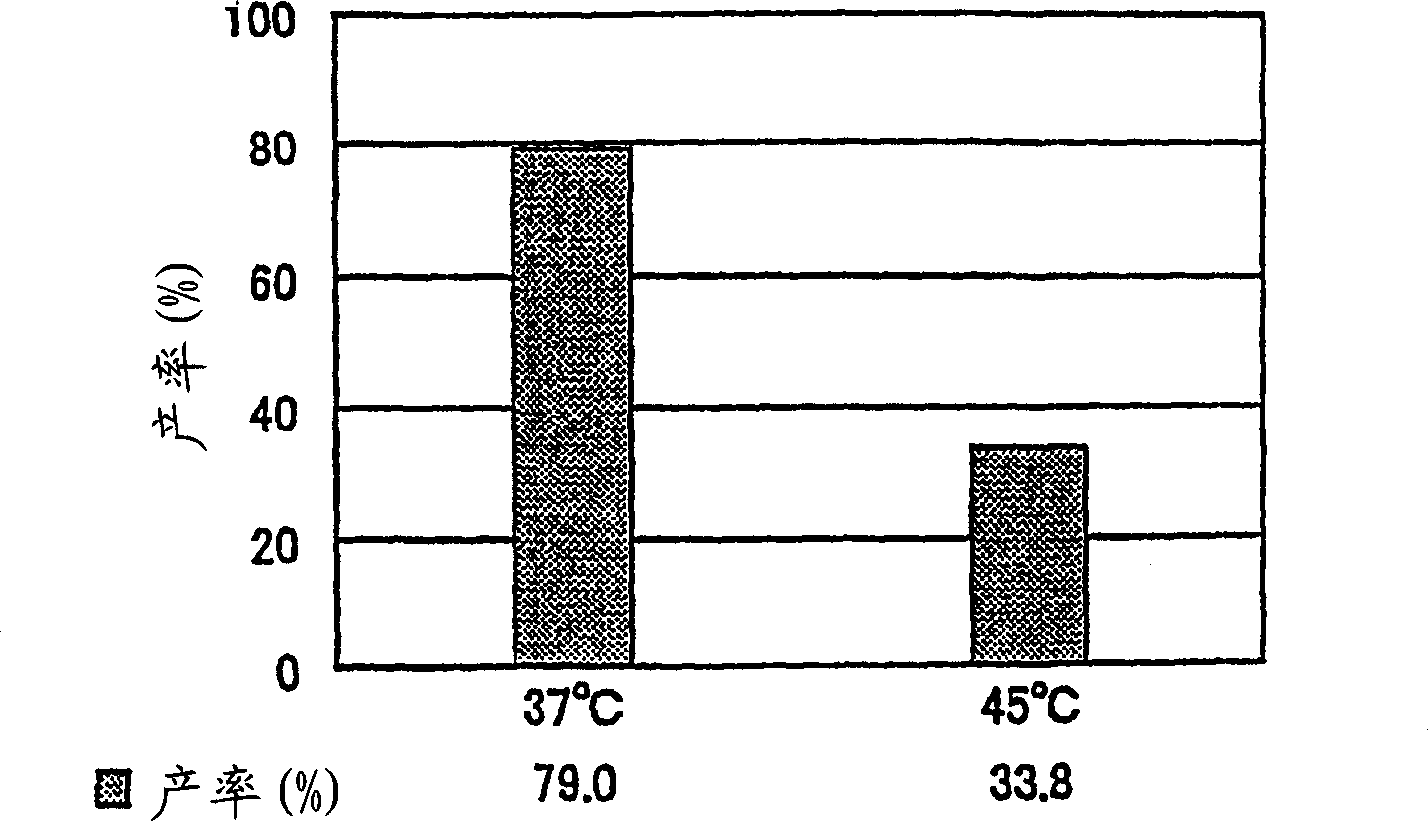
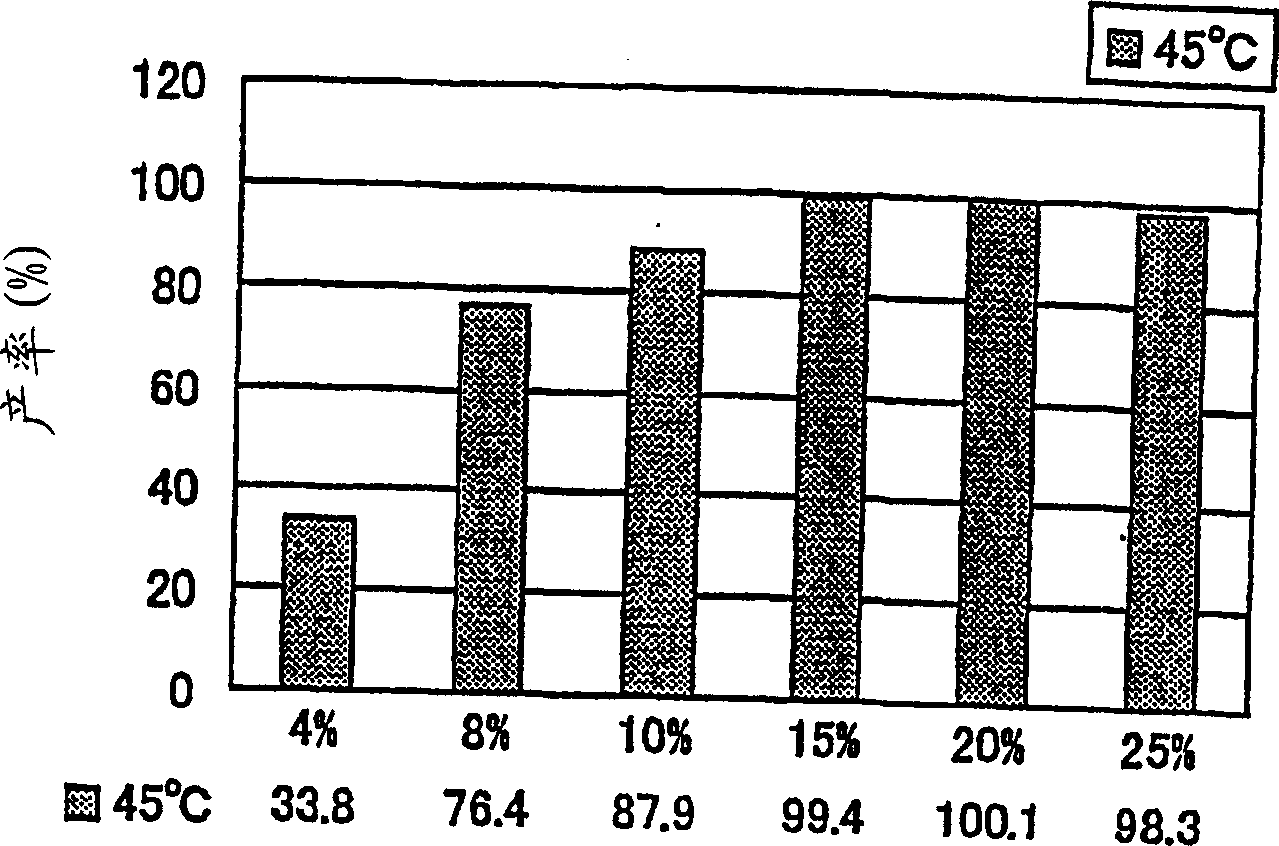
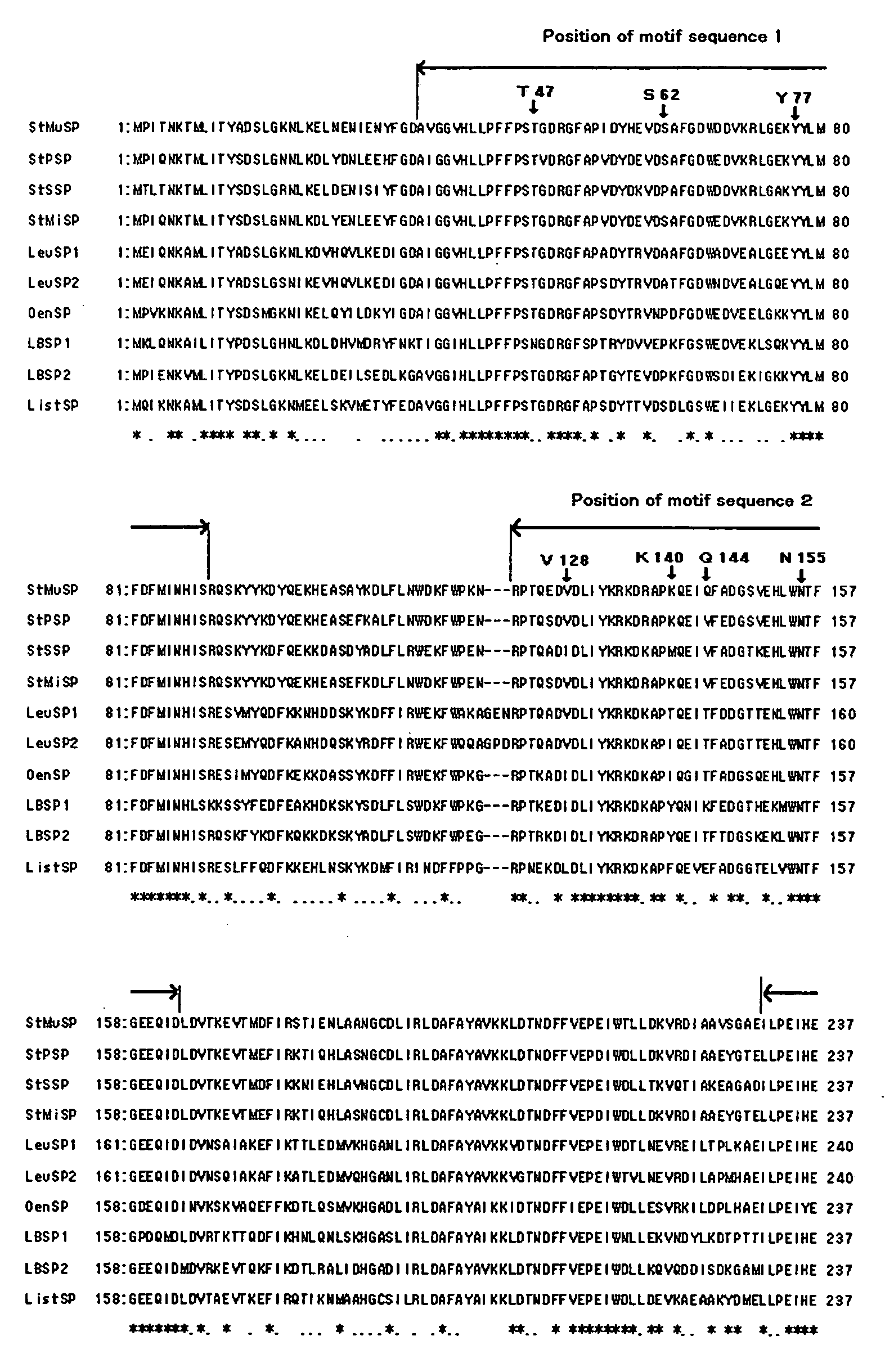
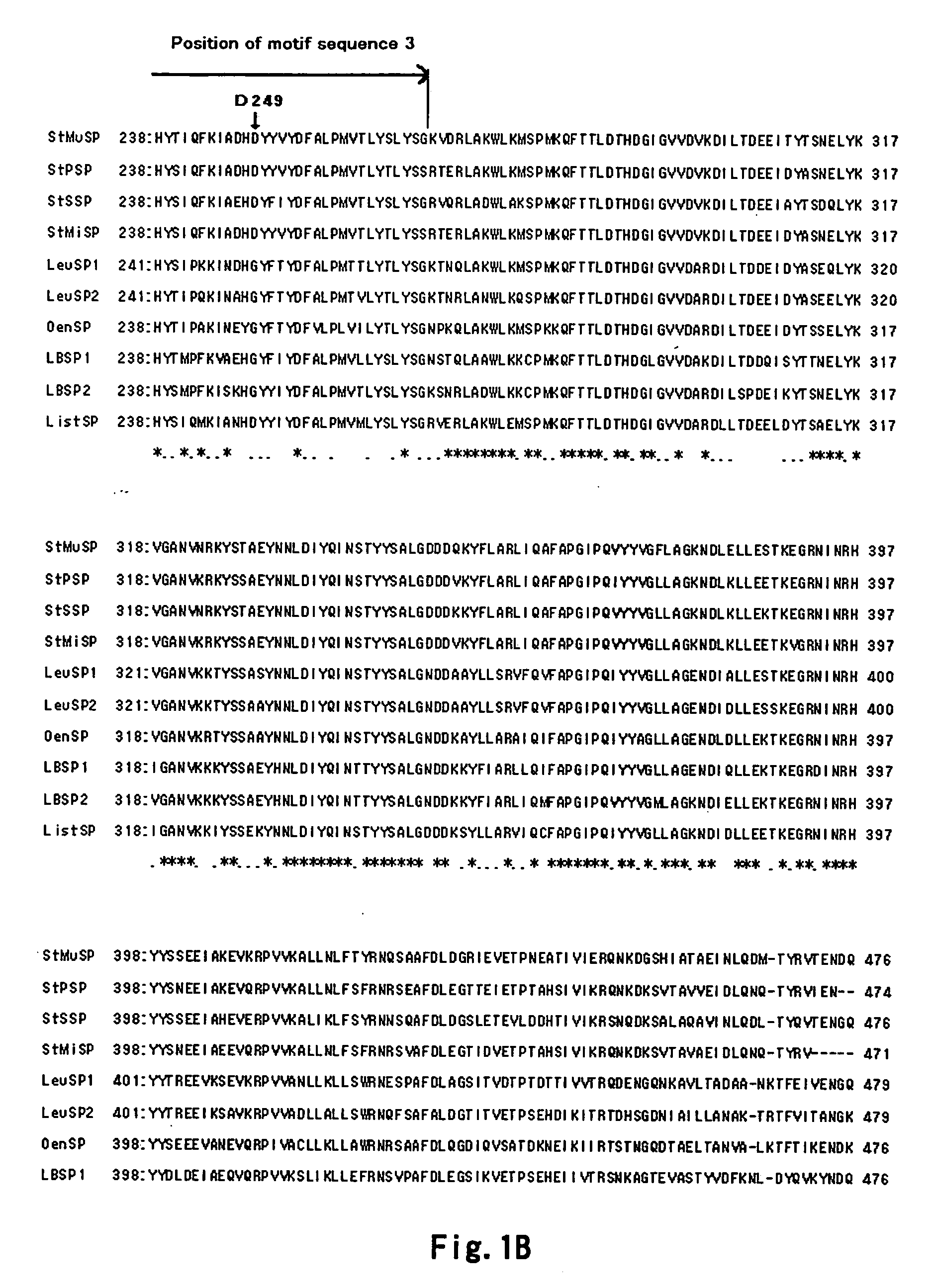
A sucrose phosphorylase (SP) having improved thermostability obtained by modifying a natural SP and a method for producing the SP having improved thermostability is provided. This SP having improved thermostability has an amino acid residue which is different from that of the natural sucrose phosphorylase, in at least one position selected from the group consisting of a position corresponding to position 14, a position corresponding to position 29 and a position corresponding to position 44 in motif sequence 1; a position corresponding to position 7, a position corresponding to position 19, a position corresponding to position 23 and a position corresponding to position 34 in motif sequence 2; and a position corresponding to position 19 in motif sequence 3, and wherein the enzyme activity of the SP having improved thermostability at 37° C., after heating the SP having improved thermostability in 20 mM Tris buffer (pH 7.0) at 55° C. for 20 minutes, is 20% or more of enzyme activity of the SP having improved thermostability at 37° C. before heating.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Method of making sucrose phosphorylase(SP) heat-stable
ActiveCN1845990AHigh activityEfficient productionTransferasesFermentationSucrose phosphorylasePhosphorylation
It is intended to provide a heat-stable sucrose phosphorylase (SP) obtained by modifying natural SP and a method of preparing this heat-stable SP. Namely, a heat-stable SP which has an amino acid residue differing from the one in natural sucrose phosphorylase at least one position selected from the group consisting of: the positions corresponding respectively to the 14-, 29- and 44-positions in the motif sequence 1; the positions corresponding respectively to the 7-, 19-, 23- and 34-positions in the motif sequence 2; and the position corresponding to the 19-position in the motif sequence 3, and, after heating in a 20 mM Tris buffer solution (pH 7.0) at 55 DEG C for 20 minutes, shows an enzymatic activity amounting to 20% or more of the enzymatic activity of the unheated heat-stable SP at 37 DEG C.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Method for preparing L-ascorbyl-2-glucoside
ActiveCN107058200ASingle productHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose phosphorylaseFermentation
The invention relates to a method for preparing L-ascorbyl-2-glucoside by virtue of an engineering strain of recombinant sucrose phosphorylase. The engineering strain of the sucrose phosphorylase is preserved in Wuhan University in Wuhan of China, postcode 430072, with preservation number of CCTCC M2016496. The engineering strain of the sucrose phosphorylase is constructed by virtue of gene recombination and site-specific mutagenesis technologies. With strain cells, obtained from fermentation, serving as a biological catalyst, AA-2G is prepared from sucrose and L-ascorbic acid in a trisodium citrate buffer solution system. According to the method provided by the invention, the sucrose, which is directly used as a glycosyl donor, is easily soluble in water and is cheap and easily available. Meanwhile, the reaction product, which mainly includes the AA-2G, is single; a yield reaches 65% or above; and additional treatment of adding saccharifying enzyme is avoided, so that production cost is reduced.
Owner:山东格得生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing sucrose phosphorylase by high-efficiency expression
ActiveCN109306357AEasy recovery and purificationEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood industrySucrose phosphorylase
The invention relates to a method for preparing sucrose phosphorylase by high-efficiency expression. The method comprises the following steps: enabling a sucrose phosphorylase SP gene and bacillus subtilis to construct a recombinant expression vector by using a vector; converting the recombinant expression vector into the bacillus subtilis to construct recombinant engineering bacteria; and performing induction culture on the recombinant engineering bacteria in a fluid medium, centrifuging a bacteria solution, and taking liquid supernatant. The method is high in yield of sucrose phosphorylase,purer in protein, easy to be recovered and purified, simple in production operation, and capable of providing convenience for industrial mass production of SP, improving the yield, saving both time and labor, and saving cost, especially providing safety guarantee for the application of the sucrose phosphorylase in food industry, and has important significance.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Recombinant E.coli (Escherichia coli) and application thereof
The invention discloses recombinant E.coli (Escherichia coli) and application thereof. The recombinant E.coli is obtained by transferring an L-VC (Vitamin C) glycosylase gene sourced from bifidobacterium longum IEF101 as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 into Escherichia coli host cells. A single glycosylated product AA-2G (2-0-alpha-D-glucosyl-L-VC) is efficiently produced by adopting a biological method through one-step catalytic conversion; the recombinant E.coli IEF-blsp101 is capable of efficiently synthesizing sucrose phosphorylase in cells, glycosylation reaction of the L-VC can be efficiently catalyzed by taking the L-VC and saccharose as substrates, 90 to 100 g / L of the AA-2G can be obtained by catalyzing within 45 to 72 hours, and the average production intensity is greater than 1.3g.L<-1>.h<-1>.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
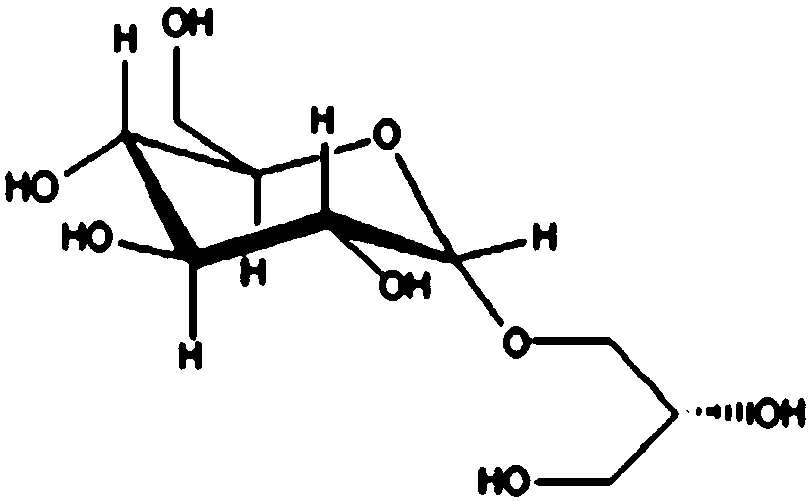
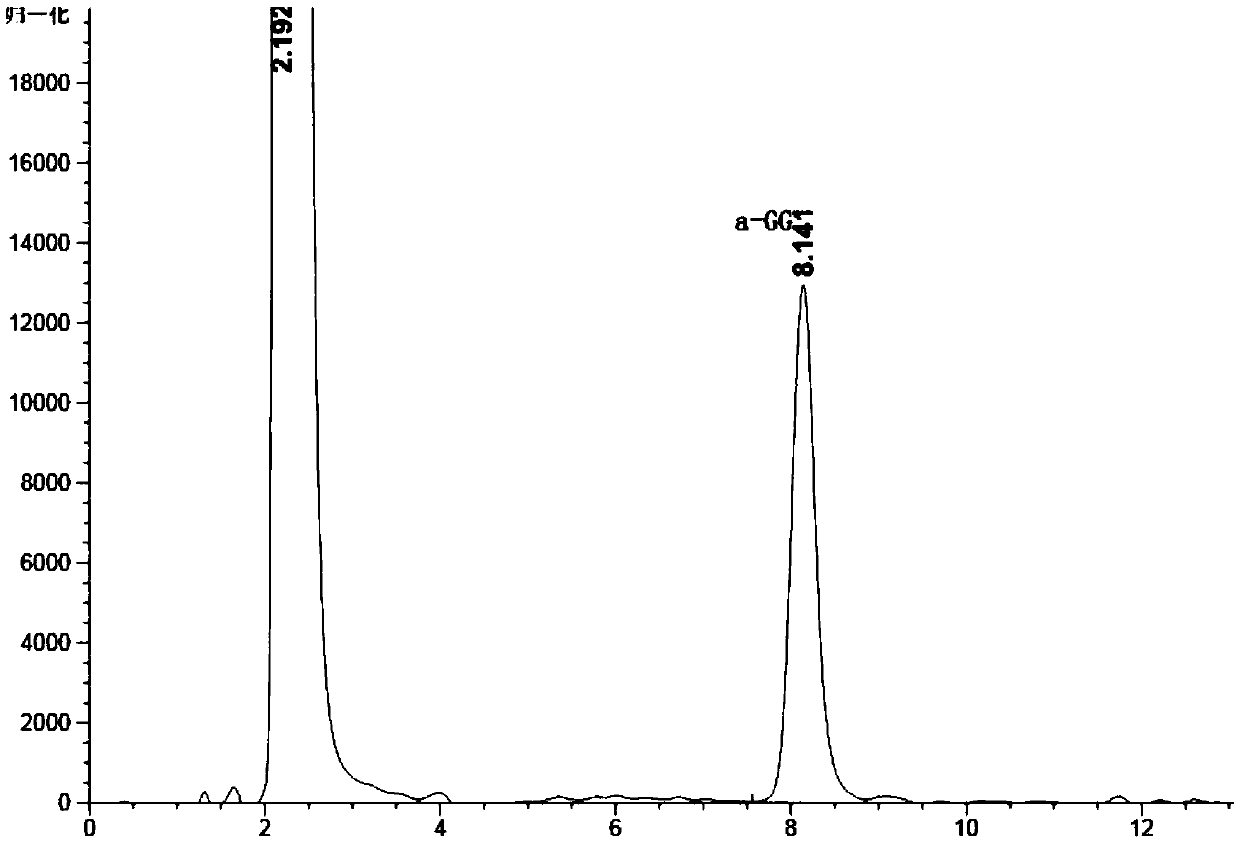
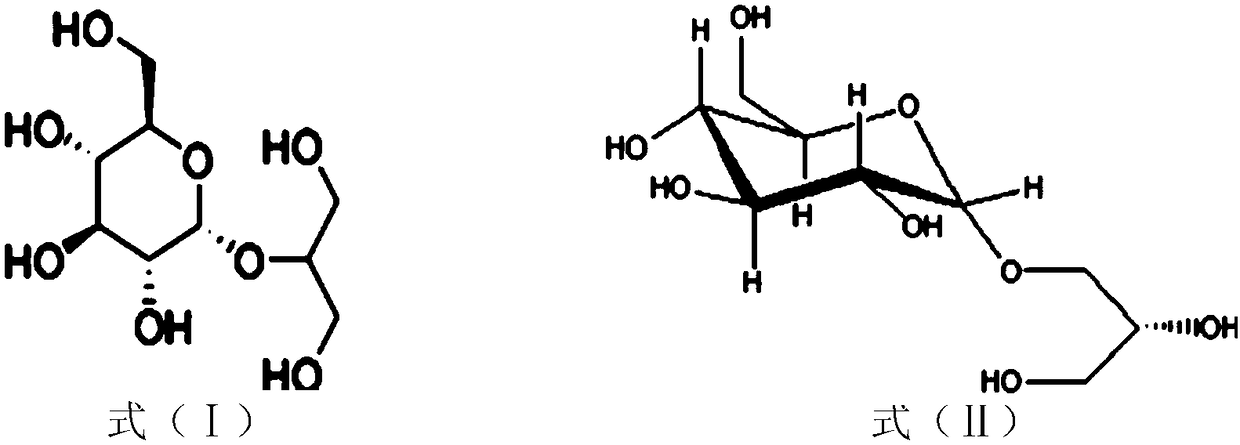
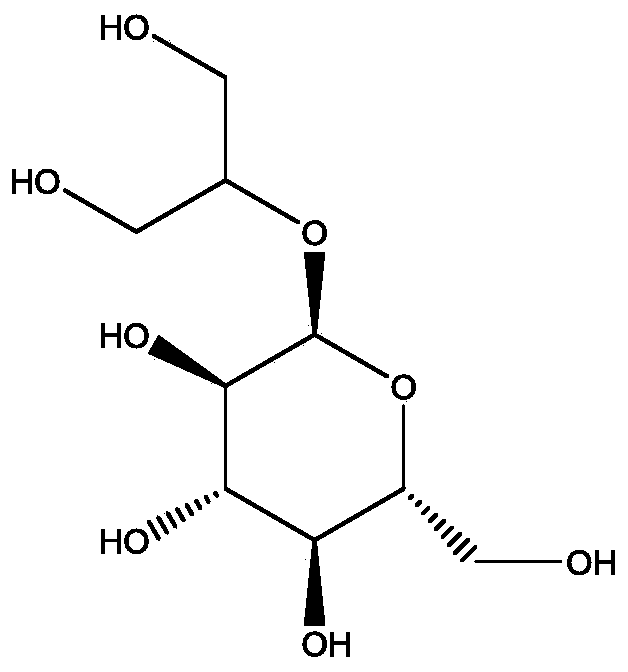
Application of glycerol-2-alpha-glucosylase in preparing 2-alpha-glyceryl glucoside
ActiveCN109988799AHigh catalytic activityHigh 2-alpha-GG contentHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses an application of glycerol-2-alpha-glucosylase in preparing 2-alpha-glyceryl glucoside, wherein an amino acid sequence of the glycerol-2-alpha-glucosylase is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The recombinant Escherichia coli IEF-bpmsp208 for producing 2-alpha-GG can efficiently synthesize sucrose phosphorylase in cells, glycerol and sucrose are taken as substrates to efficiently catalyze the glycosylation reaction of glycerol, after 18-24 hours of reaction, a 2-alpha-GG solution with a conversion rate of more than 10% can be obtained, the conversion rate of the substrate sucrose ismore than 92%, the product concentration of the 2-alpha-GG is high, the conversion rate is high, and the separation and purification of the 2-alpha-GG are facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Sucrose hosphorylase mutant with improved enzyme activity and construction method and application of sucrose phosphorylase mutant
ActiveCN110734899AIncrease enzyme activityIncreased potential for industrial applicationsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose phosphorylasePhosphorylation
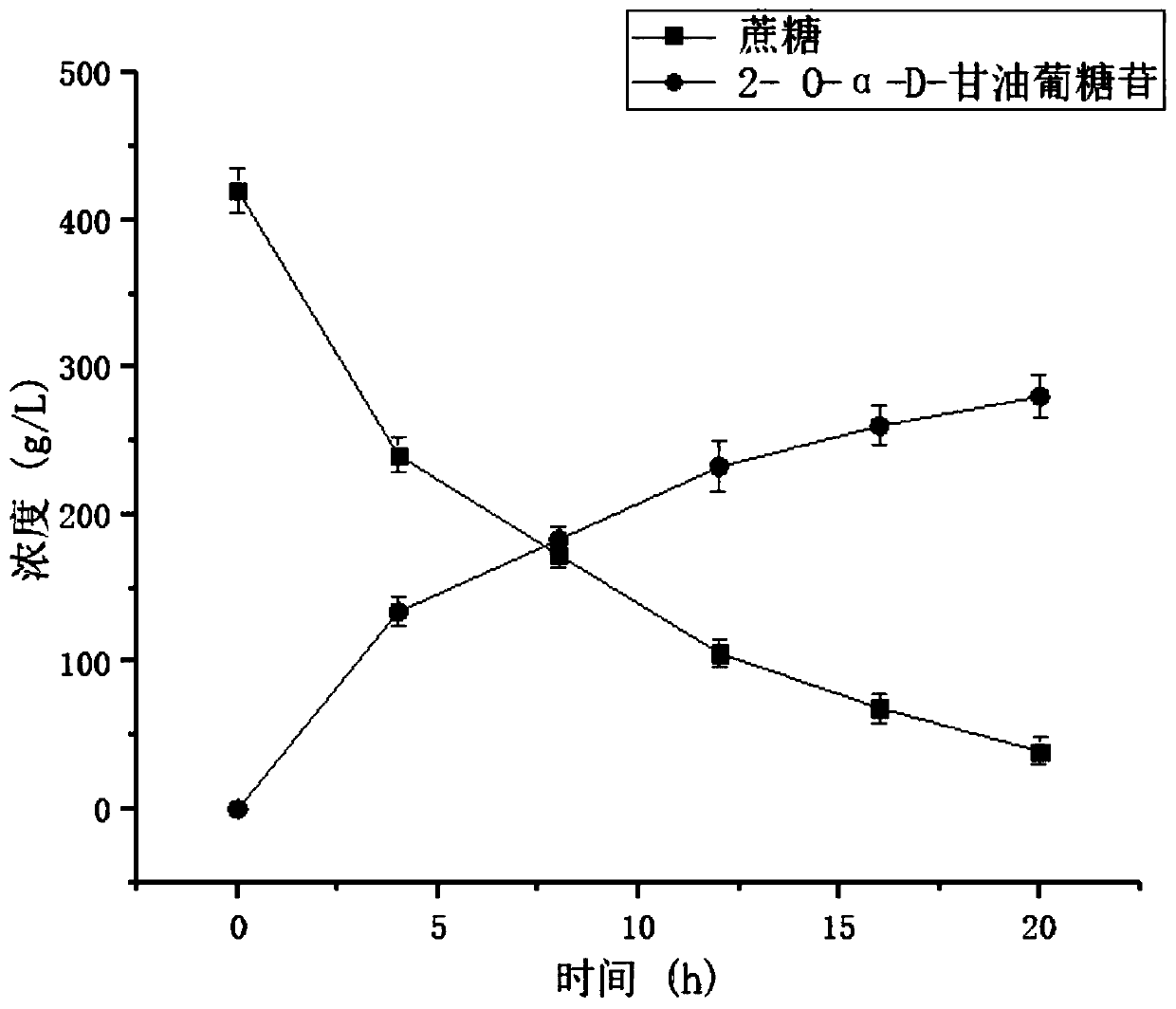
The invention relates to a sucrose phosphorylase mutant with improved enzyme activity and a construction method and application of the sucrose phosphorylase mutant, and belongs to the technical fieldof genetic engineering. The amino acid sequence of the mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. Based on sucrose phosphorylase which is derived from Leuconostoc mesenteroides, site-directed mutagenesis is performed on the mutant so as to improve the enzyme activity of sucrose phosphorylase, the mutant is expressed in Corynebacterium glutamicum, and is used as a whole-cell catalyst for production of 2-O-alpha-D-glycosylglycerol, and a large amount of 2-O-alpha-D-glycosylglycerol can be produced efficiently in a short period of time at the level of a fermenter of 5 L, so that industrial application prospects for 2-O-alpha-D-glycosylglycerol production from sucrose phosphorylase is expanded, and large-scale industrial application is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Production method and preparation method of glucans
A first method for producing glucan comprises the step of allowing a reaction solution containing sucrose, a primer, inorganic phosphate or glucose-1-phosphate, sucrose phosphorylase, and glucan phosphorylase to react to produce glucans. The maximum value of the sucrose-phosphate ratio of the reaction solution from the start of the reaction to the end of the reaction is no more than about 17. A second method for producing glucan comprises the step of allowing a reaction solution containing sucrose, a primer, inorganic phosphate or glucose-1-phosphate, sucrose phosphorylase, and glucan phosphorylase to react to produce glucans. The reaction is conducted at a temperature of about 40 C to about 70 C.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Method for Improving the Thermostability of Sucrose Phosphorylase (Sp)
ActiveUS20080206822A1High activityImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSucrose phosphorylaseChemistry
A sucrose phosphorylase (SP) having improved thermostability obtained by modifying a natural SP and a method for producing the SP having improved thermostability is provided. This SP having improved thermostability has an amino acid residue which is different from that of the natural sucrose phosphorylase, in at least one position selected from the group consisting of a position corresponding to position 14, a position corresponding to position 29 and a position corresponding to position 44 in motif sequence 1; a position corresponding to position 7, a position corresponding to position 19, a position corresponding to position 23 and a position corresponding to position 34 in motif sequence 2; and a position corresponding to position 19 in motif sequence 3, and wherein the enzyme activity of the SP having improved thermostability at 37° C., after heating the SP having improved thermostability in 20 mM Tris buffer (pH 7.0) at 55° C. for 20 minutes, is 20% or more of enzyme activity of the SP having improved thermostability at 37° C. before heating.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
Method for improving sucrose phosphorylase expression efficiency by molecular chaperone co-expression
ActiveCN109486782AImprove expression efficiencyReduce formationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInclusion bodiesSpecific enzyme
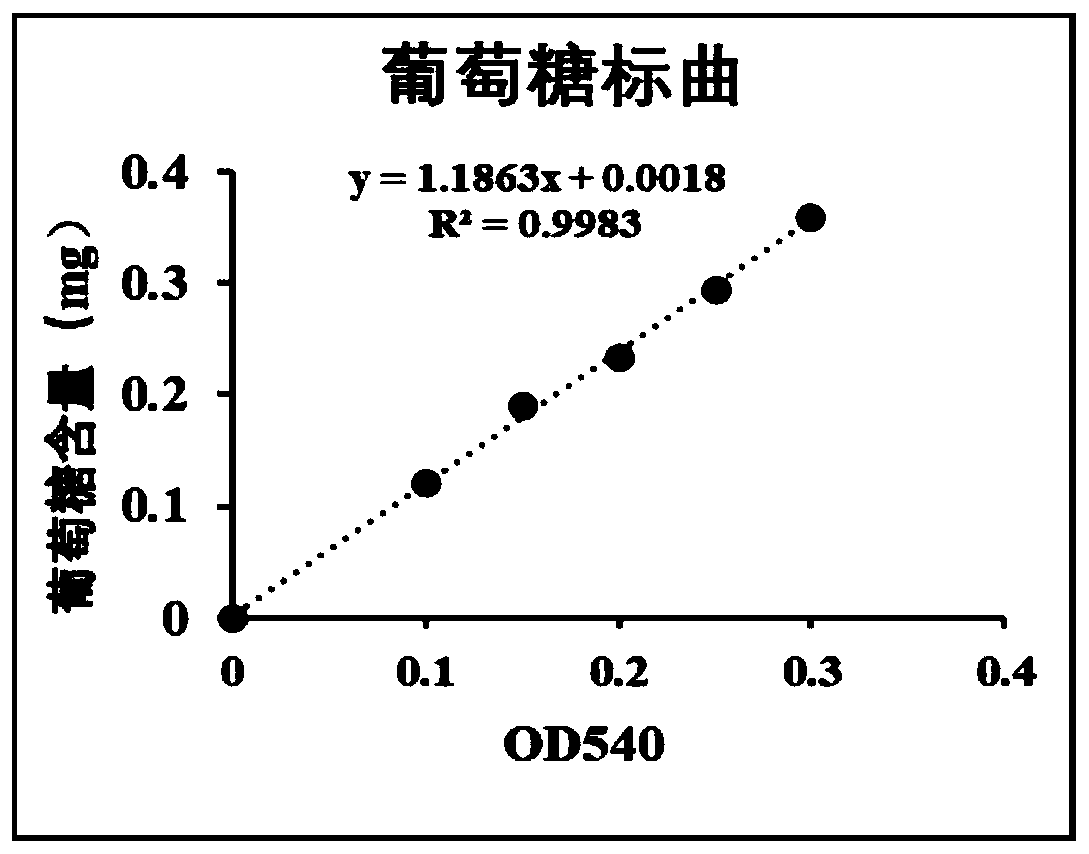
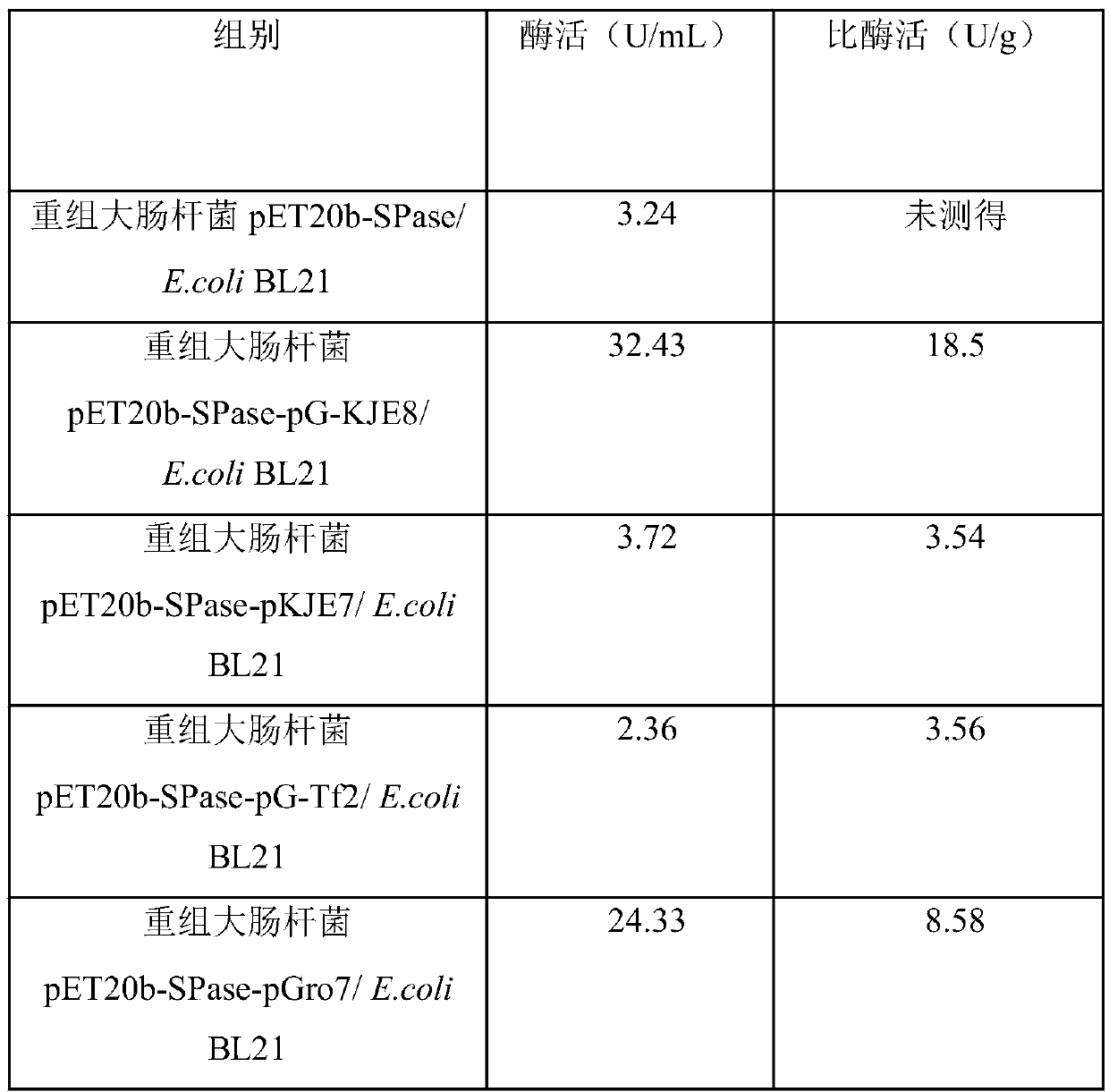
The invention discloses a method for improving the sucrose phosphorylase expression efficiency by molecular chaperone co-expression, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and enzyme engineering. According to the method, pGro7 expressed molecular chaperone protein can be used for effectively reducing formation of an inclusion body by co-expression of recombinant plasmid pET-20b-SPasewith pGro7, and improvement of SPase soluble expression level and vitality can be promoted. By optimizing the expression condition and using a molecular chaperone co-expression system, the intracellular enzyme activity of SPase can be 24.33U / mL, and the specific enzyme activity can be 6.58U / mg.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Escherichia coli for producing sucrose phosphorylase
ActiveCN110452845AStable enzyme productionPractical application is of great significanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses escherichia coli for producing sucrose phosphorylase and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. A nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 is used for constructing arecombinant plasmid pET-28a-SPase with pET-28a as a vector, the recombinant plasmid is transformed into escherichia coli BL21(DE3), and recombinant escherichia coli is constructed. Recombinant sucrose phosphorylase is produced by fermentation, the recombinant escherichia coli strain with high yield of sucrose phosphorylase is screened out by adopting an ultraviolet mutagenesis method to mutagenize the constructed recombinant escherichia coli, the enzyme activity of a supernatant on the broken walls in fermentation cells is 819.16 U / mL, the specific enzyme activity is 206.91 U / mg, the stable enzyme production can lay a foundation for further theoretical research and practical application, and practical application is significant.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
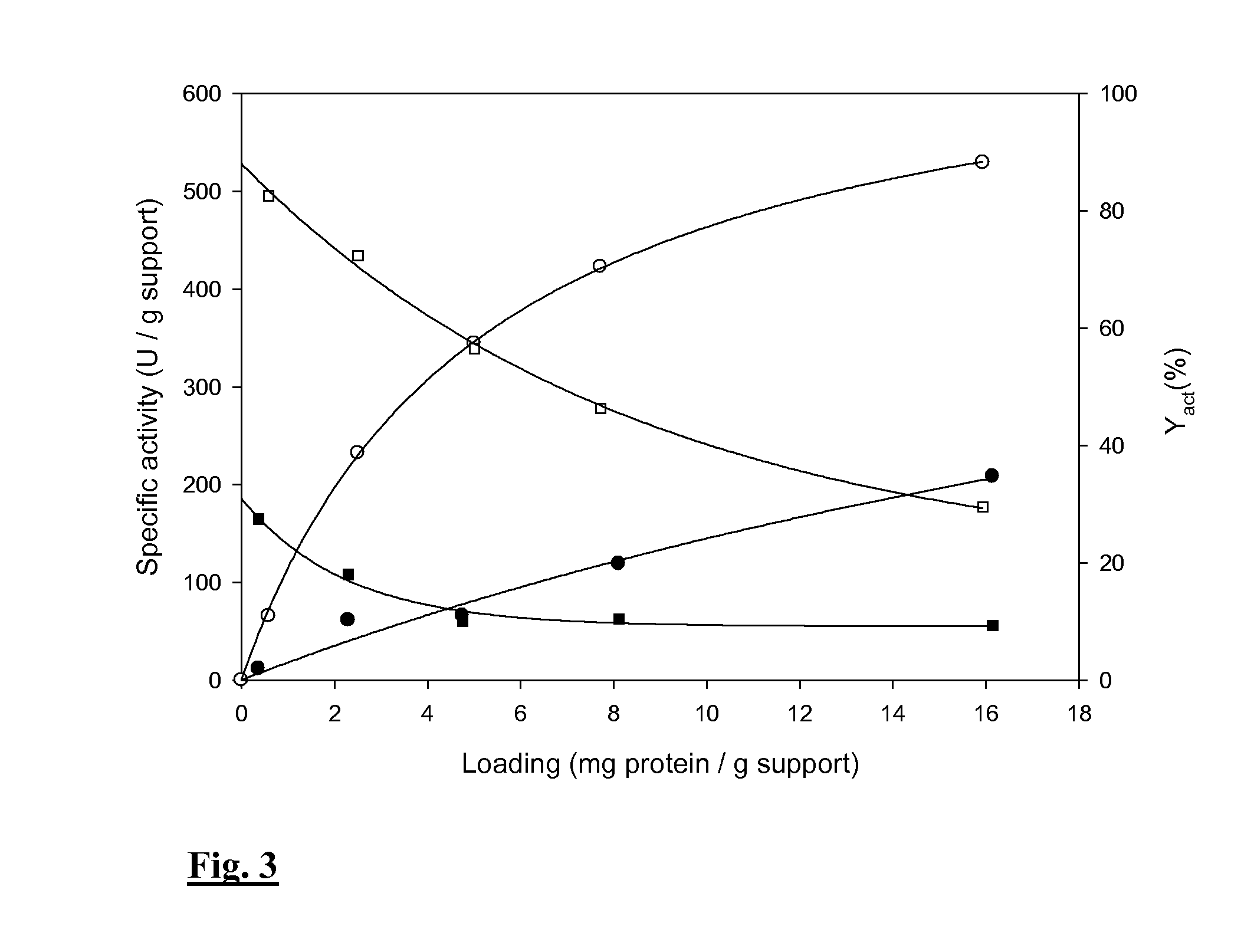
Immobilization method of sucrose phosphorylase
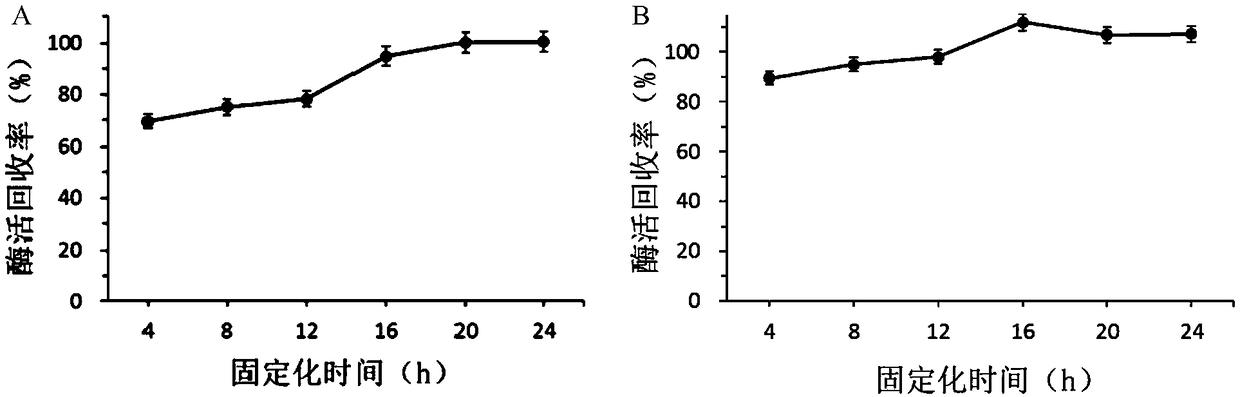
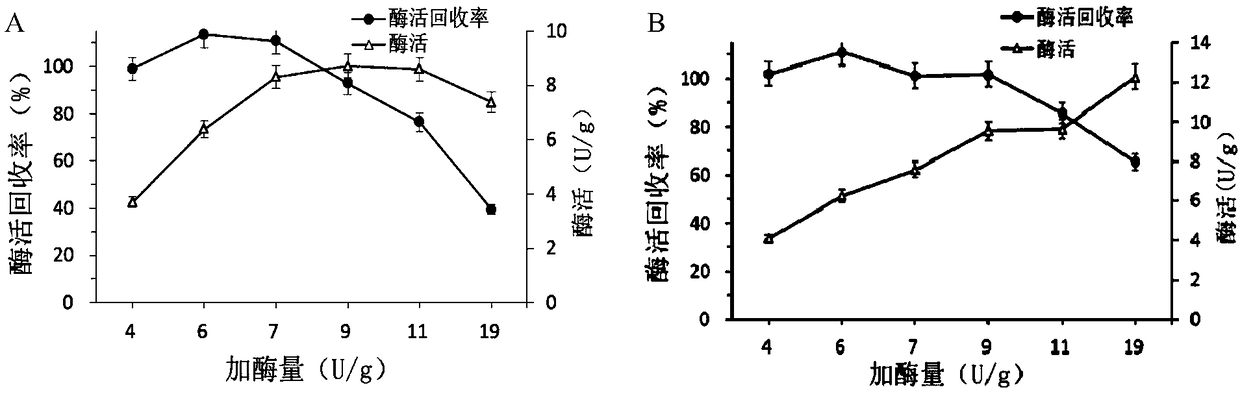
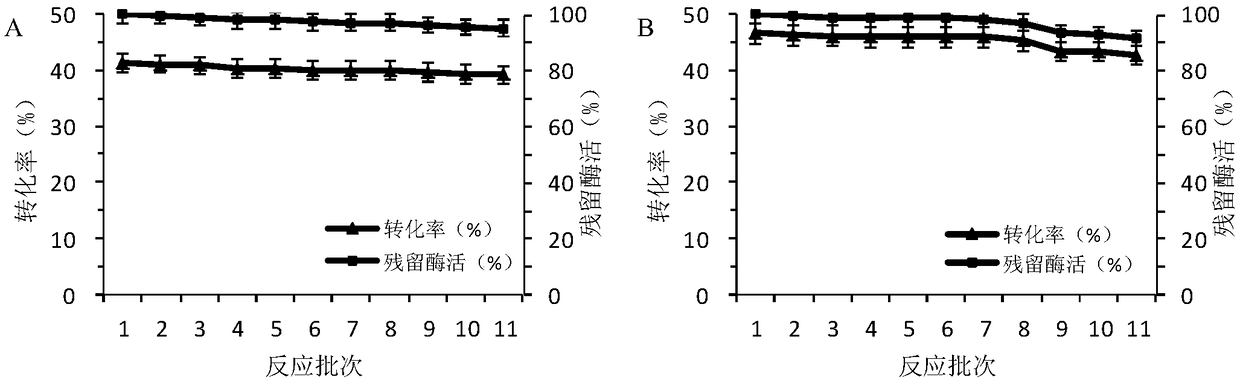
ActiveCN109371006AHigh recovery rate of enzyme activityEasy to separate and purifyOn/in organic carrierFermentationSucrose phosphorylaseSaccharophagus degradans
The invention discloses an immobilization method of sucrose phosphorylase, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the immobilization method, recombinant bacillus subtilis Spase / pBSMuL3 serves as a production bacterial strain, the enzyme activity of the LX-1000EA immobilized sucrose phosphorylase is 7.75 U / g, and the enzyme activity recovery rate reaches 110.85%; the enzyme activity of the LX-1000EA immobilized sucrose phosphorylase is 9.54 U / g, and the enzyme activity recovery rate reaches 101.82%. Within the same conversion time, continuous operation is conducted for eleven times by takingwith 0.5 M sucrose and 0.5 M glucose as a substrate, amination resin LX-1000EA immobilized Spase keeps the 39.15% of the conversion rate of 39.15% and the 94% of the residualenzyme activity of 94%; and amination resin LX-1000HA immobilized Spase keeps the 42.5% the conversion rate of 42.5% and the residual enzyme activity of 91%. The result shows that the Immobilization method is easy to operate, the enzyme activity of an immobilization enzyme has no loss, the application effect is quite good, and the immobilization enzyme immobilization method has high industrial application potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV RUGAO FOOD BIOTECH RES INST +1
Method for recycling sucrose phospholylase in alpha-arbutin production process
The invention provides a method for recycling sucrose phospholylase in an alpha-arbutin production process. Alpha-arbutin is synthesized by taking sucrose and hydroquinone as substrates under the catalysis of dissociative sucrose phospholylase rough liquid as a catalyst in the alpha-arbutin production process; after the reaction, an additive with a certain concentration is firstly added in a reaction liquid to improve the stability of the reaction liquid, then un-soluble floss materials and some large molecular proteins are filtered away by using a ceramic film, next, the dissociative sucrose phospholylase is recovered by using an ultra-filter film with a relatively small aperture, and finally the catalysis of the next batch is carried out by using the recovered sucrose phospholylase; and the purpose of recycling sucrose phospholylase is achieved by repeating the operations. The invention provides the method for recycling the sucrose phospholylase for the first time; in addition, the method has great significance in reducing film pollution, prolonging the service life of the film, reducing the production cost, and the like, so that the dissociative sucrose phospholylase has an excellent application prospect in the enzyme catalysis field.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Sucrose phosphorylase mutant and its application in the production of glycerol glucoside
ActiveCN107858335BReduce outputStrong specificityFermentationGenetic engineeringSucrose phosphorylasePhosphorylation
The invention discloses that the purpose of the invention is to provide a sucrose phosphorylase mutant and its application. A protein provided by the present invention is obtained by replacing the 341st amino acid residue of sucrose phosphorylase with leucine; the protein provided by the present invention can be the 341st amino acid residue of sucrose phosphorylase BaSP / L341W protein obtained by substituting leucine for tryptophan; the present invention significantly improves its Specificity in the production of 2‑glycerol glucoside from sucrose and glycerol as feedstock reduces the yield of the by-product 1‑glycerol glucoside. It has great application value for the production field of 2-glycerol glucoside.
Owner:NANJING HUASHI NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Technological process for synthesizing mycose by enzyme process
This invention discloses method synthesizing trehalose by enzymes. It includes steps as follows: a. clone huishuhua trehalose synthesizing enzyme gene and E. coli sucrose phosphorylase gene separately; b. construct expression vector of huishuhua trehalose synthesizing enzyme gene and E. coli sucrose phosphorylase gene separately; c. transform and express the expression vector of huishuhua trehalose synthesizing enzyme gene and E. coli sucrose phosphorylase gene separately in yeast, construct and purify the recombinant protein; d. add the said purified recombinant protein to synthesize trehalose in the reaction solution which has sucrose and glucose as main component.
Owner:李宝健
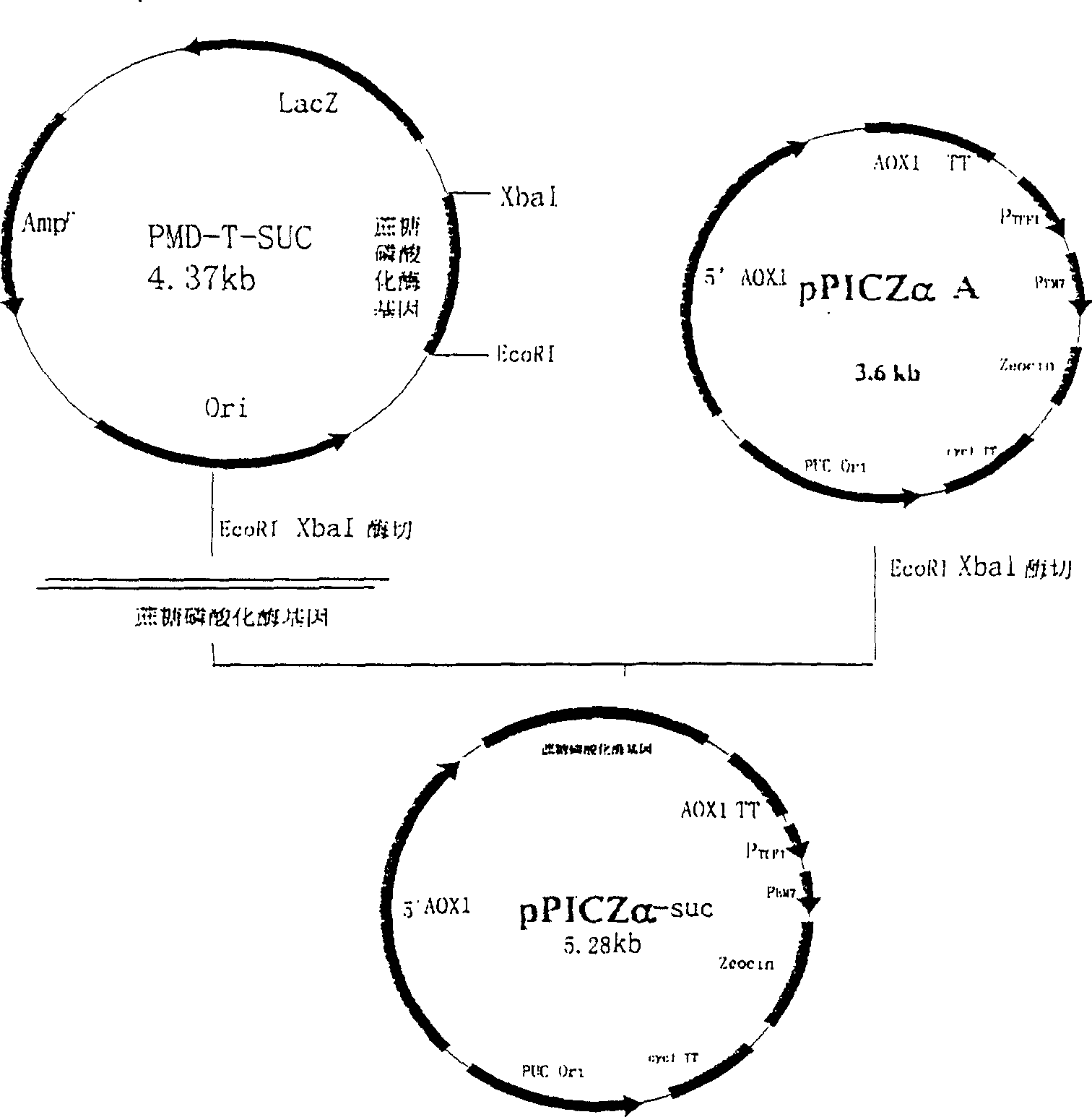
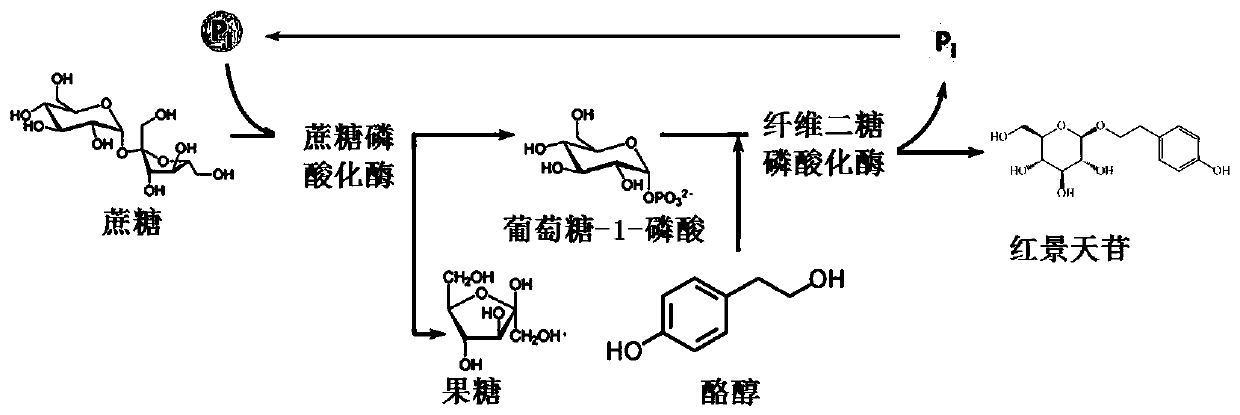
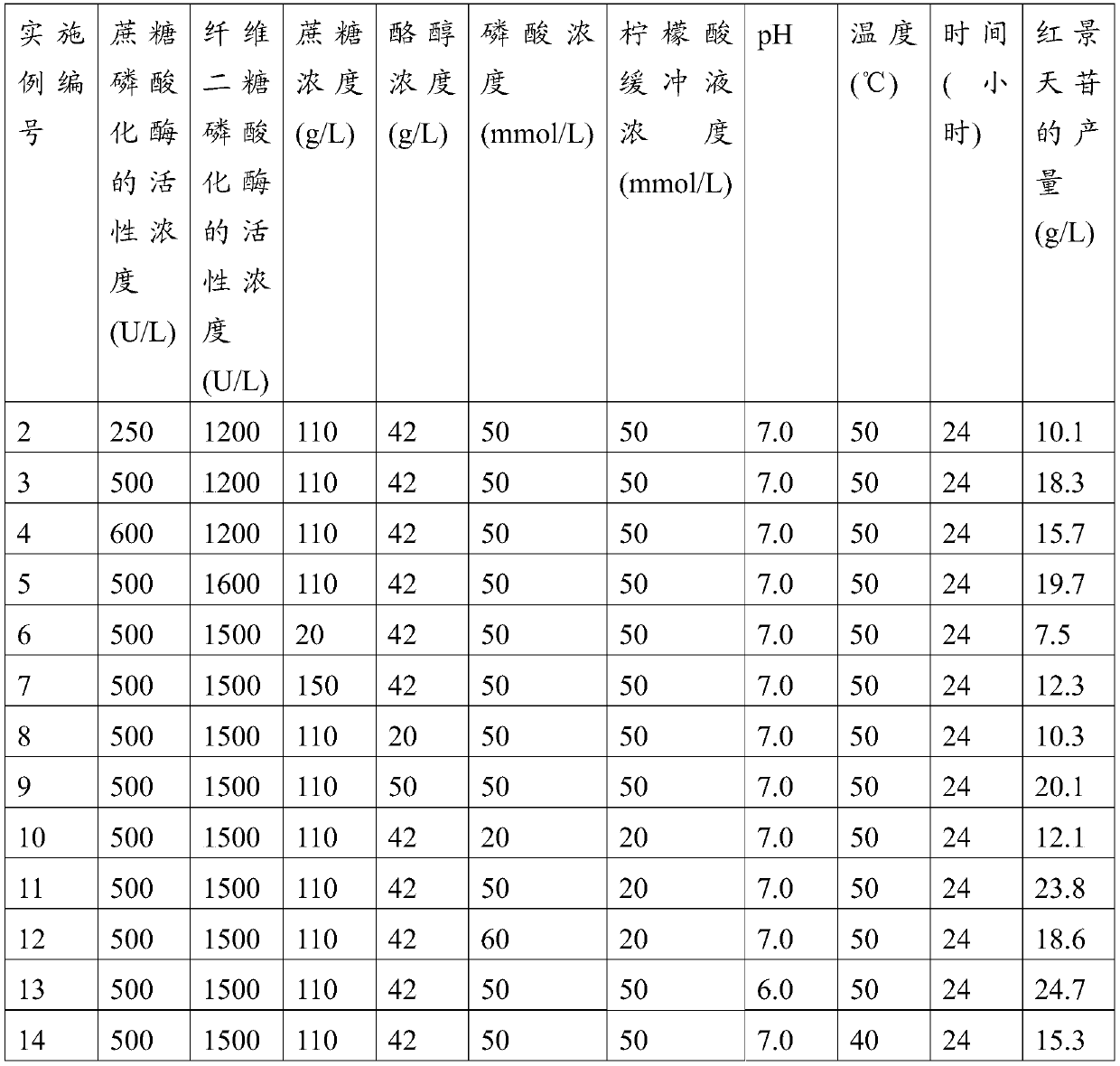
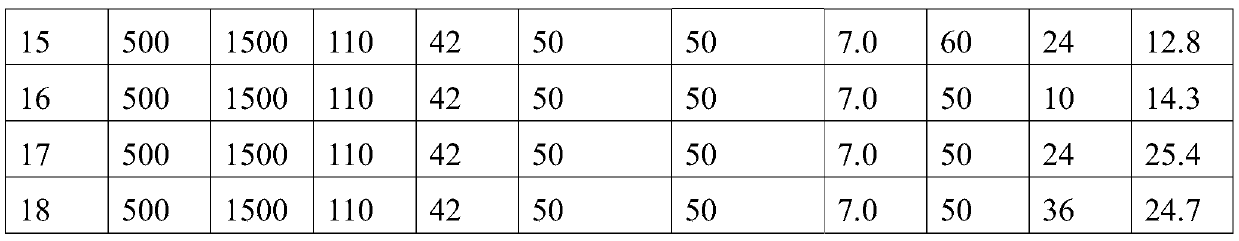
Preparation method of rhodioloside and kit
ActiveCN109694892AReduce manufacturing costReduce production stepsFermentationCellobiose phosphorylaseTyrosol
The invention discloses a preparation method of rhodioloside and a kit. The preparation method comprises following steps: mixing recombinant heatproof sucrose phosphorylase, recombinant heatproof cellobiose phosphorylase, cane sugar, tyrosol, and phosphoric acid to obtain a reaction mixture; then converting the reaction mixture at a temperature of 40 to 55 DEG C to generate rhodioloside. The preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, and high yield.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY +1
Sucrose phosphorylase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111621483AImprove thermal stabilityCosmetic preparationsBacteriaSucrose phosphorylasePhosphorylation
The present invention discloses a sucrose phosphorylase mutant and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering. A thermal stability of the sucrose phosphorylase mutant is significantly improved compared to that of a wild type. The sucrose phosphorylase mutants of T219L and I31F / T219L / S360A / T263L have better thermal stability at 50 DEGC and have a half-life of about 50 min, and the half-life of the sucrose phosphorylase mutant is about 35 min higher than that of the wild type.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing 2-O-alpha-D-glyceroglucoside by utilizing microorganisms
PendingCN111690624AIncreased potential for industrial applicationsIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 2-O-alpha-D-glyceroglucoside by utilizing microorganisms, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. An amino acid sequence of a mutant is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the mutant disclosed by the invention, site-specific mutagenesis is carried out to improve the enzyme activity of sucrose phosphorylase on the basis of sucrosephosphorylase derived from leuconostoc mesenteroides; a mutant enzyme is expressed in escherichia coli and is used as a whole-cell catalyst to produce the 2-O-alpha-D-glyceroglucoside; and a large amount of 2-O-alpha-D-glyceroglucoside can be produced within a short time at the level of a 5L fermentation tank, so that the industrial application prospect of production of the 2-O-alpha-D-glyceroglucoside by the sucrose phosphorylase can be easily expanded, and the large-scale industrial application is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Production method for sucrose phosphorylase and application of production method
ActiveCN110656077AIncreased specific enzyme activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSpecific enzyme
The invention discloses a production method for sucrose phosphorylase and an application of the production method, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The invention provides the production method for sucrose phosphorylase. The method produces the sucrose phosphorylase with high yield and high specific enzyme activity. By the method, recombinant escherichia coli is expressed in a fermentation medium containing L-arabinose, tetracycline and IPTG for 12 hours by induction, allowing enzyme activity of the sucrose phosphorylase in a supernatant of cell disruption liquid up to 32.43U / mL, andspecific enzyme activity of the produced sucrose phosphorylase up to 18.5 U / mg.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Mutant sucrose phosphorylases with improved glycosylation activity towards polyphenols
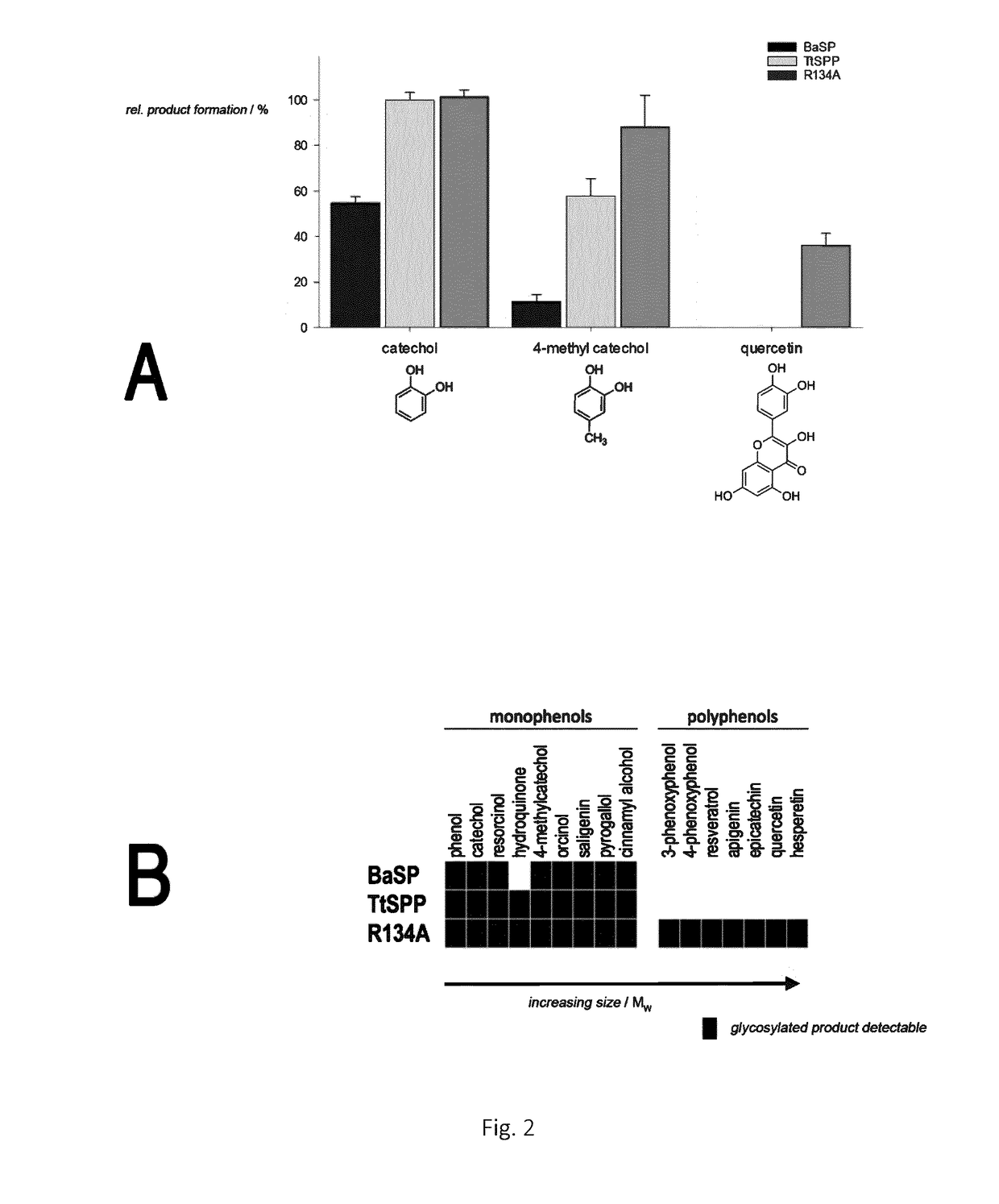
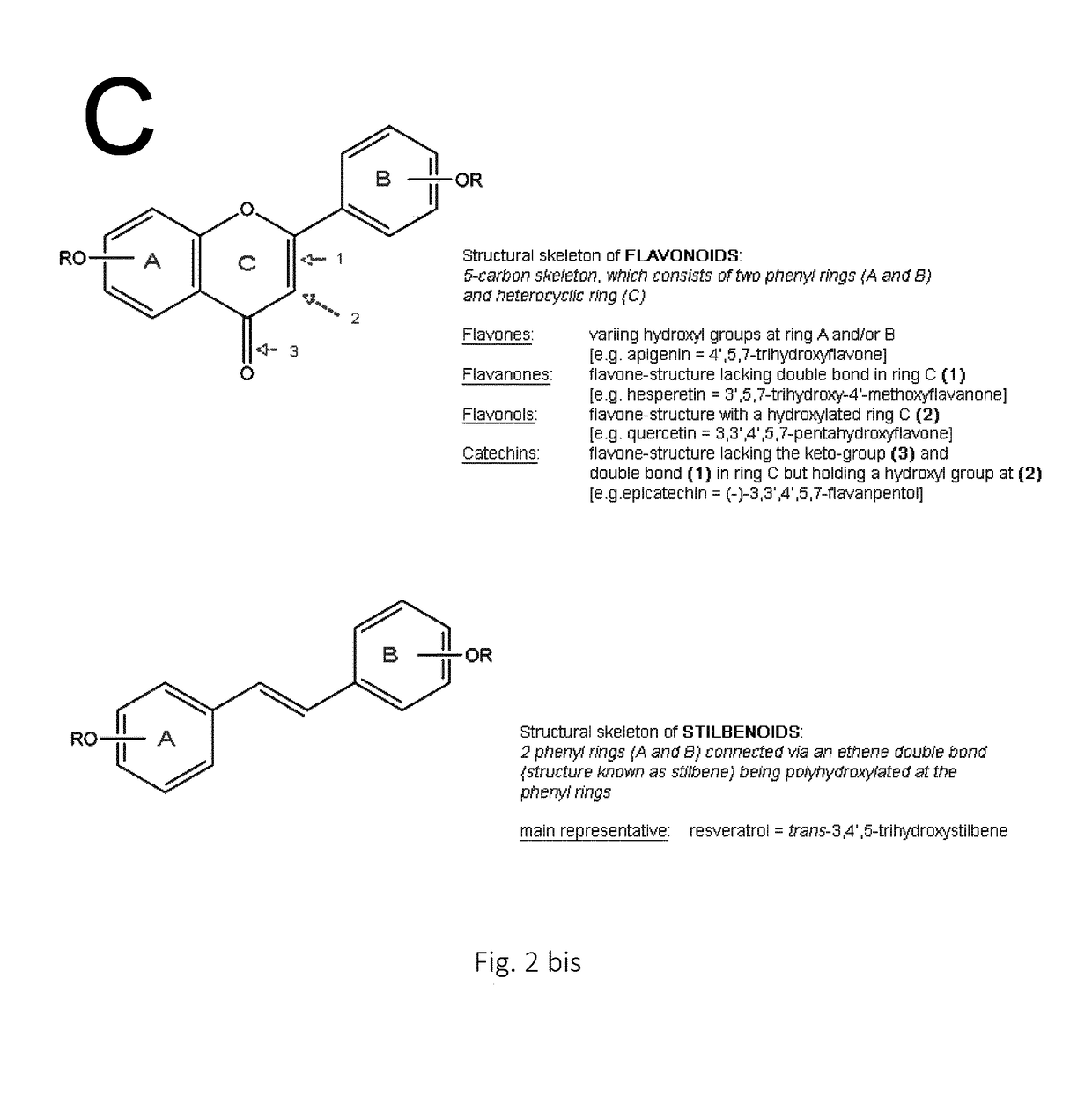
ActiveUS20180142276A1Sugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationMicroorganismSucrose phosphorylase
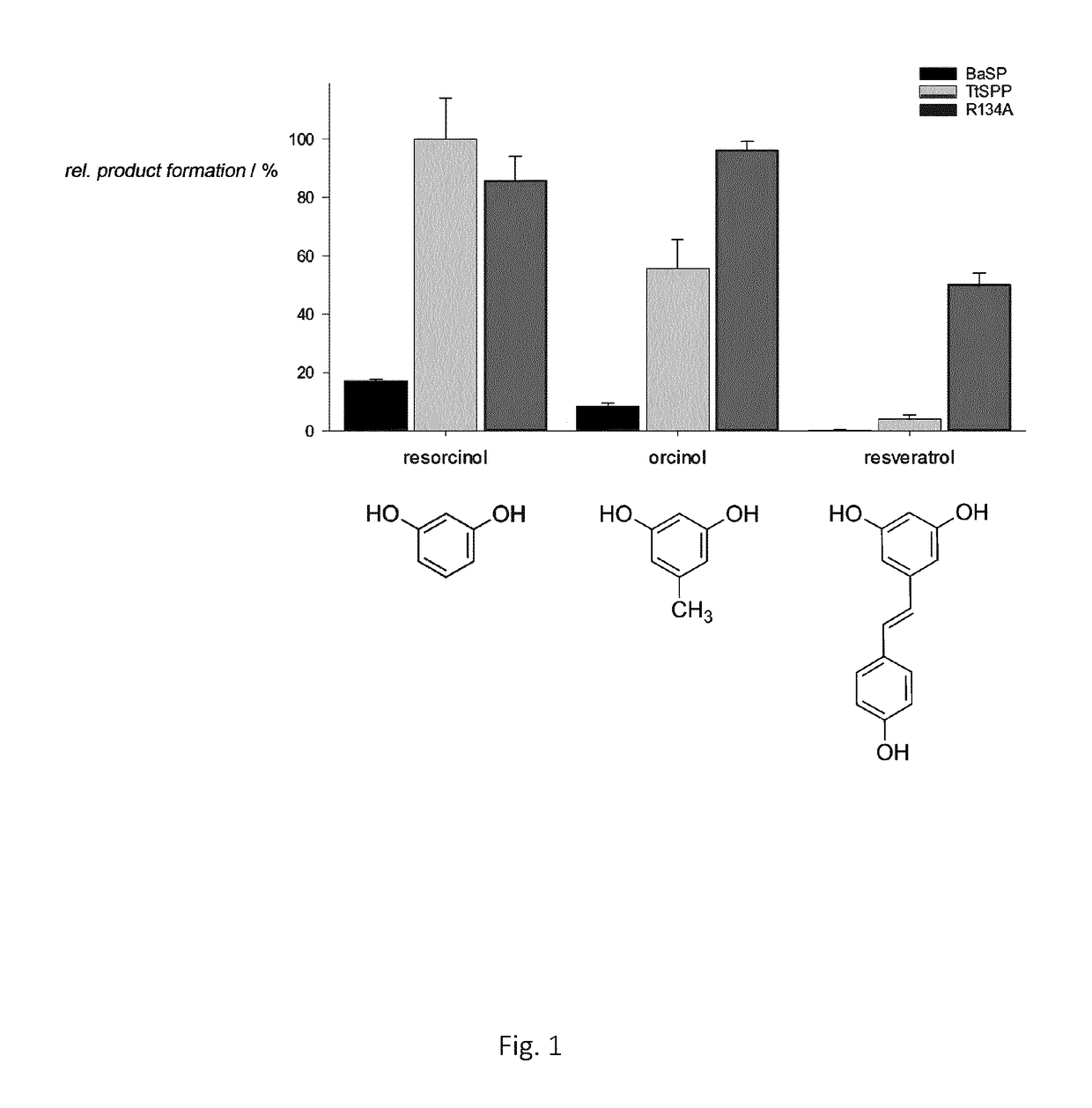
The present invention relates to glycosylating polyphenols via biocatalysis. More specifically the present invention discloses particular mutants of the thermostable sucrose phosphorylase derived from the microorganism Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum which efficiently glycosylate polyphenols such as resveratrol.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com