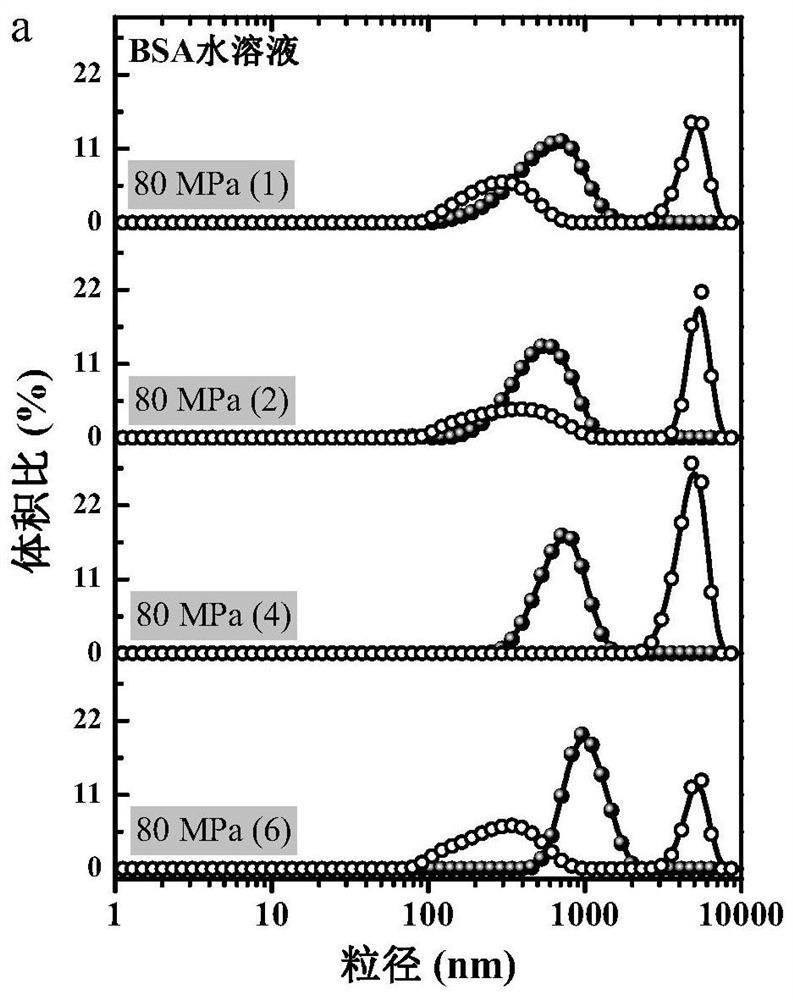
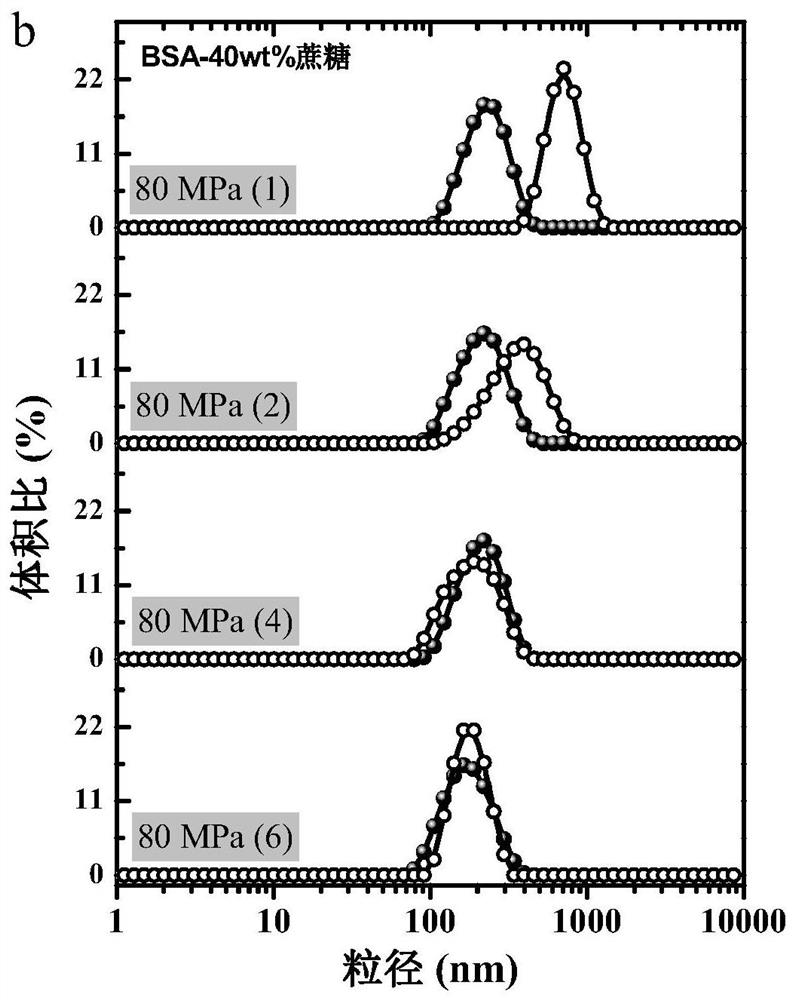
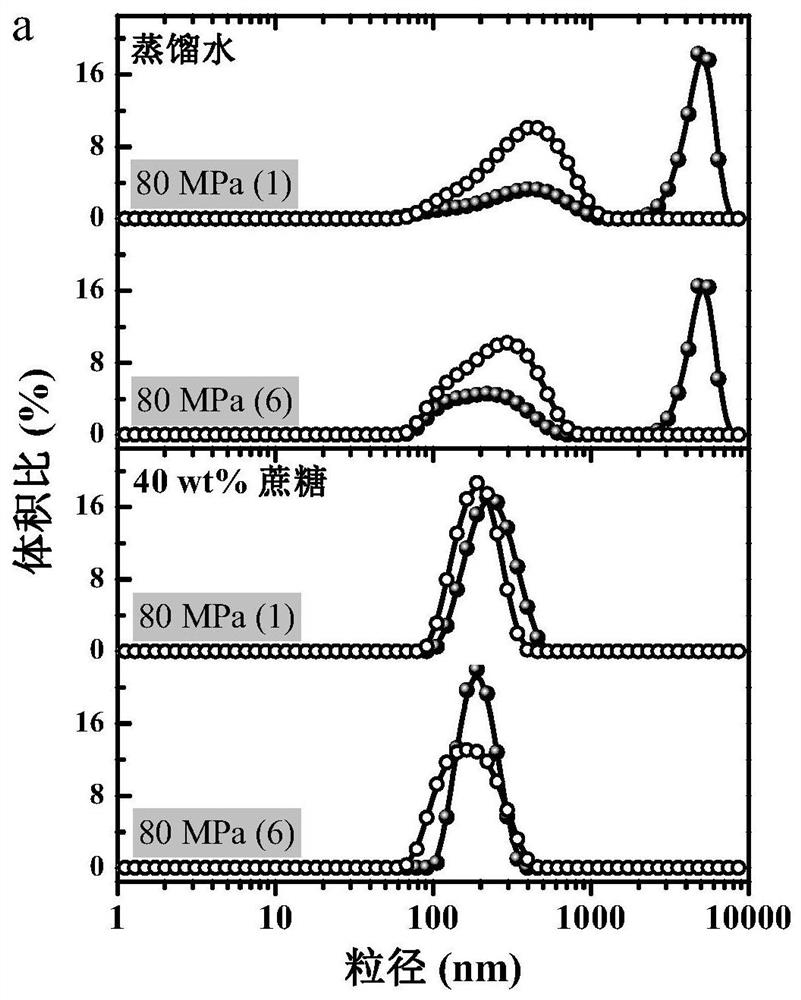
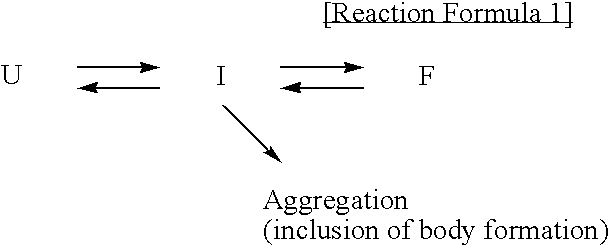
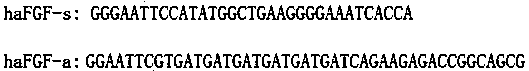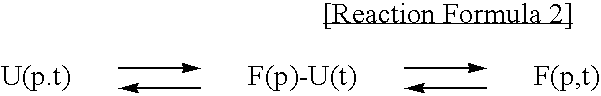Patents
Literature
81 results about "Chaperone (protein)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular biology, molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding and the assembly or disassembly of other macromolecular structures. Chaperones are present when the macromolecules perform their normal biological functions and have correctly completed the processes of folding and/or assembly. The chaperones are concerned primarily with protein folding. The first protein to be called a chaperone assists the assembly of nucleosomes from folded histones and DNA and such assembly chaperones, especially in the nucleus, are concerned with the assembly of folded subunits into oligomeric structures.
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
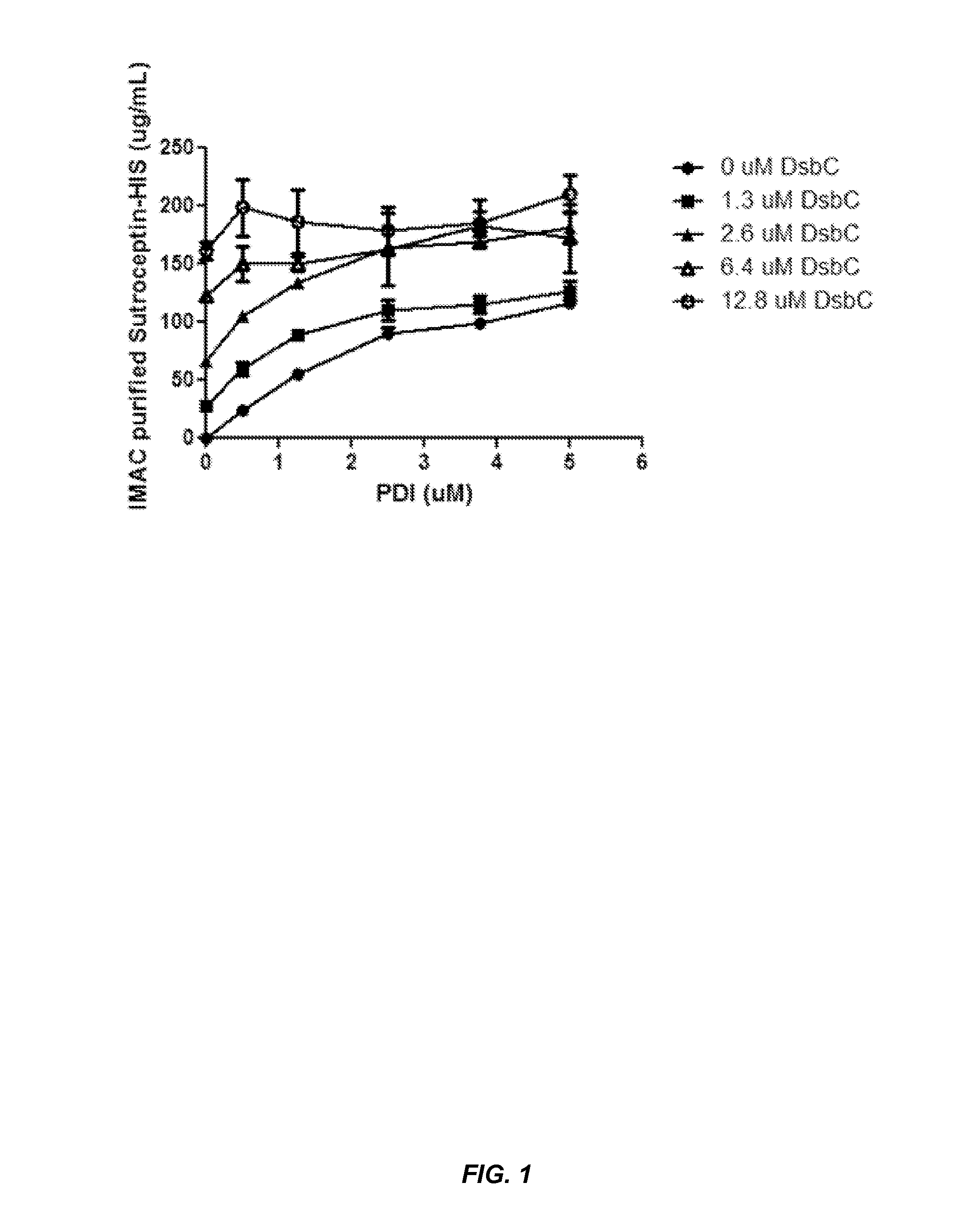
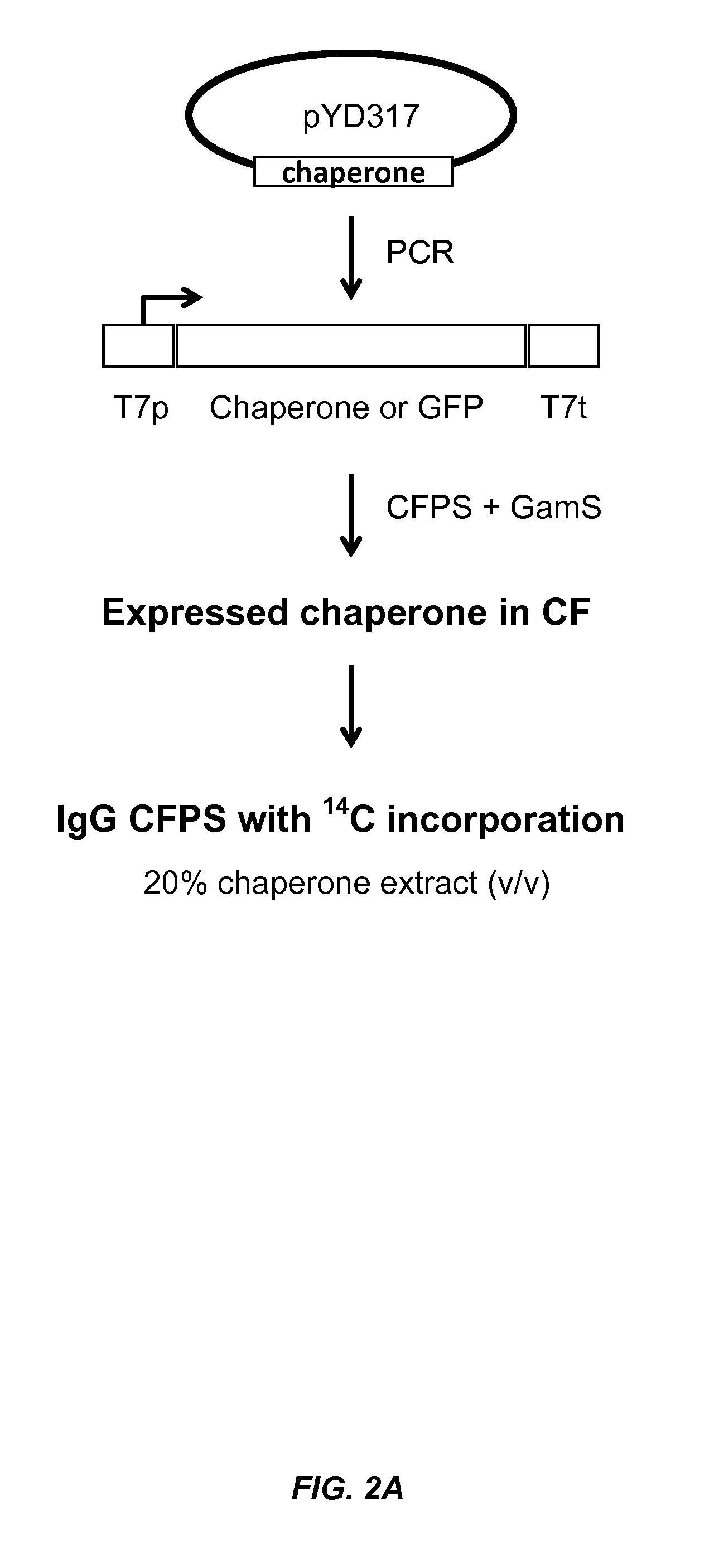
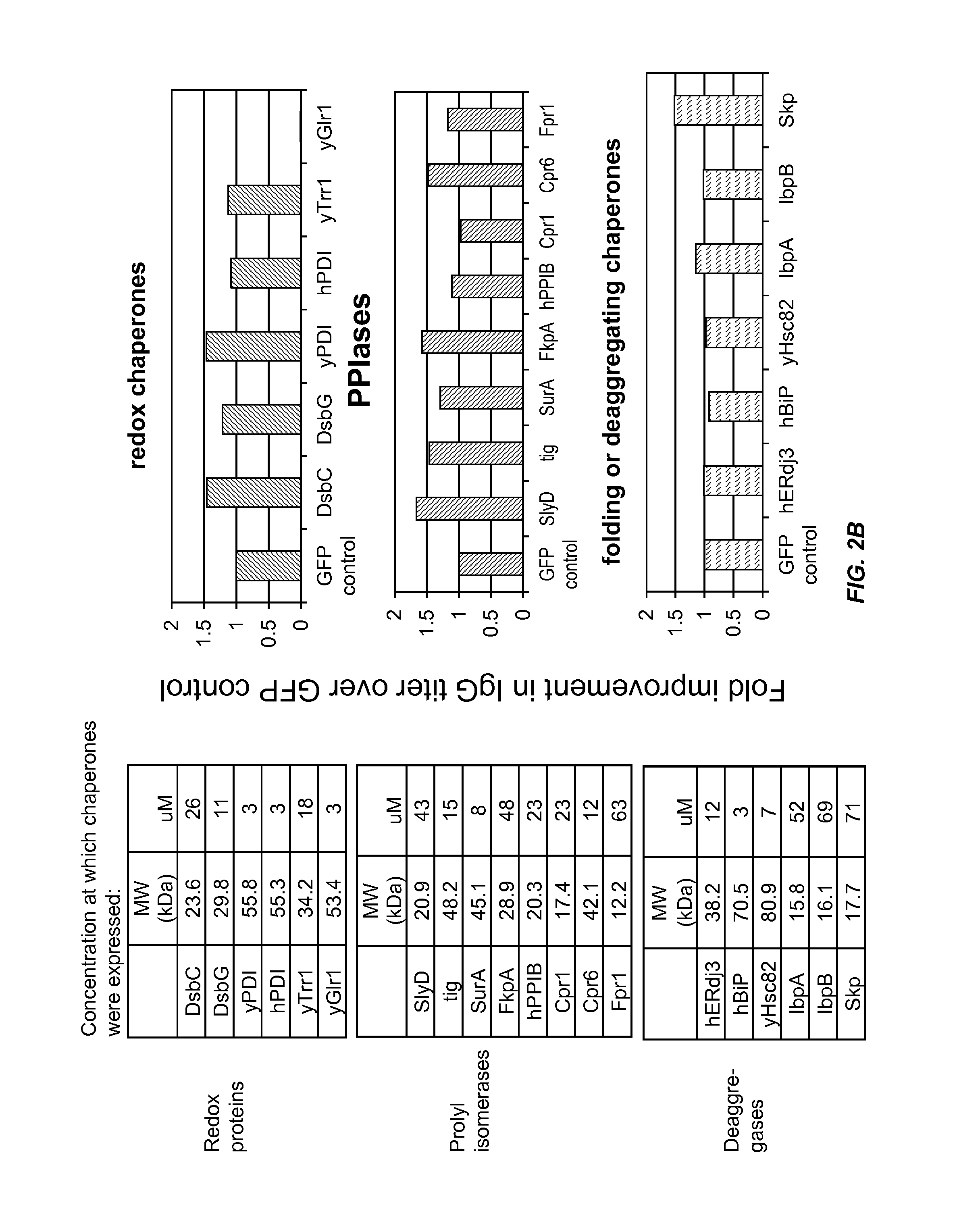
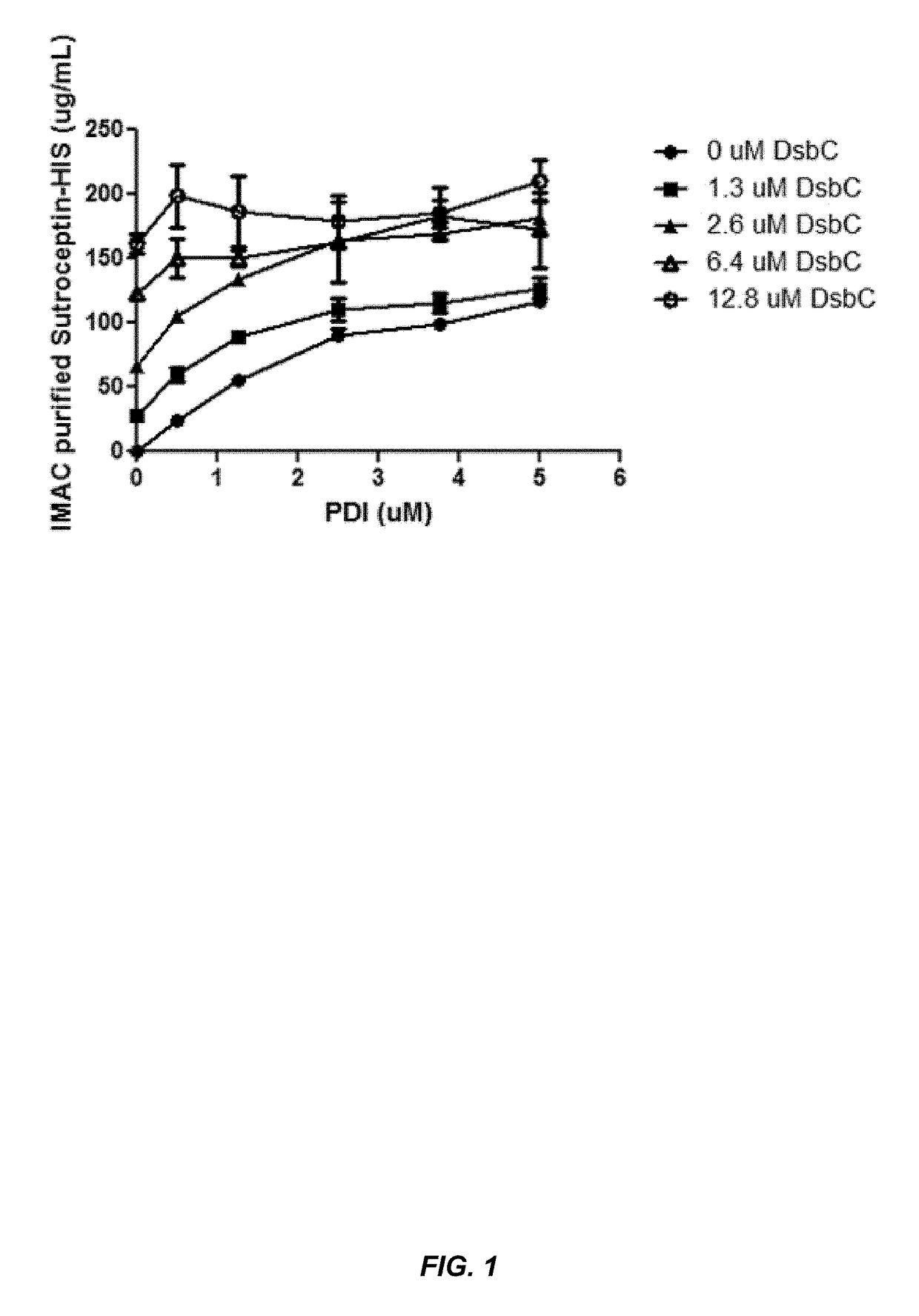
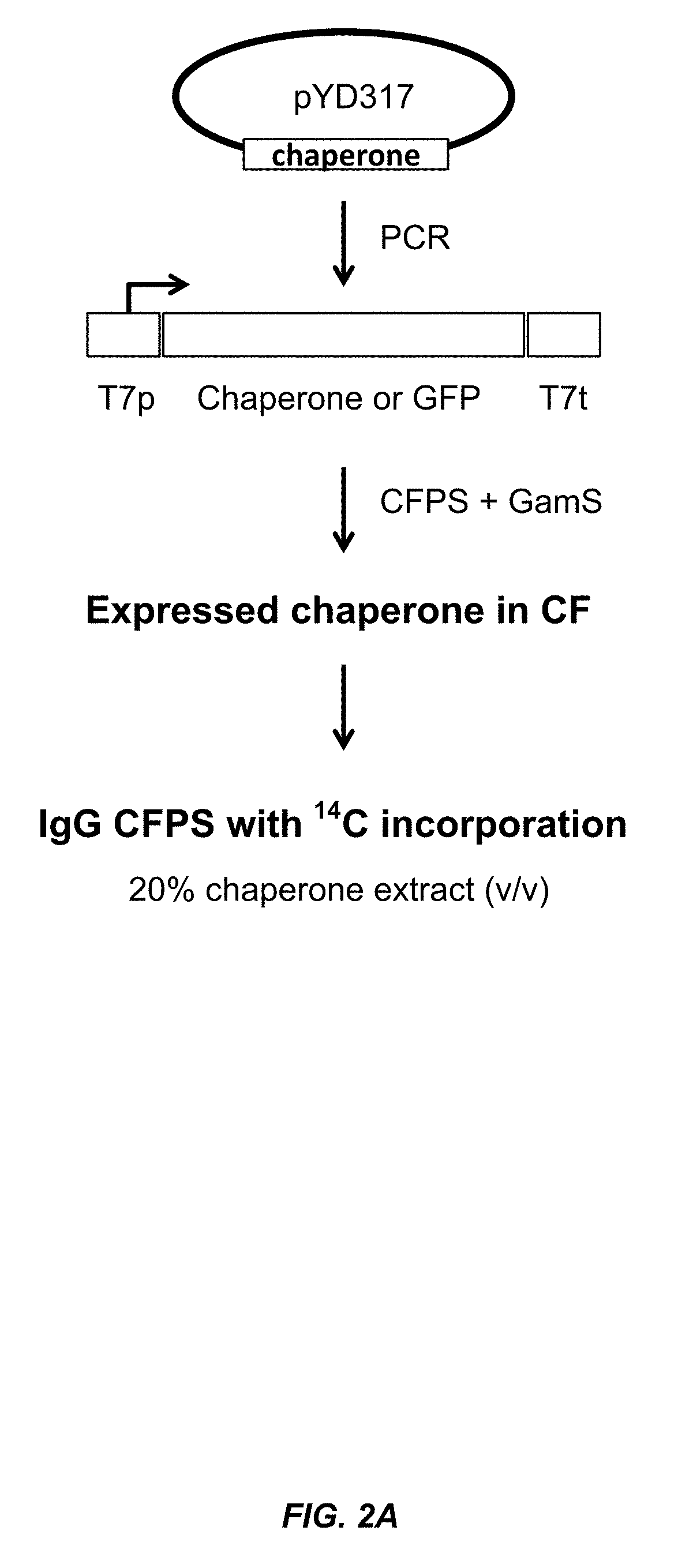
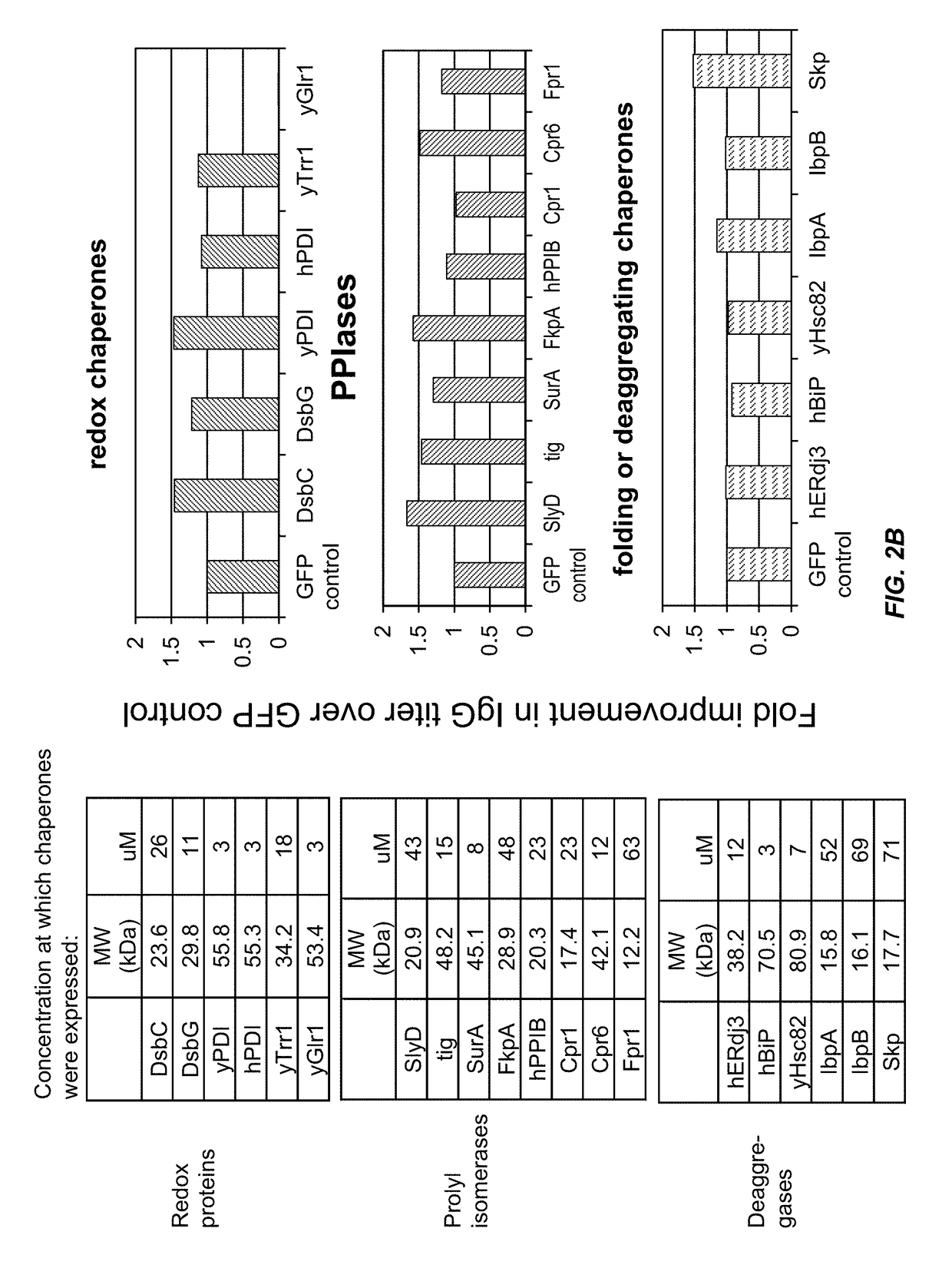
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Agents for the inhibition of virus replication through regulation of protein folding
The invention concerns agents for the treatment of acute and chronic infections with human and animal pathogenic viruses which assemble along the cell membrane and are released through budding on the surface of the cell. Hereunto count especially causative agents of infectious diseases such as AIDS, hepatitis, hemorrhagic fever, SARS, smallpox, measles, polio or the flu. The subjects of the invention are agents that contain inhibitors of the protein folding as active components. Hereunto count inhibitors of cellular folding enzymes (the enzymatic chaperones) as well as substances that disturb the folding of proteins through chemical chaperones. The following substance classes and their derivates belong thereunto: Geldanamycin, Deoxyspergualin, 4-PBA or Herbimycin A. Due to these agents the highly organised processes of the assembly and the proteolytical maturation of virus structure proteins is disturbed. As a result the release and production of infectious decendent viruses is prevented.
Owner:VIROLOGIK GMBH
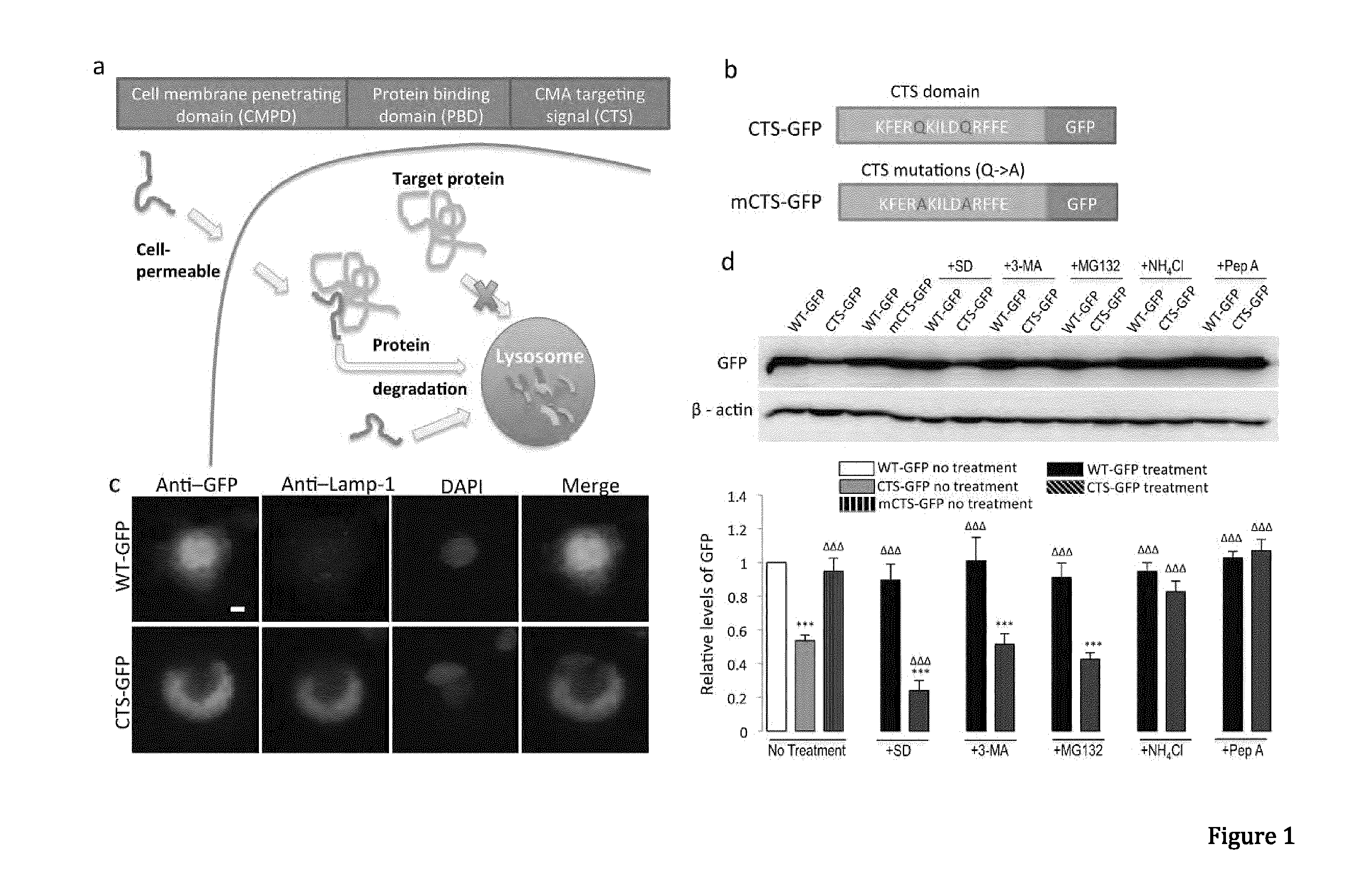
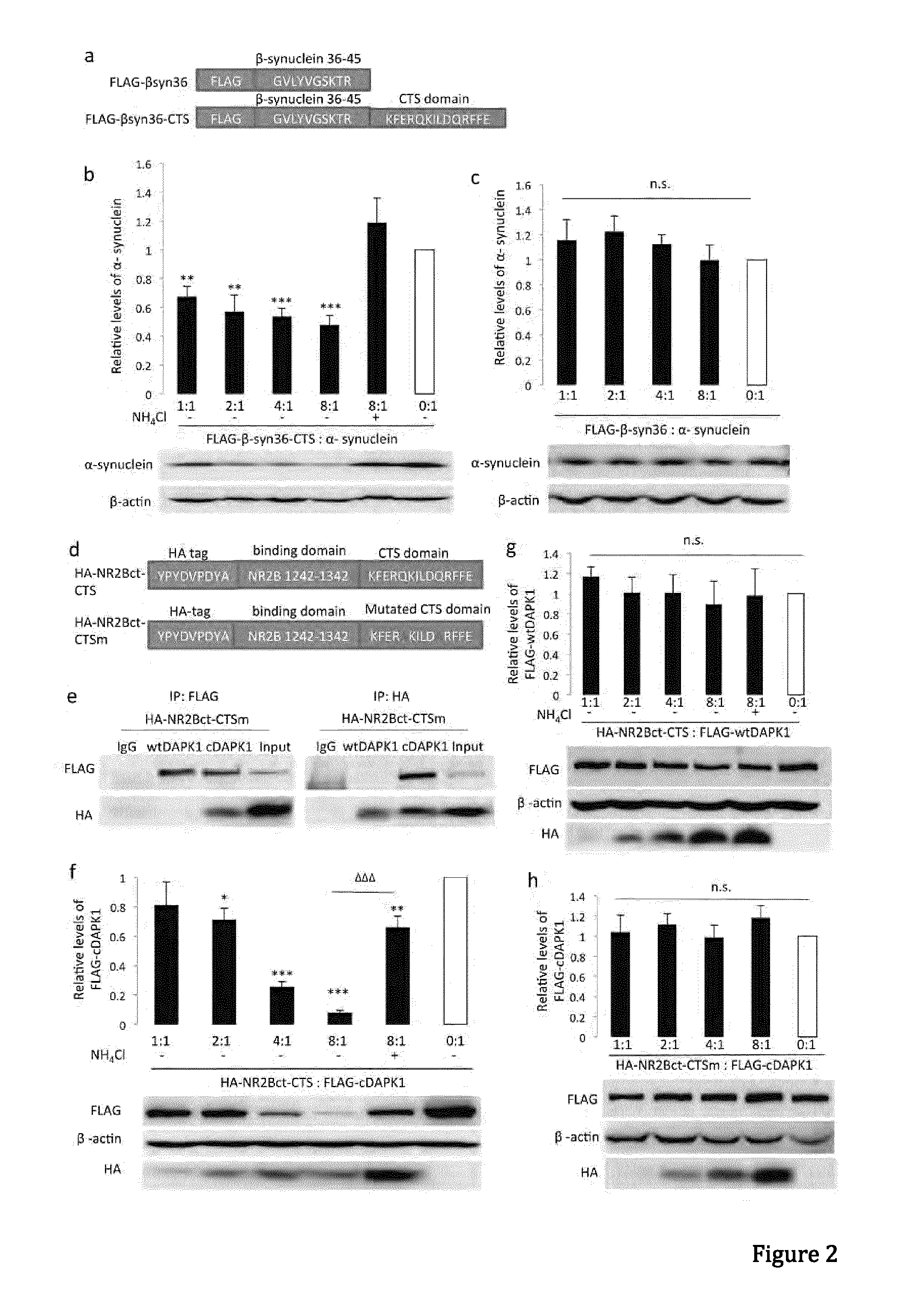
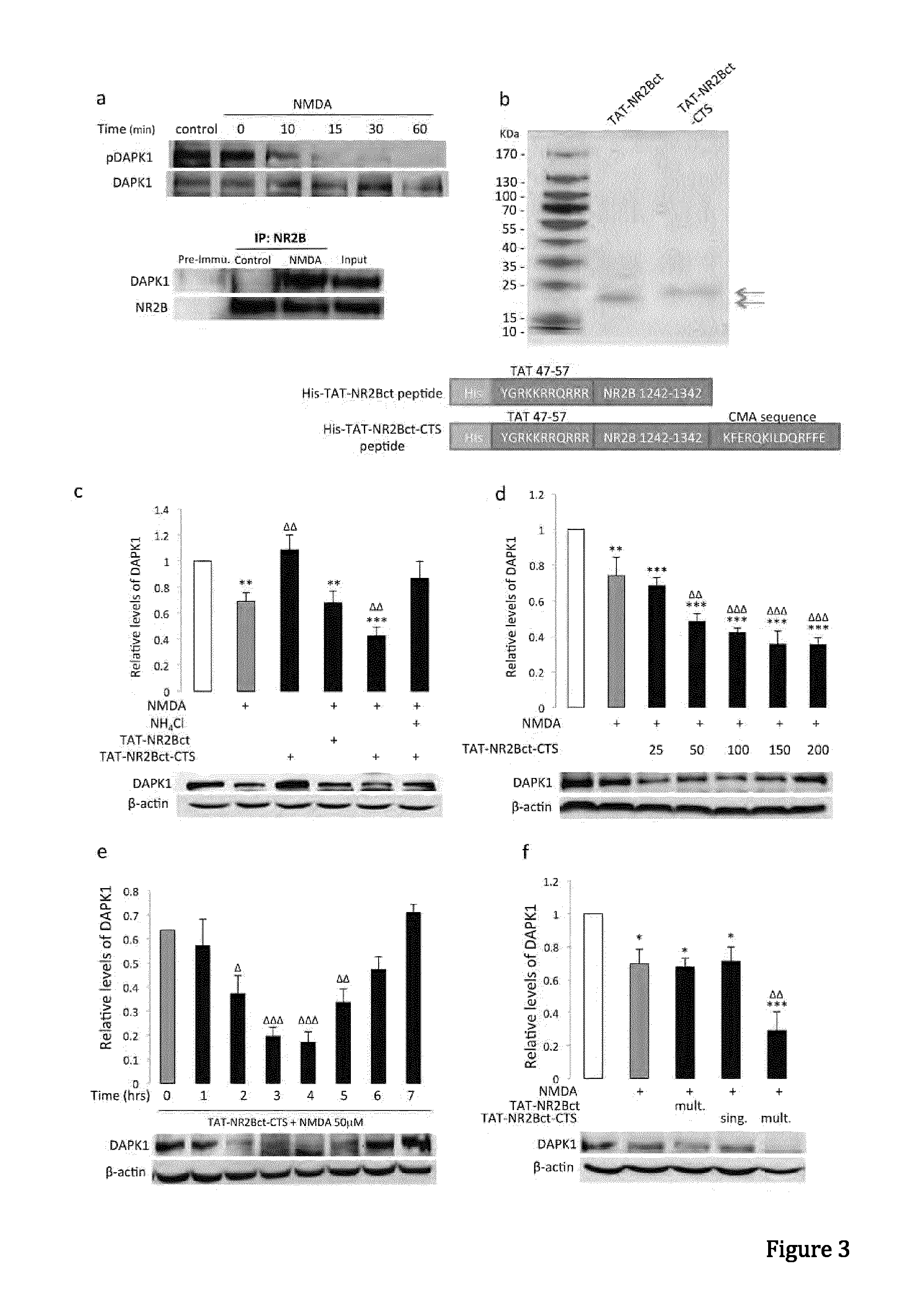
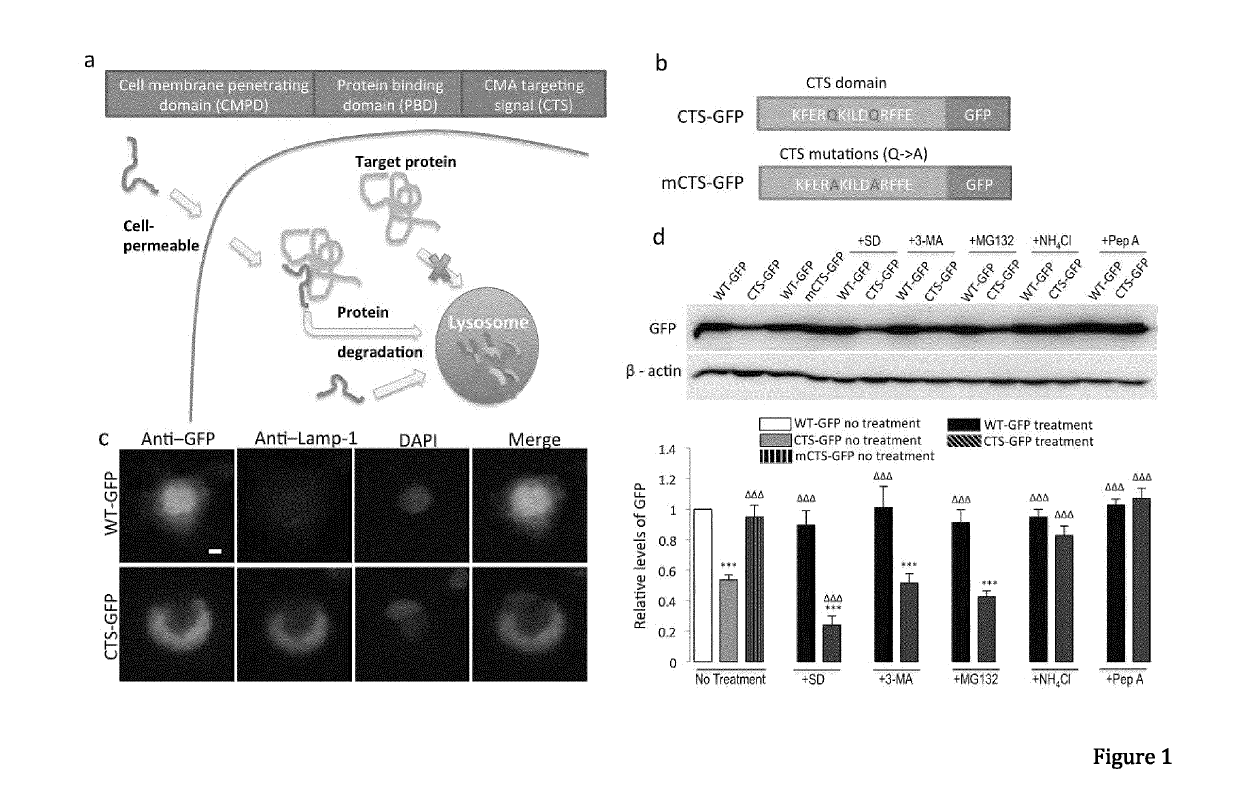
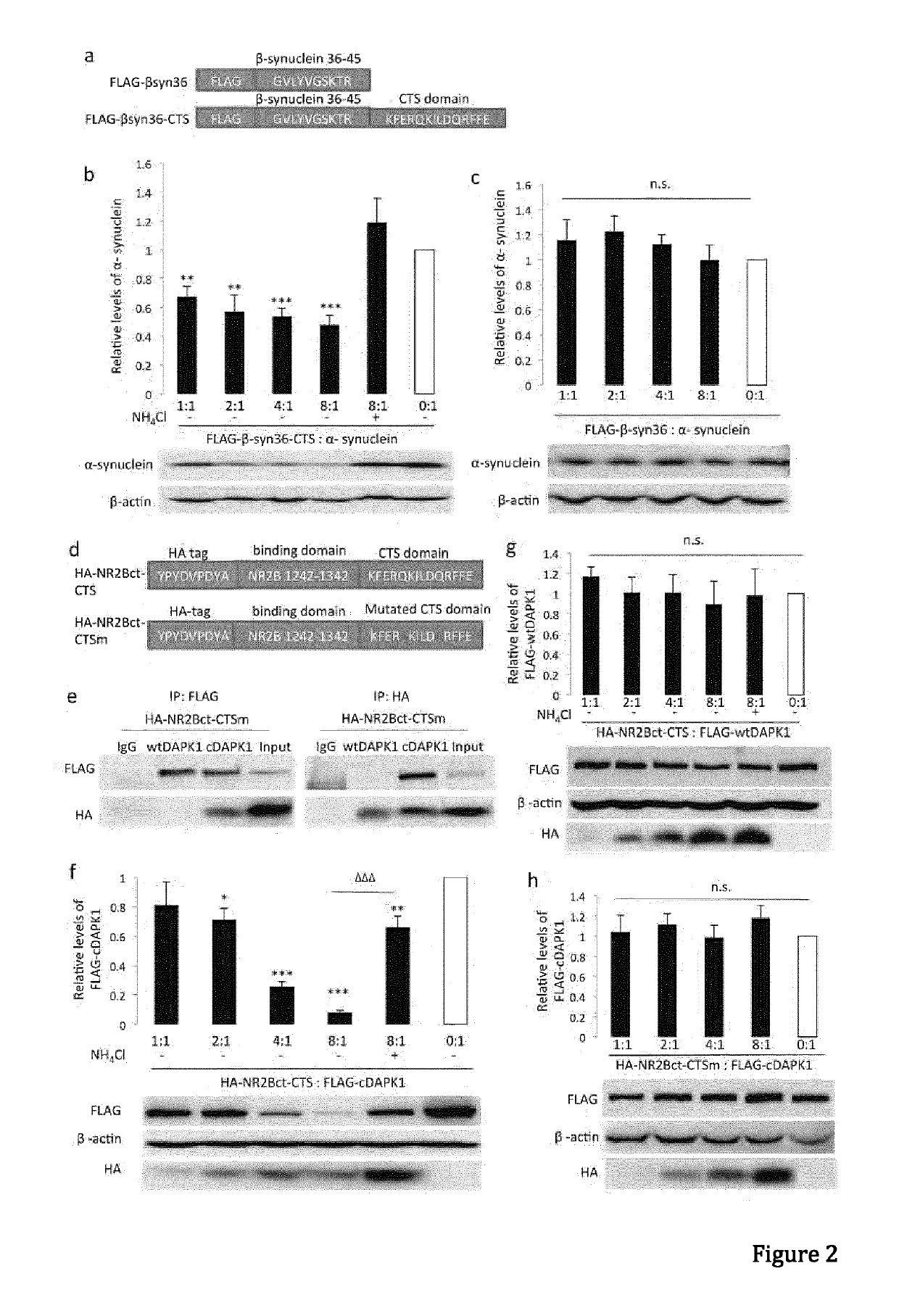
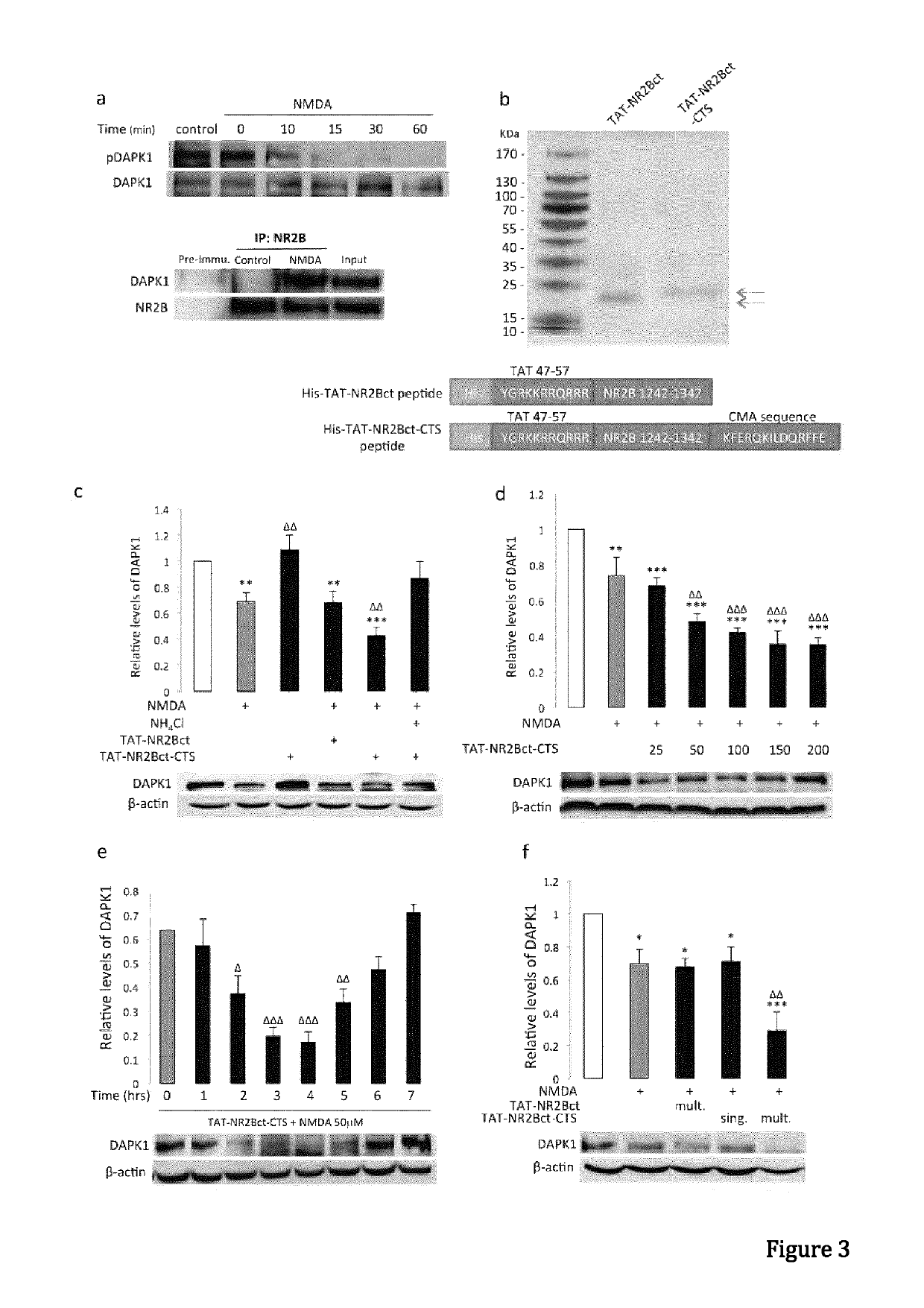
Peptide directed protein knockdown
ActiveUS20150266935A1Rapid and reversible knock-downReduced expression levelNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein target
In one aspect, the invention provides a peptide comprising a chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA)-targeting signal domain; a protein-binding domain that selectively binds to a target cytosolic protein; and a cell membrane penetrating domain (CMPD). In another aspect, the invention provides methods for reducing the intracellular expression level of an endogenous target protein in vitro and in an animal, wherein the method involves administration of the peptide. Methods are also provided for treating a pathological condition in an animal, the methods comprising administering the peptide to the animal. In one embodiment, the pathological condition is a neurodegenerative disease. In another embodiment of the invention, the target cytosolic protein is death associated protein kinase 1 and the CMPD is protein transduction domain of the HIV-1 Tat protein.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
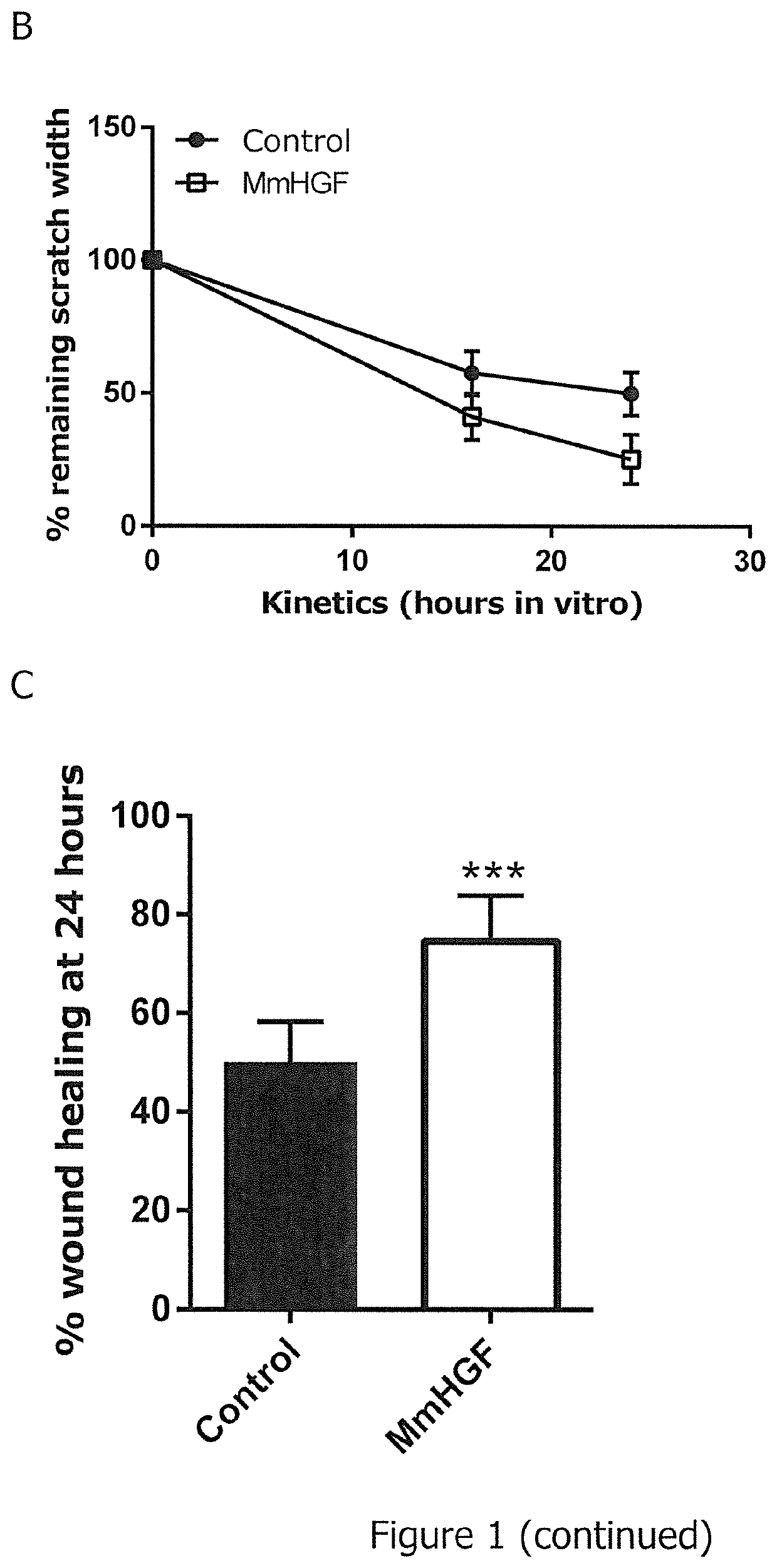
Rnas for wound healing
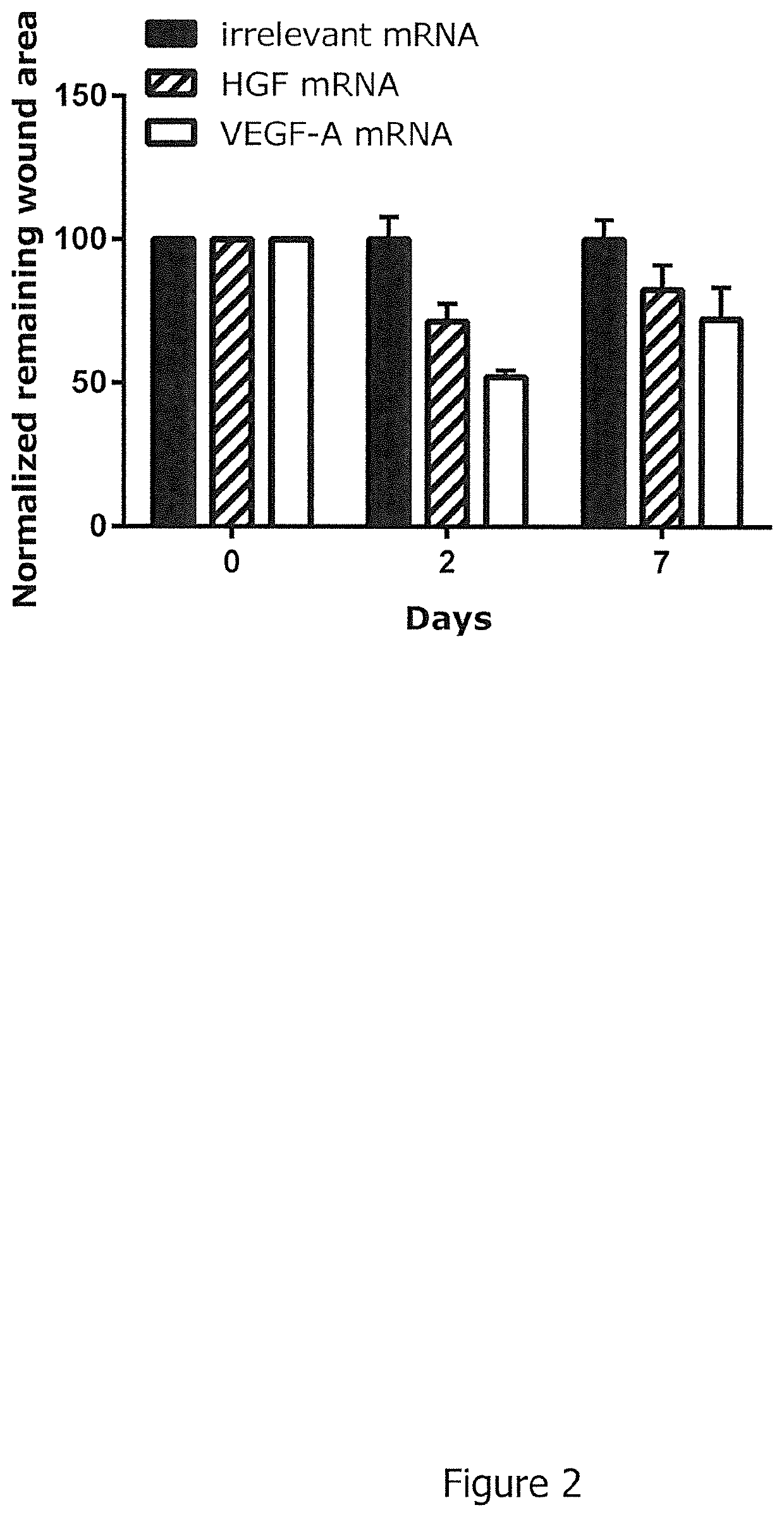
ActiveUS20200149026A1Promote wound healingPeptide/protein ingredientsDermatological disorderTherapeutic proteinReceptor
The present invention relates to an RNA encoding a therapeutic protein, in particular a collagenase, growth factor, cytokine, receptor, chaperone or signal transduction inhibitor. In particular, the present invention relates to RNA suitable for treatment of wounds, specifically for promoting wound healing. The present invention concerns such RNA as well as pharmaceutical compositions and kits and combinations comprising the RNA. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the RNA, pharmaceutical compositions, kits as disclosed herein for use in the treatment of wounds, specifically for promoting wound healing.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
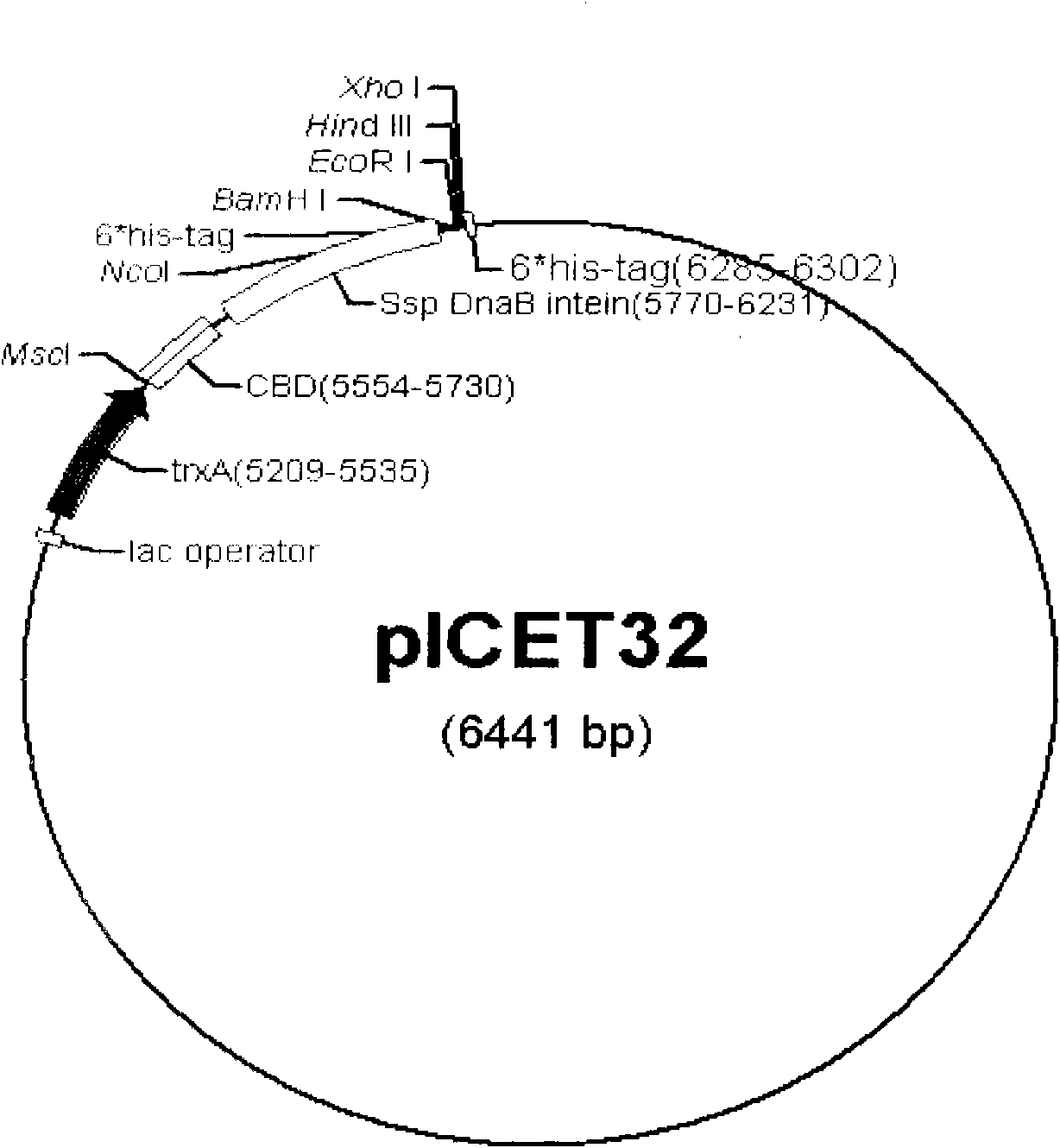
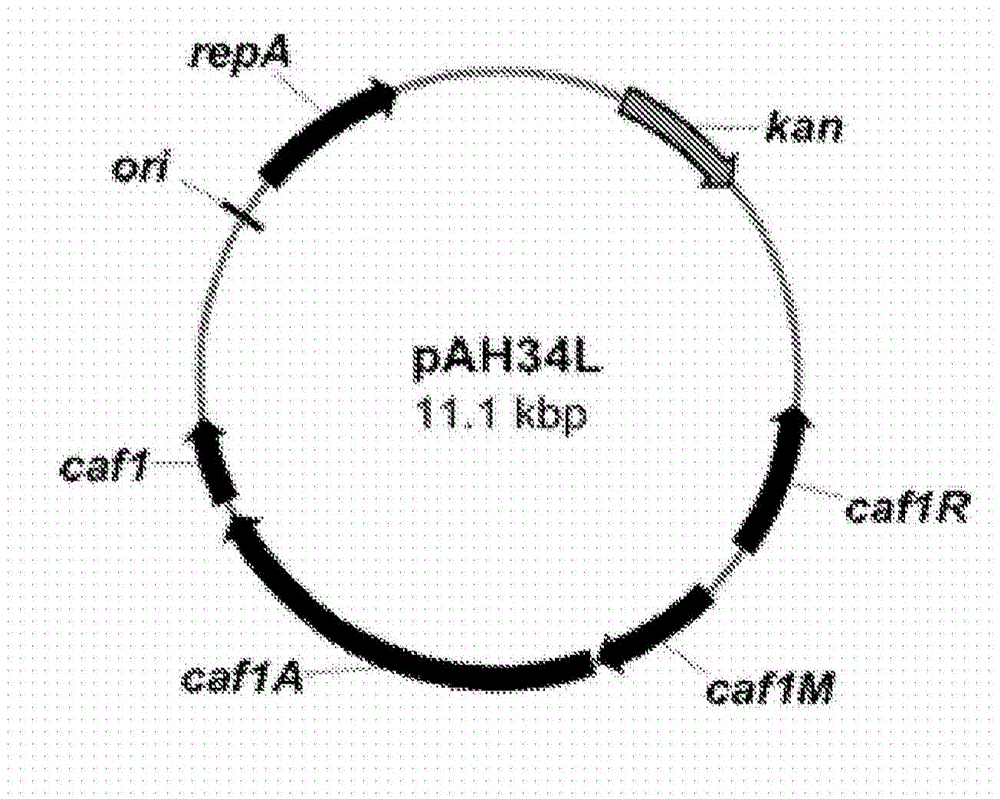
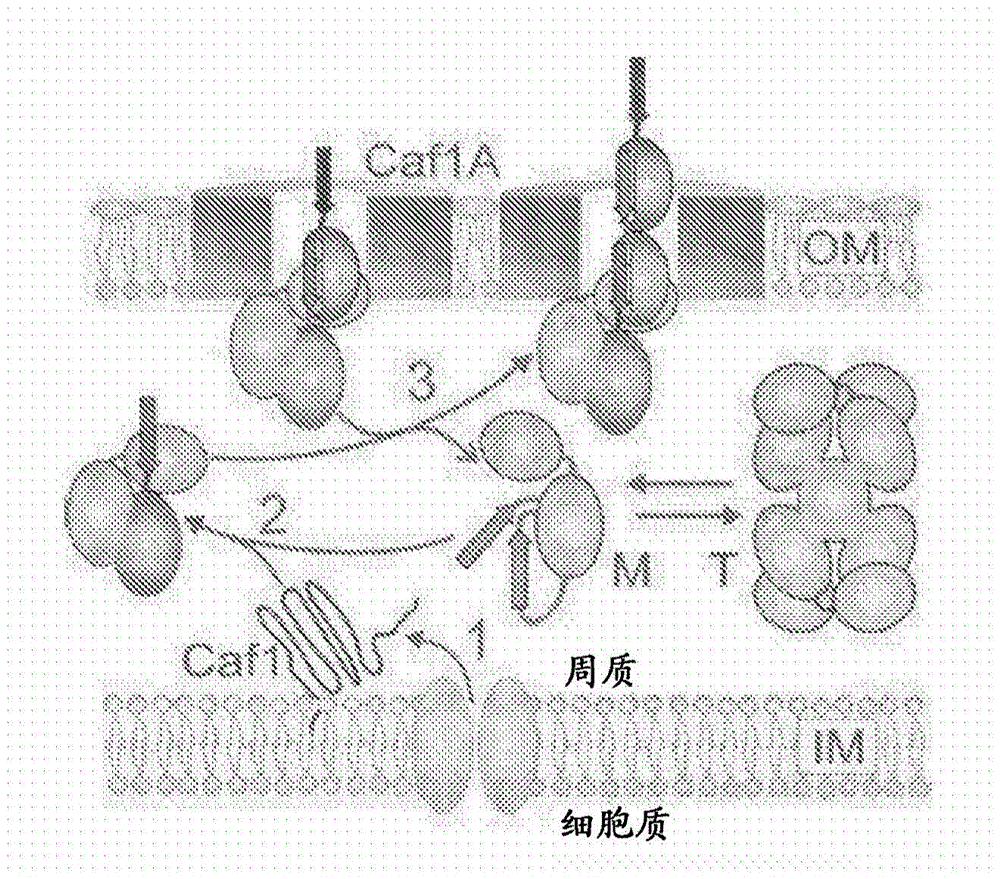
Prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN101967493AIncrease productionImprove solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetNucleotide
The invention relates to a prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof. The vector comprises: (a), a molecular chaperone for promoting the soluble expression of target protein or / and the correct folding of disulfide bonds; and (b), an encoding nucleotide sequence of intein which can be broken on peptide bonds at a C terminal. In the vector, the high-efficiency soluble expression of the target protein is promoted by the molecular chaperone, so that the target protein maintain natural bioactivity, and the self-shearing action of the intein is induced effectively under a certain condition to separate the target protein from fusion protein, and the target protein is separated and purified again to obtain the target protein with natural bioactivity economically and efficiently. The invention also relates to host cells containing the vector and application of the vector in the recombinant expression of bioactivity protein.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
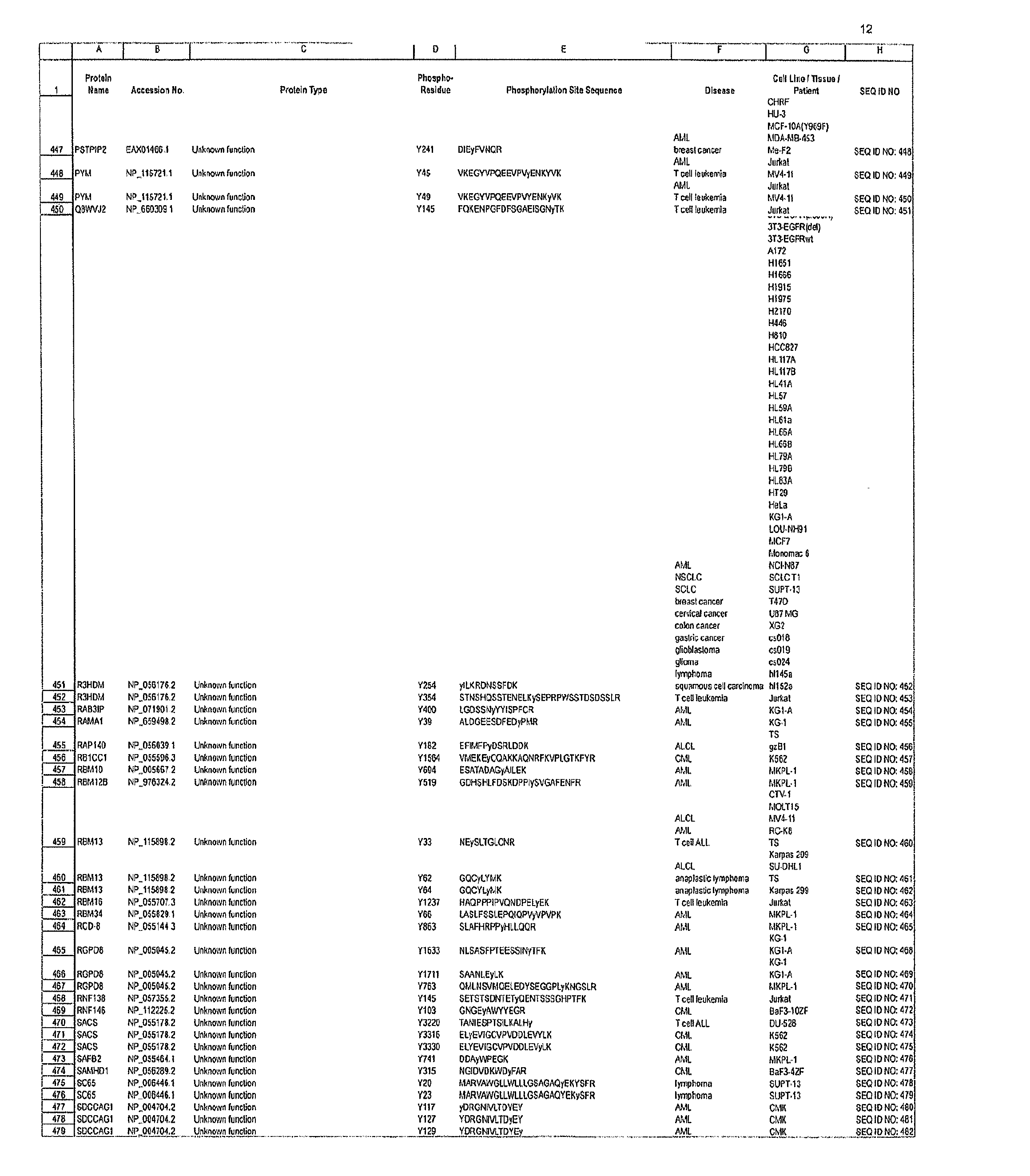
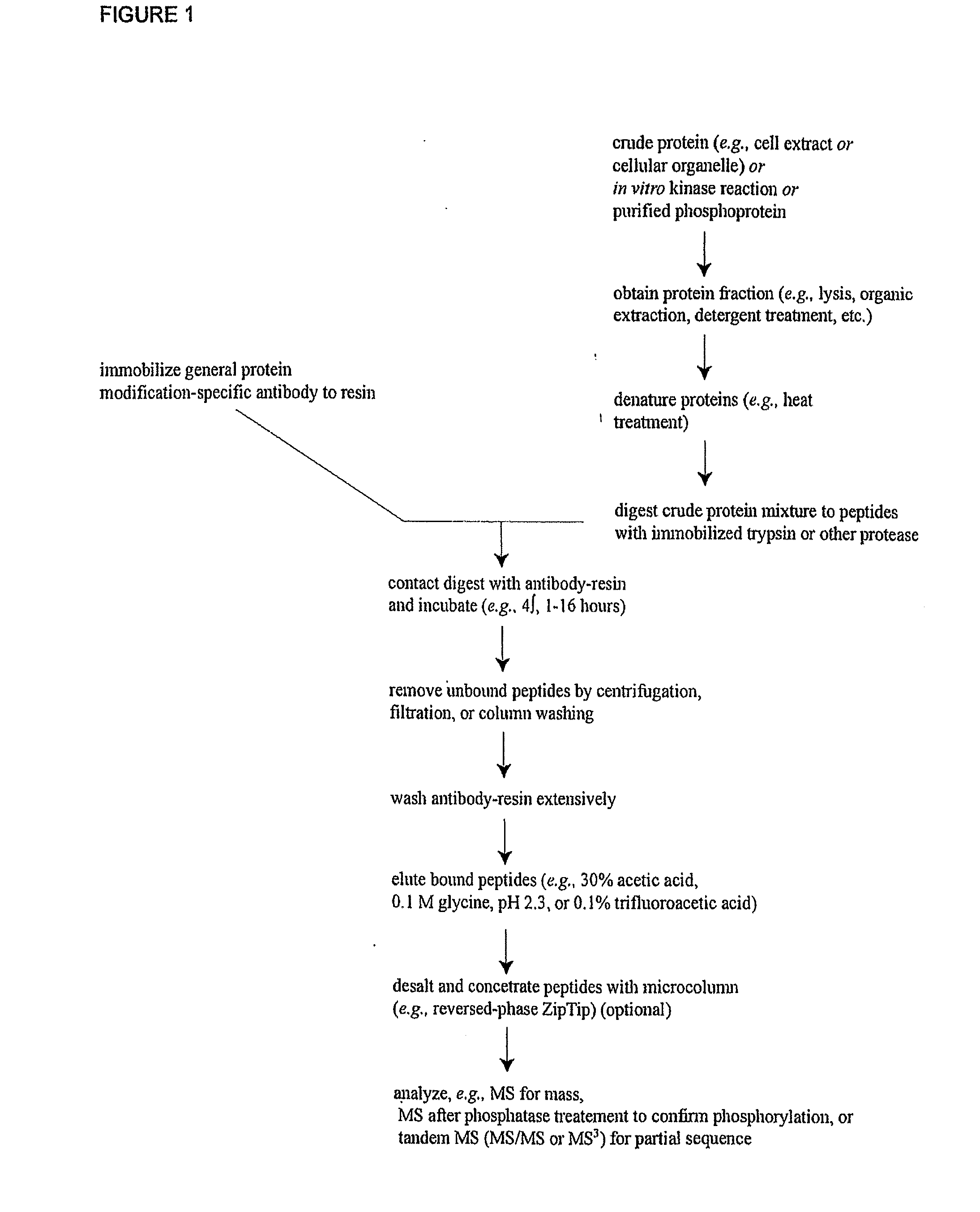
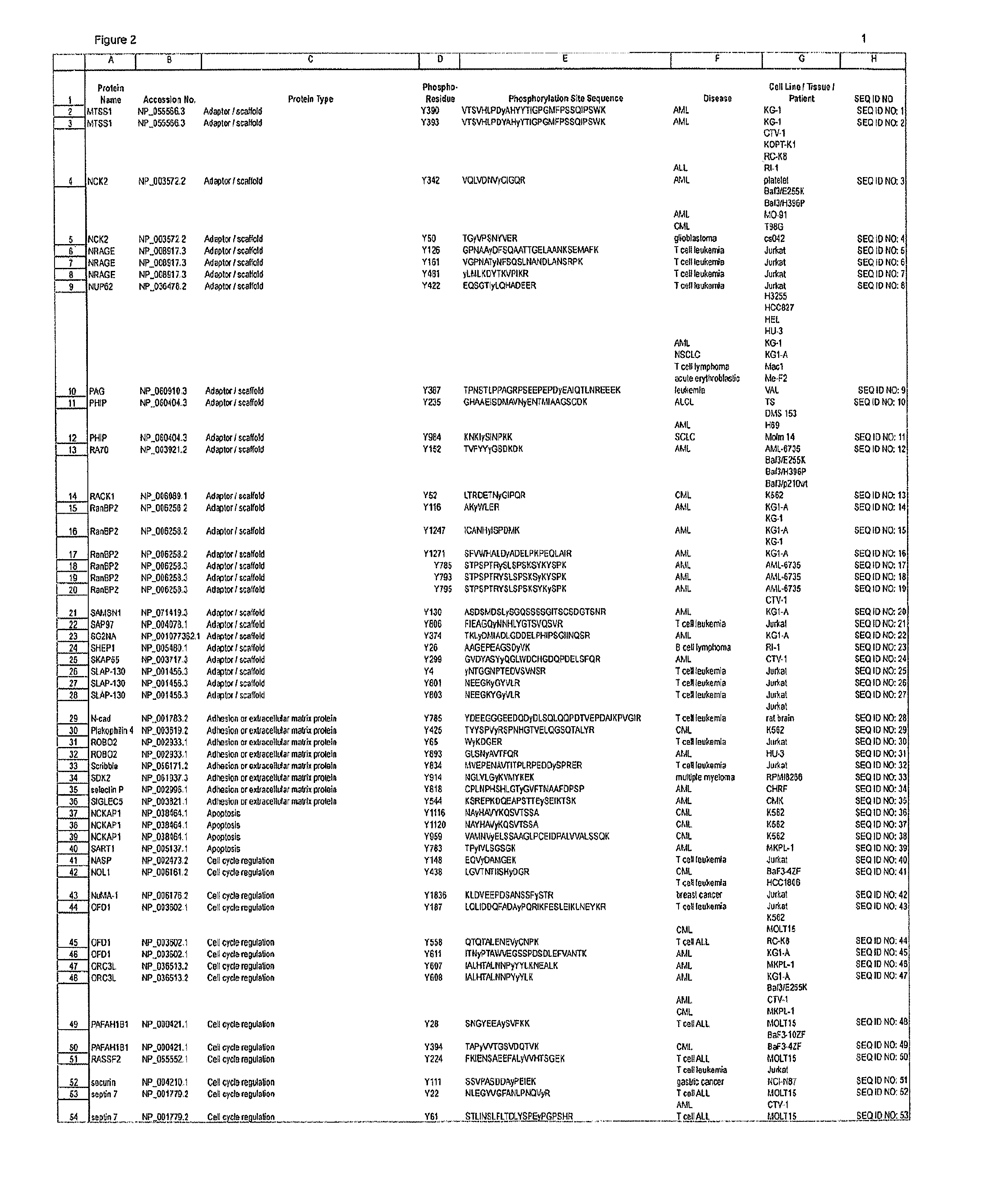
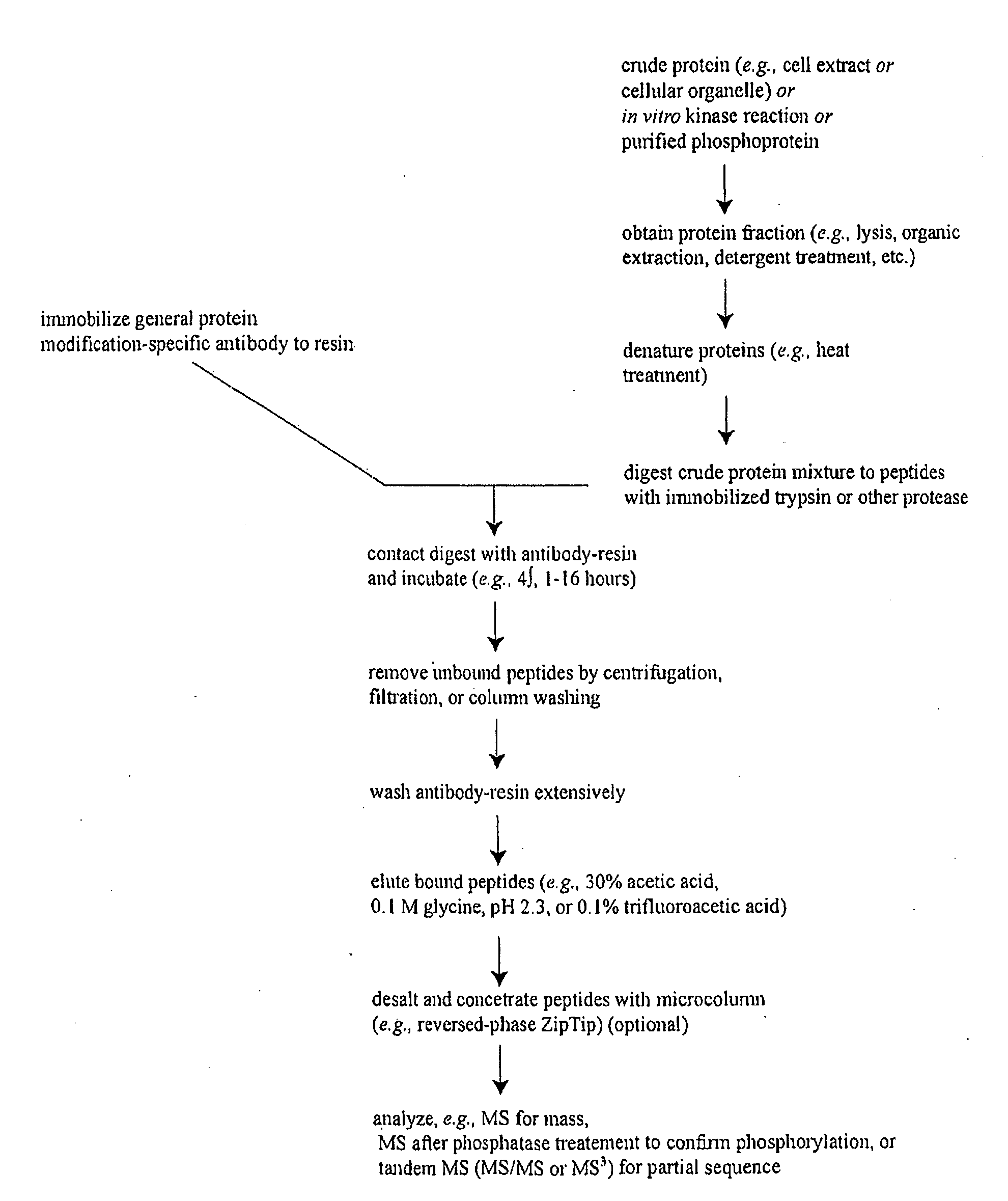
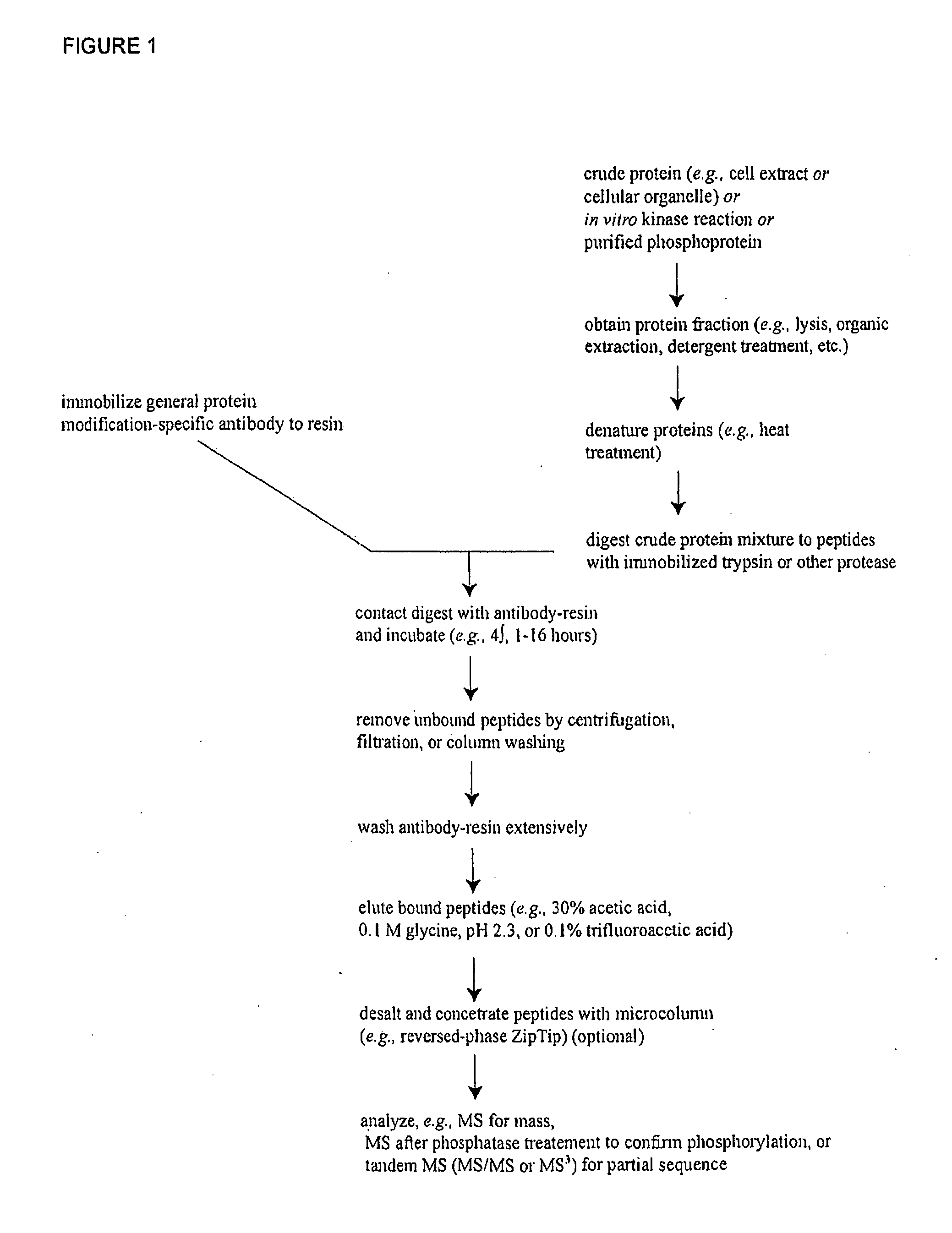
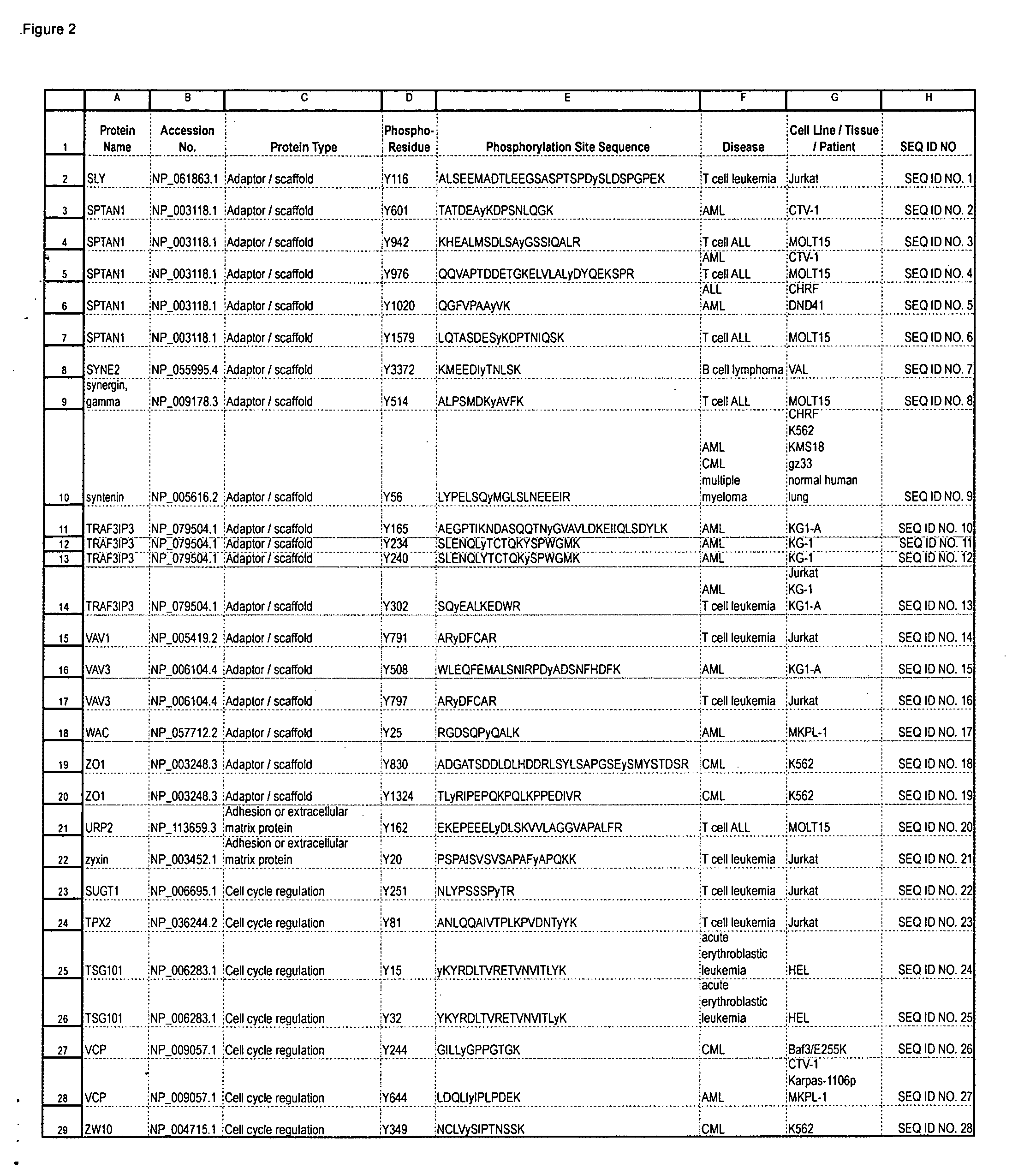
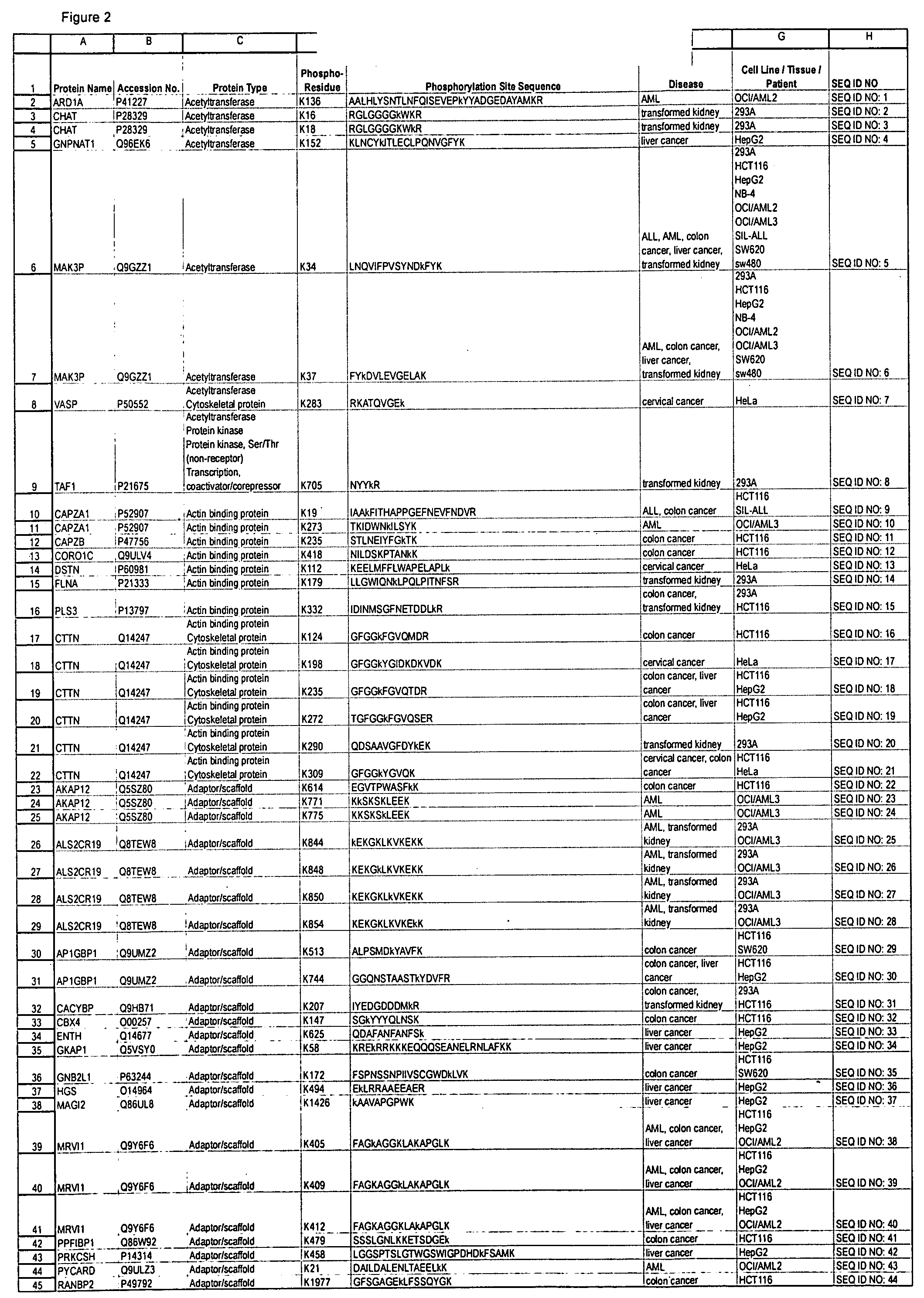
Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Signaling Pathways
ActiveUS20090258436A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEndoplasmic reticulumScaffold protein
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Method and use of producing soluble recombinant protein in colibacillus
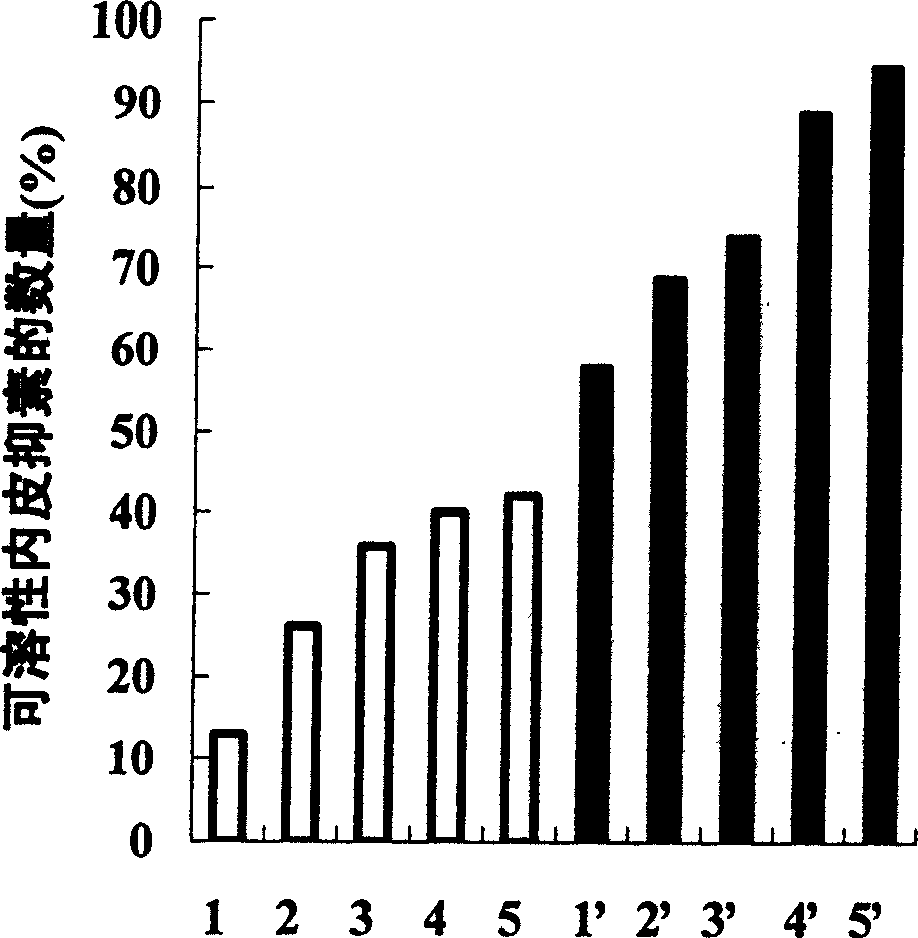
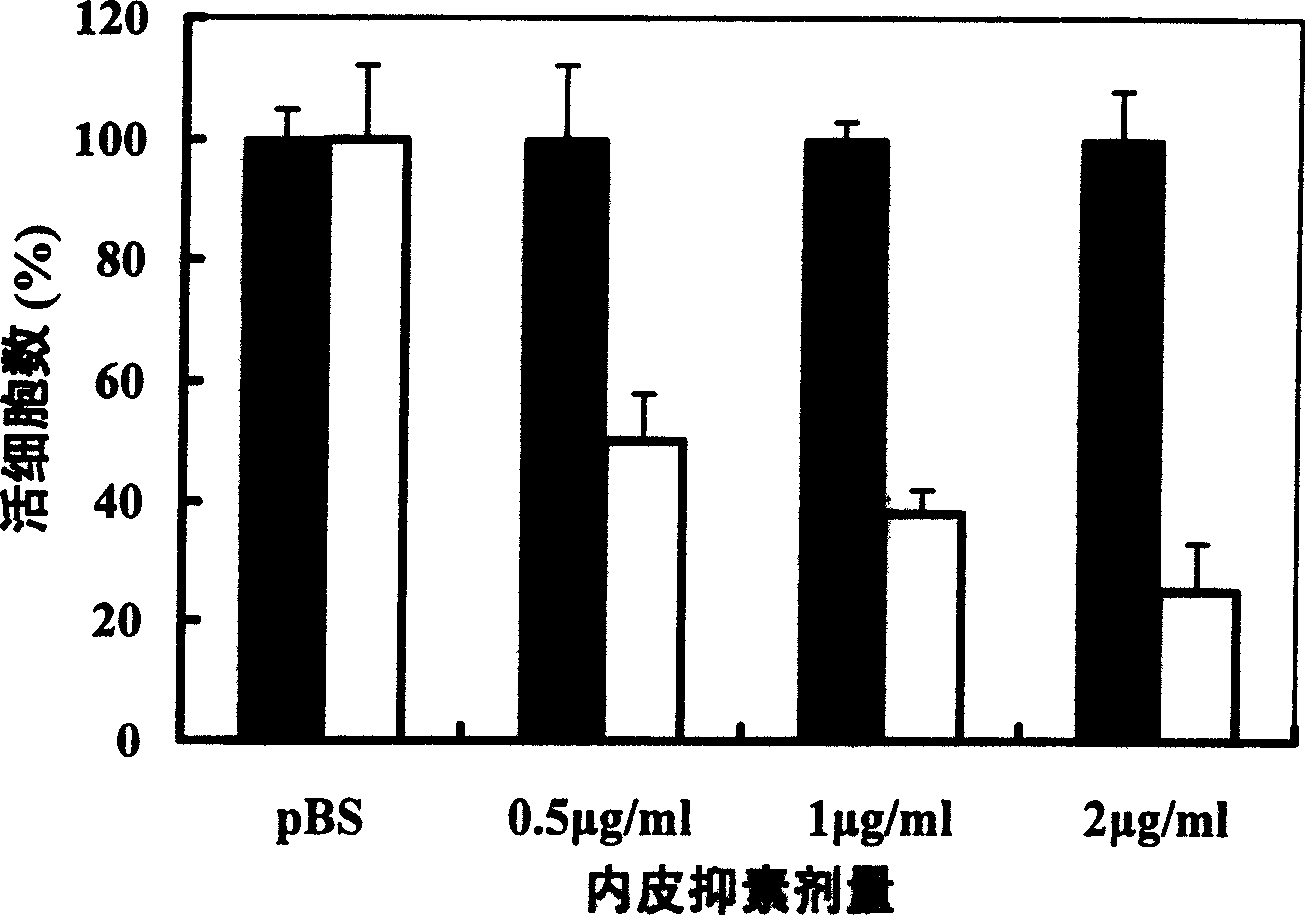
ActiveCN1614025AIncrease productionInhibit angiogenesisBacteriaFermentationBio engineeringMolecular biology
The invention was involved in that target protein expression strain and molecular partner were expressed in E.coli.at the same time at low temperature to prevent the formation of target protein inclusion body effectively and increase yields of soluble production largely. Soluble recombinant human endostatin and human angiostatin were increased largely by the technique. It provided a new simple and cheap technique to produce soluble recombinant protein with biological activity. It was applied in bioengineering pharmaceutical factory, gene engineering, biochemistry and molecular biology with high efficiency, cheap price, wide application and strong promotion.
Owner:NANJING JIRUIKANG BIOTECHNOLOGY RES INST CO LTD
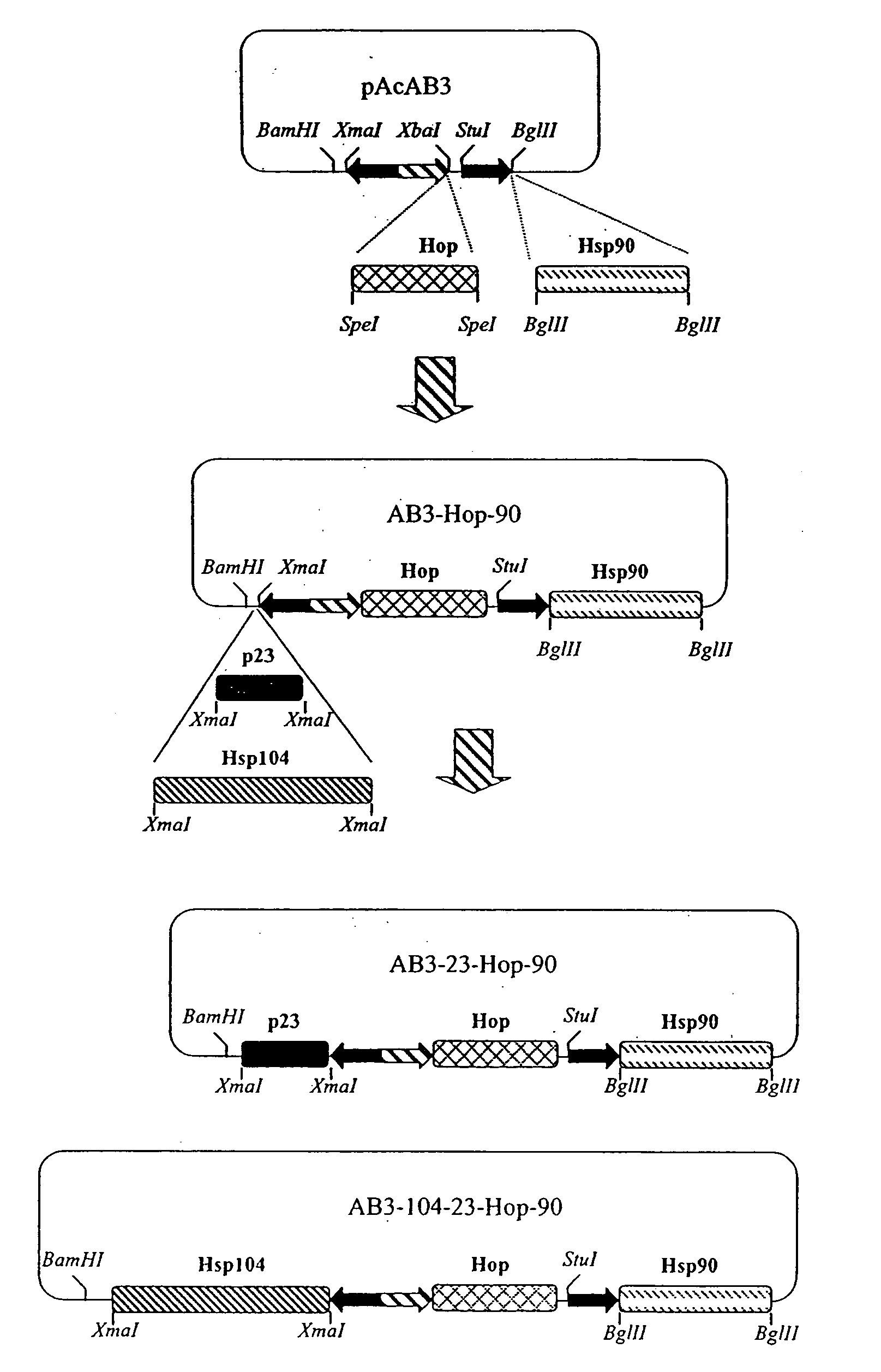
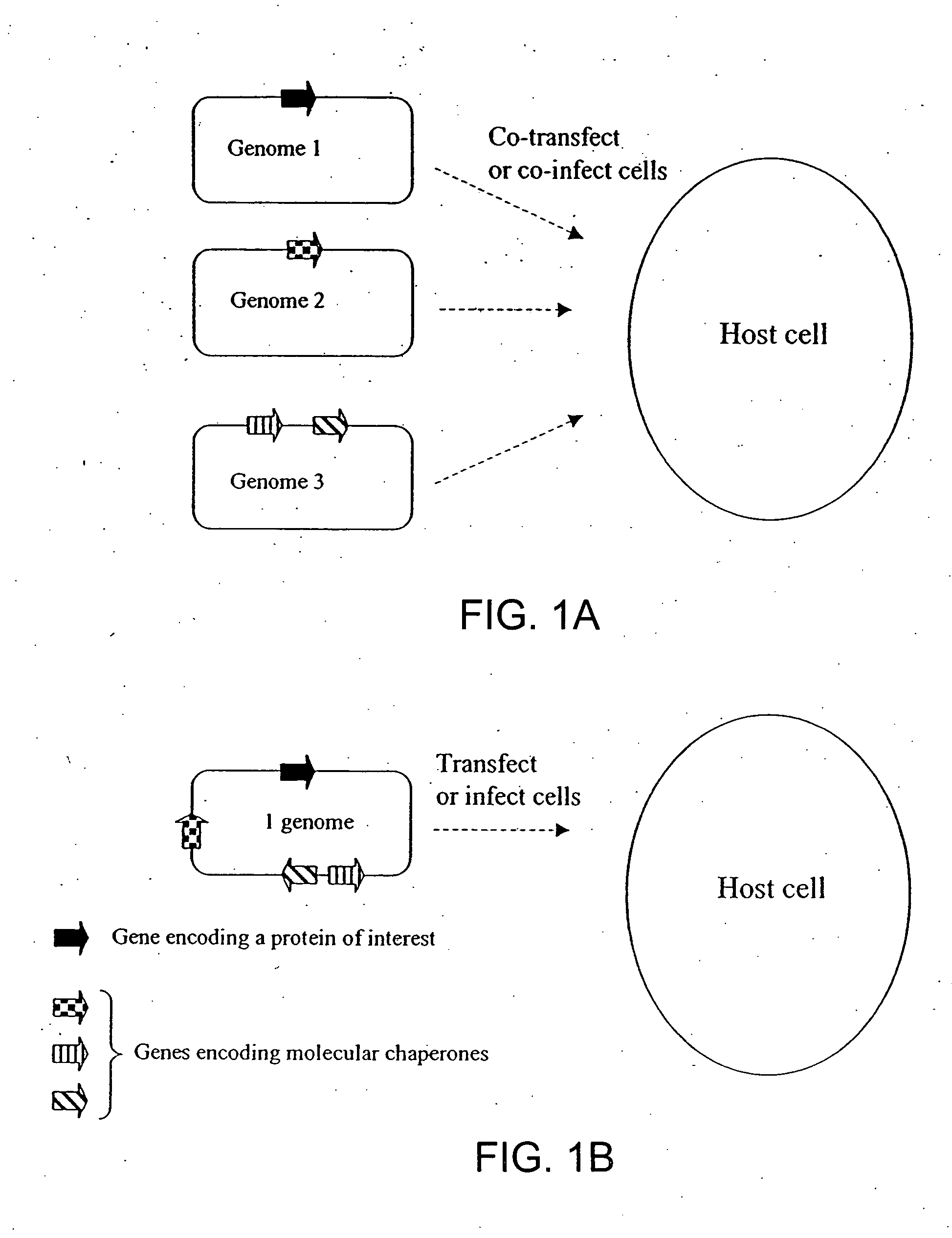
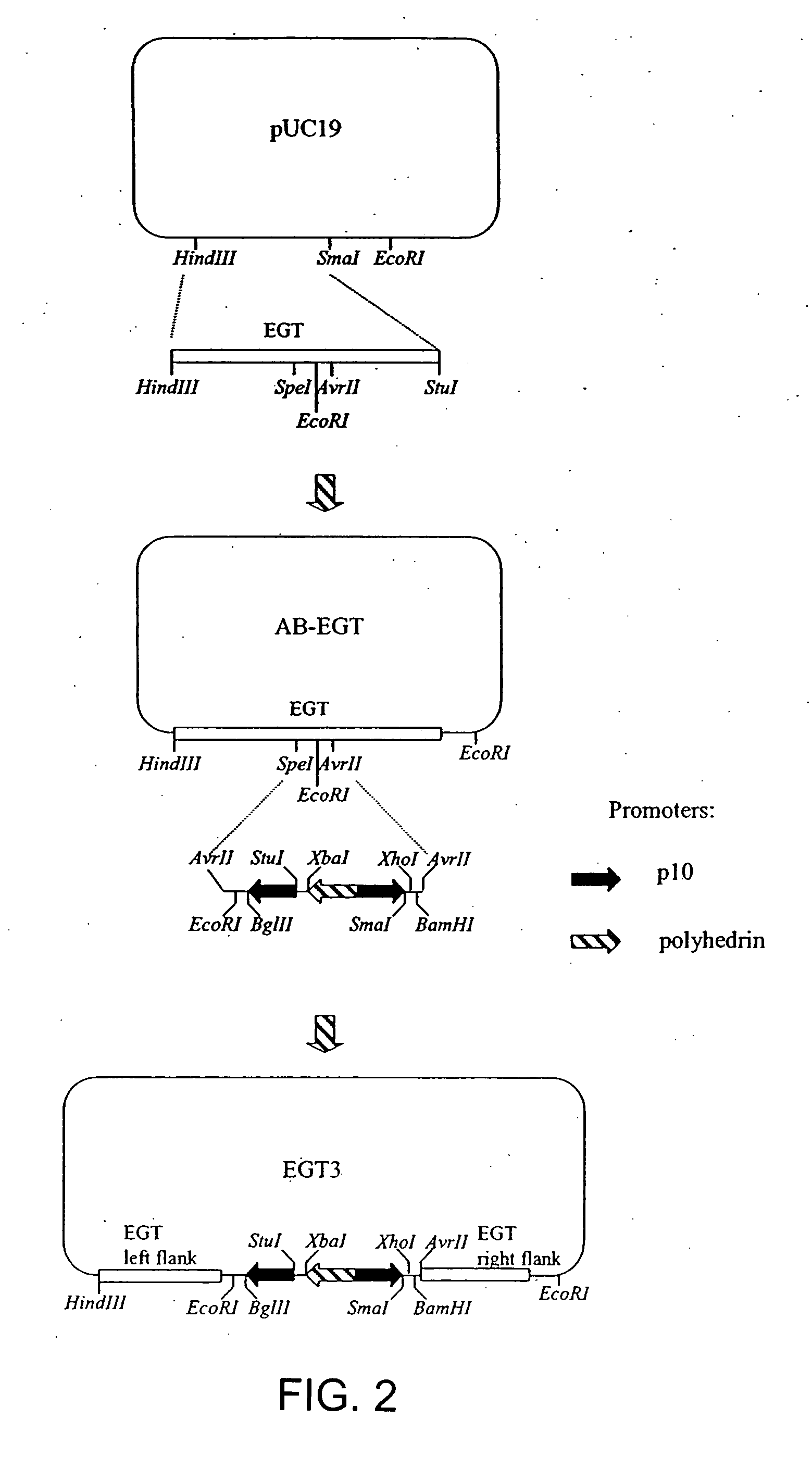
Chaperone expression genomes
InactiveUS20080057538A1Easy to foldFacilitate it co-translocationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesBiotechnologyForeign protein
A recombinant genome comprising polynucleotides encoding at least two additional molecular chaperones and a protein of interest, recombinant baculovirus vectors providing molecular chaperones and a method for producing a foreign protein using said genomes and vectors.
Owner:BELYAEV ALEXANDER S
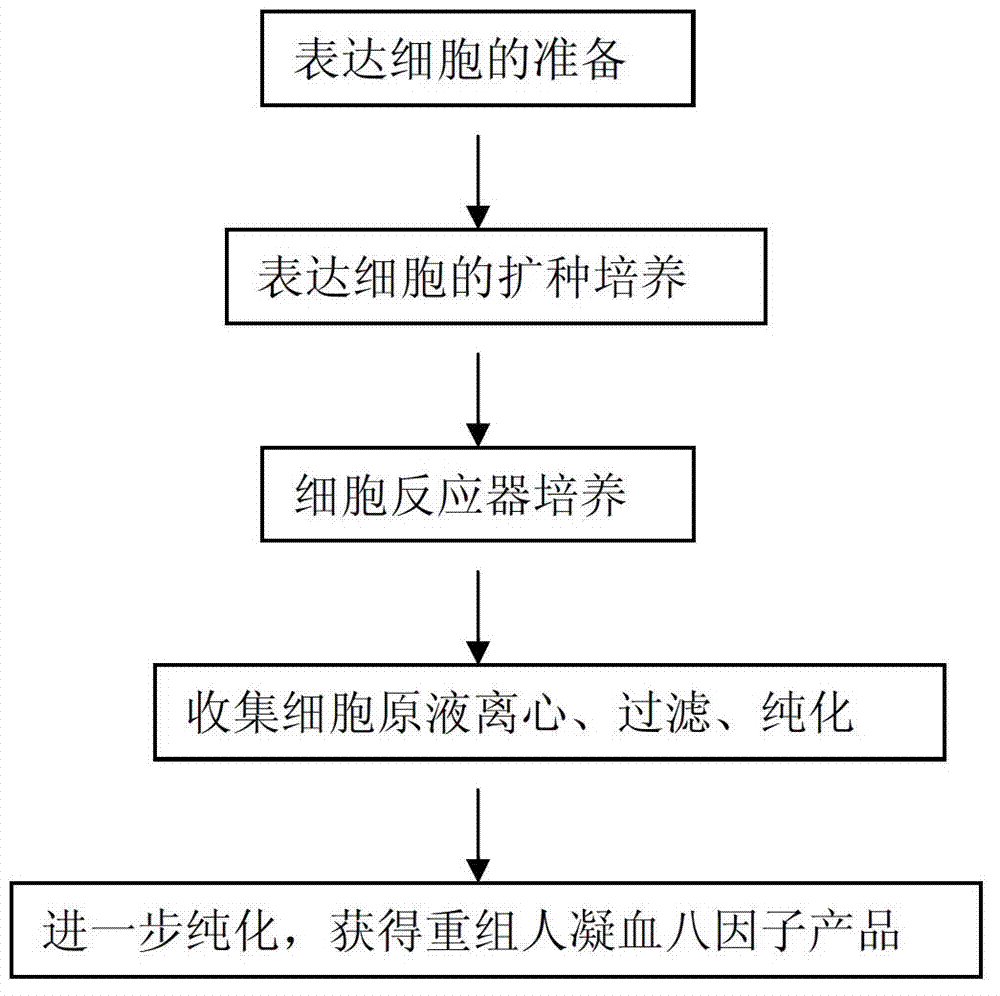
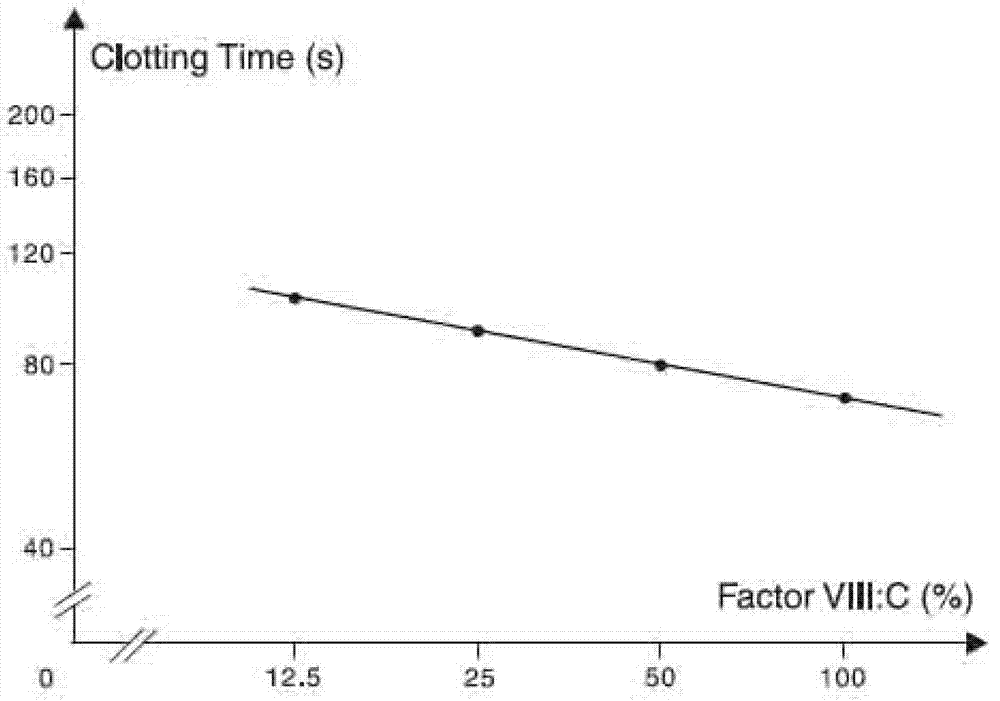
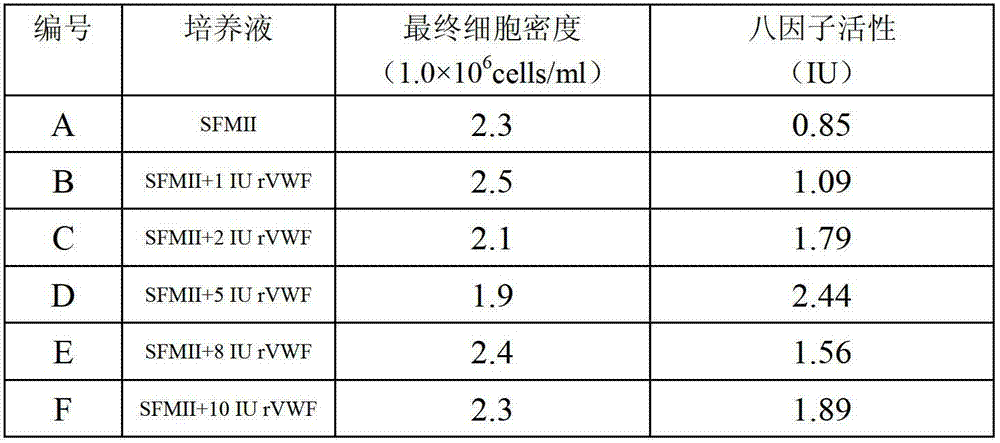
Method for effectively expressing recombinant human coagulation factor VIII
The invention relates to the technical field of biological engineering, in particular to a process method for effectively expressing a recombinant human coagulation factor VIII by utilizing mammalian cell culture. The method specifically comprises the following steps: adding an exogenous angiohemophilia factor to cell culture liquid for expressing the recombinant human coagulation factor VIII, and controlling an active ratio of the angiohemophilia factor to the human coagulation factor VIII in the cell culture liquid to be 1-10: 1 in the culture process. According to the invention, by utilizing a VWF (Von Willebrand Factor) molecule partner, which is necessary in an expression process of the recombinant human coagulation factor VIII, the newly generated human coagulation factor VIII is stabilized, the accumulating effect of the human coagulation factor VIII is improved, the technical difficulty is reduced, and the expression effect of a target protein is improved.
Owner:上海泰龙生物医药科技有限公司
Non-surgical method of treatment for cataract
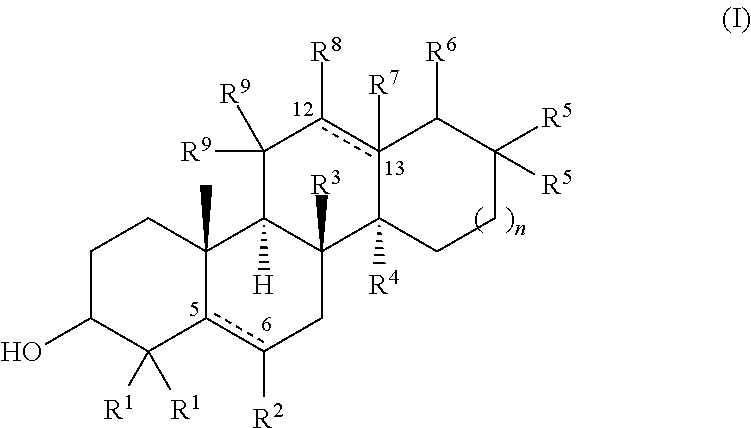
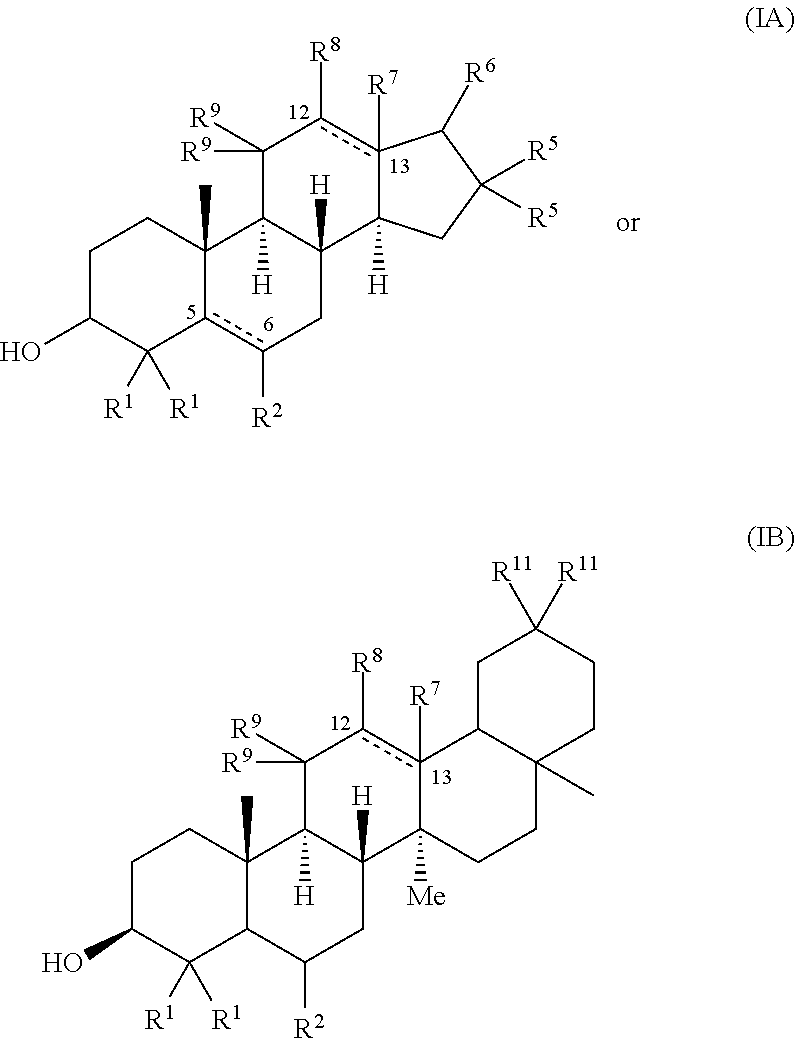
The invention provides inhibitors of α-crystallin aggregation and methods of using α-crystallin aggregation inhibitors to, e.g., treat or prevent cataracts in a subject having or at risk of developing cataracts. The invention further provides high throughput methods of screening compounds for modulation of protein thermal stability, the method comprising contacting a protein with each of a plurality of test compounds; and (b) measuring the melting transition (Tm) of the protein in the presence of each of the plurality of test compounds, wherein a compound that decreases or increases the apparent Tm by at least 2 standard deviations is identified as a pharmacological protein chaperone.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through autophagy activity mediated by ligand or arginylated bip binding to p62 zz domain
The drug action mechanisms and core techniques of the present invention are summarized in figure 1. Specifically, the invention provides malignant denatured proteins, such as mutant Huntingtin proteinor alpha-synuclein, stick together to grow into oligomer aggregates (1, 2), fibrillar aggregates (3), and ultimately inclusion bodies (4). Young neuronal cells produce a large quantity of Nt-Arg through N-terminal arginylation (5) of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones, such as BiP, and thereafter, arginylated BiP (R-BiP) comes into the cytoplasm and binds with denatured proteins (6). Nt-Arg of R-BiP, as a ligand, binds with the ZZ domain of p62 (7) to induce the structural activation of p62 (8) while the ordinarily closed inactive form of p62 is changed with an open form thereof, and thus PB1 and LC3-binding domains are exposed. On the basis of oligomerization (9) by the PB1 domain, p62 binds with the denatured protein aggregates to be concentrated to autophagically degradable aggregates, that is, p62 bodies (10). Thereafter, p62 completes autophagy targeting (11) and lysosomal proteolysis through binding with LC3 protruding on the autophagosomal membranes. In young neuronal cells, theautophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is strong, and thus the cytotoxic protein aggregates (1-5) do not accumulate, but in aged neuronal cells, the autophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is weakened, and thus the protein aggregates (1-5) accumulate, resulting in a vicious cycle. The present invention attempts to effectively remove Huntingtin and alpha-synuclein protein aggregates and the like by artificially activating p62 using low-mass ligands of the p62 ZZ domain (12, 13). Specifically, p62 binding the ligands through step 12 promotes p62-R-BiP-denatured protein oligomerization (9) and autophagy aggregate formation (10). In addition, the ligand-62 conjugates step 13 act as autophagy activators (14), to promote LC3 synthesis, the conversion of LC3-I into LC3-II, and the like, thereby promoting the formation of autophagosomes (15).
Owner:奧土择破利悟
Chimeric protein containing an intramolecular chaperone-like sequence
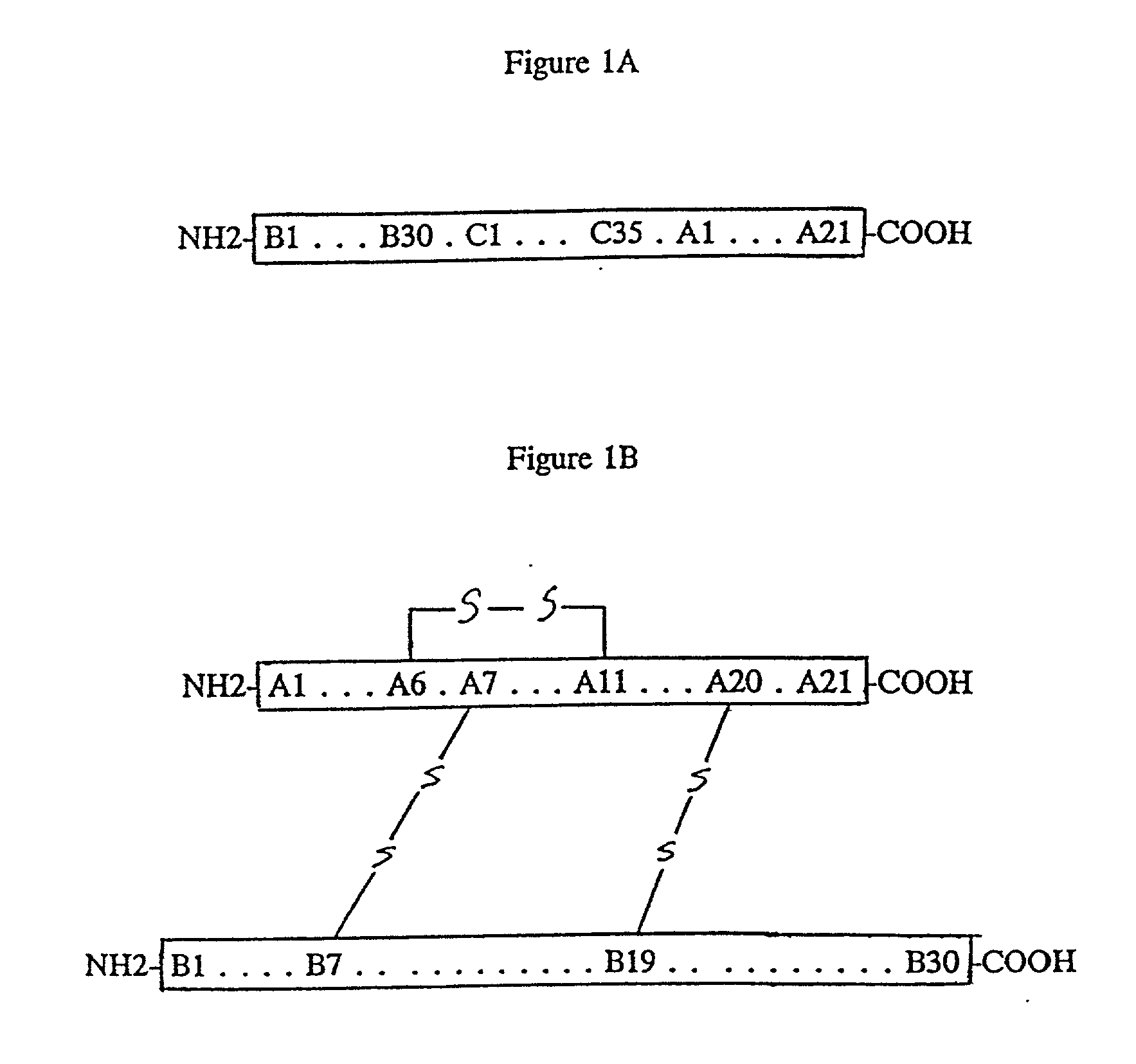
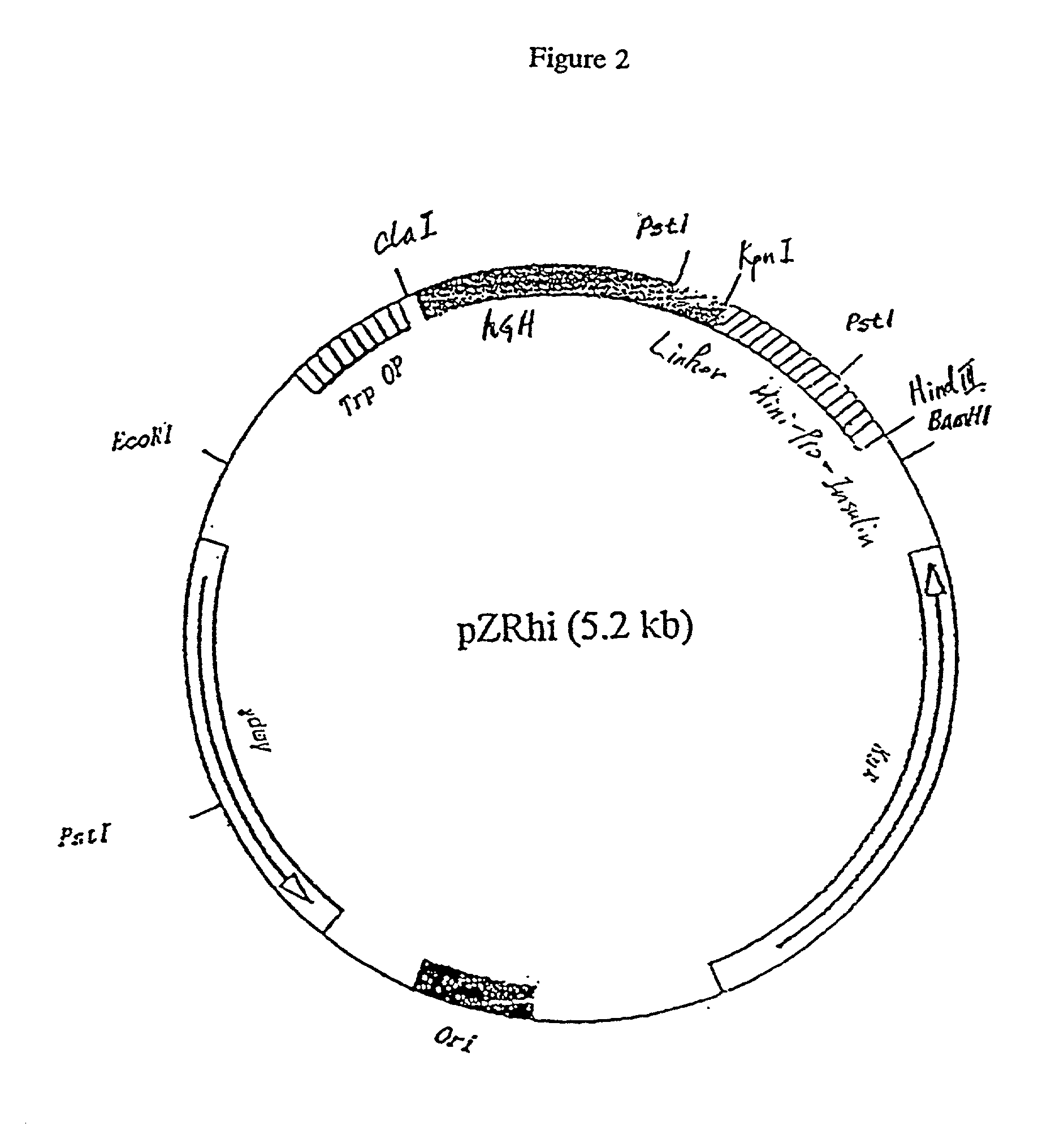
InactiveUS20020164712A1Improves insulin precursor foldingEasy to foldHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsInsulin PrecursorAmino acid
The present invention relates to a chimeric protein containing an intramolecular chaperone (IMC) like sequence linked to a target protein, preferably an insulin precursor. The present invention also relates to a process for obtaining a correctly folded insulin-precursor-containing chimeric protein, comprising, inter alia, contacting an incorrectly folded chimeric protein containing an IMC like sequence linked to an insulin precursor with at least one chaotropic auxiliary agent. The present invention further relates to an assay for screening an amino acid sequence for the ability to improve folding of an insulin precursor using a chimeric protein containing an IMC like sequence linked to an insulin precursor.
Owner:TONGHUA GANTECH BIOTECH
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100159477A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGolgi componentCell Surface Proteins
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell suface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Polypeptides for increasing mutant CFTR channel activity
InactiveUS20040115770A1Reduce deliveryFacilitates uptakeBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCompetitive bindingHsp70
The present invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing channel activity to the mutant cystic fibrosis trans-membrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR). The compositions of the invention comprise polypeptides containing CFTR sub-domains that are designed to mimic the folding defect of the full length mutant CFTR proteins, resulting in competitive binding to cytoplasmic chaperones such as Hsc / Hsp7O and Hdj2. The methods of the invention comprise transduction, or recombinant expression, of CFTR polypeptides in a cell expressing mutant CFTR. The presence of the CFTR polypeptide results in a dominant effect whereby the CFTR polypeptide competes with the endogenously expressed mutant CFTR for binding to cytoplasmic chaperones such as Hsc / Hsp70 and Hdj2. Mutant CFTR proteins include, but are not limited to, DeltaF508 CFTR. The present invention is based on the discovery that reduced binding of cytoplasmic chaperones to the endogenous DeltaF508 CFTR, mediated by the presence of CFTR polypeptides, results in restoration of plasma membrane localization and channel activity. The methods and compositions of the invention can be used to restore channel activity in cystic fibrosis subjects carrying genetic defects in the CFTR gene, such as for example, DeltaF508 CFTR.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Ire1p, novel mammalian protein, and gene encoding same
A novel polynucleotide encoding a mammalian bifunctional protein kinase\endoribonuclease referred to herein as hIre1p, is provided. hIre1p is expressed in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and upregulates the transcription of genes encoding ER protein chaperones, such as, but not limited to, glucose-related proteins (GRP's). Therapeutic, diagnostic and research methods employing the polynucleotide and protein are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Preparation method of recombinant human acidic fibroblast growth factor (haFGF) protein
ActiveCN103882047AEasy to prepareImprove product qualityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a preparation method of a recombinant protein in the field of gene engineering and in particular relates to a preparation method of a recombinant human acidic fibroblast growth factor (haFGF) protein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) designing primers according to the full-length sequence of the haFGF to obtain an original gene segment through cloning, and replacing a codon which exists in the original gene segment and is unfavourable to be expressed by escherichia coli, thus obtaining an optimized haFGF gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the optimized haFGF gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; cloning to obtain an original gene segment of a molecular chaperone PDI (protein disulfide isomerase), and replacing a codon which exists in the original gene segment and is unfavourable to be expressed by escherichia coli, thus obtaining an optimized PDI gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the optimized PDI gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2; (2) linking and cloning the optimized haFGF gene, the optimized PDI gene, tag sequences and a protease cutting site sequence into a vector to obtain an efficient expression vector through construction; or firstly constructing standby vectors of part of the sequences, and then linking the remaining sequences on part of the sequences.
Owner:杨霞
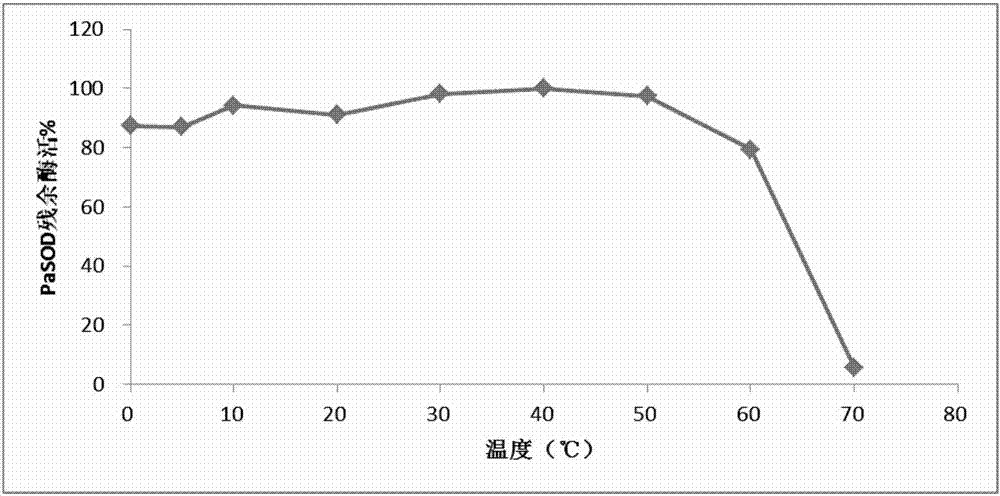
Preparation method of abyss sea cucumber sourced superoxide dismutase Cu, ZnSOD and application thereof
ActiveCN107955806AHigh purityGood energyOxidoreductasesFermentationEscherichia coliHigh concentration
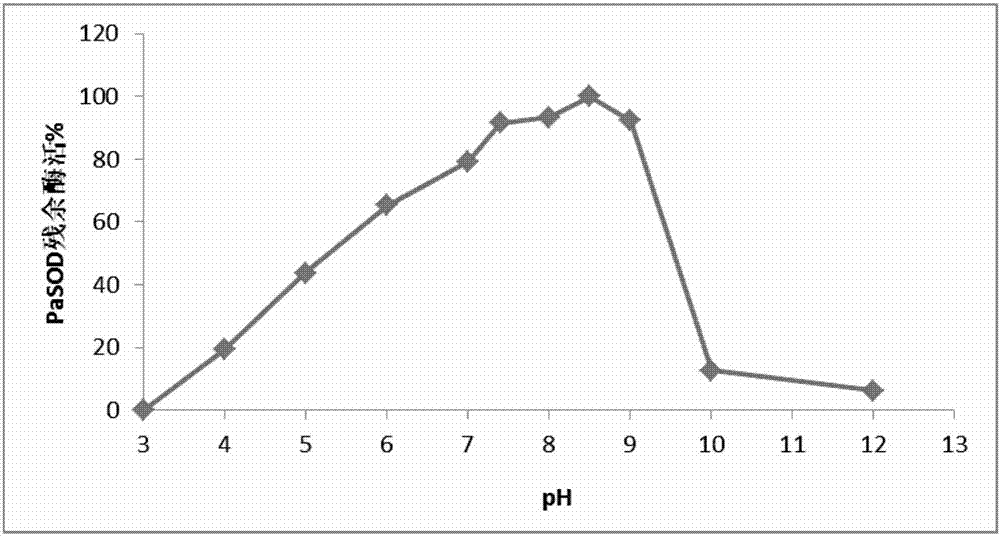
The invention discloses a preparation method of abyss sea cucumber sourced superoxide dismutase Cu, ZnSOD and application thereof. The method includes: extracting total RNA of Paelopatides sp., reversely transcribing into cDNA through RT-PCR, acquiring a gene sequence PaSOD coding superoxide dismutase through PCR amplification, establishing prokaryotic expression recombinant plasmid in pCold II vector, and guiding into chaperone Competent Cell pG-KJE8 / BL21 for recombinant protein soluble expression. Recombinant protein prepared through the method overcomes the defects that raw material sourcesare difficult to obtain and protein renaturation recycling process is complex and troublesome, purified protein is high in purity and vitality, wide in temperature suiting range and capable of resisting digestion by high-concentration digestive enzyme, and a foundation is laid for widely applying the protein in the field of biology, food, medicine and cosmetology.
Owner:INST OF DEEP SEA SCI & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant expression vector for improving soluble expression of pathogenesis-related proteins in Mongolia astragaloside
PendingCN111733178AIncreased expression of solubleHas nuclease activityPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesEscherichia coliProtein target
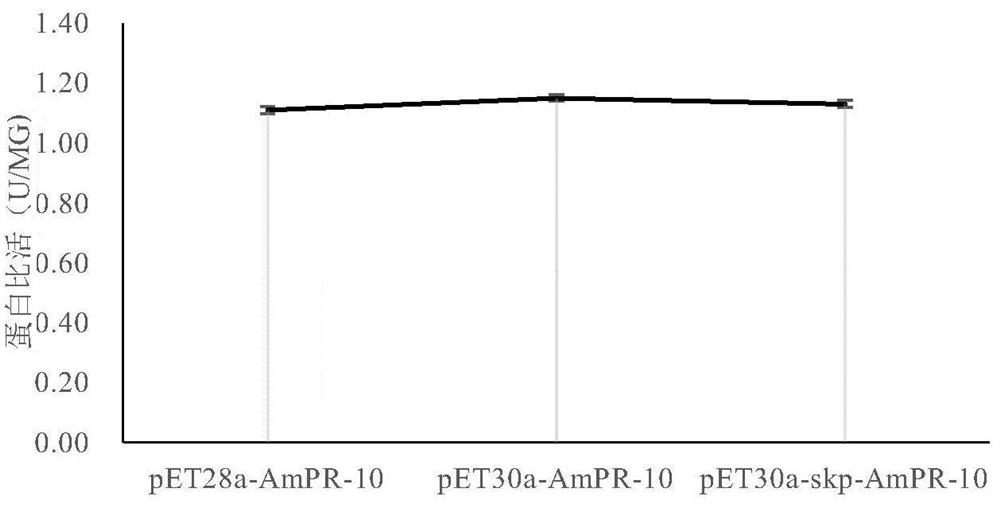
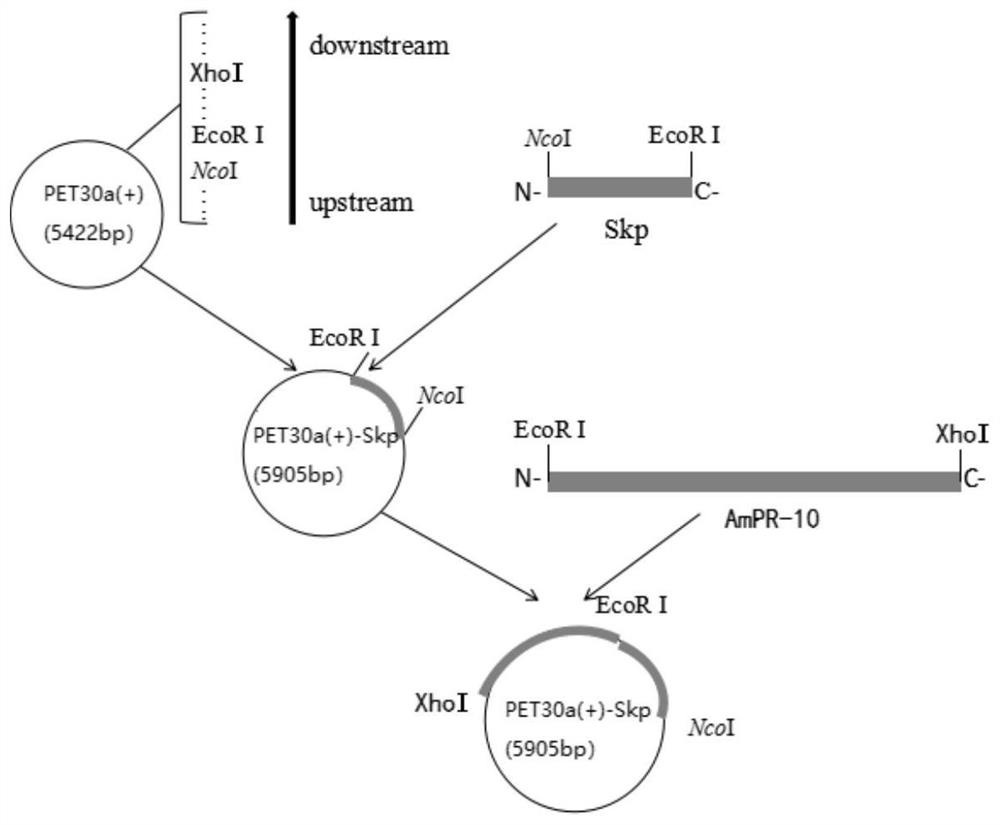
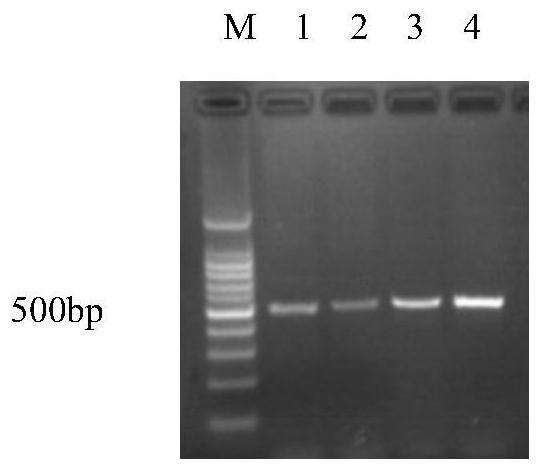
The invention discloses a recombinant expression vector for improving soluble expression of pathogenesis-related proteins in Mongolia astragaloside. The recombinant expression vector is a recombinantpET30a-skp-AmPR-10 constructed by using pET30a as a vector and modifying AmPR-10 by utilizing an escherichia coli molecular chaperone skp. According to the invention, by a method of replacing the vector and carrying out molecular chaperone modification, the soluble expression of target proteins is improved so as to fulfill the aims of saving cost and improving yield; the exogenously expressed AmPR-10 is further subjected to activity measurement so as to show that the exogenously expressed proteins also have the nuclease activity and provide reference strategies for in-vitro expression of otherhomologous related proteins; and the activity may have the important significance for researching the RNA virus resistance ability of radix astragali.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for synergistically and efficiently preparing protein-based nano-emulsion by taking polyhydroxy alcohol as molecular chaperone and prepared protein-based nano-emulsion
ActiveCN112042928AWide variety of sourcesLow production costHydrolysed protein ingredientsEmulsion deliveryOil phaseProtein
The invention discloses a method for synergistically and efficiently preparing a protein-based nano-emulsion by taking polyhydroxy alcohol as a molecular chaperone and the prepared protein-based nano-emulsion. The method comprises the following steps of dissolving protein in a polyhydroxy alcohol solution, performing uniform mixing to obtain a protein dispersion solution, performing mixing and homogenizing with an oil phase to obtain a crude emulsion, and performing emulsifying to obtain the protein-based nano-emulsion. According to the method, the functional characteristic that a polyhydroxycompound can be used as an active protective agent of enzyme or other functional proteins is utilized, and the protein and polyhydroxy alcohol are premixed, so that the original conformation of the protein in the subsequent high-energy emulsification process is effectively protected; and mixing with an oil phase is performed, and high-pressure homogenization is performed to obtain nano-scale oil-in-water emulsion with uniform particle size and good stability. The protein-based nano-emulsion provided by the invention is simple in materials, is food-grade, can be directly obtained through a convenient homogenizing means, and has an excellent protection or controlled release effect on the oil phase, so that the protein-based nano-emulsion has a wide application prospect in the fields of dailychemical products, foods, medicines and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
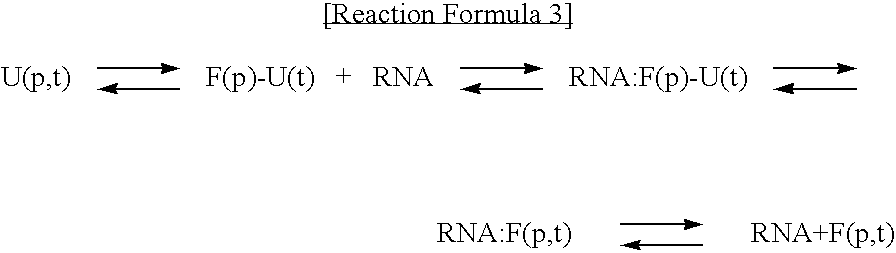
Method for improving solubility and folding efficiency of target proteins using RNA as molecular chaperone
InactiveUS20060292667A1Improve efficiencyImprove solubilityFusion with RNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityProtein target
Disclosed is a method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein linked to a RNA-binding protein by using RNA molecule as a molecular chaperone, wherein the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein. More particularly, the present invention discloses method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein by transformation of a host cell with a expression vector comprising a polynucleotide encoding the target protein linked to an RNA-binding protein; culturing the transformed host cell in an appropriate culture medium under the condition that an RNA molecule either resident inside the host cell or provided by cotransformation of the host cell with polynucleotide encoding the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein; and purifying the soluble protein from host cell lysate. The method of the present invention is very useful for production of soluble proteins for therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:XCELL THERAPEUTICS INC
Reagens for the Detection of Protein Acetylation Signaling Pathways
InactiveUS20090124023A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingCell Surface ProteinsMetabolic enzymes
The invention discloses 432 novel acetylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human protein acetylation signaling pathways, and provides acetylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these acetylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the acetylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Acetyltransferases, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Actin binding proteins, Adhesion proteins, Apoptosis proteins, Calcium-binding proteins, Cell Cycle Regulation proteins, Cell Surface proteins, DNA binding proteins, DNA replication proteins, Channel proteins, Chaperone proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, Cytoskeletal proteins, DNA repair proteins, Endoplasmic reticulum proteins, Enzyme proteins, G protein and GTPase Activating proteins, Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors, Helicase proteins, Isomerase proteins, Extracelluar matrix proteins, Hydrolases, Ligase proteins, Lipid kinases, Inhibtor proteins, Lipid Binding proteins and Lyases.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Pyranose oxidase gene constructed from molecular chaperone, protein, phchia pastoris and preparation and application of pyranose oxidase gene
PendingCN110628790AImprove expression levelHigh expressionFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastConcentration gradient
The invention belongs to preparation of a new gene, construction of engineering bacteria, and particularly relates to a pyranose oxidase gene constructed from molecular chaperone, protein, phchia pastoris and preparation and application of the pyranose oxidase gene. Genes Ero I, PDI, CNE1, SEC53 and the like in pichia pastoris are respectively cloned and connected to series derivative plasmids ofpichia pastoris expression vectors pPICZ and the like for connection, and the genes and P20 are subjected to coexpression to realize conversion into Pichia pastoris GS115 bacterial strains to be coated to YPD flats being different in bleomycin concentration gradients for inspection of effects. Through overexpression of molecular chaperone and optimization of the fermentation condition, and throughscreening and identifying, a bacterial strain with enhanced secretory expression pyranose oxidase than an original bacterial strain is obtained. For the pyranose oxidase expressed by the bacterial strain, the enzyme activity in a 10L fermenter can achieve 405U / mL, and compared with the bacterial strain without overexpression of the molecular chaperone, the enzyme activity is improved by twice, sothat a favorable foundation is established for large-scale production of the pyranose oxidase.
Owner:河北省微生物研究所有限公司
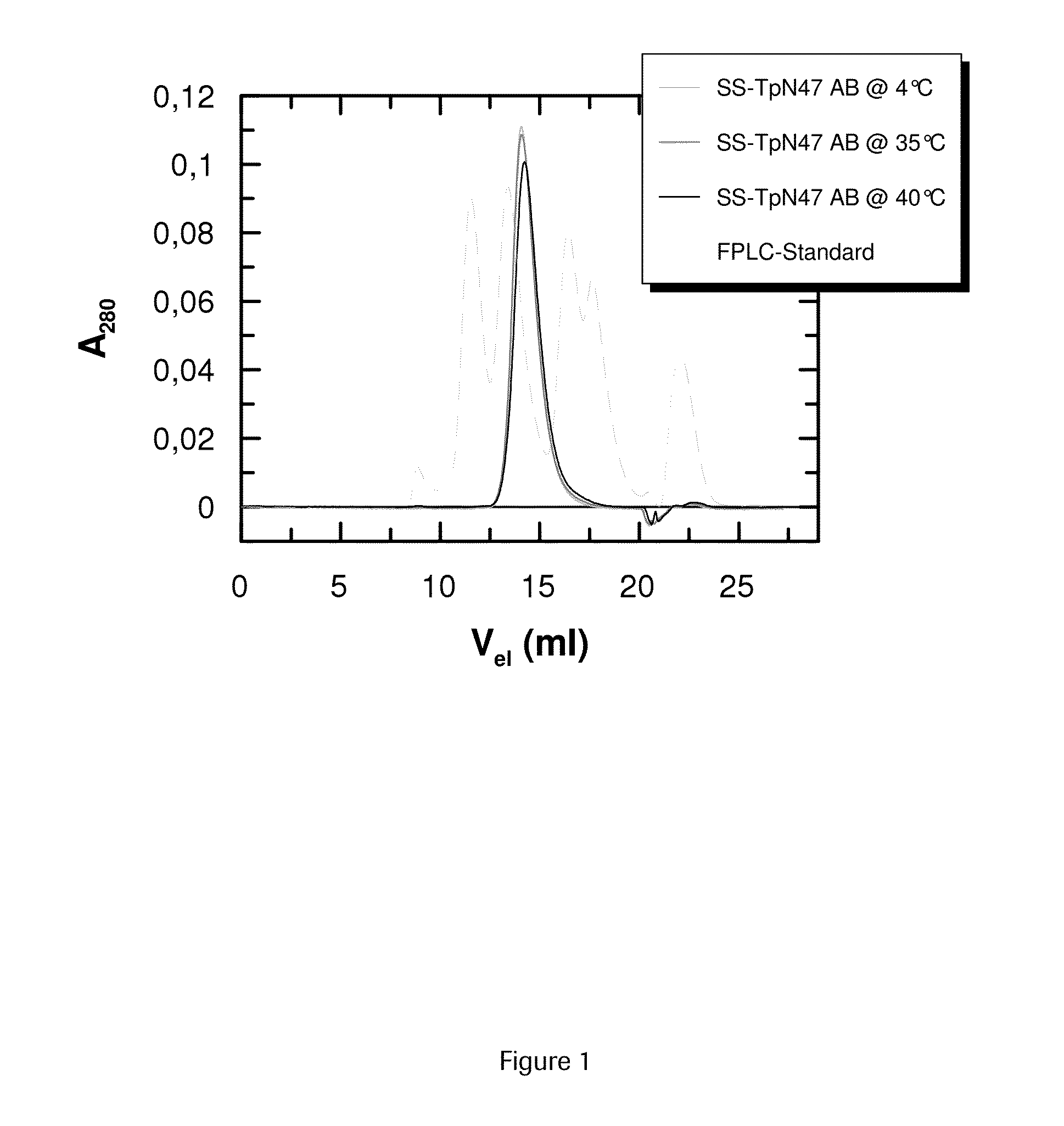
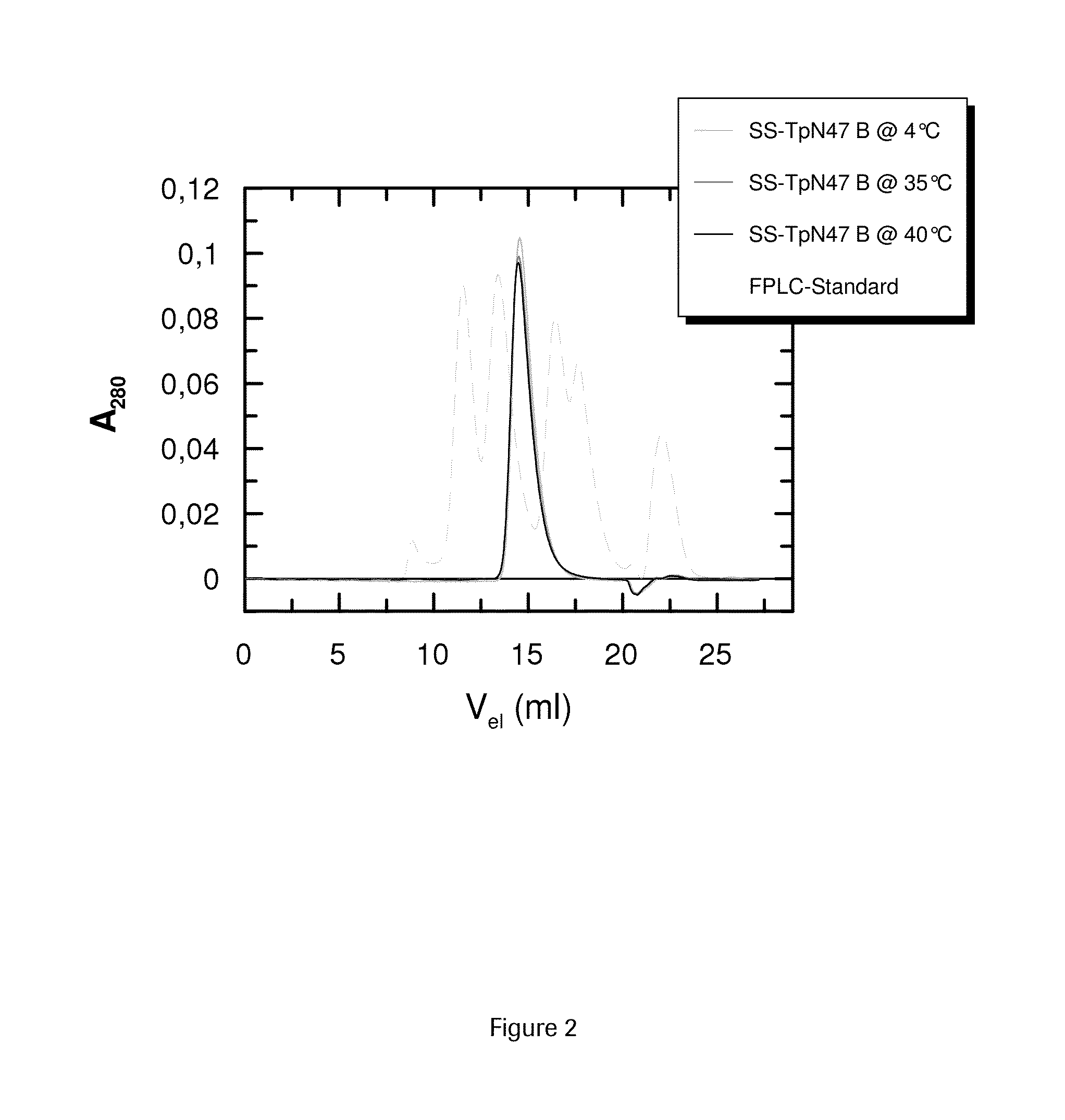
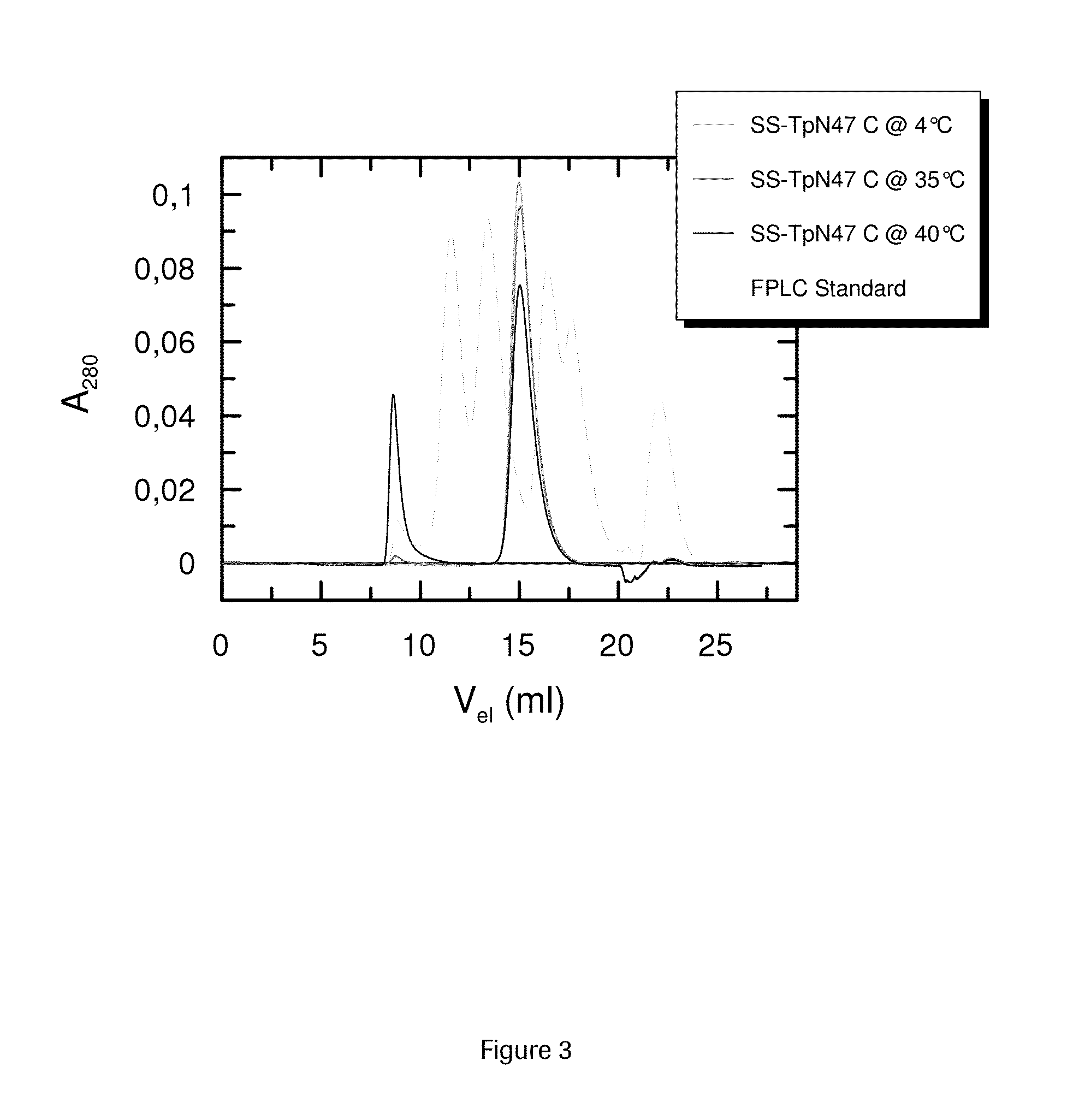
SOLUBLE IMMUNOREACTIVE TREPONEMA PALLIDUM TpN47 ANTIGENS
ActiveUS20150079604A1Improve solubilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsAntigenSpiroplasma
The invention concerns soluble variants of Treponema pallidum antigen 47 (TpN47 antigen) comprising at least domain B, or at least domains A and B, optionally domain D of the complete TpN47 protein molecule with the proviso that all antigens lack domain C (amino acid residues 224 to 351) of TpN47. The Tpn47 antigens can be fused to a chaperone. Moreover, the invention covers DNA encoding the antigens, a method of producing these antigens as well as the use of these antigens in an immunodiagnostic assay for the detection of antibodies against Treponema pallidum in an isolated sample.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Preparation of self-assembled virus-like particle by using escherichia coli to express feline parvovirus VP2 protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of vaccine preparation, relates to a novel feline parvovirus vaccine, and discloses a coding gene of a feline parvovirus VP2 protein. According to the invention, an FPV VP2 protein sequence is coded and optimized through a genetic engineering technology, a recombinant plasmid is constructed, a recombinant protein is expressed by using escherichia coli, and the FPV VP2 protein is co-expressed with four molecular chaperones respectively; and a target protein is purified by different purification methods to obtain a virus-like particle which is similar to natural viruses in size and has good hemagglutination. A new thought and a new basis are provided for novel feline parvovirus vaccines.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Raccoon dog parvovirus VP2 gene, expression vector, recombinant bacterium, method for preparing VP2 protein and assembly method
PendingCN110846326AImprove solubilityImprove immune activityBacteriaVirus peptidesNucleotideTGE VACCINE
The invention provides raccoon dog parvovirus VP2 gene, an expression vector, a recombinant bacterium, a method for preparing VP2 protein and an assembly method, and belongs to the technical field ofvaccine preparation. The raccoon dog parvovirus VP2 gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1. According to the invention, the raccoon dog parvovirus VP2 gene and a molecular chaperone arejointly transformed into ER2566 cells, and the molecular chaperone improves the correct folding rate of VP2 protein. The raccoon dog parvovirus VP2 gene provided by the invention can form high-qualityraccoon dog parvovirus-like particles. A raccoon dog parvovirus-like particle vaccine provided by the invention has a hemagglutination titer of 216 after being purified, and has a hemagglutinating property similar to that of a natural virus.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Multi-epitope fusion protein of an hcv antigen and uses thereof
ActiveUS20200148726A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenHepatitis C virus core
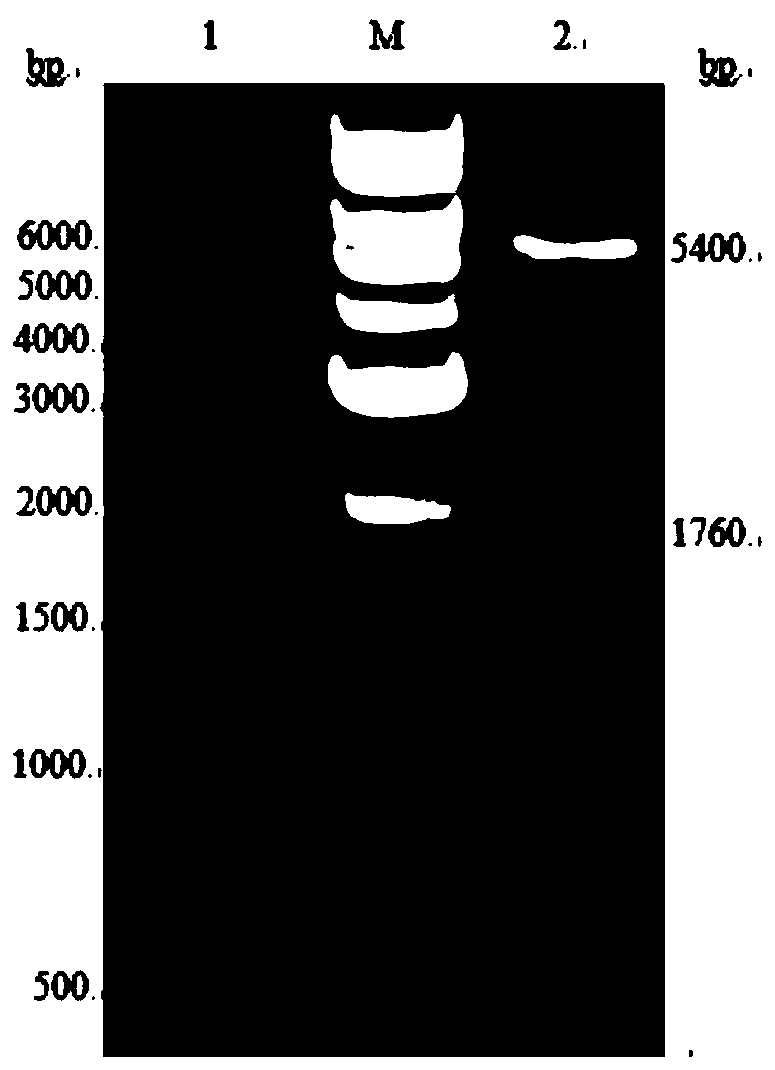
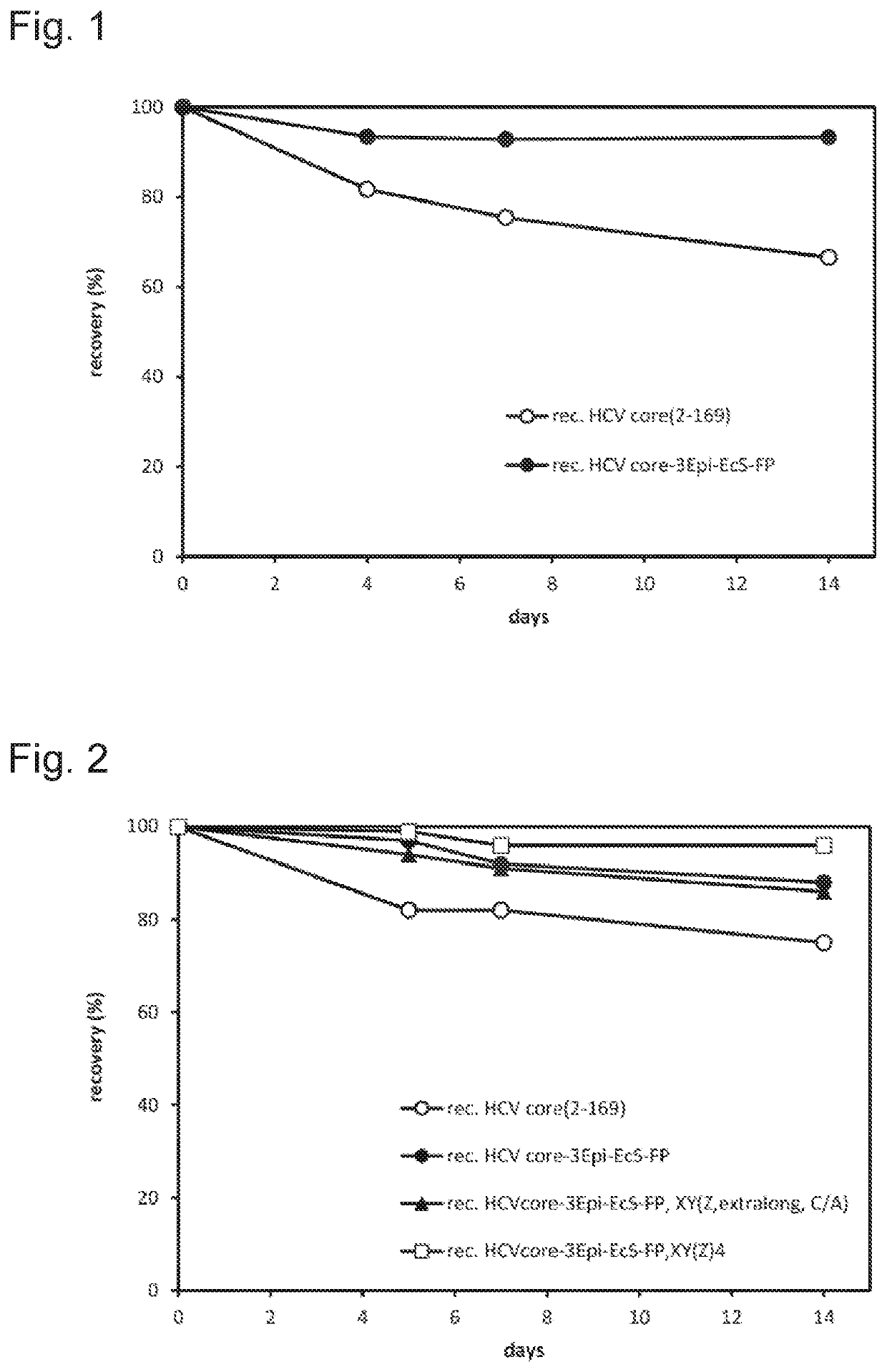
The disclosure relates to a multi-epitope fusion protein as well as to its use as calibrator and / or control in an in vitro diagnostics immunoassay for detecting HCV core antigen. The multi-epitope fusion protein has two to six different non-overlapping linear peptides present in the amino acid sequence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein, wherein each of the peptides is separated from the other peptides by a spacer consisting of a non-HCV amino acid sequence and having a chaperone amino acid sequence. No further HCV specific amino acid sequences are present in the polypeptide. A further aspect relates to a reagent kit for detecting HCV core antigen containing said multi-epitope fusion protein as calibrator or control or both.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
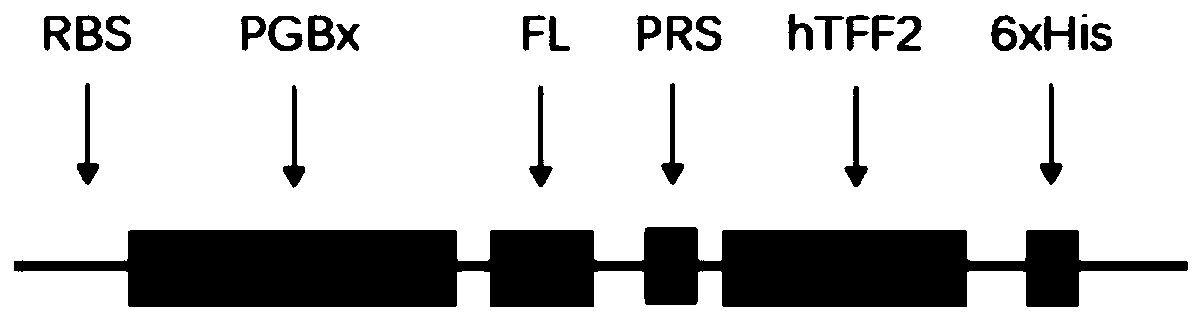
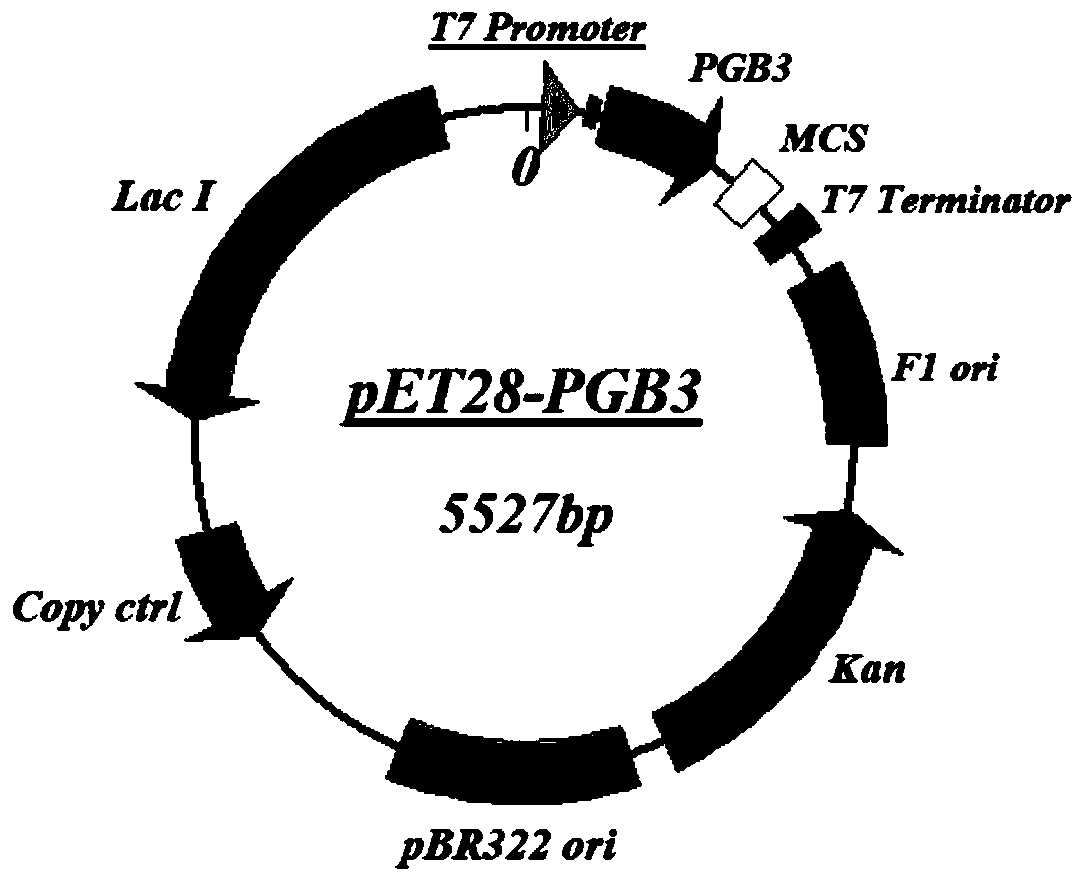
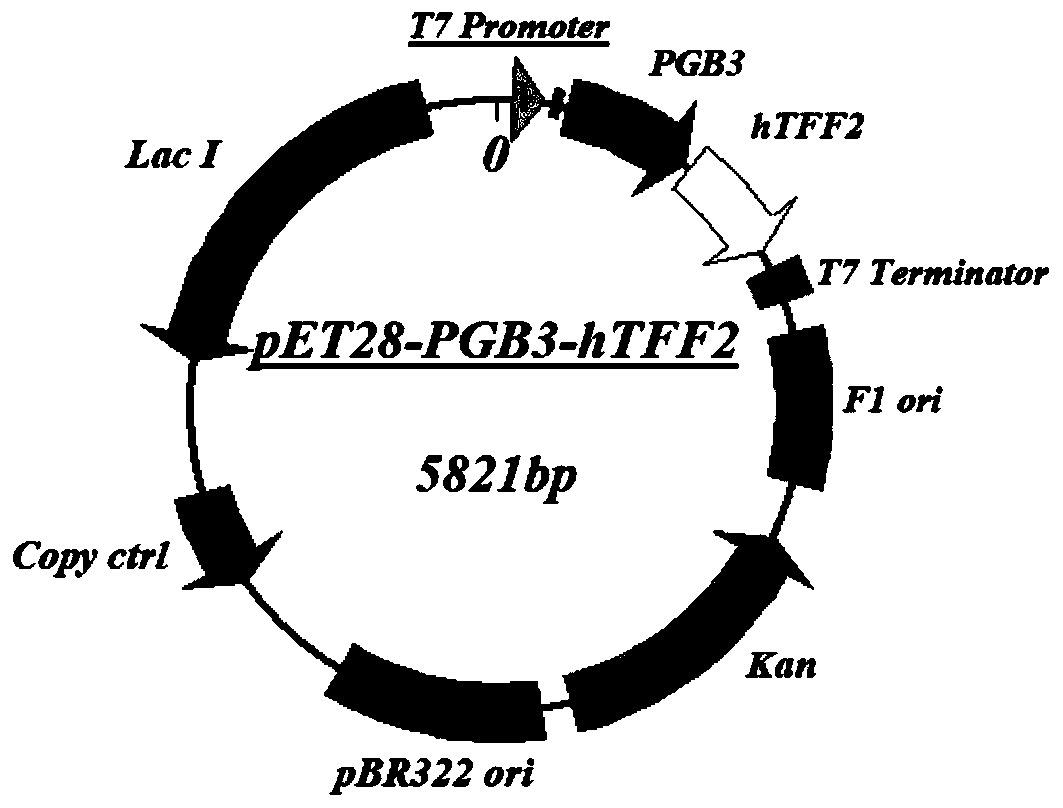
Application of PGB protein in construction of fusion protein expression vector with chaperone-like protein effect
InactiveCN110551746AFacilitate or induce foldingDepsipeptidesFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingFusion Protein ExpressionProtein target
The invention discloses application of a PGB protein in construction of a fusion protein expression vector with a chaperone-like protein effect. The fusion protein expression vector with the chaperone-like protein effect is successfully constructed by utilizing the PGB protein. For the application, by constructing a v chaperone-like protein contained pET-PGB3 expression vector and testing a targetprotein fusion protein expression vector and a target protein contained pET control vector, through contrast tests of target protein induction expressions in different recombinants, discovered that PGB has a novel chaperone-like protein function for improving the soluble expression efficiency of the target protein, so that a useful tool is provided to scientific research and industrial productionof protein expression.
Owner:因之彩生物科技(武汉)有限公司
Peptide directed protein knockdown
ActiveUS10287333B2Rapid and reversible knock-downReduced expression levelPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderDiseaseProtein target
In one aspect, the invention provides a peptide comprising a chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA)-targeting signal domain; a protein-binding domain that selectively binds to a target cytosolic protein; and a cell membrane penetrating domain (CMPD). In another aspect, the invention provides methods for reducing the intracellular expression level of an endogenous target protein in vitro and in an animal, wherein the method involves administration of the peptide. Methods are also provided for treating a pathological condition in an animal, the methods comprising administering the peptide to the animal. In one embodiment, the pathological condition is a neurodegenerative disease. In another embodiment of the invention, the target cytosolic protein is death associated protein kinase 1 and the CMPD is protein transduction domain of the HIV-1 Tat protein.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com