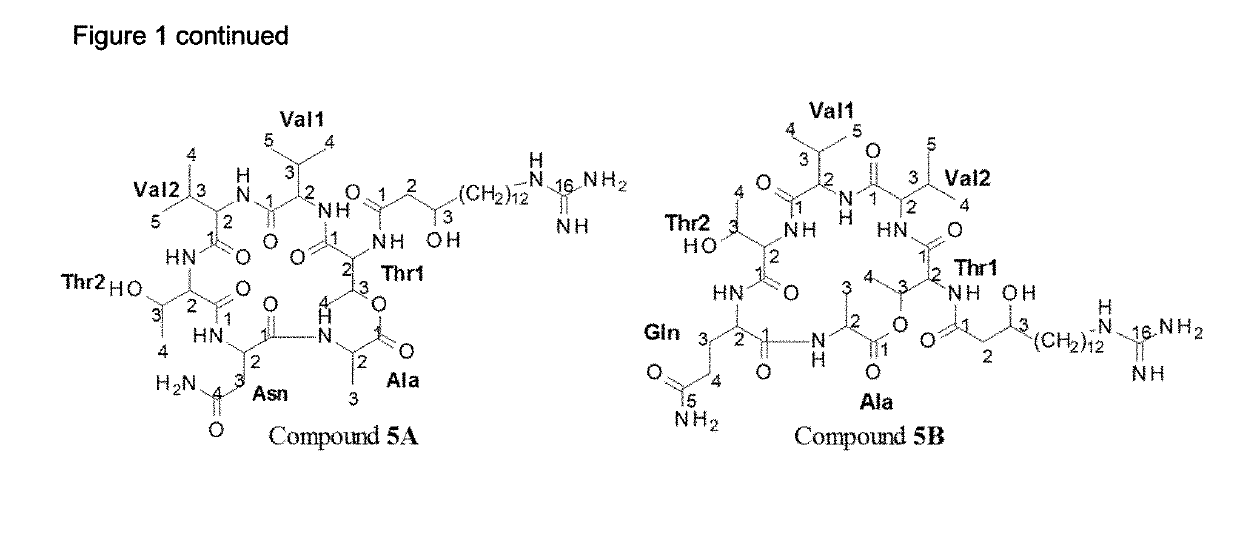
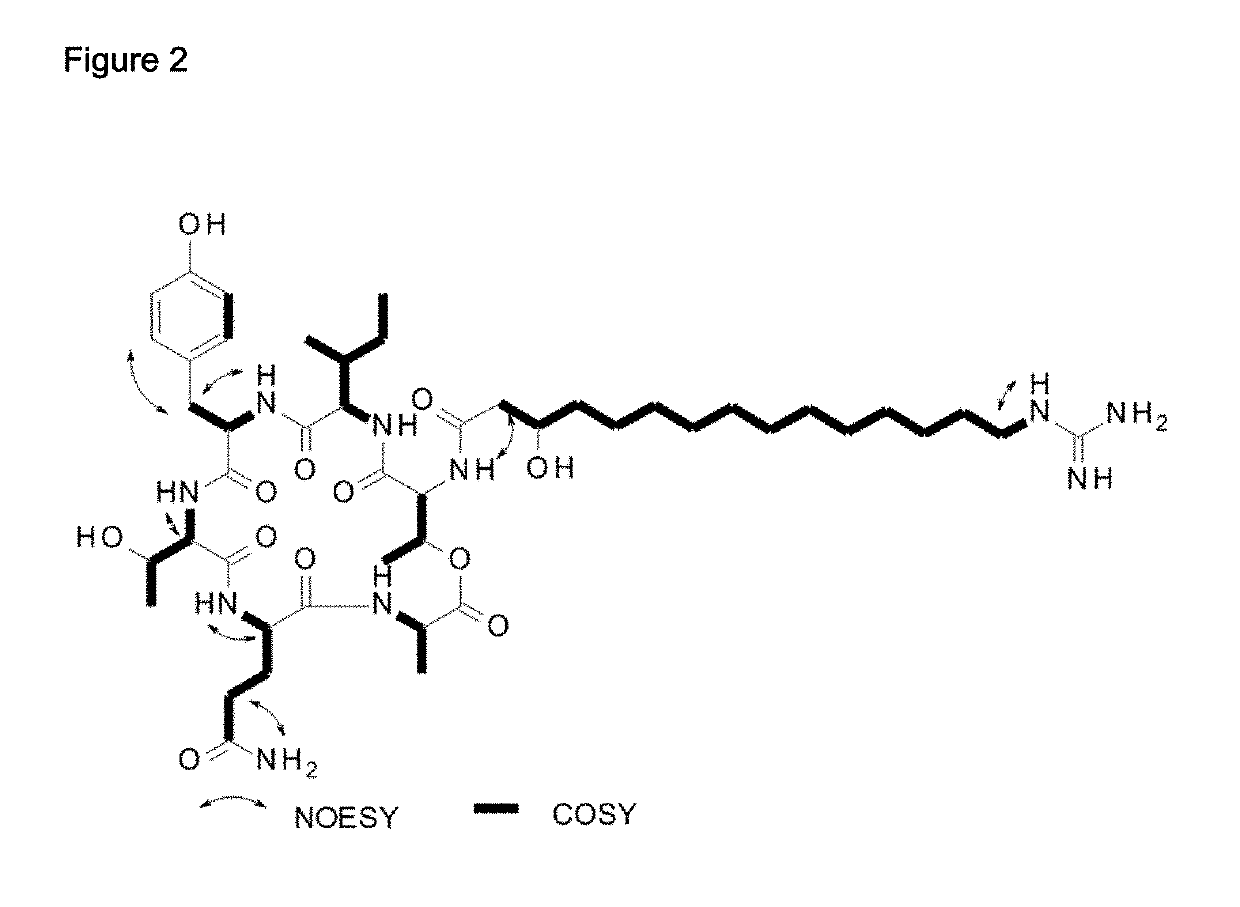
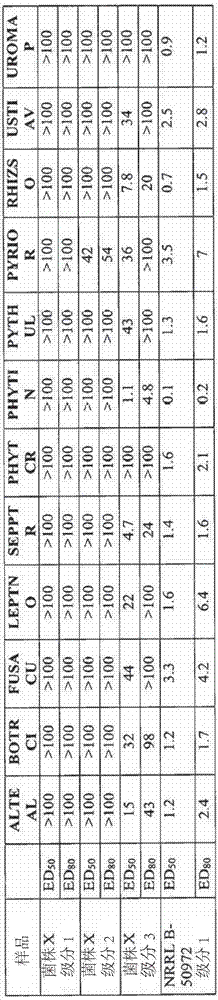
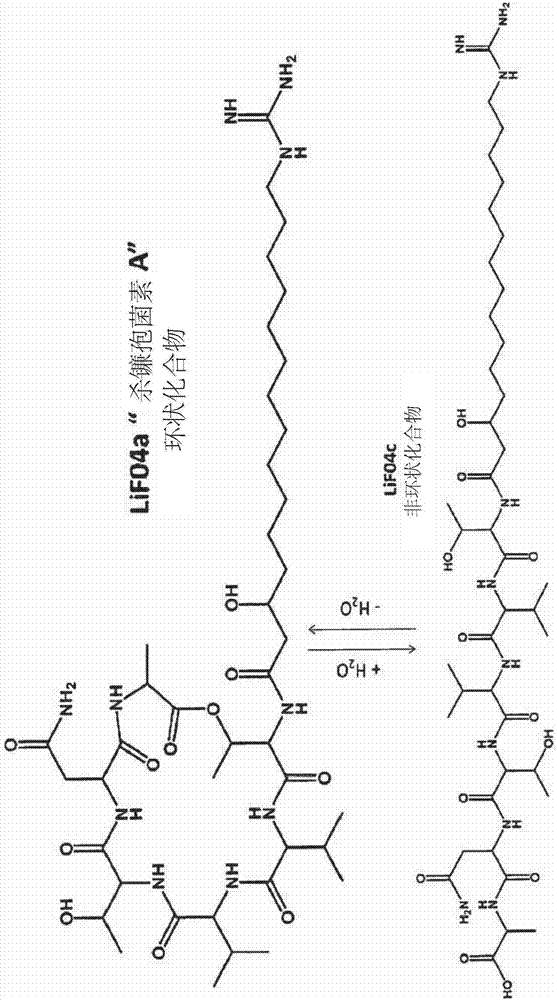
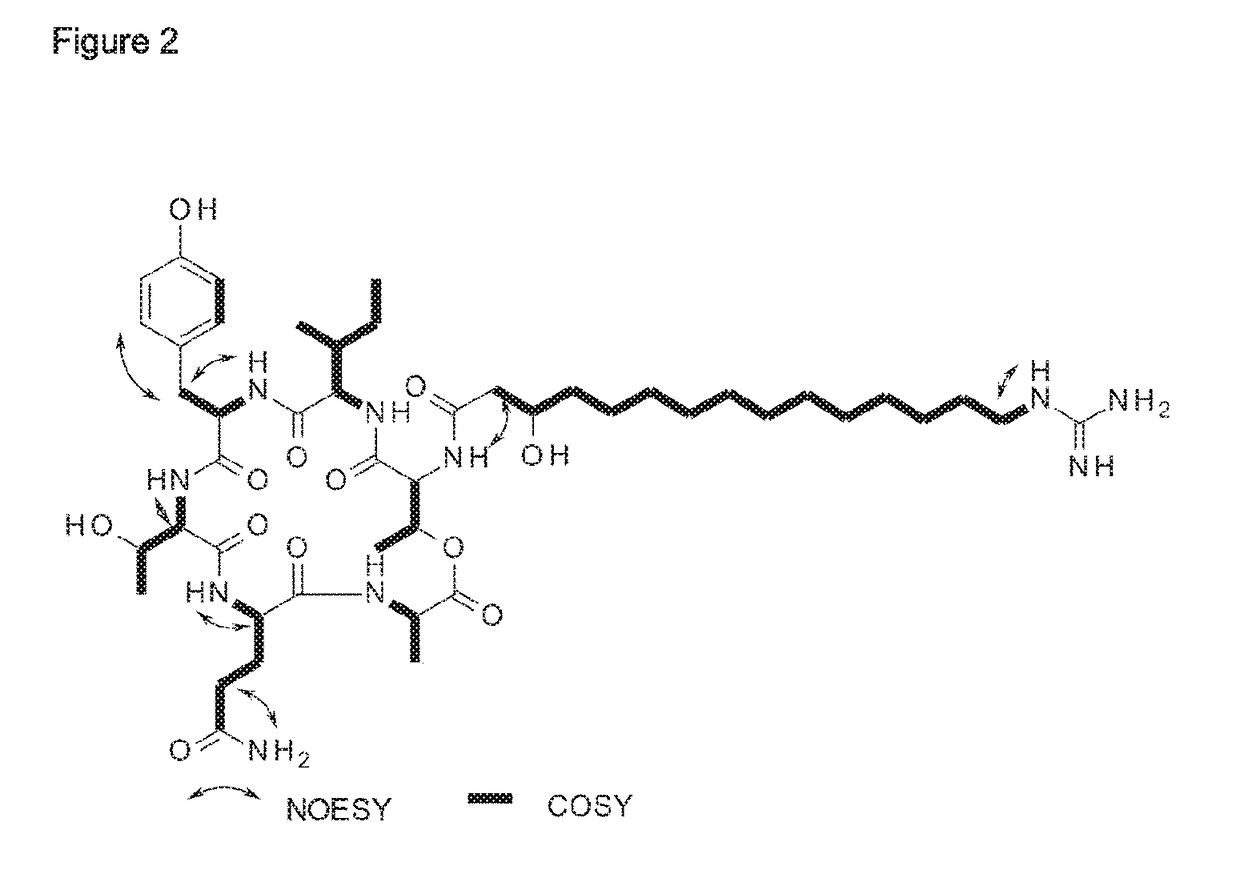
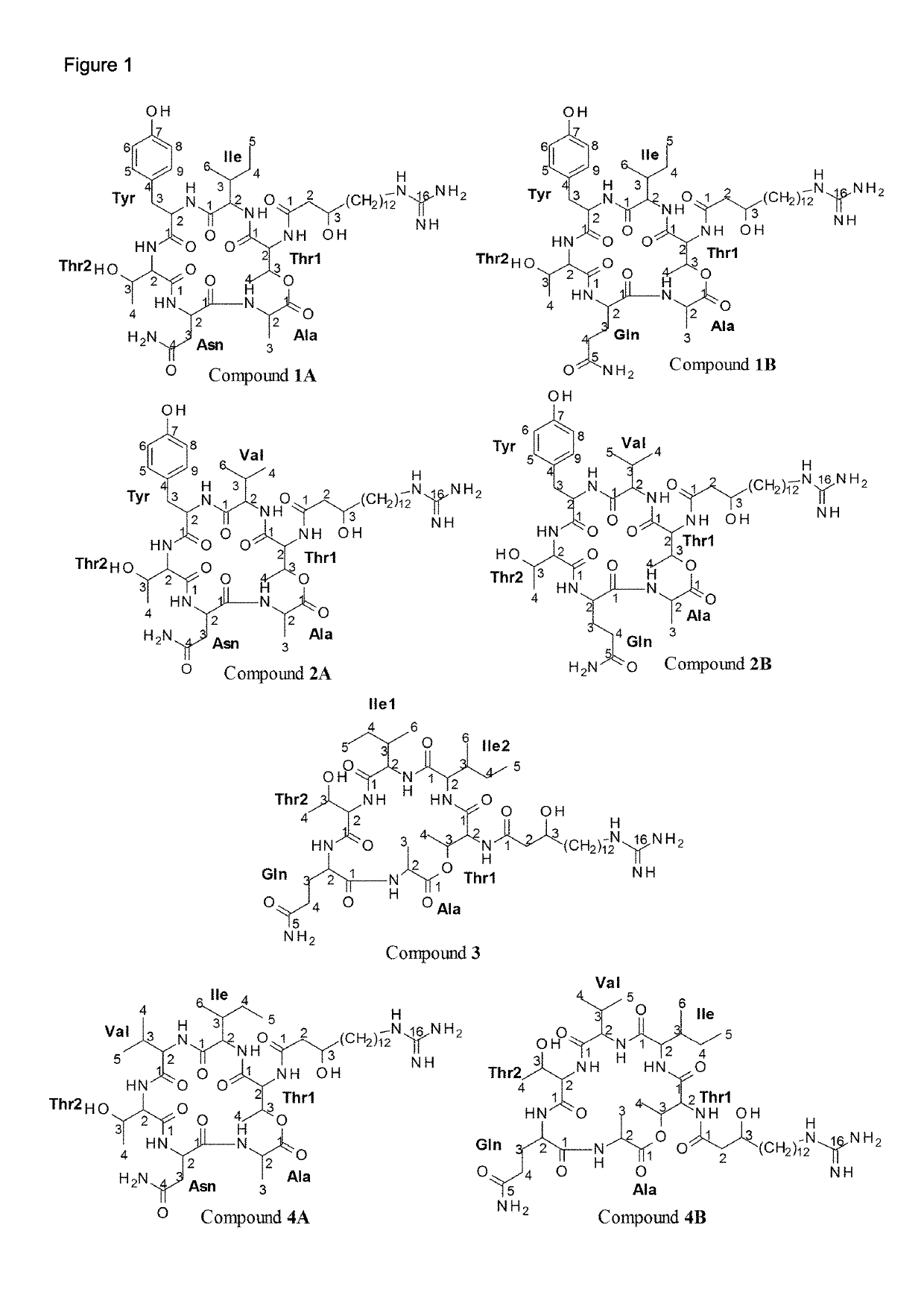
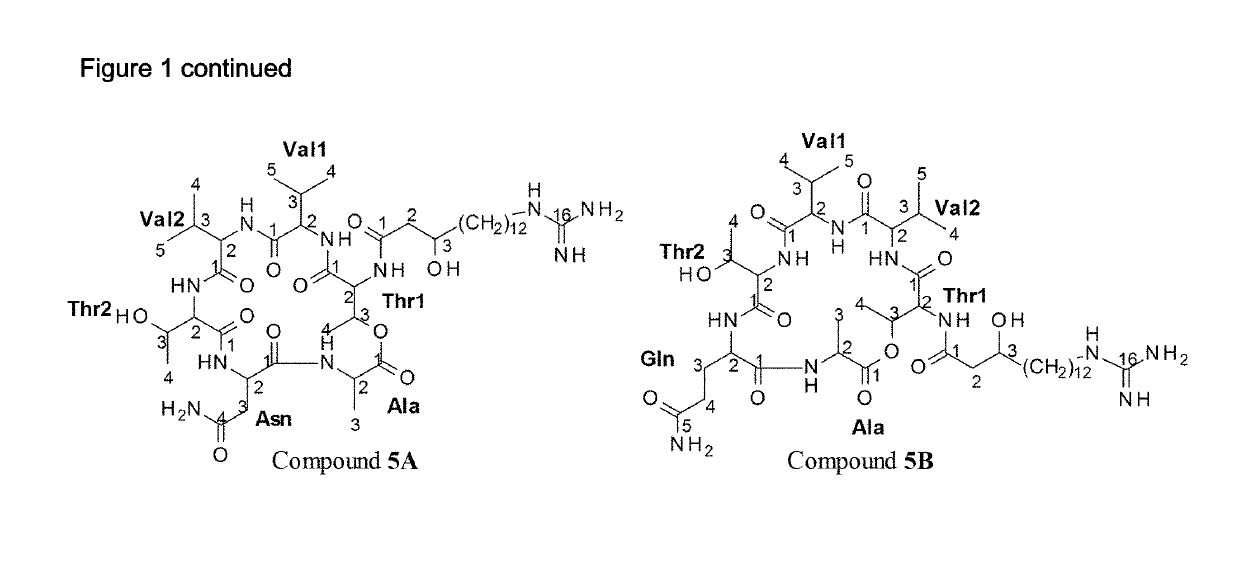
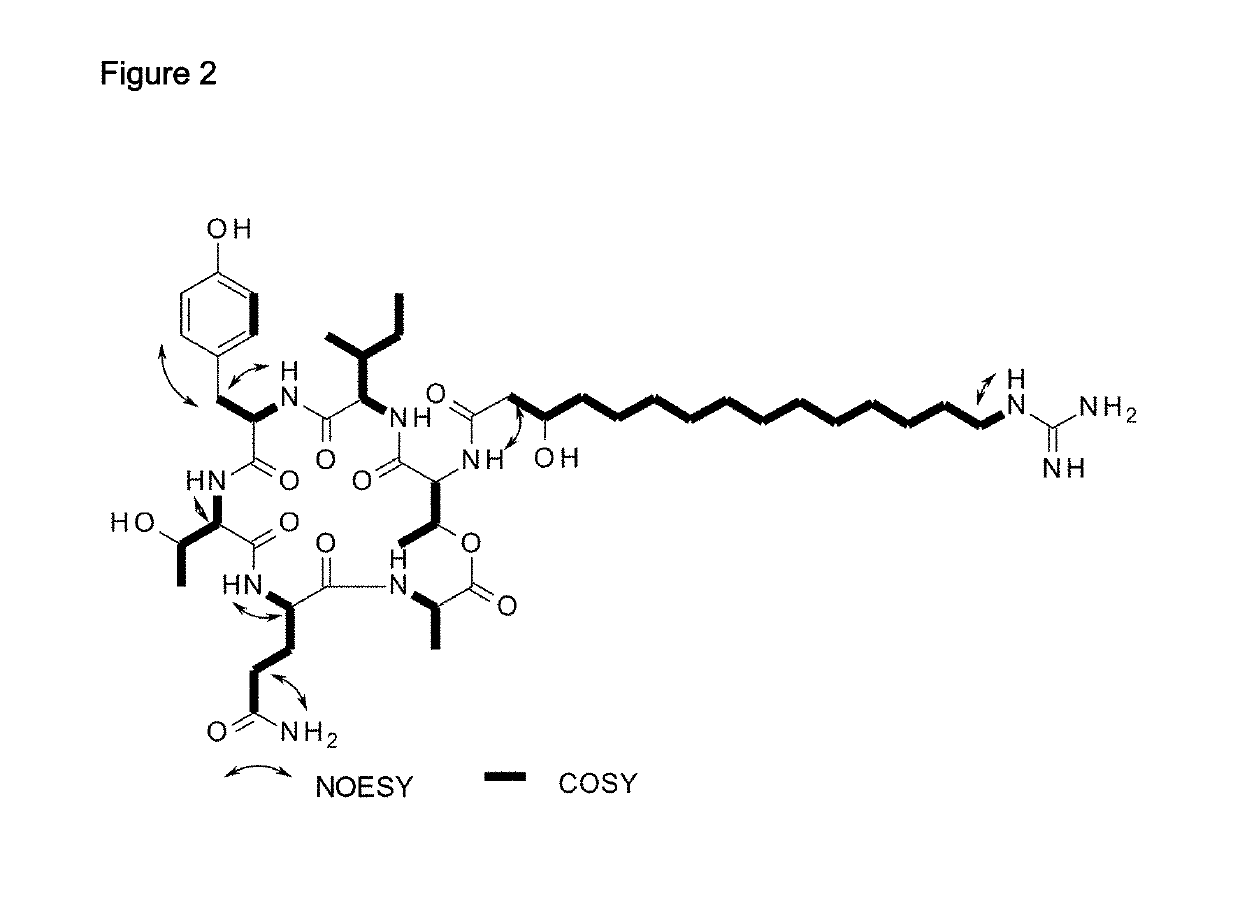
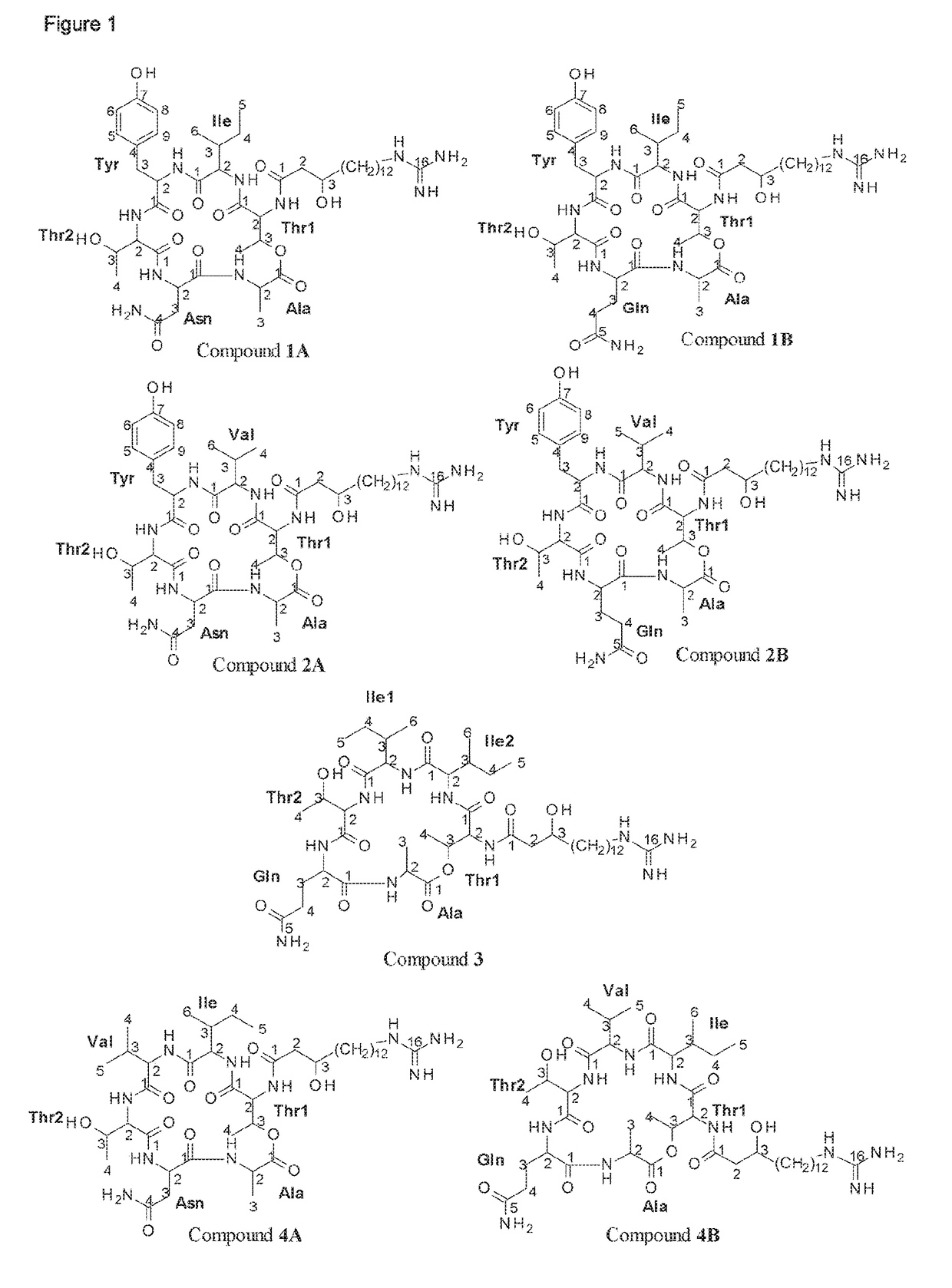
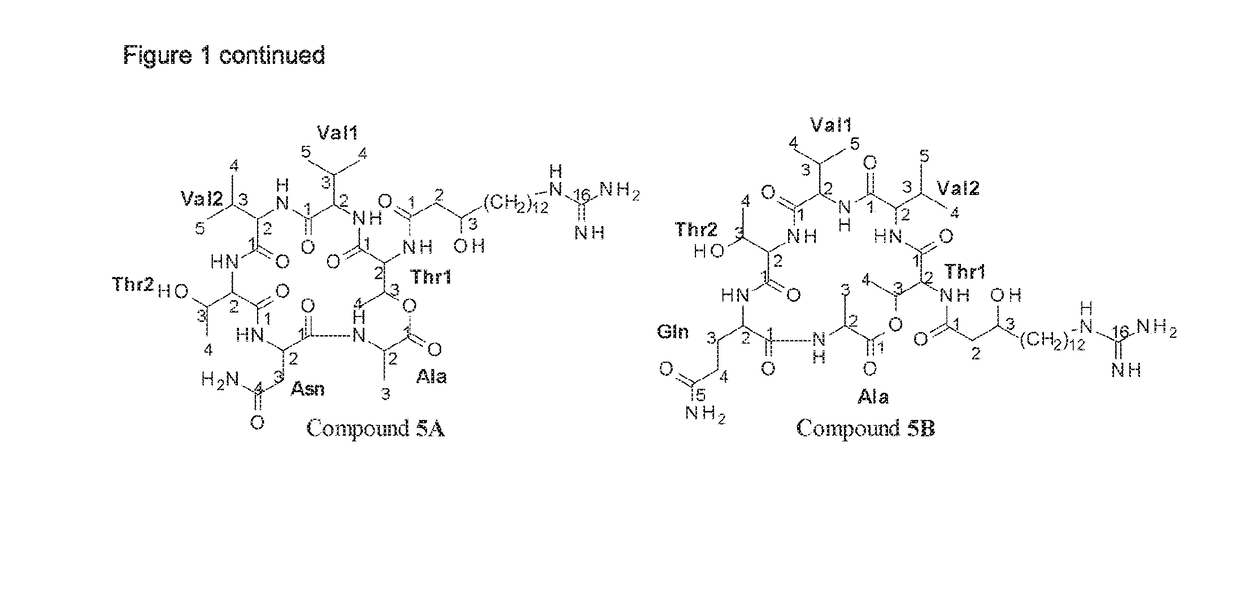
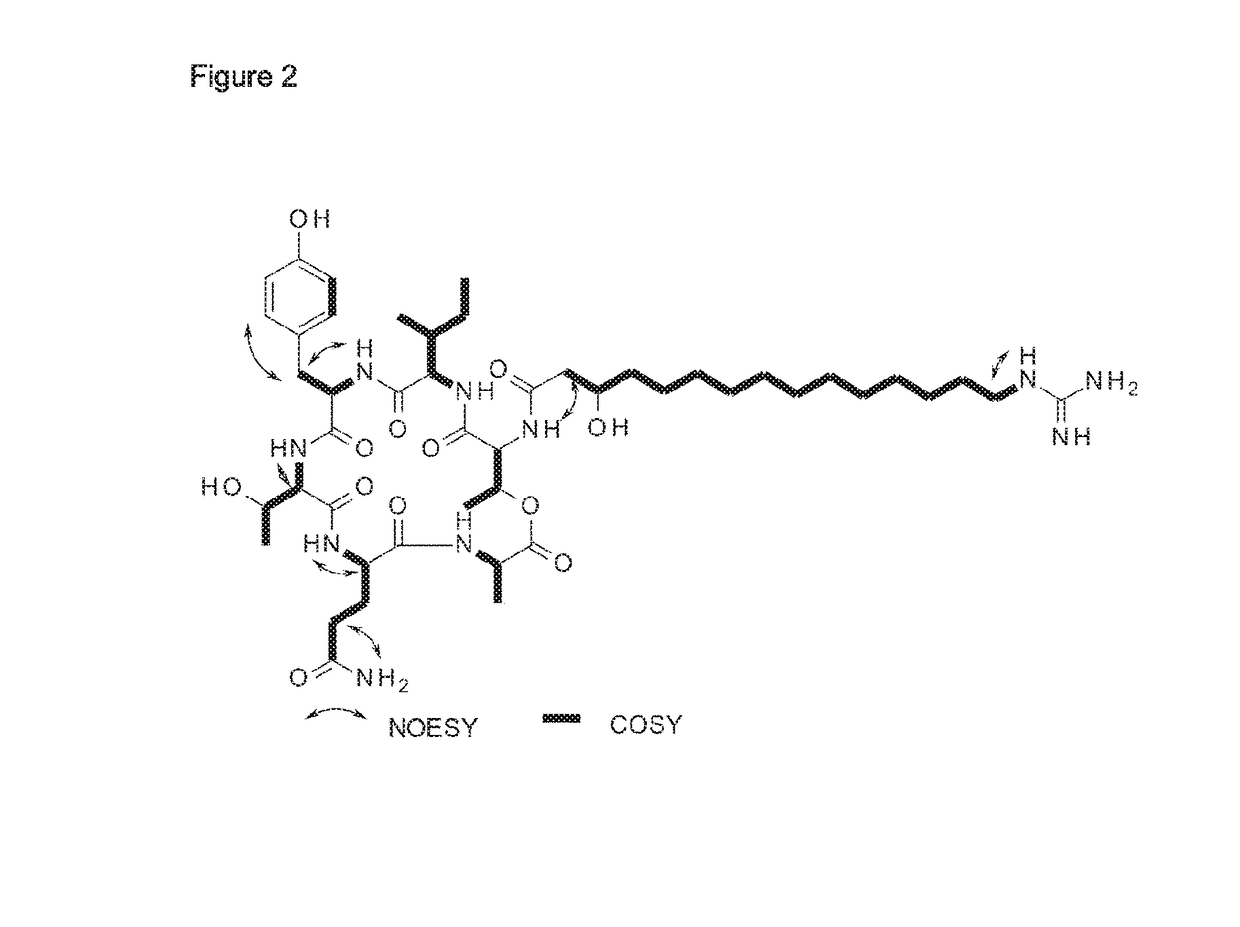
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Cell free extracts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
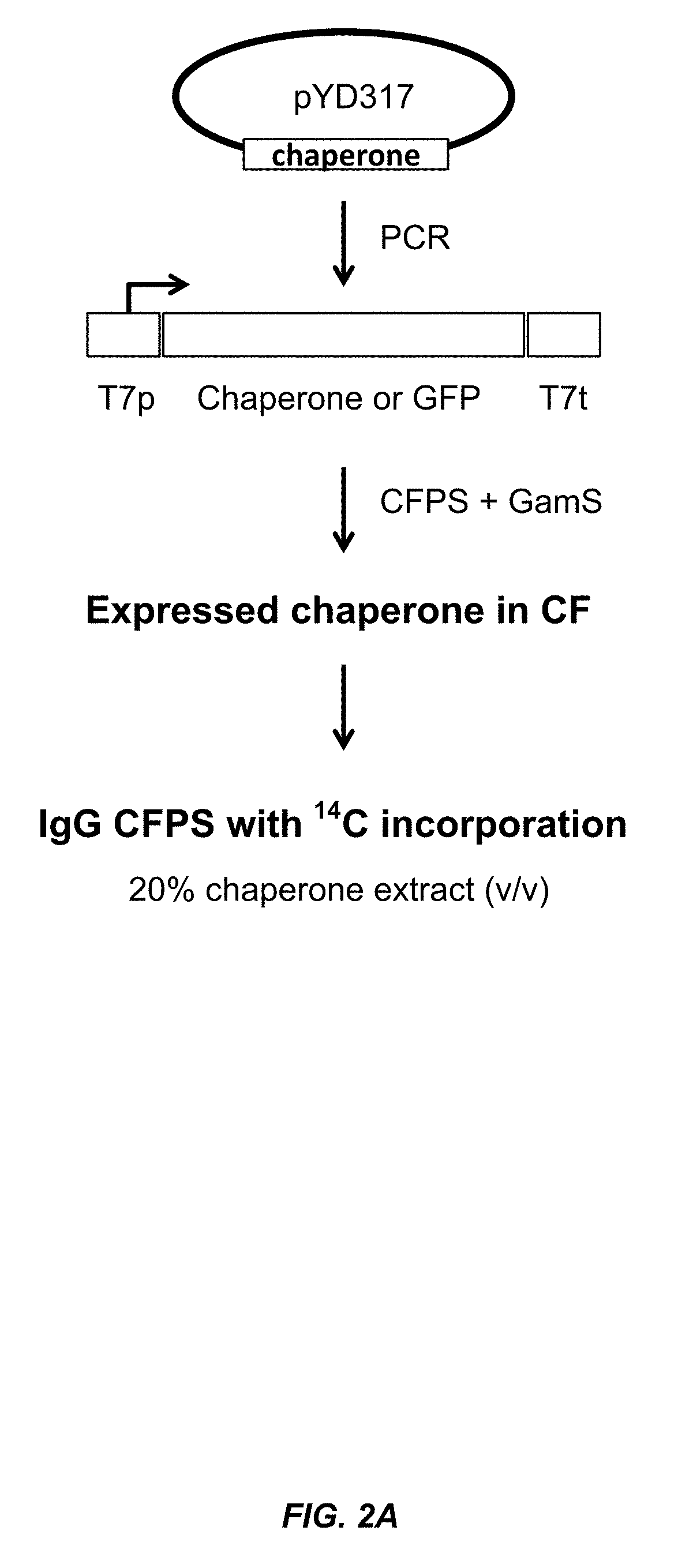
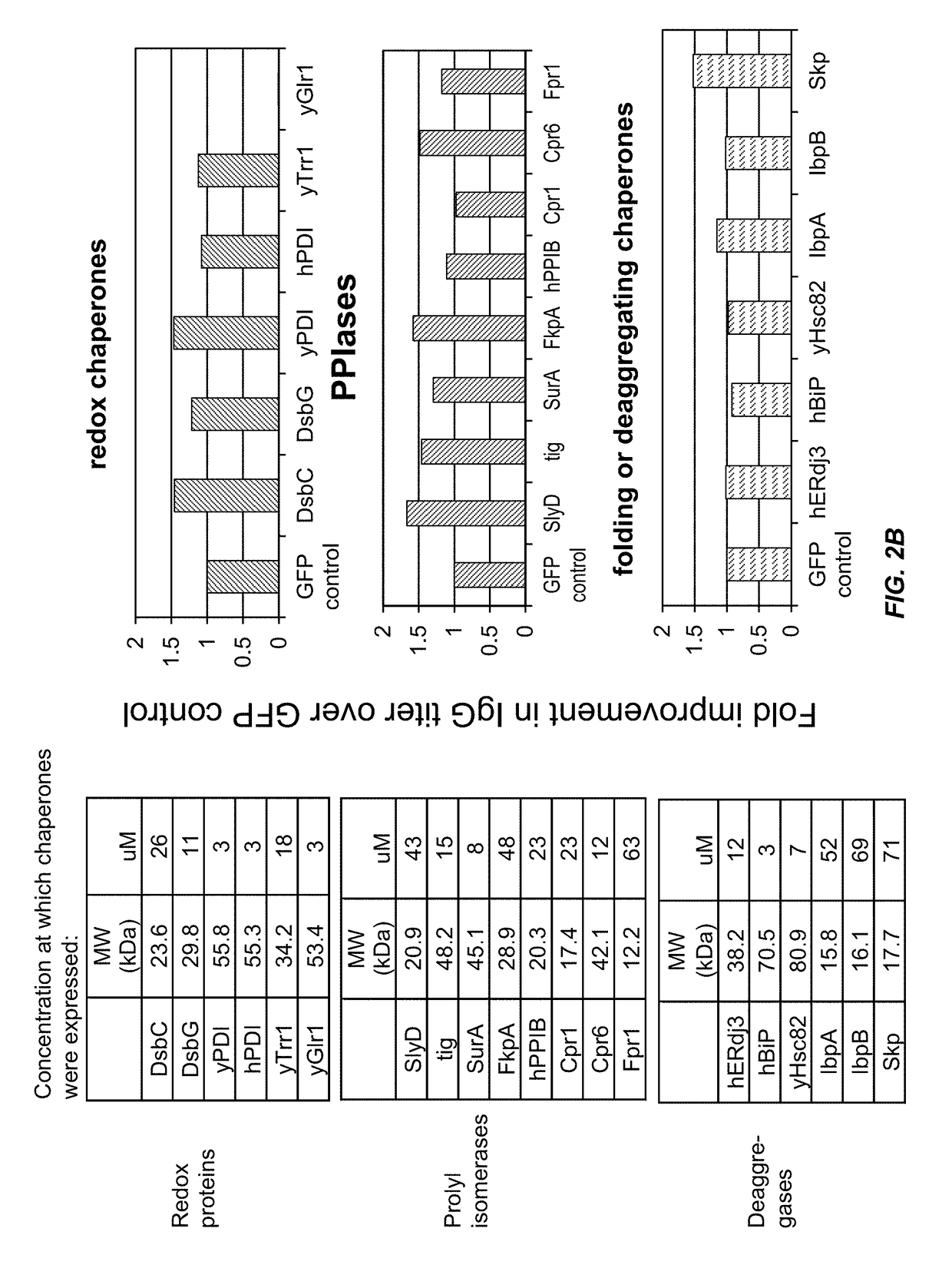
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
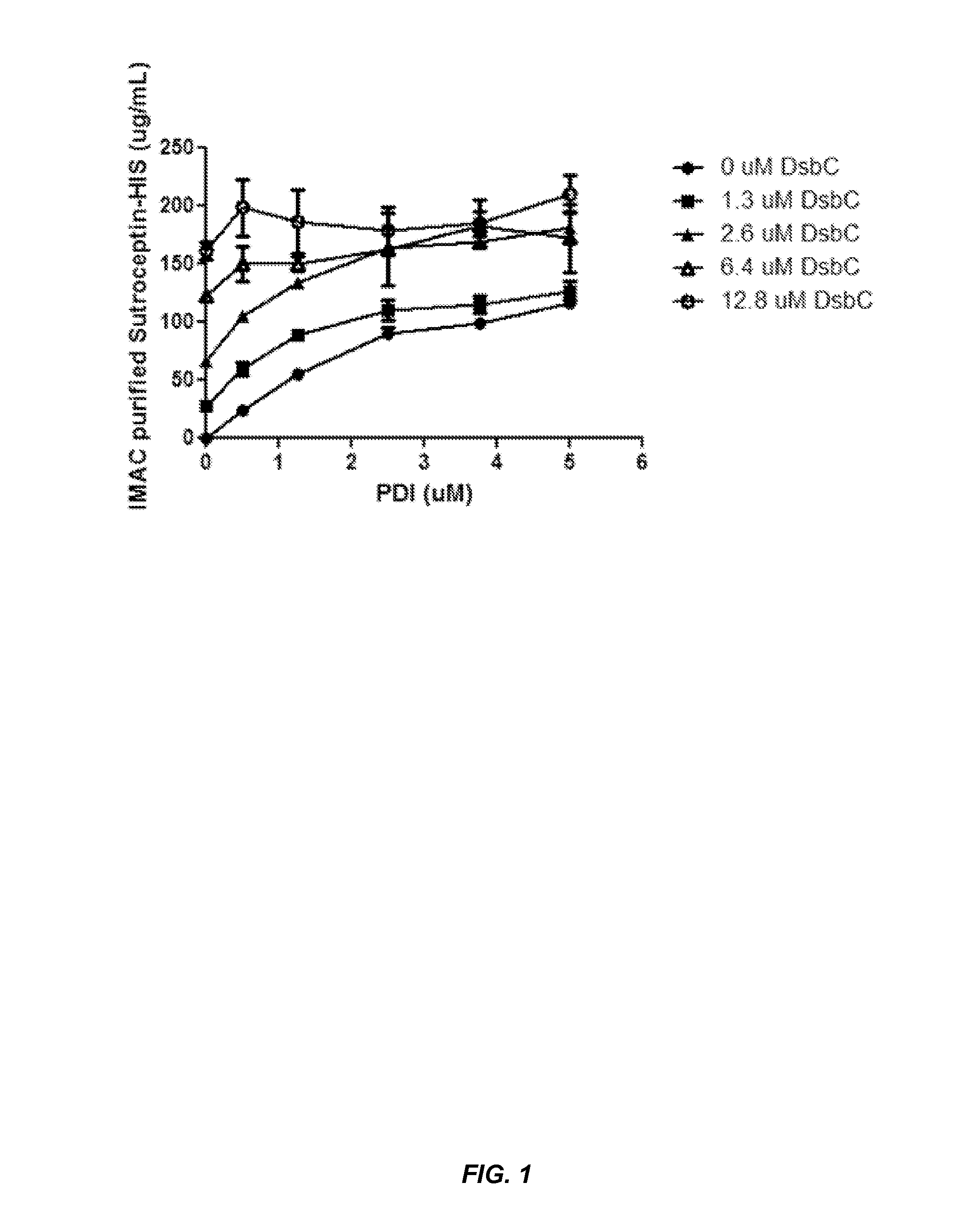
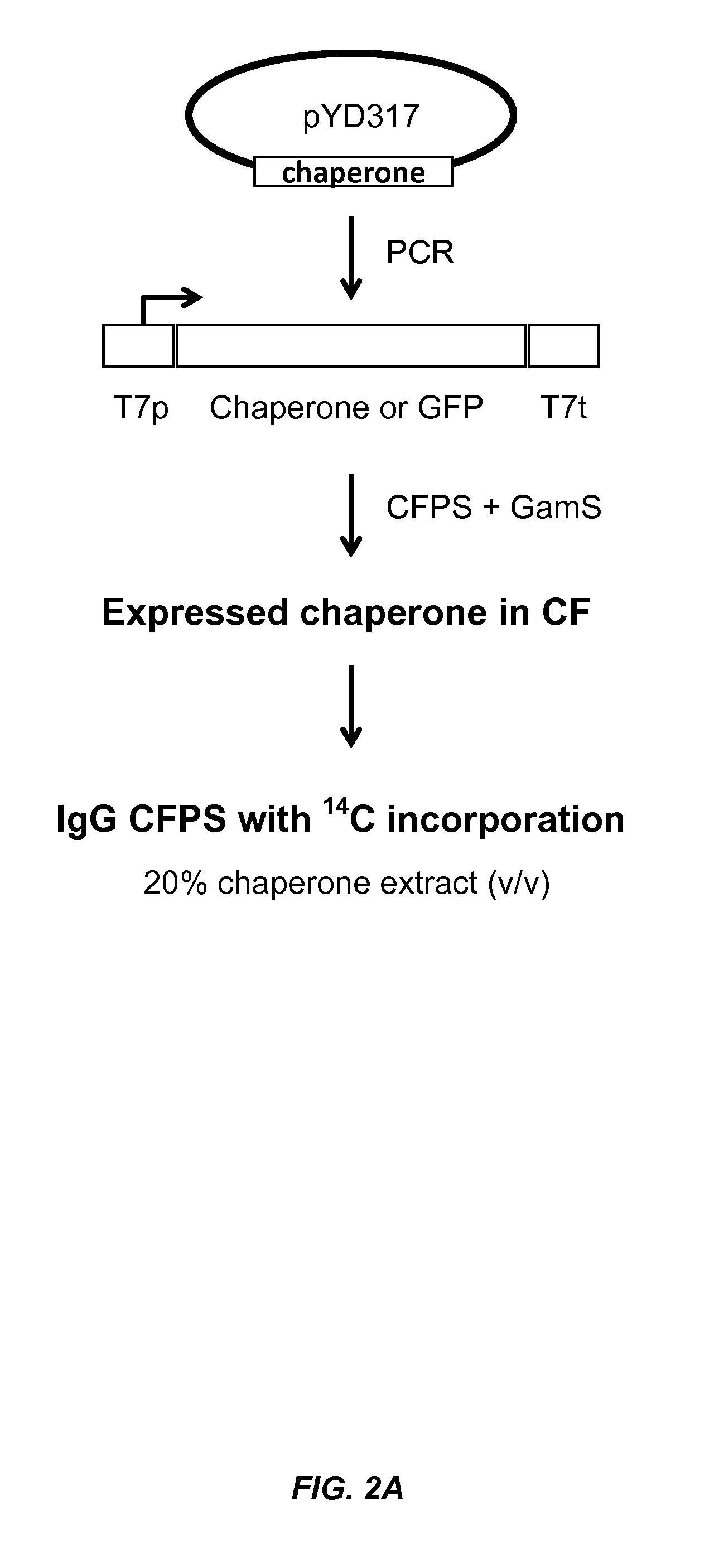
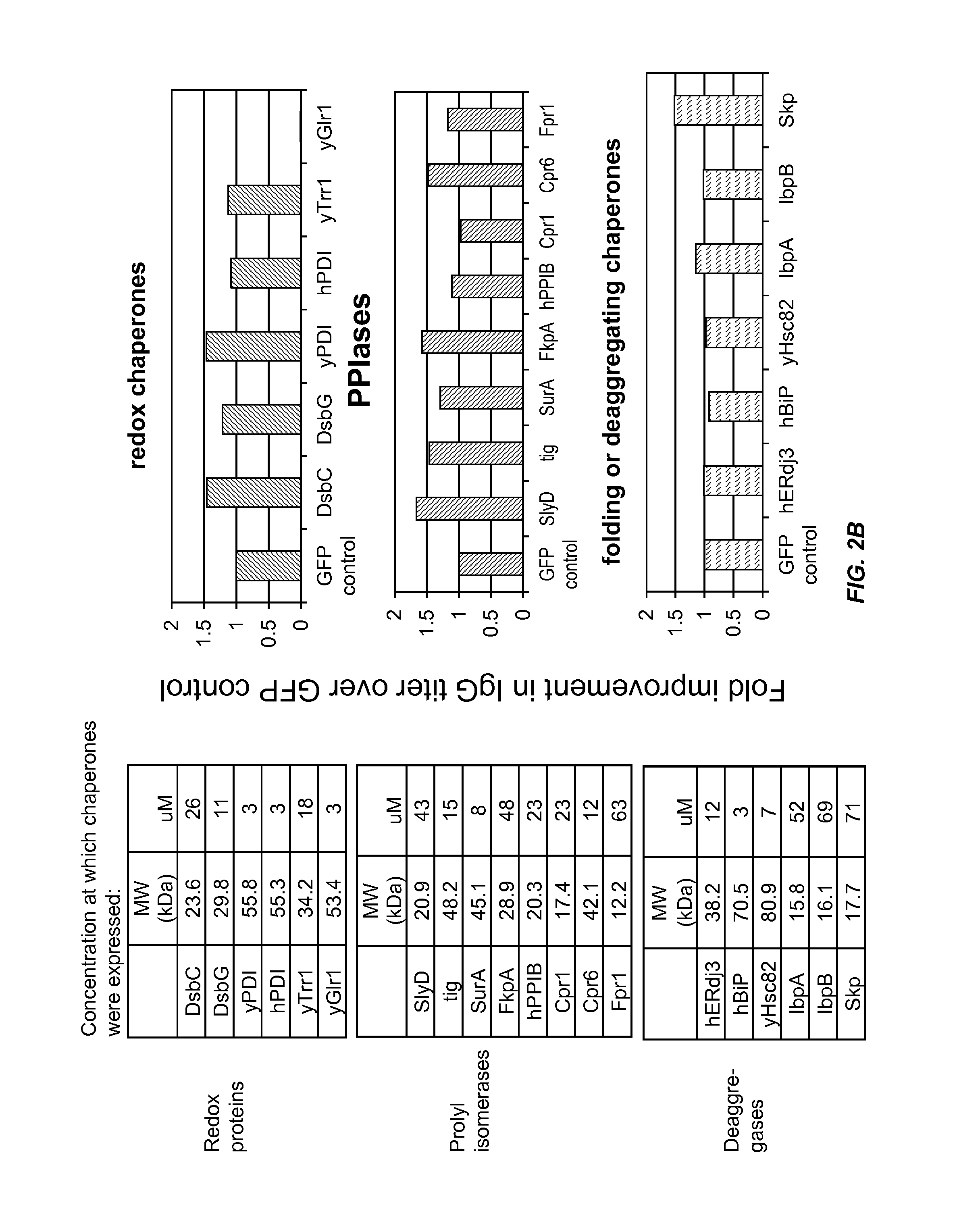
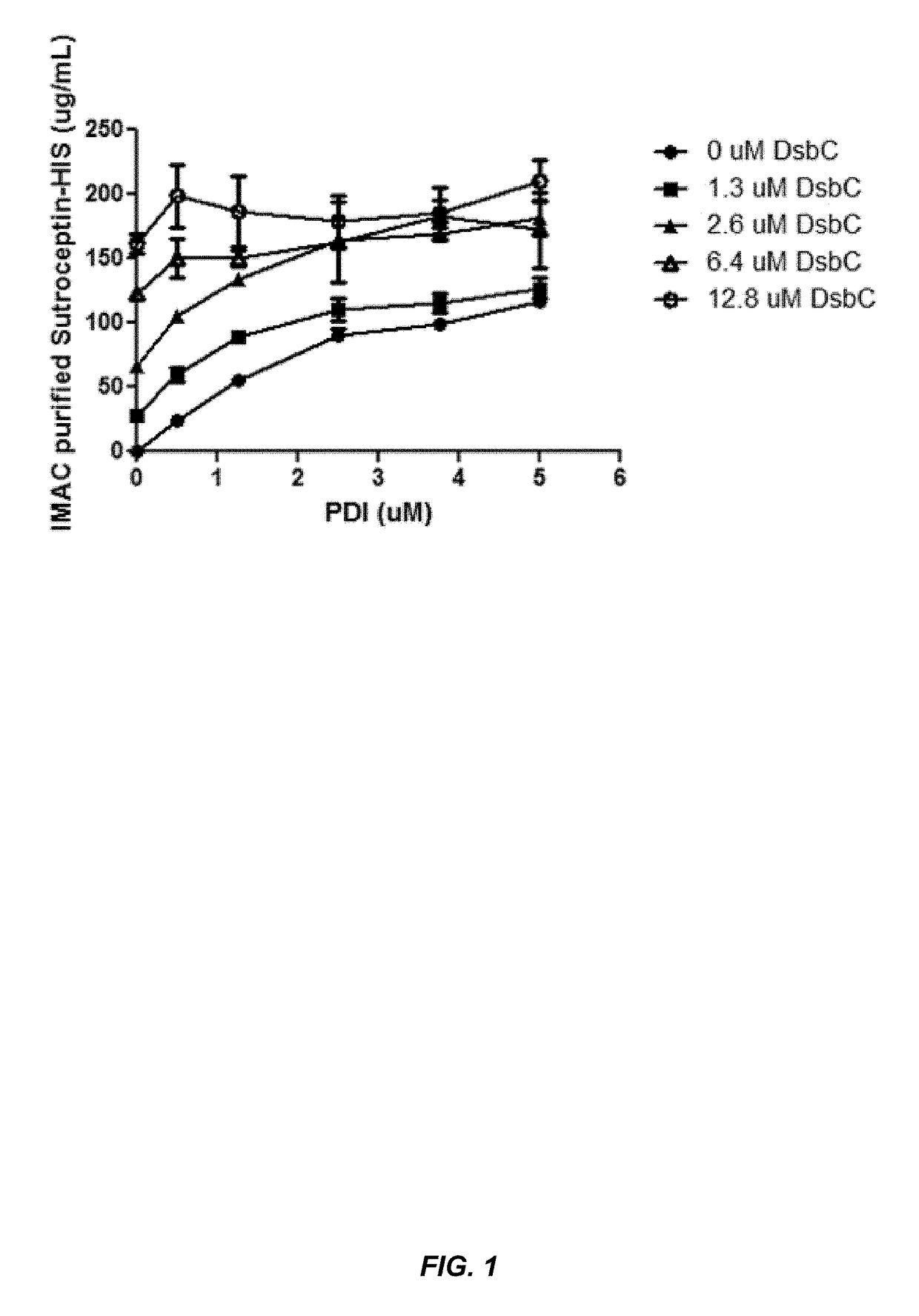
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
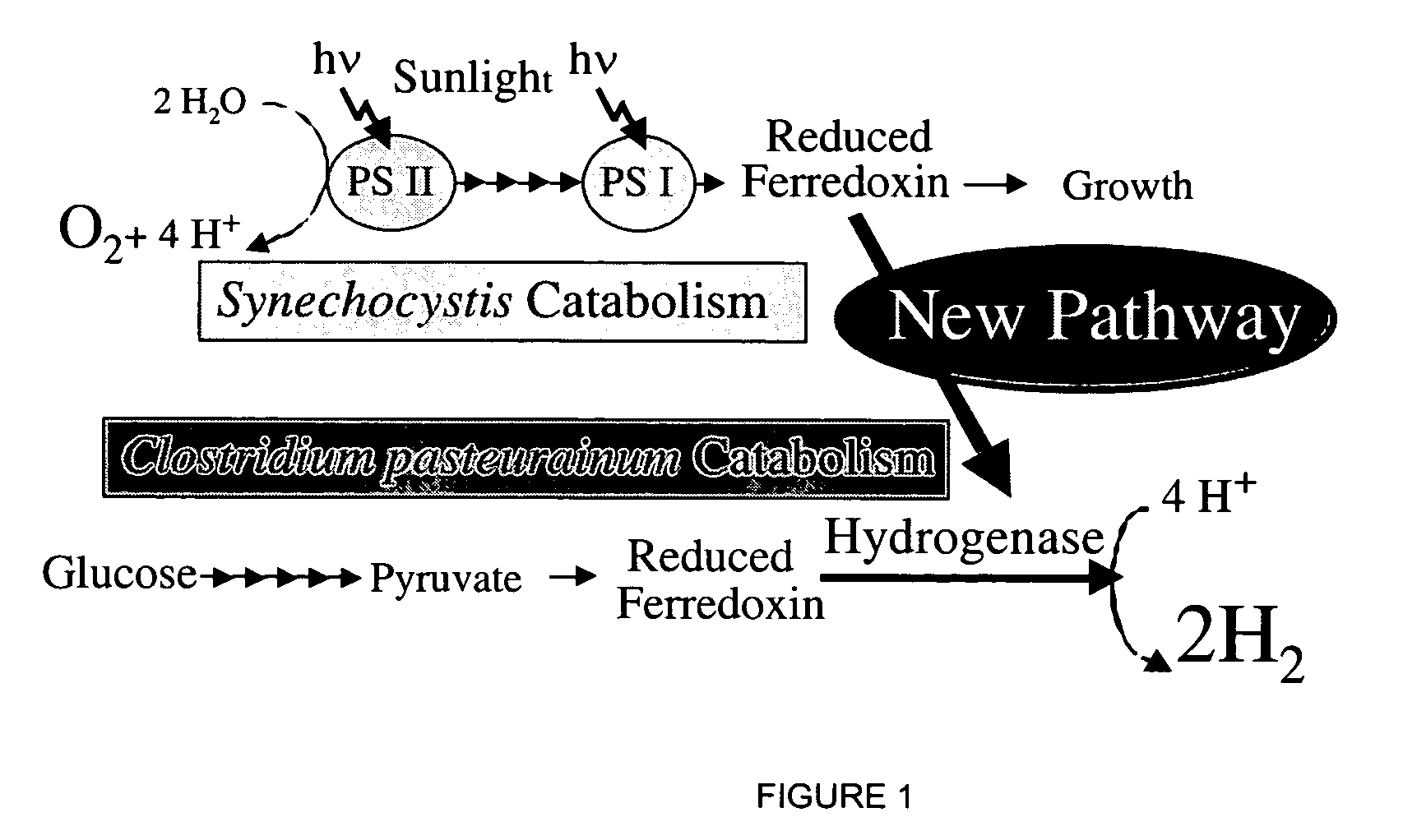
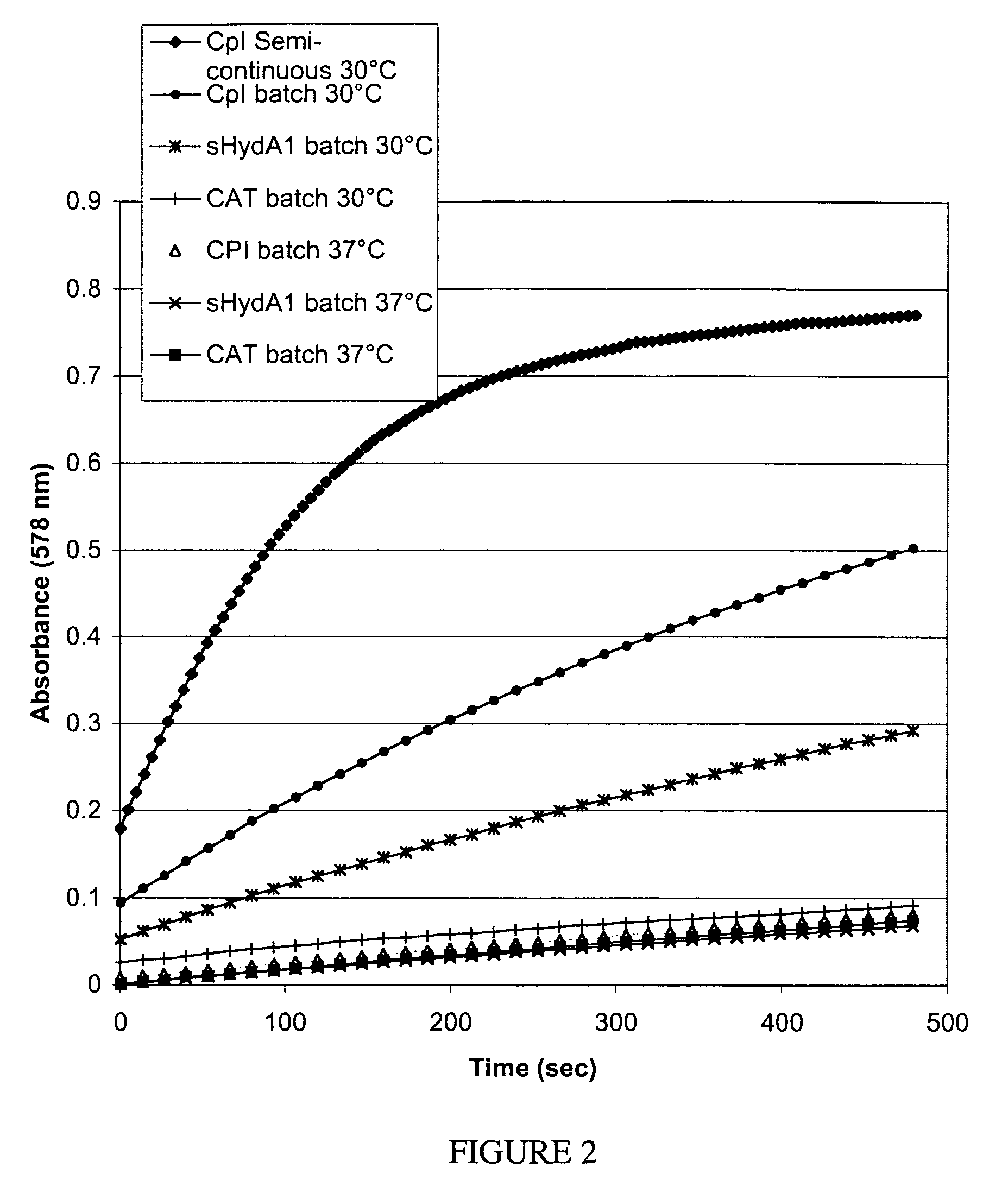
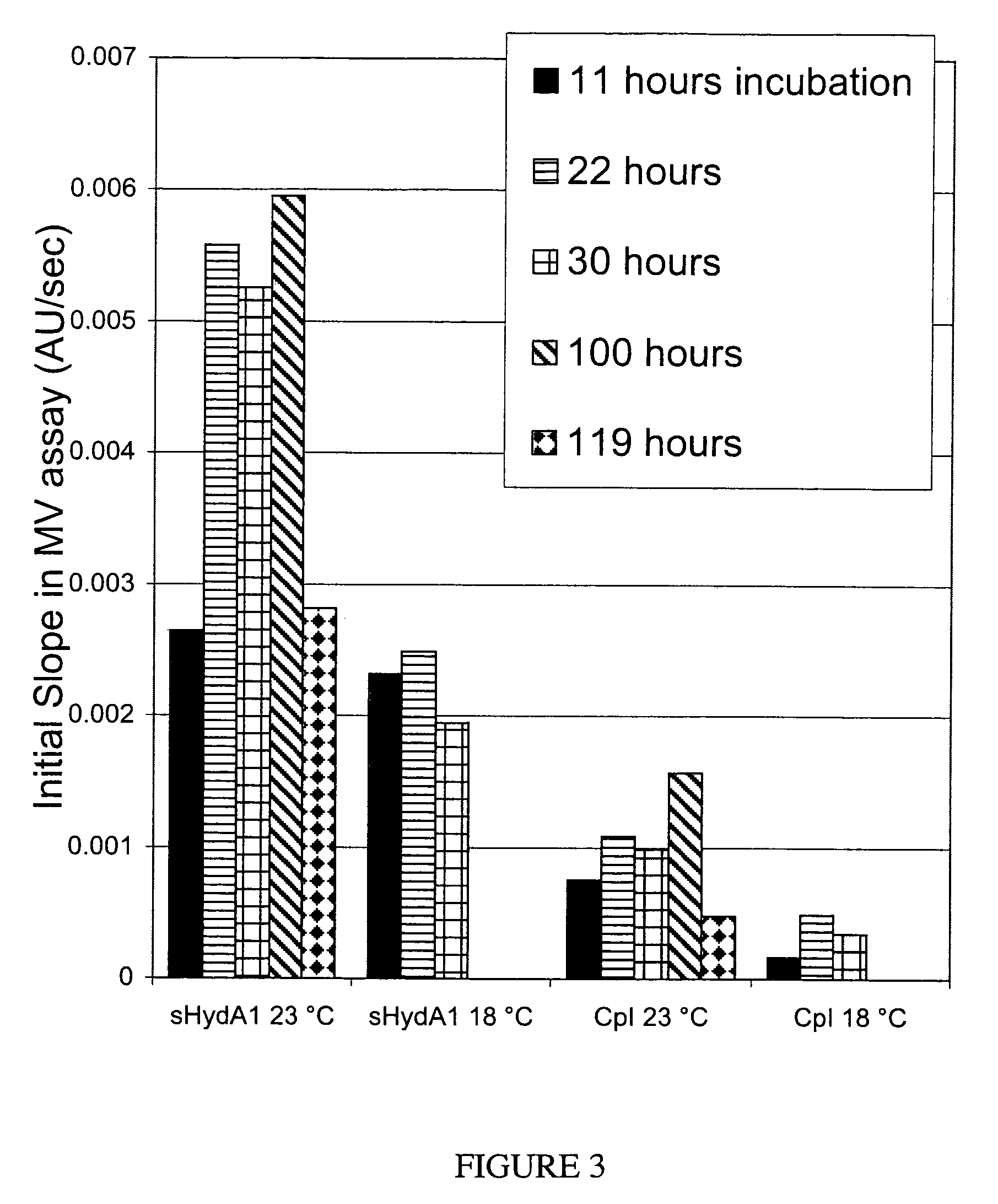
Cell-free extracts and synthesis of active hydrogenase
ActiveUS7351563B2Lower energy requirementsMore economicallySugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismCell free
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Encapsidation of Heterologous Entities into Virus-Like Particles
InactiveUS20100167981A1Improve translation efficiencyLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHeterologousVirus-like particle
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cell-free extracts and synthesis of active hydrogenase
ActiveUS20060281148A1Lower energy requirementsMore economicallyBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismCell free
Enzymatically active hydrogenase is synthesized in a cell-free reaction. The hydrogenases are synthesized in a cell-free reaction comprising a cell extract derived from microbial strains expressing at least one hydrogenase accessory protein. In some embodiments, the extracts are produced under anerobic conditions.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing with recombinant carbonyl reductase
InactiveCN102618590AAvoid inhibitionImprove conversion abilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEthyl butyrate
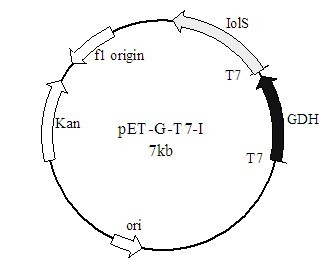
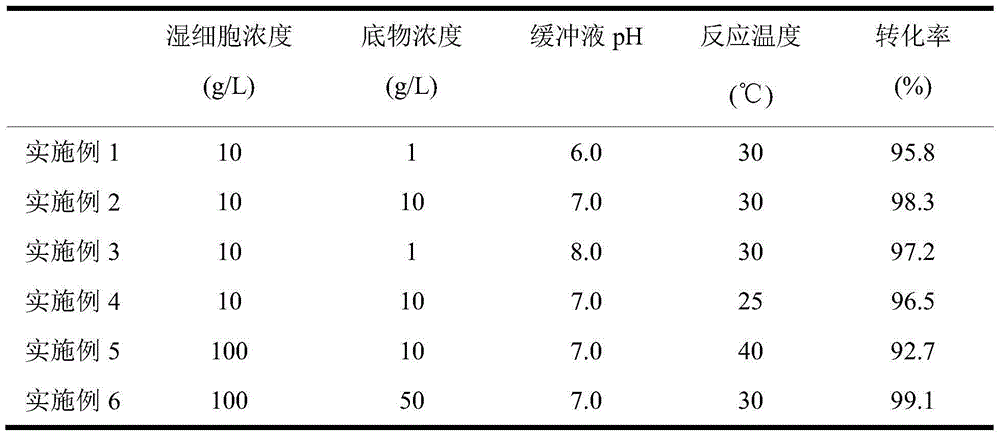
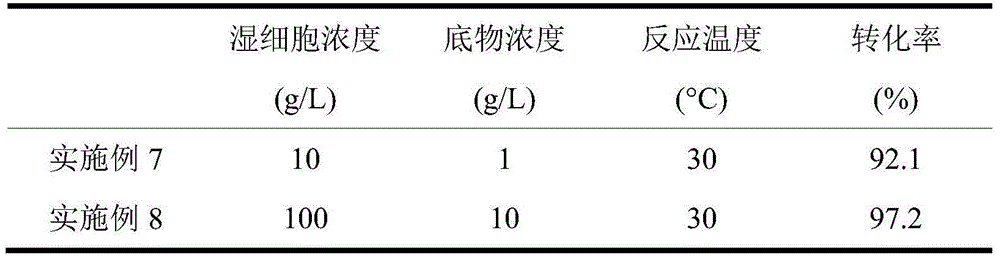
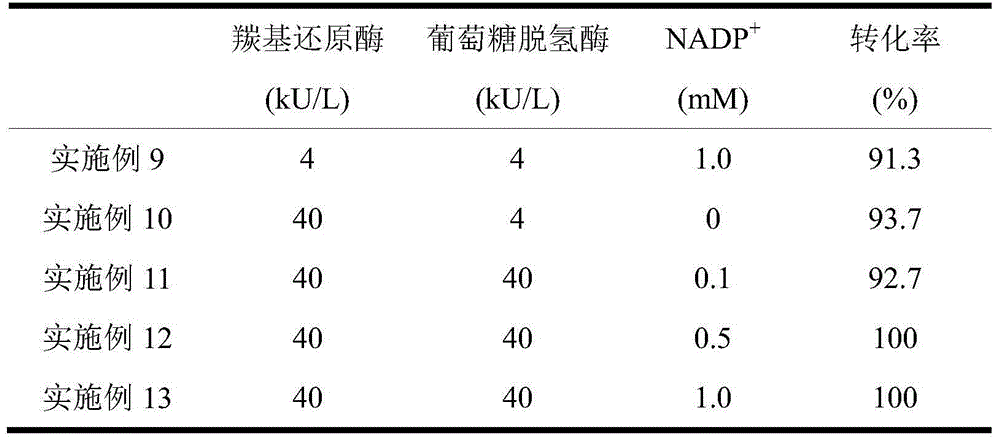
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing recombinant carbonyl reductase, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning gene segments of carbonyl reductase (IolS) and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from bacillus subtilis CGMCC NO.1.1508, expressing an IolS gene and a GDH gene in series by adopting a dual-starter method to construct a recombinant plasmid pET24a-G-T7-I, and introducing the plasmid into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); and under the condition of not adding or adding a small amount of NADP+cofactors, performing biotransformation by taking a cell-free extract of the escherichia coli recombinant plasmid as a catalyst, 2-oxo-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and glucose as a substrate to obtain (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, wherein the enantiomeric excess value of the product is higher than 99.5 percent. In the method, IolS and GDH are co-expressed, so that efficient regeneration of an intra-cellular cofactor NADP(H) is realized, production cost is lowered, and a good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Skin and hair care using extract from conditioned medium cultured by mesenchymal stem cells and other regenerative cells
InactiveUS20110177015A1Enable growthEnable maintenanceCosmetic preparationsHair removalHair streamsBiology
A method and composition for treating dermatological conditions and improving skin condition and helping hair to grow or thicken involves putting mesenchymal stem cells or other cells with regenerative properties into culture medium to induce secretion of beneficial factors such as growth factor, regulatory factors, enzymes, hormones, peptides and lymphokines into the culture medium to create conditioned medium and then extracting either a supernatant or a cell free extract of the conditioned medium to use itself or components thereof alone or with other skin or hair care reagents as a topical ointment or formula to apply to the skin or hair topically for therapeutic and cosmetic purposes.
Owner:FRIEDLANDER HYMIE
Mixtures and Compositions Comprising Paenibacillus Strains or Metabolites Thereof and Other Biopesticides
The present invention relates to novel mixtures comprising, as active components, at least one isolated bacterial strain, which is a member of the genus Paenibacillus, or a cell-free extract thereof or at least one metabolite thereof, and at least one other biopesticide. The present invention also relates to compositions comprising at least one of such bacterial strains, whole culture broth or a cell-free extract or a fraction thereof or at least one metabolite thereof, and at least one other biopesticide. The present invention also relates to a method of controlling or suppressing plant pathogens or preventing plant pathogen infections by applying such composition. The present invention also relates to mixtures of fusaricidins which are pesticidal metabolites produced by the abovementioned strains, and other biopesticides.
Owner:BASF AG
A novel paenibacillus strain, antifungal compounds, and methods for their use
The present invention relates to a composition comprising a biologically pure culture of a fungicidal Paenibacillus sp. strain comprising a variant fusaricidin synthetase lacking a functional adenylation domain in the third module. The present invention also provides a composition comprising a biologically pure culture of a fungicidal Paenibacillus sp. strain or a cell-free extract thereof comprising at least one Paeniserine and at least one Paeniprolixin. Also provided are isolated compounds and methods of treating a plant to control a plant disease with the disclosed compositions and compounds.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCI LP
Cell-free synthesis of membrane bound polypeptides
InactiveUS8183010B2High yield cell-free synthesisHigh yieldPeptidesTissue cultureCell freeMembrane bound
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Polyene Antibiotics, Compositions Containing Said Antibiotics, Method and Micro-Organisms Used to Obtain Same and Applications Thereof
InactiveUS20090221520A1Preventing polar effectClear pharmacological advantageAntibacterial agentsBiocideCell membraneAntibiotic Y
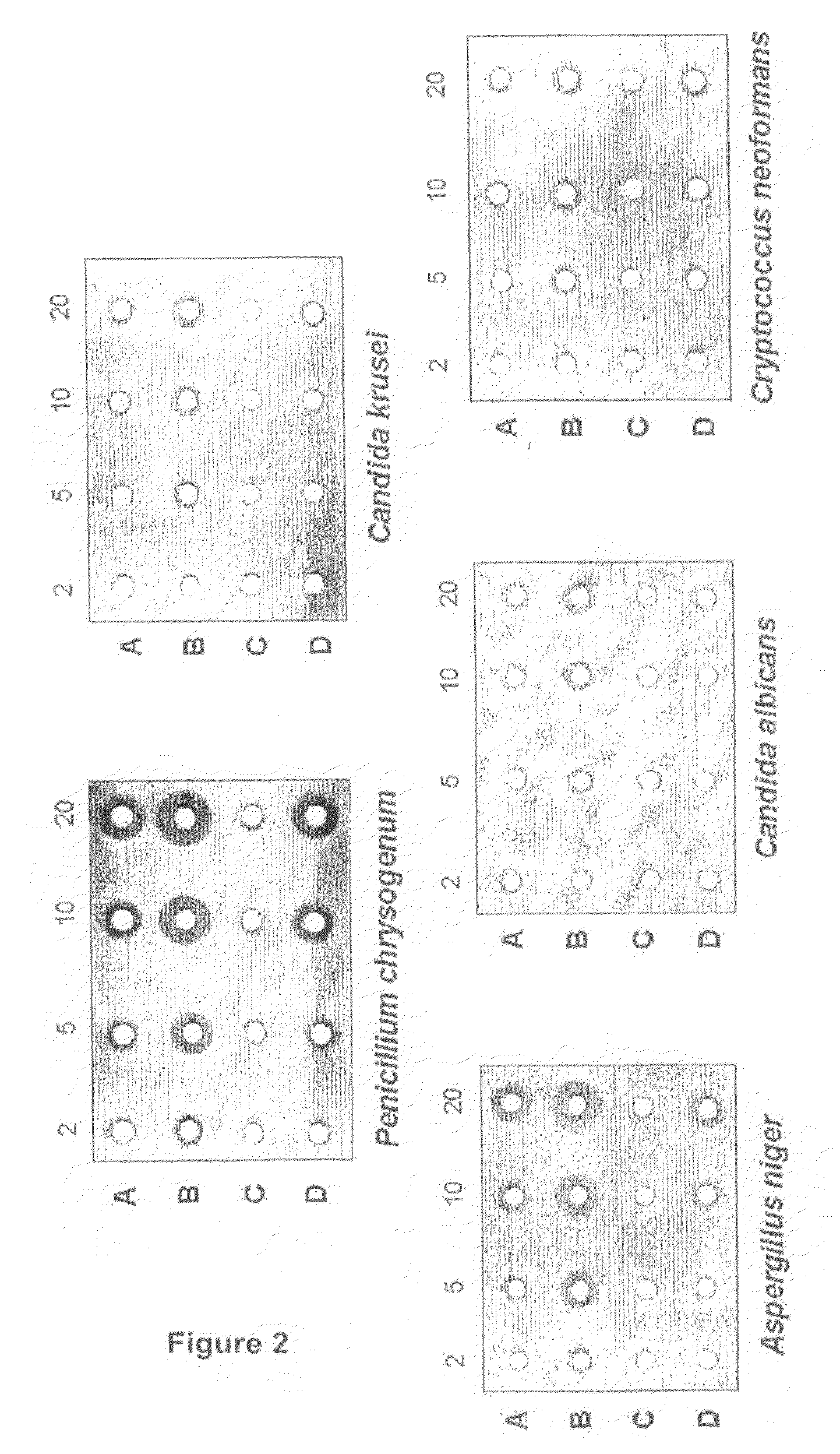
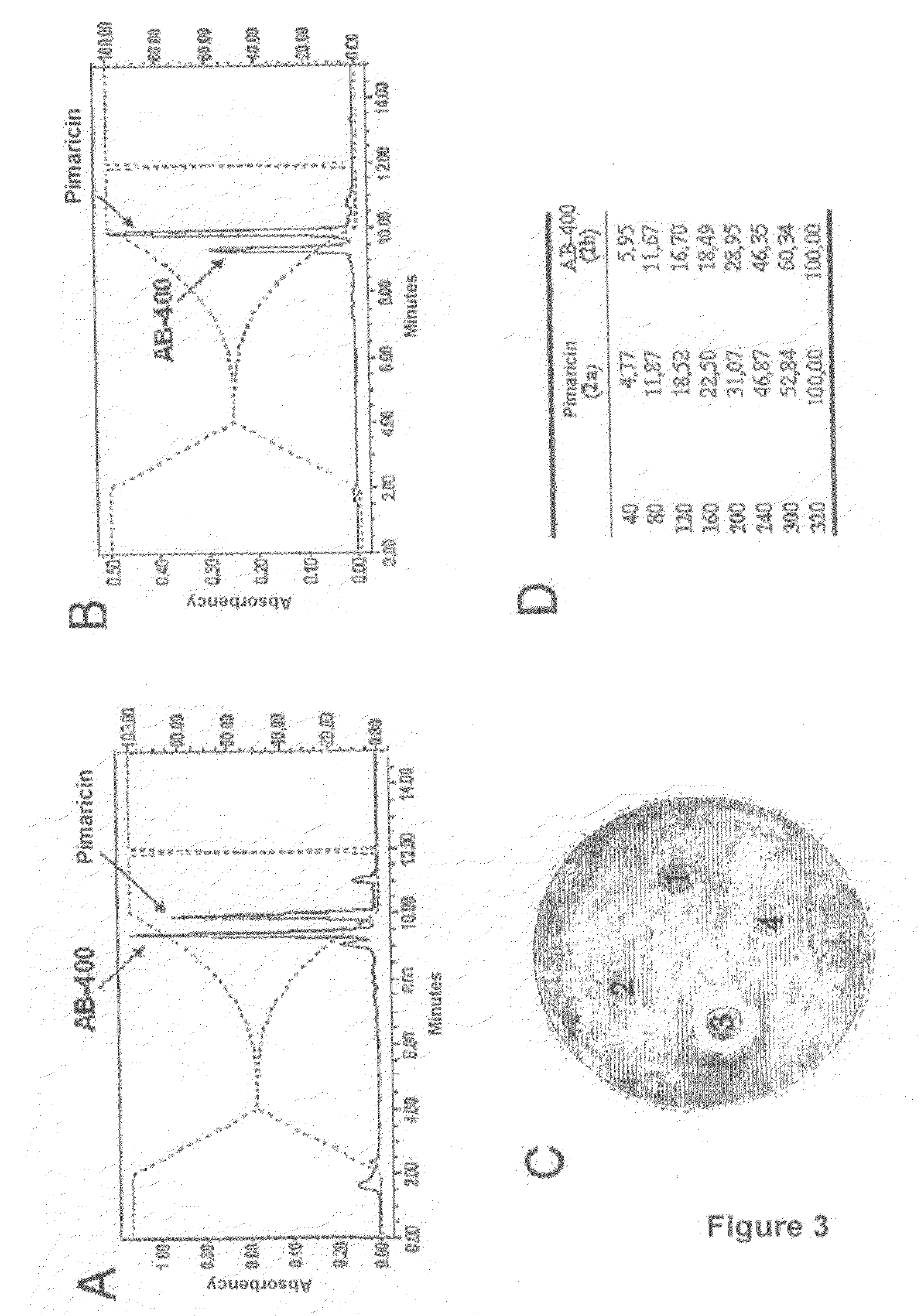
The invention relates to novel polyenes having formula (I), wherein: R1 represents alkyl C1-C3; and R2 represents a functional group selected from CH3— or CONH2— (methyl- or primary amide-). The aforementioned polyenes have a biocide action on organisms comprising cell membranes that contain ergosterol, e.g., fungi or parasites. Said compounds can be obtained using a method that consists in cultivating a producing micro-organism under conditions that enable the production thereof. In addition, the invention also relates to a mechanism for the in vitro production of amidated polyenes, consisting in incubating carboxylated polyenes with cell-free extracts (or proteinaceous fractions) of the producers of same in the presence of ATP / Mg++ and an amide- group donor compound (preferably glutamine).
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Protein discovery using intracellular ribosome display
ActiveUS20110008774A1Efficient foldingImprove stabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein-protein complexDNA
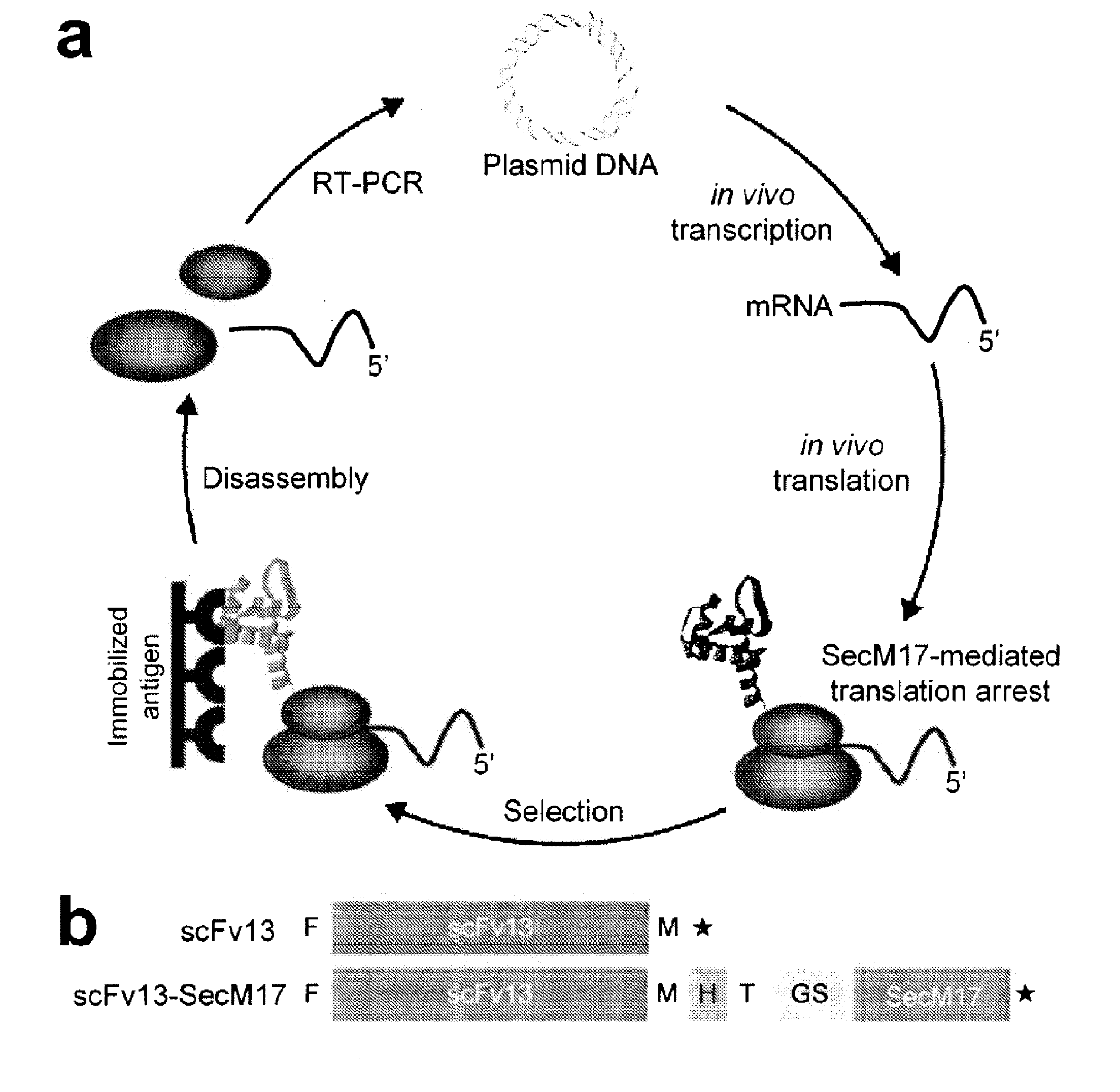
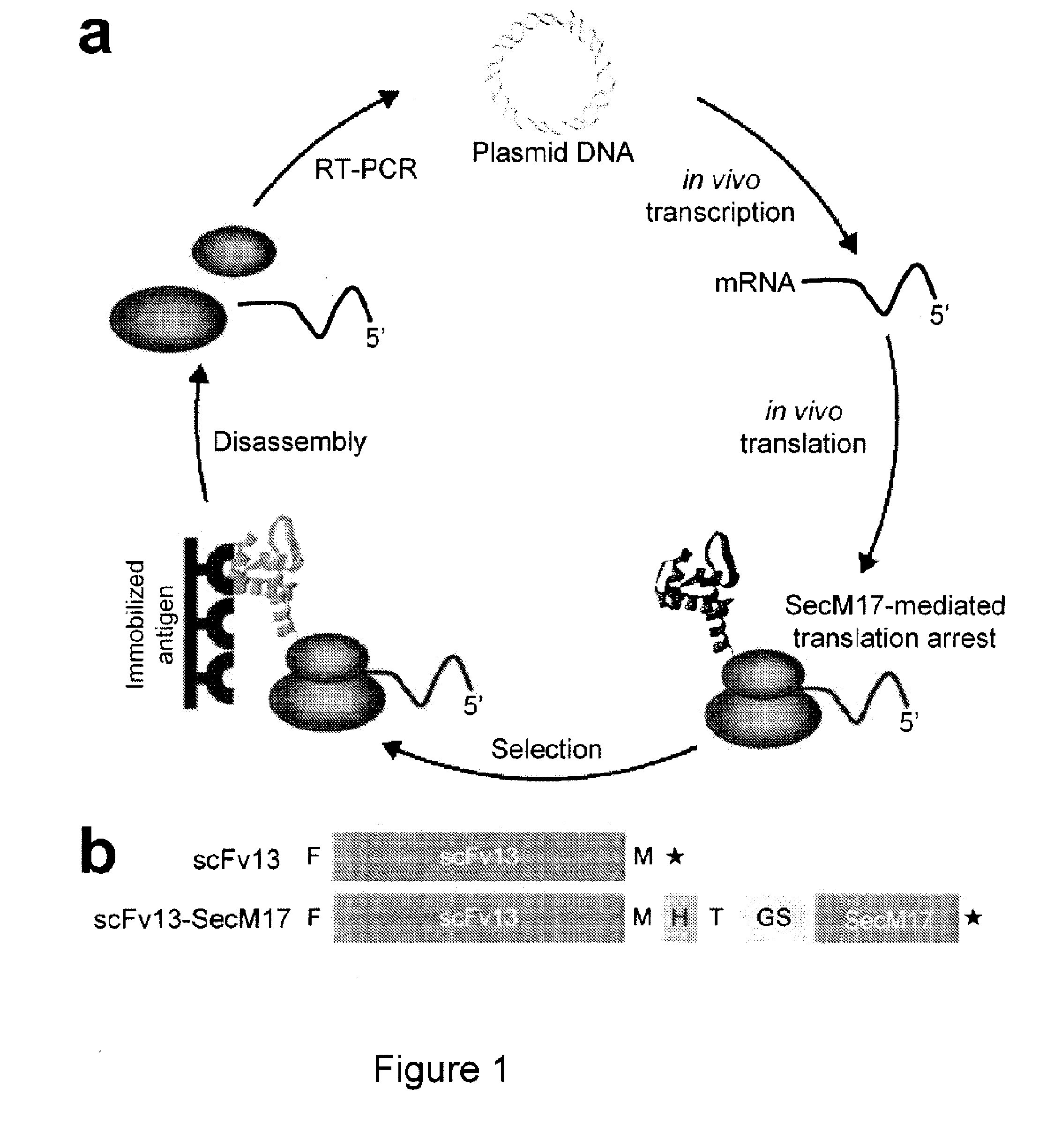
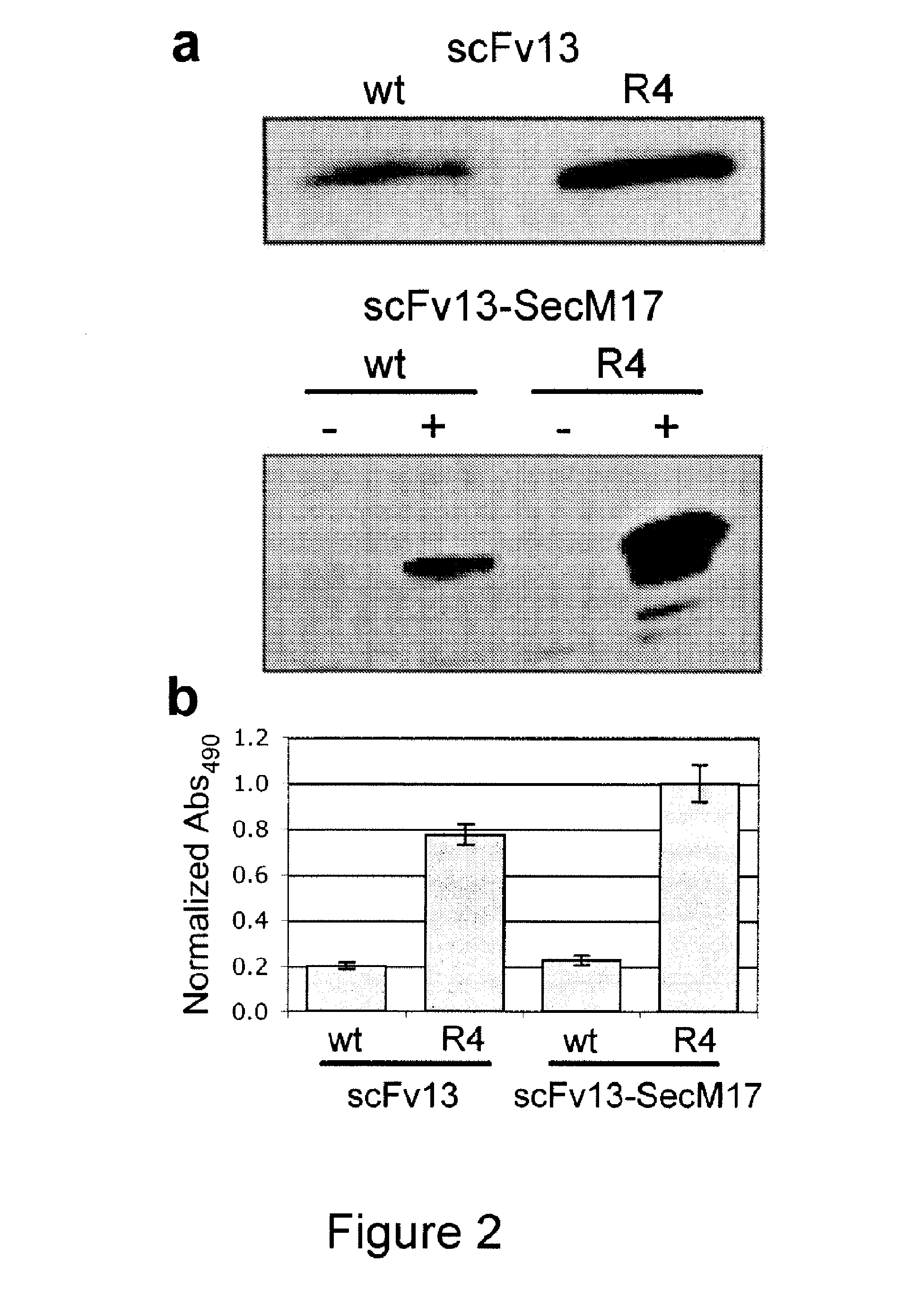
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a protein that binds to a target molecule and has intracellular functionality. This method includes providing a construct comprising a deoxyribonucleic acid molecule encoding the protein which binds to the target molecule, with the deoxyribonucleic acid molecule being coupled to a stall sequence. A host cell is transformed with the construct and then cultured under conditions effective to form, within the host cell, a complex of the protein whose translation has been stalled, the mRNA encoding the protein, and ribosomes. The protein in the complex is in a properly folded, active form and the complex is recovered from the cell. This method can be carried out with a cell-free extract preparation containing ribosomes instead of a host cell. The present invention also relates to a construct which includes a deoxyribonucleic acid molecule encoding a protein that binds to a target molecule and an SecM stalling sequence coupled to the deoxyribonucleic acid molecule. The deoxyribonucleic acid molecule and the SecM stalling sequence are coupled with sufficient distance between them to permit expression of their encoded protein, within the cell, in a properly folded, active form.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Encapsidation of heterologous entities into virus-like particles
InactiveUS8324149B2Improve translation efficiencyLower Level RequirementsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousVirus-like particle
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for in vitro site-directed mutagenesis using gene editing technologies
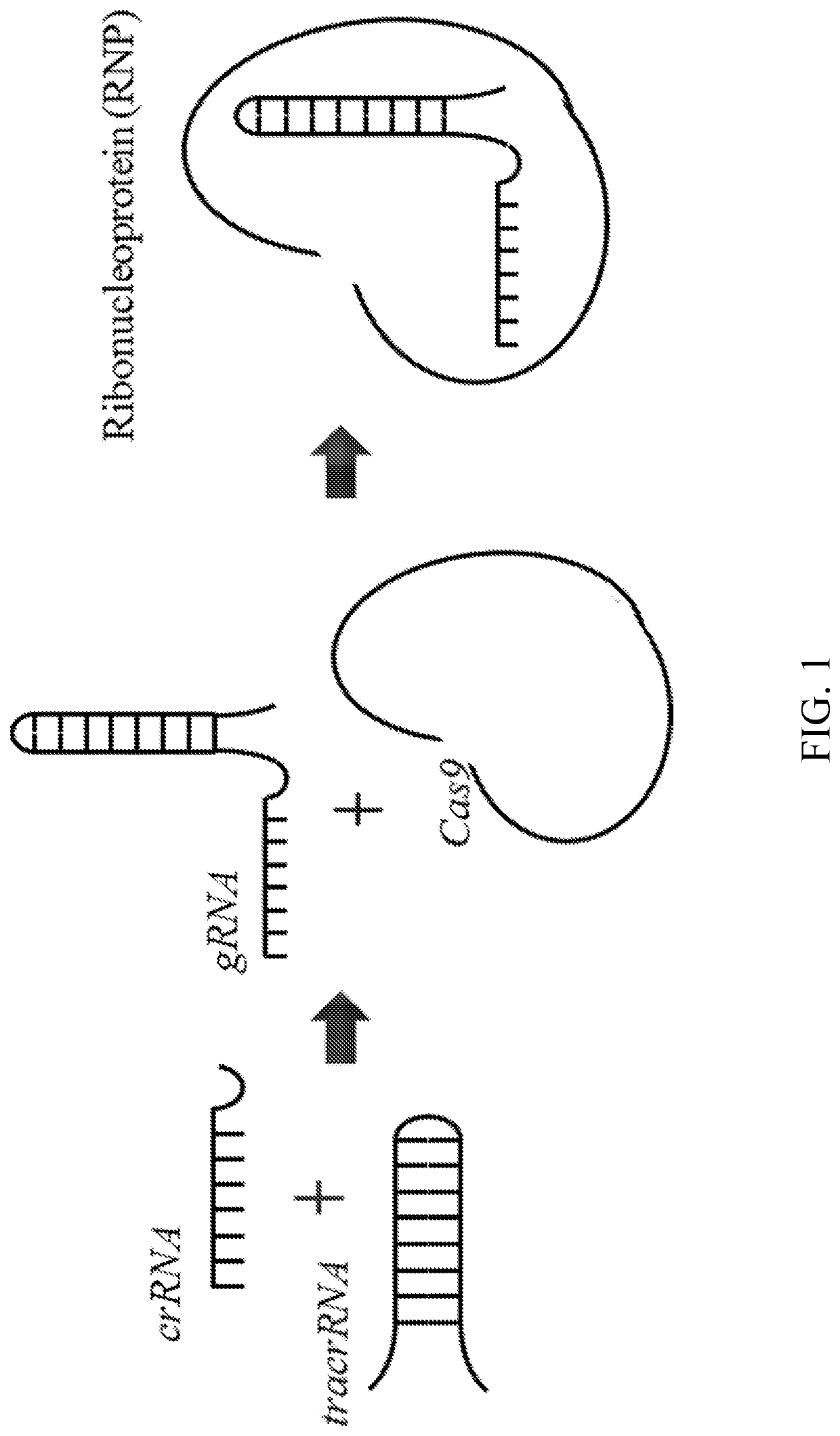
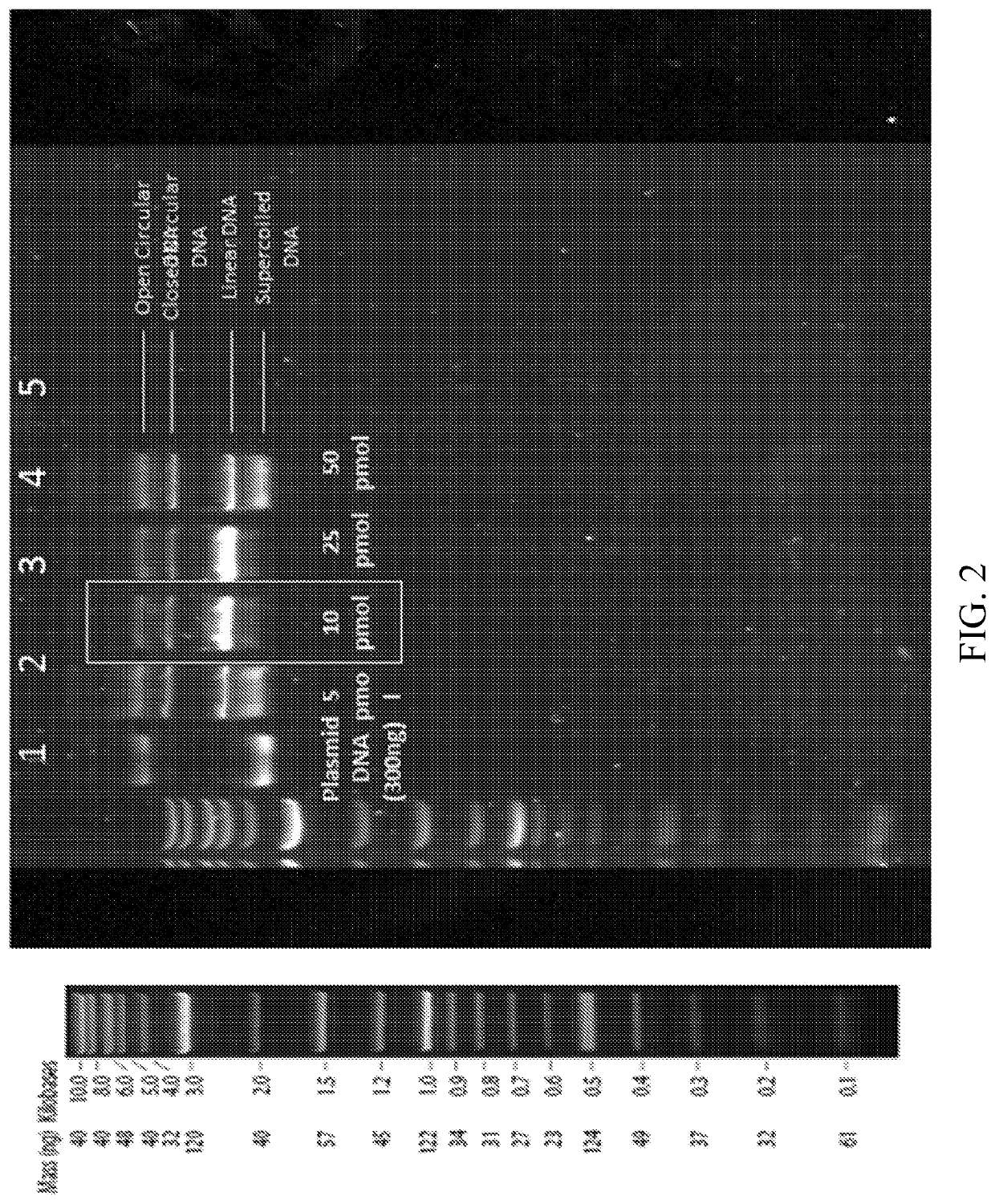
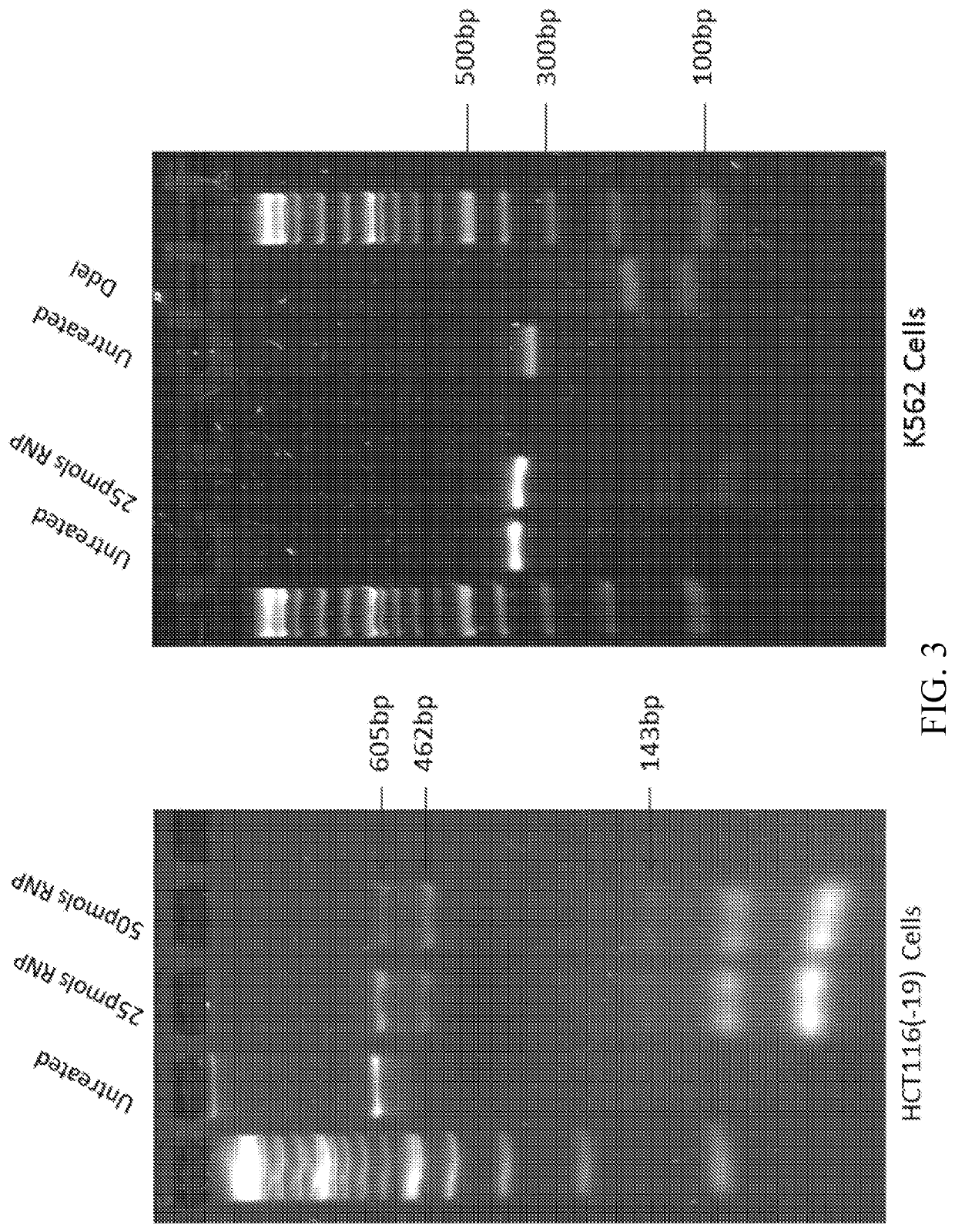
The invention relates to methods for performing in vitro site-directed mutagenesis of a targeted gene or genes. In another aspect, the invention includes in vitro site-directed mutagenesis kits comprising a ribonucleotide particle (RNP), an oligonucleotide, a buffer, a cell-free extract, and instructional material for use thereof.
Owner:F O R E BIOTHERAPEUTICS LTD +1
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Antifungal paenibacillus strains, fusaricidin-type compounds, and their use
The present invention relates to novel isolated bacterial strains, which are members of the genus Paenibacillus, originally isolated from soil and showing antagonistic activity against a broad range of pathogens and being capable of producing antimicrobial metabolites. It was found that the strains Lu16774 and Lu17007 belong to a novel subspecies named Paenibacillus polymyxa ssp. plantarum while the strain Lu17015 belongs to a novel species which is proposed to be Paenibacillus epiphyticus. The present invention also relates to microbial pesticide compositions comprising at least one of such novel bacterial strains, whole culture broth or a cell-free extract or a fraction thereof or at least one metabolite thereof, and / or a mutant of at least one of said novel bacterial strains having all the identifying characteristics of the respective bacterial strain or whole culture broth, cell-free extract, fraction and / or metabolite of the mutant thereof showing antagonistic activity against plant pathogens. The present invention also relates to a method of controlling or suppressing plant pathogens or preventing plant pathogen infections by applying such composition. The present invention also relates to novel fusaricidin-type compounds which are metabolites produced by the strains of the present invention.
Owner:BASF SE
Mixtures and compositions comprising paenibacillus strains or fusaricidins and chemical pesticides
The present invention relates to novel mixtures comprising, as active components, at least one isolated bacterial strain, which is a member of the genus Paenibacillus, or a cell-free extract thereof or at least one metabolite thereof, and at least one chemical pesticide. The present invention also relates to compositions comprising at least one of such bacterial strains, whole culture broth or a cell-free extract or a fraction thereof or at least one metabolite thereof, and at least one chemical pesticide. The present invention also relates to a method of controlling or suppressing plant pathogens or preventing plant pathogen infections by applying such composition. The present invention also relates to mixtures of fusaricidins which are pesticidal metabolites produced by the abovementioned strains, and chemical pesticides.
Owner:BASF AG
Use Of Lactic Acid Bacteria To Reduce Pathogens And As A Bio-Sanitizer
InactiveUS20140341872A1Accelerated exclusionGrowth inhibitionBiocideLactobacillusFood materialOrganism
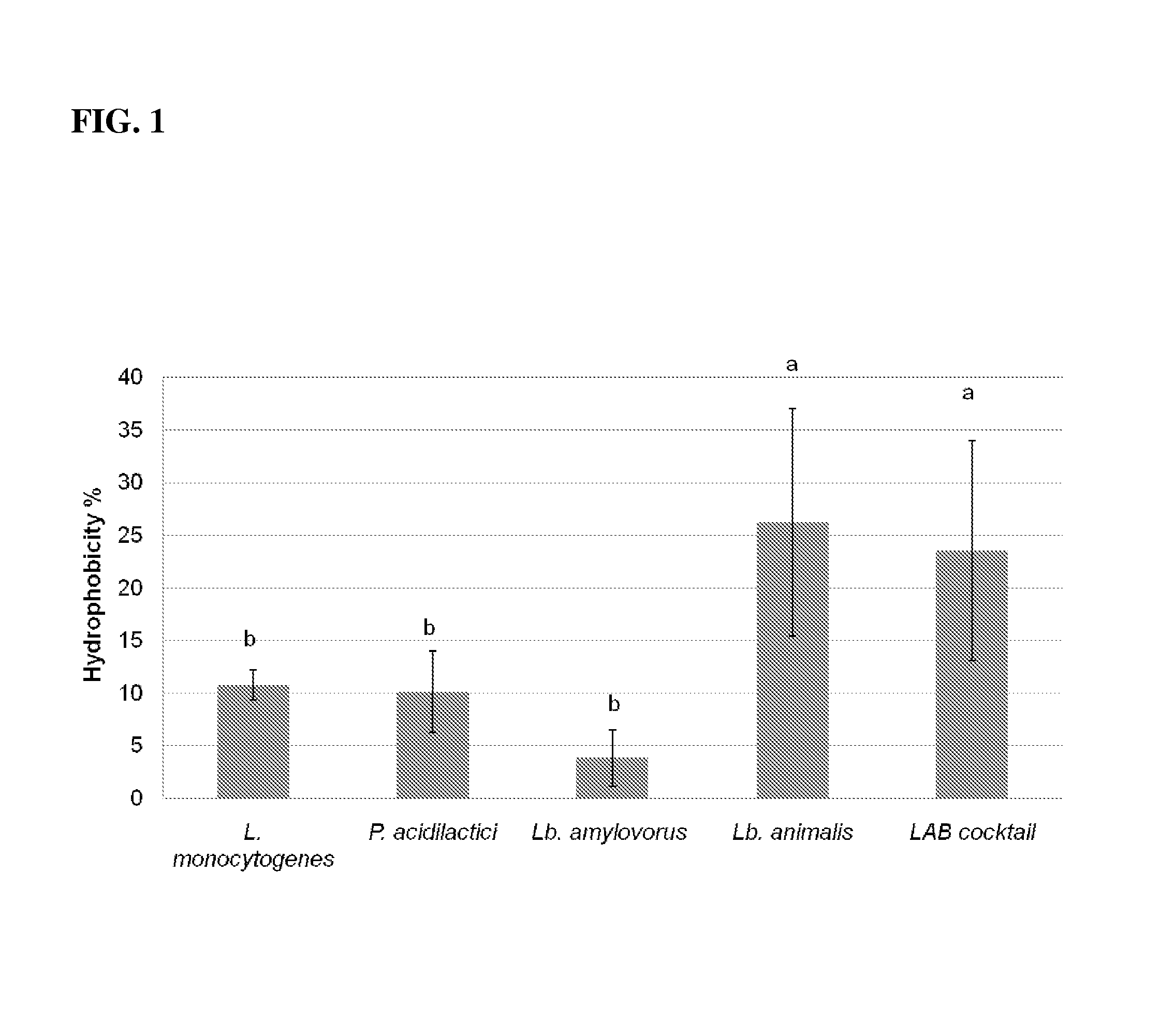
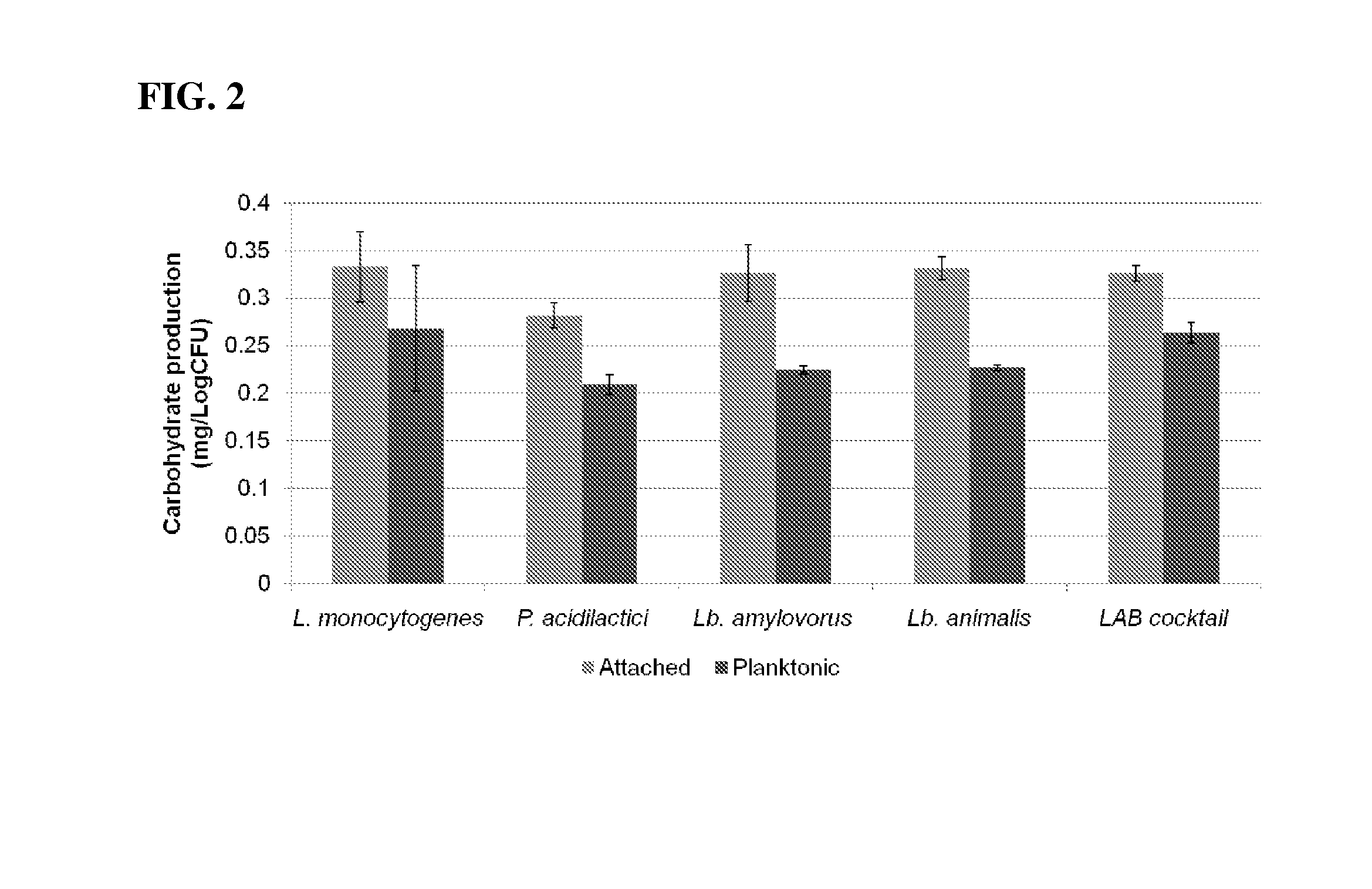
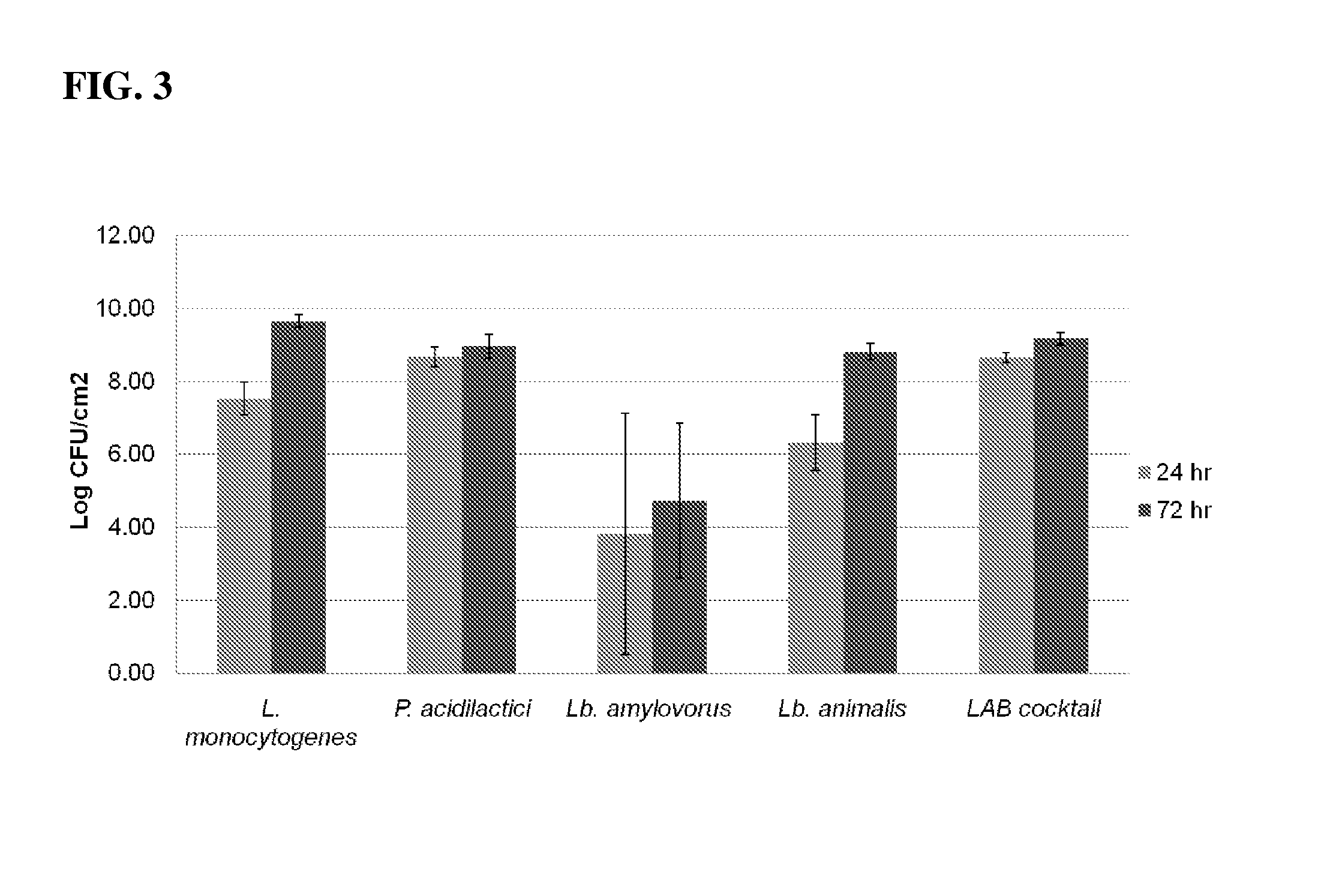
Compositions and methods are disclosed for improving food safety. One or more lactic acid producing microorganisms are shown to inhibit pathogenic contaminations on food materials. The lactic acid producing microorganisms are capable of adhering to various surfaces and may serve as a bio-sanitizing agent (or bio-sanitizer). Lactic acid producing microorganisms or cell free extract of these microorganisms may be used in an effective and natural method to prevent L. monocytogenes infection in food products, as well as in food processing facilities and equipments.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Cell-free extract and glycoprotein synthesis system
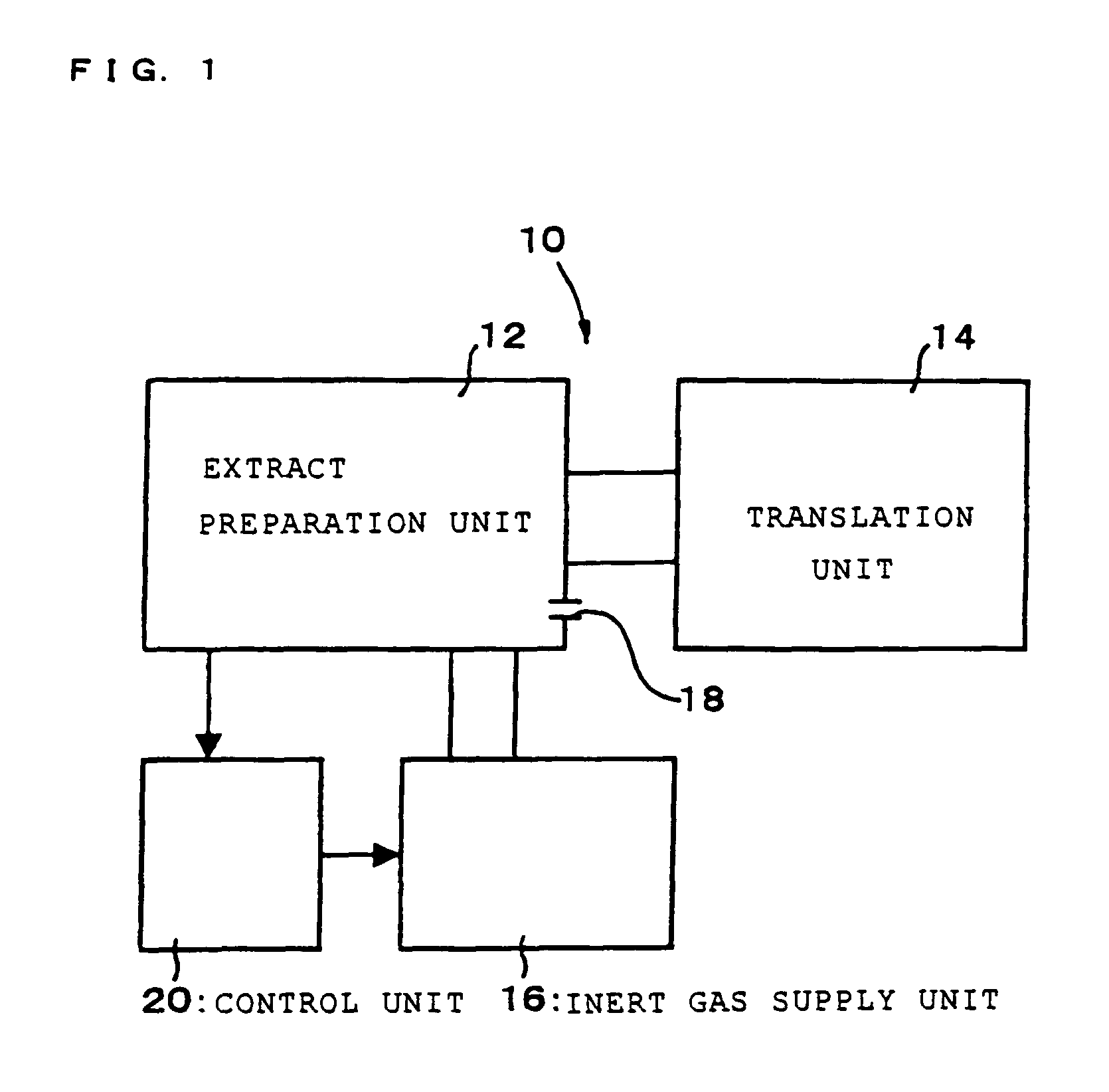
Insect cells are stored in a small gas cylinder, and the small gas cylinder is charged with nitrogen gas to pressurize the cylinder. The charged gas is exhausted at once to crush the cells to provide the objective cell extract with translation activity and glycosylation activity. As this method is gentler than the conventional cell-crushing method employing a homogenizer, in addition to translation factors, factors carrying glycosylation activity can also be recovered. As a result, an in-vitro glycoprotein synthesis system capable of performing translation to post-translation glycosylation can be produced.
Owner:TOSHIO HARA
Cell-free synthetic incorporation of non-natural amino acids into proteins
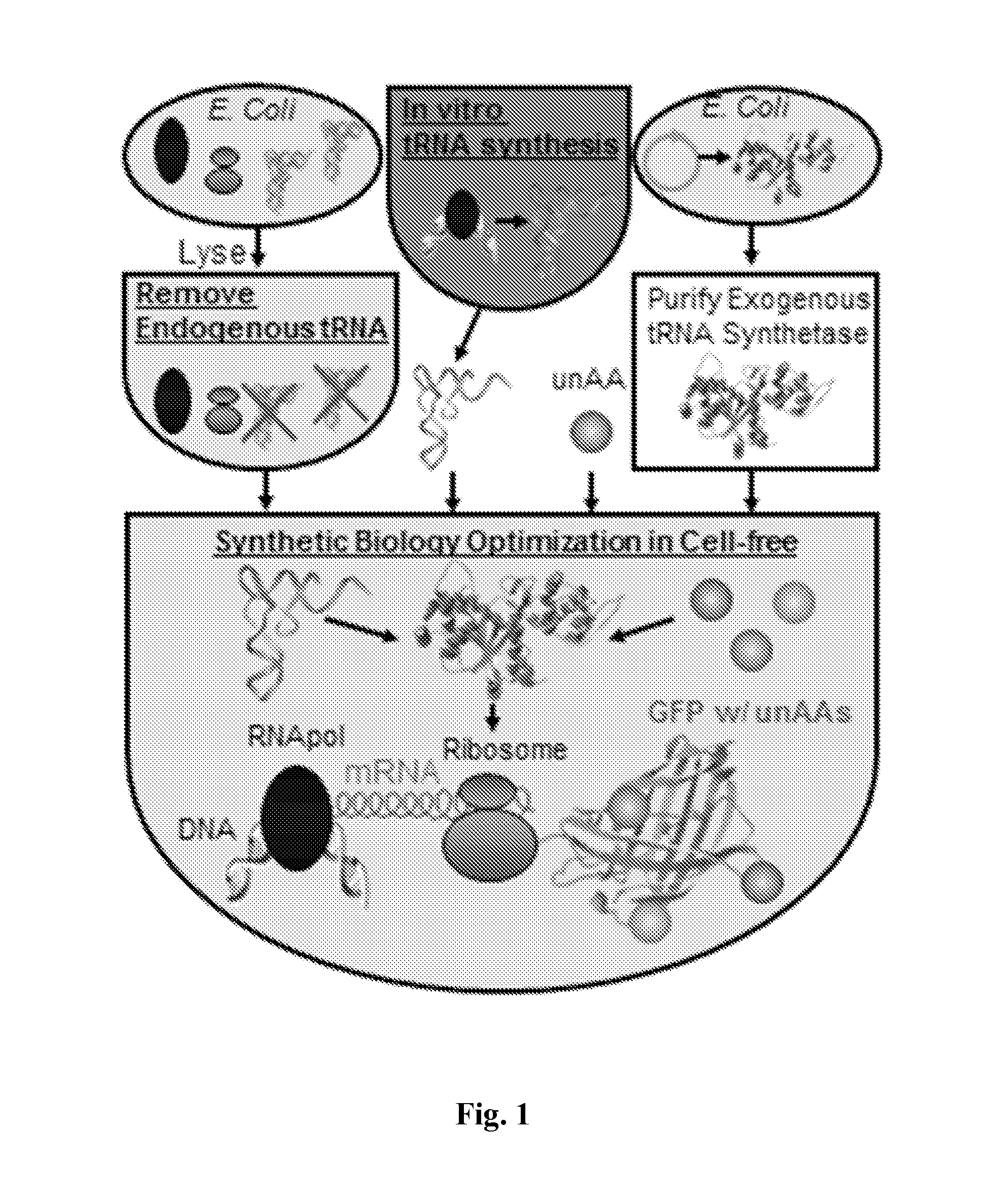
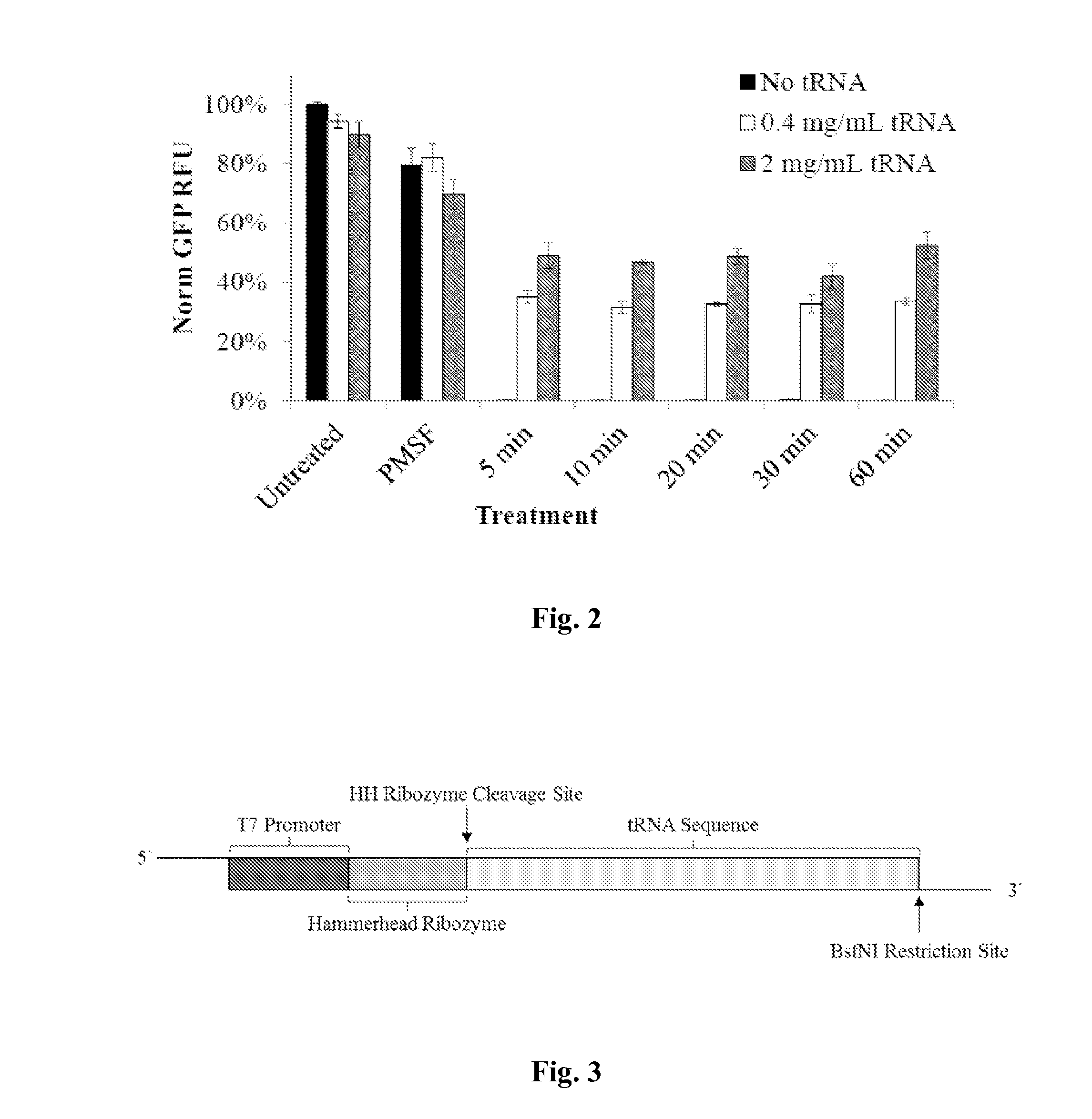
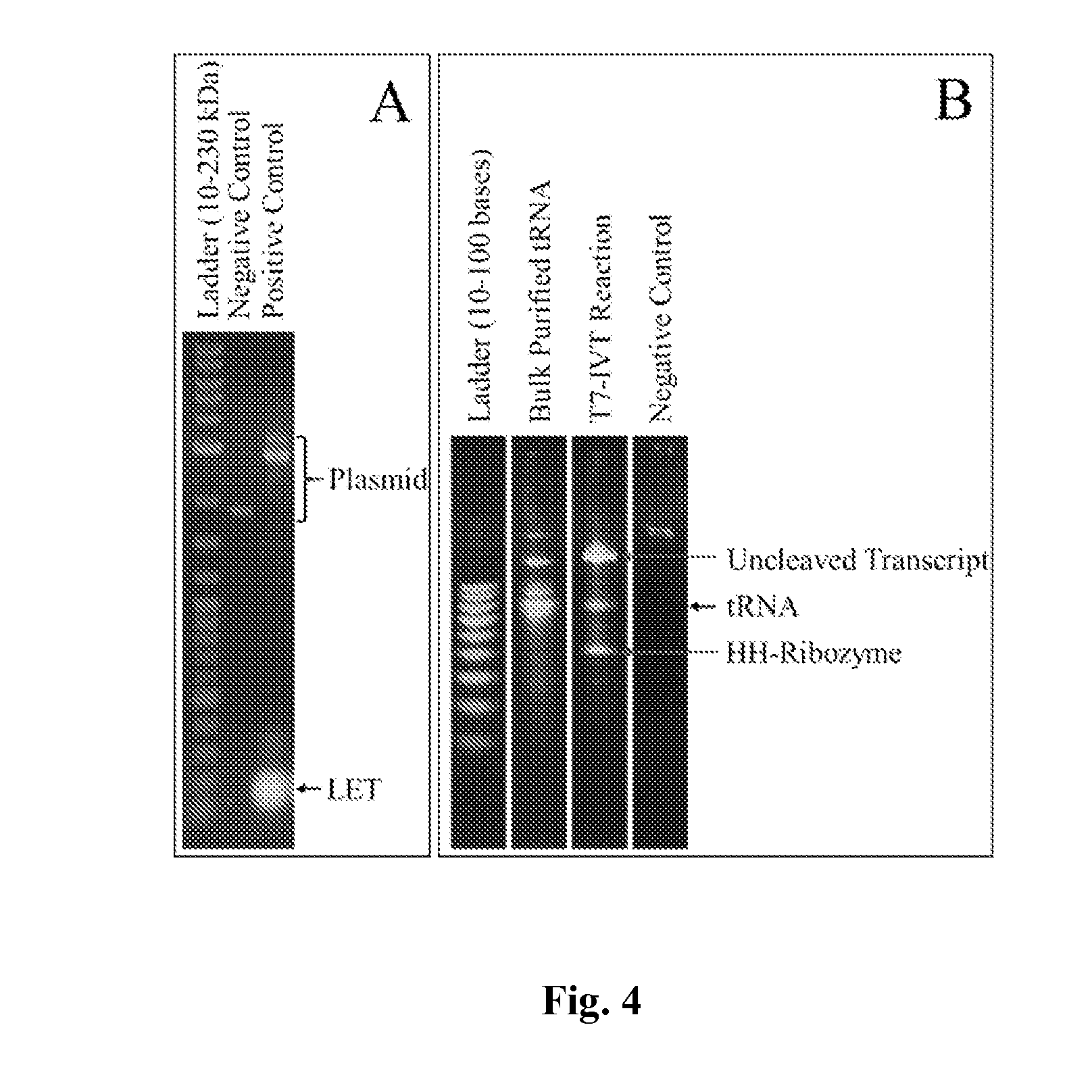
The present disclosure provides methods for incorporating at least one non-natural amino acid into a polypeptide using a cell-free protein synthesis which includes a cell-free extract and is deficient in endogenous tRNA. The methods include providing the synthesis system with at least one non-natural amino acid, at least one orthogonal tRNA and one orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase which aminoacylates the corresponding orthogonal tRNA with the non-natural amino acid. The methods may also include removing the endogenous tRNA in the cell-free protein synthesis system by treating the synthesis system with a ribonuclease to degrade the endogenous tRNA and providing the synthesis system with a minimal set of tRNAs for one or more natural amino acids and the corresponding amino-acyl tRNA synthetases, such that the lack of some tRNA will enable unique codons to encode for non-natural amino acid incorporation with no or a minimal amount of completion from the tRNA present.
Owner:BUNDY BRADLEY C +3
Lactic acid bacterium preparation and application thereof in treatment of gastric ulcer
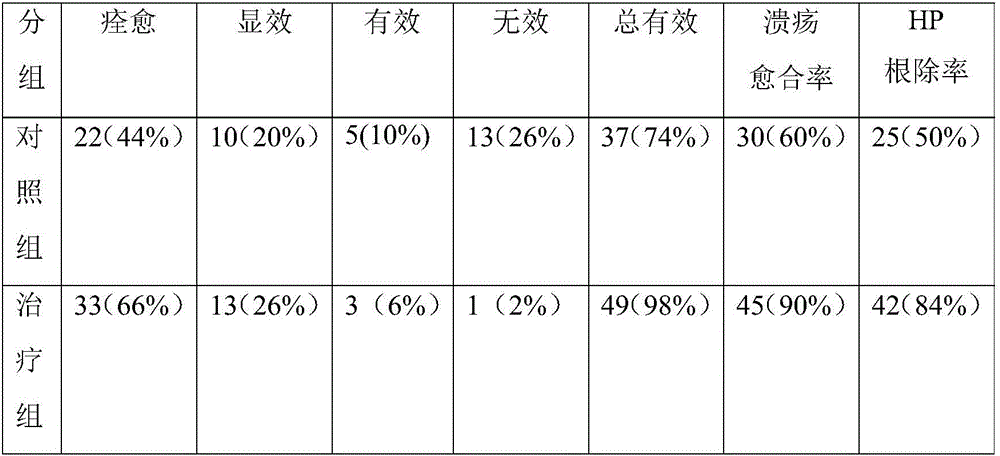
ActiveCN106381278AIncrease eradication rateImprove clearancePowder deliveryBacteriaEscherichia coliInhibition zone
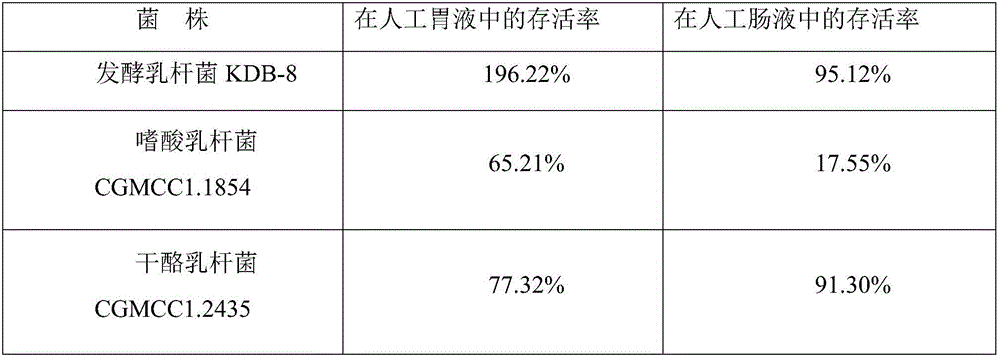
The invention relates to the technical field of microbiological screening and application and in particular provides a novel lactic acid bacterium preparation. The lactic acid bacterium preparation can be widely applied to treatment of gastric ulcer, the curative effect can be obviously improved, the cure rate of the ulcer is 90%, the eradication rate of helicobacter pylori is 84%, and the lactic acid bacterium preparation is high in tolerance to treatment and suitable for clinical application and popularization. The lactobacillus fermenti selected in the lactic acid bacterium preparation has obvious inhibitory effects on escherichia coli, salmonella and staphylococcus aureus, particularly has the strongest inhibitory effect on helicobacter pylori, and the diameter of an inhibition zone is 23mm. The lactobacillus fermenti has high tolerance to gastric acid and bile salt, and can realize effective multiplication in a gastric acid environment. The removal rate of lactobacillus fermenti KDB-8 on cholesterol is 93.2%; the survival rate of 98.5% can be maintained in 1.2mmol / L H2O2; and the scavenging rate of fermented supernatant fluid and cell-free extract on hydroxyl radicals is respectively 95.1% and 90.4%, and an undesirable technical effect is achieved.
Owner:JINAN KANGDUOBAO BIOTECH CO LTD +1
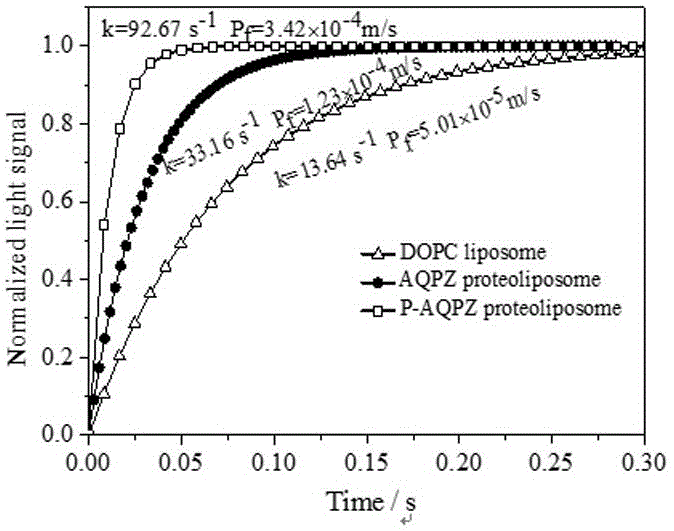
Method for compounding non-natural amino acids pPpa in escherichia coli aquaporin AQPZ
ActiveCN106084017AAvoid damageImprove soluble expression efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetCell free
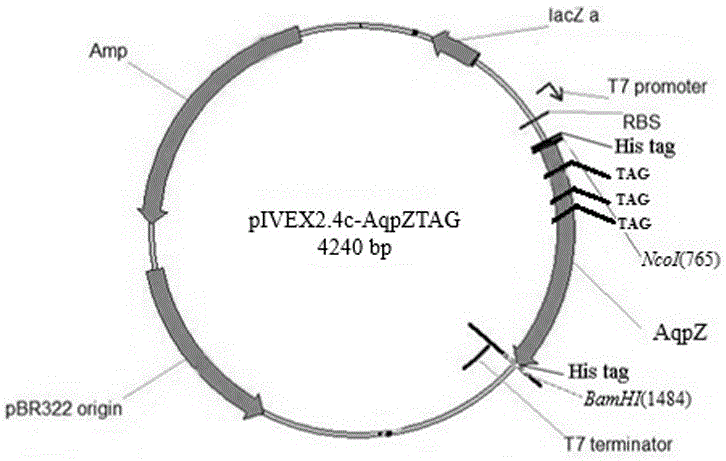
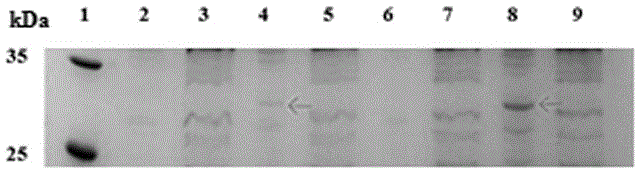
The invention provides a method for compounding non-natural amino acids pPpa in escherichia coli aquaporin AQPZ. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out site-directed mutation on tyrosine-tRNA synthetase of methanococcus jannaschii to obtain an MjpPpaRS gene; cloning the MjpPpaRS gene onto a pIVEX2.4c plasmid to obtain a recombinant plasmid pIVEX2.4c-MjpPpaRS; converting the recombinant plasmid pIVEX2.4c-MjpPpaRS and pUC-MjtRNA to escherichia coli BL21; selecting a positive transformant and fermenting to prepare escherichia coli cell-free extract; establishing a cell-free expression system; taking a pIVEX2.4c-AqpZ as a template and carrying out amber mutation on three sites including F10, F13 and F17 of the AQPZ; adding a decontaminating agent into the cell-free expression system to dissolve and express the AQPZ programmed into the pPpa; and carrying out affinity chromatography purification to obtain the AQPZ which is programmed into the pPpa at a fixed site. The AQPZ programmed into the pPpa is produced through utilizing the escherichia coli cell-free expression system, and the target protein is obtained through utilizing the affinity chromatography purification; and the non-natural amino acids are embedded, so that the affinity of the aquaporin and phospholipid is enhanced and the aquaporin is more stable after being embedded under the same condition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for biological catalyzed synthesis of optically active alkyl lactone
ActiveCN104651425AIncrease concentrationHigh optical purityMicroorganism based processesFermentationCapric Acid4-Butyrolactone
The invention relates to a method for biological catalyzed synthesis of optically active alkyl lactone. The method comprises the following steps: (1) catalyzing asymmetric reduction of a carbonyl acid to synthesize optically active hydroxy acid by using a biological catalyst; (2) in an acid environment, cyclizing the optically active hydroxy acid, thereby generating an optically active lactone compound. Freshly cultured candida parapsilosis cells or a cell-free extract is adopted as the biological catalyst for catalyzing stereoselective reduction of 4-carbonyl capric acid and 5-carbonyl capric acid, and subsequently the components are cyclized in the acid environment so as to obtain the lactone compound, so that (R)-(+)-4-hexyl-4-butyrolactone and (R)-(+)-5-amyl-5-valerolactone can be efficiently prepared. Compared with the prior art, the method is easy in preparing cells of the strain and extracts of the cells, high in stereoselectivity, simple in process for catalytic preparation of (R)-(+)-4-hexyl-4-butyrolactone and (R)-(+)-5-amyl-5-valerolactone, environment-friendly, and very good in industrial application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIFUAN ENZYME TECH +2
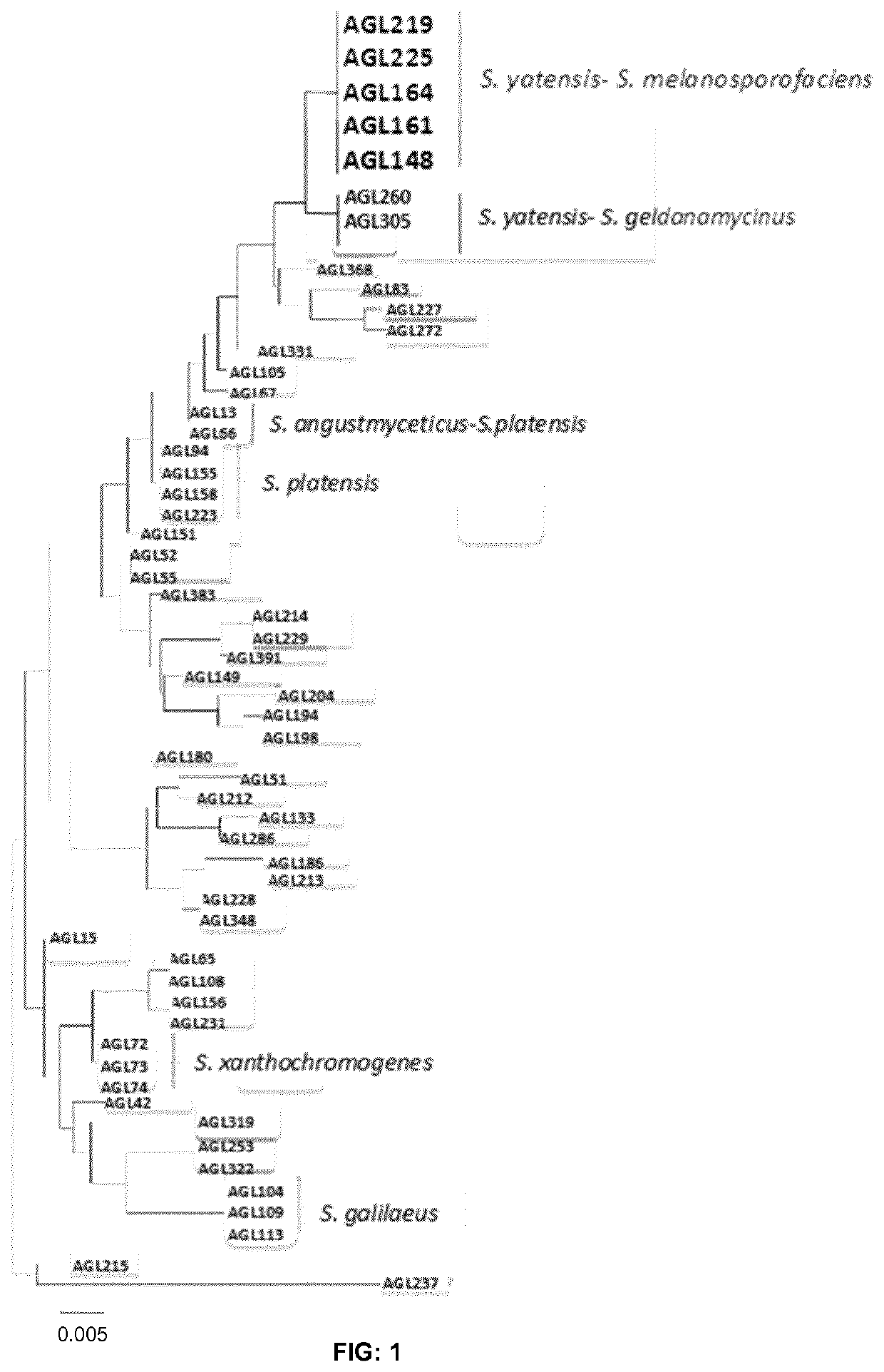
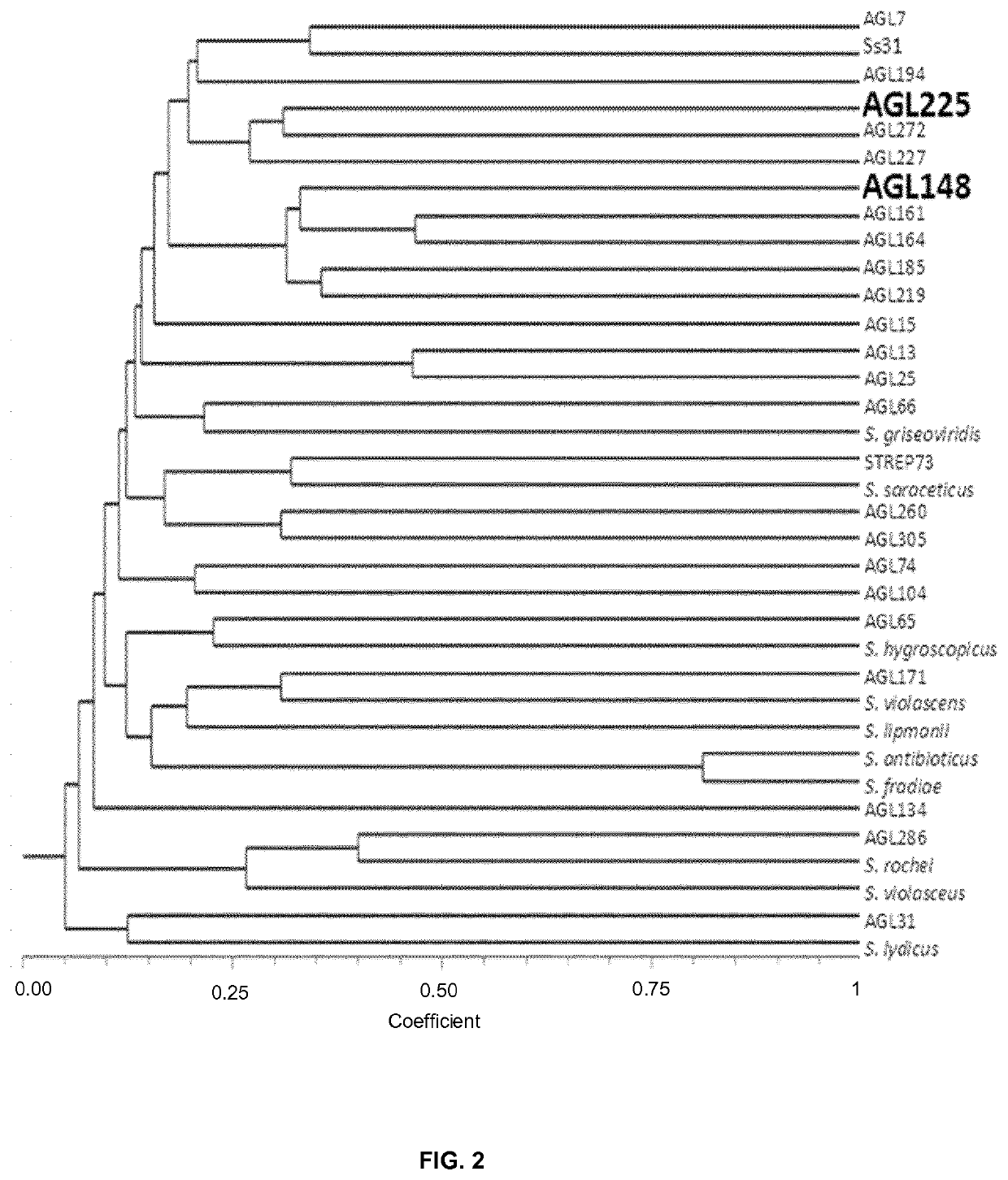
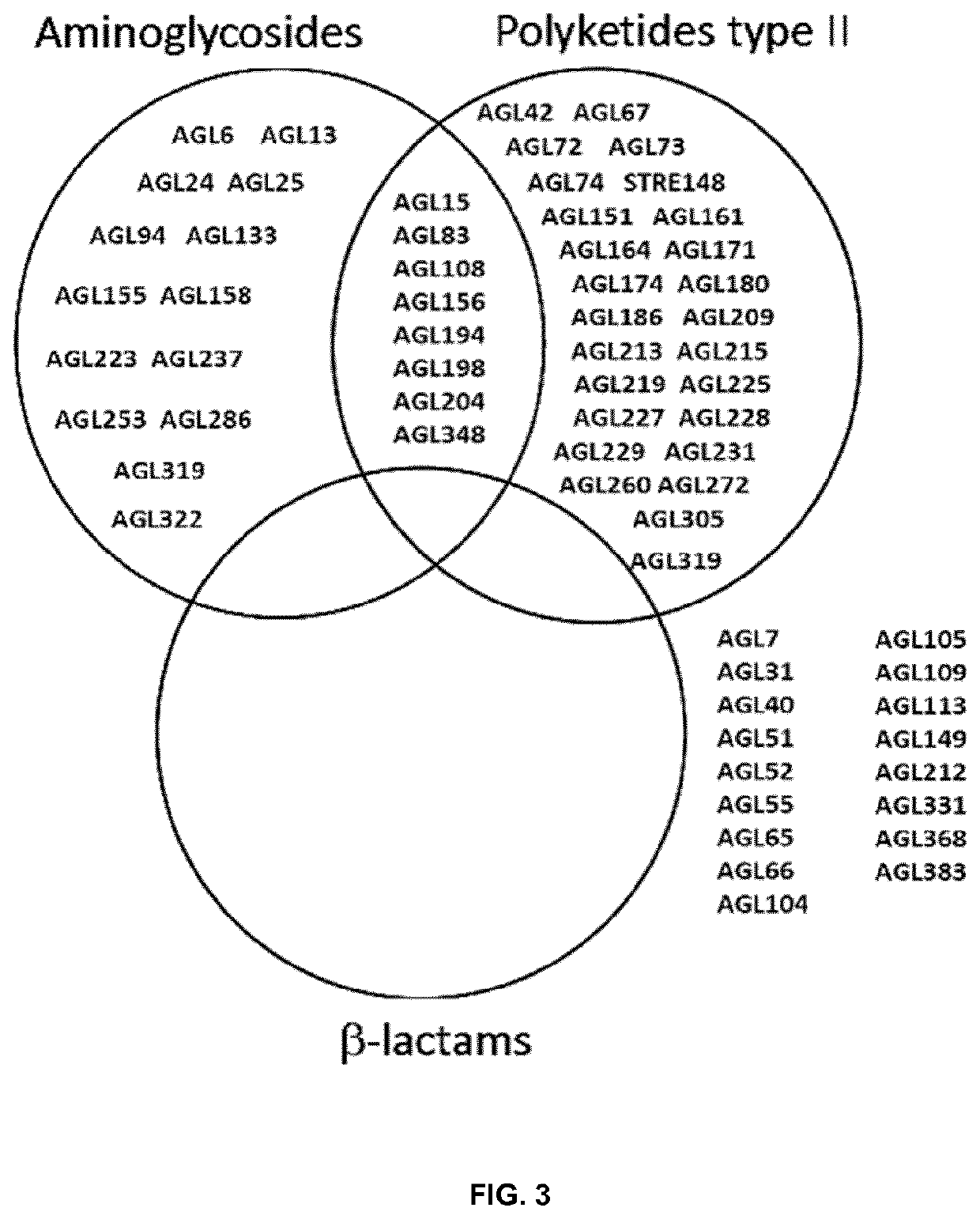
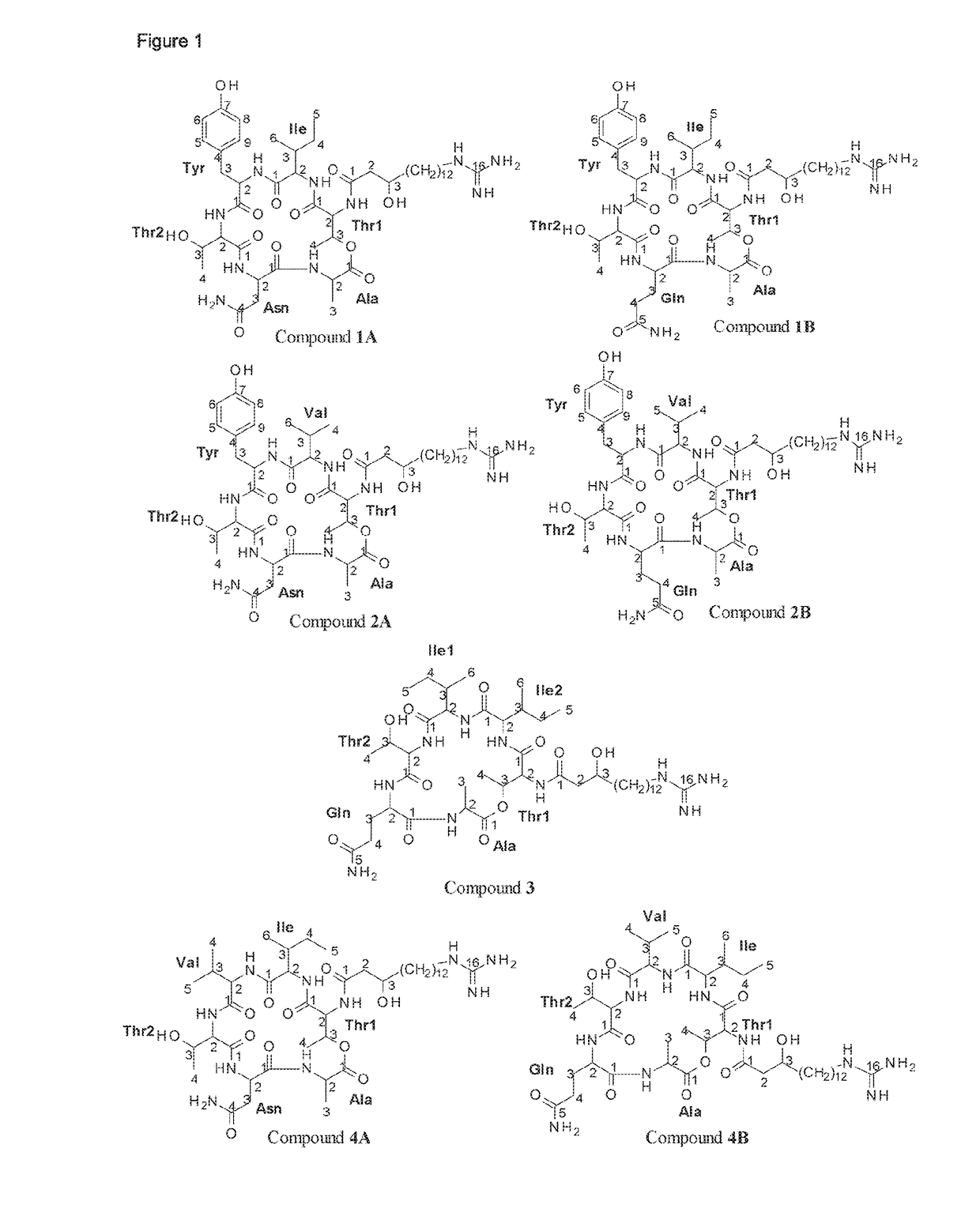
Use of compositions containing streptomyces melanosporofaciens agl225 in controlling plant diseases
The present invention refers to the strain Streptomyces melanosporofaciens AGL22 identified in the Spanish Type Culture Collection (CECT) as Streptomyces melanosporofaciens CECT9420, and the use of said strain as a pesticide in plants. Further aspects of the invention relate to suspensions and extracts of strain S. melanosporofaciens AGL225 and methods of preparing the same. Additional aspects relate to pesticidal compositions comprising S. melanosporofaciens AGL225. Finally the invention relates to a method for biological control of plant pests comprising administering to the plant strain S. melanosporofaciens AGL225, a composition including said strain or a cell-free extract derived from S. melanosporofaciens AGL225.
Owner:VICORQUIMIA SA
Antifungal paenibacillus strains, fusaricidin-type compounds, and their use
The present invention relates to novel isolated bacterial strains, which are members of the genus Paenibacillus, originally isolated from soil and showing antagonistic activity against a broad range of pathogens and being capable of producing antimicrobial metabolites. It was found that the strains Lu16774 and Lu17007 belong to a novel subspecies named Paenibacillus polymyxa ssp. plantarum while the strain Lu17015 belongs to a novel species which is proposed to be Paenibacillus epiphyticus. The present invention also relates to microbial pesticide compositions comprising at least one of such novel bacterial strains, whole culture broth or a cell-free extract or a fraction thereof or at least one metabolite thereof, and / or a mutant of at least one of said novel bacterial strains having all the identifying characteristics of the respective bacterial strain or whole culture broth, cell-free extract, fraction and / or metabolite of the mutant thereof showing antagonistic activity against plant pathogens. The present invention also relates to a method of controlling or suppressing plant pathogens or preventing plant pathogen infections by applying such composition. The present invention also relates to novel fusaricidin-type compounds which are metabolites produced by the strains of the present invention.
Owner:BASF AG
Cell-free synthesis of virus like particles
InactiveUS20090317861A1Improve assembly yieldHigh-yield synthesisFermentationBacteriophagesCell freeVirus-like particle
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
A strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use in the control of diseases caused by bacteria and fungi in plants
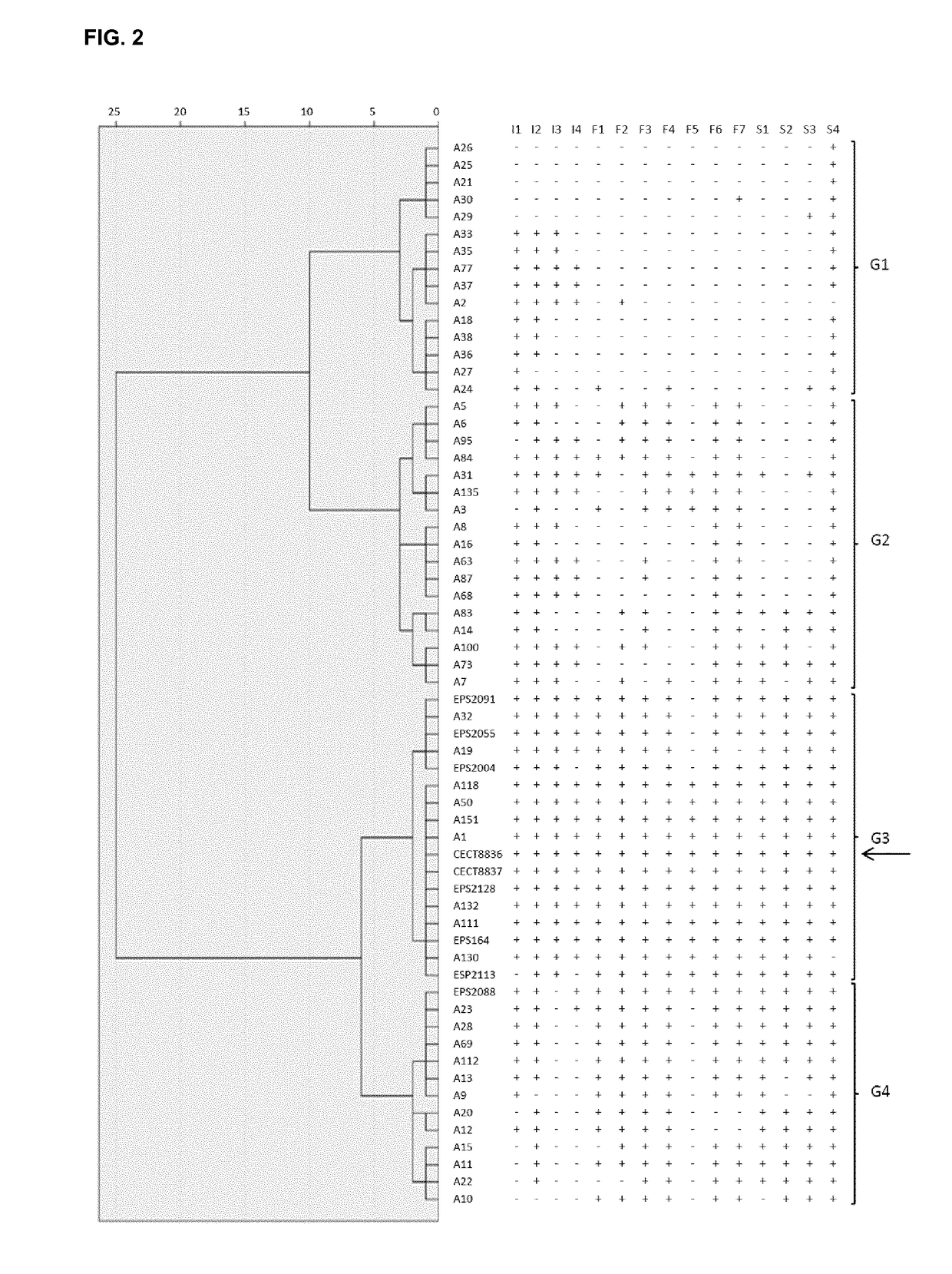
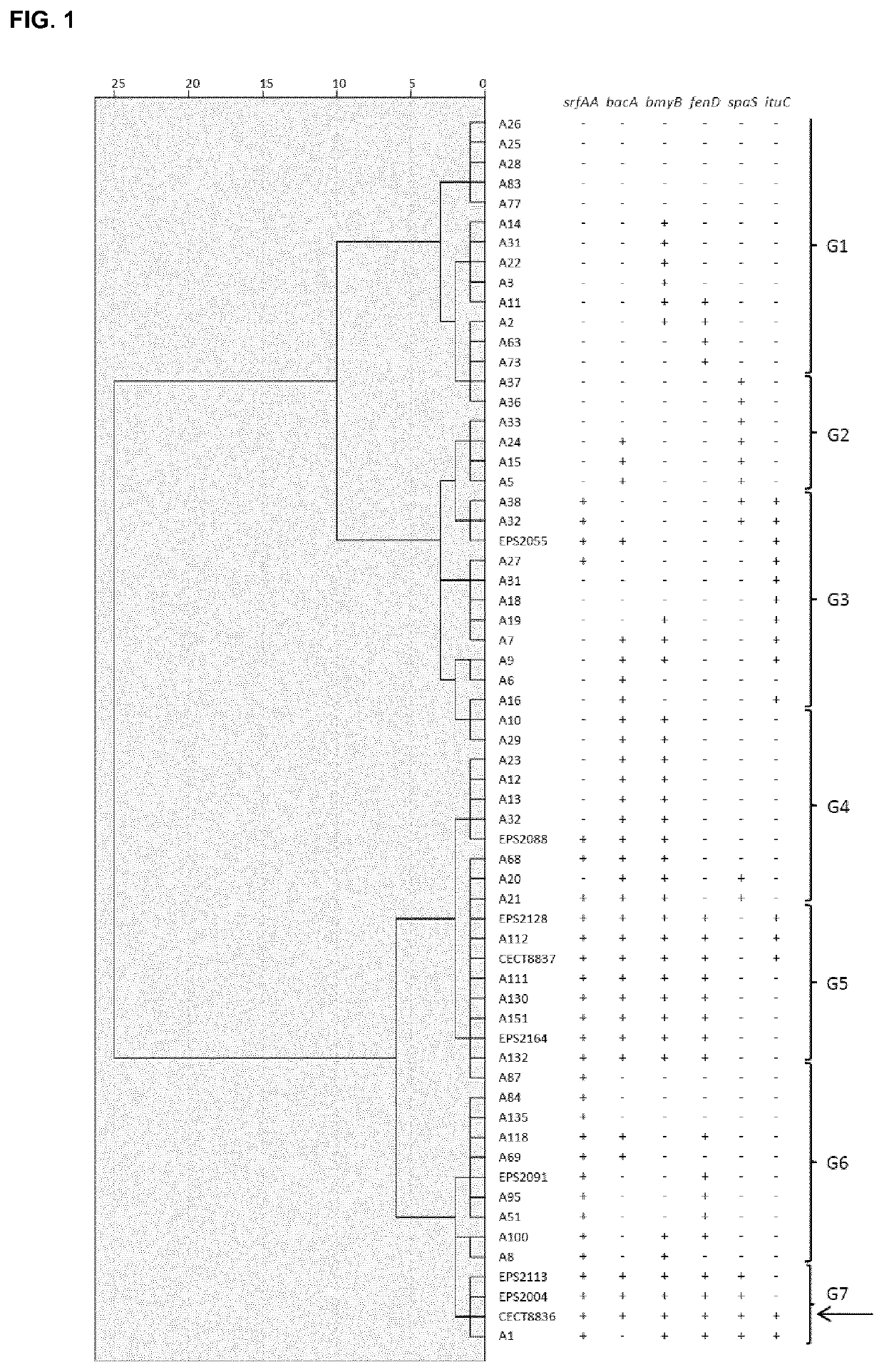
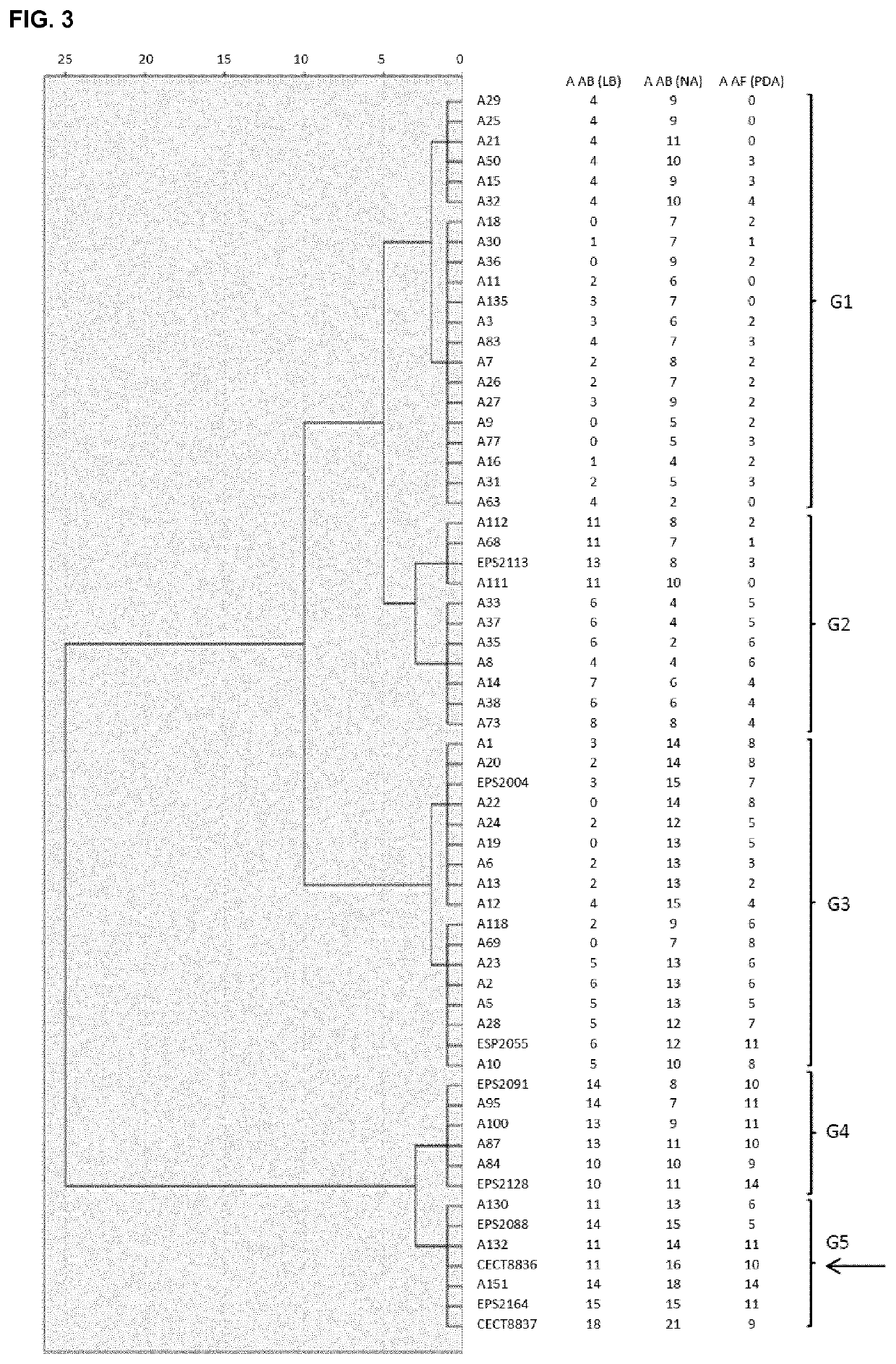
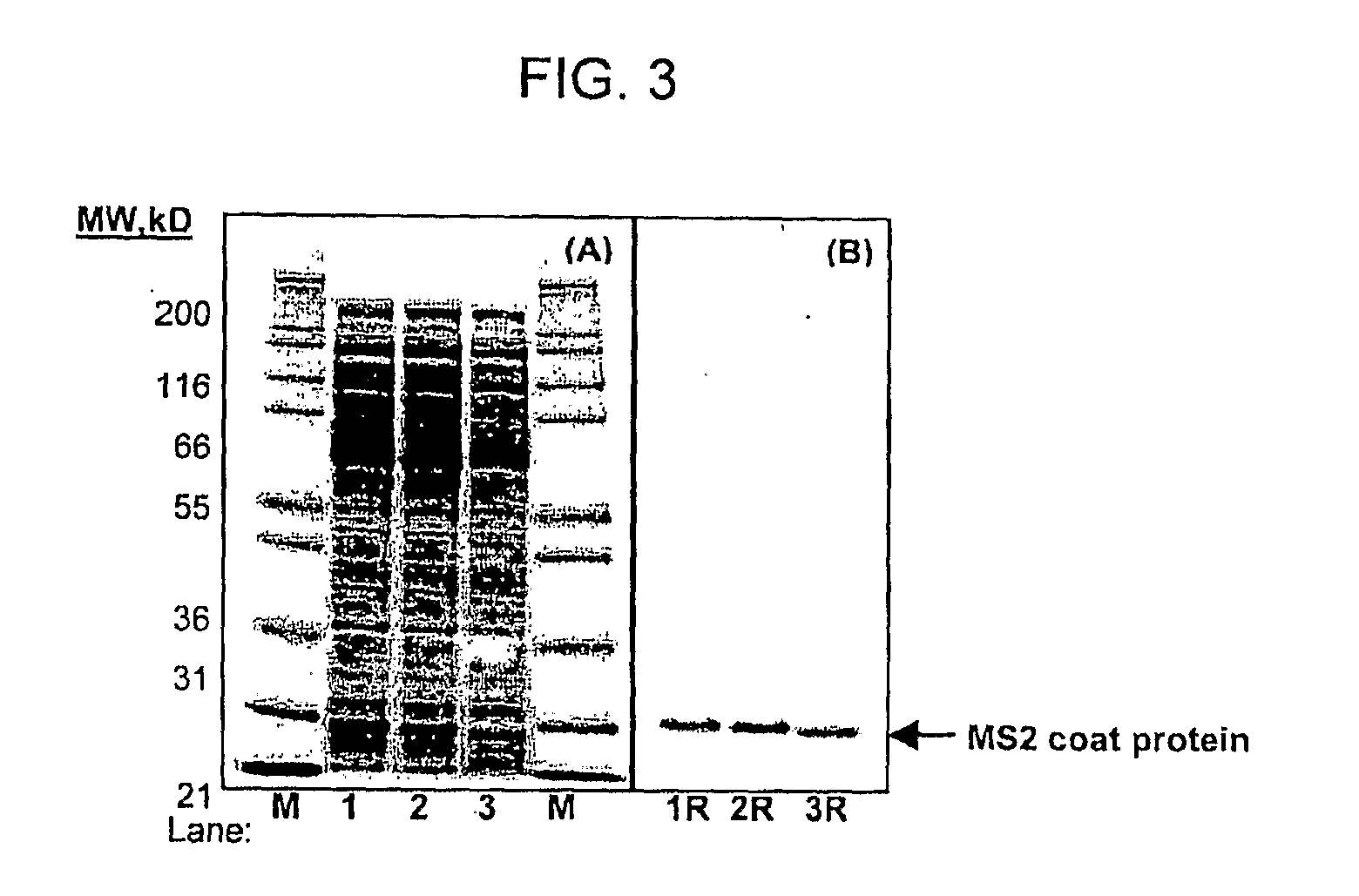
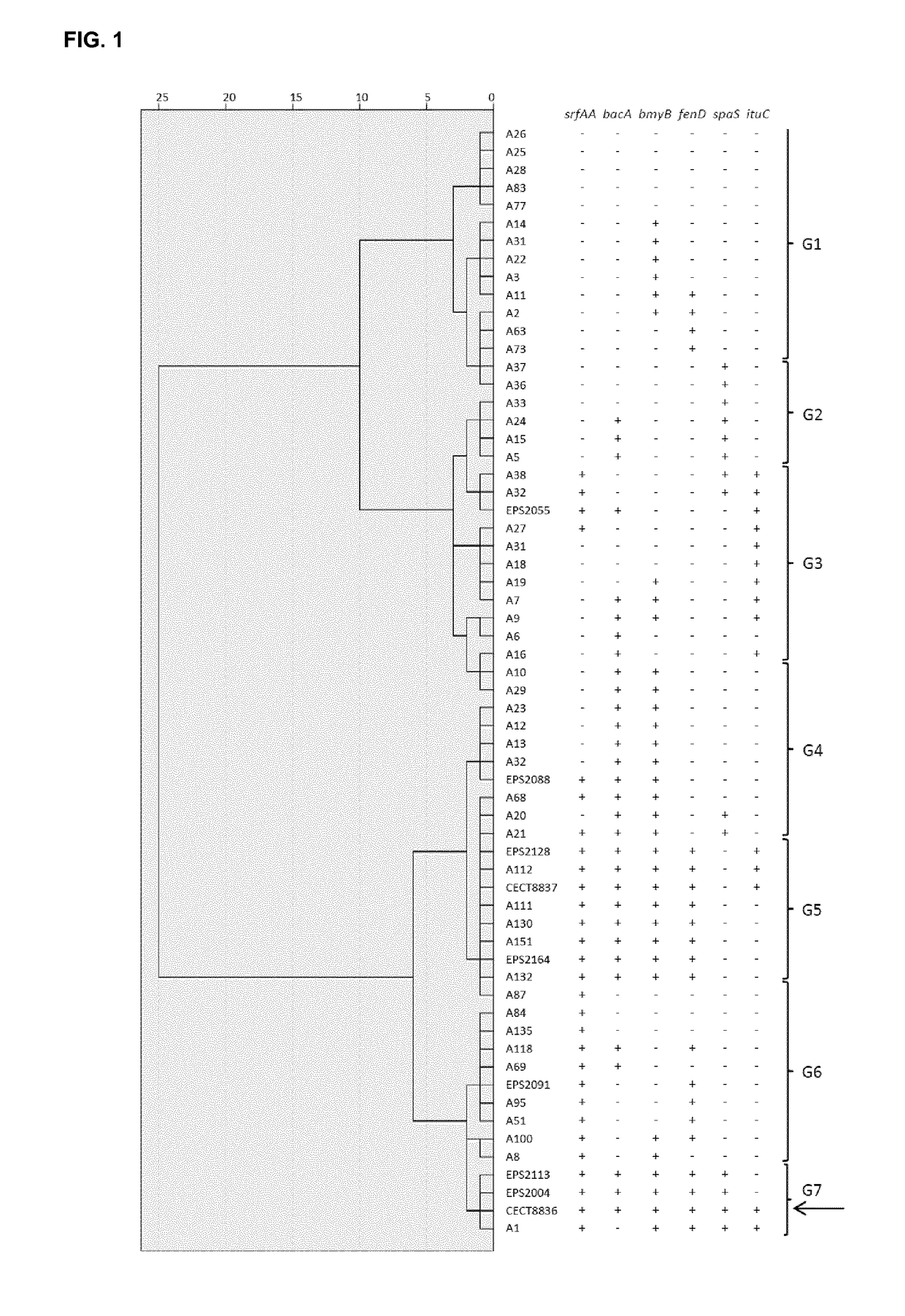
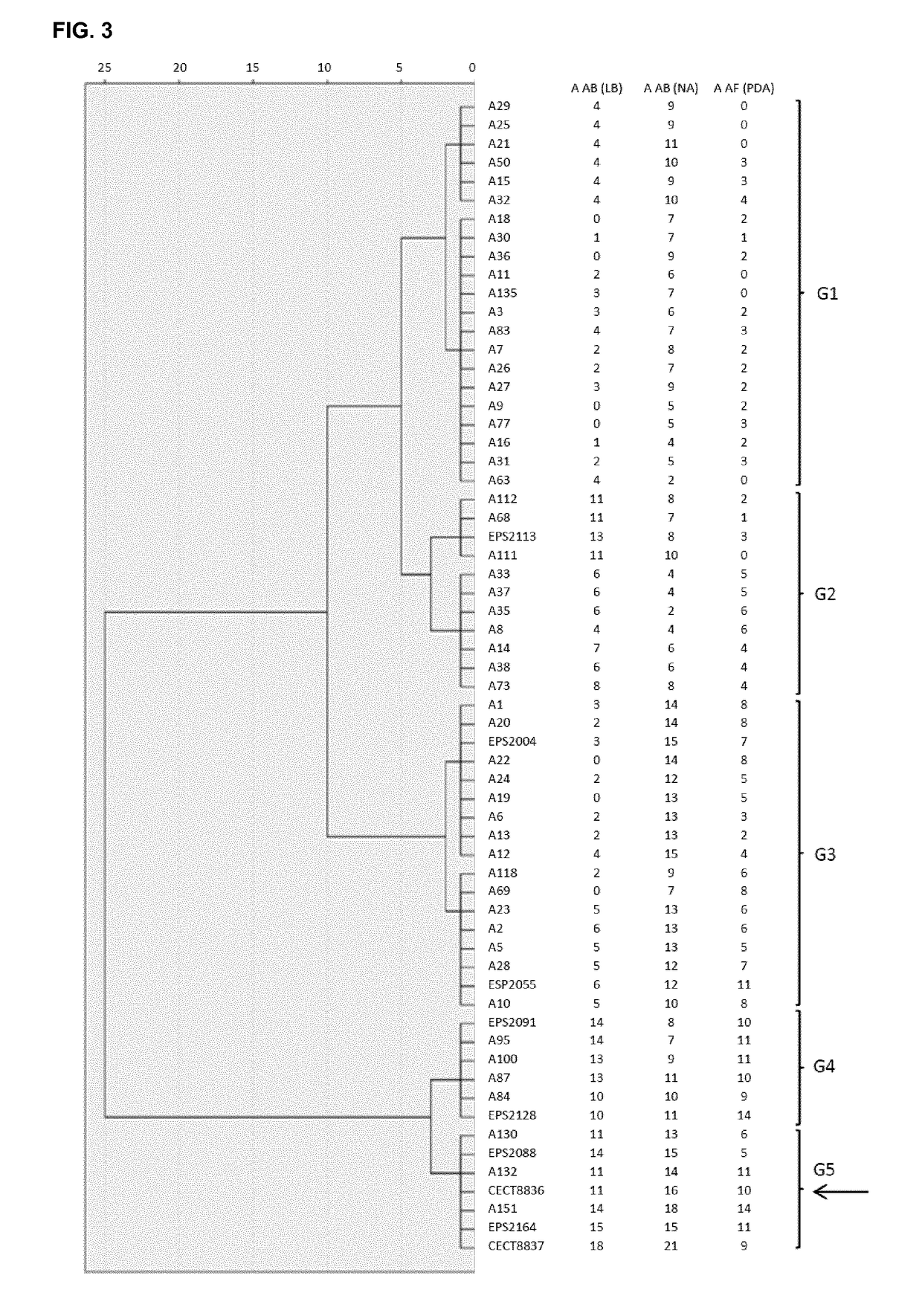
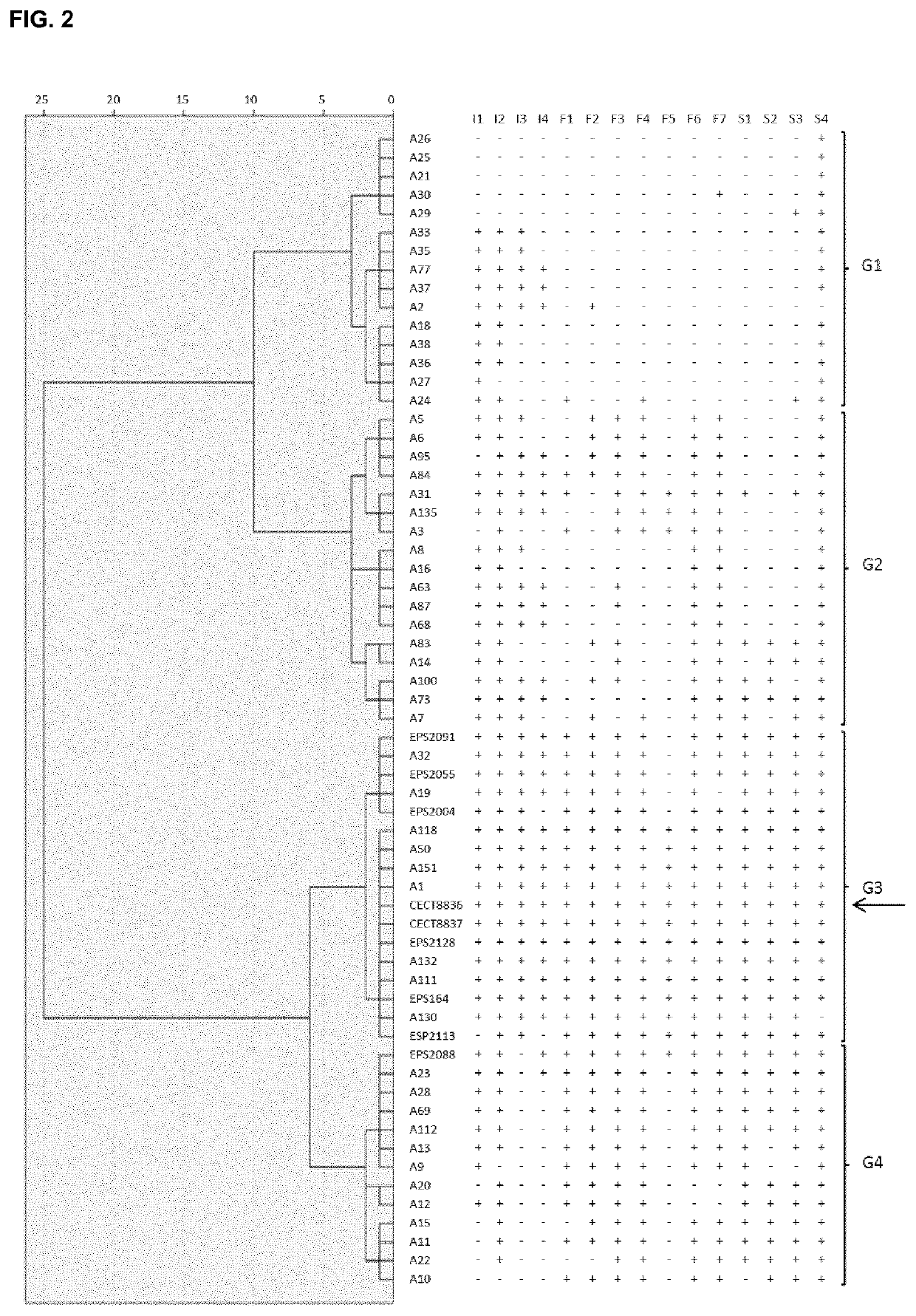
The present invention refers to the strain CECT8836 of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and mutants thereof, and the use of said strain as a pesticide in controlling plant diseases caused by fungi and bacteria. Further aspects of the invention relate to methods for preparing suspensions and extracts of the strain CECT8836 of B. amyloliquefaciens, pesticidal compositions comprising said strain and an extract of CECT8836 of B. amyloliquefaciens with antimicrobial activity. Finally the invention relates to a method for the biological control of various plant diseases caused by fungi and bacteria both in vegetable plants and in fruit trees, comprising treating these plants with the strain CECT8836 of B. amyloliquefaciens, a composition including it or a cell-free extract derived from CECT8836 of B. amyloliquefaciens.
Owner:IND QUIMICAS DEL VALLES SA
Strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use in the control of diseases caused by bacteria and fungi in plants
ActiveUS10548325B2Efficient infectionHigh antagonistic activityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyFruit tree
Owner:IND QUIMICAS DEL VALLES SA
Protein inhibitor of RAN activity and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070243169A1Inhibitory activityBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseProtein activityBiology
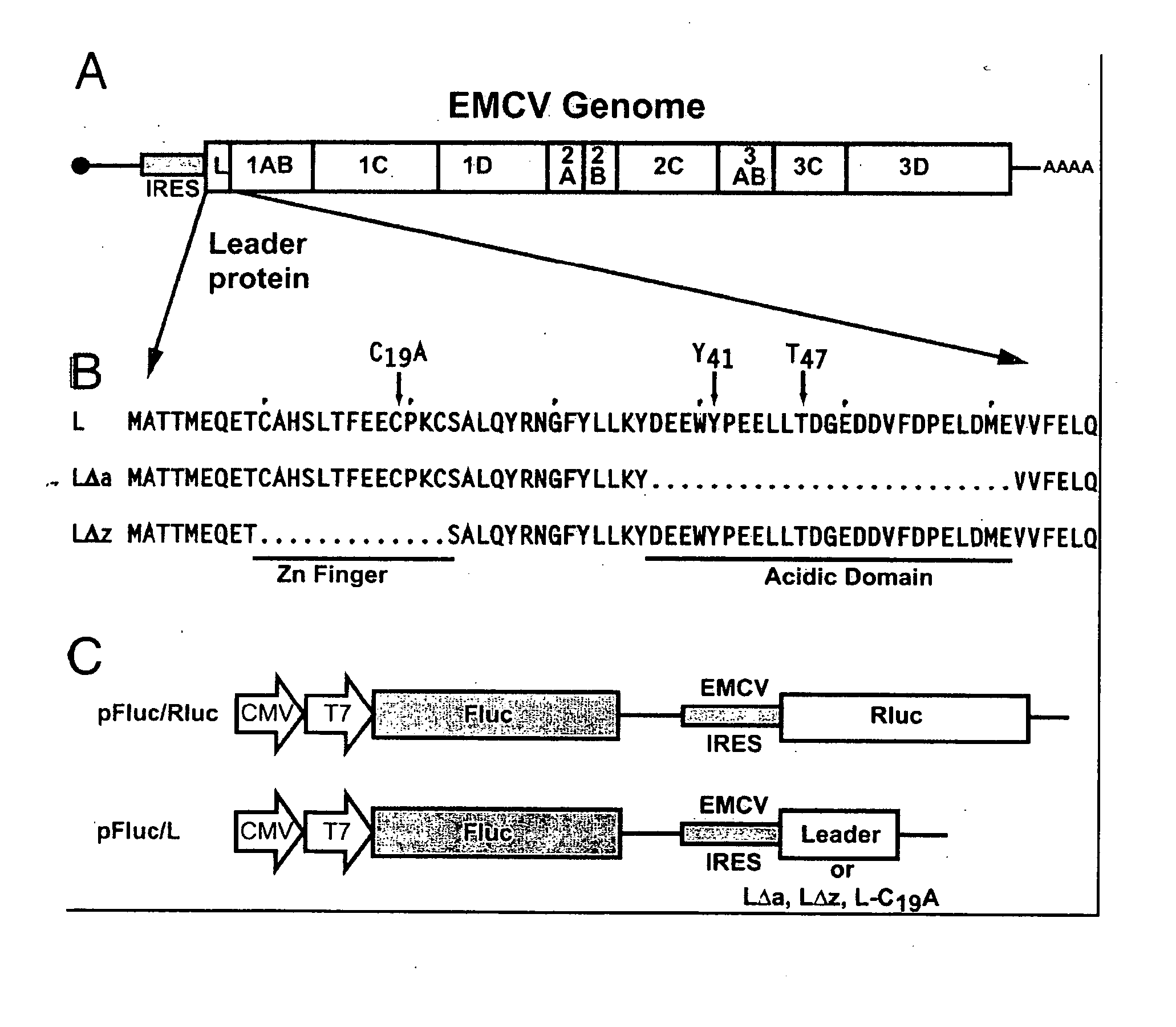
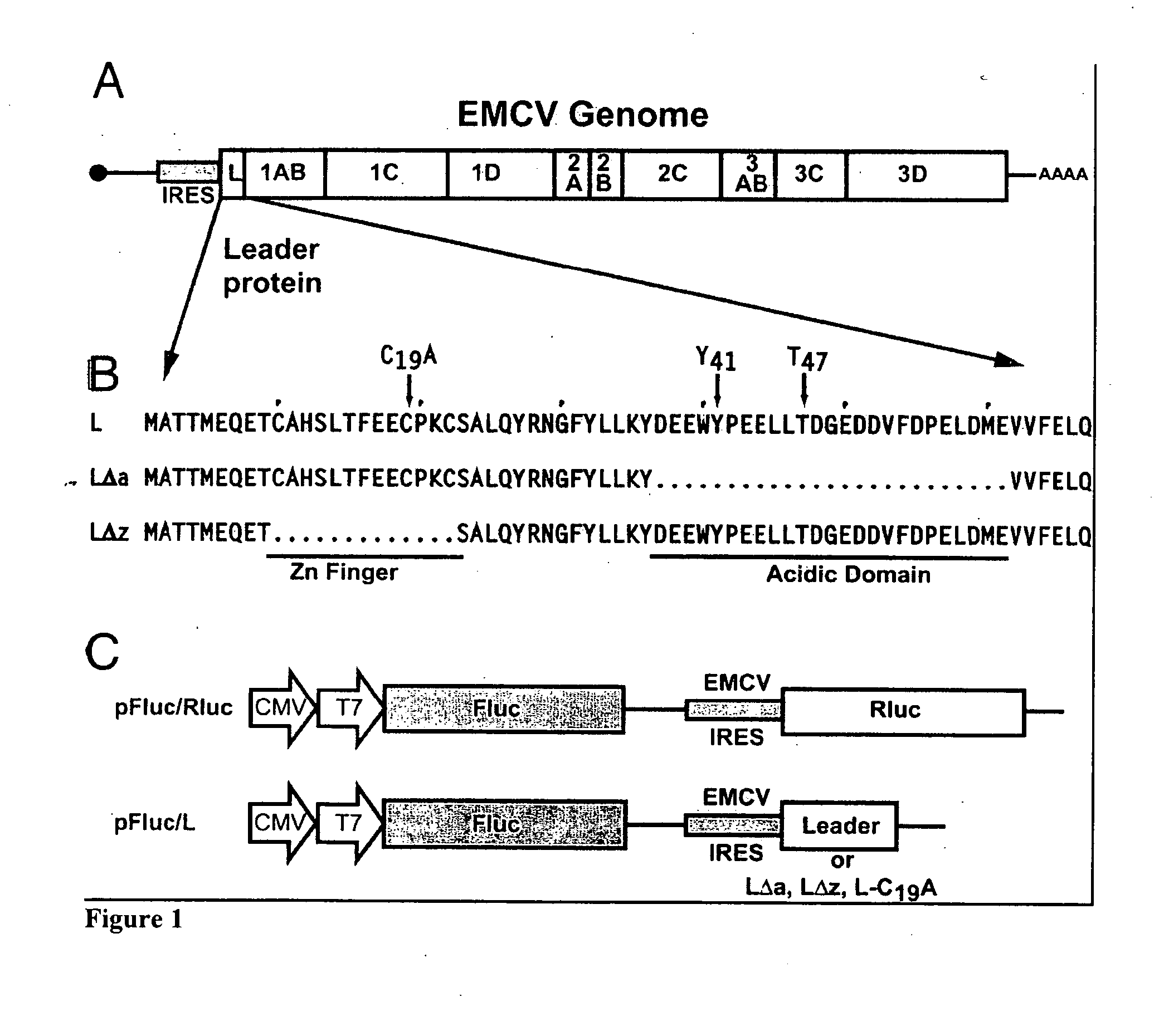
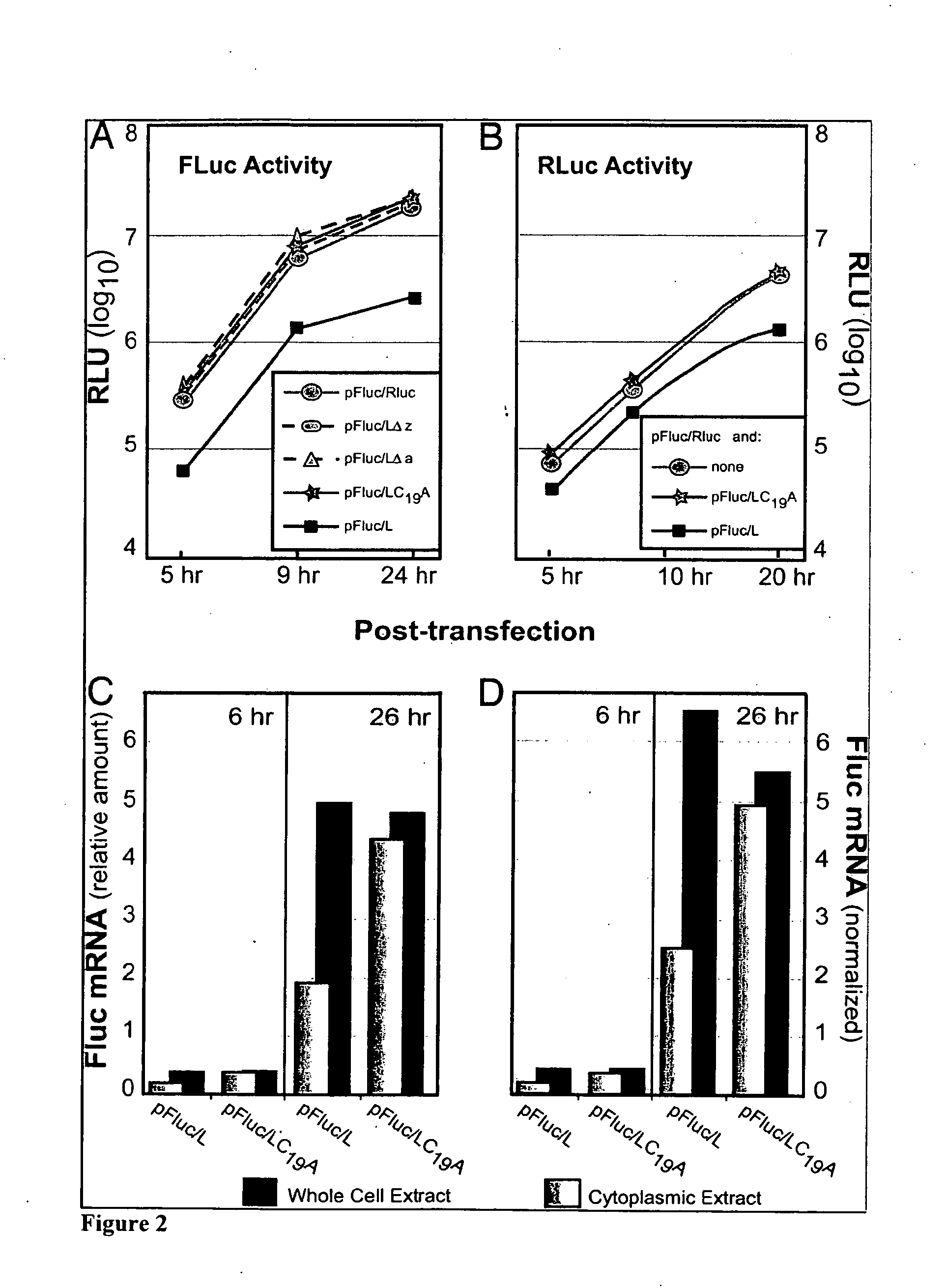
The invention provides a method of inhibiting Ran protein activity in at least one eukaryotic cell or cell-free extract, the method comprising exposing an amino acid sequence comprising at least a portion of EMCV or TMEV leader protein, wherein the amino acid sequence comprises SEQ. ID NO: 14 or SEQ. ID NO: 15, to at least one cell in an amount effective to inhibit Ran activity in the targeted cell and evaluating Ran protein activity in the cell.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Exogenous plasmid in-vitro methylation modification method used for converting different strains
InactiveCN105002162AEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBacillus licheniformisStrain specificity
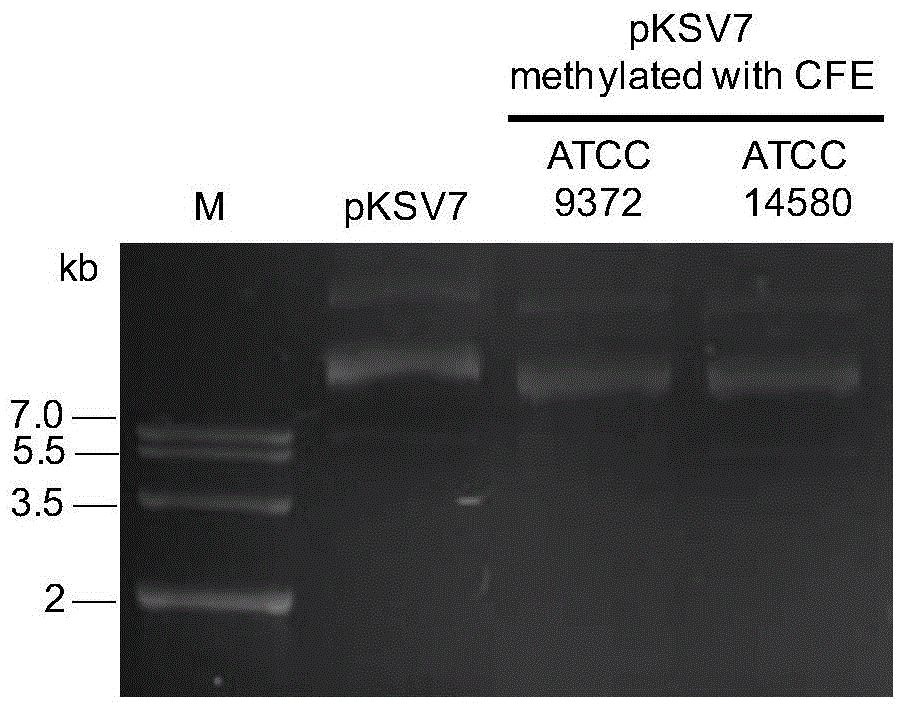
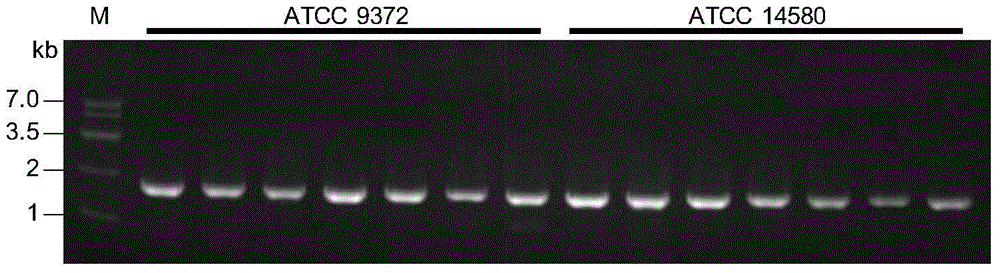
The invention discloses an exogenous plasmid in-vitro methylation modification method used for converting different strains. According to the method, cell-free extracts of bacillus subtilis or bacillus licheniformis are extracted, the cell-free extracts are used for performing in-vitro methylation modification on exogenous plasmid DNA, and therefore the plasmid DNA where methylation modification is performed can be obtained. The cell-free extracts of the bacillus subtilis or the bacillus licheniformis (the cell-free extracts include strain specificity methylase) perform in-vitro methylation modification on exogenous plasmids, and therefore the plasmid DNA where methylation modification is performed can be shifted into recipient bacteria with a restriction modification system, shear degradation caused by the recipient bacteria is avoided, and the exogenous plasmid in-vitro methylation modification method can be used for different strains and new bacteria where whole genome sequencing is not performed. The method is easy to operate.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com