Exogenous plasmid in-vitro methylation modification method used for converting different strains
An exogenous plasmid and methylation technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of inability to carry out, DNA sequence modification, restriction modification system deletion or mutation and other complicated operations, and achieve the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: the acquisition of bacterial strain cell extract;
[0026] The activated Bacillus subtilis ATCC9372 and Bacillus licheniformis ATCC14580 were respectively transferred to LB liquid medium, cultured to logarithmic growth phase at 30°C, 200r / min; centrifuged at 4°C, 5000r / min for 10 minutes to collect the bacteria, and used Wash twice with pre-cooled deionized water; resuspend the bacteria in TNM (100mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 50mM NaCl, 5mM MgCl) of 1 / 3 the volume of the original bacterial solution 2 ) buffer solution, use the ONE SHOT high-pressure cell disruptor to crush the sample under the condition of a pressure of 30kpsi; centrifuge at 5000r / min at 4°C for 10 minutes to remove cell debris, and collect the centrifuged supernatant, which is the cell extract (Cell free extracts, CFE), use immediately or aliquot and store at -70°C for later use.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: Analysis of bacterial strain restriction modification system;
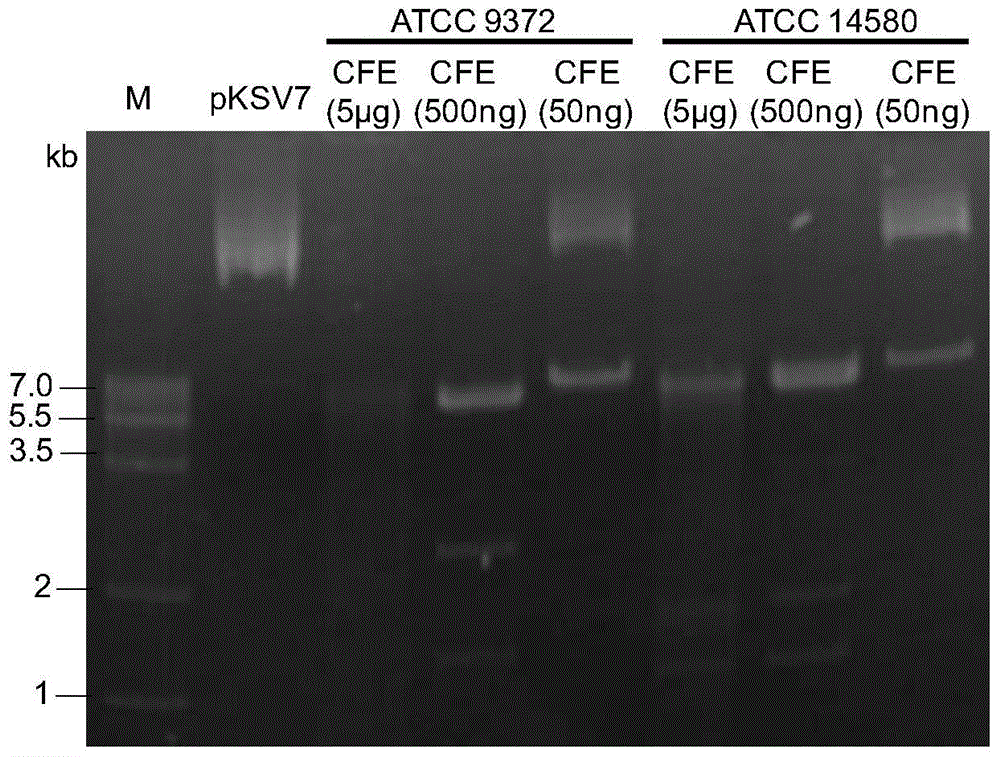
[0028] Dilute the obtained cell extracts of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 9372 and Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 14580, respectively, and perform restriction experiments according to the following system: cell extract (CFE) 10μL, plasmid DNA (pKSV7) 400-500ng, ddH 2 O up to 20 μL.
[0029] The above reaction system was well mixed and placed at 37°C for 2 hours, and then detected by gel running. Restriction analysis of plasmid pKSV7 by Bacillus subtilis ATCC9372 and Bacillus licheniformis ATCC14580 figure 1 As shown, the cell extracts of Bacillus subtilis ATCC9372 and Bacillus licheniformis ATCC14580 can degrade the exogenous plasmid pKSV7.
Embodiment 3
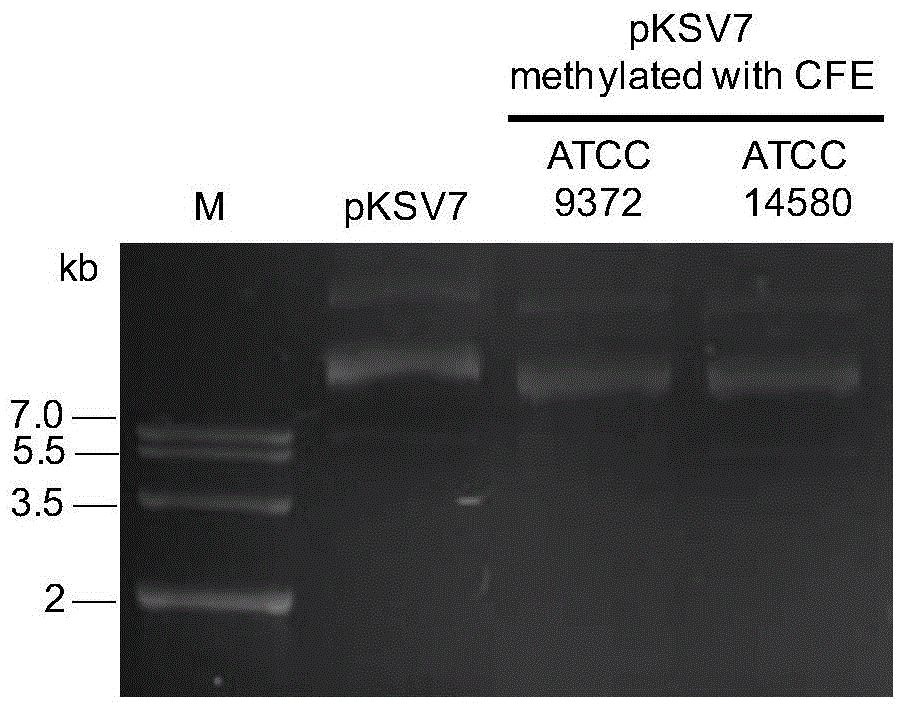
[0030] Example 3: In vitro methylation modification of exogenous plasmid DNA;
[0031] The obtained cell extracts of Bacillus subtilis ATCC9372 and Bacillus licheniformis ATCC14580 were respectively configured according to the following system for in vitro methylation modification of plasmid DNA:
[0032] Cell extract (CFE) 30μL
[0033] Plasmid pKSV712μg
[0034] EDTA (500mM, pH 8.0) 1μL
[0035] SAM (s-adenosylmethionine) (200 μM) 3 μL
[0036] DTT (dithiothreitol) (100mM) 1μL
[0037] wxya 2 O up to 100μL (SAM in the system provides methyl function)
[0038] The above reaction system was incubated at 37°C for 12 hours. During this period, SAM (200 μM) was added twice, 3 μL each time, and 1× volume of isopropanol was added, precipitated overnight at -20°C, centrifuged at 4°C for 20 minutes, and the supernatant was discarded. , add 1mL volume fraction of 70% ethanol aqueous solution to wash, dry in ultra-clean bench, redissolve in 20μL ddH 2 O, the methylation-modified...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com