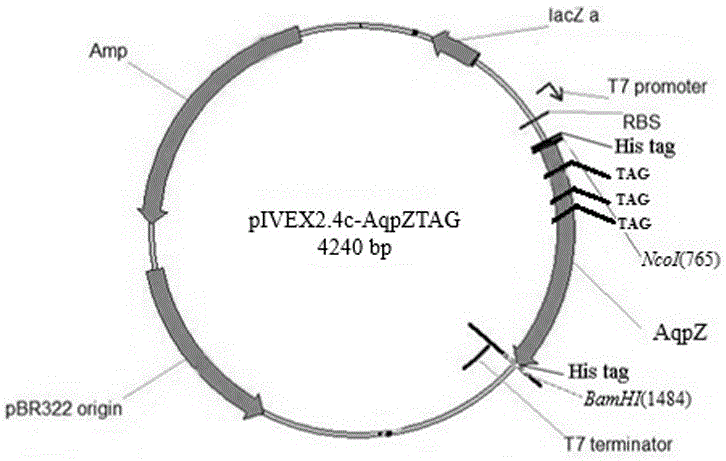
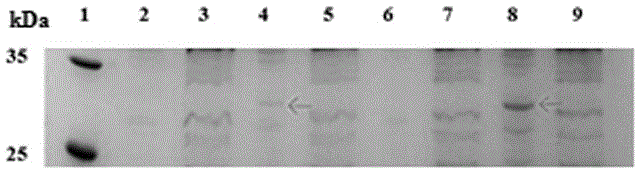
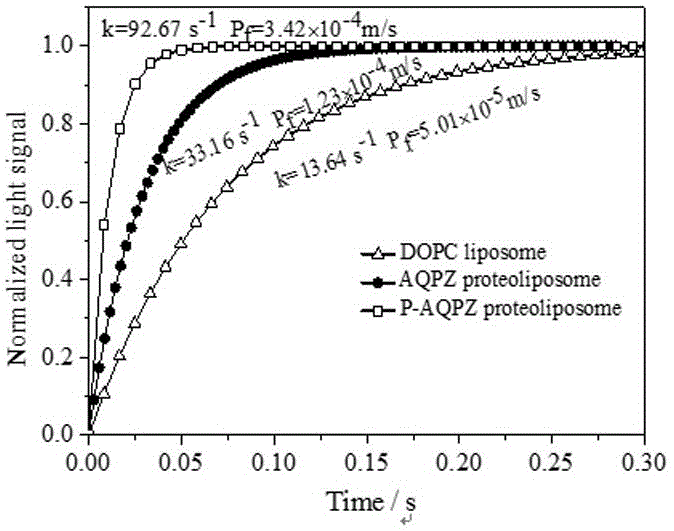
Method for compounding non-natural amino acids pPpa in escherichia coli aquaporin AQPZ
An unnatural amino acid, aquaporin technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, chemical instruments and methods, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems affecting performance and life, easy loss of protein, etc. Improve the efficiency of soluble expression and broaden the effect of thinking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of MjpPpaRS gene, comprises the following steps:
[0027] 1. Using p15a-MjtyrRS as a template, using two pairs of primers RS F2 / RS R4 and RS F4 / RS R2 to amplify two DNA fragments by PCR, and homologously recombining these two DNA fragments to obtain three site mutations (Tyr32Ala / Glu107Pro / Leu162Ala) aminoacyl tRNA synthetase plasmid. Using the above-mentioned mutant plasmid as a template, two pairs of primers, RS F1 / RS R3 and RS F3 / RS R1, were used for the second round of mutation to obtain M. tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (TyrRS), the mutated aminoacyl tRNA synthetase was named MjpPpaRS, and the p15a-MjpPpaRS plasmid was obtained. The gene sequences of the primers are shown in Table 1.
[0028] Table 1 Primers used for mutation
[0029]
[0030] 2. The PCR reaction conditions are: PCR conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 95°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 62°C for 30 seconds, extension at 70°C for 5 minutes, ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2, the preparation of Escherichia coli cell-free system extract, comprises the following steps:
[0032] 1. Simultaneously transform the recombinant vector p15a-MjpPpaRS and pUC-MjtRNA into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and select positive transformants;
[0033] 2. Pick a single colony of recombinant Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) / p15a-MjpPpaRS / pUC-MjtRNA from the plate and inoculate it in 5 mL of LB medium, and add ampicillin (Amp) with a final concentration of 50 μg / mL. Shake at 200 rpm at 37°C overnight.
[0034] 3. Transfer all the seed solutions cultivated in step 2 to two 500 mL bottles of cell-free fermentation medium, and add Amp with a final concentration of 50 μg / mL.
[0035] 4.37℃, 200rpm culture to bacterial concentration OD 600 When it reaches 0.8-1, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.5mM to induce until the bacterial concentration OD 600 When it reaches 3-4, the bacteria can be harvested.
[0036] 5. Pour the two bacterial solutions obtained...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3, the preparation of recombinant plasmid pIVEX2.4c-MjpPpaRS, comprises the following steps:
[0048] The cell-free expression vectors pIVEX2.4c and p15a-MjpPpaRS were digested with restriction endonucleases NcoI and BamHI at 37°C for 4 hours, respectively, and the digested products recovered from gel cutting were ligated overnight at 16°C and then transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells. Transformants were identified by NcoI and BamHI double enzyme digestion and sequencing, and the successfully constructed recombinant plasmid pIVEX2.4c-MjpPpaRS was obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com