Method for synergistically and efficiently preparing protein-based nano-emulsion by taking polyhydroxy alcohol as molecular chaperone and prepared protein-based nano-emulsion
A polyhydric alcohol and nanoemulsion technology, which is applied in the field of protein-based nanoemulsions, can solve the problems of easy denaturation, aggregation, emulsion stability decline, small kinetic particle size, etc., and achieve excellent protection or controlled release effects and emulsification efficiency High effect with low equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A method (experimental group) for synergistically and efficiently preparing protein-based nanoemulsions with polyhydric alcohols as molecular chaperones, comprising the steps of:
[0039] (1) Accurately weigh 1g of BSA powder (bovine serum albumin powder), disperse it in 99g of sucrose solution with a mass concentration of 40wt%, and stir continuously at room temperature for 2h to fully disperse the protein particles to obtain a protein dispersion, Adjust the pH to 7.0, add sodium azide to prevent microbial growth, the mass concentration of sodium azide in the protein dispersion is 0.02g / 100g, and place the obtained protein dispersion at 4°C for 12 hours to fully hydrate the protein , to obtain a BSA stock solution with a protein mass concentration of 1 g / 100 g.
[0040] (2) Before preparing the emulsion, stir the BSA stock solution (BSA dispersion) at room temperature for 0.5 h to return the temperature to room temperature and promote the uniform dispersion of the prot...
Embodiment 2
[0055] According to the method of the experimental group in Example 1, WPI-stabilized nanoemulsions were prepared, and the protein-removed samples were replaced with WPI powder (whey protein powder), and the homogenization times were replaced with 1 time and 6 times respectively, and other operations were the same as in Example 1. The control group in Example 2 is the protein-based nanoemulsion obtained by using the method of the experimental group in Example 2 only by using distilled water instead of 40 wt% sucrose.
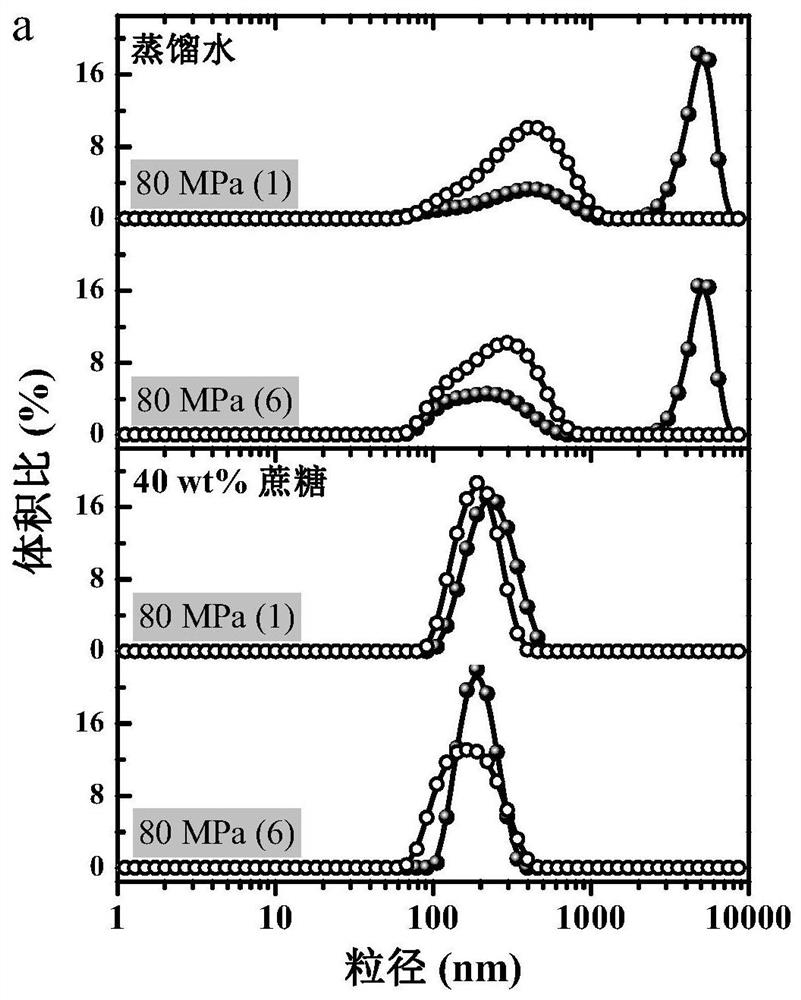
[0056] According to the scheme of this example, a stable protein-based nanoemulsion can still be efficiently prepared (Table 3). It is worth noting that due to the excellent foaming properties of WPI, small bubbles are inevitably formed during the homogenization process, and the particle size of the obtained fresh nanoemulsion is slightly larger than that of the nanoemulsion placed at room temperature for 10 hours. The contrast operation in the embodiment thus c...
Embodiment 3
[0058] According to the experimental group method of embodiment 1, prepare the stable nanoemulsion of SPI, remove protein sample and change to SPI powder (soybean protein isolate powder), homogenization number of times is changed to 1 time and 6 times respectively, other operations are the same as embodiment 1. The control group in Example 3 is a protein-based nanoemulsion obtained by using the method of the experimental group in Example 3, only using distilled water instead of 40 wt% sucrose.
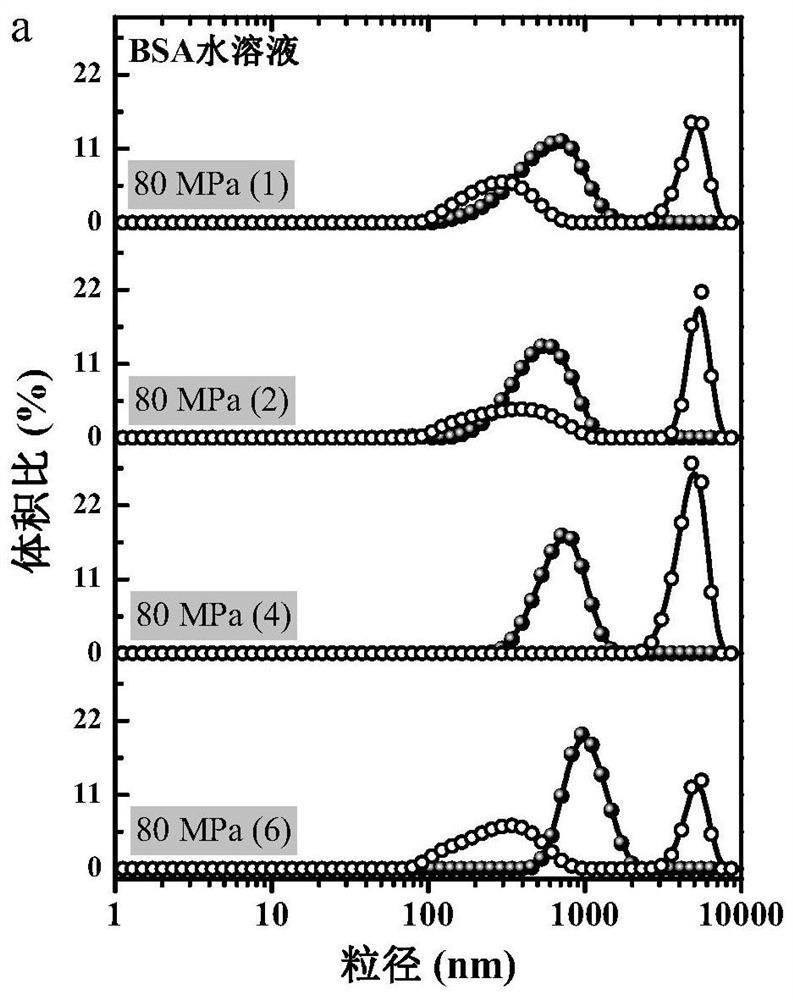
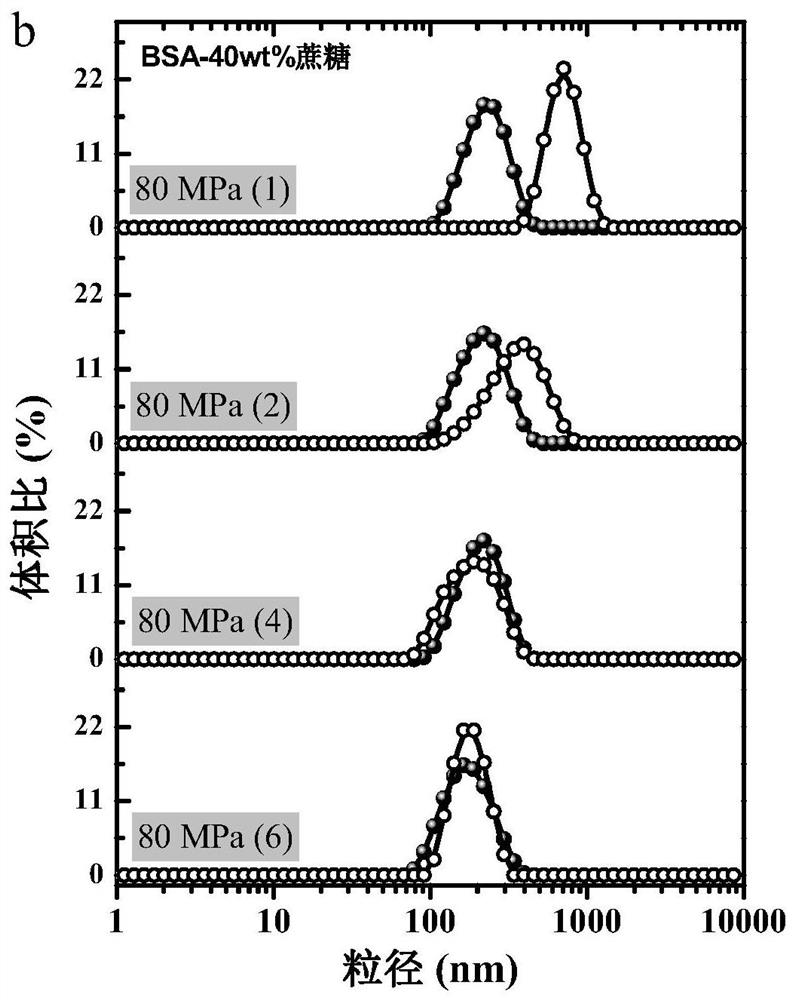
[0059] According to the scheme of this example, a stable protein-based nanoemulsion can still be efficiently produced (as shown in Table 3 below). Under the condition of high concentration of sucrose, the performance of the freshly prepared SPI-stabilized nanoemulsion is similar to that of the WPI-stabilized nanoemulsion (refer to Figure 2b shown), Figure 2b After being processed 1 time or 6 times by 80MPa microjet in embodiment 2, the particle size distribution figure of the emulsi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com