Method of making sucrose phosphorylase(SP) heat-stable
一种蔗糖磷酸化酶、耐热的技术,应用在生物化学设备和方法、植物学设备和方法、酶等方向,能够解决没有获得成功、底物特异性改变、耐热性的提高有限等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0591] (Example 1: Preparation, screening and sequencing of thermostable sucrose phosphorylase gene)
[0592] Briefly, random mutations were introduced into the sucrose phosphorylase gene derived from Streptococcus mutans, the randomly mutated gene was introduced into Escherichia coli, the randomly mutated sucrose phosphorylase was expressed, and selected from E. Escherichia coli expressing thermostable sucrose phosphorylase capable of synthesizing glucan after heating at 52.5°C for 15 minutes, the gene of thermostable sucrose phosphorylase was isolated from the Escherichia coli, and its sequence was determined.
[0593] Details as follow.
[0594] First, random mutations were introduced into the natural sucrose phosphorylase gene derived from Streptococcus mutans given in SEQ ID NO: 1 by an error-prone PCR method known to those skilled in the art to obtain a randomly mutated SP gene. Under this condition, a sucrose phosphorylase gene usually introduces 1 to 2 random mutation...
Embodiment 2A
[0601] (Example 2A: Preparation of heat-resistant sucrose phosphorylase and determination of heat resistance by site-directed mutagenesis)
[0602] (1) Preparation of thermostable sucrose phosphorylase by site-directed mutagenesis
[0603] Briefly, a library containing the combination of the above 8 mutations was prepared and screened to obtain sucrose phosphorylase with further improved thermotolerance.
[0604] In detail, an expression vector for thermostable sucrose phosphorylase was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1. In this example, a gene encoding a thermostable sucrose phosphorylase substituted at only one position that has been found to contribute to the improvement of thermosistence was prepared, and a gene encoding thermostable sucrose phosphorylase substituted at a combination of 2 to 7 positions was prepared. The gene of the sucrose phosphorylase, and the gene encoding the heat-stable sucrose phosphorylase with all the 8 positions replaced. By way of ex...
Embodiment 2B
[0626] (Example 2B: Preparation of thermostable sucrose phosphorylase with various amino acid residue substitutions and thermostable assay)
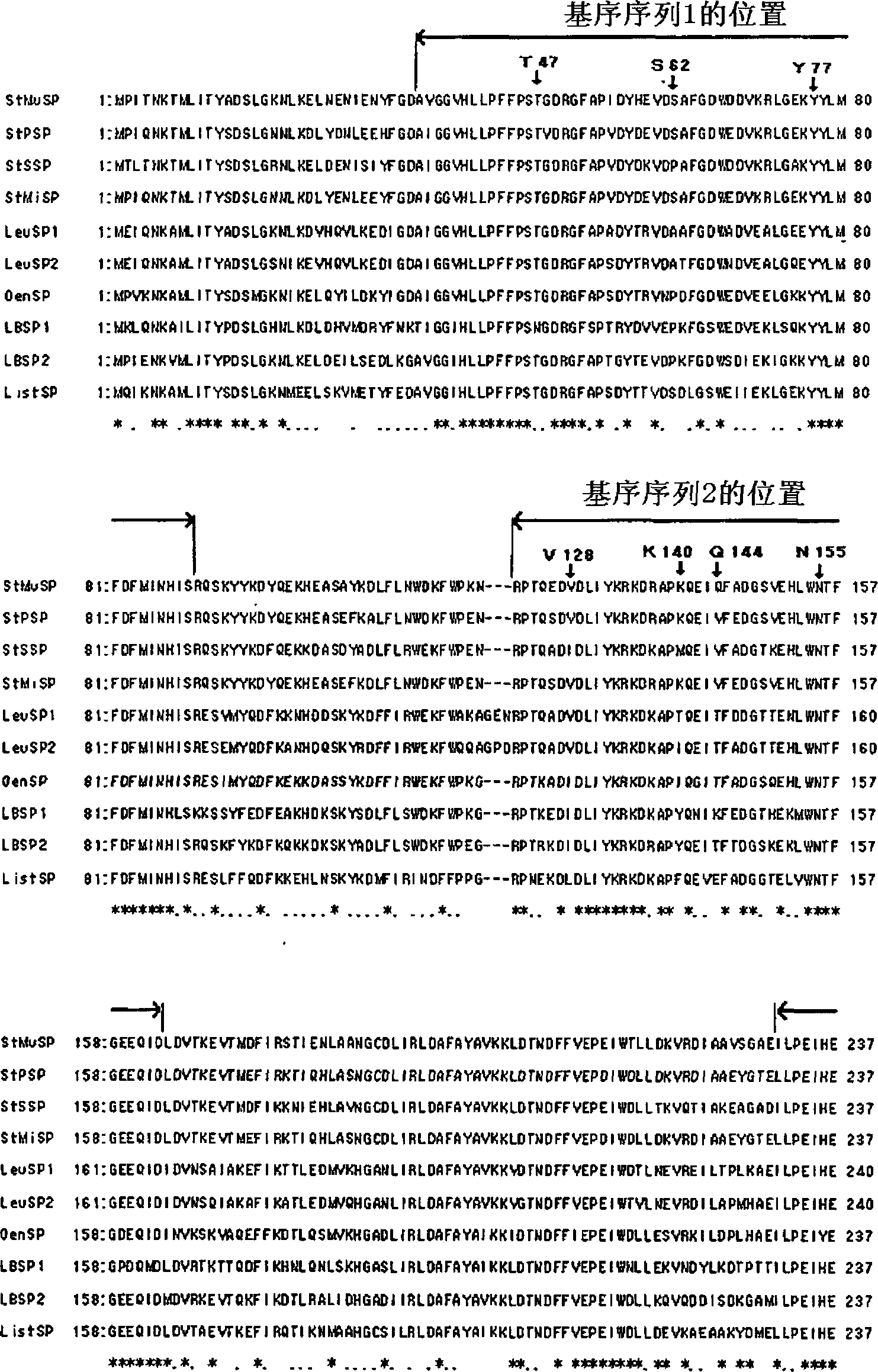
[0627] A plasmid containing the modified sucrose phosphorylase gene was prepared in the same manner as in Example 2A, except that the primers used were designed to replace one amino acid in T47, S62, Y77, V128, K140, Q144, N155 and D249 with another amino acid, and each obtained A solution of a modified SP enzyme.
[0628] The heat resistance of these modified SP enzymes was determined by measuring the remaining activity of these modified SP enzymes after heating in the same manner as in Example 2A(2)(i), except that the heating condition was 55° C. for 20 minutes. The results are shown in Table 4B below.
[0629] enzyme solution
(%)
T47S
47.3
T47I
50.0
S62P
33.4
S62A
31.0
S62K
26.3
Y77H
22.6
Y77R
34.8
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com