Lactic acid production process with fermentation and expanded bed for in-situ adsorption coupling
A technology of expanding bed and lactic acid, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low separation efficiency, bed clogging, etc., achieve high separation efficiency, improve yield and conversion rate, and relieve feedback inhibition.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
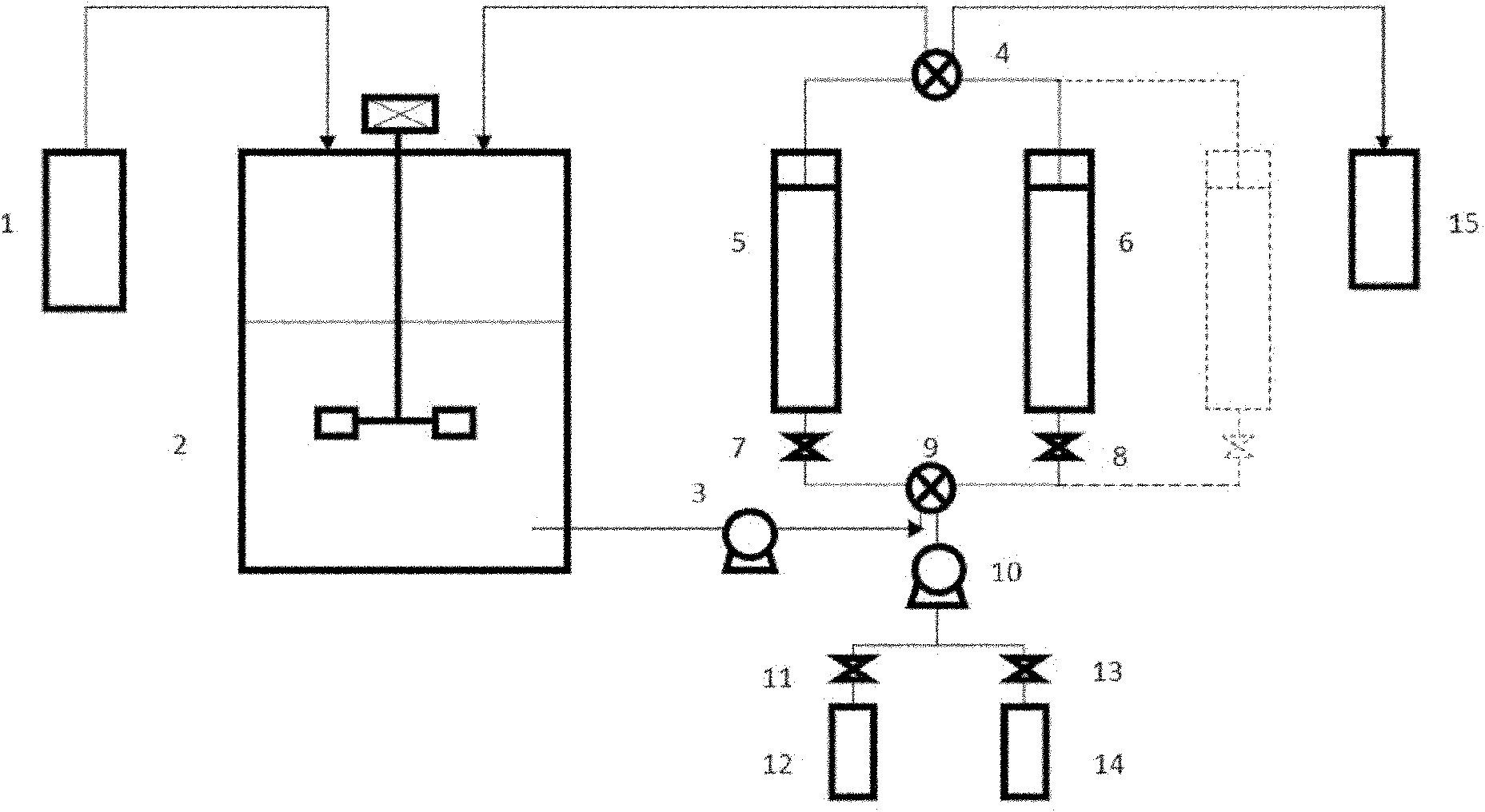
[0042] The device of the present invention includes: a high-level feeding tank, a fermentation tank, a transmission pump, a four-way valve, an expanded bed chromatography column, an eluent storage tank, a regeneration liquid storage tank, a stop valve, and a lactic acid storage tank. as attached figure 1 shown.
[0043] The device can have two or more expanded bed chromatography columns as required, the top of which is connected to the lactic acid storage tank and the circulating fluid inlet of the fermentation tank through a four-way valve; the bottom is connected to the eluent storage tank, The regeneration liquid storage tank is connected to the outlet of the circulating liquid of the fermenter;
[0044] The fermenter is equipped with a stirring device, a feeding tank and an electrode, and the bottom is respectively provided with an inlet, an air inlet and a material outlet for the fermentation circulation liquid.
[0045] The present invention is a process of utilizing e...
Embodiment 2
[0051] see figure 1 . The lactic acid production device coupled with fermentation and expanded bed in-situ adsorption of the present invention includes a fermentation tank, two parallel expanded bed chromatography columns, two transfer pumps, 4 shut-off valves, 2 four-way valves, and a high-level feeding tank , eluent storage tank, regeneration solution storage tank and lactic acid storage tank.
[0052] The fermenter 2 is connected to the No. 1 expanded bed chromatography column 5 and the No. 2 expanded bed chromatography column 6 through pipelines, and the bottom openings of the No. 1 expanded bed chromatography column 5 and the No. 2 expanded bed chromatography column 6 are respectively connected with cut-off Valves 7 and 8 are connected to the bottom outlet of fermenter 2 and eluent storage tank 12 and regeneration liquid storage tank 14 through No. 2 four-way valve 9; No. 1 expanded bed chromatography column 5 and No. 2 expanded bed The top opening of the chromatography...
Embodiment 3
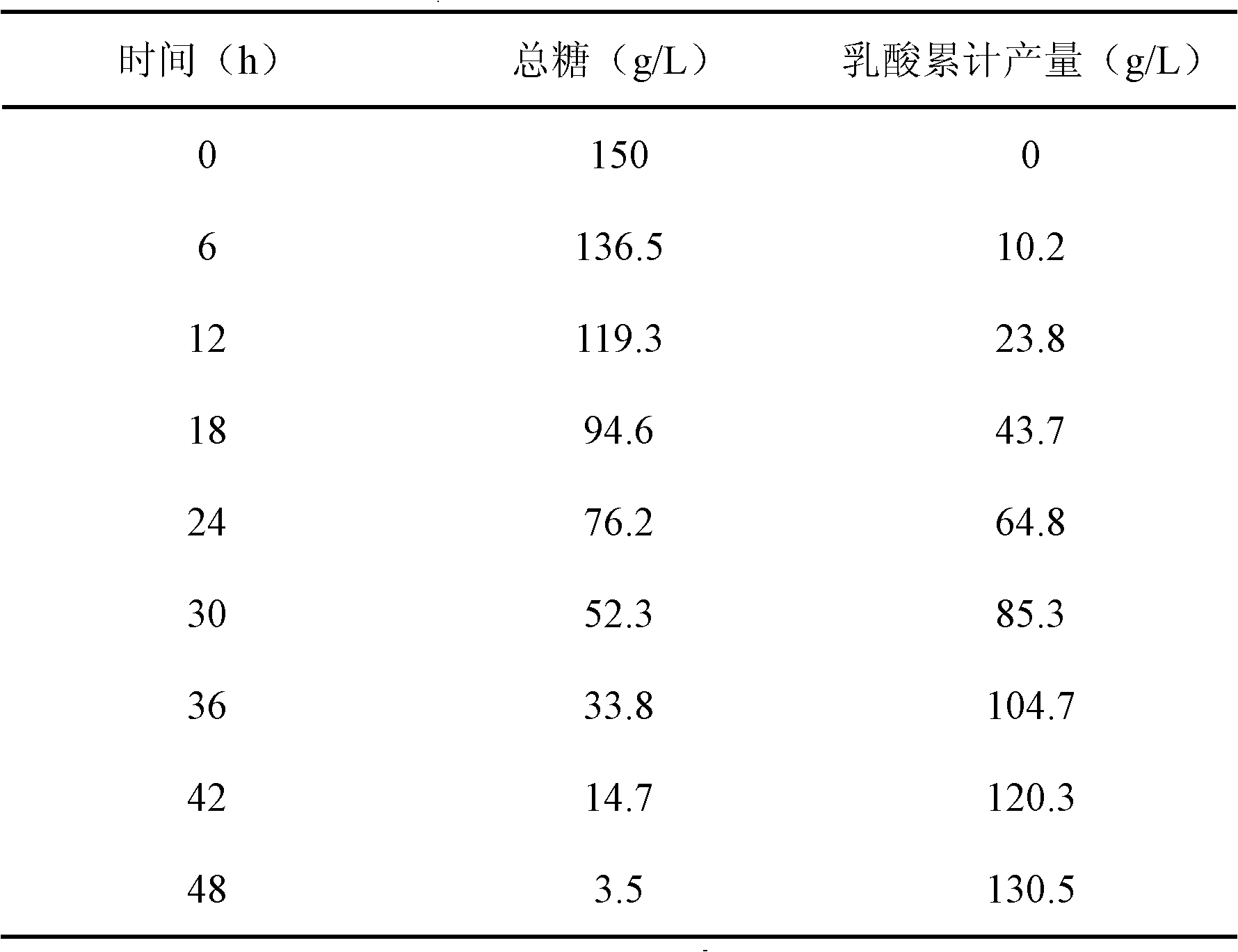
[0066] The expanded bed system described above was used. Expanded bed chromatography column coupled in situ separation batch fermentation. Depending on the initial sugar content in the culture medium, the fermentation ended within 48 hours. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0067] Table 2 In situ separation batch fermentation results
[0068]
[0069] Example 3
[0070] The types of resins used for expanded bed chromatography packed columns are shown in Table 3. The resins were first soaked in deionized water for 24 hours, and then pretreated three times with "1mol / L HCl, water, 1mol / L NaOH, water". Treat it as -OH type, and finally wash the bed with sterile water to neutral, that is, the preparation is complete. After adsorption saturation, use 10wt%-40wt% H 2 SO 4 Eluted as a desorbent. Then regenerate with 1mol / L NaOH or KOH. After one cycle of "adsorption, elution, and regeneration", the adsorption performance and resolution rate of the resin are shown in Table ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com