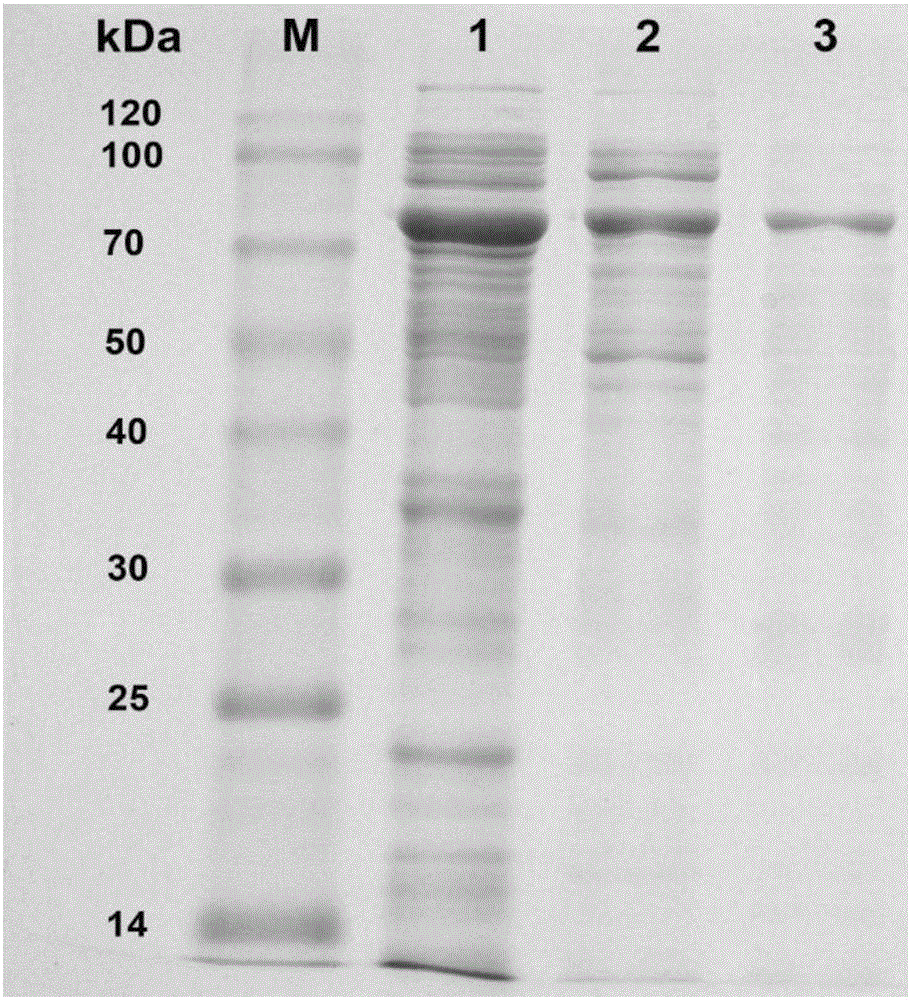
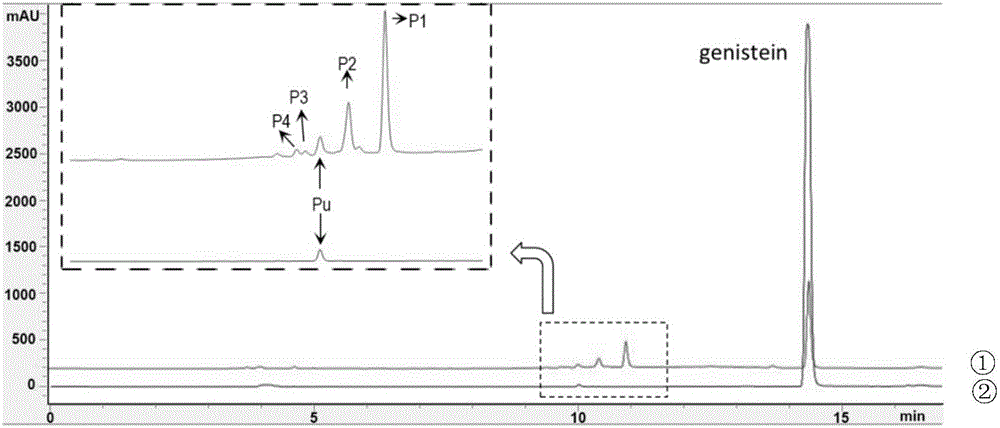
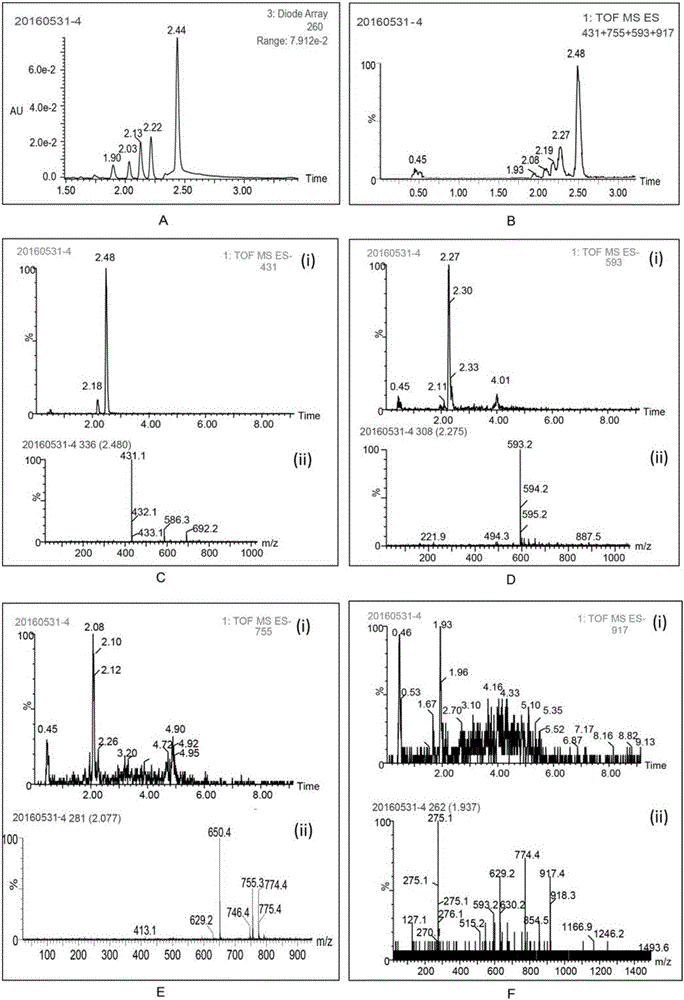
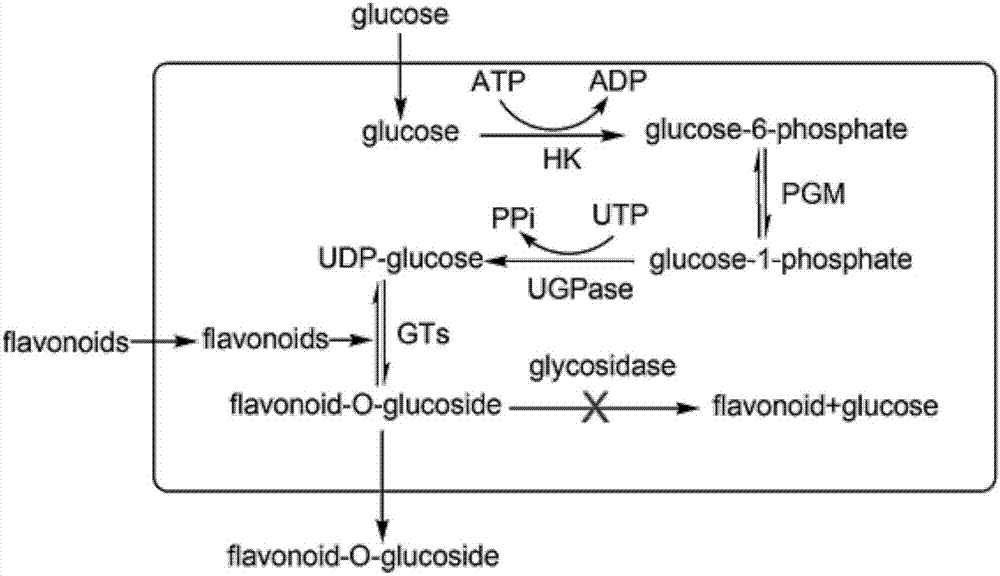
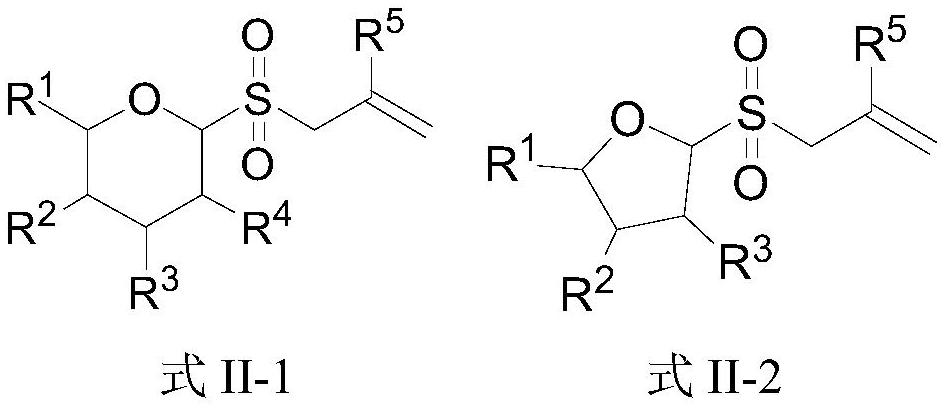
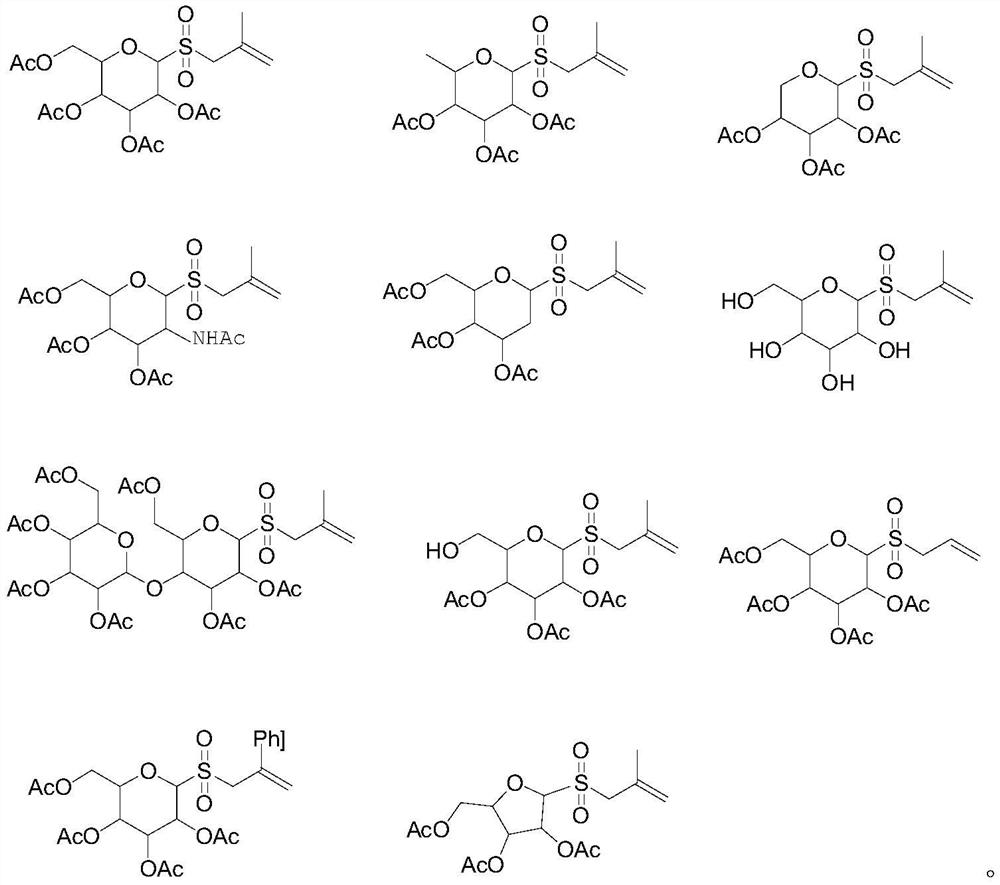
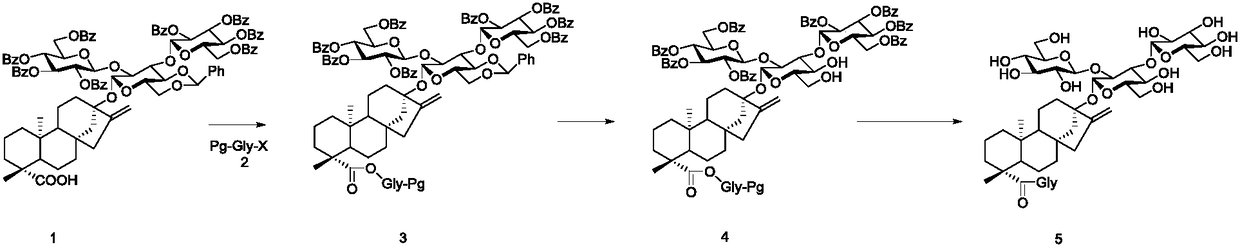
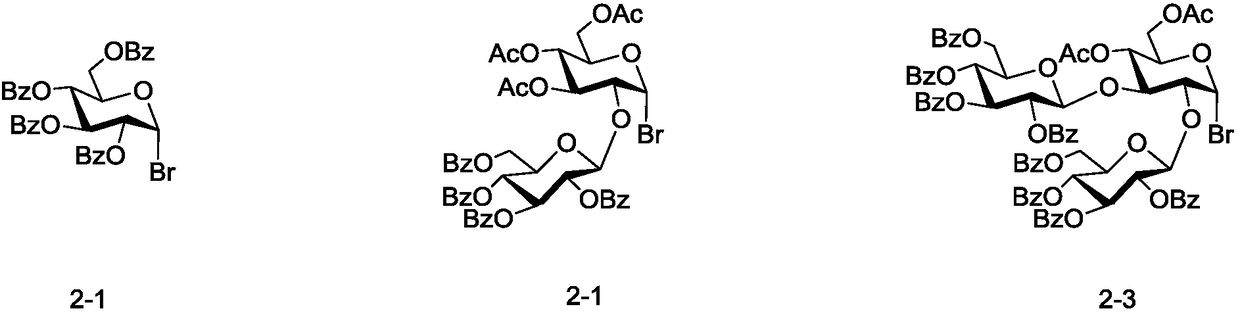
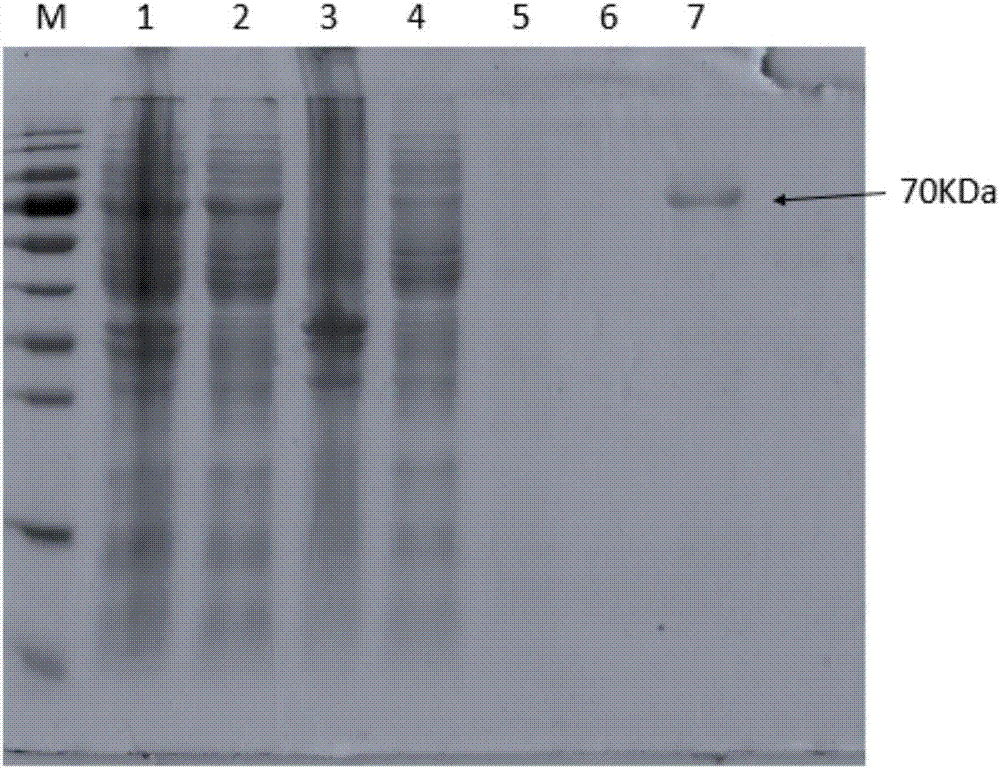
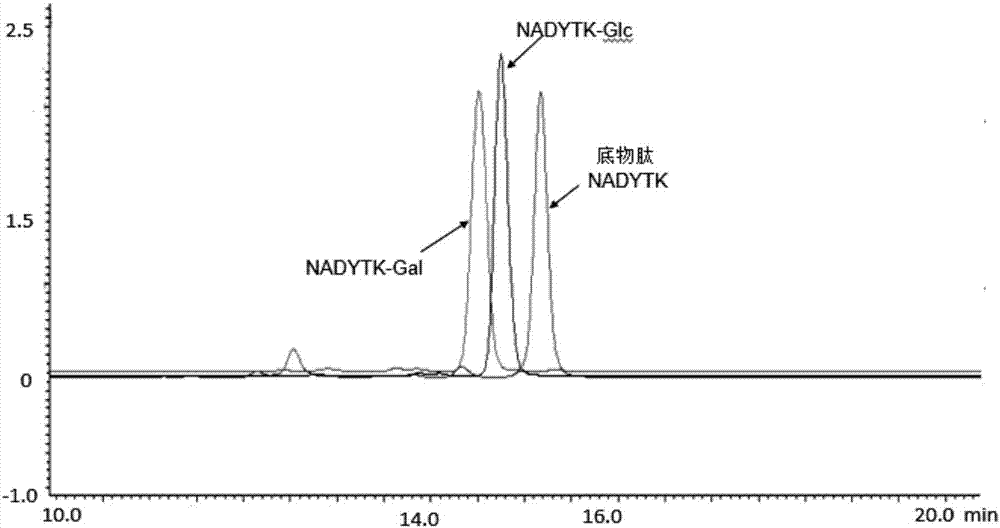
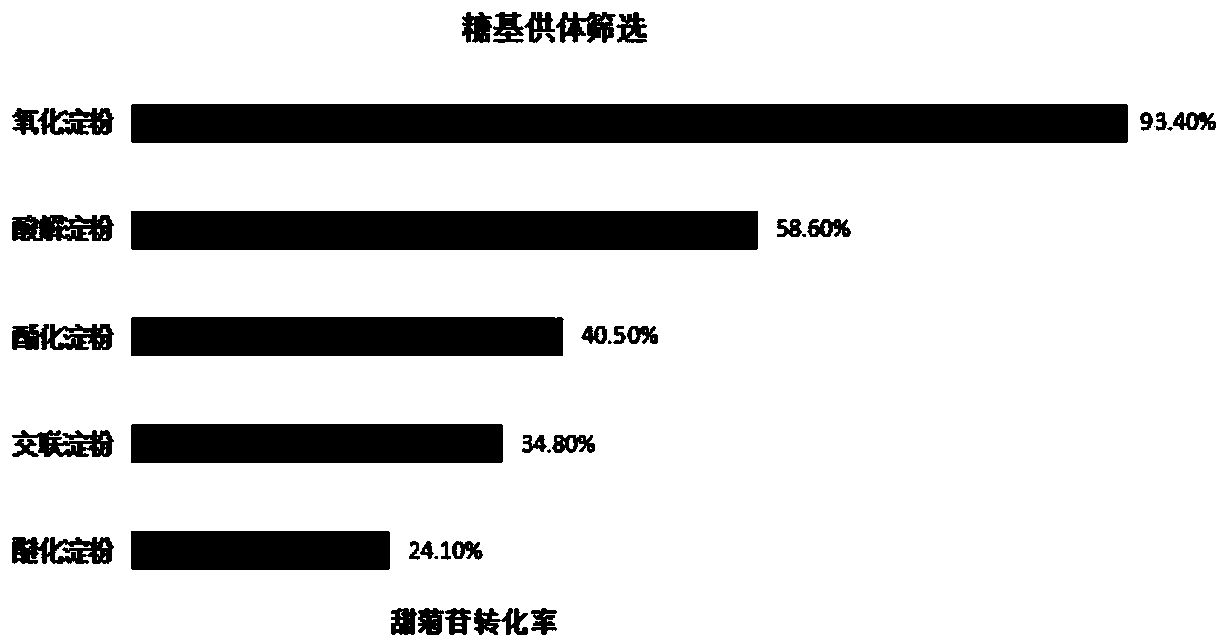
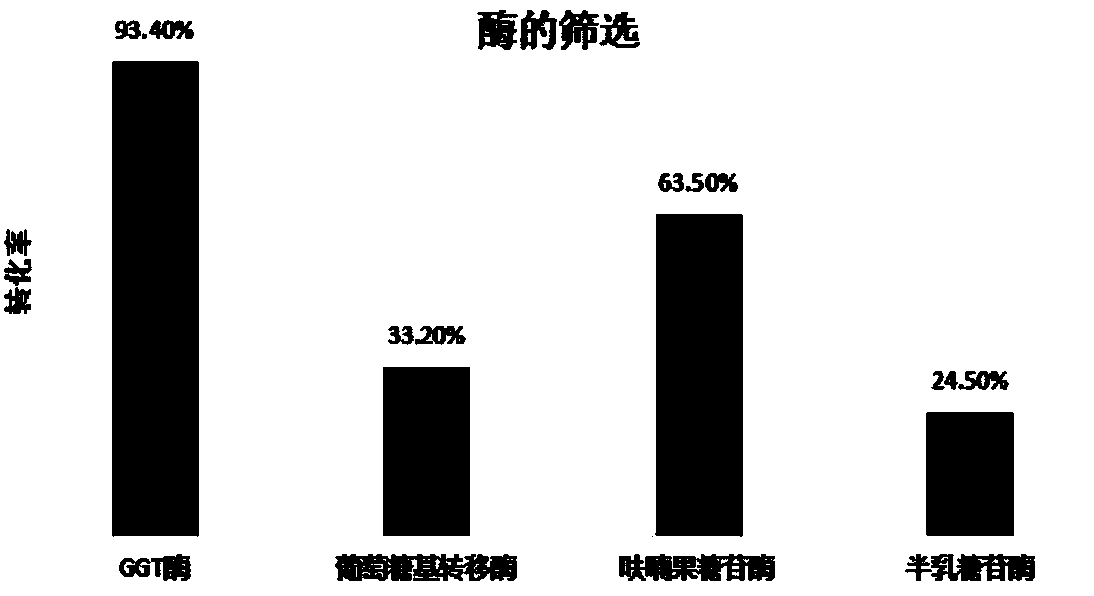
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Glycosyl donor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A glycosyl donor is a carbohydrate mono- or oligosaccharide that will react with a suitable glycosyl acceptor to form a new glycosidic bond. By convention, the donor is the member of this pair that contains the resulting anomeric carbon of the new glycosidic bond. The resulting reaction is referred to as a glycosylation or chemical glycosylation.
Glycoconjugation of polypeptides using oligosaccharyltransferases
The current invention provides polypeptides and polypeptide conjugates that include an exogenous N-linked glycosylation sequence. The N-linked glycosylation sequence is preferably a substrate for an oligosaccharyltransferase (e.g., bacterial PgIB), which can catalyze the transfer of a glycosyl moiety from a lipid-bound glycosyl donor molecule (e.g., a lipid-pyrophosphate-linked glycosyl moiety) to an asparagine (N) residue of the glycosylation sequence. In one example, the asparagine residue is part of an exogenous N-linked glycosylation sequence of the invention. The invention further provides methods of making the polypeptide conjugates that include contacting a polypeptide having an N-linked glycosylation sequence of the invention and a lipid-pyrophosphate-linked glycosyl moiety (or phospholipid-linked glycosyl moiety) in the presence of an oligosaccharyltransferase under conditions sufficient for the enzyme to transfer the glycosyl moiety to an asparagine residue of the N-linked glycosylation sequence. Exemplary glycosyl moieties that can be conjugated to the glycosylation sequence include GlcNAc, GlcNH, bacillosamine, 6-hydroybacillosamine, GalNAc, GaINH, GlcNAc-GlcNAc, GlcNAc-GlcNH, GlcNAc-Gal, GlcNAc-GlcNAc-Gal-Sia, GlcNAc-Gal-Sia, GlcNAc-GlcNAc-Man, and GlcNAc-GlcNAc-Man(Man)2. The transferred glycosyl moiety is optionally modified with a modifying group, such as a polymer (e.g., PEG). In one example, the modified glycosyl moiety is a GIcNAc or a sialic acid moiety.
Owner:RATIOPHARM GMBH +1
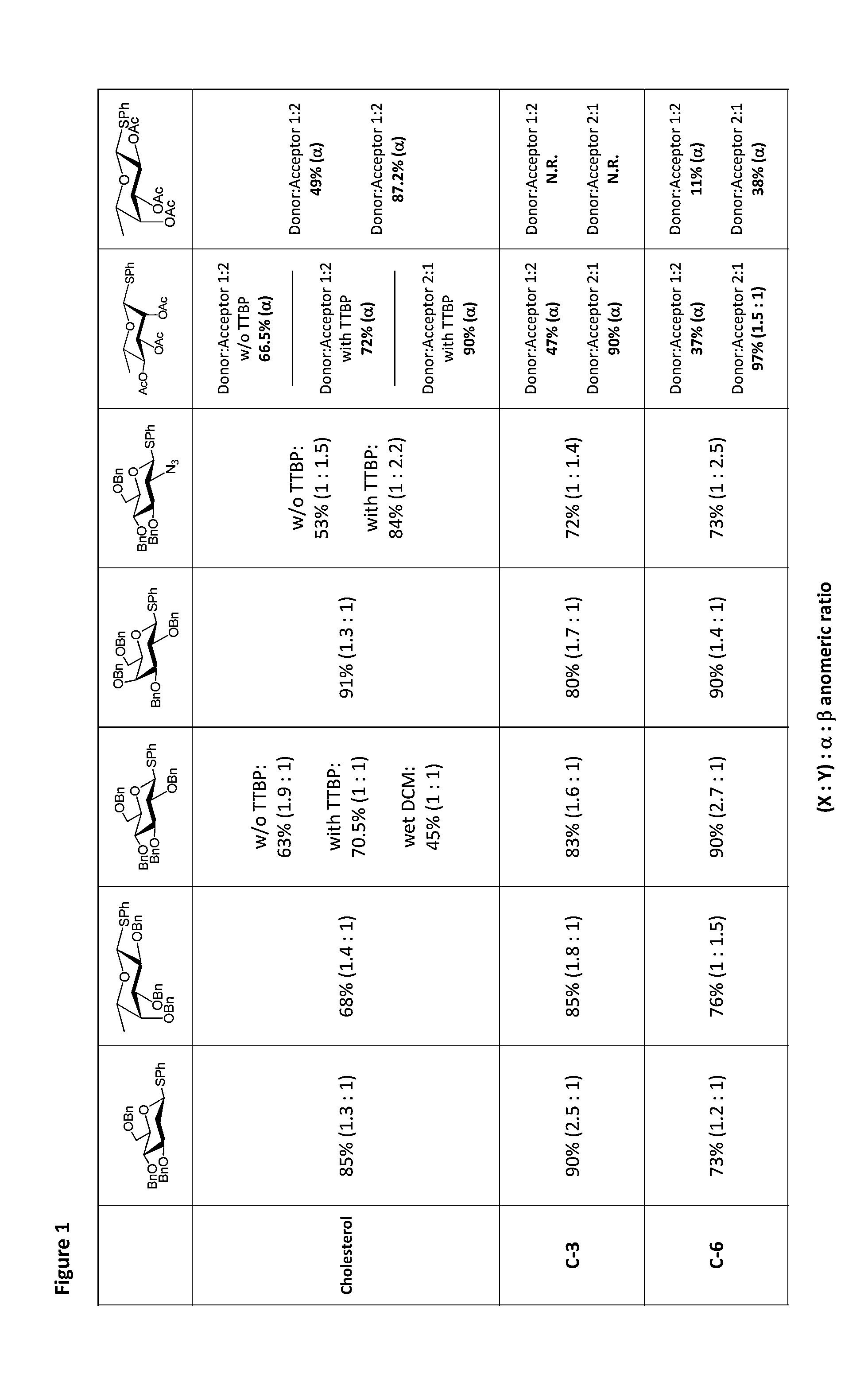
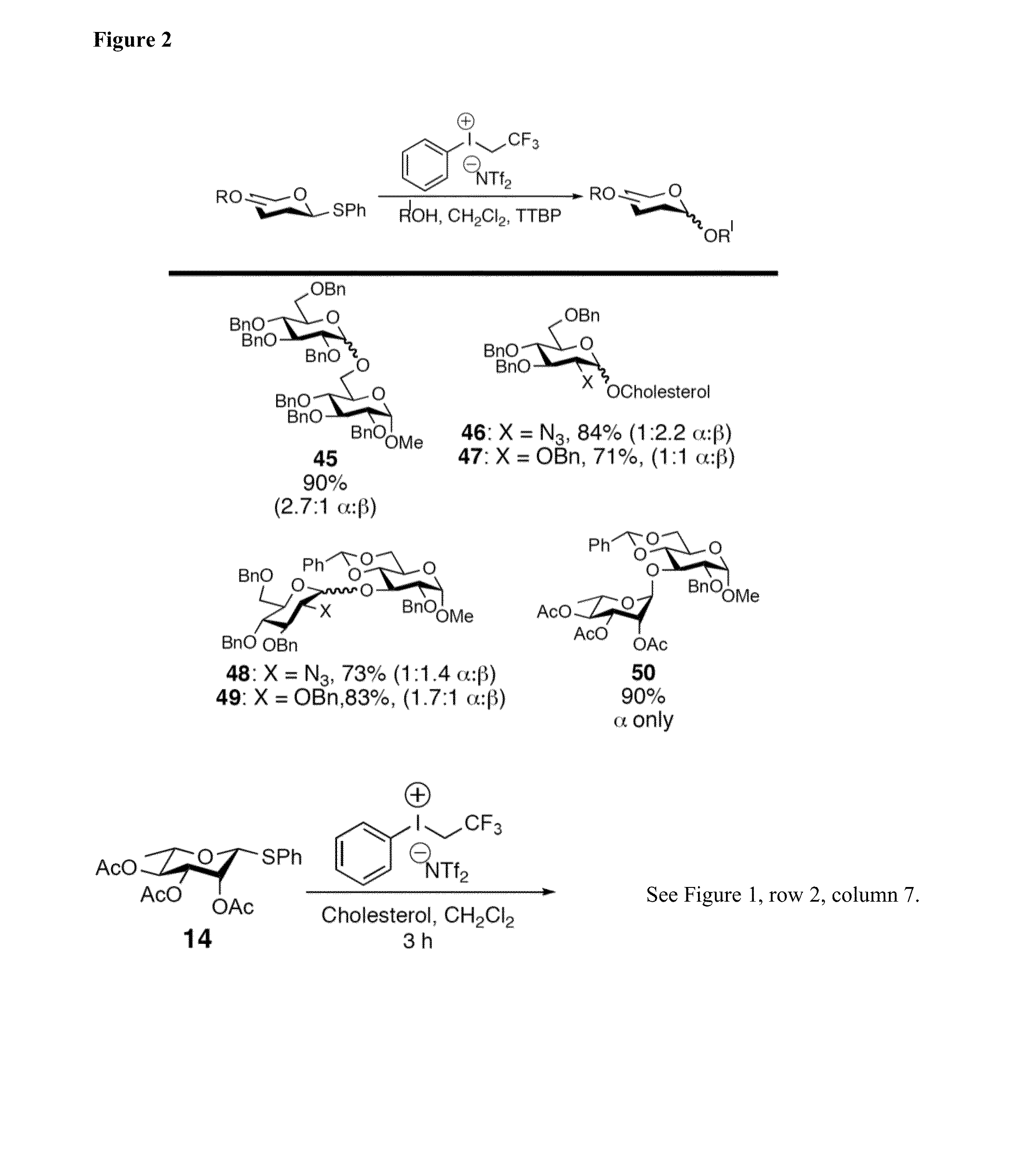
Glycosylation Reactions Using Phenyl(trifluoroethyl)iodonium Salts
Provided are methods for the preparation of glycosylation products, including those represented by formula I:Sugar-O—R′ Icomprising the step of combining R′—OH, a glycosyl sulfide glycosyl donor (“thioglycoside donor”), a hypervalent iodine alkyl-transfer activating reagent, and a base. In an embodiment, the hypervalent iodine alkyl-transfer activating reagent is (phenyl(trifluoroethyl)iodonium triflimide).
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
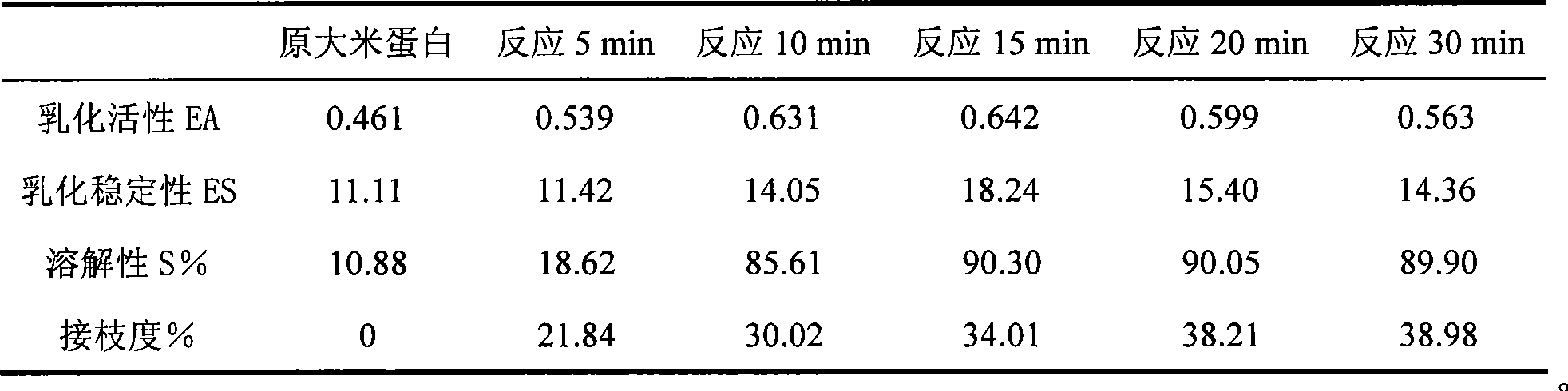
Method for improving rice protein functional property with protein-polysaccharide graft coupling technology
InactiveCN101429226AImprove functional propertiesImprove the level of comprehensive utilizationPeptide preparation methodsPhosphorylationRice protein
The invention provides a method for improving functional property of rice protein by protein-polyoses graft coupling technology, which belongs to the technical field of hydrophobicity vegetable protein modification. The method is to carry out glycosylation modification on a side product of producing rice starch and rice syrup, namely the rice protein as a raw material by different glycosyl donors through a wet method. Dissolvability, emulsibility, foamability and other functional properties of the rice protein are effectively improved and sufficiently utilized through the graft reaction of the rice protein and sugar. Compared with methods chemically modifying the vegetable protein, such as alkylation, phosphorylation, deamidization and the like, the method is safe and environment friendly, a rice protein-polyoses graft coupling product can be used as a natural macromolecular emulsifying agent or a protein nutritional reinforcing agent to sufficiently reflect and exert low sensitivity and high nutritive characteristic of the rice protein, thereby effectively expanding the application field of the rice protein. Meanwhile, the method provides theoretical reference for deep research and development of the hydrophobicity vegetable protein.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A group of glycosyl transferase, and applications thereof
InactiveCN105177100AHigh anticancer activityResolve source issuesTransferasesPlant peptidesTriterpeneTriterpenoid
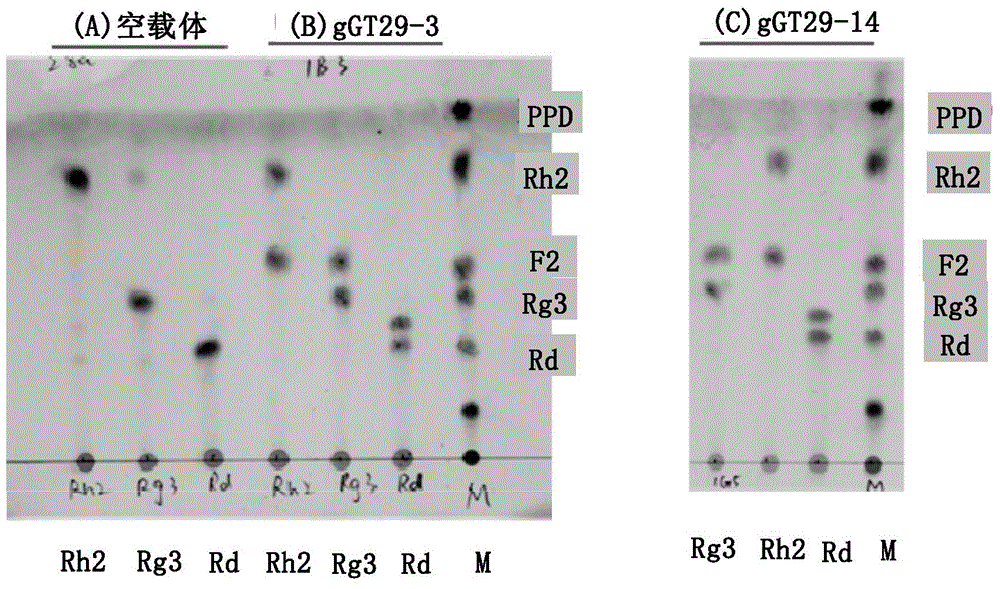
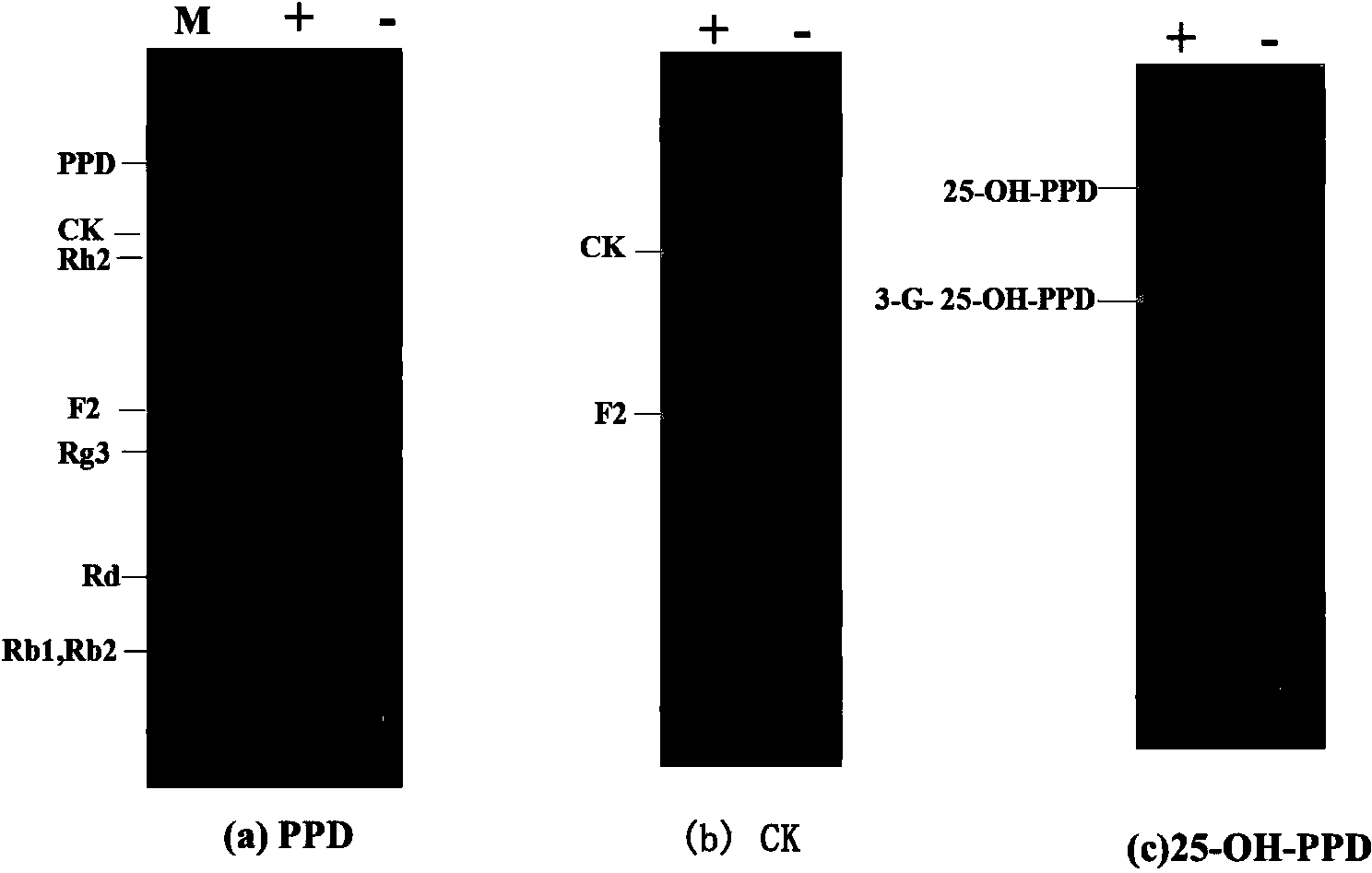
The present invention relates to a group of glycosyl transferase and applications thereof, and specifically provides applications of the glycosyl transferase gGT29-7 and a derived polypeptide thereof in terpene compound glycosylation catalysis and new saponin synthesis, wherein the glycosyl transferase can specifically and efficiently transfer the glycosyl from a glycosyl donor to the first glycosyl on C-3 site and / or C-6 site of a tetracyclic triterpene compound so as to extend the sugar chain. The glycosyl transferase of the present invention can further be used for constructing artificial ly-synthesized rare ginsenosides and a variety of new ginsenosides and derivatives thereof.
Owner:周志华
Glycosyl transferases and applications of glycosyl transferases
ActiveCN104232723ASpecific and efficient transferHas anticancer activityTransferasesFermentationTriterpeneCoa transferase
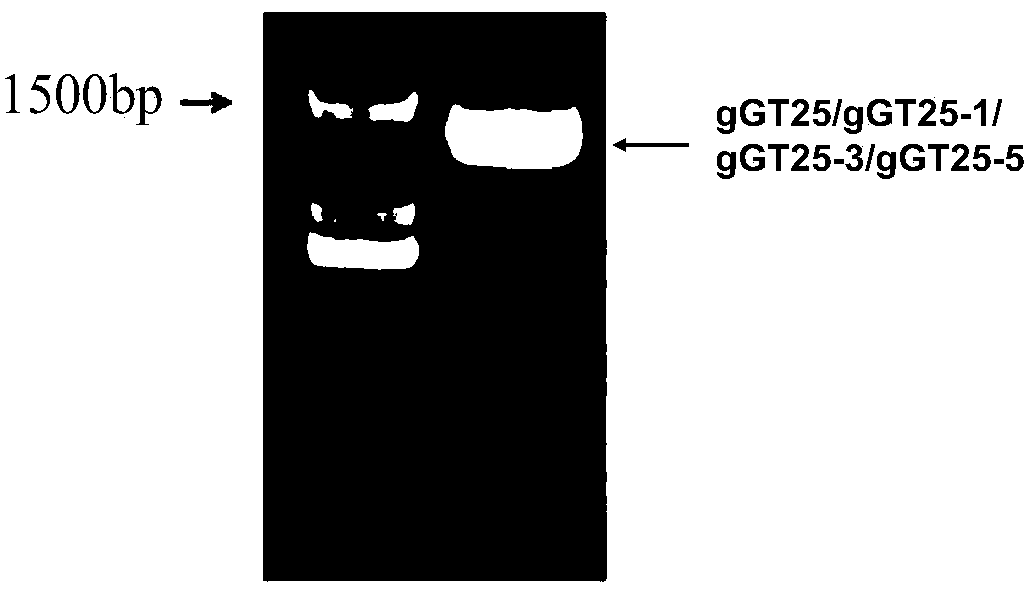
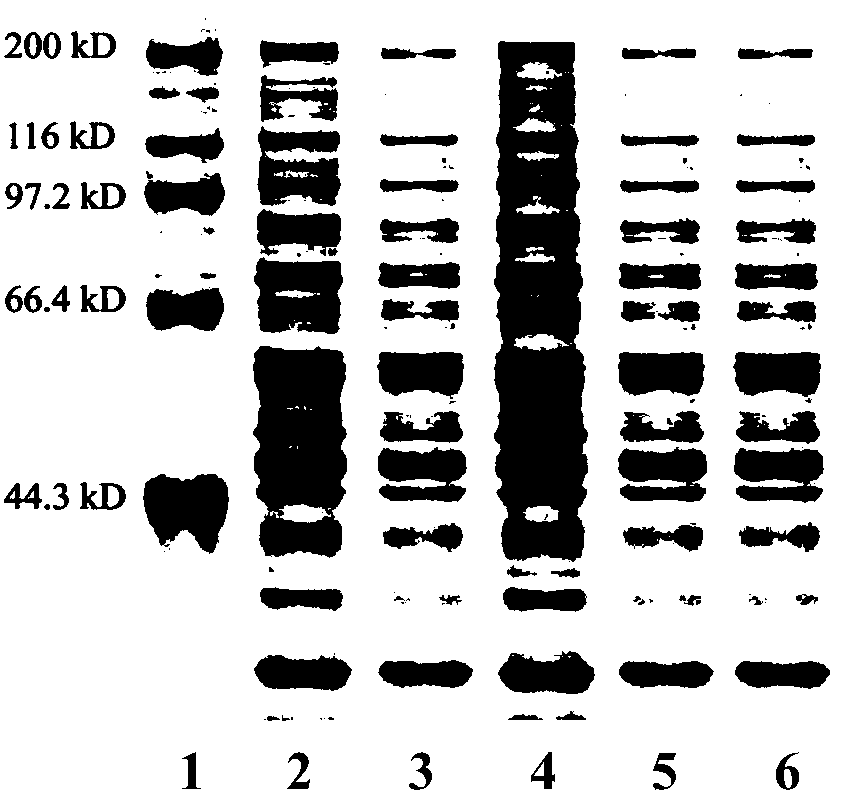
The invention relates to a group of glycosyl transferases and applications of the glycosyl transferases. Particularly, the invention provides applications of glycosyl transferases gGT25, gGT13, gGT30, gGT25-1, gGT25-3, gGT25-5, gGT29, gGT29-3, gGT29-4, gGT29-5, gGT29-6, gGT29-7, 3GT1, 3GT2, 3GT3 and 3GT4, and derived peptides of the glycosyl transferases in glycosylation catalysis and new saponin synthesis of terpenoids. The glycosyl transferases can specifically and efficiently catalyze hydroxyl glycosylation of C-20 bit and / or C-6 bit and / or C-3 of a tetracyclic triterpenoid compound substrate, and / or transfers the glycosyl groups from glycosyl donors to the first glycosyl groups of the C-3 bit and C-6 bit of the tetracyclic triterpenoid compound to extend a carbohydrate chain. The glycosyl transferases disclosed by the invention can also be applied to building synthetic rare ginsenosides and a plurality of novel ginsenosides and derivatives of the ginsenosides.
Owner:SYNBIOTECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Method for preparing low-sensitivity soybean protein powder by combination of glycosylation and enzymatic modification
The invention discloses a method for preparing low-sensitivity soybean protein powder by combination of glycosylation and enzymatic modification. The method comprises the following steps: firstly uniformly mixing soybean protein with a glycosyl donor in a certain mass ratio and then dissolving in distilled water, freezing and drying in vacuum, and putting the mixture at certain humidity and certain temperature to prepare a soybean protein glycosylation product; subsequently performing proper hydrolysis by use of a compound enzyme consisting of alkaline protease and flavorzyme, and then centrifuging and drying to obtain the low-sensitivity soybean protein powder. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that firstly, a soybean protein product prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is relatively low in antigenicity, so that soybean anaphylaxis can be reduced or eliminated; secondly, by adopting a conventional dry heating method, the preparation method is relatively simple in process, free of pollution and safe; thirdly, the method is combined with an enzymolysis method, so the reaction time is shortened and the product is free of bitter taste and other smelly flavors; finally, active substances which are easy to digest and absorb and have the functions of enhancing the immunity and reducing blood pressure can be generated during the preparation process.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
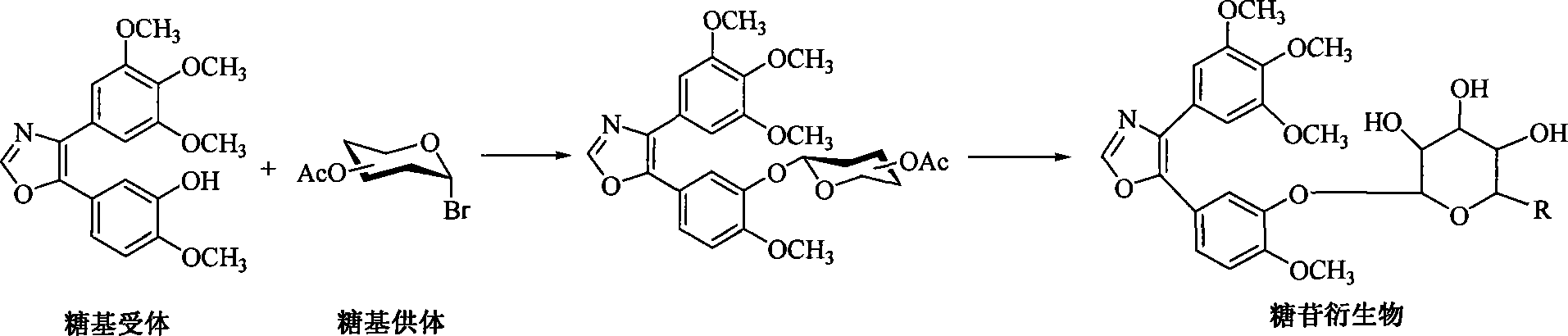
1,2-glycoside transderivative of oxazole compounds and preparation method thereof
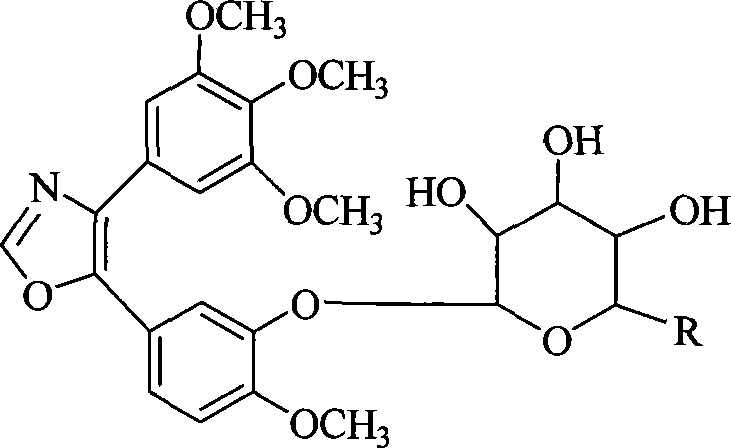
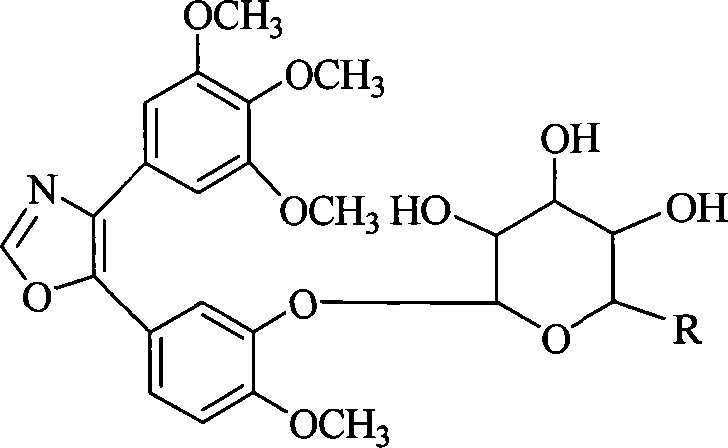
InactiveCN101230079AImprove bioavailabilityImprove targeted tumor vasculatureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilitySodium methoxide
The invention discloses 1, 2-anti form glucoside derivative of oxazole compound. During the preparation, 4-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxy phenyl)-5-(3-hydroxyl-4-methoxy phenyl oxazole is used as the acceptor of glycosyl, bromo sugar of D-glucose, D-galactose, L-arabinose, D-xylose, L-fucose or lactose with full acetyl protection, or trichlorine imine ester of L-rhamnose or D-mannose with full acetyl protection is adopted as the donator of glycosyl, glycosylation is performed with the catalysis of alkali and tetrabutyl ammonium bromide or lewis acid, to obtain glucoside derivative containing acetyl protecting group; and then the acetyl protecting group is removed by utilizing methyl alcohol and sodium methoxide, to obtain 1,2 anti-form glucoside derivative of oxazole compound. The preparation method is simple, highly effective and universal, the route is short, the water-solubility of the product is good, the bioavailability is high, thereby the glucoside derivative can be applied as antineoplastic medicine inhibiting microtubule assembly and selectively targeting tumor blood vessels.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Glycoconjugation of polypeptides using oligosaccharyltransferases
The current invention provides polypeptides and polypeptide conjugates that include an exogenous N-linked glycosylation sequence. The N-linked glycosylation sequence is preferably a substrate for an oligosaccharyltransferase (e.g., bacterial PgIB), which can catalyze the transfer of a glycosyl moiety from a lipid-bound glycosyl donor molecule (e.g., a lipid-pyrophosphate-linked glycosyl moiety) to an asparagine (N) residue of the glycosylation sequence. In one example, the asparagine residue is part of an exogenous N-linked glycosylation sequence of the invention. The invention further provides methods of making the polypeptide conjugates that include contacting a polypeptide having an N-linked glycosylation sequence of the invention and a lipid-pyrophosphate-linked glycosyl moiety (or phospholipid-linked glycosyl moiety) in the presence of an oligosaccharyltransferase under conditions sufficient for the enzyme to transfer the glycosyl moiety to an asparagine residue of the N-linked glycosylation sequence. Exemplary glycosyl moieties that can be conjugated to the glycosylation sequence include GlcNAc, GlcNH, bacillosamine, 6-hydroybacillosamine, GalNAc, GaINH, GlcNAc-GlcNAc, GlcNAc-GlcNH, GlcNAc-Gal, GlcNAc-GlcNAc-Gal-Sia, GlcNAc-Gal-Sia, GlcNAc-GlcNAc-Man, and GlcNAc-GlcNAc-Man(Man)2. The transferred glycosyl moiety is optionally modified with a modifying group, such as a polymer (e.g., PEG). In one example, the modified glycosyl moiety is a GIcNAc or a sialic acid moiety.
Owner:蔚所番有限公司
Method for glycosylation of flavonoid compounds
ActiveUS20100256345A1Effective glycosylationGood water solubilityCosmetic preparationsNervous disorderSolubilityΓ cyclodextrin
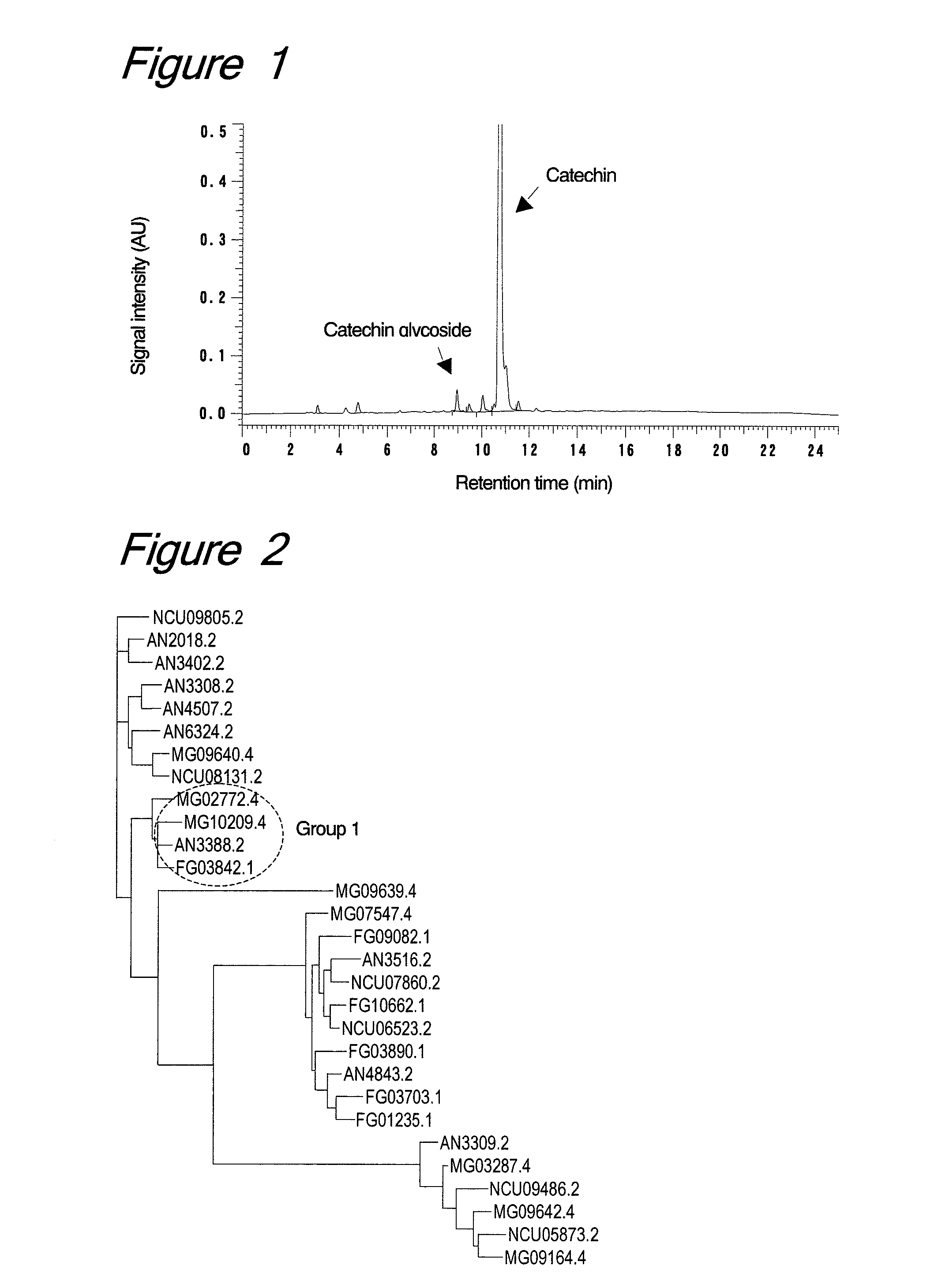
The present invention provides a method for preparing a glycoside of a flavonoid compound, which comprises the step of treating flavonoid and a glycosyl donor with an enzymatic agent having glycosylation activity and being derived from the genus Trichoderma (preferably Trichoderma viride or Trichoderma reesei). Such a flavonoid compound includes a catechin compound or a methylated derivative thereof, and the glycosyl donor includes a carbohydrate containing a maltotriose residue (preferably maltotriose, maltotetraose, maltopentaose, maltohexaose, maltoheptaose, dextrin, γ-cyclodextrin or soluble starch). Glycosides obtained by the present invention have higher water solubility, improved taste, and increased stability. The present invention also provides novel glycosides of catechin compounds, which are obtained by the method of the present invention.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for preparing L-ascorbyl-2-glucoside
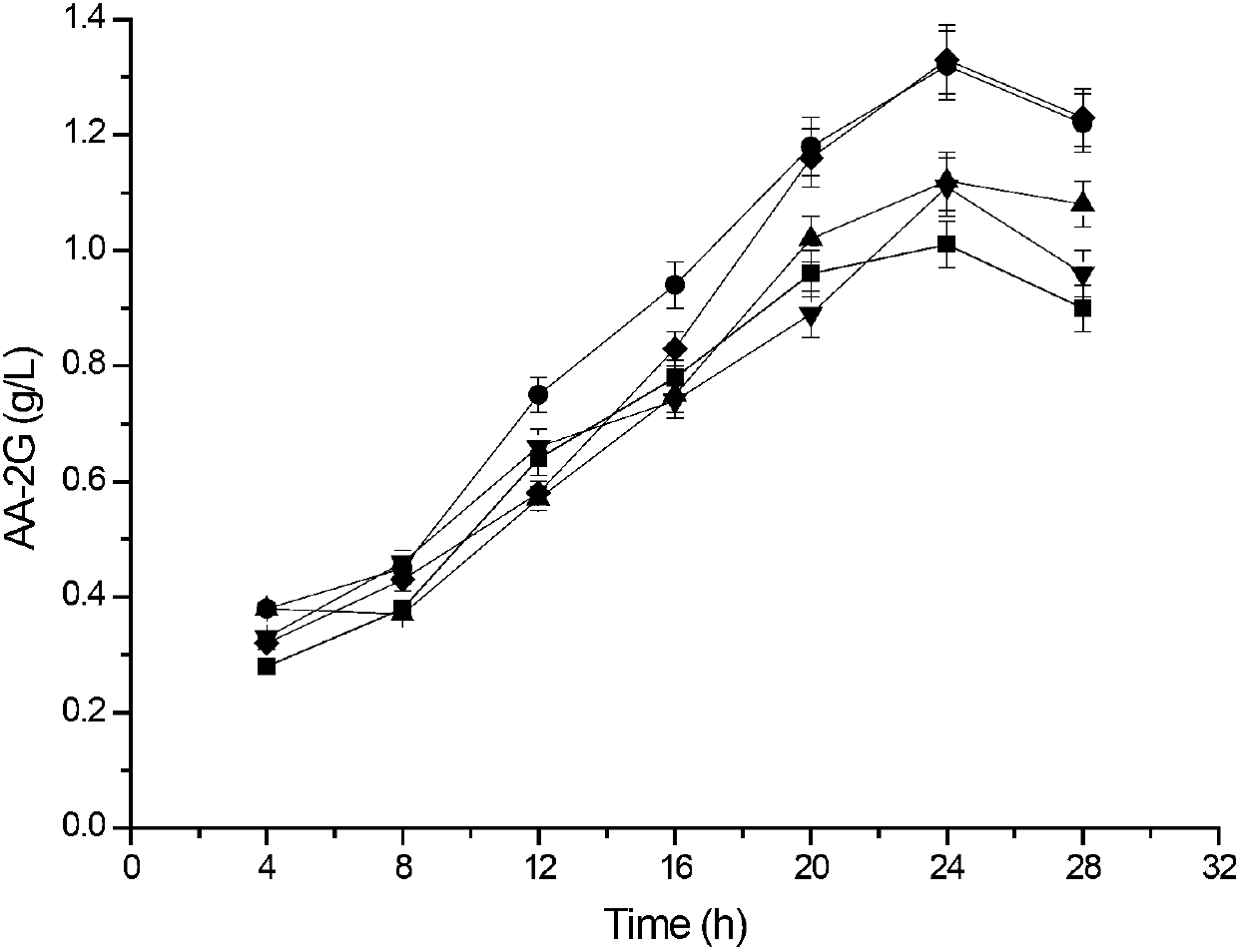
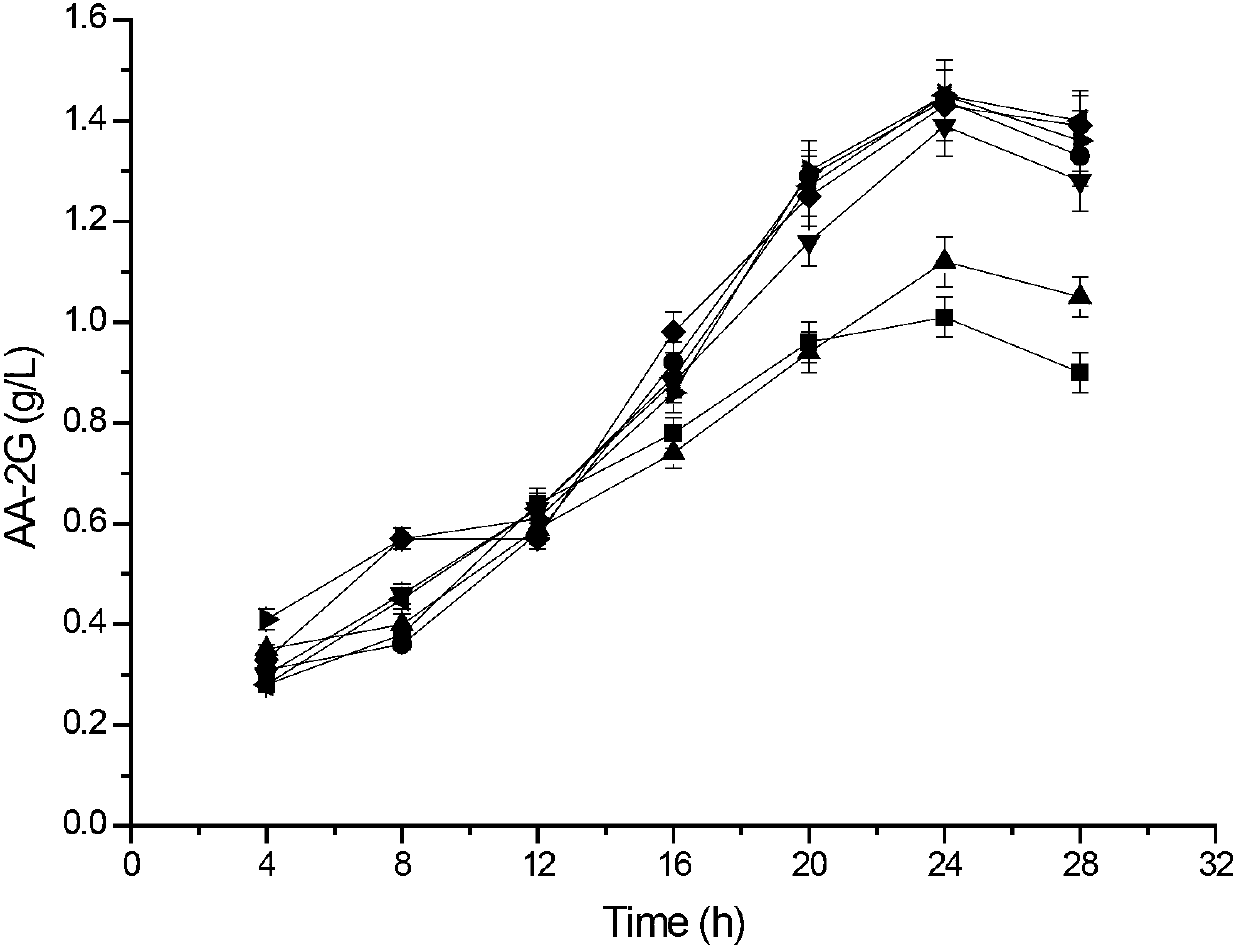
ActiveCN107058200ASingle productHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose phosphorylaseFermentation
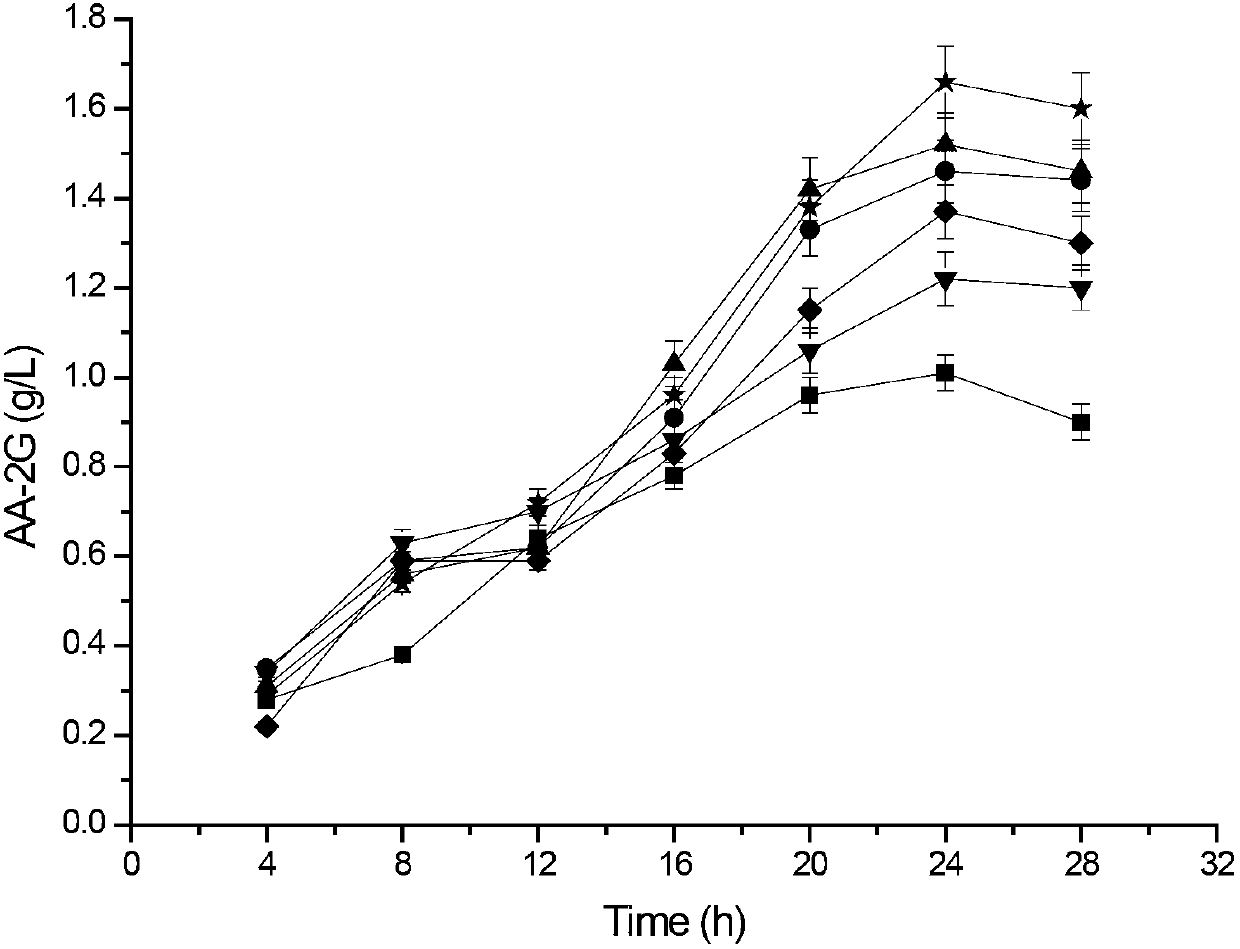
The invention relates to a method for preparing L-ascorbyl-2-glucoside by virtue of an engineering strain of recombinant sucrose phosphorylase. The engineering strain of the sucrose phosphorylase is preserved in Wuhan University in Wuhan of China, postcode 430072, with preservation number of CCTCC M2016496. The engineering strain of the sucrose phosphorylase is constructed by virtue of gene recombination and site-specific mutagenesis technologies. With strain cells, obtained from fermentation, serving as a biological catalyst, AA-2G is prepared from sucrose and L-ascorbic acid in a trisodium citrate buffer solution system. According to the method provided by the invention, the sucrose, which is directly used as a glycosyl donor, is easily soluble in water and is cheap and easily available. Meanwhile, the reaction product, which mainly includes the AA-2G, is single; a yield reaches 65% or above; and additional treatment of adding saccharifying enzyme is avoided, so that production cost is reduced.
Owner:山东格得生物科技有限公司
Method for improving water solubility of dye lignin by utilizing cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase transglycosylation reaction
The invention discloses a method for improving the water solubility of dye lignin by utilizing cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase transglycosylation reaction, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. A gene (GenBank accession no.JX412224), which is derived from P.macerans strain JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO:M208063) and optimized by a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase codon, is connected to pET20b(+) plasmid and is transferred to an E.coli BL21(DE3) cell to establish gene engineering bacteria for producing the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase. The pure cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, which is obtained through fermentation enzyme production and purification, is applied to catalytic transglycosylation reaction, alpha-cyclodextrin serves as a glycosyl donor, the dye lignin serves as glycosyl receptor, and at least four dye lignin glycosylated derivatives (Glc)n-genistein (n is equal to 1, 2, 3 and 4) are finally obtained, wherein Glc-genistein and (Glc)2-genistein are main products, in particular the water solubility of the (Glc)2-genistein is greatly improved compared with that of the dye lignin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of flavonoids compound and application thereof
ActiveCN107164253AImprove efficacyGood water solubilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydrolase Gene
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of a flavonoids compound and an application thereof. Specifically, a Beta-glycoside hydrolases gene of a chassis biological cell is removed according to the genetically engineered bacterium, and endogenous degradation of a glycosylation product is reduced; the high-expression regulation is performed to two key enzymes of glucophosphomutase (PGM) and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGP1) of the chassis biological cell for participating in the synthesis of glycosylated-donor uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-Glu), and a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene for catalyzing the flavonoid aglycones glucose glycosylation is combined so as to obtain a genetically engineered strain for effectively catalyzing the glucose glycosylation of the flavonoids compound, and finally scutellarein is used as a catalytic substrate for fermenting for 54 h in 10 L of a fermentation tank, wherein the yield of scutellarein-7-O-glucose of the glycosylation product is up to 1200 mg / L. The used strategy provides a technology reference for biologically-catalyzing chemical micromolecular glycosylation by using a microbiological method.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Glycosyltransferase mutant and method for catalytically synthesizing rebaudioside A by using same
ActiveCN112375750AIncreased expression of solubleImprove efficiencyBacteriaTransferasesSucrose synthetaseEnzyme system
The invention discloses a glycosyltransferase mutant and a method for catalytically synthesizing rebaudioside A by using the same. The amino acid sequence of original glycosyltransferase is SEQ ID NO:1. According to the experiment, Asn196, Asn78, Asn400, Asn69, Gln72, Gln198, Gln178, Gln160 and Thr319 are screened on the basis of prediction obtained by starting from surface residues Q, N and T ofUGT76G1 and combining data analysis results of solvent accessible surface area, B-factor and the like, and finally, a UGT-SuSy system of the better mutant strain 76G1_Q72E-N196D-T319E is screened outby virtue of single-point or multi-point iterative mutation in Thr81, so as to realize efficient catalytic synthesis of the rebaudioside A. The glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 or a mutant gene thereof isconnected with a sucrose synthase gene to obtain a recombinant plasmid, and a double-enzyme co-expressed recombinant strain is constructed. By constructing a double-enzyme system, regeneration of in-vivo UDPG is realized, the problem of sources of expensive glycosyl donors is effectively solved, the cost is reduced, and application of biotechnology industry is promoted. The mutant is simple to prepare, the rebaudioside A is synthesized through efficient catalysis in a short time, and the biological enzyme catalysis method is green, environmentally friendly and pollution-free and is more suitable for current green industrial processing and production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Glycosyltransferase, mutants and application thereof
The invention relates to glycosyltransferases, mutants and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides an in vitro glycosylation method provided comprisescomprising the following steps:transferring glycosyl groups of a glycosyl donor to C-3 hydroxy groups of tetracyclic triterpenoids in the presence of glycosyltransferase to form glycosylated tetracyclic triterpenoids, wherein the glycosyltransferase is glycosyltransferase or derivated polypeptide derivatives thereof shown as SEQ ID NO.4, or glycosyltransferase or derivated polypeptide derivatives thereof shown as SEQ ID NO.21.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
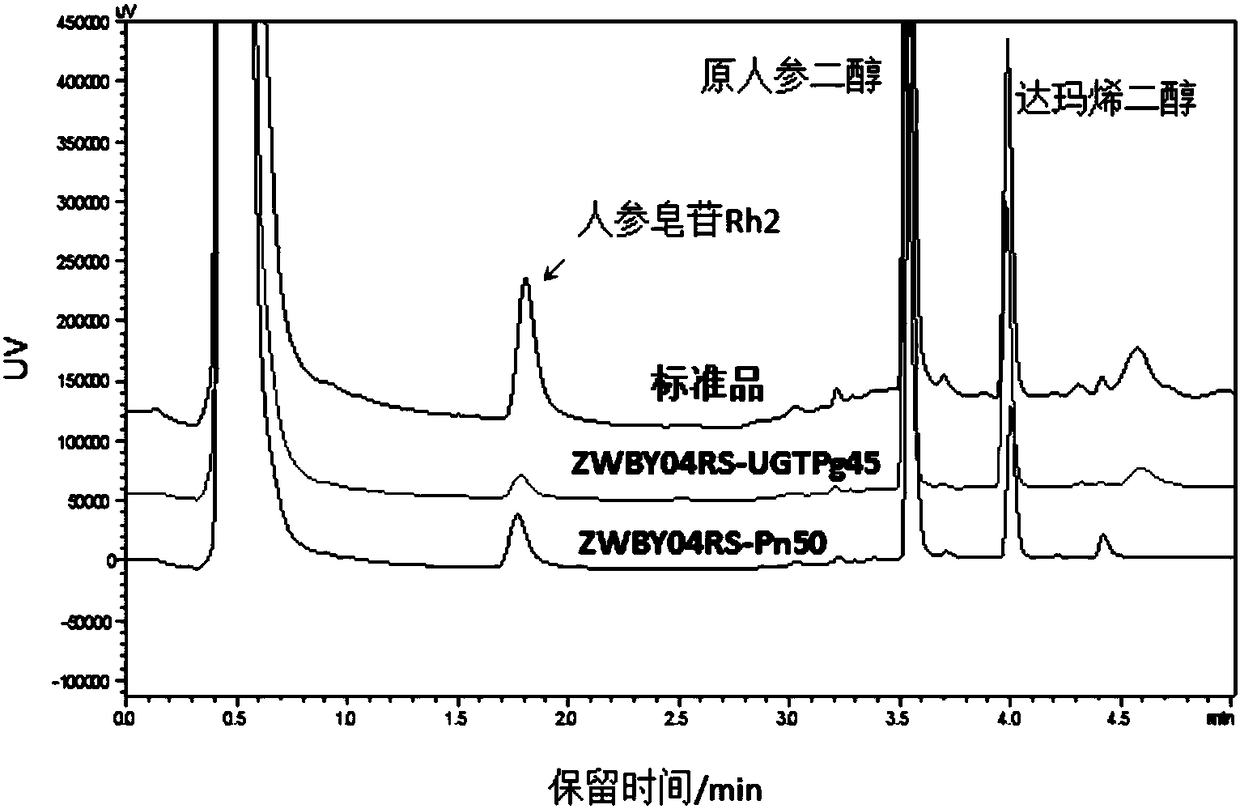
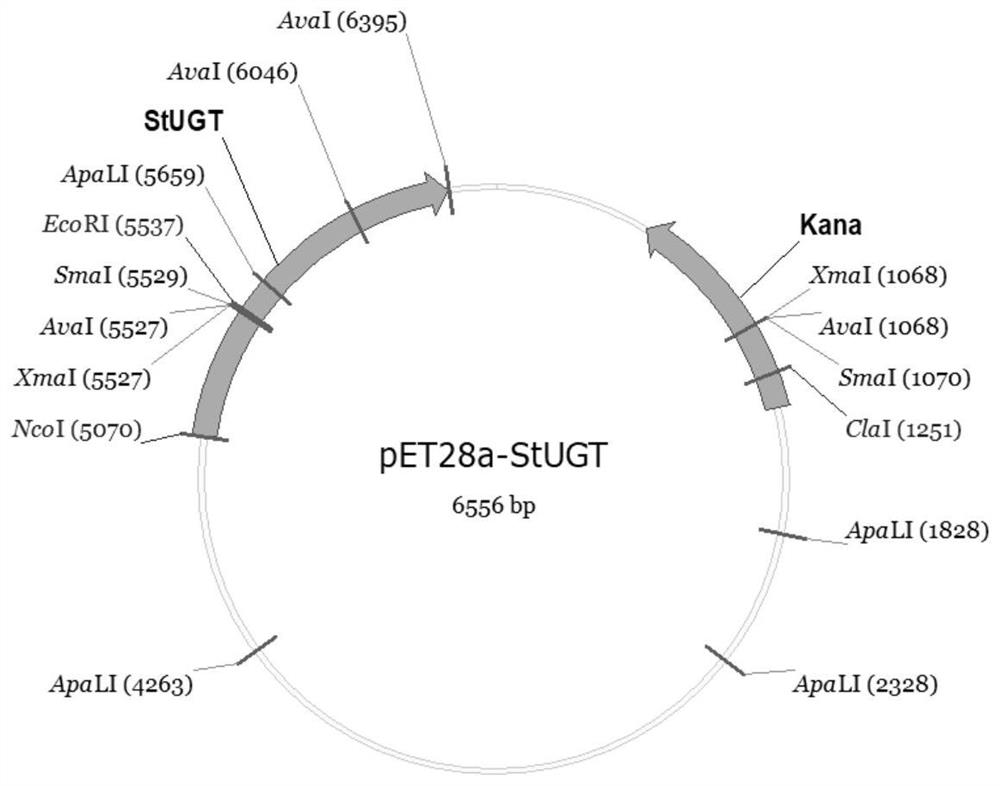
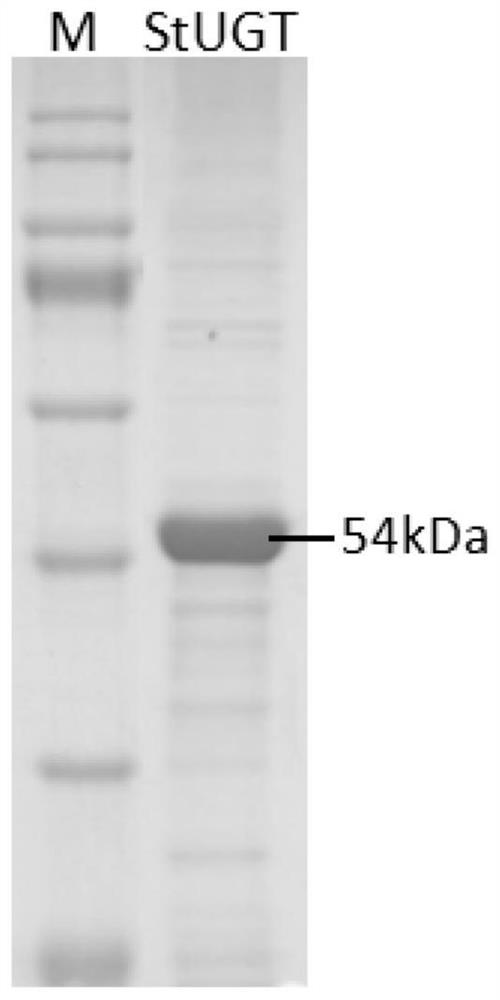
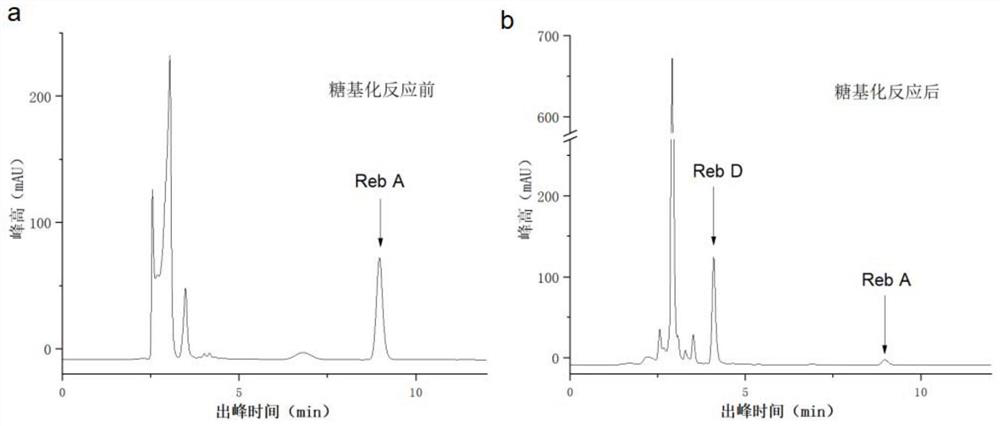
Glycosyltransferase StUGT capable of catalyzing rebaudioside A to generate rebaudioside D
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering and provides use of a nucleotide sequence for coding glycosyltransferase StUGT in preparing a recombinant protein capable of catalyzing rebaudioside A to generate rebaudioside D. The nucleotide sequence is as follows: a) a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; or a nucleotide sequence which is different from the nucleotide sequence in a) and capable of encoding an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. After a gene of the glycosyltransferase StUGT is connected to an expression vector, the gene is transferred into a host cell to obtain a recombinant bacterium. The recombinant protein takes UDPG as a glycosyl donor, the substrate rebaudioside A is catalyzed to generate rebaudioside D, and high catalytic efficiency can be achieved.
Owner:SINOCHEM HEALTH IND DEV CO LTD +1
Glycosylated and ultrasonic compound modified high-gel soy protein powder as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111227104ASimple processProcess safetyVegetable proteins working-upFood ingredient functionsIce waterPROTEIN S HEERLEN
The invention discloses glycosylated and ultrasonic compound modified high-gel soy protein powder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the glycosylated and ultrasonic compound modified high-gel soy protein powder comprises the following steps: (1), adding distilled water into protein powder and a glycosylated donor to obtain a mixture, wherein the massratio of the protein powder to the glycosylated donor is (1 to 1) to (3 to 1), uniformly stirring the mixture to prevent generation of a large quantity of bubbles so as to prepare a mixed solution with the concentration being 1 percent to 6 percent; (2), deeply inserting an ultrasonic probe into the mixed solution, controlling ultrasound output power to be 200W to 500W, controlling ultrasound treatment time to be 15 minutes to 240 minutes and setting a temperature to be 60 plus / minus 2 DEG C; and (3), taking out the reacted mixed solution after reaction is finished, and instantly putting themixed solution in ice water bath and then performing cooling to a room temperature, and performing lyophilization to obtain a sample. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, glycosylation is carried out by adopting a conventional moist heat method, the process is relatively simple, and any chemical reagents are not added, and therefore, green and no pollution can be achieved; the treatment is carried out at the same time by adopting an ultrasonic way, the glycosylation reaction time is shortened, a reaction process is easily controlled, and soy protein products subjected to compound modification has better gelation properties.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102994468AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineWild type
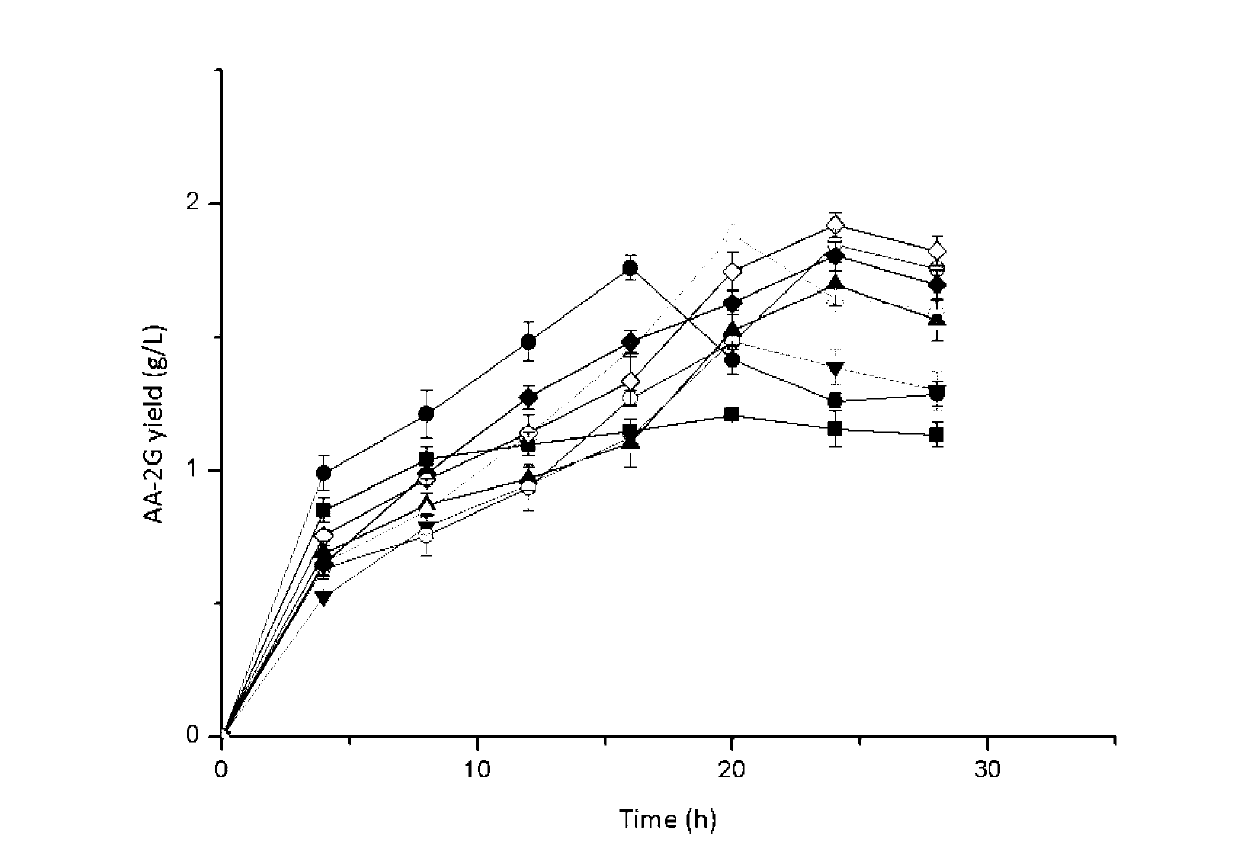
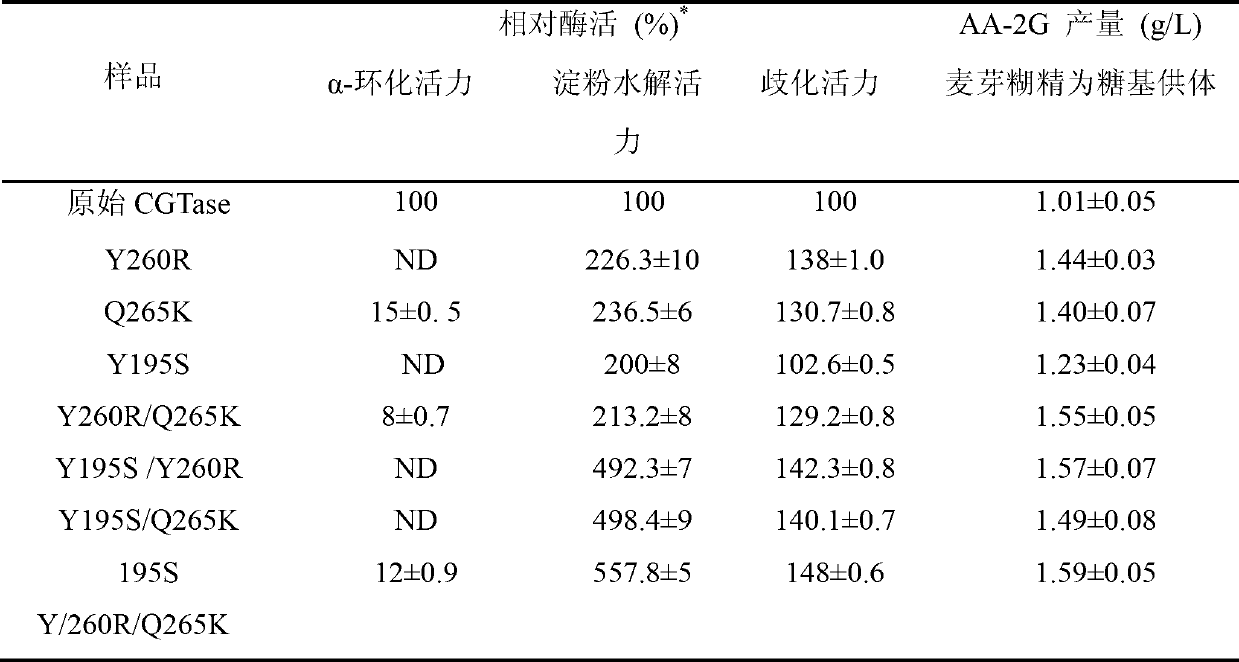
The invention discloses cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. 195-bit tyrosine (Tyr) of CGTase of P.macerans strain JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO:M208063) is replaced by serine (Ser), 260-bit tyrosine (Tyr) is replaced by arginine (Arg), and 265-bit glutamine (Gln) is replaced by lysine (Lys), so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 23 percent, 44 percent and 40 percent. According to combined mutation of the mutant strains, double mutants Y195S / Y260R, Y195S / Q265K and Y260R / Q265K and A three-point mutant Y195S / Y260R / Q265K are obtained. A Glycosyl donor is produced by the maltodextrin, so that the AA-2G yield is respectively improved by 57 percent, 49 percent, 55 percent and 59 percent; and compared with the mild type CGTase, the mutant strains facilitate the production of the AA-2G for glycosyl donors by using maltodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of glycosylated hesperetin
PendingCN110105409AImprove solubilitySolve the problem of decomposition and absorptionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilityDisaccharidase
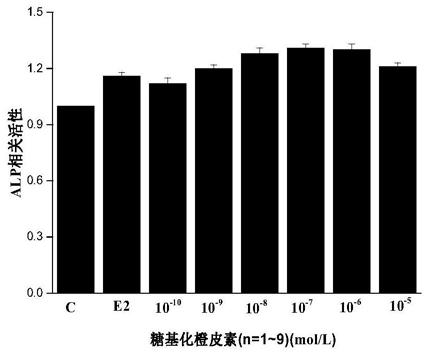
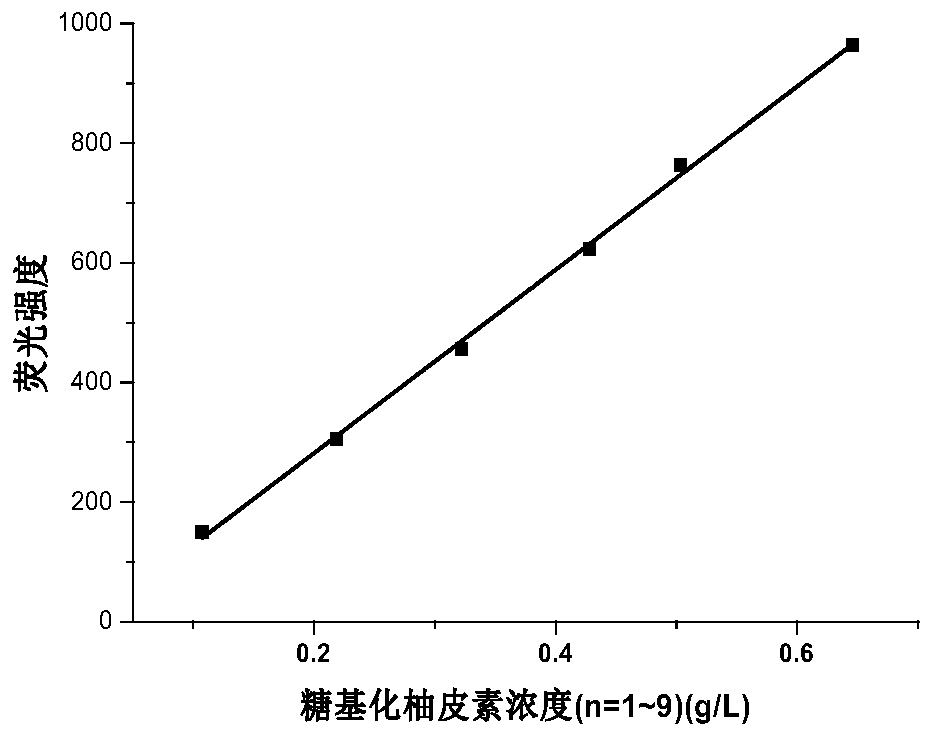
The invention provides a preparation method of glycosylated hesperetin. The preparation method comprises the specific steps that raw materials and a glycosyl donor are put into a reaction buffer solution; after the materials and the solution are mixed evenly, glycosidase and glycosyl transferase are added in a reaction system, wherein the raw materials are hesperidin, hesperetin, an extract or a conversion product of neohesperidin and a derivative thereof. According to the prepared glycosylated hesperetin, 1-9 glycosyl groups are added on a flavonoid parent, so that the solubility of the hesperetin is greatly improved, the problem of poor solubility of the hesperetin is solved, the problems about decomposition and absorption of the hesperetin in the human body are also solved, and the bioavailability of the hesperetin in citrus is greatly improved.
Owner:FOSHAN GOLDEN HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene and application thereof in preparing ginsenoside Ro
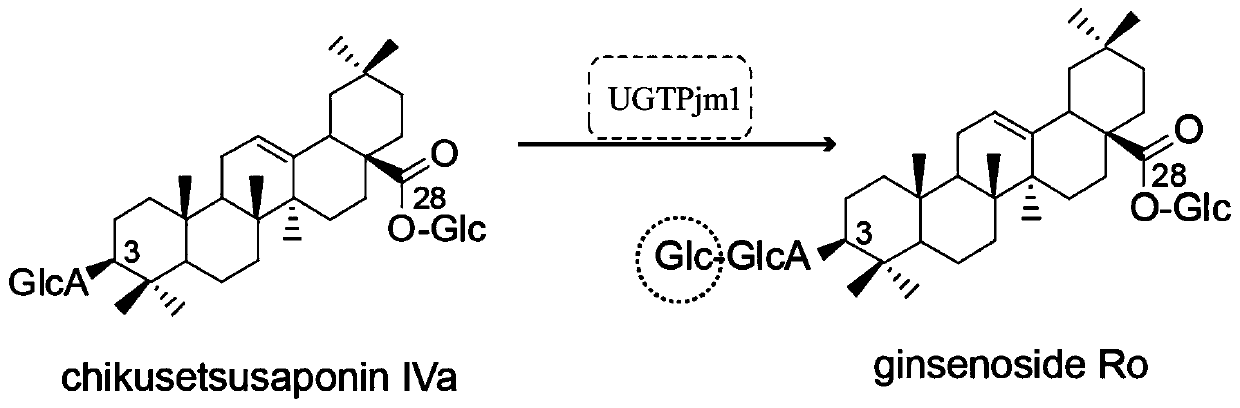
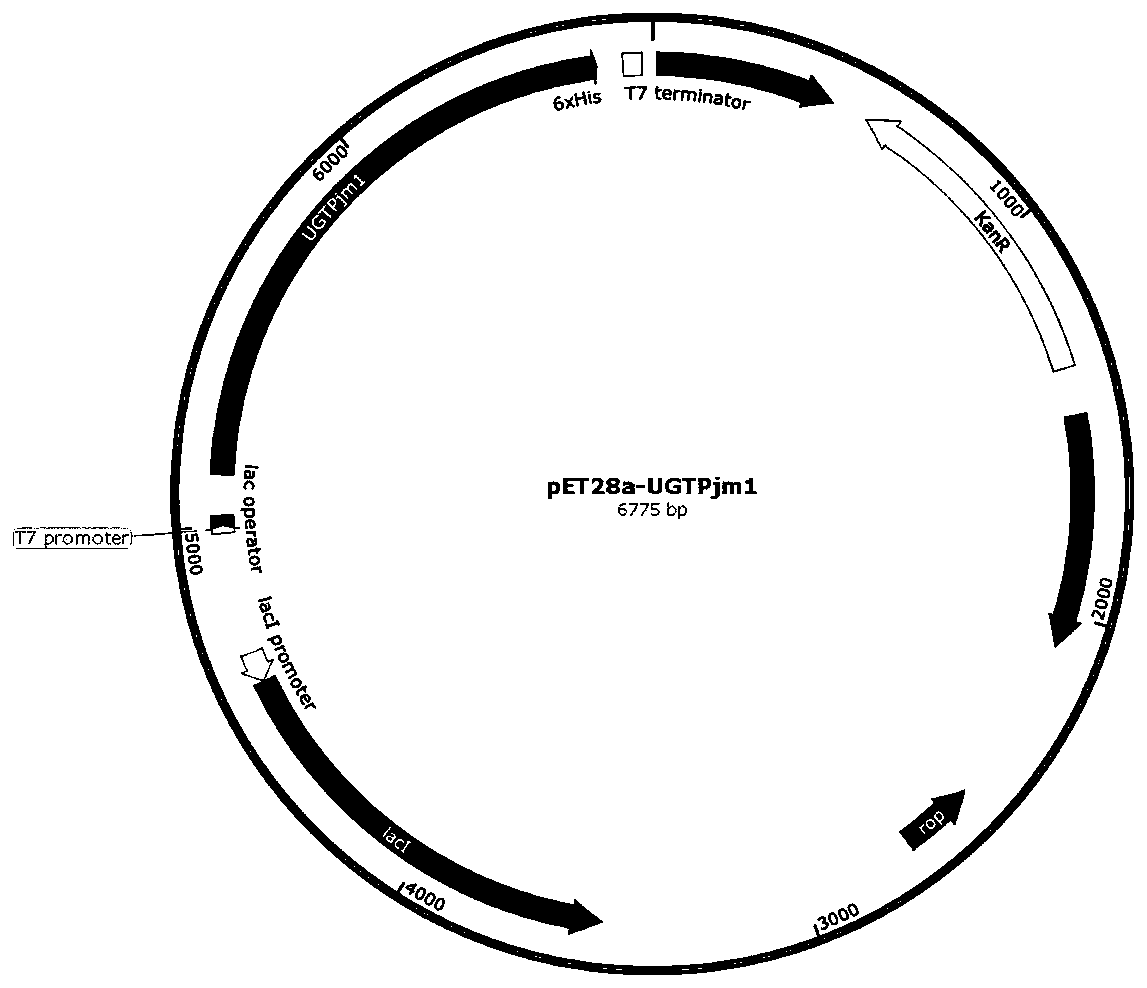
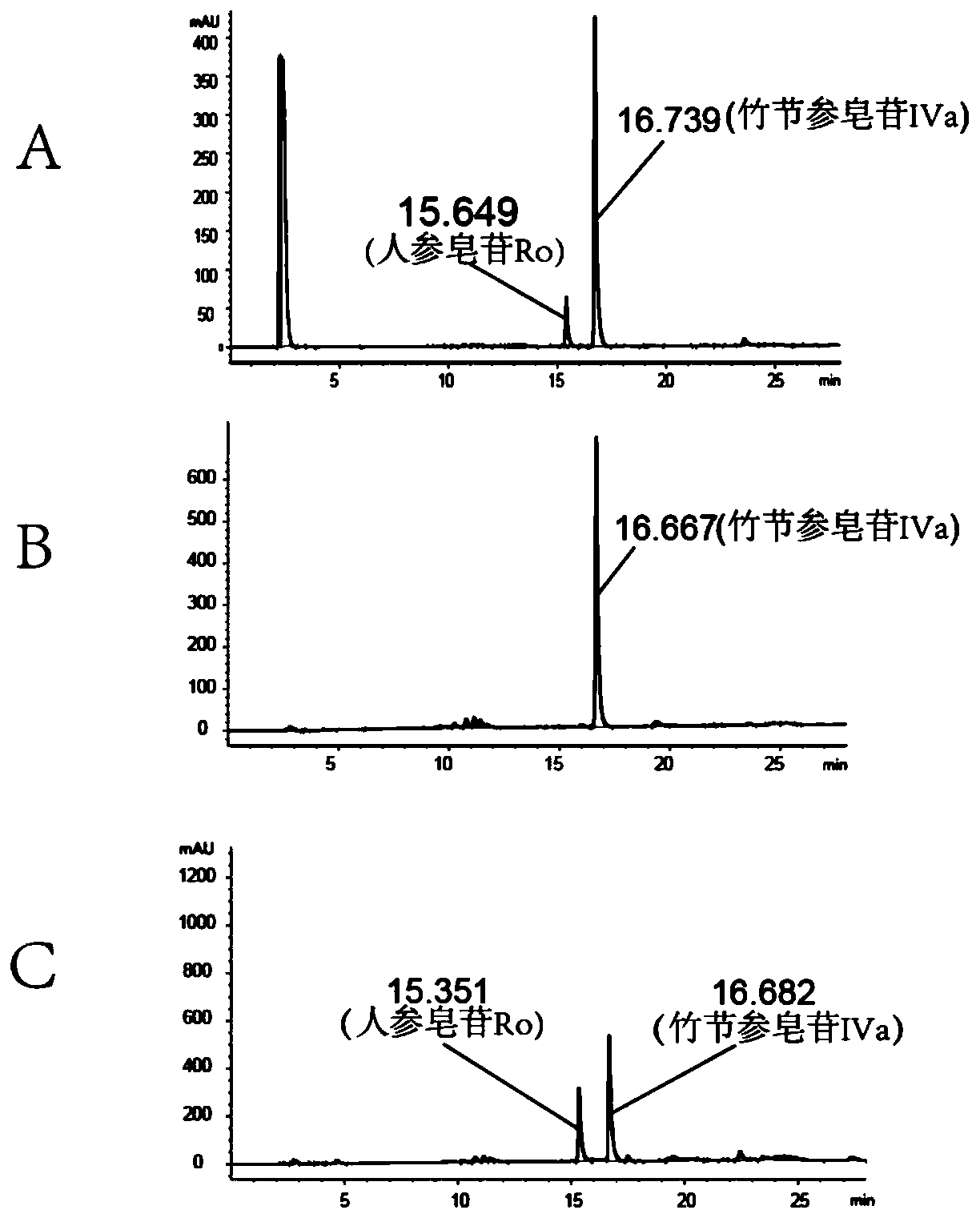
The present invention discloses a panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene and an application thereof in preparing ginsenoside Ro. A nucleotide sequence of the panax japonicus var.major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1. Panax japonicus saponin IVa and a glycosyl donor UDP-glucose are used as raw materials and a glucuronic acid group at a C3 position of the panax japonicus saponin IVa is once further glycosylated to form the ginsenoside Ro catalyzed by panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase encoded by the panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene. The biosynthesis regulation gene UGTPjm1 of the ginsenoside Ro is first identified and successfully verified. By synthesizing the ginsenoside Ro in vitro, management is more convenient, controllability is strong, demand for raw material planting can be reduced, agricultural land is saved, a production product is single, and separation and purification of the ginsenoside Ro in a late stage are facilitated. The panax japonicus var. major glycosyl transferase UGTPjm1 gene is used as a key gene for the biosynthesis of the ginsenoside Ro and can also be used for breeding studies of panax japonicus var. major and other plants.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of clostridium bolteae surface capsular polysaccharide structure derivative
ActiveCN108329362ASimple stepsLow costEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesGlycoconjugateOligosaccharide
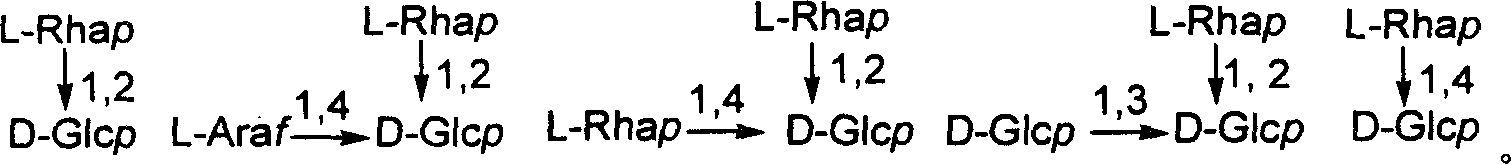
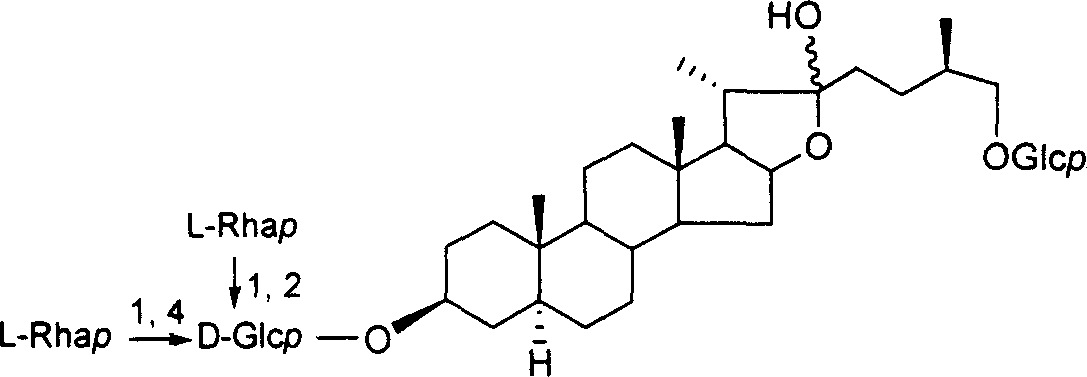
The invention discloses a preparation method of a clostridium bolteae surface capsular polysaccharide structure derivative and belongs to the field of sugar chemistry. The preparation method comprisesthe following steps: taking glucose as a glycosyl donor to obtain a target beta-glycosidic bond; then successfully synthesizing a disaccharide building block through an oxidization-reduction glucoseC-2 site method; then synthesizing a target oligosaccharide structure which takes the disaccharide building block as a repeating unit, such as the gram-positive bacterium surface capsular polysaccharide structure derivative [arrow3]-alpha-D-Manp-(1arrow4)-beta-D-Rhap-(1arrow]5-Linker. A reducing end of decaose is connected with a connecting arm and is used for connecting protein to form a glycoconjugate for carrying out immunology researches. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, time saving, labor saving and low cost; the obtained clostridium bolteae surface capsular polysaccharide structure derivative is possibly used for developing and preparing medicine related to autism.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
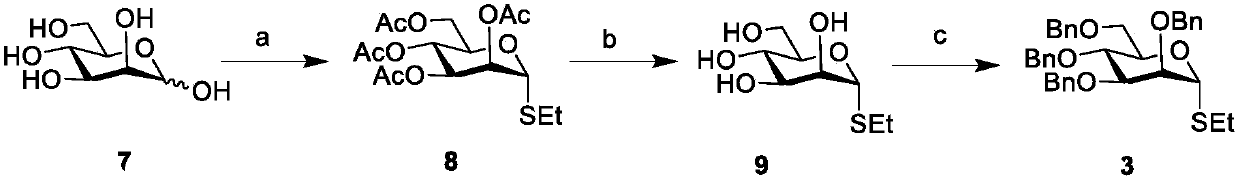
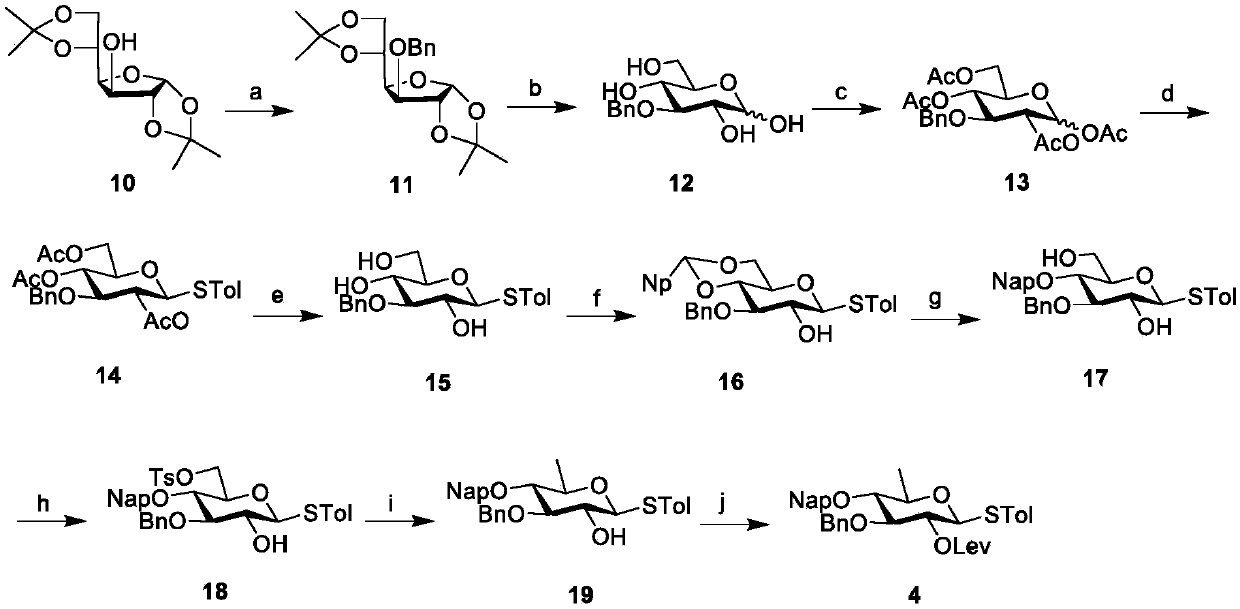
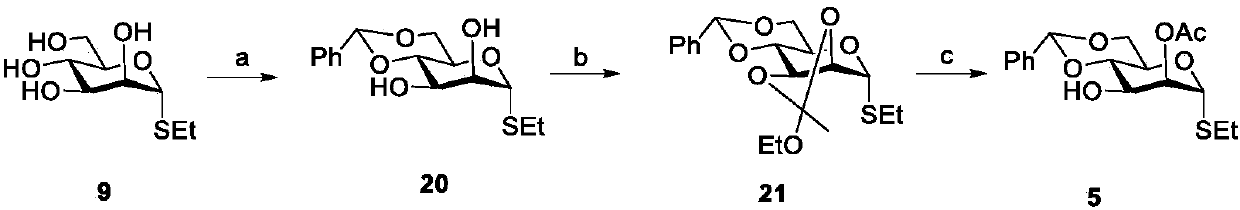
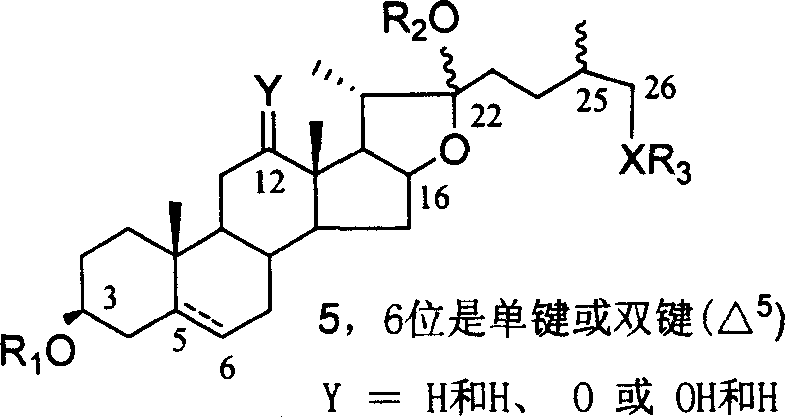
Chemical synthesis method of franosterol saponin and its derivative
The present invention relates to the new process of synthesizing furasteroid saponin and its derivative chemically with C27 helical sterane type sapogenin and various kinds of saccharide as material. The synthesis process includes the following steps: 1. synthesizing completely protected C27 helical steroid saponin through the reaction of C27 helical sterane type sapogenin and acyl radical, alkyl radical or silicon radical protected glycosyl donor; 2. reaction of completely protected helical steroid saponin and oxidant to obtain oxidized product; 3. reaction of oxidized helical steroid saponin and oxyphilic reagent to produce place 26 halogenated saponin derivative; 4. nucleophilic substitution reaction of nucleophilic reagent and the halogenated product to introduce XR3 radical; 5. reducing the place 16 carbonyl radical in saponin selectively with reductant; and 6. eliminating all the protecting radicals to obtain furasteroid saponin and its analog.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and preparation method thereof
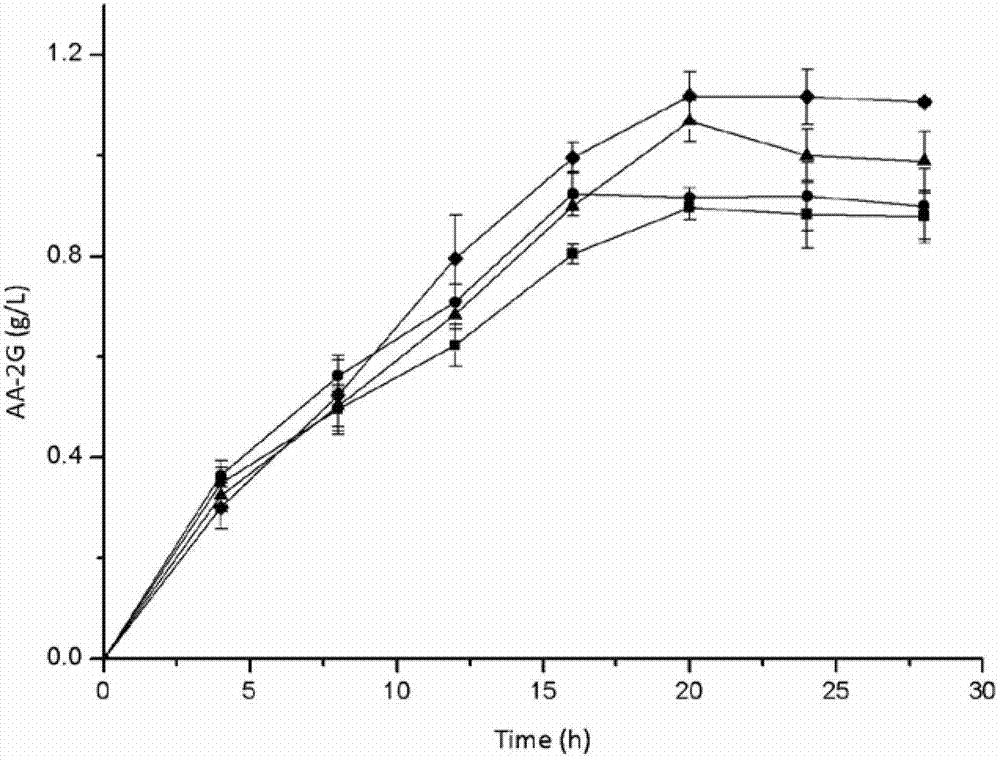
InactiveCN103122341AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesCyclodextrinWild type
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glycosyl transferase with improved maltodextrin substrate specificity and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, for CGTase derived from peanibacillus macerans, lysine at a 47th site, tyrosine at a 89th site, asparaginate at a 94th site and aspartic acid at a 196th site are respectively mutated into leucine K47L, phenylalanine Y89F, praline N94P and tyrosine D196Y, so that AA-2G yields are respectively increased by 30.7%, 10.9%, 10.0% and 31.7%. Complex mutation is carried out on the mutant strains to obtain double mutants namely K47L / Y89F, K47L / N94P, K47L / D196Y, Y89F / N94P, Y89F / D196Y and N94P / D196Y, three-point mutants namely K47L / Y89F / N94P, K47L / Y89F / D196Y, K47L / N94P / D196Y and Y89F / N94P / D196Y and a four-point mutant namely K47L / Y89F / N94P / D196Y. Yields of AA-2G produced by the mutants while maltodextrin is utilized as a glycosyl donor are respectively increased by 42.6%, 11.0%, 37.6%, 43.6%, 43.6%, 41.6%, 44.5%, 50.5%, 20.8%, 35.6% and 64.4%. Compared with the wild type CGTase, the mutants is more beneficial to production of the AA-2G while the maltodextrin is utilized as the glycosyl donor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method and application for glycosylated naringenin
PendingCN110205351AImprove solubilitySolve the problem of decomposition and absorptionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilityDisaccharidase
The present disclosure provides a preparation method for glycosylated naringenin, wherein the preparation method is characterized by particularly comprising the steps: putting raw materials and glycosyl donors into a reaction buffer solution, mixing the feed liquid evenly, and then adding glycosidase and glycosyltransferase into the reaction system, wherein the raw materials are naringin and naringenin extracts or conversion products and derivatives thereof. The glycosylated naringenin prepared by the method can have the solubility of naringenin greatly improved by adding 1-9 glycosyl groups to a flavone matrix, not only solves the problem of poor solubility of naringenin, but also solves the problem of decomposition and absorption of naringenin in a human body, and greatly improves the bioavailability of naringenin.
Owner:FOSHAN GOLDEN HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Flavones-6-hydroxylase and application thereof to scutellarin synthesis
The invention provides flavones-6-hydroxylase and application thereof to scutellarin synthesis and particularly provides flavones-6-hydroxylase which is capable of catalyzing apigenin 6-coordinate hydroxylation reaction to obtain scutellarein. In addition, the invention provides a method for preparing the scutellarein into scutellarin by adoption of glycosylated transferases and glycosyl donors.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
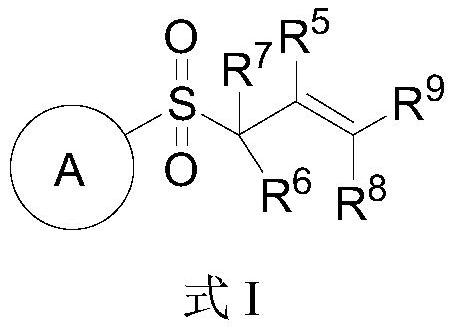
Novel glycosyl donor and thioglycoside compound, and preparation methods of thioglycoside compound
InactiveCN112279880AEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesPhoto catalyticCombinatorial chemistry
The invention provides a glycosyl donor shown as a formula I and a preparation method thereof, and further provides a thioglycoside compound shown as a formula III and a preparation method thereof. The glycosyl donor provided by the invention is novel in structure and simple in preparation method. With the glucosyl donor as a raw material, the thioglycoside compound with a special alpha configuration is prepared by utilizing a photocatalytic free radical reaction, and the preparation method is simple, mild in reaction conditions and high in yield, and has very good application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing stevioside
ActiveCN109021038AHighly economical synthesisSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationRoom temperatureProtecting group
The invention provides a convergent stevioside preparing method. The method comprises the following steps: a stevioside receptor, base and a phase transfer catalyst are dissolved in a solvent, and arereacted at room temperature for 5 to 60 minutes, a glycosyl donor 2 is added, a reaction is carried out at 40 to 60 DEG C for 10 to 18 hours, a glycosidation product is obtained with a yield being 80to 85%, and a protecting group is removed to obtain high-purity compounds Red A, Red D and Red M. The method provides a succinctly implementable strategy to facilitate the large acquisition of stevioside, especially stevioside with low content.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for improving beta-glucosidic bond stereoselectivity through bis(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) reagent activation glycosylation reaction
InactiveCN105541933AReduce dosageMild reaction conditionsSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationLeaving groupBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for improving beta-glucosidic bond stereoselectivity through a bis(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) reagent activation glycosylation reaction. According to the method, under the action of a catalytic amount of bis(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) reagent, a glycosyl donor with a leaving group being the trichloroacetic imidic acid ester group or acetylenic acid ester group is subjected to coupling with different glycosyl receptors, the using amount of the bis(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) reagent is small, the reaction condition is mild, the product yield is high, and a beta-glycosylation product can be obtained in a high-stereoselectivity mode.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Maltose substrate specificity improved cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and preparation method thereof
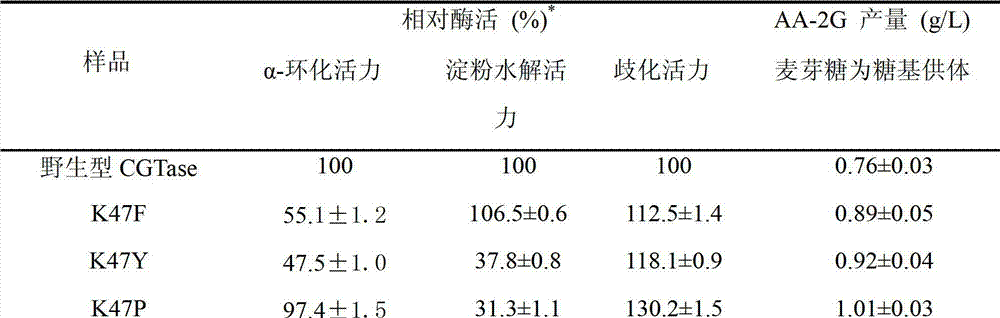
ActiveCN102965353AIncreased substrate specificityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesWild typeTyrosine
The invention discloses maltose substrate specificity improved cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The 47th lysine (Lys) of CGTase of P.macerans strain HFB05-01 (CTCC NO:M208063) is respectively replaced by phenylalanine (Phe), tyrosine (Tyr) and proline (Pro), so that the output of AA-2G is respectively improved by 17.1%, 22.1% and 32.9%. Compared with the wild CGTase, the mutant strains are more conductive to producing AA-2G for glycosyl donors by utilizing maltose, so that important industrial application prospect is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
N glycosyl transferase AaNGT and application thereof
InactiveCN107034202ATransferasesPeptide preparation methodsActinobacillus pleuropneumoniaeGlycopeptide
The invention discloses a N glycosyl transferase AaNGT. An amino acid sequence thereof is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention also discloses an application of the N glycosyl transferase AaNGT in polypeptide galactosylated modification. AaNGT is capable of supplying a simple and convenient method for the forming of glycopeptide; the capacity of AaNGT for utilizing UDP-Glc is obviously higher than that of the reported N glycosyl transferase ApNGT which is sourced from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae; the AaNGT also can transfer the special glycosyl donor UDP-GlcNH2 to the polypeptide containing N glycosylation sites, and then the other glycosyl transferases can be utilized to convert the GlcNH2 into the GlcNAc so as to form natural N glycan linking, so that a new method is supplied for the development of the glycoprotein vaccine. The invention is beneficial to the AaNGT becoming a protein modified tool enzyme.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of industrial quick production and preparation of glucosyl stevioside mixture
The invention provides a method of industrial quick production and preparation of a glucosyl stevioside mixture. The method comprises the following steps of: step I, performing enzymatic reaction: dissolving oxidized starch and stevioside, adding CGT (cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase) for the enzymatic reaction at 40-55 DEG C for 7-12h, and performing enzyme deactivation to finish the reaction, step II, performing decoloration ad deodorization, and step III, performing filtration, concentration and drying to form a product. The method takes the oxidized starch as a glycosyl donor; technical steps are reduced; a transglycosylation effect is improved; and the method is simple in technology and easy to operate, reduces requirements of industrialization on equipment and energy consumption at the same time, shortens working hours, lowers the cost and increases unit production capacity.
Owner:GUILIN NATURAL INGREDIENTS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com