Artificial site-directed mutant of paddy rice starch branching enzyme SBE3 gene and applications thereof
A technology of starch branching enzyme and rice, applied in the direction of genetic engineering, application, hydrolytic enzyme, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Selection of CRISPR / Cas9 Modified Targets
[0041] The entire genome sequence of SBE3 was scanned. The SBE3 gene has a total of 22 exons. The target sequence was located on the exon and as close as possible to the upstream as the selection criteria, and the selection of the target sequence was limited to the first 10 exons. It is required that the target sequence has an enzyme cleavage site to facilitate subsequent preliminary detection of mutation efficiency through enzyme cleavage.
[0042] Finally, after exclusion, it was determined that 3 target sequences were pre-selected, namely:
[0043] GTATCGAGAATGGGCTCCCG located in exon 5 of SBE3 gene (including SmaI restriction site);
[0044] GCAGGAGAAATCCCATACAA located in exon 8 of the SBE3 gene (including the Van91I / BseLI restriction site); and
[0045] TTCCAAAGAATCAAAAAAGCT located in exon 10 of the SBE3 gene (including the HinIII restriction site).
[0046] Since the exon 10 contains HindIII in addition ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 CISPR / Cas9 vector construction and transgenesis
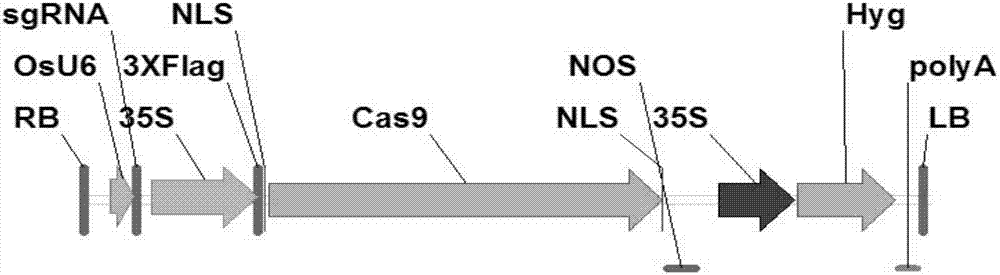
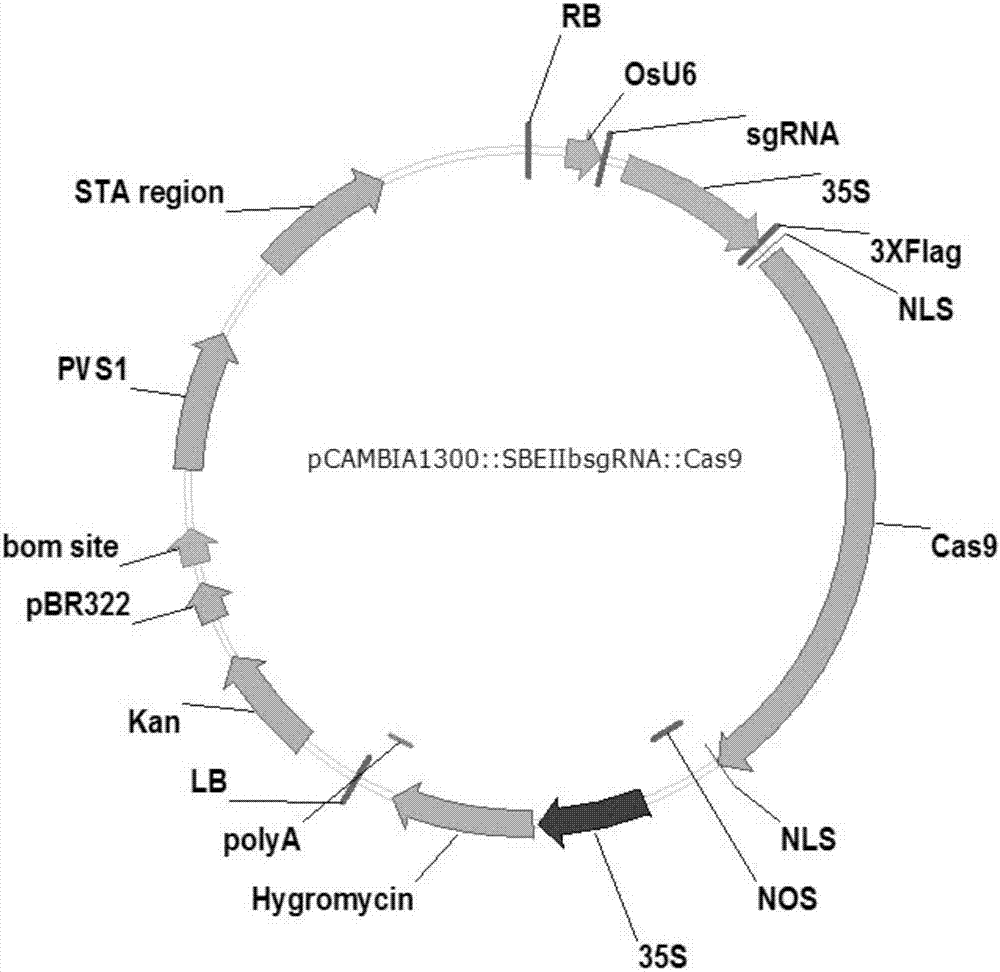
[0048] (1) Targeting sequence in exon 8 of SBE3 gene
[0049] The nucleotide sequence of exon 8 in the wild-type rice starch branching enzyme SBE3 gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The CRISPR / Cas9 modification target length is 20bp, located at bases 70-89 in exon 8, and the modification target sequence is GCAGGAGAAATCCCATACAA. The following oligonucleotides were synthesized against this targeting sequence:
[0050] SEQ ID NO.5 (SBE3-F3):
[0051] 5'-GTGTGCAGGAGAAATCCCATACAA-3'
[0052] SEQ ID NO.6(SBE3-R3):
[0053] 5'-AAACTTGTATGGGATTTCTCCTGC-3'
[0054] The sgRNA carrier OsU6-SK plasmid vector (see Zhengyan Feng et al., Efficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR / Cas system, Cell Research (2013) 23:1229–1232; from Zhu Health Lab) was digested with BbsI, and the gel was carried out. Recycle. Add the synthesized upstream and downstream primers F3 and R3 into ddHO, dilute to 10 μmol mother so...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Obtaining of CRISPR / Cas9T0 mutants
[0066] Yang Ruifang et al. used Jiangtangdao No. 1 as a high-RS gene donor material to hybridize with Miryang 23, Xiushui 123, and Hudao 55 with higher yields, and used the chalky grain characteristics of the early generations of the three hybrid populations, amylose Content (Amylasecontent, AC) and functional markers (CAPS / SpeI) for high RS rice assisted selection breeding. The research results show that the chalkiness of the grain is highly correlated with the RS content (Yang Ruifang et al., Molecular marker-assisted selection for breeding new rice varieties with high resistance starch, Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 29(12): 2259-2267 ).
[0067] Therefore, the T0 generation plants obtained in Example 1 are planted in individual plants, and the leaves of the individual plants are preserved for subsequent extraction of DNA, and the seeds are correspondingly harvested. By observing the chalkiness of T1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com