Modification method for improving slow digestion performance of starch
A slow-digesting, starch technology, applied in fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of single starch branching enzyme modification treatment conditions and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Effect of Two-stage Modification on Slowly Digestible Starch Content in Starch
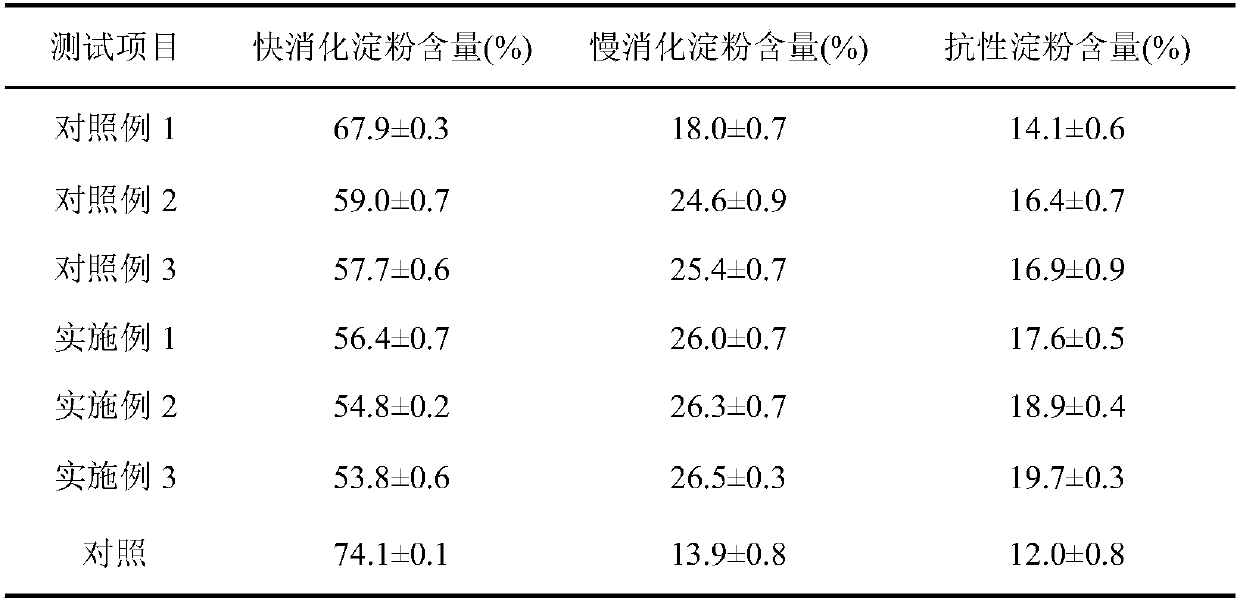
[0038] Dissolve cornstarch in water to prepare 5% starch milk, preheat at 50°C for 10min, add 30U / g starch branching enzyme, treat at 50°C for 10h, gelatinize in boiling water bath for 30min, preheat at 50°C for 10min Finally, add 30 U / g starch branching enzyme, treat at 50°C for 6 hours, stop the reaction in a boiling water bath, and freeze-dry to obtain modified starch. The results of the modified starch digestibility test are shown in Table 1.
[0039] The results of the reaction show that the two-stage modification with granular cornstarch and gelatinized cornstarch as substrates respectively, the content of slow-digestible starch in the prepared modified starch reaches 26.0%, which is 87.0% higher than that of the control. Example 3 (gelatinized cornstarch as substrate) further increased by 2.4%; fast digestible starch content increased by 23.9% compared to control example ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Effect of two-stage modification on slow-digestible starch content in starch
[0041]Dissolve cornstarch in water to prepare 5% starch milk, preheat at 50°C for 10min, add 30U / g starch branching enzyme, treat at 50°C for 10h, gelatinize in boiling water bath for 30min, preheat at 50°C for 10min Finally, add 30 U / g starch branching enzyme, treat at 50°C for 8 hours, stop the reaction in a boiling water bath, and freeze-dry to obtain modified starch. The results of the modified starch digestibility test are shown in Table 1.
[0042] The results of the reaction showed that cornstarch was modified using a two-stage modification strategy, and the content of fast-digestible starch in the prepared modified starch reached 54.8%, which was further reduced by 5.0% compared with the control example 3 (gelatinized cornstarch was the substrate). %; Slowly digestible starch content reaches 26.3%, which is further increased by 3.5% compared with control example 3 (gelatin...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Effect of Two-stage Modification on Slowly Digestible Starch Content in Starch
[0044] Dissolve cornstarch in water to prepare 5% starch milk, preheat at 50°C for 10min, add 30U / g starch branching enzyme, treat at 50°C for 10h, gelatinize in boiling water bath for 30min, preheat at 50°C for 10min Finally, add 30 U / g starch branching enzyme, treat at 50° C. for 10 h, stop the reaction in a boiling water bath, and freeze-dry to obtain modified starch. The results of the modified starch digestibility test are shown in Table 1.
[0045] The results of the reaction show that cornstarch was modified using a two-stage modification strategy, and the content of fast-digestible starch in the prepared modified starch reached 53.8%, which was further reduced by 6.8% compared with the control example 3 (gelatinized cornstarch was the substrate). %; Slowly digestible starch content reaches 26.5%, further increased by 4.3% compared with control example 3 (gelatinized corn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com