Patents
Literature
392 results about "Starch granule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
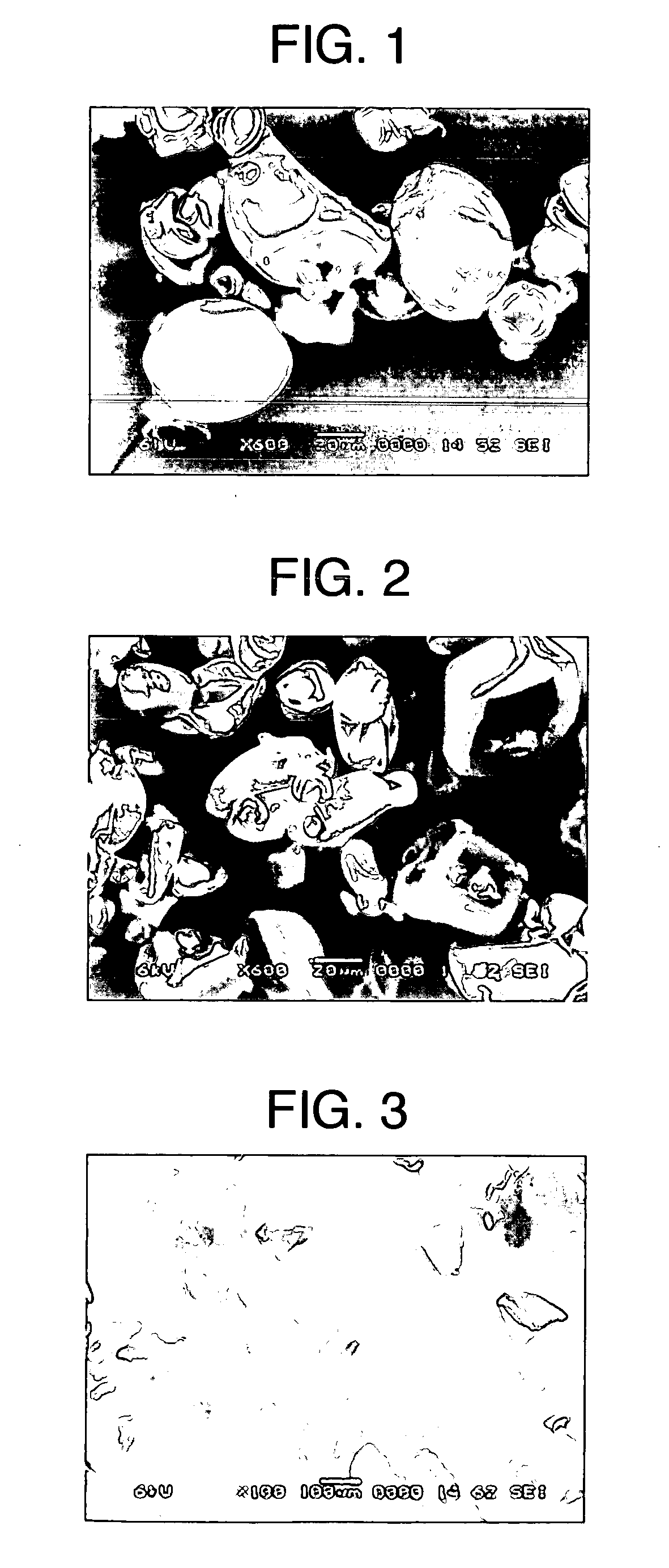
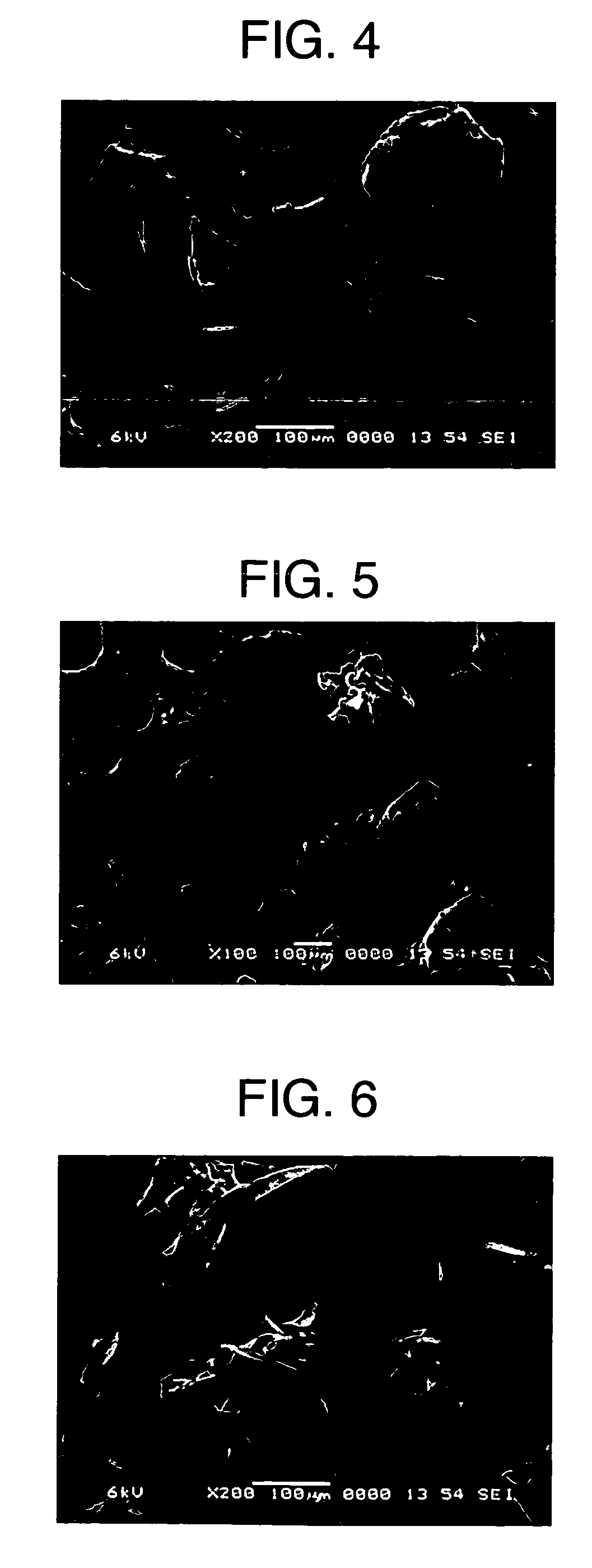
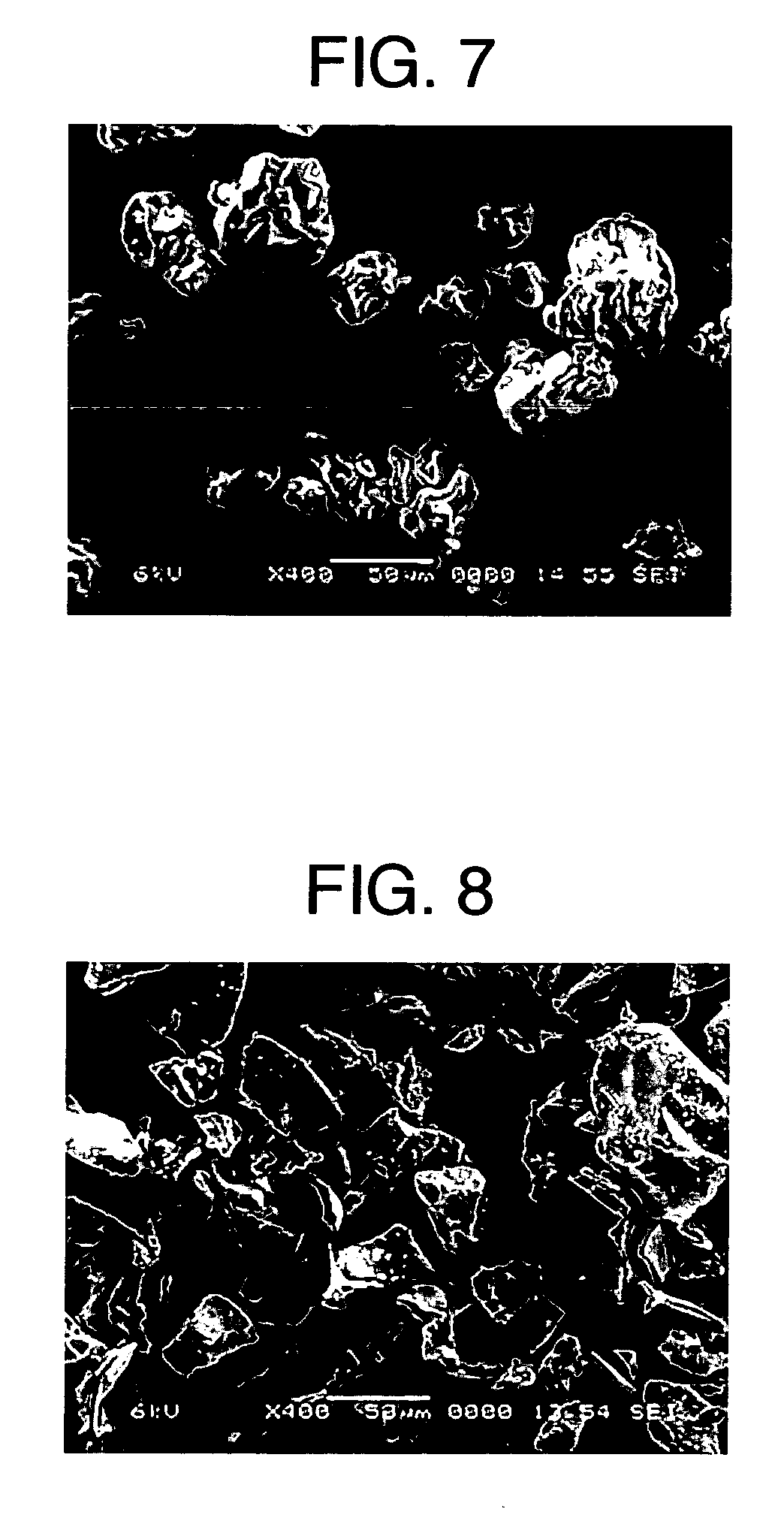
Starch granules vary in size (1 to 100 microns [μ m] in diameter) and shape, which are characteristic of their specific plant origin. Starch is the major energy reserve for plants; it is located mainly in the seeds, roots or tubers, stem pith, and fruit.
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based compositions
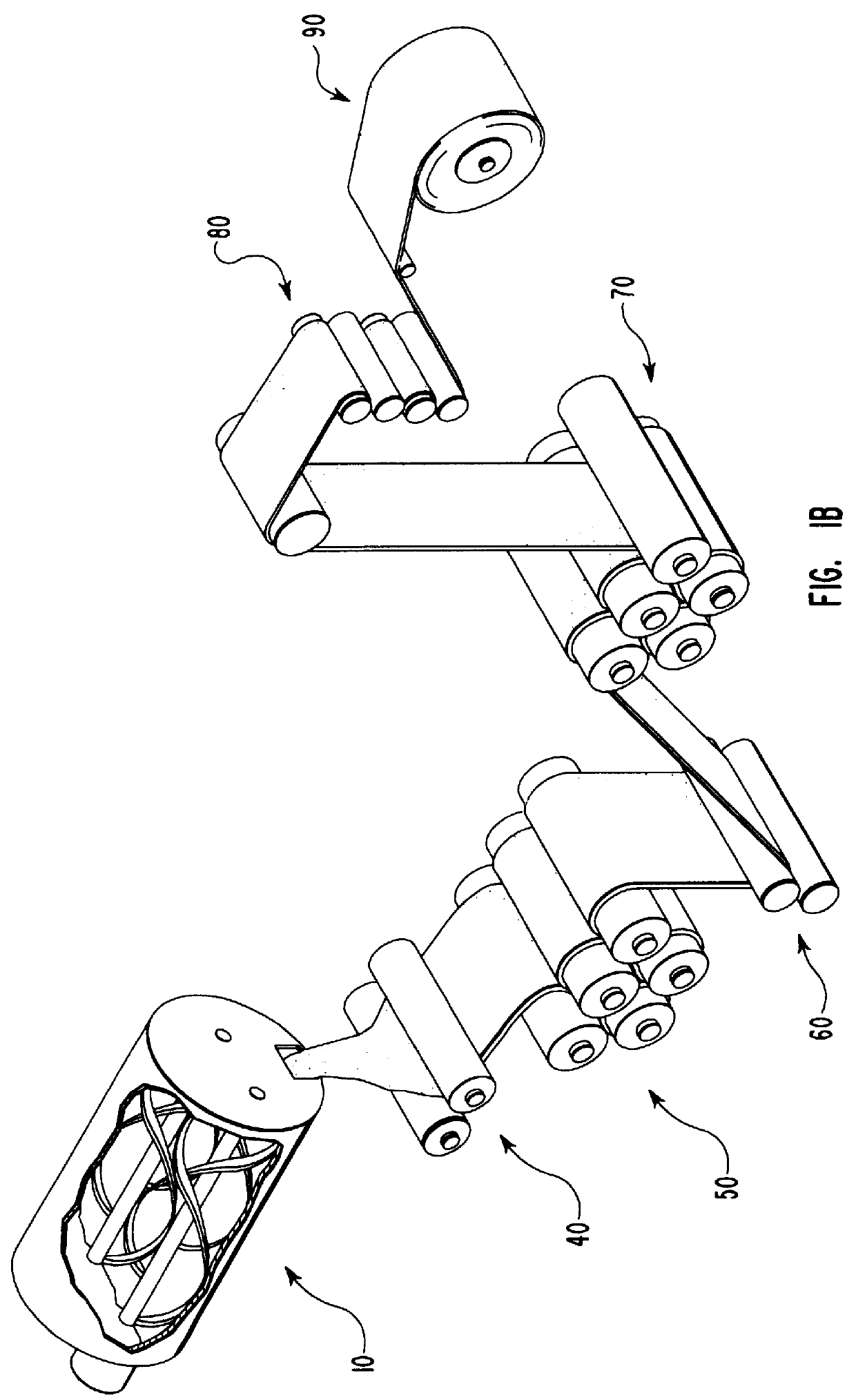
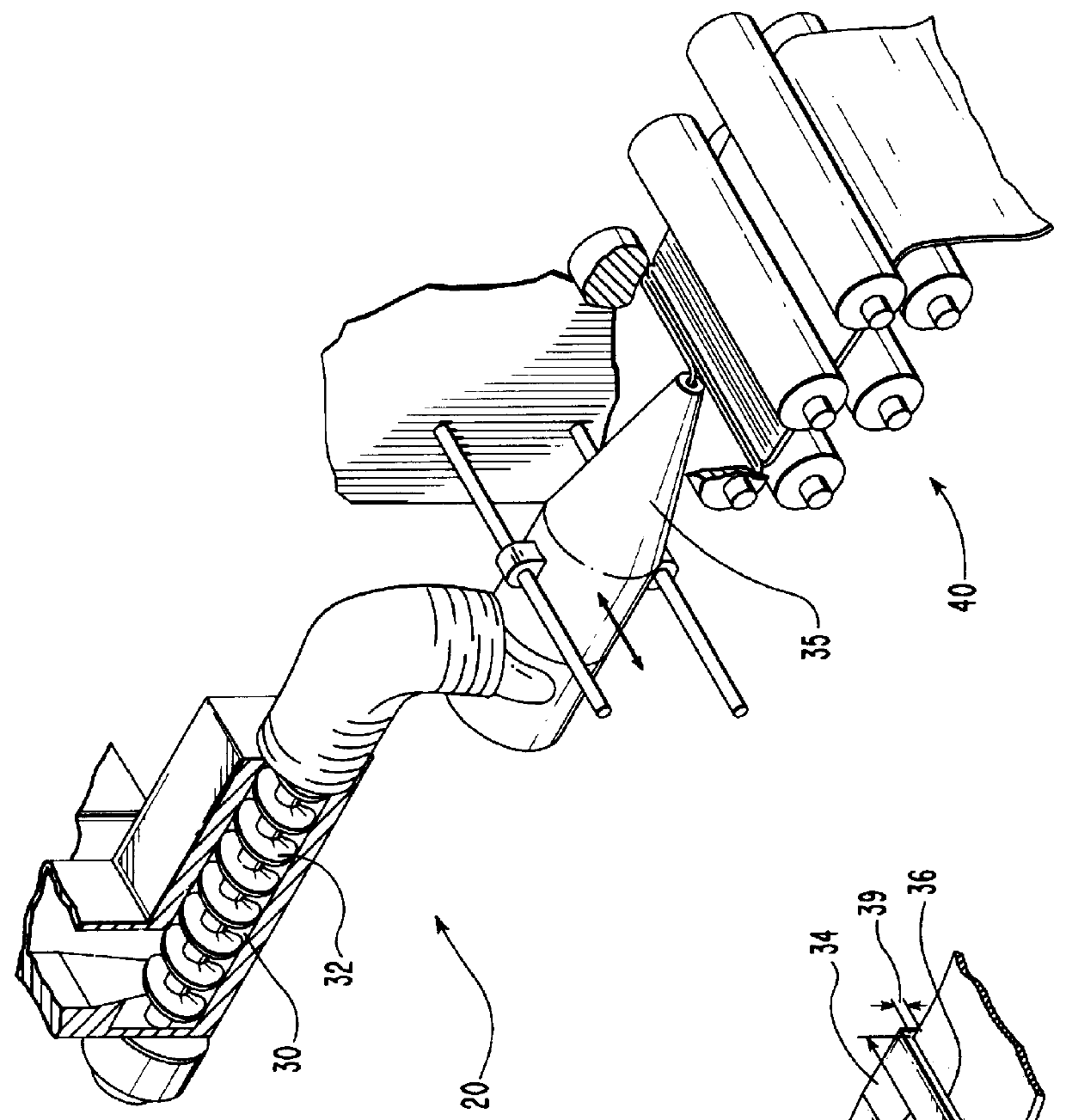
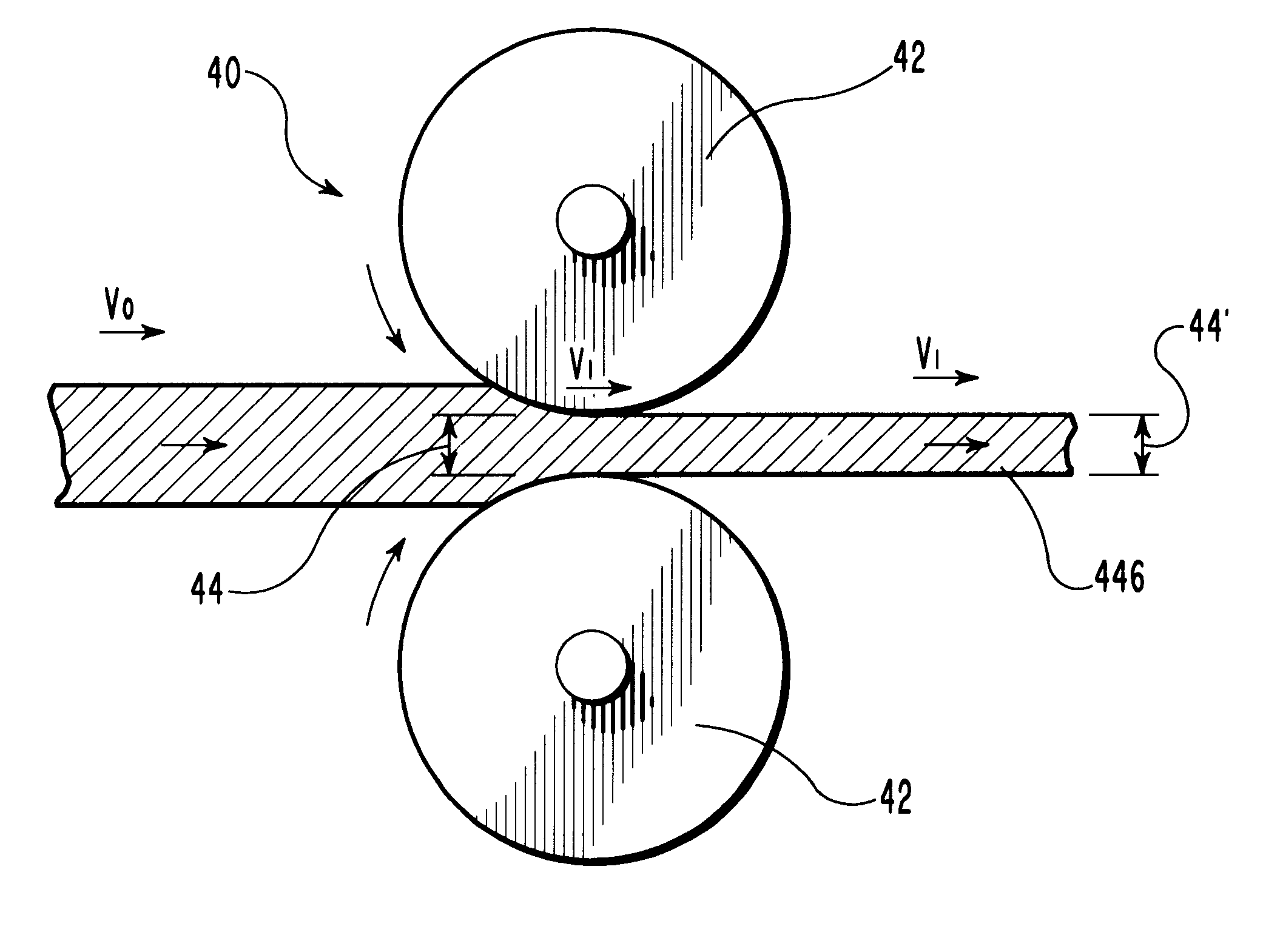
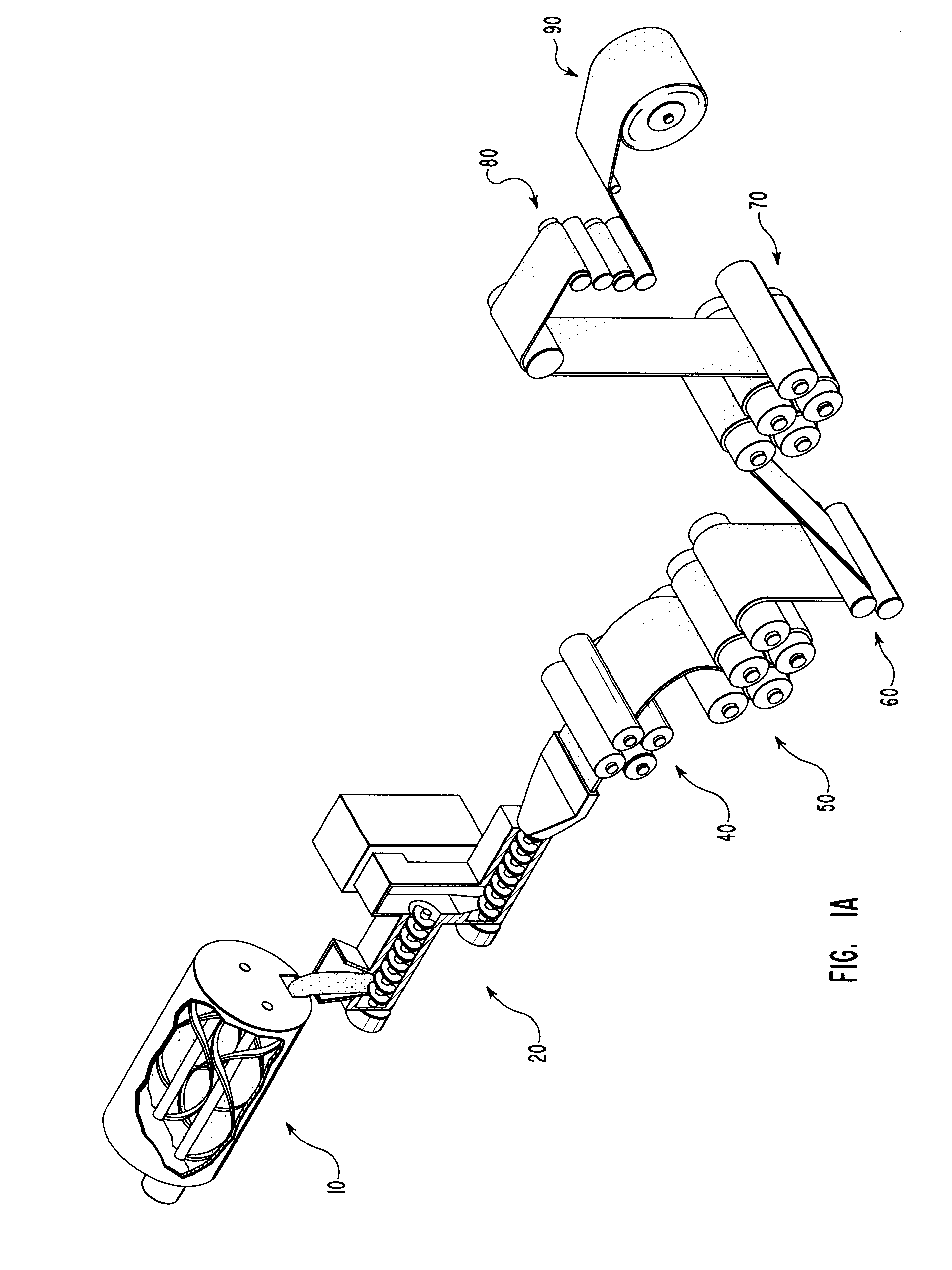
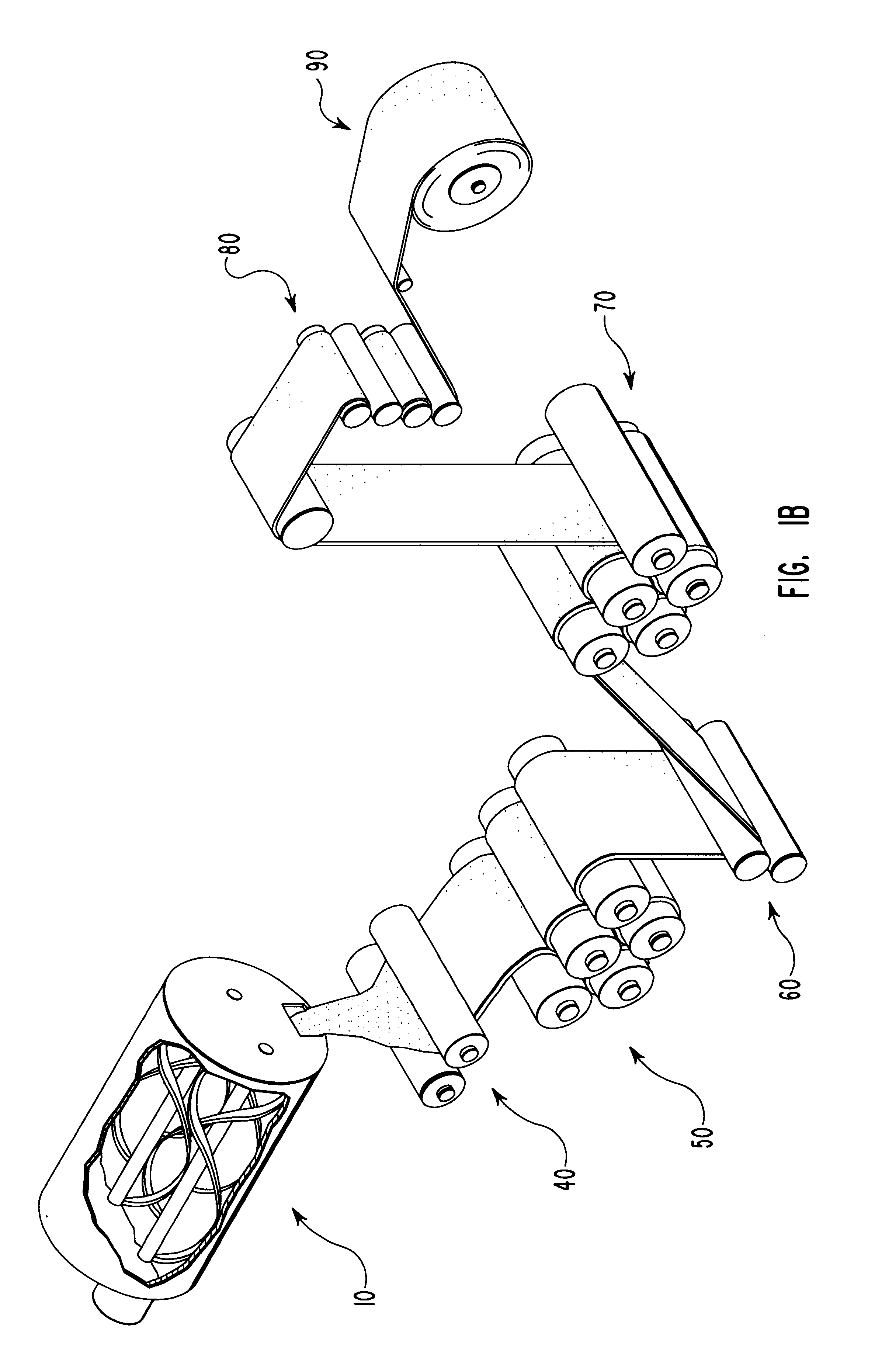
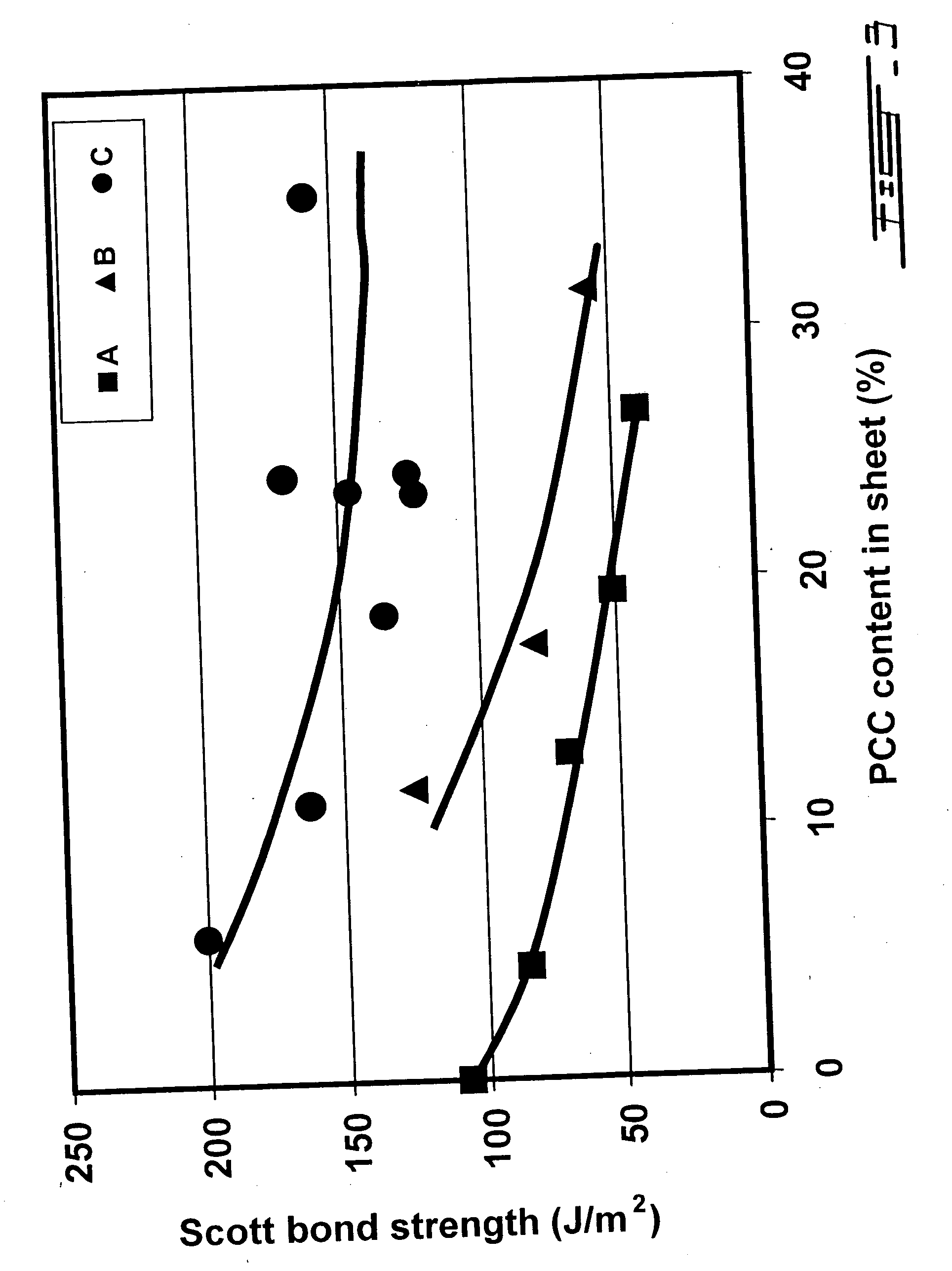
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Sheets having a starch-based binding matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix, optionally reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, a cellulosic ether, optionally fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the cellulosic ether to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and cellulosic ether form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based sheets
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Swollen starch-latex compositions for use in papermaking
InactiveUS7074845B2High retention rateEasy to drainPigmenting treatmentNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaperboardPapermaking
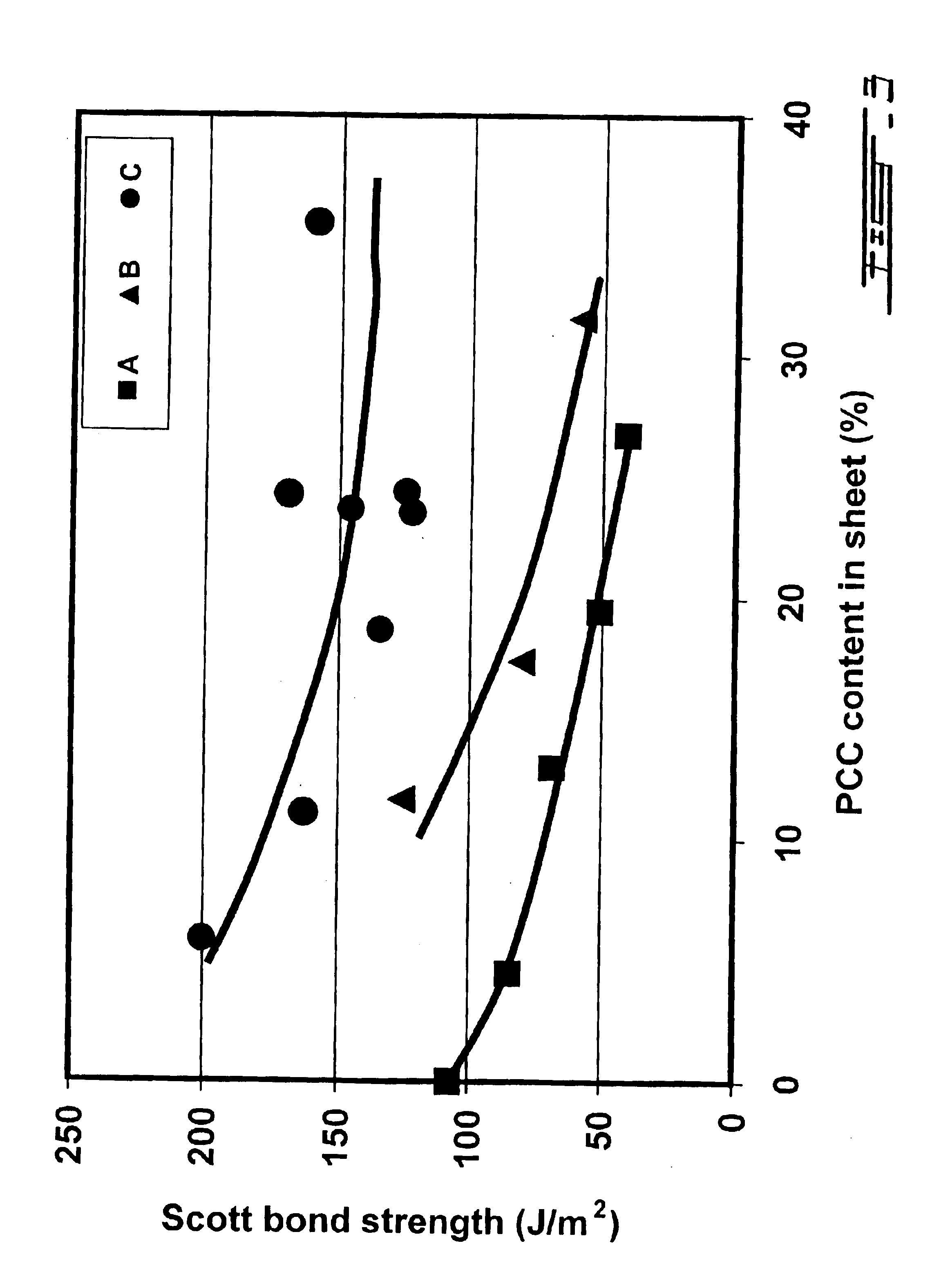
A novel filler treatment comprising the preparation of swollen starch-latex compositions, prepared in the presence or absence of co-additives, and the addition of the said composition to a filler suspension, has been developed. Use of the treated filler during papermaking improves filler retention and produces filled papers where addition of the filler has only a minimal negative effect on strength properties. The swollen starch-latex compositions can be prepared in a batch or jet cooker, or by mixing with hot water under controlled conditions (i.e., temperature, pH, mixing, mixing time) in order to make the starch granules swell sufficiently to improve their properties as a filler additive but avoiding excess swelling leading to their rupture. The swollen starch-latex composition is then rapidly mixed with the filler slurry, preferably in a static mixer, and added to the papermaking furnish at a point prior to the headbox of the paper machine. The starch-latex composition can be used with wood-free or wood-containing furnishes. The treated filler is easily retained in the web during papermaking, improves drainage, and gives sheets having good formation. Sheets made with the treated fillers have higher bonding and tensile strengths than sheets produced using filler treated with either swollen starch alone or latex alone. Retention and drainage are further improved when conventional retention aid chemicals are added to the furnish containing the treated filler. The use of swollen starch-latex compositions could allow the papermaker to increase the filler content of the paper without sacrificing dry strength properties or increasing the amount, and hence the cost, of the retention aid added. The combination of swollen starch and latex could be used as furnish additives in the manufacture of both filled grades and grades that contain no filler such as sack papers and paperboard products.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Cosmetic composition
A finisher composition that provides improved look and feel benefits to an underlying skin care product. The finisher composition is an oil-in-water emulsion that includes from 10 to 25 wt % of substantially spherical starch particles having a mean particle size of from 5 to 30 microns. The oil phase of the finisher includes a non-volatile oil present at an amount to provide a weight ratio of non-volatile oil to starch particles of from 1:10 to 3:2. The aqueous phase of the finisher includes from 20 to 85 wt % of water.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Microparticles
A process for producing parenterally administrable microparticles, in which an at least 20% by weight aqueous solution of purified amylopectin-based starch of reduced molecular weight is prepared, the solution is combined with biologically active substance, an emulsion of starch droplets is formed in an outer phase of polymer solution, the starch droplets are made to gel, and the gelled starch particles are dried. A release-controlling shell is optionally also applied to the particles. Microparticles which essentially consist of said starch, have an amino acid content of less than 50 mug and have no covalent chemical cross-linking.
Owner:PACIRA PHARMA INC
Starch branching enzymes
InactiveUS7041484B1Reduce concentrationInhibitory activitySugar derivativesTransferasesBiotechnologyStarch granule
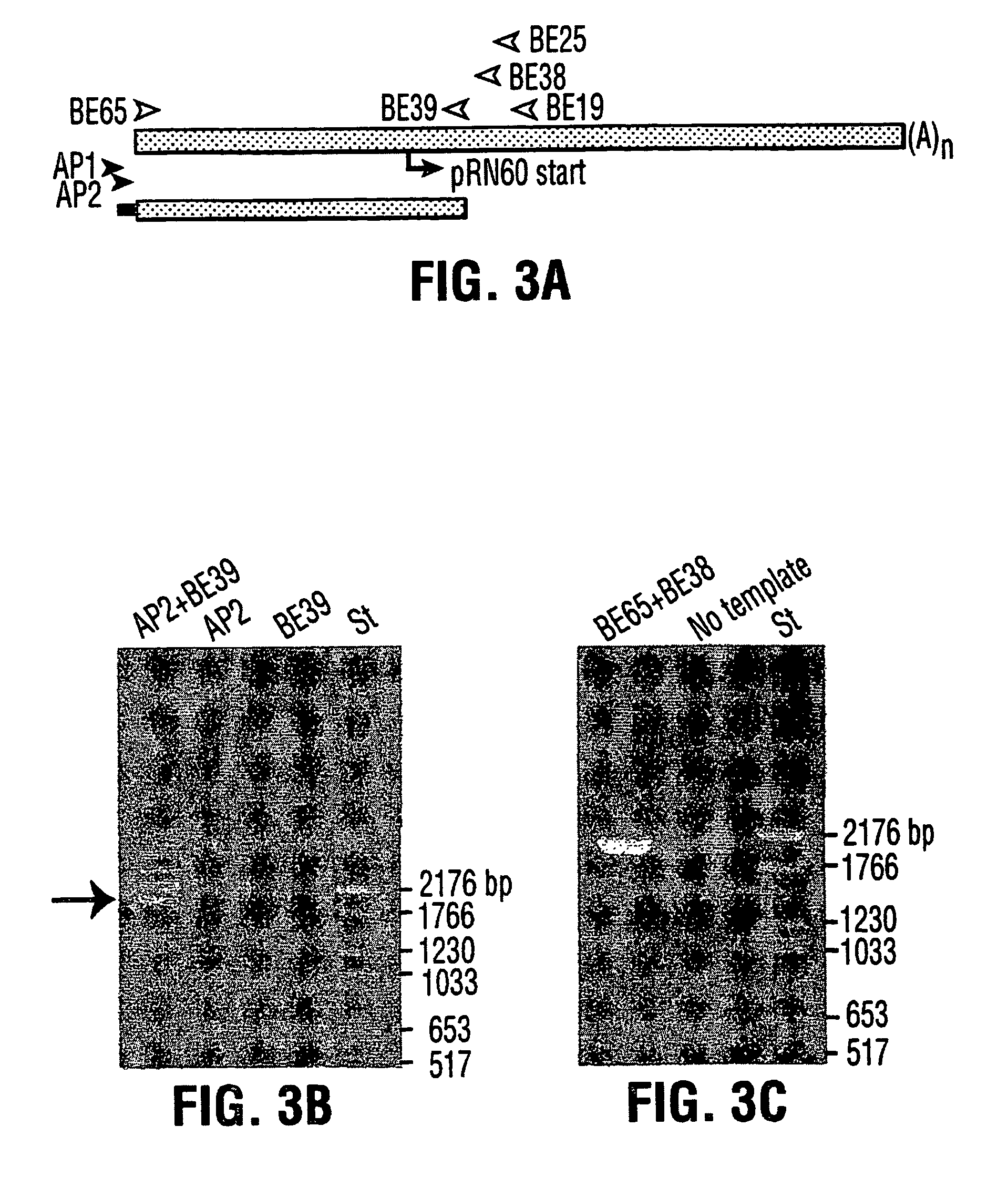
The invention provides a novel starch branching enzyme that is bound to A-type starch granules in wheat, barley, rye or triticale. The enzyme is not substantially associated with B-type starch granules. A cDNA sequence encoding an isoform of the enzyme has been isolated from the wheat cultivar Fielder and deduced amino acid sequence has been determined.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material and a preparation method thereof. The material is applied to the bone surface or bone section of a human body or an animal, and is characterized in that the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material is modified starch prepared by modifying natural starch serving as a raw material, and comprises one or more than two of modified starch granules, modified starch sponges, modified starch films, modified starch foams or modified starch glues, wherein the molecular weight of the modified starch is 15,000 to 10,000,000, and the water absorption rate is 1 to 100 times; in the natural starch serving as the raw material, the content of the amylopectin is at least no less than 70 percent of the total amount of the raw material. The invention fulfills the aim of stopping bleeding through direct spraying, daubing and pasting the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material to touch the bone bleeding surface of wound; meanwhile, the biocompatible bleed-stopping and bone healing promoting material has a function of promoting bone healing, and can be used in the bleed stopping in the sternotomy of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, spinal surgeries and joint surgeries of orthopedics department, Craniotomy and maxillo-facial surgery and the bleed stopping in the process of trauma care.
Owner:纪欣
Fabric treatment composition
ActiveUS9347022B1Fibre treatmentNon-surface-active detergent compositionsPolyethylene glycolStarch granule
A composition of a plurality of homogeneously structured particles. The particles include polyethylene glycol, perfume, and starch granules and each has a mass between about 0.95 mg and about 5 grams.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Macroporous and microporous hybrid starch granule and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101531779AHigh specific surface areaHigh selective adsorption capacityTobacco smoke filtersPolymer scienceCyclodextrin
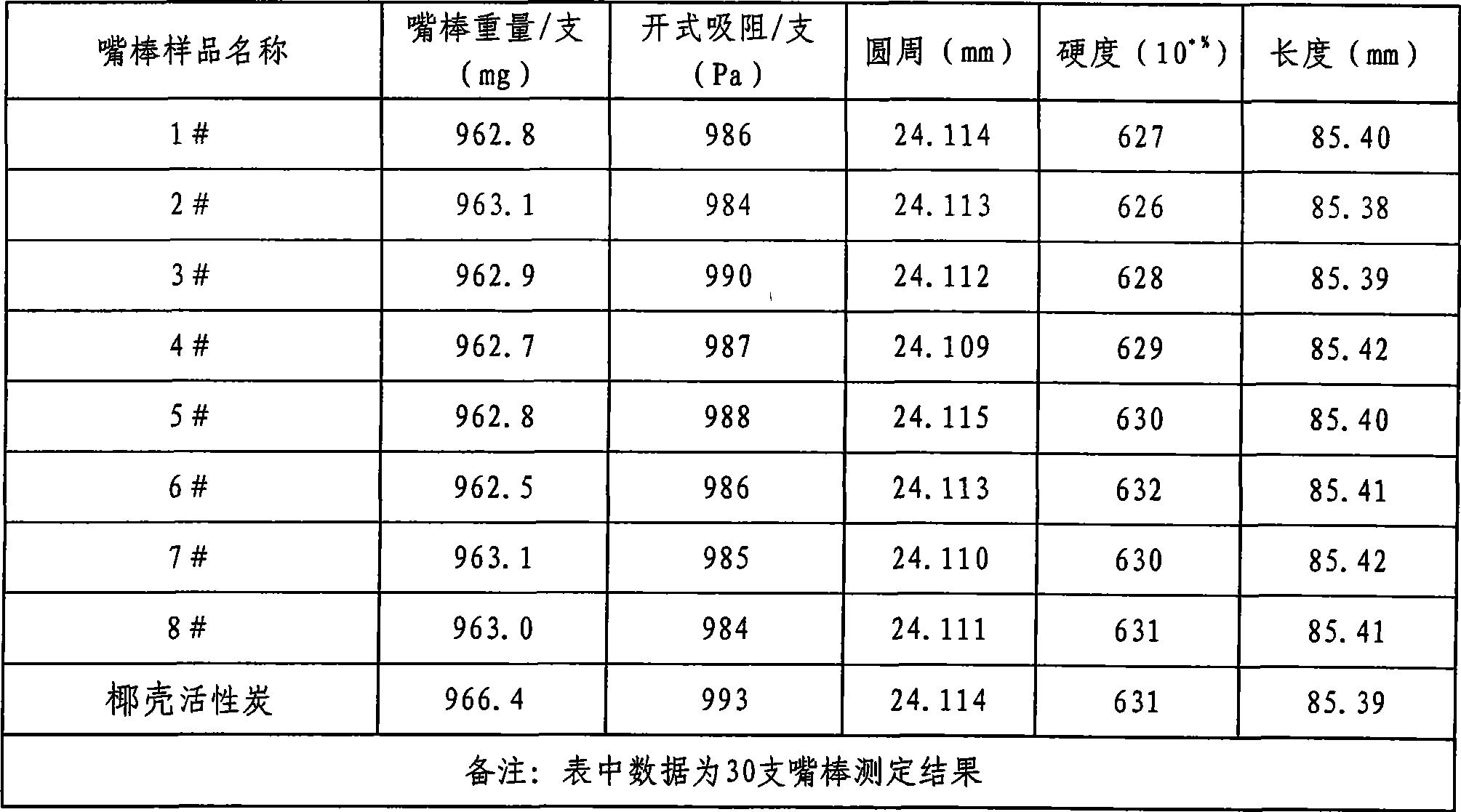
The invention discloses a macroporous and microporous hybrid starch granule and a preparation method and an application thereof; wherein, the method comprises the following steps: mixing the macroporous starch with pore diameter ranging from 0.5umm to 1.5umm with microporous starch with pore diameter ranging from 6A degree to 6.5 A degree according to the weight proportion of 0.5-4;1; then wetting, microwave drying, crashing and sifting are carried out on the mixture, thus obtaining the hybrid starch granule; the additive is superior to single modified cornstarch granule (YSQ) or beta- cyclodextrin (HH) in terms of absorption property; dualistic or ternary composite filter prepared by adding the additive to a filter element of a cigarette filter can effectively reduce delivery volume of tar, phenol, hydrocyanic acid and carbon monoxide in smoke gas and improve organoleptic quality of the cigarette, effectively improve sensory comfort of the cigarette, enhance intensity of cigarette aroma, thus enjoying good application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN RES INST OF TOBACCO SCI
Modified starch particle, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101314646AHigh specific surface areaImprove adsorption capacityTobacco smoke filtersSodium hydroxideCigarette filter
The invention discloses modified starch granules, the preparation method and the application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: stirring starch and acetic buffer solution uniformly, adding saccharifying enzyme for enzymolysis reaction, adding sodium hydroxide solution to stop the reaction, centrifugally separating to obtain paste-shape porous starch, microwave drying, pulverizing and sieving to obtain the desired modified starch granule. The modified starch granule is superior to active carbon in adsorption performance, and can be added into the filter core of a cigarette filter to prepare a binary or ternary filter, which can effectively reduce the delivery amount of tar and carbon monoxide in the smoke, improve the cigarette sense quality, effectively improve the cigarette sense comfort and improve the centralization degree of the cigarette smoke. The modified starch granule has good application prospects.
Owner:YUNNAN RES INST OF TOBACCO SCI
Microparticles
A process for producing parenterally administrable microparticles, in which an at least 20% by weight aqueous solution of purified amylopectin-based starch of reduced molecular weight is prepared, the solution is combined with biologically active substance, an emulsion of starch droplets is formed in an outer phase of polymer solution, the starch droplets are made to gel, and the gelled starch particles are dried. A release-controlling shell is optionally also applied to the particles.Microparticles which essentially consist of said starch, have an amino acid content of less than 50 μg and have no covalent chemical cross-linking.
Owner:PACIRA PHARMA INC
Flexible thermoplastic film and product thereof
The invention discloses a biodegradable polyolefin base material composition doped with thermoplastic starch granules. The material comprises 5-45% of thermoplastic starch (TSP), about 55-95% of polyolefin or polyolefin mixture and 0.5-8% of compatibilizer which has nonpolar framework and polar functional monomer or embedding section copolymer of nonpolar embedding section and polar embedding section. The invention also provides a film forming method and a packaging component prepared by the polymer material.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Concrete compositions and methods for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS6387171B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce moisture contentCeramicwareGranular starchStarch granule
Disclosed is a concrete composition that comprises water, a cementitious material, and an aggregate material, the aggregate material comprising a granular starch. In accordance with preferred embodiments of the invention, the granular starch is a washed, pre-swollen starch, and is added to the composition in an amount ranging from about 1% to about 20% by weight of the cementitious material. The starch granules are swollen in the uncured composition but liberate water and shrink to their unswollen size as the concrete cures, thus providing a cured lightweight concrete. Also disclosed is a method for preparing a concrete composition. The disclosed method comprises providing starch granules, mixing the starch granules with water and a cementitious material to form an uncured concrete composition, and subsequently curing the uncured concrete composition thus formed.
Owner:GRAIN PROCESSING CORP
Microparticles
InactiveUS20020044976A1High yieldEfficient encapsulationPeptide/protein ingredientsGlass/slag layered productsMicroparticlePolymer solution
A process for producing parenterally administrable microparticles, in which an at least 20% by weight aqueous solution of purified amylopectin-based starch of reduced molecular weight is prepared, the solution is combined with biologically active substance, an emulsion of starch droplets is formed in an outer phase of polymer solution, the starch droplets are made to gel, and the gelled starch particles are dried. A release-controlling shell is optionally also applied to the particles. Microparticles which essentially consist of said starch, have an amino acid content of less than 50 mug and have no covalent chemical cross-linking.
Owner:PACIRA PHARMA INC
Microparticles
InactiveUS20040115281A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGlass/slag layered productsMicroparticlePolymer solution
A process for producing parenterally administrable microparticles, in which an at least 20% by weight aqueous solution of purified amylopectin-based starch of reduced molecular weight is prepared, the solution is combined with biologically active substance, an emulsion of starch droplets is formed in an outer phase of polymer solution, the starch droplets are made to gel, and the gelled starch particles are dried. A release-controlling shell is optionally also applied to the particles. Microparticles which essentially consist of said starch, have an amino acid content of less than 50 mug and have no covalent chemical cross-linking.
Owner:PACIRA PHARMA INC
Production of malt
Production of malt is carried out by immersing for wheat grain, germinating and drying. It can supply sufficient hydrolase for saccharification to decompose protein into soluble nitrogen; it can supply alpha-amino-nitrogen and dissolve albuminous cell wall to degrade starch grain. It's controllable, has better physical-bio-chemical reaction and quality.
Owner:邱虎
Processing method of low-glycemic-index lotus seed starch-lipid complex
The invention relates to a processing method of a low-glycemic-index lotus seed starch-lipid complex, belonging to the field of modified starch processing. The method comprises the following steps: by using lotus seed starch as a raw material, carrying out high-pressure homogenization modification, microwave wet lamination, low-temperature cooling crystallization, alcohol washing and centrifuging, freeze-drying, pulverizing and packaging, thereby obtaining the low-glycemic-index lotus seed starch-lipid complex. The dynamic high-pressure homogenization technique is utilized to degrade the starch granules so as to form more short-chain amylose, and the amylose is subjected to microwave high-temperature lipid reaction and low-temperature cooling crystallization to form the simple helix V-shaped microcrystal starch-lipid complex. The product has the advantages of low glycemic index and high nutritive value, is free of any organic solvent, can be used as a nutrient starch additive, and has great potential in food processing.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Swollen starch-latex compositions for use in papermaking
ActiveUS20050252629A1Improve filler retentionHigh retention rateNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingPaperboard
A novel filler treatment comprising the preparation of swollen starch-latex compositions, prepared in the presence or absence of co-additives, and the addition of the said composition to a filler suspension, has been developed. Use of the treated filler during papermaking improves filler retention and produces filled papers where addition of the filler has only a minimal negative effect on strength properties. The swollen starch-latex compositions can be prepared in a batch or jet cooker, or by mixing with hot water under controlled conditions (i.e., temperature, pH, mixing, mixing time) in order to make the starch granules swell sufficiently to improve their properties as a filler additive but avoiding excess swelling leading to their rupture. The swollen starch-latex composition is then rapidly mixed with the filler slurry, preferably in a static mixer, and added to the papermaking furnish at a point prior to the headbox of the paper machine. The starch-latex composition can be used with wood-free or wood-containing furnishes. The treated filler is easily retained in the web during papermaking, improves drainage, and gives sheets having good formation. Sheets made with the treated fillers have higher bonding and tensile strengths than sheets produced using filler treated with either swollen starch alone or latex alone. Retention and drainage are further improved when conventional retention aid chemicals are added to the furnish containing the treated filler. The use of swollen starch-latex compositions could allow the papermaker to increase the filler content of the paper without sacrificing dry strength properties or increasing the amount, and hence the cost, of the retention aid added. The combination of swollen starch and latex could be used as furnish additives in the manufacture of both filled grades and grades that contain no filler such as sack papers and paperboard products.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Technology for coupling the liquefaction process of corn alcohol and the concentration process of vinasse clear liquid
ActiveCN101538588AIncrease concentrationIncrease alcohol contentFood processingBiofuelsAlcohol contentAqueous alcohol
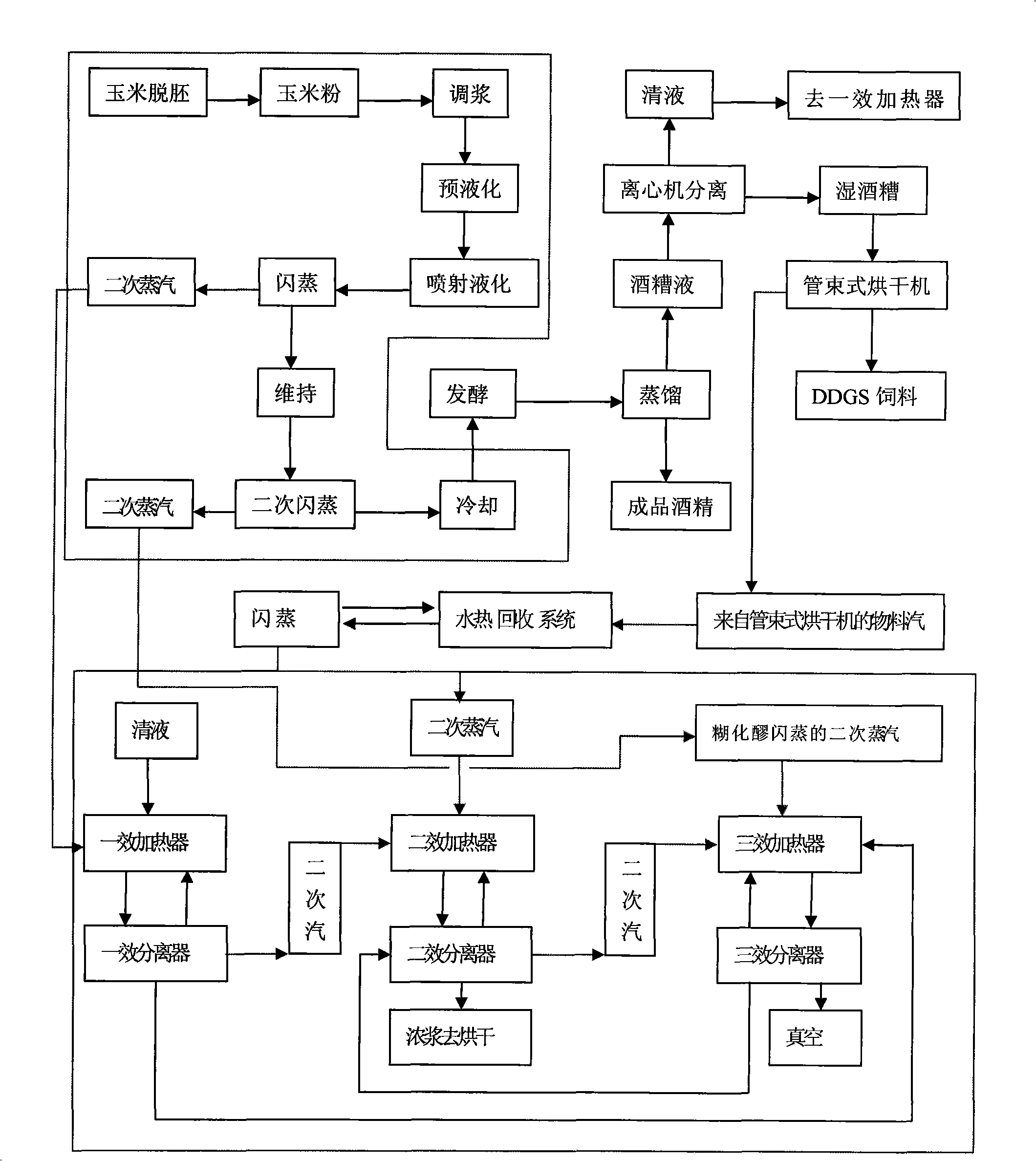
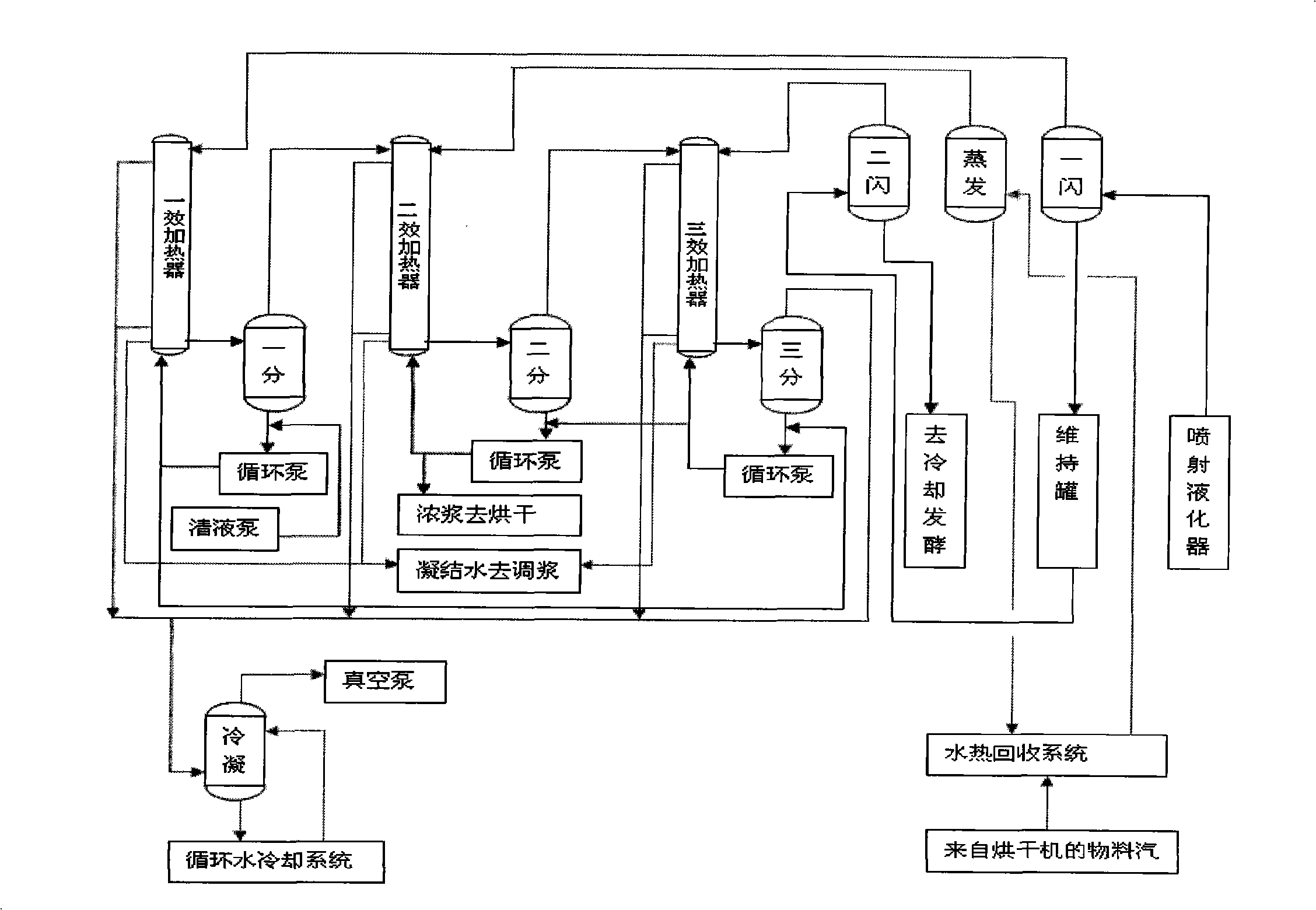
The invention belongs to the technical field of alcohol production, in particular relates to a technology for coupling the liquification process of corn alcohol and the concentration process of vinasse clear liquid. After being processed by the operations of pre-liquification and size-mixing, corn flour of the invention is sprayed and liquefied at the temperature from 105 to 135 DEG C and under the pressure from 0.1 to 0.15 MPa; starch granules are completely fractured, the gelatinization rate can reach 90 percent, and the high-temperature liquification is contributes to the increase of concentration of materials, thereby enabling the alcohol content of fermented mature mash to be improved to 14 percent (V / V); the liquefaction process and the concentration process of clear liquid are coupled, and indirect steam produced by the liquification process is used as a thermal source for the concentration process of clear liquid, thereby saving a great amount of external steam, evaporating and concentrating more clear liquid, contributing to the increase of recovery ratio of DDGS protein feed of each ton of alcohol; and vacuum equipment for the concentration process is utilized for lowering the temperature of the liquefied mash, and compared with the traditional mode of adopting a spiral plate for cooling, more cooling water can be saved.
Owner:QIANHE CONDIMENT & FOOD CO LTD
Preparation methods for high capacity biomass hard carbon anode material of sodium ion battery
InactiveCN109921018AAvoid the problem of high temperature melting and gelatinizationChange the environmentCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbonizationSodium-ion battery
The invention relates to the technical field of a secondary battery, specifically preparation methods for a high capacity biomass hard carbon anode material of a sodium ion battery. A method comprisesthe following processing steps of crushing and screening a biomass raw material to obtain precursor powder; adding a dehydrating agent, carrying out uniform mixing to obtain a mixture, and carrying out dehydration curing reaction; mixing a curved biomass precursor with a modifier, carrying out mixing by taking water as a dispersant, and carrying out drying processing to obtain a modified biomassprecursor; and carrying out pre-carbonization processing and carbonization processing in sequence. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that starch is taken as the raw material,through curving processing, the problem that the starch is melted and gelatinized due to a high temperature is effectively avoided, and doping and modification processing is carried out on cured starch granules, so a surface chemical environment and an internal structure of hard carbon are changed, and electrochemical performance of the biomass hard carbon anode material is effectively improved. Through curing reaction processing, hard carbon yield is also remarkably improved.
Owner:NINGBO SHANSHAN NEW MATERIAL TECH
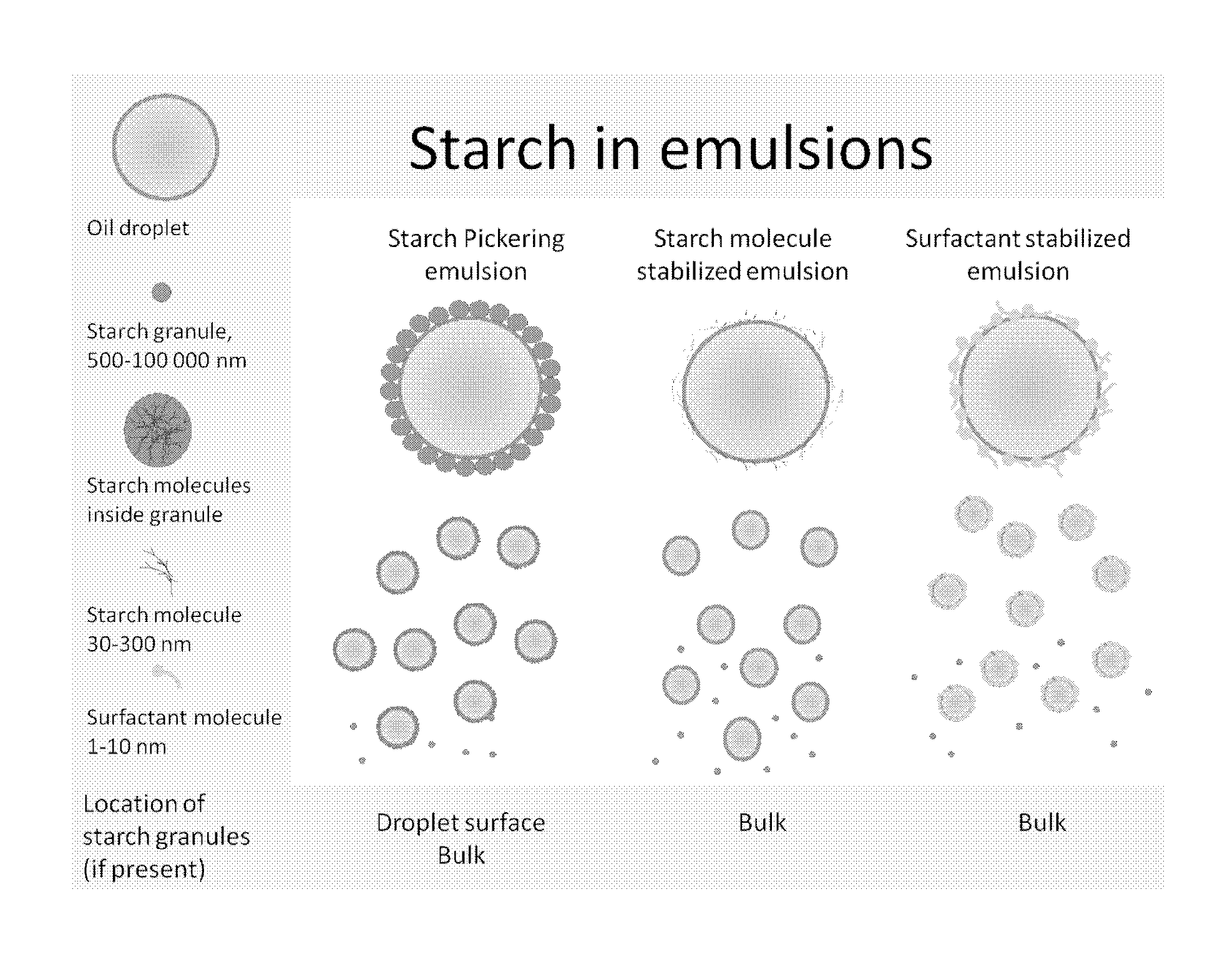
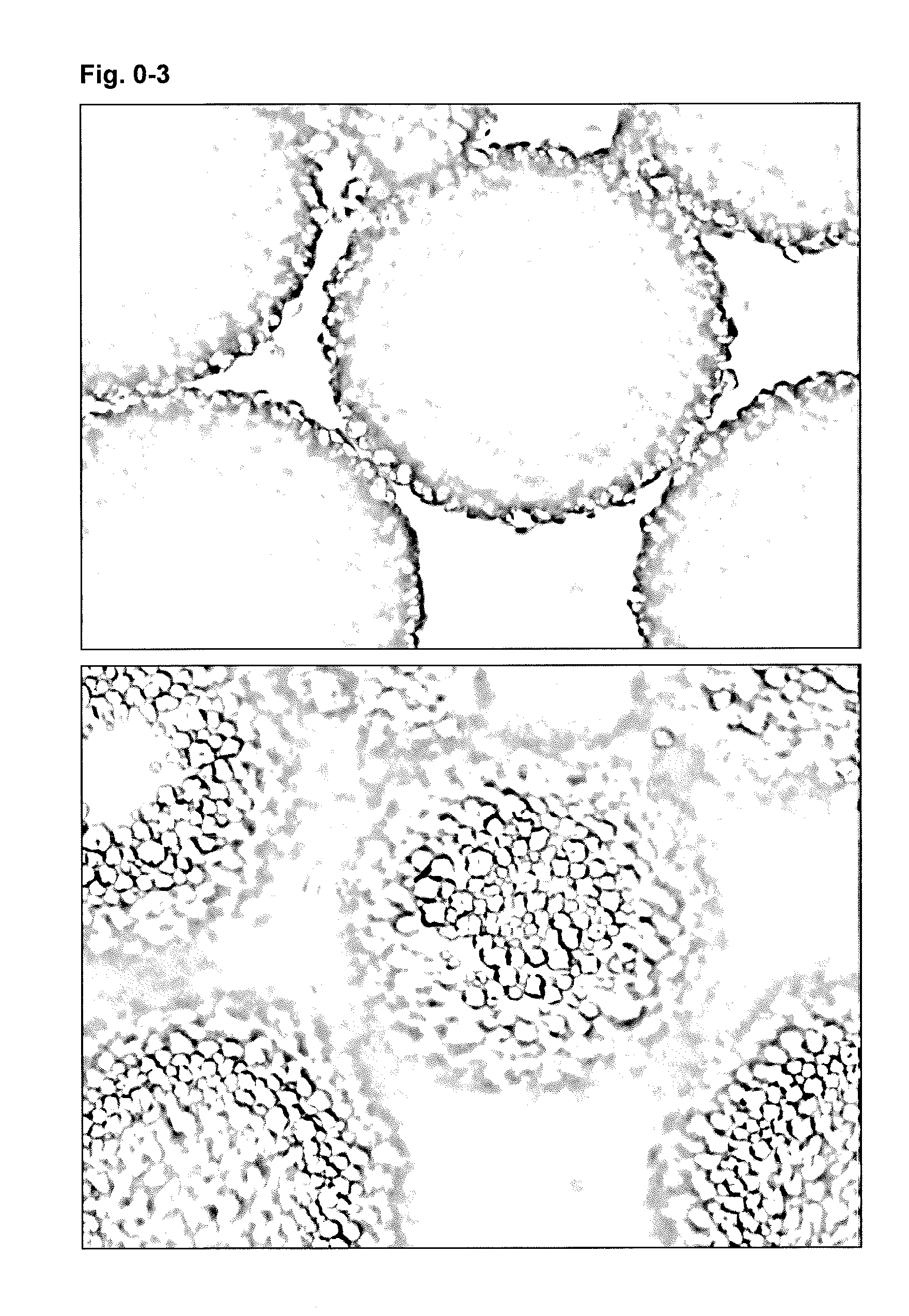
New particle stabilized emulsions and foams
InactiveUS20150125498A1Novel and useful emulsifying propertyFlexibility of systemBiocideCosmetic preparationsSolid particlePharmaceutical formulation
The present invention relates to a particle stabilized emulsion or foam comprising at least two phases and solid particles, wherein said solid particles are starch granules and said starch granules or a portion thereof are situated at the interface between the two phases providing the particle stabilized emulsion or foam. The invention further relates to the use of said particle stabilized emulsion or foam for encapsulation of substances chosen from biopharmaceuticals, proteins, probiotics, living cells, enzymes and antibodies, sensitive food ingredients, vitamins, and lipids in food products, cosmetic products, skin creams, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:SPEXIMO
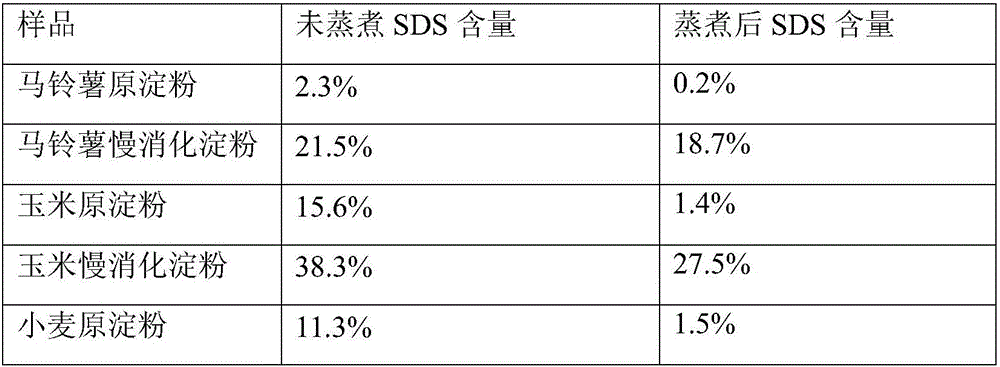
Slowly digestible starch and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106473100AAvoid contactReduce digestionFood ingredient as emulsifierDigestible starchGellan gum
The present invention discloses slowly digestible starch and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of food processing. The slowly digestible starch is prepared by using a physical embedding method, "cores" are starch granules, and "shells" are prepared by compounding sodium alginate, gellan gum and chitosan. In the low temperature, a water-in-oil aqueous emulsion is prepared, the prepared aqueous emulsion is subjected to an electrostatic spraying, the sprayed aqueous emulsion is solidified, and the solidified material is subjected to a suction filtration to obtain solid microspheres of the slowly digestible starch. The structures are monodispersed core-shell capsules. In the preparation process, the starch is always in the low temperature, the starch granules are not gelatinized, and the original SDS content is not affected. The sodium alginate / gellan gum / chitosan has good film-forming ability and flexibility, and can always cover the outer layer of the starch granules, so that the slowly digestible starch is not affected by the processing environment and the effect of the processing process in the SDS content is minimized.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Preparation method of anthocyanin emulsion with high embedding rate
ActiveCN109674751ASimple processReduce dosageOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsEmulsionEmbedding rate
The invention discloses a preparation method of anthocyanin emulsion with high embedding rate. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out esterification modification on small particle sizestarch particles with average particle size of 1 to 5 mum by using octenyl succinic anhydride to obtain modified small particle size starch particles with the substitution degree of 0.028 to 0.100; respectively dissolving an anthocyanin extract and a lipophilic emulsifier into water and oil, mixing and carrying out high-speed shearing to obtain W / O emulsion; then uniformly dispersing the modifiedsmall particle size starch particles into distilled water according to mass fraction of 1 to 8 percent (w / w), mixing a mixture with the W / O emulsion and carrying out high-speed shearing to obtain loaded anthocyanins emulsion. The anthocyanin emulsion prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has high embedding rate, simple technology, low oil content, and capability of being applied to the fields of food and beverage, cosmetic water emulsion and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
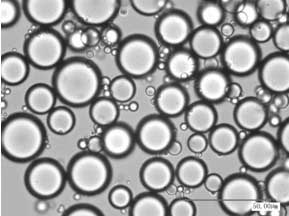
Method for preparing micro nano starch granules emulsifier and application thereof
The invention relates to a method for preparing a micro nano starch granules emulsifier and an application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of an emulsifier or a foam stabilizer. According to the invention, the product degrades raw starch by acid to obtain the micro nano starch granules, the average size of the micro nano starch granules is less than 1 mum. The micro nano starch granules can be used as the emulsifier to prepare an emulsion with high stabilization, especially prepare food and a cosmetic emulsifier.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of modified starch styptic powder
InactiveCN105457075AIncrease productivityEasy to produceAbsorbent padsBandagesCross-linkStarch Microspheres
The invention provides a preparation method of modified starch styptic powder. The prepared modified starch styptic powder is starch microspheres modified through cross-linking. The preparation technology of the modified starch styptic powder comprises the steps that starch with the molecular weight ranging from 5,000 to 3 million is dissolved in water, the mass concentration ranges from 0.01% to 10%, gelatinization is conducted for 10-200 min at 30-100 DEG C at the stirring speed ranging from 100 rpm to 6,000 rpm, and after the solution is mixed to be uniform, a cross-linking agent is added, wherein the mass ratio of the cross-linking agent to the starch ranges from 100:1 to 10:1; stirring is continuously conducted for 0.5-5 h, spray drying is conducted, the airflow velocity of spray drying ranges from 1 L / min to 100 L / min, and the air temperature is 50-200 DEG C; modified starch particles subjected to spray drying are collected, and the modified starch styptic powder microspheres with the particle size ranging from 5 micrometers to 1,000 micrometers are obtained.
Owner:WUHAN HAIJIYA BIOTECH CO LTD
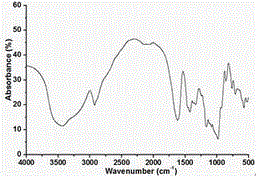
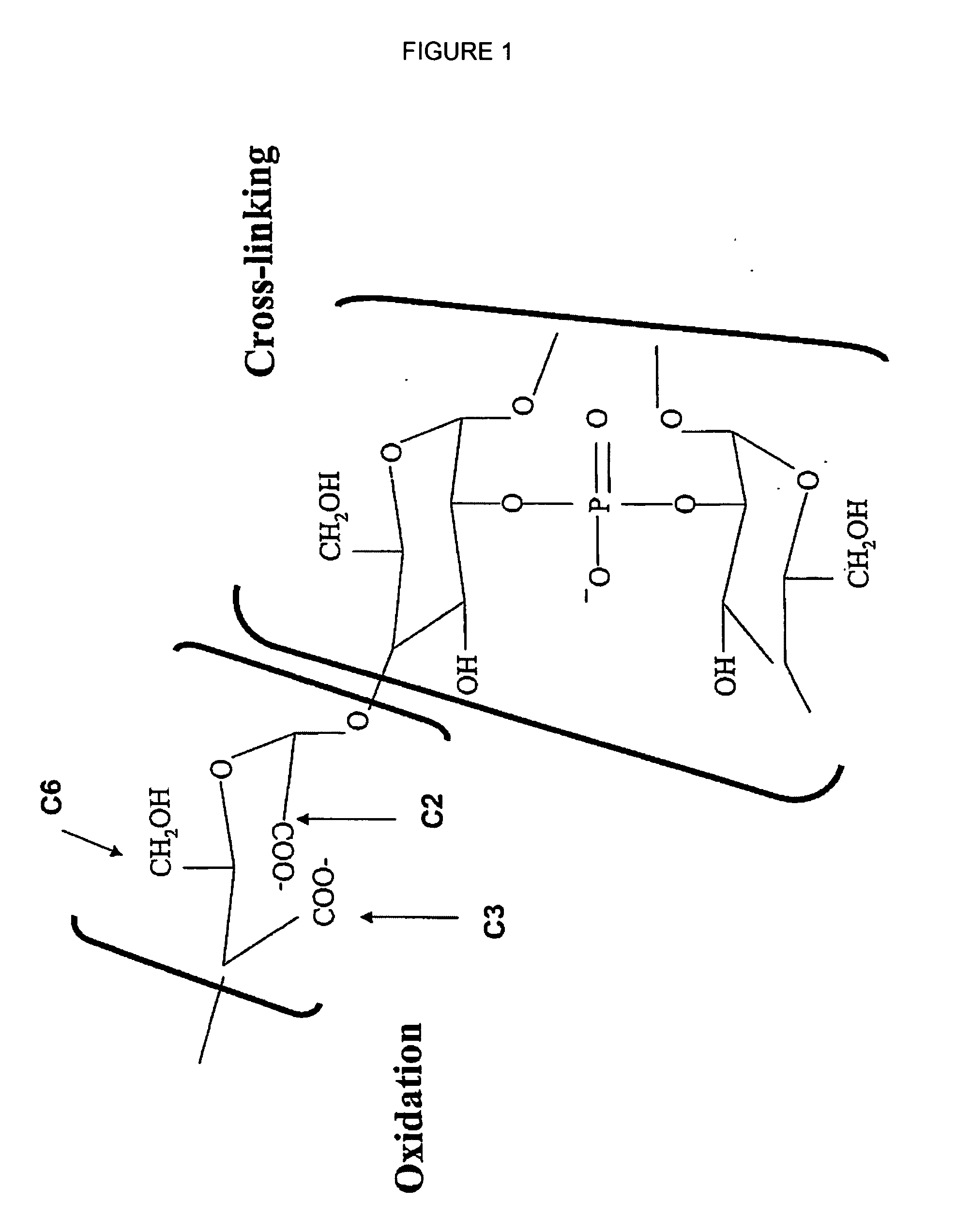
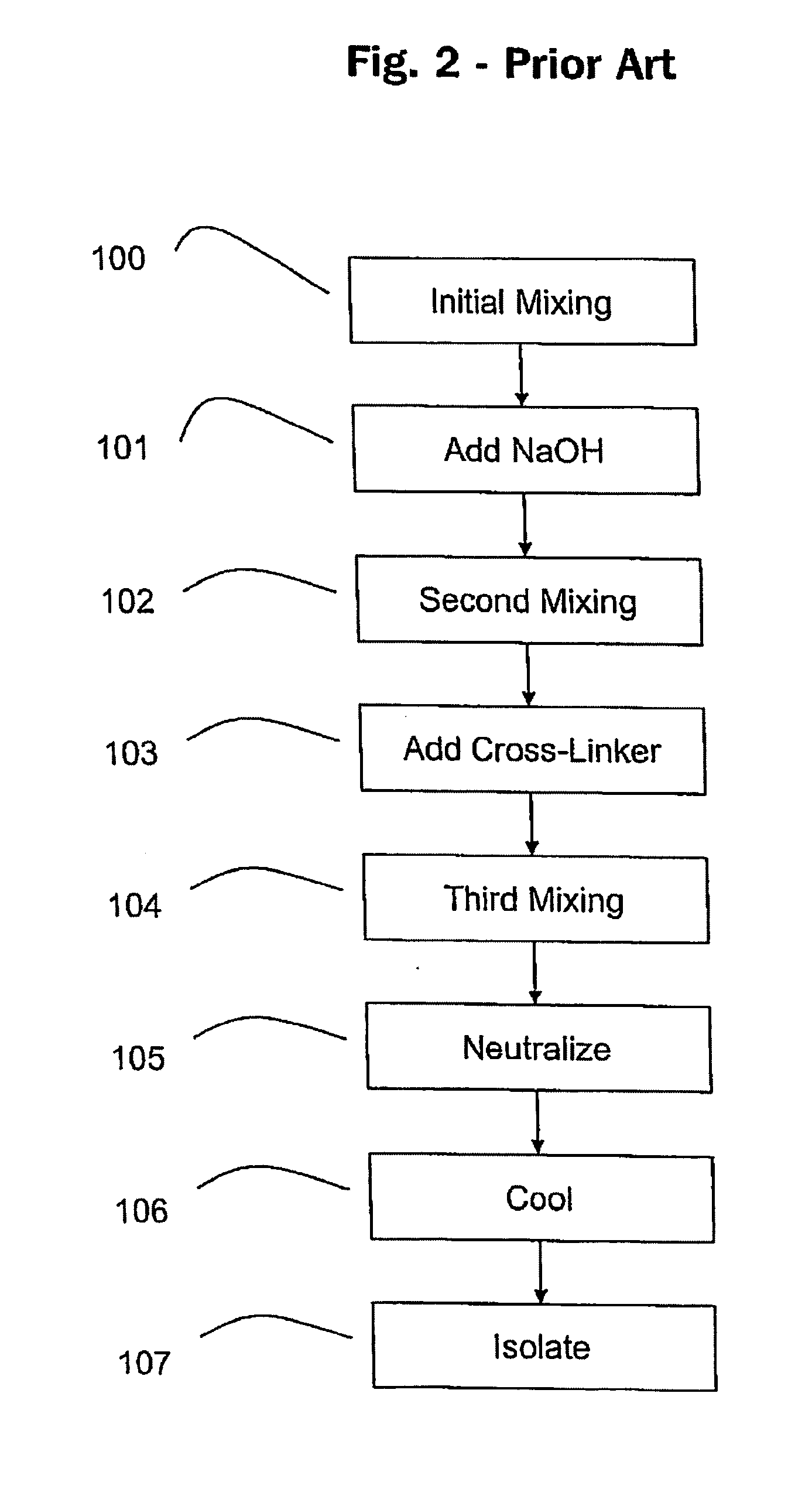
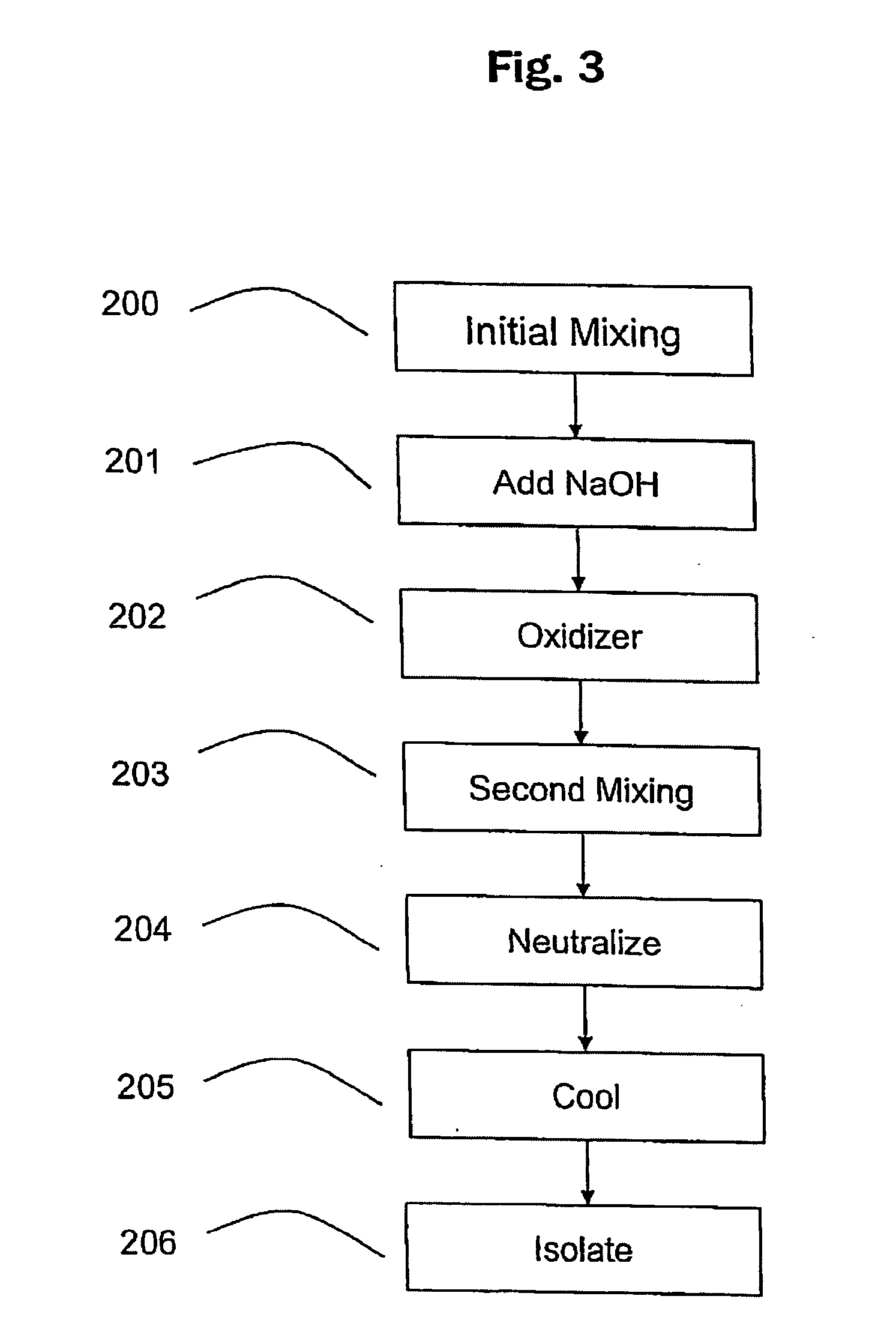
Oxidized reversibly swelling granular starch products
A rapidly-hydratable oxidized resistant starch having a cold-water hydration at least 20% greater than the resistant starch before oxidation, makeable by oxidation with an oxidizing agent selected from the group consisting of periodate, chromic acid, permanganate, nitrogen dioxide, and alkali metal hypochlorites. The starch may be made by a process for preparing a rapidly-hydratable resistant starch comprising the steps of swelling starch granules in the presence of alkali and / or heat, dispersing at least one cross-linking agent, mixing said dispersion, adding an oxidizing agent to said dispersion, and agitating said dispersion.
Owner:MGP INGREDIENTS
Functional starch powder
ActiveUS20060204569A1Satisfactory release-sustaining propertyIncrease resistanceOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePowder mixtureStarch granule
Functional starch powder of 400% or more water retention capacity, 5 hr or more collapse time and 200 g or more gel indentation load. This functional starch powder is produced through the step of heating a starch raw material in the presence of water at 60 to 150° C. so as to swell starch particles of the starch raw material and the subsequent step of drying the thus swollen starch particles so as to obtain a powder mixture comprising starch particles and, lying in the exterior thereof, amylose and amylopectin.
Owner:SANWA CORNSTARCH +1
Processing technology of lotus seed juice
ActiveCN101731709AExtended shelf lifeLower requirementFood scienceStarch granuleUltrasonic technology
The invention provides a processing technology of a lotus seed juice, aiming to solve the problem that layering and precipitation are prone to occur in lotus seed drinks. In the invention, fresh lotus seeds or quick freezing lotus seeds are washed or unfreezed and then ground into thick liquid and filtered to obtain undiluted lotus seed juice; then carrying out gelatinization in combination with ultrasonic treatment; blending, homogenizing, canning, sterilizing and cooling according to ordinary drink processing technology to obtain lotus seed juice product. In the invention, gelatinization is adopted in combination with ultrasonic technology for processing lotus seed undiluted juice, under the collective action of thermal motion and ultrasonic waves, in the lotus seed juice, starch granules degradation and starch molecule dissolving out are accelerated and dissolved out long chain starch molecules are degraded to a certain degree to form micromolecules, thus effectively preventing lotus seed starch macromolecules from aging in the process storing lotus seed juice drink and preventing layering and precipitation of the louts seed juice drink, lengthening product shelf life; in addition, in the processing technology, no high requirements are imposed on equipment, operability is good, and aging of high starchiness drinks such as the lotus seed juice can be effectively solved, therefore the processing technology is suitable for industrialized mass production of the lotus seed juice.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for producing amorphous particulate form starch by using impulse electric field
The invention discloses a method for preparing non-crystallized starch granules by using a pulse electric field. The method comprises the following steps: mixing starch with water at room temperature; stirring to form uniform starch suspension; adding electrolytes into the starch suspension until the electrical conductivity of the starch suspension is in the range of 50-2000 MuS / cm; pumping the starch suspension into a processor of the pulse electric field for non-crystallization treatment under such conditions that the electrical field intensity is 40-60 kV / cm, the pulse width is 10-100 Mus, the pulse frequency is 10-1000 Hz, the pulse waveform is square wave and the time of pulse electric field treatment is 1-1000 ms; and filtering, drying, pulverizing and screening the non-crystallized starch suspension to produce the final product. The non-crystallized starch granules are prepared at a temperature below the starch gelatinization temperature in the pulse electric field. The method has a short preparation cycle; prevents the adverse effects caused by the addition of a large amount of chemical reagents and high-temperature heating; and realizes high non-crystallization degree.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com