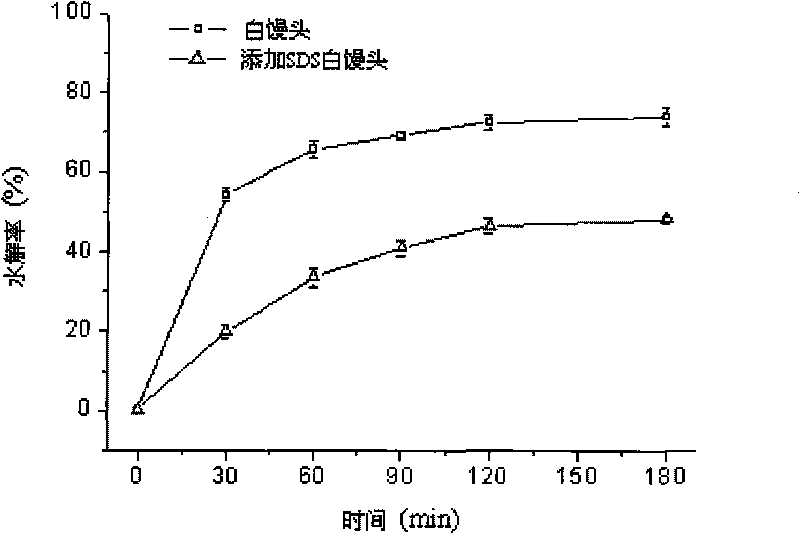
Method for producing controlled/slow release starch derivative with hypoglycemia response characteristics
A technology of starch derivatives and response characteristics, which is applied in the field of functional food additive production, can solve problems such as poor processing stability, no industrialization reports, and food safety issues, and achieve improved thermal stability, excellent product quality, and low product cost. Falling effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Mix 10g starch and 2g micronized calcium carbonate and add and disperse in 1L of high polymer mixed solution of sodium alginate and chitosan (mass ratio 0.5: 1) in 0.5% by weight; Add to the edible vegetable oil that contains 0.5% sorbitan fatty acid ester by volume ratio, the water-oil phase volume ratio is at 1: 1, stir 5min with speed 2000r / min; And solidified at room temperature (20°C) for 6 hours to obtain solid microspheres with a particle size of 15 μm; collected by filtration, washed with deionized water, and then dried with hot air at 50°C for 2 hours to obtain the finished product of the controlled-release starch derivative. The SDS measured by Englyst method was 30% higher than that of the original starch, and its content decreased by 2% after high-pressure cooking treatment, and the GI was 43%.
Embodiment 2
[0030] 150g of starch and 20g of micronized calcium lactate are mixed evenly and added and dispersed in 1L of high polymer mixed solution of carrageenan and chitosan (mass ratio 6: 1) in 1L weight percent; after it is mixed evenly, press The volume ratio is added to the edible vegetable oil containing 3% sorbitan fatty acid ester, the water-oil phase volume ratio is at 1: 5, stirs 12min with speed 1000r / min; Curing at room temperature (30°C) for 2 hours to obtain solid microspheres with a particle size of 64 μm; collecting by filtration, washing with deionized water, and drying with hot air at 30°C for 12 hours to obtain the finished product of the controlled-release starch derivative. The SDS measured by Englyst method is 25% higher than that of the original starch, and its content is reduced by 0.5% after high-pressure cooking treatment. The GI measured by the in vitro simulation experiment is 38%.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Mix 80g of starch and 10g of micronized calcium citrate and add and disperse it into 1L of high polymer mixed solution of sodium alginate and chitosan (mass ratio 10:1) with a weight percentage of 9%; mix it evenly Add to the edible vegetable oil that contains 5% sorbitan fatty acid ester by volume ratio afterward, water-oil phase volume ratio is at 1: 10, stirs 20min with speed 200r / min; , and solidified at room temperature (15° C.) for 10 hours to obtain solid microspheres with a particle size of 145 μm; collected by filtration, washed with deionized water, and then dried with hot air at 45° C. for 7 hours to obtain the finished product of the controlled-release starch derivative. The SDS measured by Englyst method is 24% higher than that of the original starch, and its content is reduced by 0.9% after high-pressure cooking treatment. The GI measured by the in vitro simulation experiment is 49%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com