Glucan branching enzyme and coding gene and application thereof
A technology encoding gene and glucan, applied in application, genetic engineering, glycosyltransferase and other directions, can solve the problems of difficulty in being degraded, accelerated aging rate of starch products, and reduced effective utilization of starch raw materials, and achieves good low temperature. Adaptability, excellent enzymatic properties, and strong substrate specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of glucan branching enzyme gene
[0043] 1. PCR amplification of the conserved region of the glucan branching enzyme gene genome
[0044] Genomic DNA of Rhizomucor miehei (Rhizomucor miehei) CAU432 was used as a template, with degenerate primers GBEDF and GBEDR, and Ex Taq DNA polymerase was used for PCR amplification to obtain PCR amplification products.
[0045] PCR reaction conditions: 94°C for 5min; 94°C for 30s, 60°C to 55°C (0.5°C decrease for each cycle) for 30s, 72°C for 1min, a total of 10 cycles; 94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C for 1min, 20 cycles Cycle; 72°C, 10min.
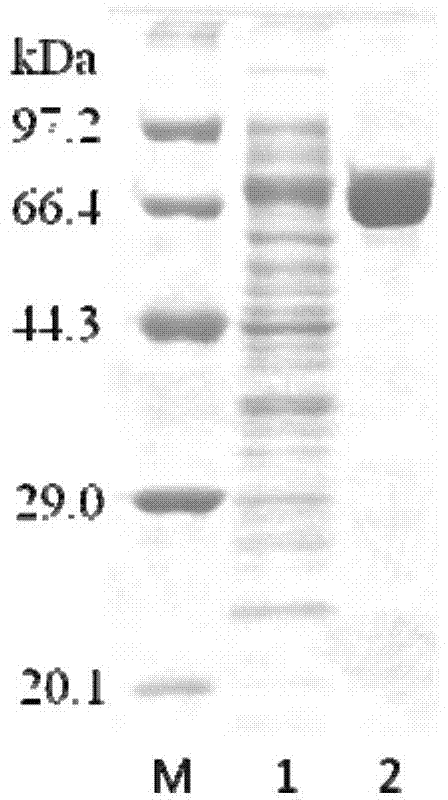
[0046] The PCR amplification product was detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and there was a specific band at about 460bp, which was recovered and connected to the pMD18-T vector, transformed into E.coli DH5α by heat shock method, and identified by colony PCR Subsequent sequencing. The sequencing results were searched and compared by NCBI BLAST, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2, the preparation of recombinant dextran branching enzyme
[0065] 1. Construction of recombinant bacteria
[0066] (1) Design and synthesize the following primers
[0067] RmGBEF: 5'-ATTCCG GAATTC ATGCTTACCGACGACTTTG-3'
[0068] (The underlined sequence is the recognition site for EcoRI digestion)
[0069] RmGBER: 5'-ATTCCG CTCGAG CTAATCTGCTTTTTCCCAATACA-3'
[0070] (The underlined sequence is the XhoI restriction recognition site)
[0071] (2) Extract the mRNA of Rhizomucor miehei CAU432 and reverse transcribe it into cDNA, use the cDNA as a template, and use RmGBEF and RmGBER as primers to carry out PCR amplification to obtain PCR amplification products.
[0072] PCR reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 55°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 2 min and 30 s, a total of 30 cycles; total extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0073](3) EcoRI and XhoI double-digest the PCR amplification product t...
Embodiment 3
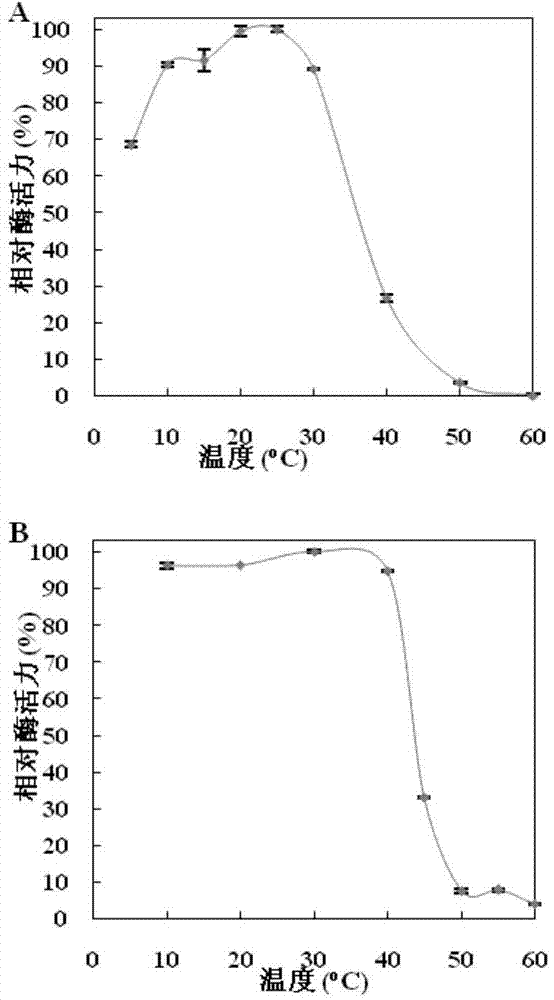
[0088] Example 3, Properties of Recombinant Glucan Branching Enzyme (RmGBE)
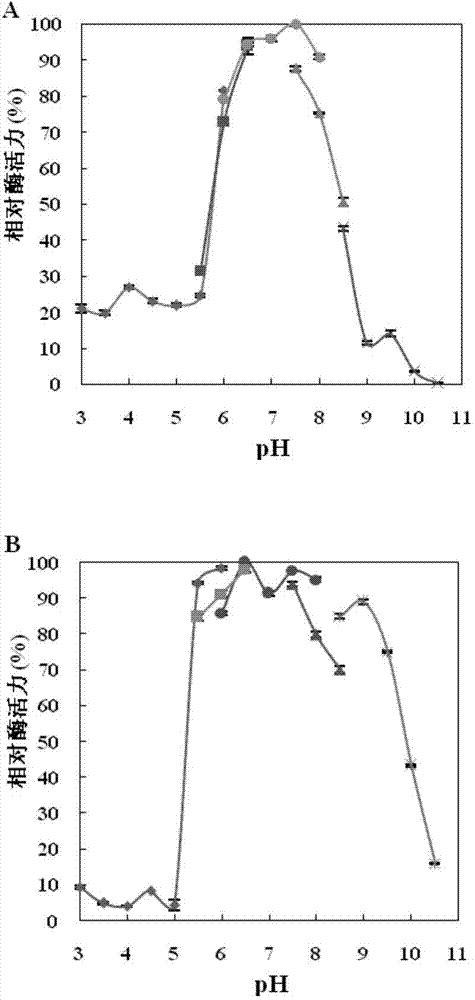
[0089] 1. Determination of the optimal pH of RmGBE: Glucan branching enzyme (RmGBE) enzyme solution and amylose (purchased from Sigma) were dissolved in five buffer systems with different pH values as follows: citric acid / sodium citrate Buffer (pH3.0-6.0), MES (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid) buffer (pH5.5-6.5), disodium hydrogen phosphate / sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH6.0 -8.0), Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.0-9.0), glycine / sodium hydroxide buffer (pH8.6-10.6), and then measure the enzyme activity of dextran branching enzyme at 25°C. The highest activity point was taken as 100%, and the relative enzyme activity at each pH was calculated. The result is as figure 2 As shown in A.
[0090] 2. Determination of the pH stability of RmGBE: Dilute the glucan branching enzyme (RmGBE) enzyme solution with the above five buffer solutions with different pH values, and treat the diluted enzyme solution...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com