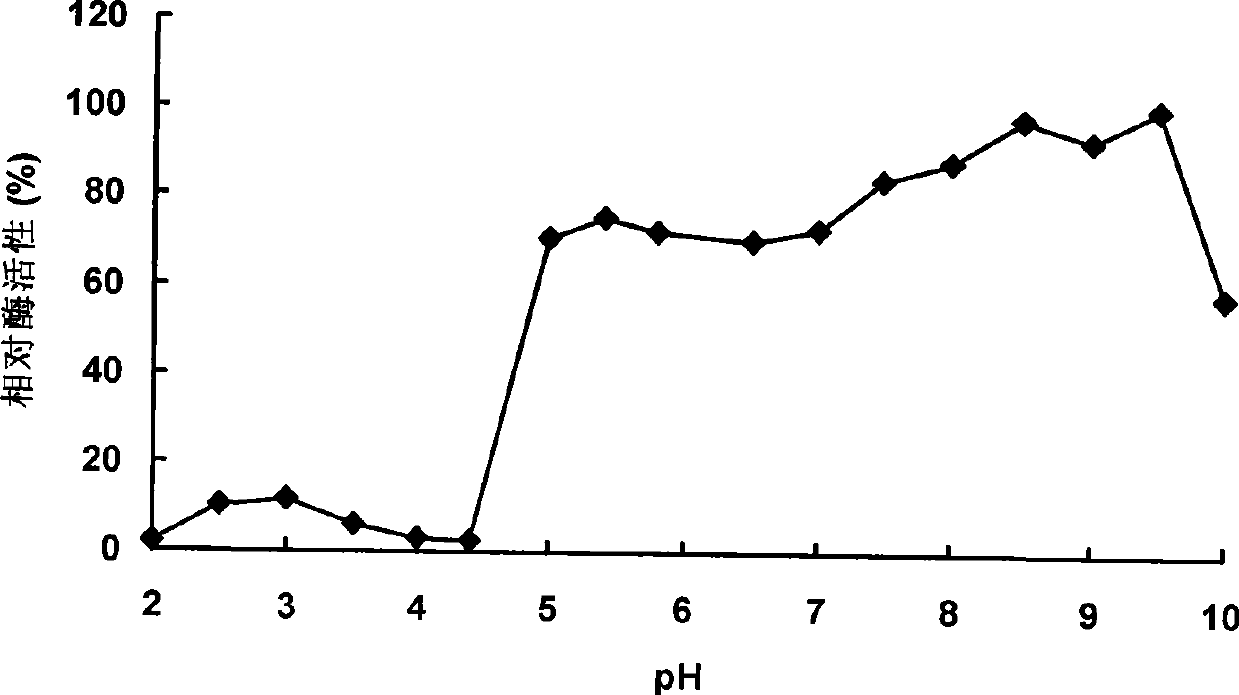
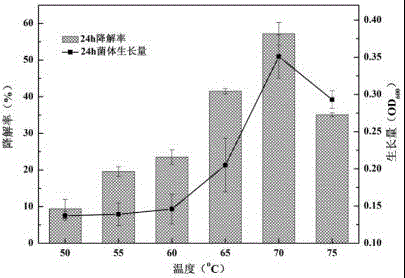
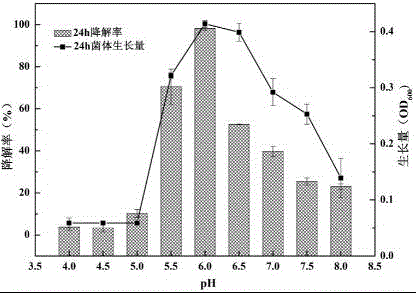
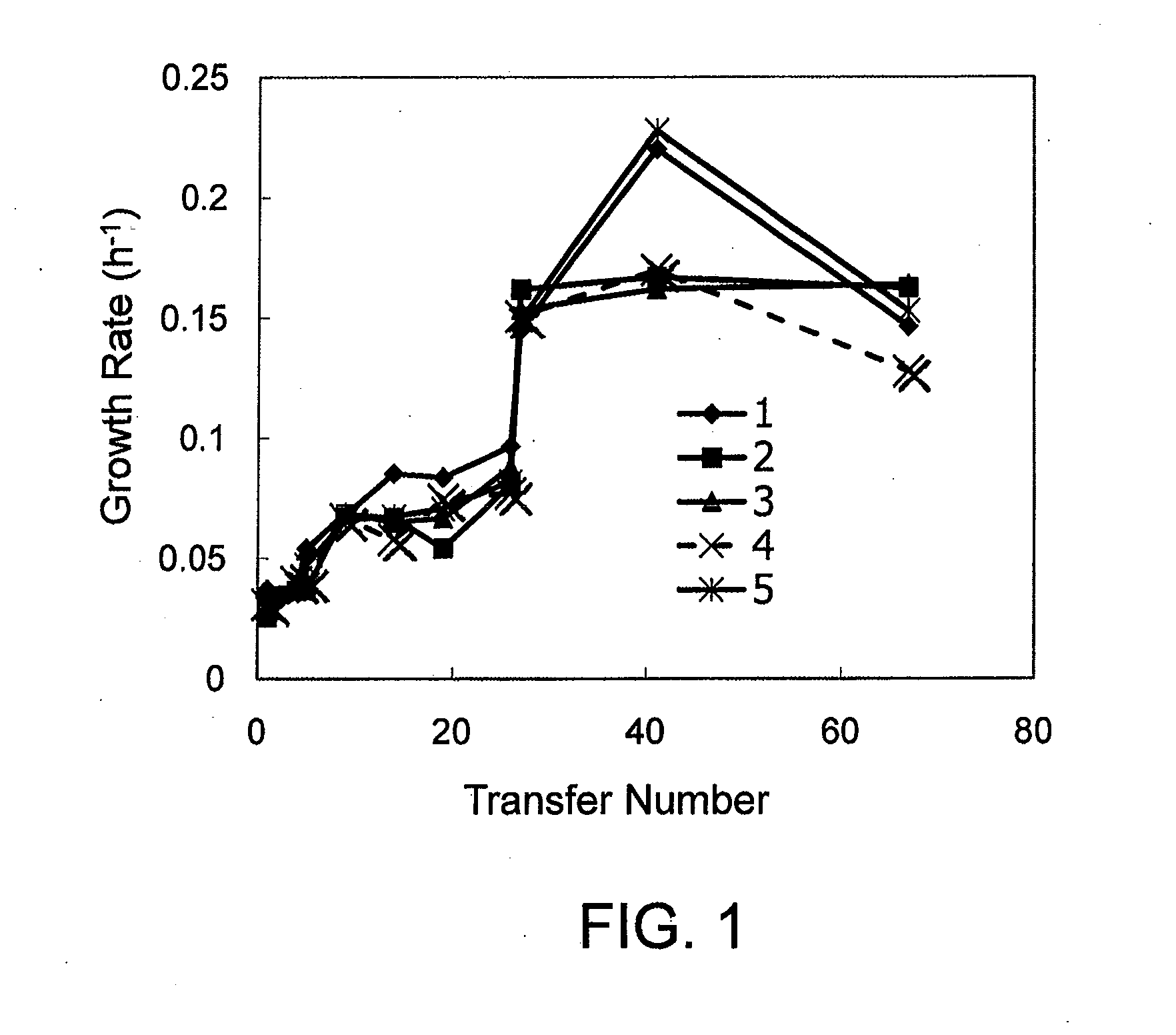
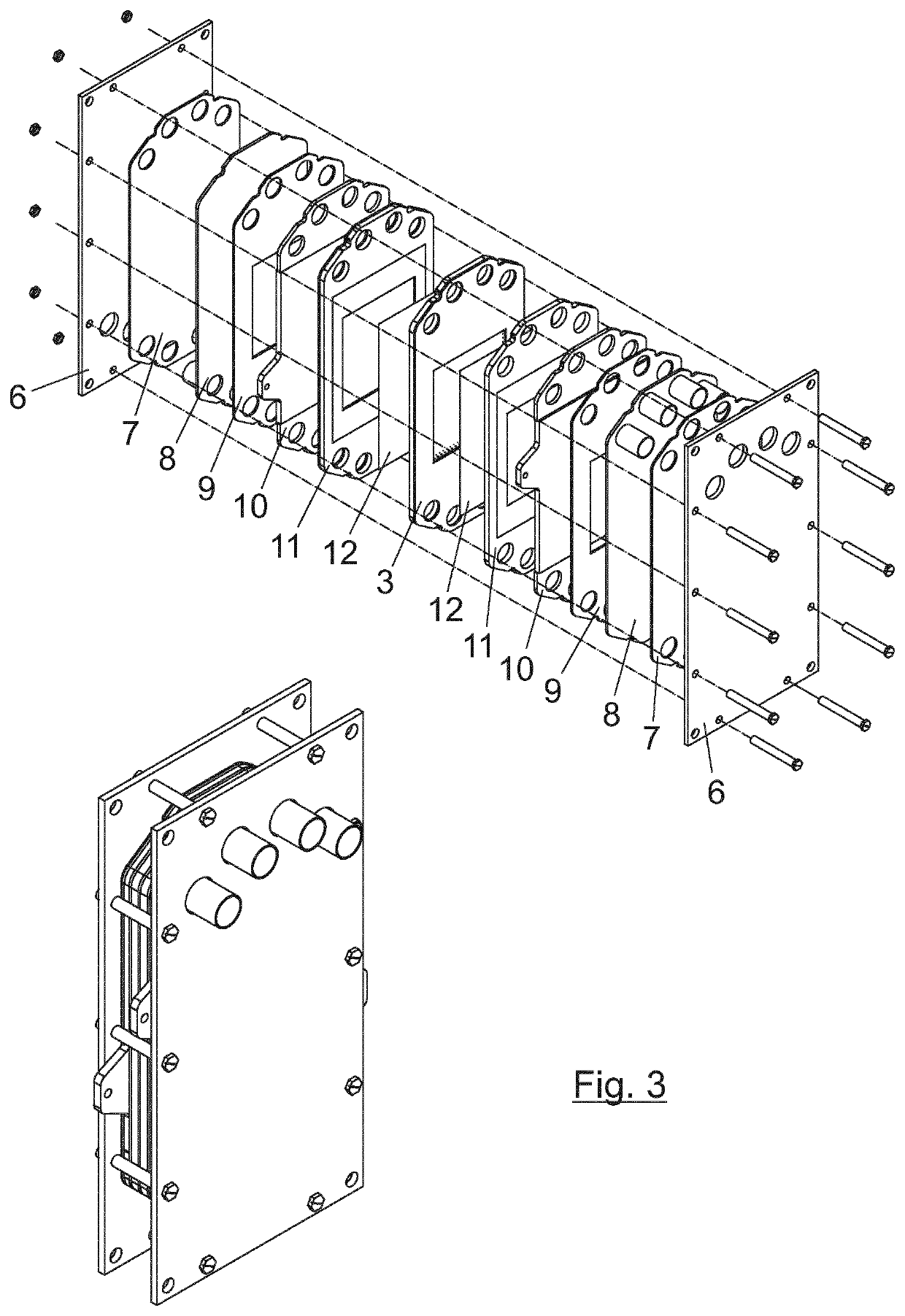
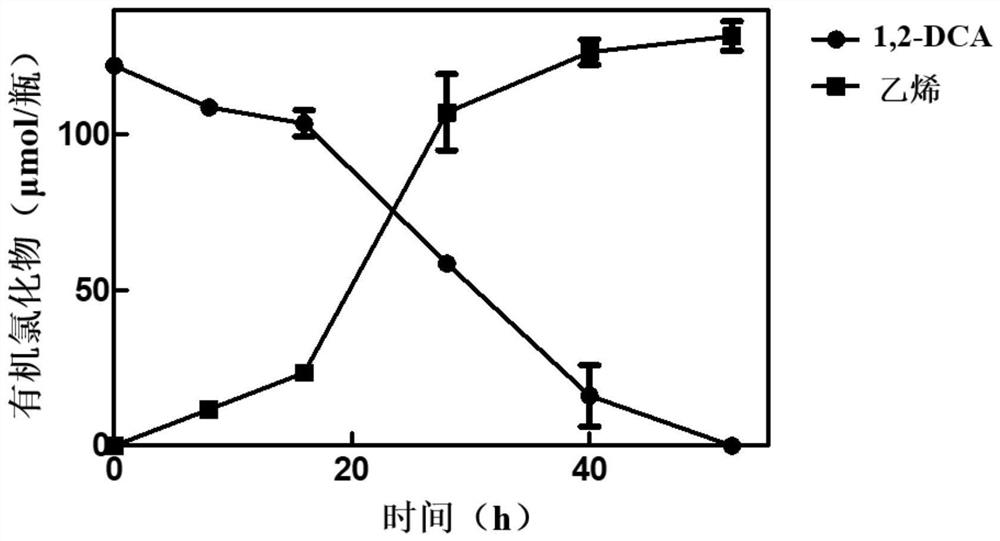
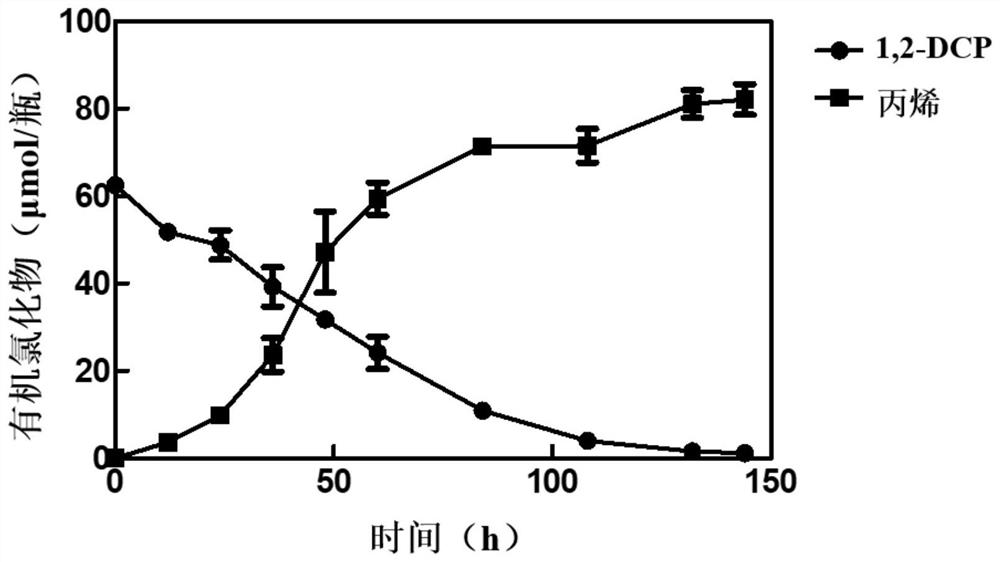
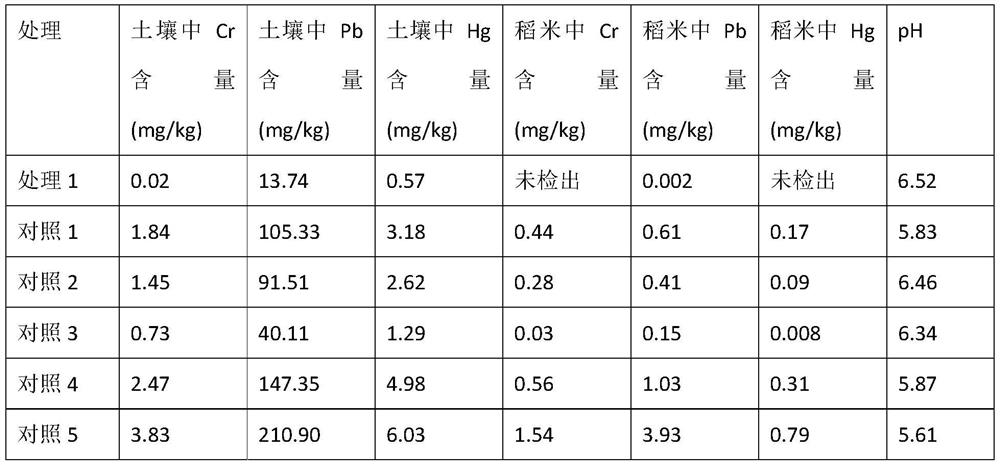
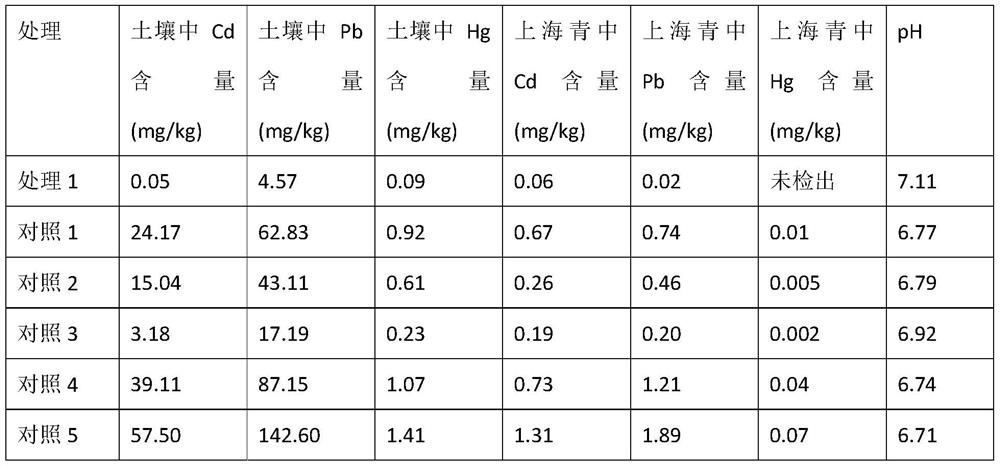
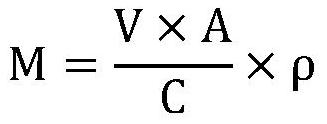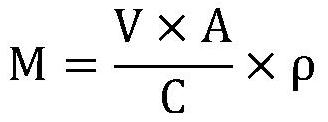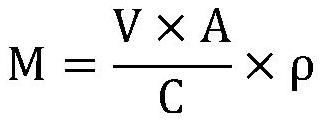Patents
Literature
44 results about "Geobacter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Geobacter is a genus of Proteobacteria. Geobacter species are anaerobic respiration bacterial species which have capabilities that make them useful in bioremediation. Geobacter was found to be the first organism with the ability to oxidize organic compounds and metals, including iron, radioactive metals, and petroleum compounds into environmentally benign carbon dioxide while using iron oxide or other available metals as electron acceptors. Geobacter species are also found to be able to respire upon a graphite electrode. They have been found in anaerobic conditions in soils and aquatic sediment.
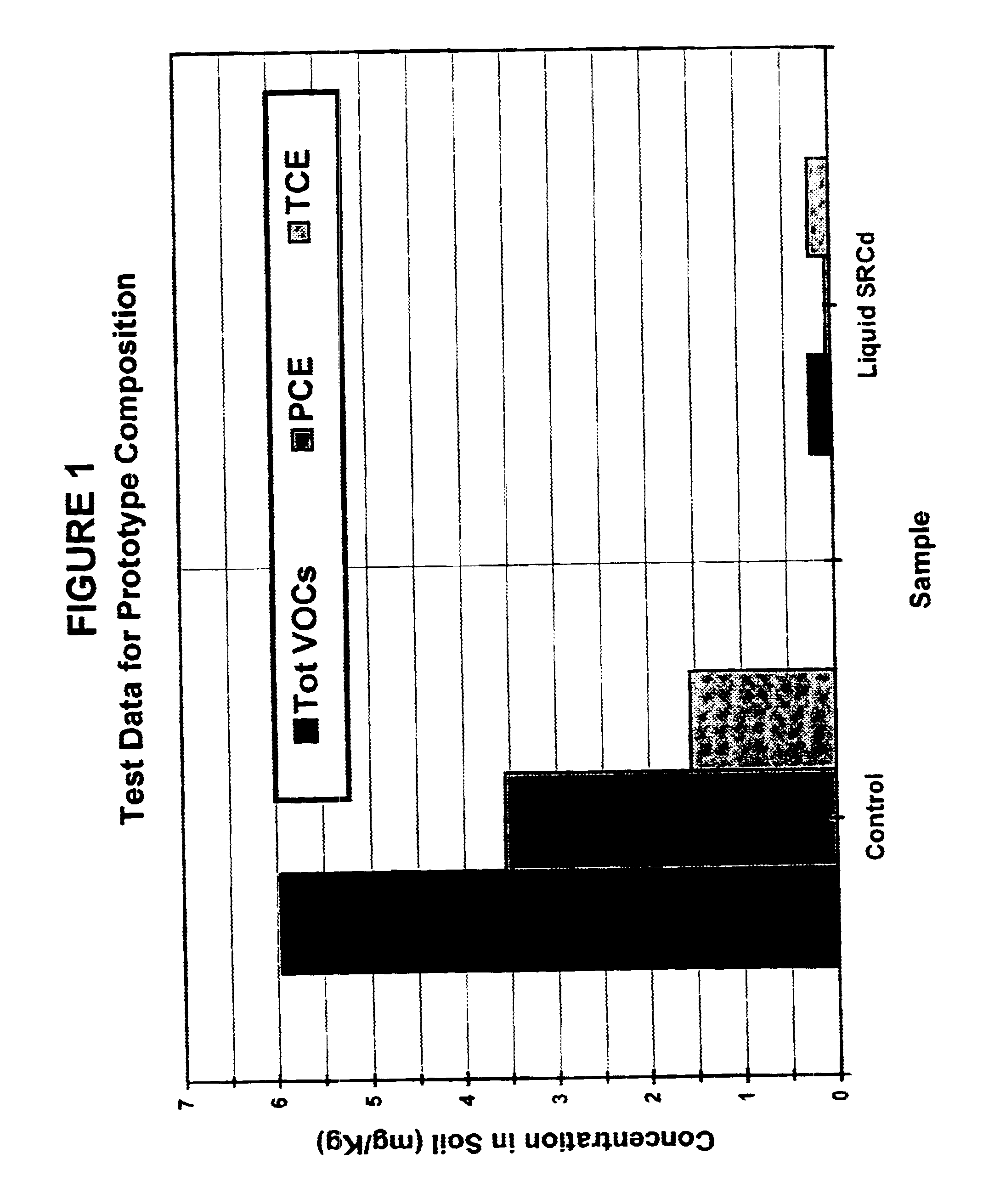
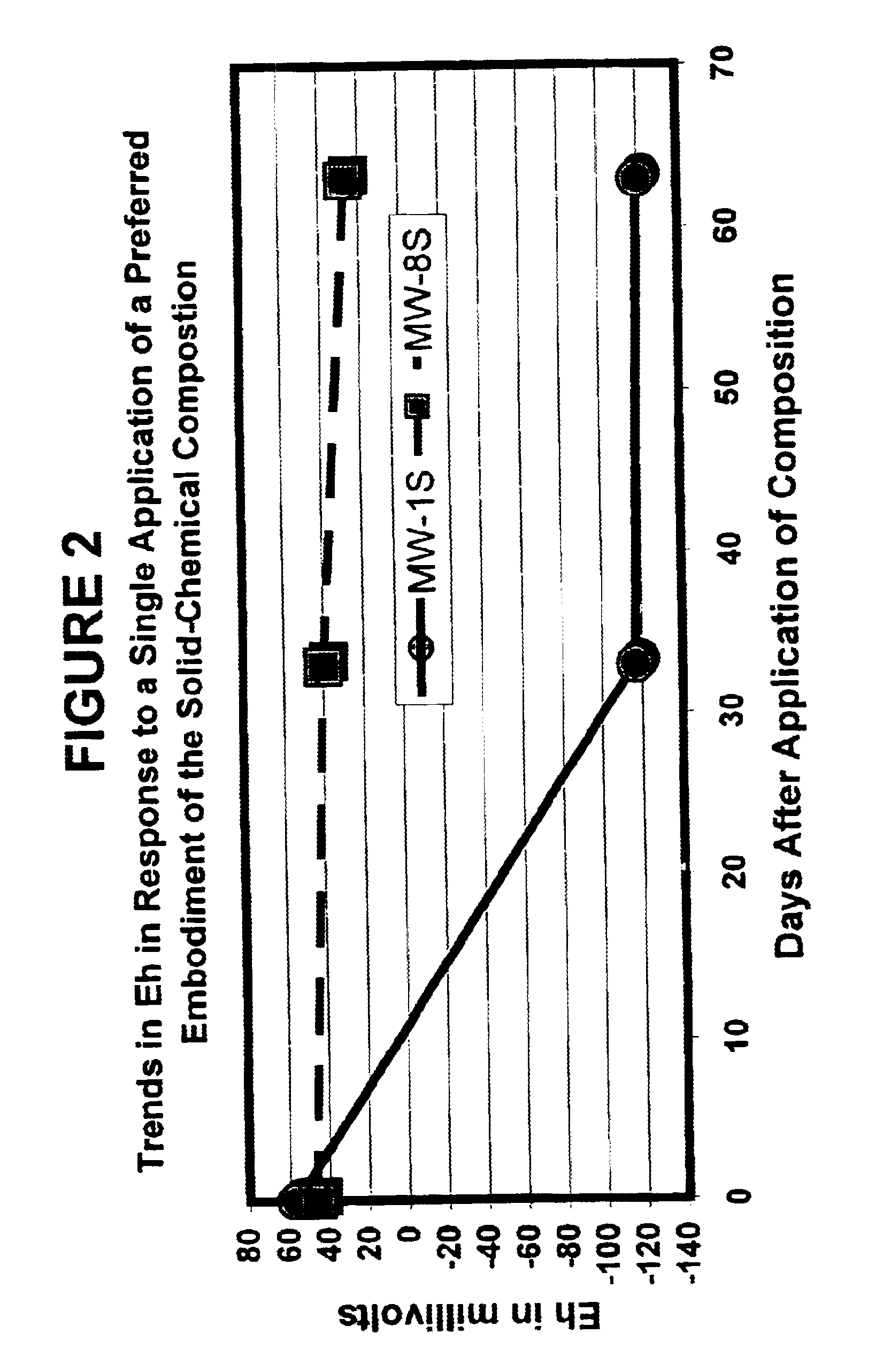
Solid-chemical composition for sustained release of organic substrates and complex inorganic phosphates for bioremediation
InactiveUS6620611B2Improve solubilityIncreasing speed and effectivenessBacteriaWater treatment compoundsPseudomonasTrichoderma spp
A slow-release solid chemical composition for environmental bioremediation is provided. The composition comprises a source of soluble organic substrates which include sugars, soluble organic polymers and mixtures of them in an amount of 7% to 90%, insoluble organic substrates an amount of 10% to 70%, complex inorganic phosphates in an amount of 0.5% to 7% and soluble organic salts in an amount of 2% to 70%. The insoluble organic substrates include fibrous plant materials, starches, cellulosic materials and mixtures of these substrates. The complex inorganic phosphates include ringed metaphosphates, linear polyphosphates and mixtures. The organic salts include lactates, formates, acetates, citrates, etc. Also the composition further comprises microorganisms which include Bacillus spp., Rhizobium spp., Bradyrhibzobium spp., Fibrobacter spp., Clostridium spp., Pseudomonas. spp., Geobacter spp., Arthrobacter spp., Nocardia, spp., aspergillus spp., Trichoderma spp., Candida spp., Yarrowia spp. and combinations of these microorganisms. The composition can be prepared in various forms, including granules, briquettes, pellets, tablets or capsules.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Neutral phytase PHYMJ11 and gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the genetic engineering field, especially to a land bacillus Pedobacter sp. MJ11 with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 2503 and a neutral phytase PHYMJ11, a gene thereof, a recombinant vector containing the same and its application. The invention provides the neutral phytase PHYMJ11 with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 and a gene phyMJ11 for coding said neutral phytase. The neutral phytase obtained in the invention has the optimum pH value 7. 0 and simultaneously has a high enzymatic activity in a range of pH5-9. The ability for hydrolyzing a phytate phosphorus in a bean pulp of the phytase in a neutral condition is better than the present used phytase, which enables the phytase in the invention to apply to a fresh water fish feed stuff.
Owner:WUHAN SUNHY BIOLOGICAL
Sulfadimidine degrading bacterium S-07 and screening method thereof
The invention relates to a sulfadimidine degrading bacterium S-07 degraded by microorganisms and a screening method thereof. The sulfadimidine degrading bacterium S-07 is verified as Geobacillus, and the Genbank registration number of the bacterium 16S rDNA is KU588289. The sulfadimidine degrading bacterium is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 21st, 2016, and the preservation number of the sulfadimidine degrading bacterium is CGMCC No. 12382. The sulfadimidine degrading bacterium S-07 well grows within the temperature range of 50-75 DEG C, has quite strong tolerance to sulfadimidine, and can efficiently degrade sulfadimidine in a liquid phase and a solid phase. The bacterium can be used for degrading and removing sulfadimidine residues in livestock excrement or sludge high-temperature compost, the removal rate is larger than 95%, and the sulfadimidine degrading bacterium S-07 has good industrial application prospects and environment benefits.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
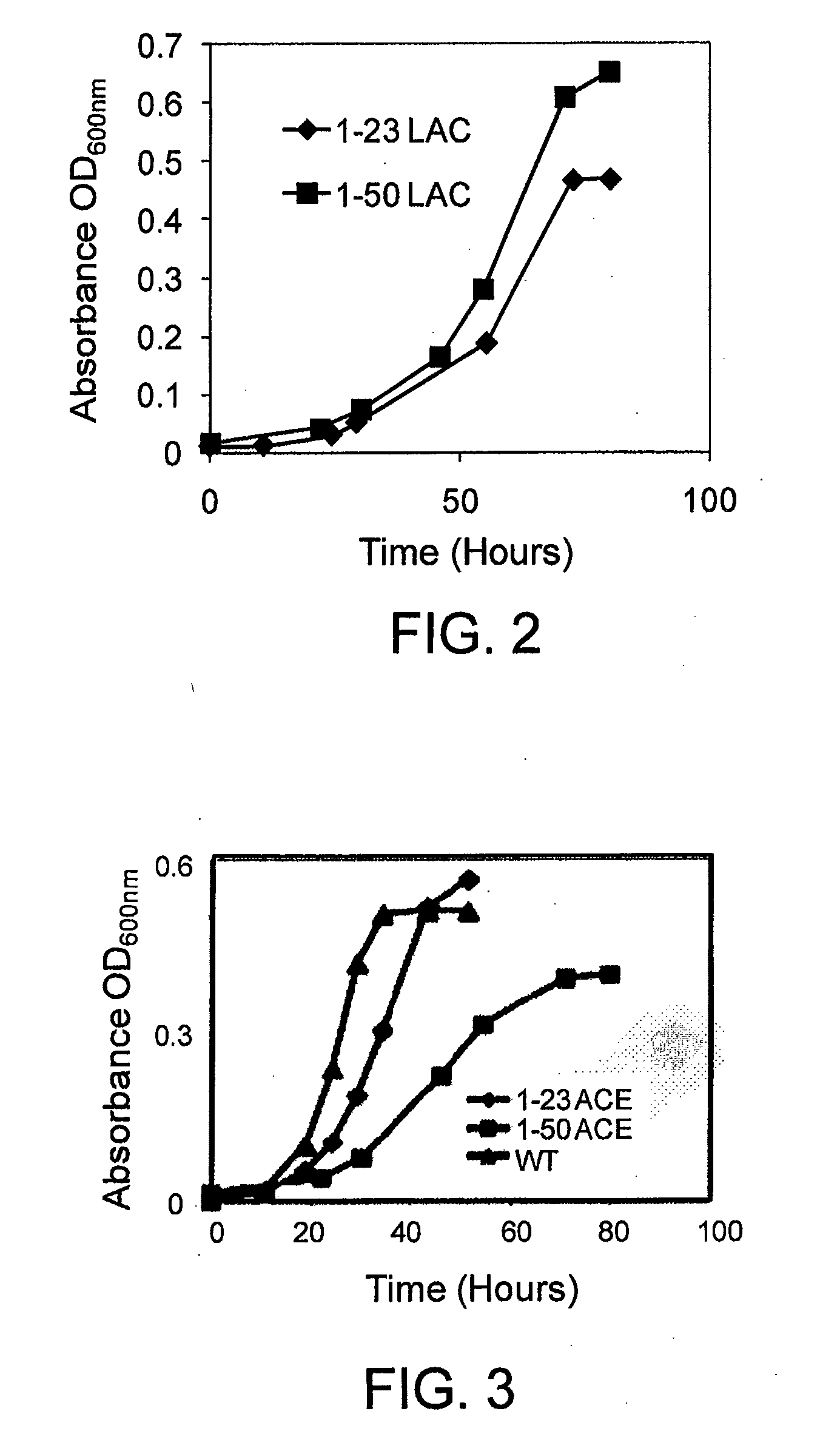
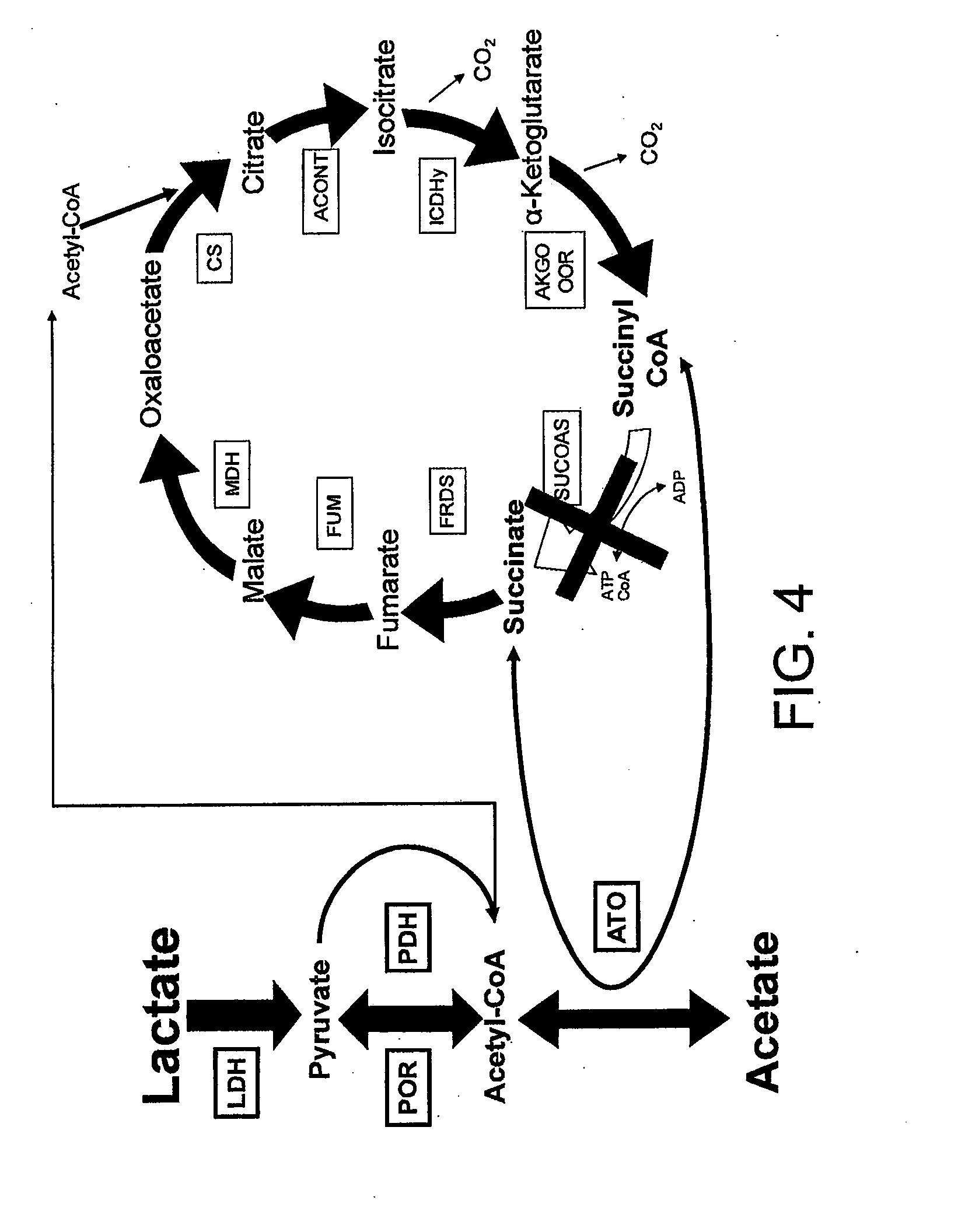
Geobacter Strains That Use Alternate Organic Compounds, Methods of Making, and Methods of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20110151544A1Improving in situ bioremediationEfficient use ofBacteriaUnicellular algaeElectron donorIn situ bioremediation
In preferred embodiments, the present invention provides new isolated strains of a Geobacter species that are capable of using a carbon source that is selected from C3 to C12 organic compounds selected from pyruvate or metabolic precursors of pyruvate as an electron donor in metabolism and in subsequent energy production. In other aspects, other preferred embodiments of the present invention include methods of making such strains and methods of using such strains. In general, the wild type strain of the microorganisms has been shown to be unable to use these C3 to C12 organic compounds as electron donors in metabolic steps such as the reduction of metallic ions. The inventive strains of microorganisms are useful for improving bioremediation applications, including in situ bioremediation (including uranium bioremediation and halogenated solvent bioremediation), microbial fuel cells, power generation from small and large-scale waste facilities (e.g., biomass waste from dairy, agriculture, food processing, brewery, or vintner industries, etc.) using microbial fuel cells, and other applications of microbial fuel cells, including, but not limited to, improved electrical power supplies for environmental sensors, electronic devices, and electric vehicles.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Microorganism continuously-fermenting corn stalk hydrolysate power generation method and battery
ActiveCN107623139AEfficient resource utilizationBiochemical fuel cellsHydrolysateMoorella thermoacetica
The invention relates to a microorganism continuously-fermenting corn stalk hydrolysate power generation method and a battery. The method comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing corn stalks to obtain corn stalk hydrolysate; fermenting the corn stalk hydrolysate in an anaerobic environment by utilizing a Moorella thermoacetica bacterial solution to obtain a culture solution; and injecting the culture solution and sulfur reduced geobacter bacterial solution into a double-chamber container isolated by a proton exchange membrane, reacting in an anaerobic environment, and outputting electricpower from an electrode of the double-chamber container. The battery comprises a double-chamber container isolated by a proton exchange membrane, an anode and a cathode which are arranged in two chambersof the double-chamber container, as well as N2-CO2 mixed gas, sulfur reduced geobacter bacterial solution and the culture solution obtained by fermenting the corn stalk hydrolysate with the Moorella thermoacetica in the double-chamber container. The agricultural waste corn stalks are converted into electric power by virtue of a bioengineering way, so that the high-efficiency recycling of the agricultural wastes is realized while the environment-friendly power generation is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Two-phase anaerobic treatment device and process for establishing direct interspecies electron transfer based on ethanol-type fermentation
InactiveCN107555591AImprove efficiencyImprove decomposition rateWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesDecompositionHigh load
The invention discloses a two-phase anaerobic treatment device and process for establishing direct interspecies electron transfer based on ethanol-type fermentation. The process comprises the following steps: respectively taking a fully mixed anaerobic digester and an up-flow anaerobic sludge bed reactor as an acidification phase and a methanogenesis phase; respectively controlling the hydraulic retention time of the acidification phase and the methanogenesis phase, and the pH and temperature in the device; regulating the fermentation pH of the acidification phase to be 4.0 to 4.5 by using 2 to 4mol / L HCI solution, and running the process. The two-phase anaerobic treatment device and process can achieve the following effects of improving the content of ethyl alcohol in an acidized product;improving the abundance of geobacter in granule sludge of the methanogenesis phase and promoting the establishment of direct interspecies electron transfer with methanogens; accelerating the decomposition rate of organic acid and alcohol substances in the methanogenesis phase; mitigating the acidity accumulation and syntrophism metabolism stasis of the methanogenesis phase caused by high organicloading; and improving the methanogenesis efficiency. The technology has the advantages of low investment cost, simple operation, remarkable improvement effect, and can be applied to the upgrading andrebuilding of the existing two-phase anaerobic process for improving the resistance to high load wastewater impact.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
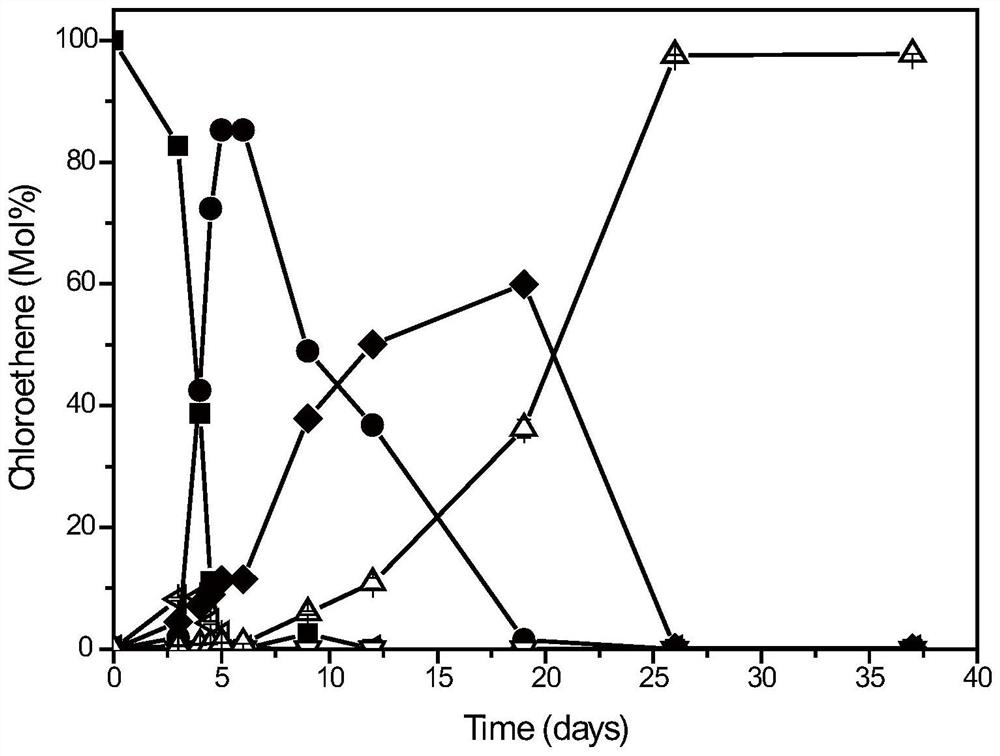
Method for enriching and separating perchloroethylene (PCE) dechlorinating bacteria and application
InactiveCN111676147APromote growthGuaranteed survivalBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
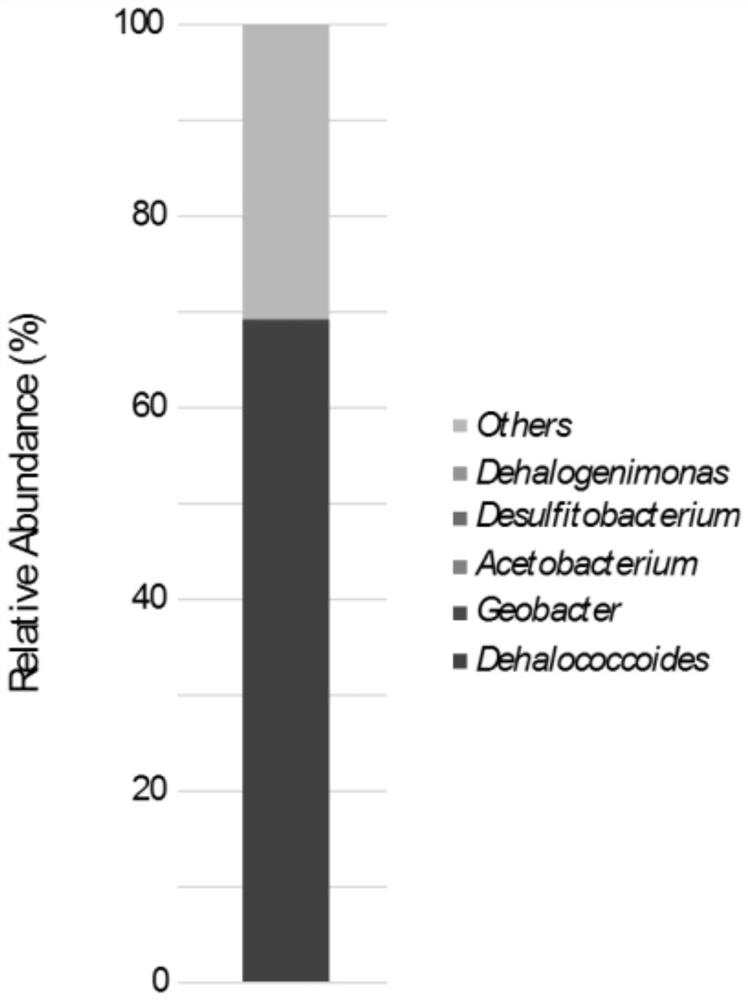
The invention discloses a method for enriching and separating perchloroethylene (PCE) dechlorinating bacteria and application. The invention realizes efficient enrichment culture of PCE complete dechlorinating bacteria, PCE can be completely dechlorinated after 26 days by using the dechlorinating mixed bacteria obtained by the enrichment method, the dechlorinating mixed bacteria show excellent dechlorinating effects, and the abundance of Dehalococoides in the dechlorinating mixed bacteria reaches 68.87%; and efficient PCE dechlorinating bacteria Geobacter is obtained by separation and purification from the enriched dechlorinating mixed bacteria by further using an ecology principle. The method provides favorable technical guidance for realizing efficient enrichment and separation of halogenated organic matter dehalogenation functional microorganisms and obtaining engineering bacterial agents, and has important application value in the technical field of halogenated organic matter anaerobic microorganism remediation.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
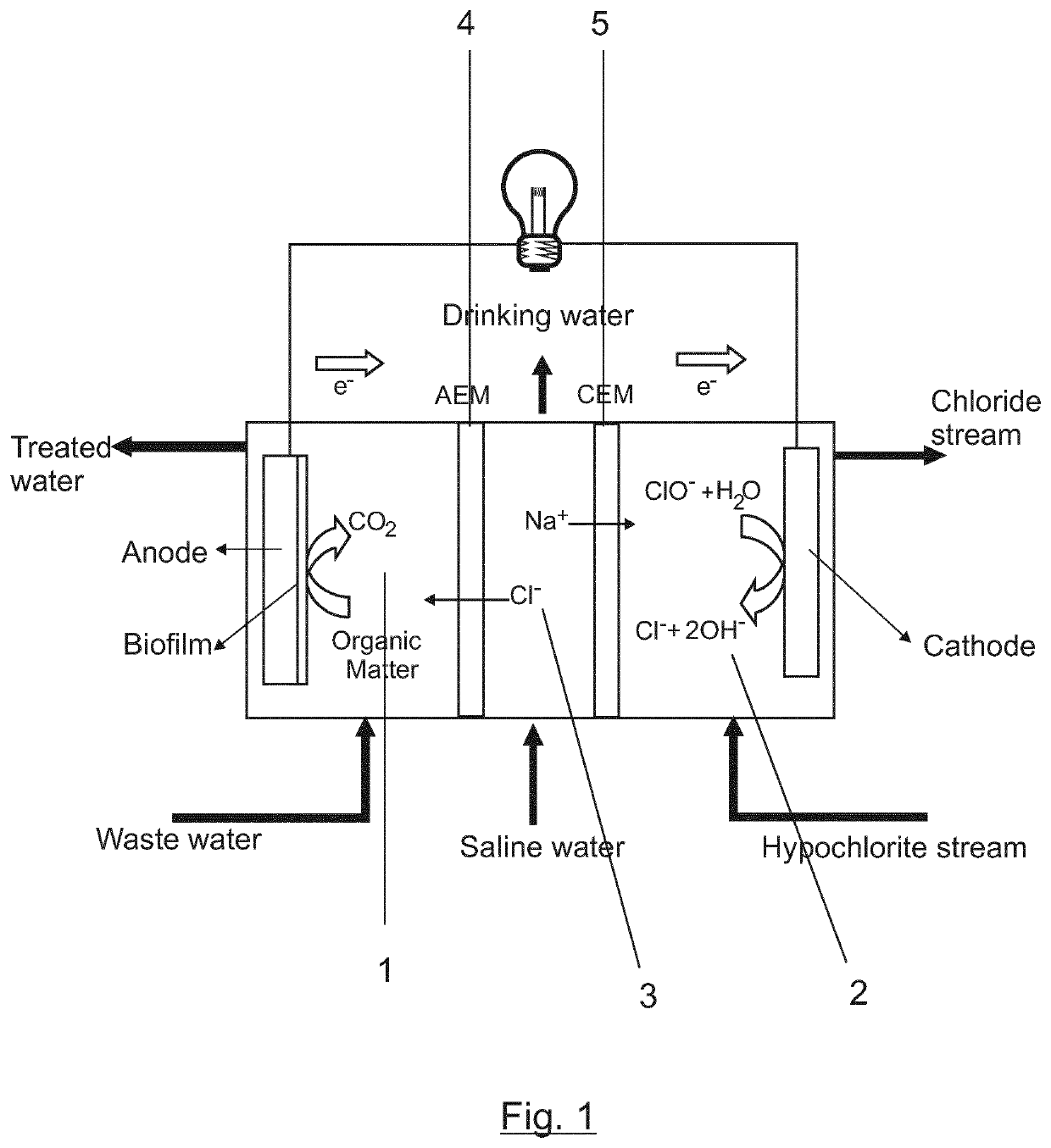
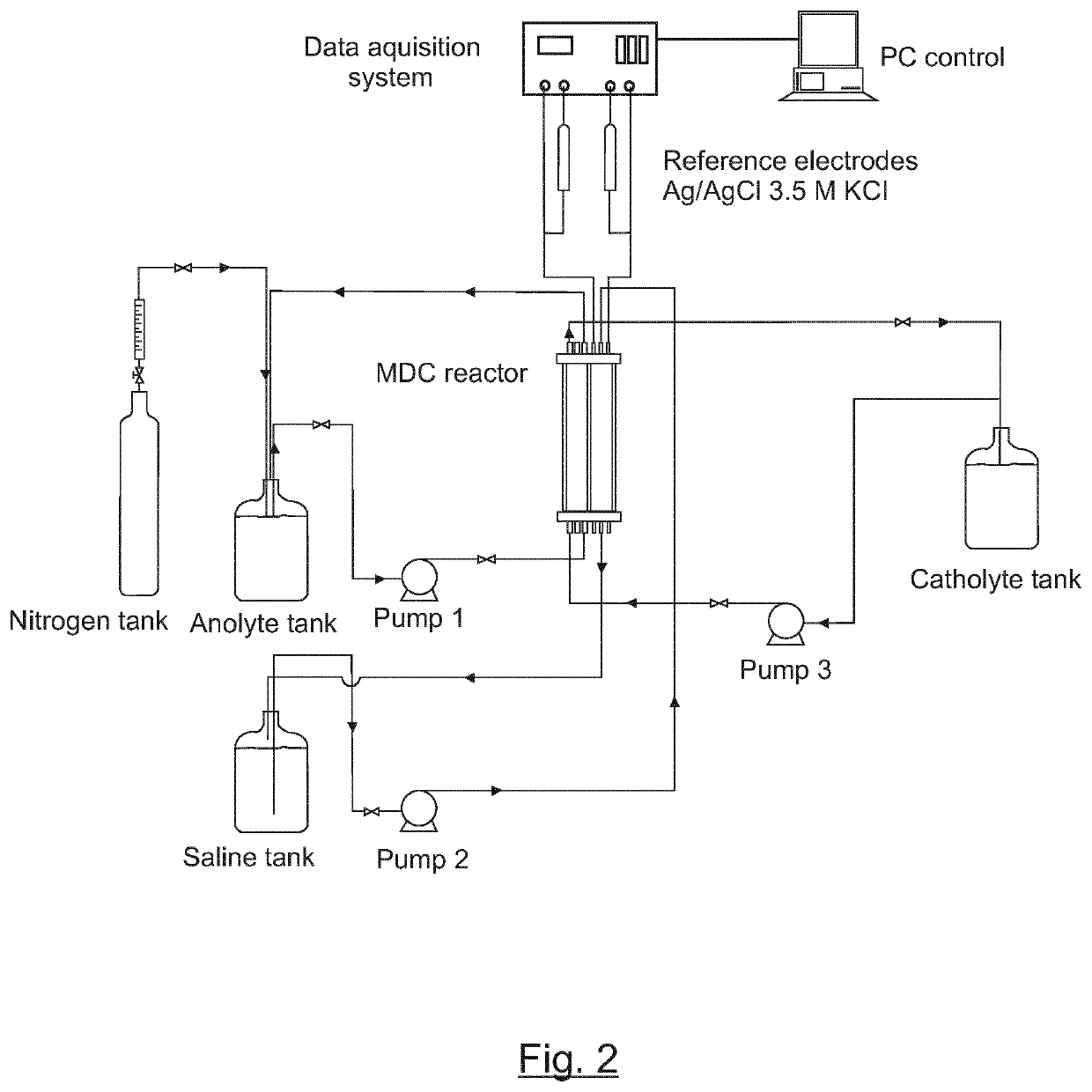
Method of desalination and wastewater treatment in a microbial desalination cell reactor
ActiveUS10954145B2Increase productionHigh energyMembranesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesMicroorganismDesalination
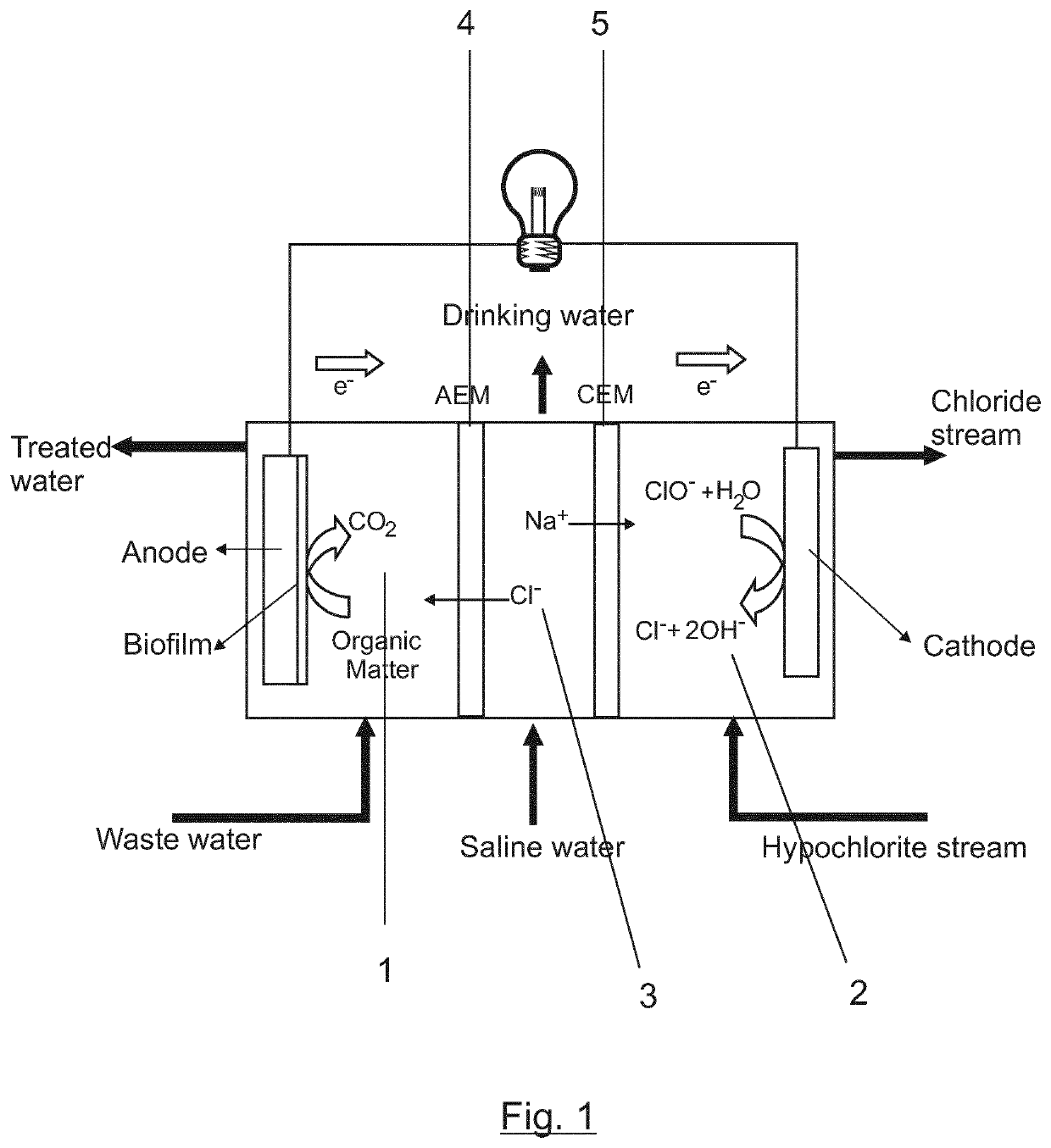
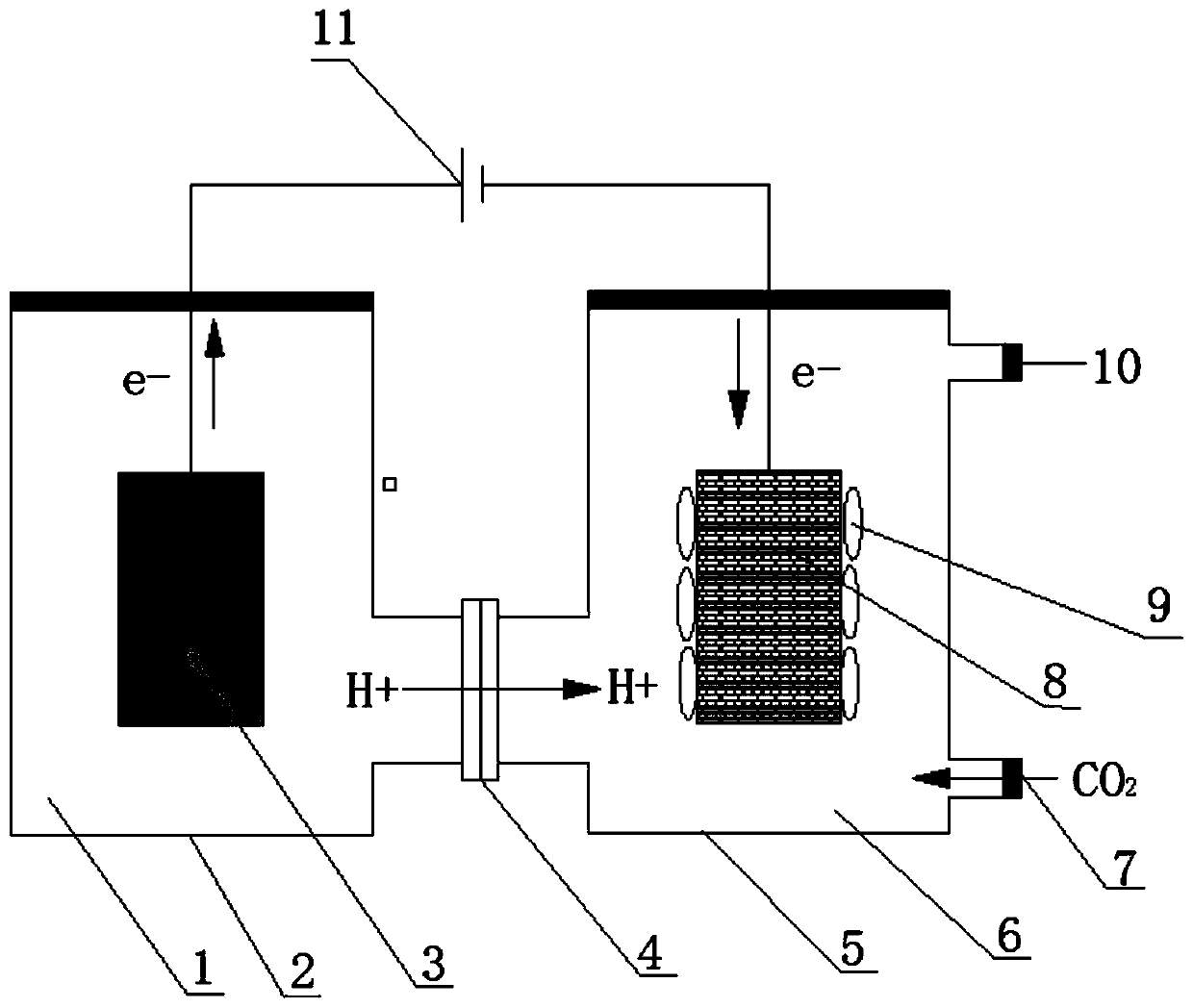
Method of desalination and wastewater treatment in a microbial desalination cell reactor is provided, the microbial desalination cell reactor has three compartments, an anodic compartment, a cathodic compartment and a saline compartment, the method is carried out by (a) adding electrically conductive particles or electrically conductive material in the anodic compartment and cathodic compartment, (b) adding bacteria species of the genus Geobacter in the anodic compartment and several solutions in the compartments (c) replacing the solutions in the cathodic compartment and in the saline compartment and (d) oxidizing organic matter present in wastewater by bacteria from the genus Geobacter in the anodic compartment and desalinating the solution in the saline compartment and (e)after 20 to 30 operation cycles, replacing the solution in the saline compartment by a solution of hypochlorite salt.
Owner:FCC AQUALIA +1
Immobilized bactericide capable of realizing in-situ restoration of polluted sediment and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108624530AIncrease abundanceGood removal effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSediment
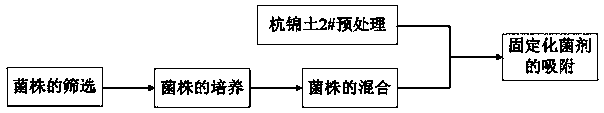
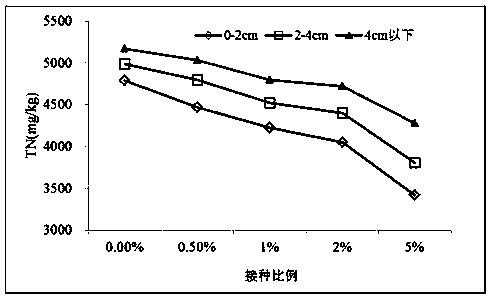
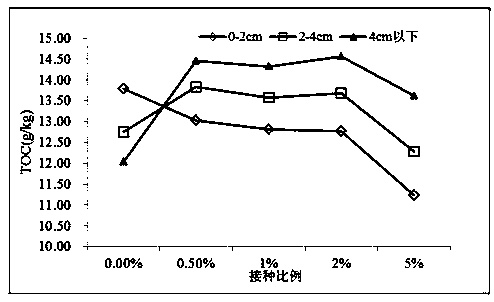
Immobilized bactericide capable of realizing in-situ restoration of polluted sediment is composed of Hangjin clay 2# loaded conductive microorganisms. A preparation method of the immobilized bactericide includes: 1), pretreating Hangjin clay 2# to obtain granular filler; 2), subjecting conductive microorganism strains to enlarged culture to obtain a to-be-inoculated bacteria solution, proportionally adding Hangjin clay 2# pretreated in the step 1, mixing in an anaerobic condition, standing, and removing supernatant to obtain the immobilized bactericide, wherein the conductive microorganism strains include geobacter sulfurreducens, geobacter metalreducens and shewanella spp.. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the immobilized bactericide and application of the immobilized bactericide in in-situ restoration of the polluted sediment.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for synthesizing organic matter by catalytically reducing CO2 through MES biological cathode
InactiveCN110484931ASolve resource problemsCellsElectrolytic organic productionMicrobial electrosynthesisElectron
The invention provides a method for synthesizing an organic matter by catalytically reducing CO2 through an MES biological cathode. A biological cathode is prepared in a microbial electrosynthesis system, CO2 is introduced into a cathode chamber for cyclic aeration, and the polarization potential range is set to be -0.6 V to -1.0 V (vs.Ag / AgCl). Microorganisms Acetobacterium, Candida sp. S and Geobacter which are domesticated and cultured on the cathode can directly obtain electrons from the electrode or hydrogen generated by the electrode to reduce CO2 and synthesize organic matters. The rateof synthesizing organic matters by reducing CO2 is high, and the method has important application value for CO2 fixed conversion and synthesis of organic chemicals.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Devices and methods for generating electrical current from methane
Methods, microbial fuel cells and microbial consortia for generating electrical current are provided according to the present invention which include providing a microbial consortium to an anode chamber of a microbial fuel cell, wherein the microbial CN consortium includes: 1) an engineered methanogen that contains a heterologous nucleic acid sequence encoding methyl-coenzyme M reductase derived from an anaerobic methane oxidizer, 2) an exoelectrogen microbe that produces electrically-conductive appendages and / or one or more types of electron carrier, and 3) a sludge, methane-acclimated sludge, a sludge isolate component, a methane-acclimated sludge isolate component chosen from Paracoccus spp., Geotoga spp., Geobacter spp., Methanosarcina spp., Garciella spp., humic acids; or a combination of any two or more thereof.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Biological-agent fuel cell
InactiveCN103337651AImprove electricity production efficiencyGood symbiosisCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsBacillus licheniformisEngineering
The invention discloses a biological-agent fuel cell. The biological-agent fuel cell comprises microbial fuel, wherein the microbial fuel is formed by mixing bacillus pumilus, bacillus licheniformis, rhodopseudomonas palustris, pseudomonas aeruginosa, sulfuric-reducing geobacter and sulfolobus propionate. The biological-agent fuel cell disclosed by the invention has the advantages that by selection of proper electricity-generating microbes, the electricity-generating efficiency of the microbes is greatly improved; and due to better symbiotic synergy among multiple microbes, the defects of low efficiency and single substrate and the like of single electricity-generating microbes in the prior art are overcome, so that the application prospect is good.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Method for extracting geobacter extracellular polymeric substances
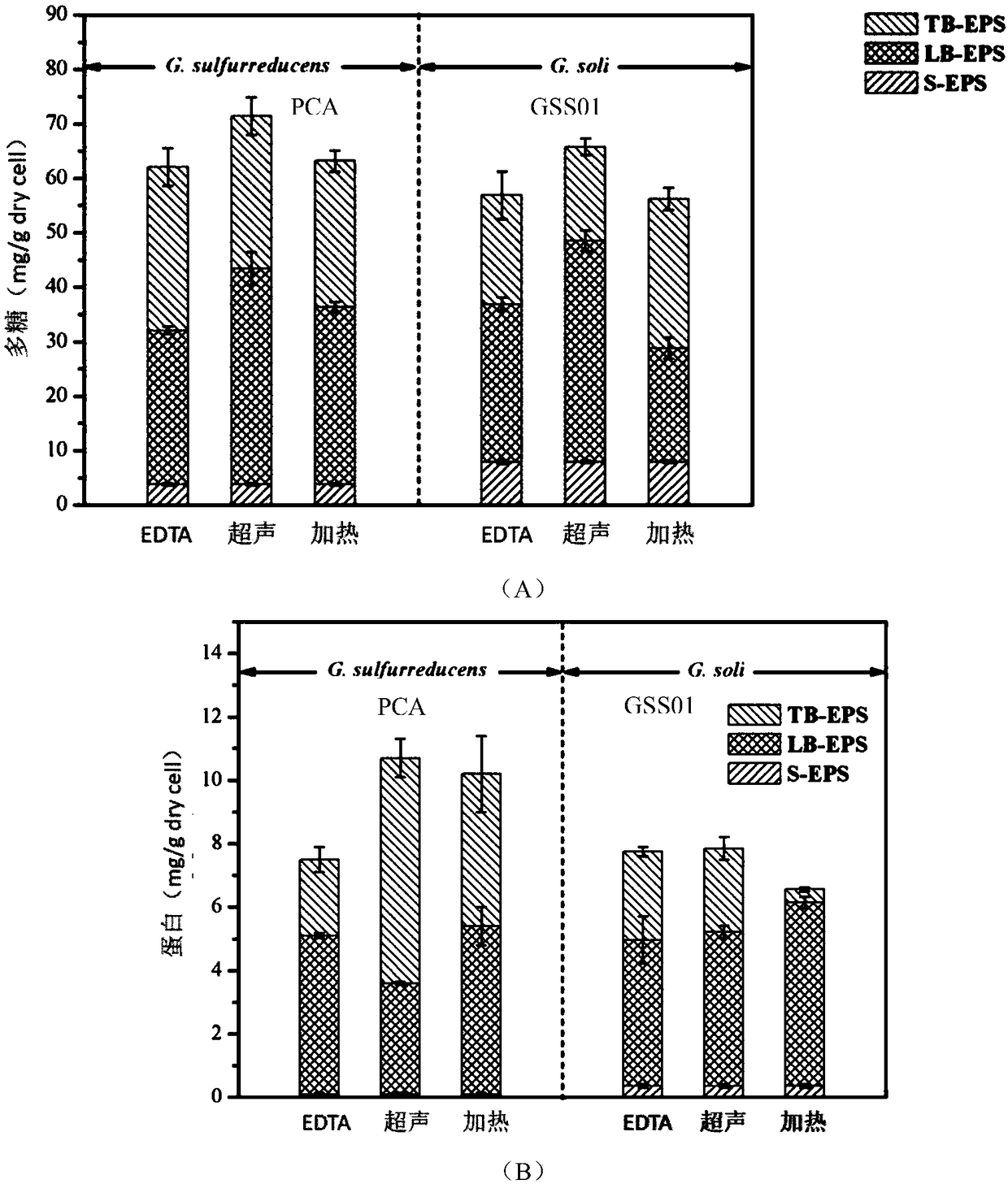
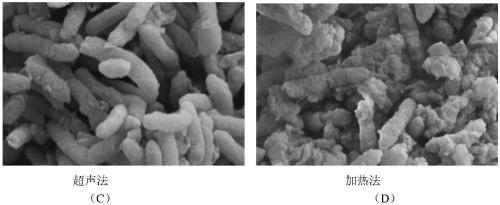
InactiveCN109111499AEasy extractionAvoid damagePeptide preparation methodsMicrobial fuel cellMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for extracting geobacter extracellular polymeric substances. A microbial fuel cell is utilized to culture a biological film, ultrasound and centrifugation are combinedto extract the geobacter extracellular polymeric substances in a layered mode, and soluble S-EPS, loosely bound EPS (LB-EPS) and tightly bound EPS (TB-EPS) can be extracted out. Bacteria damage in anextracting process is effectively reduced, and the extracting amount of the extracellular polymeric substances is improved. According to the method, the characteristics of the geobacter extracellularpolymeric substances are represented for the first time, and the extracted geobacter extracellular polymeric substances is favorable for environmental pollution rehabilitation; furthermore, the method has a certain application prospect in extracellular electron transfer pathways and environment rehabilitation.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for improving biofilm culturing efficiency of biofilter for treating high-nitrate wastewater
PendingCN112062290AShorten the start-up periodSolve the problem of poor film hanging effectWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentActivated sludgeBiological filter
The invention discloses a method for improving biofilm culturing efficiency of a biological filter for treating high-nitrate wastewater, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. Themethod comprises the following operation steps of: 1, carrying out amplification culture and high-nitrate wastewater adaptability culture on geobacterium; 2, synchronously adding the cultured geobacillus and low-concentration activated sludge into a biological filter according to an equal mass ratio, and carrying out biofilm culturing; and 3, maintaining continuous water inflow of the biologicalfilter until biofilm culturing is completed. According to the invention, the abundance and bacterial extracellular polymeric substances of the geobacillus are increased by carrying out high-nitrate adaptability culture on the geobacillus and adding the cultured geobacillus into the reactor, and the growth speed, microbial activity and viscosity of microorganisms are improved, so that the biofilm culturing efficiency of the biofilter for treating the high-nitrate wastewater is improved; and the formed biological film is firm and high in impact load resistance, and has an excellent wastewater treatment effect.
Owner:光大水务科技发展(南京)有限公司 +1
Method for in-situ fluorescent labeling of geobacillus
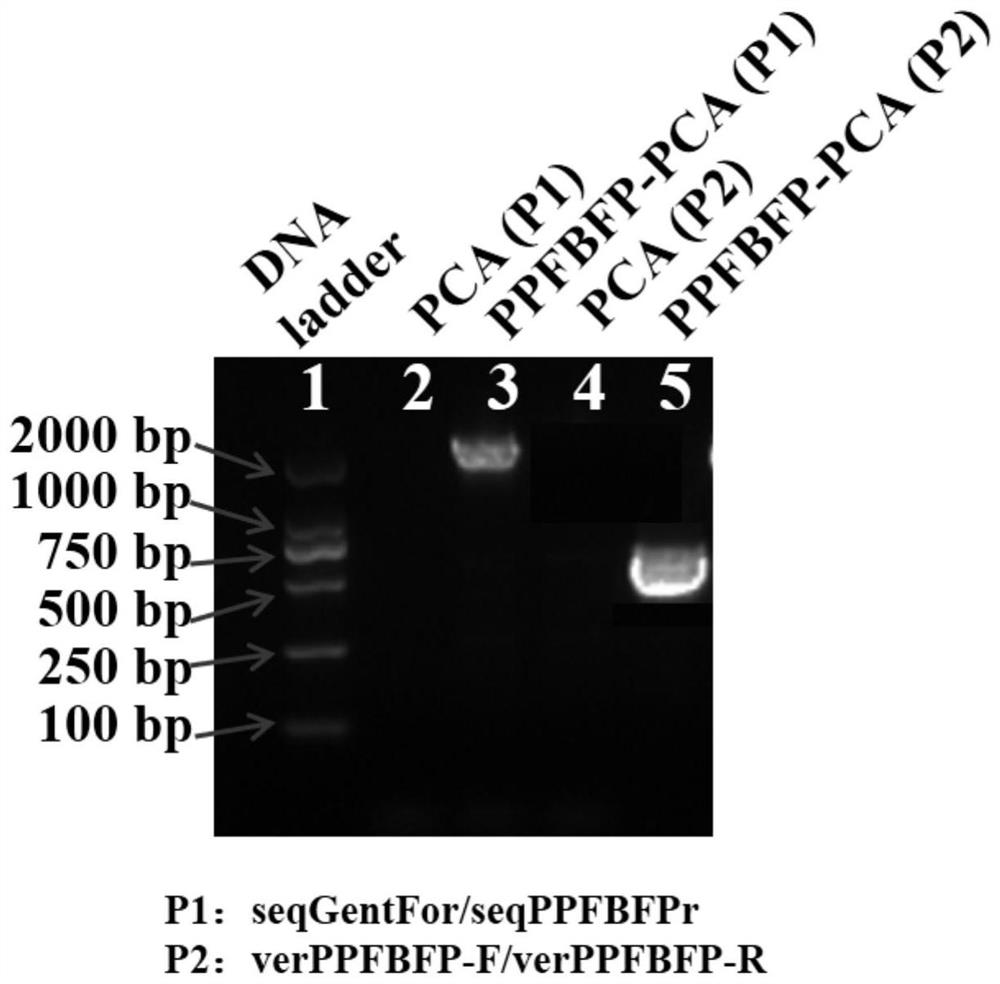
ActiveCN111411064AReal-time observation of motion trajectoryReal-time observation of film formation processBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescent proteinGene
The invention provides a method for in-situ fluorescent labeling of geobacillus. The method includes transferring a PpFbFP fluorescent protein gene into geobacillus. The PpFbFP fluorescent protein label is not influenced by oxygen, can make the labeled geobacillus strain fluoresce under anaerobic conditions, and has a long half-life, and can realize long-term real-time observation of movement trajectory, film forming process and group behavior of the geobacillus.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Geobacteraceae sulferreducens Geo-LYY strain for dehalogenation of halogenated organic compounds and dye decoloration and application thereof
ActiveCN111269854AEfficient dechlorination effectAchieve complete depigmentationBacteriaWater contaminantsTetrachloroethyleneMicroorganism
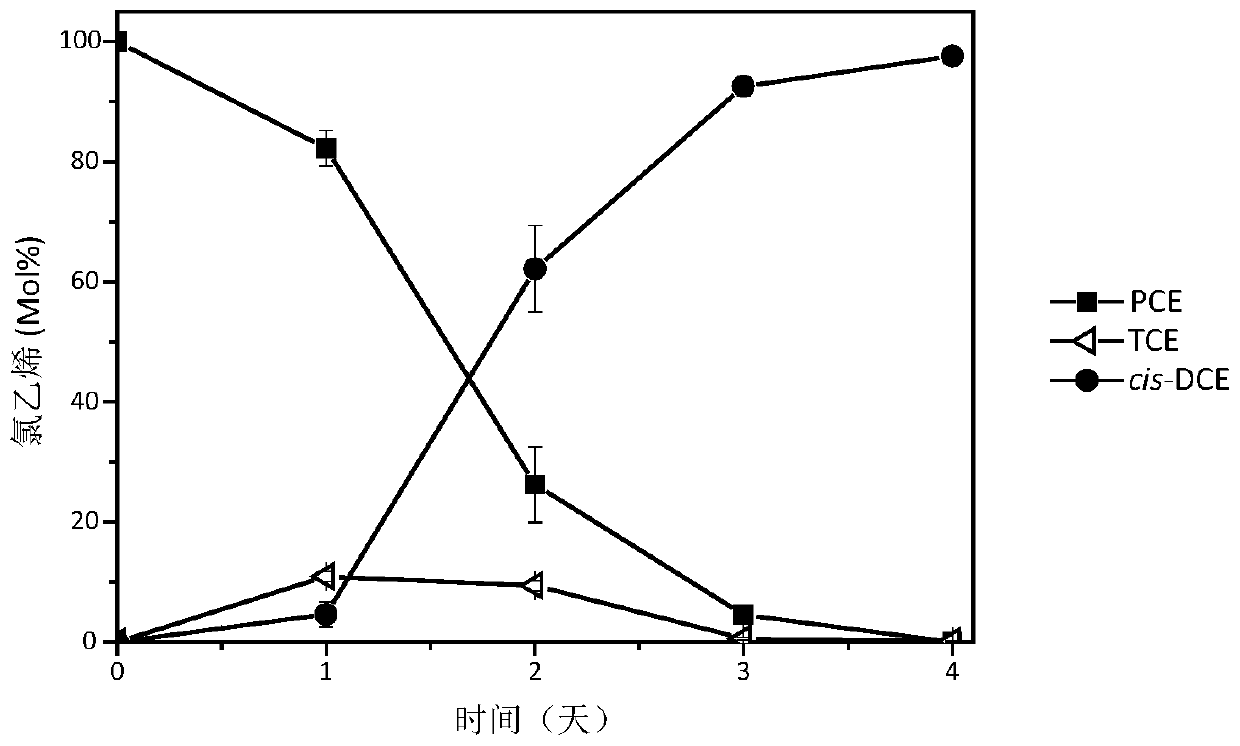
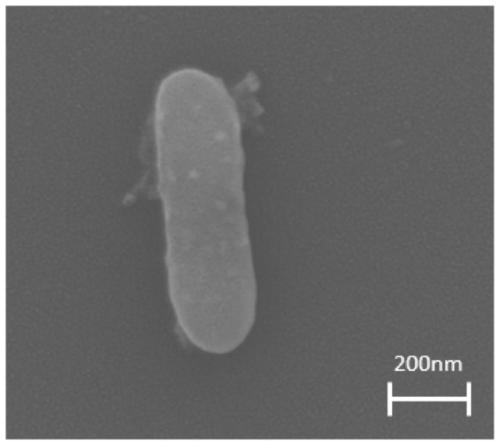
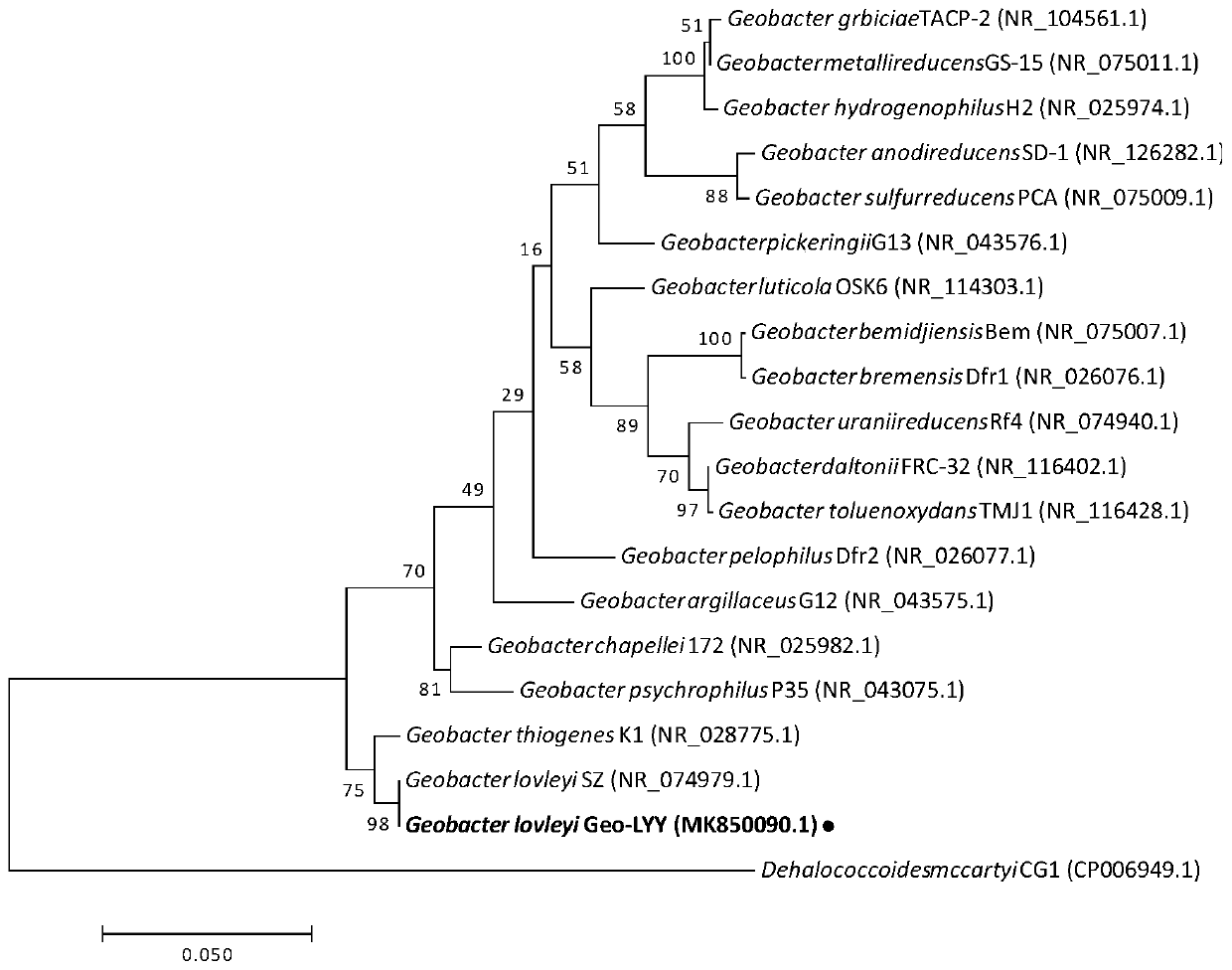
The invention discloses a Geobacteraceae sulferreducens Geo-LYY strain for dehalogenation of halogenated organic compounds and dye decoloration and application of the Geobacteraceae sulferreducens Geo-LYY strain. According to the invention, a strain of Geobacteraceae sulferreducens LYY with halogenated organic compound dehalogenation and dye decolorization capabilities is obtained through screening and separation; the strain was preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on February 17, 2020, and the preservation number of the strain is GDMCC No: 61003. The Geobacteraceae sulferreducens LYY can tolerate the pressure of environmental conditions of high-concentration tetrachloroethylene, antibiotics, heavy metal Cu<2+> and heavy metal Cd<2+>, the efficient dechlorination effect of tetrachloroethylene is kept, and the Geobacteraceae sulferreducens LYY can achieve the effect of completely decoloring azo dyes AO7; therefore, the Geobacteraceae sulferreducens LYY has a good application prospect in dehalogenation of halogenated organic compounds or preparation of halogenated organic compound dehalogenation microbial inoculum and dye decoloration or preparation of a dye decoloration agent.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Water body remediation microbial inoculum and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a composition for preparing a water body remediation microbial inoculum. The composition comprises a fermentation substrate, first fermentation powder and second fermentationpowder, wherein the first ferment powder comprises bacillus subtilis, saccharomycetes and actinomycetes; wherein the second ferment powder is prepared from bifidobacterium album, compost agrobacteriumtumefaciens and Fluviicola taffensis. The invention also relates to a water body remediation microbial inoculum and a preparation method thereof. According to the composition and the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the fermentation time is shortened, the cost is saved, and the obtained water body remediation microbial inoculum is obviously better in removal of nitrogen and phosphorus as well as organic matters. In the aspects of nitrogen removal and phosphorus removal, the microbial inoculum provided by the invention can remove ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in seriously polluted water more quickly, and finally reaches class II and class III water quality standards. In the aspect of COD removal, the microbial inoculum can treat V-type water to reach the standard of I-type water quality.
Owner:WUHAN EZHENGNONG SCI & TECH
Method of desalination and wastewater treatment in a microbial desalination cell reactor
ActiveUS20200010345A1Increase productionHigh energyMembranesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesMicroorganismDesalination
Method of desalination and wastewater treatment in a microbial desalination cell reactor is provided, the microbial desalination cell reactor has three compartments, an anodic compartment, a cathodic compartment and a saline compartment, the method is carried out by (a) adding electrically conductive particles or electrically conductive material in the anodic compartment and cathodic compartment, (b) adding bacteria species of the genus Geobacter in the anodic compartment and several solutions in the compartments (c) replacing the solutions in the cathodic compartment and in the saline compartment and (d) oxidizing organic matter present in wastewater by bacteria from the genus Geobacter in the anodic compartment and desalinating the solution in the saline compartment and (e)after 20 to 30 operation cycles, replacing the solution in the saline compartment by a solution of hypochlorite salt
Owner:FCC AQUALIA +1
Methods and compositions for treating cancer
PendingCN113645981ABacteria material medical ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrevotellaBacteroides salyersiae
Described herein are methods and compositions for treating cancer and for predicting a subjects' response to combination checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Aspects of the disclosure relate to a method of treating cancer and / or reducing toxicity to a therapy in a subject comprising administering to the subject a composition comprising at least one isolated or purified population of bacteria belonging to one or more of the genera Flavonifractor, Dielma, Akkermansia, Alistipes, Bacteroides, Butyricimonas, Vampirovibrio, Tyzzerella, Parabacteroides distasonis, Fournierella, Fournierella massiliensis, Eisenbergiella tayi, Tissierellales, Hungateiclostridium thermocellum, Dorea formicigenerans, Caloramator coolhaasi, Muricomes, Geosporobacter, Prevotella paludivivens, Lactobacillus secaliphilus, Bacteroides fmegoldii, Lactobacillus johnsonii, Parapedobacter composti, and Anaerotignum lactatifermentans and wherein the method further comprises treating the subject with a combination of (i) a PD-1, PDL1, or PDL2 inhibitor and (ii) a CTLA-4, B7-1, or B7-2 inhibitor.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Novel organic halide respiration geobacter and application thereof
ActiveCN112111420AHas the ability to degradeBacteriaWater contaminantsBacterial strainBioremediation
The invention relates to the microbiological field, and discloses novel organic halide respiration geobacter and application of the novel organic halide respiration geobacter in bioremediation of chloralkane pollutants. A geobacter IAE bacterial strain is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (culture collection number CGMCC) on July 7, 2020, wherein the addressis No. 3, 1 Courtyard No., Beichenxi Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the zip code is 100101, and the collection number is 1.5298.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heavy metal passivation and soil remediation type microbial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113861997AReduce contentThe combination ratio is reasonableAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesMicroorganismSoil science
The invention relates to a heavy metal passivation and soil remediation type microbial agent and a preparation method thereof. The heavy metal passivation and soil remediation type microbial agent contains various microorganisms such as bacillus subtilis, bacillus megatherium, bacillus mucilaginosus, metal reduction geobacter and the like, and is loaded by a composite carrier prepared from an inorganic carrier and an organic carrier. After the heavy metal passivation and soil remediation type microbial agent is applied to soil, the microbial agent can stably survive and reproduce in the carrier, so that heavy metals in the soil can be effectively remedied, and the carrier contains silicon, calcium and magnesium elements, so that the pH value of the soil can be adjusted, and the heavy metals in the soil can be passivated.
Owner:创想未来生物工程(北京)有限公司 +1
Geobacterium engineering strain for passivating heavy metals and construction method of geobacterium engineering strain
ActiveCN114410559AStrong toleranceImprove residual problemsBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMetallic sulfideEnvironmental engineering
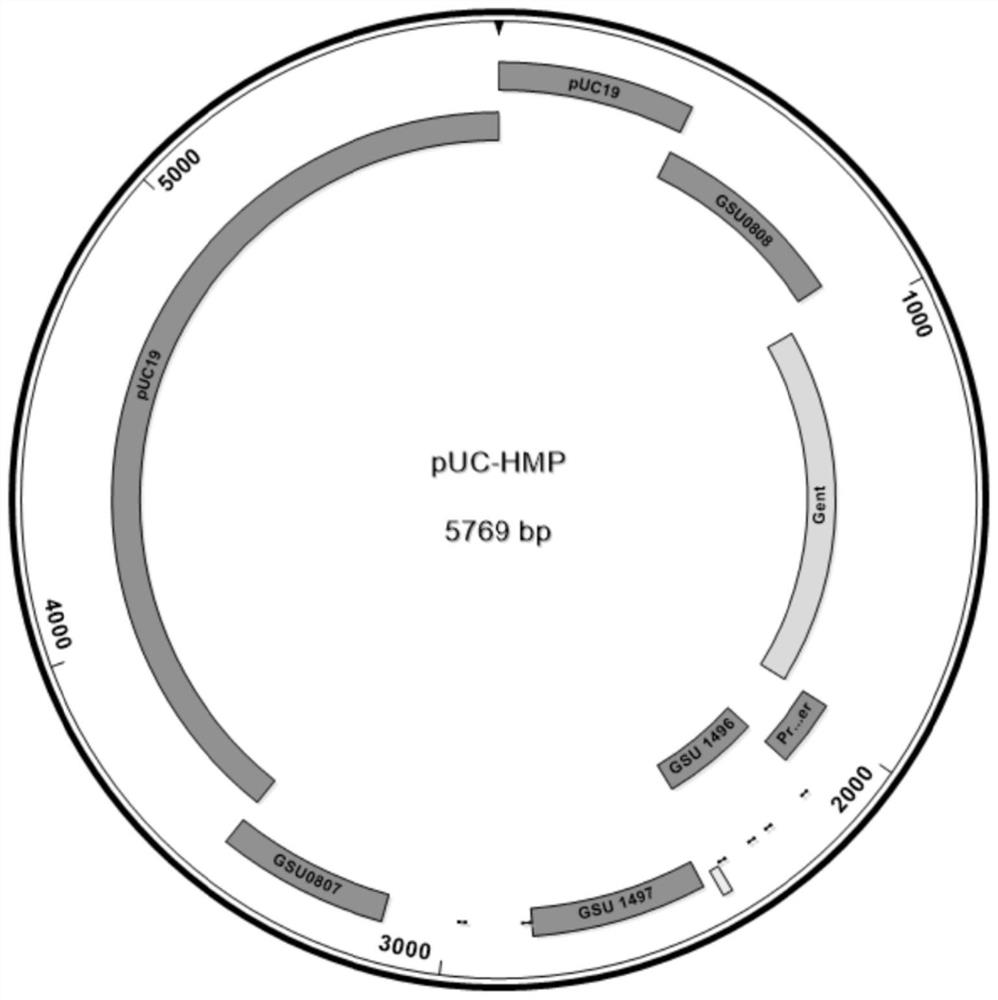
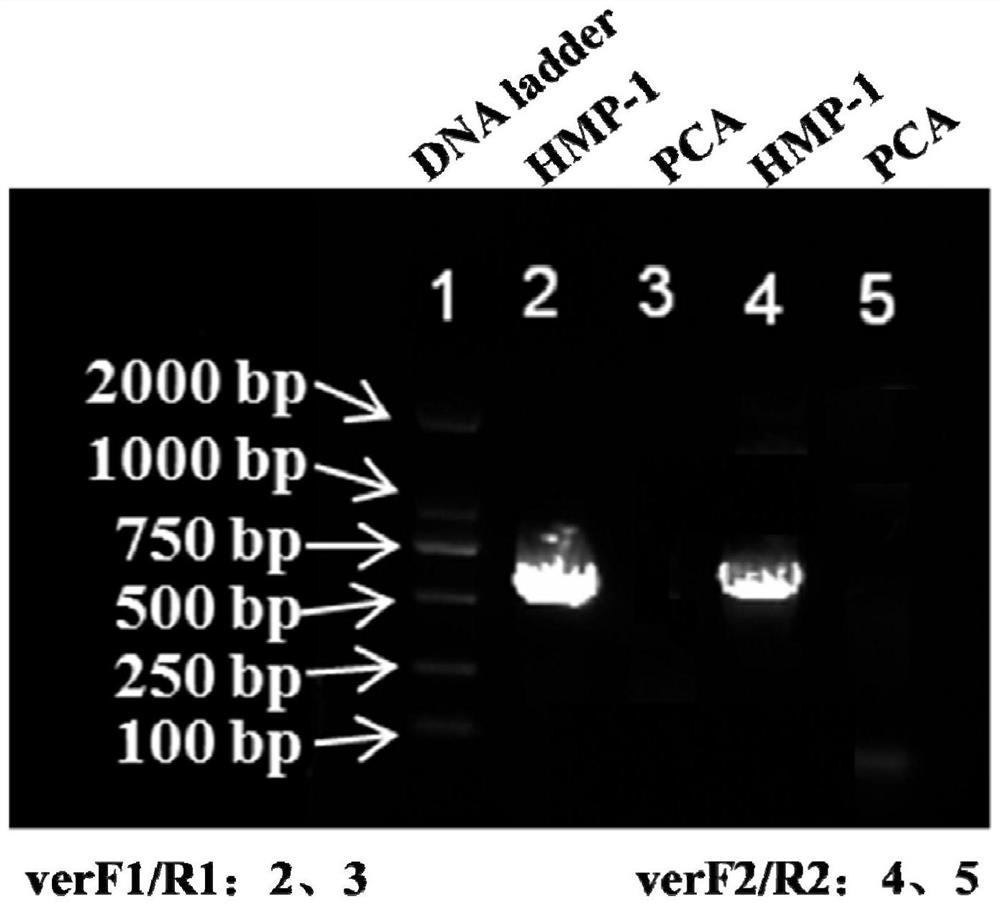
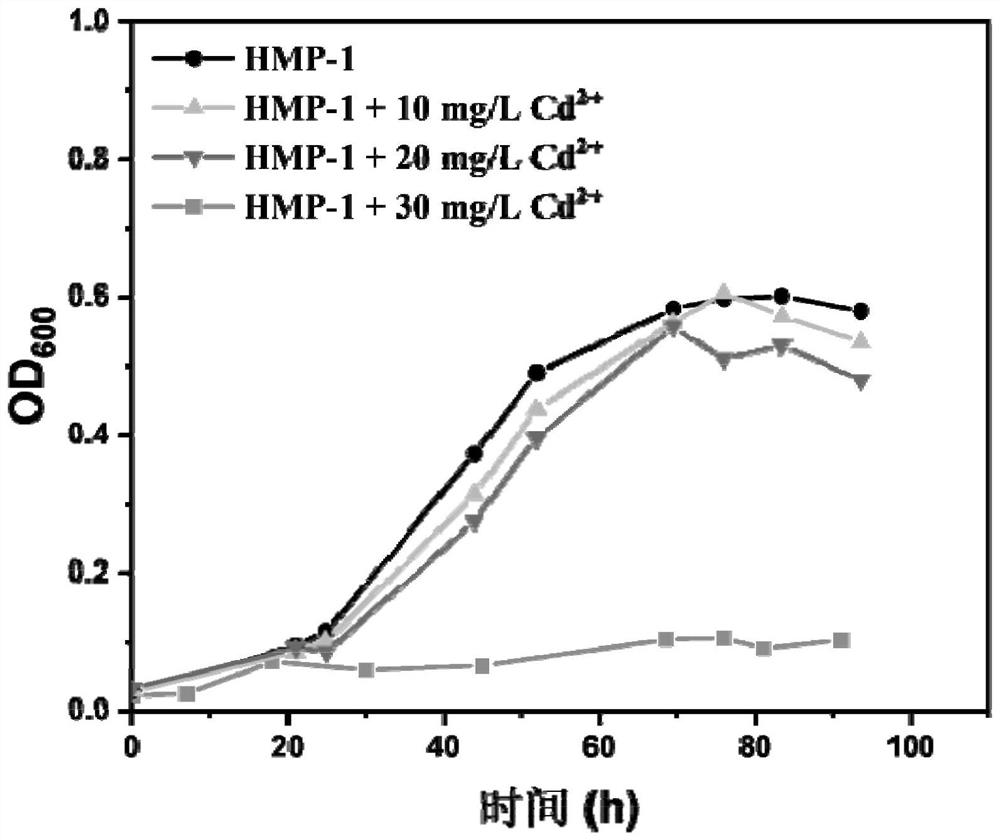
The invention discloses a geobacter engineering strain for passivating heavy metals and a construction method of the geobacter engineering strain, the geobacter engineering strain for passivating the heavy metals is Geobacter sulfurreducens HMP-1, and is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is GDMCC NO.62189. The invention further discloses a construction method of the geobacter engineering strain for passivating the heavy metals. According to the heavy metal passivated geobacterium engineering strain, cysteine is marked on the pilus surface, and the cysteine in the pilus is combined with heavy metal ions to quickly form metal sulfide precipitates, so that the heavy metal removal rate reaches 70% or above under the condition of not depending on any substrate or highly enriched heavy metal plants, and the heavy metal removal rate can reach 70% or above under the condition of not depending on any substrate or highly enriched heavy metal plants. Therefore, the problem of Cd < 2 + > residue in the environment can be effectively improved, and the defects that the existing microbial remediation effect on heavy metals is unstable and the remediation process is limited by many conditions are overcome.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Microbial continuous fermentation corn stalk hydrolyzate production method and battery
ActiveCN107623139BEfficient resource utilizationBiochemical fuel cellsBiotechnologyElectrical battery
The invention relates to a microorganism continuously-fermenting corn stalk hydrolysate power generation method and a battery. The method comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing corn stalks to obtain corn stalk hydrolysate; fermenting the corn stalk hydrolysate in an anaerobic environment by utilizing a Moorella thermoacetica bacterial solution to obtain a culture solution; and injecting the culture solution and sulfur reduced geobacter bacterial solution into a double-chamber container isolated by a proton exchange membrane, reacting in an anaerobic environment, and outputting electricpower from an electrode of the double-chamber container. The battery comprises a double-chamber container isolated by a proton exchange membrane, an anode and a cathode which are arranged in two chambersof the double-chamber container, as well as N2-CO2 mixed gas, sulfur reduced geobacter bacterial solution and the culture solution obtained by fermenting the corn stalk hydrolysate with the Moorella thermoacetica in the double-chamber container. The agricultural waste corn stalks are converted into electric power by virtue of a bioengineering way, so that the high-efficiency recycling of the agricultural wastes is realized while the environment-friendly power generation is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
A method for in situ fluorescence labeling of Geobacter
ActiveCN111411064BReal-time observation of motion trajectoryBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyFluorescent protein
The invention provides a method for in situ fluorescence labeling of Geobacter. The PpFbFP fluorescent protein gene is transferred into Geobacter. The PpFbFP fluorescent protein marker of the present invention is not affected by oxygen, and can make the labeled Geobacter under anaerobic conditions. The strain fluoresces and has a long half-life, which enables long-term real-time observation of the movement trajectory, film formation process and group behavior of Geobacter.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for degrading protein by co-culture of proteiniphilum acetatigenes and geobacter sulfurreducens
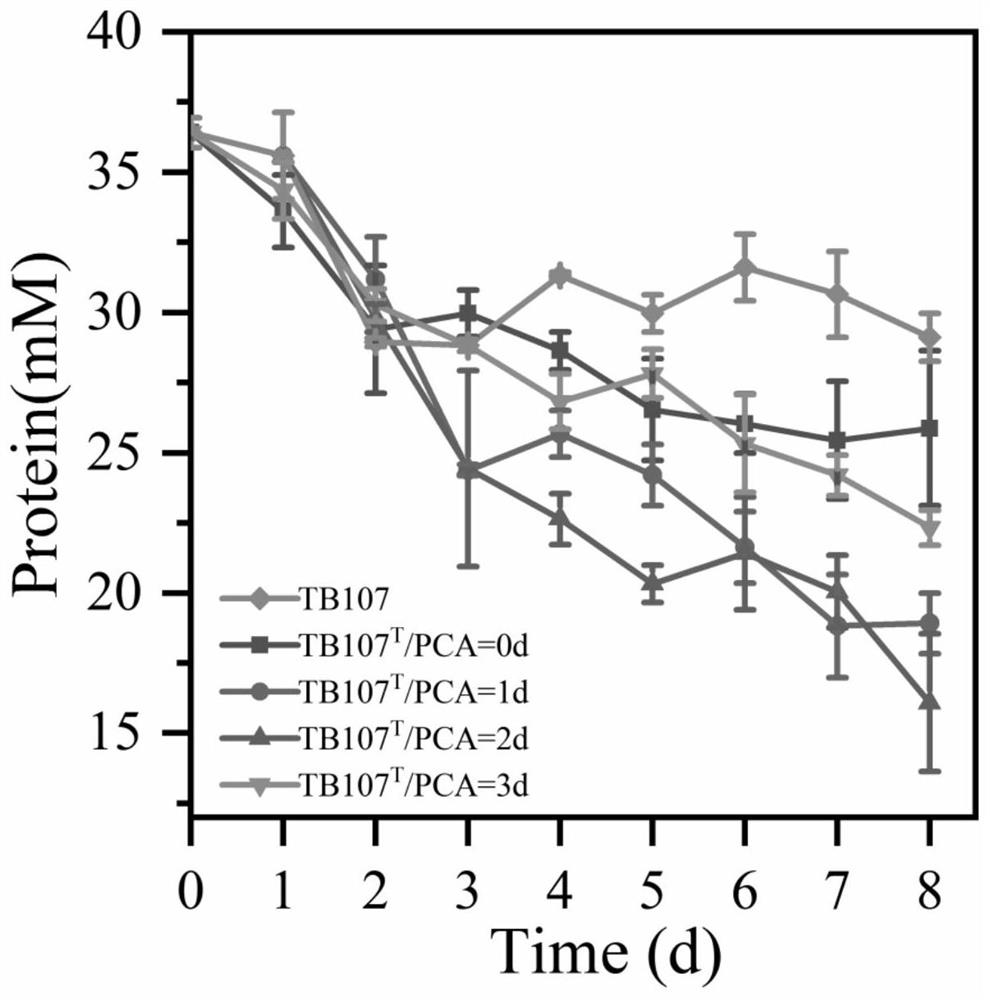
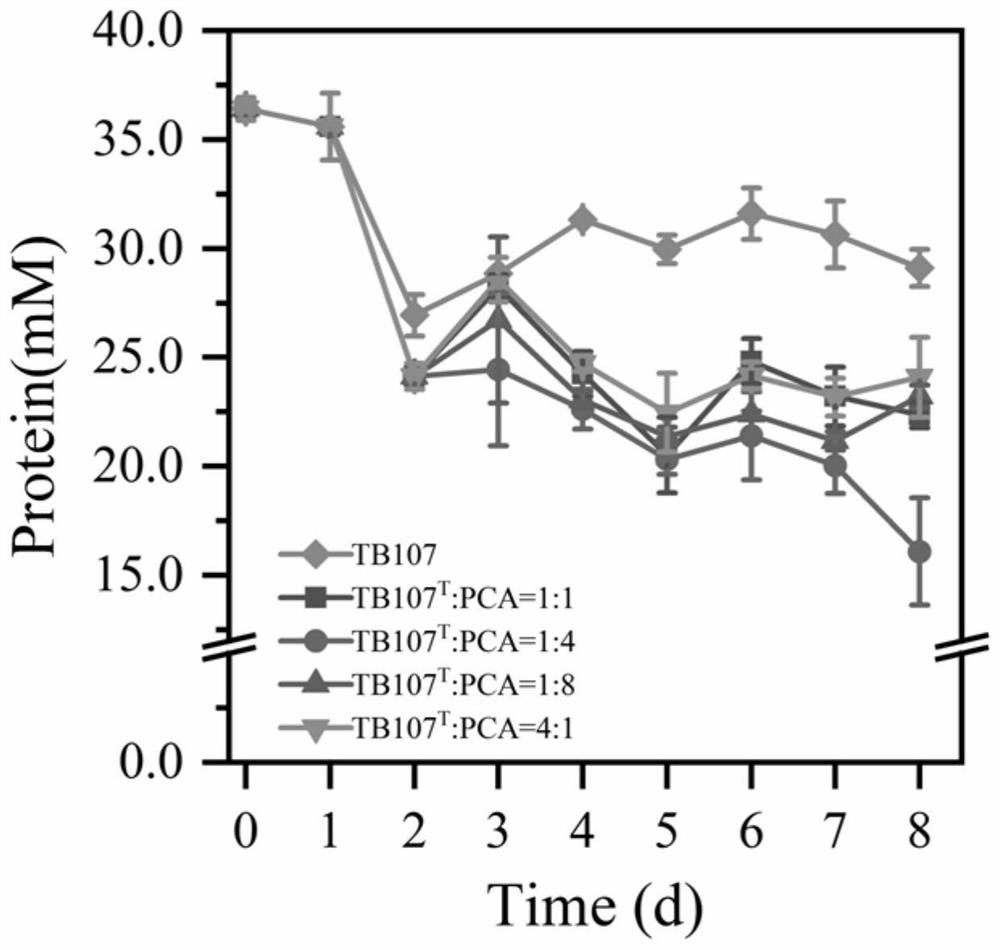
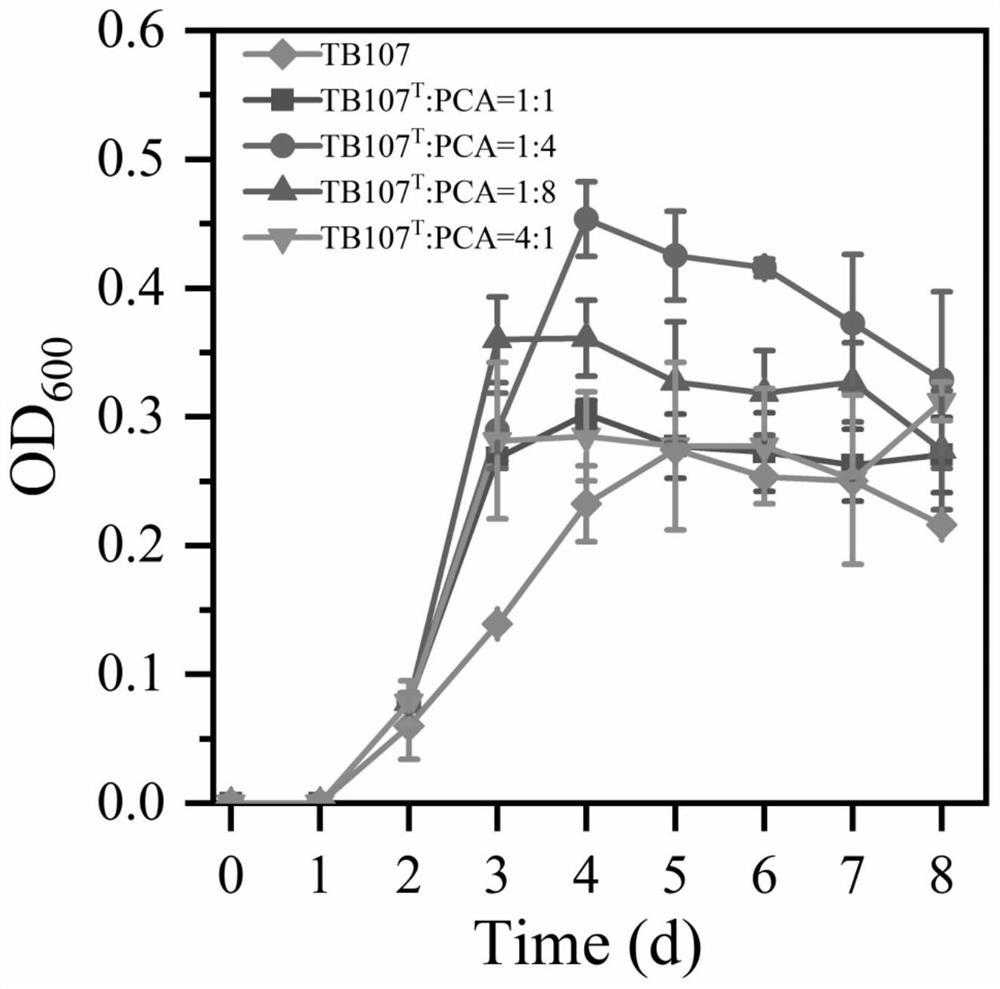
PendingCN113897318AAvoid pollutionAvoid complexityBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyWAS PROTEIN
The invention discloses a method for degrading a protein by co-culture of proteiniphilum acetatigenes and geobacter sulfurreducens. The method comprises the following specific steps: S1, firstly inoculating the proteiniphilum acetatigenes in a culture solution, and then inoculating the geobacter sulfurreducens; S2, protein degradation effect: observing the degradation effect of protein inoculated with mixed bacteria for different days and different in inoculation proportions, and the result shows that the co-culture of the two bacteria is far better than pure culture of the proteiniphilum acetatigenes in terms of protein degradation effect; wherein the proteiniphilum acetatigenes and the geobacter sulfurreducens are inoculated in a proportion of 1: 4, the protein degradation rate of a co-culture system where the proteiniphilum acetatigenes grows for 2 days firstly and then the geobacter sulfurreducens is inoculated is the highest, the degraded proteiniphilum acetatigenes of the invention are protein degradation bacteria and can generate acetic acid, and the acetic acid can be used as a substrate of the sulfur-reducing geobacter and can be used as a substrate of the geobacter sulfurreducens. Compared with other protein degrading bacteria, the mixed system can degrade more proteins, and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Sludge fermentation process for pig raising wastewater
PendingCN113072248ASpeed up decompositionImprove processing efficiencyWaste water treatment from animal husbandryTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectrical conductorMethanobacter
The invention discloses a sludge fermentation process for pig raising wastewater. A precipitation tank and a fermentation tank are sequentially included from left to right, a feeding pipe is arranged on one side wall of the upper end of the precipitation tank, the lower end of the precipitation tank is communicated with the lower end of the fermentation tank through a material guiding pipe, and a wastewater collecting device is arranged in the precipitation tank. The wastewater collecting device can discharge and collect upper-layer wastewater in the settling tank; and a material passing pipe is arranged on one side wall of the upper end in the fermentation tank, anaerobic sludge particles can be introduced into the material passing pipe, a stirring device is arranged on the fermentation tank, a carbon rod layer is arranged on the stirring device, and the carbon rod layer is electrically connected with an external power supply through a wire. The carbon rod layer is used as a conductor material and intervenes in electron transfer between anaerobic oxidation bacteria and methane bacteria, so that electrons generated by decomposing organic matters by geobacterium are directly utilized by methanogens, carbon dioxide is reduced into methane, the methane yield and the sludge decomposition speed are increased, the sludge treatment efficiency is improved, and the investment is saved.
Owner:江西清绿环保有限公司
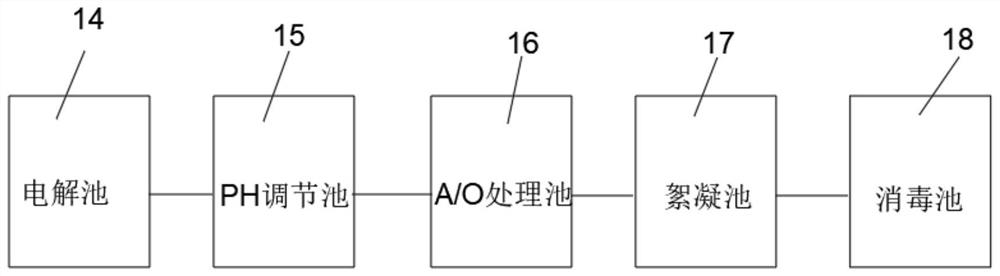
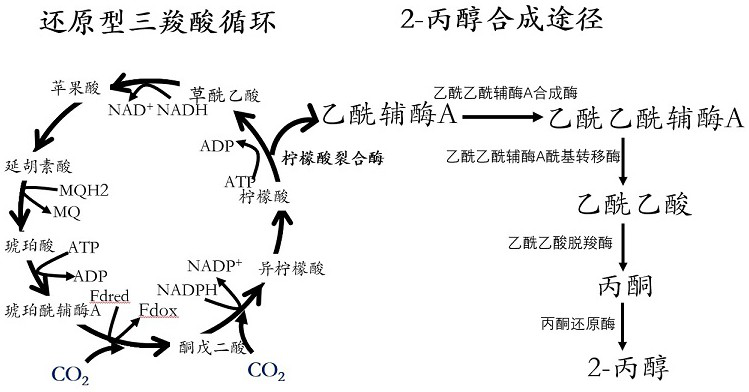
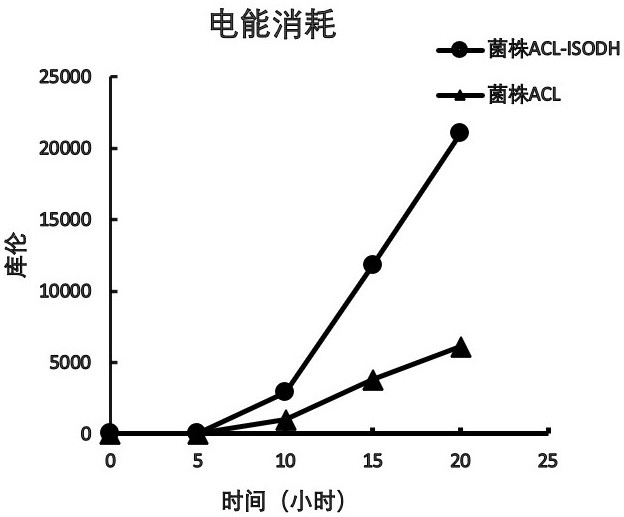
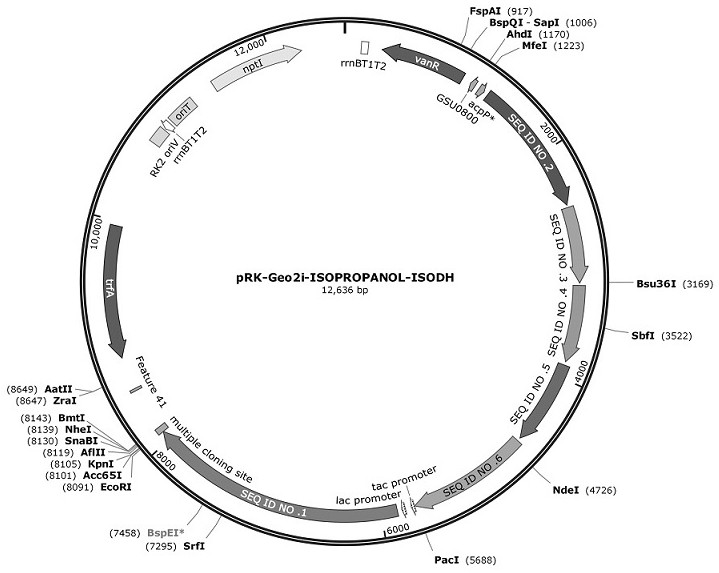
Utilize electrical energy to fix co 2 And engineering bacteria for synthesizing isopropanol and construction method
ActiveCN114561416BEfficient conversionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIsocitrate Dehydrogenase (NAD+)
The present invention provides a method for designing and constructing high-efficiency use of electrical energy to fix CO by using synthetic biotechnology. 2 And the method and application of engineering bacteria for synthesizing isopropanol. The method of designing and constructing engineering bacteria is to be able to utilize electric energy and CO. 2 electroactive microorganisms Geobacter sulfurreducens ACL is the chassis. In the chassis strain, isocitrate dehydrogenase and isopropanol synthesis pathway-related enzymes are efficiently expressed by plasmids. It has been verified by experiments that the strain constructed by this method can efficiently utilize electricity and CO. 2 Synthesis of isopropanol.
Owner:深圳中科翎碳生物科技有限公司
Wheat endophyte and an application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of microbial application, and particularly relates to a wheat endophyte and an application thereof. The specific technical features are characterized in that the wheat endophyte is preserved on CGMCC on August 6th, 2018, and preserved at the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, No.1 yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China, with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 13938. The endophyte can be applied to the control of plant diseases, especially for the control of wheat diseases and watermelon fusarium wilt. The invention provides a brand new species of the geobacter strain, which has obvious effects in controlling plant diseases, and may have other unknown effects. The geobacter strain has important promotion value for the healthy growth and yield increase of various economic crops, and has research significance and guiding value for studying the effect of fungi on plant diseases.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
A kind of microbial electrode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112838221BExcellent electron transfer propertiesImprove power generation performanceCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsBiotechnologyAminophenylboronic acid
The present invention relates to the field of microbial fuel cells, in particular to a microbial electrode and a preparation method thereof, wherein, a preparation method of a microbial electrode comprises the following steps: placing the acidified substrate in an aqueous solution containing a coupling agent, and adding phenylboronic acid substances to obtain an activated substrate; soaking the activated substrate in glucose solution, and then co-cultivating it with electroactive microorganisms to obtain a microbial electrode; the coupling agent is 1 A mixture of ‑ethyl‑3‑(3‑dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide and N‑hydroxysuccinimide; the phenylboronic acid is 3‑aminophenylboronic acid or 4‑dimethylaminobenzene Any one of boric acid; the electroactive microorganism is any one or both of Geobacter or Shewanella. Due to the electroactive biofilm covered on the surface of the microbial electrode prepared by the present invention, the surface has excellent electron transfer properties, thereby significantly improving the electricity generation performance of the microbial electrode.
Owner:DATANG ENVIRONMENT IND GRP
Pure bacteria Geobacter genus microbe electrochemical system capable of being easily started in aerobic environment
InactiveCN110343602AImprove securityWide applicabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenusBiology
The invention relates to a microbial cultivation technology, and provides a pure bacteria Geobacter genus microbe electrochemical system capable of being easily started in an aerobic environment. Thesystem takes a moulding carbon electrode material or an electrode material for modifying amorphous carbon as a carrier of an electrochemically active biofilm, and takes a purely cultured Geobacter genus microbe as an inoculum, a culture solution is configured by a PBS solution, a substrate and an aerobic culture medium; the microbe electrochemical system is operated under aerobic conditions, and the headspace oxygen partial pressure is characterized in that PO20 is greater than 0 and less than or equal to 21%; a substrate of the culture solution is acetic acid, ethanol or glucose; an aerobic culture agent is a mixture of one or more of ferric salt, fumarate, hexavalent chromium salt, pentavalent vanadium salt or hexavalent uranium salt. The system uses a method of adding the aerobic culture agent for the first time to aerobic culture of Geobacter genus microbe in the electrochemical system, which is more suitable for practical application, and has the advantages of high safety, universal applicability, and simple operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com