Method for extracting geobacter extracellular polymeric substances
A technology of extracellular polymers and geobacteria, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of changes in the characteristics of extracellular polymers and the lack of uniform standards for extraction methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
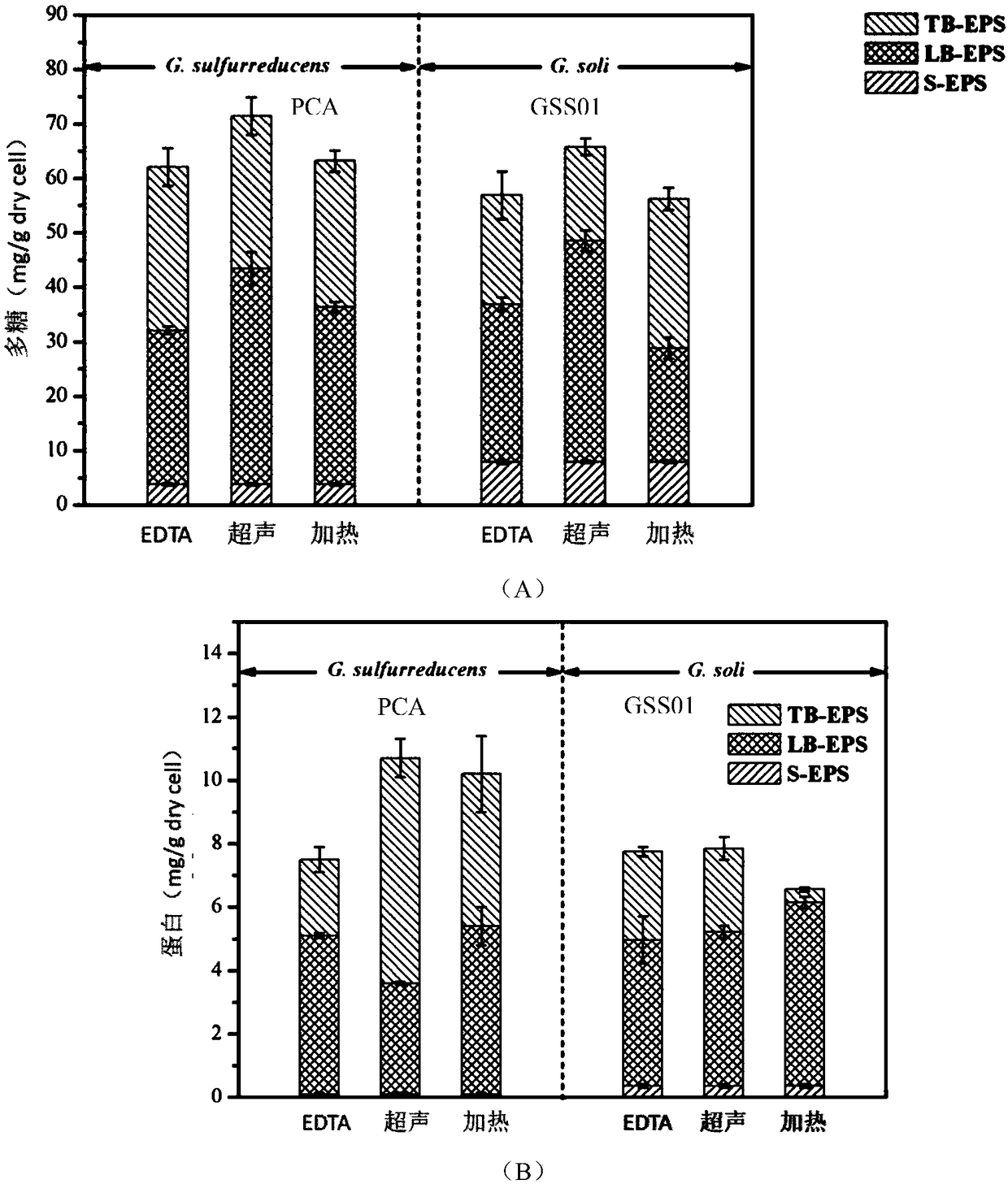
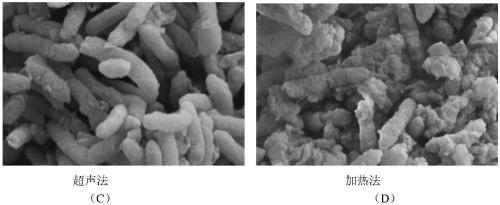
[0031] 1) Use the CHI1010C electrochemical workstation to cultivate the anode biofilm. The microbial fuel cell adopts a three-electrode system, in which the saturated calomel electrode is the reference electrode, and the 15mm*10mm*5mm cuboid graphite plate is the working electrode and the counter electrode. The electrochemical workstation runs Amperometric In i-t Curve mode, when the current runs to the highest point in the third cycle, the electrochemical workstation stops running. Disassemble the battery, remove the working electrode graphite plate, take the electrolyte to obtain soluble EPS (S-EPS), and rinse the graphite plate electrode with 0.9% NaCl solution to remove the soluble EPS (S-EPS) on the graphite plate. Scrape off the biofilm on the graphite plate, suspend it in 0.9% NaCl solution to get the biological suspension, take a certain volume of the suspension to measure the OD600 value, take a certain volume of the suspension and dry it, calculate its density, and ca...
Embodiment 2
[0035] 1) Use the CHI1010C electrochemical workstation to cultivate the anode biofilm. The microbial fuel cell adopts a three-electrode system, in which the saturated calomel electrode is the reference electrode, and the 15mm*10mm*5mm cuboid graphite plate is the working electrode and the counter electrode. The electrochemical workstation runs Amperometric In i-t Curve mode, when the current runs to the highest point in the third cycle, the electrochemical workstation stops running. Disassemble the battery, remove the working electrode graphite plate, take the electrolyte to obtain soluble EPS (S-EPS) S-EPS, and rinse the graphite plate electrode with 0.9% NaCl solution to remove the soluble EPS (S-EPS) on the graphite plate. ). Scrape off the biofilm on the graphite plate, suspend it in 0.9% NaCl solution to get the biological suspension, take a certain volume of the suspension to measure the OD600 value, take a certain volume of the suspension and dry it, calculate its densi...
Embodiment 3
[0039]1) Use the CHI1010C electrochemical workstation to cultivate the anode biofilm. The microbial fuel cell adopts a three-electrode system, in which the saturated calomel electrode is the reference electrode, and the 15mm*10mm*5mm cuboid graphite plate is the working electrode and the counter electrode. The electrochemical workstation runs Amperometric In i-t Curve mode, when the current runs to the highest point in the third cycle, the electrochemical workstation stops running. Disassemble the battery, remove the working electrode graphite plate, take the electrolyte to obtain soluble EPS (S-EPS) S-EPS, and rinse the graphite plate electrode with 0.9% NaCl solution to remove the soluble EPS (S-EPS) on the graphite plate. ). Scrape off the biofilm on the graphite plate, suspend it in 0.9% NaCl solution to get the biological suspension, take a certain volume of the suspension to measure the OD600 value, take a certain volume of the suspension and dry it, calculate its densit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com