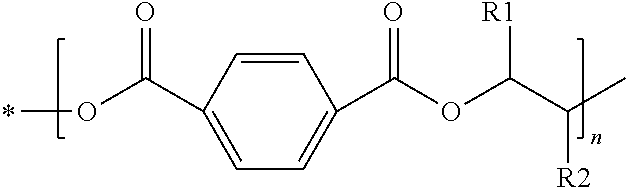
Patents
Literature
203 results about "Extracellular polymeric substance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
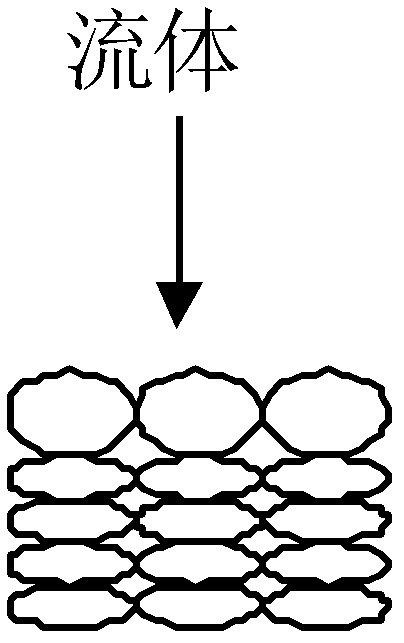
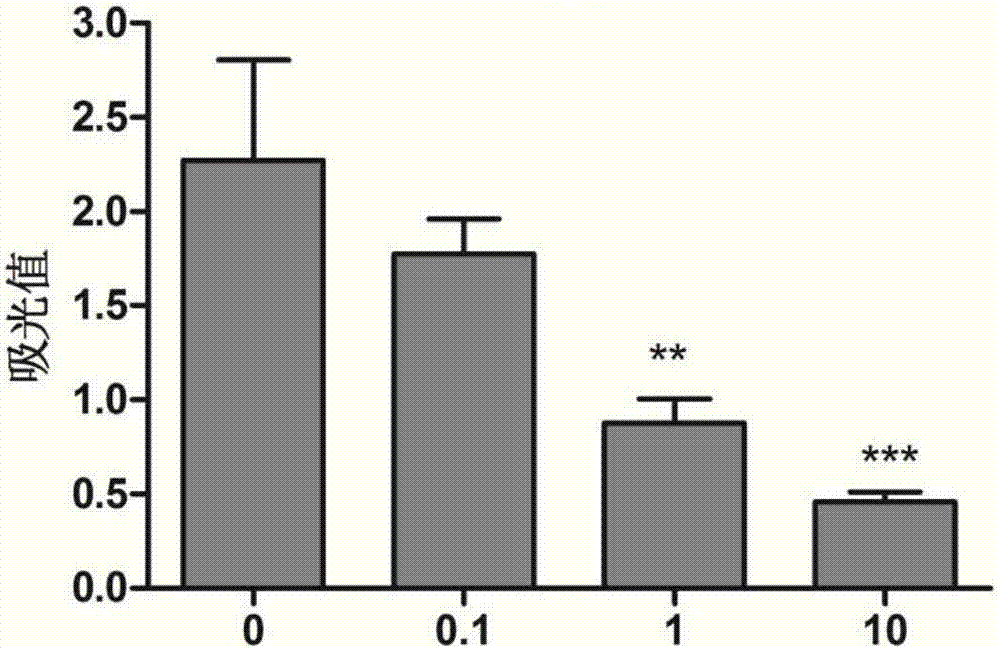
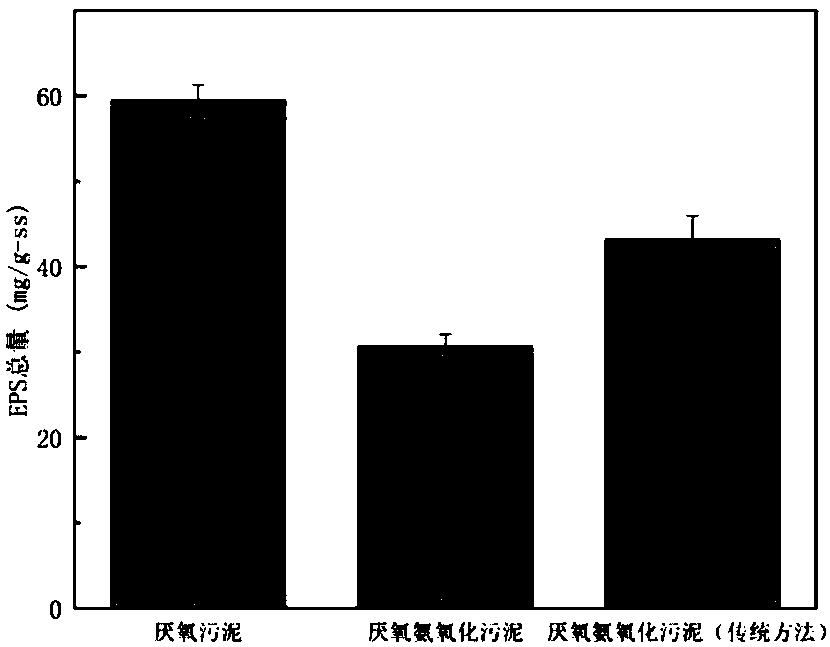
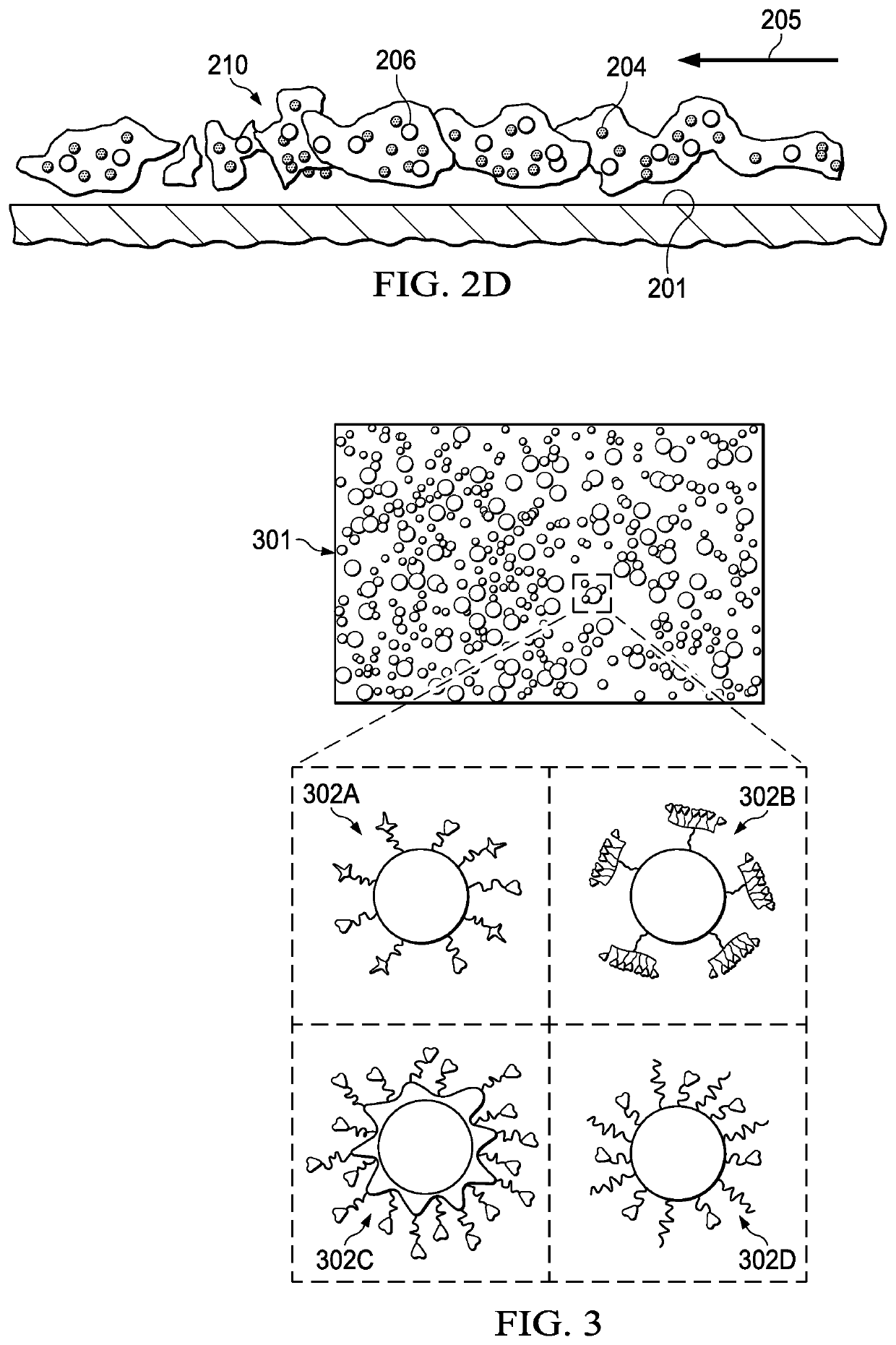
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental component that determines the physiochemical properties of a biofilm.
Wastewater treatment process
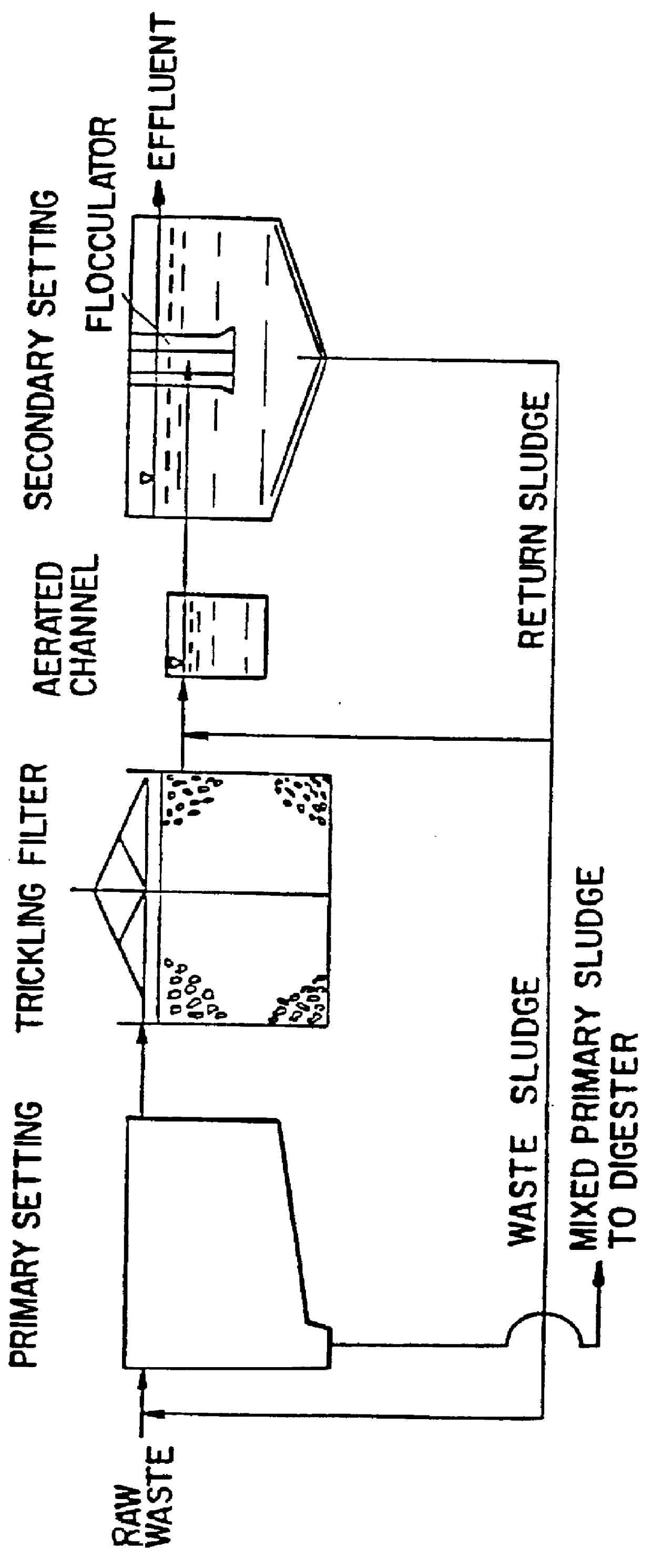
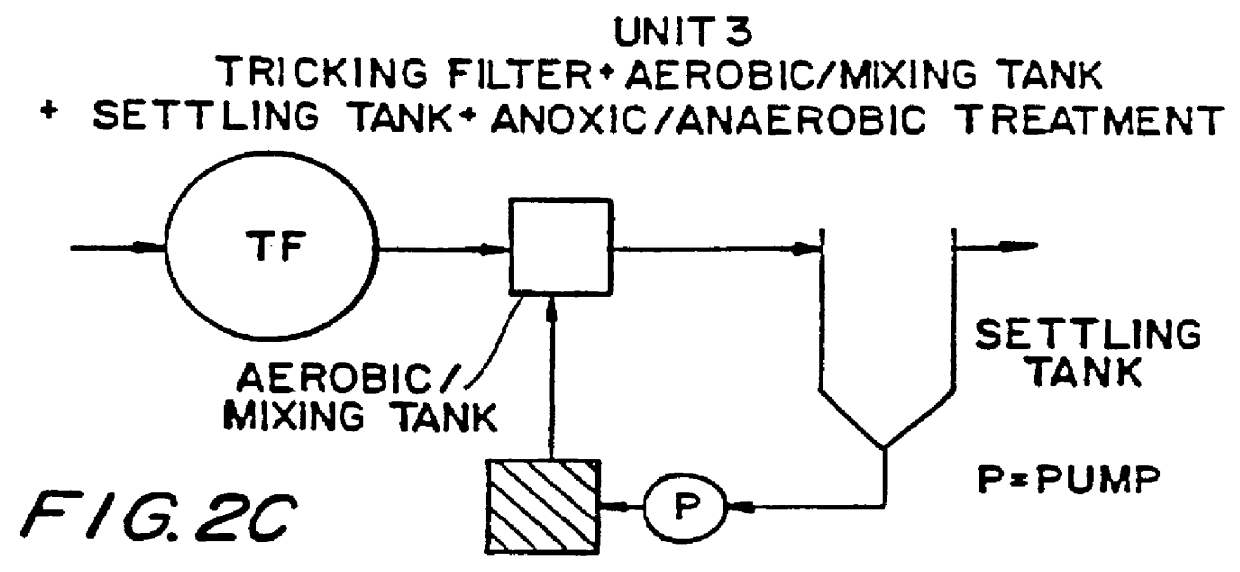
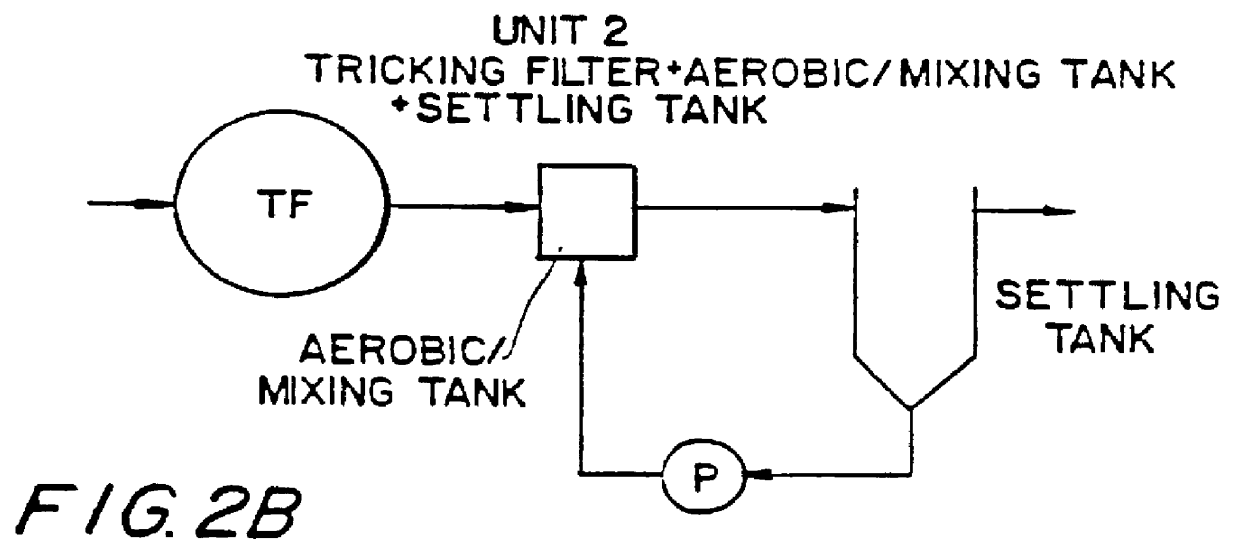
InactiveUS6113788AImprove efficiencyFacilitated releaseTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSludgePhosphate
A wastewater treatment process having improved solids separation characteristics and reduced biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) in the purified wastewater comprising the steps of: passing wastewater through a main aerobic biological oxidation zone and therein oxidizing a portion of the BOD a portion of the ammonia nitrogen content (NH3-N); passing the effluent from said aerobic biological oxidation zone to an aerobic / mixing zone and therein mixing said effluent with effluent from the anoxic / anaerobic zone; passing the effluent from said aerobic / mixing zone to a settling zone and therein separating purified wastewater having reduced BOD and suspended solids, and sludge containing suspended solids; passing a portion of the sludge formed in the settling zone and volatile acids to an anoxic / anaerobic zone and therein increasing the extracellular polymer content of said sludge, the release of phosphorus into solution and the reduction of nitrate nitrogen to molecular nitrogen gas; and recycling an effective amount of the effluent from said anoxic / anaerobic zone to said aerobic / mixing zone. In an alternative embodiment, a volatile acid is added to a zone to which no additional oxygen has been added that is in the flow path from the main aerobic biological oxidation zone or, alternatively, it may be added to the anoxic / anaerobic zone and the thus-treated effluent is passed to the aerobic / mixing zone wherein phosphate is removed from the effluent.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
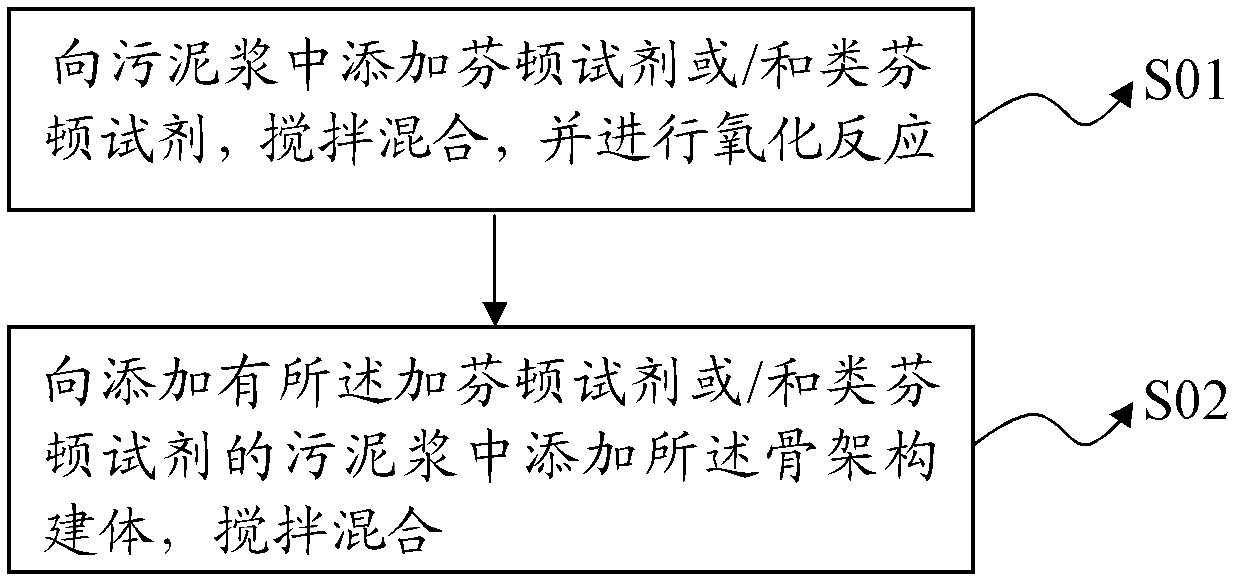
Sludge-dewatering compound conditioning agent and application method thereof
ActiveCN102381828AAchieve deep dehydrationShorten spin timeSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationPOLYMER SUBSTANCEFenton reagent
The invention provides a sludge-dewatering compound conditioning agent and an application method thereof. The sludge-dewatering compound conditioning agent comprises a Fenton reagent or / and similar Fenton reagent and a skeleton construct, and the weight ratio of the Fenton reagent or / and similar Fenton reagent and the skeleton construct is 1: (0.05-300); and the skeleton construct adopts a powder body. The application method comprises the following steps: adding the Fenton reagent or / and similar Fenton reagent into sludge slurry, and mixing for oxidation; and adding the skeleton construct into the sludge slurry with the Fenton reagent or / and similar Fenton reagent, and mixing. Due to synergy of the Fenton reagent or / and similar Fenton reagent and the powder type skeleton construct, extracellular polymeric substances in sludge can be destructed effectively, the compressibility of organic substances can be reduced, and the sludge dewatering performance of the sludge-dewatering compound conditioning agent can be improved greatly. The procedures of the application method are simple, the conditions can be controlled easily, the sludge dewatering time can be shortened, and the large-scale treatment of the sludge can be realized.
Owner:UNIVERSTAR SCI & TECH SHENZHEN +1
Method for treating chronic wounds with an extracellular polymeric substance solvating system
Chronic wounds may be treated by debriding necrotic and other devitalized tissue from the wound, and applying to the wound an extracellular polymeric substance solvating system comprising a metal ion sequestering agent, surfactant and buffering agent. The solvating system disrupts biofilms which may be present in the wound and aids or enables the resumption of normal healing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Joint-conditioning dehydration method for sludge
InactiveCN102910793AImprove dehydration effectIncrease solid contentSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationParticulatesFenton reagent
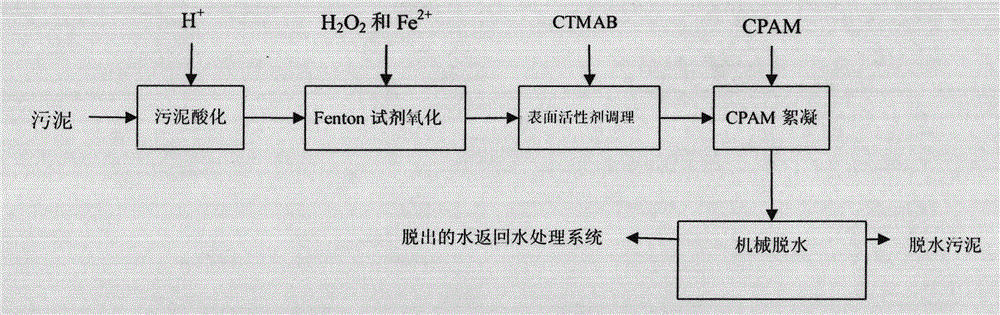
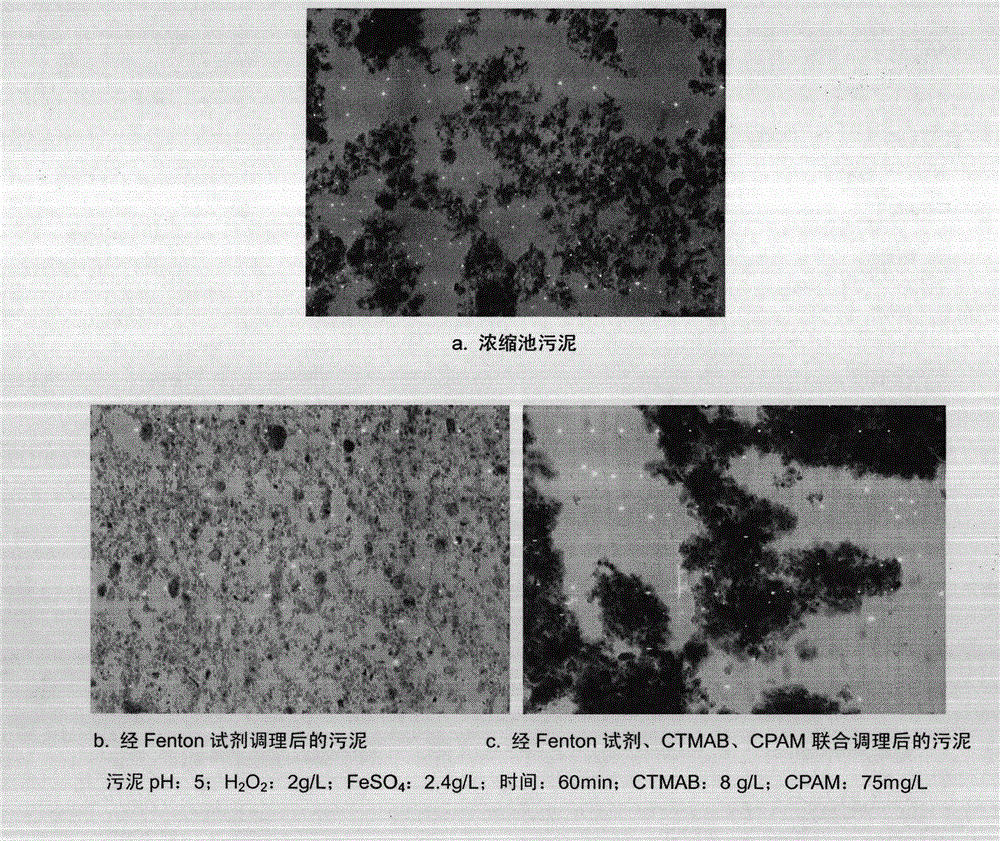
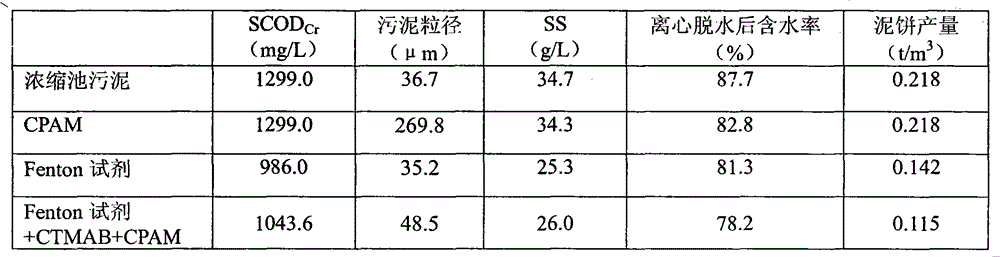
The invention is named as 'a joint-conditioning dehydration method for sludge', belonging to the technical field of environmental engineering and sludge treatment. The joint-conditioning dehydration method comprises the following steps of: adding H202 and FeSO4 into the sludge (with pH being equal to 5) acidified by mineral acid, degrading organic matter by virtue of strong oxidation of a Fenton reagent, and dissolving and cracking microbial cells and extracellular polymeric substances in the sludge; adding a surfactant CTMAB (Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide) into the sludge to reduce the surface tension of the sludge and change the surface characteristics of the sludge, and transforming a part of interstitial water into free water; and flocculating sludge particulates with disperse structure, small particle diameter and large specific surface area by virtue of flocculation action of polyacrylamide (CPAM) to the sludge particulates. After the sludge is subjected to joint conditioning of the Fenton reagent, the surfactant and the CPAM, the moisture content of the sludge after being centrifugally dewatered is reduced to 78.2% from 87.7%, and the output of mud cakes is reduced to 0.115t / m<3> from 0.218t / m<3>, therefore, the dehydration property of the sludge can be improved remarkably, the investment and operation costs are reduced effectively, and an ideal sludge reduction goal is reached.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Compound conditioning and deep dewatering method of sludge
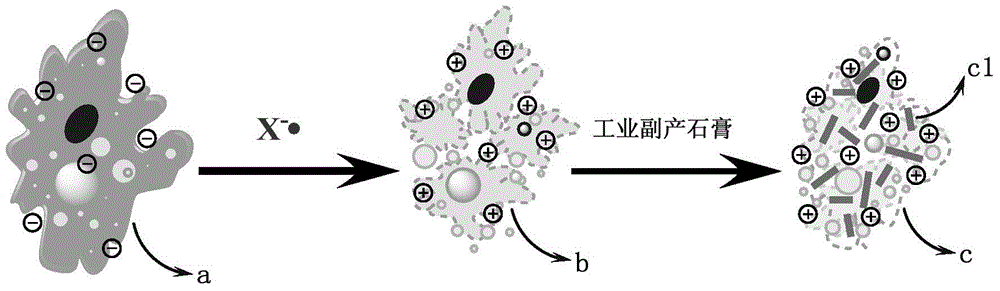
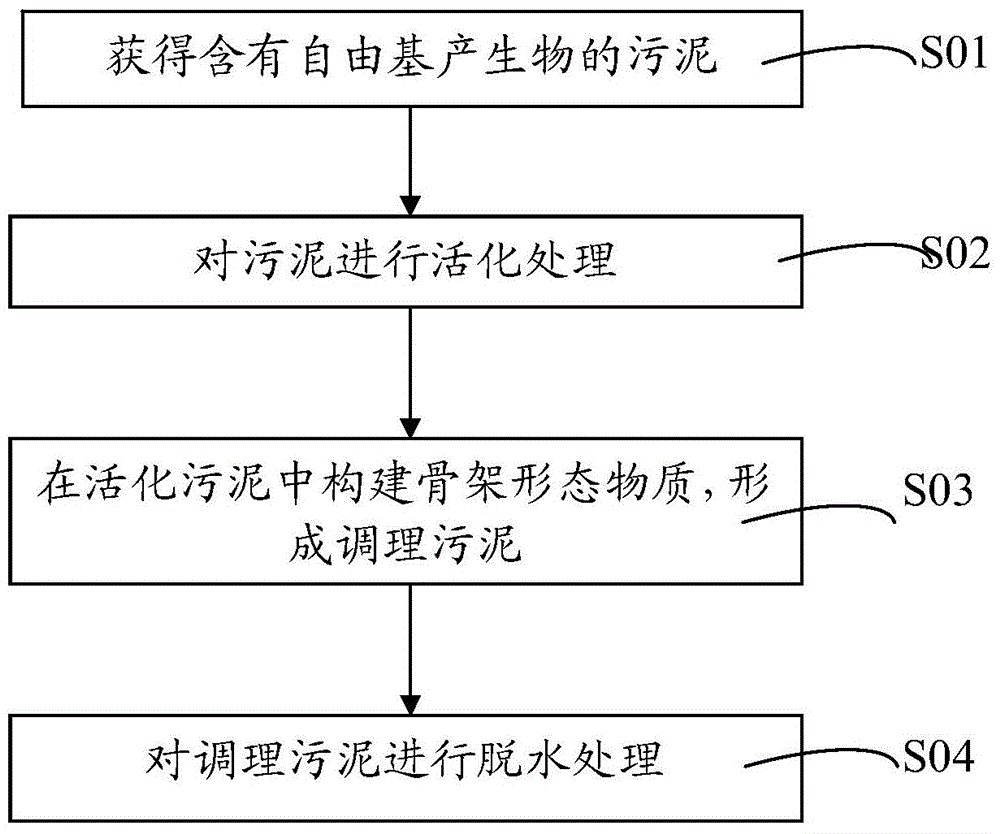
ActiveCN104649533AGood conditionSimple processSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationHydration reactionPorosity
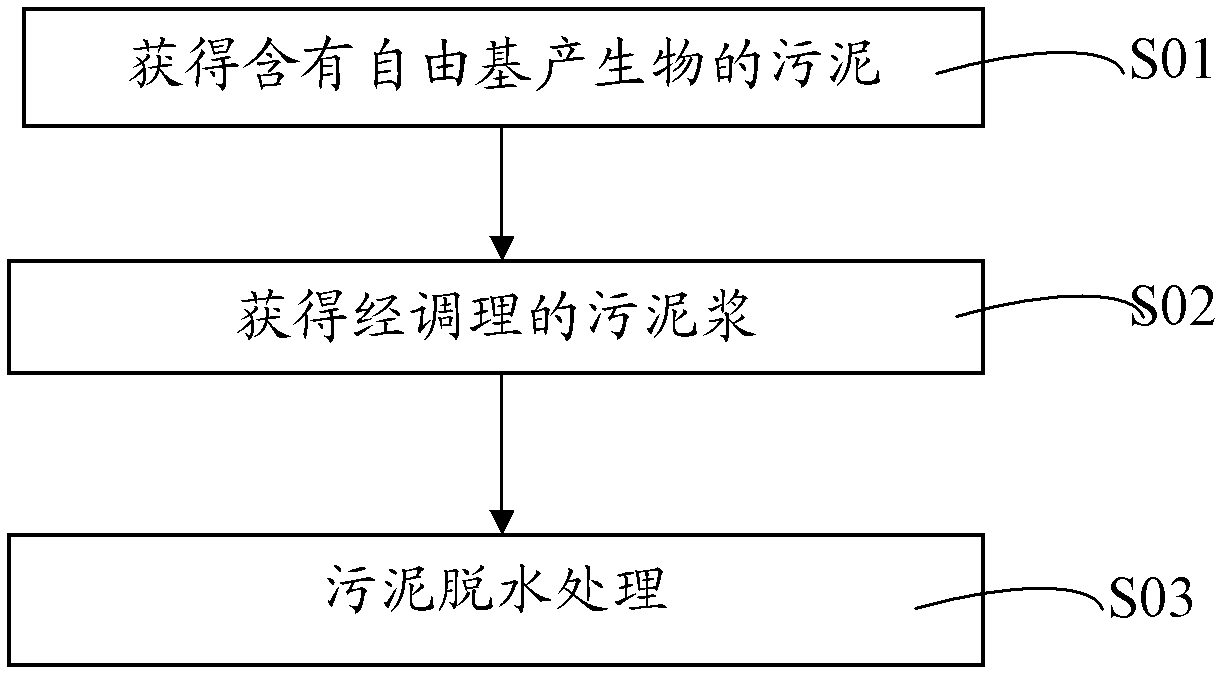
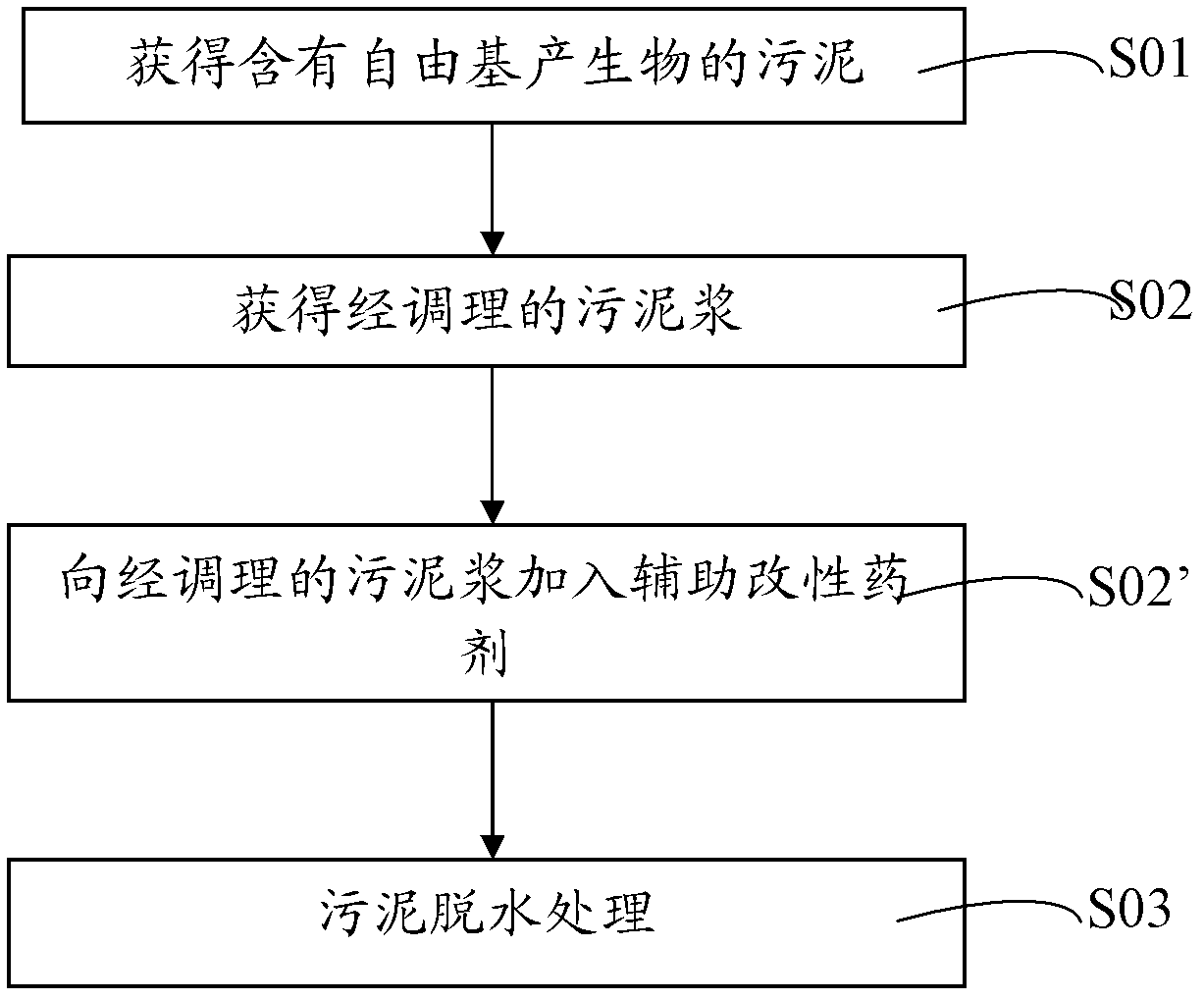
The invention provides a sludge deep dewatering method. The sludge deep dewatering method comprises the following steps: obtaining sludge containing a free radical generating substance; adding an activator to the sludge containing the free radical generating substance for activation, thereby obtaining the activated sludge; adding industrial byproduct gypsum to the activated sludge for mixing treatment, thereby forming conditioned sludge containing a new skeleton form substance; and performing dewatering treatment on the conditioned sludge. According to the sludge deep dewatering method, zero-valent iron or nano zero-valent iron is taken as the activator to react with the free radical generating substance to generate active free radicals, and therefore, the extracellular polymeric substance of the sludge can be effectively damaged and the filtering property of the sludge can be improved on one hand, and on the other hand, ions after the activation reaction is completed are capable of directly promoting the industrial byproduct gypsum to perform a hydration reaction, and the new substance morphology of the skeleton form can be controlled; the skeleton structure is capable of remarkably increasing the porosity of the sludge, and therefore, the deep dewatering of the sludge is realized.
Owner:UNIVERSTAR SCI & TECH SHENZHEN +1
Method for treating chronic wounds with an extracellular polymeric substance solvating system
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Method for treating surplus sludge produced after biological treatment of wastewater
InactiveCN104193127AReduce moisture contentReduce dehydration operating costsSludge treatmentPotassium persulfatePersulfate
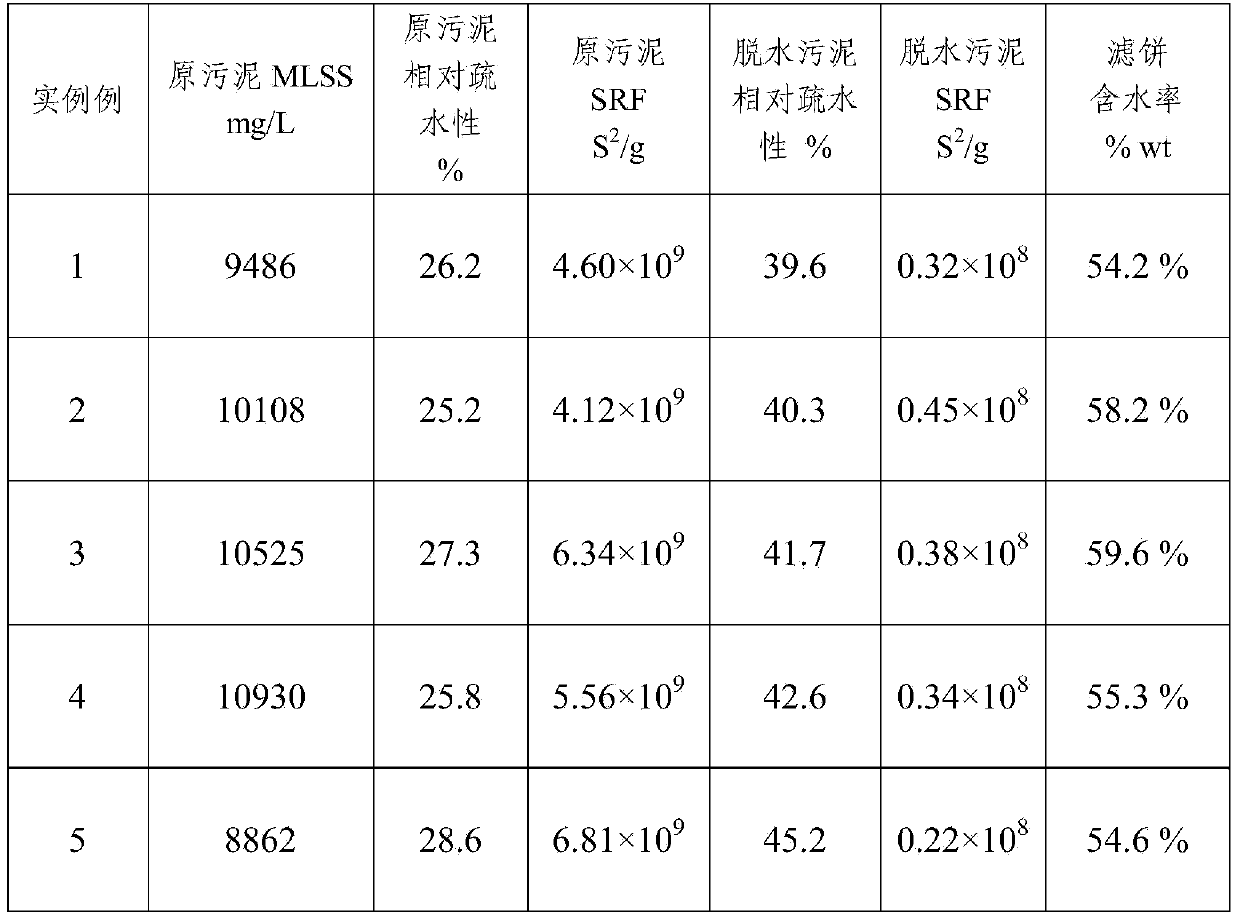
The invention provides a method for treating surplus sludge produced after biological treatment of wastewater. By adding a ferrous sulfate solution, a sodium persulfate solution or a potassium persulfate solution, and industrial coal ash, the sludge is treated to obtain a filter cake and a filter liquor. Compared with the prior art, adding divalent ferric salt and heating synergize to stimulate the persulfate to produce a free sulfate radical having a strong oxidizing property, the free sulfate radical is used to efficiently break a microbial cell in the sludge, then the microorganism is inactivated, the adhesive action with an extracellular polymeric substance is remarkably weakened, the extracellular polymeric substance is then stripped, the bond-state water is released, and the structure and the surface hydrophobicity of the sludge flocculant are changed; after the industrial coal ash is added, the permeability of the filter cake is improved, and the filter cake can play the role of a filter aid. According to the method, the specific resistance of the sludge is as low as (0.2-0.5)*108S<2> / g, the moisture content of the dehydrated filter cake is as low as 40-60%, the secondary pollution caused by common flocculants like polyacrylamide is reduced, the operating cost for the dehydration of the sludge is lowered, original processing equipment can be used to implement the method without any transformation, the operation is convenient, and the dehydrated sludge is directly backfilled or is used to produce a ceramsite or building material.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Method using biochar-based microalgae composite absorbent to remove heavy metals
InactiveCN106076278AHigh recovery rateFast adsorption rateOther chemical processesWater contaminantsHigh concentrationPOLYMER SUBSTANCE
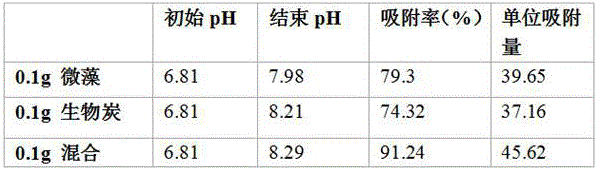
The invention provides a heavy metal removing method using biochar as the substrate material and fixing microalgae to the biochar carrier to form a composite absorbent. The method is characterized in that extracellular polymeric substances secreted by the microalgae under an inhibition condition are used as the binder, and micro-grade algae cells are attached to the surfaces of the multiple pores of the biochar to form the composite absorbent; the composite absorbent utilizes the advantage that the biochar can absorb the heavy metals fast and uses the live algae cells to absorb the heavy metals through metabolism in a long-term and effective manner so as to increase the absorption effect on water with high-concentration heavy metals. Accordingly, the method is high in heavy metal removing rate, easy in recycling and low in application cost.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Sludge deep dehydration method
ActiveCN103319066ADeep dehydrationImprove filtering effectSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBound waterFiltration
The invention provides a sludge deep dehydration method comprising the following steps: adding 1-10%, based on the dry weight of sludge slurry, of a free radical production into the sludge slurry, and stirring to mix; adding a transition metal salt activator, a magnesium salt activator and / or an aluminum salt activator to the sludge slurry containing the free radical production, carrying out an activation reaction to form active free radicals, and treating by the active free radicals to obtain a conditioned sludge slurry; and dehydrating the conditioned sludge slurry. Through the sludge deep dehydration method, the active free radicals are produced by reacting the transition metal salt, the magnesium salt and / or the aluminum salt and the like with the free radical production, on one hand, can effectively destroy sludge extracellular polymeric substances, alter surface properties of sludge particles, improve the filtration performance of the sludge, and reduce the sludge bound water content; on the other hand, the active free radicals can active ions produced after the completion of the reaction, can be combined with sludge particles, can improve the strength of sludge flocs, are favorable to the sludge dehydration process, so as to realize the sludge deep dehydration.
Owner:UNIVERSTAR SCI & TECH SHENZHEN +1
Method for controlling membrane pollution in membrane bioreactor
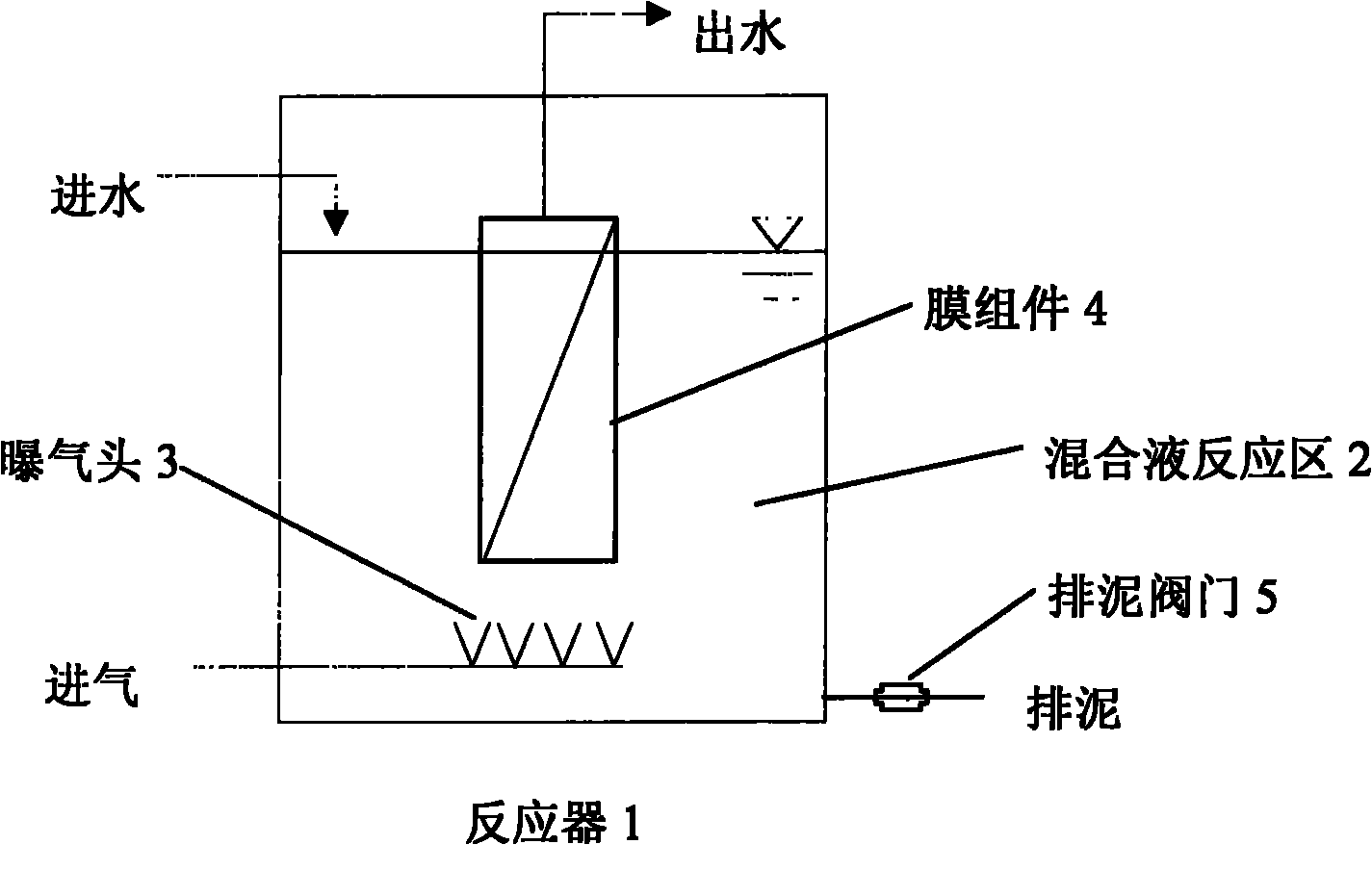
InactiveCN101905918APollution Mitigation and ControlReduced service lifeWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisSustainable biological treatmentChemistryExtracellular polymeric substance
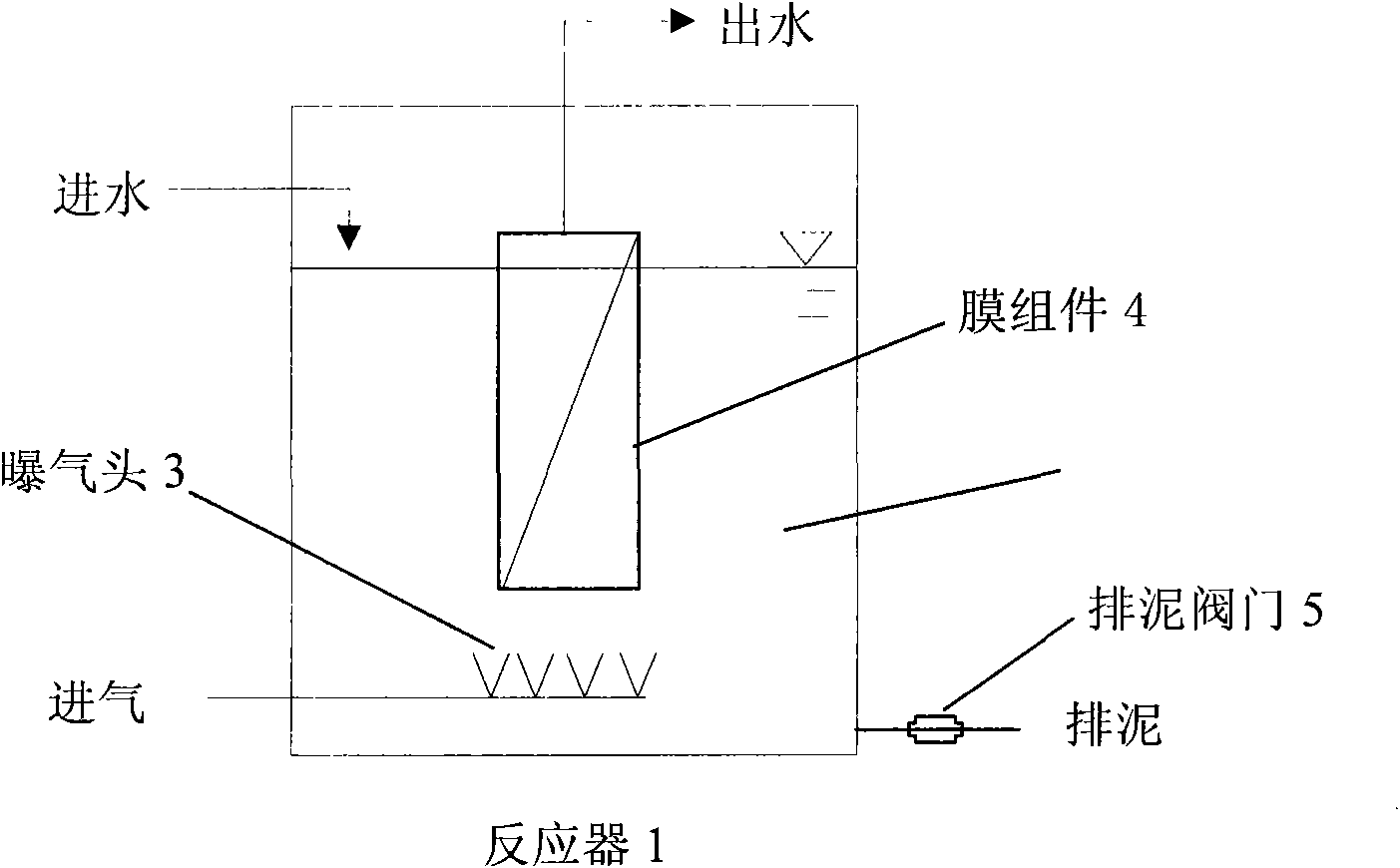
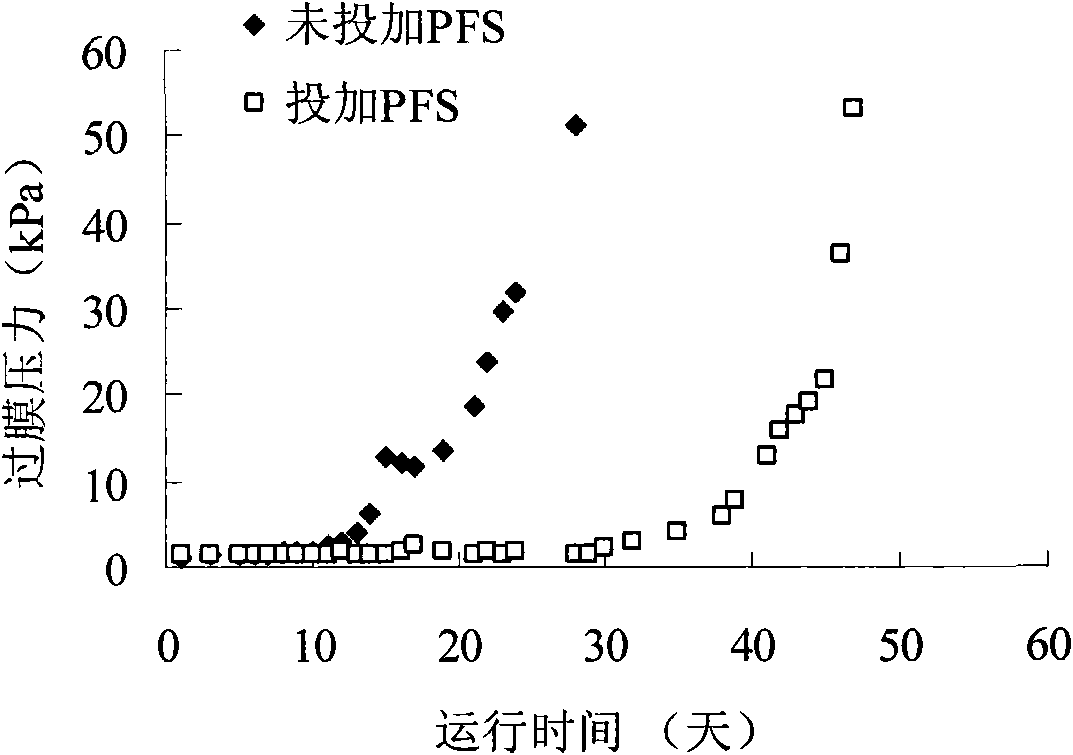
The invention belongs to a water and wastewater treating technology, and particularly to a method for controlling the membrane pollution in a membrane bioreactor, which comprises the following steps of: adding a certain concentration of polyferric sulfate as an inorganic flocculating agent, regulating and controlling the property of a sludge mixed liquid in the membrane bioreactor, and then discharging a proper amount of treated sludge mixed liquid to realize the control of the membrane pollution. Particularly for the sludge mixed liquid with fine sludge grains and high EPS (Extracellular Polymeric Substance) concentration after long-term operation, the method can be used for effectively regulating and controlling the sludge performance, alleviating the membrane pollution and prolonging the membrane cleaning period.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
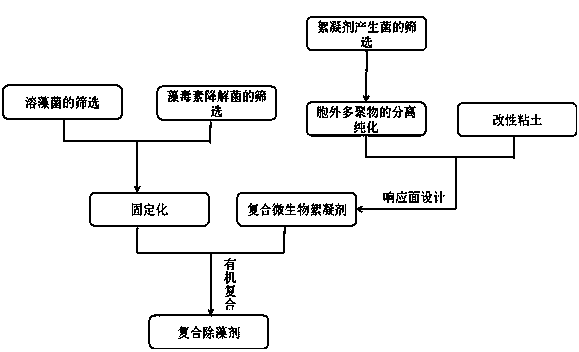
Preparation method of compound microbial algaecide
InactiveCN104140963ANo negative impactLow priceMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierBiotechnologyNatural ecosystem
The invention discloses a preparation method of a compound microbial algaecide. The method comprises the following steps: reasonably combining separated and purified extracellular polymeric substances, kaolin and the like so as to prepare a compound microbial flocculant; then fossilizing separated alga dissolving bacteria and algal toxin degrading bacteria; finally, reasonably compounding the compound microbial flocculant with the fossilized alga dissolving bacteria and algal toxin degrading bacteria so as to prepare the compound microbial algaecide. The compound microbial algaecide is good in alga killing effect and algal toxin degrading effect; source materials adopted during the preparation of the compound microbial algaecide are low in cost, so that the compound microbial algaecide is low in preparation cost and harmless to natural ecosystems. The prepared compound microbial algaecide is organically integrated with functions of flocculation-type alga removing, microbial alga dissolving and micro-biological degradation of algal toxin, so that the safe and efficient treatment of water blooms is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for forming non-biological granular sludge in heavy metal waste water treatment process
ActiveCN103288191AStable structureAccelerated settlementWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSludgeWater quality
The invention discloses a method for forming non-biological granular sludge in a heavy metal waste water treatment process, belonging to the environmental engineering field. Chemical sludge obtained in a heavy-metal-containing waste water treatment process is flocculent suspended state sludge mostly, stability, settleability and dehydration property are poorer, and effluent quality and technology operating efficiency are seriously influenced. Inspired by an induction kernel hypothesis and an extracellular polymeric substance hypothesis for forming the biological granular sludge, an improved parallel flow charging control crystallization process is applied in the invention, a heavy metal precipitation reaction mechanism is changed, and seed crystals and a flocculating agent are added, so that the non-biological heavy metal granular sludge is obtained. The method for forming the non-biological granular sludge has the advantages that an operation cycle is short, a flow path is simple, operation is easy, stability of the heavy metal chemical sludge can be effectively improved, moisture content of settled sludge is reduced by 7-8% compared with common flocculent sludge, and settling rate is increased by 4-5 times.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
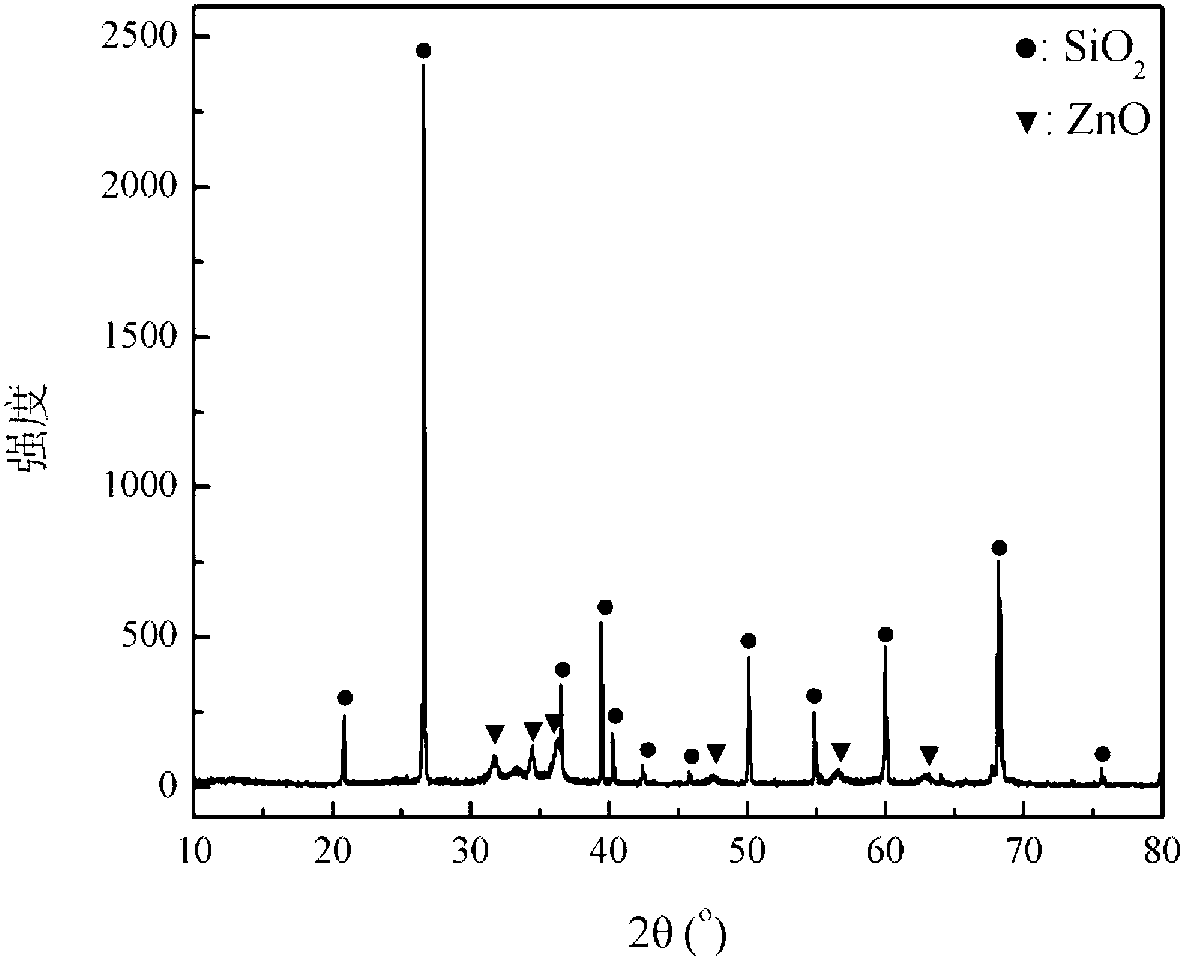
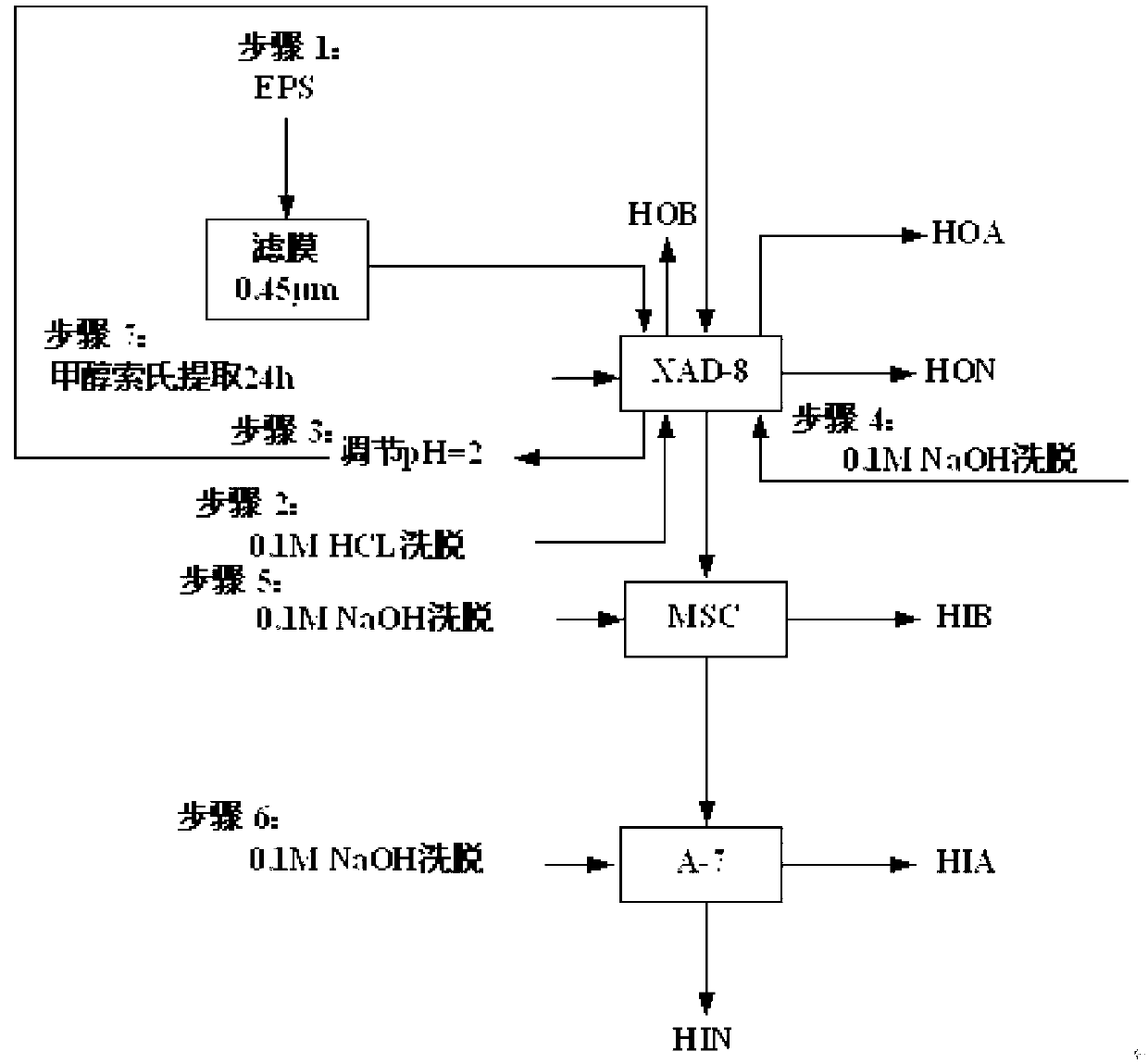
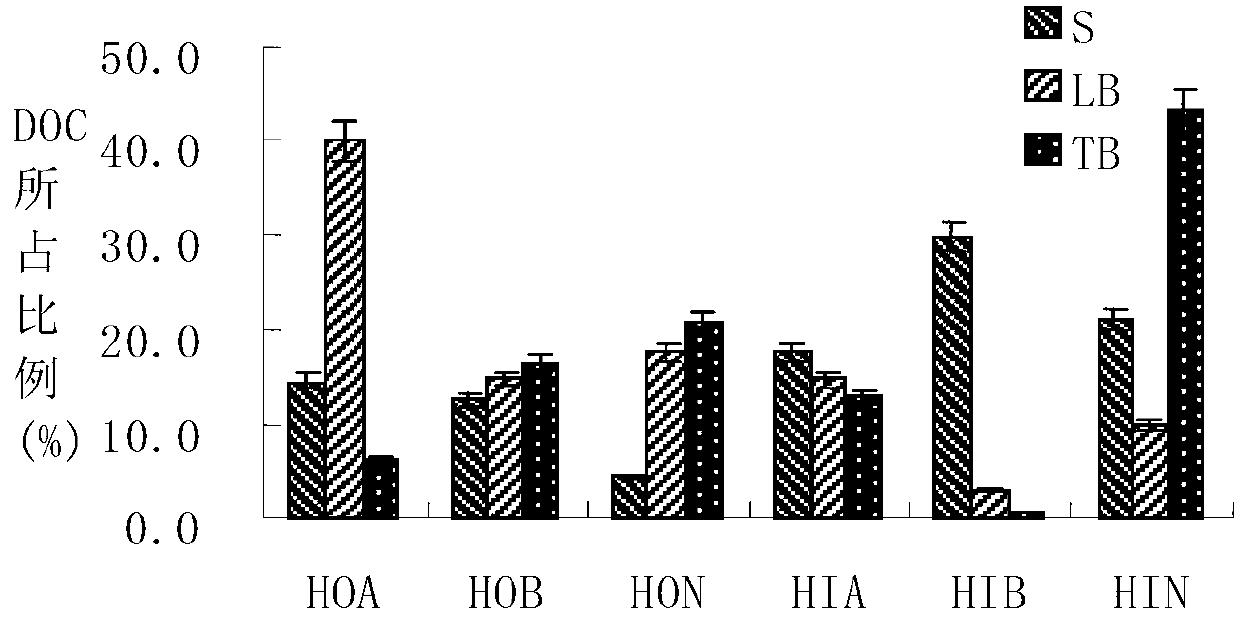
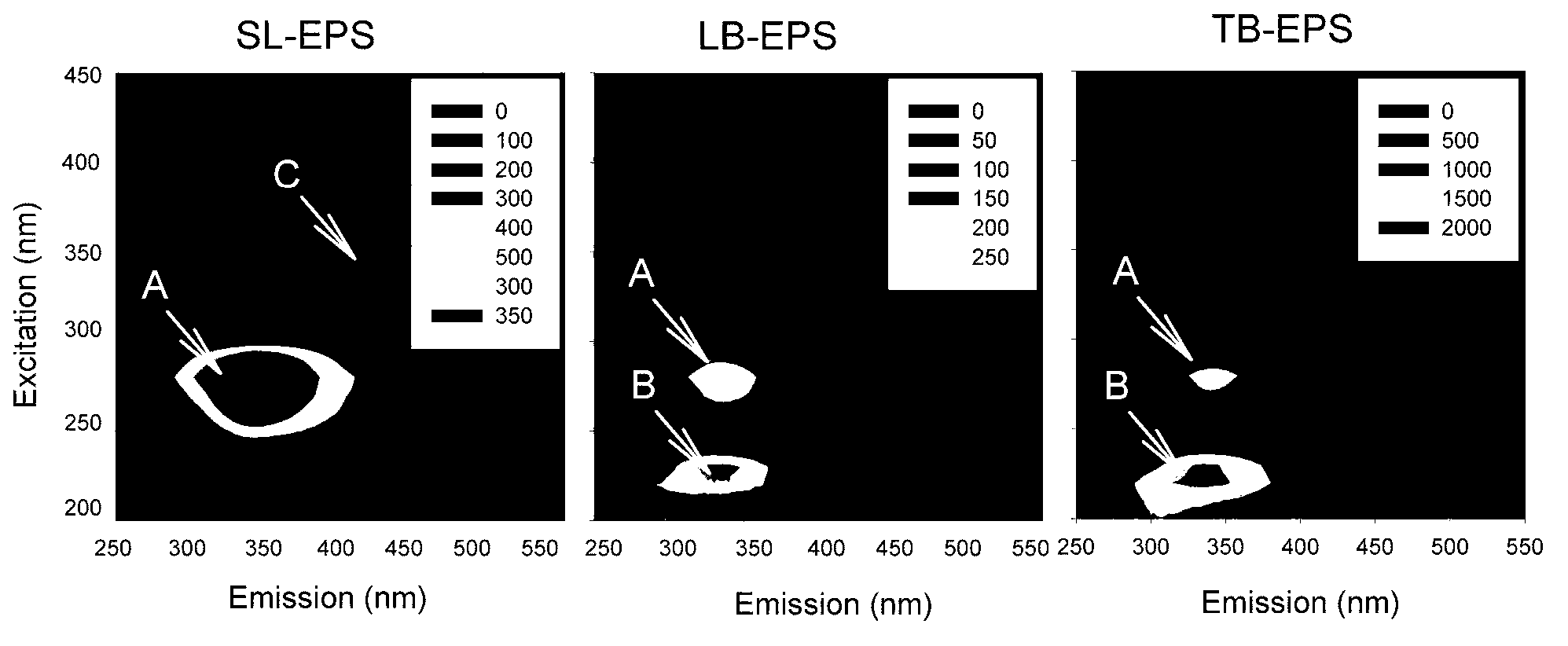
Biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance extraction and grading analysis method of biological membrane reactor
ActiveCN103272404ANo pollutionSolve the problem of unsystematic feature analysisCation exchanger materialsComponent separationPOLYMER SUBSTANCEBiochemistry
The invention discloses a biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance extraction and grading analysis method of a biological membrane reactor. The biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance extraction and grading analysis method comprises the following steps of: extracting biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance mucus, loose extracellular polymeric substance and tight type extracellular polymeric substance; respectively carrying out chromatography grading on the biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance mucus, loose extracellular polymeric substance and tight type extracellular polymeric substance by adopting XAD-8 adsorption resin, MSC cation exchange resin and Duolite A-7 anion exchange resin; and carrying out system analysis on each graded component of the biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance mucus, loose extracellular polymeric substance and tight type extracellular polymeric substance. By adopting the biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance extraction and grading analysis method, the problems that the original biological membrane structural characteristics are destroyed in general biological membrane stripping, synchronous separation of biological membrane extracellular polymeric substance and hydrophilic, hydrophobic and acid and alkaline substances is difficult and characteristic analysis is not systematic can be solved.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
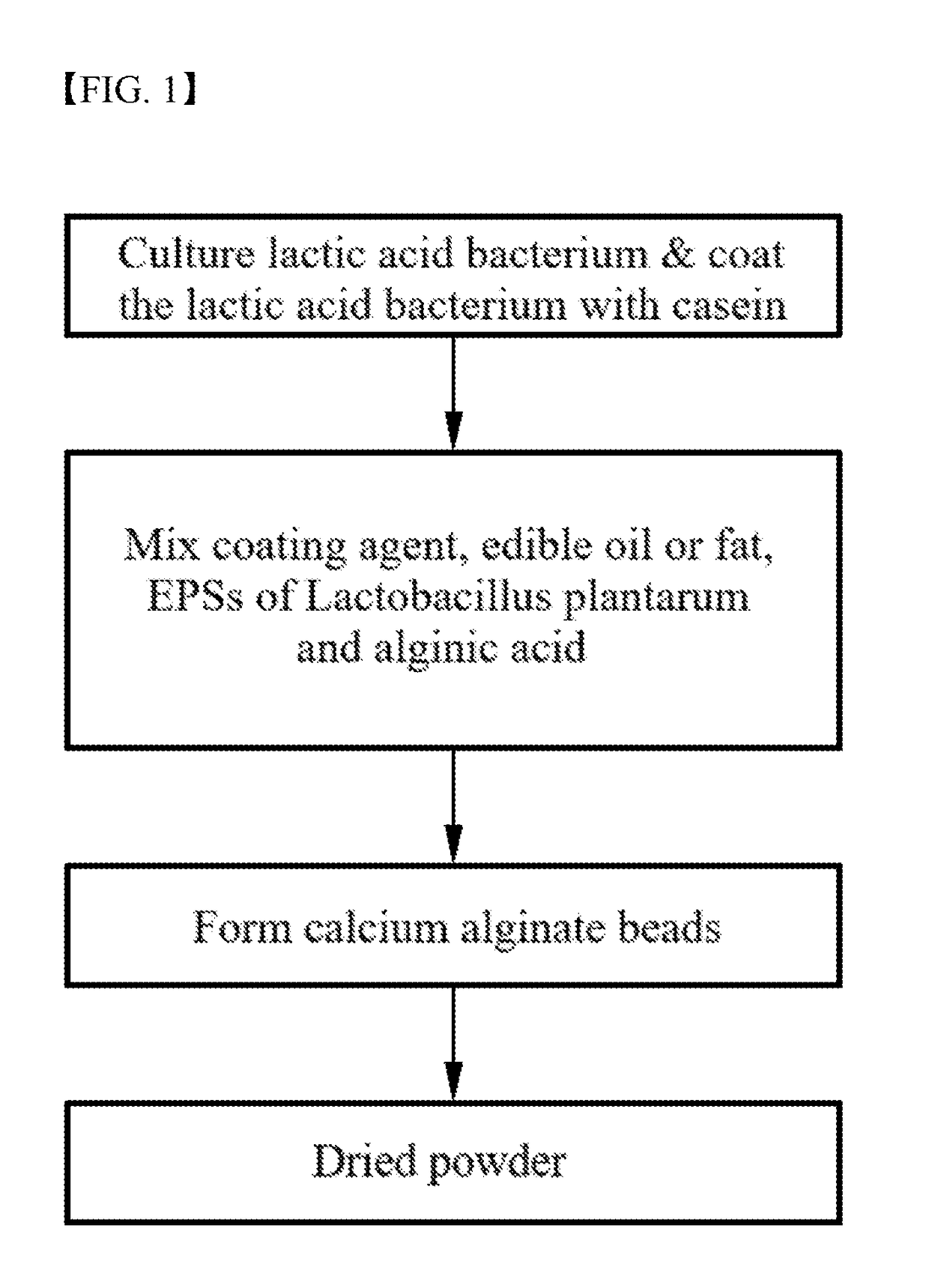
Coating method of lactic acid bacteria with increased intestinal survival rate
InactiveUS20190029311A1Good storage stabilityImproved intestinal survivalMilk preparationLactobacillusLactic acid bacteriumPOLYMER SUBSTANCE
This application relates to a coating method of lactic acid bacteria and a lactic acid bacteria complex produced by the coating method, the coating method comprising: (a) a step of culturing lactic acid bacteria in a medium including casein and coating the lactic acid bacteria with casein; (b) a step of mixing the casein-coated lactic acid bacteria with a solution comprising a coating agent, an edible oil, an extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) of Lactobacillus plantarum and alginic acid; and (c) a step of adding the mixture of step (b) to a calcium-containing solution to form alginic acid-calcium beads, wherein the alginic acid-calcium beads contain the casein-coated lactic acid bacteria, the coating agent, the edible oil, and the EPS of Lactobacillus plantarum.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
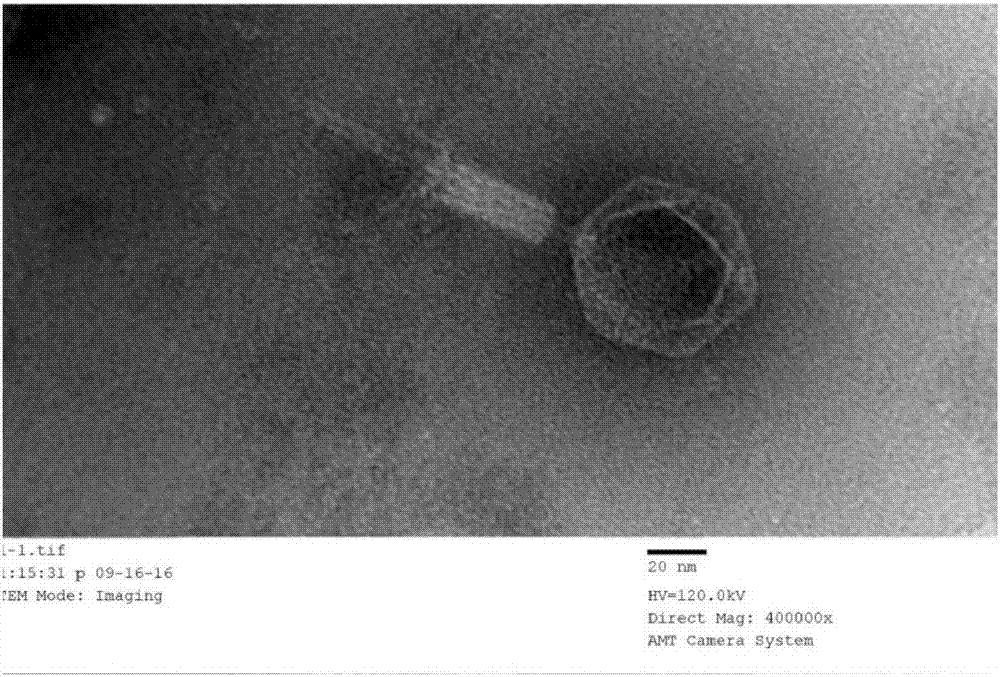
Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage and application thereof
ActiveCN106929481AStrong cracking abilityEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideDisinfectantsBacteroidesAntibiotic Y
The invention provides pseudomonas aeruginosa phage and application thereof. According to the pseudomonas aeruginosa phage, the strain name is vB_PaeM_QKL1, the preservation number is CGMCC No.13381, the classification name is pseudomonas aeruginosa phage, and the pseudomonas aeruginosa phage was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) in December 8th, 2016. The invention also provides application of the pseudomonas aeruginosa phage. Degrading enzyme of an extracellular polymeric substance exists in the caudal spine of the pseudomonas aeruginosa phage and can crack cell envelope to crack biofilm generating bacteria so as to completely remove the bacterial biofilm; the pseudomonas aeruginosa phage provided by the invention has remarkable inhibition effect on a pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm, can break the pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm, and also can be combined with antibiotics and the common chemical detergents.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for relieving blockage of constructed wetland
InactiveCN105776550ARestore poresImprove hydraulic conductivityClimate change adaptationSustainable biological treatmentConstructed wetlandPOLYMER SUBSTANCE
The invention discloses a method for relieving blockage of a constructed wetland. The method comprises the steps as follows: A, the blockage is desolventized: 0.09-0.15 g / L of a biosurfactant, namely, rhamnolipid is dosed into inflow water of the wetland, inflow water enters the wetland and remains for desolventizing of the blockage of the wetland, the hydrophobic group end of rhamnolipid is bound with an organic group of an extracellular polymeric substance, the hydrophilic end is bound with pore water in the constructed wetland, and large-particle blockages connected by the extracellular polymeric substance are dispersed and solubilized; B, the blockages are eluted out of a wetland system: the wetland is emptied; C, the desolventizing action generates positive effects: the solubilizing and dispersing effects of rhamnolipid destroy the structure of the extracellular polymeric substance, so that bound enzymes are released, and contact among microorganisms, the enzymes and substrates is promoted; D, according to the condition of the wetland, desolventizing is performed for a plurality of times on the constructed wetland which begins to show a trend in blockage or is blocked till the blockage condition is improved. The method is easy to use, an appropriate amount of rhamnolipid is directly dosed into the inflow water of the wetland, the inflow water enters the wetland and remains for an appropriate period, and the method is suitable for recovery of the wetland which begins to show a trend in blockage or is blocked.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Flocculating agent for simulating composition of microorganism extracellular polymeric substances and application method thereof
ActiveCN103803690APromote formationImprove settlement performanceWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSludgeTyrosine
The invention relates to a flocculating agent for simulating composition of microorganism extracellular polymeric substances and an application method thereof. The flocculating agent is formed by compounding microorganism exopolysaccharides (sodium alginate, xanthan gum and pulullan) and hydrophobic amino acid (tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine), the weight ratio (ammonia acid / polysaccharide) is 2-8, the optimal ratio is 8, and the concentration of the flocculating agent in the system when in charging is controlled at 20-40mg / L. The flocculating agent has the characteristics that the bridging attraction effect of the exopolysaccharide and the hydrophobic attraction effect of the hydrophobic amino acid can be adequately played after all components are compounded, so that the formation of non-biological particle sludge in the heavy metal waste water treatment process can be effectively promoted by integrating the bridging attraction effect and the hydrophobic attraction effect. Compared with the flocculent sludge, the flocculating agent has the advantages that the settleability of the non-biological particle sludge can be increased by 2-5 times, and the weakness of the difficulty in solid-liquid separation in the heavy metal waste water treatment process and toxicity and harm of the traditional macromolecular flocculating agent can be overcome.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Aerobiotic heterotrophic bacteria extracellular polymeric substance for removing stress of heavy metals and preparation method
PendingCN105886580AEffective induction ofIncrease productionWater contaminantsFermentationPOLYMER SUBSTANCEBio engineering
The invention relates to the technical fields of bioengineering and wastewater treatment and particularly relates to an extracellular polymeric substance, a heavy metal treating agent and a heavy metal treating method. A preparation method of the extracellular polymeric substance comprises the steps of carrying out heavy metal stress treatment on aerobiotic heterotrophic bacteria when the aerobiotic heterotrophic bacteria are cultured, and removing a culture medium, heavy metals and thalluses, so as to obtain the extracellular polymeric substance. The extracellular polymeric substance provided by the invention has outstanding capacity for removing specific heavy metals and can be applied to the treatment of heavy metal wastewater.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
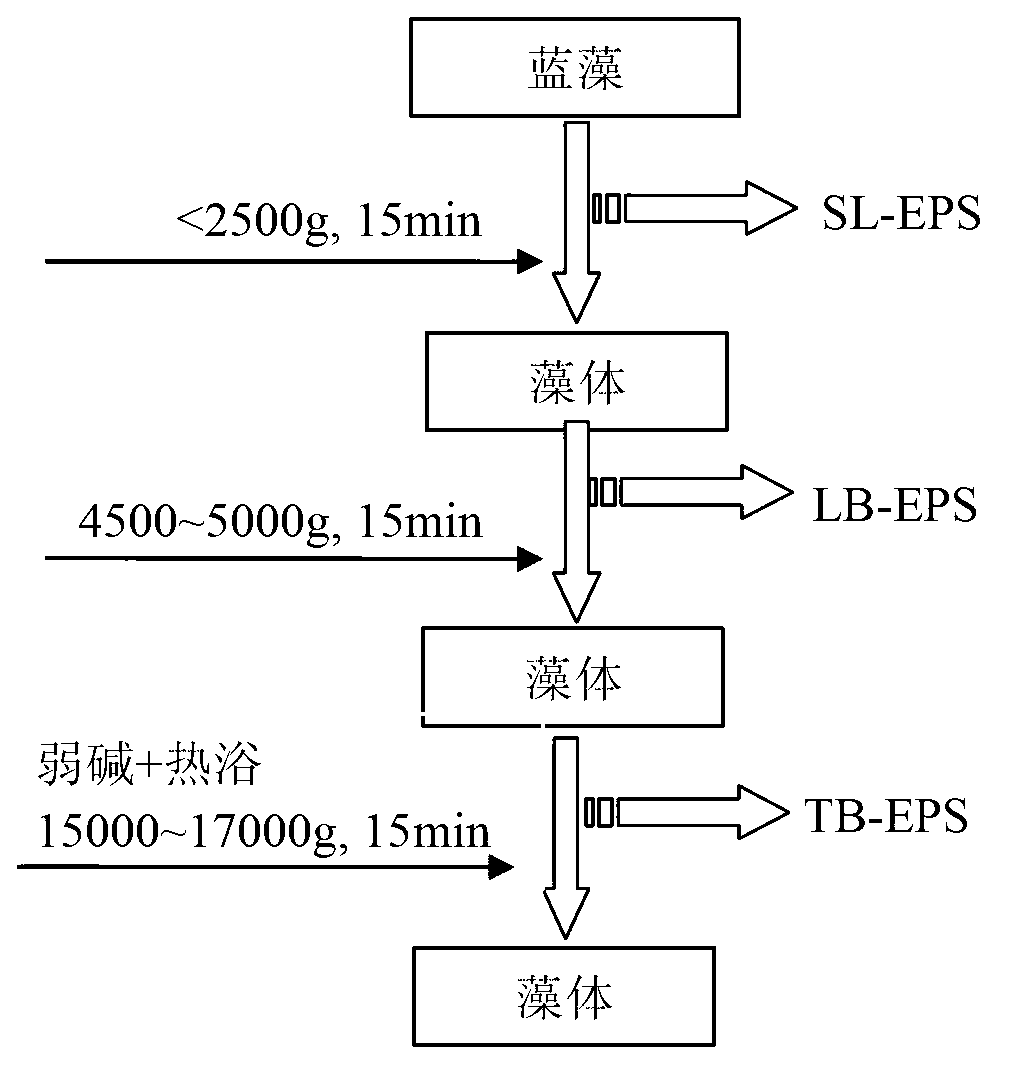
Method for extracting blue-green algae extracellular polymeric substance in grading manner
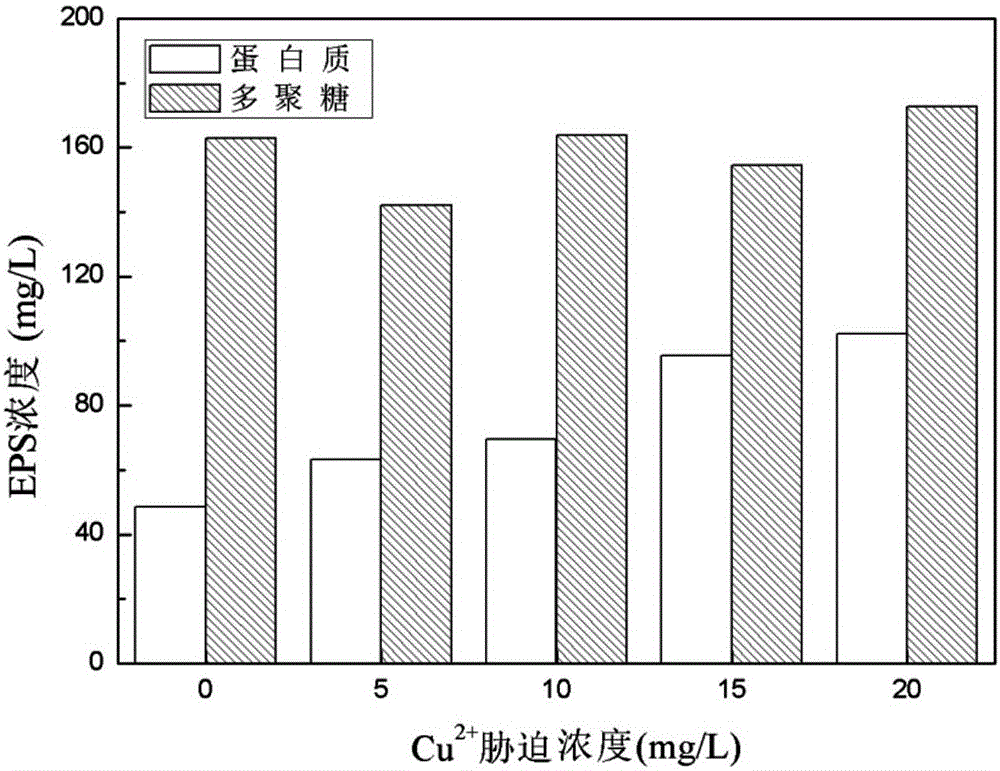
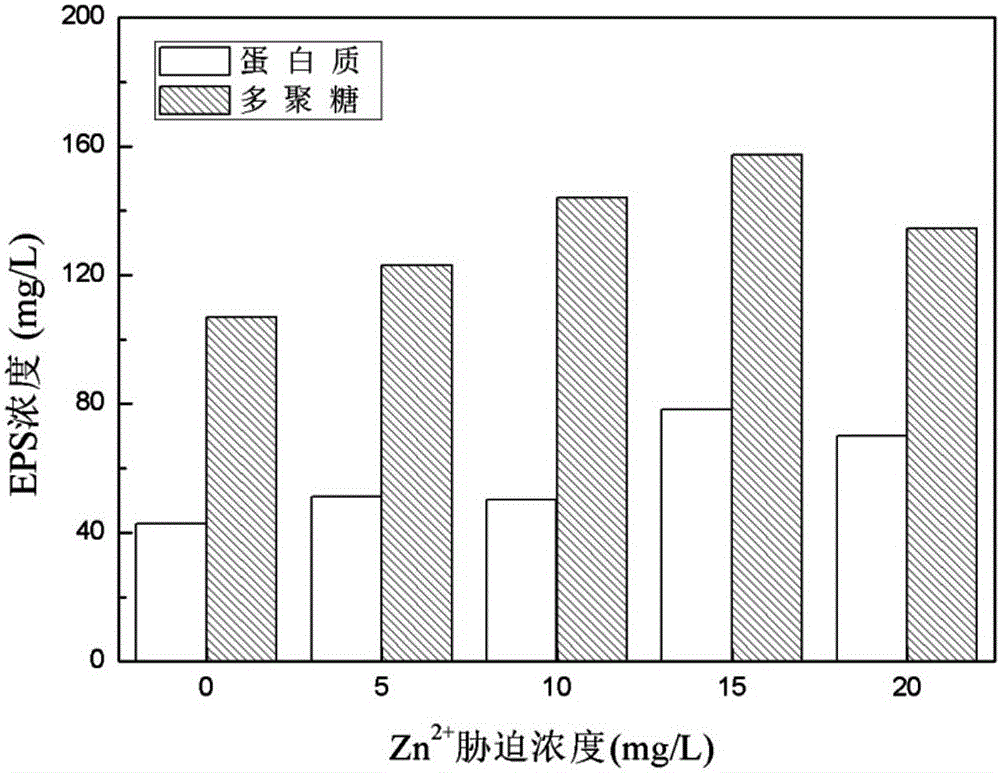
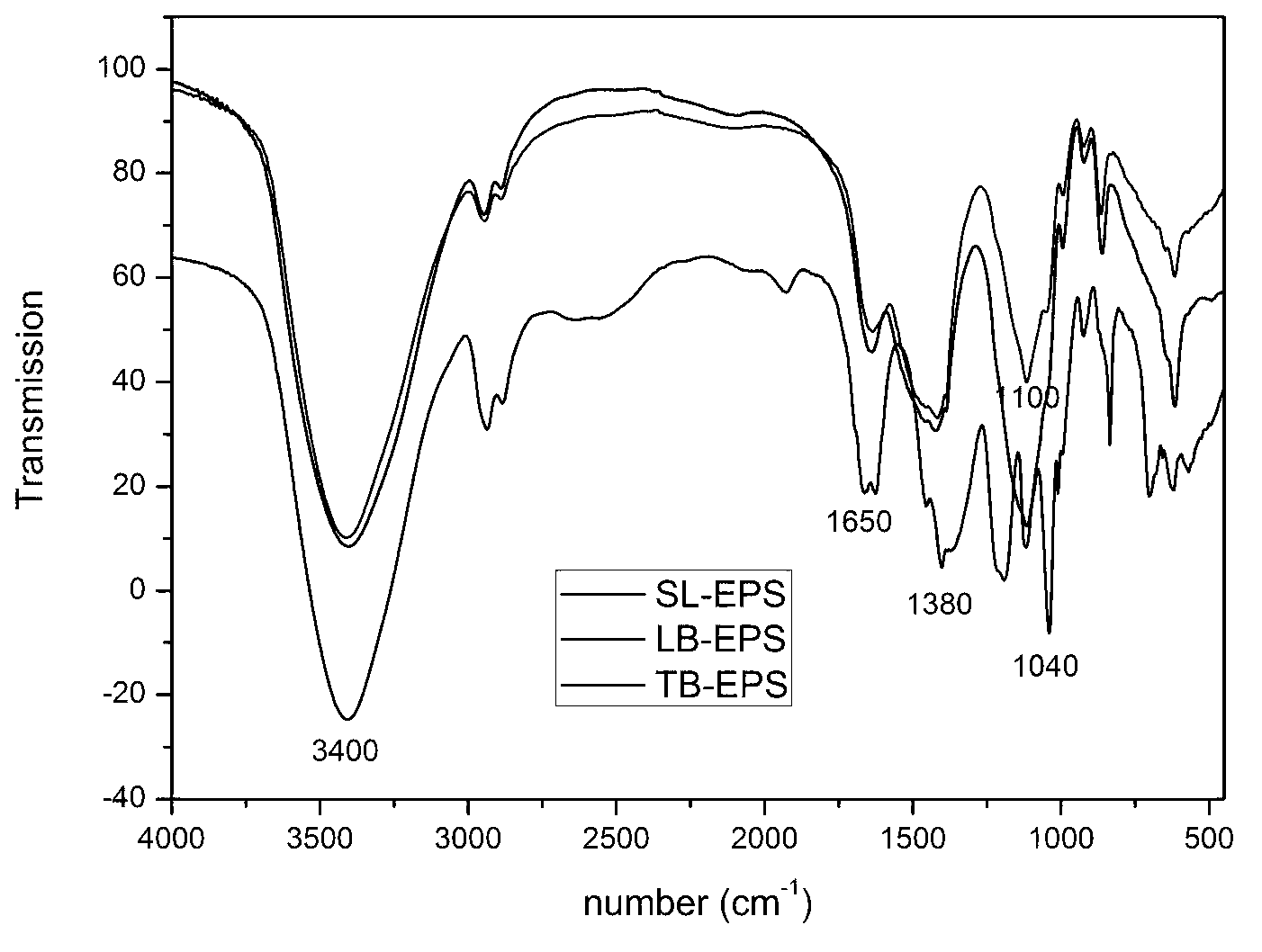
InactiveCN103304626AGuaranteed stabilityDeepen understandingPeptide preparation methodsLow speedPOLYMER SUBSTANCE
The invention relates to an operation method for extracting a blue-green algae extracellular polymeric substance in a grading manner. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out middle / low-speed eccentric shearing to obtain a soluble and loosely combined type extracellular polymeric substance; and secondly, extracting a tightly combined type extracellular polymeric substance in a mode of subalkaline hot bath with the combination of high-speed eccentric shearing. The physical and chemical analysis result shows that the soluble and loosely combined type extracellular polymeric substance contains a small amount of organisms, and the tightly combined type extracellular polymeric substance contain a great amount of organisms; and three-dimensional fluorescence and infrared spectroscopy result shows that the soluble extracellular polymeric substance is only composed of polysaccharide, protein substances and humus substances, and the loosely combined and tightly combined extracellular polymeric substances only consist of polysaccharide and protein substances. The invention discloses an operation method for grading extraction of the blue-green algae extracellular polymeric substance. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the cyanobacterium is free of damage, the cyanobacterium is analyzed in different grades, and the like; and the method has high guiding significance in industrial application of the blue-green algae extracellular polymeric substance.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
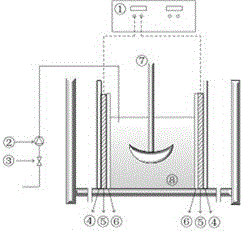
Sludge conditioning-horizontal alternating current field dewatering method and device
InactiveCN106242211ALow costShort conditioning timeSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationBound waterSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a sludge conditioning-horizontal alternating current field dewatering method and device. The method is completed in a conditioning and dewatering integrated device, the synergistic effect of alternating-current electric field disintegration and sulfate radical free radical oxidation is used, so that the sludge is subjected to homogenization disintegration, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) are decomposed, part of bound water is converted into free water, and then the bound water and the free water are uniformly removed under the electroosmosis action of the horizontal alternating current field. The method comprises the following steps: adding a zero-valent iron (Fe<0>) and persulfate into the sludge, applying an alternating current field for sludge conditioning, then performing sedimentation and horizontal alternating current field dewatering. The integrated device comprises a conditioning dewatering tank, an alternating current power supply, a mechanical stirrer, a sludge conveying pump and a valve. The conditioning dehydration method disclosed by the invention is high in dehydration efficiency; the moisture content of the dewatered sludge can be reduced to 80%; the corresponding integrated device is compact in structure, simple to operate and capable of recycling the conditioner.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
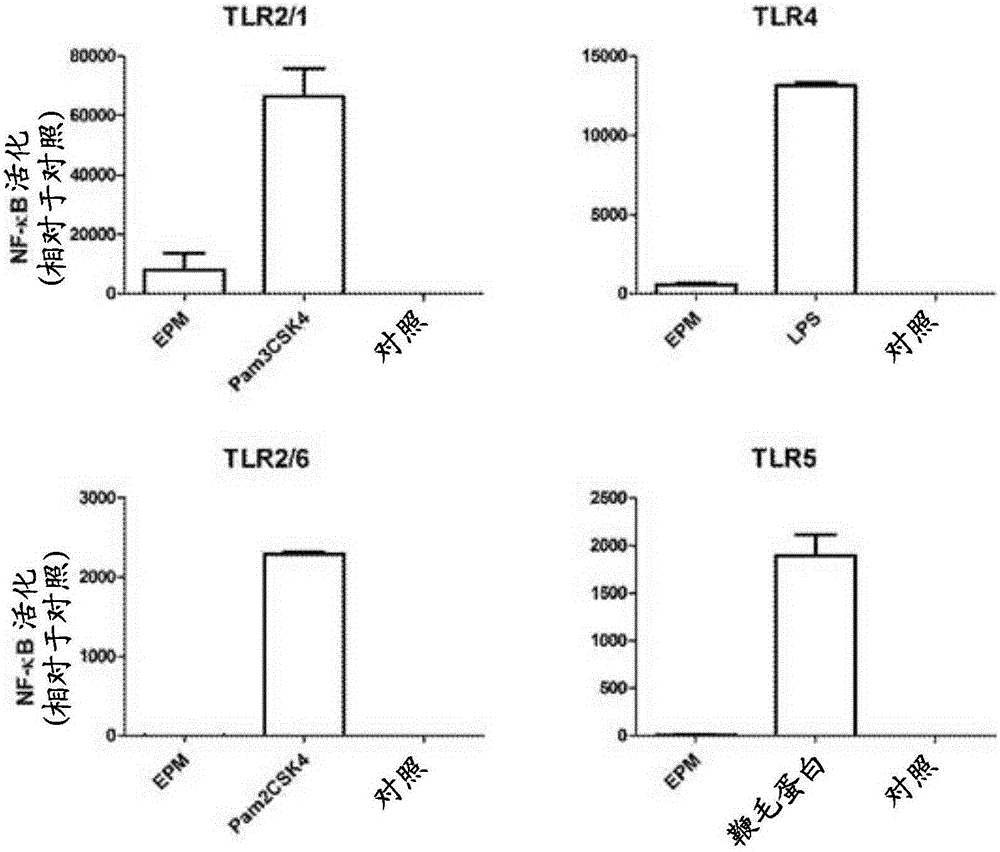
Use of faecali bacterium prausnitzii htf-f (dsm 26943) to suppress inflammation.
InactiveCN105228635AAntipyreticBacteria material medical ingredientsFaecalibacterium prausnitziiBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to medicine, particularly immunology and gastroenterology. Specifically, it relates to probiotic bacteria and extracts thereof for therapeutic use for the treatment of inflammatory disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease. Provided is a composition comprising as active ingredient Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strain HTF-F (DSM 26943) or an extract thereof comprising extracellular polymeric matrix (EPM), and an acceptable carrier, diluent or excipient. Also provided is an anti-inflammatory composition comprising EPM extracted from F. prausnitzii strain HTF-F, and a method for preparing the same.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN +3
Method for extracting extracellular polymeric substance of zoogloea
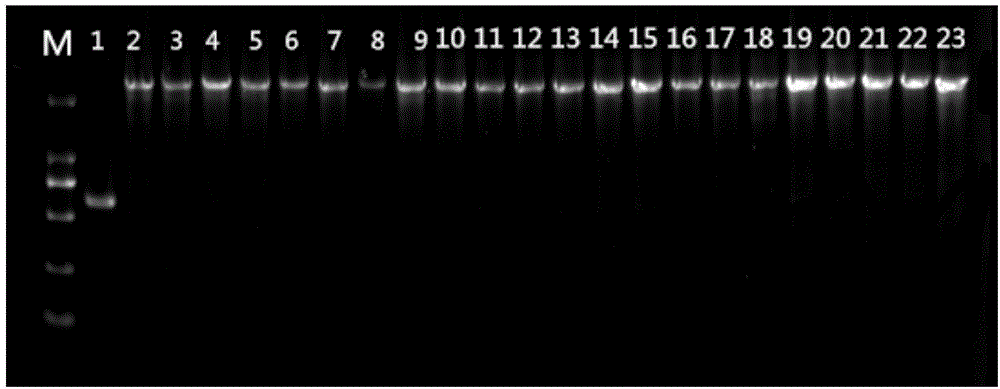
ActiveCN108129547AAchieve separate extractionEfficient extractionPeptide preparation methodsDNA preparationSlime layerZoogloea
The invention provides a method for efficiently extracting an extracellular polymeric substance of activated sludge. The method comprises cleaning, extracting a slime layer by a centrifugal method, extracting a loosely bound extracellular polymeric substance (LB-EPS) by a high-speed centrifugal method and extracting a tightly bound extracellular polymeric substance (TB-EPS) by a formaldehyde-acetic acid potassium acetate heating method. The method has the beneficial effects that the method provided by the invention can be used for simply, conveniently and quickly extracting the extracellular polymeric substance of the activated sludge, moreover, can be used for avoiding the decomposition of protein and polysaccharide, which is caused when a cellular content is dissolved out into an extracting solution and is extracted, and the purity of an extract is furthest guaranteed.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
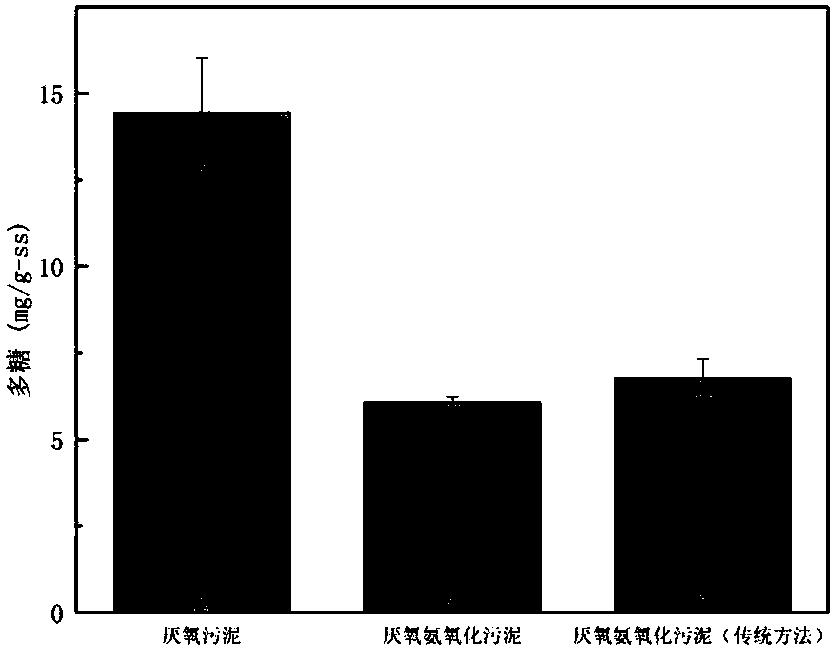
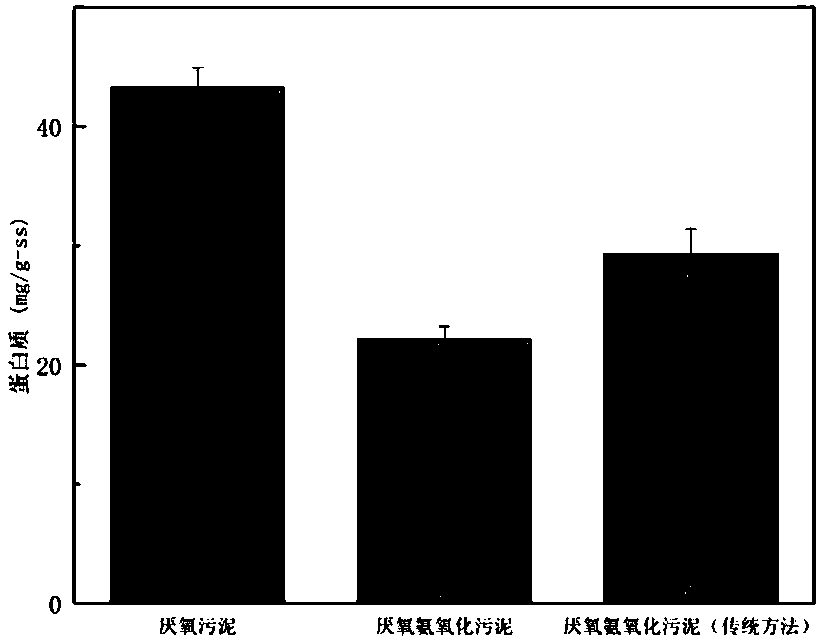
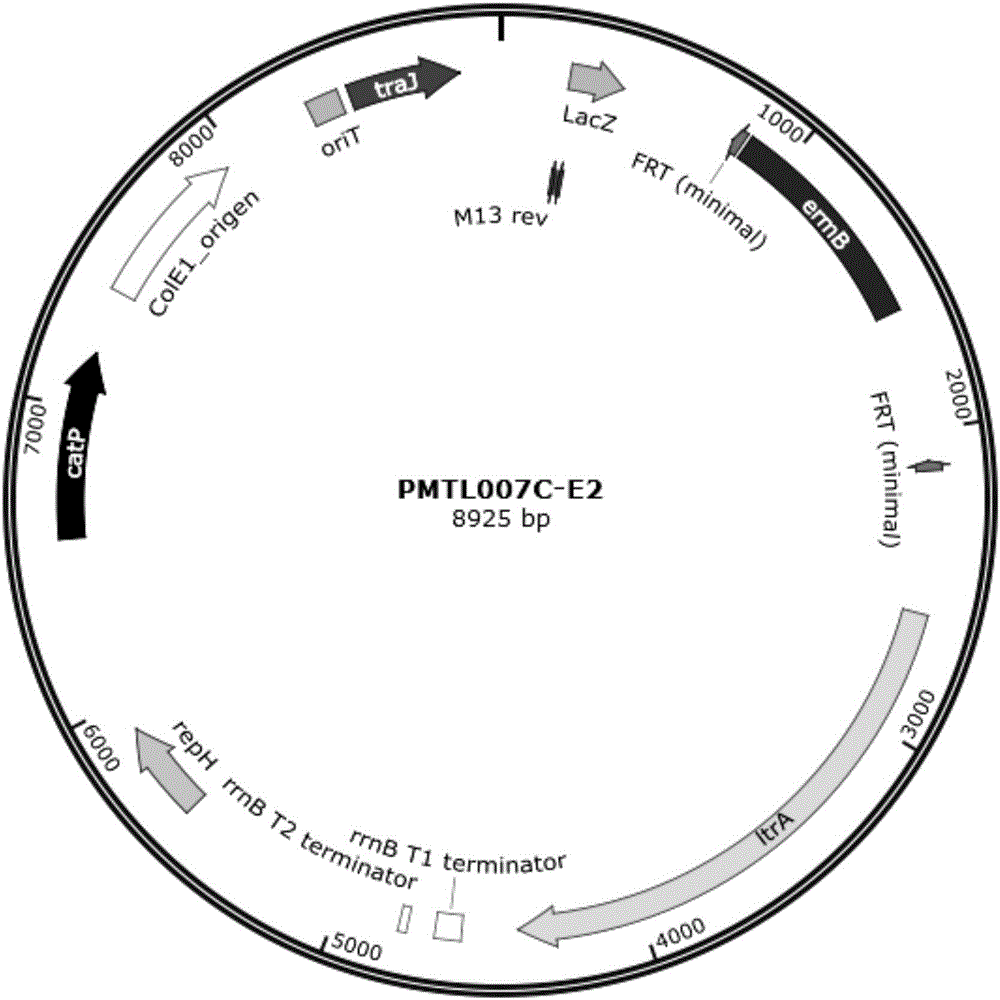
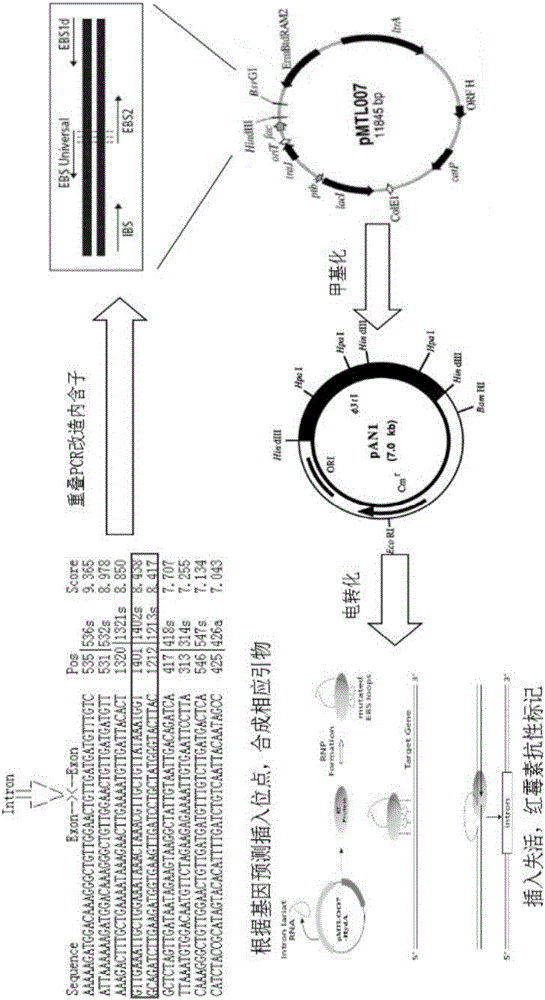
Method for regulating and controlling synthesis of EPS (extracellular polymeric substance) of clostridium acetobutylicum
The invention discloses a method for regulating and controlling synthesis of an extracellular polymeric substance of clostridium acetobutylicum. The method is characterized in that an intron sequence is interpolated into a gene Spo0A of the clostridium acetobutylicum by using a type II intron gene knockout technology. The invention provides a simple and efficient method for regulating and controlling EPS (Extracellular Polymeric Substance) synthesis; a recombinant strain obtained based on the method is relatively good in regulating and controlling effect on the EPS; in case of taking glucose as a carbon source, when cultivated in an anaerobic bottle with the volume of 100 ml by using a slide biomembrane cultivation method, a clostisdium acetobutylicum biomembrane is 5.81 mum in thickness, and the thickness of a strain biomembrane cultivated under the same condition is 24.6 mum.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for enhancing anaerobic fermentation of algal waste liquid to generate methane
The invention relates to a method for enhancing anaerobic fermentation of algal waste liquid to generate methane. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly adopting a centrifugation method to extract extracellular polymeric substances of anaerobic sludge; mixing and adding the algal waste liquid and anaerobic sludge into an anaerobic bioreactor; adjusting the nutritive ratio of C / N / P in the anaerobic bioreactor, wherein the inflowing water quality after the nutritive ratio is adjusted is as follows: COD is 20000-25000mg / L, C / N / P is (100-200):5:1, and pH value is 6.0-9.0; and after preheating, preparing the extracted extracellular polymeric substances and NiCL2.6H2O into mixed liquid A and adding the mixed liquid A into the anaerobic bioreactor. The method has the advantages that necessary trace element Ni for growing the methanogen is chelated into a dissolved-state biological promoter for utilization of the methanogen, the chemical precipitation action is overcome, the utilization ratio of the trace element is increased, the gas generation ratio for anaerobic fermentation of the algal waste liquid is increased to the maximum extent, the adding amount of the promoter is less, the cost is low and the operation is simple.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
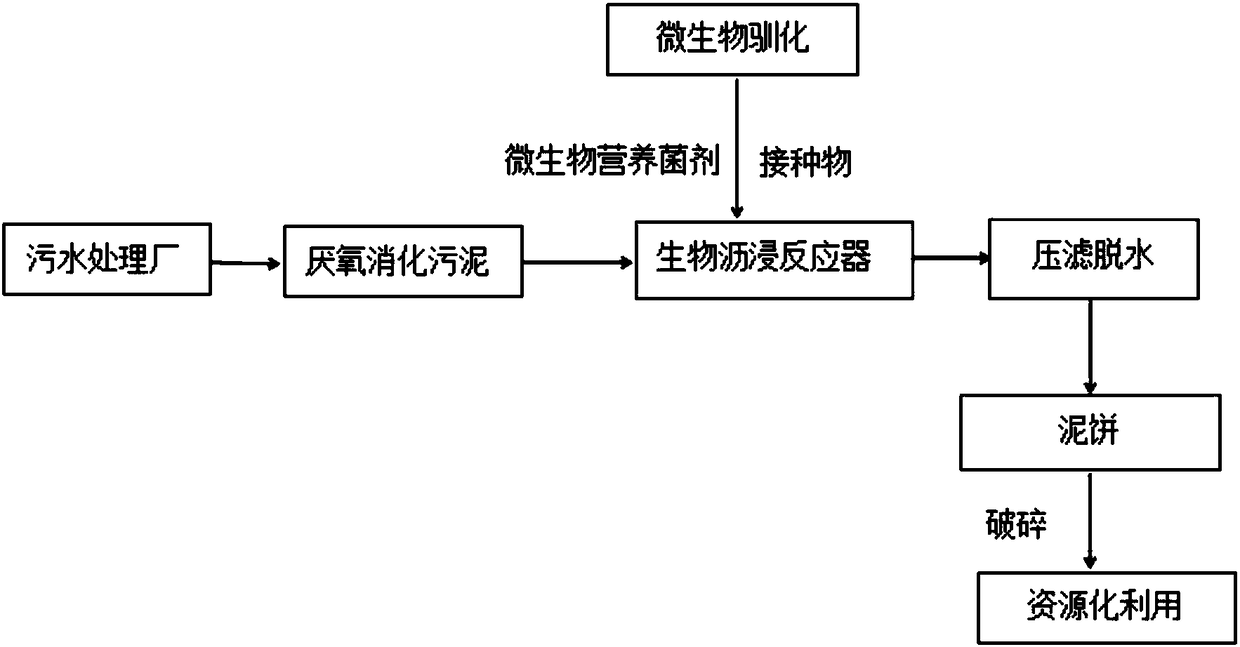
Compound microbial liquid for treating anaerobic digested sludge and novel bioleaching method
ActiveCN108083597AGuaranteed dehydration efficiencyDetox inhibitionFungiSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBiologyWater content
The invention discloses a bioleaching method for anaerobic digested sludge and belongs to the technical field of sludge treatment. Bioleaching work flora is compounded by introducing new microbial strains, continuous domestication is performed, an inoculum obtained through domestication is mixed with the anaerobic digested sludge for bioleaching treatment, the new microbial strains are used for degrading small-molecular organic acids and secreting surface active materials to rapidly remove EPSs (extracellular polymeric substances) wrapping surfaces of sludge cells, bioleaching reaction time isshortened to 12-24 h, the sludge obtained after bioleaching directly enters a plate-and-frame filter press for dehydration, and a mud cake with water content lower than 60% is obtained. The method adopts simple process, no chemical reagent is needed due to complete dependence on action of microbes, and the method has the advantages of high dehydration efficiency, low operation cost and low technological operation difficulty.
Owner:南京贝克特环保科技有限公司
Acoustically excited encapsulated microbubbles and mitigation of biofouling
Provided herein is a universally applicable biofouling mitigation technology using acoustically excited encapsulated microbubbles that disrupt biofilm or biofilm formation. For example, a method of reducing biofilm formation or removing biofilm in a membrane filtration system is provided in which a feed solution comprising encapsulated microbubbles is provided to the membrane under conditions that allow the encapsulated microbubbles to embed in a biofilm. Sonication of the embedded, encapsulated microbubbles disrupts the biofilm. Thus, provided herein is a membrane filtration system for performing the methods and encapsulated microbubbles specifically selected for binding to extracellular polymeric substances (EFS) in a biofilm.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
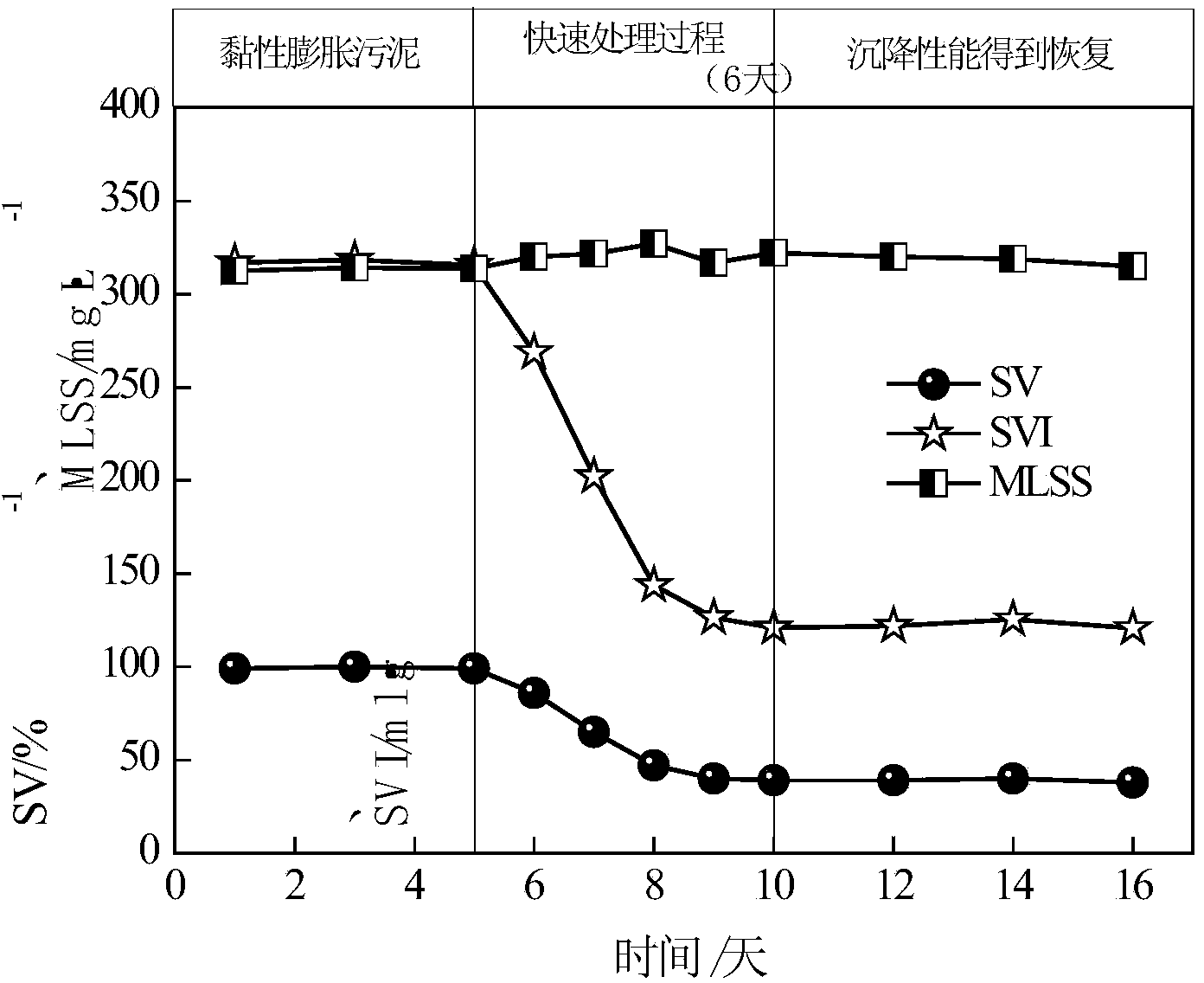
Method for rapidly solving sticky sludge bulking problem
ActiveCN103408142AAccelerated settlementImprove settlement performanceTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesProcess systemsZeta potential
The invention relates to a method for rapidly solving sticky sludge bulking problem and belongs to the field of biochemical wastewater treatment. For a sticky sludge bulking problem caused by a high organic load, a means that inflow water supply is diluted and an operation mode of a reactor is changed is adopted, so that a system operates under the conditions of low inflow water organic load and high substrate concentration gradient; the sludge settleability is controlled in real time and conditions are improved in real time by detecting parameters such as a sludge volume index, an extracellular polymeric substance and a Zeta potential in an operation process. Practice shows that the sludge settleability can be obviously improved by continuously operating the method for rapidly solving the sticky sludge bulking problem for 2-8 days; in a later operation process, recurrence of the sticky sludge bulking problem can be effectively prevented by improving an inflow water and operation mode of a system. The method for rapidly solving the sticky sludge bulking problem has the advantages of short period, low recurrence rate, low economic cost and small influence on sludge activity and can be taken as an alternative scheme for rapidly and efficiently solving the sticky sludge bulking problem in an activated sludge process system.
Owner:中山公用水务投资有限公司
Oxidation-oriented catalyst used for sludge treatment
InactiveCN103028426APromote generationPromote digestionSludge treatment by oxidationOther chemical processesSorbentDecomposition
The invention provides an oxidation-oriented catalyst used for sludge treatment. The oxidation-oriented catalyst for sludge treatment comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5-45% of metal compound and 55-95% of adsorbent. The oxidation-oriented catalyst comprises the metal compound, so that the oxidation-oriented catalyst can be used as an oxidation initiator to promote the generation of hydroxyl radicals and decompose organic matters in sludge; the oxidation-oriented catalyst comprises the adsorbent, so that the oxidation-oriented catalyst has a larger specific surface area and a strong adsorption capacity and can efficiently adsorb solid granular matters in the sludge from gas or liquid; and during the sludge treatment, an acidity and alkalinity regulator is not required to be added into the oxidation-oriented catalyst, so that membrane condensation on the surface of a microbial extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) is avoided, membrane rupture and decomposition of the EPS in the sludge are facilitated, and thus the sludge treatment efficiency is improved.
Owner:湖南清和环保技术有限公司
Cleaning compositions having an enzyme system
ActiveUS20170355931A1Enhance the stain-removal and/or malodor-reducing benefits of a nuclease enzymeOrganic/inorganic per-compounds compounding agentsSoap detergent compositionsEnzyme systemCleansing Agents
Cleaning compositions having an enzyme system, where the enzyme system includes a nuclease enzyme, an extracellular-polymer-degrading enzyme, and a cleaning adjunct. Methods of making and using such cleaning compositions. Use of an extracellular-polymer-degrading enzyme.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for alleviating density of float sludge of silt port by using heterotrophic bacteria microorganisms
ActiveCN104743761ASlow down the compaction speedLow running costBiological sludge treatmentContaminated waterways/lakes/ponds/rivers treatmentMicroorganismPOLYMER SUBSTANCE
The invention discloses a method for alleviating density of float sludge of a silt port by using heterotrophic bacteria microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps: I) screening heterotrophic bacteria which can generate extracellular polymeric substances and alleviate float sludge of the silt port from float sludge of the silt port; and II) generating the extracellular polymeric substances by heterotrophic bacteria and carrying out interaction on extracellular polymeric substances and the float sludge of the silt port so as to alleviate the dense speed of the float sludge of the silt port. By selecting the heterotrophic bacteria microorganisms of the float sludge of the silt port, interaction on extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and the float sludge of the silt port is carried out to alleviate the dense speed of the float sludge of the silt port, so that the application period of navigational depth is prolonged, the maintaining and dredging period can be prolonged, the operational cost of port enterprises is lowered, and the economical benefit is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST FOR WATER TRANSPORT ENG M O T
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com