Method for extracting blue-green algae extracellular polymeric substance in grading manner
An extracellular polymer and fractional extraction technology, applied in the field of cyanobacterial extracellular polymer extraction, can solve the problems of large differences in extraction operating conditions, poor comparability of results, etc., to ensure cell integrity, improve yield, and high extraction efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
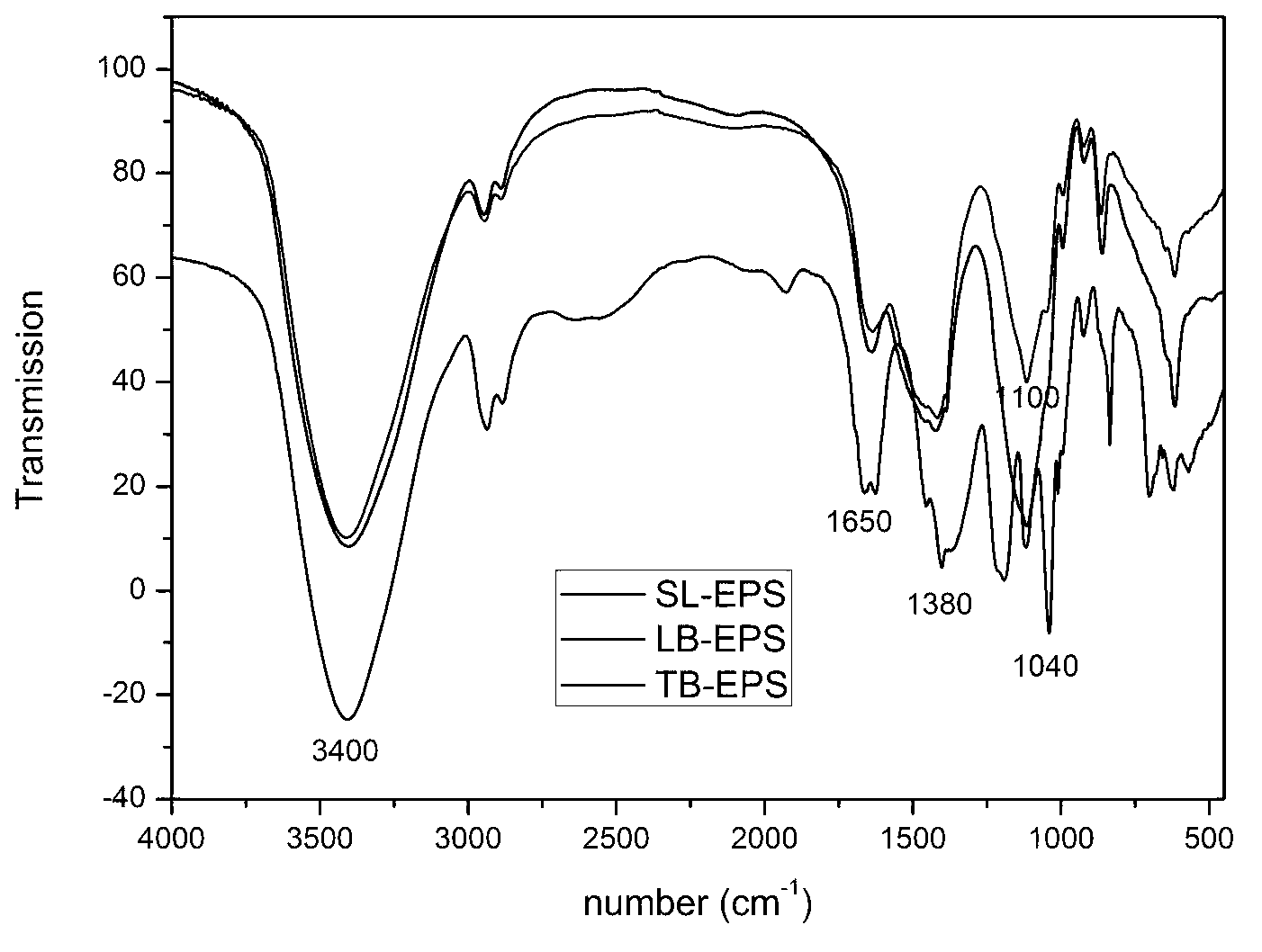
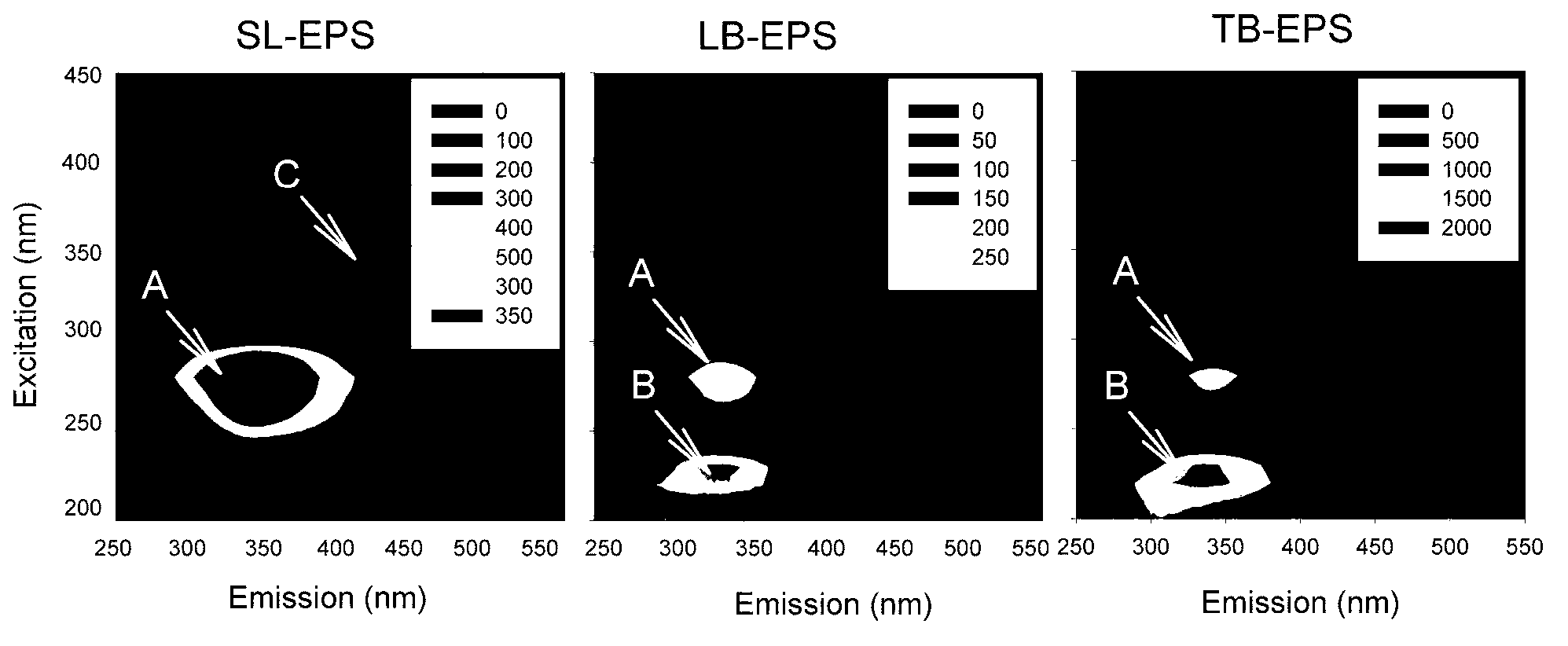
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
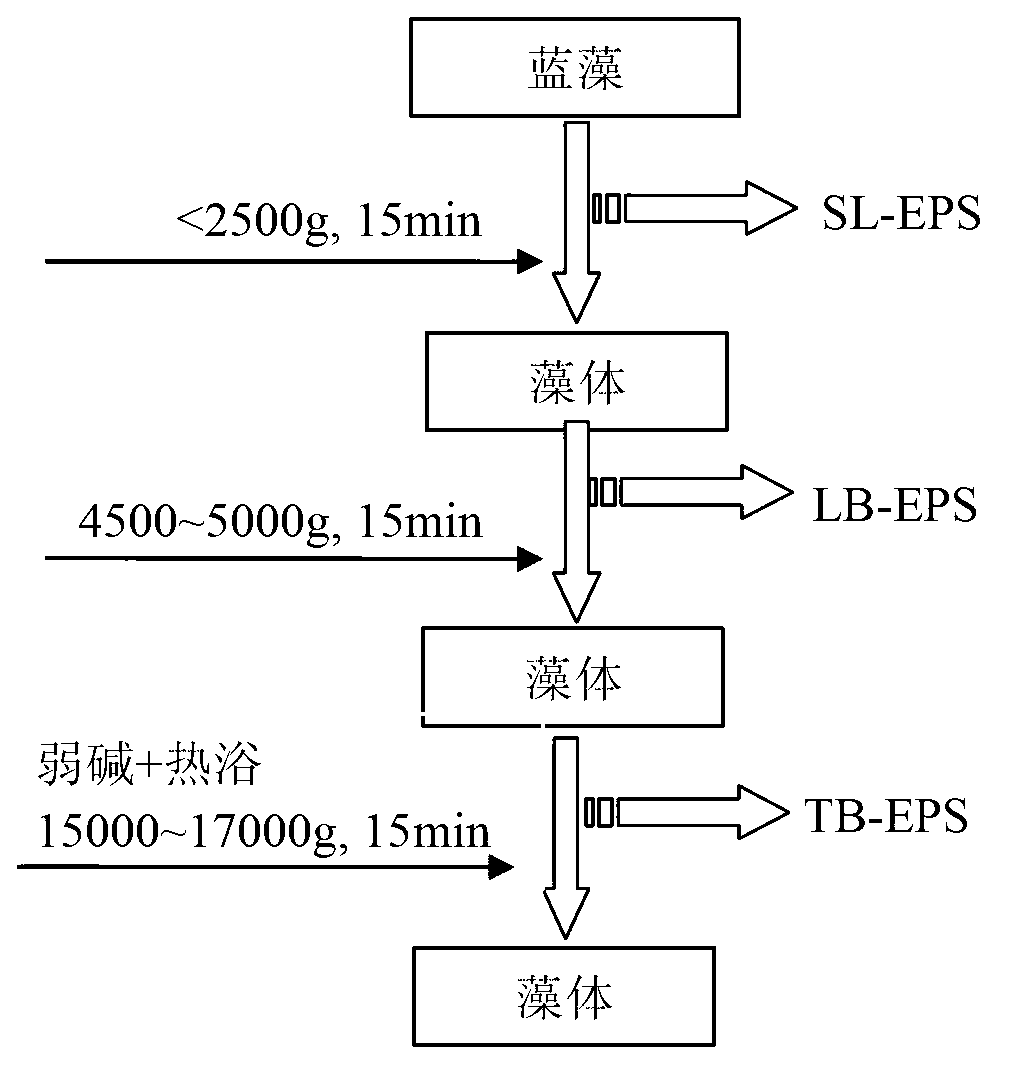
[0030] Take a sample of cyanobacteria water body in Taihu Lake in summer. The biomass of cyanobacteria is 0.8g / L. After the cyanobacteria water sample is collected, it is placed in a refrigerator at 4°C, and the extracellular polymer is fractionated and extracted within 12 hours. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0031] (1): Extraction of soluble and loosely bound extracellular polymers from cyanobacteria
[0032] Take a certain amount (50ml) of cyanobacteria water samples and centrifuge at 2500g centrifugal force for 15min at 4°C. The supernatant collected is SL-EPS; Centrifuge at 4500g for 15 minutes, and the collected supernatant is LB-EPS; add 0.05% NaCl buffer solution to the original volume of the solid sample, and proceed to the next step.
[0033] (2): Extraction of tight-binding extracellular polymers from cyanobacteria
[0034] Use 40% NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the algal cells to be extracted to 9.0, equilibrate for 10 minutes, and then place t...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Take the cyanobacteria water samples in Taihu Lake in autumn. The cyanobacteria biomass is 0.5g / L. After the cyanobacteria water samples are collected, they are placed in a 4°C refrigerator, and the extracellular polymers are fractionated and extracted within 12 hours. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0042] (1): Extraction of soluble and loosely bound extracellular polymers from cyanobacteria
[0043] Take a certain amount (50ml) of cyanobacteria water samples and centrifuge at 2000g centrifugal force for 15min at 4°C. The collected supernatant is SL-EPS; add 0.07% NaCl buffer solution to the original volume of solid samples, Centrifuge at a centrifugal force of 5000g for 15 minutes, and the collected supernatant is LB-EPS; add 0.07% NaCl buffer solution to the original volume of the solid sample, and proceed to the next step.
[0044] (2): Extraction of tight-binding extracellular polymers from cyanobacteria
[0045] Use 35% KaOH solution to adjust the...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Microcystis aeruginosa was cultivated indoors to obtain a culture solution of Microcystis aeruginosa, and the algae biomass was determined to be 0.15 g / L. Samples were subjected to the following steps:
[0051] Take a certain amount (50ml) of the culture solution sample and centrifuge at 2500g centrifugal force for 15min at 4°C, and the collected supernatant is SL-EPS; add 0.08% NaCl buffer solution to the original volume of the solid sample, Centrifuge at 4500g for 15 minutes, and the collected supernatant is LB-EPS; add 0.08% NaCl buffer solution to the original volume of the solid sample, and proceed to the next step.
[0052] (2): Extraction of tight-binding extracellular polymers from cyanobacteria
[0053] Use 40% KaOH solution to adjust the algae cells to be extracted to pH 8.0, balance for 10 minutes, and then place the algae liquid to be extracted at 55 o C constant temperature hot water reaction for 30min. Take it out and cool it immediately, and centrifuge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com