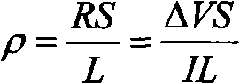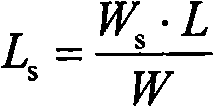Patents
Literature
103 results about "Interstitial water" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interstitial water. 1. n. [Geology] Water that occurs naturally within the pores of rock. Water from fluids introduced to a formation through drilling or other interference, such as mud and seawater, does not constitute interstitial water. Interstitial water, or formation water, might not have been the water present when the rock originally formed.
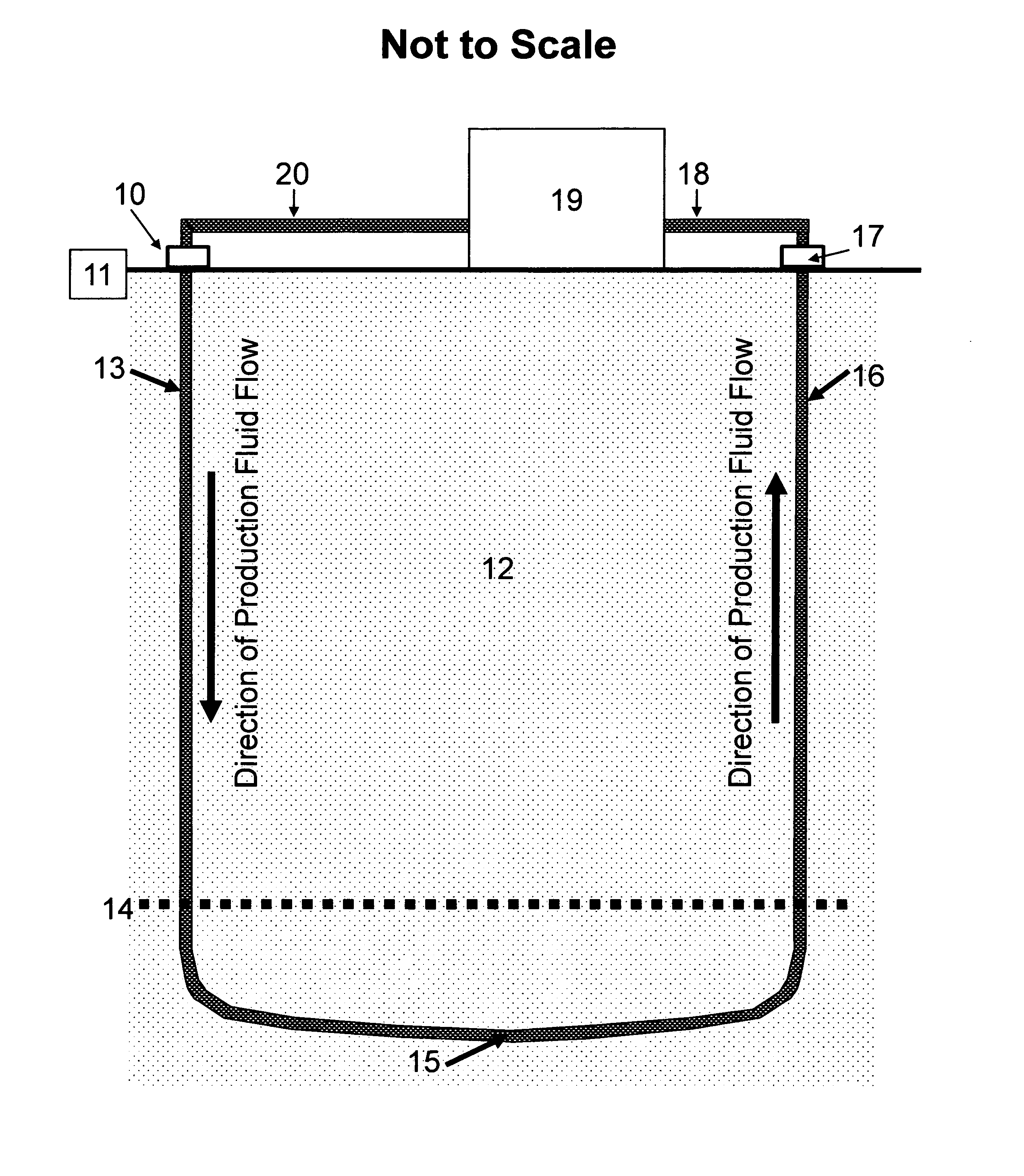
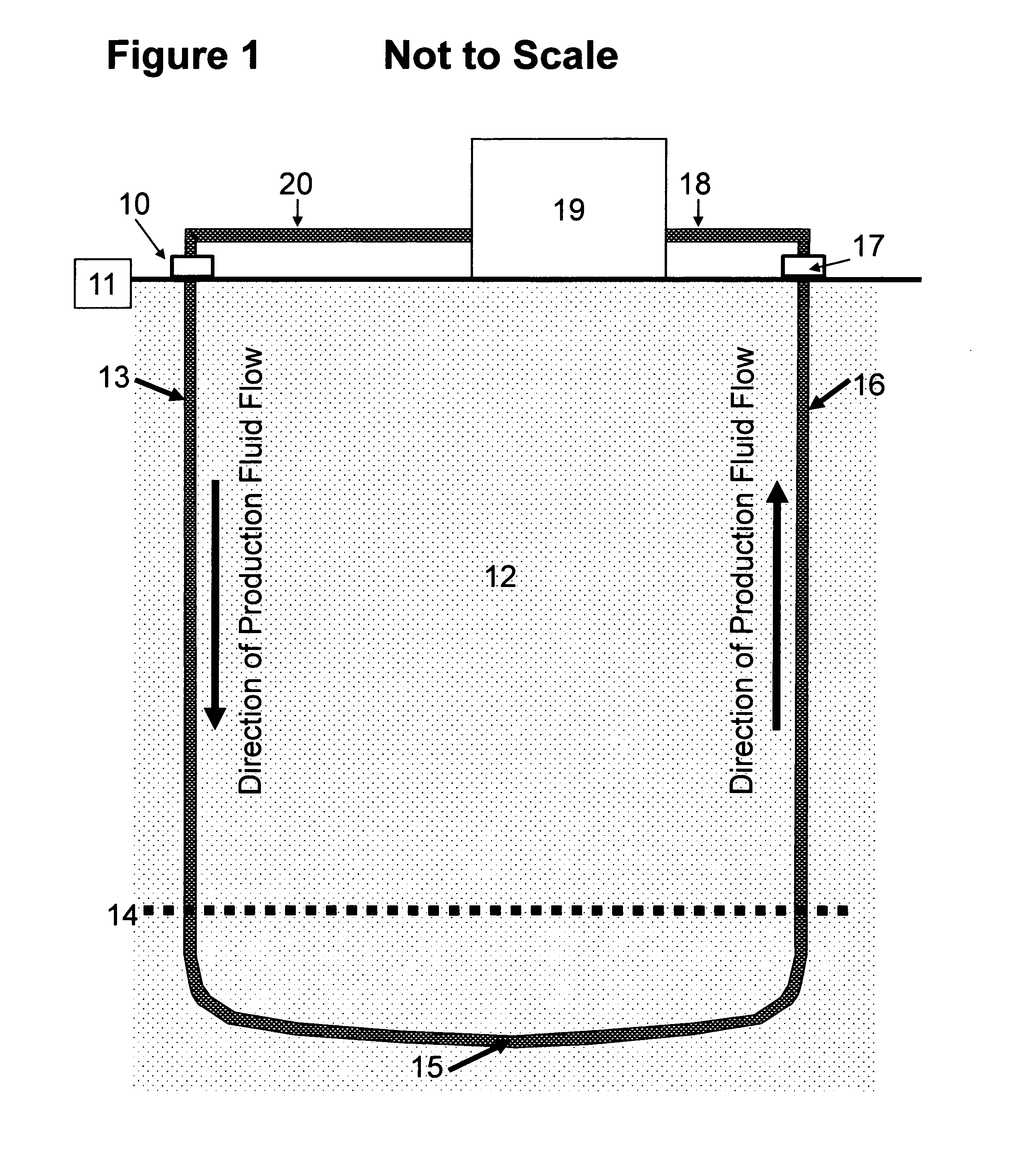
Loop geothermal system
InactiveUS20110048005A1Direct contact guaranteeRapidly and easily changeOther heat production devicesGeothermal energy generationInterstitial waterPorosity
One embodiment of a system of geothermal energy production containing a production fluid circulated entirely within a continuous subterranean pipeline (13 and 16) while below the earth's surface (11) so that the production fluid is heated, via the encasing pipe, by surrounding subterranean hot rock (12). By directing the heated production fluid through said continuous subterranean pipeline up to the earth's surface and through a power plant (19), energy can be produced from the hot production fluid.This system enables energy production from subterranean rock formations of moderate temperature at moderate depths because any production fluid, such as water, hydrocarbon, or refrigerant, can be used to optimize energy production. Furthermore, natural porosity and permeability of the subterranean rock formations at moderate depths may provide sufficient natural circulation of interstitial water to assist in heat transfer from large volumes of hot rock without the need of inducing artificial fractures.
Owner:MCHARGUE TIMOTHY REED
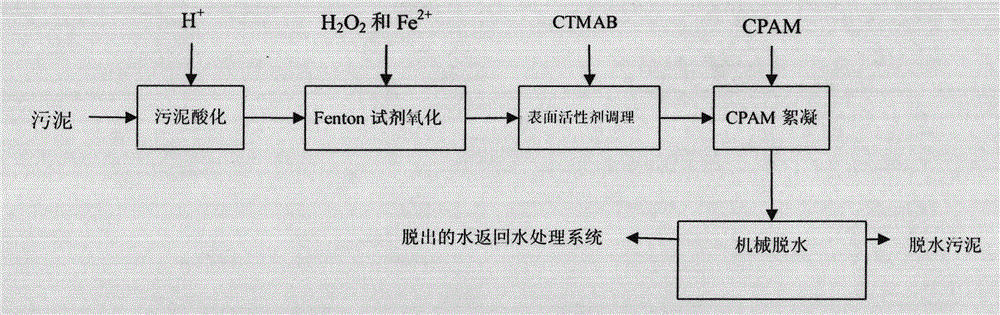
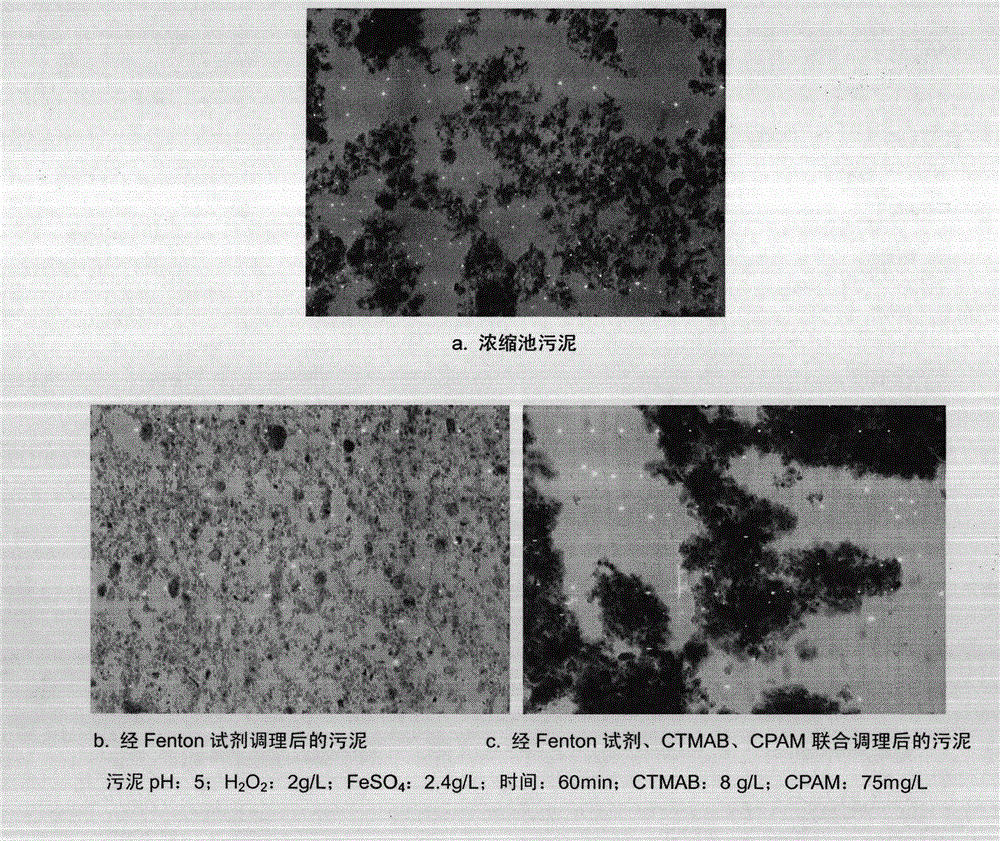
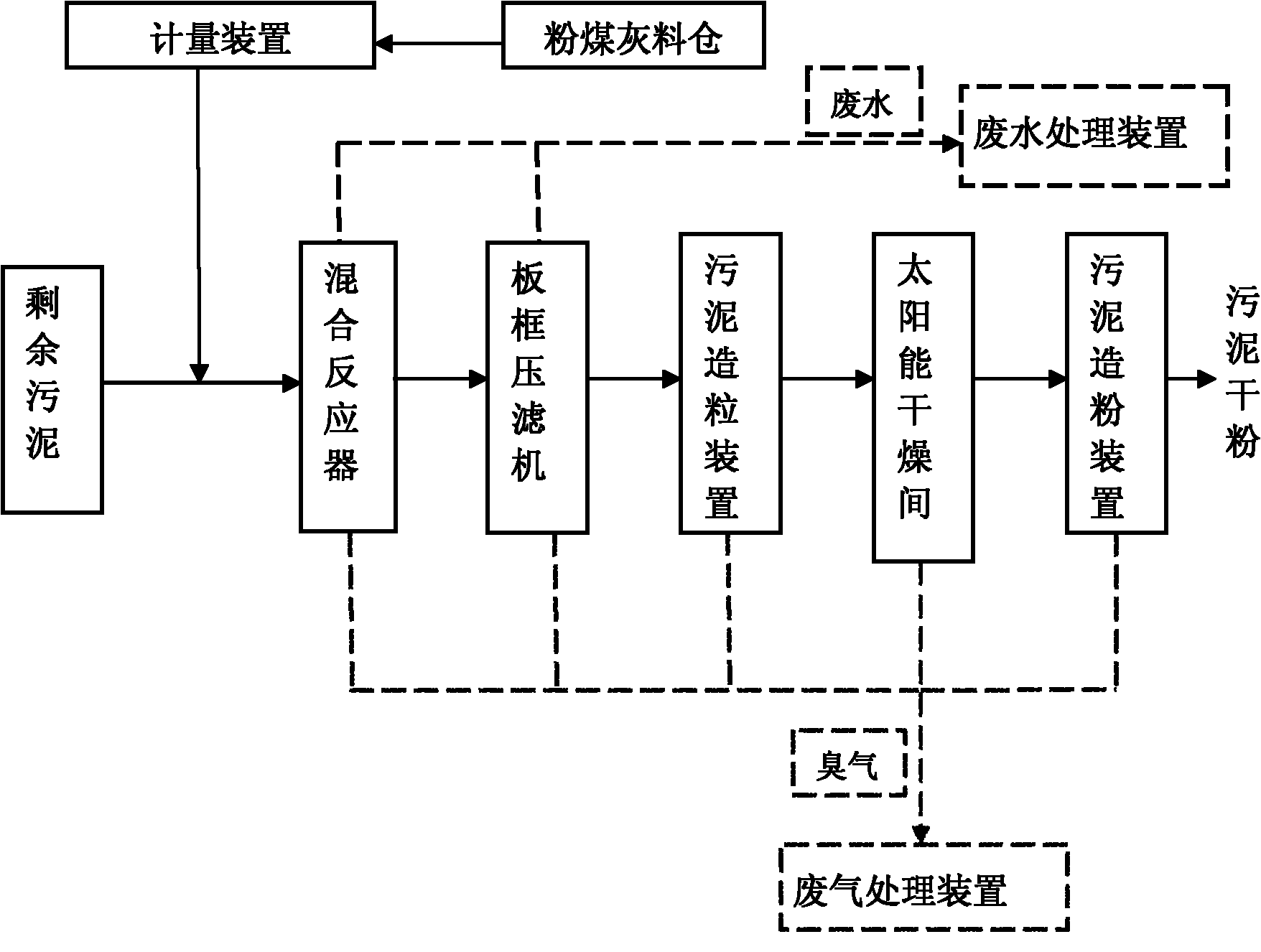
Joint-conditioning dehydration method for sludge
InactiveCN102910793AImprove dehydration effectIncrease solid contentSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationParticulatesFenton reagent
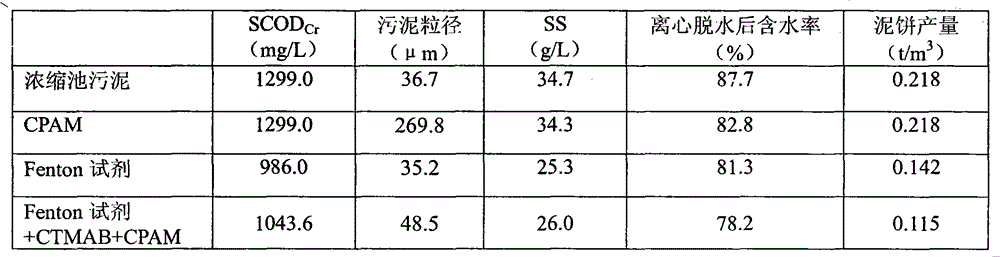
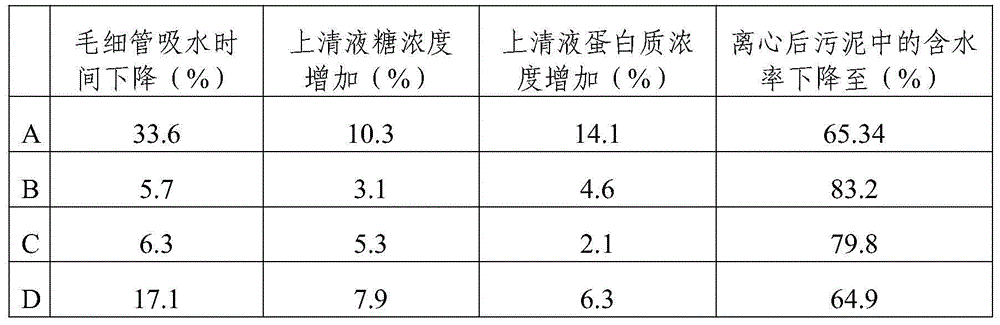
The invention is named as 'a joint-conditioning dehydration method for sludge', belonging to the technical field of environmental engineering and sludge treatment. The joint-conditioning dehydration method comprises the following steps of: adding H202 and FeSO4 into the sludge (with pH being equal to 5) acidified by mineral acid, degrading organic matter by virtue of strong oxidation of a Fenton reagent, and dissolving and cracking microbial cells and extracellular polymeric substances in the sludge; adding a surfactant CTMAB (Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide) into the sludge to reduce the surface tension of the sludge and change the surface characteristics of the sludge, and transforming a part of interstitial water into free water; and flocculating sludge particulates with disperse structure, small particle diameter and large specific surface area by virtue of flocculation action of polyacrylamide (CPAM) to the sludge particulates. After the sludge is subjected to joint conditioning of the Fenton reagent, the surfactant and the CPAM, the moisture content of the sludge after being centrifugally dewatered is reduced to 78.2% from 87.7%, and the output of mud cakes is reduced to 0.115t / m<3> from 0.218t / m<3>, therefore, the dehydration property of the sludge can be improved remarkably, the investment and operation costs are reduced effectively, and an ideal sludge reduction goal is reached.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Quick measurement method for different forms of water in sludge
ActiveCN103308543ASimple and fast operationQuick measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceInterstitial waterActivated sludge
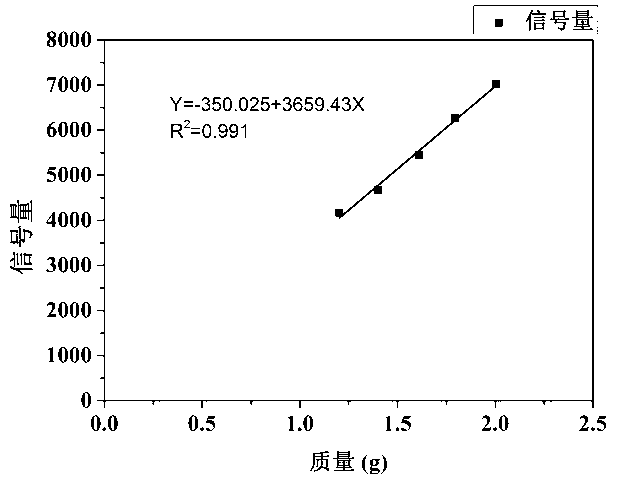
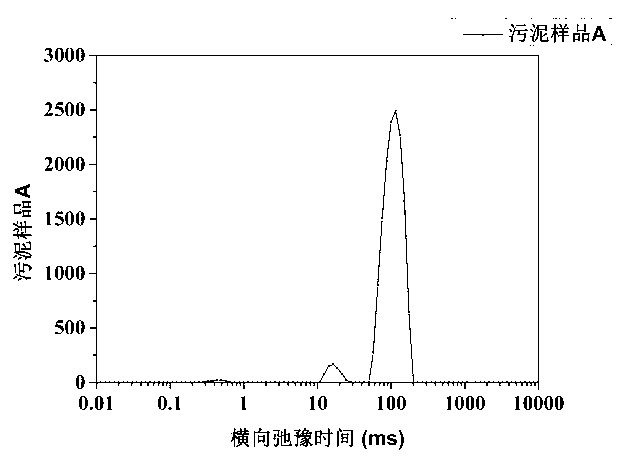
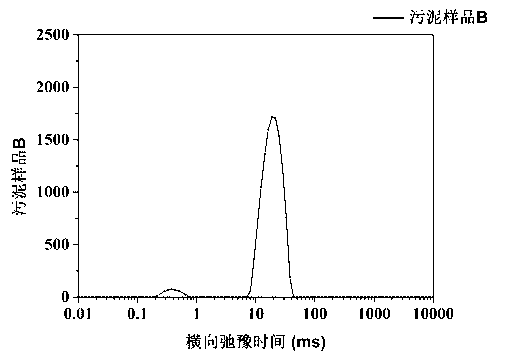
The invention discloses a quick measurement method for different forms of water in sludge. The quick measurement method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on the sludge to obtain a transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of different forms of water in the sludge; (2) stewing and settling activated sludge, preparing a standard sample by supernatant liquid at equal mass interval, and constructing a standard curve; (3) according to the obtained standard curve, matrixing the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time of the sludge to obtain three different forms of water, namely free water mass, interstitial water mass and surface combined water mass in the sludge; and (4) drying the sludge to be measured until the weight is balanced, subtracting the final mass from the initial mass, and calculating the fourth form of water in the sludge, namely the internal combined water mass. Compared with the conventional method, the quick measurement method for measuring the content of different forms of water in the sludge by a nuclear magnetic resonance technology has the advantages of short experiment time, harmlessness to experiment samples, precision of measurement and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Integral treatment utilization method for sludge produced from water works
InactiveCN101215192AIncrease humidityIncreased rainfallSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningClimate change adaptationInterstitial waterSludge
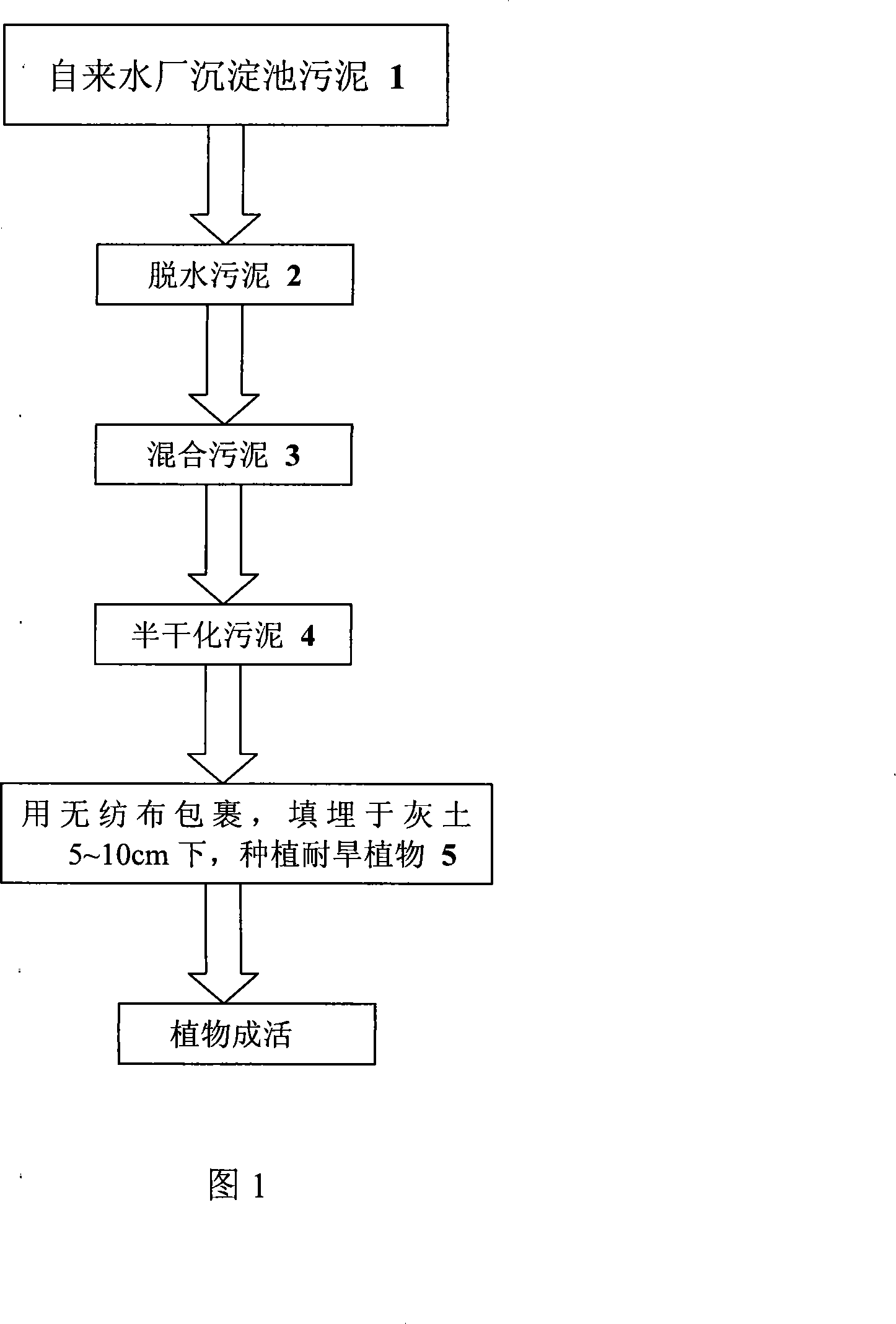
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively processing and utilizing sludge produced by water supply works. The technical problems which need to be resolved by the invention are solidification and improvement for desert soil, better harnessing for deserts and changing the sludge which is in need of money to harness originally into resource. The technical scheme of resolving the problems comprises: 1) employing the sludge produced by the water supply works to remove a majority of interstitial water in the sludge via gravitional settling and concentrating, and obtaining dewatered sludge, 2) adding additives in the dewatered sludge to form blended sludge, 3) piling the blended sludge in a bar pile which is 1.5 meters in width and 1 meter in height, stacking retting for 7-15 days and forming half-dewatered sludge after fermentation, 4) using a crusher to process the half-dewatered sludge into granules, wherein the maximum granular size of the sludge granules does not exceed 8 centimeters, then wrapping the sludge granules with non-woven fabrics, controlling volume of each bag of the sludge granules at a scale of 0.05-0.5 cubic meter, then burying dispersedly the sludge granules in the place which are 5-10 centimeters below desert dirt. The invention is mainly adapted for processing and handling the sludge produced by the water supply works.
Owner:浙江大洲固体废物处置研究所
Liquefaction phenomenon prediction system
InactiveUS20030177834A1Vibration measurement in solidsForce measurementHorizontal stressPore water pressure
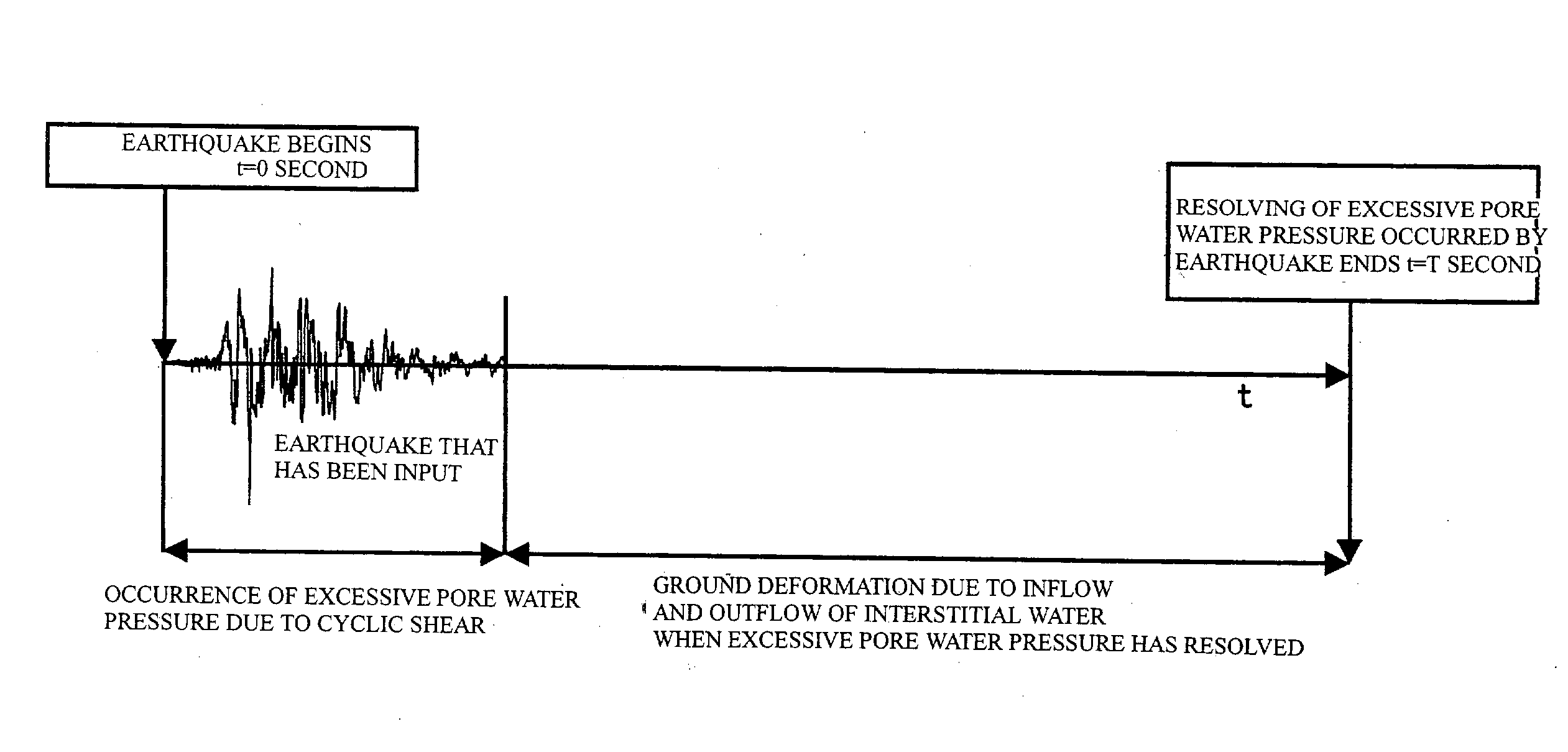
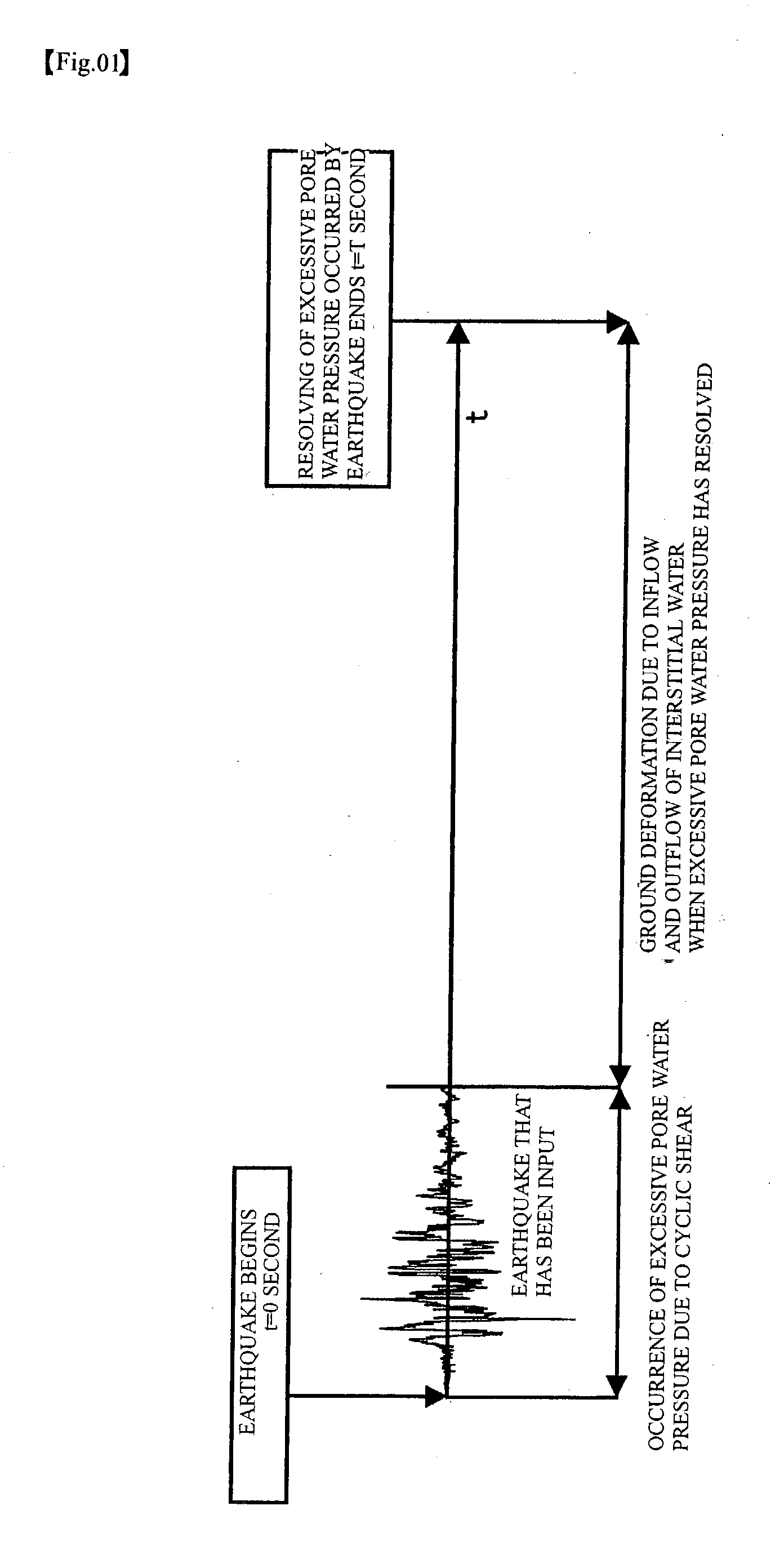
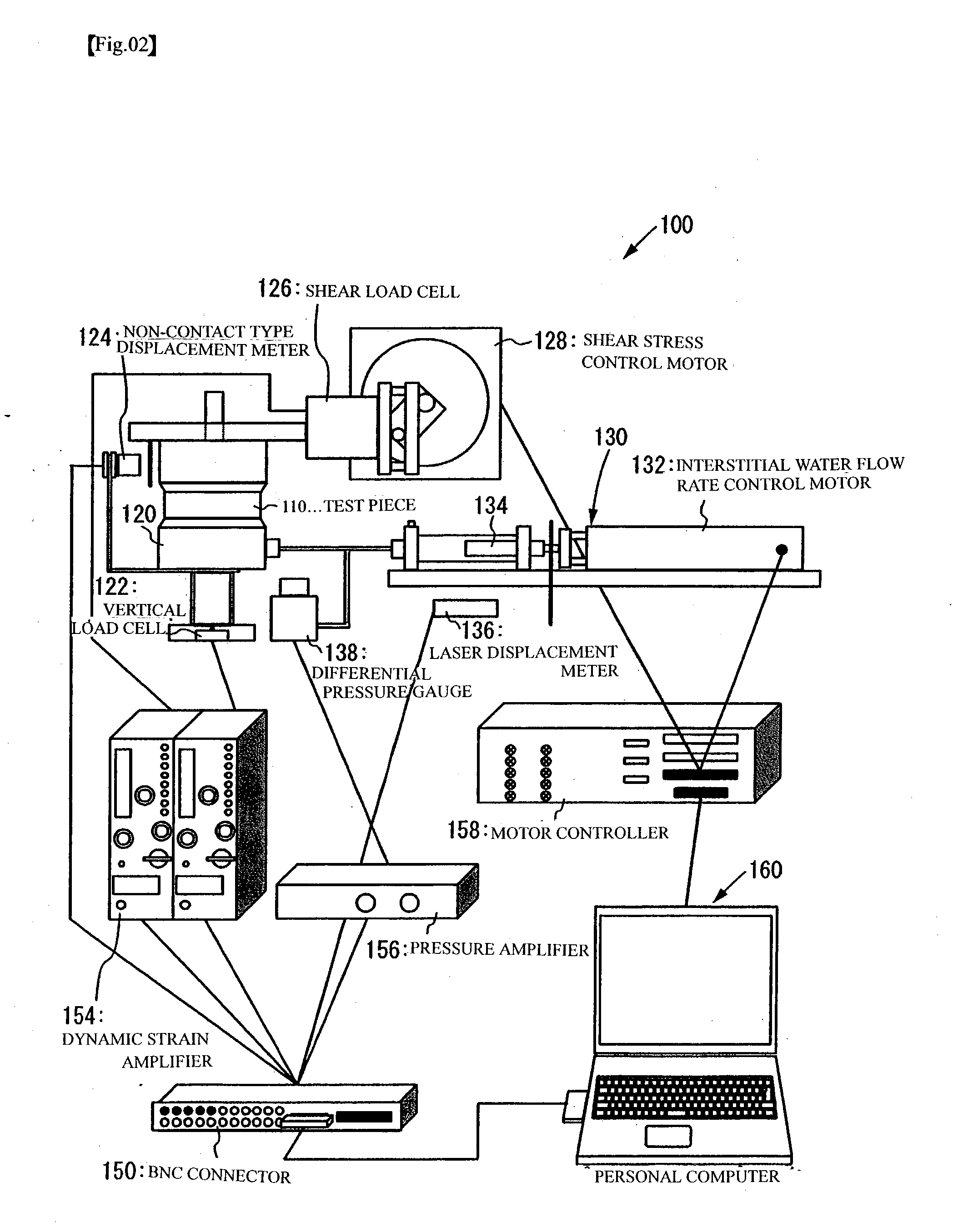
To predict residual settlement quantity and residual horizontal deformation quantity of ground where a liquefaction phenomenon has occurred due to earthquake. Soils in situ (stratum B to stratum D) are sampled from ground, and are made to be element test object stratums. A stratum whose characteristic is well-known, or the like may be substituted for a numerical model (stratum A). Next, setting of input conditions is performed, and vertical stress, horizontal stress and initial shear stress, which are equivalent to applied load that the ground at a depth of the point suffers, are worked on to each stratum. This recreates a stress status of soil before earthquake occurs. Then, shear displacement and the movement quantity of interstitial water by earthquake are given to the test piece, and the quantity of shear stress and pore water pressure, which have occurred, is obtained. In the element test execution stratum, displacement computed for stratum element and the movement quantity of interstitial water are actually given to each element to measure restoring force and the pore water pressure. By sequentially repeating the steps, it is possible to simulate the behavior of the liquefaction phenomenon.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD
Electrokinetic remediation contaminated soil display system
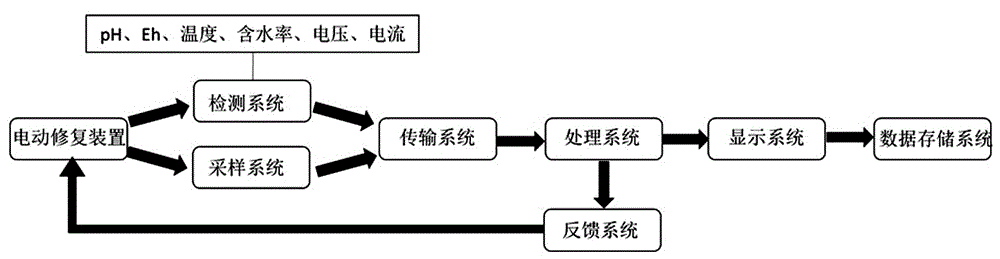
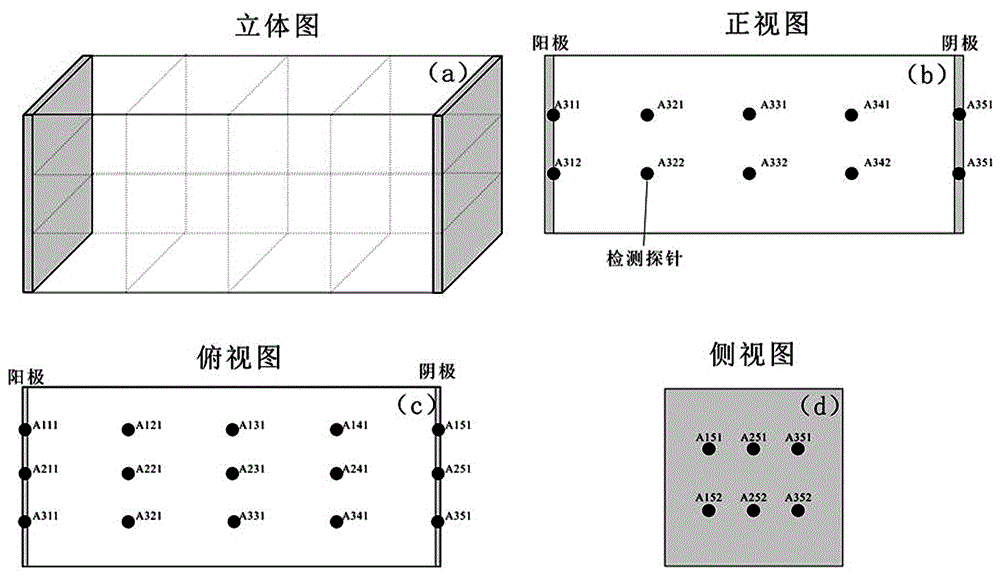
ActiveCN106734174AReal-time understanding of repair statusEasy to monitor real-timeMeasurement devicesContaminated soil reclamationInterstitial waterElectrokinetic remediation
The invention discloses an electrokinetic remediation contaminated soil display system. The system comprises a detection subsystem, a real-time sampling subsystem, a transmission subsystem, a treatment subsystem, a display subsystem, a recording and storing subsystem and a feedback subsystem. By means of the electrokinetic remediation contaminated soil display system, multiple sensors are effectively integrated, detection, displaying and storing of electric field intensity, pH, Eh, moisture content, temperature and soil interstitial water heavy metal concentration at any position in an electrokinetic remediation treatment box can be achieved, and the later-period data processing is facilitated. The electrokinetic remediation contaminated soil display system is of great significance in knowing soil remediation conditions, improving electrokinetic remediation efficiency, reducing manual work amount for monitoring soil remediation and reducing maintaining cost.
Owner:INST OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
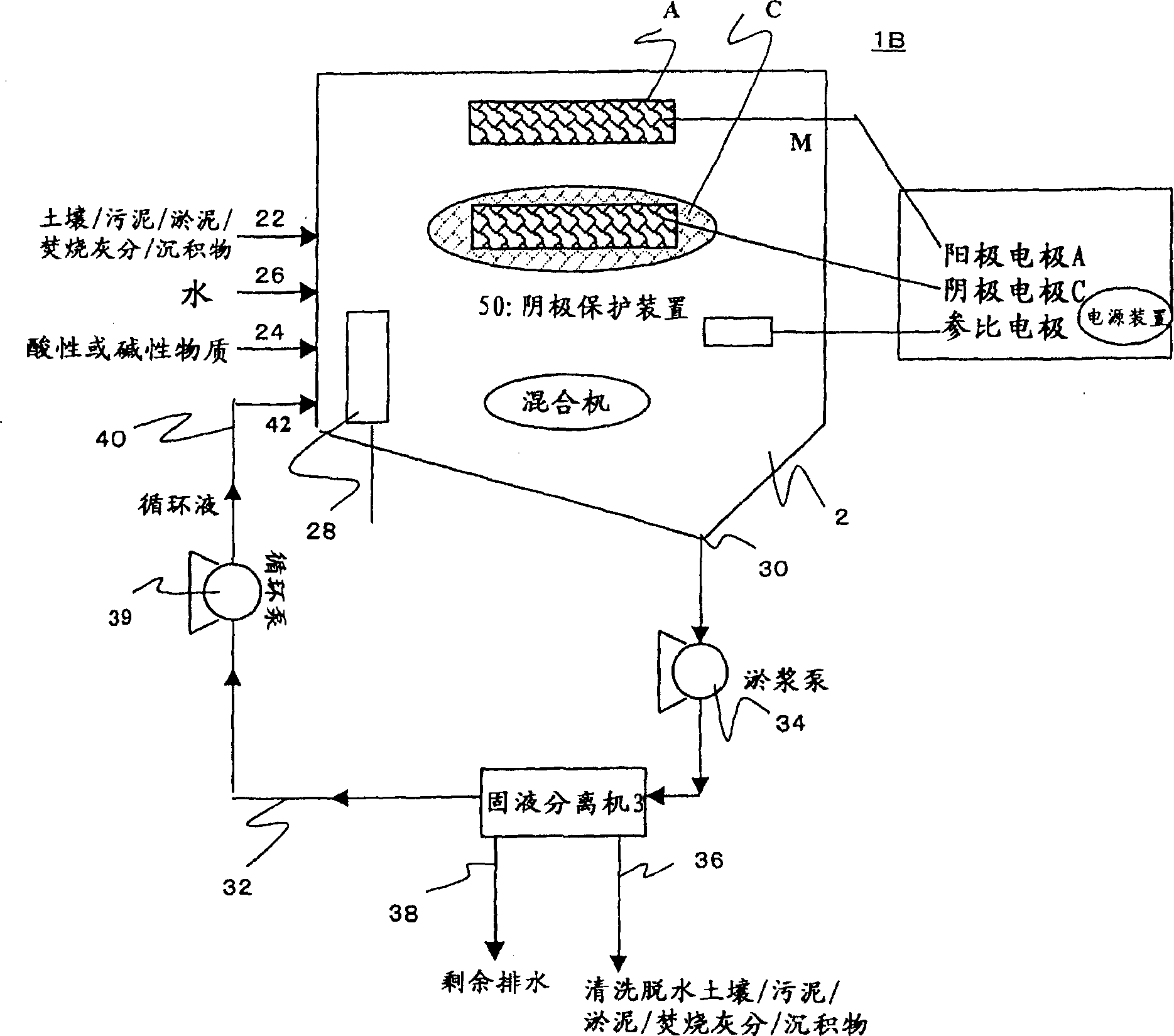
Clarification method and apparatus for material contaminated with heavy metals
InactiveUS20070142693A1Reduce concentrationEliminate the risk of contaminationContaminated soil reclamationElectrolysisSludge
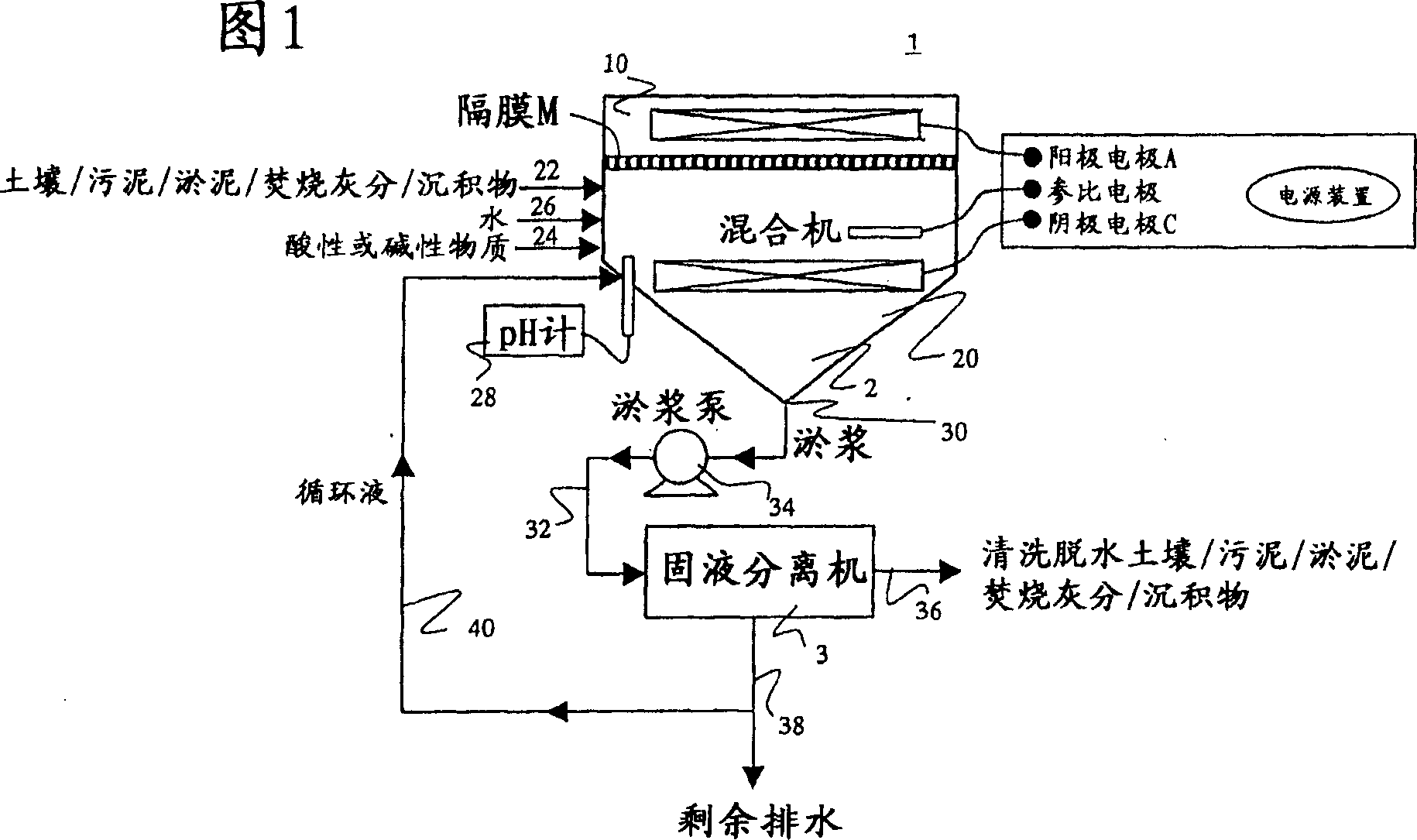
A clarification method and apparatus, which can reliably remove heavy metals, including their sparingly soluble fractions, from a contaminated solid material containing the heavy metals, such as soil, sludge, sediments, wastes, or incineration ash, are provided. A reaction vessel 2 is divided into an anode zone 10 containing an anode A, and a cathode zone 20 containing a cathode C, by a diaphragm M provided between the anode A and the cathode C. The cathode zone 20 is supplied with a contaminated solid material containing heavy metals via a contaminated solid material supply means 22, an acidic substance or an alkaline substance via an acidic substance or alkaline substance supply means 24, and in some cases, water via a water supply means 26. A slurry of their mixture is maintained in the condition of a reducing atmosphere and a strongly acidic or strongly alkaline atmosphere to dissolve the heavy metals and electrolytically deposit the heavy metals on the surface of the cathode, thereby separating the heavy metals from the contaminated solid material and interstitial water.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Process for treating excess sludge by utilizing fly ash
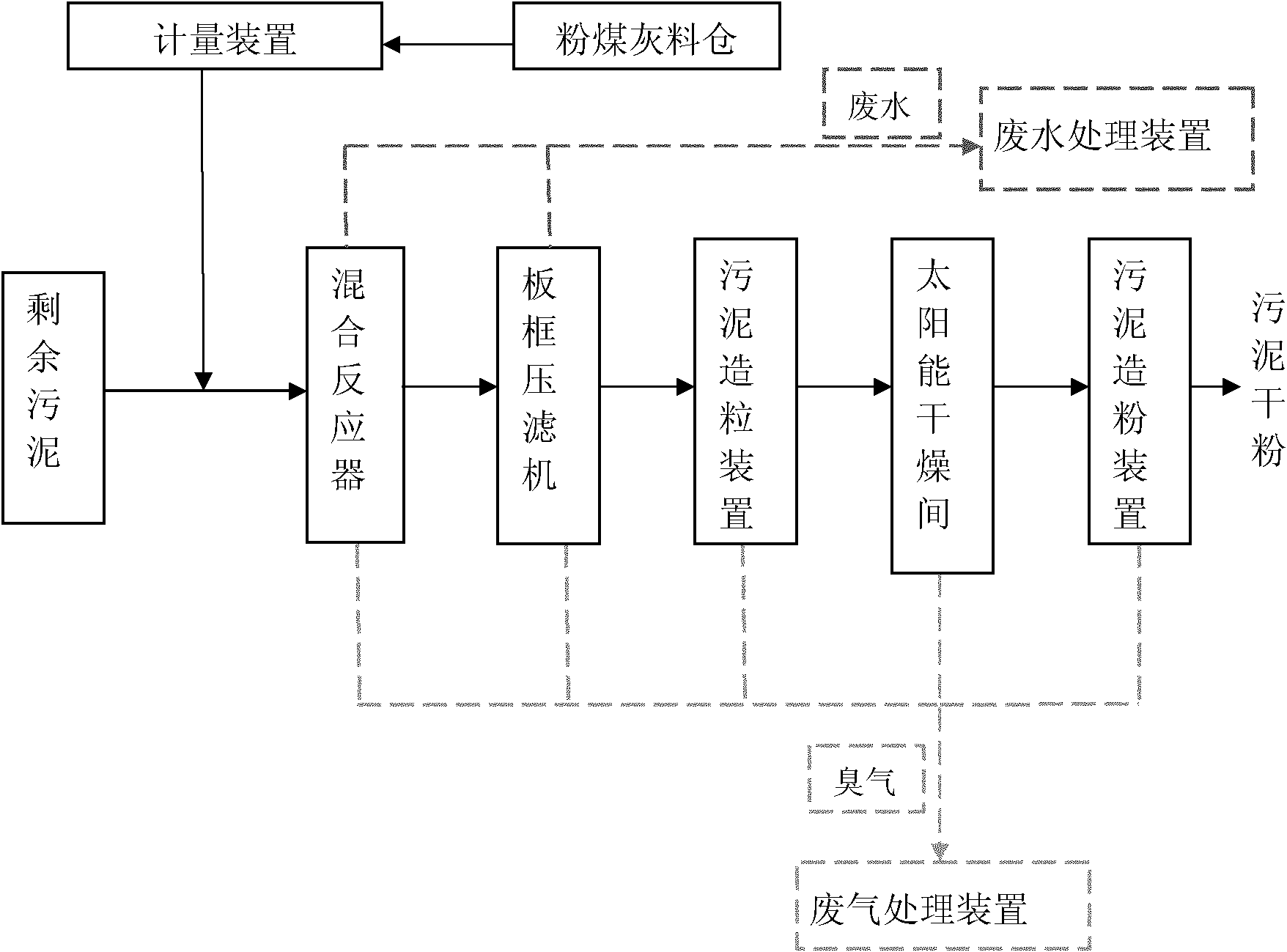
ActiveCN102161562ALoose textureWell-developed poresSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWaste processingBound waterSolar drying
The invention relates to a process for treating excess sludge by utilizing fly ash. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: 1, feeding excess sludge to be treated which has the water content of between 80 and 90 percent, and fly ash in an amount which is 20 to 50 percent based on the mass of the excess sludge into a mixing agitator; fully mixing and reacting for 5 to 15min; feeding into a plate and frame dehydrator for dehydration to obtain sludge of which the water content is reduced to be between 35 and 45 percent; crushing the sludge into coarse particles with the particle size of between 3 and 5mm by using a sludge granulation device; feeding the sludge particles into a solar drying room, and drying for 24 to 48h at the temperature of above 40 DEG C and under the humidity of below 15 percent to ensure that the water content of the sludge is reduced to between 8 and 15 percent; and treating by sludge pulverization equipment and a high-speed airflow collision technology, wherein the particle size of sludge powder is 150 to 300 meshes and the water content is 5 to 10 percent after the treatment. The method has the advantages that: interstitial water, adsorbed water and capillary bound water in the excess sludge are absorbed into the fly ash; due to the characteristic of high permeability coefficient of the fly ash, the water in the fly ash is easily discharged; and the secondary pollution to the environment is avoided by appropriately treating the excess sludge.
Owner:北京方兴科创环境科技有限公司
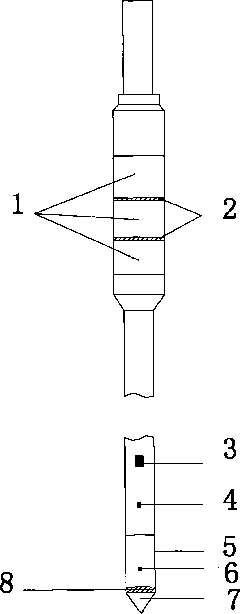
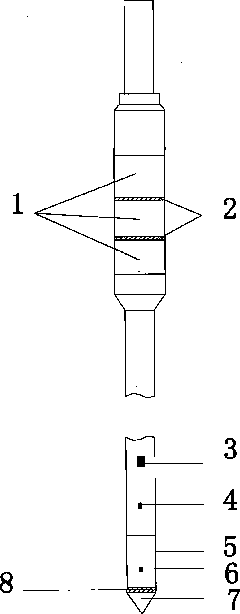
Resistivity static sounding probe
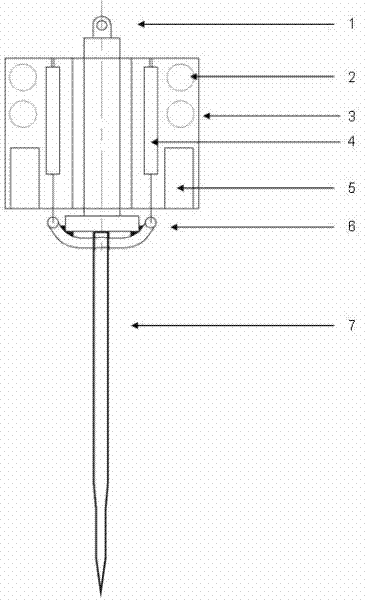
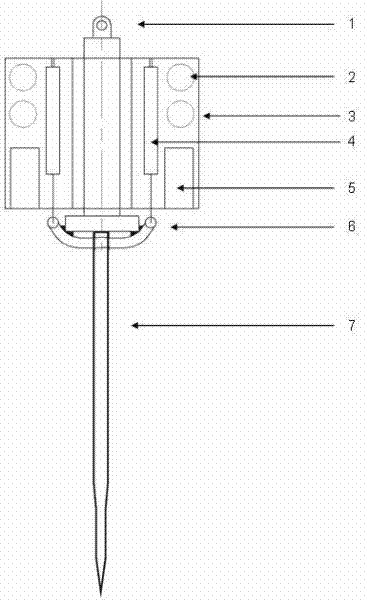
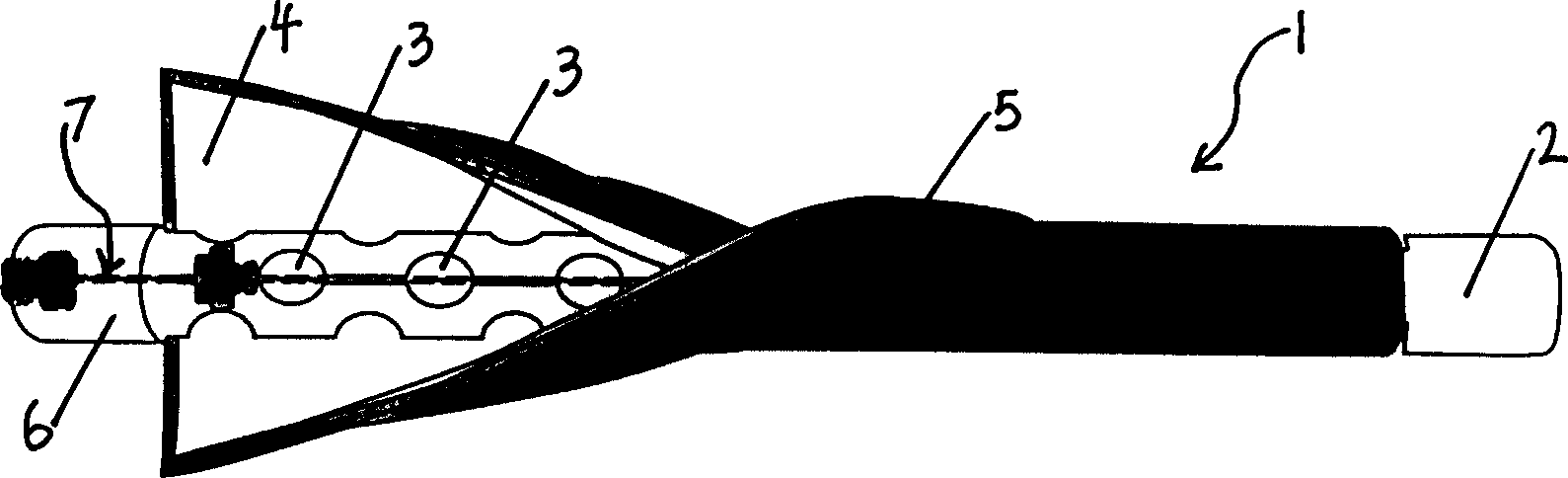
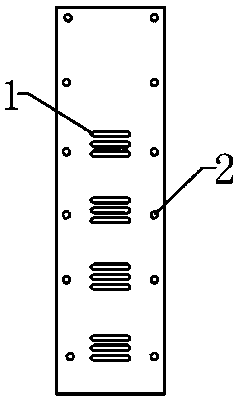
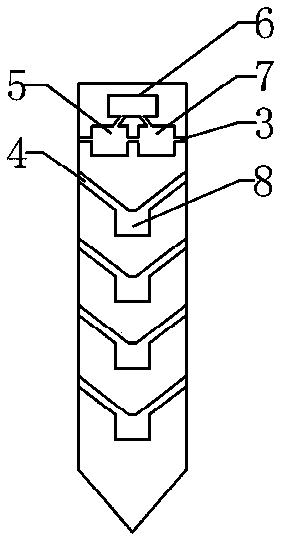
The invention discloses a resistivity static sounding probe. The periphery of the first half section of the resistivity static sounding probe is wrapped with two annular electrodes (2), and both sides of the annular electrodes (2) are provided with insulating layers (1); the second half section of the resistivity static sounding probe is provided with a three-component seismic detector (3); the lower part of the three-component seismic detector (3) is provided with a clinometer (4); a friction drum (5) is positioned below the clinometer (4); the middle of the friction drum (5) is provided with an interstitial water pressure sensor (6); a probe (7) is connected below the friction drum (5); and a pore-pressure filter ring (8) is positioned at the connection position of the friction drum (5) and the probe (7). The resistivity static sounding probe has the advantages of home position, fastness, accuracy, economy and the like and provides a powerful detection tool for the foundation treatment practice of civil engineering.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Submarine sediment interstitial water in-situ acquisition system
InactiveCN102221485ARealize in-situ long-term continuous layered collectionImprove time resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesInterstitial waterOcean bottom
The invention relates to a submarine sediment interstitial water in-situ extraction system, which can realize the long-term continuous in-situ layered acquisition of sediment interstitial water samples. The system consists of a lifting joint, floating balls, a bracket, releasers, fluid acquirers, connecting parts and a layered penetration connecting elements, wherein the lifting joint is positioned above the bracket; the layered penetration connecting element is positioned below the bracket, and is formed by assembling penetration connecting elements and filtering rings; the filtering rings are arranged between the connecting parts; sampling ports of each filtering ring are connected with the fluid acquirers by pipelines respectively; and the fluid acquirers, the releasers and the floating balls are arranged on the bracket respectively. After sampling is finished, a releaser deck unit transmits a releasing instruction to the releasers on board to separate the fluid acquirers from an in-situ layered penetration part, and the fluid acquirers float up to the sea surface for recycling. The system realizes the long-term continuous in-situ layered acquisition of sediment interstitial water, and can continuously acquire time sequence samples of a year by once deployment and recycling operation.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Electro-osmotic dewatering technology for biological sludge
InactiveCN105016601AReduce moisture contentIncrease the rate of dehydrationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningInterstitial waterDewatered sludge
The invention relates to an electro-osmotic dewatering technology for biological sludge, which comprises the following steps: 1)mechanical dewatering treatment; 2) electro-osmotic dewatering pretreatment; 3)electro-osmotic dewatering treatment; 4)dewatering filtrate recovery; and 5) dewatering filter cake collection. The water content of the dewatering filter cake obtained in the above steps is less than 55%. The method has the beneficial effect that the dewatering technology employs a surfactant and a flocculating agent for complex formulation, water content of the dewatered sludge is reduced, and sludge dewatering rate is increased. According to the invention, a mechanical dewatering step is carried out so that free water and interstitial water in sludge can be removed, the water content is reduced to 75-80%, then an electro-osmotic dewatering step is carried out, so that electro-osmotic dewatering time is saved, service life of an electrode is increased, and loss can be reduced.
Owner:霍普科技(天津)股份有限公司
Microwave and PAM (Polyacrylamide) flocculating agent combined sludge dewatering method
InactiveCN102659297AReduce dosageLow additional costSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningInterstitial waterBound water
A microwave and PAM (Polyacrylamide) flocculating agent combined sludge dewatering method relates to a sludge dewatering method. The microwave and PAM (Polyacrylamide) flocculating agent combined sludge dewatering method aims at solving the technical problem that according to the traditional sludge dewatering method, as the addition quantity of a flocculating agent is large, the cost of sludge treatment is increased. The microwave and PAM (Polyacrylamide) flocculating agent combined sludge dewatering method comprises the following steps: carrying out microwave radiation on sludge passing through a sludge concentration tank for 50s under the conditions of 2450MHZ frequency and 700w power, then adding a PAM flocculating agent, wherein the addition proportion is that 4mL of the PAM flocculating agent is added in 100mL of sludge, the concentration of the PAM flocculating agent is 1g / L, and carrying out centrifugal or filter-press dewatering, thereby finishing the sludge dewatering. According to the microwave and PAM flocculating agent combined sludge dewatering method, sludge particles are accelerated to move and mutually collide under the effect of the microwave radiation on sludge floc so that the sludge floc is damaged and part bound water and interstitial water in the sludge floc are released, then the sludge particles can rapidly become unstable and flocculate by using the PAM flocculating agent for conditioning, thereby leading the effect of sludge dewatering to be better, and simultaneously reducing the addition quantity of the flocculating agent.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of purifying matter contaminated by heavy metal and apparatus therefor
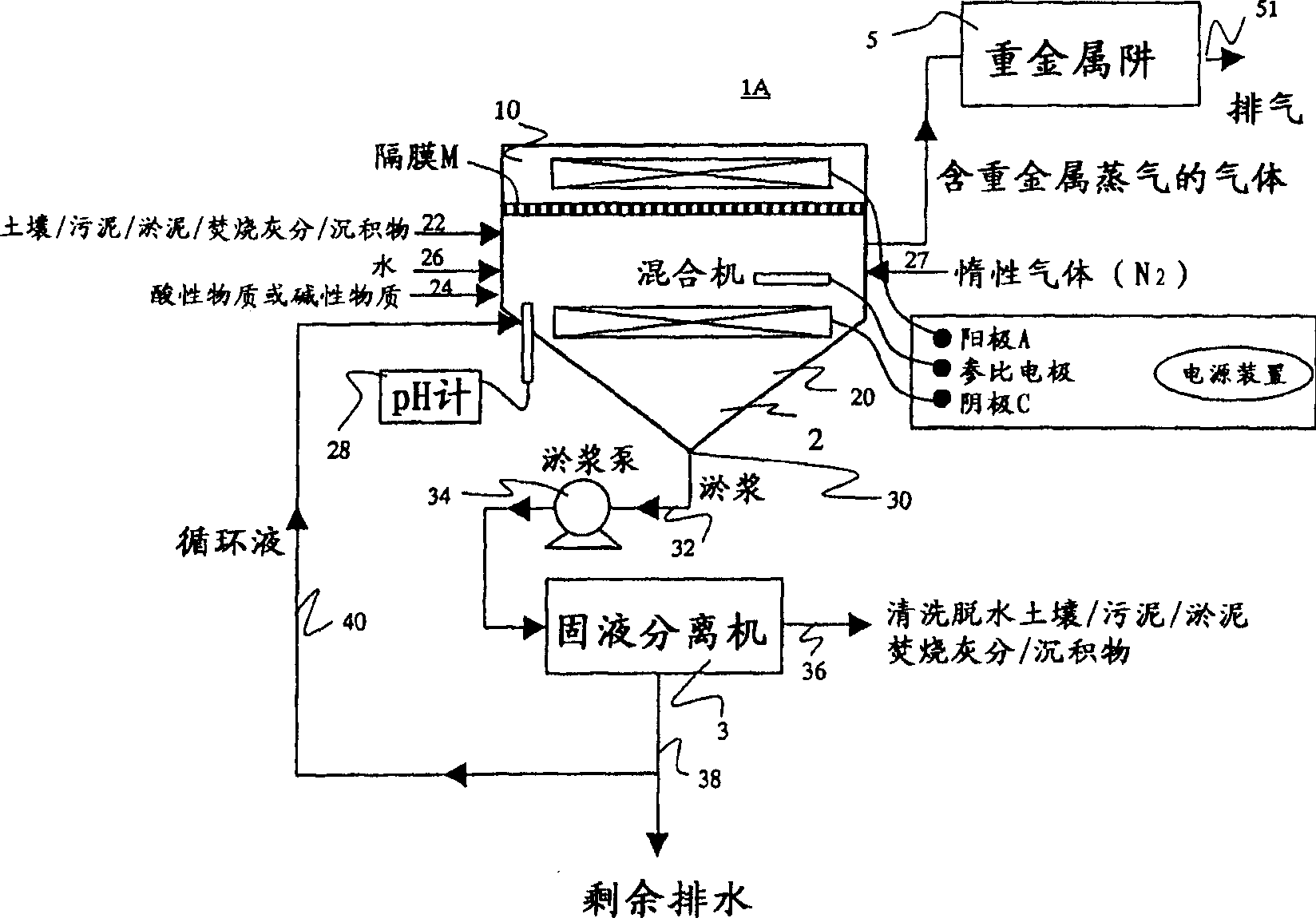
InactiveCN1863607AReduced contact efficiencyReduce the efficiency of electrolysisSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationPurification methodsSludge
A purification method and apparatus in which even hardly soluble fractions of heavy metals contained in solid contaminated matters can be securely removed from solid contaminated matters, such as soil, sludge, sediment, waste and ash. Reaction vessel (2) is separated into anode section (10) including anode electrode (A) and cathode section (20) including cathode electrode (C) by means of diaphragm (M) interposed between the anode electrode (A) and the cathode electrode (C). Into the cathode section (20), there are fed solid contaminated matters containing heavy metals via solid contaminated matter supply means (22) and acid or alkali materials via acid or alkali material supply means (24) optionally together with water via water supply means (26). The resultant mixture in slurry form is maintained in a combination of reducing atmosphere and strongly acid or strongly alkali atmosphere so as to effect heavy metal leaching and electrodeposition on cathode electrode surface. The heavy metals are separated from the solid contaminated matters and interstitial water.
Owner:EBARA CORP
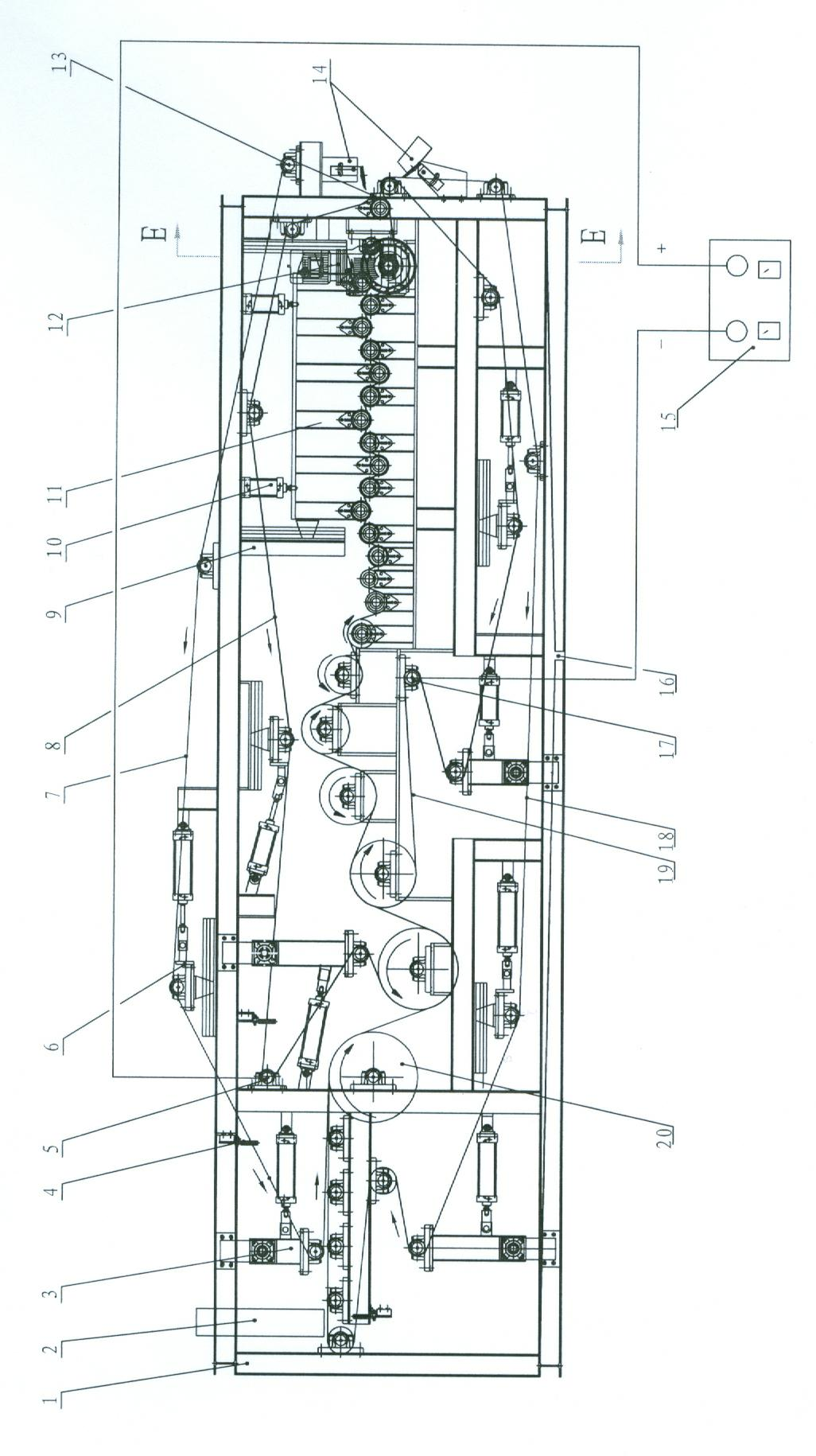
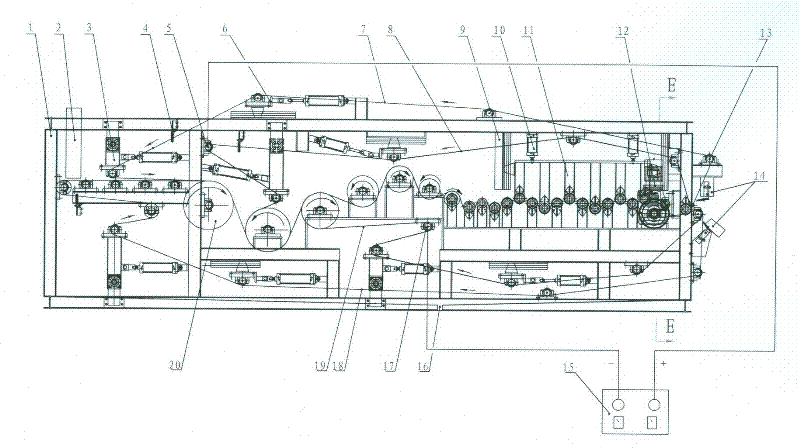
Electrolytic filtering/squeezing integrated sludge dewatering machine
ActiveCN102115302AIncrease productivitySmall footprintSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge cakeInterstitial water
The invention discloses an electrolytic filtering / squeezing integrated sludge dewatering machine which comprises a primary squeezing and filtering region, an electrolytic filtering region, an electrolytic squeezing region and an external direct current power source, wherein the primary squeezing and filtering region, the electrolytic filtering region and the electrolytic squeezing region are sequentially arranged with one anther by taking a frame as a carrier. The sludge fallen from a hopper is primarily squeezed and filtered to remove the free water contained in the sludge. A driven upper filter strip and a driven lower filter strip are respectively and externally leaned against an upper squeezing strip and a lower squeezing strip connected the two poles of a direct current power source, so that the sludge clamped between the upper squeezing strip and the lower squeezing strip is electrolyzed, and the interstitial water and the cellular water in the sludge flow to the negative pole when the electric charge flows, i.e. the electrophoresis. The incompletely-dried sludge is carried into the electrolytic squeezing region and is forced under the condition that the sludge is stilled electrolyzed to accelerate the dewatering. By sequentially reducing the diameters of a plurality of the roll shafts and by adopting an installation technology measure that the adjoining roll shafts are installed in a misplaced way up and down, the machine can dewater by sequentially forcing, so that the dryness of a sludge cake is improved. The machine is particularly suitable for treating the biochemical active sludge precipitated by the urban domestic sewage or the industrial sewage.
Owner:江苏百新环境工程有限公司
Process for removing interstitial water from a wastewater sludge
InactiveUS20050109713A1Suitable lengthReduced pHSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningMultistage water/sewage treatmentInterstitial waterSludge
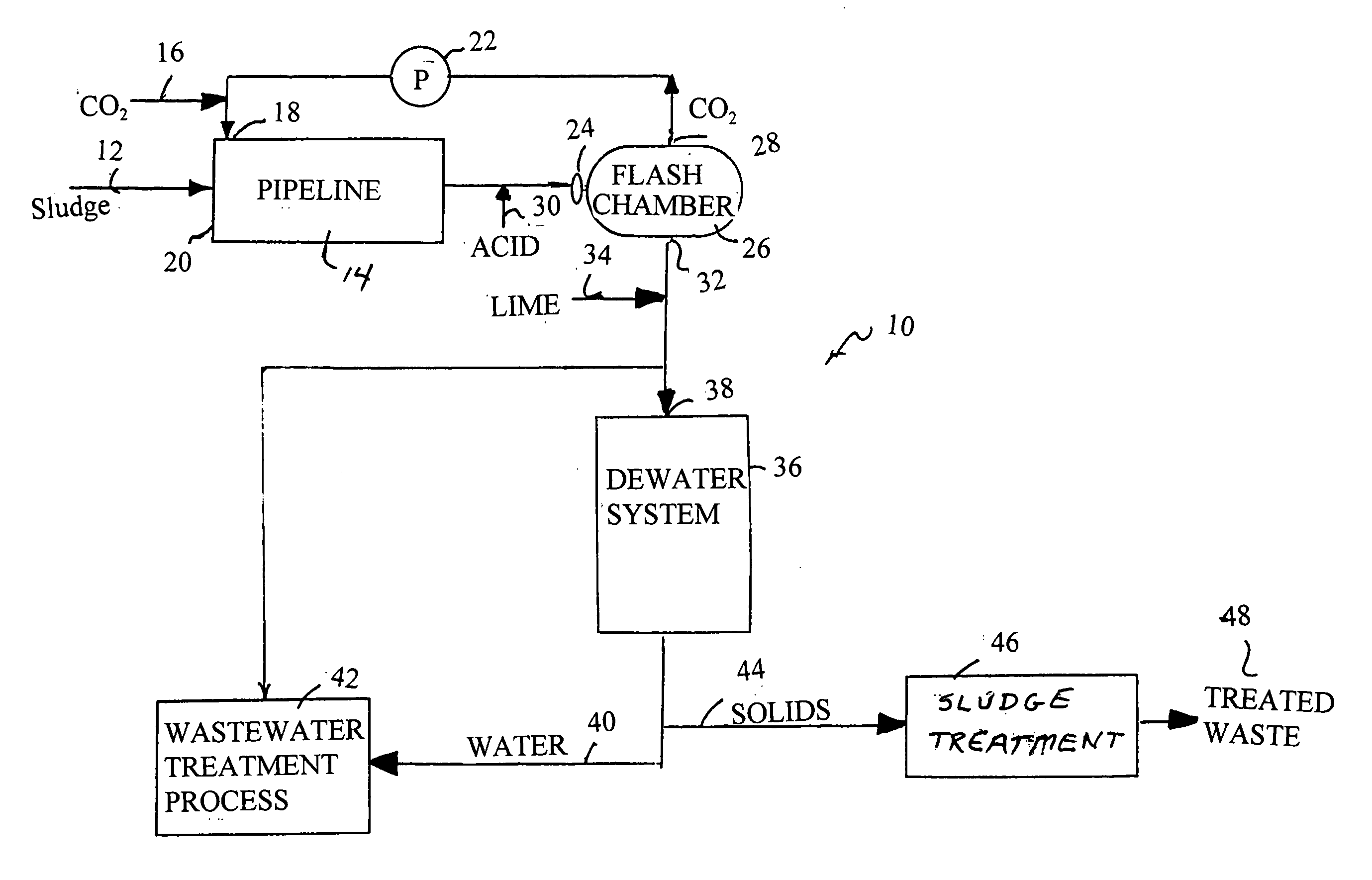
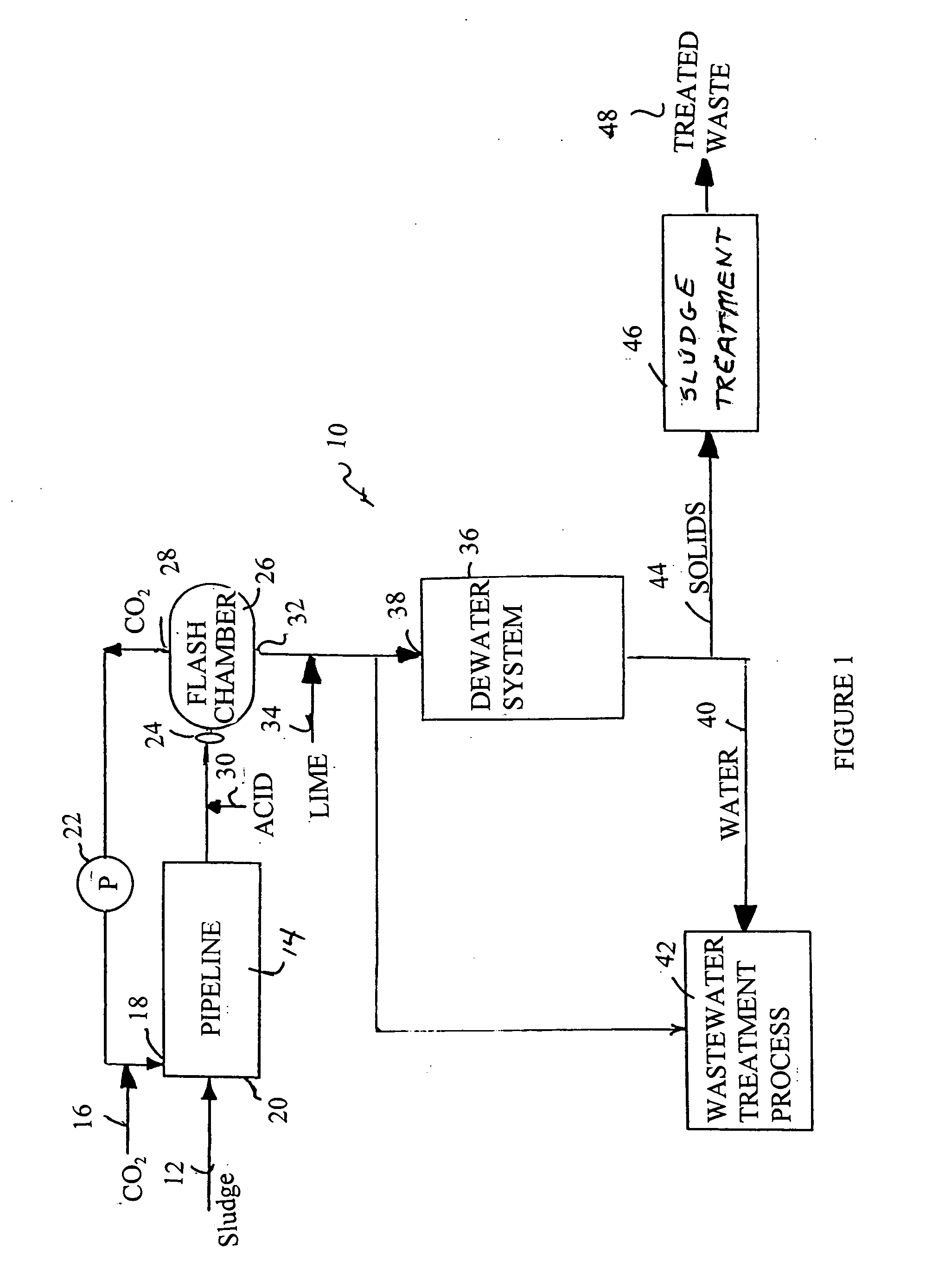
A process for removing water from sludge has the steps of passing the sludge through a chamber, injecting carbon dioxide gas under pressure into the chamber as the sludge passes through the chamber, and flashing the carbon dioxide-injected sludge through an orifice into a vessel so as to release carbon dioxide gas from the sludge. The flashed sludge is returned to a digester or is dewatered to remove water from the sludge. The carbon dioxide gas is injected at no less than 14.7 p.s.i.a. of pressure.
Owner:SHEPHERD SAMUEL L +1
Method for conditioning urban sludge by agent compounding
InactiveCN108083609AImprove dehydration effectCalorific valueSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningElectrochemical sludge treatmentDewatered sludgeMoisture
The invention discloses a method for conditioning urban sludge by agent compounding. The method comprises (1) adjusting pH through an acid solution, then adding iron powder and activated carbon powderinto sludge, carrying out full stirring mixing, starting an aeration device to condition and transferring a part of substances in the sludge into the liquid phase, (2) adding a persulfate into the sludge conditioned in the previous step, activating the persulfate through ferrous ions, oxidizing to break the sludge so that combined water, adsorbed water, interstitial water and free water in the sludge are partially separated, the dewaterability is improved and SCOD, proteins and polysaccharide in the sludge are increased, and (3) after sludge conditioning, carrying out mechanical dewatering toobtain dewatered sludge. The method can reduce the moisture content of the urban sludge from 97 to 99% to 55 to 60%, greatly reduce the specific resistance and volume of the sludge, greatly improve the combustion calorific value, realize harmlessness, stabilization, reduction and recycling of sludge and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of sodium-rich anhydrous prussian blue analogue material
InactiveCN109292795ALow costImprove responseIron cyanidesCell electrodesFiltrationSodium-ion battery
The invention relates to a sodium-rich anhydrous prussian blue analogue material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using potassium ferrocyanide or sodium ferrocyanide, sodium chloride and manganese chloride as precursors for preparing a prussian blue analogue, so that a turbid liquid is formed; collecting solid materials in the turbid liquid by using a centrifugation and suction filtration method, and carrying out water washing until no residual sodium chloride exists in the product, so that a sodium-rich prussian blue analogue is obtained; grinding the prepared sodium-rich prussian blue analogue into powder, laying the powder in a square boat, and placing the square boat in a constant-temperature zone of a tubular furnace for calcining; and taking one or a mixture ofmore selected from N2, He an Ar as an inert gas source, heating the tubular furnace to 180 DEG C at a heating speed of 1-10 DEG C / min, carrying out heat preservation for 2-3 hours to remove interstitial water, and carrying out cooling to room temperature along with the furnace after the heat preservation is finished, so that the sodium-rich anhydrous prussian blue analogue material is obtained. The prepared composite material of prussian blue analogue is applied to positive poles of sodium-ion batteries.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Efficient treatment system of oil sludge
ActiveCN105152503AReduce viscosityReduce chance of stickingCombination devicesSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningCombustion chamberOil sludge
The invention discloses an efficient treatment system of oil sludge. The TPH (total petroleum hydrocarbons) content of the oil sludge treated is less than 1%. The oil sludge enters a dryer with a stirrer and an outer heating coil and is subjected together with hydrogen separated by a nitrogen making machine, to heat exchanging via heat transfer oil, a resulting product is subjected with oil sludge directly to convection drying, cracking heat of a thermal desorption unit performs on indirect heating on the oil sludge through the outer heating coil of the dryer, viscosity of the oil sludge is decreased after free water, interstitial water and part of light gases are removed, chances that the oil sludge cake in the heat desorption unit are also slimmed, and long-term running of the thermal desorption unit is guaranteed; the dryer with the stirrer and the outer heating coil uses the cracking heat of the thermal desorption unit, thus energy is saved; gases subjected to oil removal, dust removal and odor removal are used as fuels for a combustor, thus energy is saved; high-hydrogen gas from the dryer with the stirrer and the outer heating coil separates oil and water through bubbles generated by an air flotation machine, oil-water separation is efficient, and the separated oil is used as a fuel for the combustor, thus energy is saved.
Owner:大连爱德摩设备制造有限公司
Modified nitrogen control material prepared from lake sediments, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106000283AGood effectIncrease cation exchange capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsFreeze-dryingRaw material
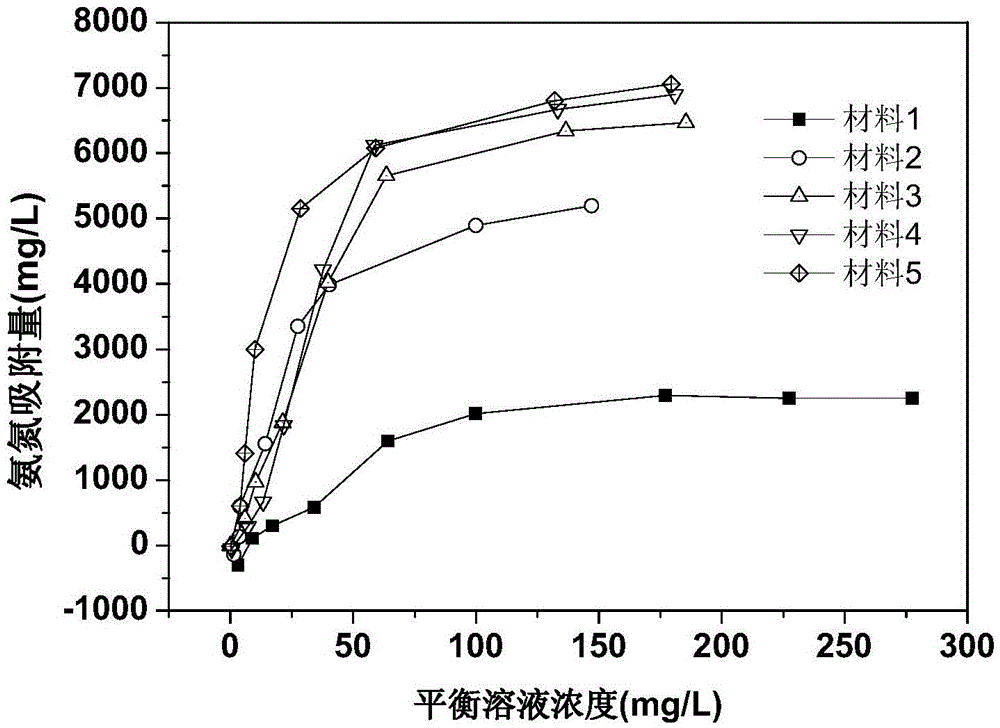
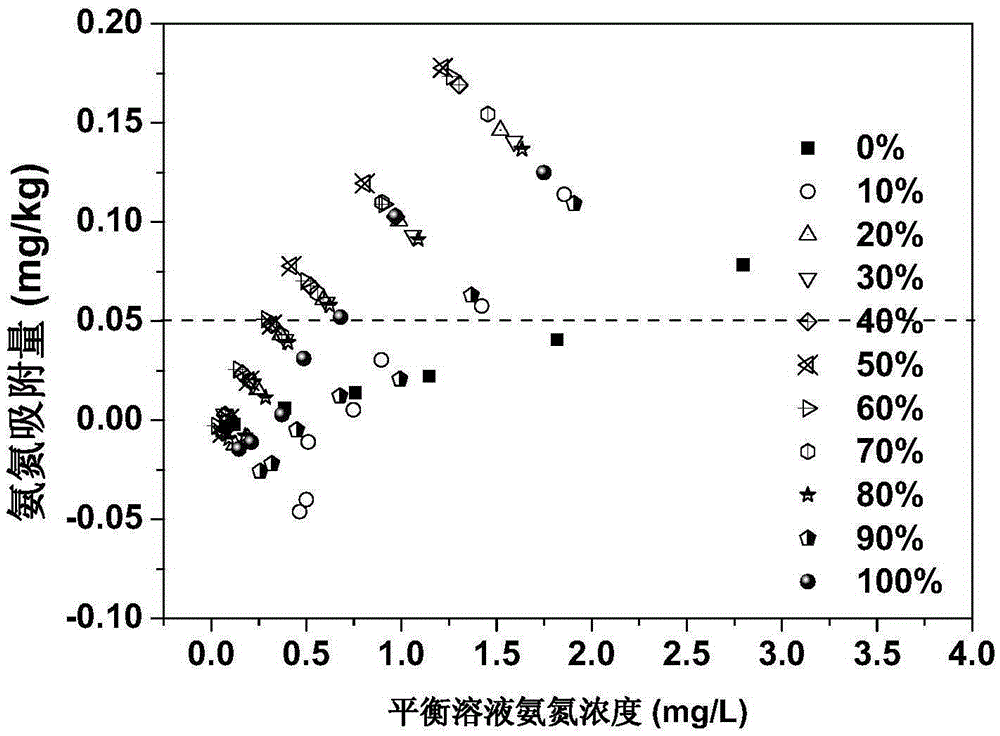
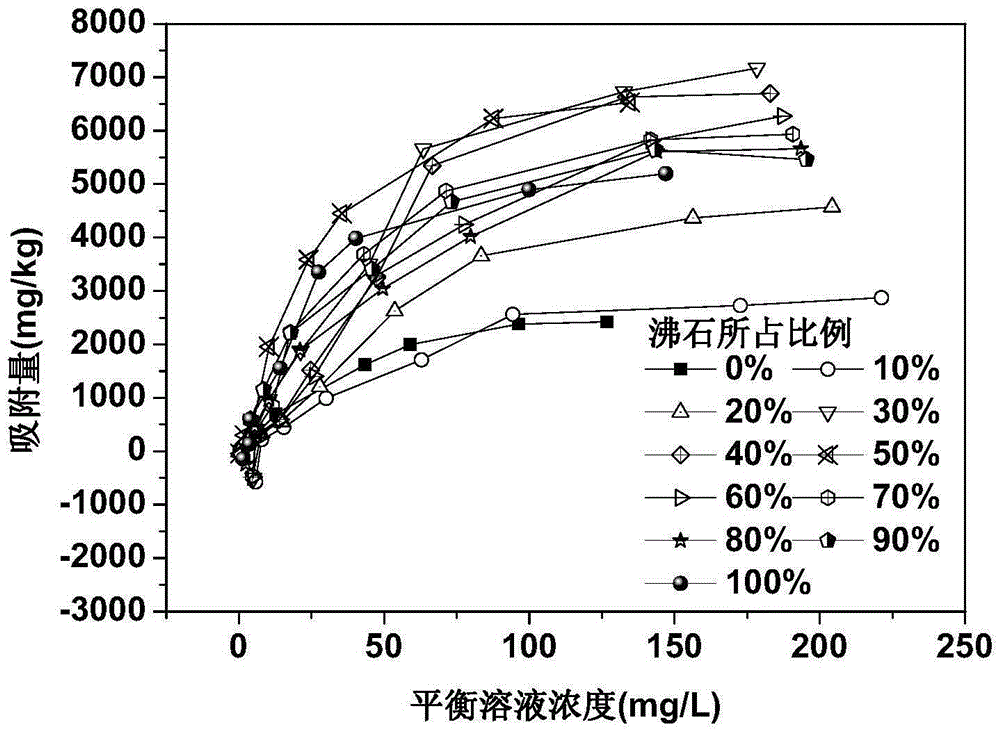
The invention relates to a modified nitrogen control material prepared from lake sediments, a preparation method and application thereof. The method includes: collecting lake sediments, conducting freeze drying, grinding and sieving for standby use; then subjecting the treated lake sediments to constant temperature heating treatment, then performing cooling, and adding zeolite into the sediments in proportion, mixing the materials evenly, then adding a mixed solution of a salt solution and an alkaline solution, carrying out oscillation impregnation modification, then conducting filtering and cooling to obtain residue, i.e. the sediment modified nitrogen control material. The method provided by the invention adopts lake sediments as the raw materials, the prepared modified nitrogen control material has significantly enhanced ammonia nitrogen adsorption performance, especially has good ammonia nitrogen removal effect on lake sediment interstitial water, the materials are cheap, the safety is high, the social and economical benefits are good, also the material has no ecological risk to lake water, is energy saving and environment-friendly, and can be applied to the lake sediment-water interface nitrogen pollution control field.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for improving water-removing performance of urban sludge by coupling treatment of ultrasonic wave and chitosan
InactiveCN104926064AReduce usageShorten the timeSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningLow speedBound water
The invention relates to the technical field of improvement on the water-removing performance of sludge and particularly relates to a method for improving the water-removing performance of urban sludge by coupling treatment of ultrasonic wave and chitosan. The method comprises the following steps: firstly adopting acid liquor to adjust the pH value, adding the chitosan, then stirring for a period of time at high speed, stirring for 10-15 minutes at low speed, then adopting ultrasonic treatment, further enabling bound water, absorbed water, interstitial water and free water in the sludge to be partially removed and further enabling the water content in the sludge to be reduced from more than 98% to less than 68%, and the capillary water absorption time of sludge is reduced. The method has the advantages that the content of polysaccharide and protein in supernatant liquor of sludge treatment is increased, the water-removing performance of the sludge and the quality of the removed water are improved, the operation is simple, the energy consumption is low and the cost is low.
Owner:ZUNYI NORMAL COLLEGE
Denitrification sulphur removal-based in-situ black-odorous riverway bottom mud oxidization technology
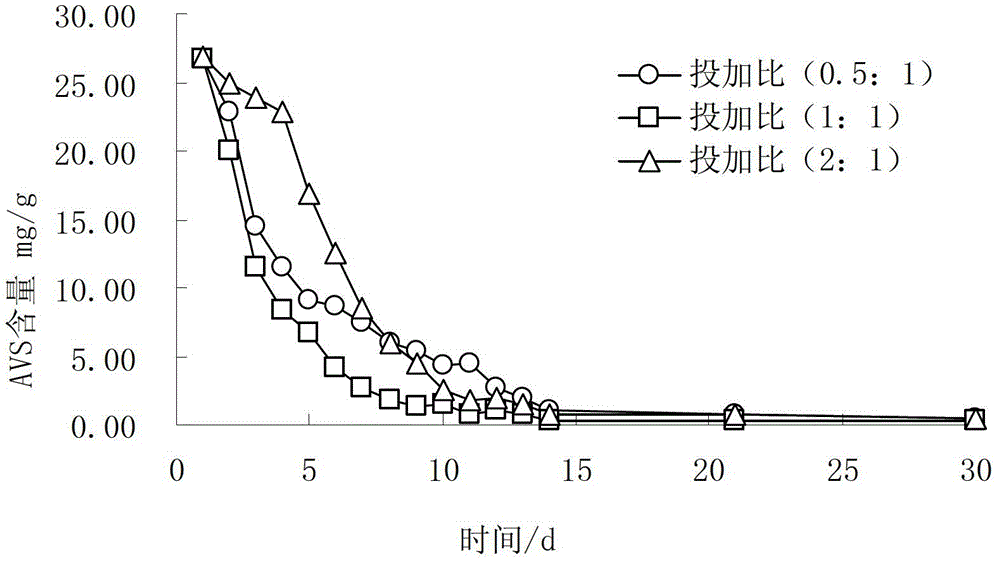
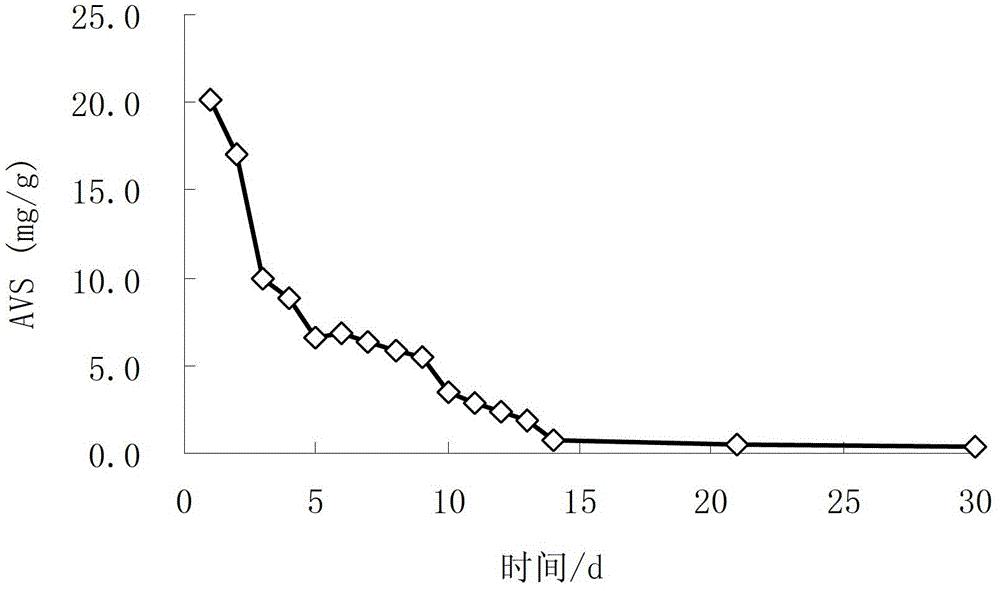
ActiveCN103332836AFacilitated releaseInhibition releaseSludge treatment by oxidationBiological sludge treatmentInterstitial waterSulfur
The invention discloses a denitrification sulphur removal-based in-situ black-odorous riverway bottom mud oxidization technology. The technology comprises the steps of: feeding a bottom mud oxidant, a bottom mud ammonia nitrogen extracting agent and a bottom mud acid-base conditioning agent into the black-odorous riverway in a wet-process or dry-process manner, the feeding quantity of the bottom mud oxidant ranges from (0.5-2):1 according to the mass ratio of the bottom mud oxidant and sulfide in the bottom mud, the feeding quantity of the bottom mud ammonia nitrogen extracting agent needs to meet the condition that the initial concentration of the bottom mud ammonia nitrogen extracted and released in interstitial water achieves more than 50mg / L, and the feeding quantity of the mud ammonia nitrogen extracting agent needs to meet the condition that the initial pH of the bottom mud is controlled to be 6.0-8.0. The sulfur, nitrogen and phosphorus of the mud can be synchronously removed, the blackness and odor of the riverway can be fast eliminated, the release of the bottom mud nitrogen and phosphorus can be inhibited, and the quality of water-in-water body can be improved; and the problem of eliminating the secondary release of bottom mud nitrogen in the black and odorous treatment process can be solved. The method is applicable to comprehensive treatment of a riverway (surge) taking organic matters, sulfide, nitrogen and phosphorus as mainly serious pollution sources.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for improving slurry-forming ability of sludge and coal-water slurry by cracking sludge flocculation through ultrasonic waves
InactiveCN107164003ASmall granularityReduce slurry viscositySludge treatmentLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCoal waterFlocculation
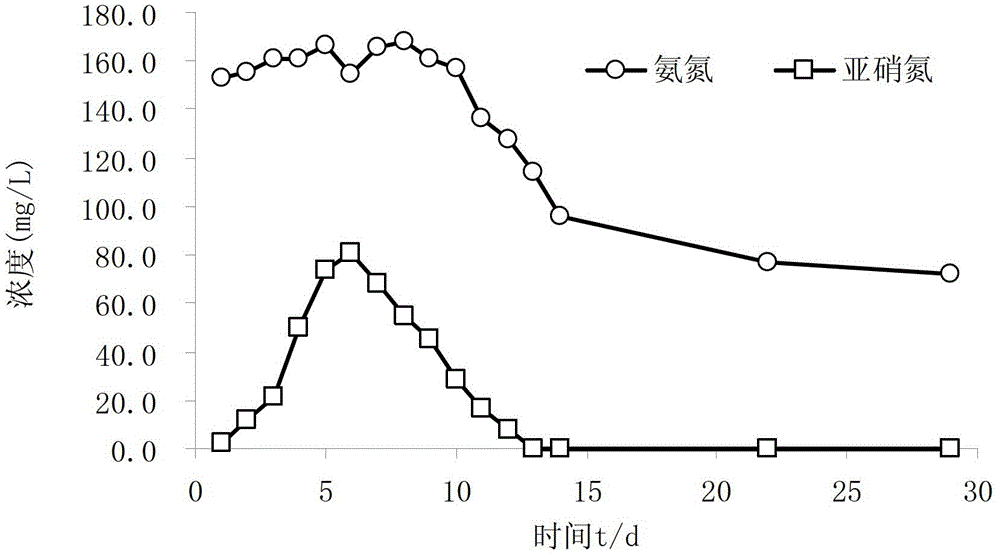
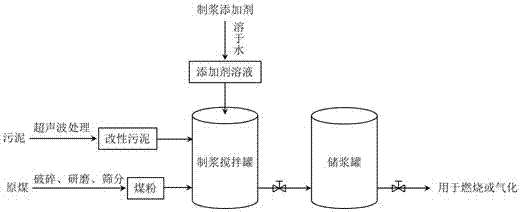
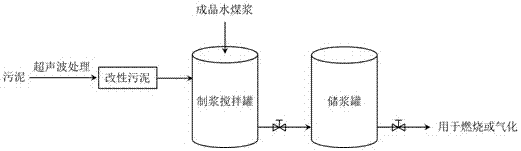
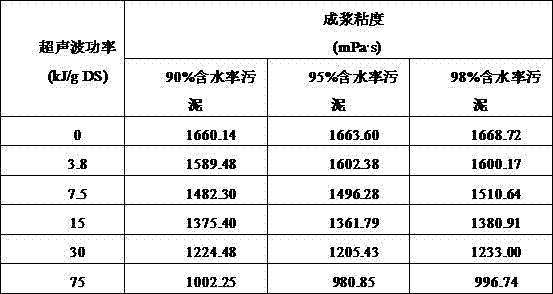
The invention discloses a method for improving slurry-forming ability of sludge and coal-water slurry by cracking sludge flocculation through ultrasonic waves. The ultrasonic waves are used for modifying sludge, microbial cell walls in a sludge floc structure and the sludge are broken by high-temperature high-pressure environments and shearing action generated by ultrasonic cavitation action, sludge particle granularity is reduced, part of interstitial water is released, the modified sludge is mixed with coal, slurry-forming additives, water and the like to prepare the sludge and coal-water slurry, or finished coal-water slurry is doped into the modified sludge and uniformly stirred to prepare the sludge and coal-water slurry. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the slurry-forming viscosity of the sludge and coal-water slurry can be obviously reduced, slurry-forming concentration is increased, the sludge and coal-water slurry with excellent slurry-forming ability is obtained, treatment time is short, operation is convenient, and the method is applicable to large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method for measuring nonlinear isothermal-adsorption curve of cohesive soil
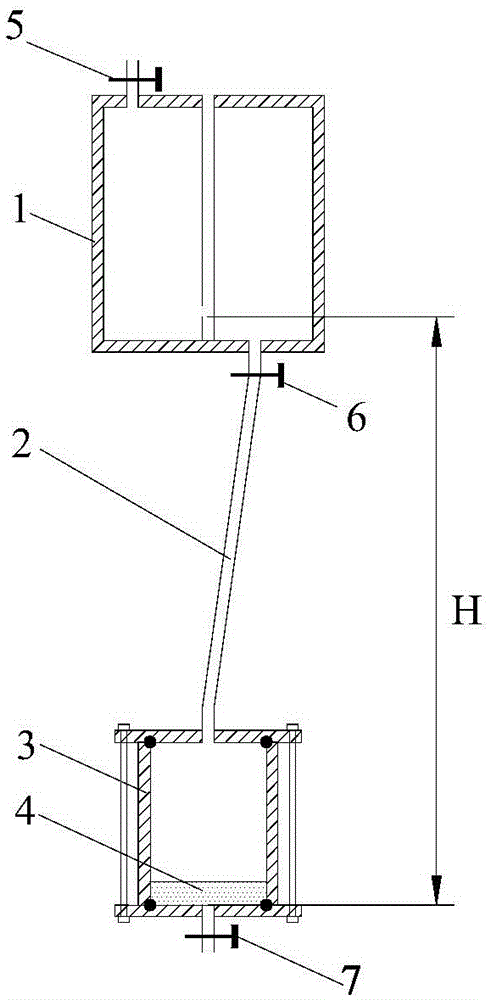
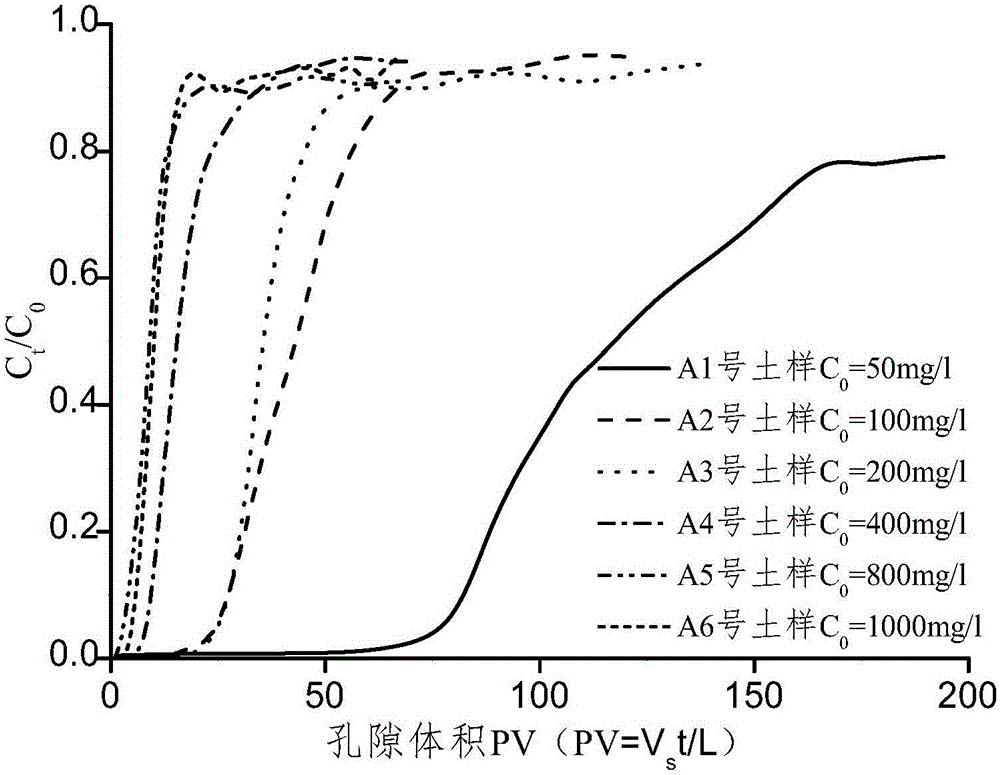
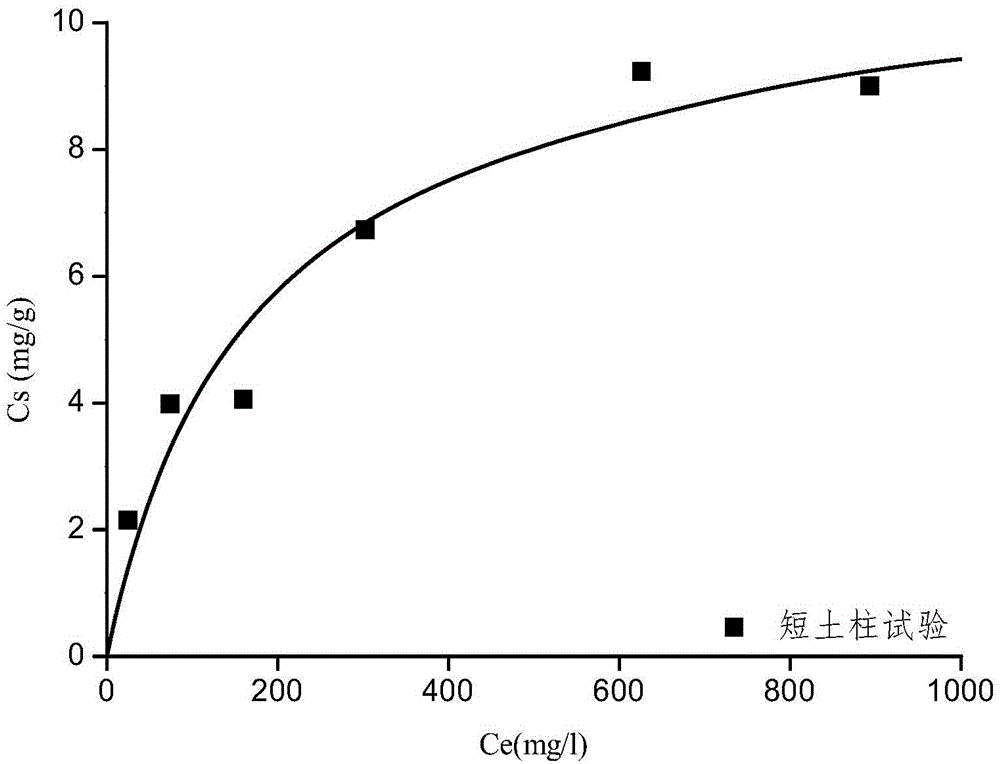
ActiveCN105021547AImprove reliabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsInterstitial waterEngineering
The invention discloses method for measuring a nonlinear isothermal-adsorption curve of cohesive soil. Through compression and consolidation, a batch of short earth-pillars of 2 cm high are prepared; the short earth-pillars are respectively connected to Markov bottles filled with different concentrations of target pollutant solutions; a short earth-pillar breakdown test is carried out at constant head so as to obtain an outflow curve of a target pollutant at different source concentrations and concentration of pollutants in interstitial water of the short earth-pillars after outflow concentration is stable; slice digestion is carried out on each short earth-pillar after the outflow concentration is stable, total amount of pollutants adsorbed in the short earth-pillars is measured, and the nonlinear isothermal-adsorption curve of the short earth-pillars is obtained by fitting of test data points of different pollution source concentrations. By the method, the nonlinear isothermal-adsorption curve of target pollutants in earth-pillars of cohesive soil can be directly obtained within a short period of time. In addition, the test method is reliable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Sediment interstitial water in-situ sampling method and apparatus
The invention relates to a method and a device for sampling deposits interstitial water. The method comprises steps of: (1) installing a solid-phase micro-extraction device in the cavity of a water exchanging device, or connecting one end of the water exchanging device with a water pipe which is connecting with the cavity and sealed matching with the water exchanging device; (2) embedding the water exchanging device into deposits per requirement, making the water pipe extend out the ground, employing a water pump to pump the interstitial water via the water pipe or getting out the water exchanging device to get the interstitial water via the micro-extraction.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sediment/zeolite nitrogen control material prepared from lake sediment, method and application thereof
ActiveCN106006814ALarge specific surface areaOptimize total pore volumeOther chemical processesAluminium silicatesFreeze-dryingDesorption
The invention relates to a sediment / zeolite nitrogen control material prepared from lake sediment, a method and application thereof. The method includes: collecting lake sediment as the raw material, conducting freeze drying, grinding and sieving to obtain sediment powder for standby use; taking zeolite, conducting grinding and sieving to obtain zeolite powder for standby use; then subjecting the treated sediment powder to constant temperature heating treatment, and then performing cooling for standby use; adding the zeolite powder into the sediment powder in proportion, mixing the substances evenly, then adding water to infiltrate the mixed raw materials, carrying out extrusion molding and roasting so as to obtain the sediment / zeolite nitrogen control material. The method provided by the invention adopts lake sediment as the raw material, and combines zeolite, so that the sediment / zeolite nitrogen control material has significantly improved ammonia nitrogen adsorption performance and significantly decreased ammonia nitrogen desorption capacity. The raw materials are cheap, the safety is high, the social and economical benefits are good, also the material has no ecological risk to lake water, is energy saving and environment-friendly, and can significantly reduce the ammonia nitrogen concentration of sediment interstitial water in the application process to achieve the purpose of impeded control of lake sediment ammonia nitrogen release.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Electro-osmosis sludge dewatering system
InactiveCN104973747AImprove dehydration effectIncrease profitSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningElectricityInterstitial water
The invention aims to provide an electro-osmosis sludge dewatering system. According to the technical scheme, the electro-osmosis sludge dewatering system comprises a feed system, a sludge dewatering system and a discharge system. Sludge with 80% water content which is produced from a sludge treatment plant undergoes caching, and the whole set of feed system with sludge caching equipment is assembled at the front end of electro-osmosis equipment. Thus, utilization rate of sludge which enters the dewatering system can be raised effectively. An electro-osmosis sludge dewaterer is adopted as a sludge dewaterer. According to the electro-osmosis sludge dewaterer, dewatering is realized by the phenomenon that sludge particles and water molecules are separated and move in opposite polarity directions. By an extra direct-current electric field and through sludge high-drying dewatering equipment for removing through a certain mechanical pressure a part of interstitial water and absorbed water which cannot be removed by mechanical filter-press in materials, water content of active excess sludge is reduced below 60%. Dewatered sludge is thin mud cakes which are beneficial to later deep drying and natural airing. Thus, aerobic composting or combustion disposal can be carried out.
Owner:霍普科技(天津)股份有限公司
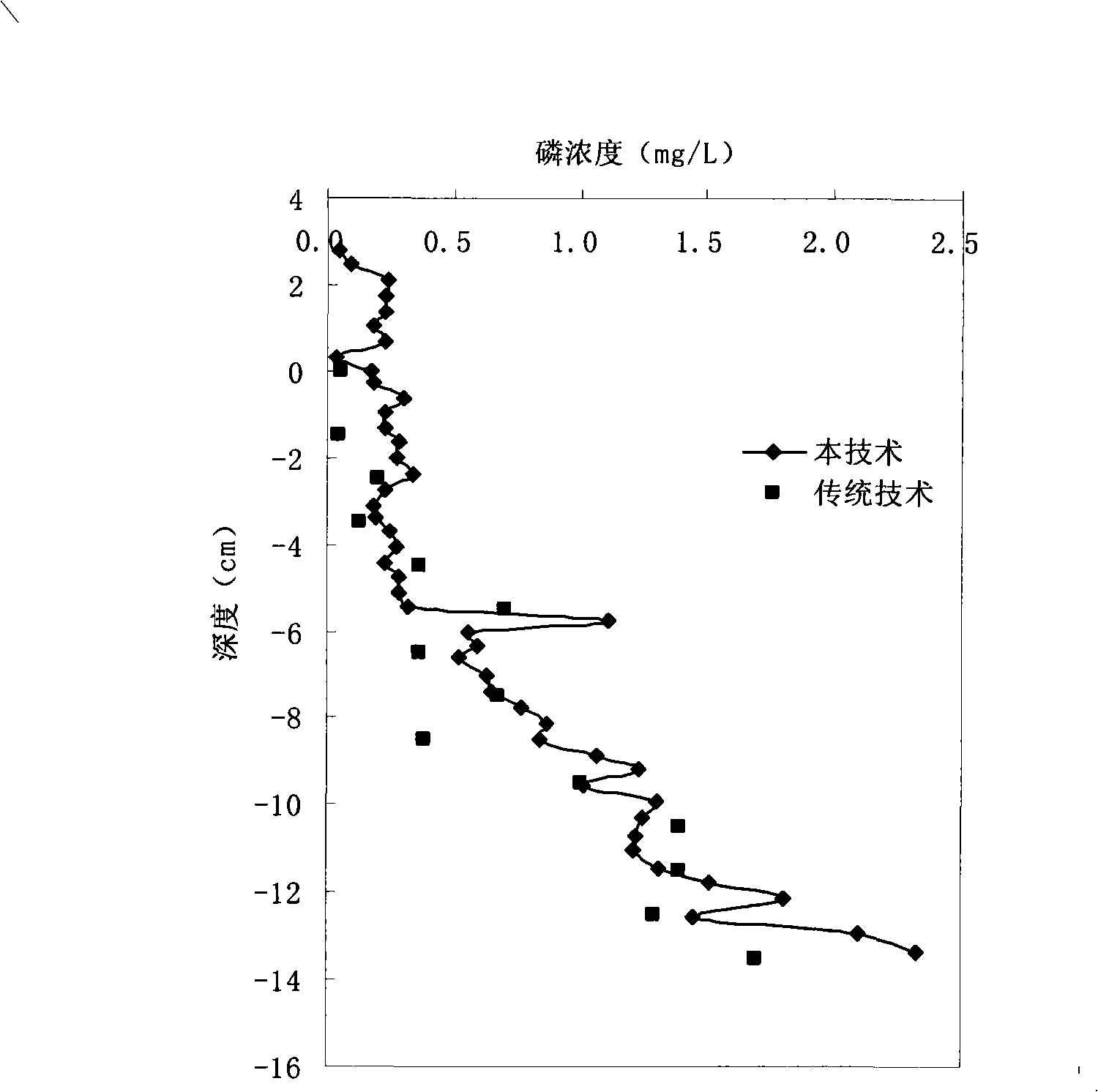
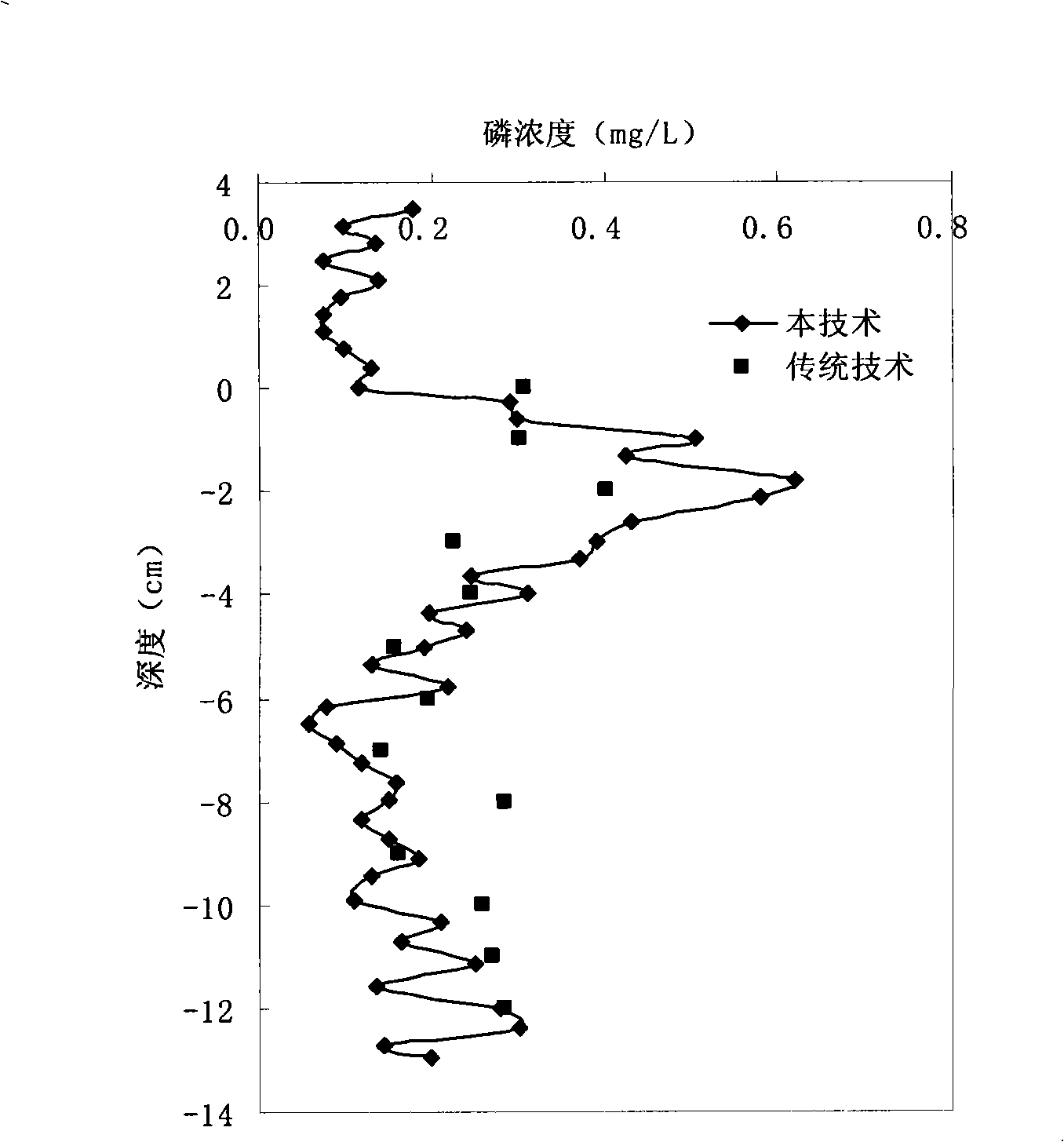
High precision in situ acquisition and analysis method as well as apparatus of sediment clearance phosphorus in water
InactiveCN101303276AEasy to analyzeSimplify deviceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWithdrawing sample devicesMalachite greenMalachite green stain
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
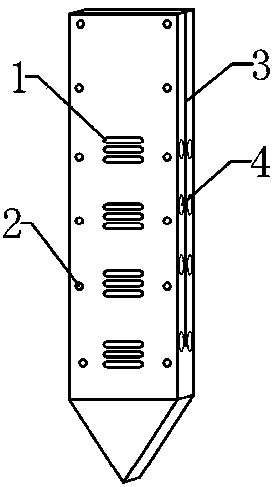
In-situ monitor device for synchronously analyzing physico-chemical property of hyporheic zone and using method thereof
The invention discloses an in-situ monitor device for synchronously analyzing the physico-chemical property of a hyporheic zone and a using method thereof. The device mainly comprises a cuboid main body, wherein a tip part for inserting into the hyporheic zone is arranged at the lower end of the main body, a plurality of interstitial water passive sampling chambers are distributed inside the mainbody along the height direction, and sampling openings communicated with the interstitial water passive sampling chambers are respectively formed in front and rear surfaces of the main body; the sampling openings are covered with dialysis membranes which are compressed through a grating plate; a plurality of sensor fixing grooves are arranged above the interstitial water passive sampling chambers,monitoring sensors are embedded in the sensor fixing grooves, sensing probes of the monitoring sensors extend into the interstitial water passive sampling chambers, and signal cables are connected with a data processing module through cable slots; and a storage battery module is used for supplying electricity to the data processing module and the monitoring sensors, and the data processing moduleand the storage battery module are positioned at the top inside the main body. The device can be used for synchronously and nondestructively monitoring physical and chemical properties of the hyporheic zone, and has the advantages of accurate monitor and convenience in use.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
Electrolytic filtering/squeezing integrated sludge dewatering machine
ActiveCN102115302BTo achieve the purpose of removalImprove dehydration efficiencySludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge cakeInterstitial water
The invention discloses an electrolytic filtering / squeezing integrated sludge dewatering machine which comprises a primary squeezing and filtering region, an electrolytic filtering region, an electrolytic squeezing region and an external direct current power source, wherein the primary squeezing and filtering region, the electrolytic filtering region and the electrolytic squeezing region are sequentially arranged with one anther by taking a frame as a carrier. The sludge fallen from a hopper is primarily squeezed and filtered to remove the free water contained in the sludge. A driven upper filter strip and a driven lower filter strip are respectively and externally leaned against an upper squeezing strip and a lower squeezing strip connected the two poles of a direct current power source,so that the sludge clamped between the upper squeezing strip and the lower squeezing strip is electrolyzed, and the interstitial water and the cellular water in the sludge flow to the negative pole when the electric charge flows, i.e. the electrophoresis. The incompletely-dried sludge is carried into the electrolytic squeezing region and is forced under the condition that the sludge is stilled electrolyzed to accelerate the dewatering. By sequentially reducing the diameters of a plurality of the roll shafts and by adopting an installation technology measure that the adjoining roll shafts are installed in a misplaced way up and down, the machine can dewater by sequentially forcing, so that the dryness of a sludge cake is improved. The machine is particularly suitable for treating the biochemical active sludge precipitated by the urban domestic sewage or the industrial sewage.
Owner:江苏百新环境工程有限公司
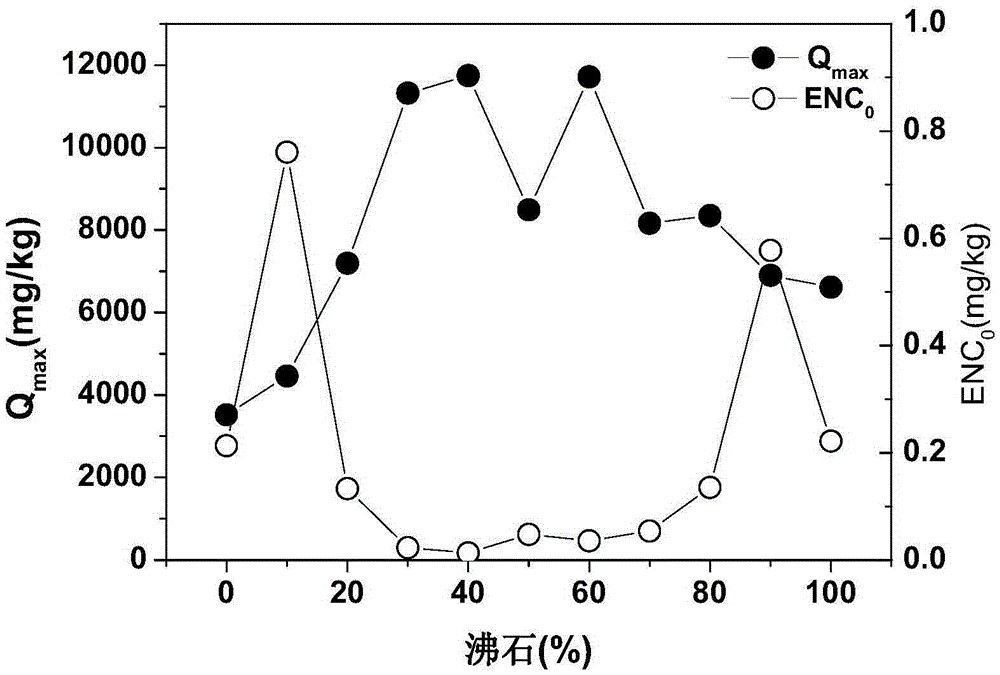
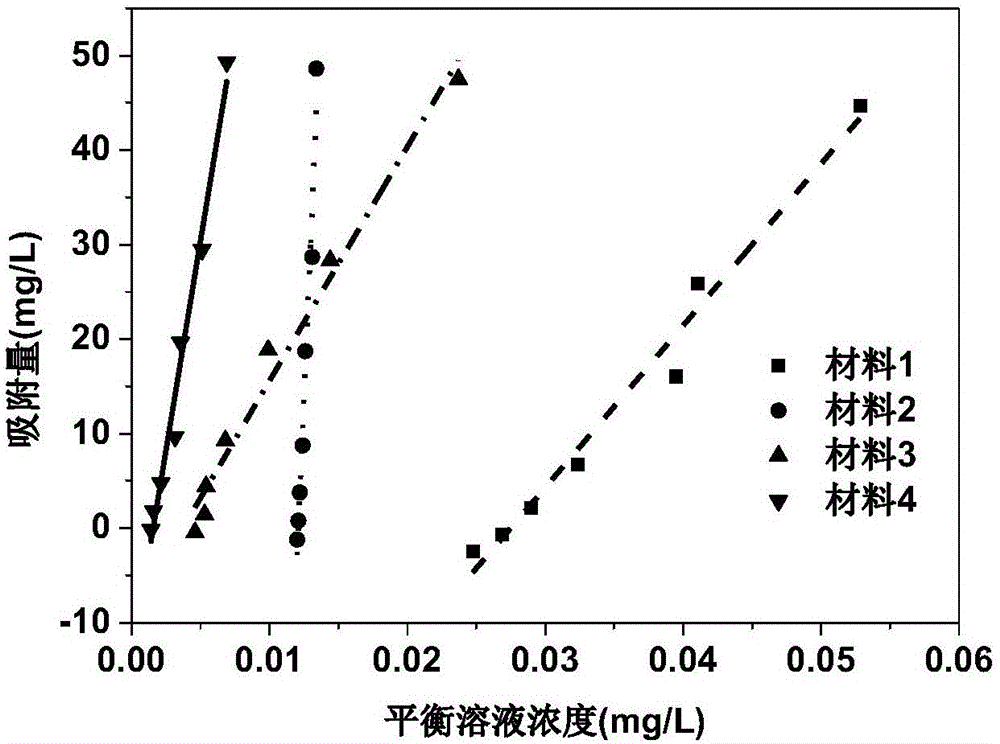
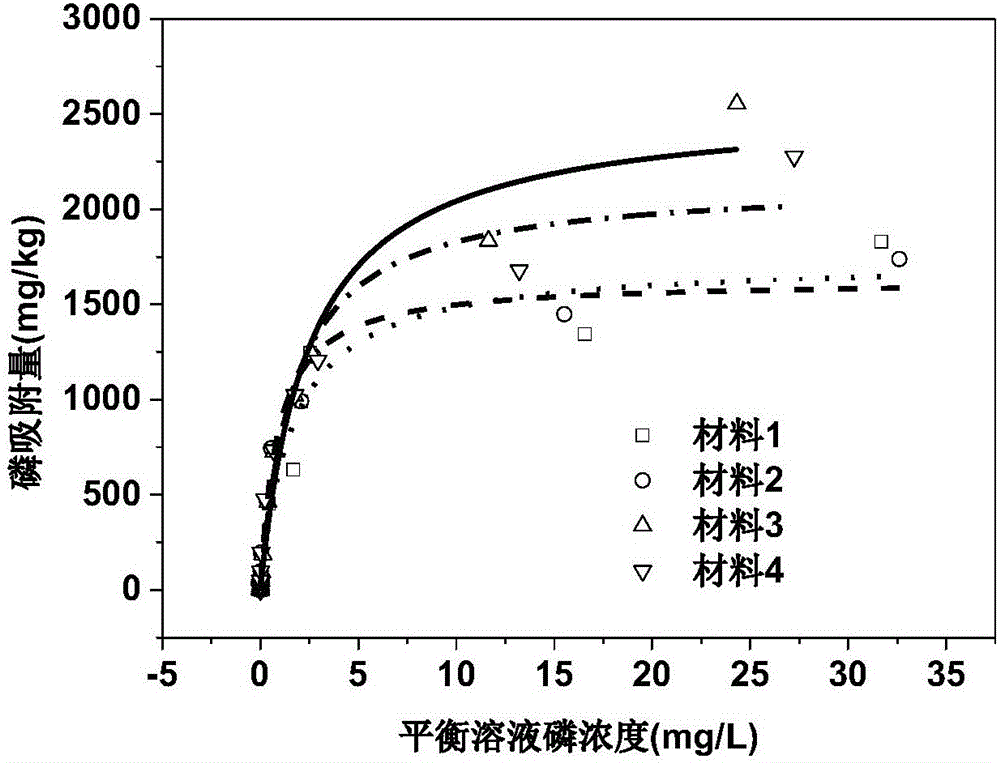
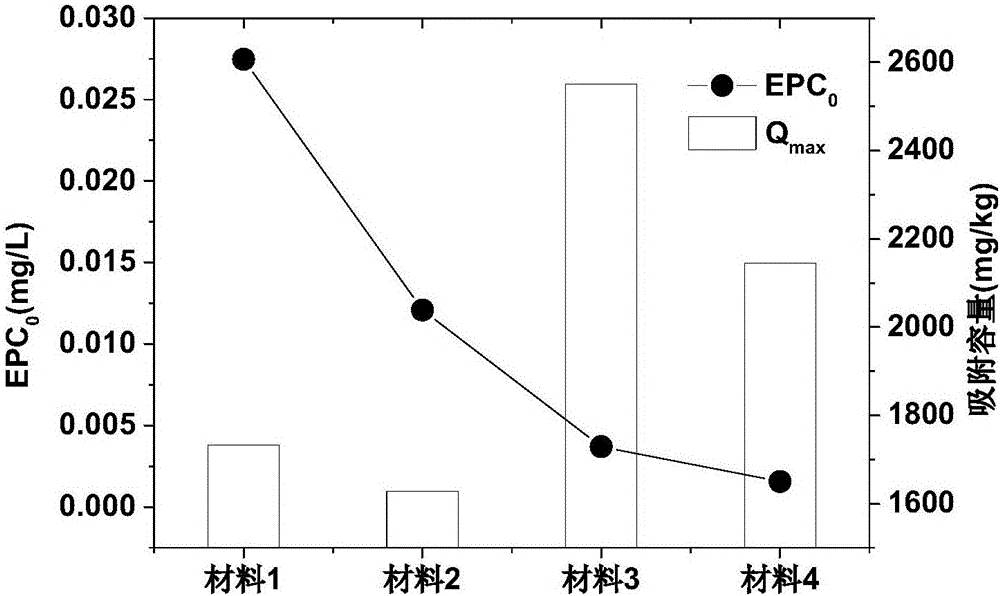
Preparation method and application of efficient removing materials for interstitial water phosphate of sediments
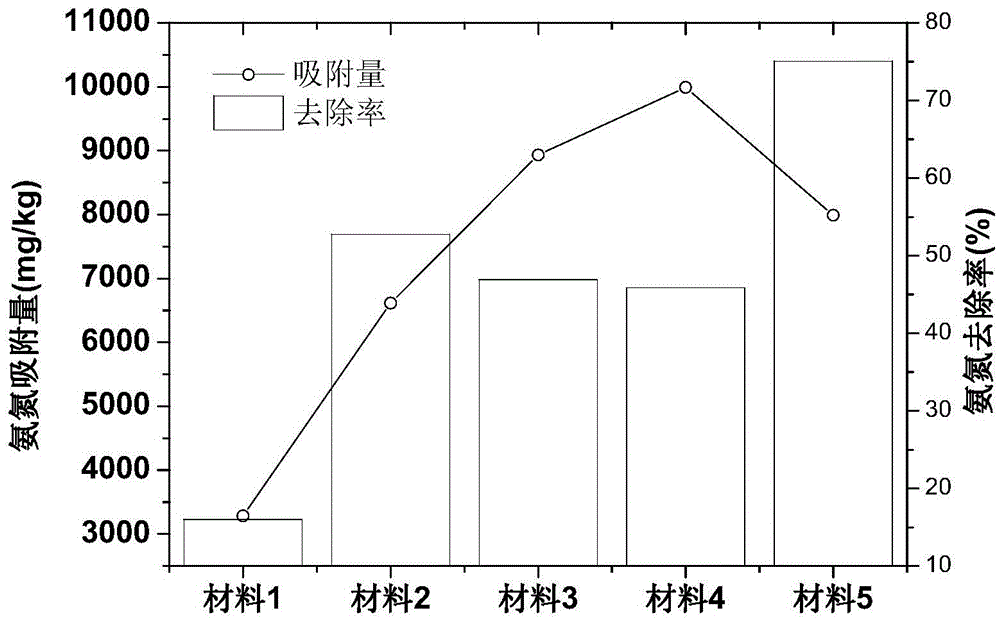
ActiveCN106311129ALess materialHigh porositySludge treatmentOther chemical processesPhosphateDesorption
The invention provides preparation method and application of efficient removing materials for interstitial water phosphate of sediments. Lake sediments are initiatively taken as basic materials of the materials and are subjected to calcination and alkaline washing, then the obtained material is mixed with kaolin, and mixed powder obtained is modified via ferric salt and then pore-forming agents are added for granulation and calcination shaping is peformed, and the low EPCo value and high Qmax value efficient removing materials for the interstitial water phosphate of the sediments are obtained. Concentration of the interstitial water phosphate of the sediments can be effectively cut down through the materials, and release of the phosphate of the sediments-water interfaces is restrained; desorption capacity of phosphate of the materials is weak and adsorption capacity is large, so that effective resistance and control of the materials on the sediments-water interfaces can be truly realized; the materials are low in cost, good in social and economic benefits, high in security, free of ecological risk on lake water, energy saving and environment friendly and remarkable in control effect on the sediments-water interfaces of different lakes of the Dian Lake during application.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com