Denitrification sulphur removal-based in-situ black-odorous riverway bottom mud oxidization technology
A technology of denitrification, sulfur removal, and in-situ oxidation, which is applied in the oxidation treatment of sludge, sludge treatment, biological sludge treatment, etc. pollution and other problems, to achieve the effect of quickly eliminating black odor, promoting the release, and inhibiting the release of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
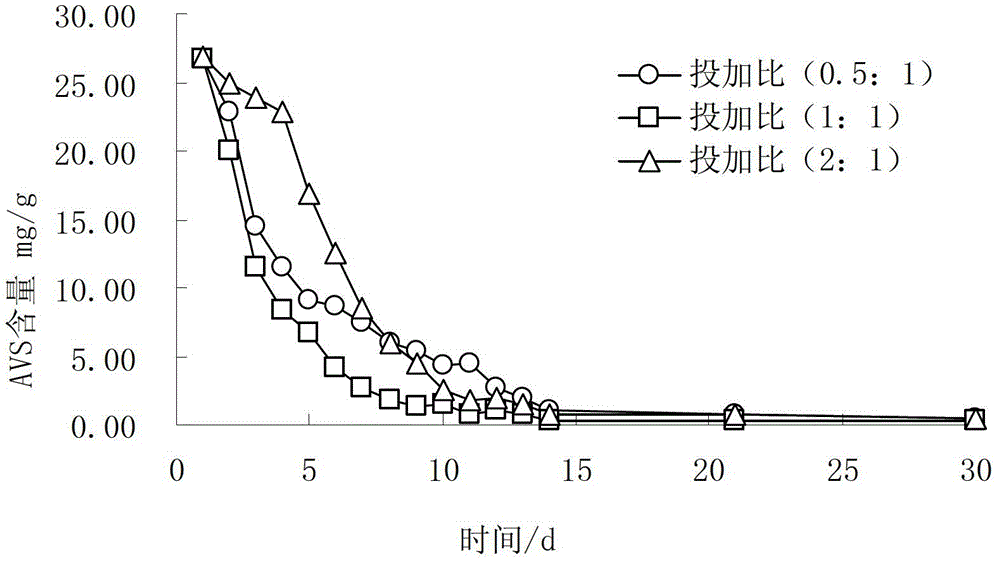
[0024] The content of 26mg AVS / g bottom mud in the bottom mud of present embodiment black-stinky river course (welling), according to the mass ratio of the content of sulfide (AVS) in bottom mud oxidant calcium nitrate and bottom mud, to black-stinky river gushing The mass ratios of calcium nitrate and sulfide in the dry method were 0.5:1, 1:1 and 2:1 respectively; the dosage of acid-base regulator lime was used to control the initial pH of the sediment to 7.5. The above-mentioned sediment oxidant and acid-base regulator are directly mixed with the sediment through the ejector by hydraulic or mechanical stirring, and the in-situ oxidation process of the black and odorous river (welling) sediment based on denitrification and desulfurization is implemented. The results are as follows: figure 1 shown. figure 1 It is the time-varying graph of bottom mud sulfide content after different calcium nitrate dosages are processed in the bottom mud in-situ oxidation process of embodiment 1...
Embodiment 2
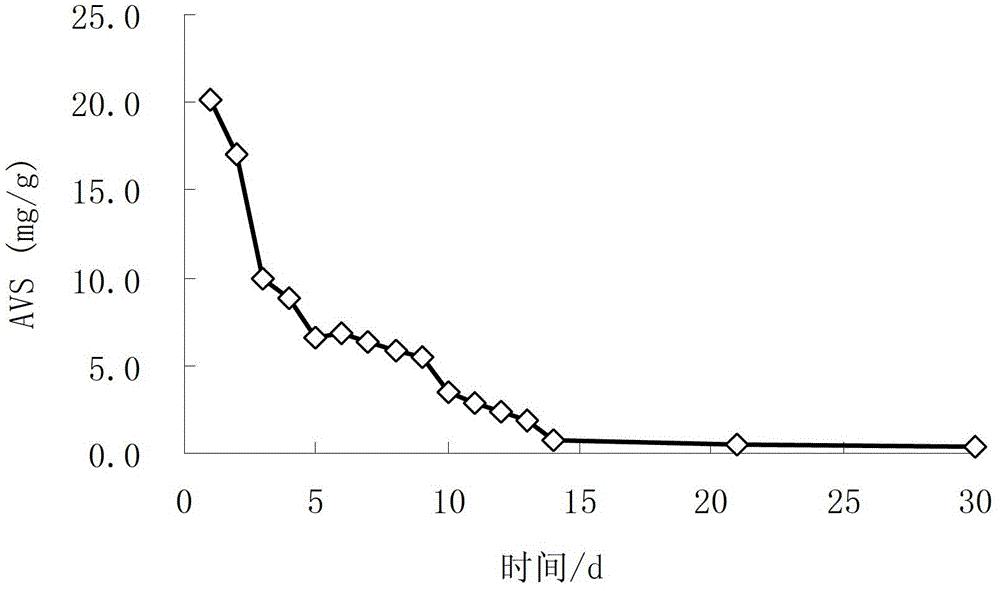
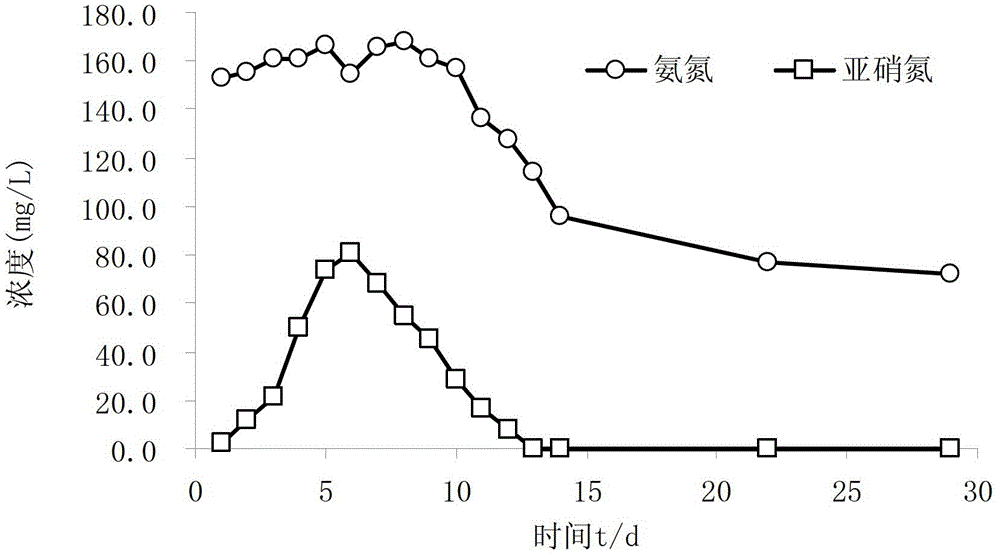
[0028] This embodiment is carried out in a closed system of bottom mud (only bottom mud and intermittent water, no overlying water), the content of sulfide in the bottom mud of black and smelly rivers (welling) is 20mg AVS / g bottom mud, and the total nitrogen content of bottom mud is 2485.5mg / kg. According to the mass ratio of the sediment oxidant and the content of sulfide (AVS) in the sediment, the mixture of the sediment oxidant sodium nitrate and calcium nitrate is added to the black-smelly river flushing method, and the mass ratio of the dosage to the sulfide content The mass ratio of sodium nitrate to calcium nitrate is 0.5:1, and the dosage of potassium chloride as a bottom sludge ammonia nitrogen extraction agent is 150 mg / L to promote the release of bottom sludge ammonia nitrogen. The dosage of dilute nitric acid as an acid-base regulator is used to control the initial pH of the sediment to 6.0. First, stir and dissolve the sediment oxidant, sediment ammonia nitroge...
Embodiment 3
[0030]In this embodiment, the content of sulfide in the bottom mud of the black-smelly river course (welling) is 16 mg AVS / g bottom mud, and the total nitrogen content of the bottom mud is 2358.5 mg / kg. According to the mass ratio of the sediment oxidant and the content of sulfide (AVS) in the sediment, the mixture of the sediment oxidant sodium nitrate and calcium nitrate is added to the black-smelly river flushing method, and the mass ratio of the dosage to the sulfide content is 2:1, wherein the mass ratio of sodium nitrate to calcium nitrate is 1:1, and the dosage of sodium chloride as an ammonia nitrogen extraction agent from sediment is 200 mg / L to promote the release of ammonia nitrogen from sediment. If the initial When the concentration of ammonia nitrogen exceeds 200mg / L, there is no need to add it. The dosage of dilute nitric acid as sediment acid-base regulator is to control the initial pH of sediment to 6.5. First, stir and dissolve the sediment oxidant, sediment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com