Method for increasing activity of GAD (Glutamate Decarboxylase) by using D101 macroporous adsorption resin
A technology of glutamic acid decarboxylase and adsorption resin, which is applied in the biological field and can solve the problems of high cost of gamma-aminobutyric acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] A kind of method of improving glutamic acid decarboxylase activity with D101 macroporous adsorption resin of the present invention comprises the following steps:
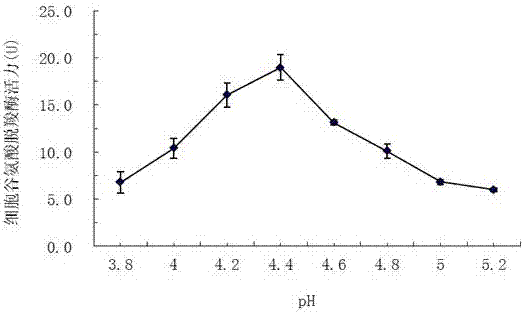
[0065] ①. Dissolve L-glutamate monosodium (monosodium glutamate) in 0.2mol / L acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, adjust the pH to 4.2-4.6, and prepare 0.2mol / L-0.3mol / L L-glutamic acid Monosodium solution, as substrate solution;
[0066] ②. Pretreat the D101 macroporous adsorption resin with 95% ethanol and distilled water according to the instructions of the resin, and then balance it with the substrate solution;
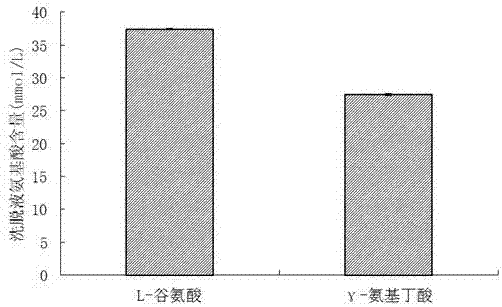
[0067] ③. According to step ②, the mass of D101 macroporous adsorption resin balanced: the volume of substrate solution: the volume of Enterococcus faecium GDMCC 60203 bacterial suspension is mixed in a ratio of 1:1:1, and the mixture is glutamic acid decarboxylase compound Transformation reaction system;
[0068] ④. React the mixture in step ③ in 80r / min, 37℃~43℃ water bath shaker or stir...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A kind of method of improving glutamic acid decarboxylase activity with D101 macroporous adsorption resin of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0072] ①. Dissolve L-glutamic acid in 0.2mol / L acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, adjust the pH to 4.2-4.6, and prepare a 0.2mol / L-0.3mol / L L-glutamic acid solution as a substrate solution;
[0073] ②. Pretreat the D101 macroporous adsorption resin with 95% ethanol and distilled water according to the instructions of the resin, and then balance it with the substrate solution;
[0074] ③. According to step ②, the mass of D101 macroporous adsorption resin balanced: the volume of substrate solution: the volume of Enterococcus faecium GDMCC 60203 bacterial suspension is mixed in a ratio of 1:1:1, and the mixture is glutamic acid decarboxylase compound Transformation reaction system;
[0075] ④. React the mixture in step ③ in 80r / min, 37℃~43℃ water bath shaker or stir at 37℃~43℃ at low speed or stand fo...
Embodiment 3
[0078] A kind of method utilizing D101 macroporous adsorption resin of the present invention to improve glutamic acid decarboxylase activity comprises the following steps:
[0079] ①. Dissolve L-glutamate monosodium (monosodium glutamate) in 0.2mol / L acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, adjust the pH to 4.2-4.6, and prepare 0.2mol / L-0.3mol / L L-glutamic acid Monosodium solution, as substrate solution;
[0080] ②. Pretreat the D101 macroporous adsorption resin with 95% ethanol and distilled water according to the instructions of the resin, and then balance it with the substrate solution;
[0081] ③. The mass of D101 macroporous adsorption resin balanced according to step ②: volume of substrate solution: volume of Enterococcus faecium GDMCC 60203 glutamate decarboxylase free enzyme solution is 1:1:1 and the three are mixed, and the mixture is gluten Amino acid decarboxylase complex transformation reaction system;
[0082] ④. React the mixture in step ③ in 80r / min, 37℃~43...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com