Genetically engineered bacterium for producing polyhydroxybutyric acid-valerate as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
An amino acid and coding gene technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems that the performance of strains cannot reach commercial production, increase production costs, and complicate the control process, etc., and achieve fermentation process Ease of control, low cost of raw materials, and safe strains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
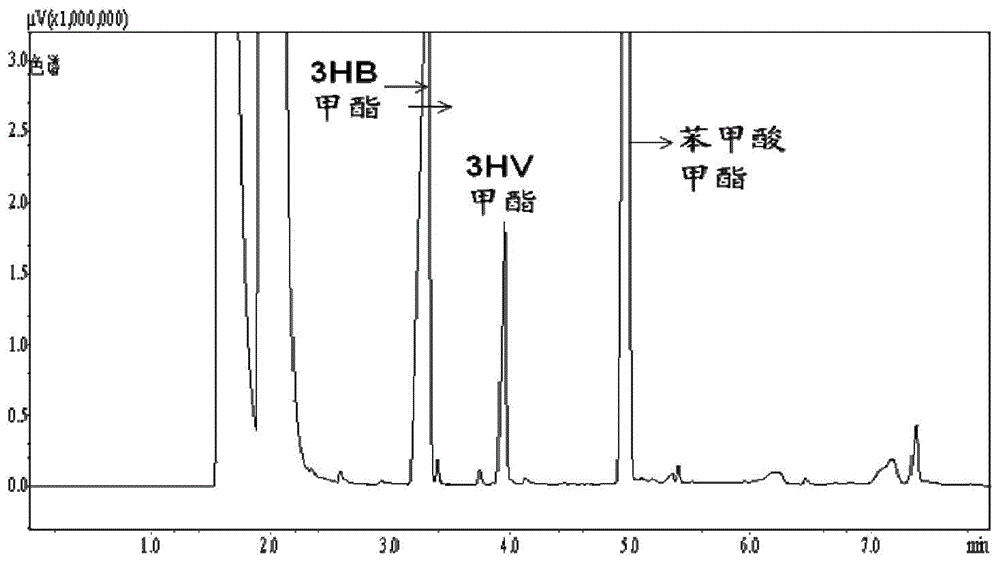
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] Preparation method of basal medium: each liter of basal medium contains 6.7g Na 2 HPO 4 2H 2 O, 1.5g KH 2 PO4, 1g(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 0.2g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 1ml of trace elements and 20g of glucose.
[0050] Contains 0.3g H per liter of trace elements 3 BO 3 , 0.2g CoCl 2 , 0.1g ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.03g MnCl 2 4H 2 O, 0.02g NaMoO 4 2H 2 O, 0.02g NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O, 0.01g CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O, 0.01g CaCl 2 2H 2 O and 0.06g Fe(NH 4 ) 2 (SO 4 ) 2 .
Embodiment 1
[0051] The construction of the gene knockout vector of embodiment 1, prpC1 and prpC2
[0052] 1. Construction of prpC1 gene knockout vector
[0053] Using the genomic DNA of Ralstonia eutropha H16 as a template, PCR amplification was performed using prpC1df / prpC1dr primers. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0054] prpC1df: 5'-TAGATCTCAAGCGCGCCGGCTACCGGGCC-3';
[0055] prpC1dr: 5'-TTCTAGACAGGTCGAACTTCAGCACGCGCT-3'.
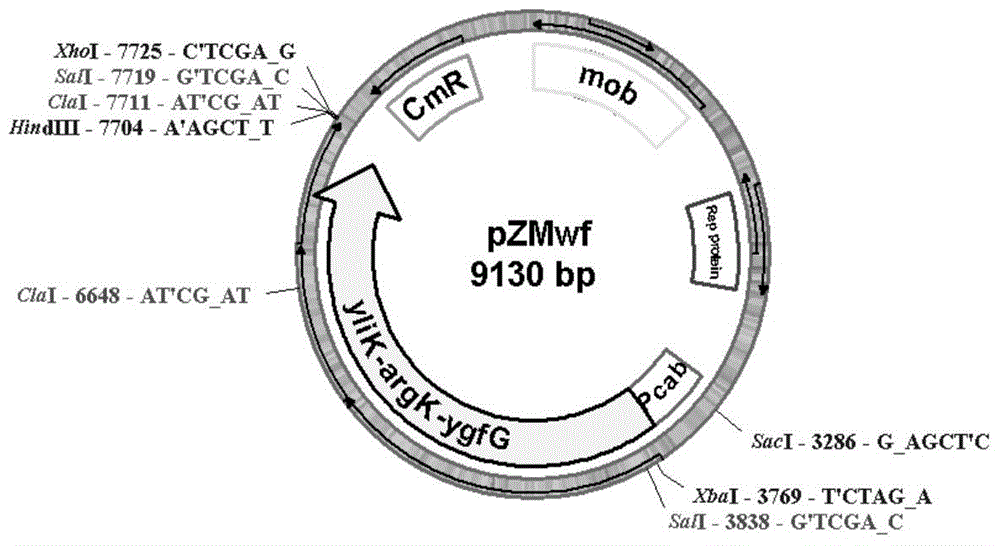
[0056] The amplified fragment with a size of 3222bp was connected to the plasmid pMDT19-simple, and the resulting recombinant vector was designated as pMD19-prpC1. The recombinant vector pMD19-prpC1 was transformed into E. coli DH5α, single colonies were picked, and the plasmid was extracted for sequencing. Sequencing results show that the sequence of the PCR amplification product is shown as sequence 1 in the sequence listing, which contains DNA fragments of the prpC1 gene and its two homologous arms. The nucleotide sequence of the prpC1 gene is shown in ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2, Construction of prpC1 and prpC2 gene knockout strains
[0067] 1. Construction of prpC1 knockout strain
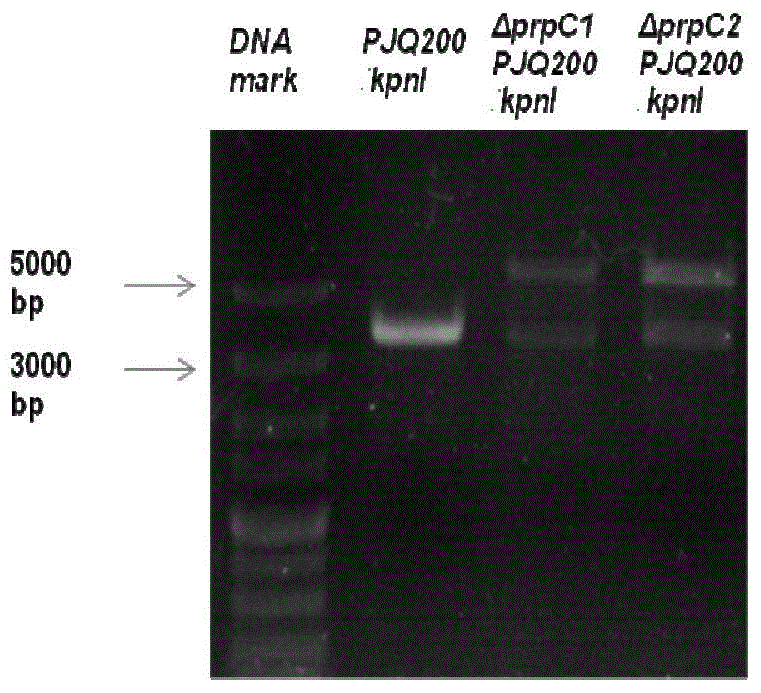
[0068] Gene knockout was performed by the method of conjugal transfer. The pJQ200mp18Tc::ΔprpC1 knockout vector was transformed into E.coli S17-1, spread on the LB plate containing tetracycline, and the correct transformant was selected and named ΔprpC 1pJQ200 / S17-1.
[0069] ΔprpC 1pJQ200 / S17-1 was used as the donor bacteria for conjugative transfer and the recipient bacteria Rem-1 for conjugative transfer. The process of conjugative transfer is as follows: first, the recipient bacteria Rem-1 was inoculated in PG medium, and cultured at 30°C until the OD value was 1.0; the donor bacteria ΔprpC 1pJQ200 / S17-1 was inoculated in LB culture based on 37°C culture, and the growth When the OD value is 0.4, take 100 μl of the culture solution of the recipient bacteria and the donor bacteria, and centrifuge at 3000 rpm to remove the supernatant, suspend and mix ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com