Construction method of yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium for producing citric acid or itaconic acid by using acetic acid
A technology of Yarrowia lipolytica and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve unseen problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
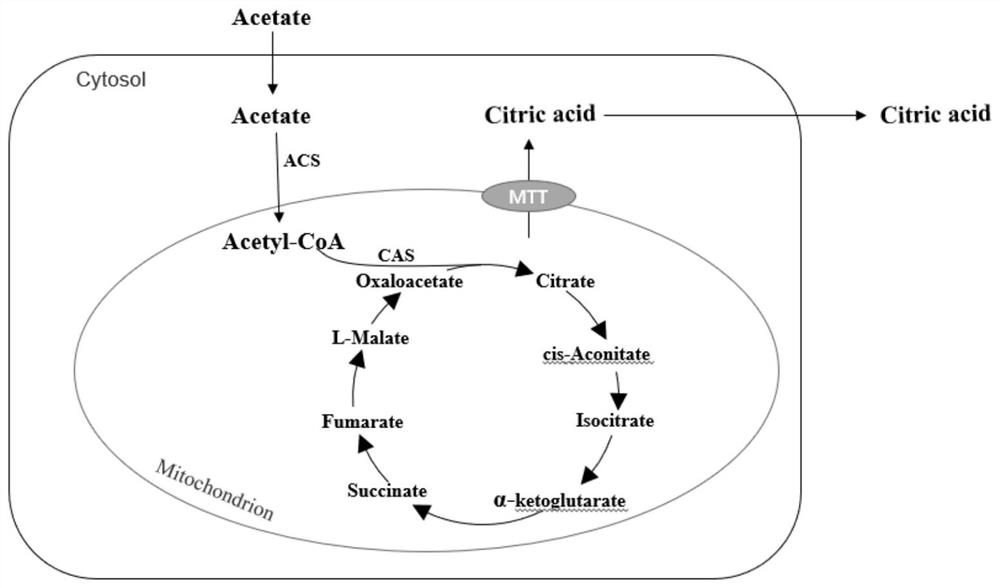
[0041] Embodiment 1 uses acetic acid as carbon source to produce the construction of Yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacterium of citric acid
[0042] A. Construction of plasmid PYcam
[0043](1) The citric acid synthase gene CAS and the acetyl-CoA synthetase gene ACS are all derived from the genome of Yarrowia lipolytica. The corresponding citrate synthase gene CAS and acetyl-CoA synthetase gene ACS were amplified by PCR above, which were derived from the mitochondrial carboxylic acid transporter gene MTT of Aspergillus terreus, and connected to the vector PYLXP' in turn to obtain the recombinant plasmid PYcam, whose nucleoside The acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.5.
[0044] Primer sequences used in Table 1
[0045]
[0046] B. Yarrowia lipolytica transformation of plasmid pYcam
[0047] The transformation method of the plasmid is the lithium acetate yeast transformation method commonly used in yeast transformation.
[0048] The specific way is:
[0049...
Embodiment 2
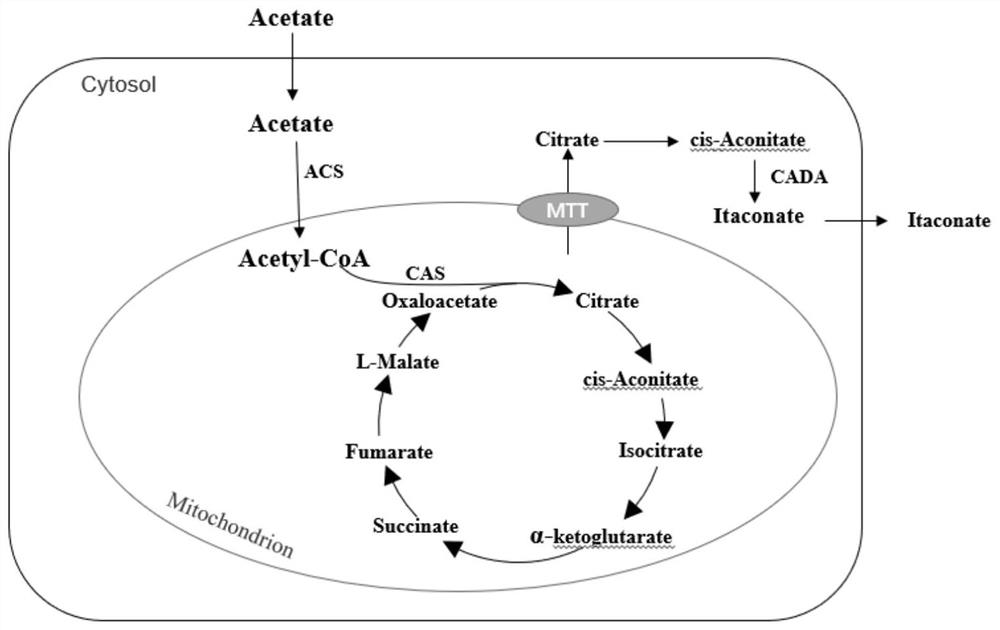
[0057] Example 2 Production of itaconic acid Yarrowia lipolytica genetically engineered bacteria using acetic acid as a carbon source
[0058] A, construction of plasmid PYcama
[0059] (1) The citric acid synthase gene CAS and the acetyl-CoA synthetase gene ACS are all derived from the genome of Yarrowia lipolytica. The corresponding citrate synthase gene CAS and acetyl-CoA synthetase gene ACS were amplified by PCR above, which were derived from the mitochondrial carboxylate transporter gene MTT and aconitic acid decarboxylase gene CADA of Aspergillus terreus, and were sequentially connected to the vector PYLXP' The obtained recombinant plasmid is PYcama, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.6, and the sequence used is shown in Table 1.
[0060] B. Yarrowia lipolytica transformation of plasmid pYcam
[0061] The transformation method of the plasmid is the lithium acetate yeast transformation method commonly used in yeast transformation.
[0062] The speci...
Embodiment 3
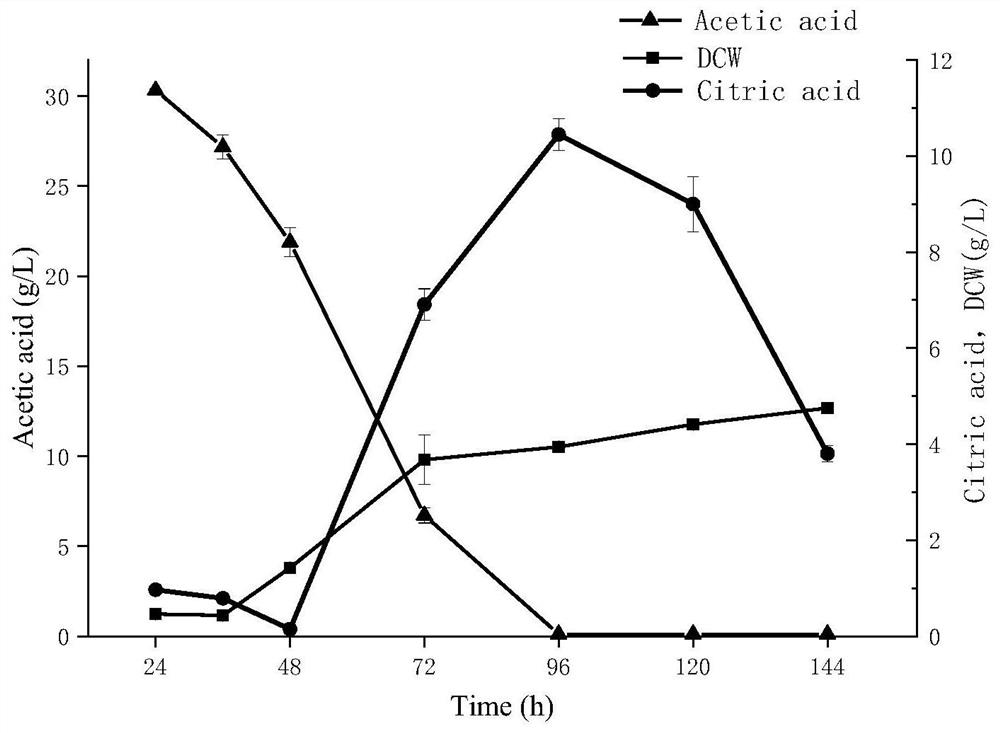
[0071] Example 3 Experiment of YLA01 strain producing citric acid by fermenting acetic acid as carbon source
[0072] 1. Experimental material: strain YLA01
[0073] 2. Experimental method:
[0074] Seed medium: acetic acid leucine deficient medium, YNB1.5 g / L, acetic acid 23 g / L, ammonium sulfate 4.6 g / L, CSM-leu0.8 g / L. Sterilize at 121°C for 25 minutes.
[0075] Fermentation medium: acetic acid leucine deficient medium, YNB1.7 g / L, acetic acid 41 g / L, ammonium sulfate 0.825 g / L, CSM-leu 0.69 g / L. Sterilize at 121°C for 25 minutes.
[0076] Inoculate the strain YLA01 in 5mL of seed medium, and cultivate it for 48 hours at 28°C and 220rpm, take 100μL of seed liquid, inoculate it in 50mL of fermentation medium, and cultivate it at 28°C and 220rpm After 144 hours, the concentration of citric acid and the remaining amount of acetic acid in the fermentation broth were measured.
[0077] 3. Product detection method
[0078] Citric acid is easily soluble in water, so the prod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com