Construction and applications of corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain for producing L-homoserine
A technology of Corynebacterium glutamicum and homoserine, applied in the field of fermentation engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
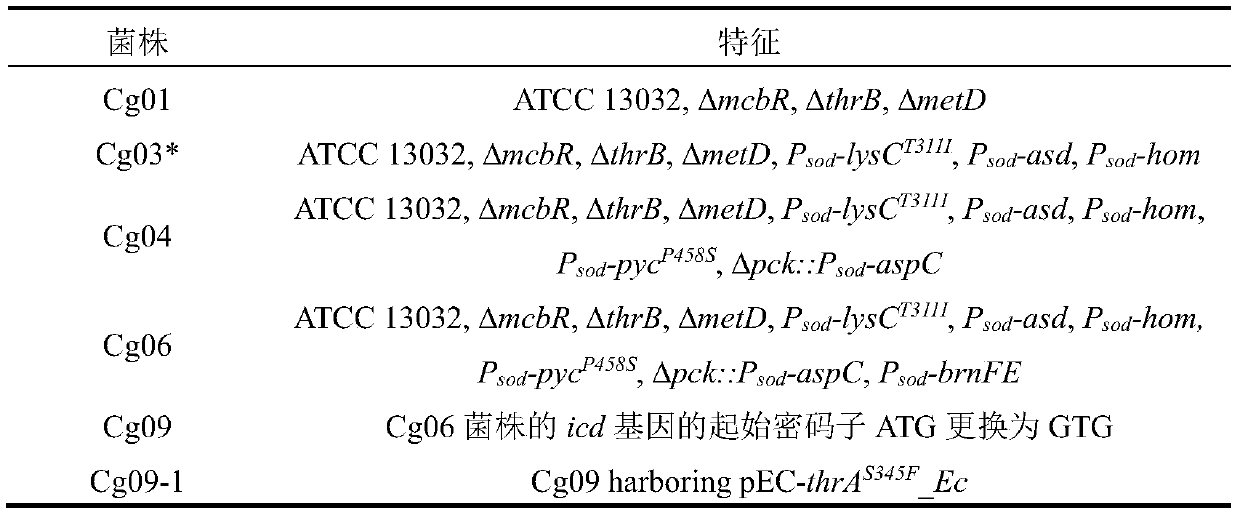
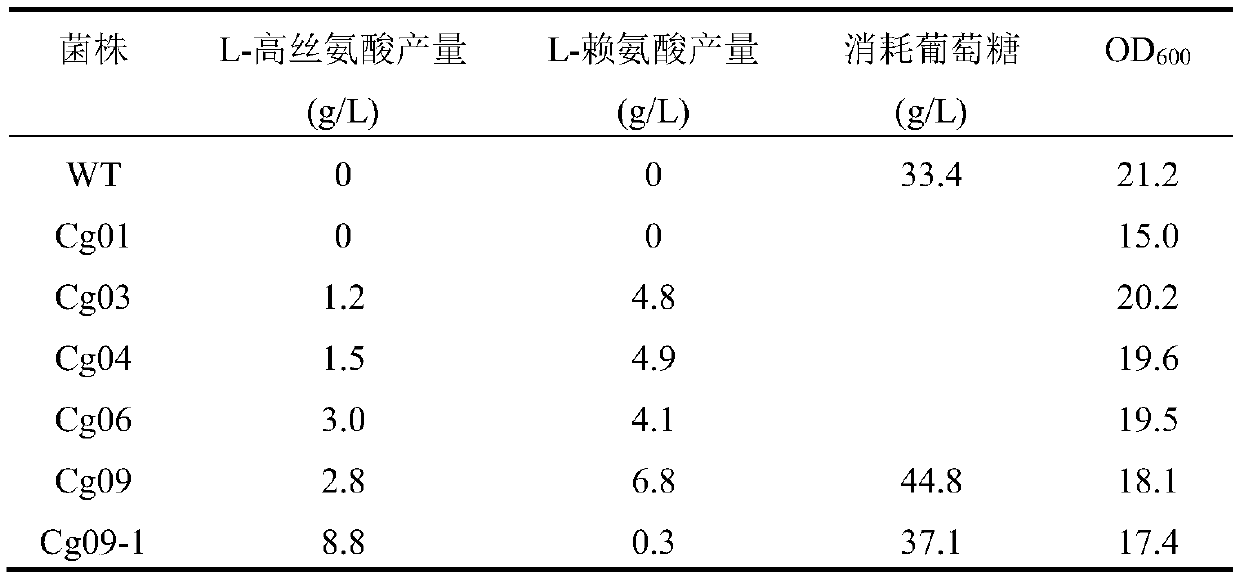
[0040] Embodiment 1: Construction of bacterial strain Cg01
[0041] 1. Construction of gene knockout plasmid
[0042] The plasmid pK18mobsacB was digested with restriction endonucleases HindIII and BamHI to obtain a linearized pK18mobsacB fragment;
[0043] According to Corynebacterium glutamicum genome (NCBI accession number is NC_003450.3), synthetic nucleotide sequence is as shown in the fragment mcbR-U of SEQ ID NO.1; Nucleotide sequence is as the fragment mcbR shown in SEQ ID NO.2 -D; the knockout plasmid pK-mcbR was obtained by assembling mcbR-U, mcbR-D and linearized pK18mobsacB by Gibson assembly method;
[0044] The fragment thrB-U with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.3 and the fragment thrB-D with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.4 were assembled with linearized pK18mobsacB by Gibson assembly to obtain a knockout plasmid pK-thrB;
[0045] The fragment metD-U with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.5 and the fragment metD-D with the nuc...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: the construction of bacterial strain Cg03
[0051] 1. Plasmid construction
[0052] The plasmid pK18mobsacB was digested with restriction endonucleases Hind III and BamH I to obtain a linearized pK18mobsacB fragment;
[0053] The fragment lysC(P)-U whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.7, the fragment lysC(P)-D whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.8, and the nucleotide sequence such as SEQ ID NO. The fragment Psod shown in ID NO.11 was assembled with linearized pK18mobsacB by Gibson assembly method to obtain the expression plasmid pK-lysC(P);
[0054] The fragment hom(P)-U whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.9, the fragment hom(P)-D and Psod whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.10 are assembled by Gibson, Assembly with linearized pK18mobsacB to obtain overexpression plasmid pK-hom(P);
[0055] Use primers lysC(m)-U-R and lysC(m)-D-F to perform site-directed mutagenesis on plasmid pK-lysC(P) by PCR, and replace...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3: the construction of bacterial strain Cg04
[0063] 1. Plasmid construction
[0064] The plasmid pK18mobsacB was digested with restriction endonucleases Hind III and BamH I to obtain a linearized pK18mobsacB fragment;
[0065] The fragment pyc(P)-U whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.12, the fragment pyc(P)-D whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.13, and the fragment Psod and Linearized pK18mobsacB was assembled to obtain the expression plasmid pK-pyc(P);
[0066] The fragment aspC(P)-U with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.14, the fragment aspC(P)-D with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.15, the fragment Psod, The fragment aspC with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.16 was assembled with the linearized pK18mobsacB to obtain the expression plasmid pK-aspC(P);
[0067] Use the primers pyc(m)-F and pyc(m)-F to perform site-directed mutation on the plasmid pK-pyc(P), replace the proline at position 458 of py...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com