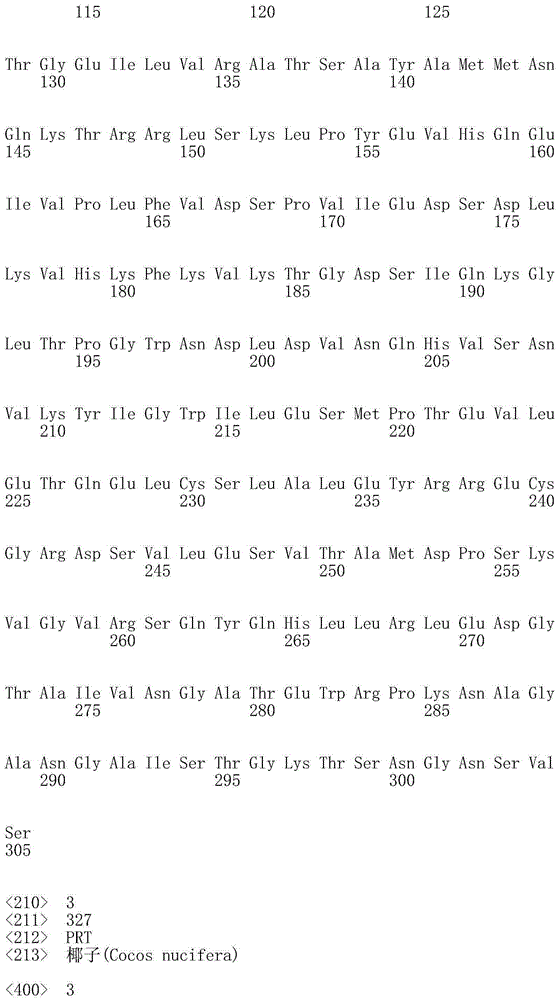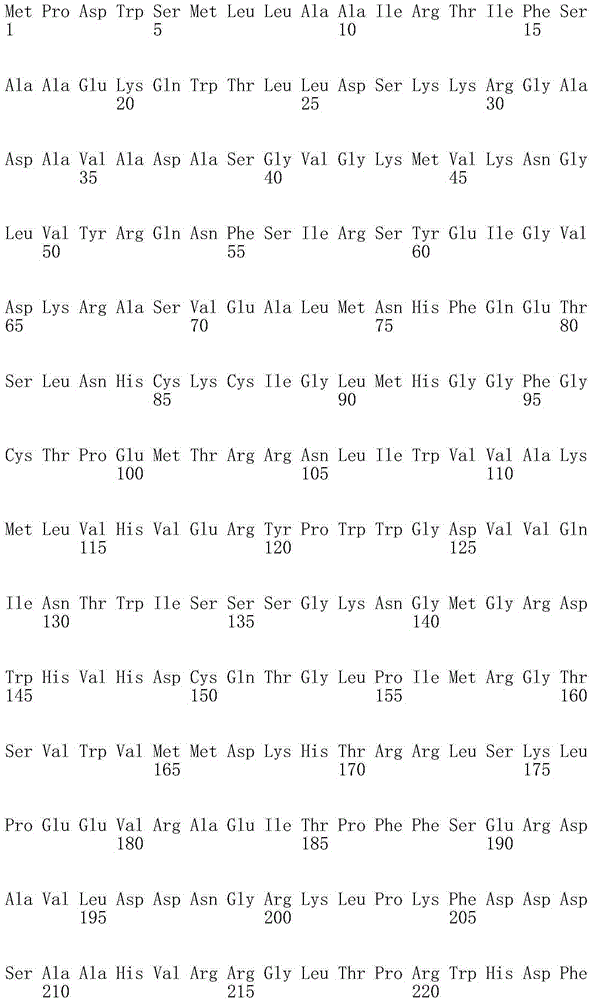Fatty acid and derivatives production
A fatty acid and derivative technology, applied in biosynthesis, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as difficult control of composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Construction of plasmids for the production of fatty acids using R. eutropha
[0059] To construct a plasmid for the production of fatty acids from R. eutropha, 3 synthetic expression cassettes consisting of the following components were synthesized:
[0060] R. eutropha groEL Ribosome binding site of gene (SEQ ID NO: 1), gene encoding thioesterase from Calyx chinensis ChFATB2 (SEQ ID NO:2), which has been 5'-truncated at the plastid targeting sequence, Escherichia coli rrnB The terminator (SEQ ID NO:5) of gene, wherein in the translation of Laueria eutropha, is used for ChFATB2The coding region of is codon-optimized (RBSRegroEL-ChFATB2-T; SEQ ID NO: 6).
[0061] R. eutropha groEL The ribosome binding site (SEQ ID NO: 1) of gene, coding comes from coconut ( Cocos nucifera ) thioesterase gene CnFATB3 (SEQ ID NO:3), Escherichia coli rrnB The terminator (SEQ ID NO:5) of gene, wherein in the translation of Laueria eutropha, is used for CnFATB3 The coding ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Introduction of plasmids for fatty acid production in Laueria eutropha
[0066] The plasmids from above were transfected into competent E. coli S17-1 cells in which conjugative transfer of plasmids from R. eutropha among other strains was possible. For this purpose, Spotmating conjugation using the respective plasmids was performed (e.g. FRIEDRICH et al., 1981), in which E. coli strain S17-1 was the donor and R. eutropha H16 (reclassified as Alcaligenes eutropha , DSMZ428) and R. eutropha PHB-4 (reclassified as Alcaligenes eutropha, DSMZ541) are recipients. Zygotes were obtained in all cases carrying the respective plasmids and the corresponding strains were named as follows:
[0067] R. eutropha H16PbBr-ChFATB2, R. eutropha H16PbBr-CnFATB3, R. eutropha H16PbBr-UcFATB1, R. eutropha PHB-4-PbBrChFATB2, R. eutropha PHB- 4-PbBrCnFATB3, and R. eutropha PHB-4-PbBrUcFATB1.
Embodiment 3
[0069] Quantification of fatty acids
[0070] Quantification of caprylic acid, 3-hydroxycapric acid, capric acid, lauric acid, 3-hydroxymyristic acid, myristic acid, palmitoleic acid, palmitic acid, oleic acid, and stearic acid in fermentation samples by An internal calibration of HPLC-ESI / MS was performed and internal standards were used: caprylic acid, 3-hydroxycapric acid, capric acid, lauric acid, 3-hydroxymyristic acid, myristic acid, palmitoleic acid, stearic acid D3 Lauric Acid (Methyl-D3, 99%), and D3 of Palmitic, Oleic, Stearic Acids (D3-Methyl, 98%).
[0071] Use the following equipment:
[0072] ●HPLC system: Surveyor (ThermoFisherScientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA), composed of SurveyorMS pump, SurveyorAutosamplerPlus and SurveyorSurveyorPDA
[0073] ●Mass spectrometer: TSQVantageHESIII-source (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA)
[0074] HPLC column: XBridge BEHC8, 100x2.1 mm, particle size: 2.5 microns, pore size 130 Å (Waters, Milford...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com