PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
A compound and polyketide technology, applied in the field of preparation and use of the non-bacterial PUFAPKS system disclosed in this paper, identification of bacteria and non-bacterial microorganisms containing the PUFAPKS system, can solve problems such as difficult plant expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
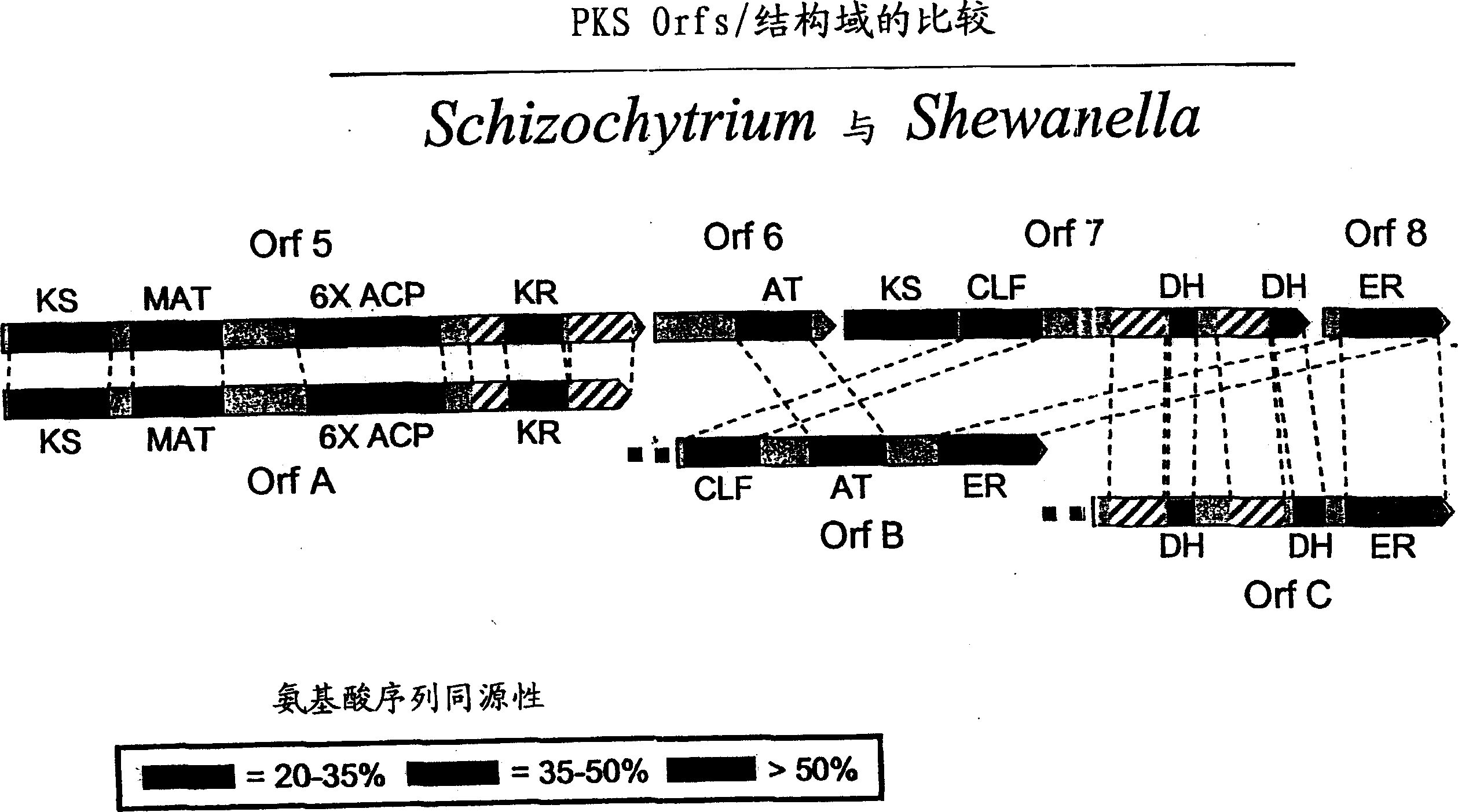
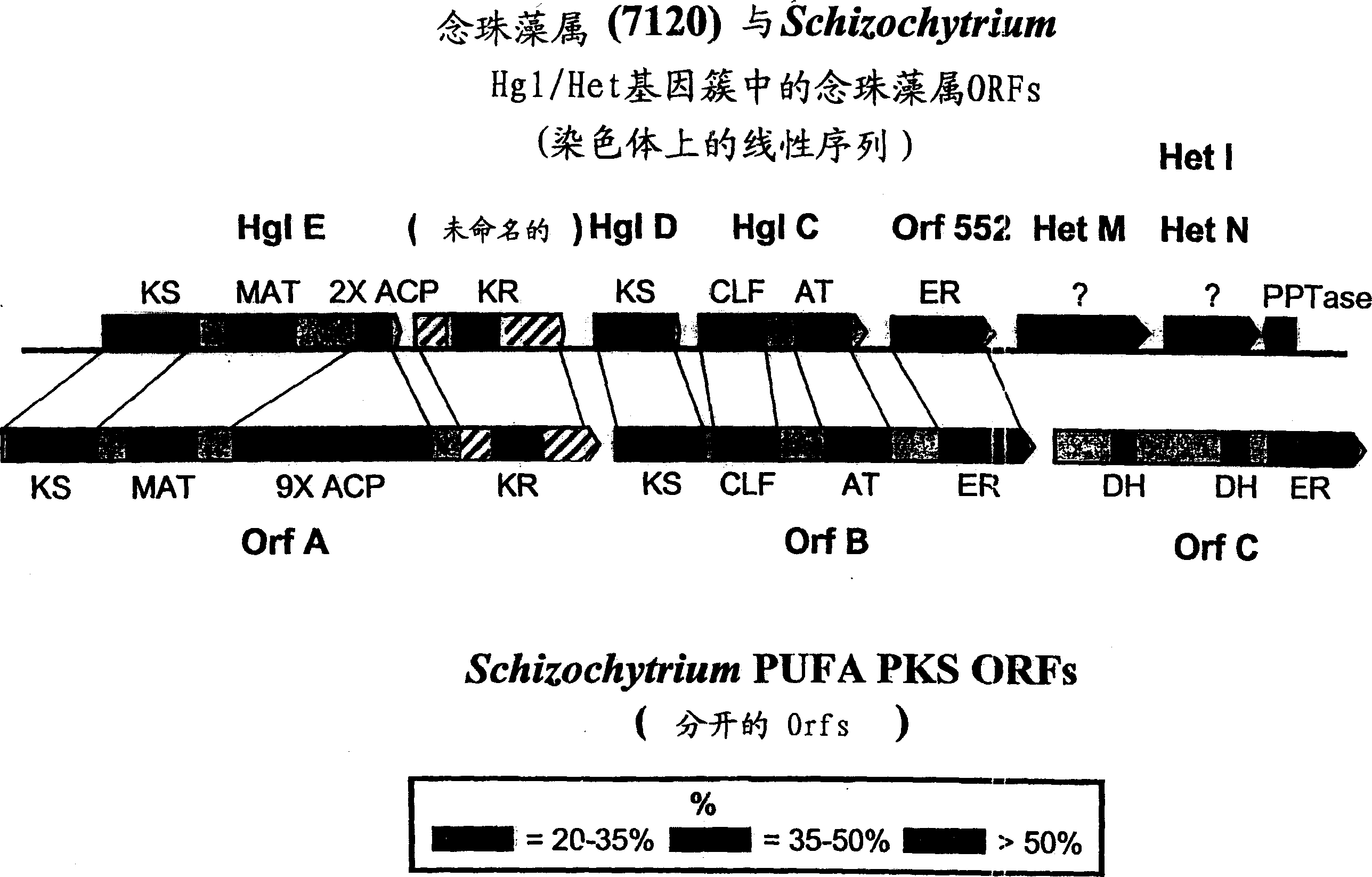
[0241] The following example describes further analysis of PKS related sequences from Schizochytrium.
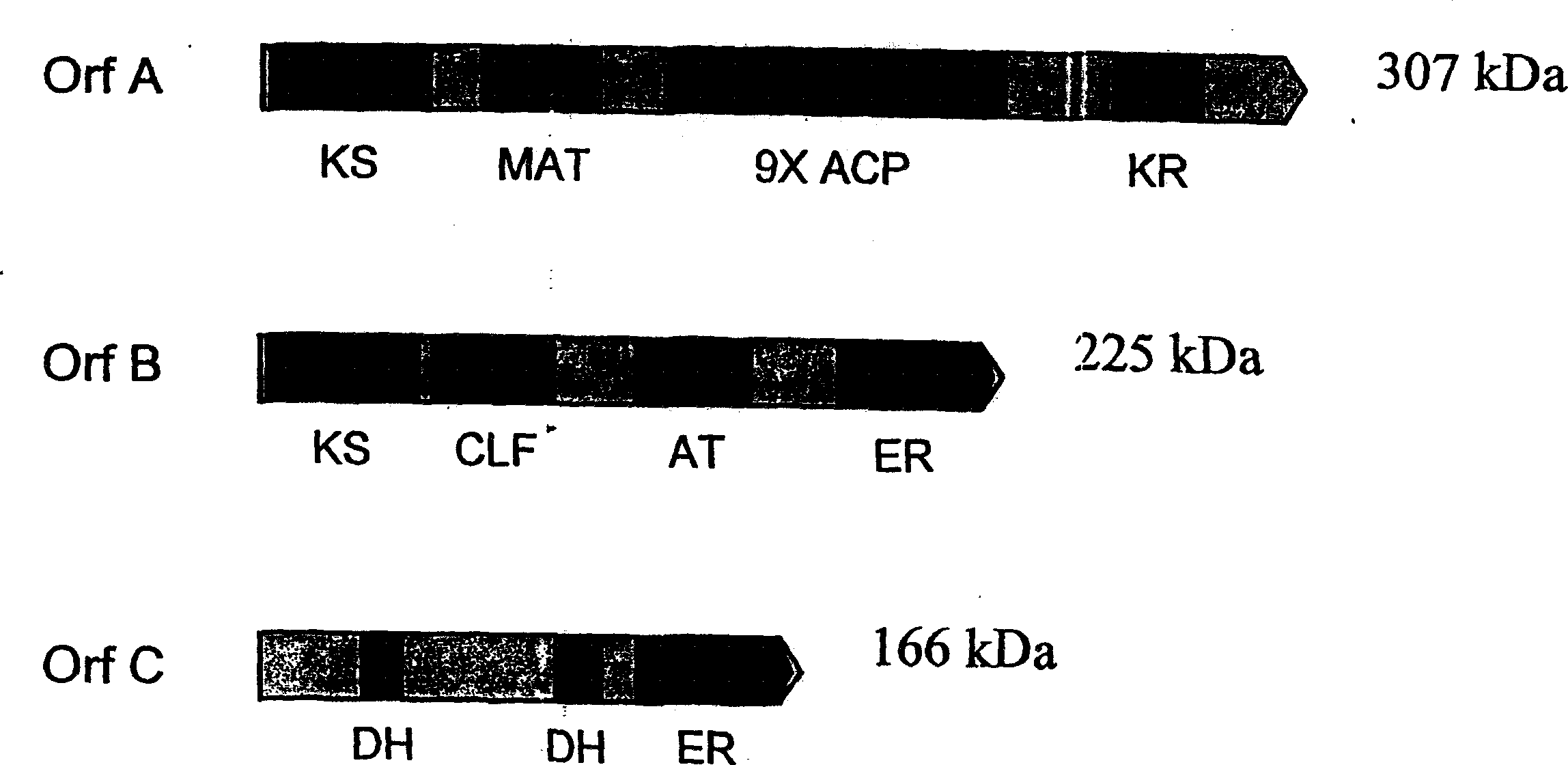
[0242] The inventors sequenced the full-length genome containing all three open reading frames (Orfs) in the Schizochytrium PUFA PKS system using the general methods outlined in Examples 8 and 9 of PCT Publication No. WO 0042195 and US Application Serial No. 09 / 231,899 DNA. The biologically active domain in the Schizochytrium PKS protein is in figure 1 is described graphically. The domain structure of the Schizochytrium PUFA PKS system is described in more detail below.
[0243] Open reading frame A (OrfA) :
[0244] The complete nucleotide sequence of OrfA is represented herein as SEQ ID NO:1. OrfA is a sequence of 8730 nucleotides (not including the stop codon), which encodes a sequence of 2910 amino acids, represented herein as SEQ ID NO:2. There are 12 domains within OrfA:
[0245] (a) a β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase (KS) domain;
[0246] (b) a malonyl-CoA:ACP acyltr...
Embodiment 2
[0289] The following examples describe the identification of three other non-bacterial organisms containing the PUFAPKS system according to the invention using the screening method of the invention.
[0290] Thraustochytrium 23B (ATCC 20892) was cultured following the screening method described in US Provisional Application Serial No. 60 / 298,796 and described in detail herein.
[0291] A biologically plausible screening system (using shake flask cultures) for the detection of microorganisms containing PUFA-producing PKS systems was performed as follows:
[0292] Place a 2 mL culture of the microorganism of the strain to be tested in a 250 mL baffled shake flask containing 50 mL of medium (aerobic treatment), and place another 2 mL culture of the same strain in a 250 mL unbaffled flask containing 200 mL of medium plate in shake flasks (anoxic treatment). Both shake flasks were placed on a shaker at 200 rpm. After 48-72 hours of incubation, the cultures were harvested by centr...
Embodiment 3
[0328] The following examples demonstrate that DHA and DPA synthesis in Schizochytrium does not involve membrane-bound desaturases or fatty acid elongases, as has been described for other eukaryotes (Parker-Bames et al., 2000, supra; Shanklin et al., 1998, cited above).
[0329] Schizochytrium accumulates large amounts of triacylglycerol rich in DHA and meningoleic acid (DPA; 22:5ω6); for example, 30% of dry weight DHA+DPA. In eukaryotes that synthesize 20- and 22-carbon PUFAs via elongation / desaturation pathways, the molecular repertoire of 18-, 20- and 22-carbon intermediates is quite large, so using [ 14 In vivo labeling experiments with C]-acetate revealed clear precursor-product kinetics of the predicted intermediates. Additionally, exogenous radiolabeled intermediates provided to the organism are converted to final PUFA products.
[0330] 2-day-old cultures were initially supplemented with a single pulse of [1- 14 C] Acetate. Cell samples are then harvested by centri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com