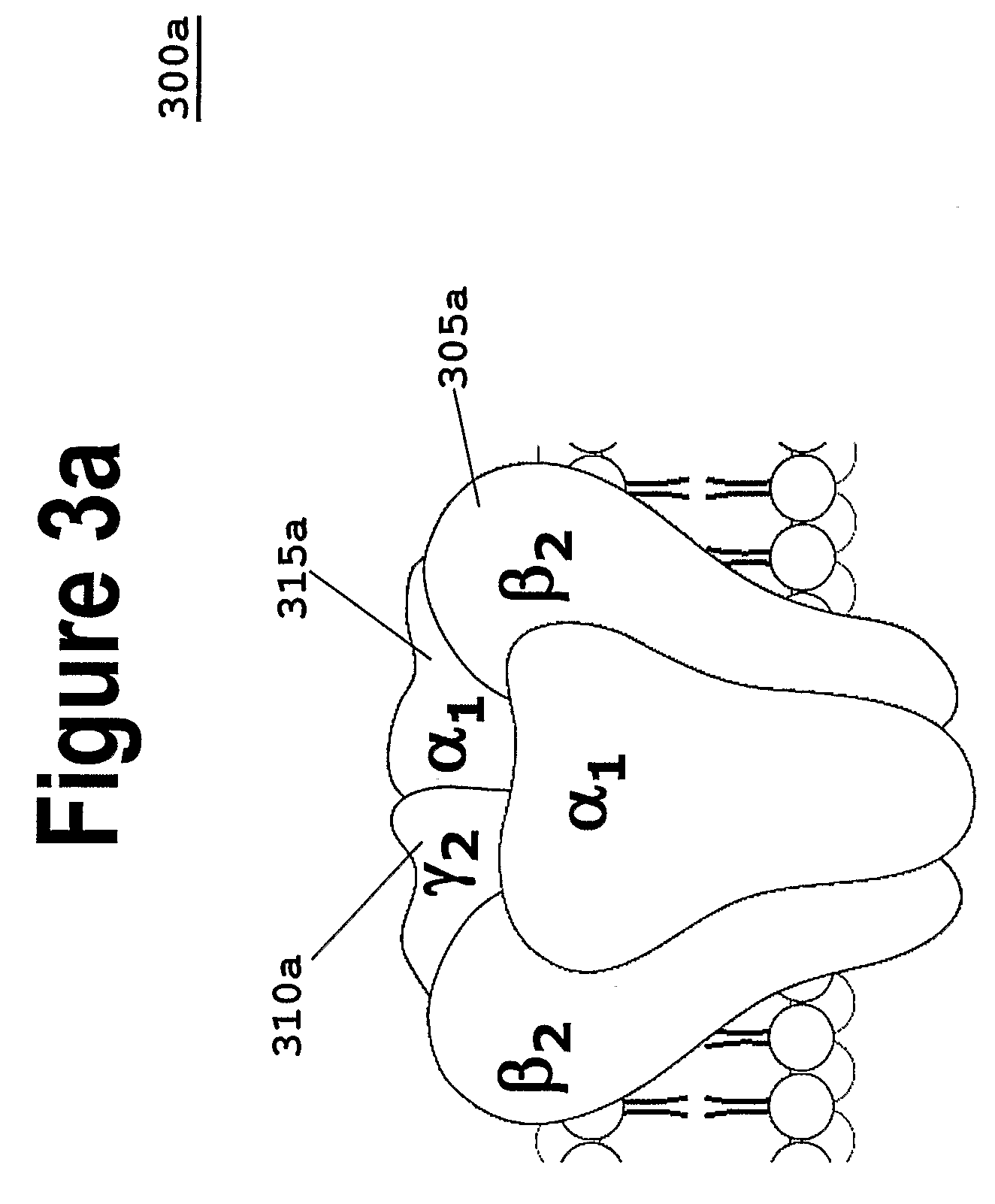
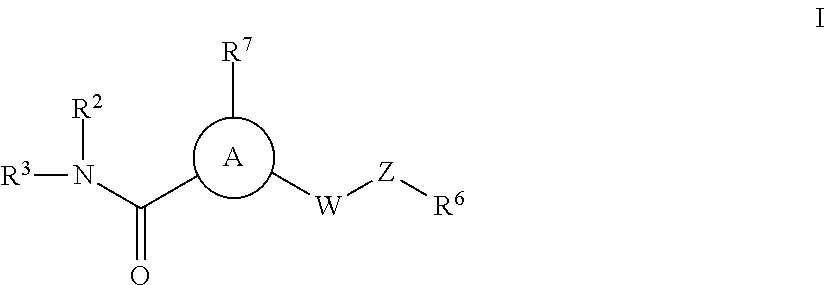
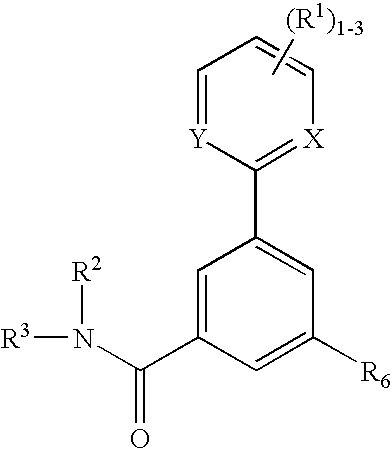
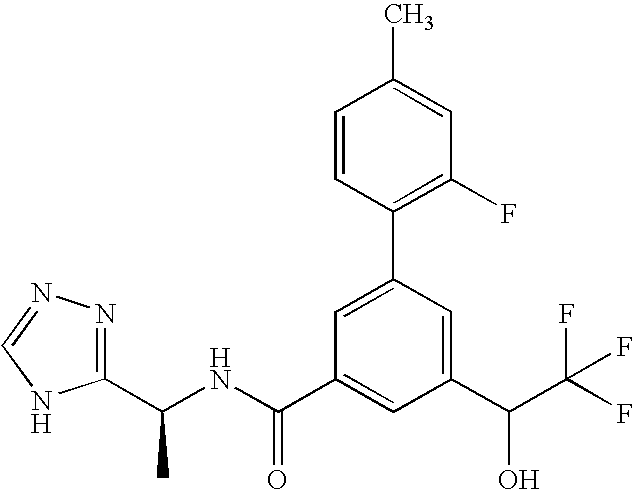
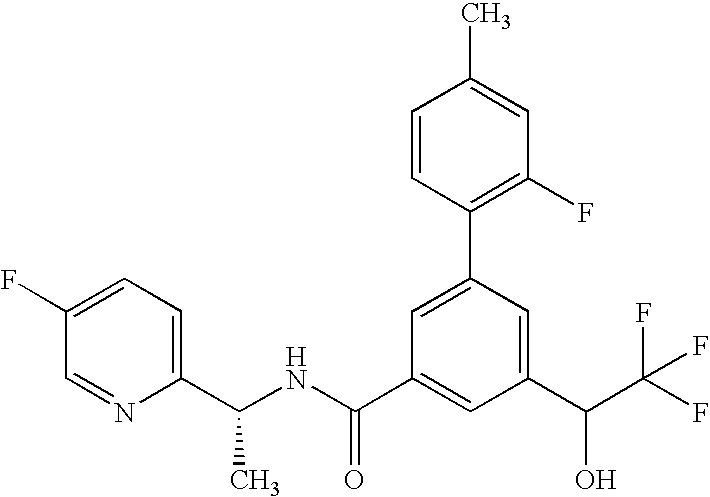
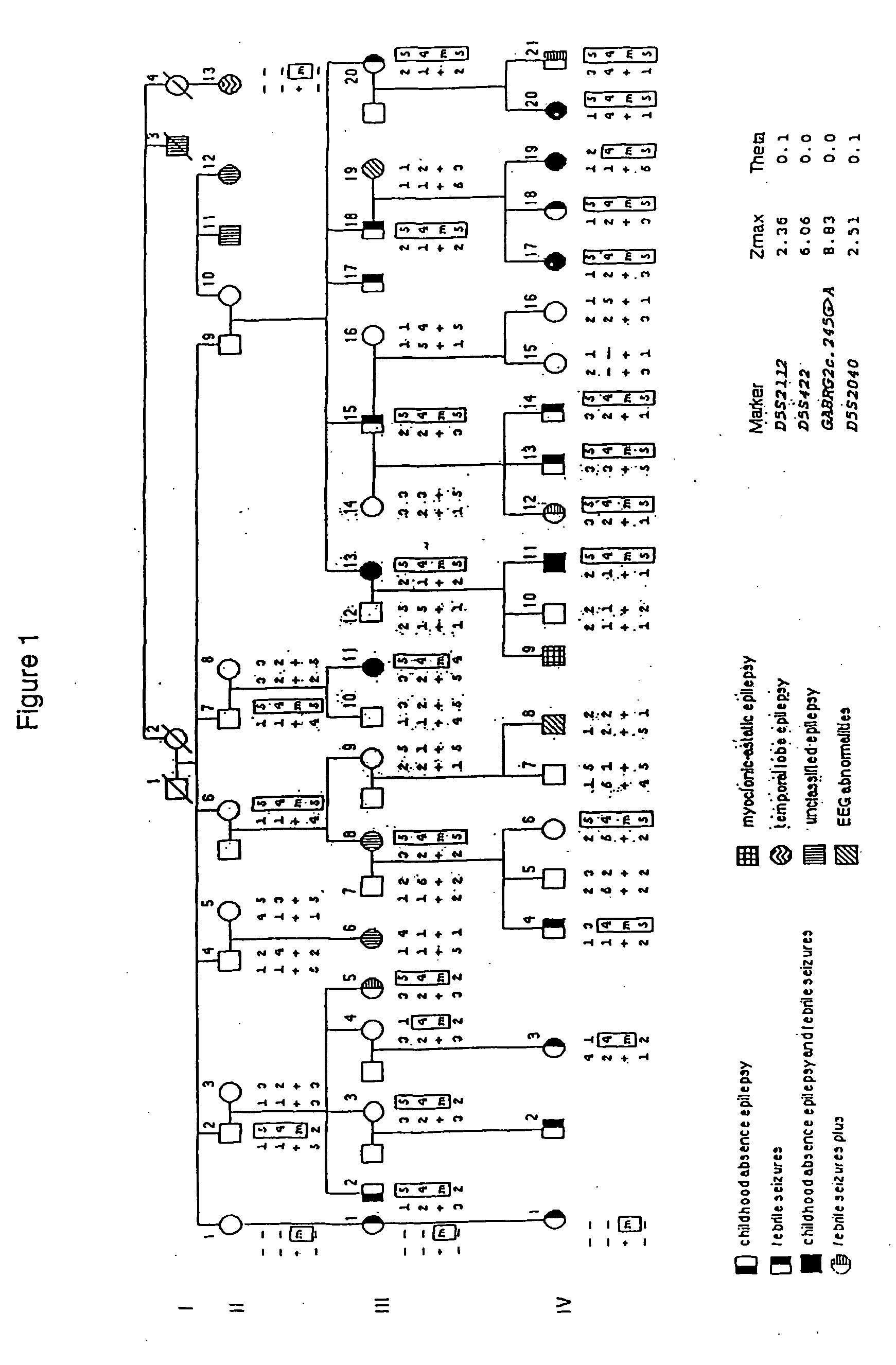
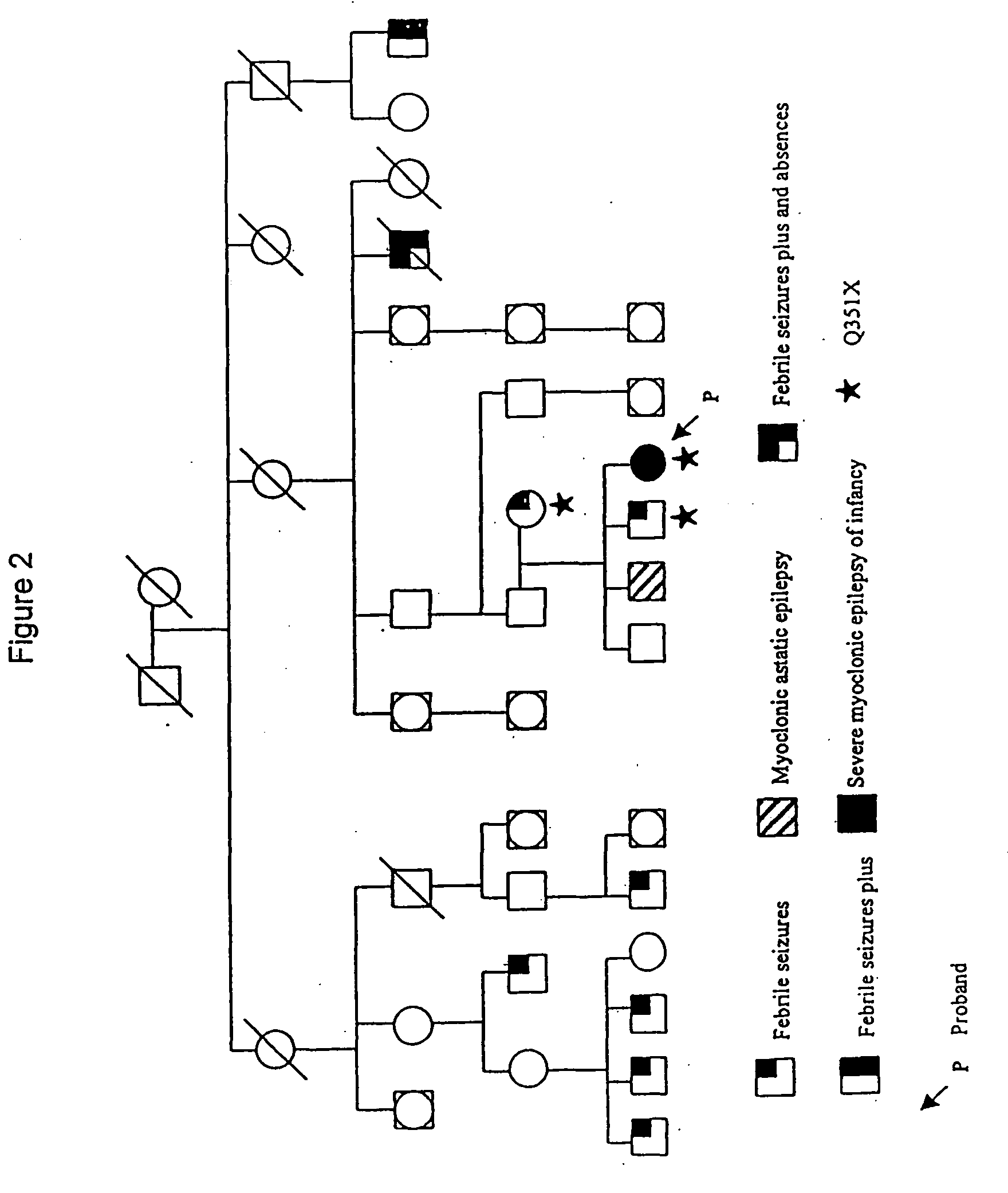
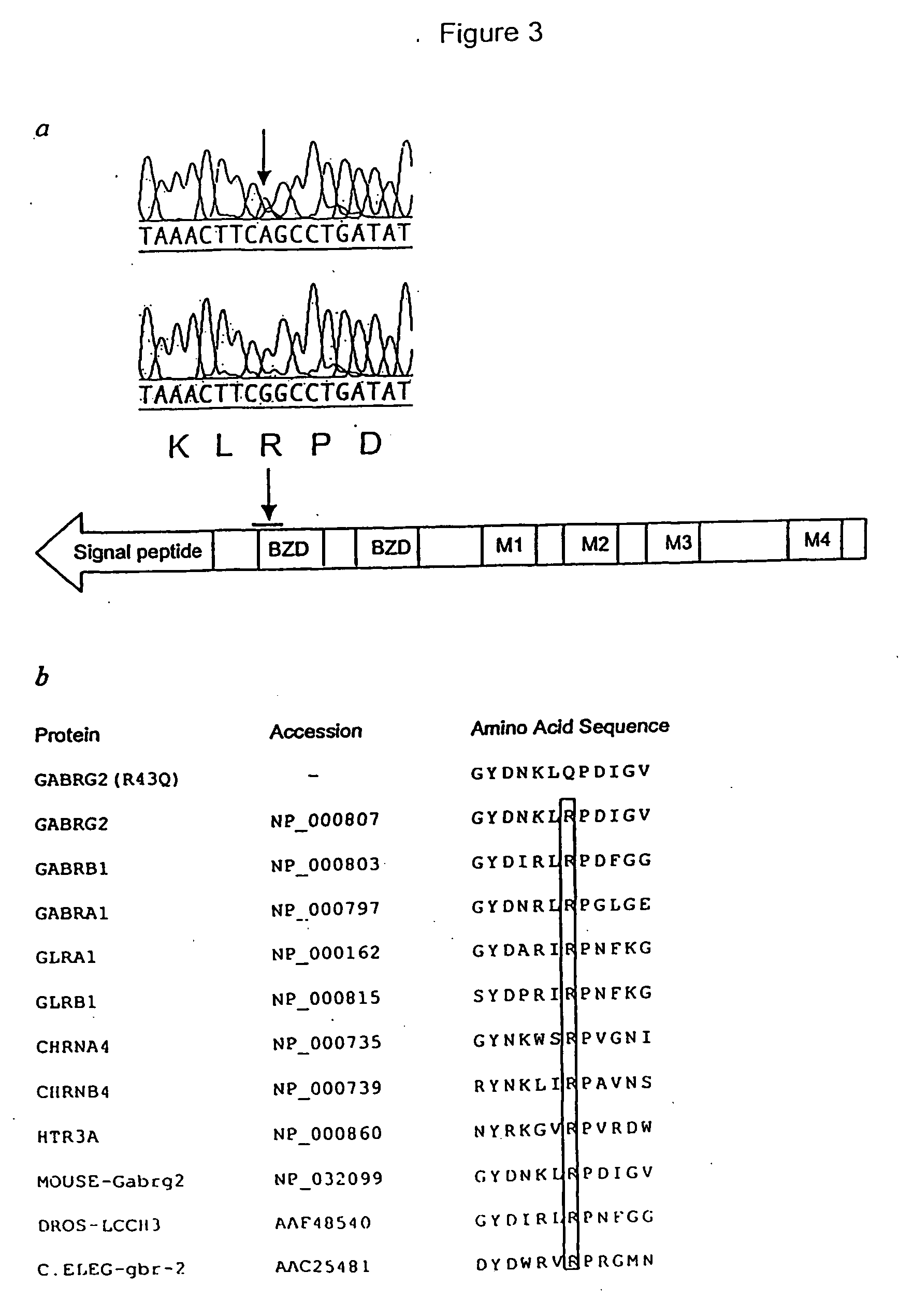
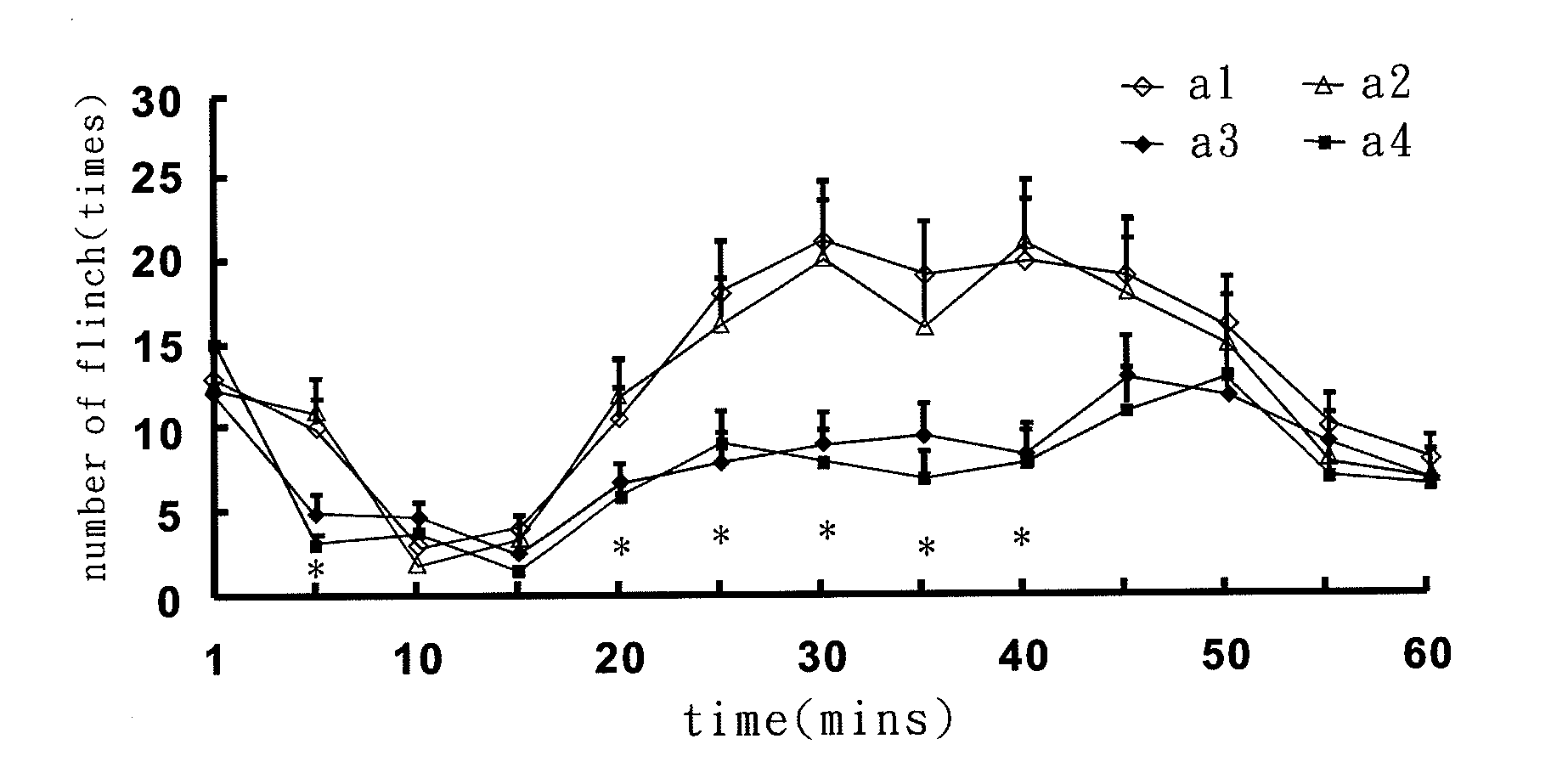
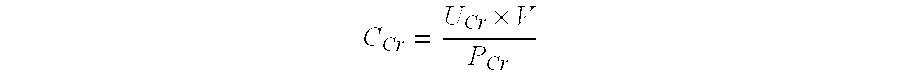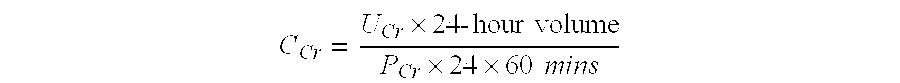Patents
Literature
52 results about "Receptor subunit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
IL3R.alpha. antibody conjugates and uses thereof
ActiveUS8163279B2Reduce in quantityReduce the numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellAntibody conjugate
The present invention provides antibodies that bind to the IL-3 receptor alpha subunit alpha (Il3Rα) chain, and compositions comprising such antibodies. The present invention provides methods for inhibiting or reducing an IL3Rα-expressing cell population, the methods comprising contacting a population of IL3Rα-expressing cells (e.g., cancer cells and / or cancer stem cells) with an antibody that binds to IL3Rα. The present invention also provides antibody conjugates comprising an antibody that binds to an IL3Rα chain linked to a cytotoxic agent or anticellular agent and compositions comprising such conjugates. The present invention also provides methods for preventing, treating and / or managing a disorder associated with IL3Rα-expressing cells (e.g., a hematological cancer), the methods comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an antibody that binds to IL3Rα.
Owner:STEMLINE THERAPEUTICS
Methods of and Compositions For the Prevention of Anxiety, Substance Abuse, and Dependence
InactiveUS20080207601A1Prevent addictionAvoid dependenceBiocideNervous disorderSubstance abuserDrug withdrawal symptoms
Compositions for reducing dependency and addiction to substances of abuse are provided. Chloride channels such as the GABAA receptors are altered under conditions of dependency and withdrawal such that the electrophysiological properties of the GABAA receptor containing neurons are altered thereby providing a pathophysiological condition resulting in symptoms of dependency and withdrawal such as anxiety. Specifically, under conditions of withdrawal the relative ratio of the a1 receptor subunit decreases relative to the a4 receptor subunit. Endogenous neurosteroid production is also associated with the molecular changes underlying the alterations of GABA-gated chloride channels. Compositions of at least two compounds including at least one inhibitor of neurosteroid production are useful for treating the pathophysiology of addiction, dependency and substance abuse withdrawal.
Owner:HYTHIAM
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in sepsis patients. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7, Beta-2-glycoprotein 1, Metalloproteinase inhibitor 2, Alpha-1 Antitrypsin, Leukocyte elastase, Serum Amyloid P Component, C-X-C motif chemokine 6, Immunoglobulin A, Immunoglobulin G subclass I, C-C motif chemokine 24, Neutrophil collagenase, Cathepsin D, C-X-C motif chemokine 13, Involucrin, Interleukin-6 receptor subunit beta, Hepatocyte Growth Factor, CXCL-1, -2, -3, Immunoglobulin G subclass II, Metalloproteinase inhibitor 4, C-C motif chemokine 18, Matrilysin, C-X-C motif chemokine 11, and Antileukoproteinase as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker assays of renal injury in the sepsis patient.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
P2x3, receptor antagonists for treatment of pain
The subject invention relates to novel P2X3 receptor antagonists that play a critical role in treating disease states associated with pain, in particular peripheral pain, inflammatory pain, or tissue injury pain that can be treated using a P2X3 receptor subunit modulator.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
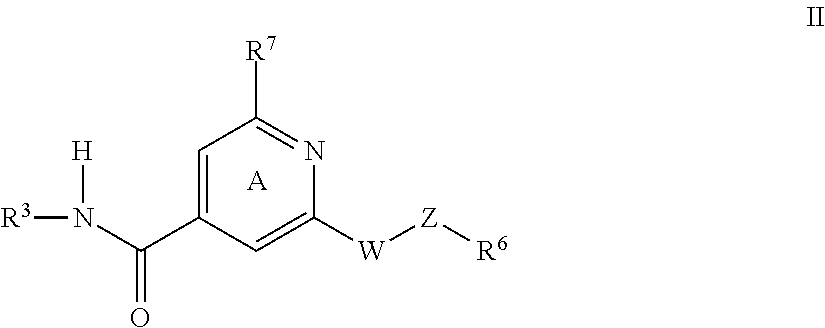
Interleukin-2 derivative
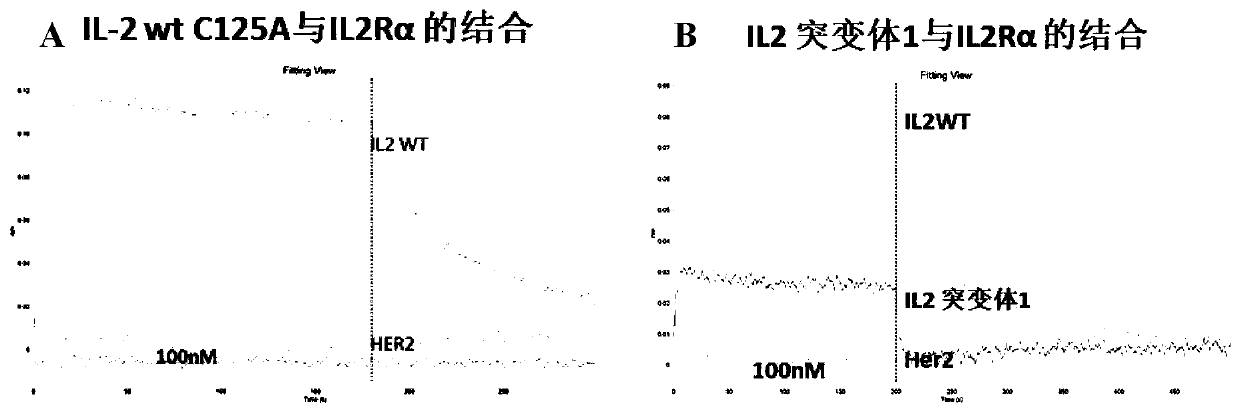
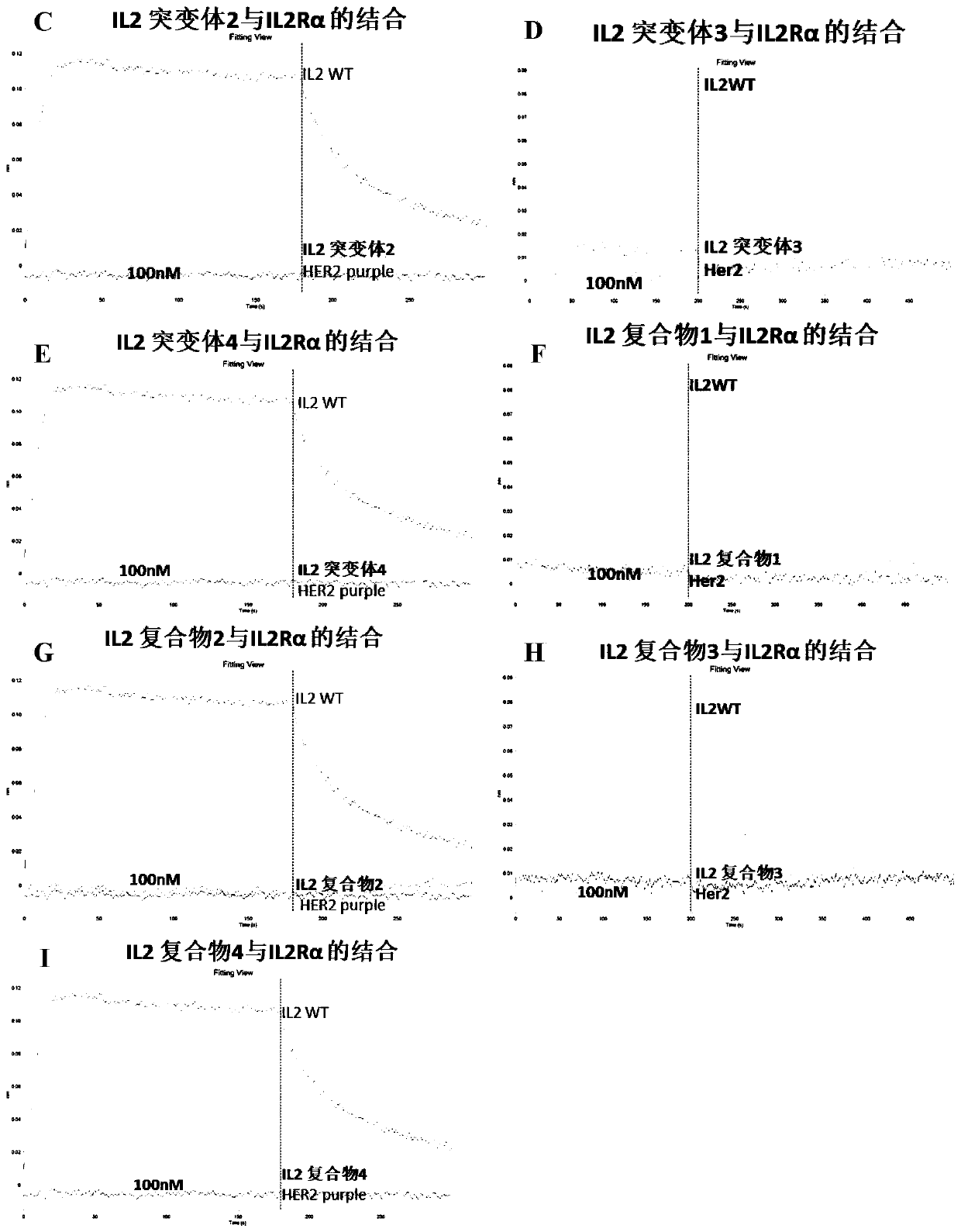
ActiveCN111018961AAvoid binding structuresReduce or eliminate toxic side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDisulfide bondingReceptor subunit
The invention discloses an IL-2 derivative. At least one cysteine residue is introduced on the basis of wild type IL-2, the binding plane of the IL-2 derivative and an alpha receptor subunit is partially or completely blocked, and meanwhile, the affinity to a beta and gamma receptor subunit compound is basically reserved. The invention also discloses the compound. The compound comprises: the IL-2derivative, wherein a third cysteine residue is introduced into the IL-2 derivative on the basis of wild type IL-2; and a blocking module, wherein a fourth cysteine residue is arranged on or introduced to the blocking module. The third cysteine residue on the IL-2 derivative and the fourth cysteine residue on the blocking module form an intermolecular disulfide bond in order to form the IL-2 derivative and blocking module compound, so the binding plane of the IL-2 derivative and the alpha receptor subunit is partially blocked or completely blocked, and the affinity to the beta and gamma receptor subunit compound is substantially retained.
Owner:LETO LAB CO LTD
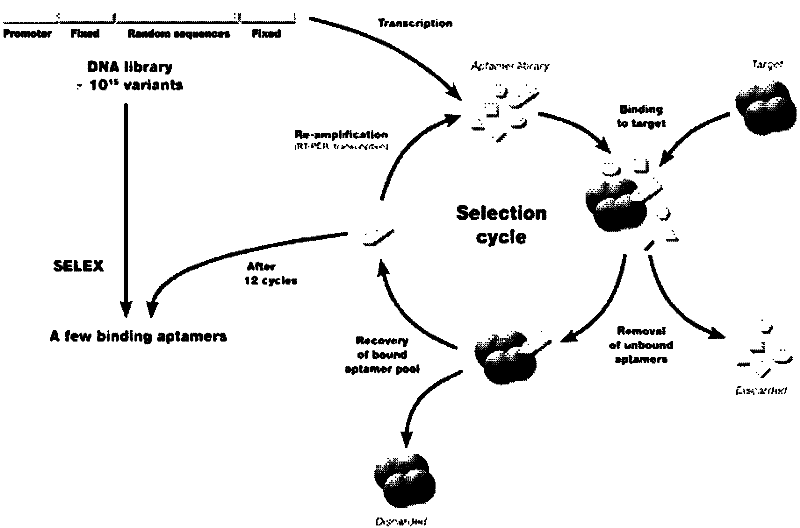
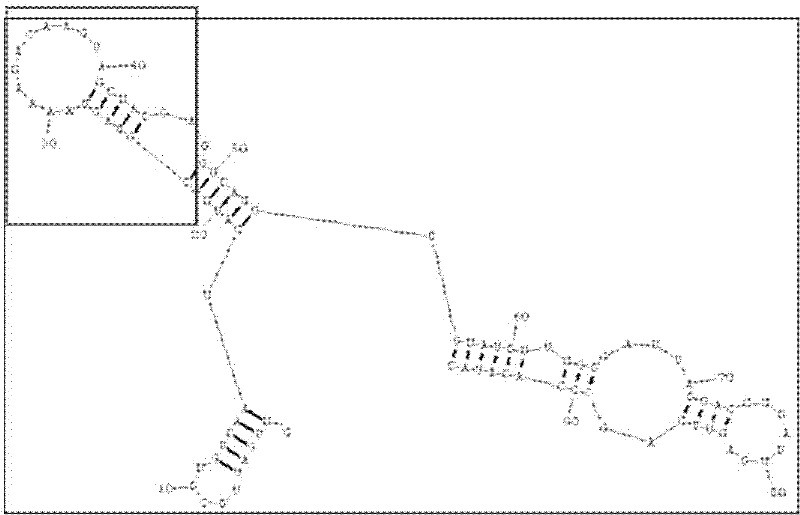
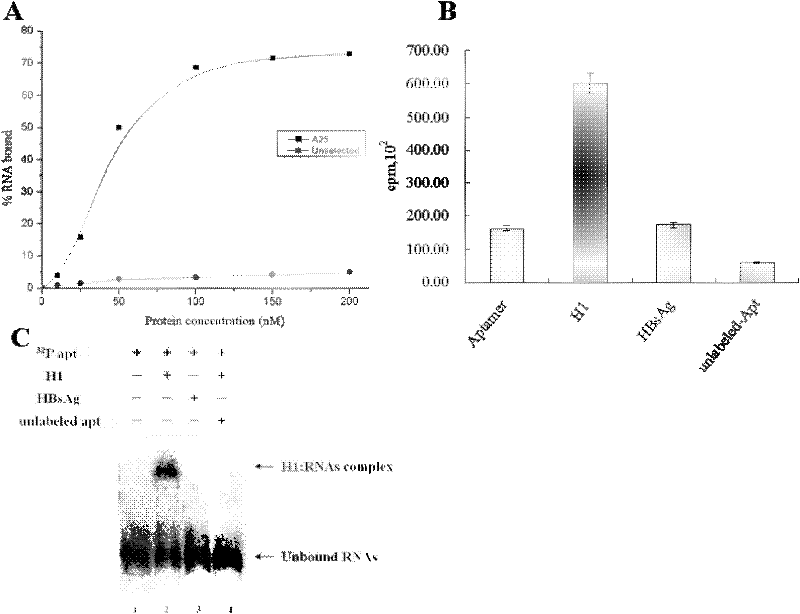
RNA aptamer of targeting hepatocyte and nucleotide sequence thereof
The invention discloses a RNA aptamer of a targeting hepatocyte and a nucleotide sequence thereof, and relates to the field of hepatic disease diagnosis and treatment. The RNA aptamer provides a novel specific and efficient molecule of a targeting hepatocyte for the field of hepatic disease diagnosis and treatment. In the invention, through using the new combinatorial chemical technology SELEX, and taking hepatic ASGPR (asialoglycoprotein receptor) large subunits as target proteins, an RNA aptamer which can specify the ASGPR is screened from a single-stranded RNA random library. The aptamer can be formed into a special stemloop structure in a random sequence region thereof, combines with big liver ASGP receptor subunit H1 protein with high specific affinity and can combine to liver cells in a targeted mode by high specific affinity. The RNA aptamer provides a new choice for developing a liver disease targeted diagnostic reagent and treatment drug.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
P2X3 receptor antagonists for treatment of pain
The subject invention relates to novel P2X3 receptor antagonists that play a critical role in treating disease states associated with pain, in particular peripheral pain, inflammatory pain, or tissue injury pain that can be treated using a P2X3 receptor subunit modulator.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
P2x3 receptor antagonists for treatment of pain
The subject invention relates to novel P2X3 receptor antagonists that play a critical role in treating disease states associated with pain, in particular peripheral pain, inflammatory pain, or tissue injury pain that can be treated using a P2X3 receptor subunit modulator.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
P2x3 receptor antagonists for treatment of pain
The subject invention relates to novel P2X3 receptor antagonists that play a critical role in treating disease states associated with pain, in particular peripheral pain, inflammatory pain, or tissue injury pain that can be treated using a P2X3 receptor subunit modulator.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Methods And Compositions Comprising A Viral Vector For Expression Of A Transgene And An Effector
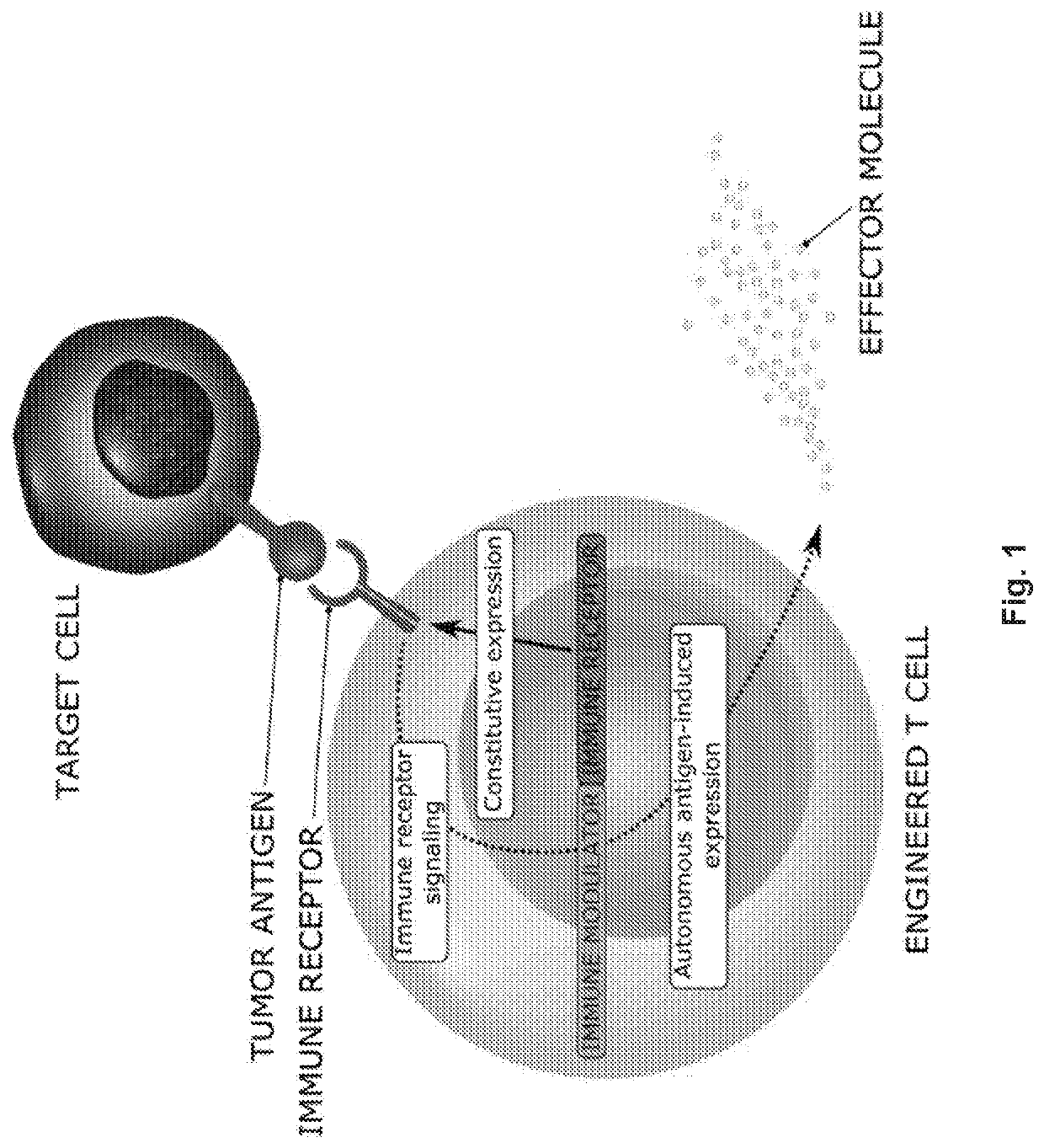
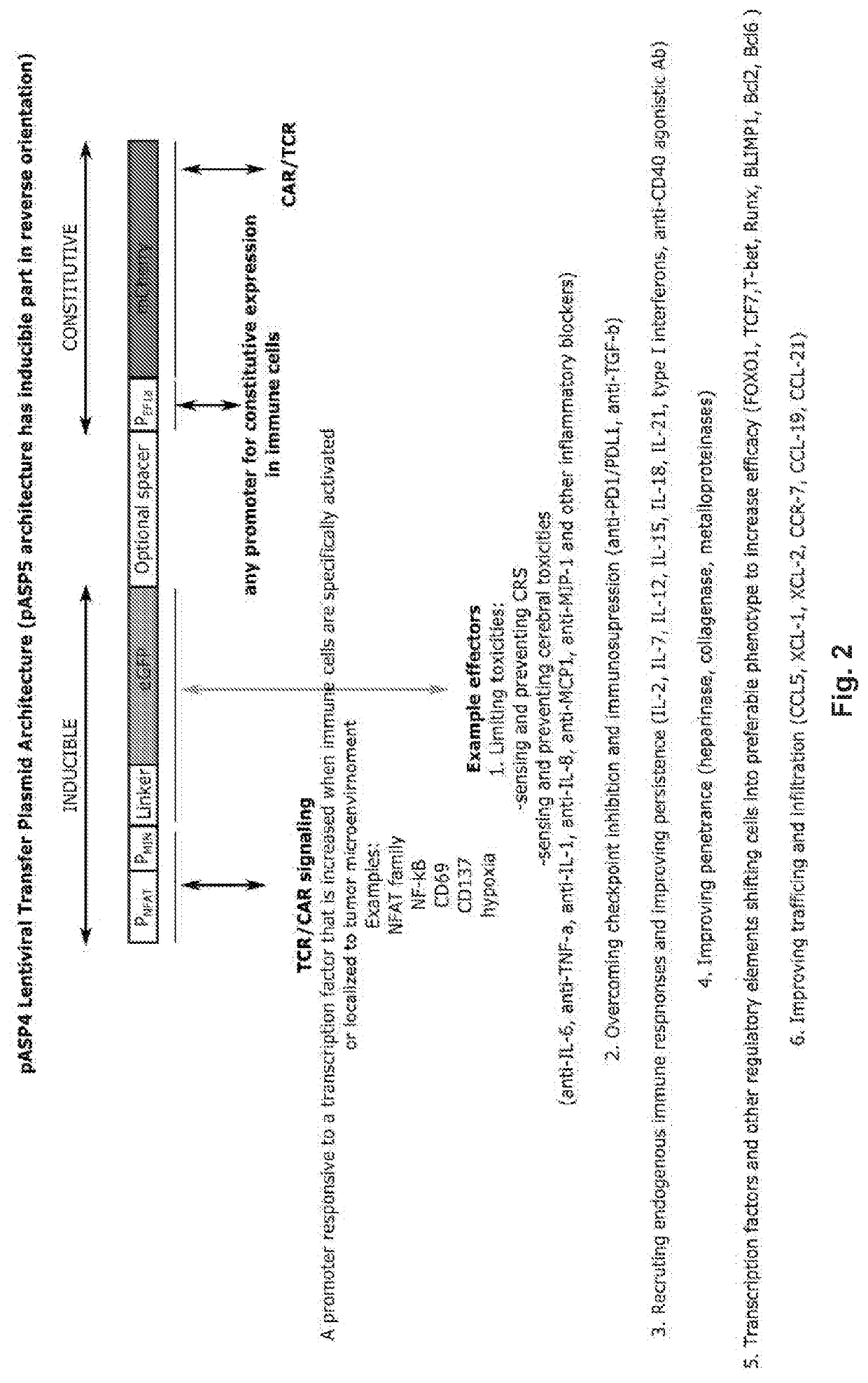
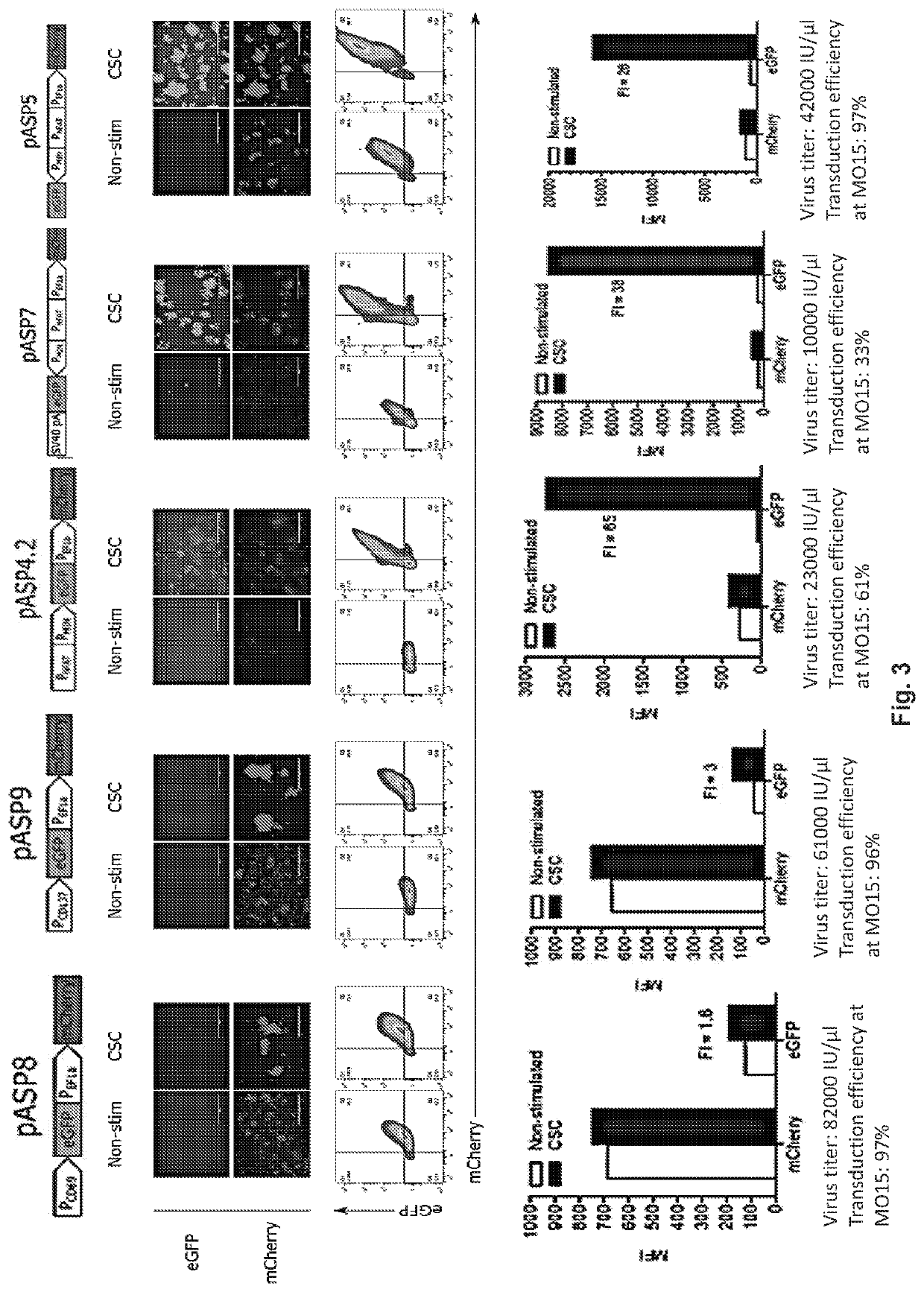
The present invention relates to compositions and methods comprising a single viral vector comprising both a first polynucleotide comprising a constitutive promoter operably linked to a nucleic acid encoding at least one transgene, wherein one of the at least one transgenes encodes a receptor or receptor subunit, a receptor fusion protein or a fluorescent marker; and a second polynucleotide comprising an inducible promoter operably linked to a nucleic acid encoding an effector. Also provided are engineered cells comprising the viral vector and methods for generating the engineered cells comprising the viral vector. Also provided is site-specific integration of the genetic element into the a gene locus by means of a CRISPR-related system. Further provided are methods for treating a patient having a disease, a disorder or condition associated with expression of an antigen, the method comprising administering to the patient an effective amount of a composition comprising the engineered cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
P2X3, receptor antagonists for treatment of pain
The subject invention relates to novel P2X3 receptor antagonists that play a critical role in treating disease states associated with pain, in particular peripheral pain, inflammatory pain, or tissue injury pain that can be treated using a P2X3 receptor subunit modulator.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
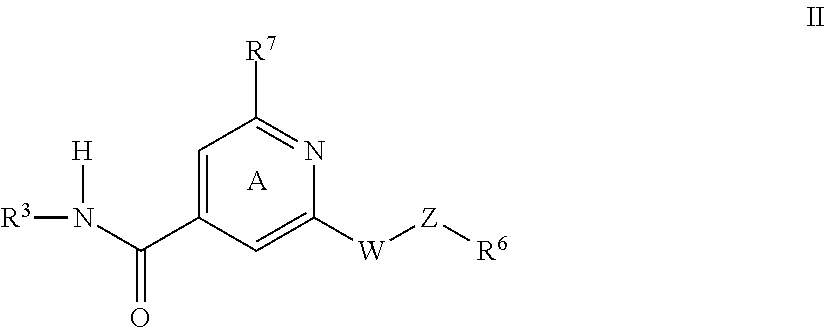
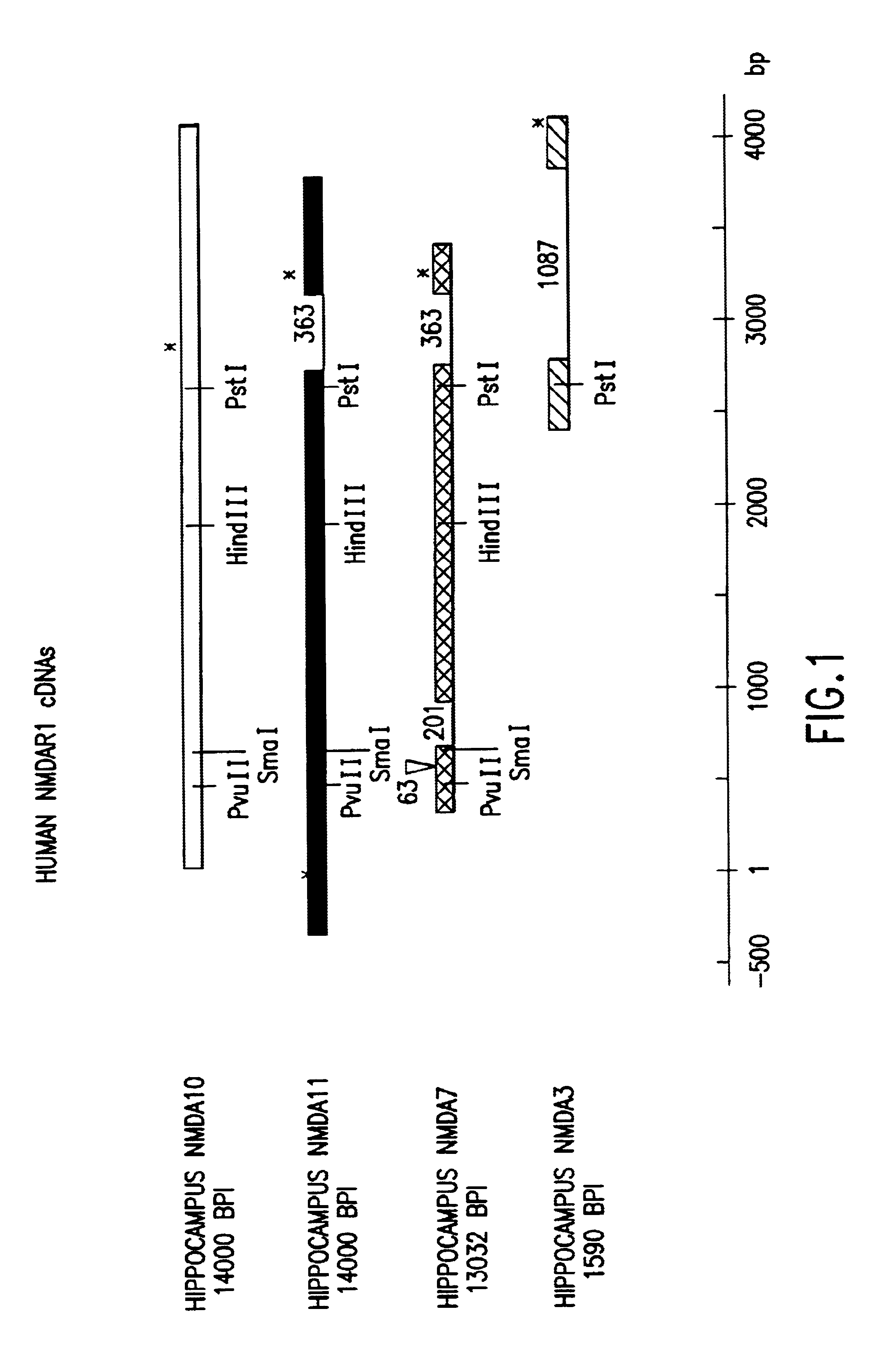
Nr3b nmda receptor subunit compositions and related methods
InactiveUS20050153287A1High expressionReduce functionTissue cultureFermentationNR1 NMDA receptorReceptor subunit
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Novel GABAB receptor DNA sequences
DNA encoding a novel human GABAB receptor subunit, HG20, as well as the protein encoded by the DNA, is provided. Also provided is DNA encoding a novel murine GABAB receptor subunit, GABABR1a, as well as the protein encoded by the DNA. Heterodimers of HG20 protein and GABABR1a protein that form a functional GABAB receptor are disclosed. Methods of identifying agonists and antagonists of the GABAB receptor are also provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +3
Cation conducting gabaa receptors and their use
This invention relates to cation conducting GABAA receptors, mutated GABAA receptor subunits, polynucleotide sequences encoding mutated subunits, expression vectors comprising the mutated subunits, host cells capable of expressing the mutated subunits, drug screening methods, and chemical substances identified by the drug screening methods of the invention.
Owner:JENSEN MARIANNE LERBECH +2
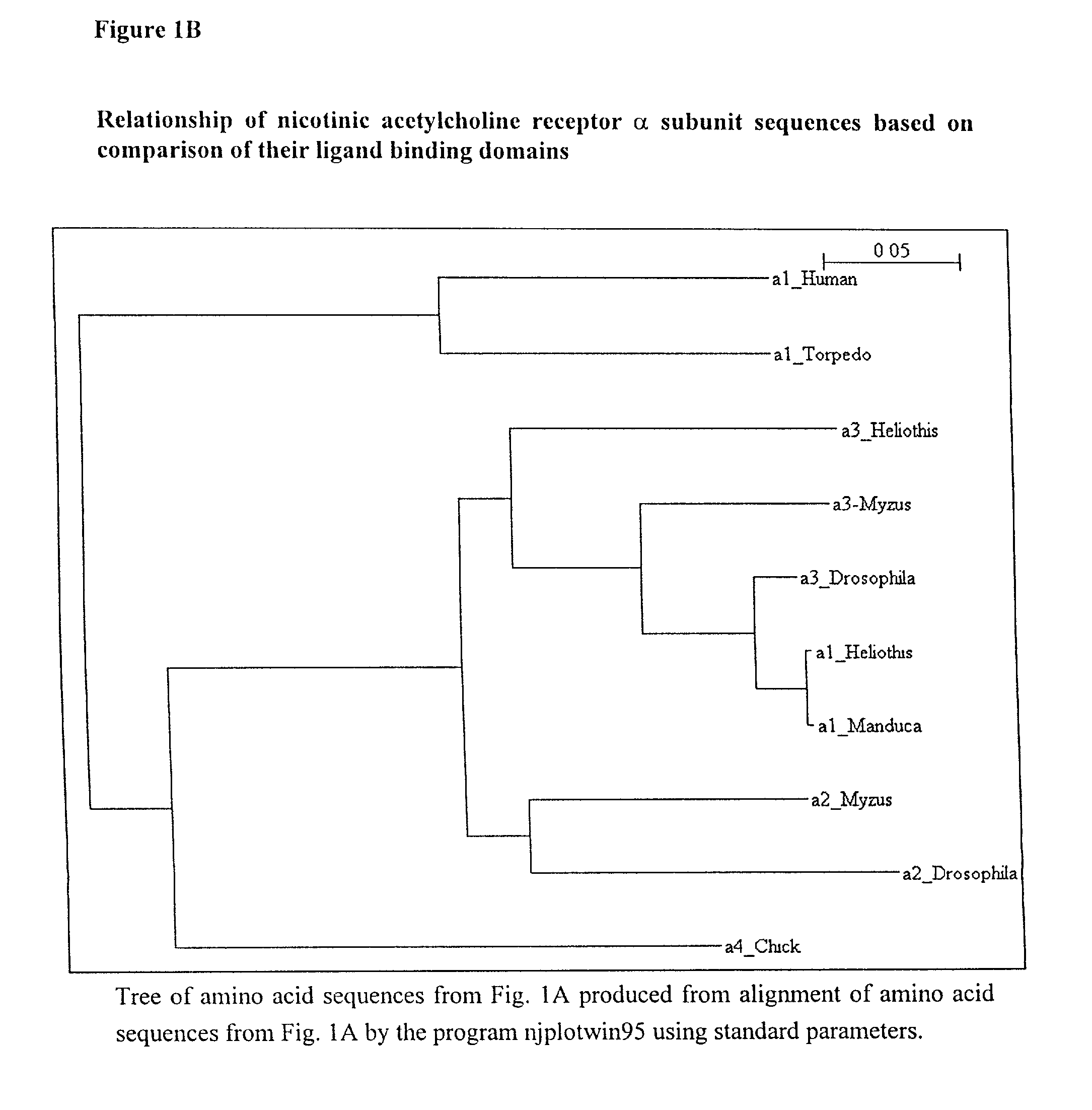
Genomic DNA fragments containing regulatory and coding sequence for the beta2-subunit of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and transgenic animals made using these fragments or mutated fragments
Several genes encoding subunits of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors have been cloned and regulatory elements involved in the transcription of the ∝:2 and ∝:7-subunit genes have been described. Yet, the detailed mechanisms governing the neuron-specific transcription and the spatio-temporal expression pattern of these genes remain largely uninvestigated. The β2-subunit is the most widely expressed neuronal nicotinic receptors subunit in the nervous system. We have studied the structural and regulatory properties of the 5′ sequence of this gene. A fragment of 1163 bp of upstream sequence is sufficient to drive the cell-specific transcription of a reporter gene in both transient transfection assays and in transgenic mice. Deletion analysis and site-directed mutagenesis of this promoter reveal two negative and one positive element. The positively acting sequence includes one functional E-box. One of the repressor elements is located in the transcribed region and is the NRSE / RE1 sequence already described in promoters of neuronal genes.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
P2x3, receptor antagonists for treatment of pain
The subject invention relates to novel P2X3 receptor antagonists that play a critical role in treating disease states associated with pain, in particular peripheral pain, inflammatory pain, or tissue injury pain that can be treated using a P2X3 receptor subunit modulator.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
P2X3 receptor antagonists for treatment of pain
The subject invention relates to novel P2X3 receptor antagonists that play a critical role in treating disease states associated with pain, in particular peripheral pain, inflammatory pain, or tissue injury pain that can be treated using a P2X3 receptor subunit modulator.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
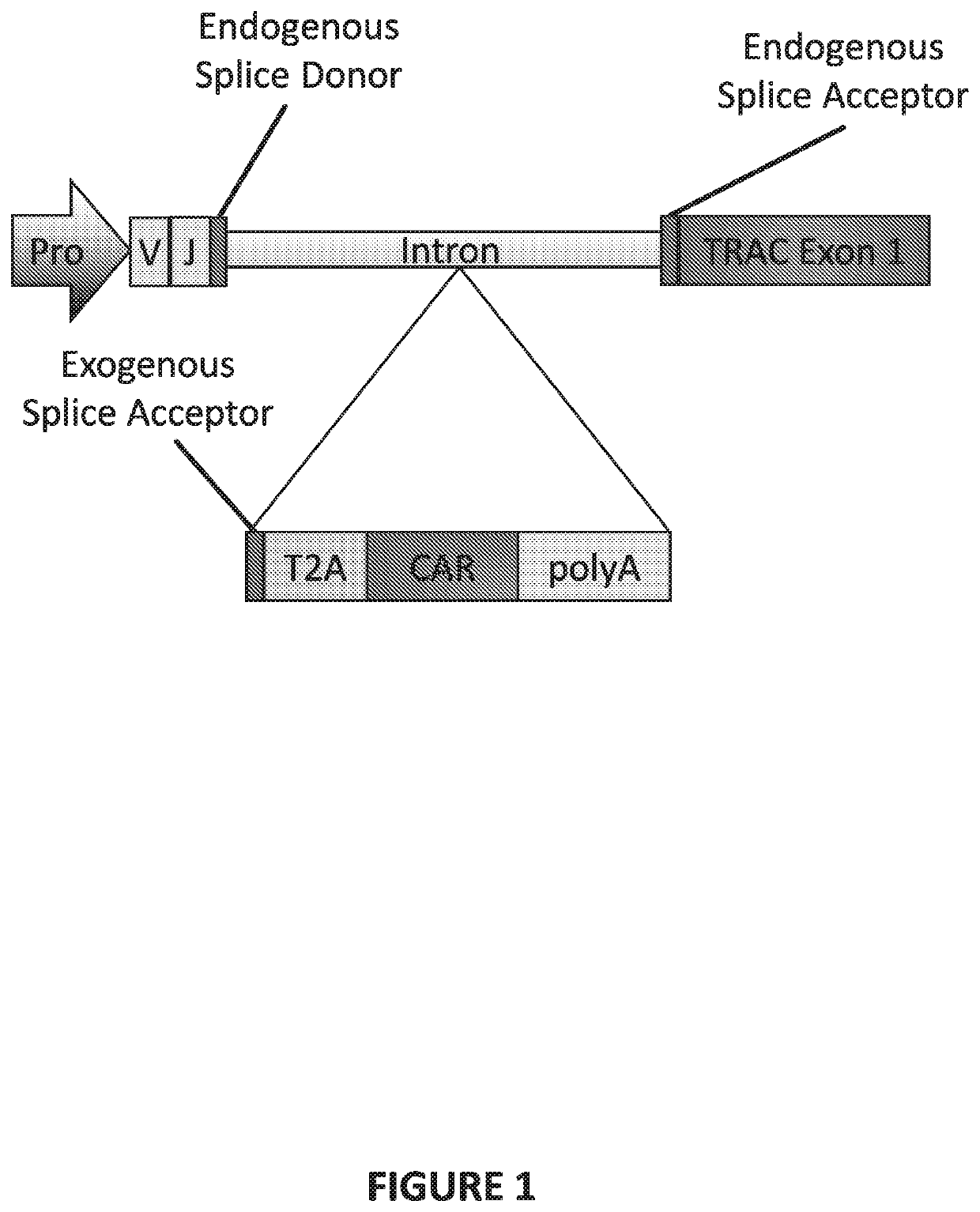
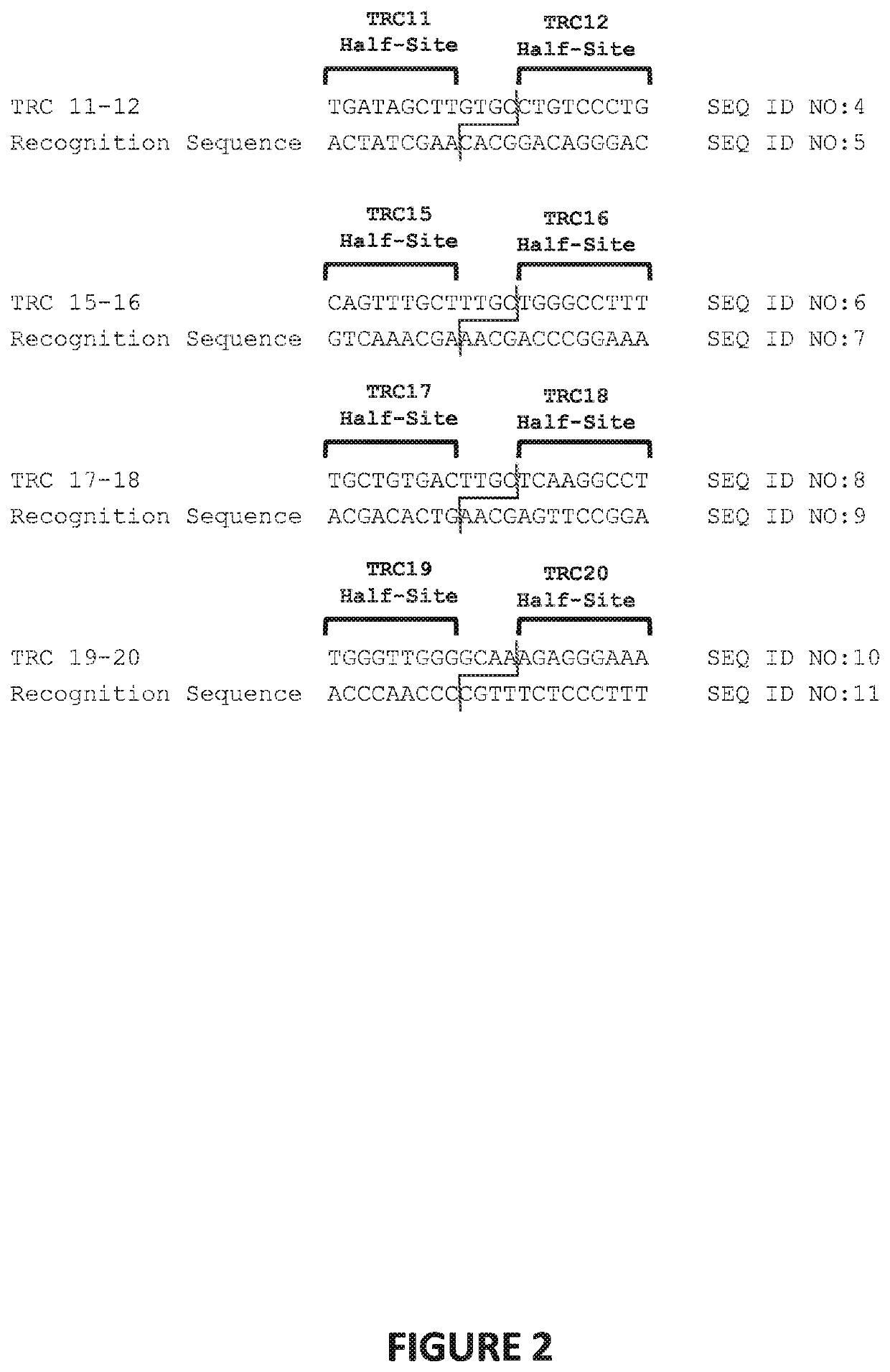
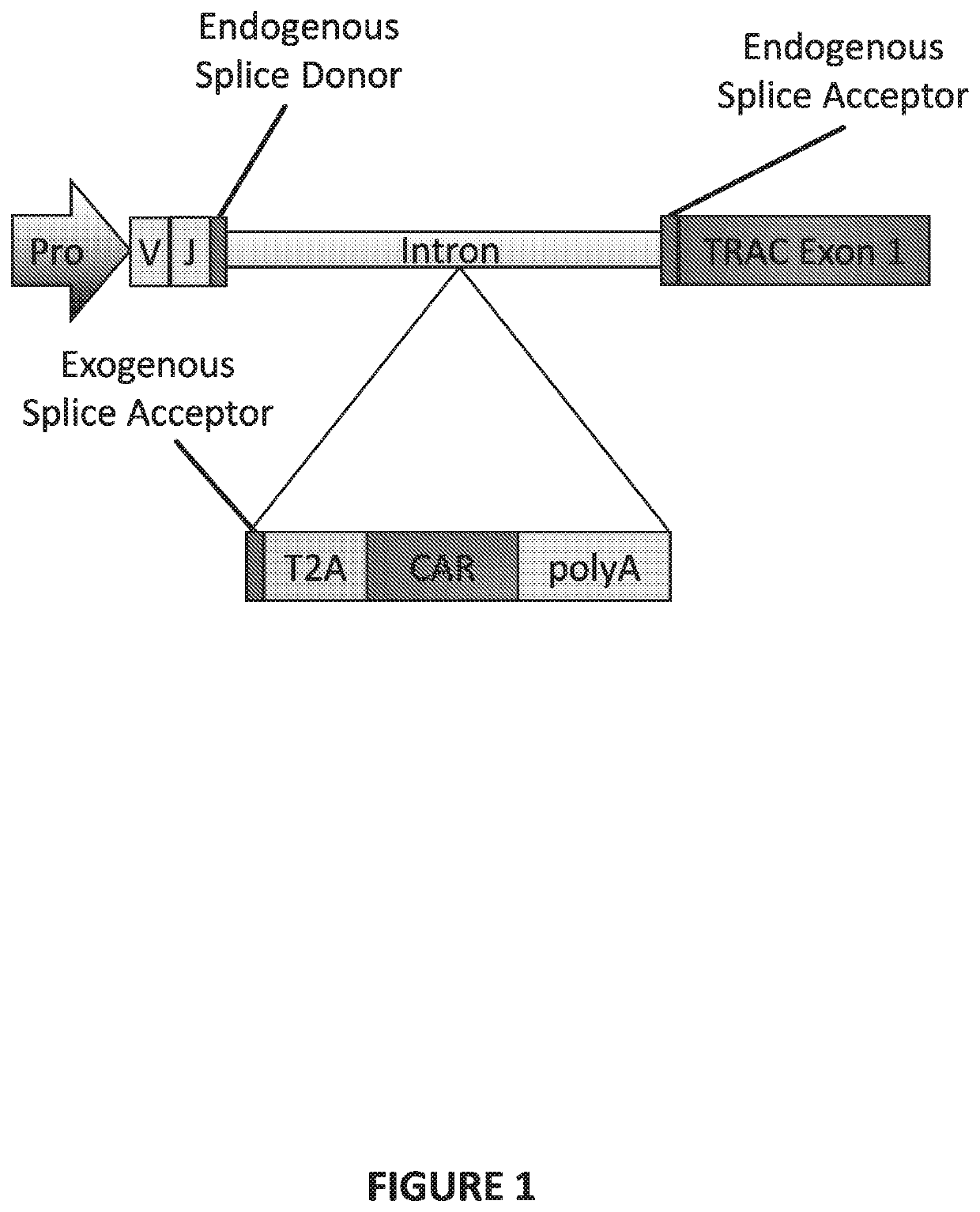
Genetically-modified t cells comprising a modified intron in the t cell receptor alpha gene
ActiveUS20200123516A1Reduces surface expressionDecrease cell surface expressionImmunoglobulin superfamilyHydrolasesT-Cell Receptor Alpha GeneAntigen receptors
The present invention provides a genetically-modified T cell comprising in its genome a modified human T cell receptor alpha gene. The modified T cell receptor alpha gene comprises an exogenous sequence of interest inserted into an intron within the T in cell receptor alpha gene that is positioned 5′ upstream of TRAC exon 1. The exogenous sequence of interest can comprise an exogenous splice acceptor site and / or a poly A signal, which disrupts expression of the T cell receptor alpha subunit. The sequence of interest can also include a coding sequence for a polypeptide, such as a chimeric antigen receptor. Additionally, the endogenous splice donor site and the endogenous splice acceptor site flanking the intron are unmodified and / or remain functional. The invention further provides compositions and methods for producing the genetically-modified cell, and populations of the cell, and methods for the treatment of a disease, such as cancer, using such cells.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
Genetically-modified T cells comprising a modified intron in the T cell receptor alpha gene
ActiveUS11053484B2Reduces surface expressionReduce expressionImmunoglobulin superfamilyHydrolasesAntigen receptorT-Cell Receptor Alpha Gene
The present invention provides a genetically-modified T cell comprising in its genome a modified human T cell receptor alpha gene. The modified T cell receptor alpha gene comprises an exogenous sequence of interest inserted into an intron within the T cell receptor alpha gene that is positioned 5′ upstream of TRAC exon 1. The exogenous sequence of interest can comprise an exogenous splice acceptor site and / or a poly A signal, which disrupts expression of the T cell receptor alpha subunit. The sequence of interest can also include a coding sequence for a polypeptide, such as a chimeric antigen receptor. Additionally, the endogenous splice donor site and the endogenous splice acceptor site flanking the intron are unmodified and / or remain functional. The invention further provides compositions and methods for producing the genetically-modified cell, and populations of the cell, and methods for the treatment of a disease, such as cancer, using such cells.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
Methods and compositions relating to chimeric nicotinic receptor subunits
A chimeric nAChR receptor subunit polypeptide having a substitution of at least about 15% of the native amino acid sequence of the subunit in the area of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain is provided, as well as polynucleotides encoding the polypeptide. Vectors, host cells, and related methods for evaluating compounds are also provided.
Owner:TARGACEPT INC +1
Gabaa receptor epsilon subunits
The present invention relates to a novel GABAA receptor ε subunit (GABRE) and an alternative transcript thereof (ET2). More specifically, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding human GABRE and ET2 receptor subunits. ET2 and GABRE polypeptides are also provided, as are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of ET2 and GABRE activities. Also provided are diagnostic methods for detecting aberrant GABRE and ET2 expression, as well as therapeutic methods for treating disorders involving ET2 and GABRE.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Mutation associated with epilepsy
InactiveUS20060088913A1Decreased functional densityInhibitory responseOrganic active ingredientsFungiReceptor subunitMammal
An isolated mammalian DNA molecule encoding a mutant γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor subunit, wherein a mutation event selected from the group consisting of point mutations, deletions, insertions and rearrangements has occurred and said mutation event disrupts the functioning of an assembled GABAA receptor, or an otherwise functional fragment or homologue thereof.
Owner:WALLACE ROBYN +4
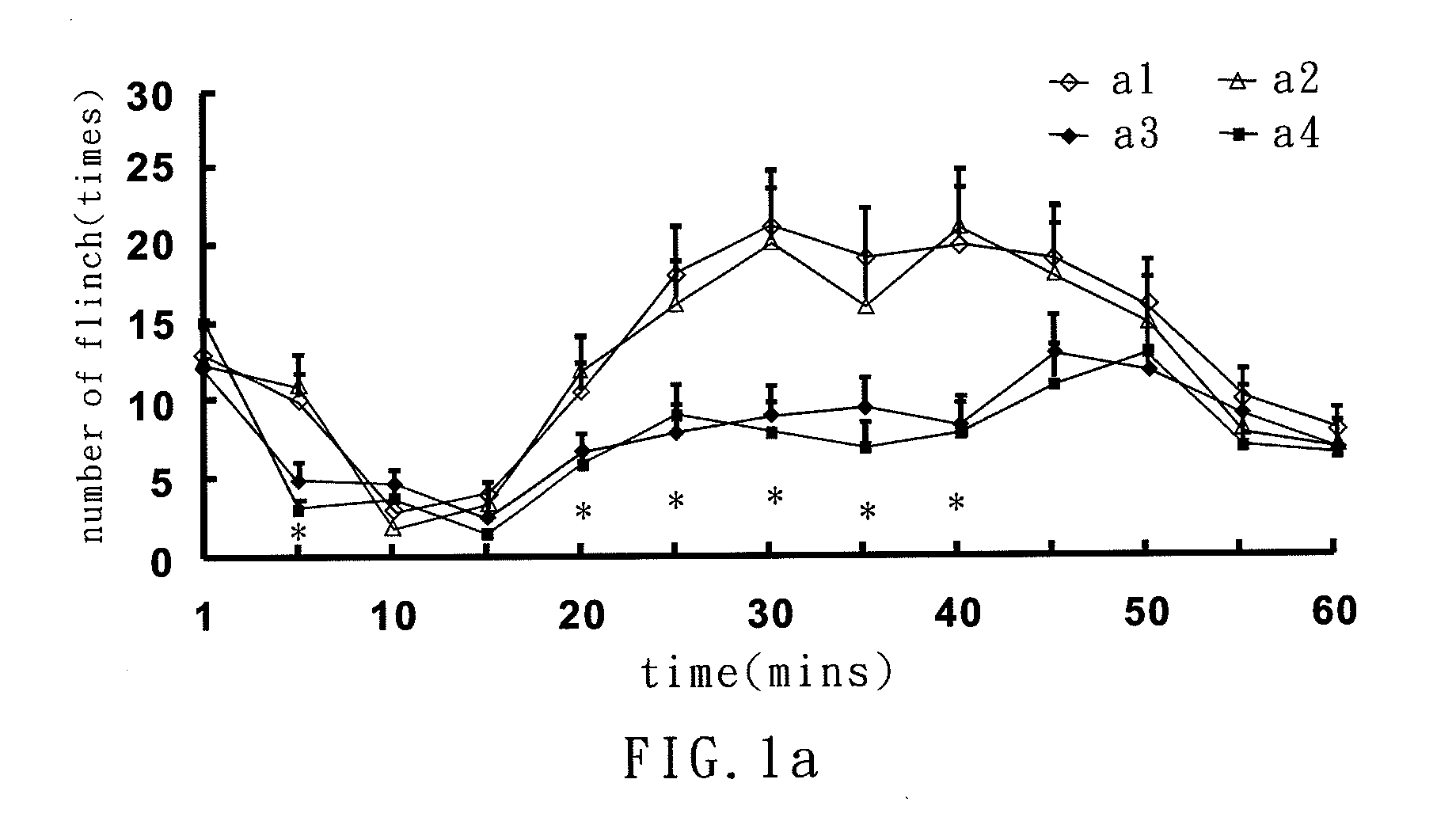
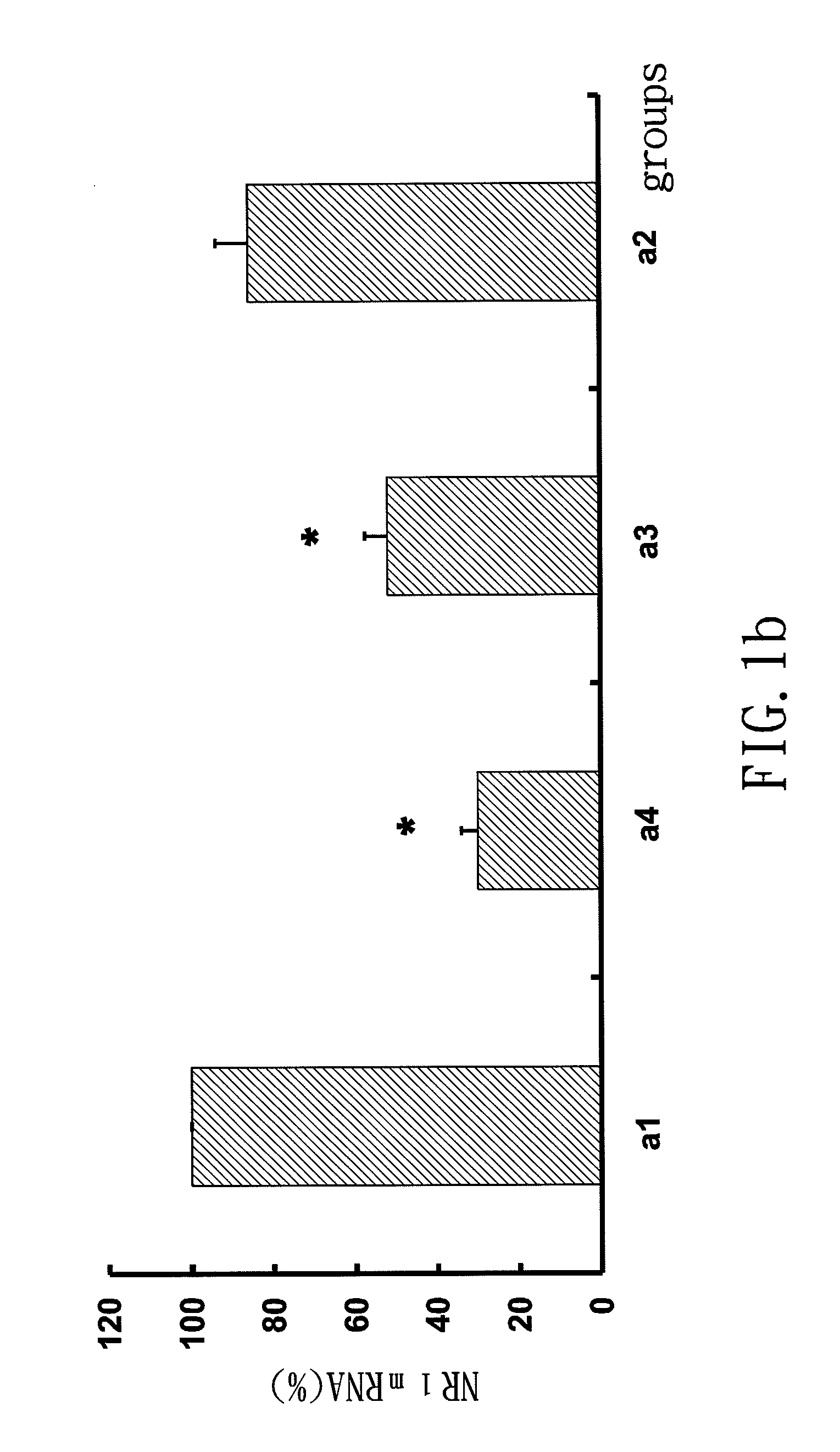
Small interfering RNA for gene knockdown of the subcutaneous n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor nr1 subunit, and it's application on pharmaceutics
ActiveUS20110263676A1Avoid effectHigh efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesBurning PainN-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
A small interfering RNA for gene knockdown of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit comprises 21 to 25 ribonucleic acids, which are homologous to the RNA sequence of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit. A method of using the small interfering RNA, applying the small interfering RNA on subcutaneous tissues temporary interfere with the genetic expression of the NMDA receptor NR1 subunit in hypoderm. A use of the small interfering RNA on pharmaceutics, applying the small interfering RNA manufacture into new analgesic drugs for moderating the inflammatory pain or intolerable chronic pain, especially on clinical chronic pain and burn pain patients. An analgesic drug for skin inflammatory pain comprising: the small interfering RNA and a siRNA acceptable vehicle.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Cation conducting GABAA receptors and their use
InactiveUS7282344B2High throughput drug screeningFungiNervous disorderReceptor subunitScreening method
This invention relates to cation conducting GABAA receptors, mutated GABAA receptor subunits, polynucleotide sequences encoding mutated subunits, expression vectors comprising the mutated subunits, host cells capable of expressing the mutated subunits, drug screening methods, and chemical substances identified by the drug screening methods of the invention.
Owner:SANIONA
Acetylcholine receptor subunits
InactiveUS7198942B2Easy to liftAltered propertyBacteriaFermentationAcetylcholine receptorAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to modified acetylcholine receptor subunits, to nucleic acids coding modified acetylchloine receptor subunits, and to methods for finding active ingredients for crop protection and active pharmaceutical ingredients for treating humans and / or animals.
Owner:BAYER AG
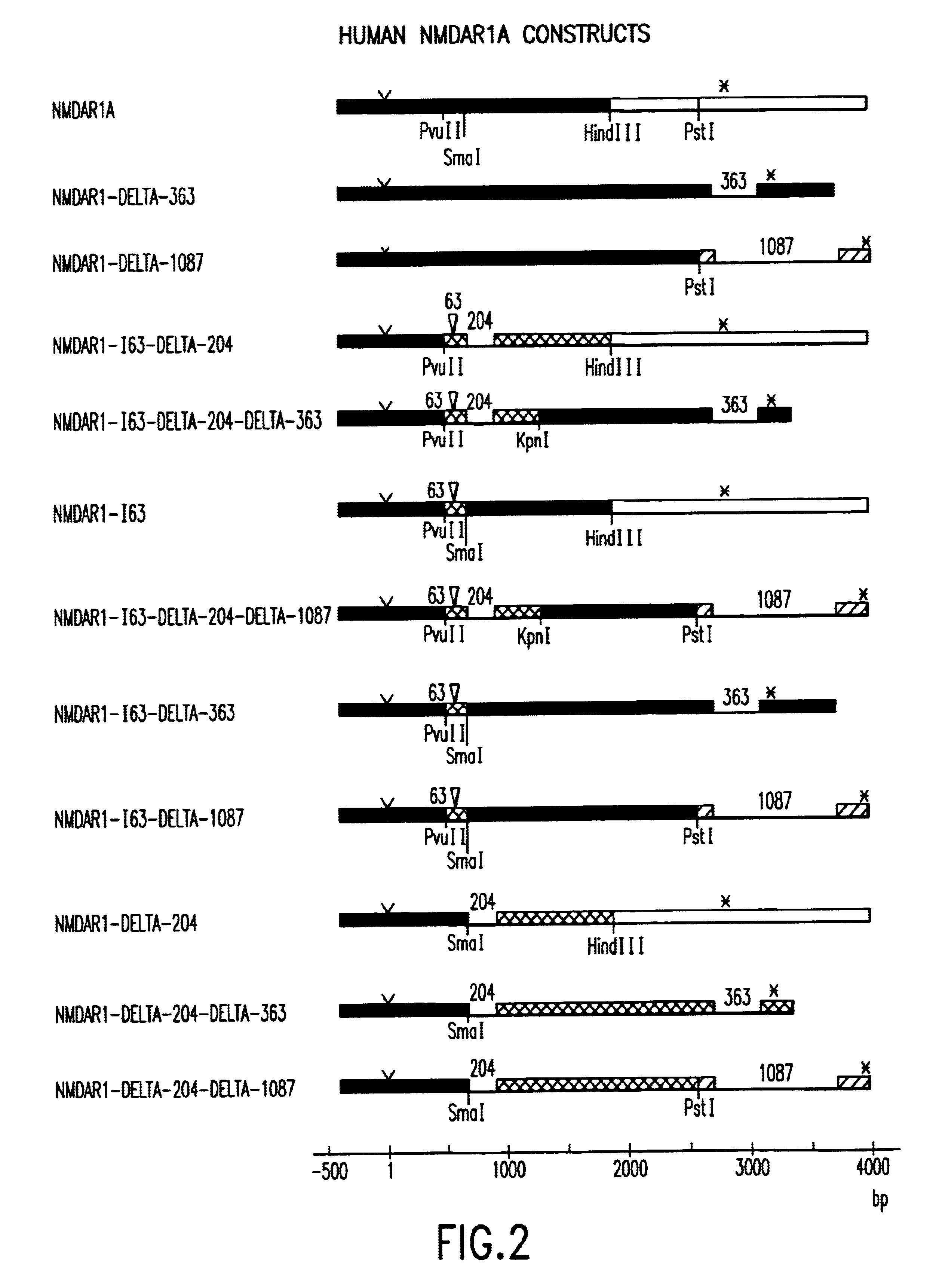
Human N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits nucleic acids encoding same and uses therefor
InactiveUS6956102B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganism based processesNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
Provided herein are nucleic acids encoding human NMDA receptor protein subunits and the proteins encoded thereby. In one aspect of the invention, the nucleic acids encode provides In a preferred embodiment, the invention nucleic acids encode MNDAR1, NMDAR2A, NMDAR2B, NMDAR2C and NMDAR2D subunits of human NMDA receptors. The disclosed nucleic acids are also useful as probes, thus enabling those skilled in the art, to identify and isolate related human receptor subunits. Functional glutamate receptors can be assembled, in accordance with the present invention, from a plurality of one type of NMDA receptor subunit protein (homomeric) or from a mixture of two or more types of subunit proteins (heteromeric). Also provided are methods for using the disclosed receptor subunits to identify and characterize compounds which affect the function of such receptors, e.g., agonists, antagonists, and modulators of glutamate receptor function. Methods for determining whether unknown protein(s) are functional as NMDA receptor subunits are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Composition and pharmacology of novel alpha6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
InactiveUS20090068642A1Useful pharmacological characteristicStably transfectedMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsReceptor subunitMuscarinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) comprising the α6 receptor subunit; nucleic acids, including vectors, comprising subunit incoding sequences; cells expressing the nAChRs of the invention; and methods of screening compounds are provided.
Owner:TARGACEPT INC
Subunit-selective nucleic acid inhibitors of glutamate receptors
Inhibitors of AMPA-type glutamate ion channels are useful as biochemical probes for structure-function studies and as drug candidates for a number of neurological disorders and diseases. Disclosed herein is the identification of an RNA inhibitor or aptamer by an in vitro evolution approach and characterization of its mechanism of inhibition on the sites of interaction by equilibrium binding and on the receptor channel-opening rate by a laser-pulse photolysis technique. The aptamer of the invention is a noncompetitive inhibitor of AMPA-type glutamate ion channels, one that selectively inhibits the GluA2Qflip AMPA receptor subunit without any effect on other AMPA receptor subunits or on kainate or NMDA receptors. Furthermore, the aptamer preferentially inhibits the closed-channel state of GluA2Qflip with a KI=1.5 μM or by ˜15-fold over the open-channel state. The potency and selectivity of this aptamer rival those of small molecule inhibitors. Together, these properties make the aptamers of the present invention promising water-soluble, highly potent, GluA2 subunit-selective drugs.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
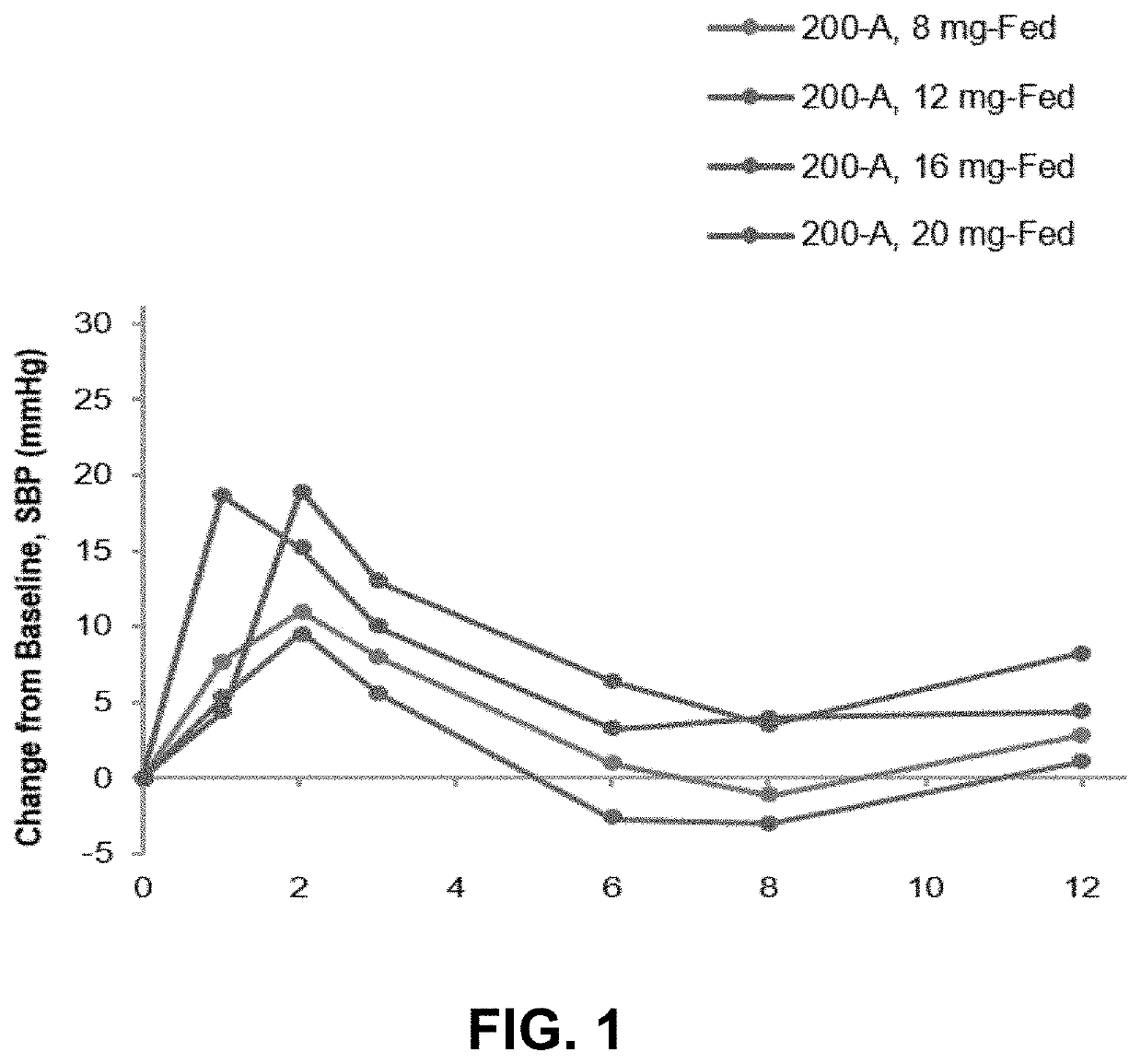
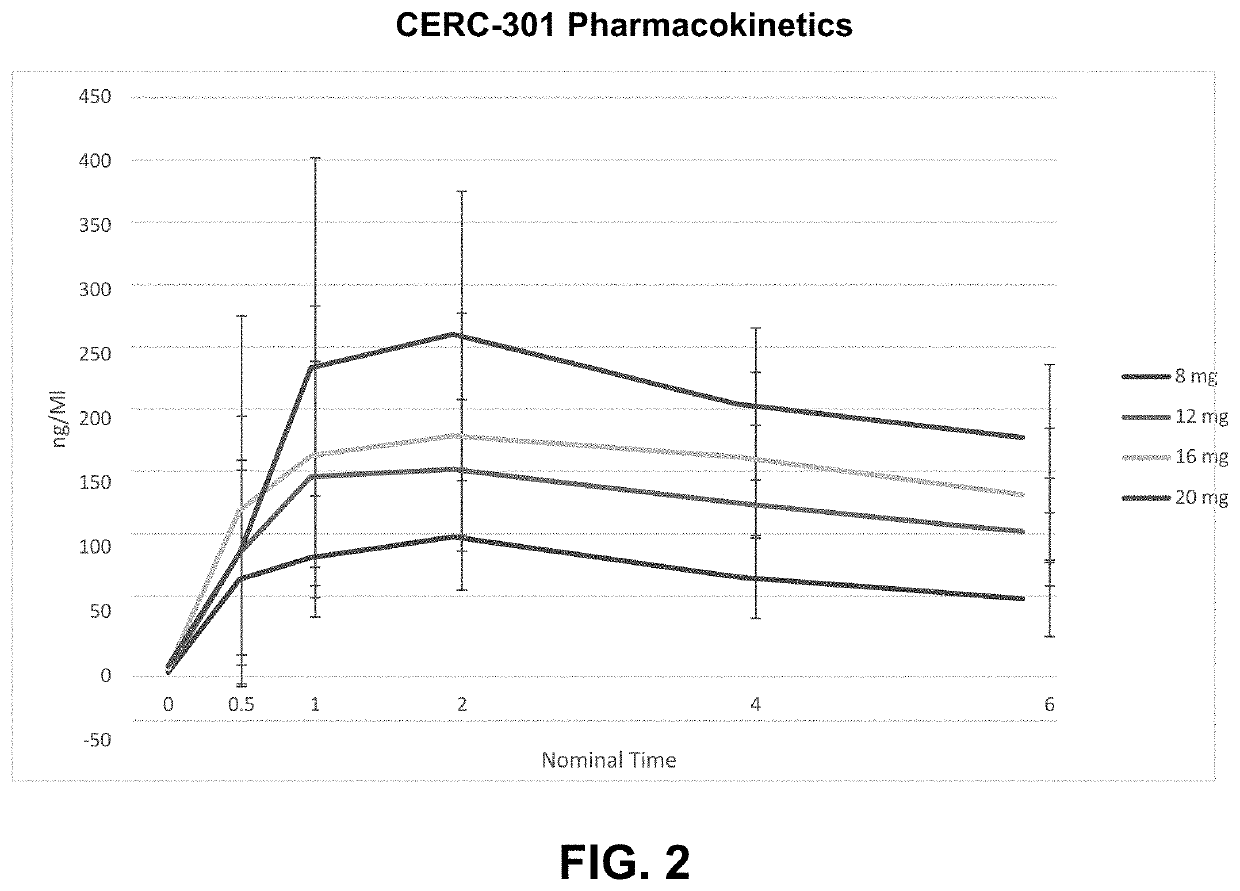
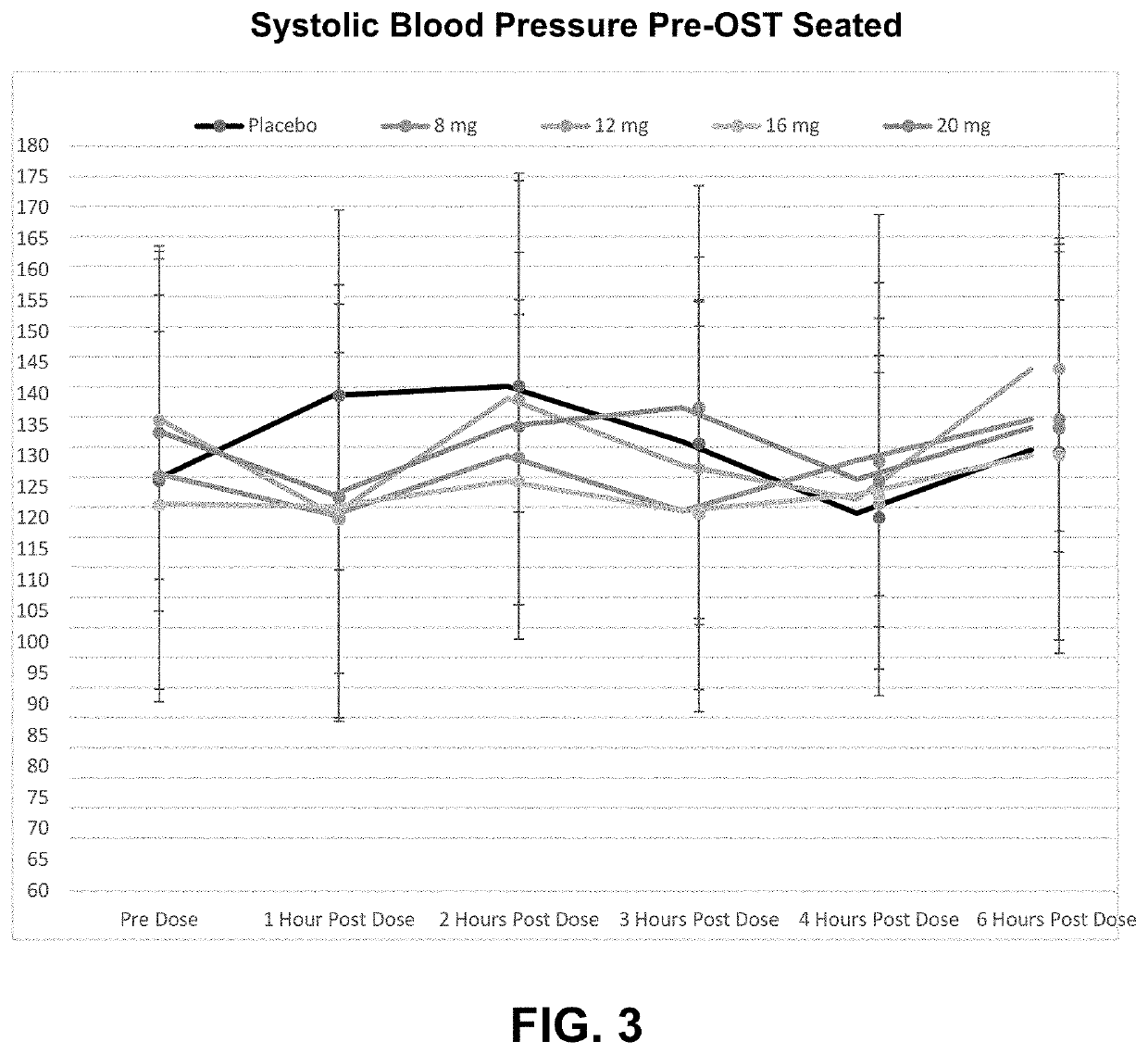
Methods for treating symptomatic orthostatic hypotension
PendingUS20220168301A1Long-term effective therapeutic treatmentImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryReceptor subunitAspartic acid
The present disclosure provides a method for treating symptomatic orthostatic hypotension using a potent selective antagonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B (NMDA-GluN2B or NR2B).
Owner:CERECOR INC
IL-2alpha receptor subunit binding compounds
Owner:MEDIKINE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com