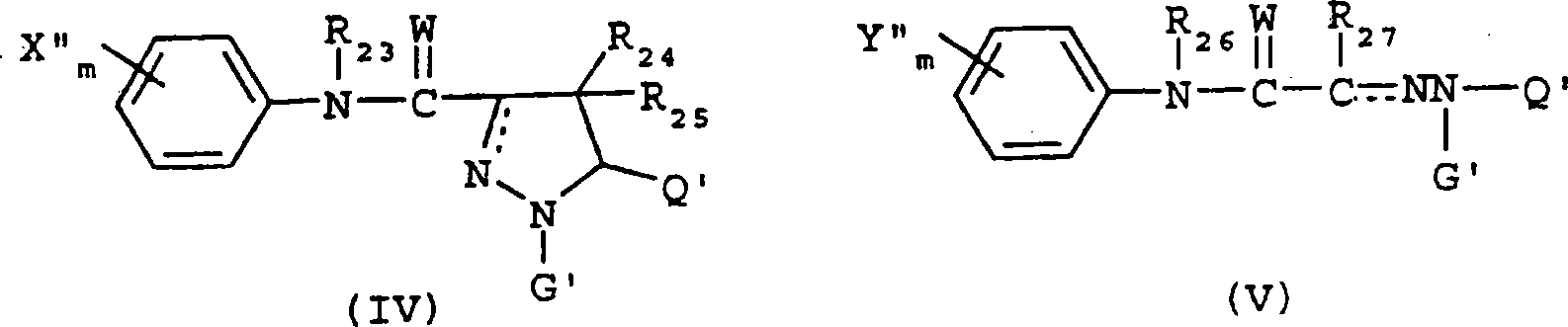Patents
Literature
140 results about "Acetylcholine receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An acetylcholine receptor (abbreviated AChR) is an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter.
Novel m3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20070179180A1BiocideOrganic chemistryMuscarinic receptor siteMuscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
Method of Improving Treatments in Rheumatic and Arthritic Diseases
Improved treatments of joint diseases, such as, e.g. osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, and pain, wherein a strontium-containing compound is administered alone or in combination with one or more second therapeutically and / or prophylactically active substances, selected from the group consisting of bisphosphonates, glucosamine, pallitative agents, analgesic agents, disease modifying anti-rheumatic compounds (DMARDs), selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), aromatase inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs), COX-2 inhibitors, COX-3 inhibitors, opioids, inhibitors / antagonists of IL-1, inhibitors / antagonists of TNF-alpha, inhibitors of matrix metallo-proteinases (MMPs), cathepsin K inhibitors, inhibitors / antagonists of RANK-ligand, statins, glucocorticoids, chondroitin sulphate, NMDA receptor antagonists, inhibitors of interleukin-I converting enzyme, Calcitonin gene related peptide antagonists, glycine antagonists, vanilloid receptor antagonists, inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthetase (iNOS), N-acetylcholine receptor agonists, neurokinin antagonists, neuroleptic agents, PAR2 receptor antagonists and anabolic growth factors acting on joint tissue components. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a strontium-containing compound and a second therapeutically and / or prophylactically active substance as defined above.
Owner:OSTEOLOGIX AS
M3muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
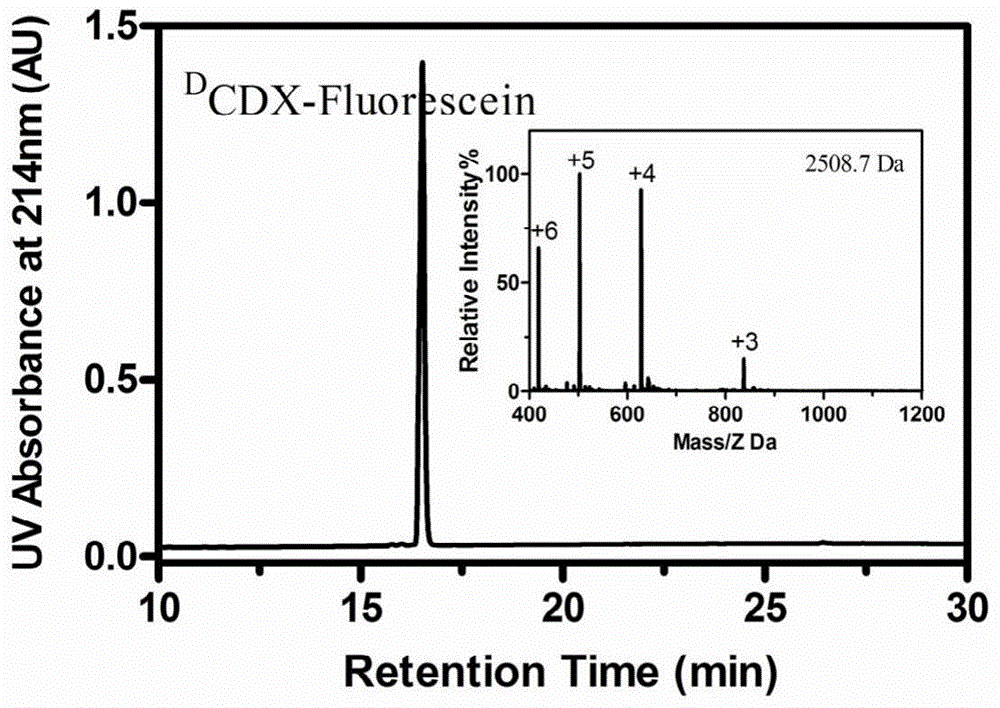
Acetylcholine receptor-mediated targeting D-configuration polypeptide and application thereof
ActiveCN104558117AHigh binding activityImprove stabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderDiseaseIn vivo
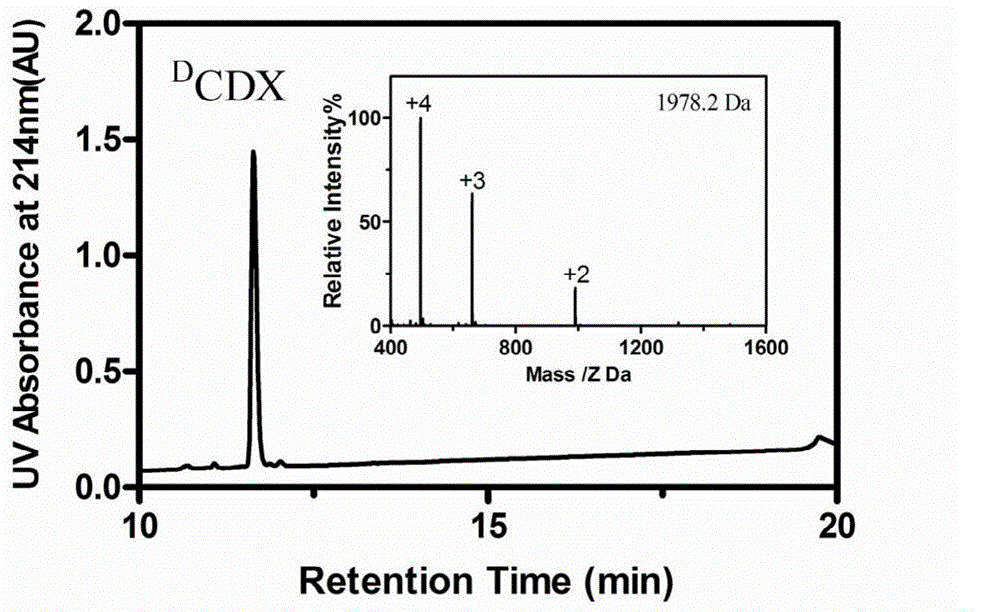
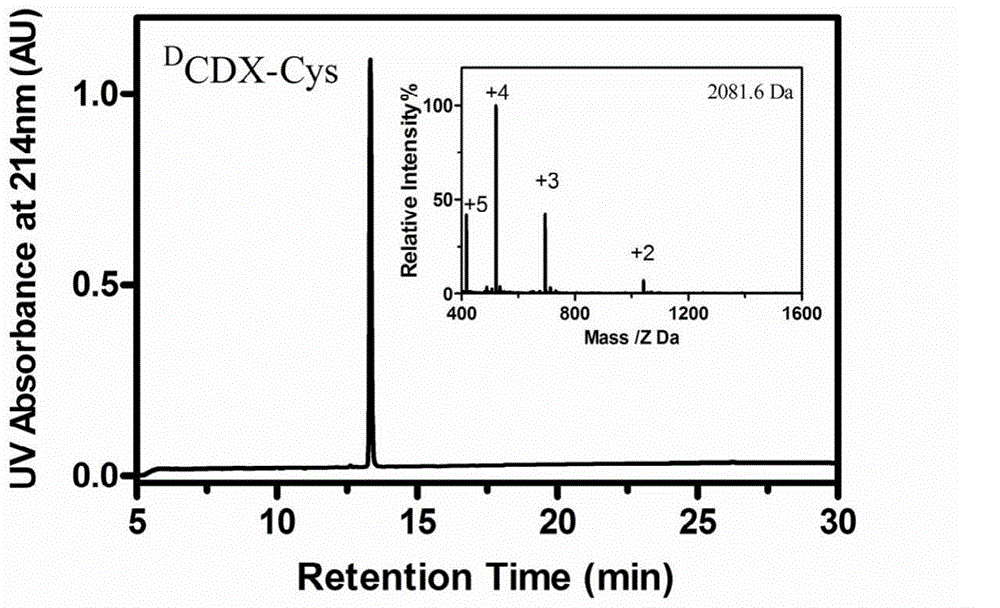
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to D-configuration polypeptide with high stability and capable of realizing mediated targeting of acetylcholine receptor high-expression cells and crossing corresponding barrier membranes and a nano drug delivery system thereof as well as an application in in-vivo and in-vitro brain targeting and in treatment of brain diseases and the like. Test results indicate that DCDX and the acetylcholine receptor are combined with IC50 to obtain 84.5nM which is stable in serum and tolerates hydrolysis of protease; the model drug carried by DCDX is specifically taken in by the positive cells expressing the acetylcholine receptor and has an ability of crossing the barrier formed by the kind of cells; and the nano drug delivery system made of a DCDX-modified polymer carrier material can deliver the entrapped model drug to the target tissue while the drug effect is remarkably improved. The D-configuration polypeptide DCDX provided by the invention can mediate active targeting of the drug or nano drug delivery system and has a good application prospect in the diagnosis and treatment of multiple diseases.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
M3 muscarinic acetylchoine receptor antagonists
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
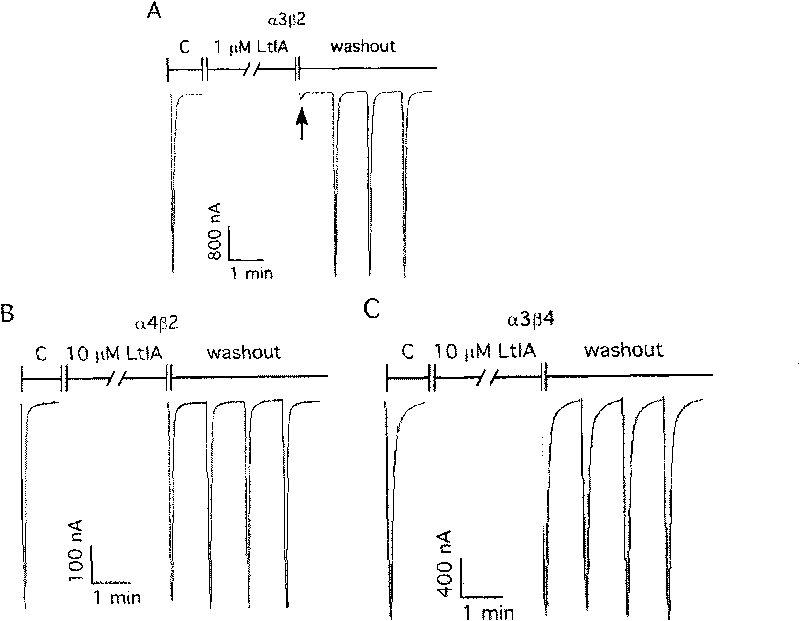
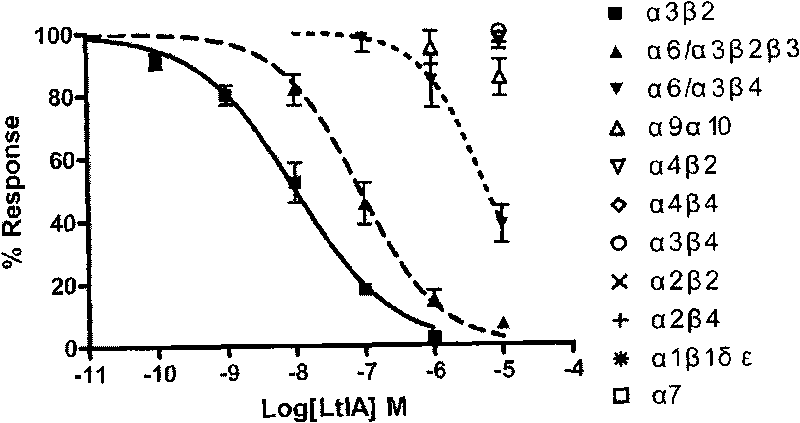
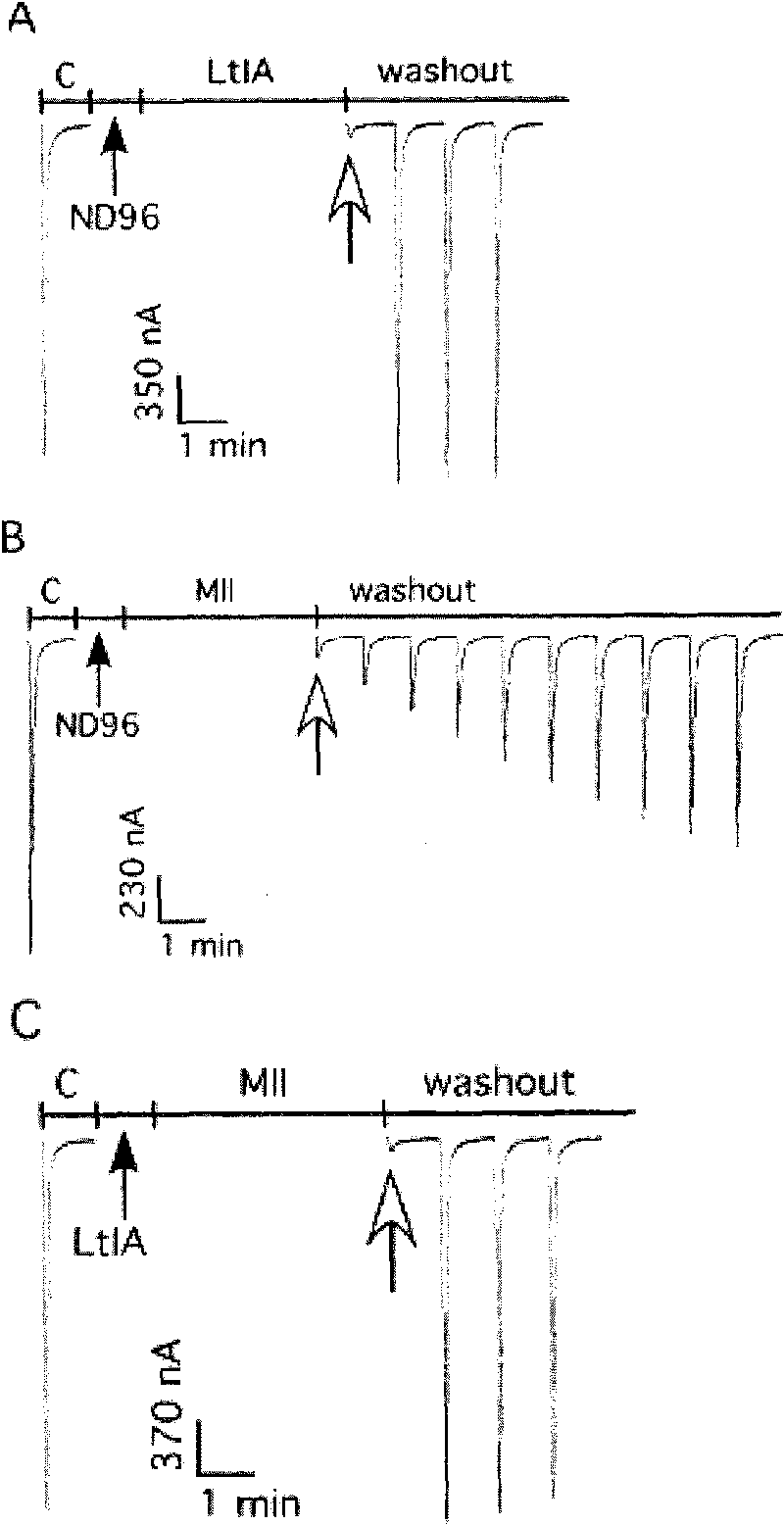
Alpha-conotoxins from Hainan province for specific blockage of acetylcholine receptor and application thereof
InactiveCN101745097ANervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscarinic acetylcholine receptorAlpha-Conotoxin
The invention relates to alpha-conotoxins from Hainan province for specific blockage of a acetylcholine receptor and application thereof, in particular to application of alpha-conotoxins LtIA for specific blockage of (alpha)2(beta)3. nAChRs, application of alpha-conotoxins TxIB for specific blockage of (alpha)9(beta).10 nAChRs, related pharmaceutical compositions and the like.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
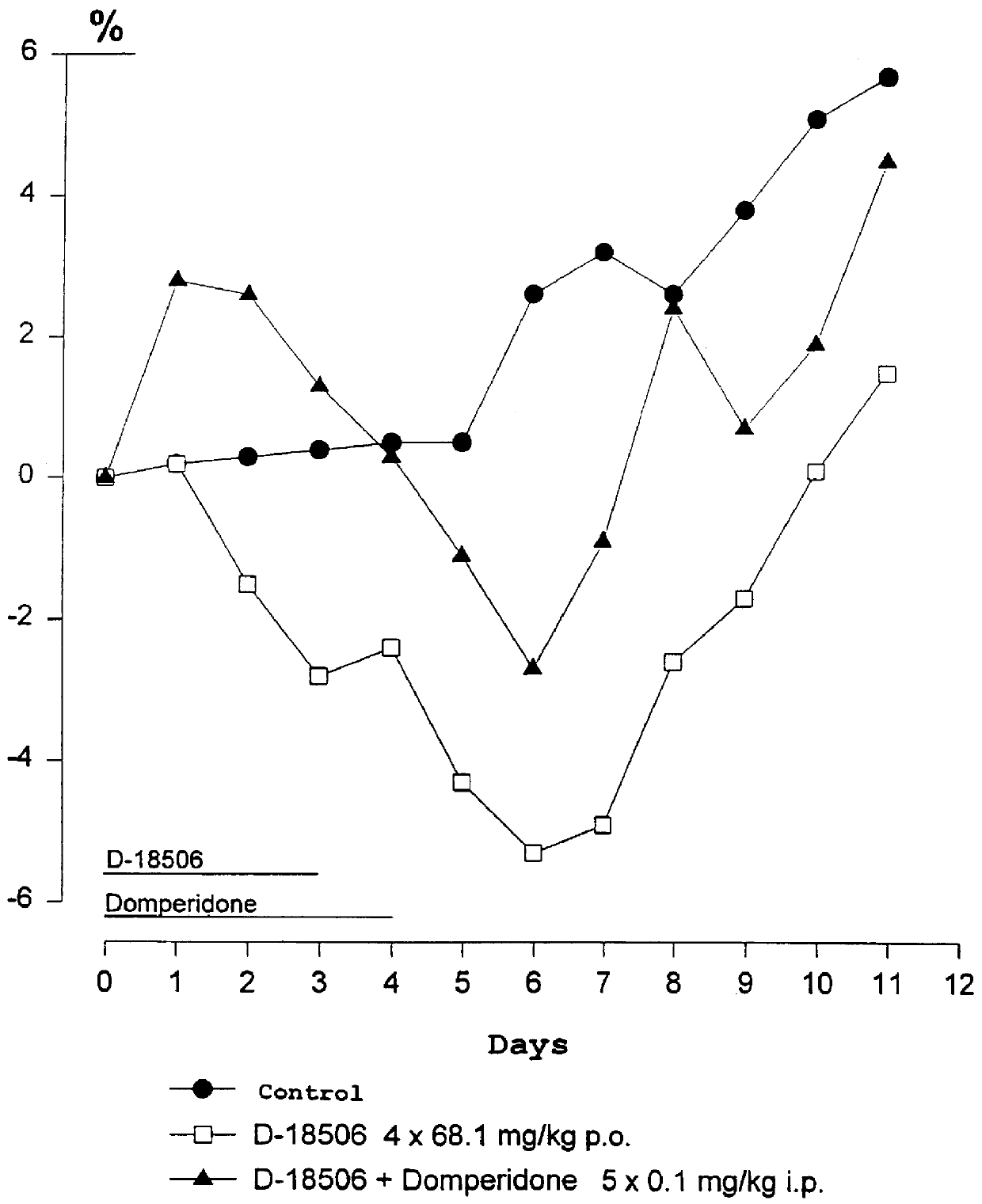
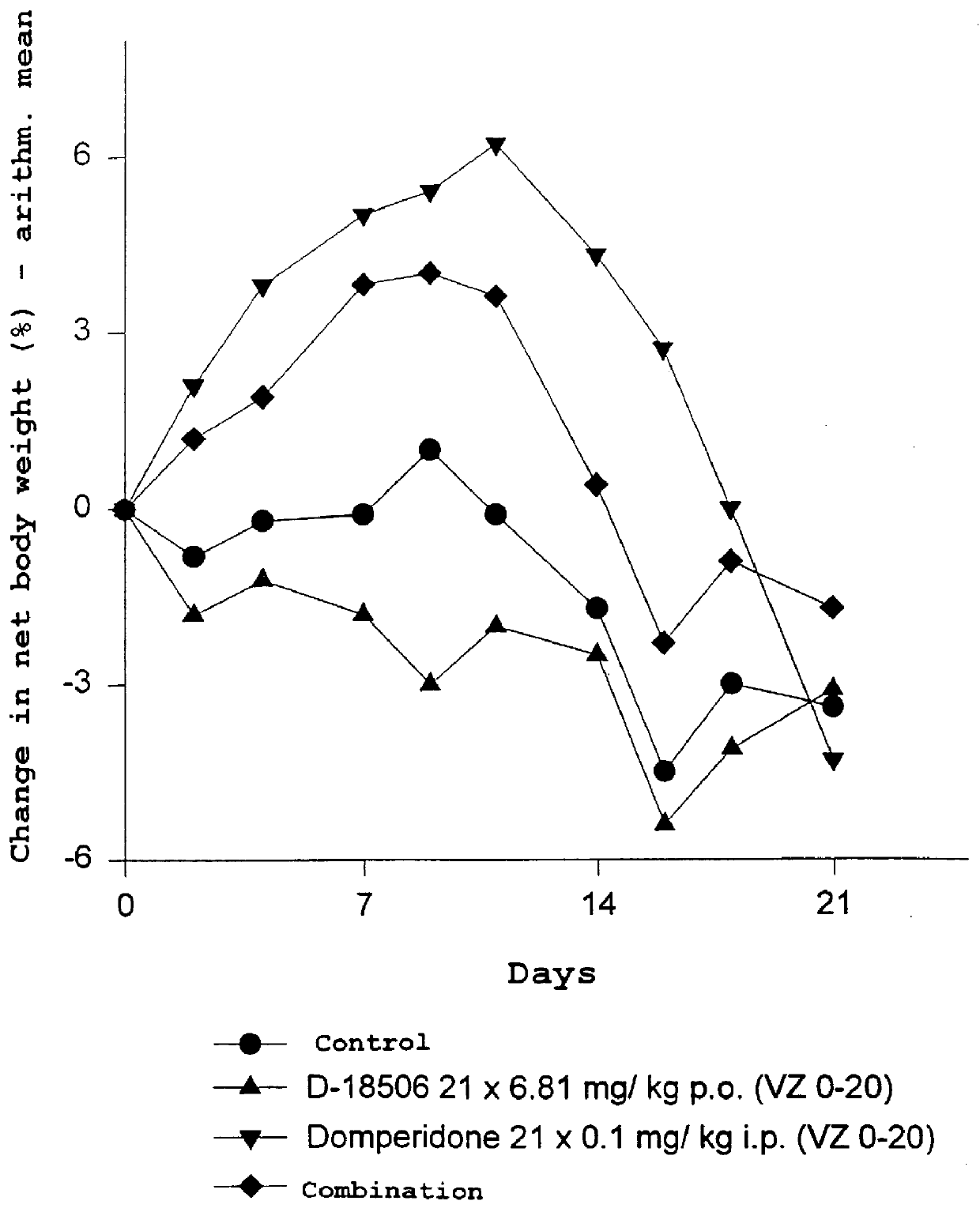
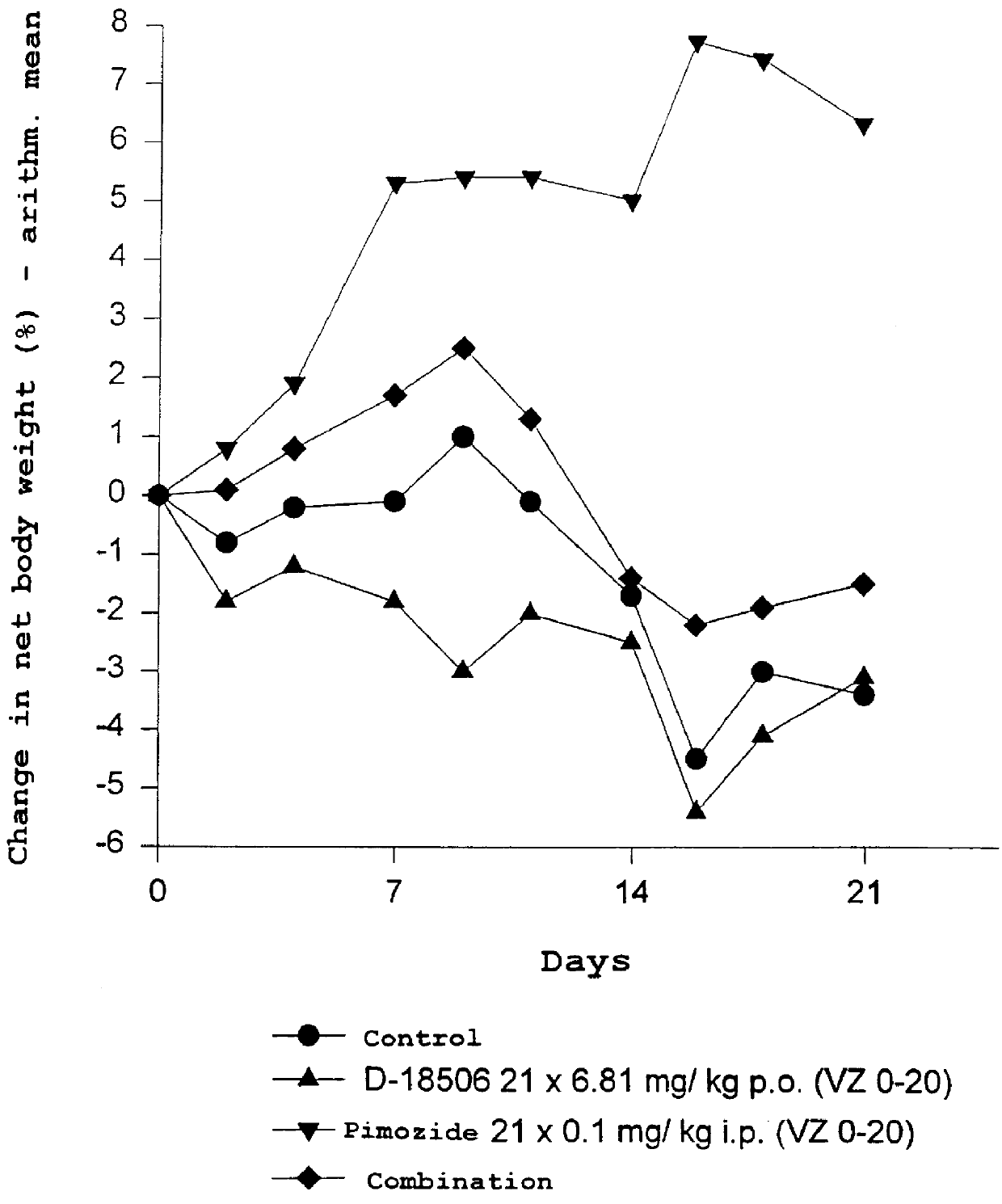
Use of dopamine receptor antagonists in palliative tumor therapy
The side effect of decrease in body weight caused by the alkylphosphocholines such as miltefosine can be antagonized by certain acetylcholine receptor antagonists such as domperidone and pimozide. The combination of alkylphosphocholine plus the antagonist does not have any effect on the anti-tumor action of the alkylphosphocholine. The combination also caused no new side effects in the animals.
Owner:AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH
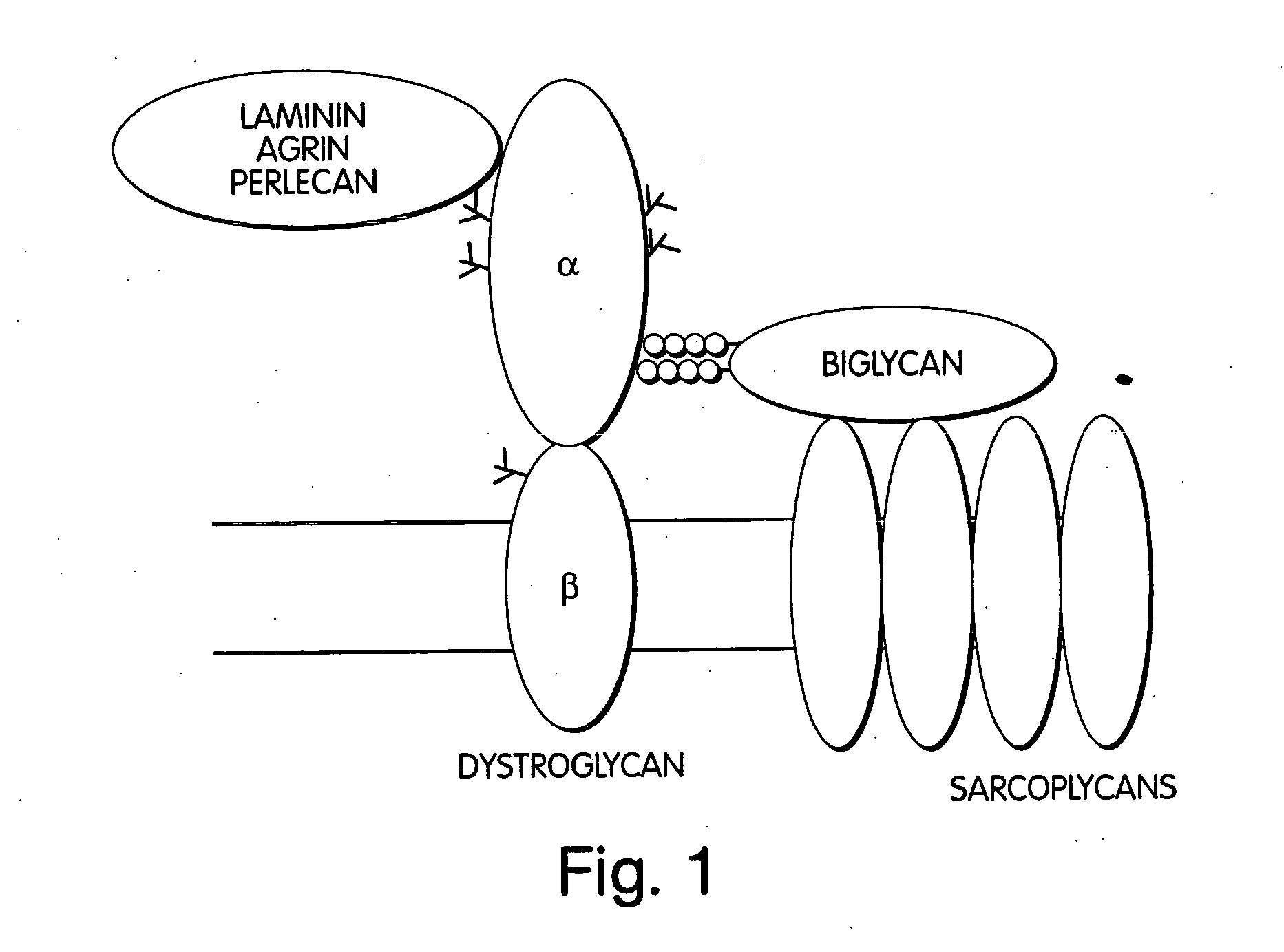
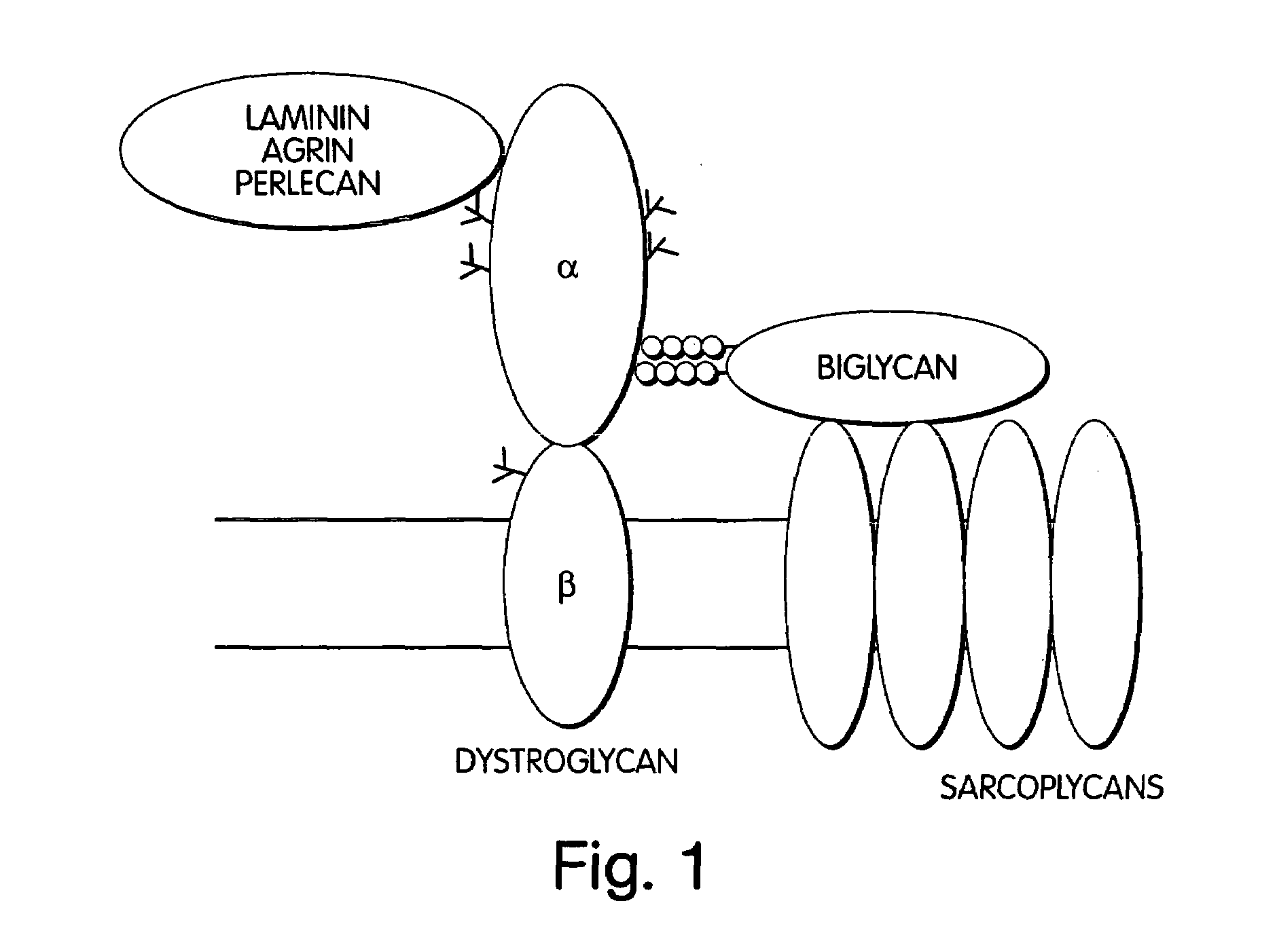
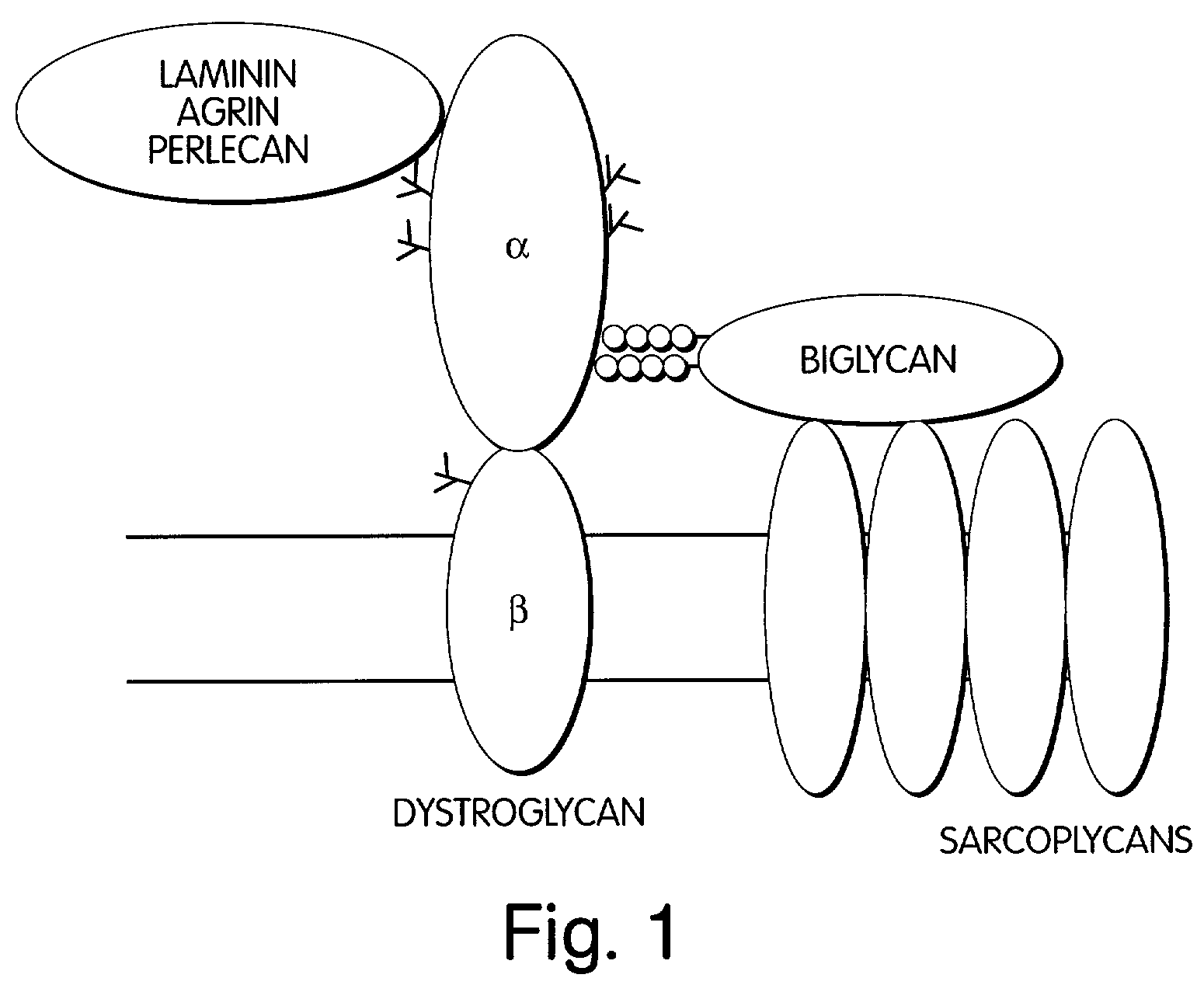
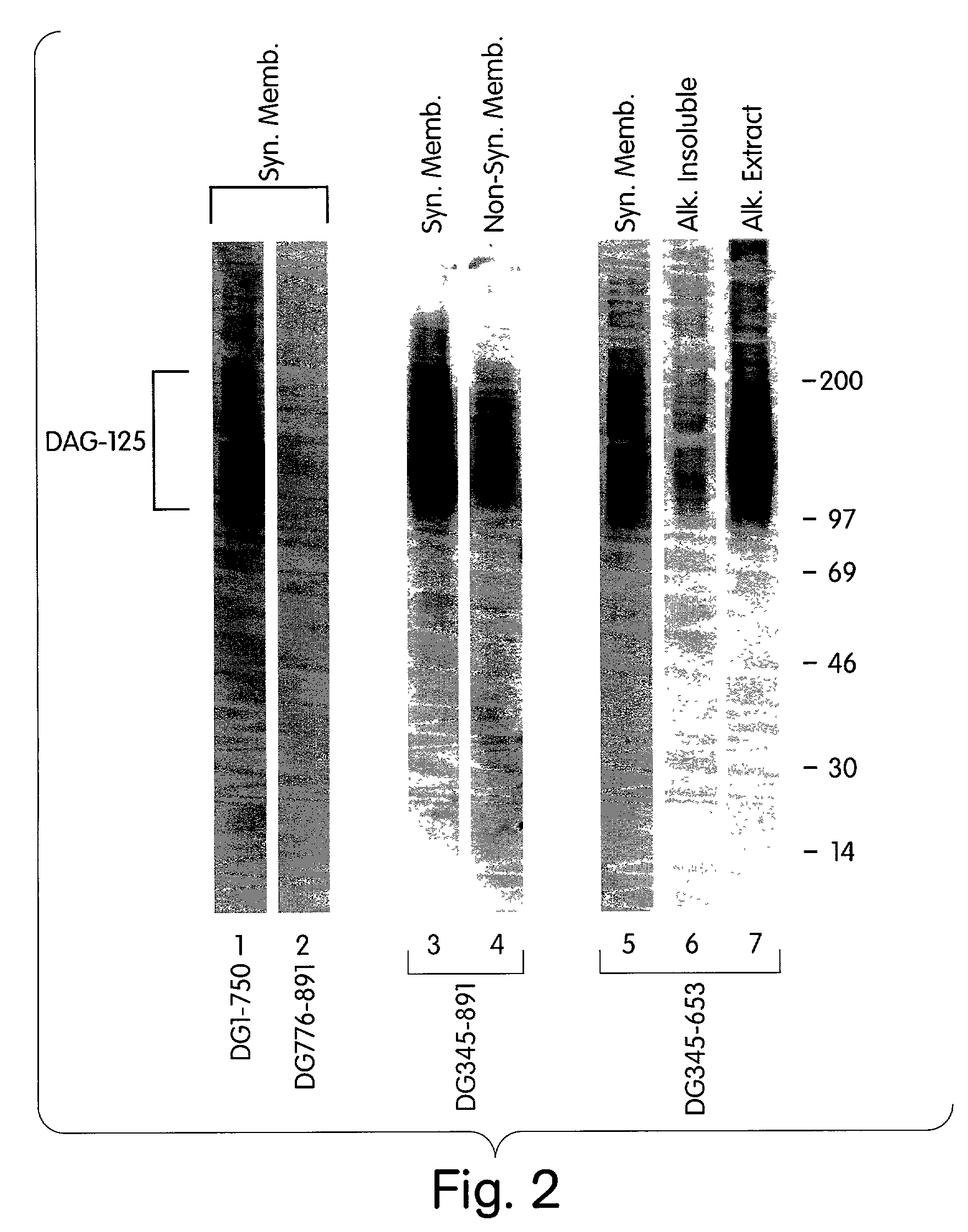
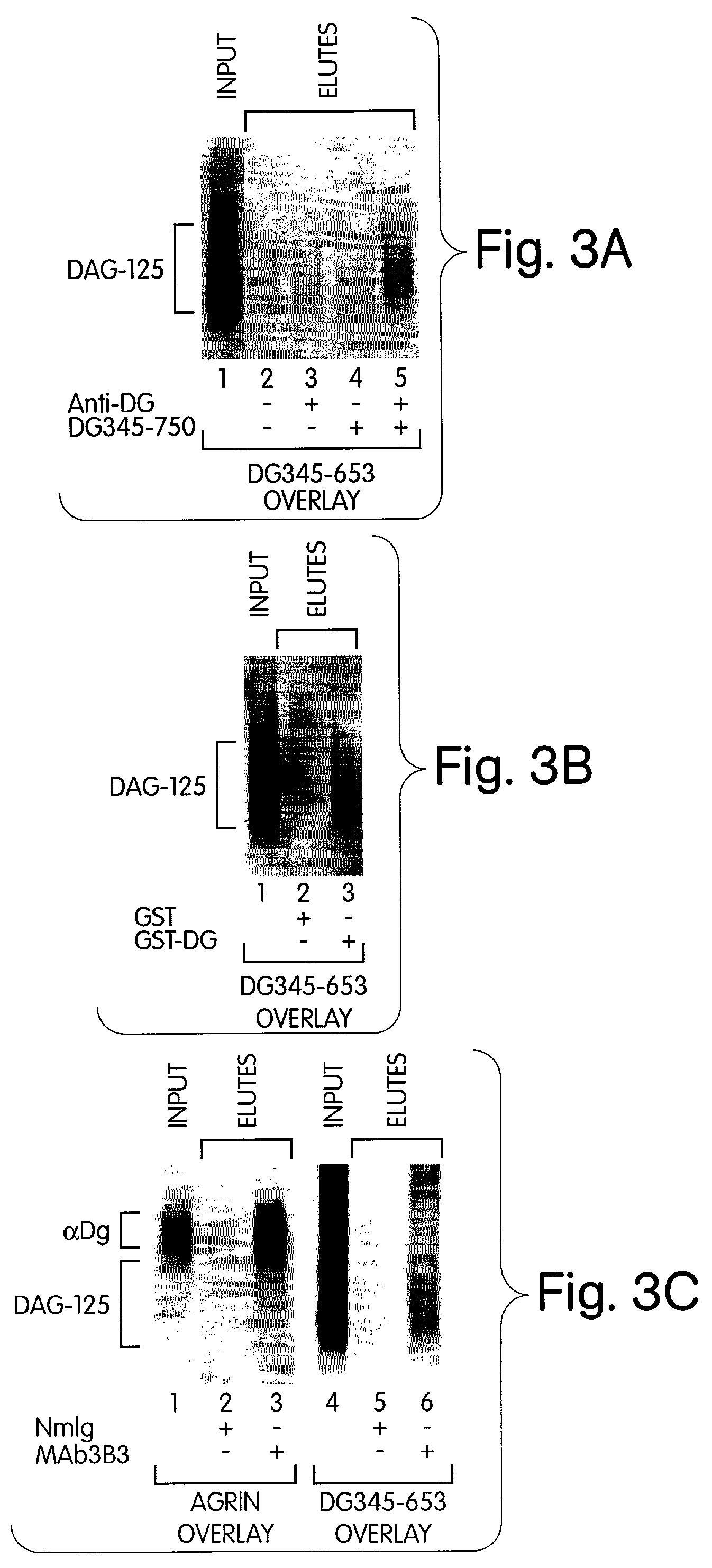
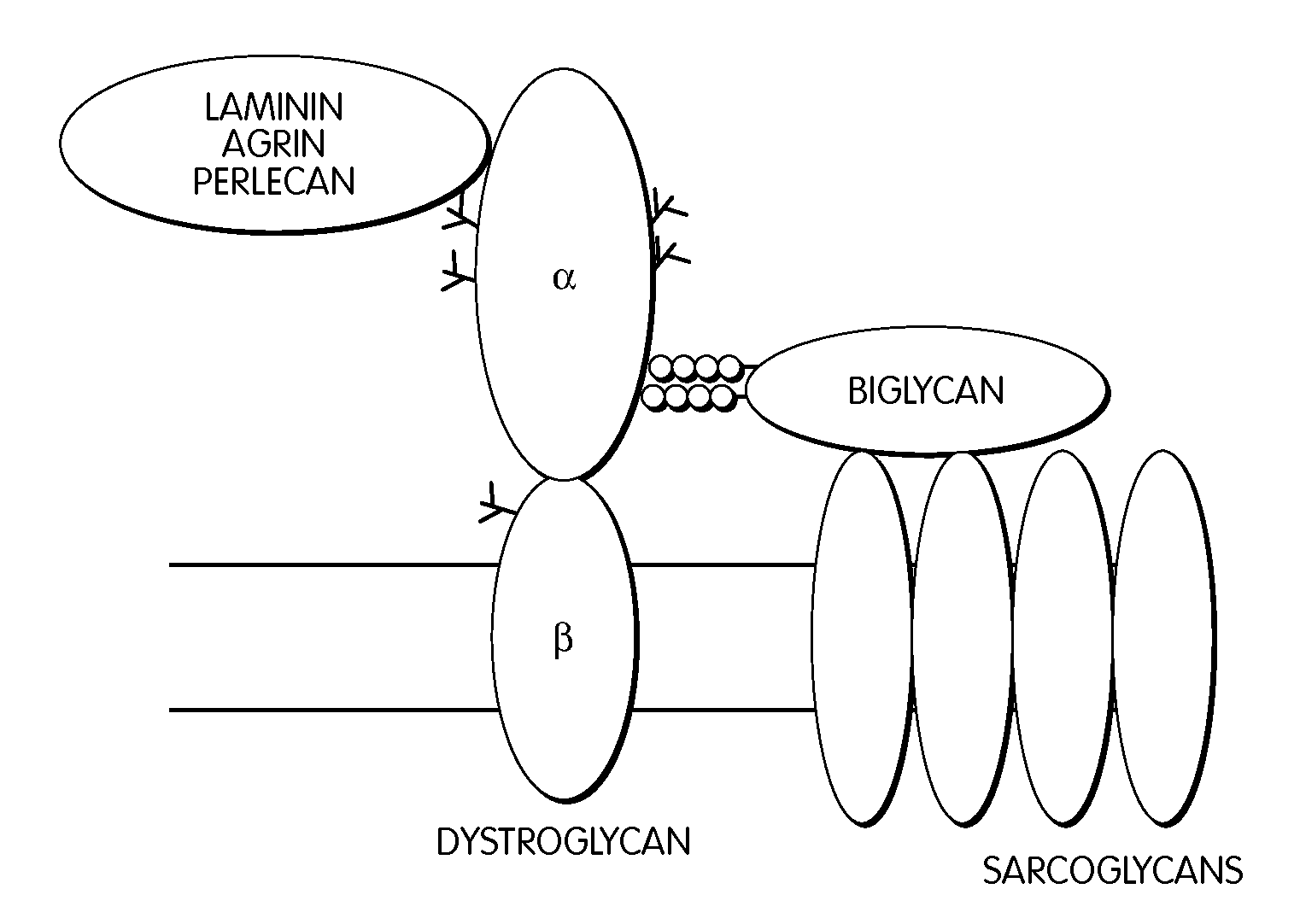
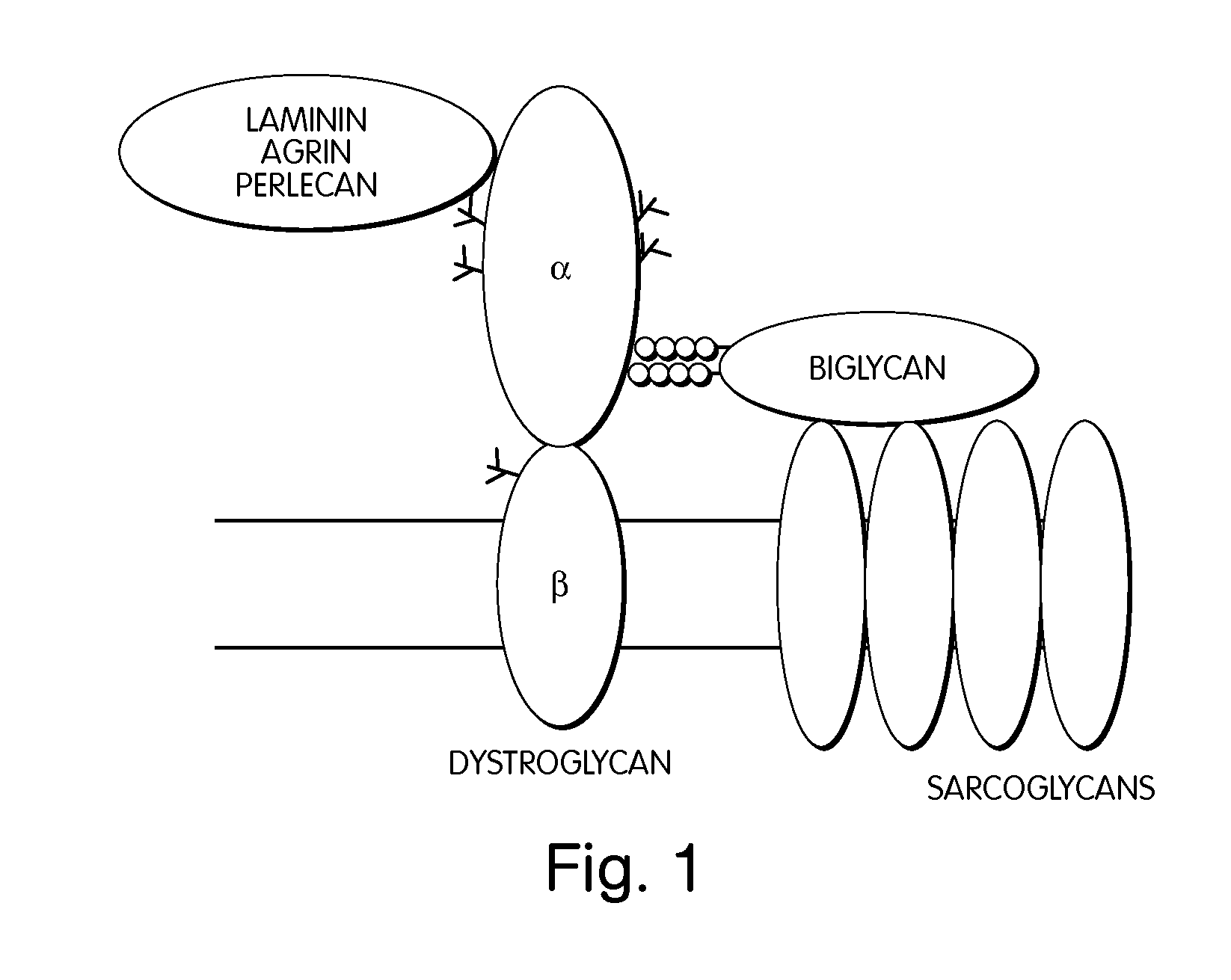
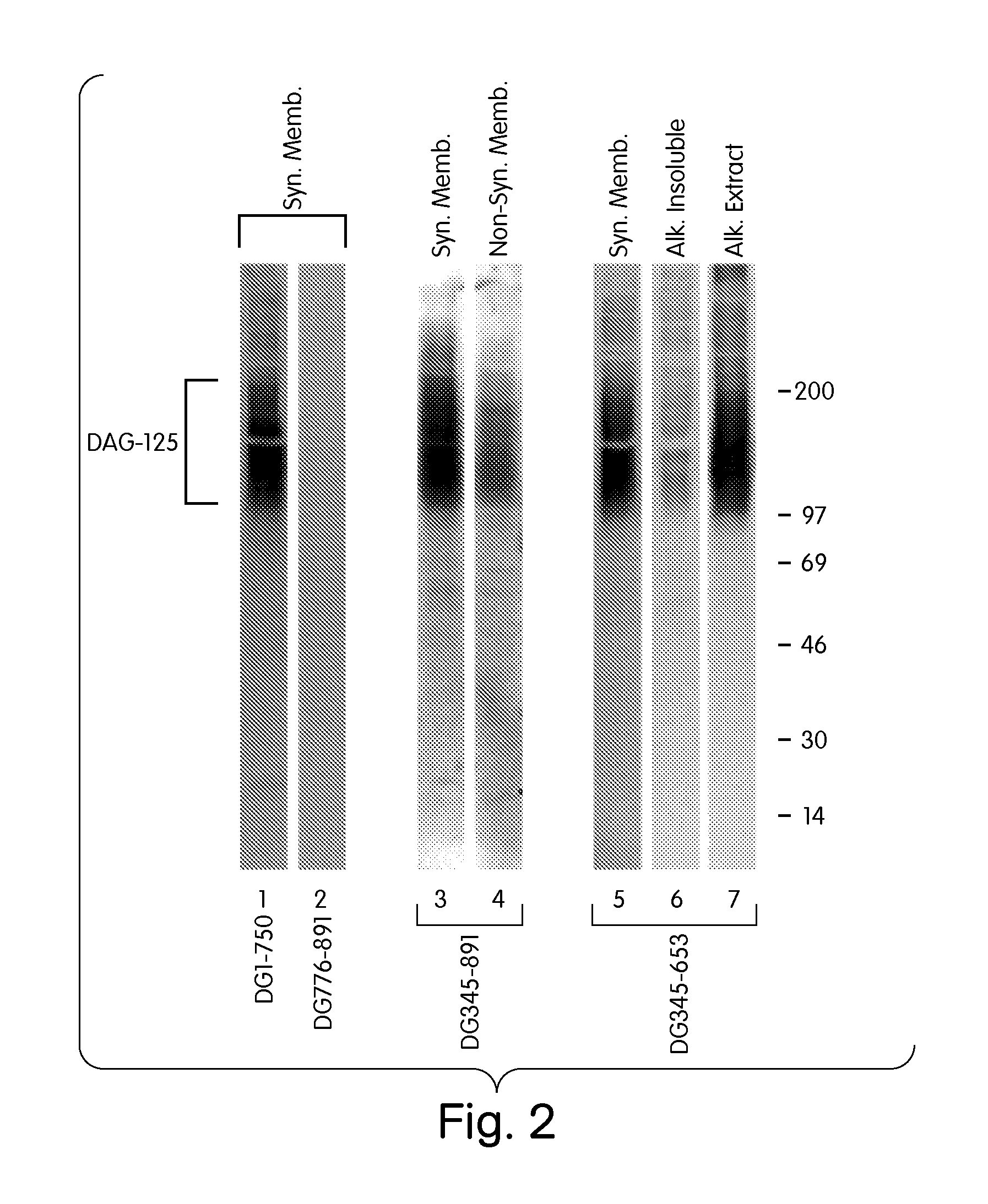
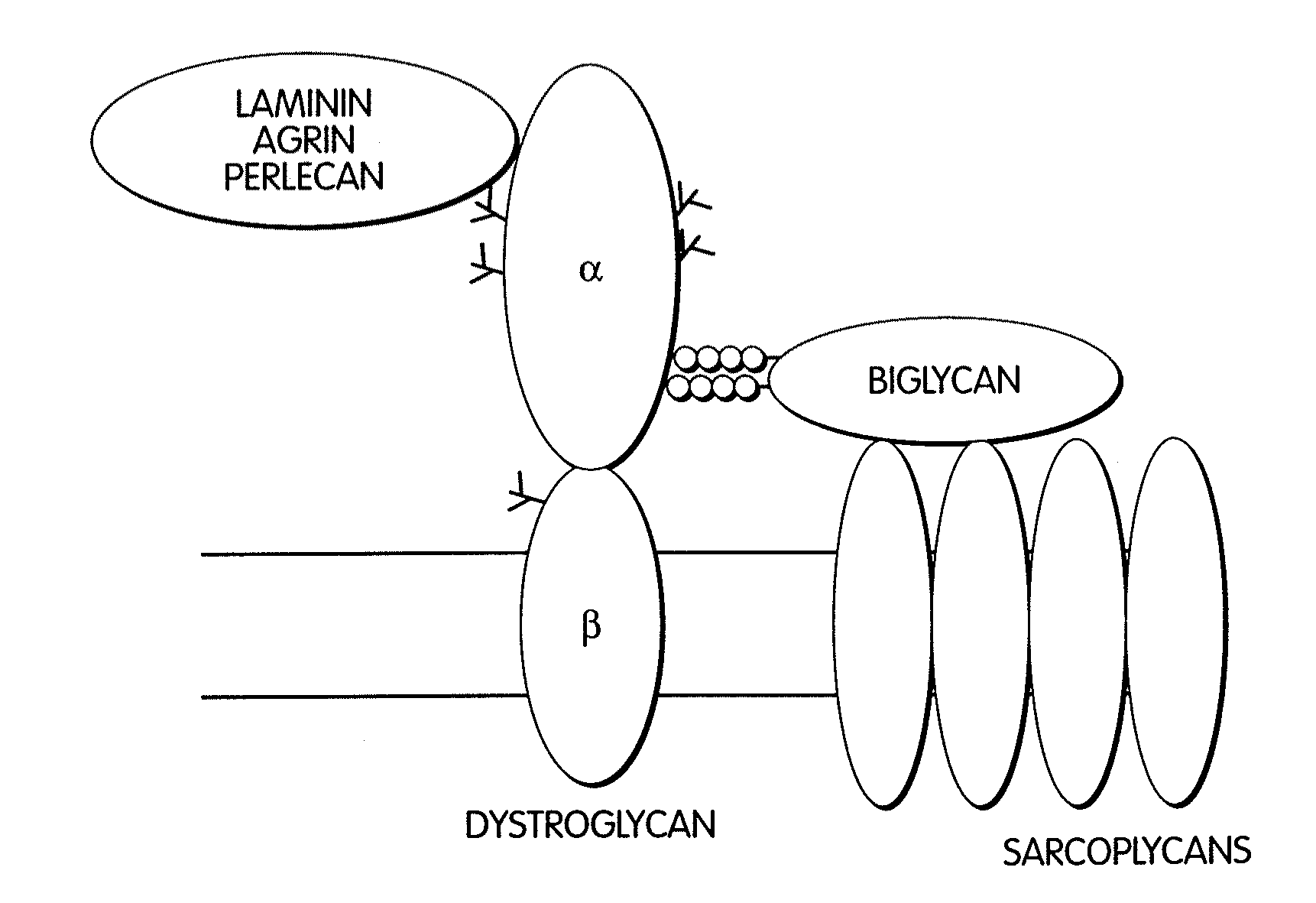
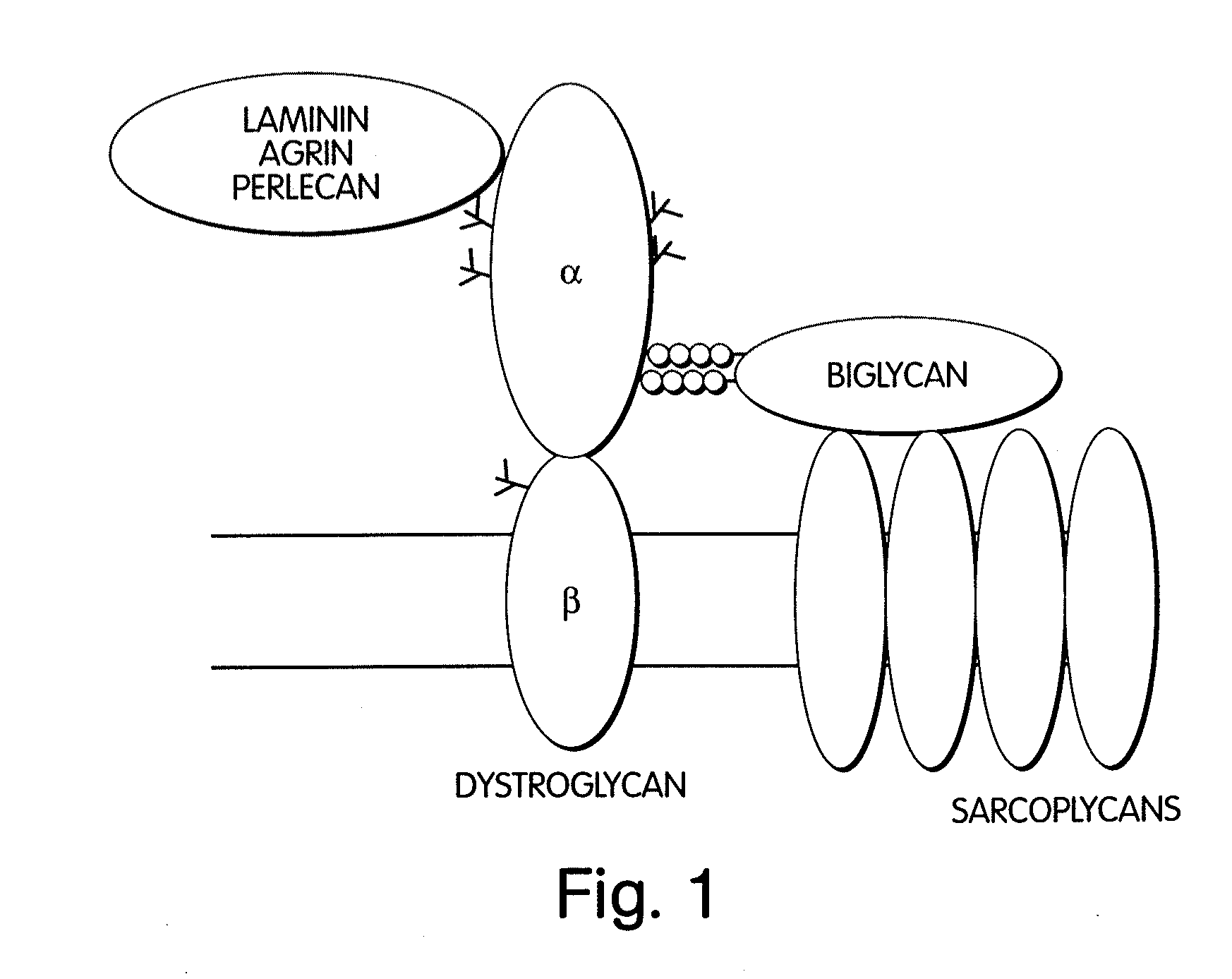
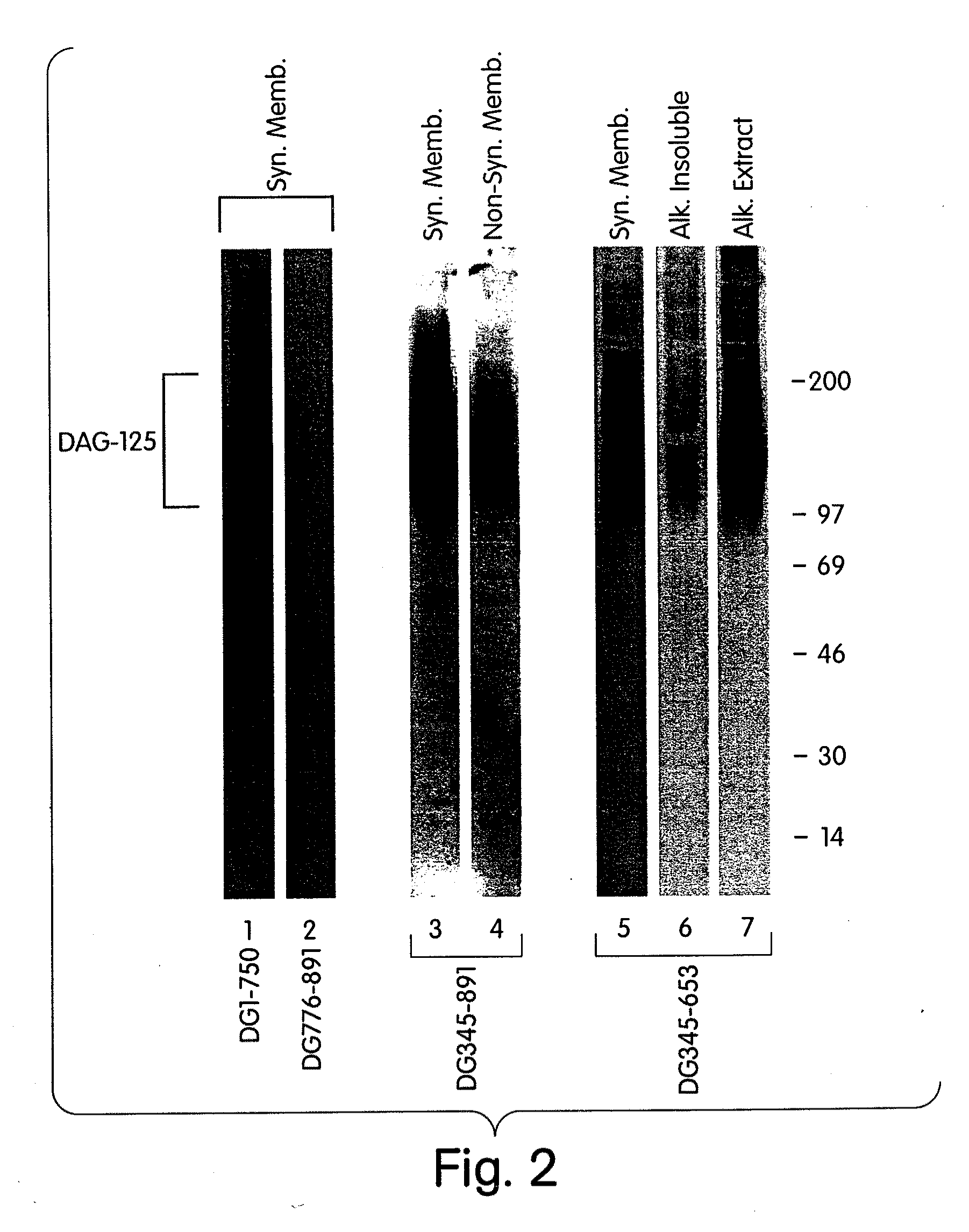
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
InactiveUS20050059580A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifeHormone peptidesSnake antigen ingredientsNervous systemBiglycan
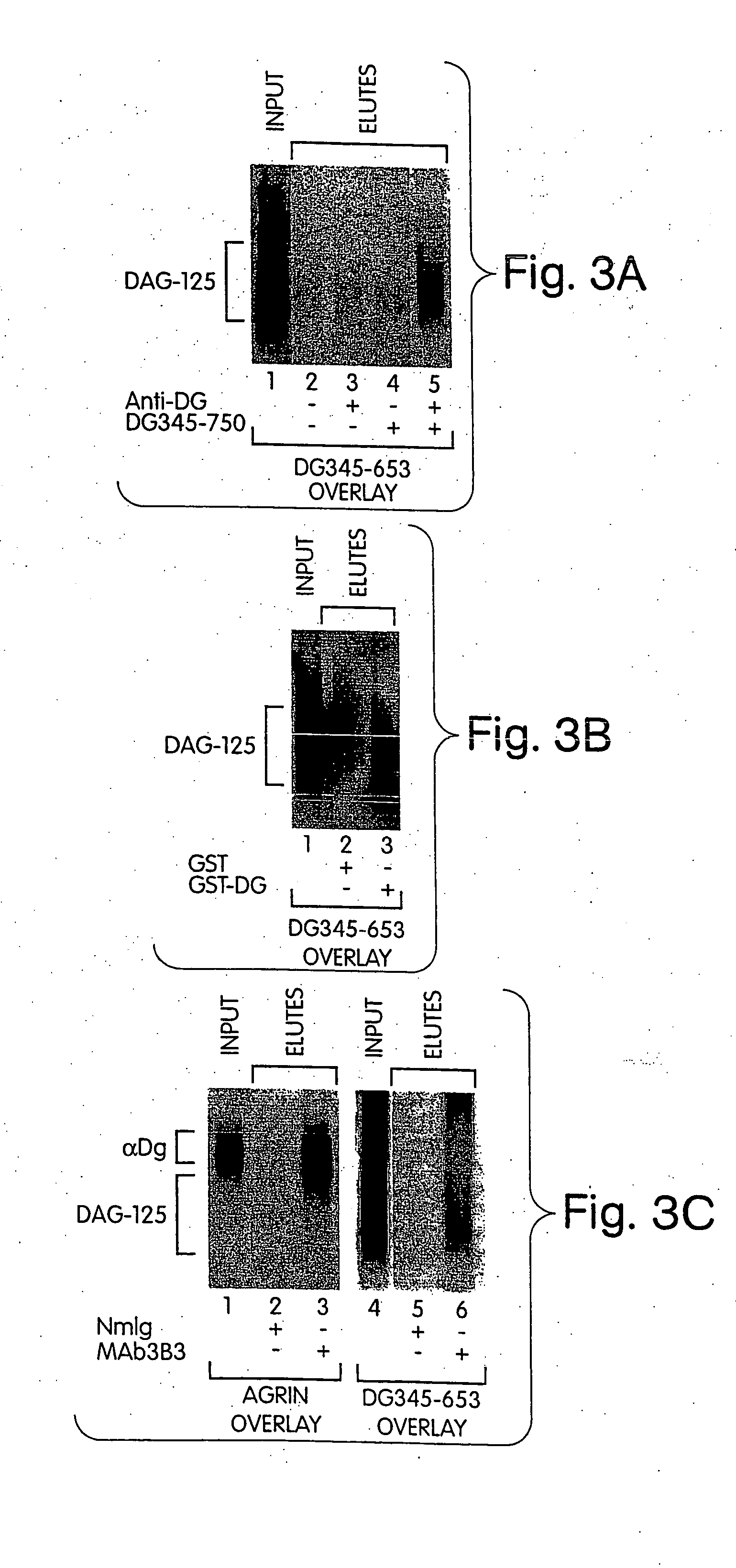
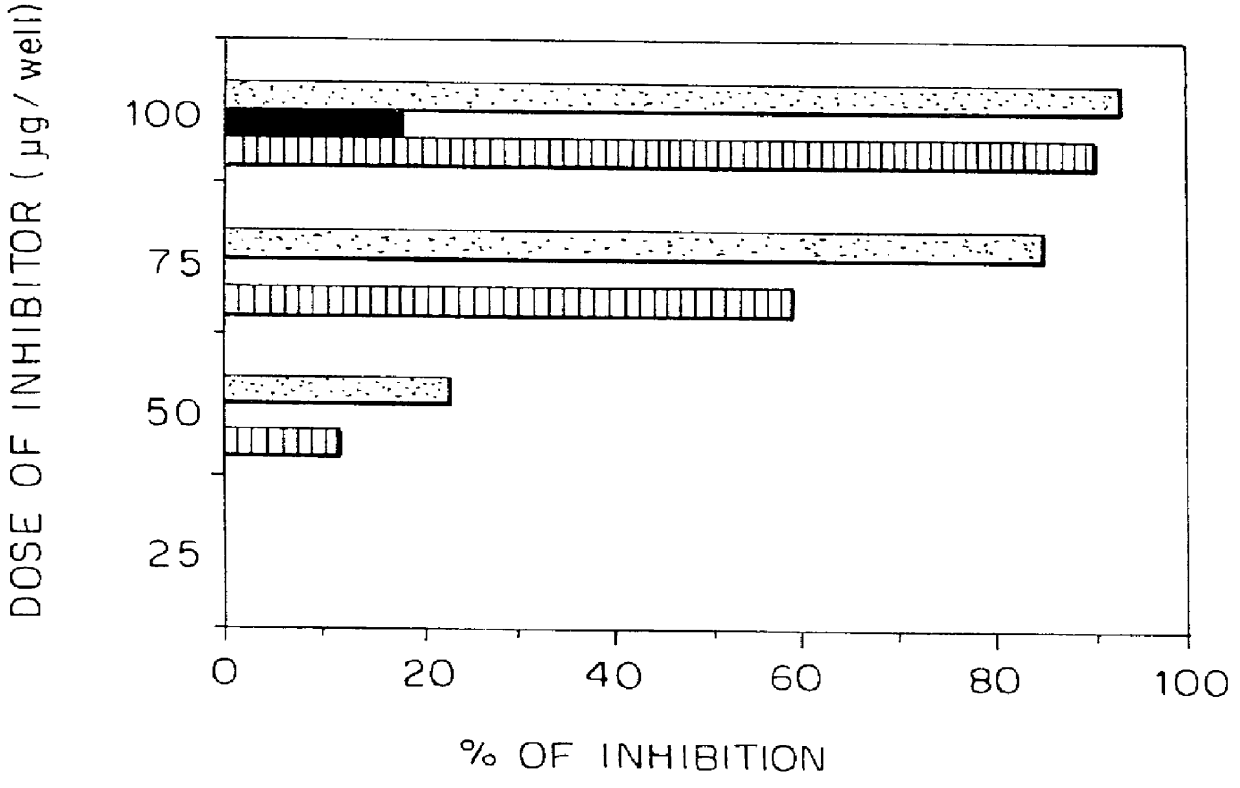
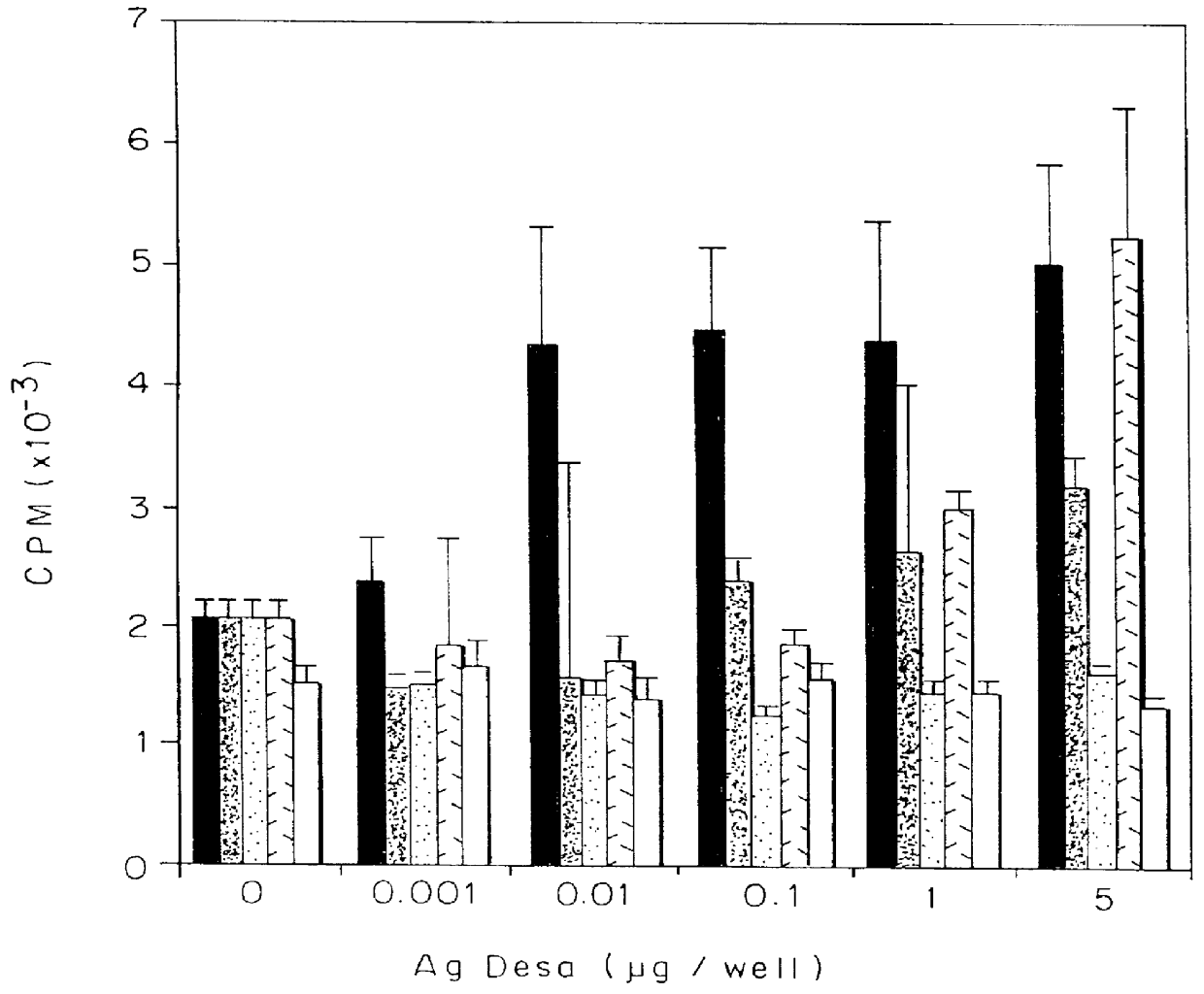
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Examples of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Alpha-conotoxin peptide, and medical composition, preparation method and purpose thereof
The invention belongs to the fields of biochemistry and molecular biology, relates to an alpha-conotoxin peptide, and a medical composition, a preparation method and a purpose thereof, also relates to a propeptide of the conotoxin peptide, a nucleic acid construct, an expression vector, a transformed cell and a fusion protein, and also relates to a method for blocking acetylcholine receptors and a pharmaceutical purpose of the conotoxin peptide. The alpha-conotoxin peptide can specifically block the acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) (such as alpha3beta2 nAChR), has high analgesic activity and addiction withdrawal activity and has a good application prospect in the aspects of preparing analgesics, smoking cessation or drug treatment medicines and the like.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
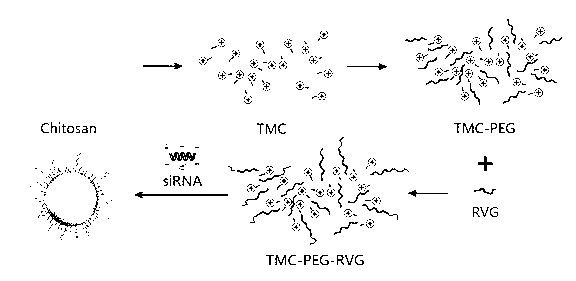
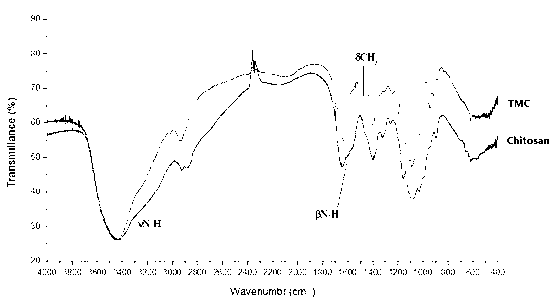
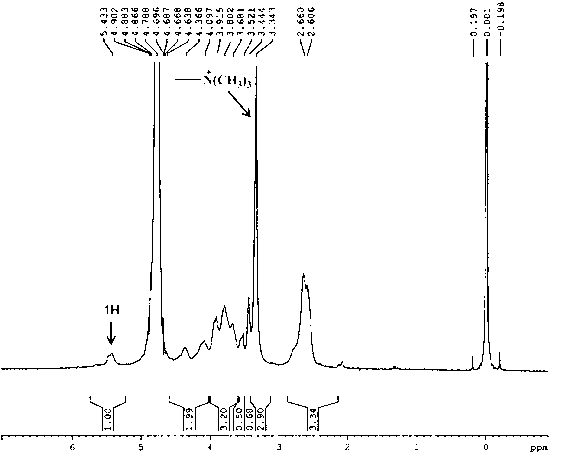
Trimethyl chitosan-graft-polyethylene glycol/nucleic acid brain-targeting micellar and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and relates to an acetylcholine-receptor-mediated trimethyl chitosan-graft-polyethylene glycol / nucleic acid brain-targeting micellar and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, trimethyl chitosan-graft-polyethylene glycol-brain-targeting functional peptide is obtained through the steps that: chitosan is sequentially subjected to quaternary ammonium modification such that trimethyl chitosan is obtained; the amino group of trimethyl chitosan is subjected to a reaction with an active group of two-end-activated polyethylene glycol, such that trimethyl chitosan-graft-polyethylene glycol is obtained; and another active group of polyethylene glycol is subjected to a reaction with brain-targeting functional peptide RVG. According to the invention, ion composite micellar is adopted as a carrier, and brain-targeting functional peptide RVG is adopted as a targeting molecule, such that nucleic acid medicine can actively target and position through blood-brain barrier and brain. The ion composite micellar provided by the invention is formed through static composition of positively charged trimethyl chitosan-graft-polyethylene glycol-brain-targeting functional peptide and negatively charged nucleic acid. With the invention, nucleic acid medicine defects such as easy in-vivo degradation, poor stability, and low transfection efficiency are solved.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Synergistic insecticidal compositions
InactiveUS20080125420A1Improve protectionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSodium Channel AntagonistsCarbamate
The present invention provides a synergistic insecticidal composition comprising as essential active ingredients a neuronal sodium channel antagonist in combination with one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of pyrethroids, pyrethroid-type compounds, recombinant nucleopolyhedroviruses capable of expressing an insect toxin, organophosphates, carbamates, formamidines, macrocyclic lactones, amidinohydrazones, GABA antagonists and acetylcholine receptor ligands.Also provided are methods for synergistic insect control and crop protection.
Owner:TREACY MICHAEL FR +4
Synergistic insecticidal compositions
InactiveUS20080125421A1Improve protectionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSodium Channel AntagonistsCarbamate
Owner:TREACY MICHAEL FR +4
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
InactiveUS7335637B2Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifeBiocideHormone peptidesAcetylcholine receptorMedicine
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Examples of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
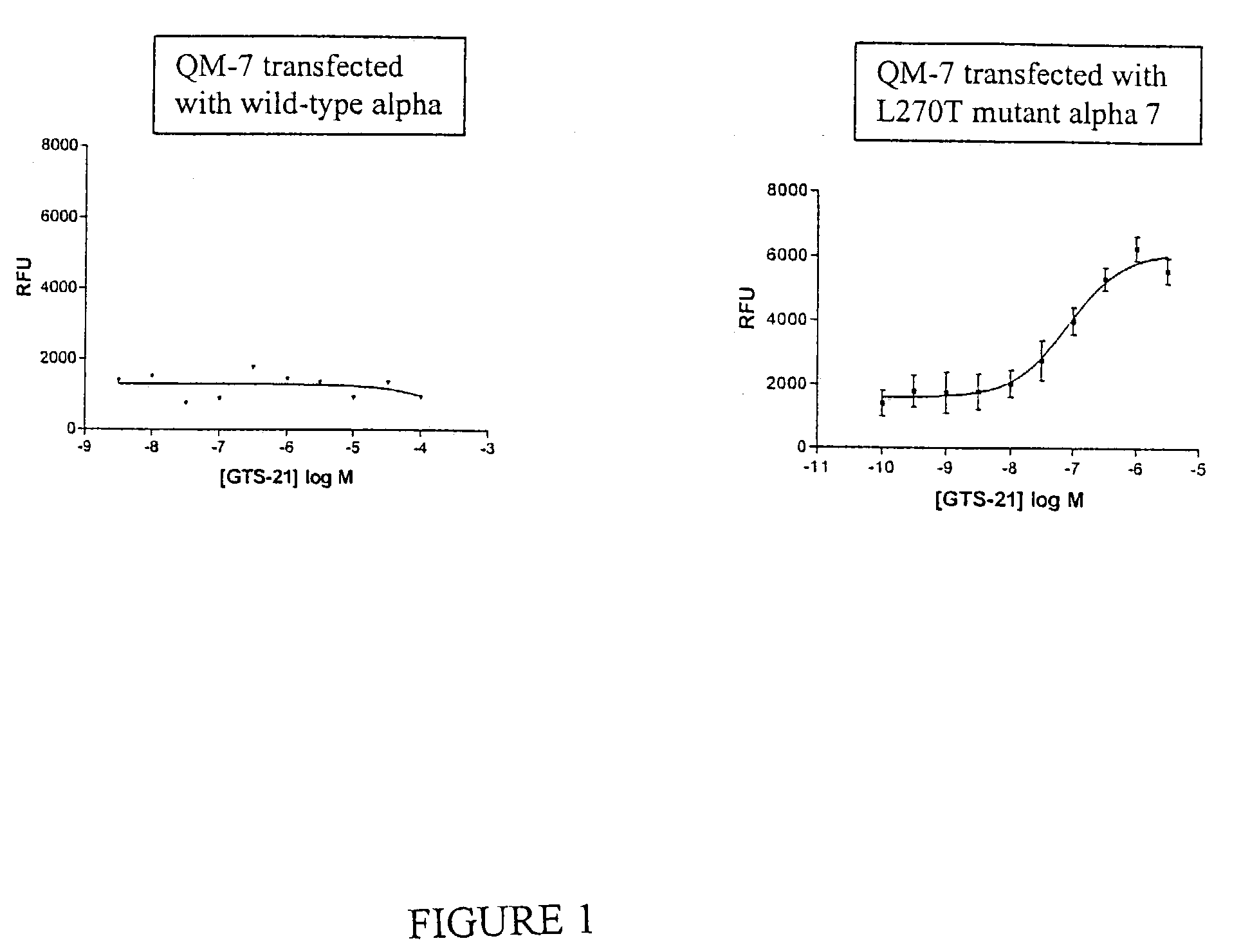
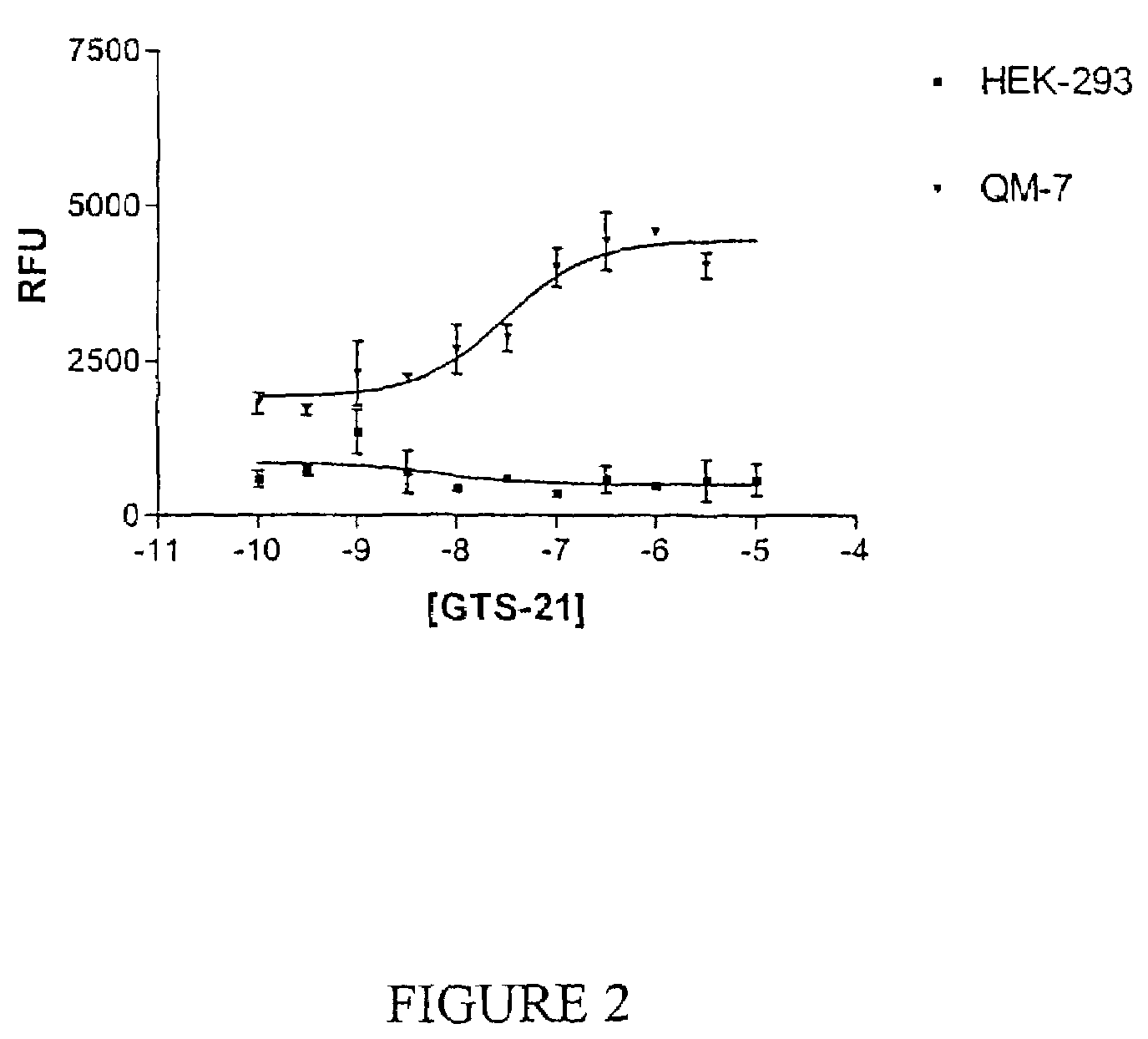
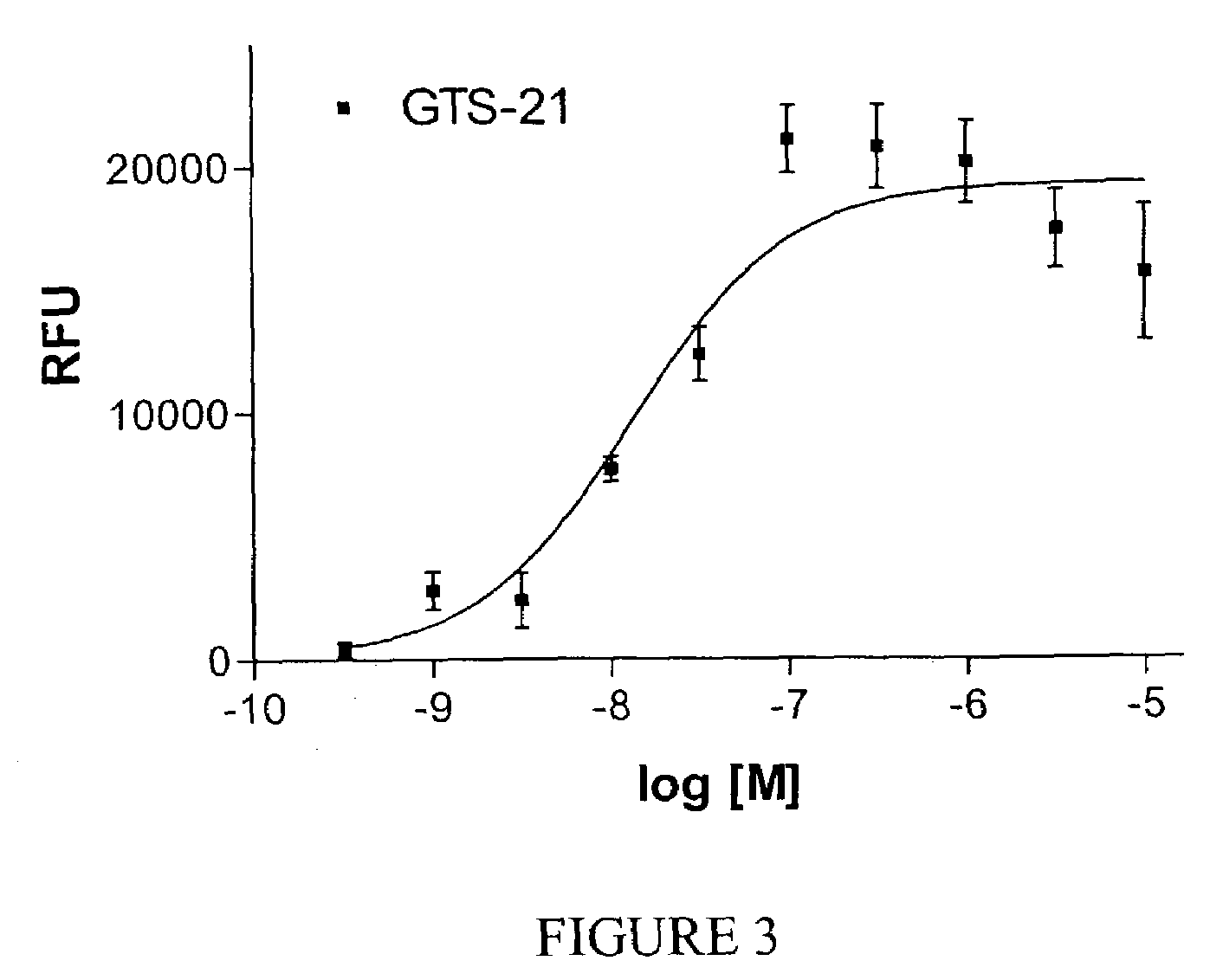
QM-7 and QT-6 cells transfected with mutant cell surface expressed channel receptors and assays using the transfected cells
InactiveUS7358057B2Less stringentEffective functionDrug screeningFermentationAcetylcholine receptorCell biology
The present invention relates e.g., to QM-7 or QT-6 cells comprising a heterologous mutant nicotinic α7 acetylcholine receptor and / or a nucleic acid encoding it, or a fragment or variant thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the mutant nicotinic α7 acetylcholine receptor subunit has a mutation in the M2 domain. QM-7 and QT-6 cells of the invention are useful for, e.g., assays such as high throughput assays that measure the influx of cations, such as Ca++ ions, into a cell. Such assays can be used, e.g., to identify agents that modulate the expression and / or activity of a mutant cell-surface-expressed channel receptor (e.g., the nicotinic α7 receptor), and which thus modulate, e.g., among other functions, processes involved in the central nervous system, such as learning and memory.
Owner:MEMORY PHARMA CORP
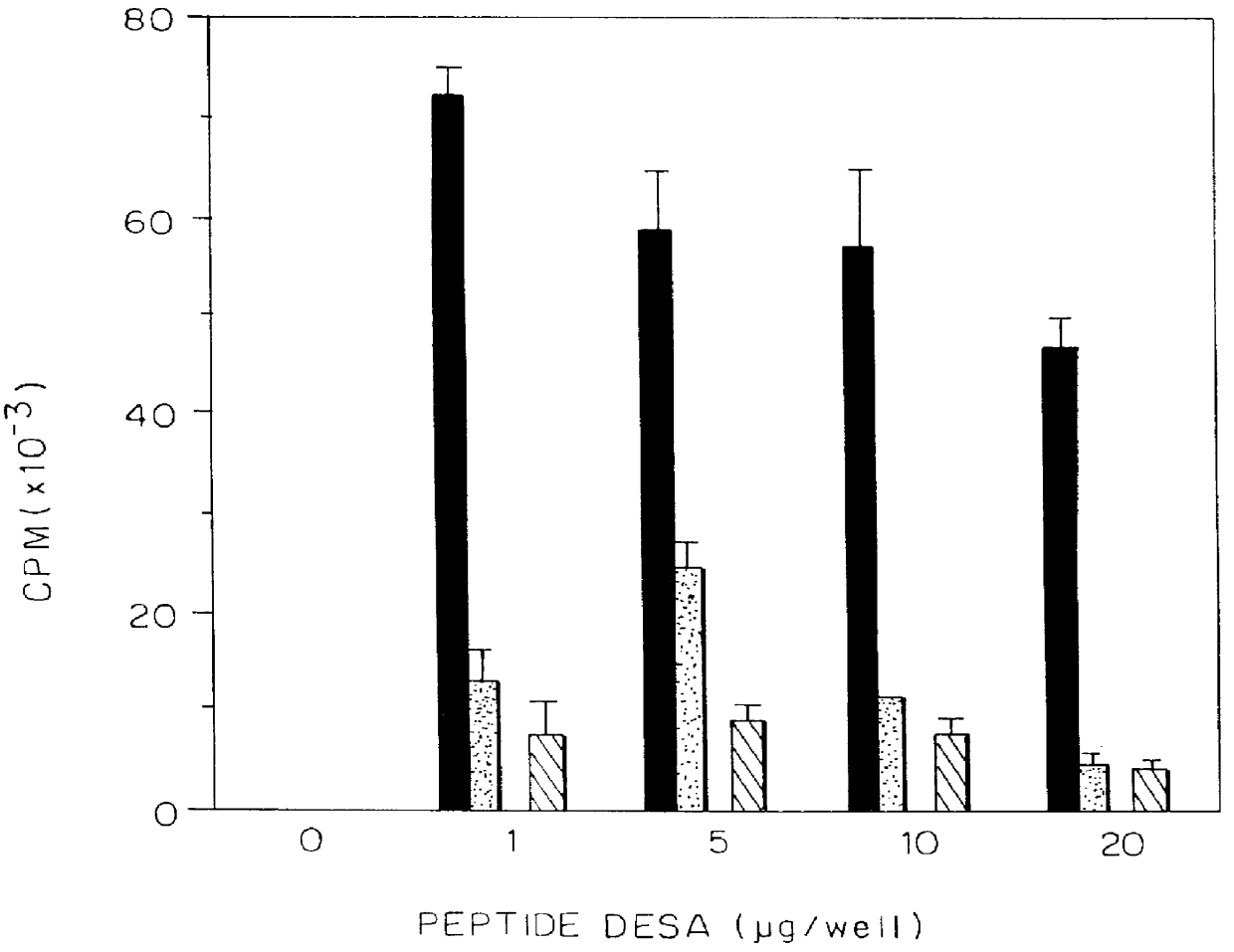
Synthetic peptides for the treatment of myasthenia gravis
Peptides having at least nine amino acid residues each including an amino acid sequence which corresponds to position p200-208 or p262-266 of the human acetylcholine receptor alpha -subunit, but differing therefrom by one or more amino acid substitutions, are disclosed. These peptides inhibit the proliferative response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to the myasthenogenic peptides p195-212 and p259-271 and are suitable for treatment of subjects afflicted with myasthenia gravis.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Ginseng and antler muscle strengthening pills and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to ginseng and antler muscle strengthening pills and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of natural Chinese herbal medicine. The type of drugs can regulate immune function, improve acetylcholine receptor function and strengthen muscle contraction ability. The drug formula is used for moistening lung, regulating qi, promoting production of fluid, strengthening spleen, strengthening kidney, replenishing essence, nourishing blood, soothing liver, strengthening muscle and increasing strength. The pills can effectively inhibit abnormal autoimmunity response and solve the acetylcholine transfer disorder. The pills have significant efficacy for myasthenia gravis.
Owner:宋水清
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Example of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Treatment of muscular dystrophies and related disorders
InactiveUS20110053854A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderSynapseDisease
The invention provides, among other aspects, compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of collagen VI; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); and disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
New conopeptide, medicinal composition and uses thereof
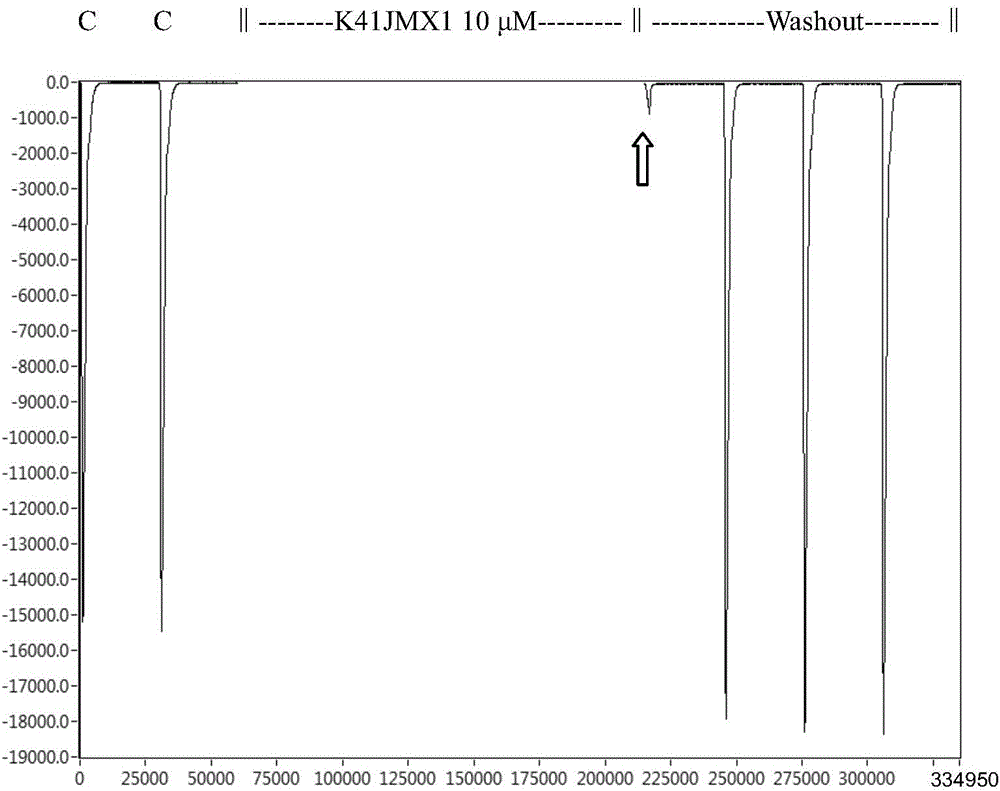
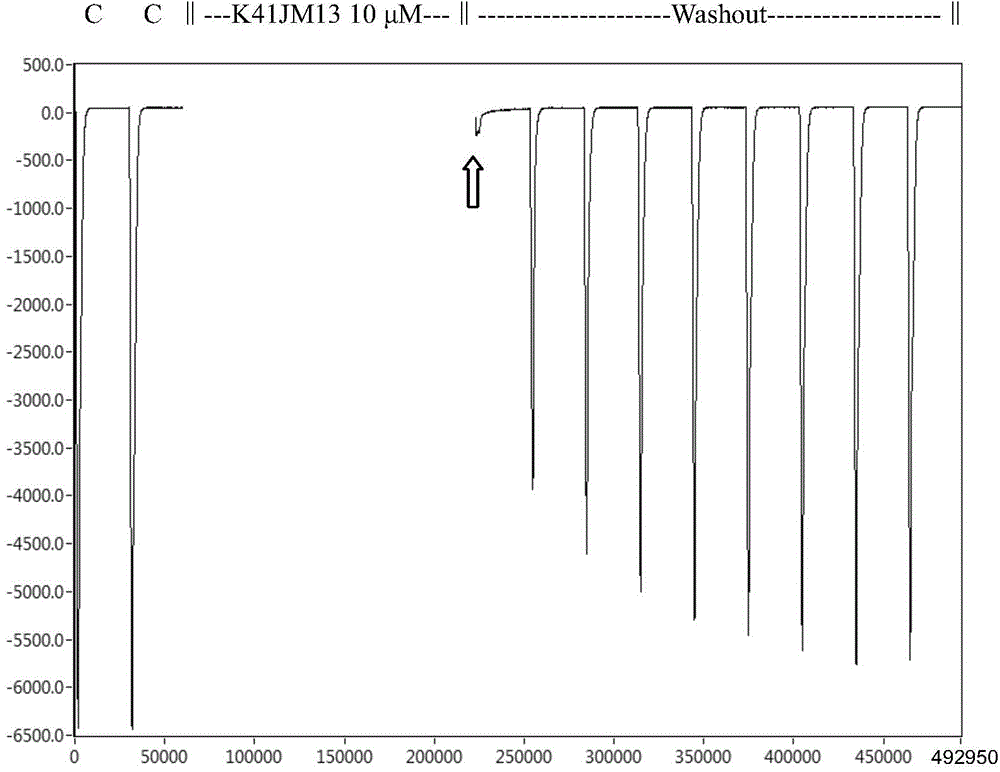
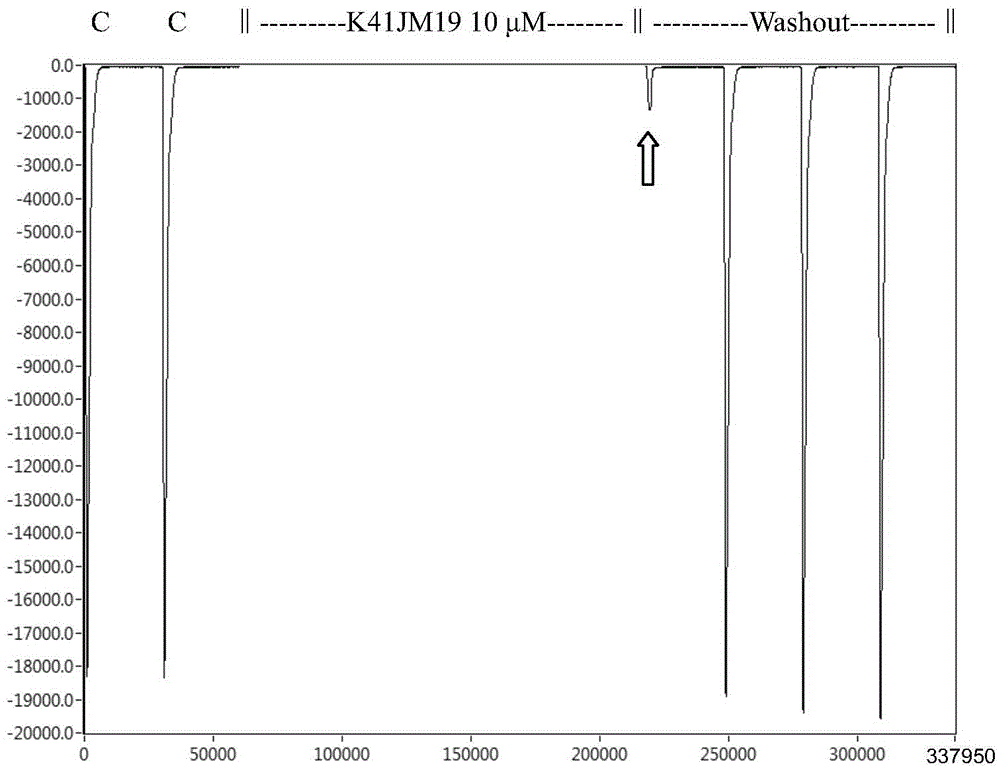
ActiveCN105985410AHas analgesic activityGrowth inhibitionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyLung cancer
The invention belongs to the fields of biochemistry and molecular biology, relates to a new conopeptide, and a medicinal composition, a preparation method and uses thereof, also relates to a nucleic acid construct, an expression vector of the nucleic acid construct, a converted cell of the expression vector and a fusion protein of the conopeptide, and further relates to a method for blocking out an acetylcholine receptor, and pharmaceutical uses of the conopeptide. The new conopeptide K41JM and analogs thereof can specifically block out the acetylcholine receptor (nAChRs) (such as alpha9alpha10nAChR), have can treat neuralgia, cancer chemotherapy, breast cancer, lung cancer, wound healing, encephalomyelitis, epilepsy and ischaemia, and have good application prospects in the preparation of pain easing medicines, anticancer medicines and neuroscience tool medicines.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
InactiveUS20100130405A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifeCompound screeningNervous disorderBiglycanBecker's muscular dystrophy
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Example of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Synergistic insecticidal compositions
The present invention provides a synergistic insecticidal composition comprising as essential active ingredients a neuronal sodium channel antagonist in combination with one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of pyrethroids, pyrethoid-type compounds, recombinant nucleopolyhedroviruses capable of expressing an insect toxin, organophosphates, carbamates, formamidines, macrocyclic lactones, amidinohydrazones, GABA antagonists and acetylcholine receptor ligands. Also provided are methods for synergistic insect control and crop protection.
Owner:BASF AG
Conotoxin alphaD-GeXXA gene, and polypeptide and applications thereof
ActiveCN106367421AIncreased ability to inhibit acetylcholine receptorsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsConotoxinAcetylcholine receptor
The present invention provides a conotoxin alphaD-GeXXA gene, and a polypeptide and applications thereof, wherein the conotoxin alphaD-GeXXA gene is derived from South China Sea Strategoconus generalis, and the encoded conotoxin alphaD-GeXXA mature peptide can spontaneously form a homodimer so as to non-competitively inhibit acetylcholine receptors, such that the peptide has good application prospects in preparation of drugs or reagents for inhibition of acetylcholine receptors.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +2
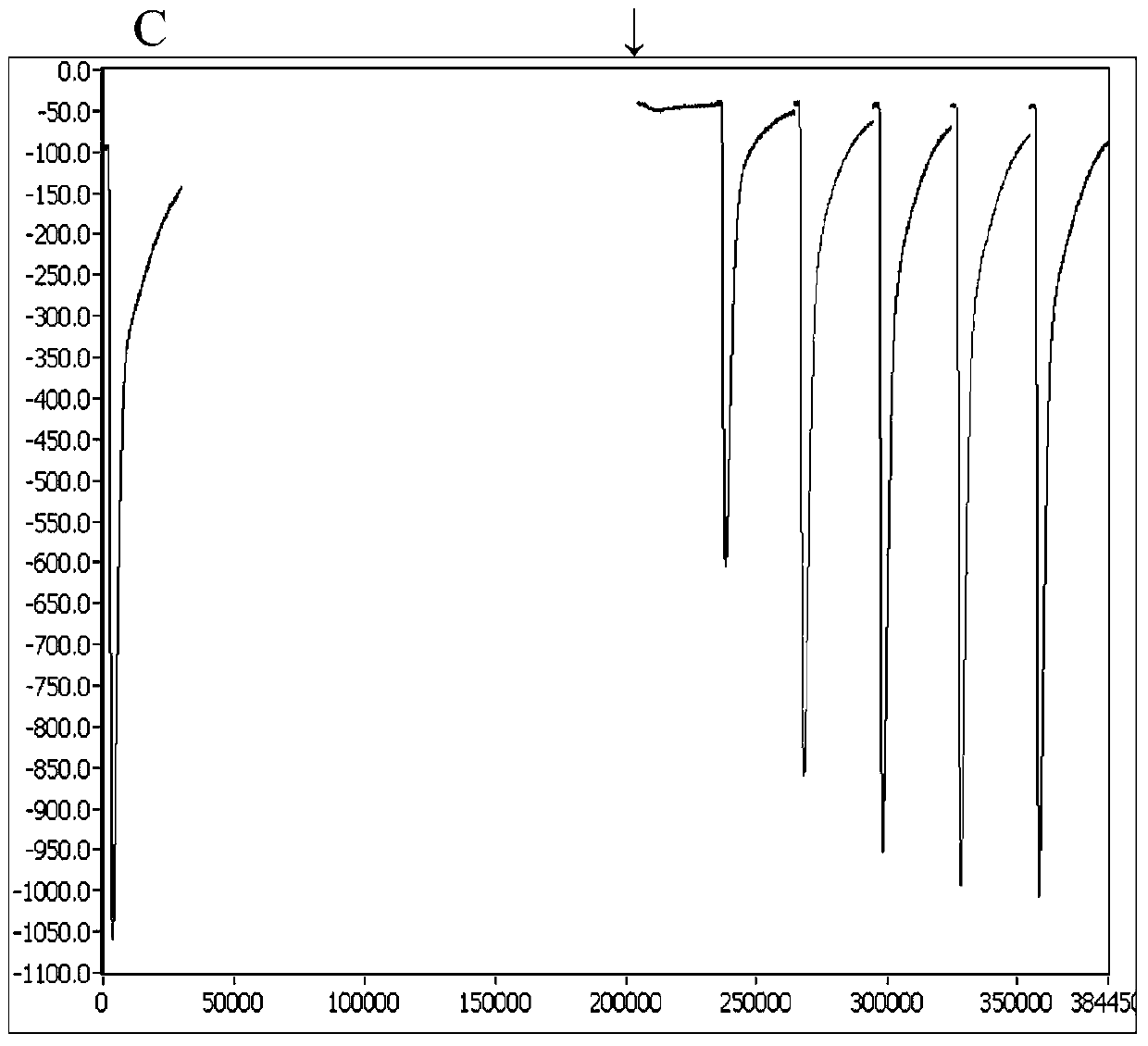
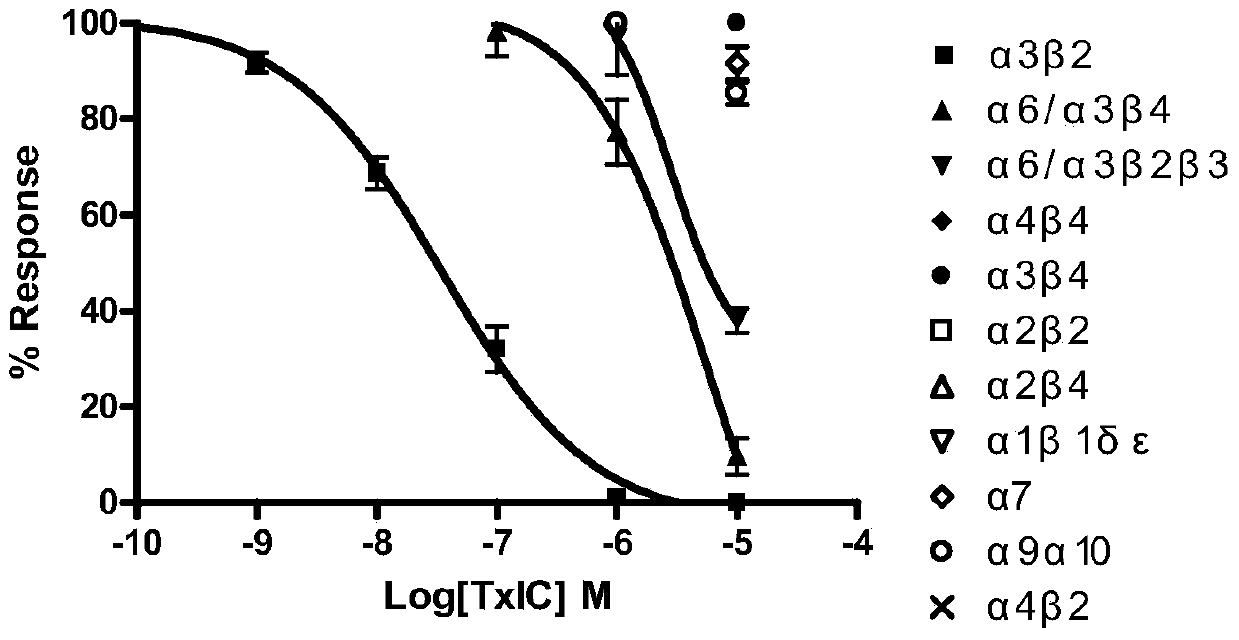
Alpha-conotoxin TxIC, medicinal composition thereof, preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN104262461AStrong analgesic activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsConotoxinAcetylcholine receptor
The invention belongs to the fields of biochemistry and molecular biology, and relates to alpha-conotoxin TxIC, a medicinal composition thereof, a preparation method thereof and an application. The invention further relates to a propeptide of conotoxin, a nucleic acid construct thereof, an expression vector thereof and a transformed cell, and a fused protein thereof. The invention further relates to a method for blocking an acetylcholine receptor and a pharmaceutical use of the conotoxin. The alpha-conotoxin disclosed by the invention can be used for specifically blocking the acetylcholine receptor (nAChRs) (such as alpha3beta2nAChR), has high analgesic activity and addiction withdrawal activity, and has a good application prospect on the aspect of preparation of analgesics, smoking addiction withdrawal medicaments or drug addiction withdrawal medicaments and the like.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
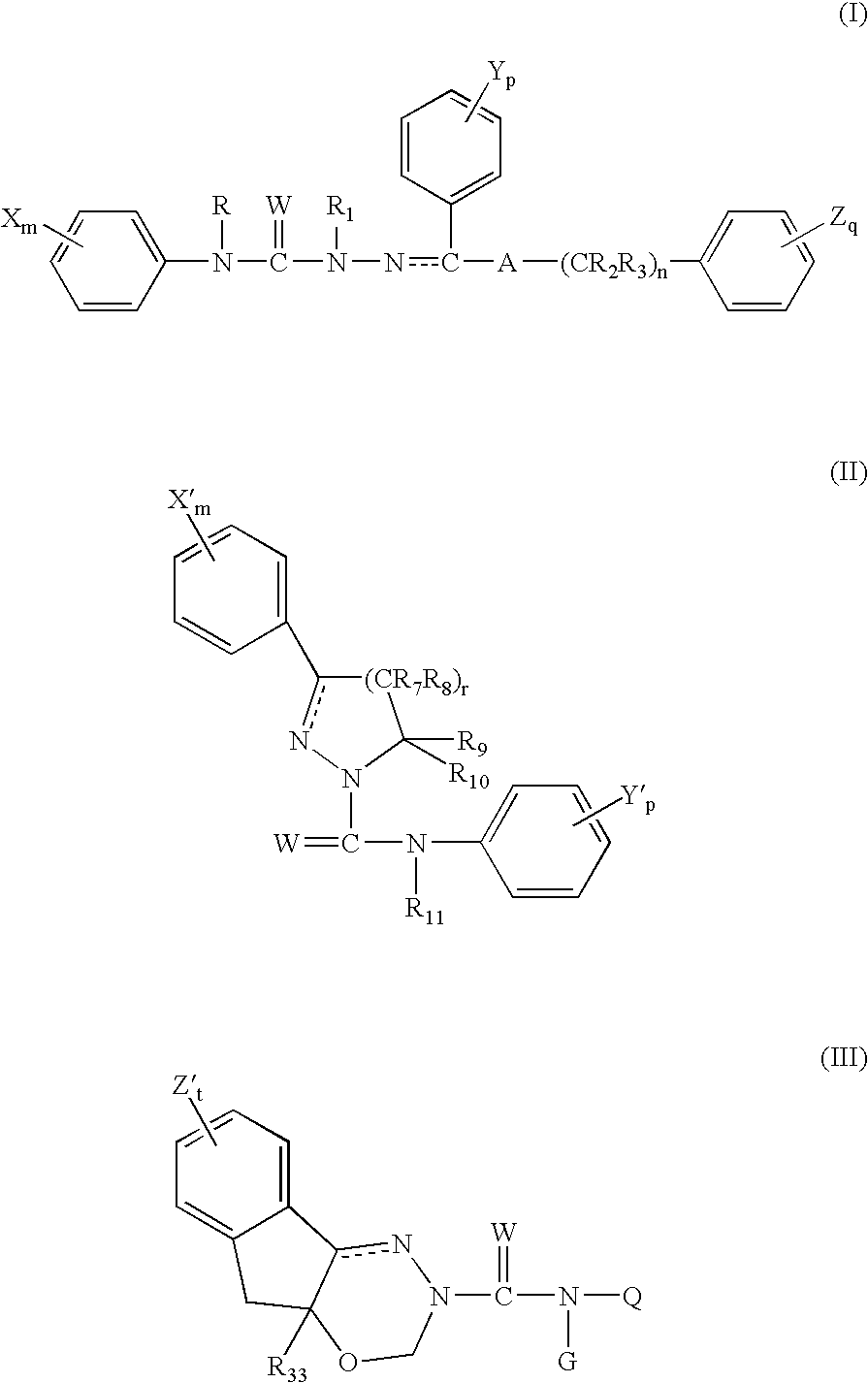
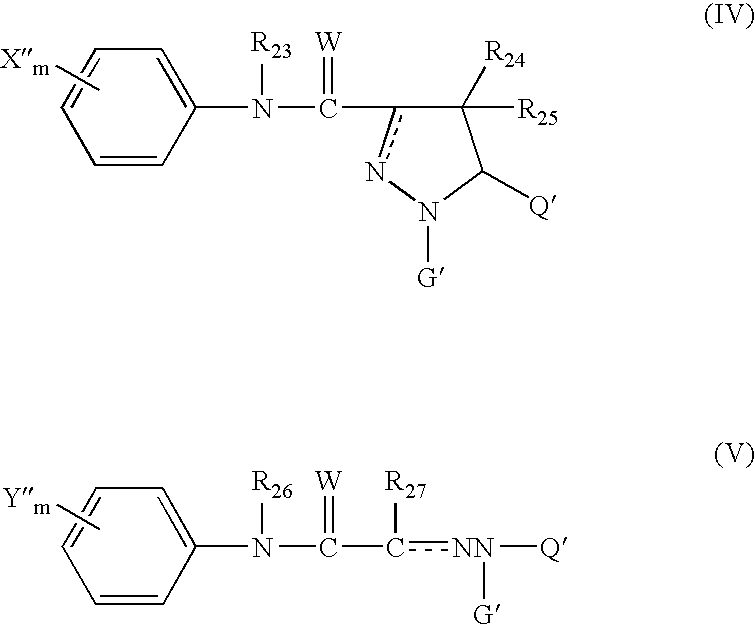
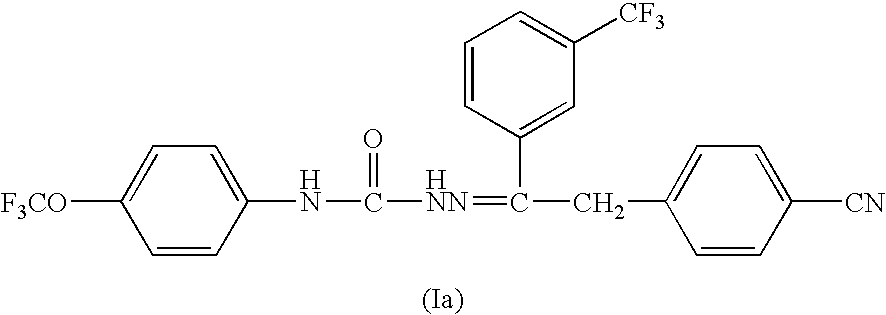
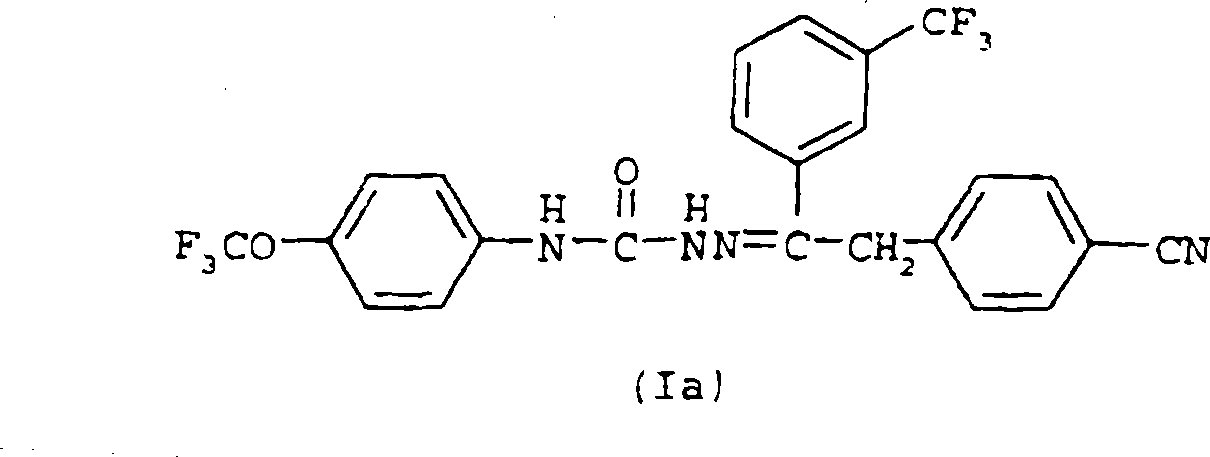
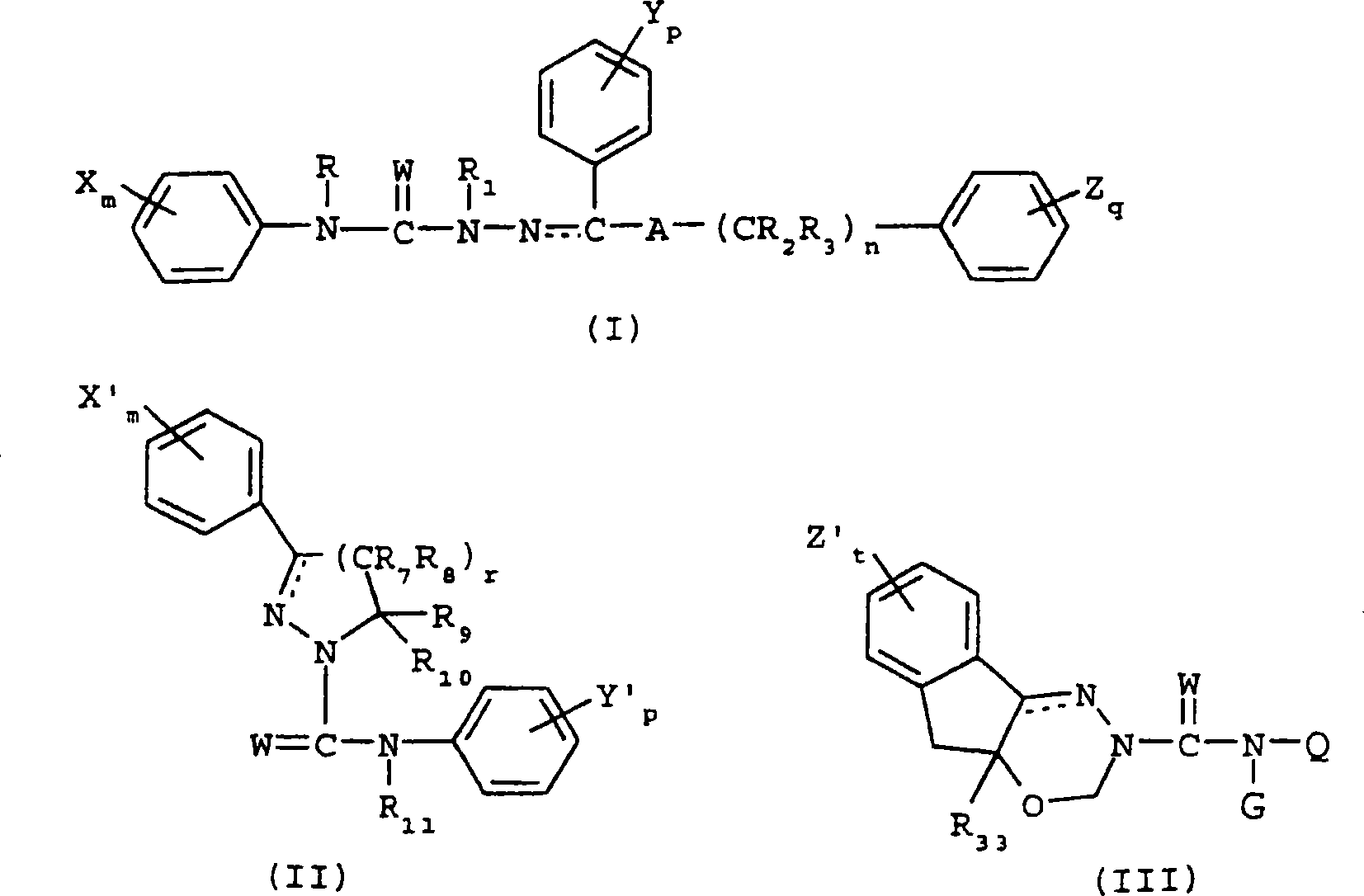
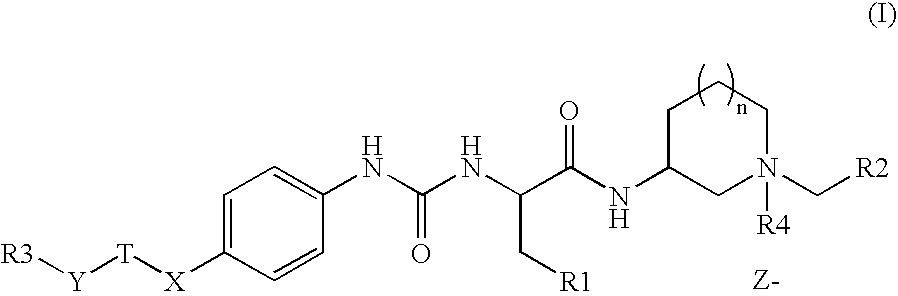
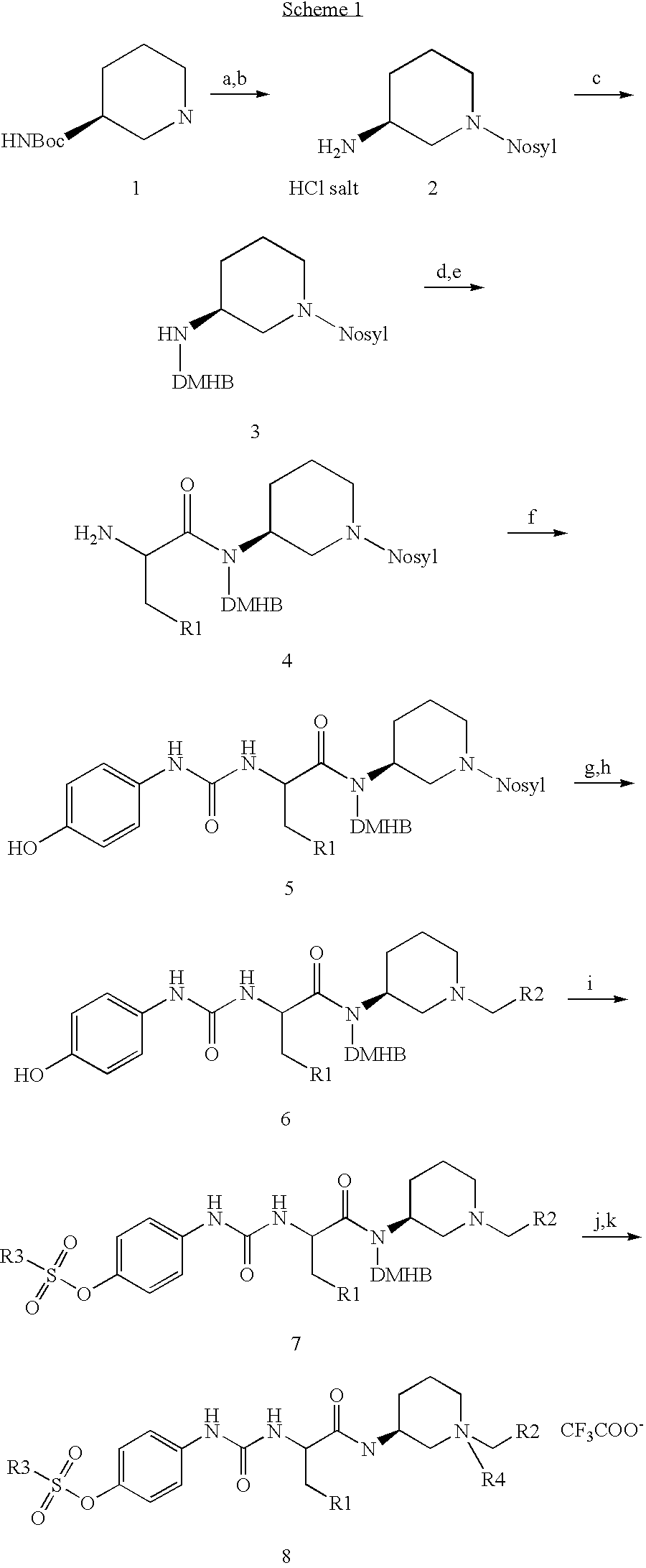
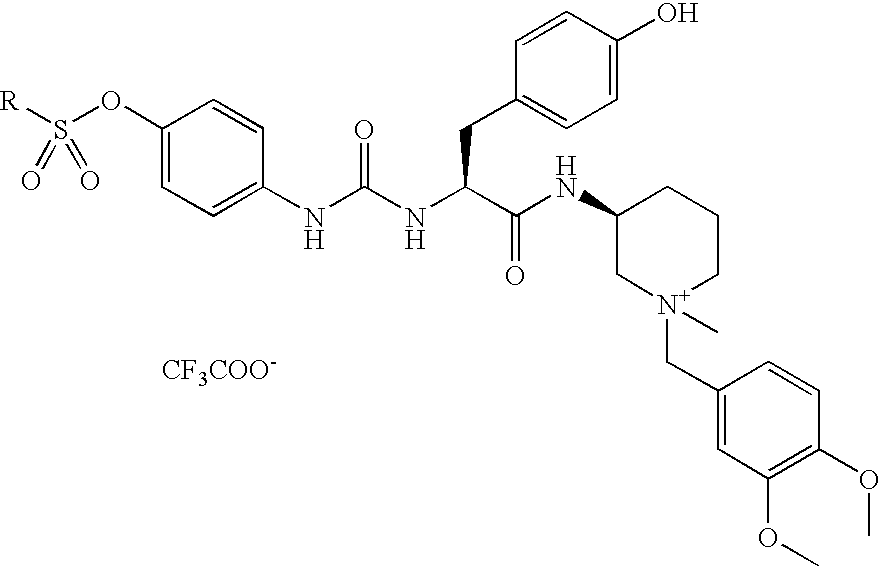
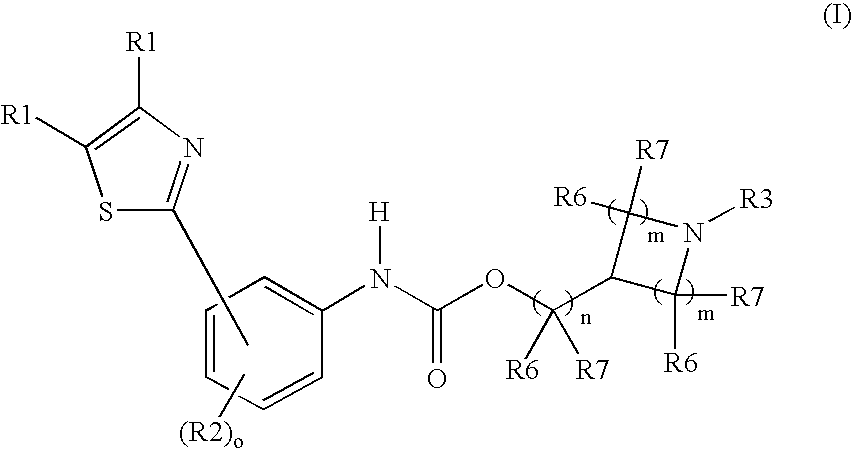
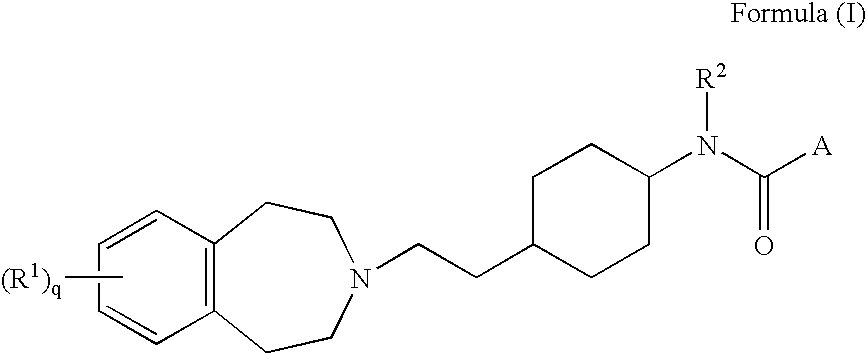
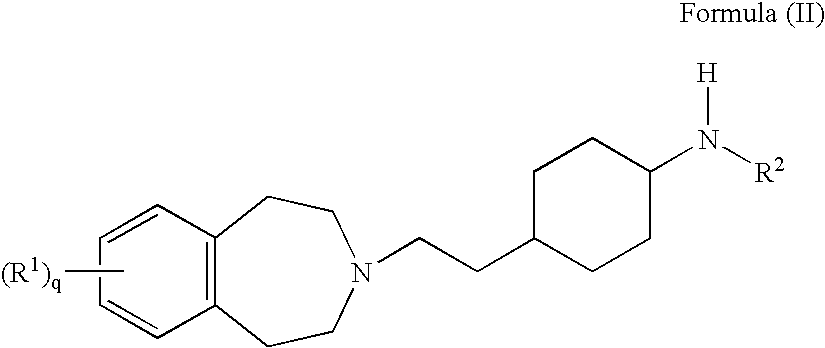
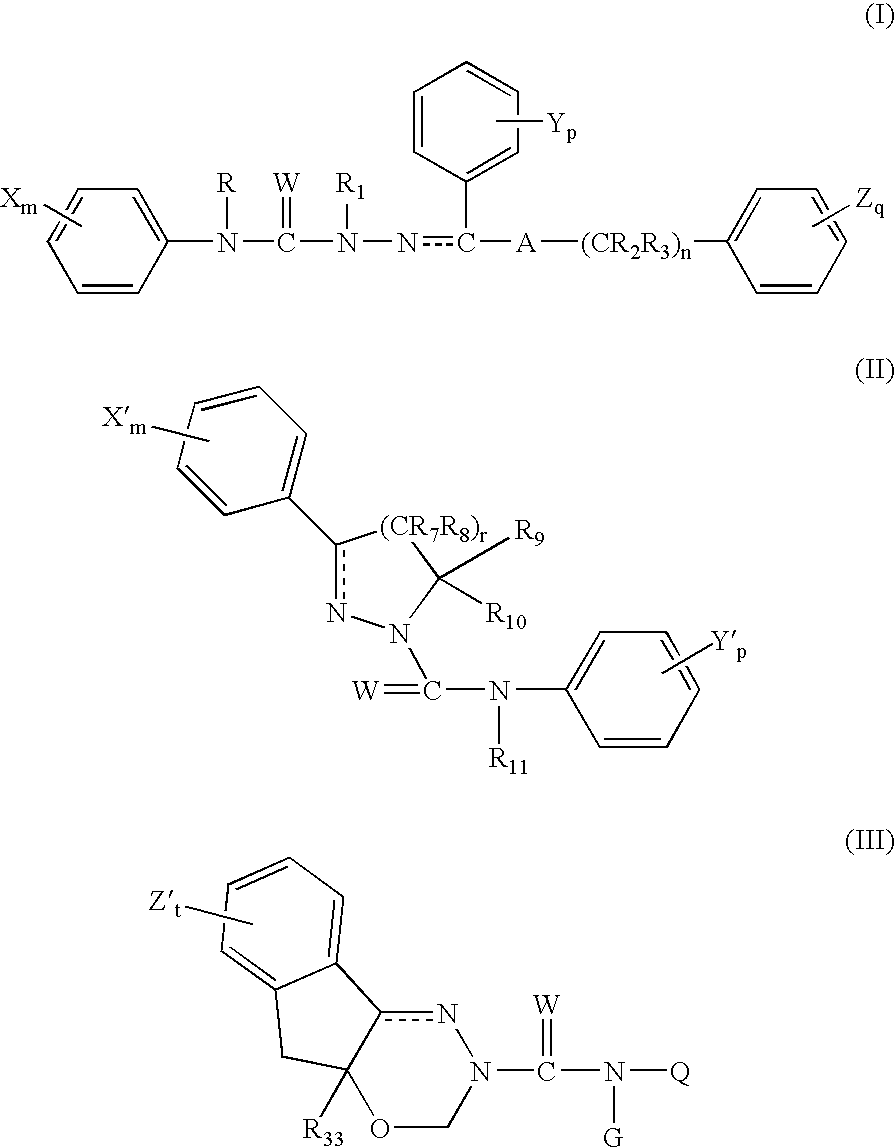
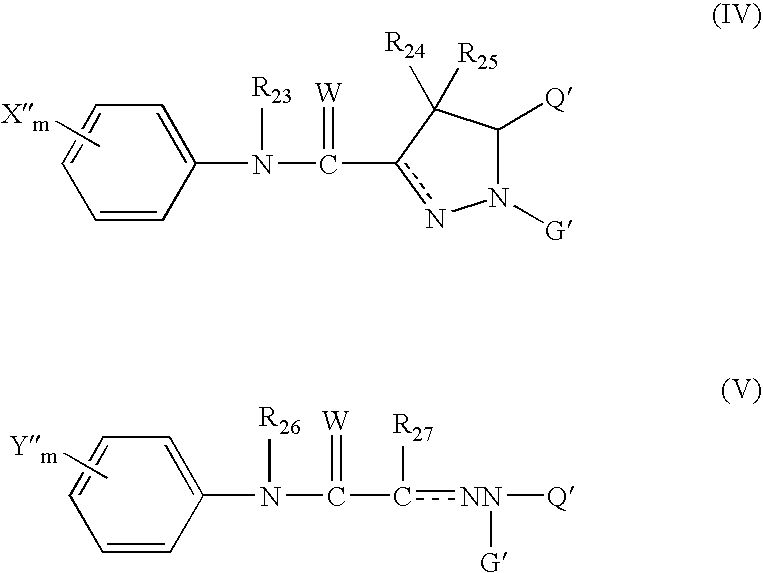
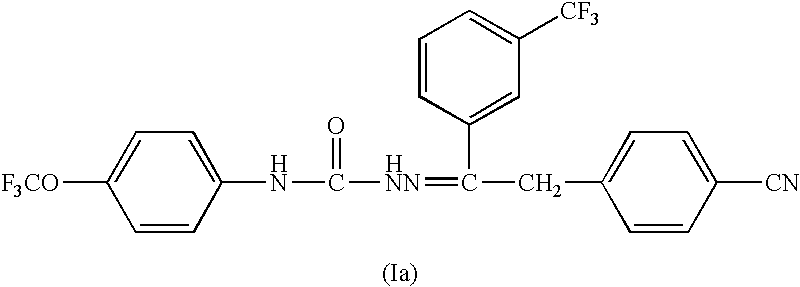
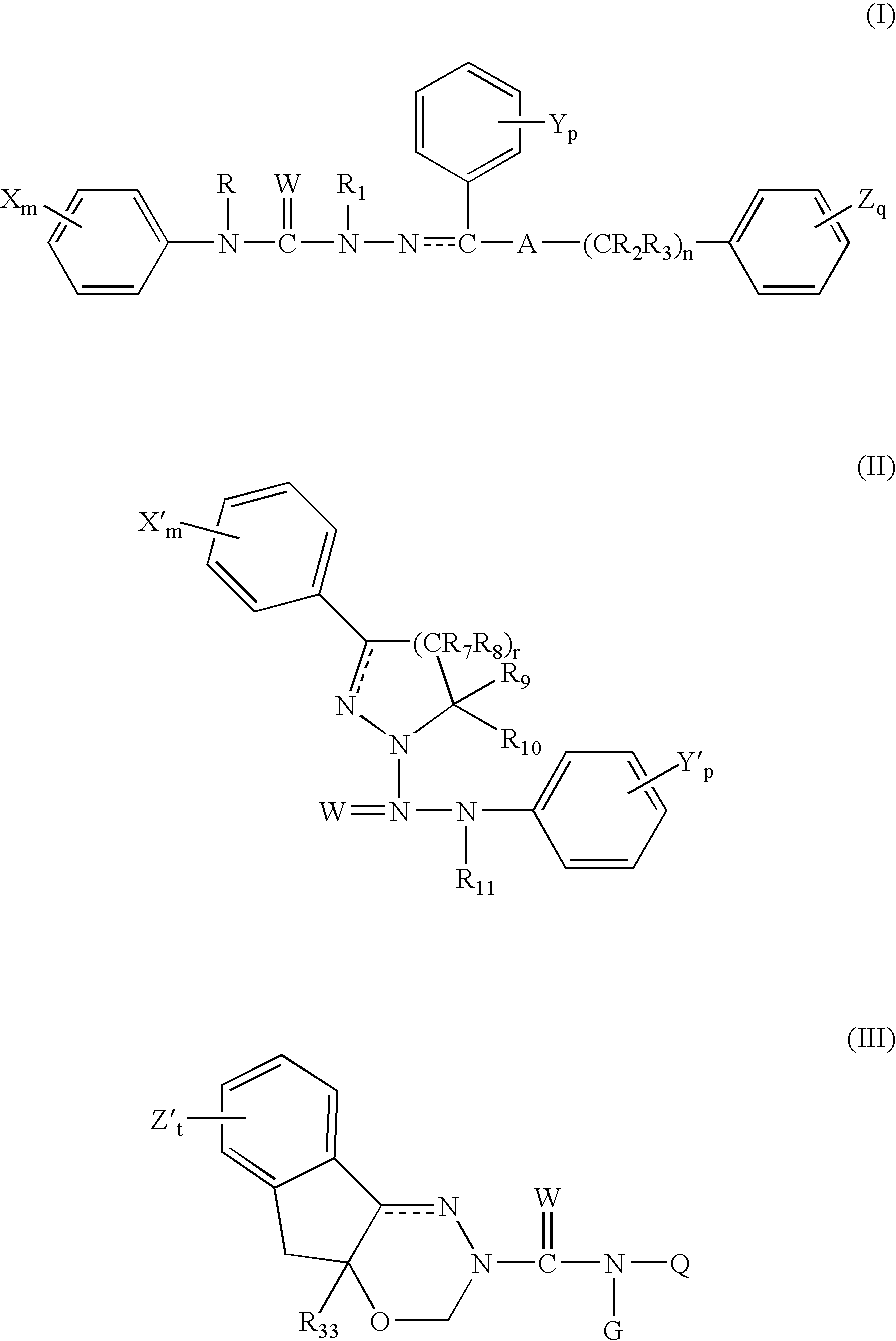
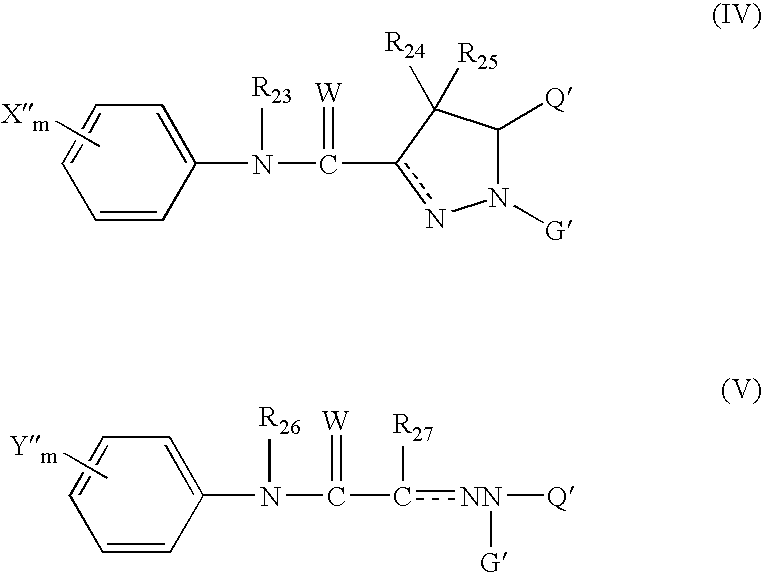
6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-B]pyridin-5-one allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
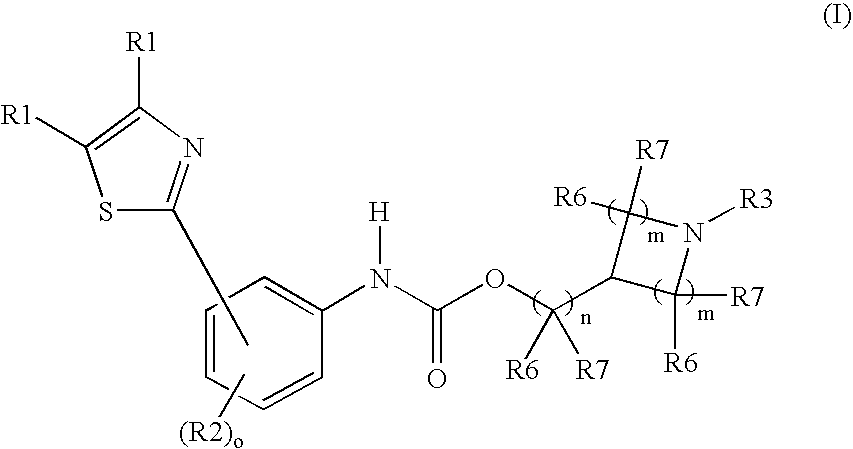
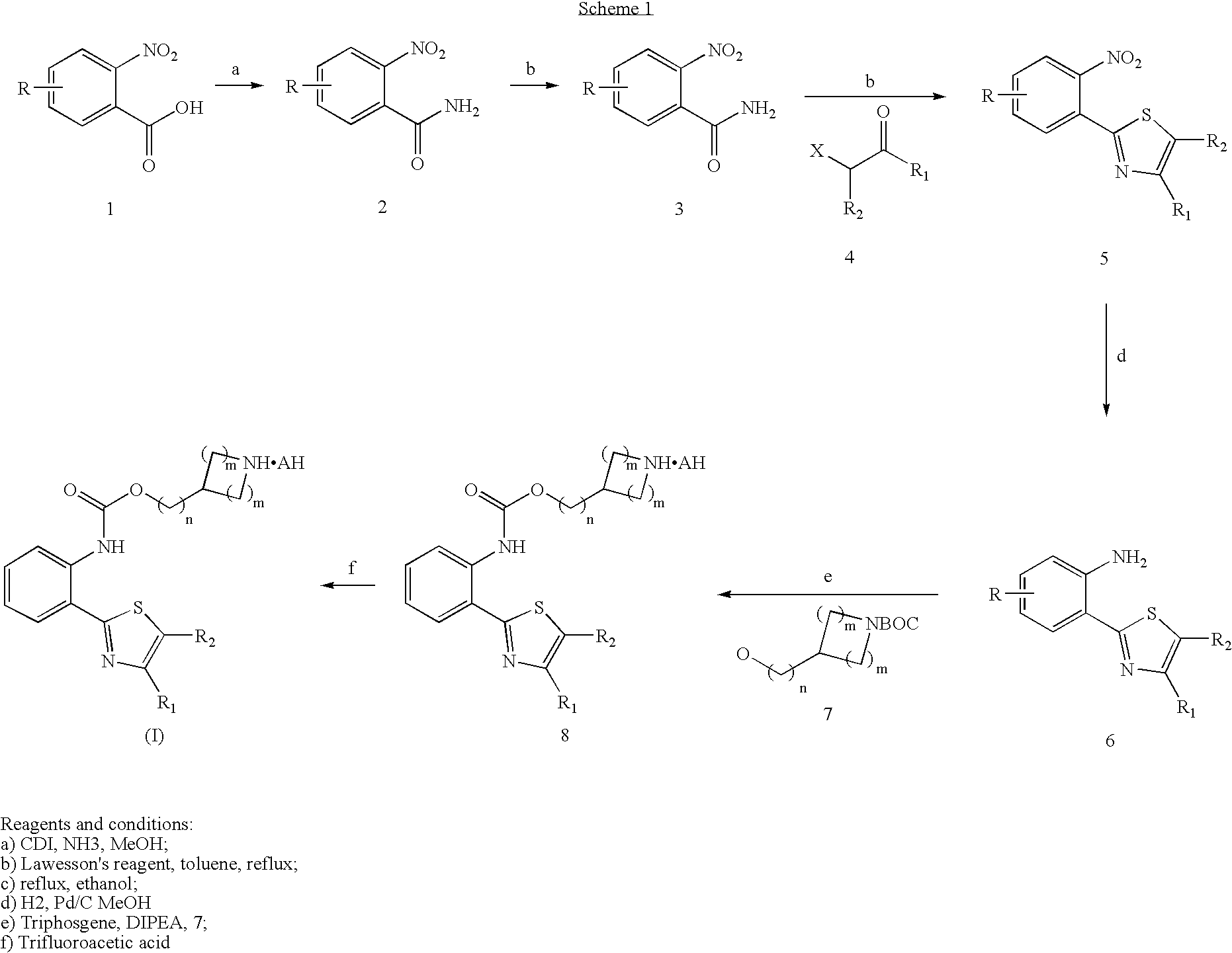
The present invention is directed to 6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5-one compounds which are allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The present invention is also directed to uses of the compounds described herein in the potential treatment or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders and diseases in which M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are involved. The present invention is also directed to compositions comprising these compounds. The present invention is also directed to uses of these compositions in the potential prevention or treatment of such diseases in which M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are involved.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
Peptide capable of transporting DNA to target neurocytes and brain
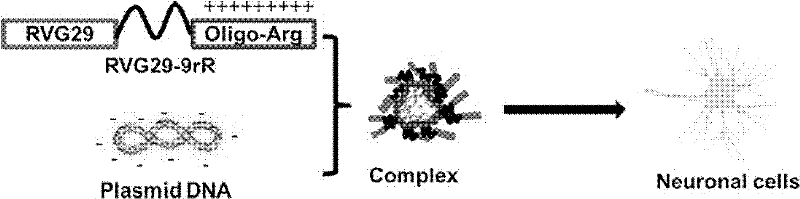
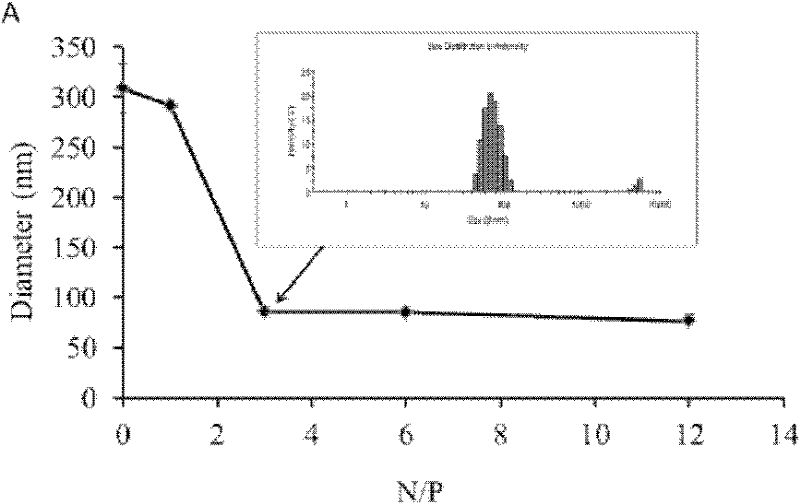
InactiveCN102250222ASolving difficulties that are difficult to be transported to the brain and expressedSmall sizeDepsipeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsAcetylcholine receptorDrug carrier
The invention discloses a peptide capable of transporting a DNA to target neurocytes and brain and belongs to the field of biological science and medicine carriers. The peptide is formed by combining a target sequence, a connecting sequence and a DNA combining sequence, wherein the target sequence is an acetylcholine receptor identifying ligand; and the DNA combining sequence is 9-poly-L-arginine, and the amino acid sequence of the 9-poly-L-arginine is represented by SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence list. The peptide can transport the DNA to the target neurocytes and brain.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
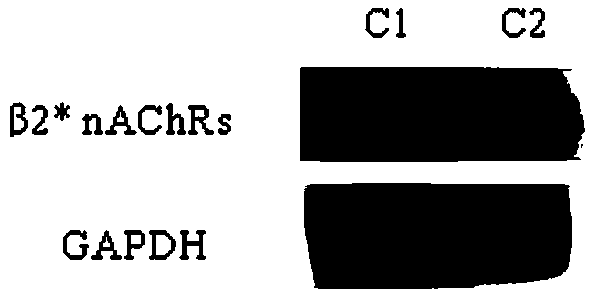
Method for determining expression quantity of nicotine acetylcholine receptors in rat lymphocytes
InactiveCN111208306AEfficient removalSolve the phenomenon of strip bandwidth smearingDisease diagnosisBiological testingAcetylcholine receptorWestern blot
The invention belongs to the field of life science research, and specifically relates to a method for detecting the expression quantity of nicotine acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in peripheral bloodlymphocytes of rats, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) separating peripheral blood lymphocytes of rats; 2) acquiring cell total protein, concentration determination and sample preparation; and 3) detecting the expression quantity of the nAChRs in the lymphocytes by a western blot (WB) experiment. According to the invention, the detection of the protein expression in theanimal peripheral blood in real time can be realized by determining the protein in the peripheral blood lymphocytes, and the kit has important significance for the research of nicotine addiction biomarkers.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY +1
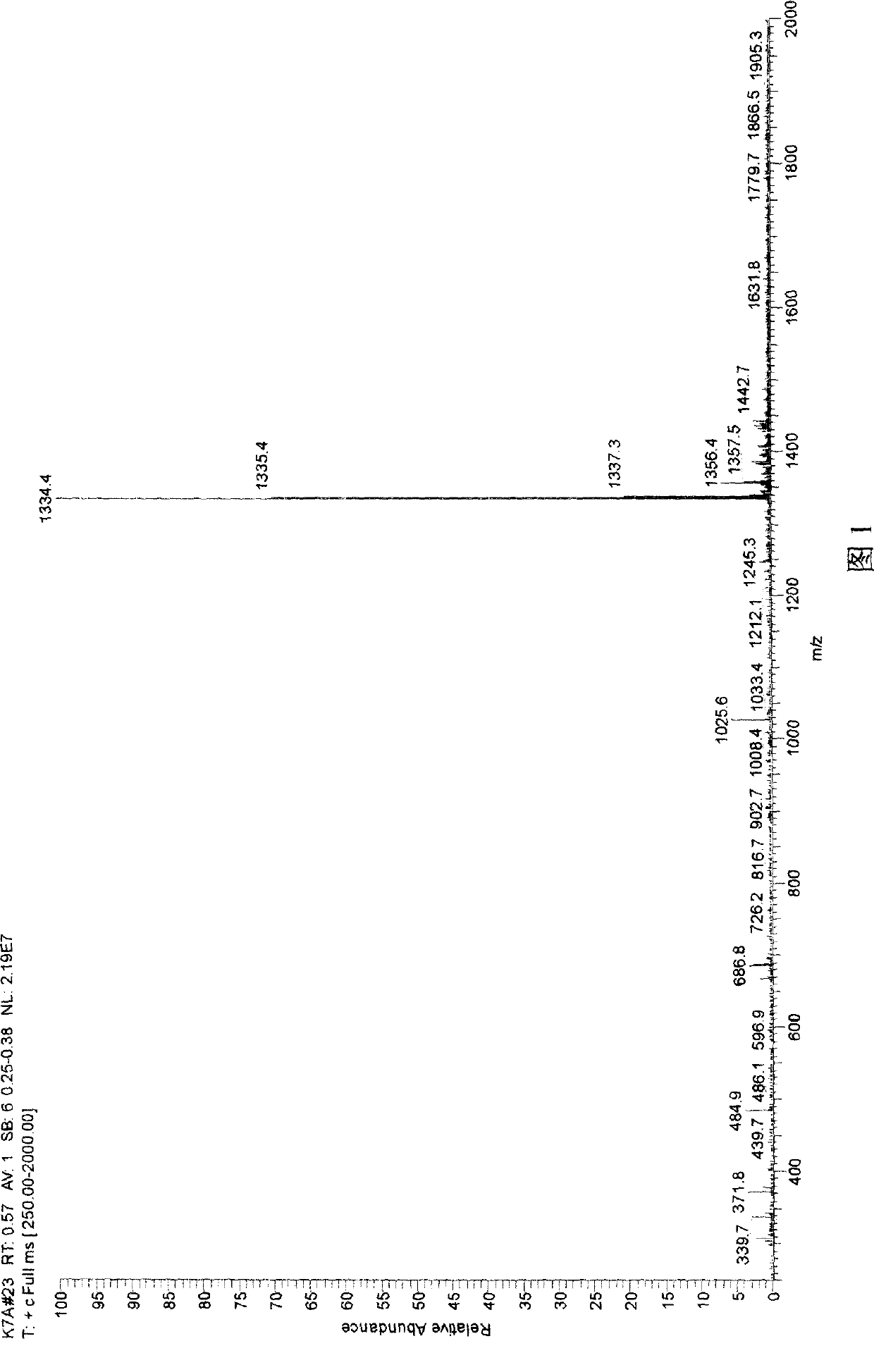
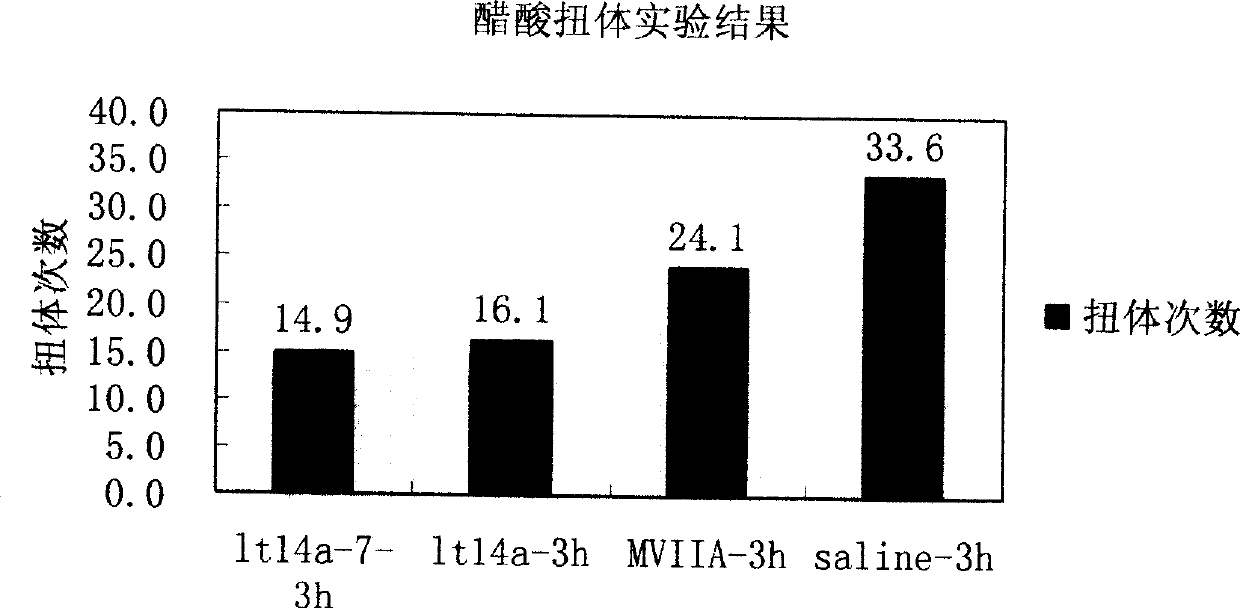
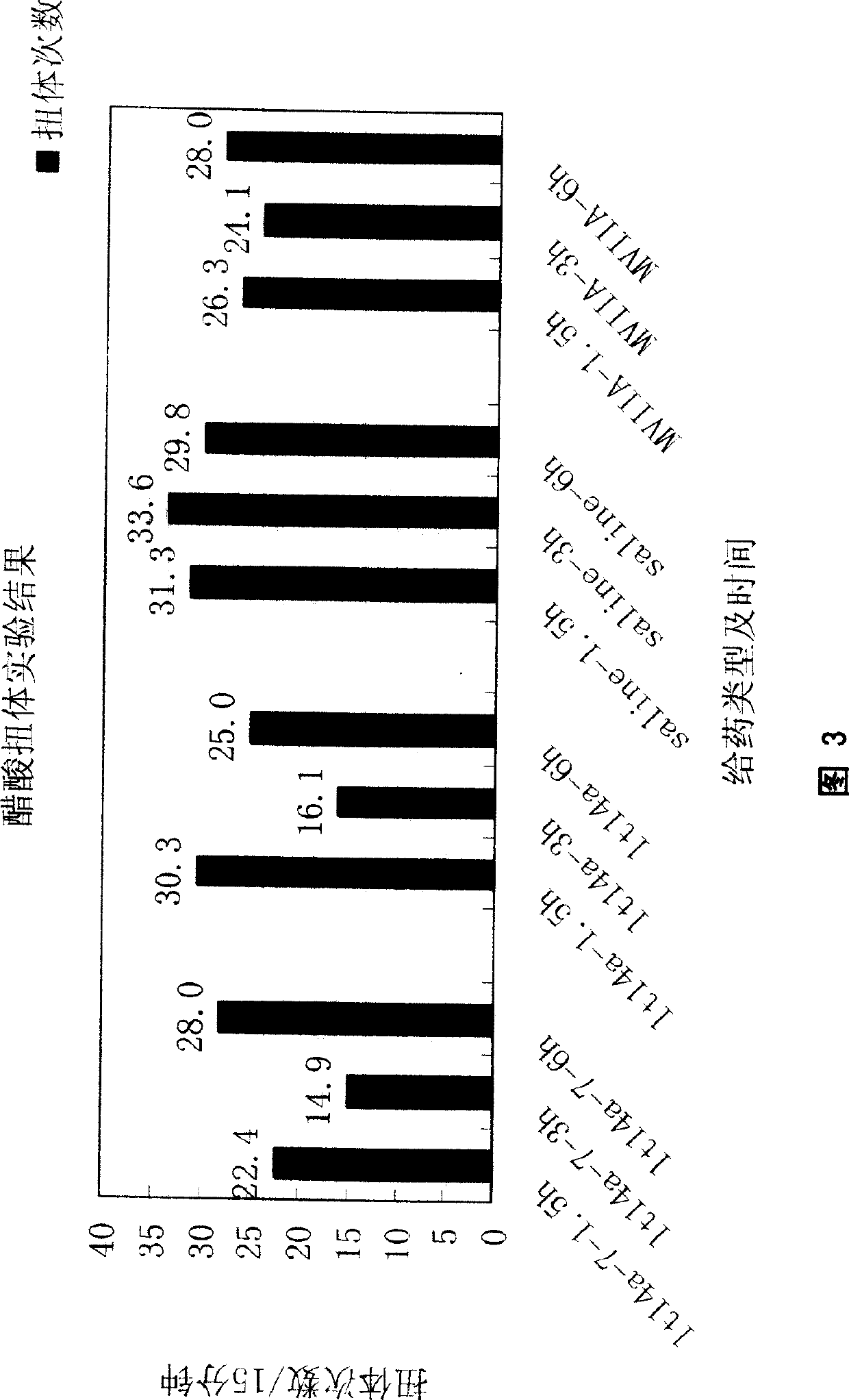
Signal conotoxin mutant polypeptides compound lt14a-7, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101372507AImprove superioritySite-specificNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseChemical synthesis
The invention relates to a mutant polypeptide compound lt14a-7 of South China Sea conus littertus linnaeus toxin lt14a, the preparation technology and application of the polypeptide. The peptide is obtained by replacing seventh lysine with lactamine through mature conotoxin lt14a, so as to be called as lt14a-7 (A is used for replacing the seventh K); the amino acid sequence direction is MCPPLCAPSCTNC from N end to C end. The lt14a-7 is prepared by the chemosynthesis method, and the polypeptide has the activity of antagonism neuron type acetylcholine receptor, important value in the development of analgesics, and good effect in the treatment of chronic pain caused by some diseases and receptor study.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Synergistic insecticidal compositions
InactiveUS20080108639A1Improve protectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSodium Channel AntagonistsCarbamate
The present invention provides a synergistic insecticidal composition comprising as essential active ingredients a neuronal sodium channel antagonist in combination with one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of pyrethroids, pyrethroid-type compounds, recombinant nucleopolyhedroviruses capable of expressing an insect toxin, organophosphates, carbamates, formamidines, macrocyclic lactones, amidinohydrazones, GABA antagonists and acetylcholine receptor ligands. Also provided are methods for synergistic insect control and crop protection.
Owner:TREACY MICHAEL FR +4
Synergistic insecticidal compositions
The present invention provides a synergistic insecticidal composition comprising as essential active ingredients a neuronal sodium channel antagonist in combination with one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of pyrethroids, pyrethroid-type compounds, recombinant nucleopolyhedroviruses capable of expressing an insect toxin, organophosphates, carbamates, formamidines, macrocycliclactones, amidinohydrazones, GABA antagonists and acetylcholine receptor ligands. Also provided are methods for synergistic insect control and crop protection.
Owner:BASF SE
Geminal substituted quinuclidine amide compounds as agonists of alpha-7 nicotonic acetylcholine receptors
InactiveUS20170369486A1Significant positive effectIncrease awarenessOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAcetylcholine receptorCognitive defects
The present invention relates to novel geminal substituted quinuclidine amide compounds, and pharmaceutical compositions of the same, that are suitable as agonists or partial agonists of α7-nAChR, and methods of preparing these compounds and compositions, and the use of these compounds and compositions in methods of maintaining, treating and / or improving cognitive function. In particular, methods of administering the compound or composition to a patient in need thereof, for example a patient with a cognitive deficiency and / or a desire to enhance cognitive function, that may derive a benefit therefrom.
Owner:AXOVANT SCI GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
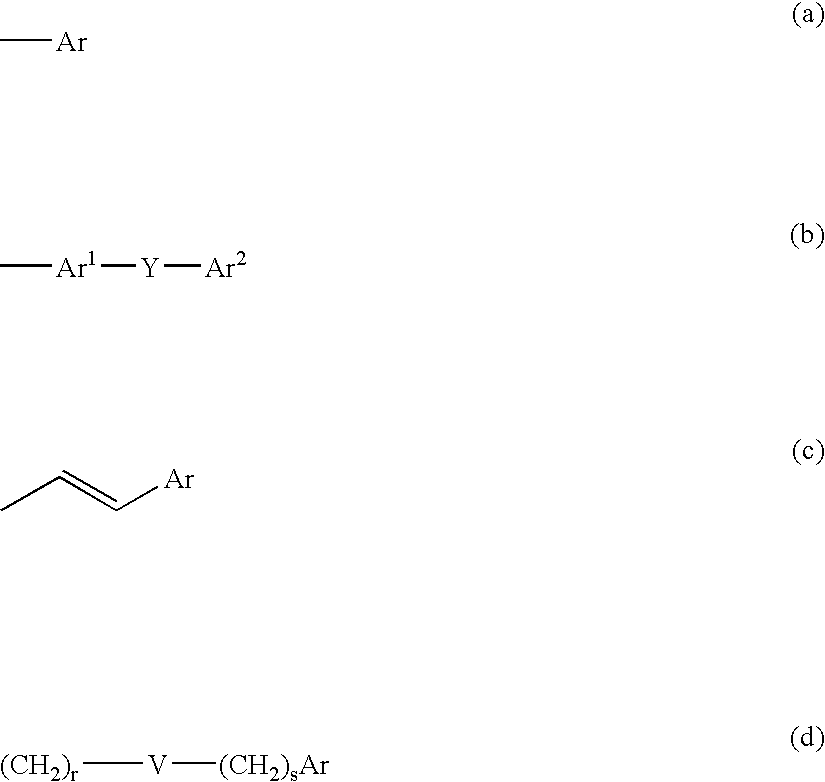
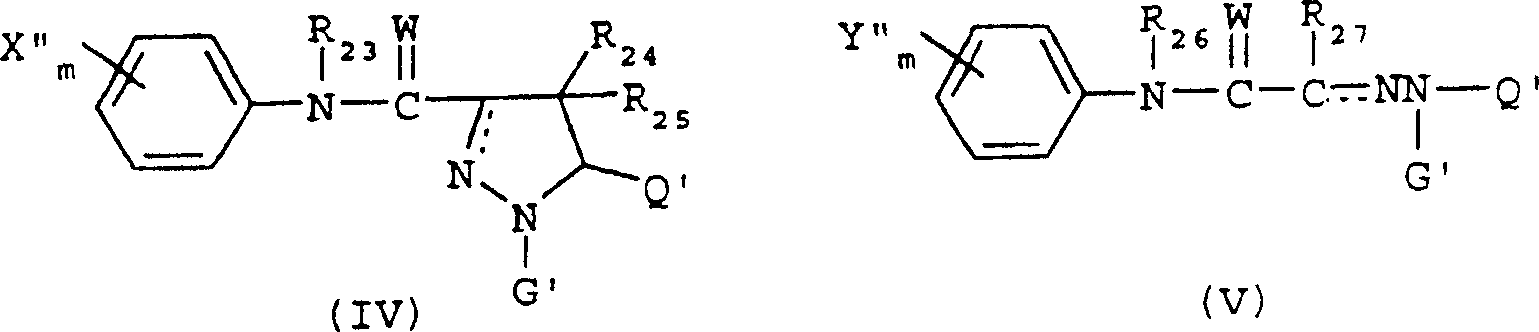
![6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-B]pyridin-5-one allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-B]pyridin-5-one allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ab30fb2-8fca-4493-8169-99a8cdaeecbf/US10329289-C00001.png)
![6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-B]pyridin-5-one allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-B]pyridin-5-one allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ab30fb2-8fca-4493-8169-99a8cdaeecbf/US10329289-C00002.png)
![6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-B]pyridin-5-one allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-B]pyridin-5-one allosteric modulators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5ab30fb2-8fca-4493-8169-99a8cdaeecbf/US10329289-C00003.png)