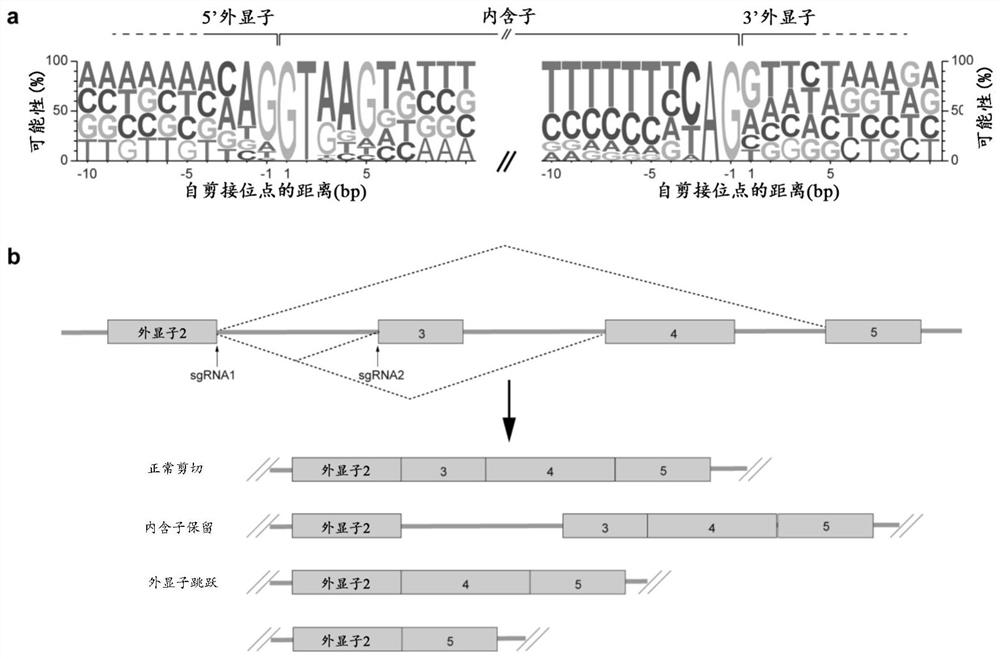
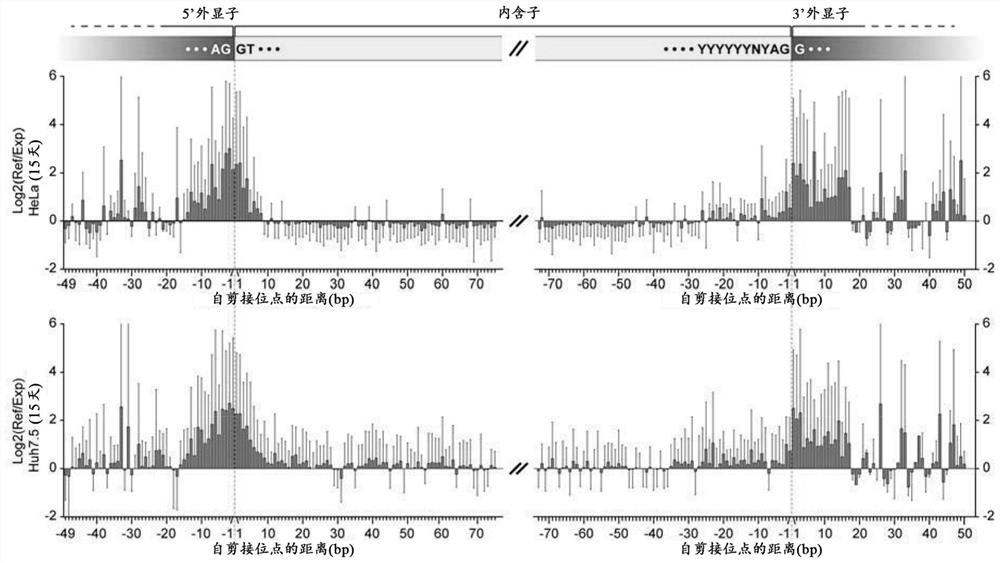
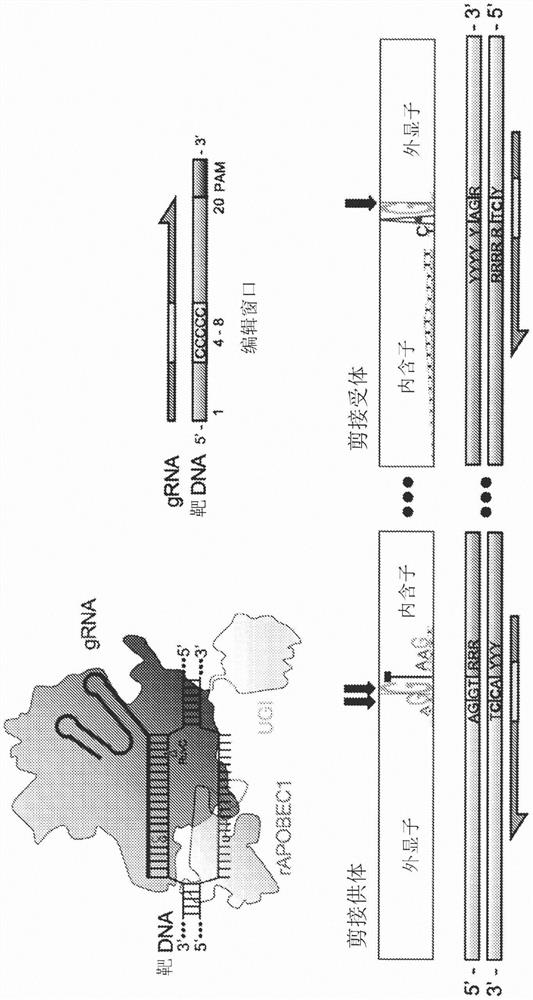
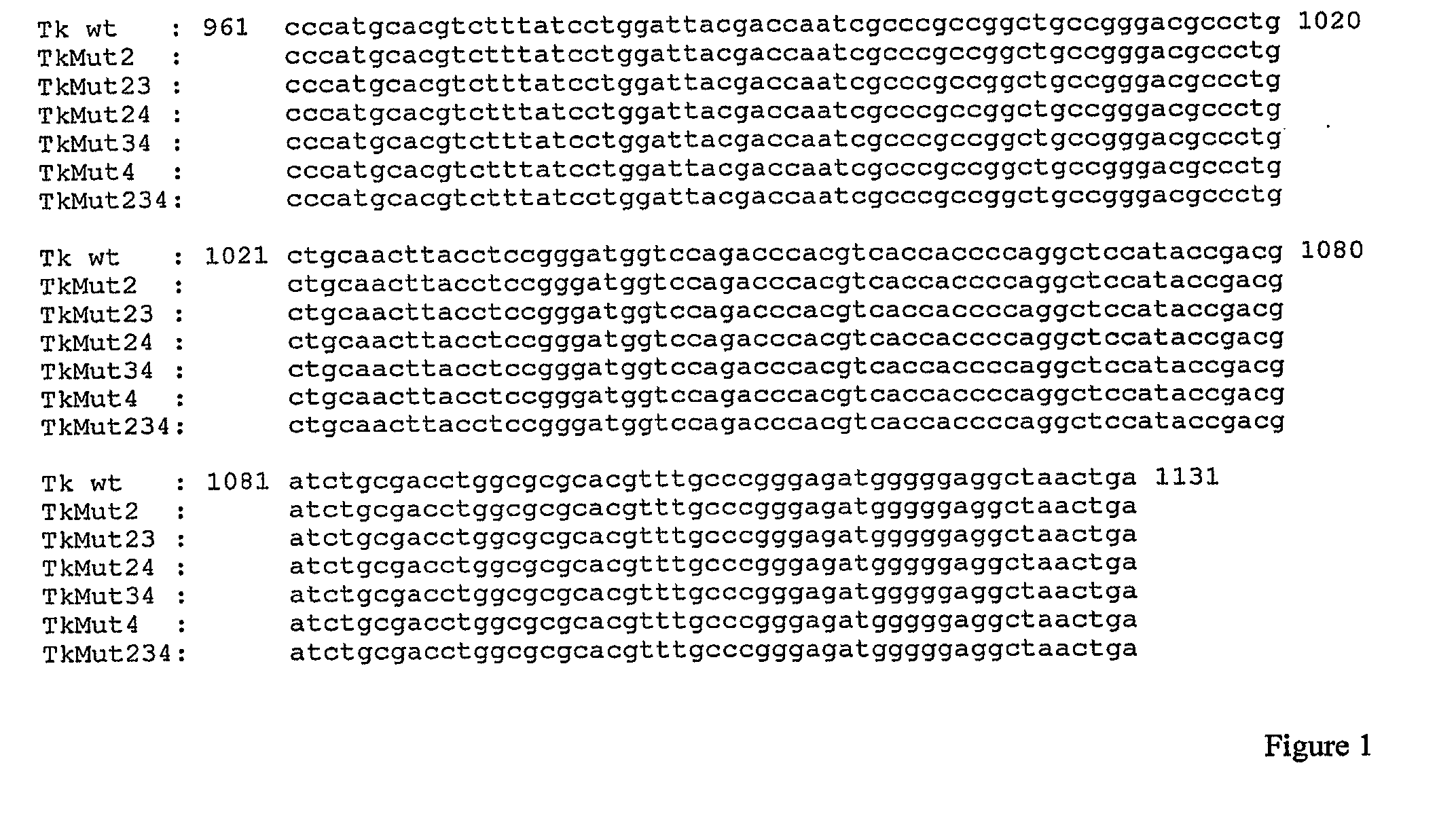Patents
Literature
40 results about "Splice Donor Site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
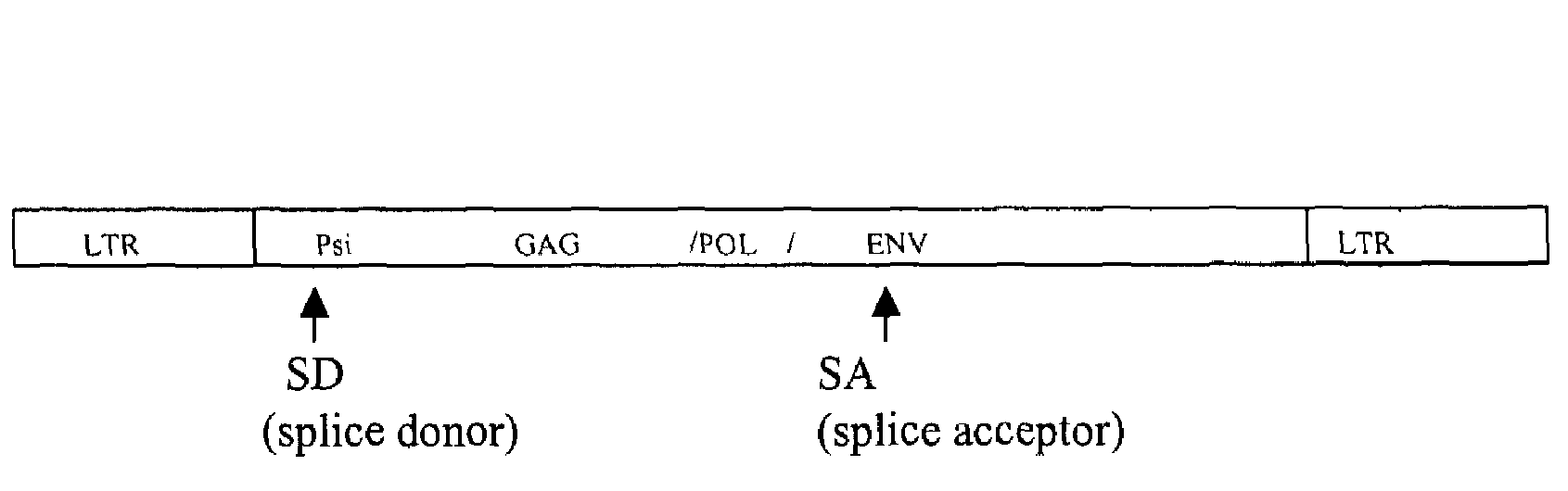
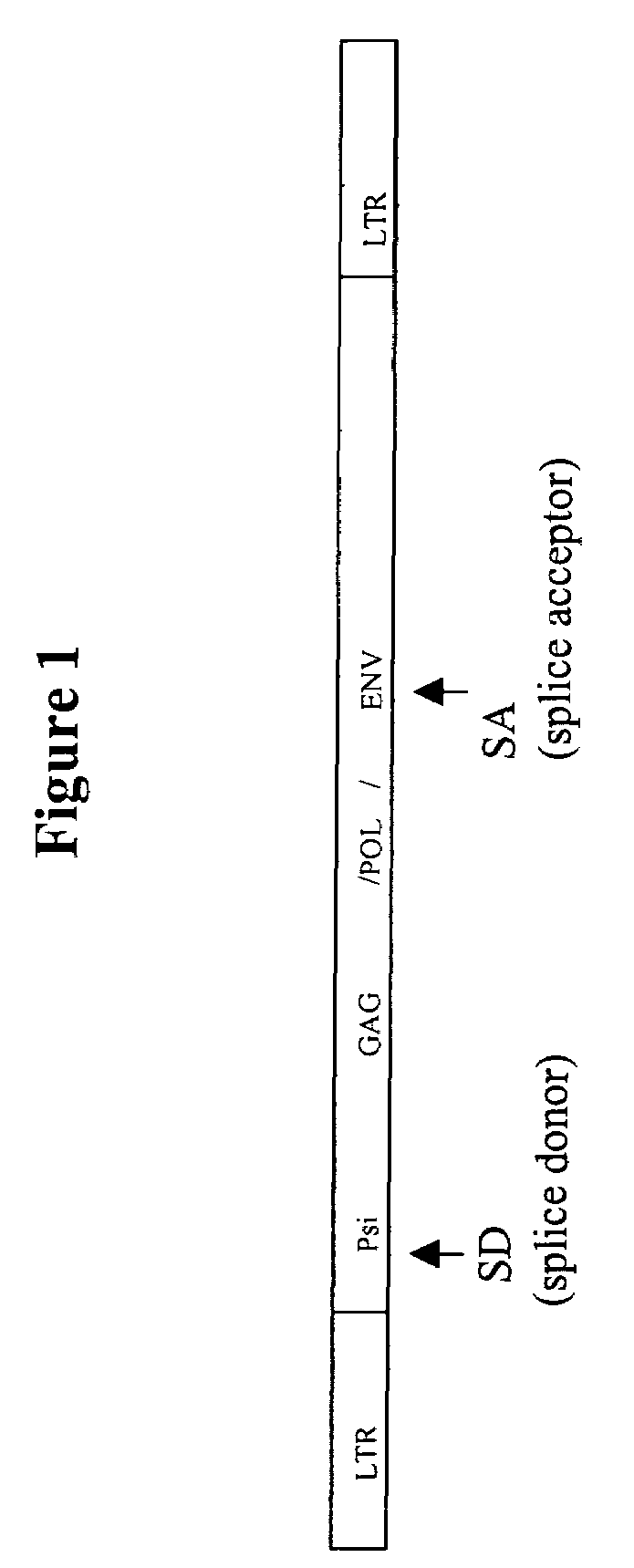
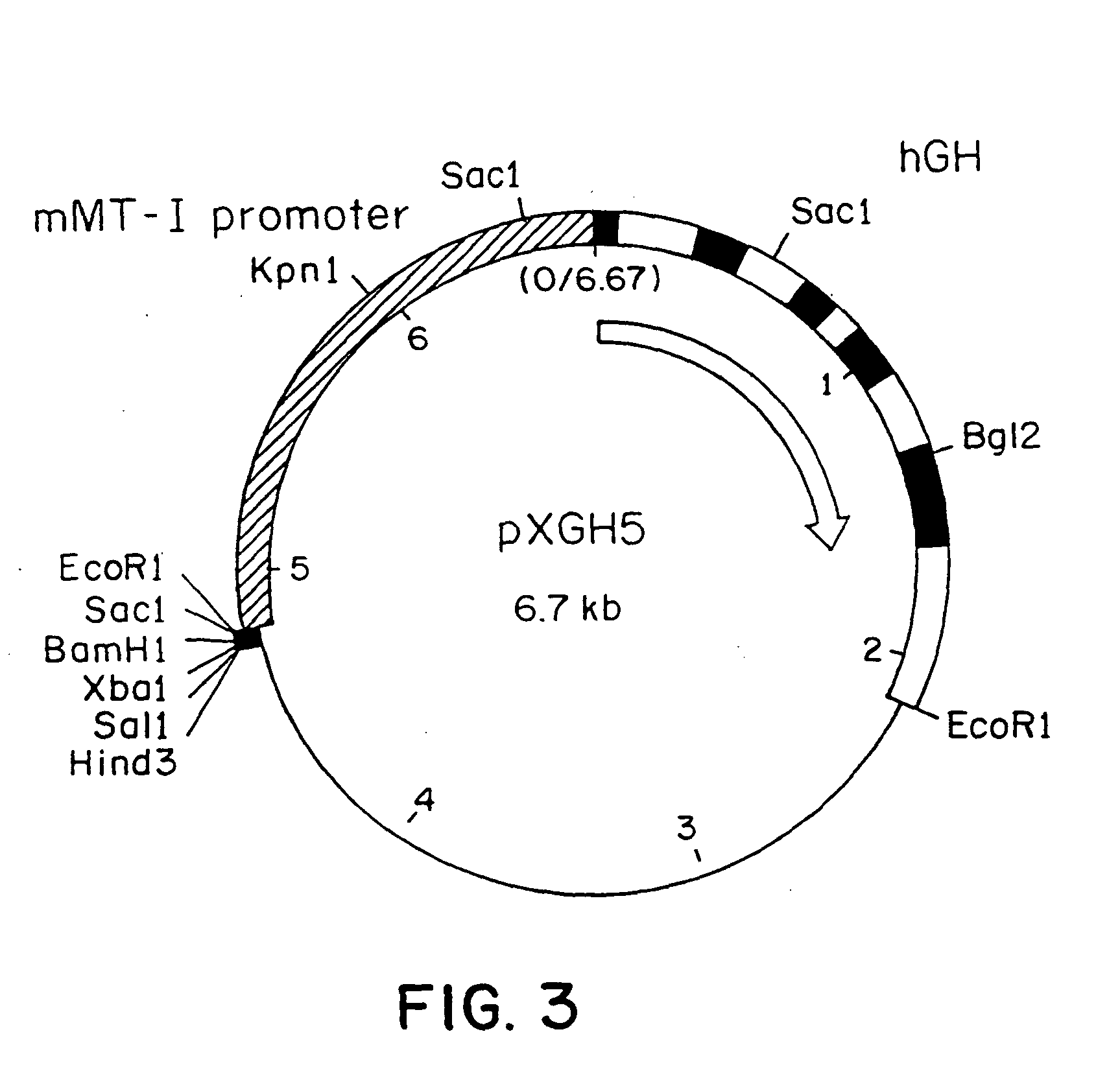
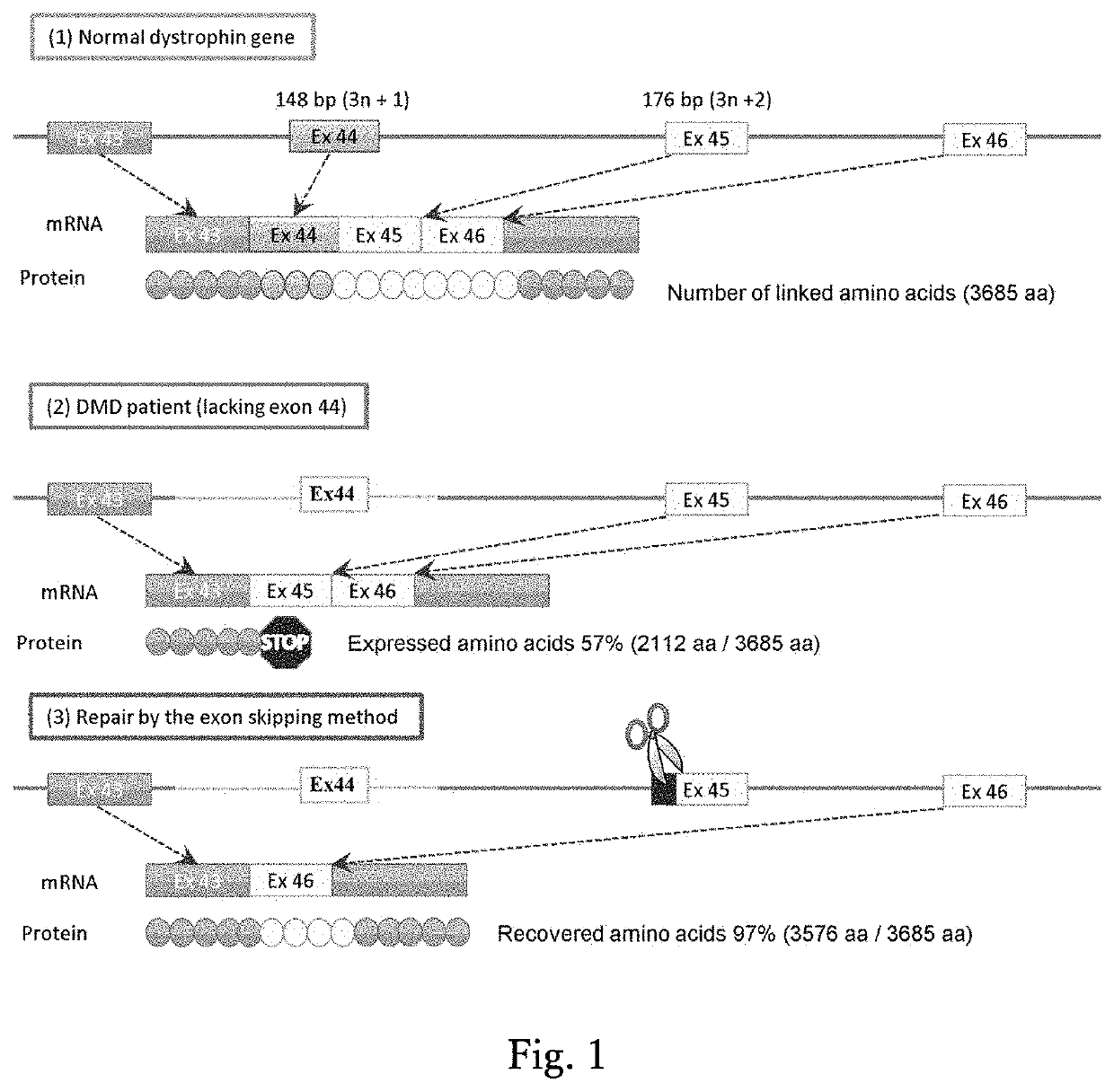
Retroviral vectors comprising a functional splice donor site and a functional splice acceptor site
InactiveUS7303910B2Efficient expressionIncrease rangeSsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
A retroviral vector is described. The retroviral vector comprises a functional splice donor site and a functional splice acceptor site; wherein the functional splice donor site and the functional splice acceptor site flank a first nucleotide sequence of interest (“NOI”); wherein the functional splice donor site is upstream of the functional splice acceptor site; wherein the retroviral vector is derived from a retroviral pro-vector; wherein the retroviral pro-vector comprises a first nucleotide sequence (“NS”) capable of yielding the functional splice donor site and a second NS capable of yielding the functional splice acceptor site; wherein the first NS is downstream of the second NS; such that the retroviral vector is formed as a result of reverse transcription of the retroviral pro-vector.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
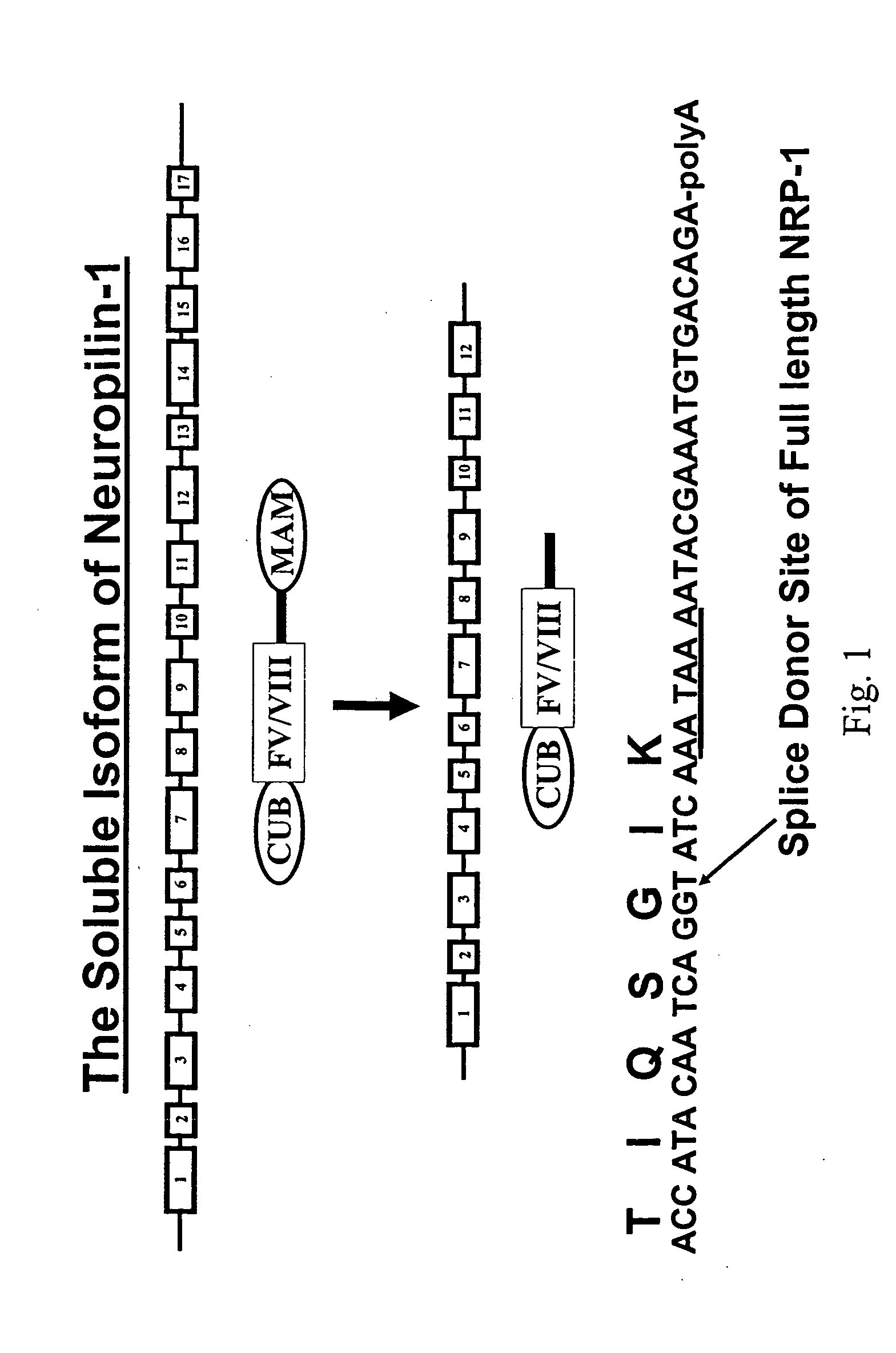
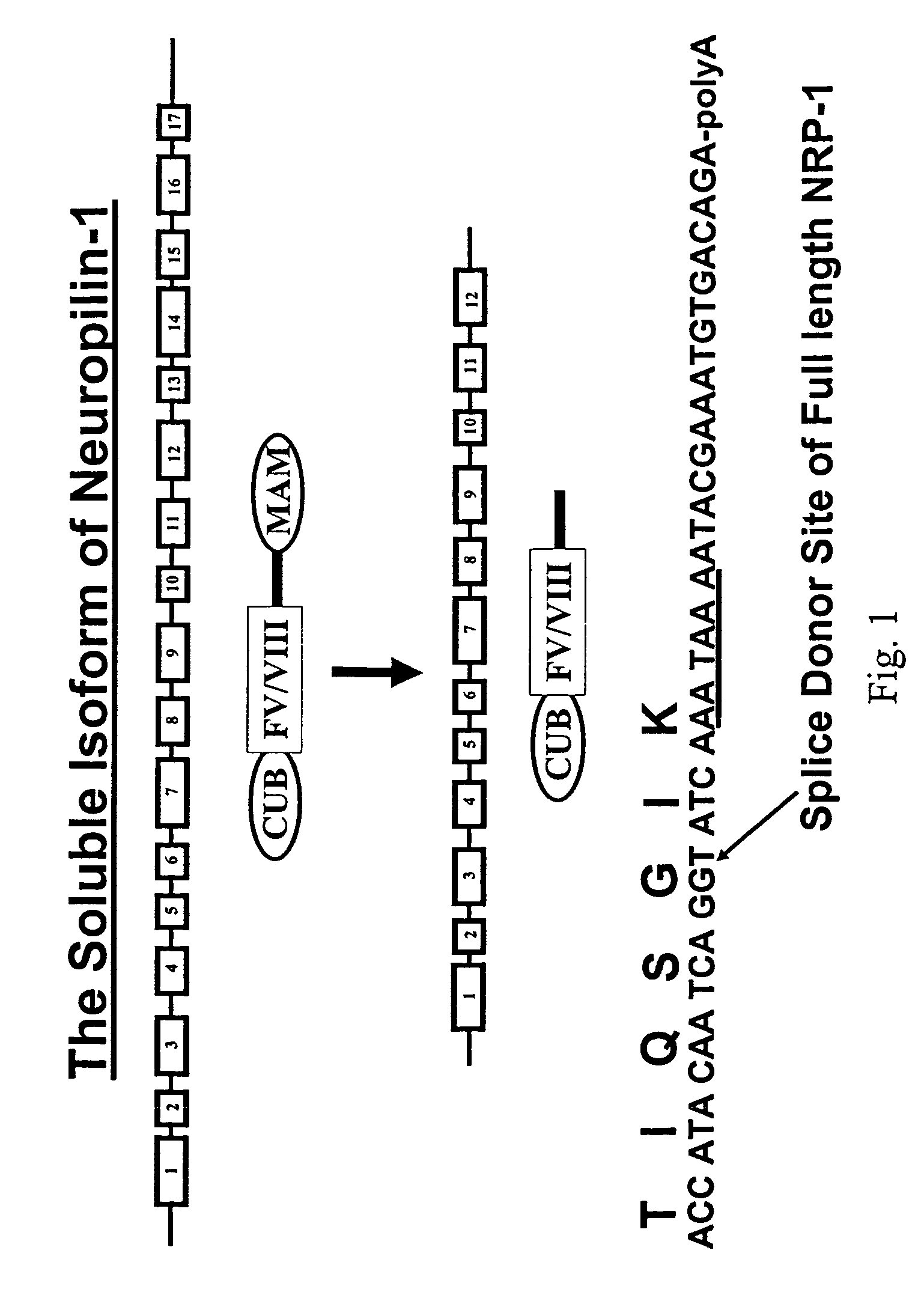
Human soluble neuropilin-1 primary polyadenylation signal and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050175591A1Easy to transportImprove translationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsPoly-A RNANucleotide
The human soluble neuropilin-1 (sNRP) polyadenylation signal (sNRP-poly(A)), situated downstream of the GT splice donor site of intron 12 of the full-length neuropilin-1 gene, also functions as the termination codon for sNRP. This 17 nucleotide sequence efficiently facilitates addition of poly(A) tails to RNAs expressed in cells. The present invention shows that this optimally succinct sequence has similar activity to the SV40 polyadenylation signal that is currently used in expression vectors. By using this shorter dual termination / polyadenylation signal and avoiding the need for large and cumbersome polyadenylation signals, expression vectors may be engineered to carry considerably larger genes.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Method of producing transcripts using cryptic splice sites
The invention is directed to a method of preparing a nucleic acid sequence with a modified splice site usage profile, which employs the use of a nucleic acid sequence comprising a cryptic splice donor site. The invention also provides a method of producing an alternate form of an RNA molecule encoded by a nucleic acid sequence, which nucleic acid sequence comprises a cryptic splice donor site, a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, and a splice acceptor site.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
Polypeptide producing cells
ActiveUS8354516B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationPoly-A RNA
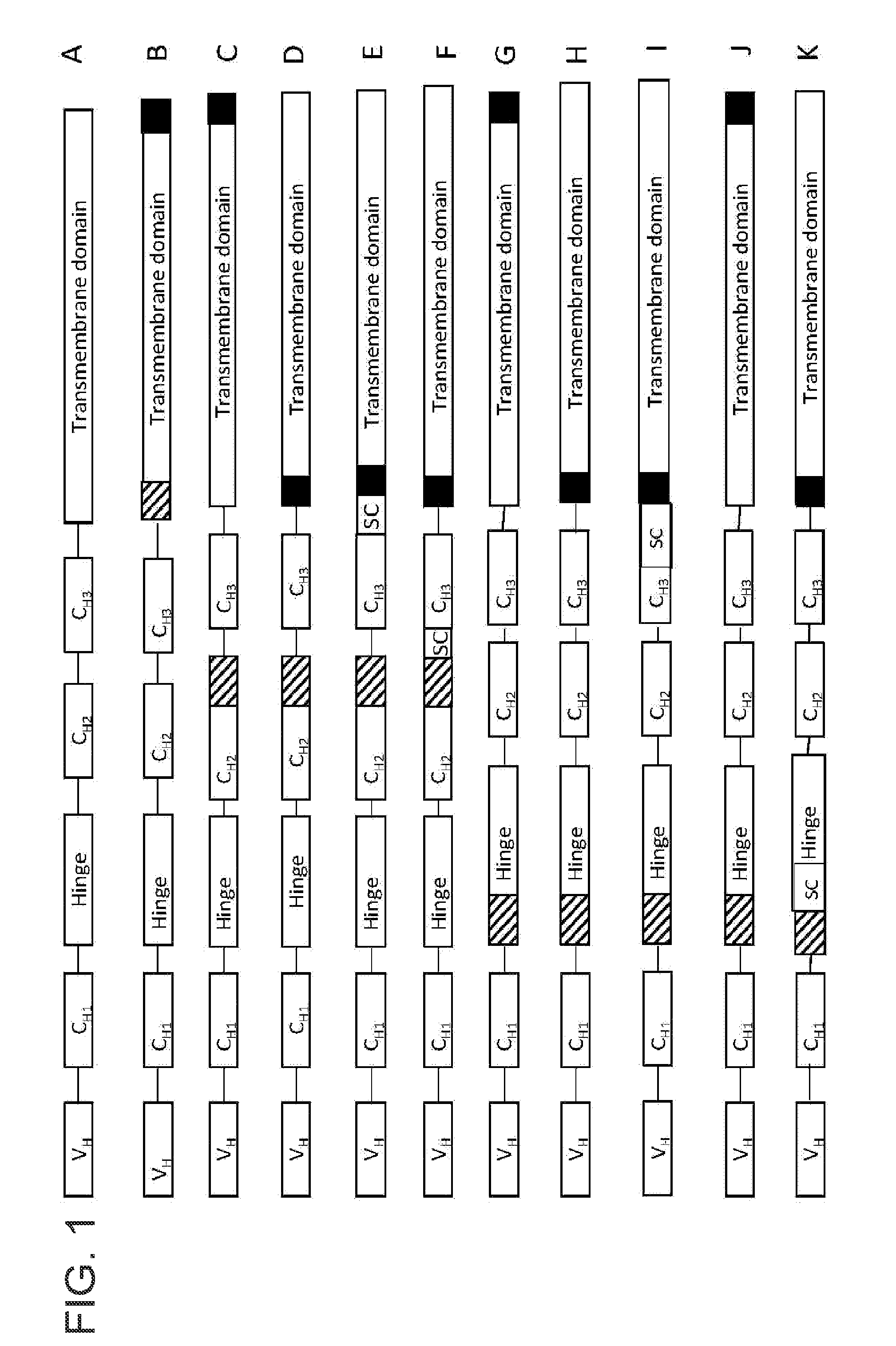
The current invention describes a nucleic acid comprising in a 5′ to 3′ direction a) a first nucleic acid encoding a heterologous polypeptide without an in frame stop codon, b) a second nucleic acid beginning with a 5′ splice donor site and terminated by a 3′ splice acceptor site comprising an in frame translational stop codon and a polyadenylation signal, and c) a nucleic acid encoding i) at least a fragment of a transmembrane domain, or ii) a signal peptide for a GPI-anchor.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
DNA construct for effecting homologous recombination and uses thereof
The invention relates to constructs comprising: a) a targeting sequence; b) a regulatory sequence; c) an exon; and d) an unpaired splice-donor site. The invention further relates to a method of producing protein in vitro or in vivo comprising the homologous recombination of a construct as described above within a cell. The homologously recombinant cell is then maintained under conditions which will permit transcription and translation, resulting in protein expression. The present invention further relates to homologously recombinant cells, including primary, secondary, or immortalized vertebrate cells, methods of making the cells, methods of homologous recombination to produce fusion genes, methods of altering gene expression in the cells, and methods of making a protein in a cell employing the constructs of the invention.
Owner:TRANSKARYOTIC THERAPIES
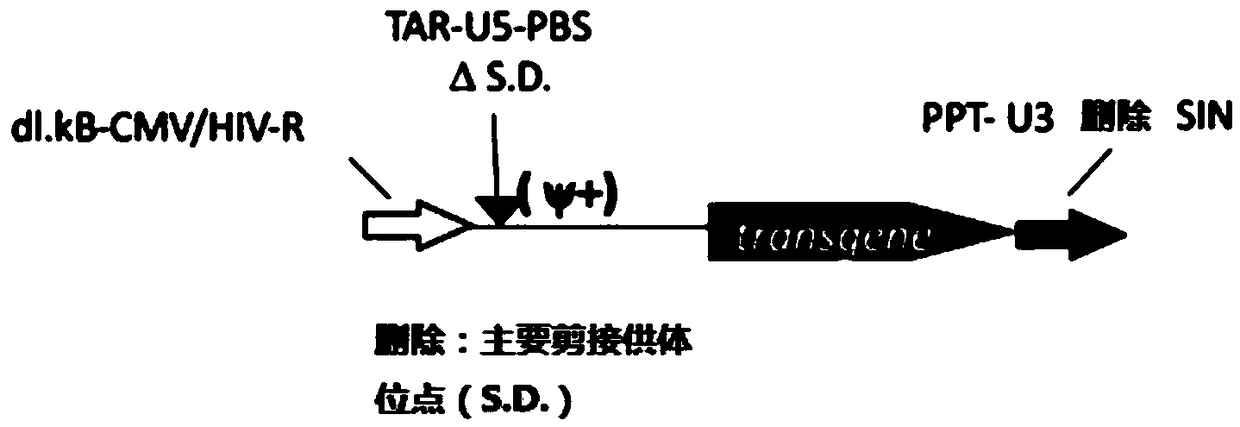
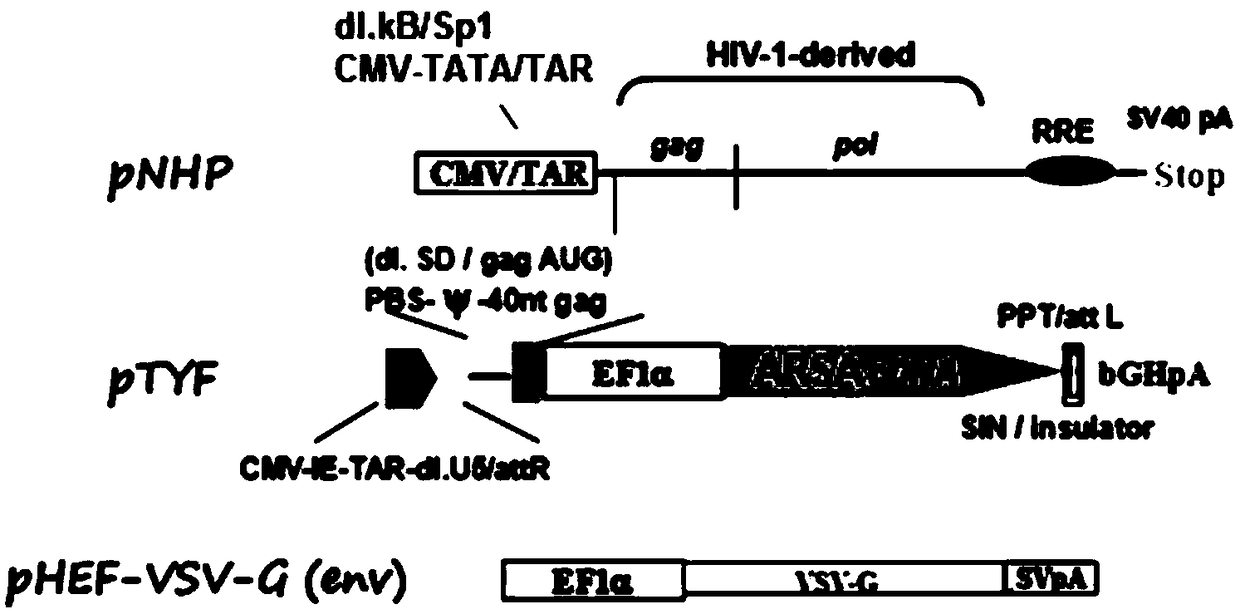
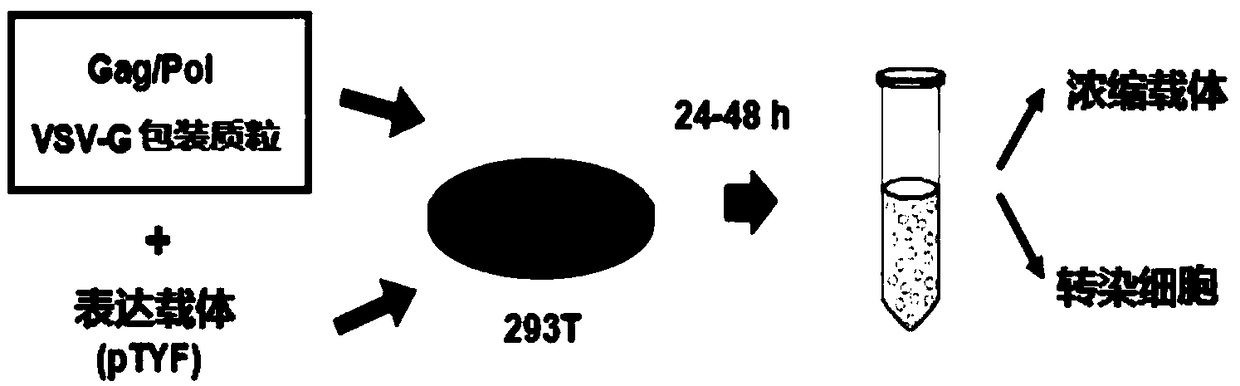
MLD (metachromatic leukodystrophy) lentiviral vector, lentivirus and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108707627AImprove securityEfficient deliveryNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCereblonLentivirus
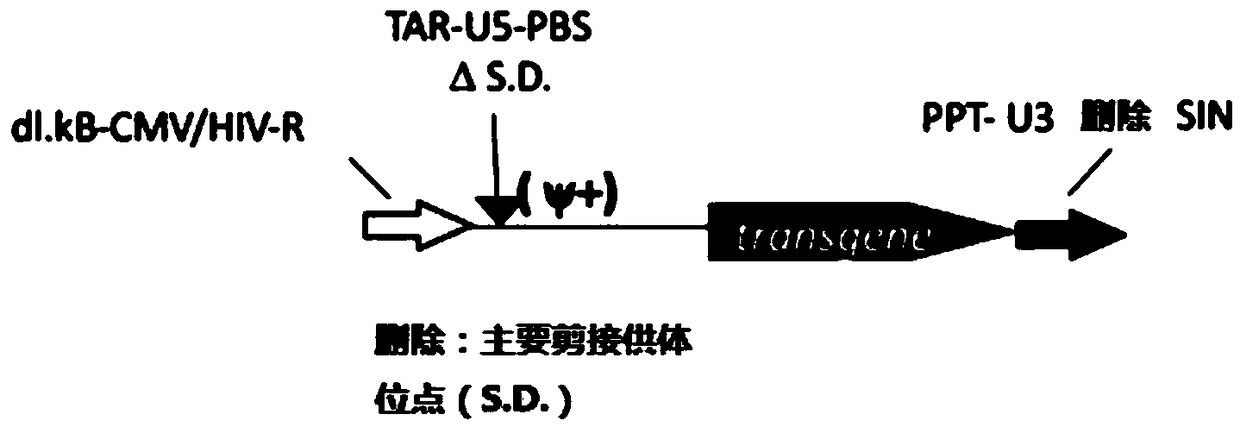
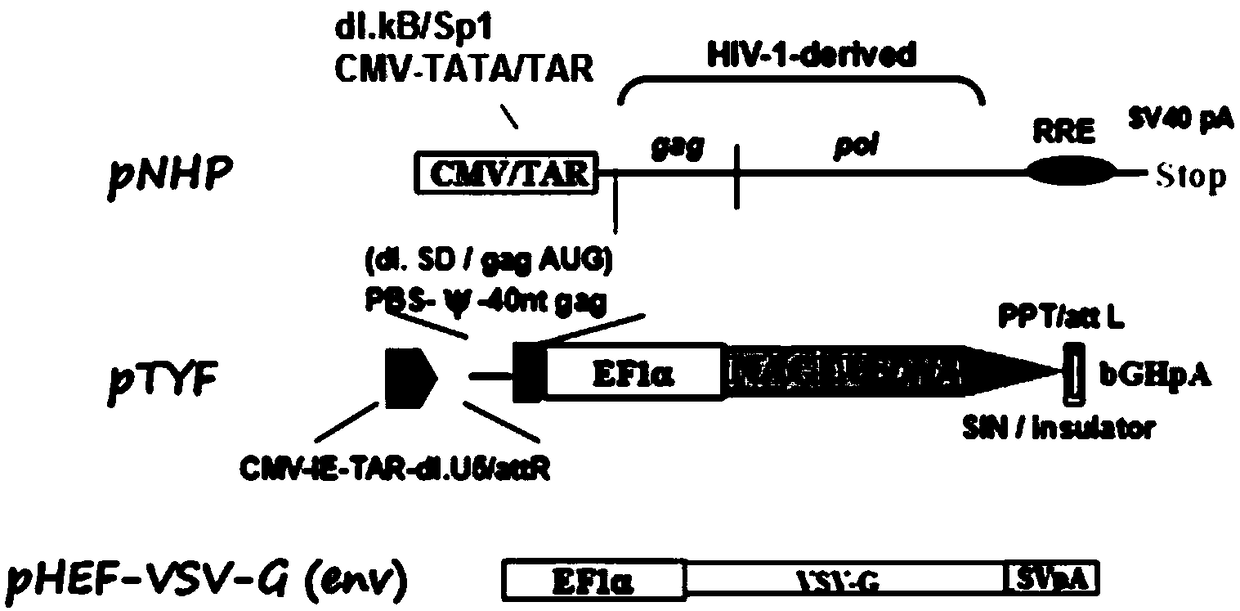
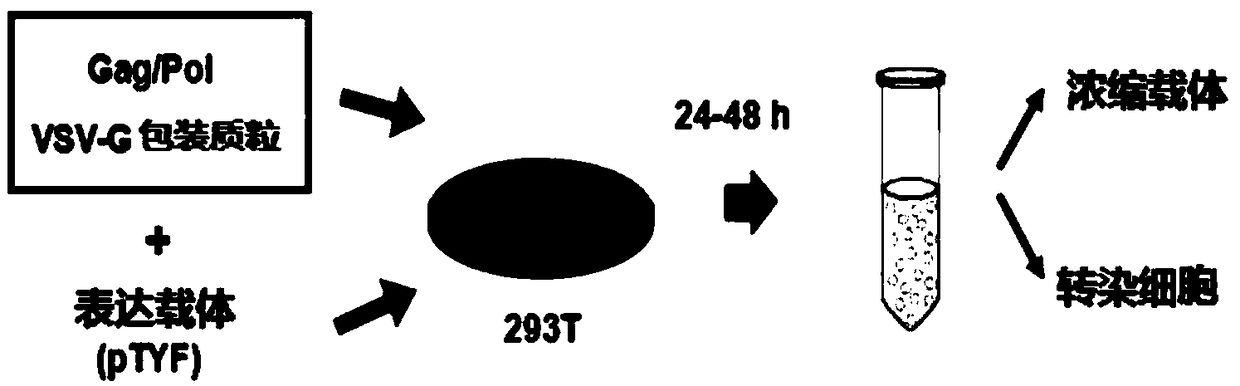
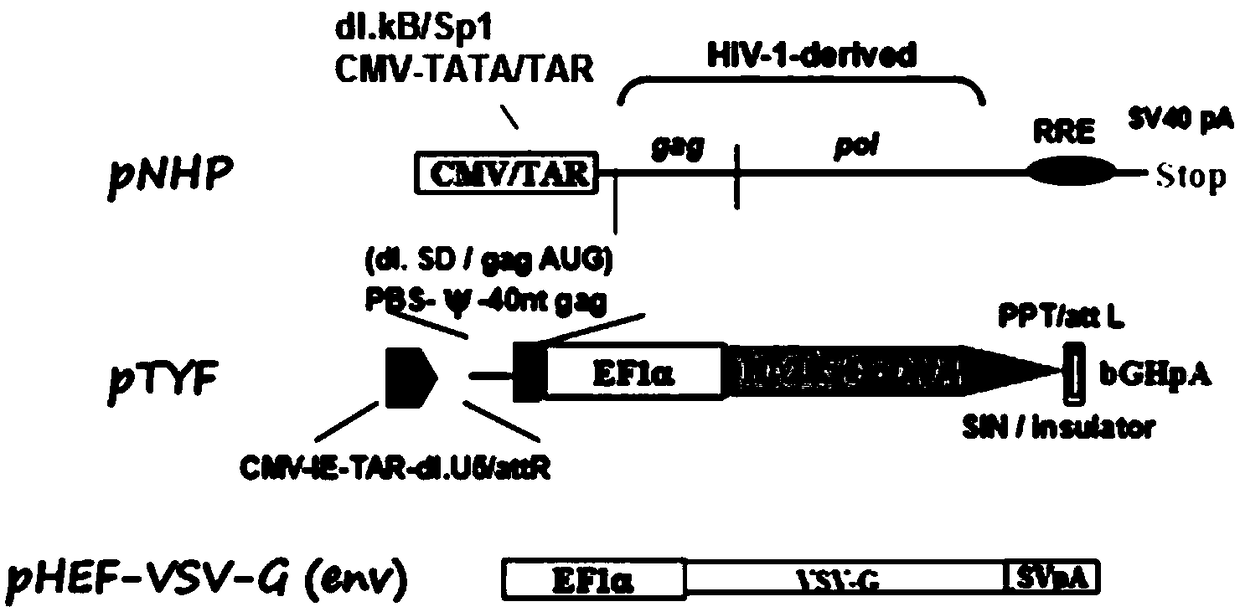
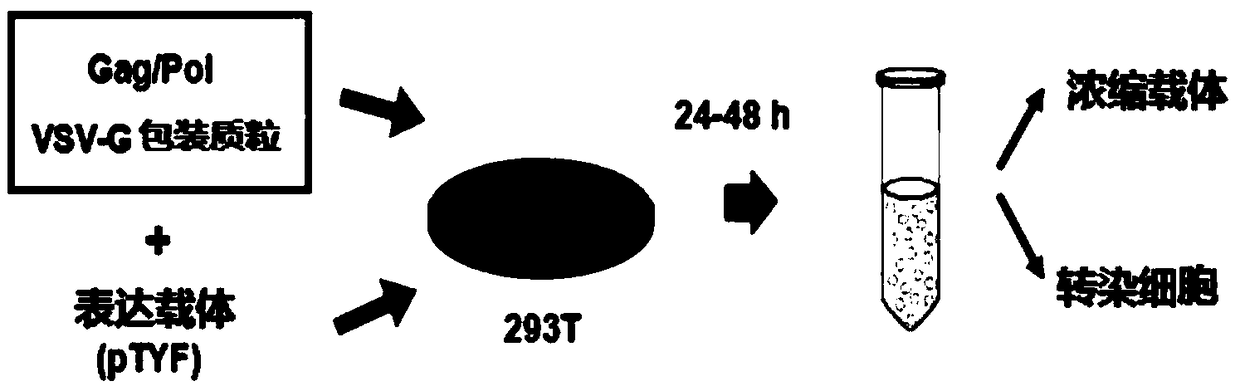
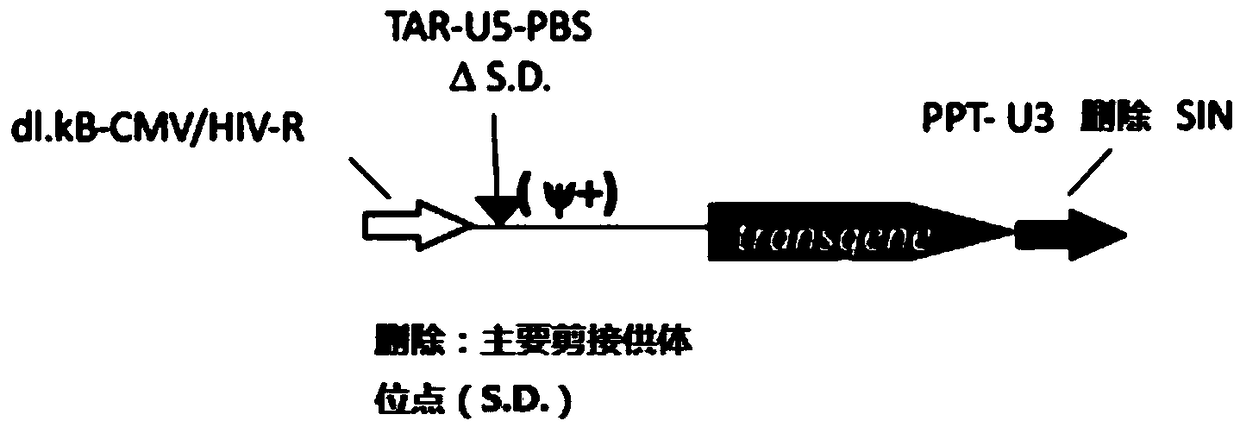
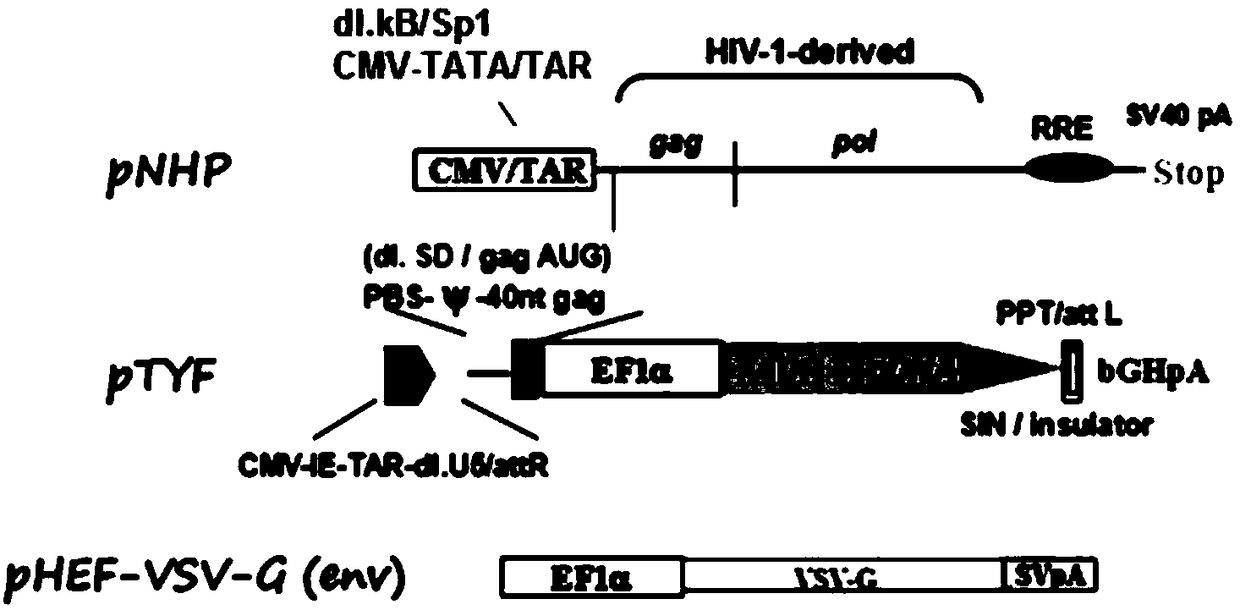
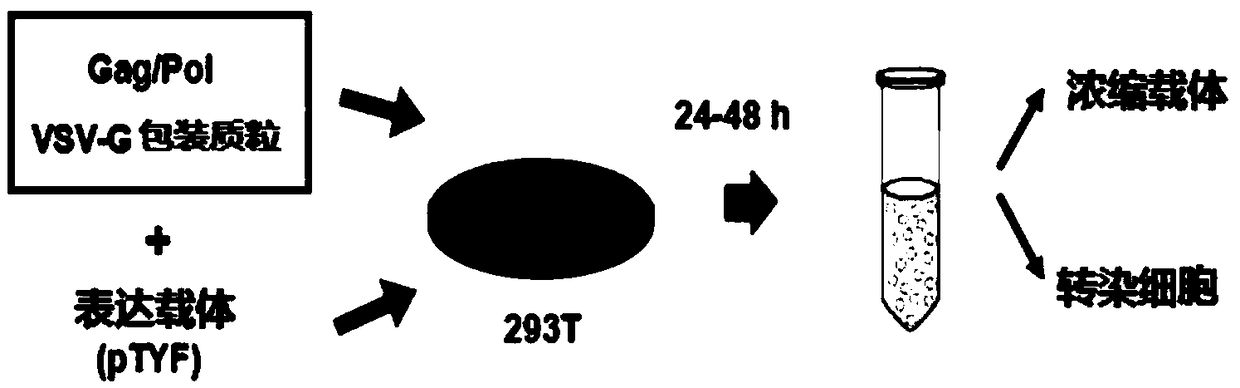
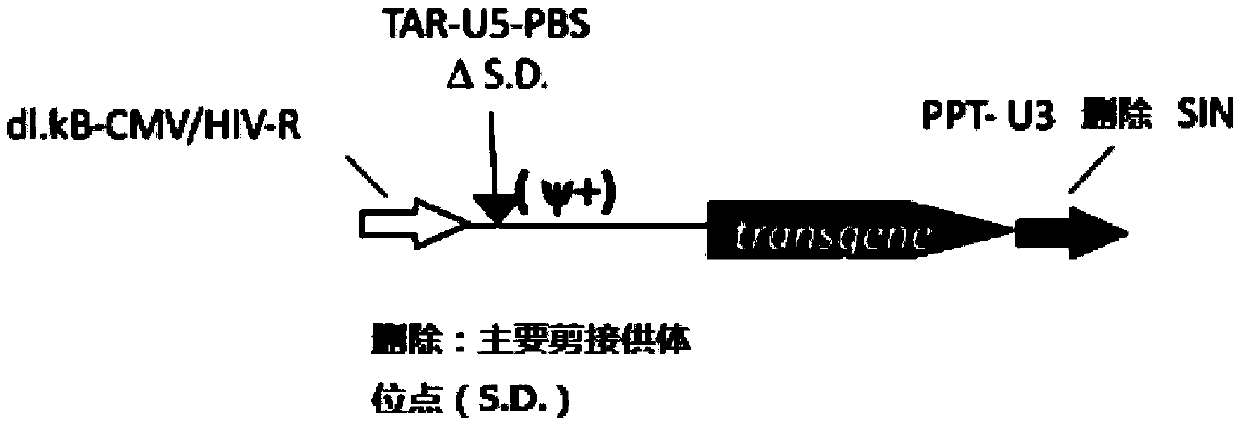
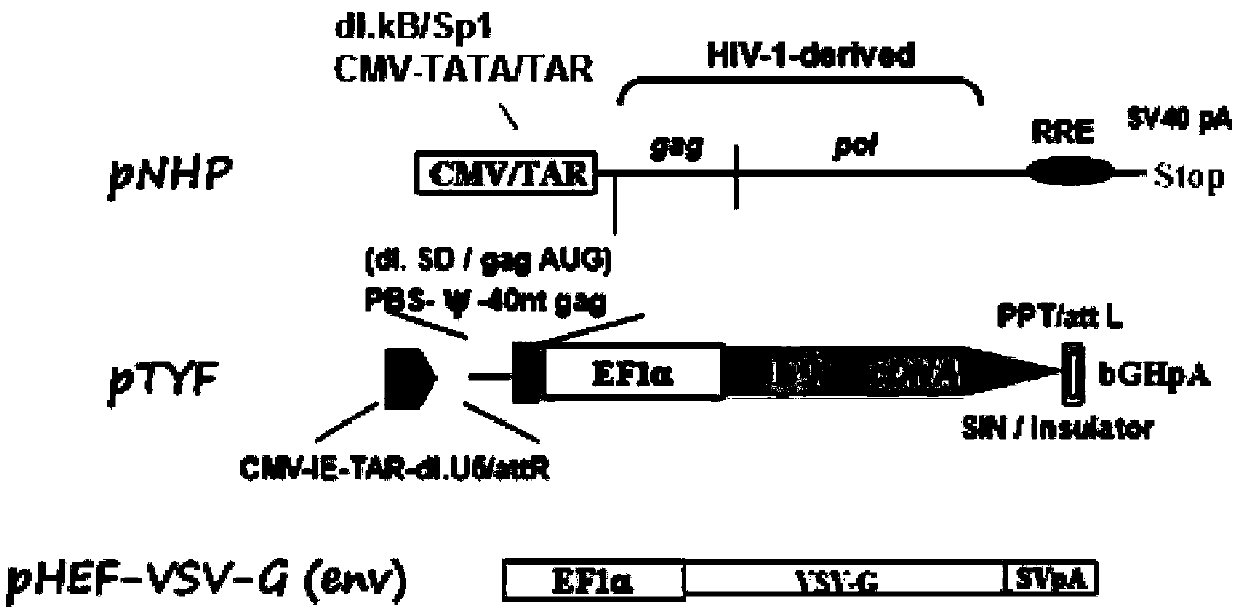
The invention provides an MLD (metachromatic leukodystrophy) lentiviral vector, a lentivirus and a preparation method and application thereof. The lentivirus vector is modified for splicing donor sites at the 5' end of pTYF lentiviral vector, wherein the lentiviral vector further comprises ARSA (arylsulfatase A )genes. The ASRS genes are specifically linked on the basis of the modified lentivirusvector, efficient gene transmission can be achieved while security is ensured, expression of the ARSA genes in transgenic brain cells is significantly increased, and normal gene transmission in the process of MLD gene therapy can be efficiently completed.
Owner:SHENZHEN GENO IMMUNE MEDICAL INST
Integration vectors
InactiveUS20060024819A1Improve stabilityHigh throughput screeningNucleic acid vectorFermentationGene trappingSplice Donor Site
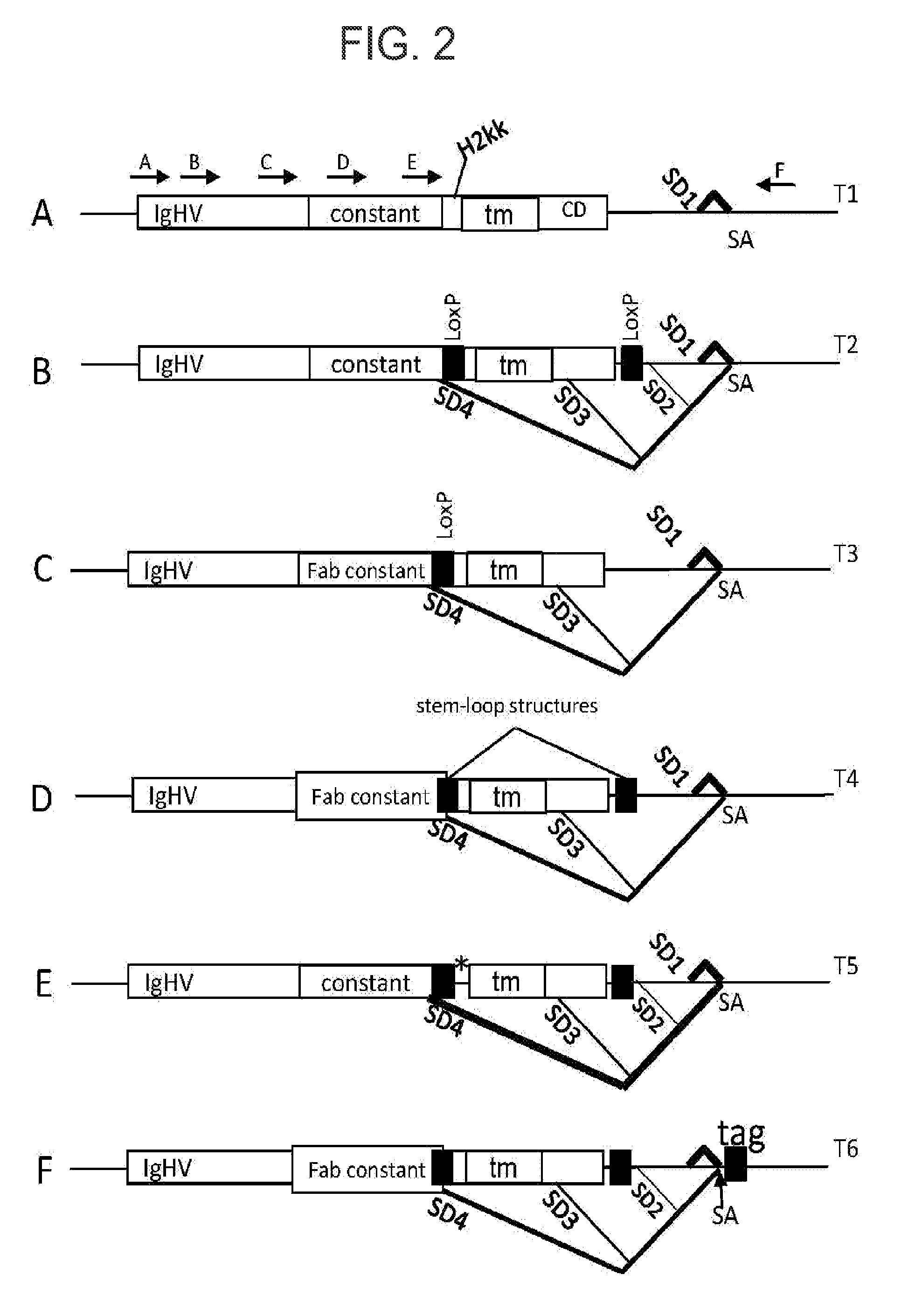
The invention relates to integration vectors for modifying a target genomic region comprising, in a 5′ to 3′ direction, a splice acceptor site, a 3′ hybrid recognition site, and a marker sequence (i.e., a 5′ gene trap vector); or alternatively comprising, in a 5′ to 3′ direction, a marker sequence; a 5′ hybrid recognition site; and a splice donor site (i.e., a 3′ gene trap vector). The integration vector, upon insertion into the target genomic region is capable of producing a recombinant RNA transcript that is comprised of a hybrid recognition site for a selection molecule. The hybrid recognition site of recombinant RNA produced from insertion of the 5′ gene trap vector is comprised of a 5′ hybrid recognition site derived from genomic sequence and a 3′ hybrid recognition site derived from vector sequence. The hybrid recognition site of recombinant RNA produced from insertion of the 3′ gene trap vector is comprised of a 5′ hybrid recognition site derived from vector sequence and a 3′ hybrid recognition site derived from genomic sequence. The selection molecule selects recombinant cells comprising the integration vector inserted within the target genomic region.
Owner:FINNEY ROBERT E
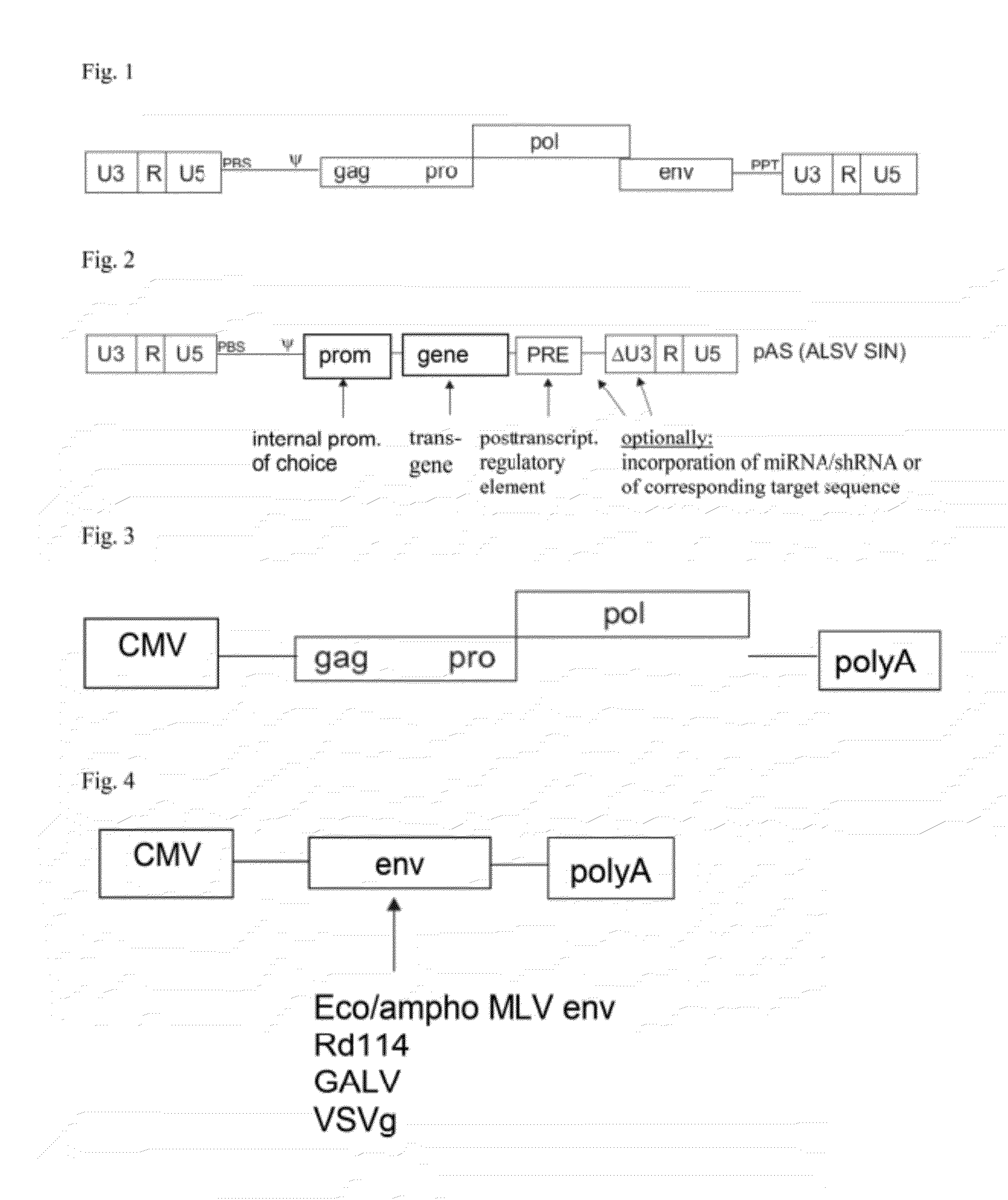
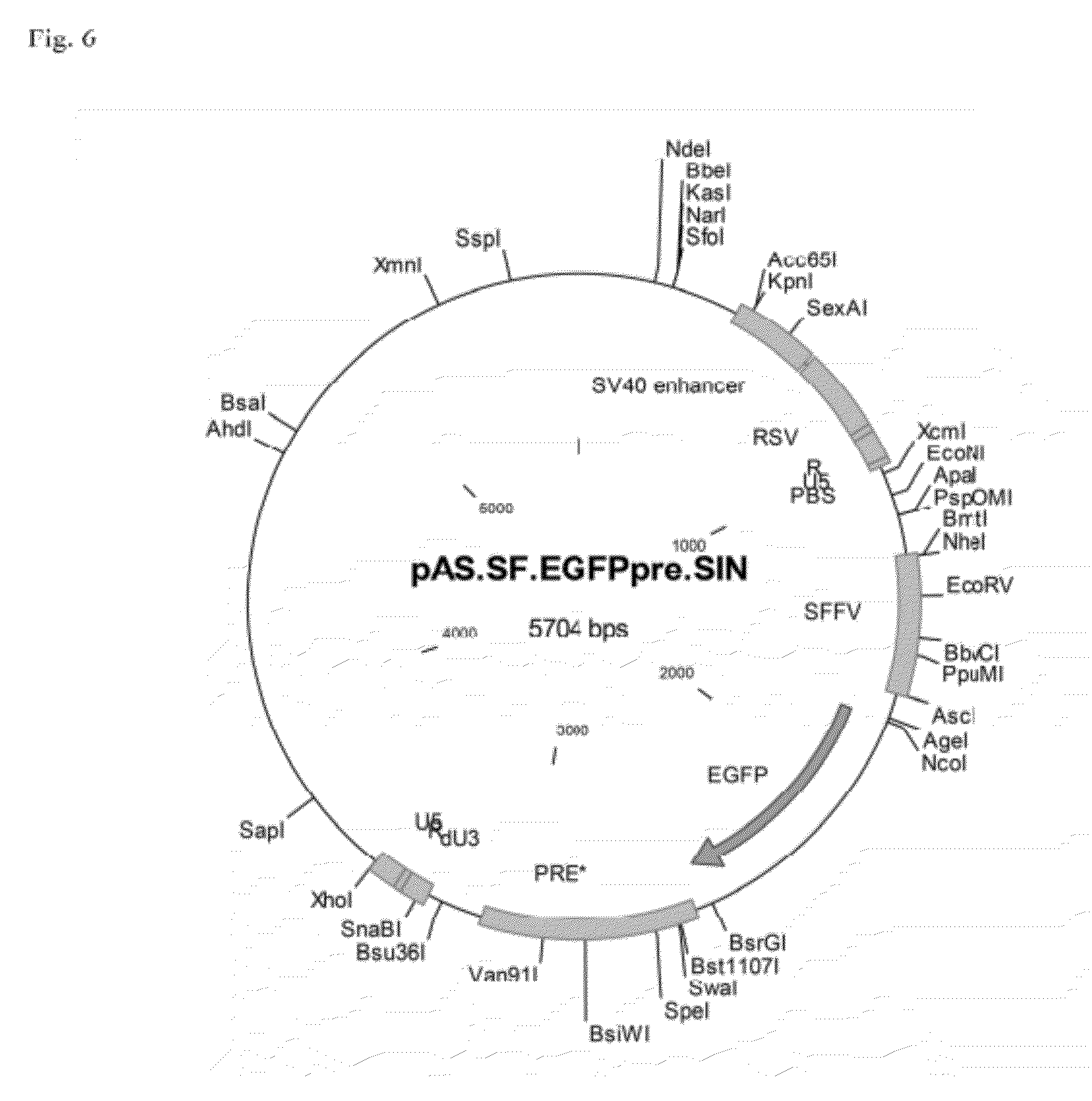
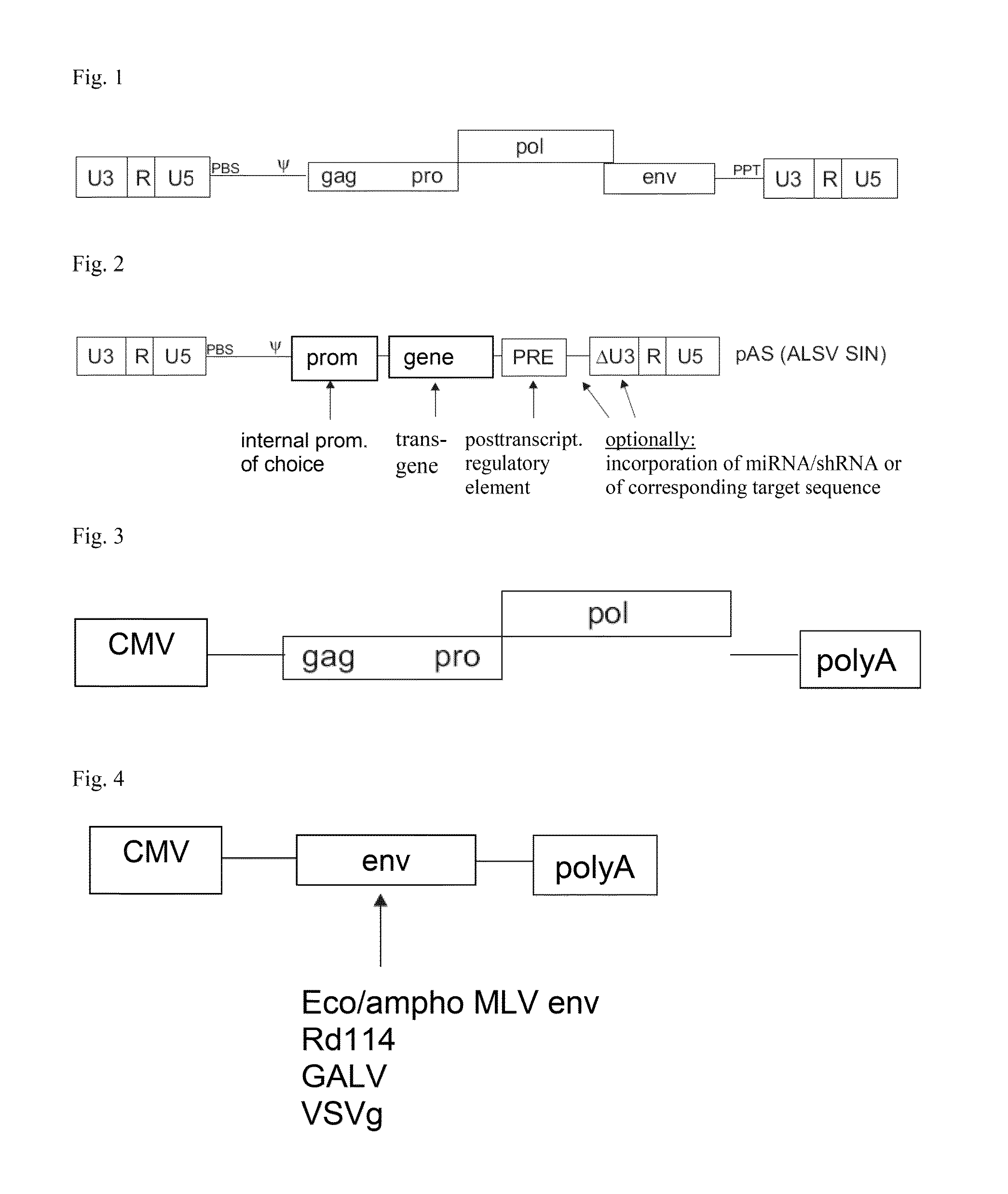
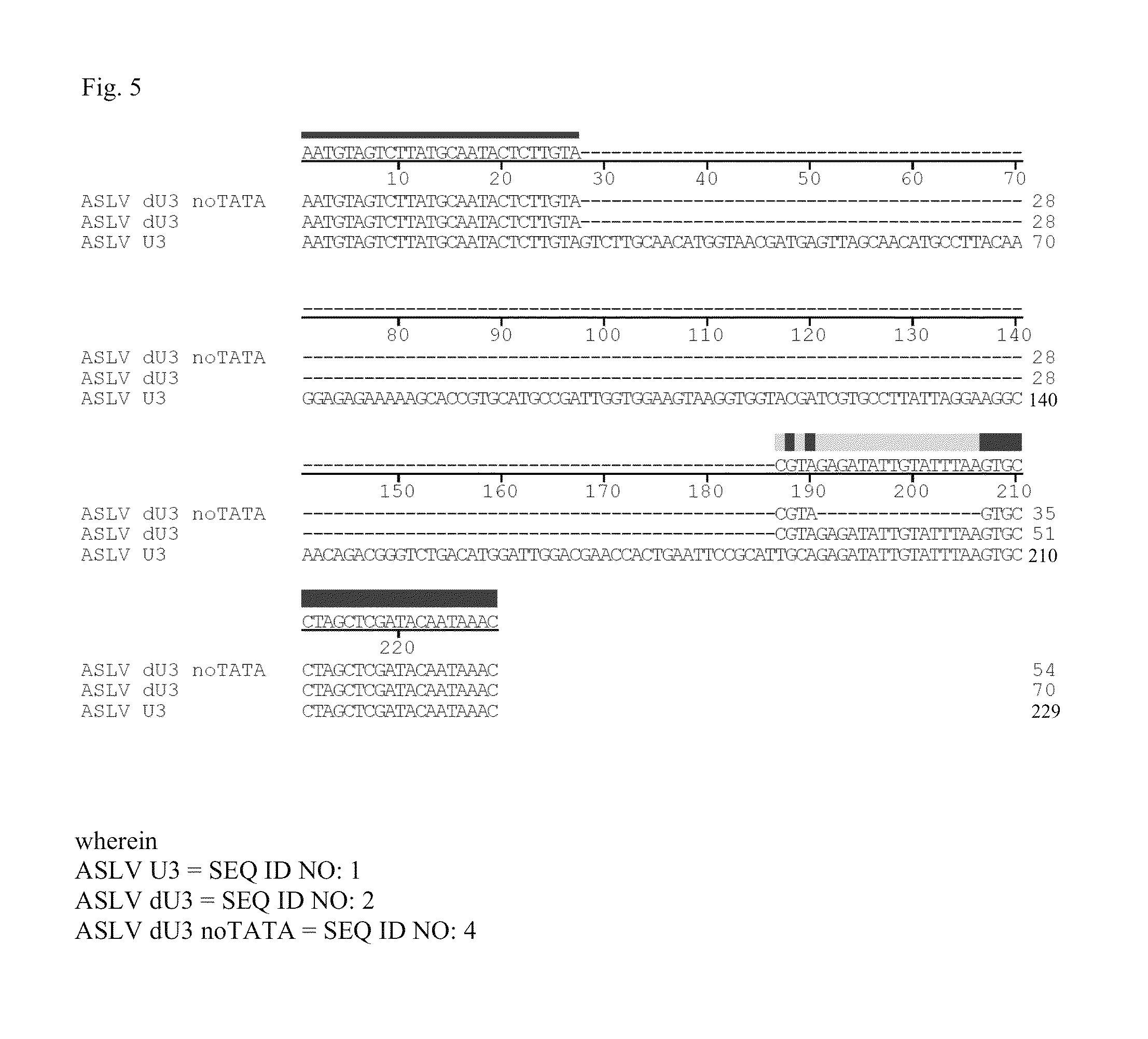
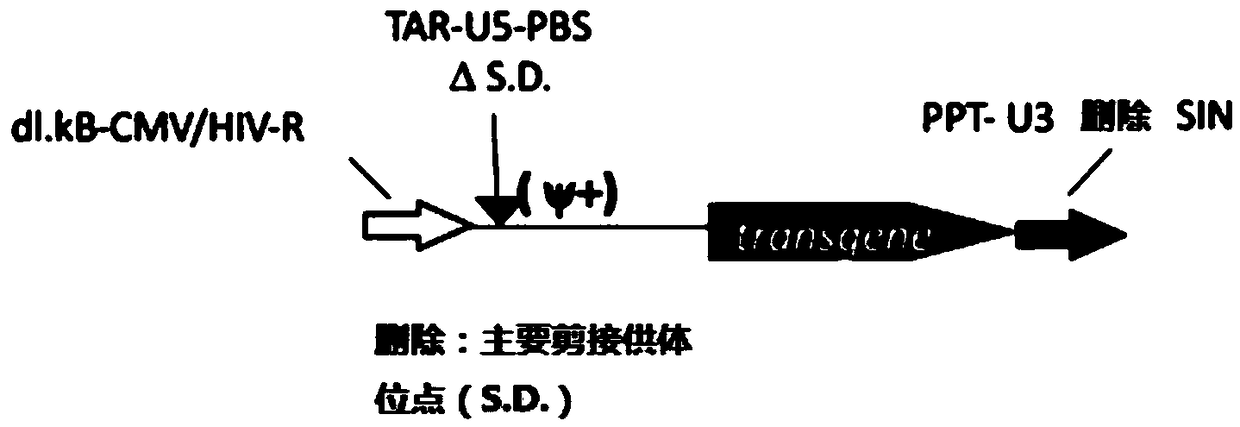
Aslv vector system
ActiveUS20120172418A1Efficiently translatedRisk minimizationSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsVector systemAvian leukosis viruses
The invention provides a viral self-inactivating (SIN) vector on the basis of the avian sarcoma leukosis virus (ASLV) as well as a split-packaging system comprising in addition to the SIN vector a first helper plasmid serving for the expression of the viral fusion protein gag-pol and a second helper plasmid serving for the expression of the retroviral envelope protein (env). The first and second helper plasmid, for example contained in a packaging cell line or transiently transfected, serve for the generation of non-replicating (RCR-incompetent) viral particles containing RNA having a SIN LTR according to the invention at the 3′ terminus, wherein the RNA can have a therapeutically effective section which e.g. is denoted a transgene. This 3′ SIN LTR contains an extensive deletion of the U3 region which in the course of the reverse transcription is copied into the 5′ LTR. In addition, in the SIN vector all coding regions of ASLV as well as the retroviral splice donor site are removed.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
Recombinant influenza viruses and uses thereof
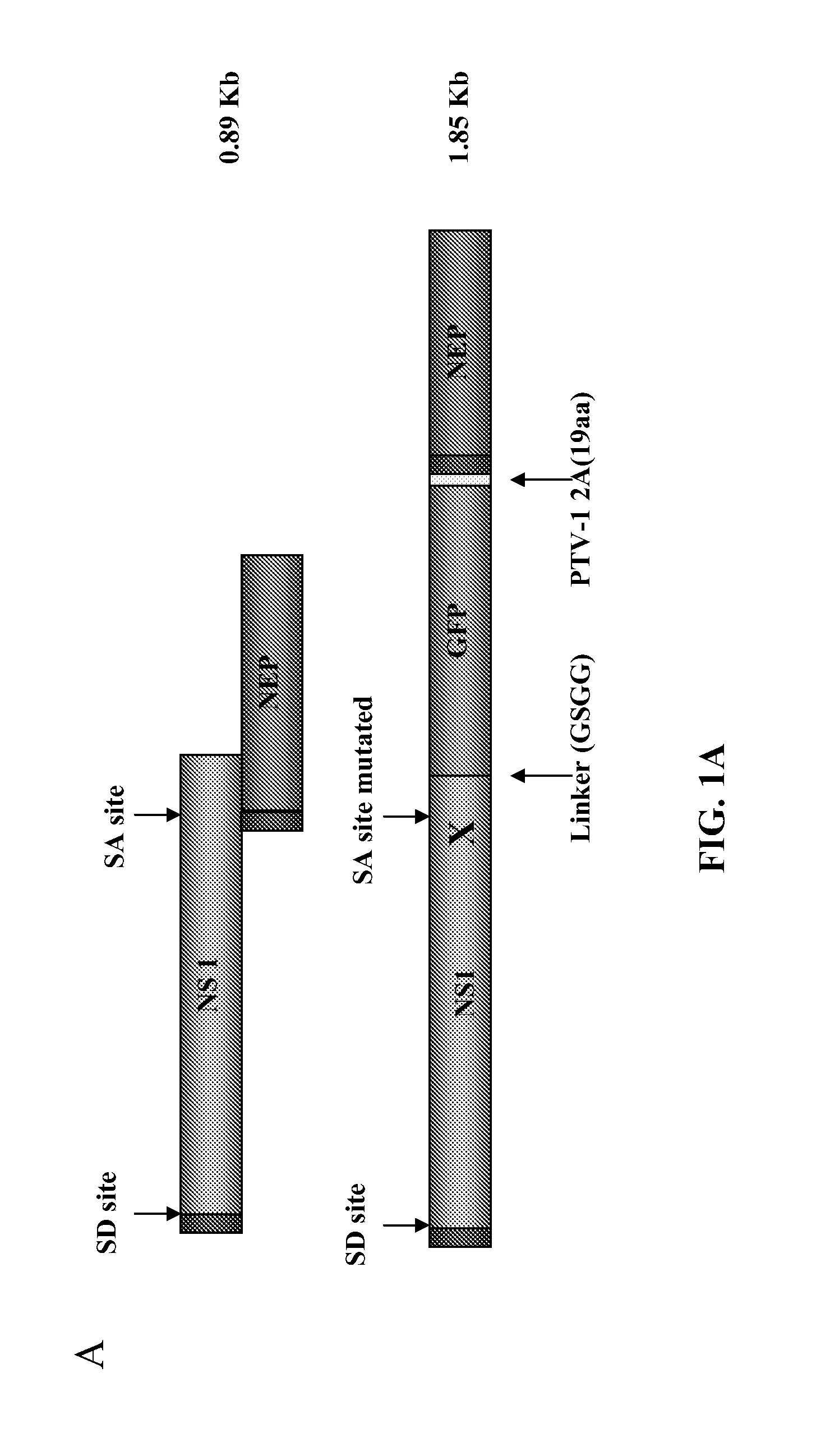
ActiveUS20120251568A1Reduction and amelioration in severityShorten the construction periodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideHeterologousDisease
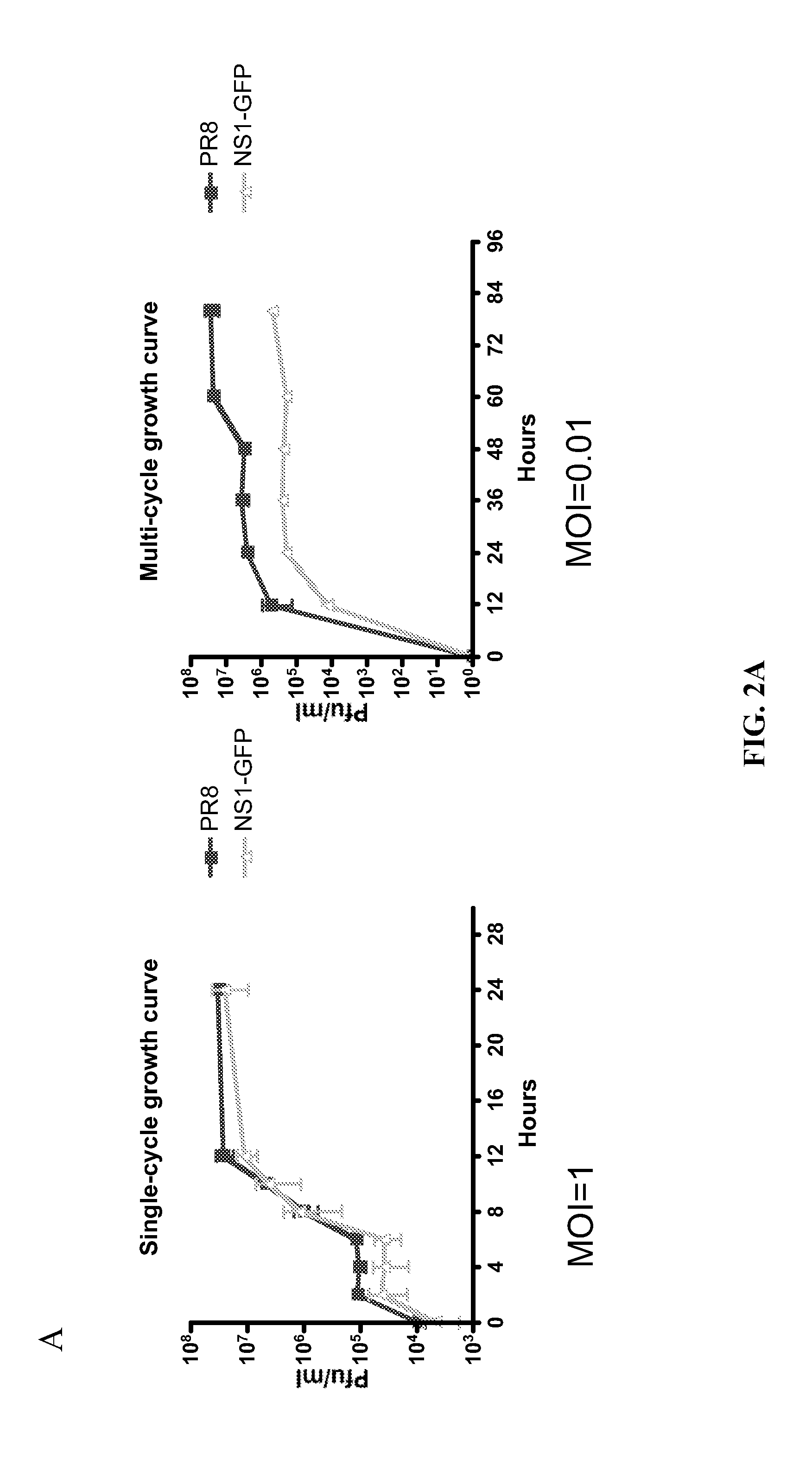
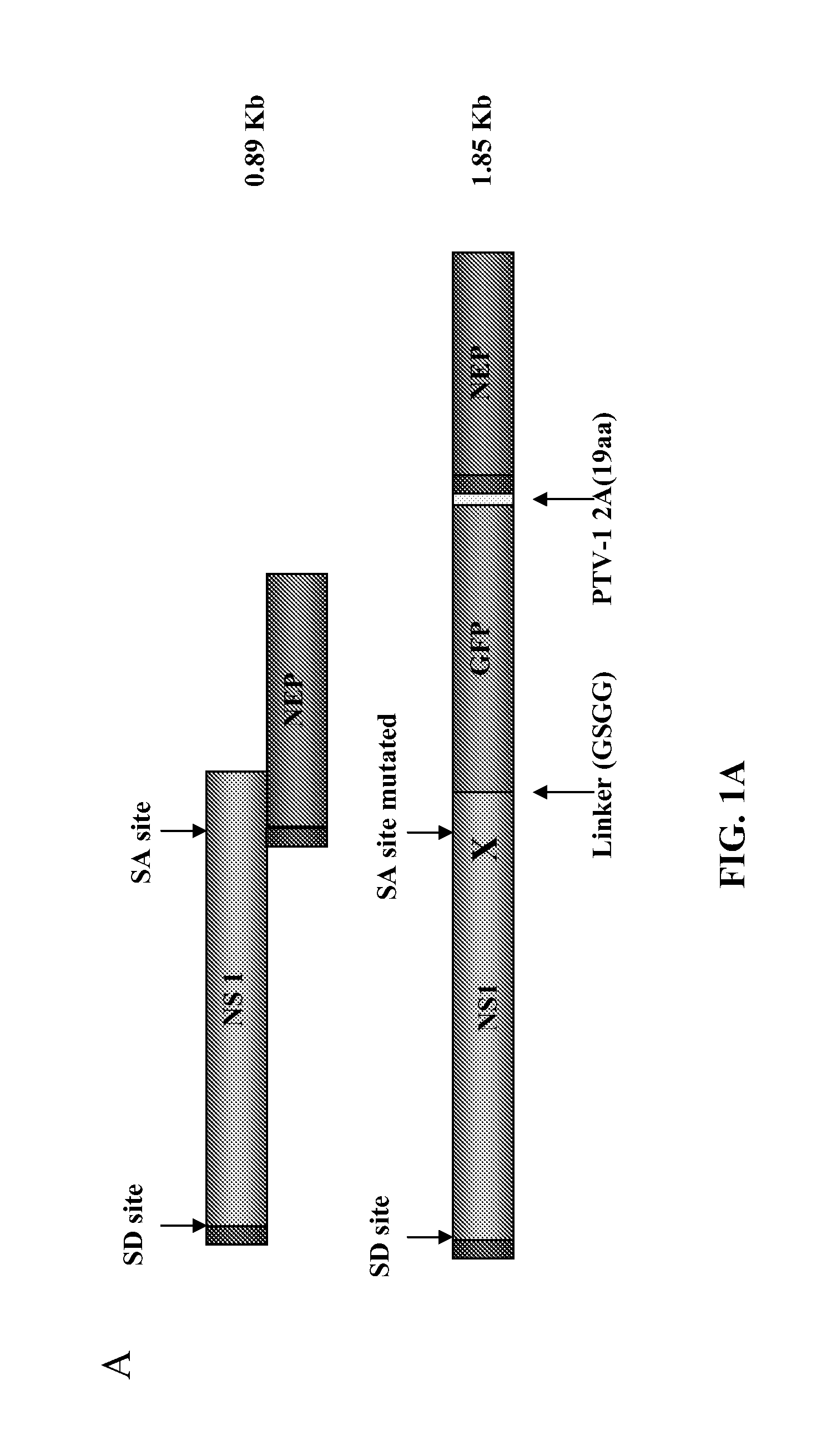
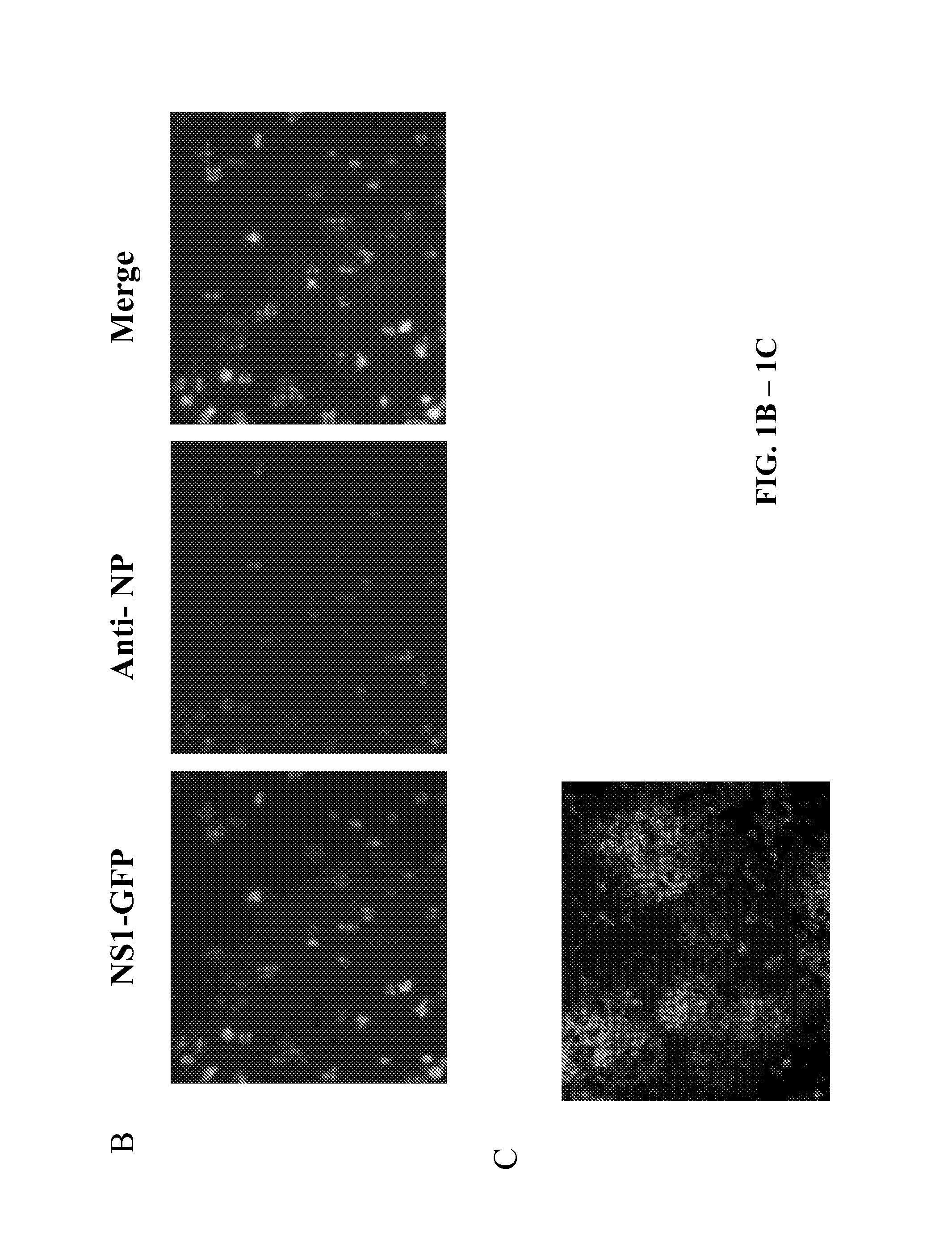
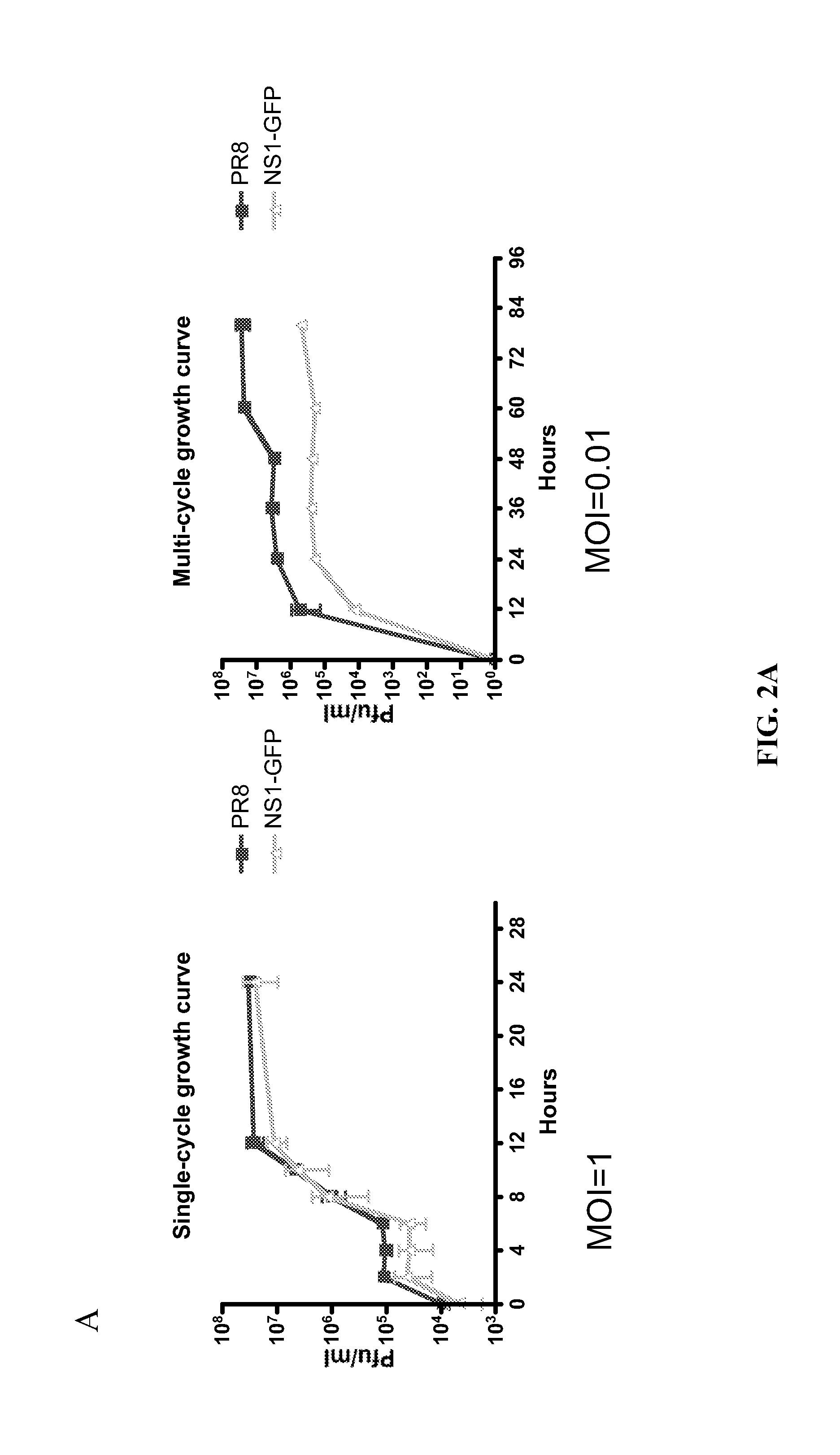
Described herein are modified influenza virus NS gene segments and nucleic acid sequences encoding such modified influenza virus NS gene segments. In certain embodiments, a modified influenza virus NS gene segment described herein comprises an influenza virus NS 1 open reading frame (ORF) lacking a stop codon, a heterologous nucleotide sequence, a 2A autoproteolytic cleavage site or another cleavage site, an NEP ORF, wherein the gene segment has one or more mutations in either the splice acceptor site, splice donor site, or both the splice acceptor and splice donor sites that prevents splicing of mRNA. Also described herein are recombinant influenza viruses comprising a modified influenza virus NS gene segment and the use of such viruses. The recombinant influenza viruses may be use in the prevention and / or treatment of influenza virus disease or as a delivery vector.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Lymphohematopoietic engineering using cas9 base editors
PendingUS20210040507A1Easily damagedGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNABase JEngineered genetic
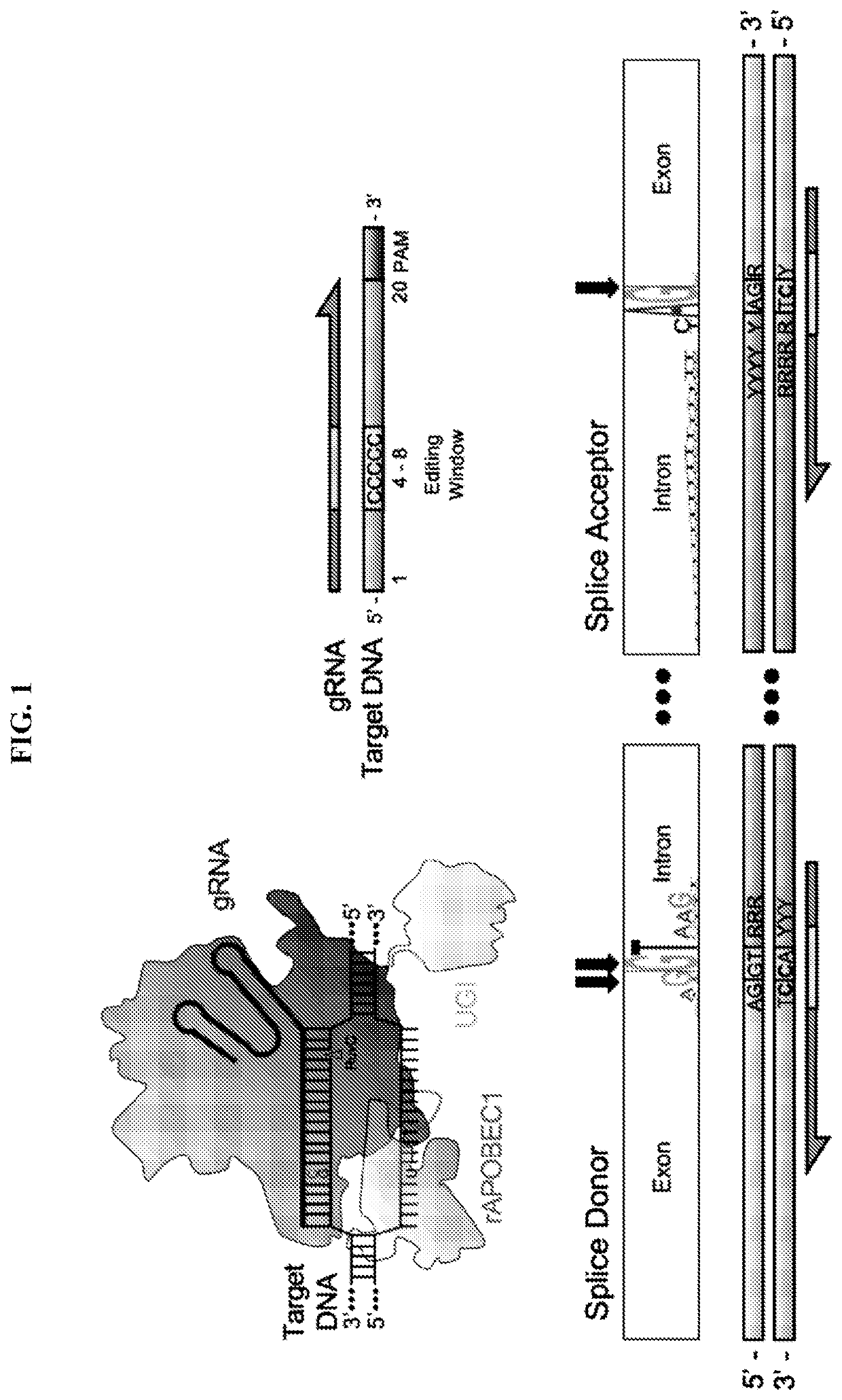
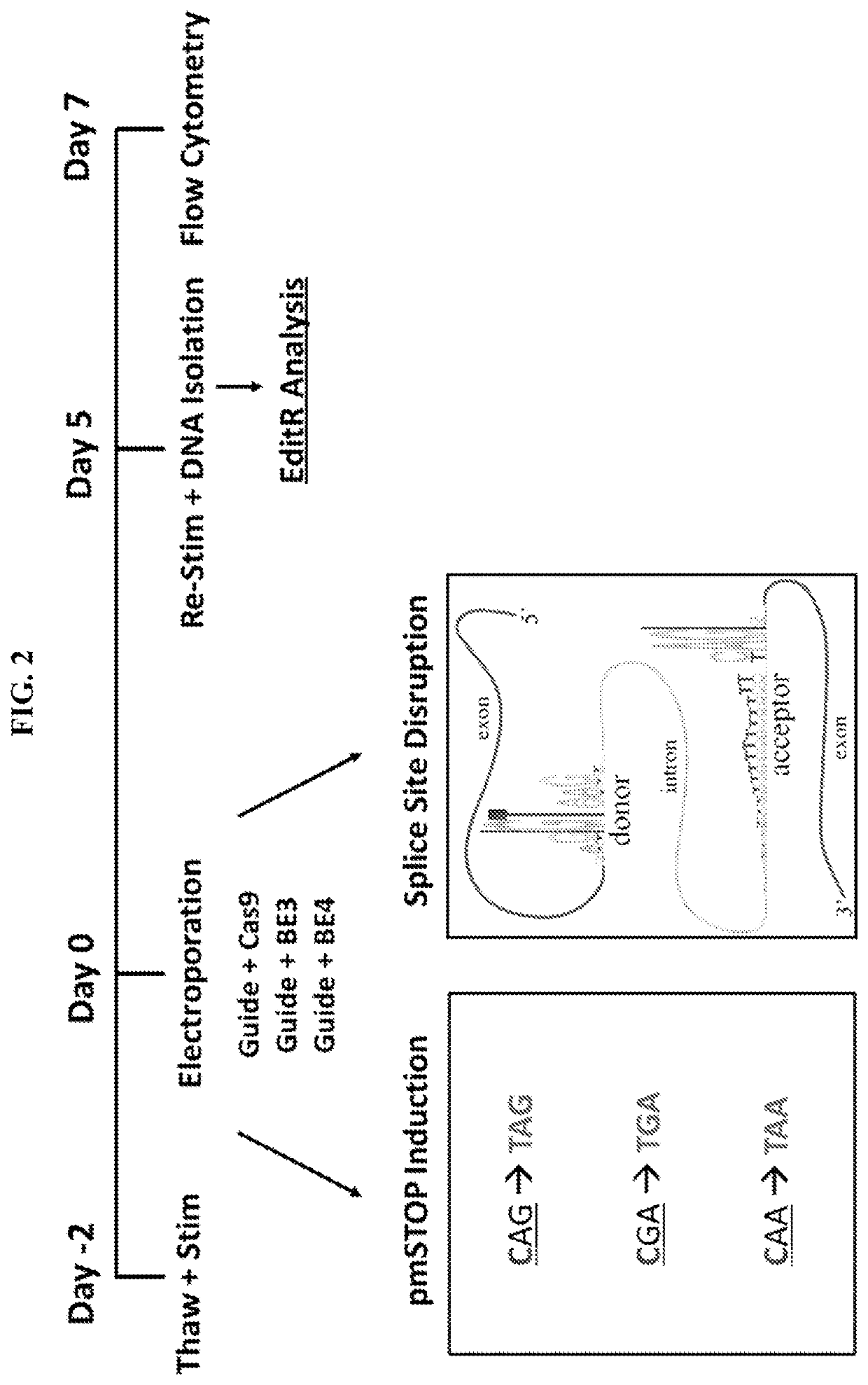
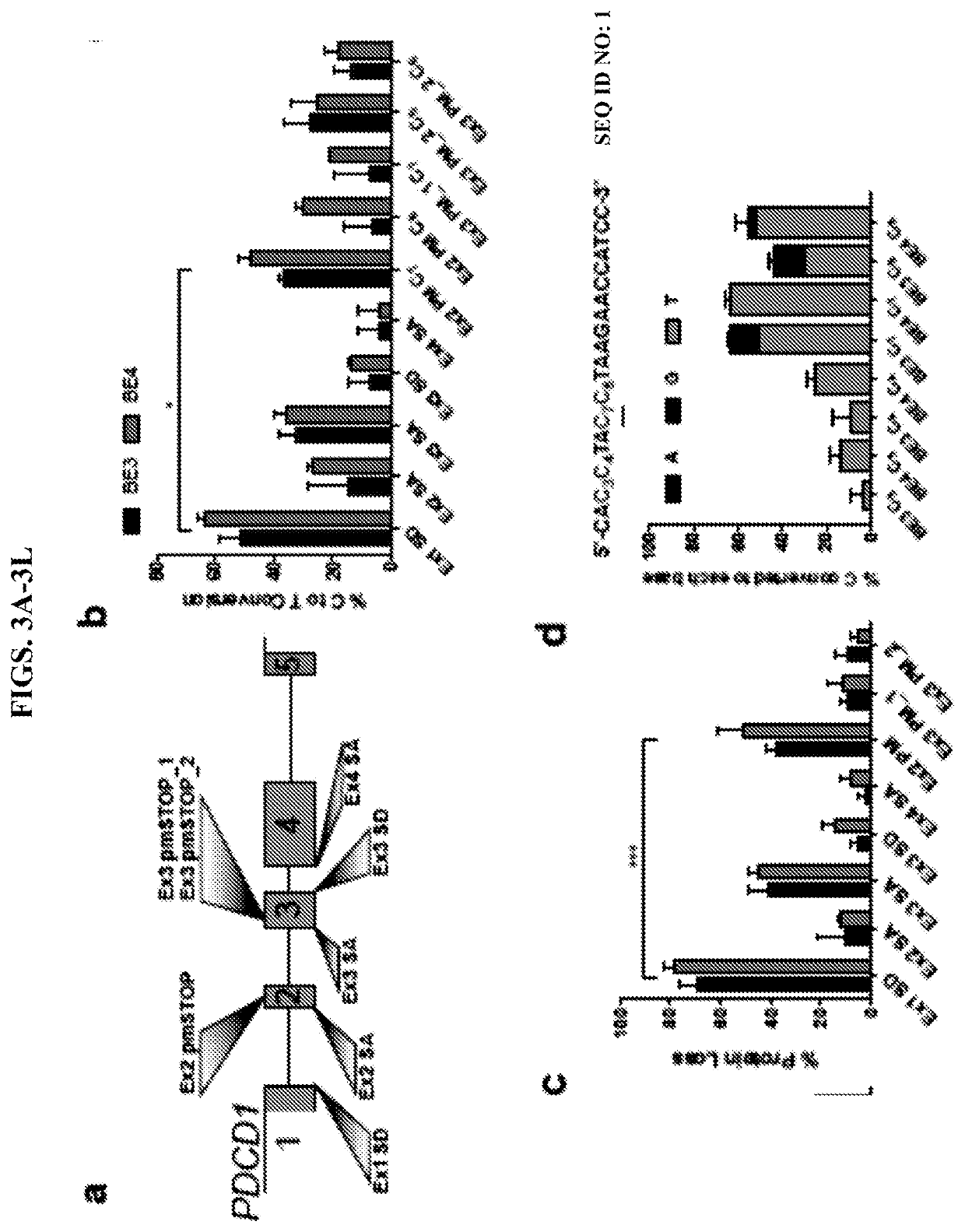
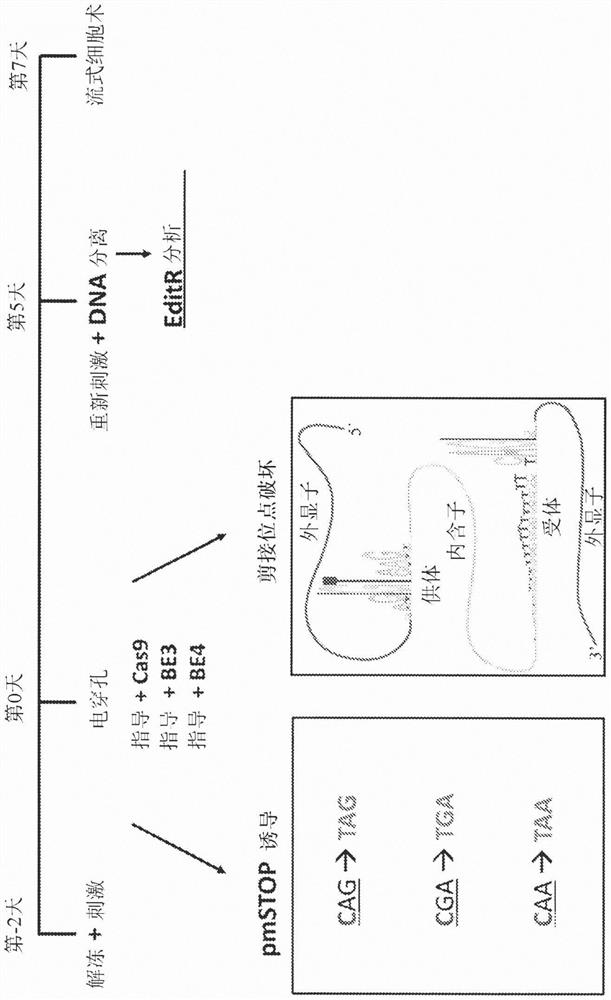
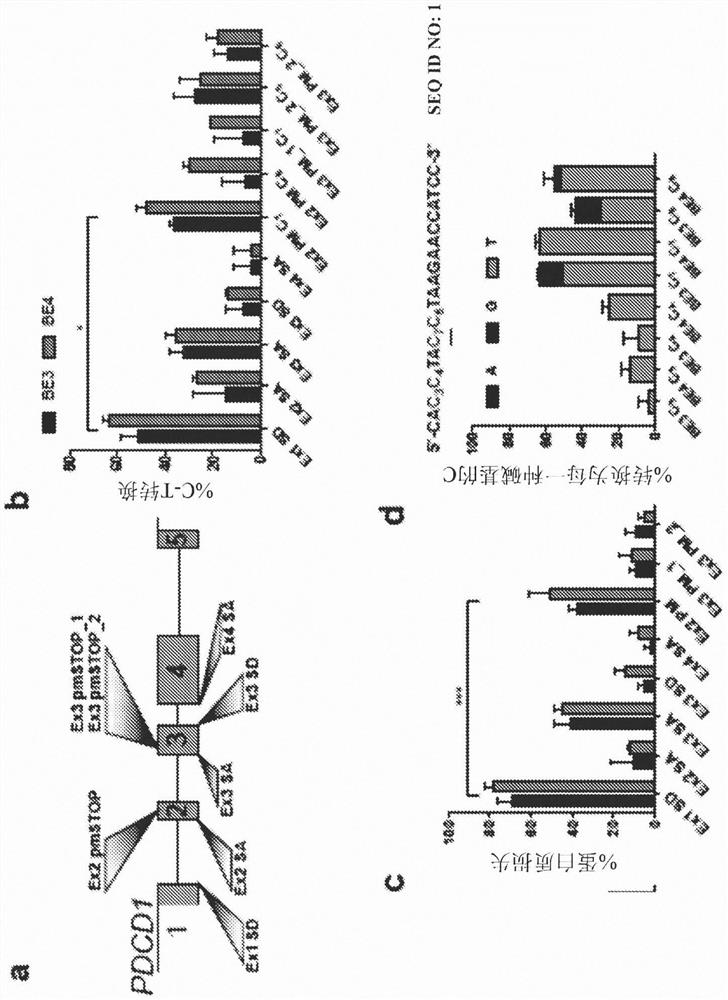
Provided herein are methods and systems for targeted gene disruption (knock-out, missense mutation) and targeted gene knock-in in mammalian cells using base editors and guide RNAs (gRNAs) designed to target splice acceptor-splice donor sites. Also provided herein are universally acceptable genetically engineered cells comprising targeted disruptions in immunotherapy-related genes and comprising a CAR / TCR for therapeutic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
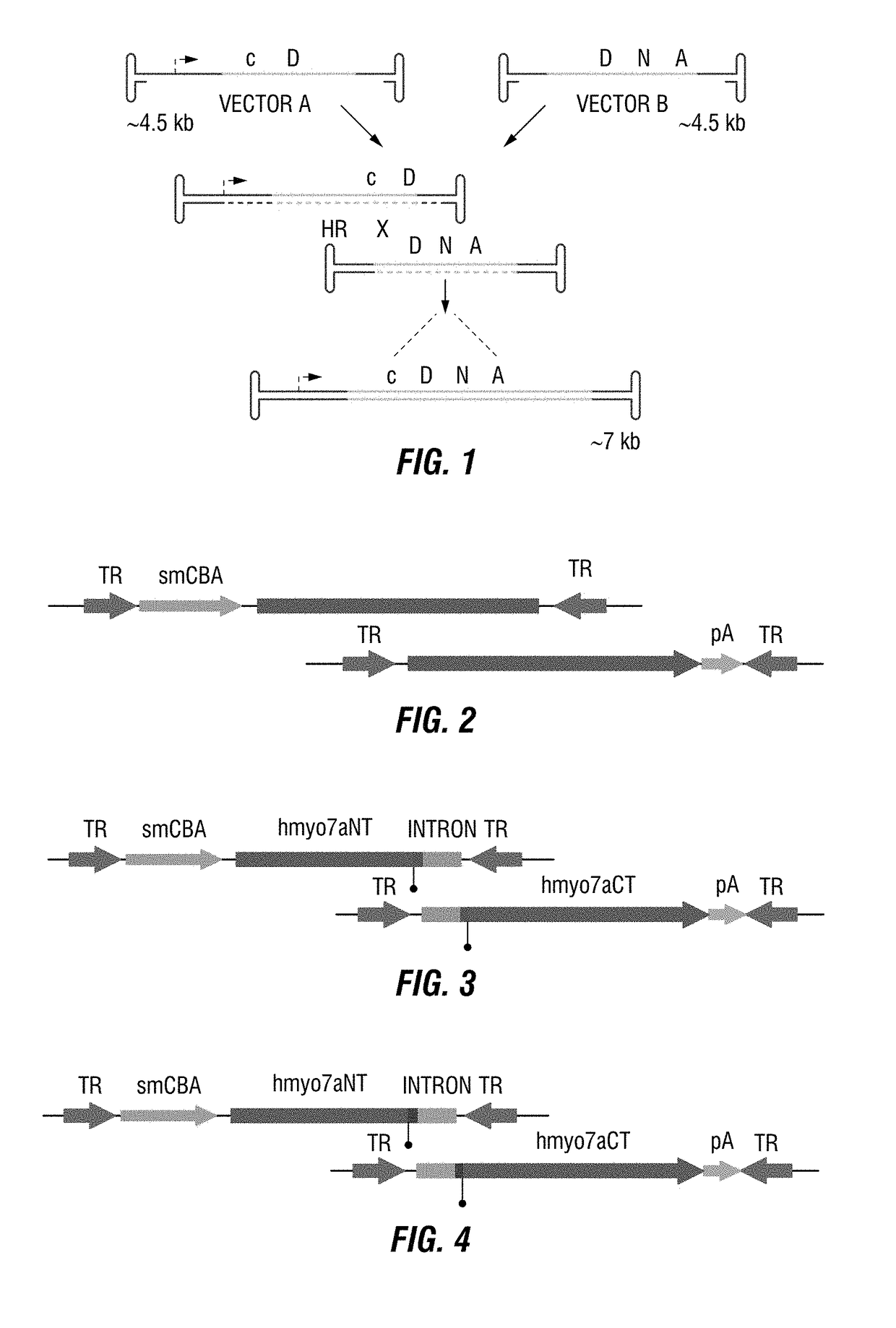
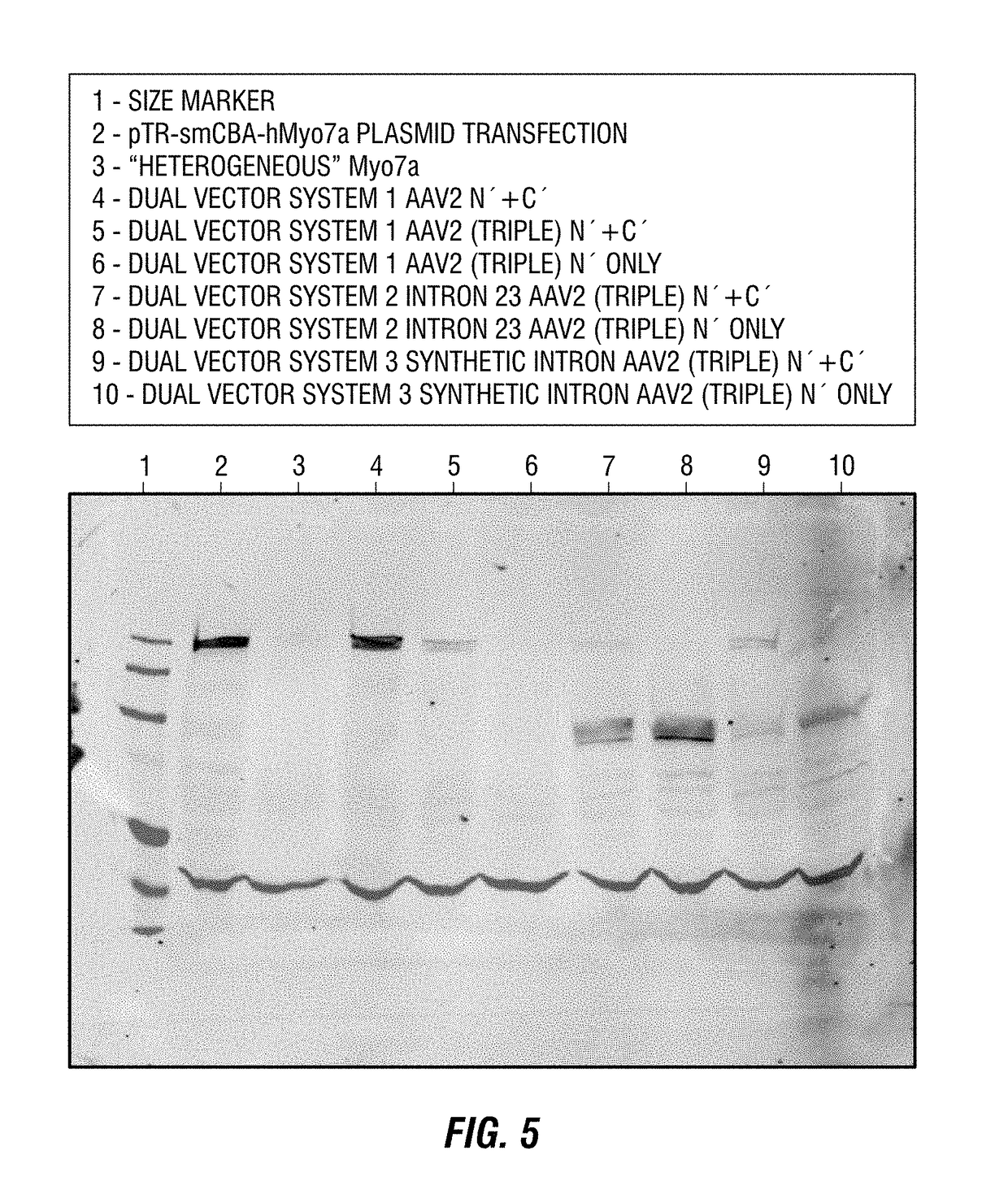
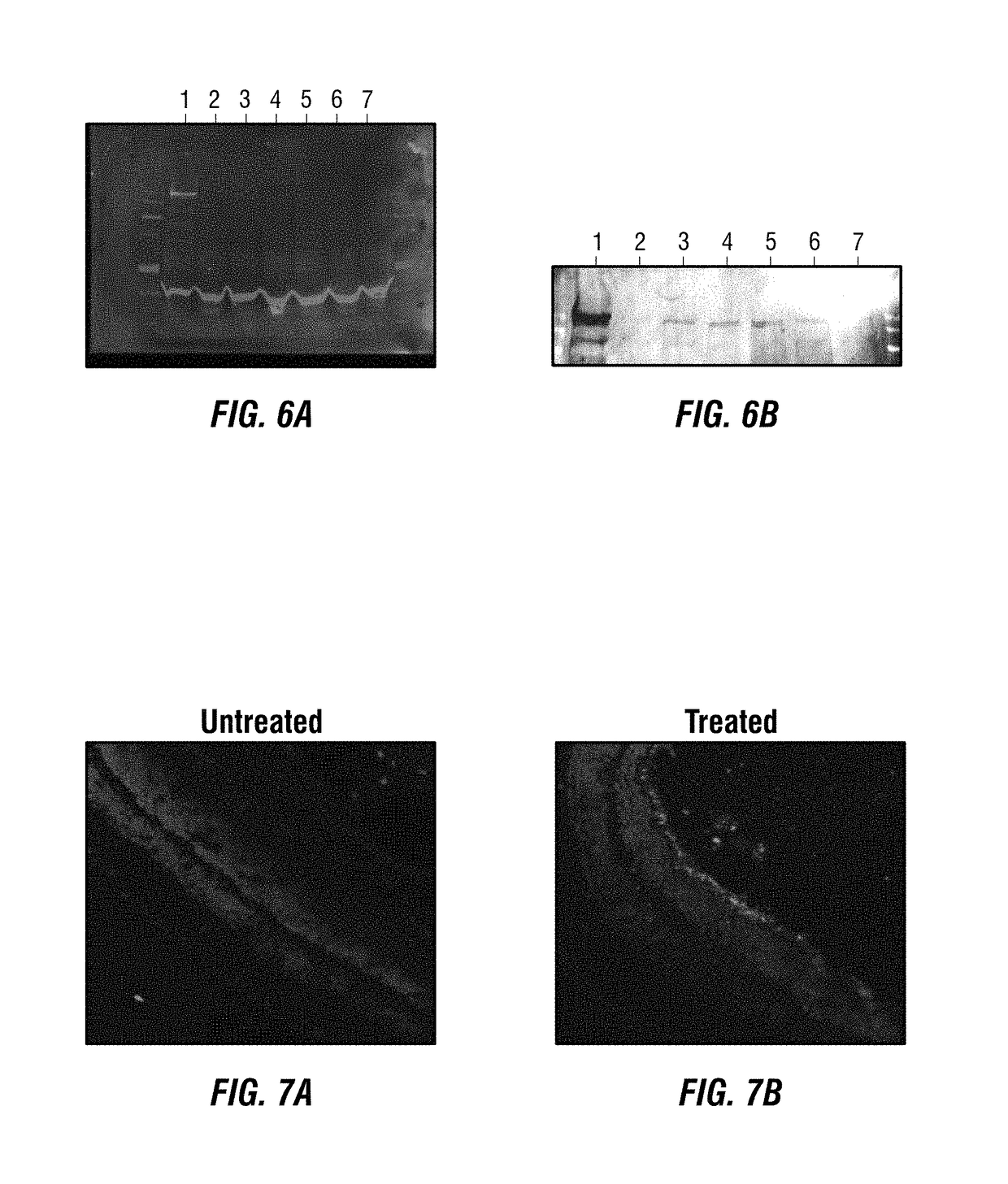
Dual-AAV vector-based systems and methods for delivering oversized genes to mammalian cells
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
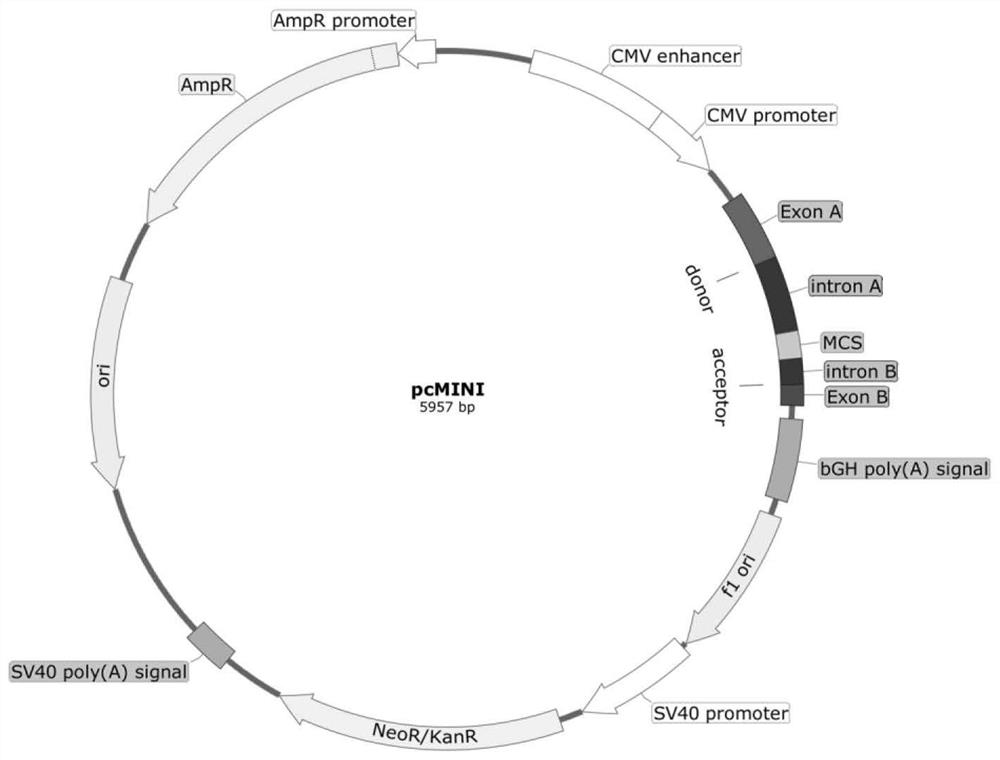
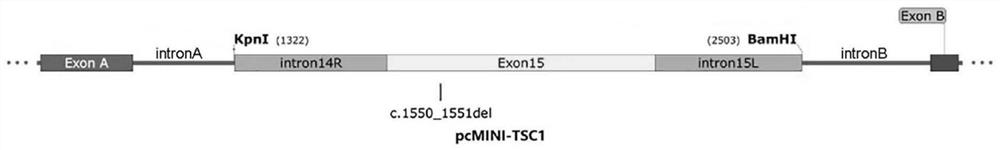
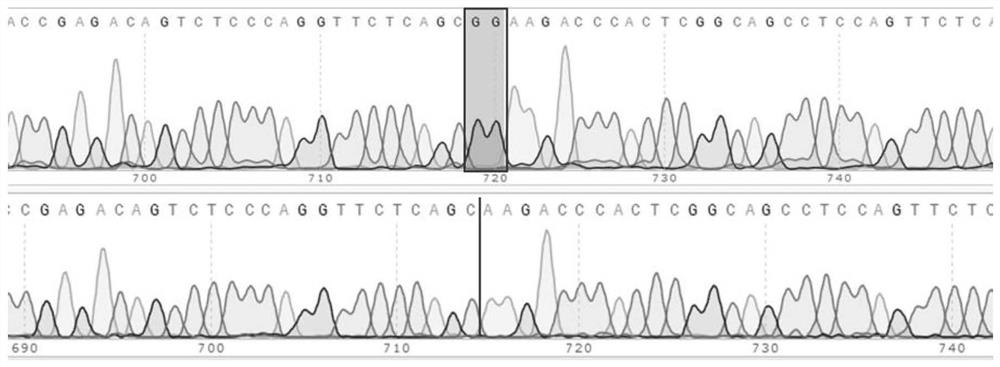
PcMINI vector as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN113736812ASimple and fast operationEfficient constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenes mutationCloning Site
The invention discloses a pcMINI vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pcMINI vector is formed by modifying a vector pcDNA3.1+, the pcMINI vector comprises a CMV enhancer, a PCMV promoter, a multiple cloning site (MCS), an exon-intron gene fragment and a BGH_PA_terminator terminator, and the multiple cloning site (MCS) is used for being inserted into a gene fragment with mutation at an exon-intron combination position. According to a pcMINI vector system, detection on different gene mutations can be achieved only by replacing inserted DNA fragments, the application range is wide, and the operation is easy and convenient; according to the constructed pcMINI vector, dNA fragments needing to be inserted are smaller, and vector construction is more efficient and faster; and meanwhile, an intron element of the pcMINI vector comprises an efficient splicing acceptor and a splicing donor site, so that effective RNA splicing of an inserted DNA fragment can be ensured. The invention provides a complete and feasible prokaryotic mRNA abnormal splicing verification method based on the pcMINI vector.
Owner:武汉翼康基因科技有限公司 +1
ASLV vector system
ActiveUS8642570B2Risk minimizationEfficiently translatedSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsVector systemAvian leukosis viruses
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
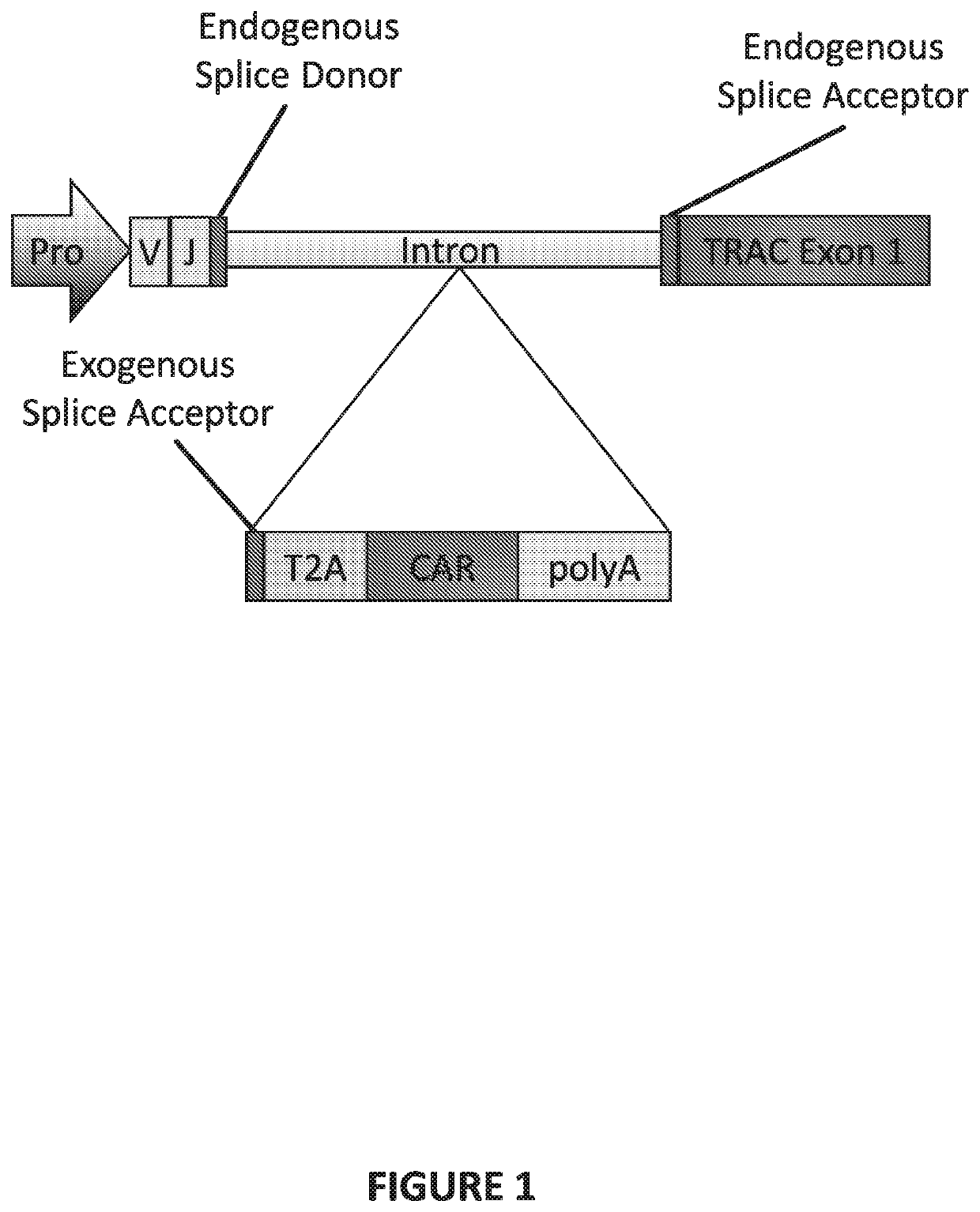
Genetically-modified t cells comprising a modified intron in the t cell receptor alpha gene
ActiveUS20200123516A1Reduces surface expressionDecrease cell surface expressionImmunoglobulin superfamilyHydrolasesT-Cell Receptor Alpha GeneAntigen receptors
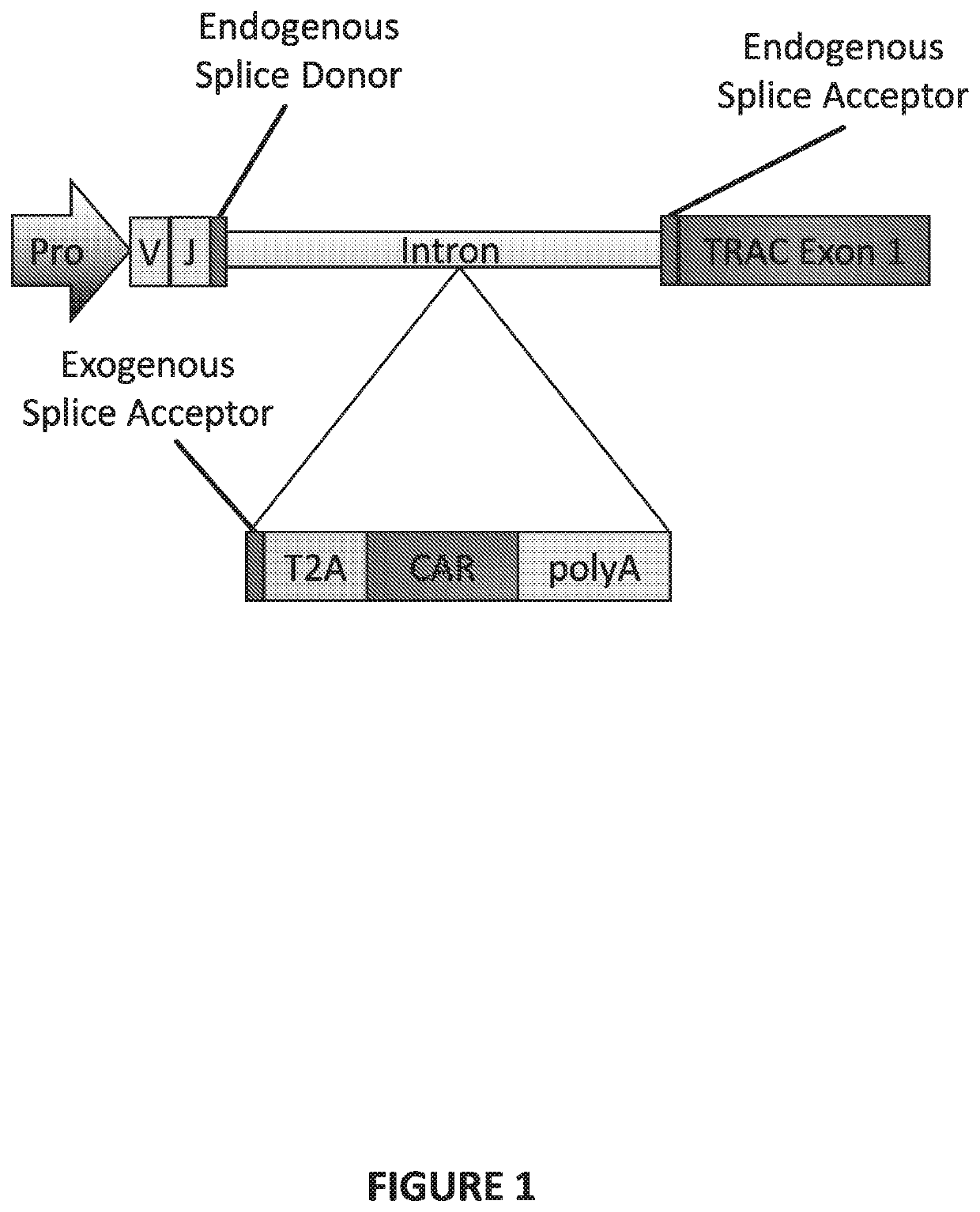
The present invention provides a genetically-modified T cell comprising in its genome a modified human T cell receptor alpha gene. The modified T cell receptor alpha gene comprises an exogenous sequence of interest inserted into an intron within the T in cell receptor alpha gene that is positioned 5′ upstream of TRAC exon 1. The exogenous sequence of interest can comprise an exogenous splice acceptor site and / or a poly A signal, which disrupts expression of the T cell receptor alpha subunit. The sequence of interest can also include a coding sequence for a polypeptide, such as a chimeric antigen receptor. Additionally, the endogenous splice donor site and the endogenous splice acceptor site flanking the intron are unmodified and / or remain functional. The invention further provides compositions and methods for producing the genetically-modified cell, and populations of the cell, and methods for the treatment of a disease, such as cancer, using such cells.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
Barley Lipoxygenase 1 Gene, Method of Selecting Barley Variety, Material of Malt Alcoholic Drinks and Process For Producing Malt Alcoholic Drink
InactiveUS20080193593A1Improved flavor stabilityImprove foam stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPurineHordeum vulgare
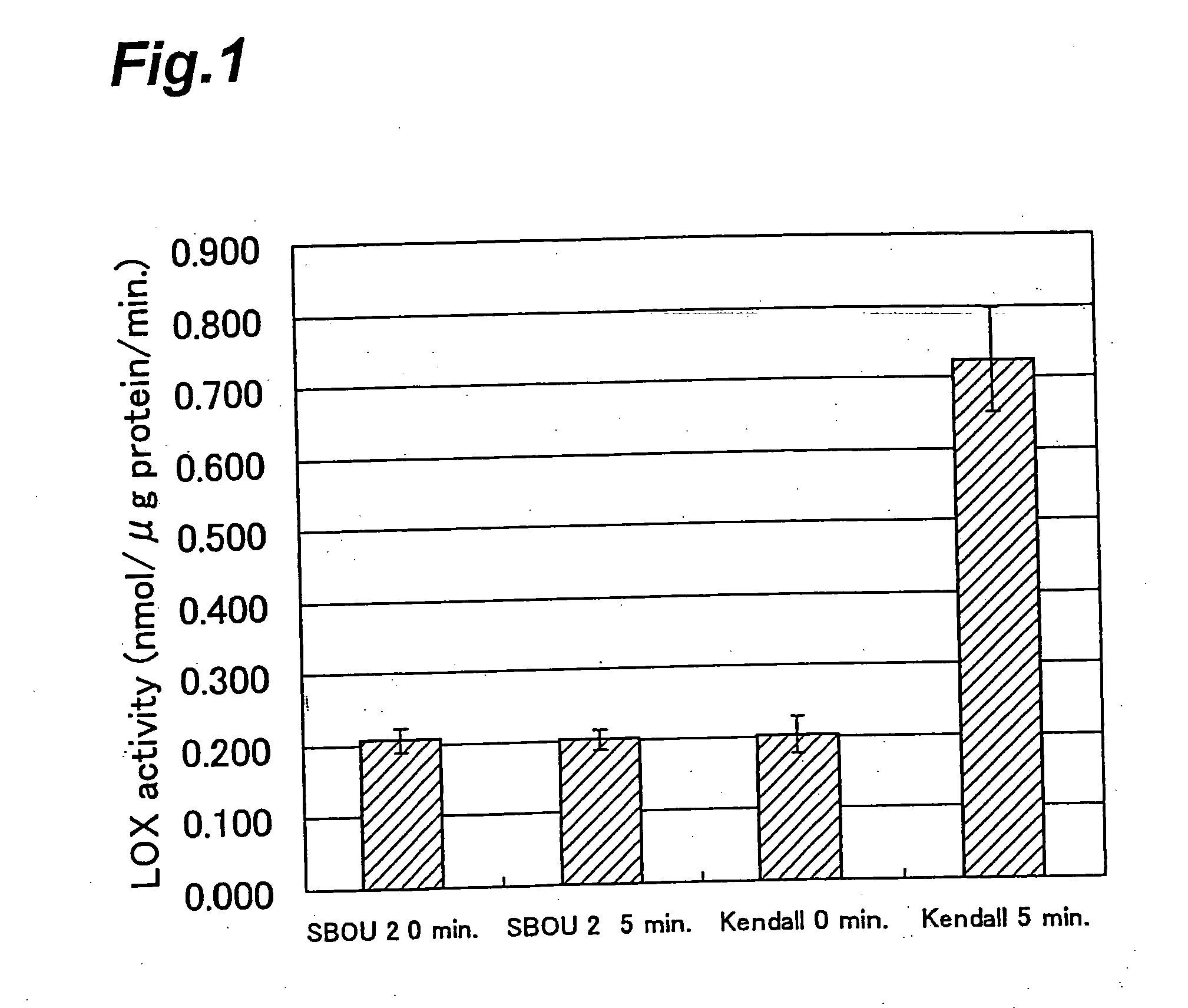
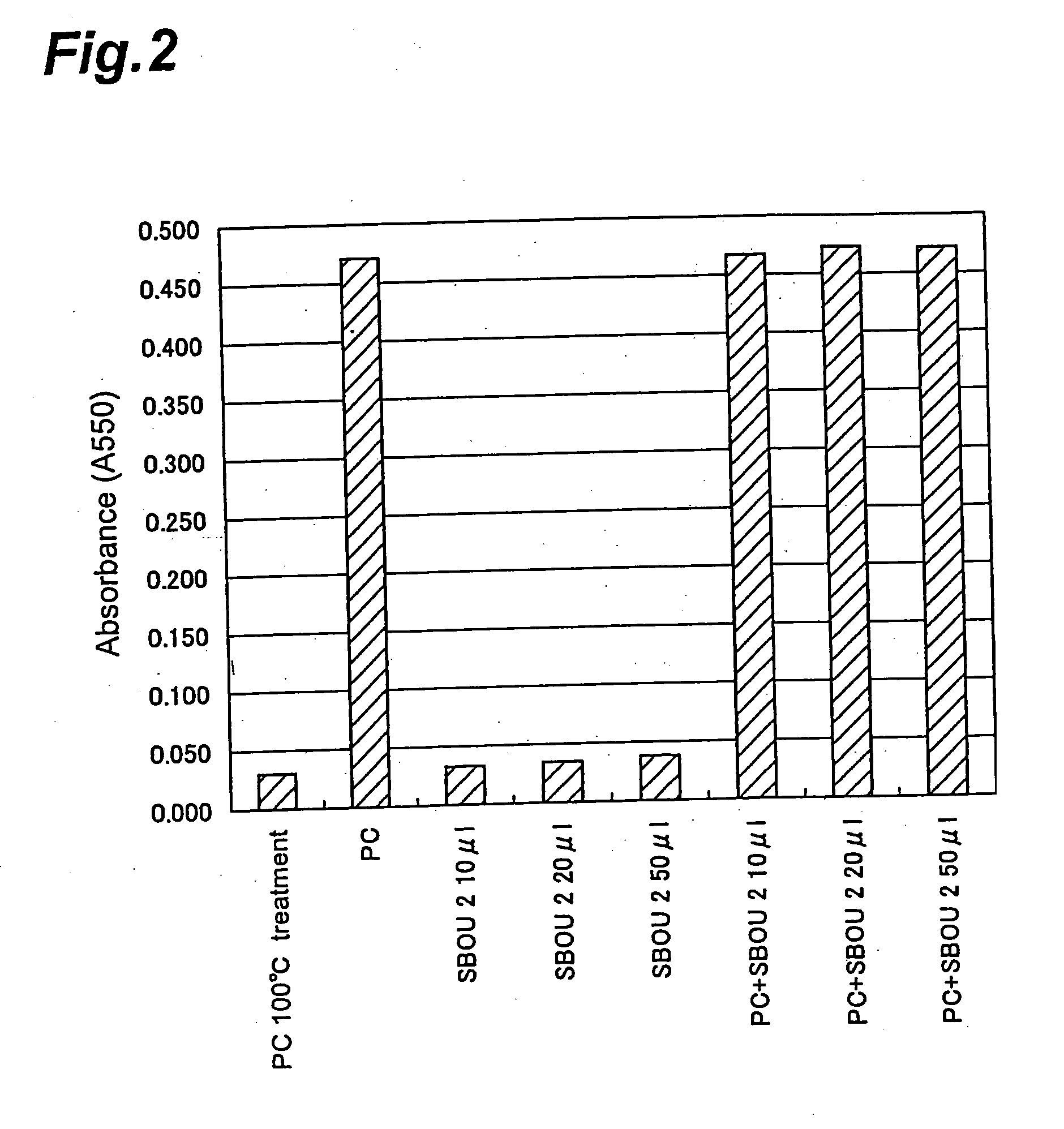
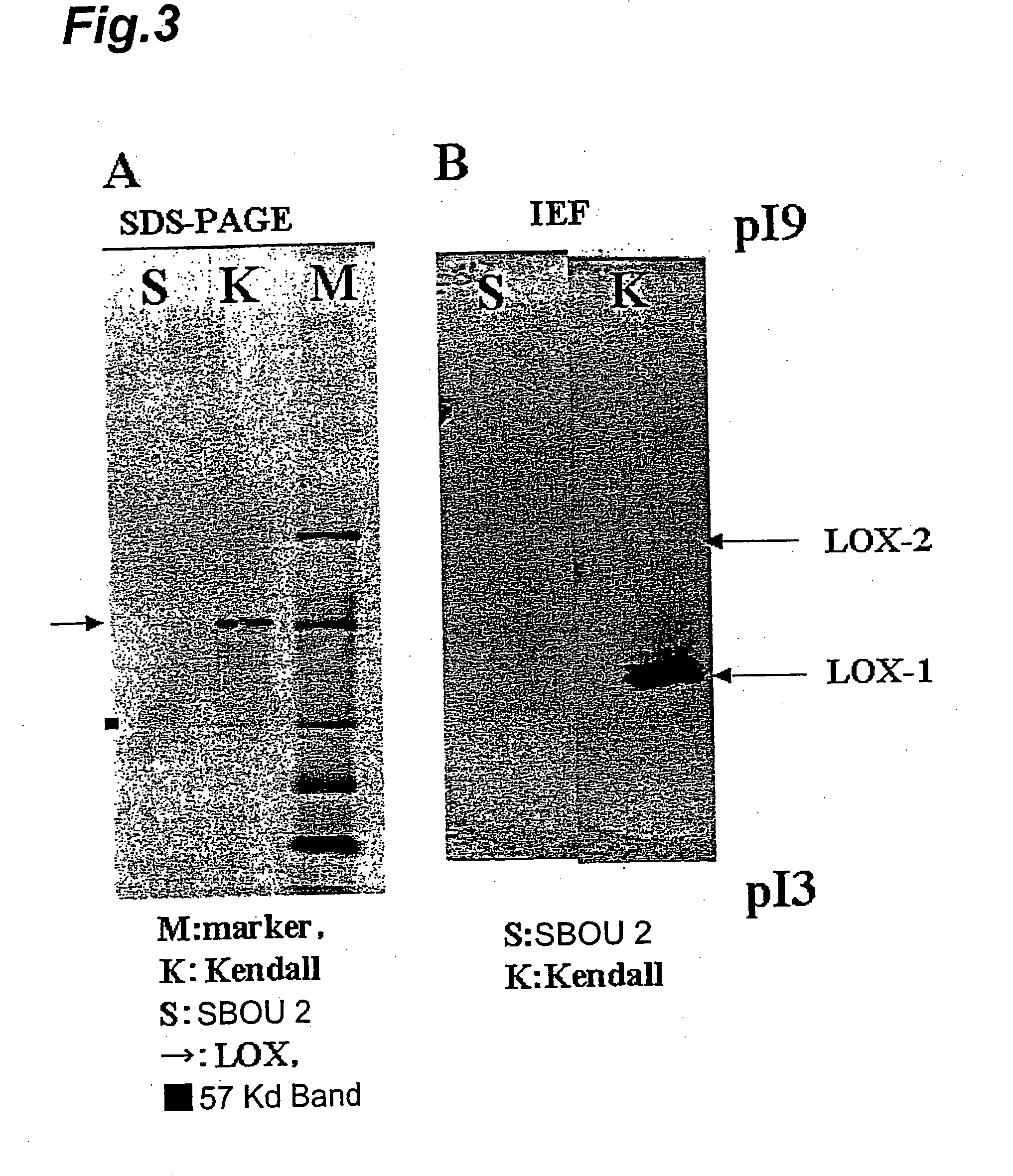
A selection method for barley lipoxygenase-1 deficient barley, comprising a step of distinguishing the barley lipoxygenase-1 deficient barley by whether or not the guanine at the splicing donor site of the 5th intron of the barley lipoxygenase-1 gene is mutated to a different base; and a method for production of malt alcoholic beverages using a material for malt alcoholic beverages derived from barley obtained by the selection method.
Owner:SAPPORO BREWERIES
Recombinant influenza viruses and uses thereof
ActiveUS9217157B2Reduction and amelioration in severityShorten the construction periodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideHeterologousDisease
Modified influenza virus NS gene segments and nucleic acid sequences encoding such modified influenza virus NS gene segments are described. In certain embodiments, a modified influenza virus NS gene segment comprises an influenza virus NS 1 open reading frame (ORF) lacking a stop codon, a heterologous nucleotide sequence, a 2A autoproteolytic cleavage site or another cleavage site, an NEP ORF, wherein the gene segment has one or more mutations in either the splice acceptor site, splice donor site, or both the splice acceptor and splice donor sites that prevents splicing of mRNA. Also recombinant influenza viruses comprising a modified influenza virus NS gene segment and the use of such viruses are described. The recombinant influenza viruses may be used in the prevention and / or treatment of influenza virus disease or as a delivery vector.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Genetically-modified T cells comprising a modified intron in the T cell receptor alpha gene
ActiveUS11053484B2Reduces surface expressionReduce expressionImmunoglobulin superfamilyHydrolasesAntigen receptorT-Cell Receptor Alpha Gene
The present invention provides a genetically-modified T cell comprising in its genome a modified human T cell receptor alpha gene. The modified T cell receptor alpha gene comprises an exogenous sequence of interest inserted into an intron within the T cell receptor alpha gene that is positioned 5′ upstream of TRAC exon 1. The exogenous sequence of interest can comprise an exogenous splice acceptor site and / or a poly A signal, which disrupts expression of the T cell receptor alpha subunit. The sequence of interest can also include a coding sequence for a polypeptide, such as a chimeric antigen receptor. Additionally, the endogenous splice donor site and the endogenous splice acceptor site flanking the intron are unmodified and / or remain functional. The invention further provides compositions and methods for producing the genetically-modified cell, and populations of the cell, and methods for the treatment of a disease, such as cancer, using such cells.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
Sanfilippo B syndrome lentiviral vector, lentivirus and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108715867AImprove securityComplete efficientlyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLentivirusSanfilippo B syndrome
The invention provides a Gaucher lentiviral vector, a lentivirus and a preparation method and application thereof. The lentiviral vector is obtained by modifying a splicing donor site at the terminal5' of a pTYF lentiviral vector and further comprises NAGLU gene. The NAGLU gene is specifically connected in on the basis of the lentiviral vector after being modified, so that more efficient genetictransmission can be realized while safety is ensured, expression of the NAGLU gene in brain related cells is improved, and transmission of normal gene in the process of Sanfilippo B syndrome gene therapy can be completed more efficiently.
Owner:SHENZHEN GENO IMMUNE MEDICAL INST
Method for inducing exon skipping by genome editing
ActiveUS20210087555A1Effective treatmentEfficient analysisHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionBase JGenetics
A method of skipping a target exon of a gene of interest in a genome uses CRISPR-Cas and guide RNA. The guide RNA contains a spacer sequence such that the site of cleavage by the CRISPR-Cas is positioned within 80 bases from the splice donor site immediately before the target exon or the splice acceptor site immediately after the target exon.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Human soluble neuropilin-1 primary polyadenylation signal and uses thereof
InactiveUS7557197B2Easy to transportImprove translationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
The human soluble neuropilin-1 (sNRP) polyadenylation signal (sNRP-poly(A)), situated downstream of the GT splice donor site of intron 12 of the full-length neuropilin-1 gene, also functions as the termination codon for sNRP. This 17 nucleotide sequence efficiently facilitates addition of poly(A) tails to RNAs expressed in cells. The present invention shows that this optimally succinct sequence has similar activity to the SV40 polyadenylation signal that is currently used in expression vectors. By using this shorter dual termination / polyadenylation signal and avoiding the need for large and cumbersome polyadenylation signals, expression vectors may be engineered to carry considerably larger genes.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
X-SCID lentivirus carrier, lentivirus as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108728494AImprove securityHigh transfection efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesGene deliveryLentivirus
The invention provides an X-SCID lentivirus carrier, lentivirus as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the lentivirus carrier, transformation is conducted on a donor splicing site of the 5' end of a pTYF lentivirus carrier, wherein the lentivirus carrier further comprises an IL-2RgammaC gene. On the basis of the transformed lentivirus carrier, the IL-2RgammaC gene isspecifically connected, so that not only is the safety ensured, but also more efficient gene transmission is achieved, thus the expression quantity of the IL-2RgammaC gene in transgenic related cellsis obviously improved, and transferring of normal genes in an X-SCID gene therapy process is completed more efficiently.
Owner:SHENZHEN GENO IMMUNE MEDICAL INST
Lentiviral vector of mucopolysaccharidosis, lentivirus, and preparation method and application of lentiviral vector
InactiveCN108795985AImprove securityEfficient deliveryHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryLentivirus
The invention provides a lentiviral vector of mucopolysaccharidosis, a lentivirus, and a preparation method and application of the lentiviral vector. The lentiviral vector is prepared by modifying a splicing donor site at the 5' end of a pTYF lentiviral vector, and also includes an MPS II gene. On the basis of the modified lentiviral vector, the MPS II gene is specifically linked in, thereby achieving more efficient gene delivery while ensuring safety, significantly increasing the expression quantity of the MPS II gene in transgenic brain-related cells, and more efficiently completing the transmission of normal genes during the gene therapy of mucopolysaccharidosis.
Owner:SHENZHEN GENO IMMUNE MEDICAL INST
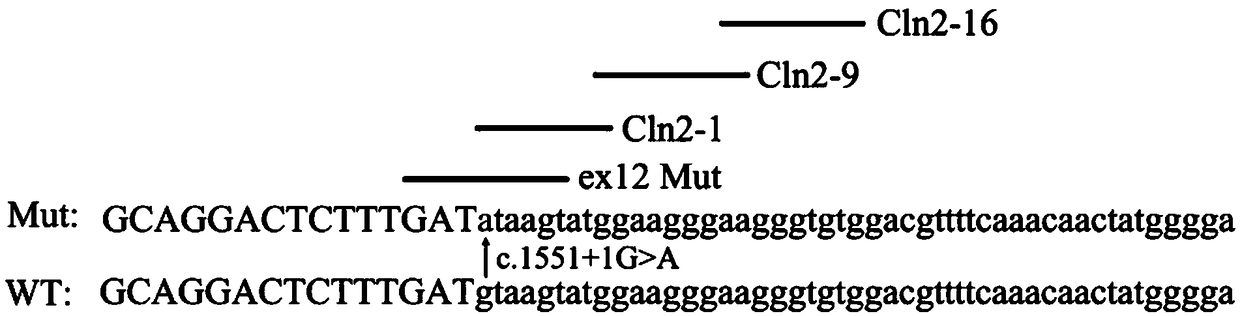
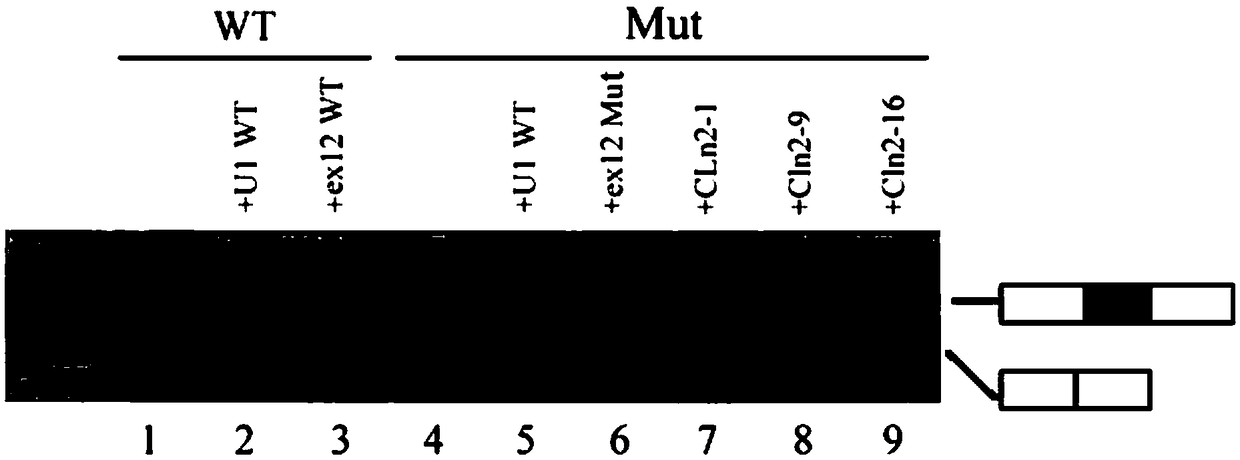
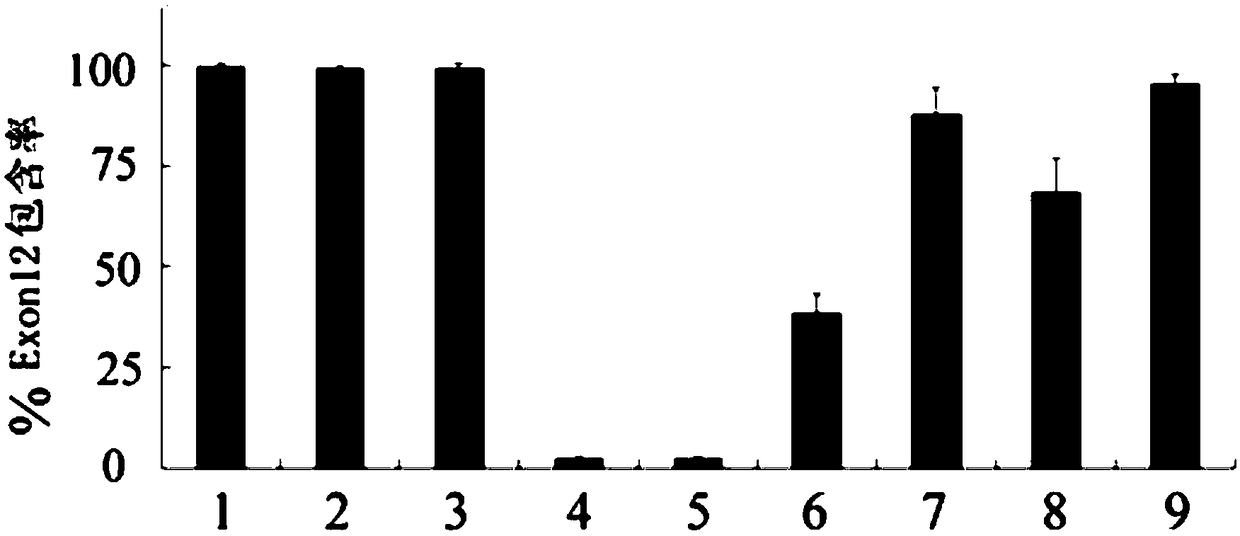
U1-snRNA for repairing TPP1 gene Pre-mRNA aberrant splicing and application of U1-snRNA
ActiveCN109486813AGain splicing repair efficiencyInhibit abnormal mRNA expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseSide effect
The invention discloses a U1-snRNA for repairing TPP1 gene splicing defects and a vector containing a base sequence for expressing the U1-snRNA. The base sequence for expressing the U1-snRNA sequentially comprises a U1-snRNA initial basic group, a sequence complemented with a TPP1 gene Exon12 donor splicing site or a downstream intron sequence target and a U1-snRNA downstream sequence, and the U1-snRNA downstream sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.20. The U1-snRNA is from a nucleic acid molecule prepared according to a TPP1 gene donor splicing site or donor splicing site downstream intron sequence. By the aid of a U1-snRNA technique, U1-snRNA of a target gene serves as a target medicine, and repairing is implemented in the splicing process of Pre-mRNA, so that aberrant mRNA expression caused by splicing site mutation is effectively restrained. The U1-snRNA has the advantages of high specificity, high efficiency and small side effect, can make up for the deficiency of current treatment means of diseases caused by aberrant splicing and possibly serves as a new method for treating specific types of diseases in the near future.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Thymidine kinase
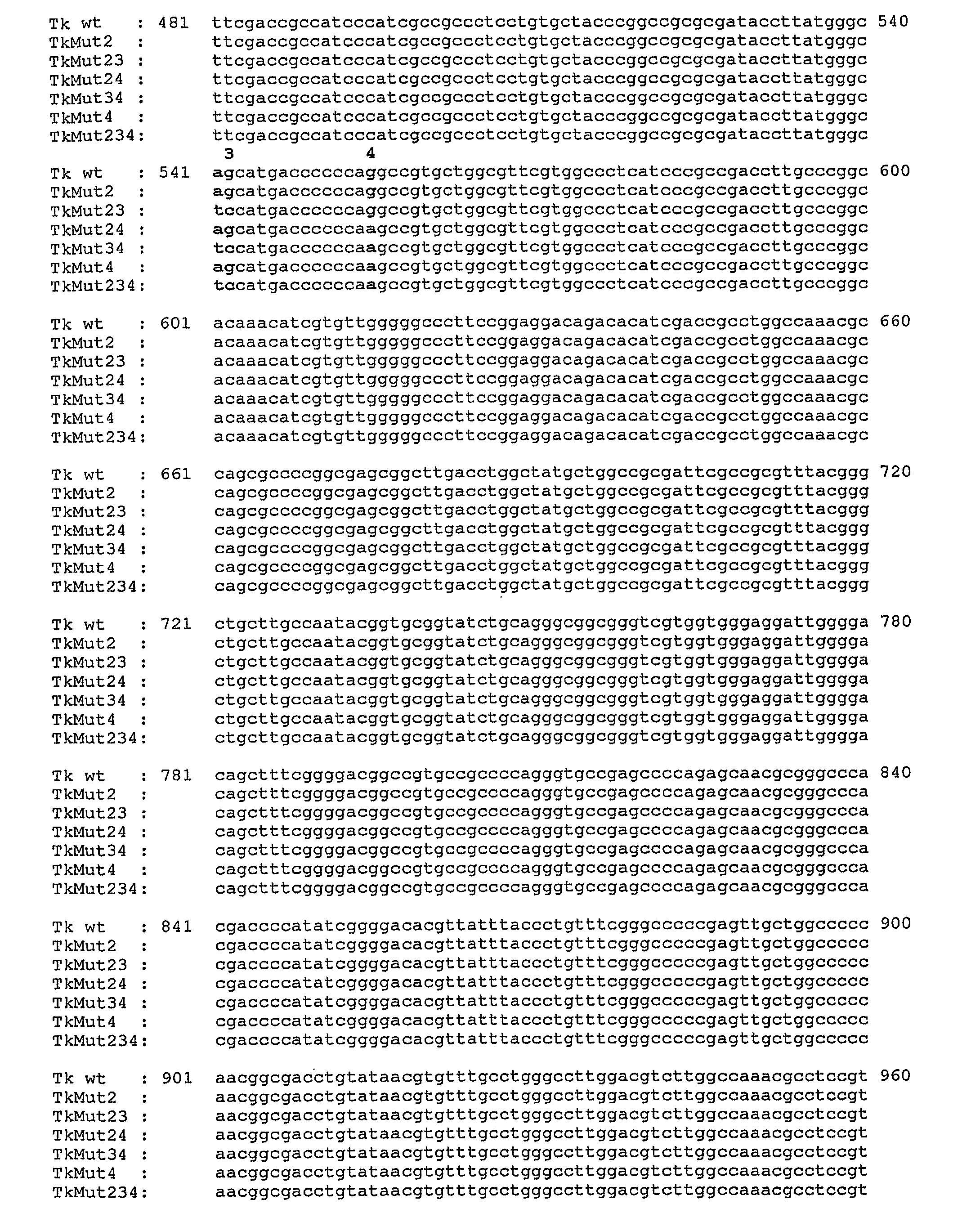
ActiveUS20130028876A1Avoid stitchingGreat proportionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
A polynucleotide comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a thymidine kinase wherein at least one of the nucleotides corresponding to the splice donor site nucleotides is replaced by another nucleotide and wherein the nucleotides of the splice acceptor sites are not altered.
Owner:MOLMED SPA
Method for screening and identifying functional lncrnas
PendingUS20210163936A1Eliminate functionReduced activityHydrolasesReverse transcribing RNA virusesGeneticsGenome
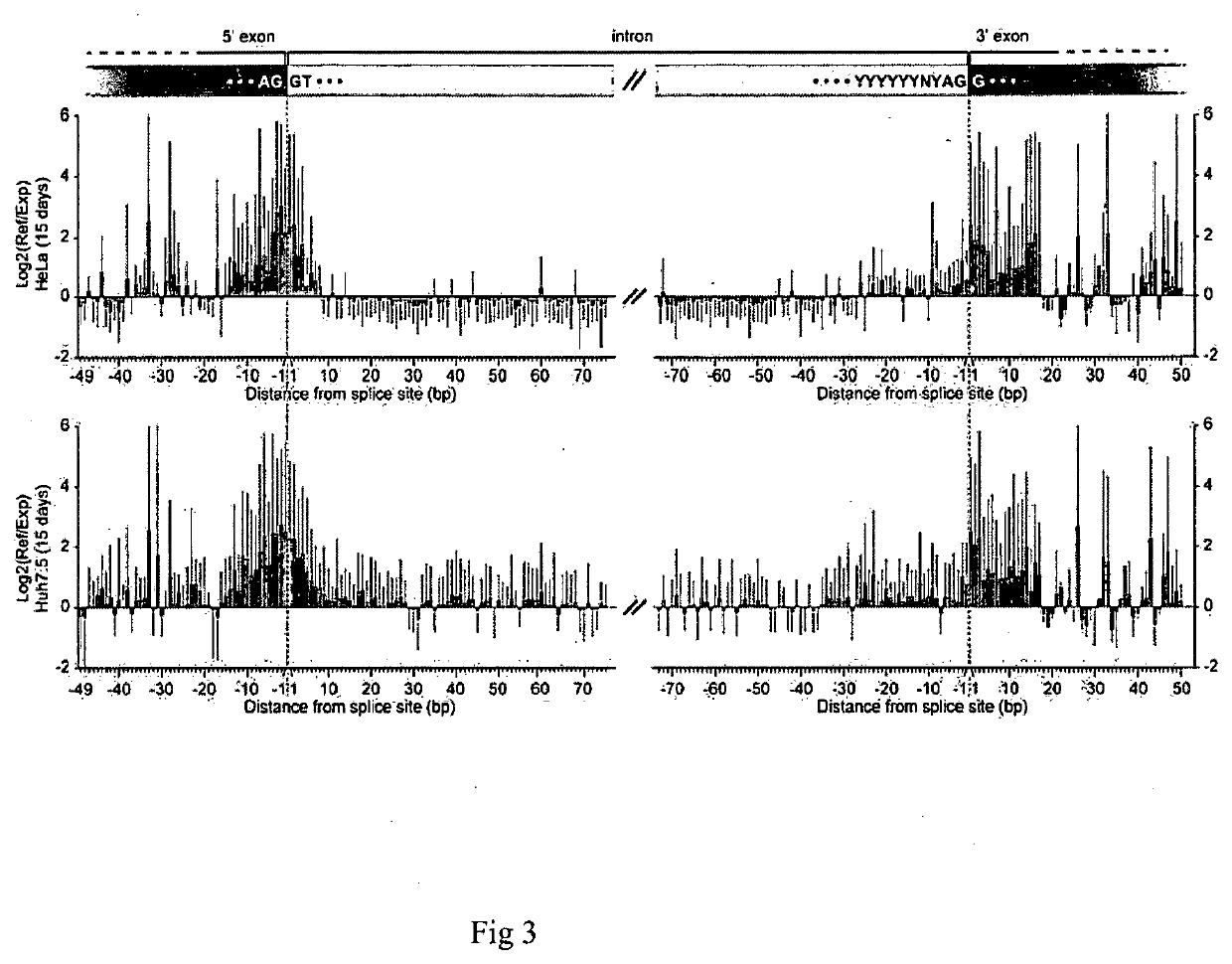
Provided is a high-throughput method for screening or identifying long non-coding RNAs by CRISPR system, which uses paired guide RNA targeting the genomic sequence within the region spanning −50 bp to +75 bp surrounding a splice donor site or a splice acceptor site of a long non-coding RNA.
Owner:EDIGENE BIOTECH INC +1
Type B hemophilia lentiviral vector, lentivirus and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108676815AImprove securityComplete efficientlyPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLentivirusGenetics
The invention provides a type B hemophilia lentiviral vector, a lentivirus and a preparation method and application thereof. The lentiviral vector is obtained by modifying a splicing donor site of a 5' end of the pTYF lentiviral vector, wherein the lentiviral vector further comprises an FIX gene. The FIX gene is specifically connected on the basis of the modified lentiviral vector, the safety canbe ensured and more efficient gene transmission is realized, so that the expression amount of the FIX gene in bone marrow related cells is remarkably increased, and the transmission of normal genes ina gene treatment process of type B hemophilia can be more efficiently finished.
Owner:SHENZHEN GENO IMMUNE MEDICAL INST
Method for Screening and Identifying Functional lncRNAs
Provided is a high-throughput method for screening or identifying long non-coding RNAs by CRISPR system, which uses paired guide RNA targeting the genomic sequence within the region spanning -50 bp to+75 bp surrounding a splice donor site or a splice acceptor site of a long non-coding RNA.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Lymphohematopoietic engineering using cas9 base editors
PendingCN112292139AGenetically modified cellsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBase JMissense mutation
Provided herein are methods and systems for targeted gene disruption (knock-out, missense mutation) and targeted gene knock-in in mammalian cells using base editors and guide RNAs (gRNAs) designed totarget splice acceptor-splice donor sites. Also provided herein are universally acceptable genetically engineered cells comprising targeted disruptions in immunotherapy-related genes and comprising aCAR / TCR for therapeutic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Thymidine kinase
ActiveUS8357788B2Avoid stitchingGreat proportionAntibacterial agentsTransferasesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
A polynucleotide comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a thymidine kinase wherein at least one of the nucleotides corresponding to the splice donor site nucleotides is replaced by another nucleotide and wherein the nucleotides of the splice acceptor sites are not altered.
Owner:MOLMED SPA
Non-integrating DNA vectors for the genetic modification of cells
InactiveUS20200277624A1Improving establishment efficiencyImproving transgene expressionNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionPolynucleotidePromoter
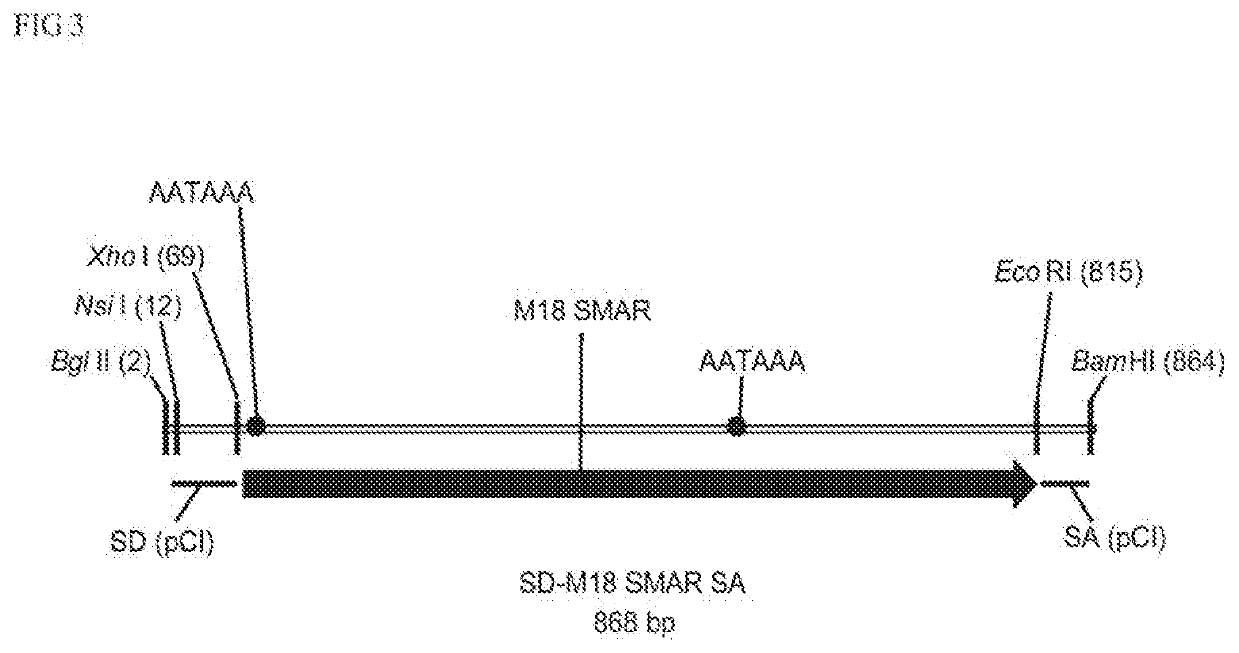
The present invention relates to a polynucleotide comprising at least one promoter and an S / MAR element, wherein said S / MAR element is located downstream of said promoter in the 3′ UTR of the transcription unit and wherein the said S / MAR element is flanked by a 5′ splice donor site and a 3′ splice acceptor site; the present invention further relates to a composition comprising said polynucleotide, and to the polynucleotide for use in medicine and for use in treating genetic disease.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com