Method for Screening and Identifying Functional lncRNAs
A functional and purposeful technology, applied in the field of screening and identification of functional lncRNAs, can solve problems such as destruction, laborious scale-up, and lack of scale-up
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0096] Materials and methods
[0097] 1. Cells and Reagents
[0098] The HeLa cell line from Z. Jiang's laboratory (Peking University) was cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Gibco C11995500BT). The Huh 7.5 cell line from the laboratory of S. Cohen (Stanford University School of Medicine) was cultured in DMEM (Gibco) supplemented with 1% MEM non-essential amino acids (NEAA, Gibco 1140-050). K562 cells from H. Wu laboratory (Peking University) and GM12878 cells from Coriell cell bank were cultured in RPMI1640 medium (Gibco11875-093). All cells were supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, CellMaxBL102-02) and 1% penicillin / streptomycin at 37°C in 5% CO 2 cultivated in.
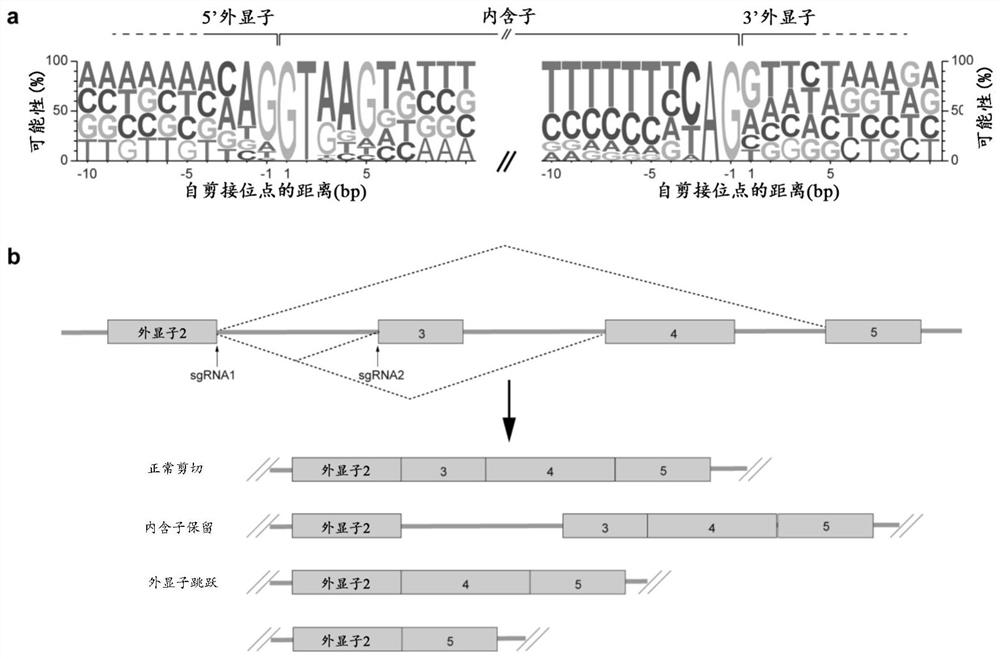
[0099] 2. Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) to test for intron retention or exon skipping
[0100] Cloning of sgRNA into a lentiviral expression vector carrying a CMV promoter-driven mCherry marker, followed by transduction of HeLa by viral infection at MOIOC cell 1-4 , 72 hours ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com