Patents
Literature
399 results about "Embryo tail" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human embryos have a tail that measures about one-sixth of the size of the embryo itself. As the embryo develops into a fetus, the tail is absorbed by the growing body.
Seed specificity highly effective promoter and its application
InactiveCN101063139AReduce adverse effectsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Simulation dog tail swinging installment
InactiveUS20110003528A1Low costReduce frictionDollsSelf-moving toy figuresEngineeringControl circuit
A simulation tail swinging installment includes a base plate, an electromagnetic coil disposed on the base plate, a battery module configured for supplying power to the electromagnetic coil, and a control circuit coupled to the battery module. The simulation tail swinging installment further includes a furcated component having two arms disposed with respect to the electromagnetic coil, with the two arms located on opposite sides of the electromagnetic coil, respectively. Each of the arms includes a permanent magnet positioned in correspondence with the electromagnetic coil. The furcated component is mounted to the base plate through a pivot connected to the base plate. A first driving cable and a second driving cable are attached to the two arms, respectively. The first driving cable and the second driving cable extend through and along two side portions of a simulation tail and secured to a distal end of the simulation tail.
Owner:TSUI KING LAM
Transient Transfection with RNA
ActiveUS20080260706A1Lymphocyte transfectabilitySimilar efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryDNA construct
A method of mRNA production for use in transfection is provided, that involves in vitro transcription of PCR generated templates with specially designed primers, followed by polyA addition, to produce a construct containing 3′ and 5′ untranslated sequence (“UTR”), a 5′ cap and / or Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES), the gene to be expressed, and a polyA tail, typically 50-2000 bases in length. This RNA can efficiently transfect different kinds of cells. This approach results in increased efficiency (fidelity and productivity) of mRNA synthesis and is less time consuming because it does not require cloning, and also consequently eliminates the unwanted errors and effects related to RNA made on DNA templates obtained with cloning techniques. The results of transfection of RNAs demonstrate that RNA transfection can be very effective in cells that are exceedingly difficult to transfect efficiently with DNA constructs. Further, the levels of gene expression following mRNA transfection are consistent from cell to cell in an experiment and these levels can be controlled over a wide range simply by changing the amount of mRNA that is transfected, and without obvious cytotoxic effects due to the levels of RNA per se. Due to high efficiency the cells can be simultaneously transfected with multiple genetic constructs. The method can be used to deliver genes into cells not- or only poorly transfectable for DNA, in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for storing information in DNA
InactiveUS20050053968A1Microbiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHuman DNA sequencingPresent method
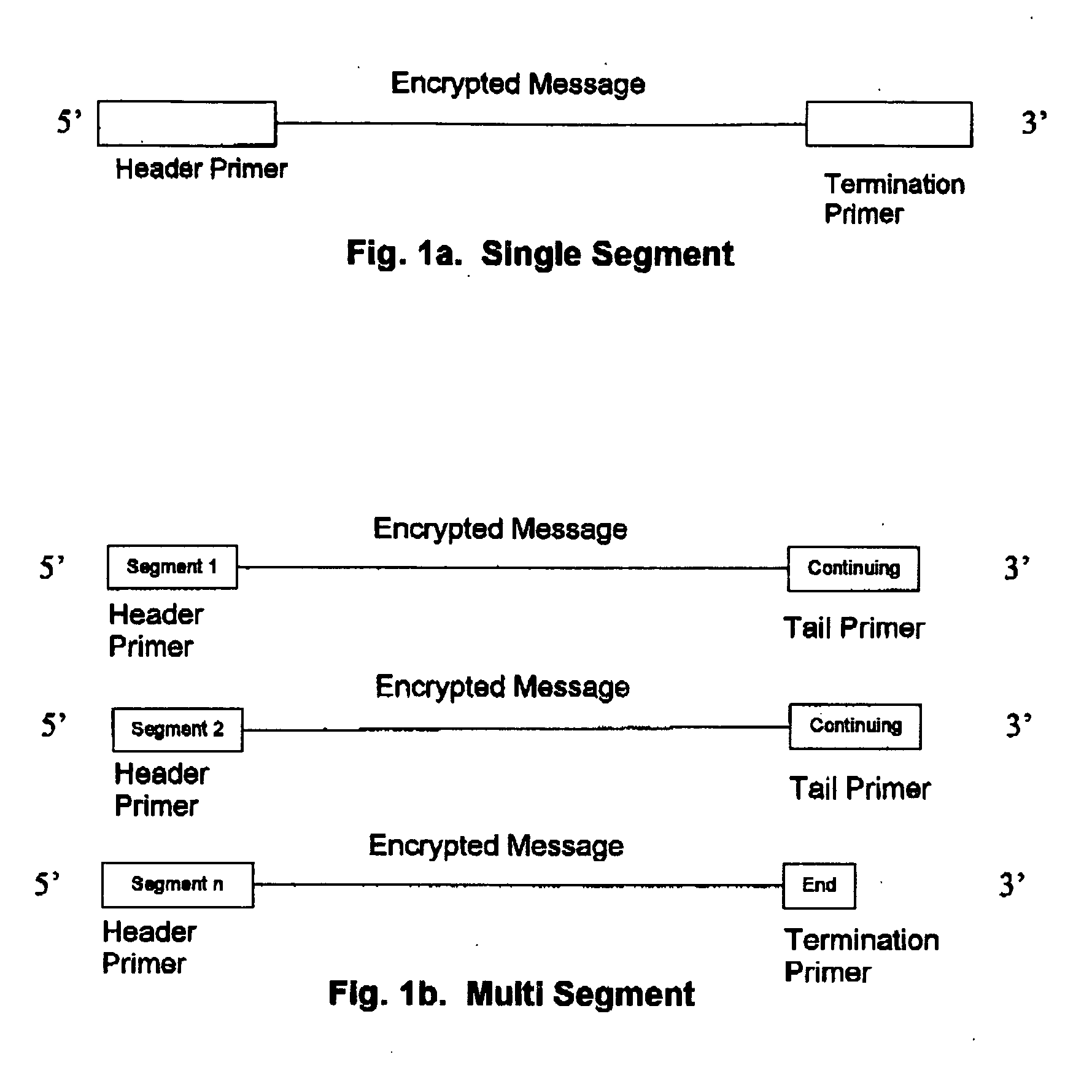
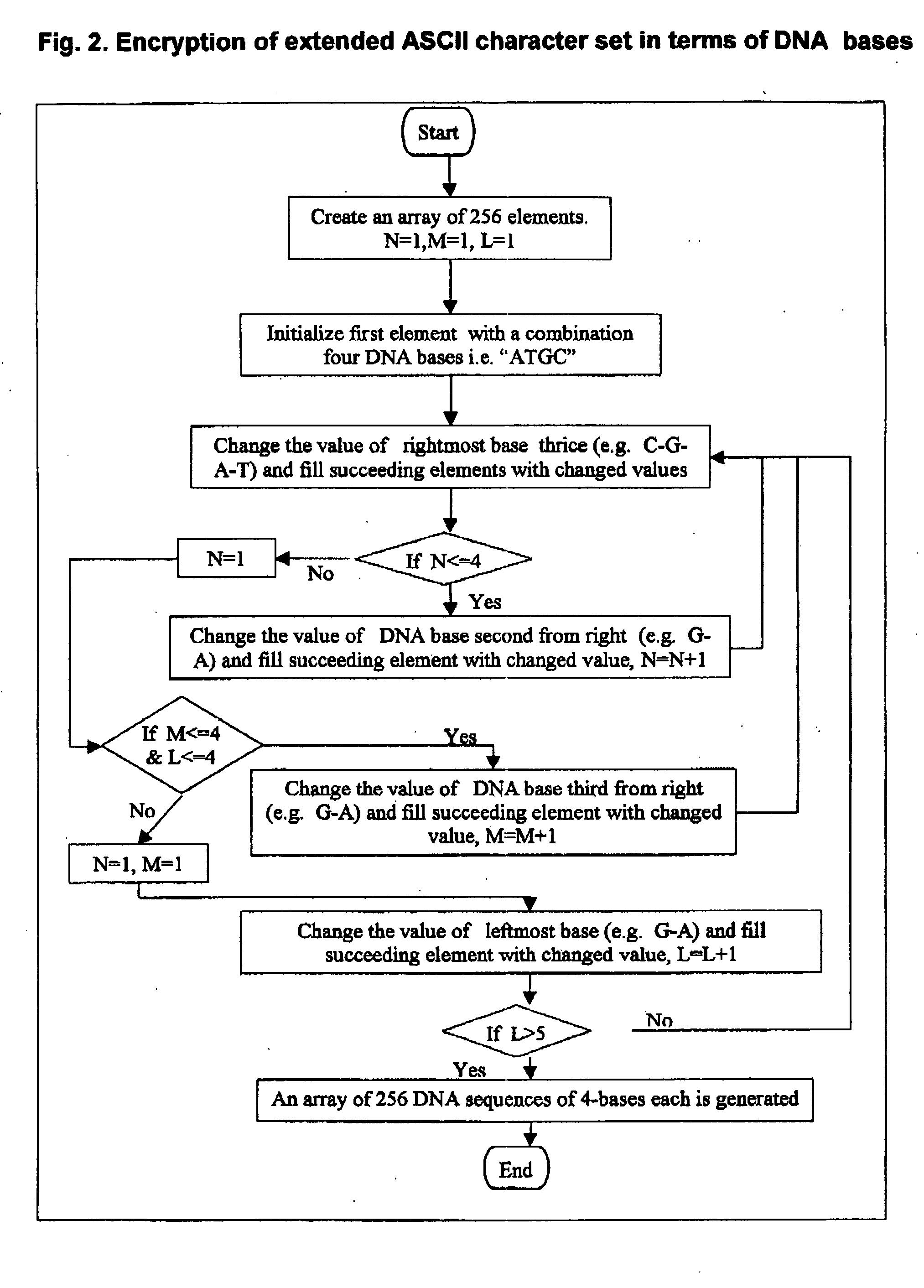
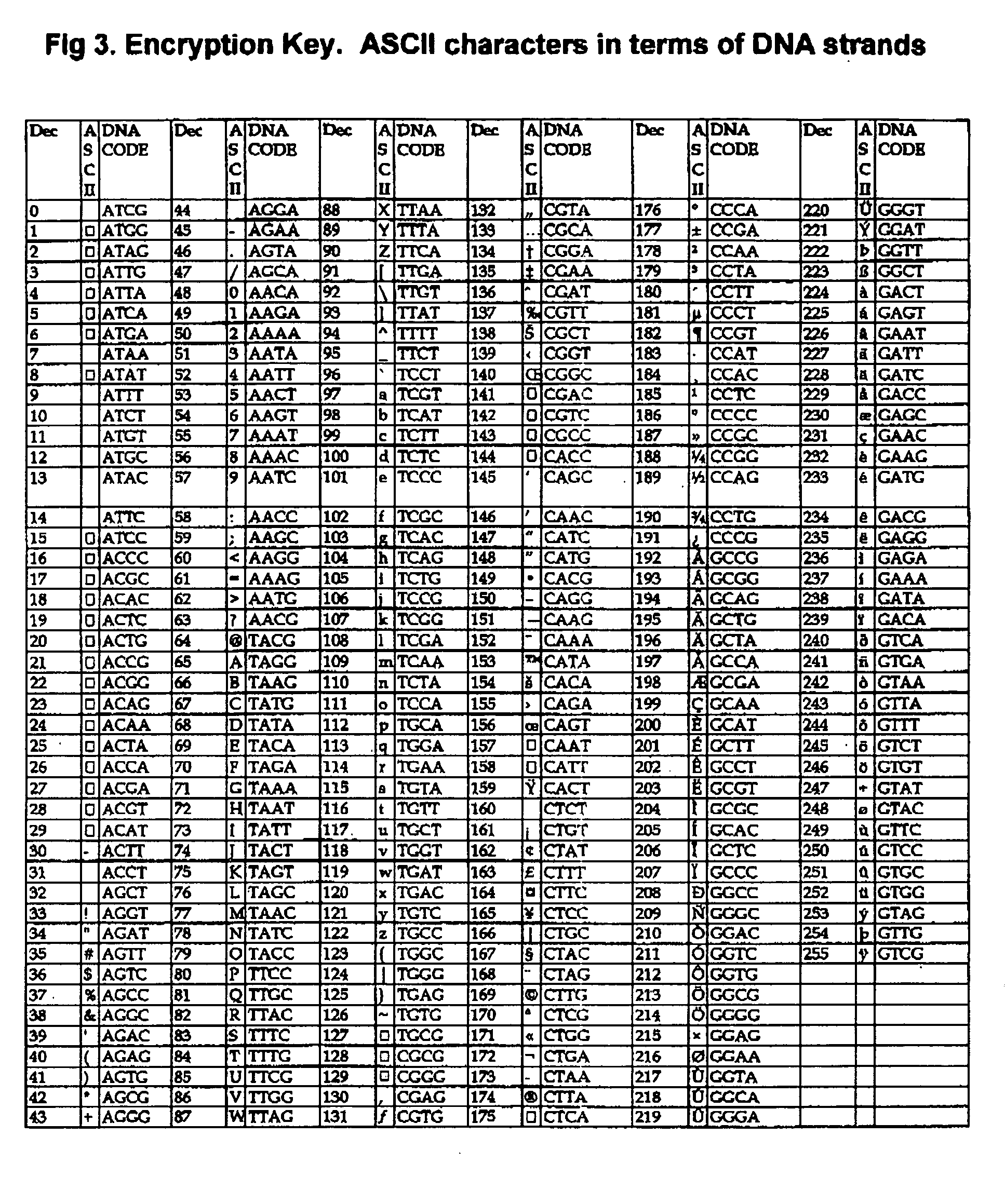
DNA is a natural molecular level storage device. Molecular storage devices use each molecule or part of it for storing a character. Thus it is possible to store information million of times than presently used storage devices. For example a JPEG image (i.e. flag of India) having file size of 1981 Bytes can be encrypted using 7924 DNA bases which occupies about 2694.16 nanometers In other words flag of India can be encrypted 8.07×105 times in human genome which comprises 6.4×109 DNA bases and occupy a tiny volume of about 0.02 μm3. A method for storing information in DNA has been developed which includes software and a set of schemes to encrypt, store and decrypt information in terms of DNA bases. The main advantages of the present method over exiting art is that it addresses complete set of extended ASCII characters set and thereby, encryption of all kind of digital information (text, image, audio etc.). First of all, information is, encrypted along with carefully designed sequences known as header and tail primers at both the ends of actual encrypted information. This encrypted sequence is then synthesized and mixed up with the enormous complex denatured DNA strands of genomic DNA of human or other organism.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method of making a glass envelope
InactiveUS20070128967A1Easy to understandElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesFritLight beam
A method of minimizing stress in an OLED device laser sealing process using an elongated laser beam. A laser beam having an intensity distribution which decreases as a function of distance from the longitudinal axis of the beam is passed through a mask to create an elongated beam having a length-wise intensity distribution which decreases as a function of distance from the axis of the beam and a substantially constant width-wise intensity distribution. The elongated beam is traversed over a line of frit disposed between two substrates. The tails of the length-wise intensity distribution provide for a slow cool down of the frit as the beam traverses the line of frit.
Owner:CORNING INC
Sterol-Modified Amphiphilic Lipids
Disclosed are sterol-modified amphiphilic lipid compounds having two or more hydrophobic tails of which at least one is a sterol. Also disclosed are the processes for the synthesis of these compounds, compositions comprising such compounds, and the use of such compounds in delivery of an agent of interest, e.g., therapeutics, imaging agents, contrast materials for ultrasound applications, vaccines, biosensors, nutritional supplements and skin care products.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for targeted inactivation of HIV cell surface receptors
InactiveUS20110262406A1Avoid infectionReduce viral loadBiocideOrganic active ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusTail
Compositions for targeted mutagenesis of cell surface receptors for HIV and methods of their use are provided herein. The compositions include triplex-forming molecules that displace the polypyrimidine strand of target duplex and form a triple-stranded structure and hybrid duplex in a sequence specific manner with the polypurine strand of the target duplex. The triplex-forming molecules include a mixed-sequence “tail” which increases the stringency of binding to the target duplex, improves the frequency of modification at the target site, and reduces the requirement for a polypurine:polypyrimidine stretch. Methods for using the triplex-forming molecules in combination with one or more donor oligonucleotides for targeted modification of sites within or adjacent to genes that encodes cell surface receptors for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are also disclosed. Methods for ex vivo and in vivo prophylaxis and therapy of HIV infection using the disclosed compositions are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
High performance fan tail heat exchanger
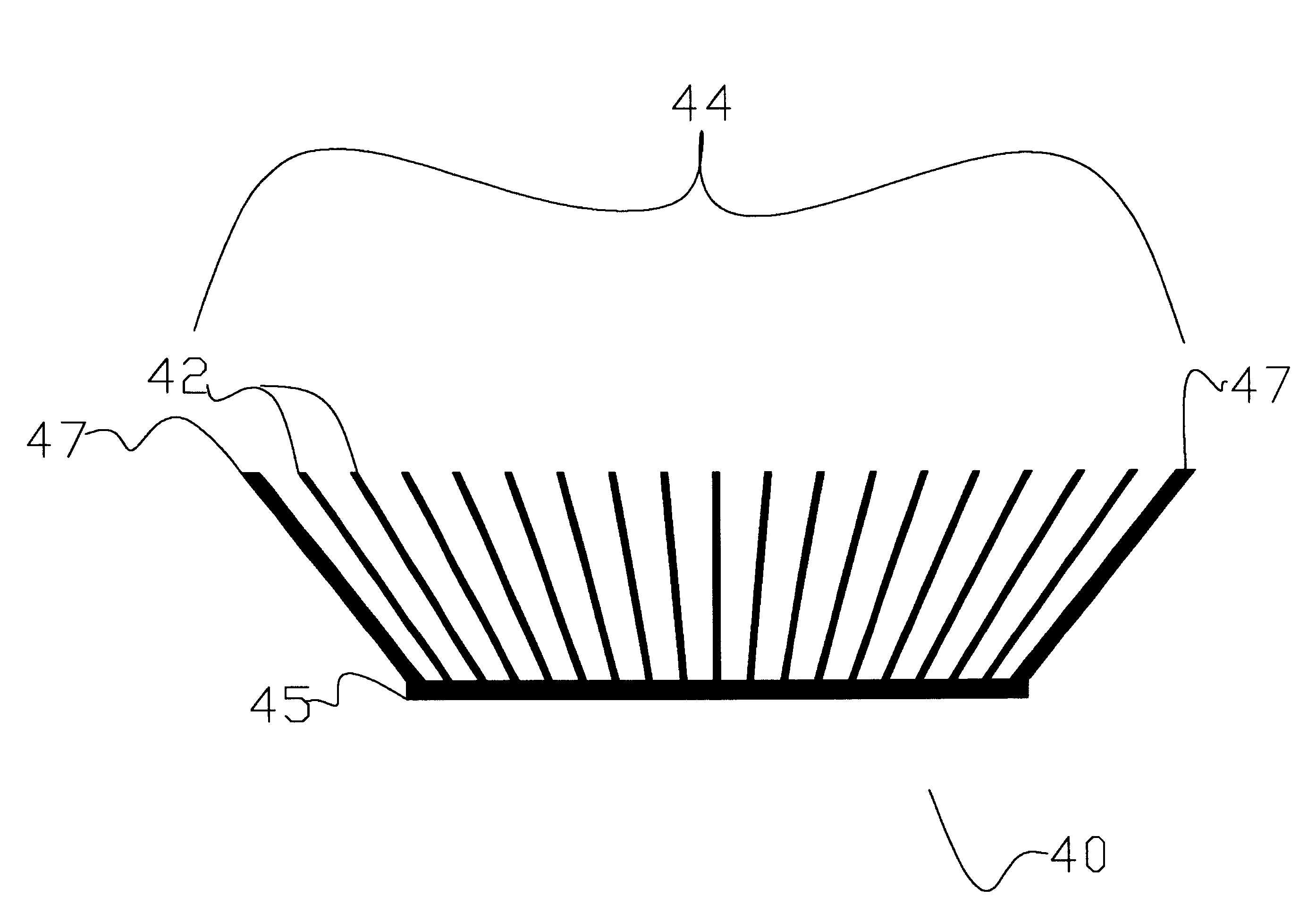
InactiveUS6308771B1Increased control volumeOptimize volumeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAcute angleEngineering
A novel plate fin heat exchanger adapted for high and low velocity fluid flows for dissipating heat from a heat generating component. The heat exchanger comprises an array of fins being affixed to and in thermal communication with a thermally conductive base, wherein the fins are arranged in a fan tail configuration for minimizing flow bypass, and further providing reduced thermal resistance for fluid passing through the fin field. The fins are affixed to and in thermal communication with the base at an acute angle, such that the effective width of the array of fins exceeds the width of the base. The enlarged effective width of the fin array in comparison to conventional heat exchanger provides an increased volume for fluid flow, thereby allowing a greater volume of fluid to enter the fin field and a greater surface area of plate fins for cooling the fluid passing through the heat exchanger. In addition, the heat exchanger comprises a fin density of at least ten fins per inch or greater of base length thereby providing a narrow channel heat exchanger with a fan tail. The aspect ratio of the individual channels between the fins, as compared to parallel fins affixed perpendicular to the base through an extrusion method, generates a reduced pressure drop across the heat exchanger. Accordingly, the heat exchanger of the present invention expands the envelope of cooling performance provided by fluid flow over an array of thermally conductive plates.
Owner:ADVANCED THERMAL SOLUTION
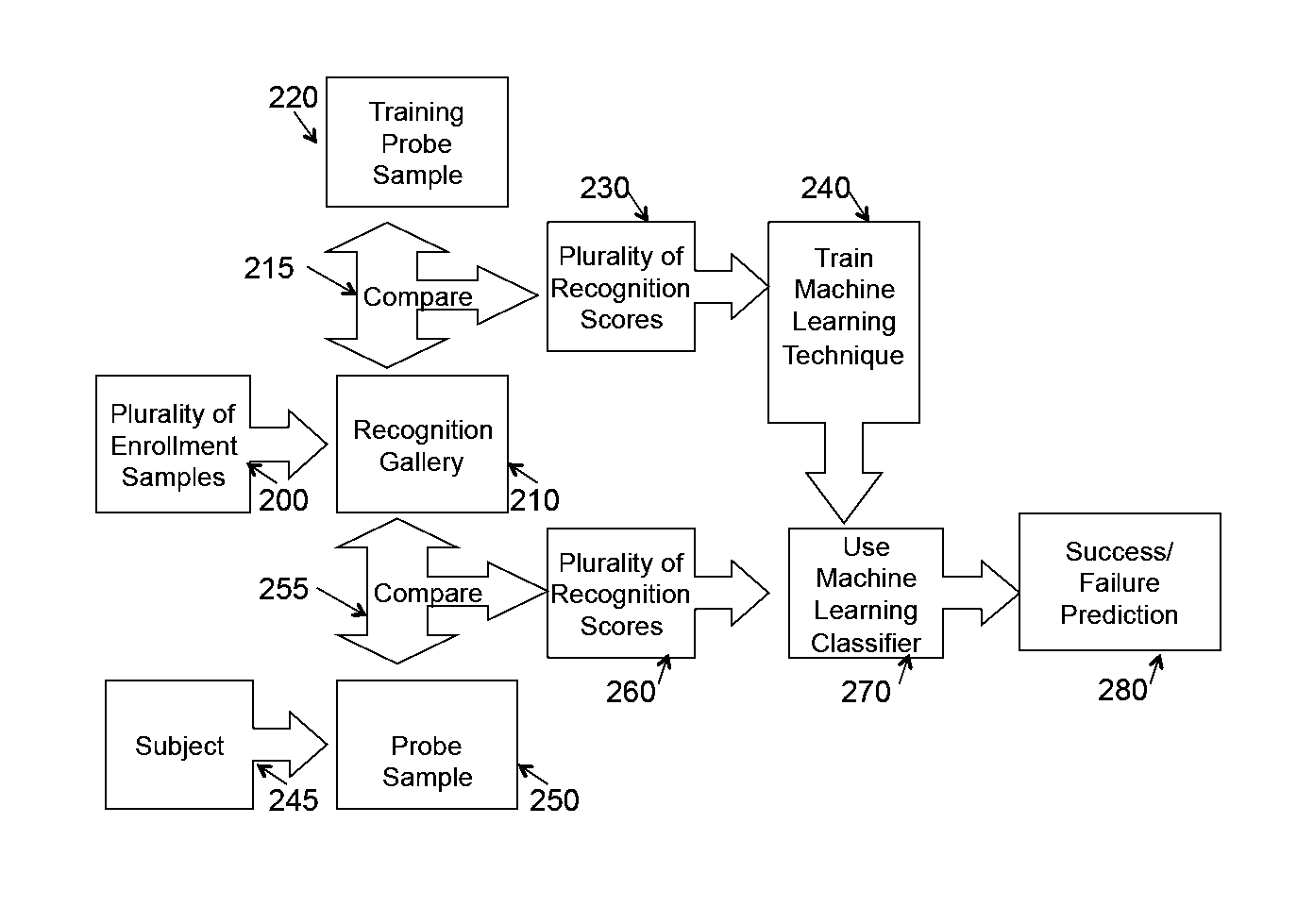
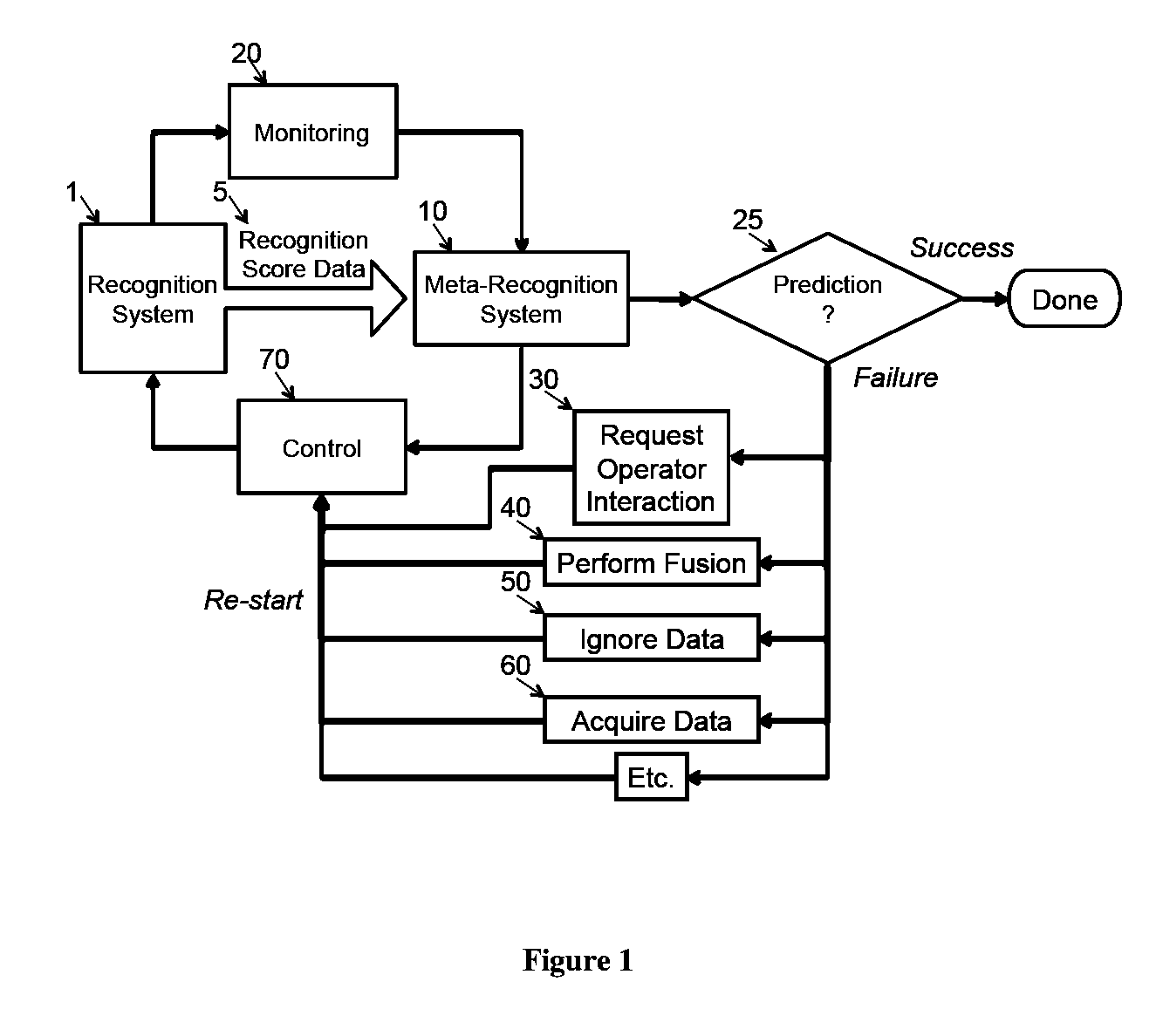
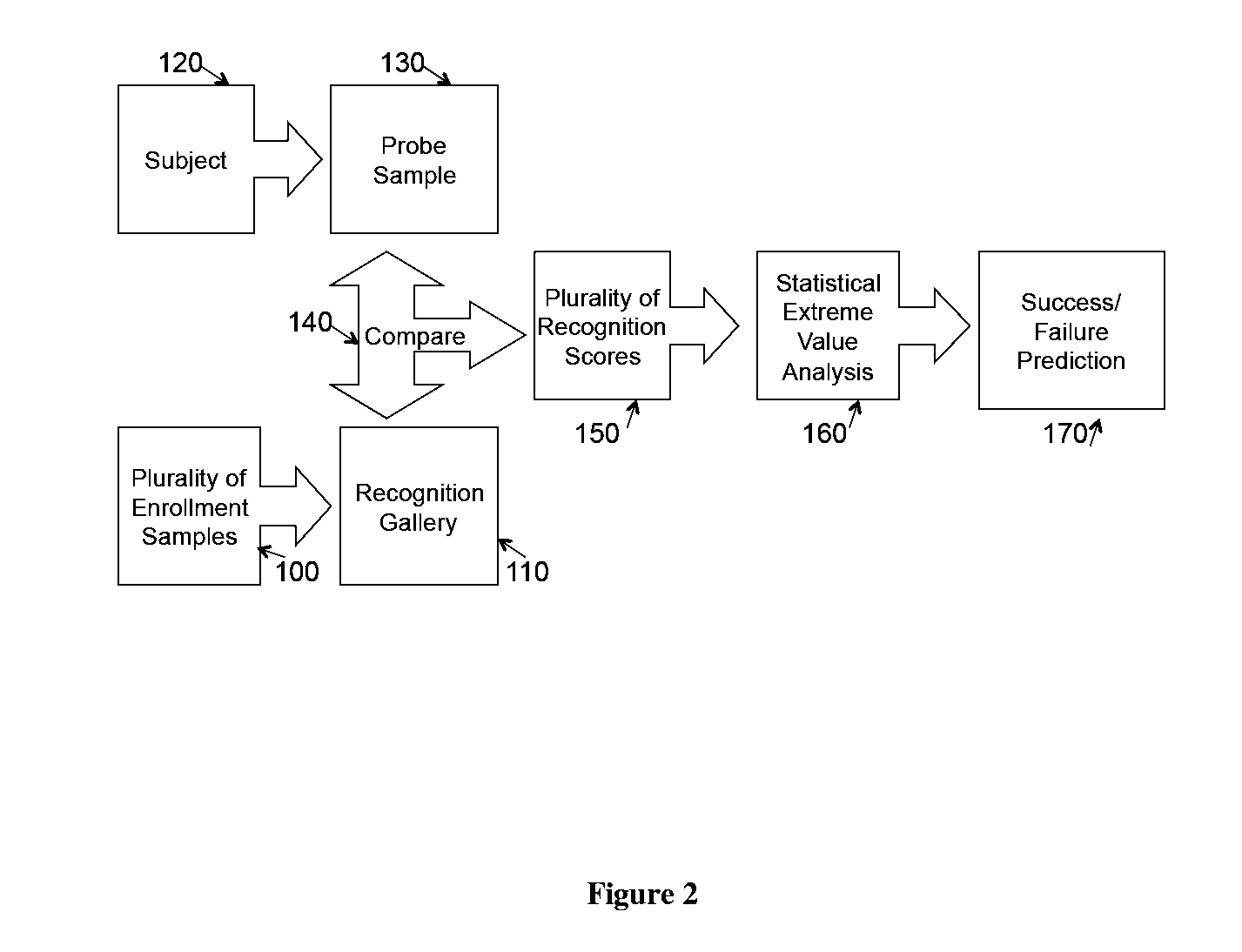
System and appartus for failure prediction and fusion in classification and recognition
InactiveUS20110106734A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsLearning methodsComputer science
The present invention relates to pattern recognition and classification, more particularly, to a system and method for meta-recognition which can to predict success / failure for a variety of different recognition and classification applications. In the present invention, we define a new approach based on statistical extreme value theory and show its theoretical basis for predicting success / failure based on recognition or similarity scores. By fitting the tails of similarity or distance scores to an extreme value distribution, we are able to build a predictor that significantly outperforms random chance. The proposed system is effective for a variety of different recognition applications, including, but not limited to, face recognition, fingerprint recognition, object categorization and recognition, and content-based image retrieval system. One embodiment includes adapting machine learning approach to address meta-recognition based fusion at multiple levels, and provide an empirical justification for the advantages of these fusion element. This invention provides a new score normalization that is suitable for multi-algorithm fusion for recognition and classification enhancement.
Owner:BOULT TERRANCE +2
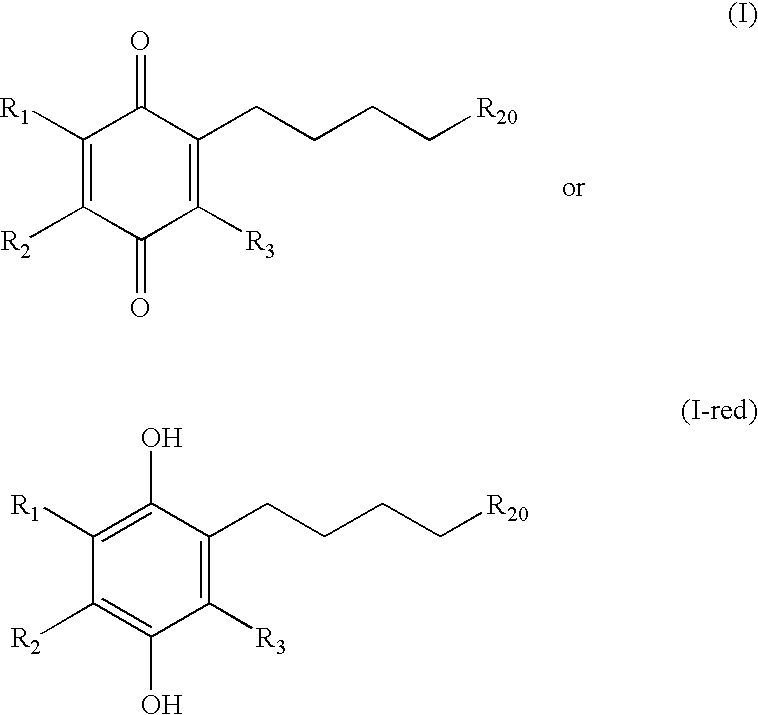
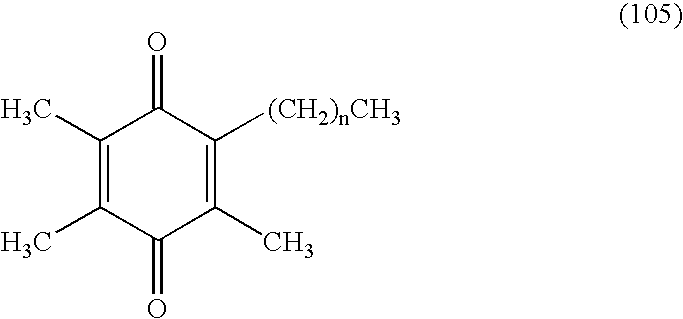
Tail variants of redox-active therapeutics for treatment of mitochondrial diseases and other conditions and modulation of energy biomarkers
ActiveUS20070072943A1Lower Level RequirementsExercise toleranceAntibacterial agentsBiocideKearn sayre syndromeFriedreichs ataxia
Methods of treating or suppressing mitochondrial diseases, such as Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA), Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON), mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactacidosis, stroke (MELAS), or Kearns-Sayre Syndrome (KSS) are disclosed, as well as compounds useful in the methods of the invention. Energy biomarkers useful in assessing the metabolic state of a subject and the efficacy of treatment are also disclosed.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
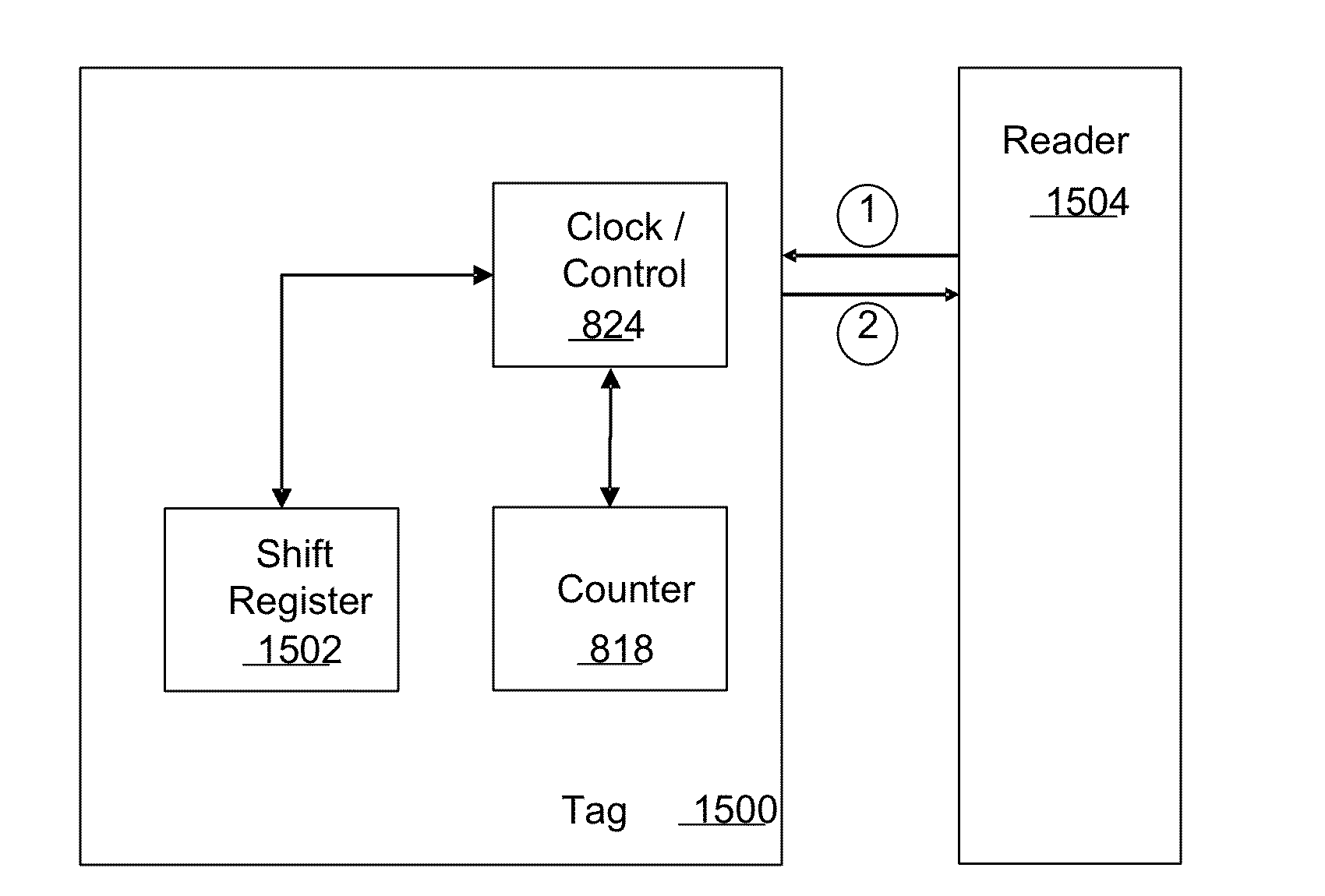
RADIO FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION (RFID) MOISTURE TAG(S) and SENSORS with EXTENDED SENSING via CAPILLARIES
ActiveUS20160267769A1Increase flexibilityNear-field transmissionRoof coveringAntenna impedanceImpedance matching
Embodiments of the present invention provide a passive radio frequency identification (RFID) moisture sensor. This moisture sensor includes one or more antenna structures having a tail. The tail is operable to transport a disturbance such as, but not limited to fluid or moisture from a monitored location wherein the antenna has an impedance and varies with proximity to the disturbance. An integrated circuit couples to the antenna structure. This IC includes a power harvesting module operable to energize the integrated circuit, an impedance-matching engine coupled to the antenna, a memory module, and a wireless communication module. The impedance-matching engine may vary a reactive component to reduce a mismatch between the antenna impedance and the IC and produce an impedance value (sensor code) representative of the reactive component impedance. The memory module stores the impedance value (sensor code) until the wireless communication module communicates with an RFID reader and sends the impedance value / sensor code to the RFID reader. The RFID reader may then determine an environmental condition such as the presence of moisture or fluids at the tail of the RFID sensor. This sensor may deploy several antenna and / or tails sensitive to unique disturbances. These tails may be used to monitor different locations as well as different types of fluids. In one particular embodiment, the disturbance is a fluid or moisture within the gutter of a vehicle body.
Owner:RFMICRON
Compositions and methods for treating neoplasia, inflammatory disease and other disorders
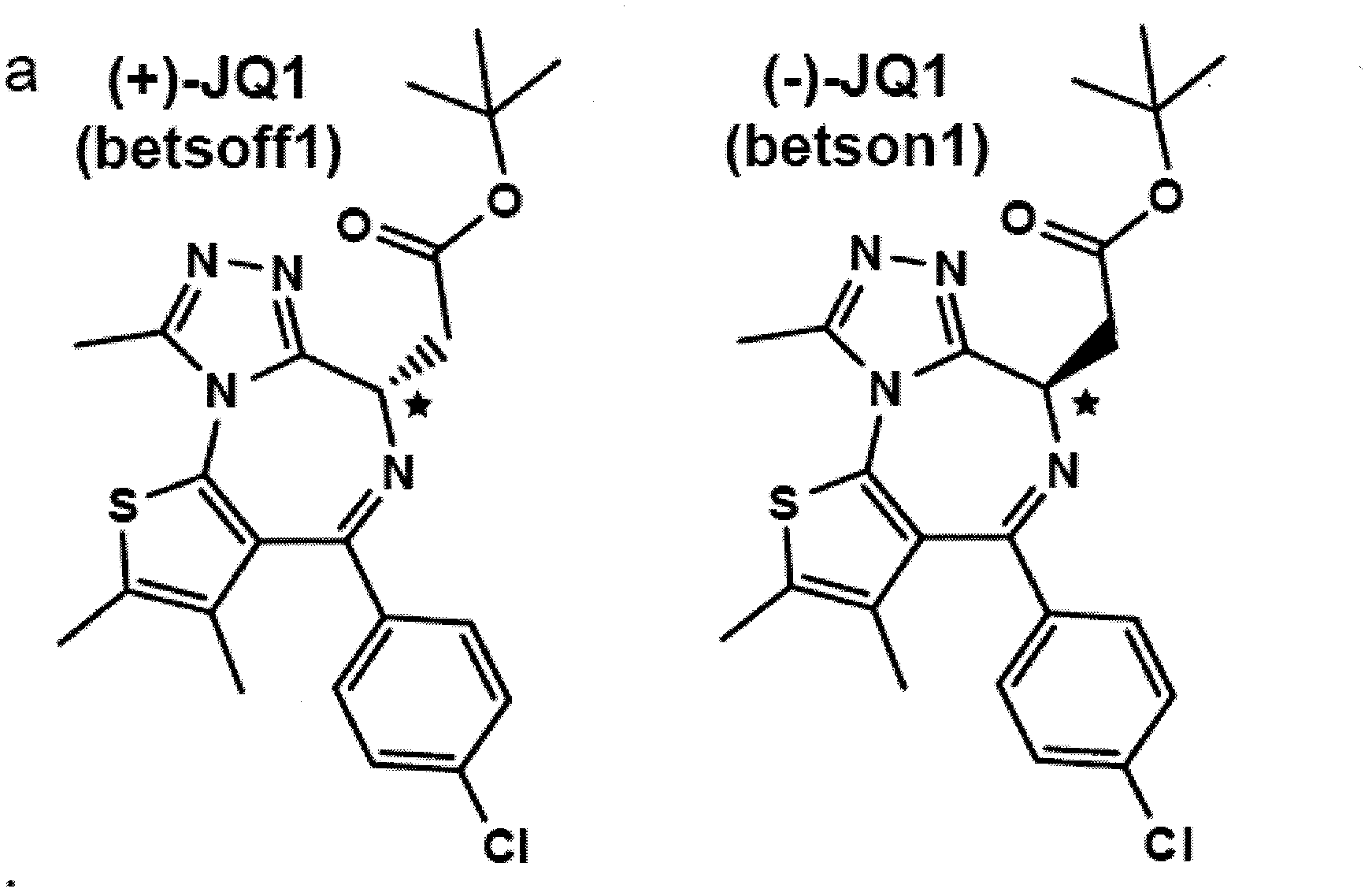
The invention features compositions and methods for treating or preventing a neoplasia. More specifically, the invention provides compositions and methods for disrupting the interaction of a BET family polypeptide comprising a bromodomain with chromatin (e.g., disrupting a bromodomain interaction with an acetyl-lysine modification present on a histone N-terminal tail).
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
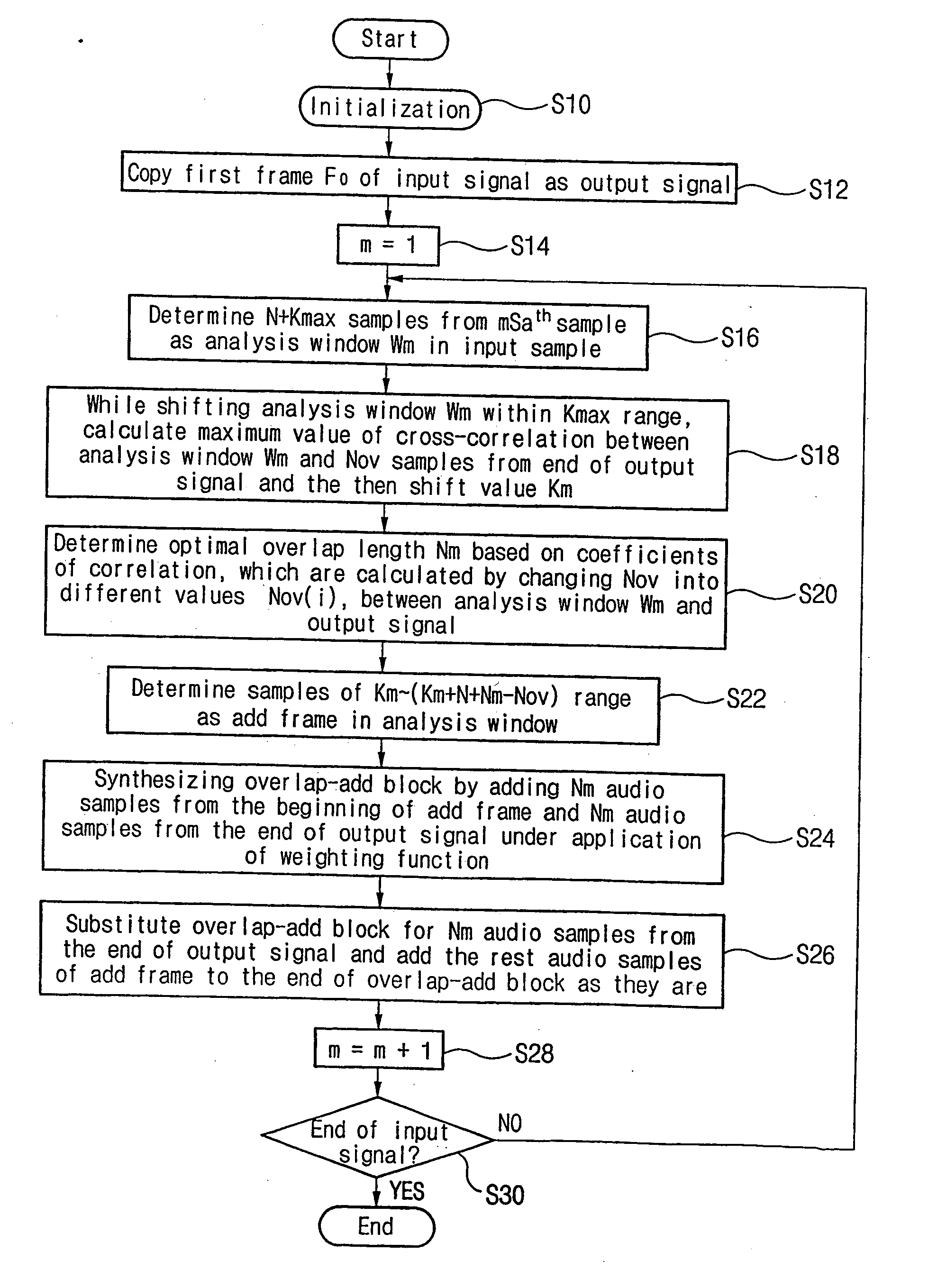
Audio signal time-scale modification method using variable length synthesis and reduced cross-correlation computations
InactiveUS20050273321A1Reduce the amount of calculationSpeech analysisCorrelation coefficientVariable length
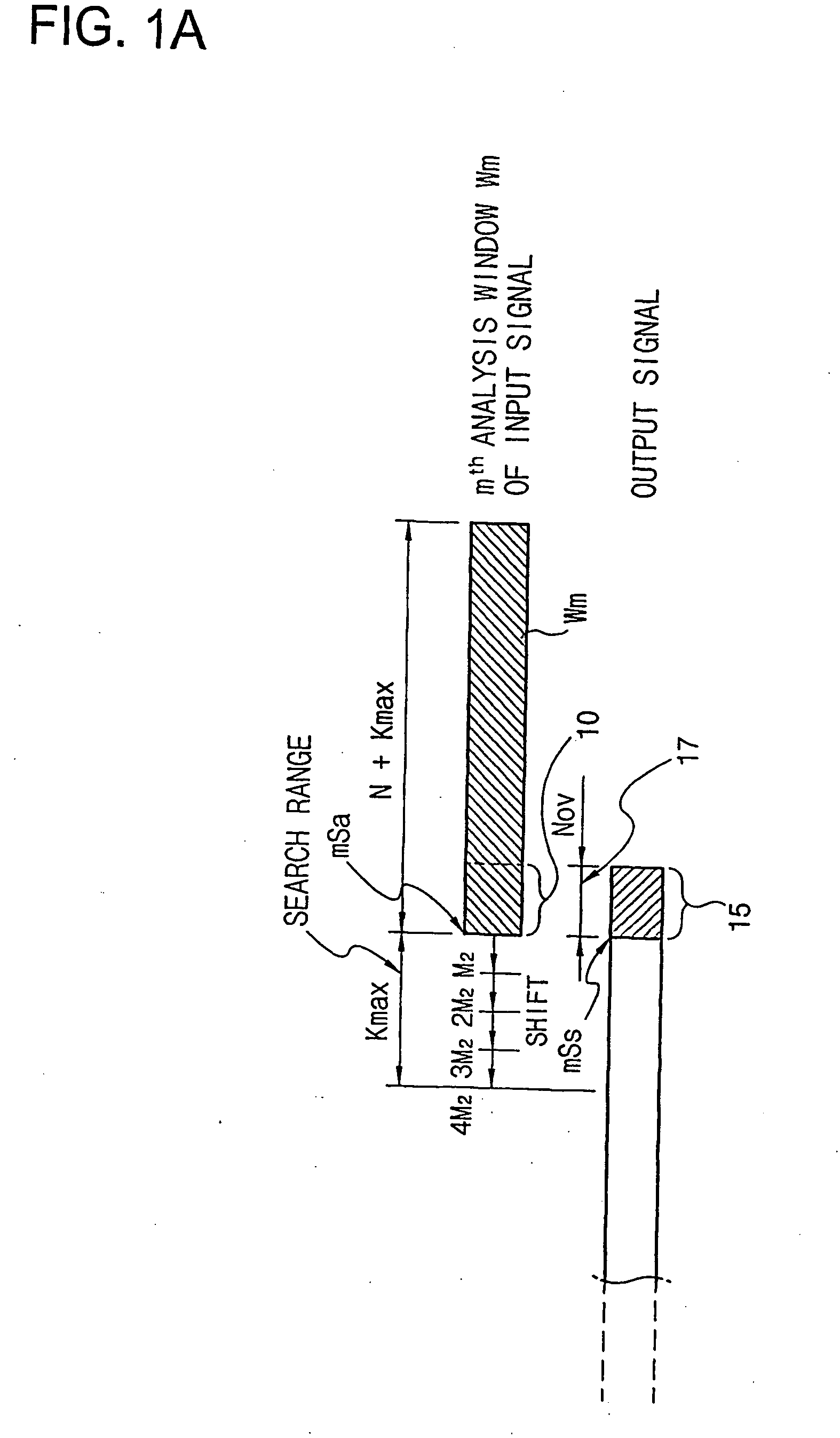
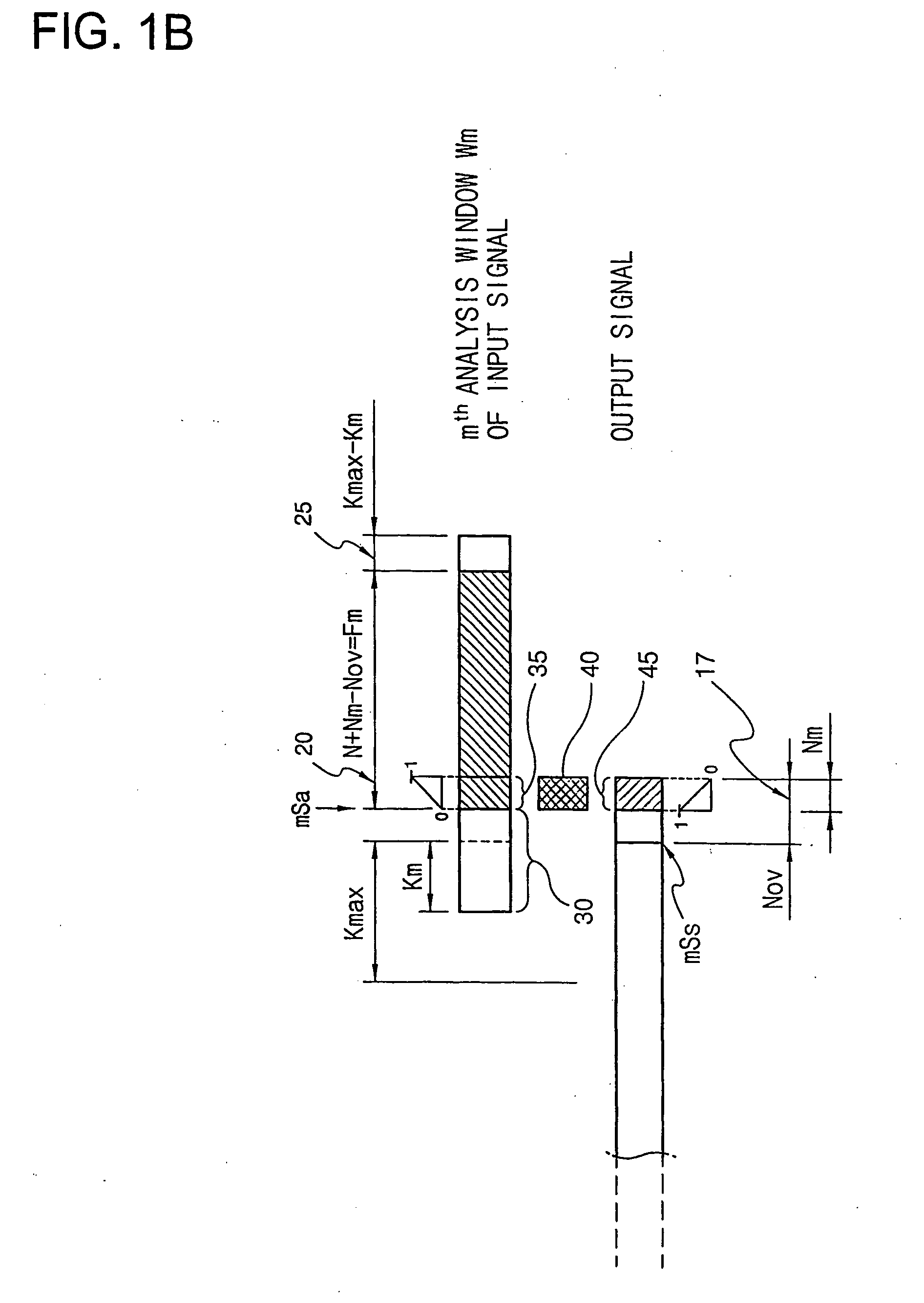
Disclosed is an audio signal time-scale modification which utilizes variable length synthesis for the improvement of output audio quality and reduced cross-correlation computations for the reduction of computation loads to a processor. An analysis window consisting of N+Kmax audio samples is selected from an input audio samples and is shifted by the predetermined interval along output audio samples to find optimal shift Km, which ensures best cross-correlation between Nov audio samples of the analysis window and last Nov audio samples of the output audio samples and a particular value of Nm at which a coefficient of correlation between them is larger than a reference value or is the maximum one among a plurality of coefficients of correlation calculated with varying the value of Nov. The audio samples involved in the calculation of cross-correlation are down-selected by the predetermined ratio from Nov audio samples of the analysis window and last Nov audio samples of the output audio samples, respectively. The analysis window may also be shifted by the plurality of audio samples per one shift. The audio samples ranged region (Km+Nov−Nm)th sample in the analysis window is determined as an add frame. The existing last Nm audio samples of the output audio samples are replaced with new Nm audio samples obtained by weighting and adding the overlapped parts, i.e., the first Nm audio samples of the add frame and the last Nm audio samples of the output audio samples, while remaining part of the add frame is simply appended to the tail of the new Nm audio samples in the output audio samples.
Owner:CHOI WON YONG
Slitting tool
A tool for slitting an elongate sheath from about an elongate member that is disposed within a longitudinally extending lumen of the sheath includes a longitudinally extending tail portion projecting rearward of a slitting edge and a nose portion of the tool; a lower surface of the nose portion is disposed beneath the slitting edge for engaging a portion of the elongate member. The tail portion of the tool, approximately aligned with the sheath lumen when the lower surface engages the elongate member and a leading edge of the nose portion is within the sheath lumen, is sized to fit within the sheath lumen after the sheath is slit by the slitting edge. A passageway between the nose portion and the tail portion allows a proximal segment of the elongate member to bend away from the tail portion when the elongate member is engaged by the nose portion.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Automobile compound waterproof tail light
InactiveUS20060028830A1Easy to useLow powerNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLight head
An automobile compound waterproof taillight includes a bottom base, a main light base, a side light base and a sealing cap. A main light set, a license plate light set, a side light set, and a car width indicating light set are all arranged in the bottom base and separated with caps from one another to clearly show which light is used. The interior of the bottom base is filled with waterproof glue to keep all components therein sealed to keep them from getting wet so as to prolong its service life.
Owner:LUCIDITY ENTERPRISE
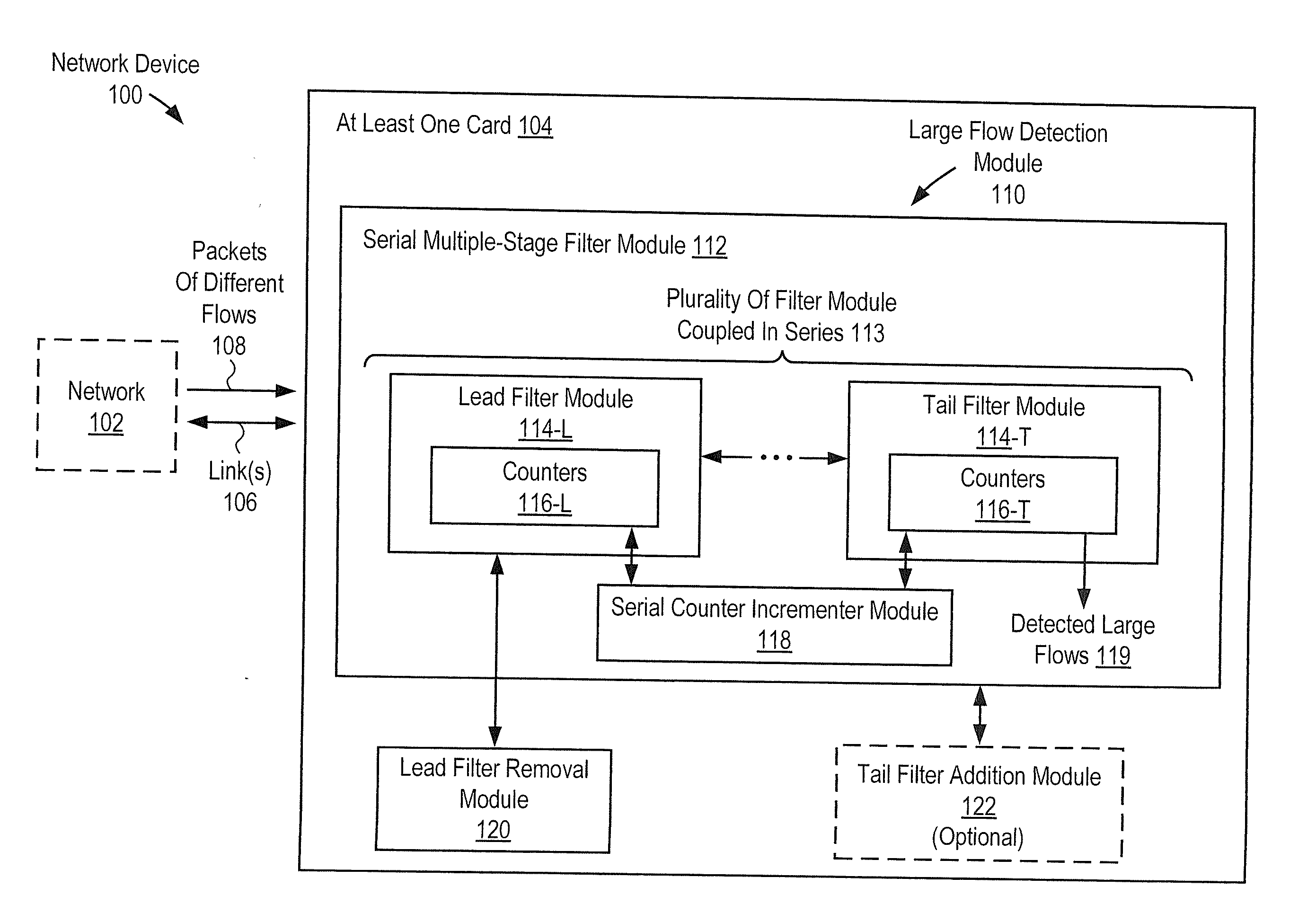
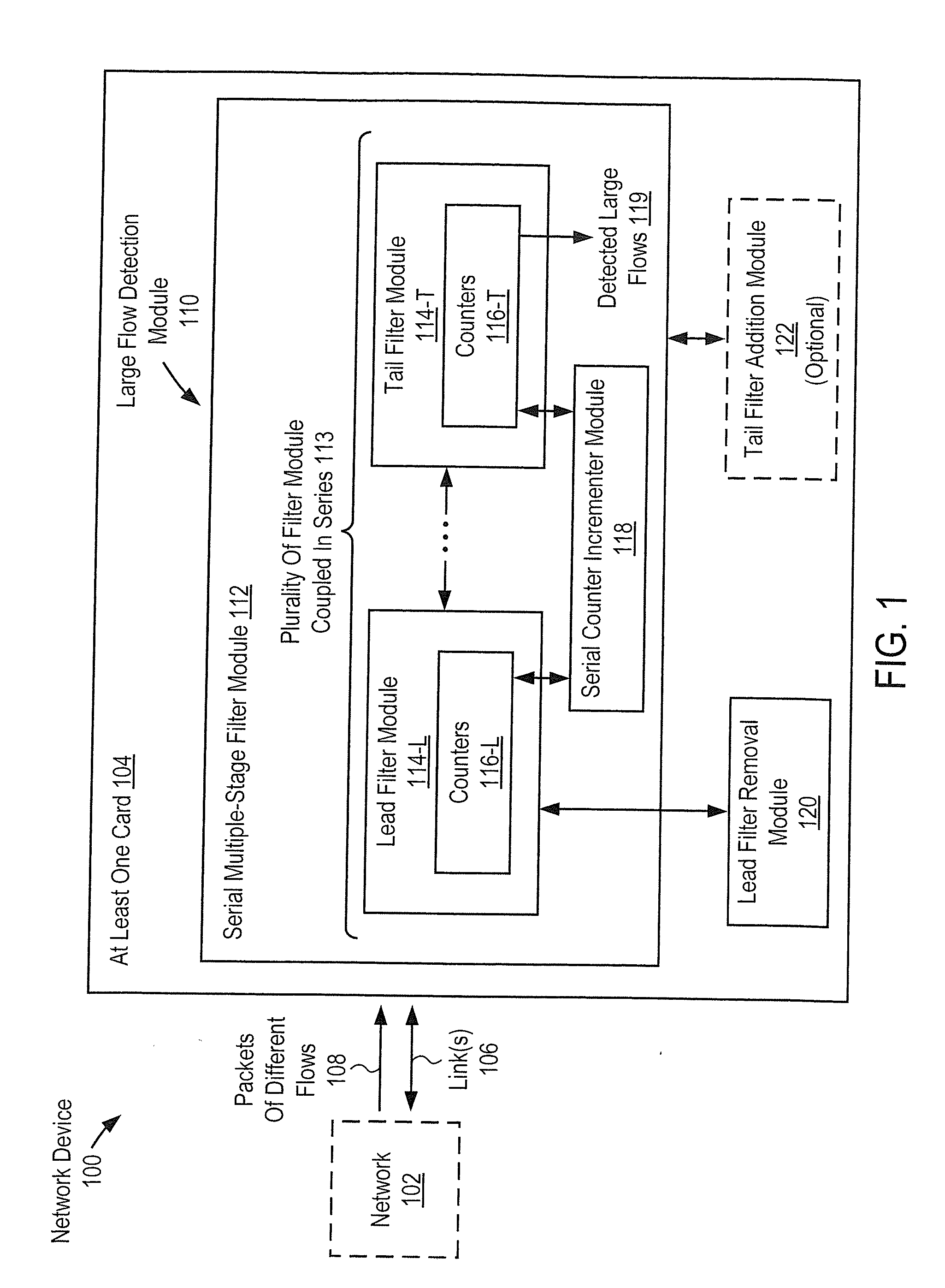
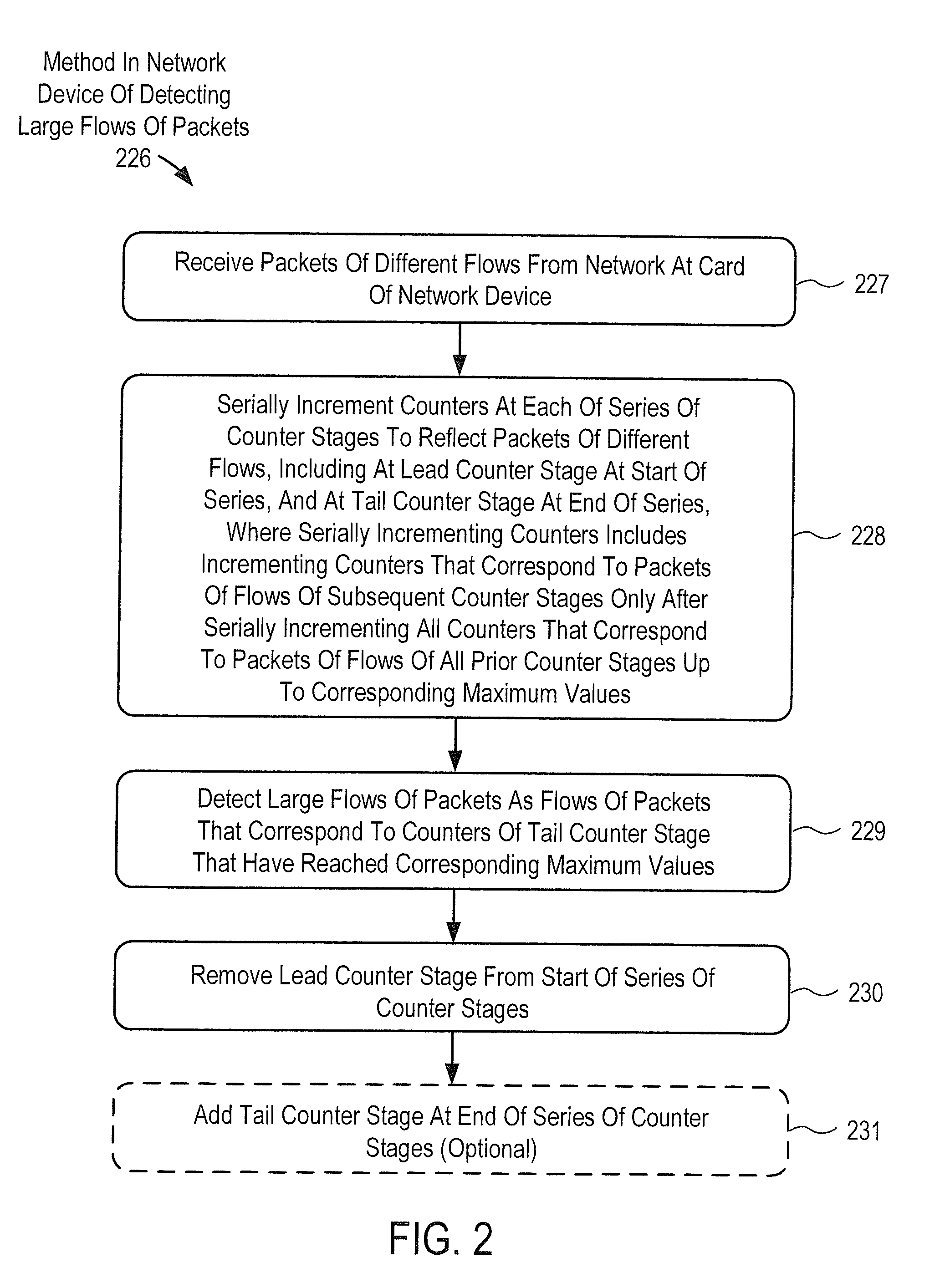
Removing lead filter from serial multiple-stage filter used to detect large flows in order to purge flows for prolonged operation
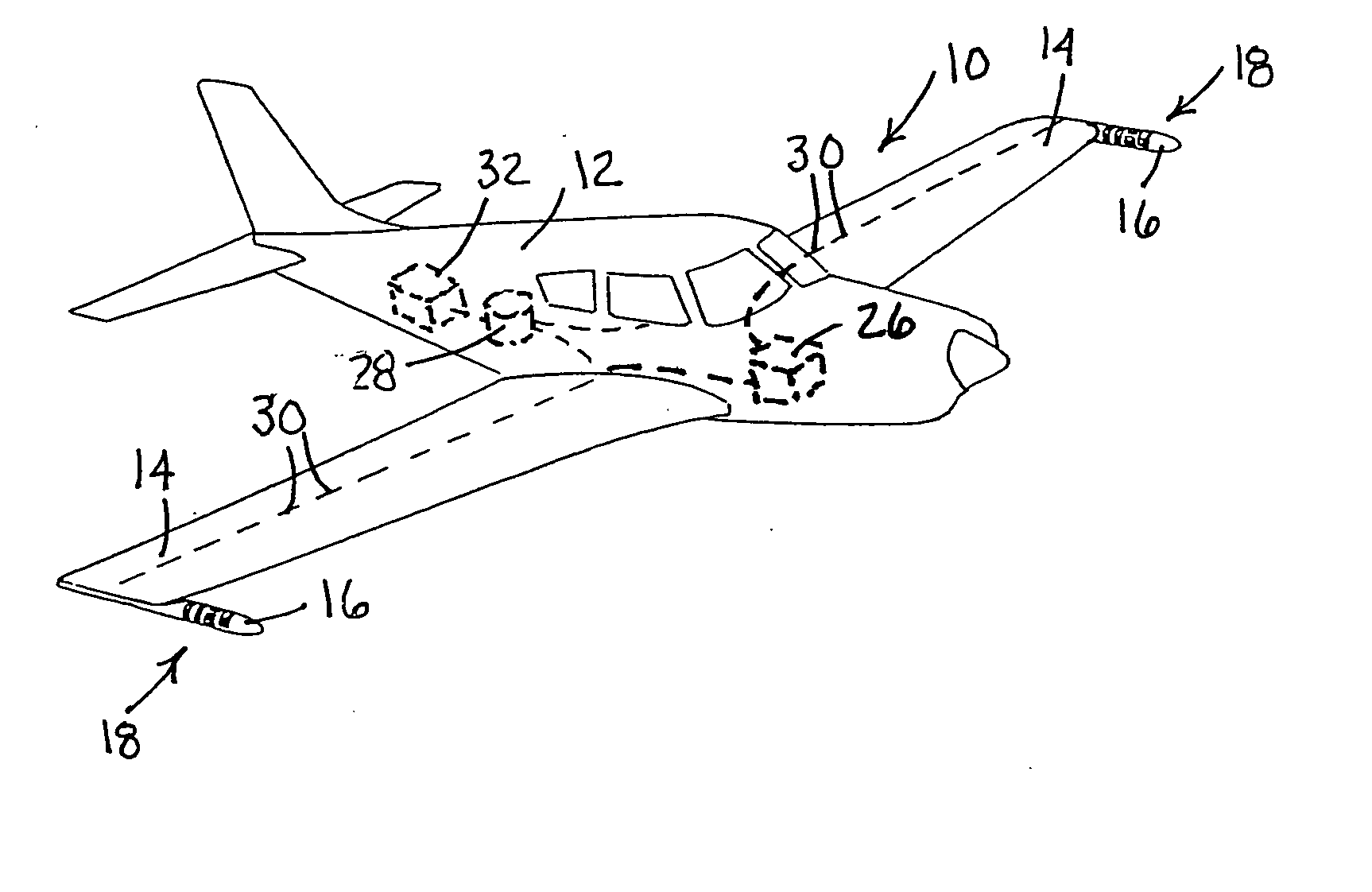
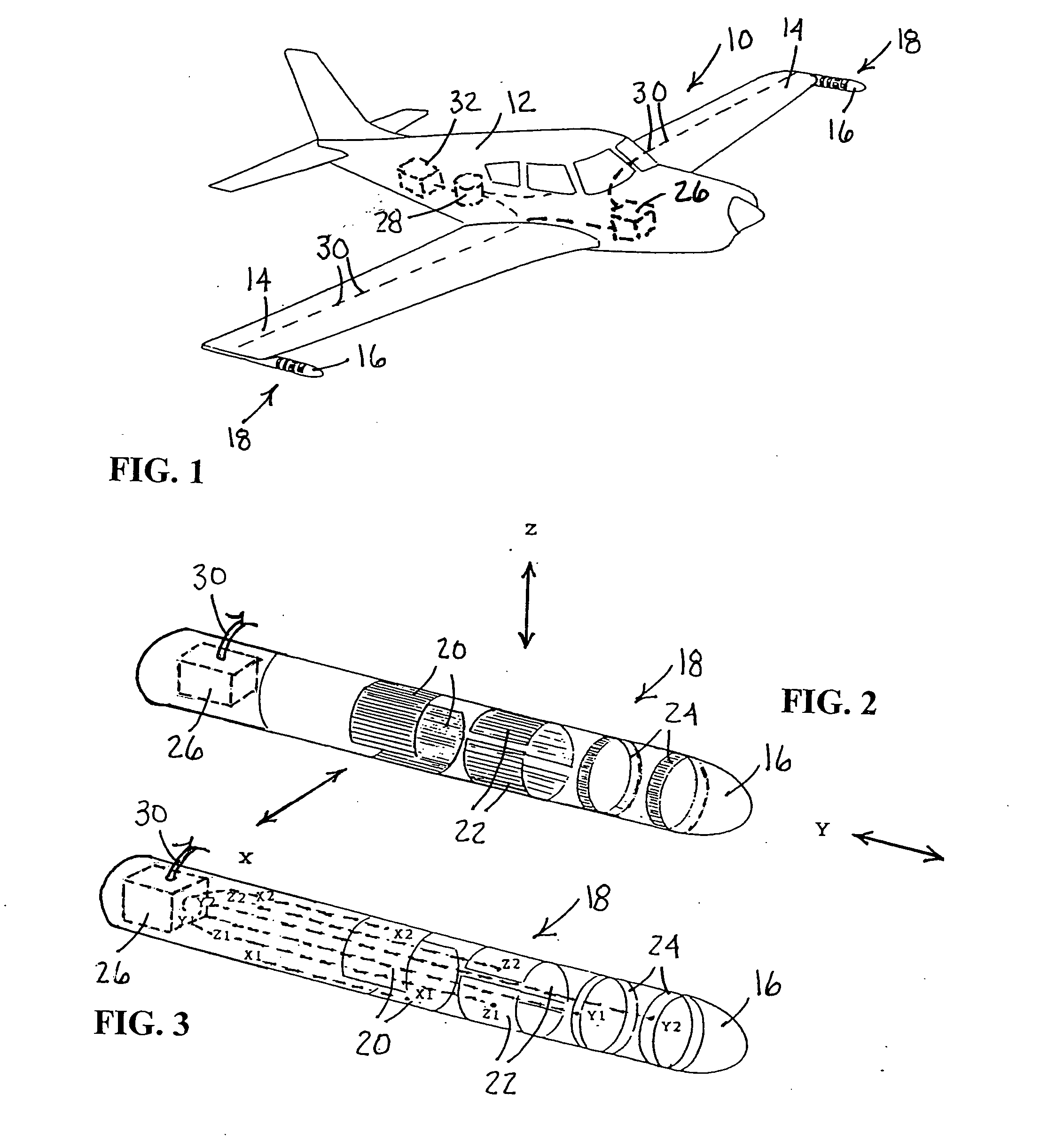
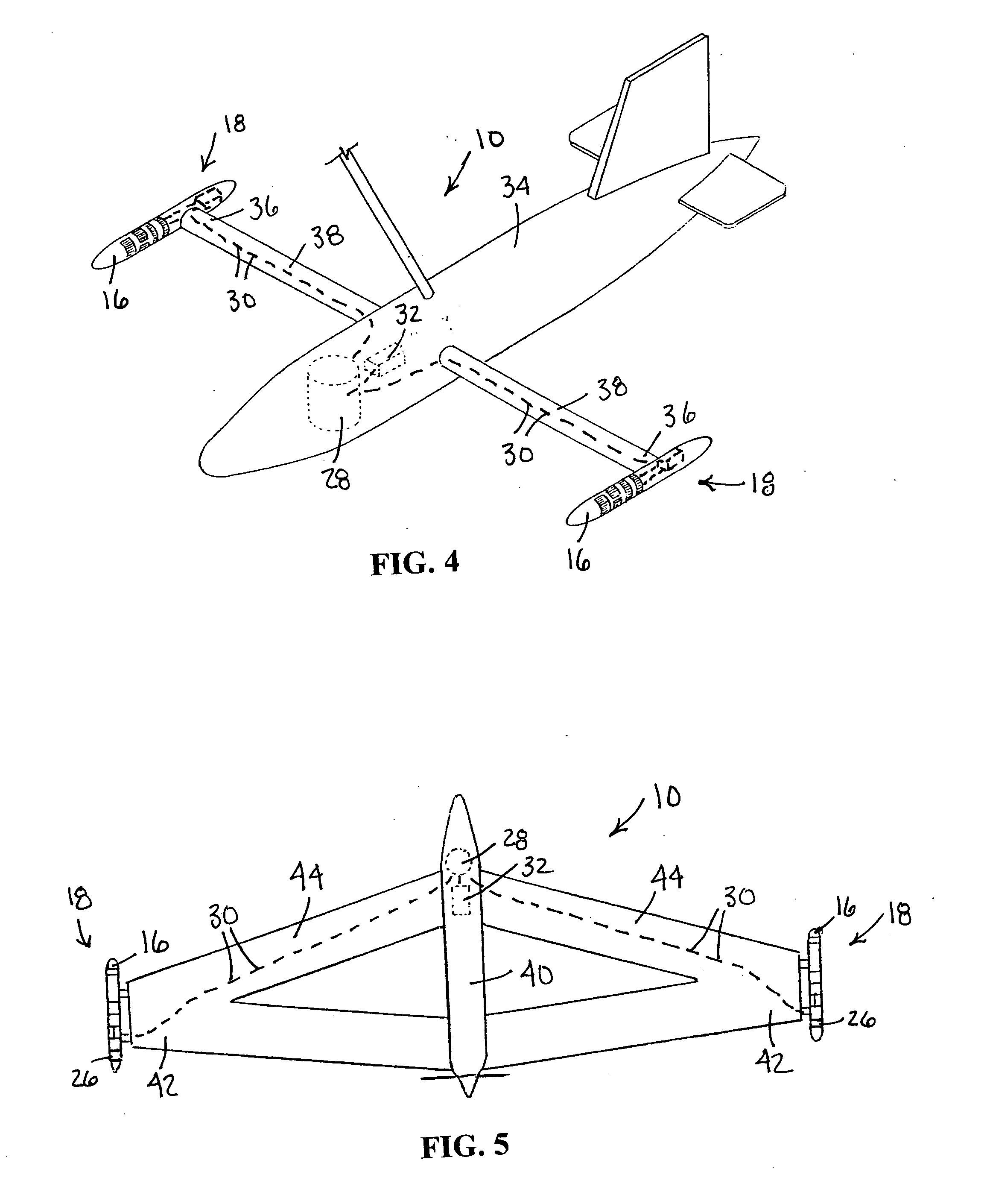
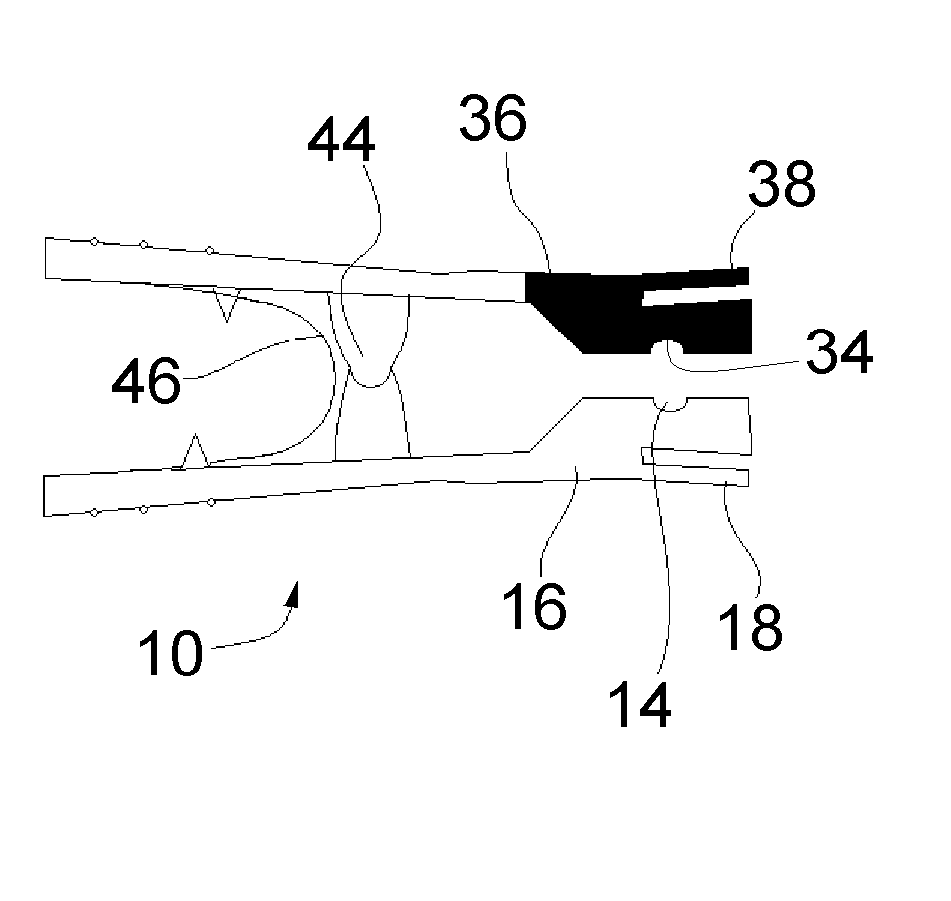
ActiveUS20150016255A1Avoid discontinuitiesHigh trafficError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEmbryo tailComputer science
A network device to detect large flows includes a card to receive packets of flows. The device includes a large flow detection module including a serial multiple-stage filter module including series filter modules including a lead filter module and a tail filter module. Each filter module includes counters. The serial filter module is to serially increment the counters to reflect the flows, and is to increment counters that correspond to flows of subsequent filter modules only after all counters that correspond to the flows of all prior filter modules have been incremented serially up to maximum values. The serial filter module is to detect flows that correspond to counters of the tail filter module that have been incremented up to maximum values as the large flows. The large flow detection module includes a lead filter removal module to remove the lead filter module from the start of the series.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for obtaining sheep with different hair colors on basis of CRISPR/Cas9 and sgRNA of targeted ASIP gene
ActiveCN105950626AStrong specificityPrecise targeted modificationHydrolasesMicroinjection basedAnimal scienceGenome editing
The invention discloses a method for obtaining sheep with different hair colors on the basis of CRISPR / Cas9 and sgRNA of a targeted ASIP gene. The invention provides sgRNA (ASIP-sgRNA) capable of achieving specific and targeted modification of a sheep ASIP gene, and the sgRNA (ASIP-sgRNA) is RNA as shown from the third nucleotide to the 22<nd> nucleotide of 5' tail end of a sequence 4 of a sequence list or RNA with the nucleotides from the third nucleotide to the 22<nd> nucleotide of the 5' tail end of the sequence 4 of the sequence list. The ASIP-sgRNA particularly can be the RNA as shown in the sequence 4 of the sequence list. The invention further provides a method for obtaining sheep with changed hair colors. The method comprises the following steps that co-transfection of sgRNA capable of achieving specific and targeted modification of the sheep ASIP gene and Cas9mRNA on sheep cells is conducted, and therefore the sheep ASIP gene is deleted, and the sheep with the changed hair colors are obtained. According to the method for obtaining the sheep with different hair colors on the basis of CRISPR / Cas9 and sgRNA of the targeted ASIP gene, a CRISPR / Cas9 genome-editing technology is combined with a microinjection technology, and an effective technological means is provided for artificially changing the hair colors of the sheep.
Owner:新疆畜牧科学院生物技术研究所
EphA2, hypoproliferative cell disorders and epithelial and endothelial reconstitution
InactiveUS20050049176A1Convenient treatmentReduces and avoids unwanted effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticCell layerInflammatory Bowel Diseases
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management, or prevention of a hypoproliferative cell disorder, especially those disorders relating to the destruction, shedding, or inadequate proliferation of epithelial and / or endothelial cells, particularly interstitial cystitis (IC) and lesions associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of one or more agents that are antagonists of EphA2. In certain embodiments, the EphA2 antagonistic agent of the invention decreases EphA2-endogenous ligand binding, upregulates EphA2 gene expression and / or translation, increases EphA2 protein stability or protein accumulation, decreases EphA2 cytoplasmic tail phosphorylation, promotes EphA2 kinase activity (other than autophosphorylation or ligand-mediated EphA2 signaling), increases proliferation of EphA2 expressing cells, increases survival of EphA2 expressing cells, and / or maintains / reconstitutes epithelial and / or endothelial cell layer integrity. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more EphA2 antagonistic agents of the invention either alone or in combination with one or more other agents useful for therapy for a hypoproliferative cell disorder. Diagnostic methods and methods for screening for therapeutically useful agents are also provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
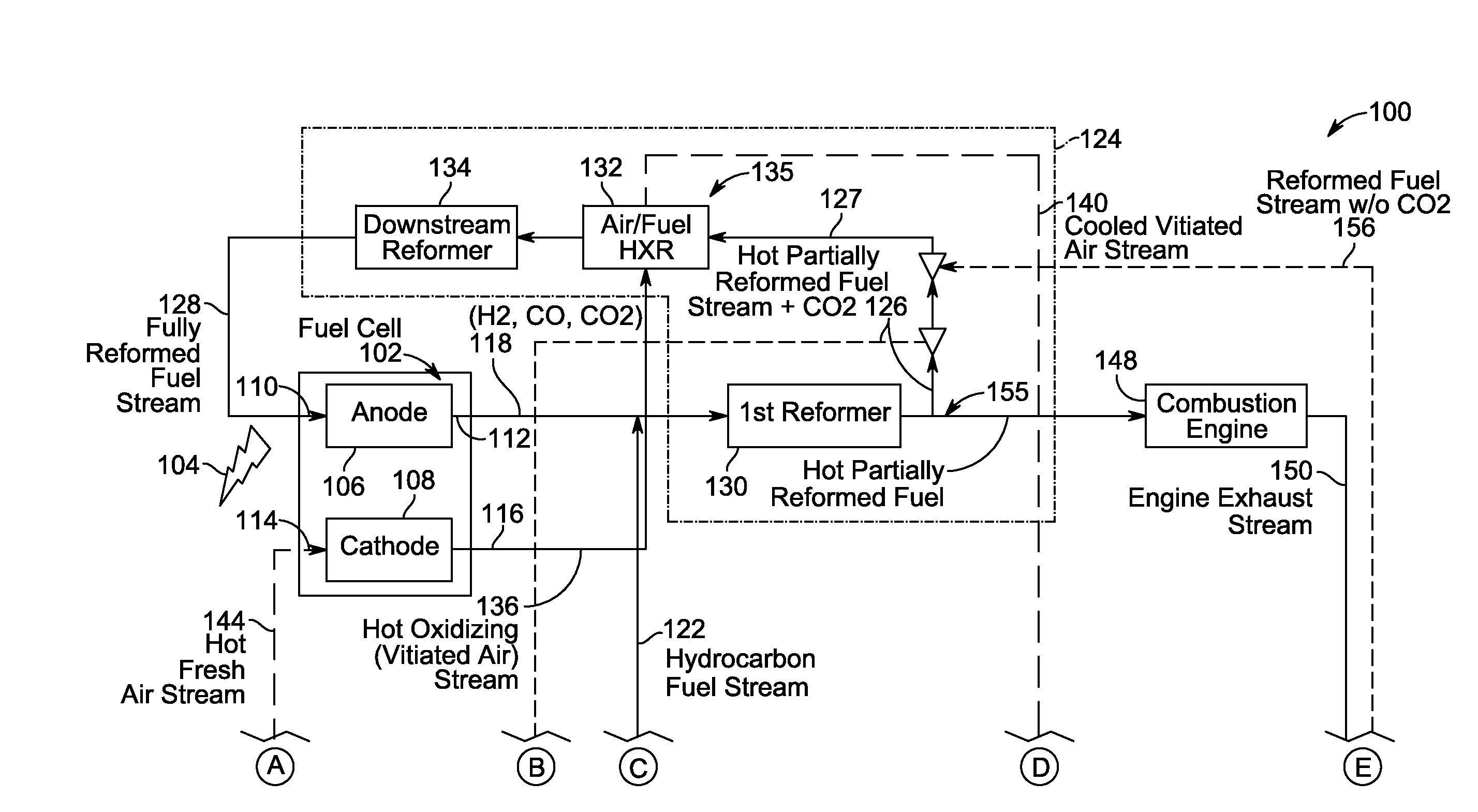
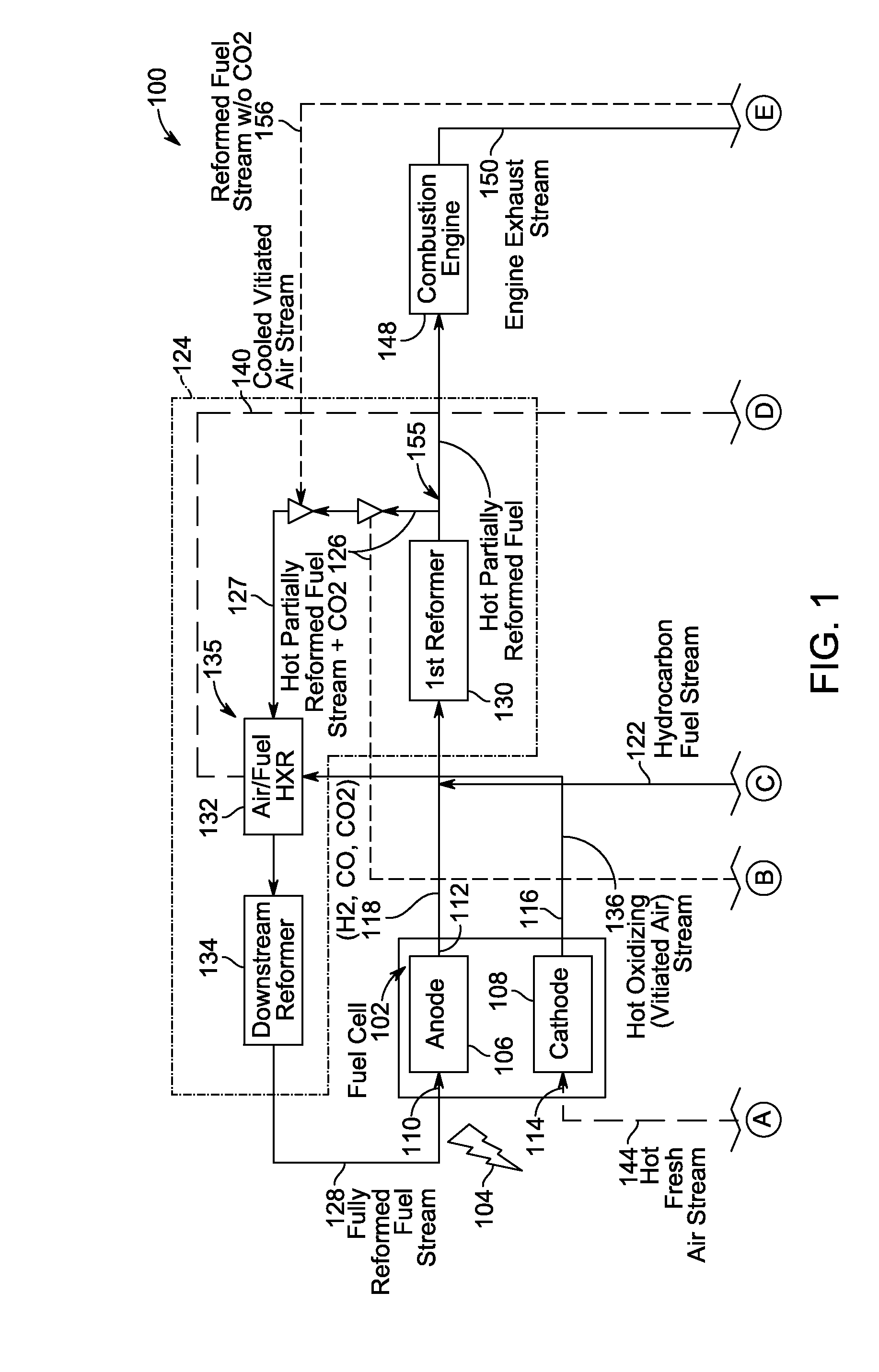
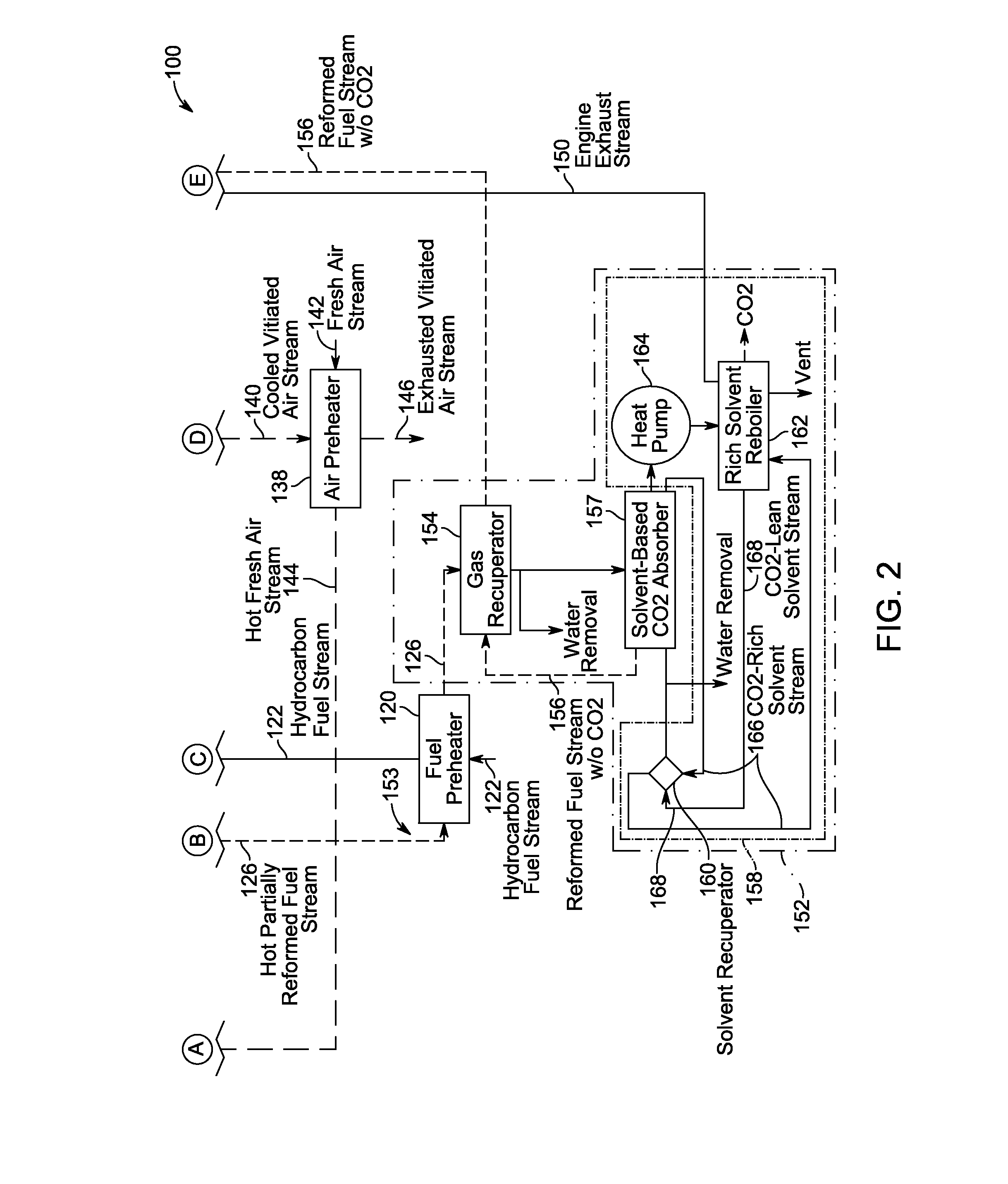
Fuel cell reforming system with carbon dioxide removal
A power generation system includes a fuel cell including an anode that generates a tail gas. The system also includes a hydrocarbon fuel reforming system that mixes a hydrocarbon fuel with the fuel cell tail gas and to convert the hydrocarbon fuel and fuel tail gas into a reformed fuel stream including CO2. The reforming system further splits the reformed fuel stream into a first portion and a second portion. The system further includes a CO2 removal system coupled in flow communication with the reforming system. The system also includes a first reformed fuel path coupled to the reforming system. The first path channels the first portion of the reformed fuel stream to an anode inlet. The system further includes a second reformed fuel path coupled to the reforming system. The second path channels the second portion of the reformed fuel stream to the CO2 removal system.
Owner:CUMMINS ENTERPRISE LLC
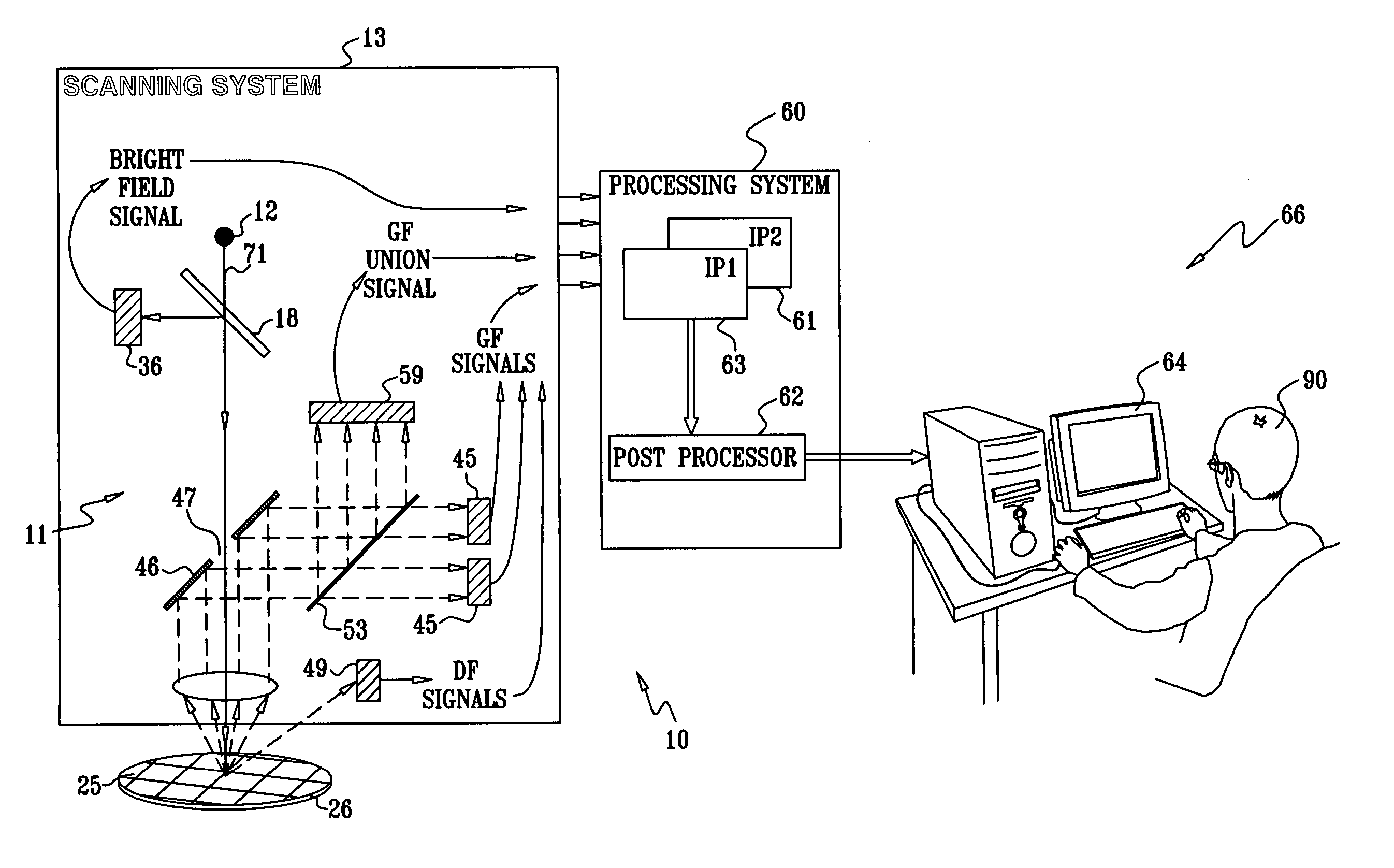
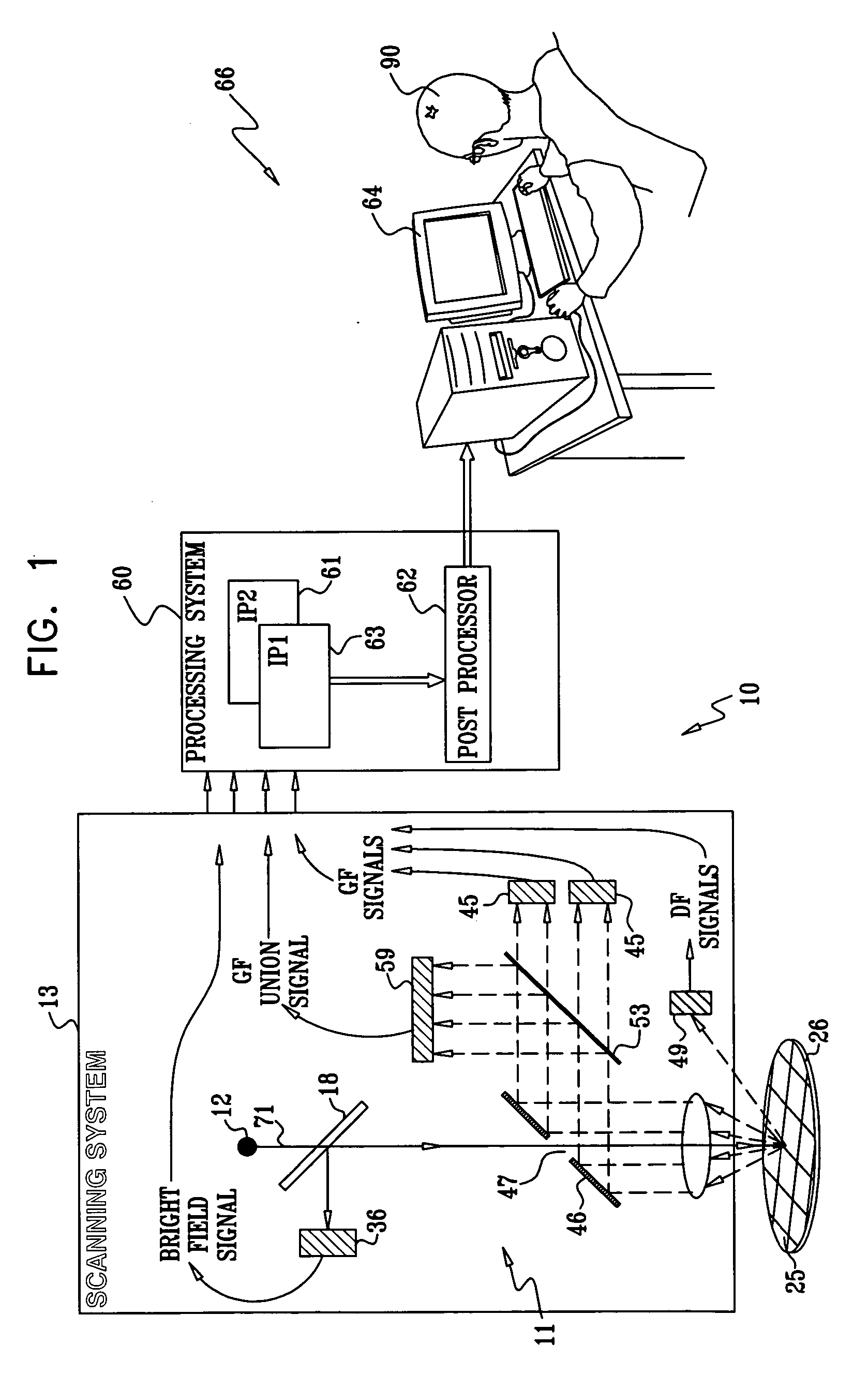
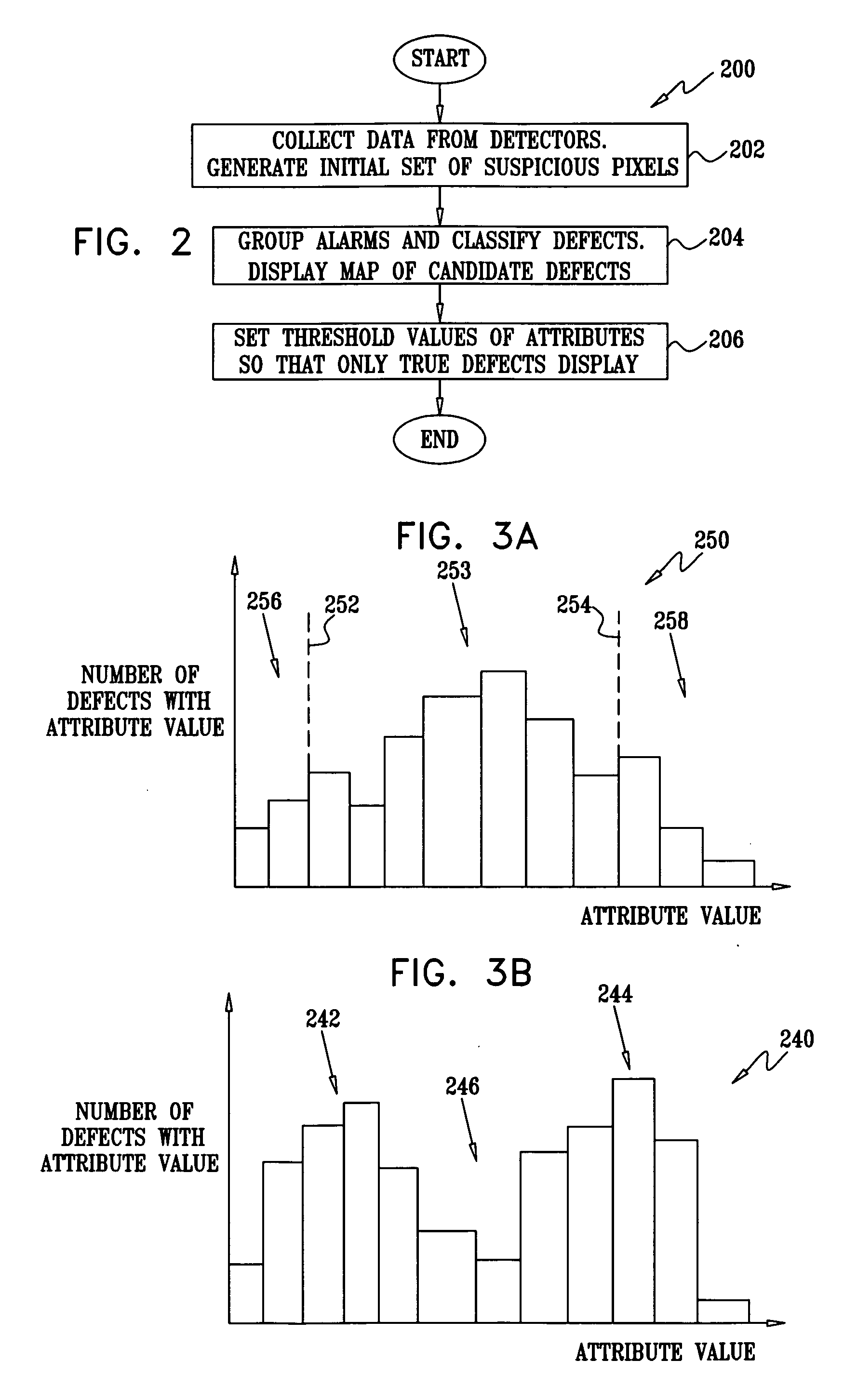
Method for filtering nuisance defects
A method for inspecting a sample, consisting of receiving a definition of image attributes that are characteristic of defects, and processing an image of the sample so as to identify candidate defects on the sample. The method further includes forming distributions of values of the respective attributes from the candidate defects, and selecting a set of the candidate defects that are characterized by respective candidate attribute values that fall in one or more tails of the distributions. The selected set is presented to a human operator, and respective classifications of the candidate defects in the selected set are received from the operator. A definition of the one or more tails of the distributions is refined responsively to the classifications. The method may be used as a filter to remove false alarms, or nuisances. The method may also be used to categorize the candidate defects into two or more classes.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Primer middle sequence interference PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology
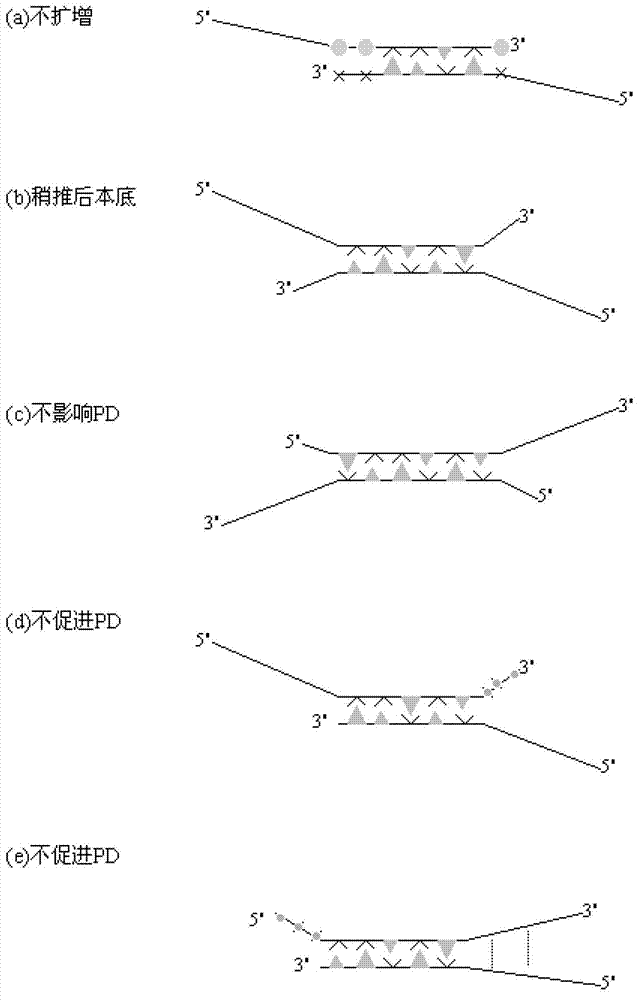
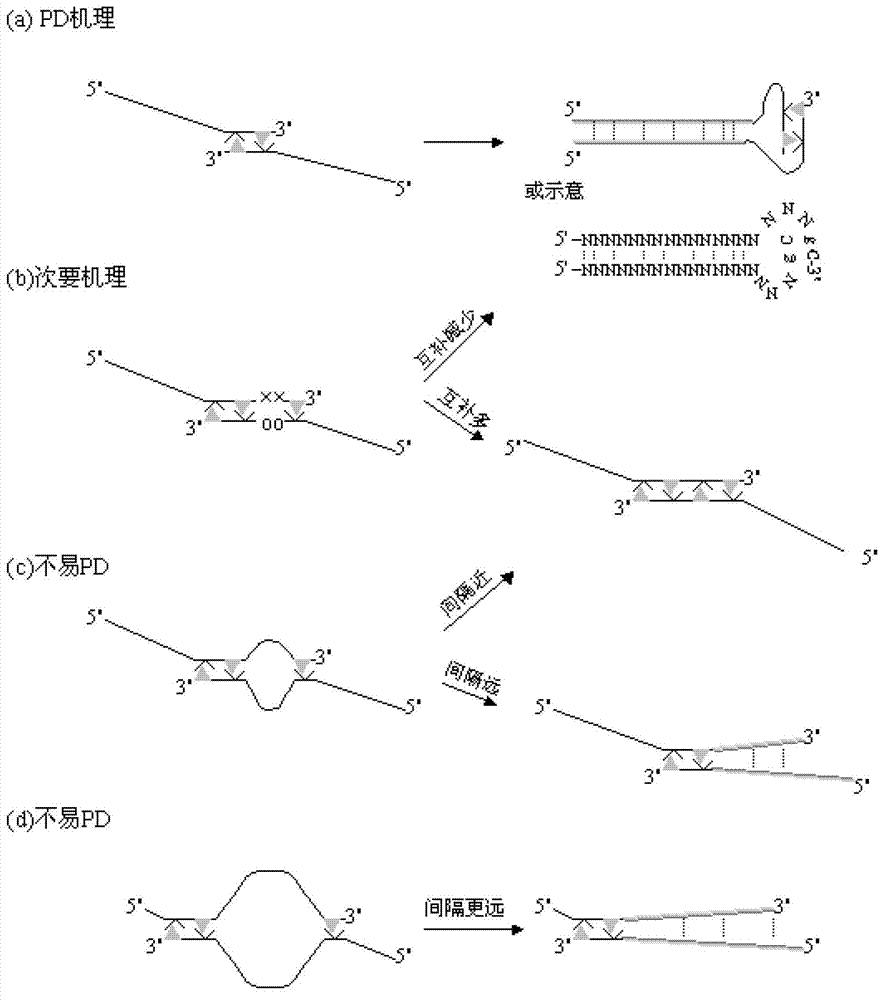
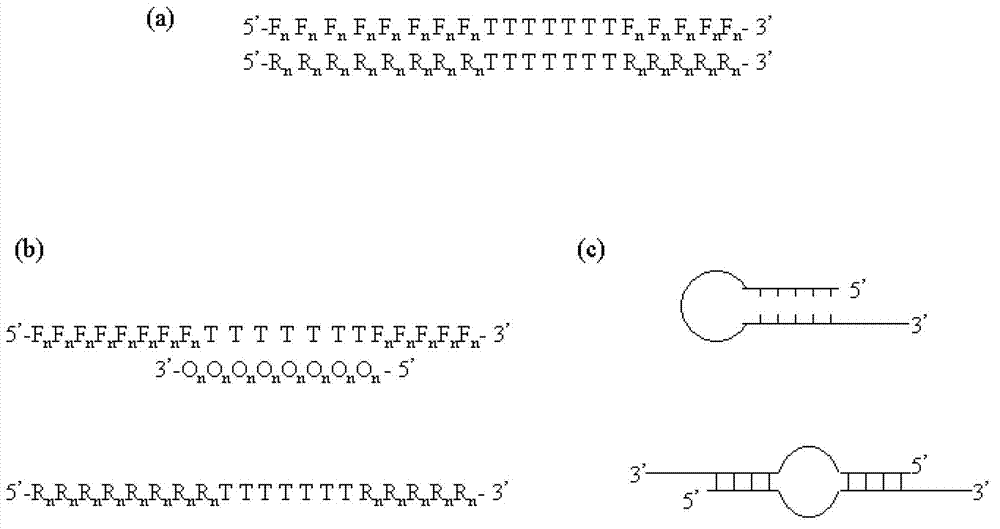
InactiveCN103114131AHigh Sensitivity FeaturesQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceFluorescence
The invention relates to a primer middle sequence interference PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology. The improved PCR technology is characterized in that one segment of relatively non-complemented or same-sequence basic group primer molecules in the intermediate domain of primers perform the antisense interference inside and outside so as to competitively destroy the polymerization among the primers to selectively inhibit the primer dimer (PD) from being amplified. For the interference of the intermediate domain of the primers, based on the primers optimally selected by the conventional design principle, the technology that the intermediate domain (ID) of a pair of the primers are in parallel but are not complemented with each other or are in the same sequence or / and the technology that ID antisense oligonucleotides (Oligo) are added into the primers to perform the interference action or / and the Oligo antonymy is carried out in the primer molecules via the ID so as to perform the interference action are adopted, or the combined technology of the three types of the technologies is adopted. As a result, only the ID of the primers is interfered while the target specific amplification is not influenced; the combining force acting on the minority of base-group pairing hydrogen bonds at the tail end and the base-group hydrogen bonds outside the tail end due to the action of the primers is dispersed to a maximum extent, so that the PD is selectively inhibited. Therefore, the PD accumulation in the PCR system is avoided. If the mineral oil is additionally used, the sealed primers can slowly release the hot starting and the UDG pretreatment so as to prevent aerosol glue as a byproduct of the PCR system from causing the pollution. Consequently, the nucleic acid is amplified reliably and the real-time fluorescence PCR is quantified accurately.
Owner:珠海市坤元科技有限公司
Cas9 nuclease G915F and application thereof
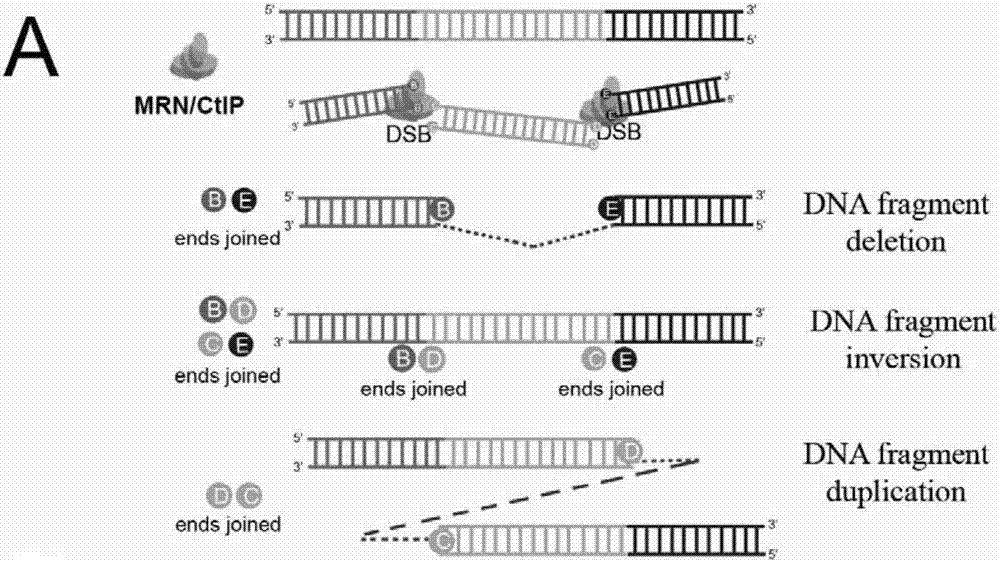
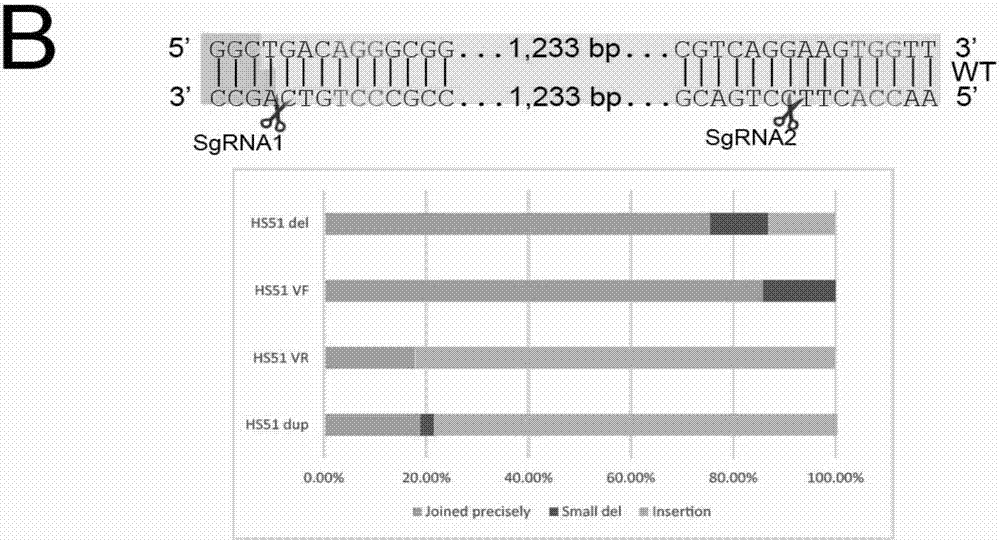
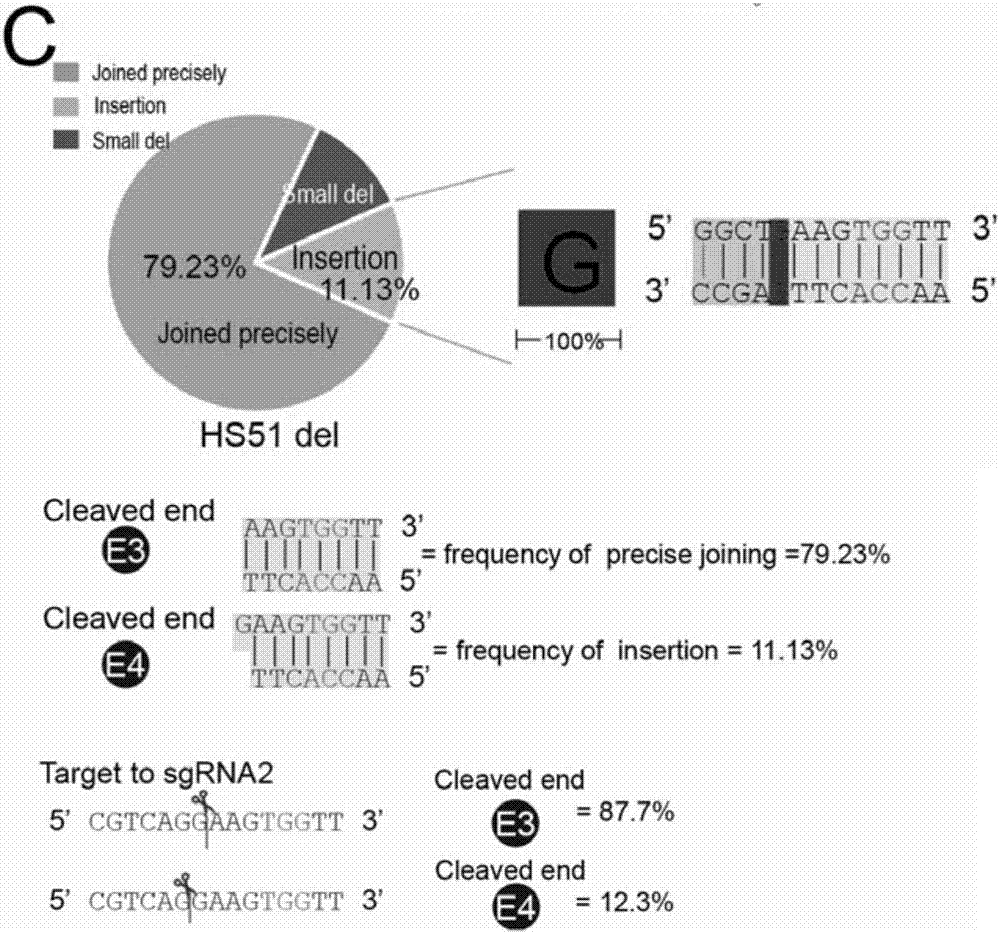
The invention belongs to the technical field of biologics, and particularly relates to a Cas9 nuclease G915F and application thereof. The Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-G915F) has activity of Cas9 nuclease and is applicable to a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system, and the Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-G915F) is prepared by mutating glycine at a 915th site of wild Cas9 nuclease into phenylalanine. When the Cas9 nuclease (Cas9-G915F) is adopted to cut double chains of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), protruding fractured tail ends can be generated, an alkali group complemented with the protruding fractured tail ends can be added in a filling connection mode, and precise edition on specific positions of genome DNA fragments can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Double-barreled bullpup pump-action shotgun
ActiveUS9115954B1Great contributionFiring/trigger mechanismsMissile propulsionEngineeringShotgun pellet
A double-barreled bullpup pump-action shotgun has a frame with two forward-extending barrels arranged side-by-side, a pair of tube magazines, each positioned beneath a respective barrel, an action attached to the frame and operable to load ammunition from the tube magazines to the barrels, and a trigger assembly attached to the frame, the action being located at least in part behind the trigger assembly, and the trigger assembly including a trigger linkage to connect the trigger assembly to the action and to operate the hammers behind the bolts. The action may be a pump action. The trigger assembly may include a plurality of hammer trips, each having a sloped forward surface. The trigger assembly may include a plurality of sears having tails, and the sloped surfaces of the hammer trips may lift the tails of the sears during a portion of a complete cycle of the action.
Owner:CONNECTICUT SHOTGUN MFG
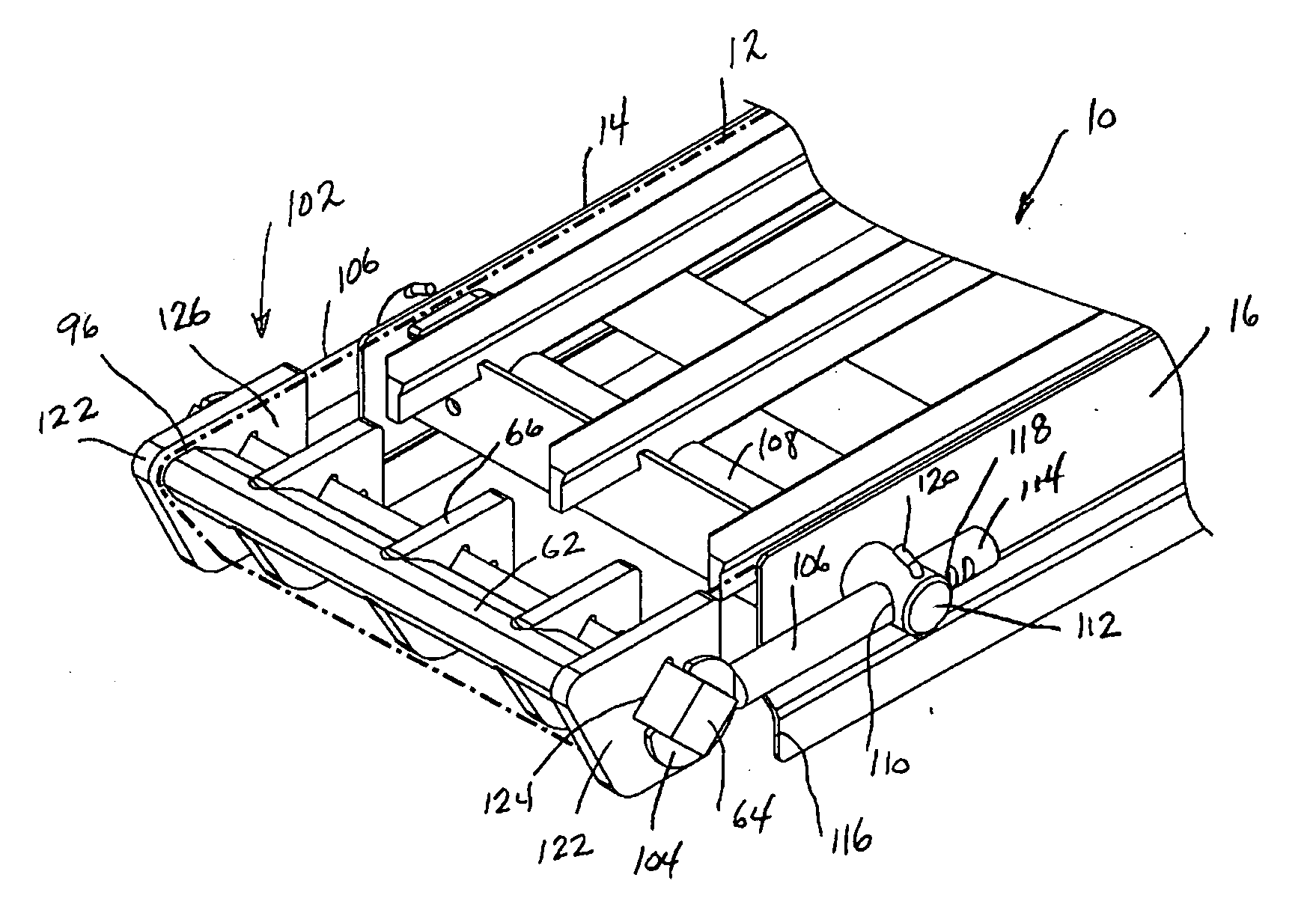
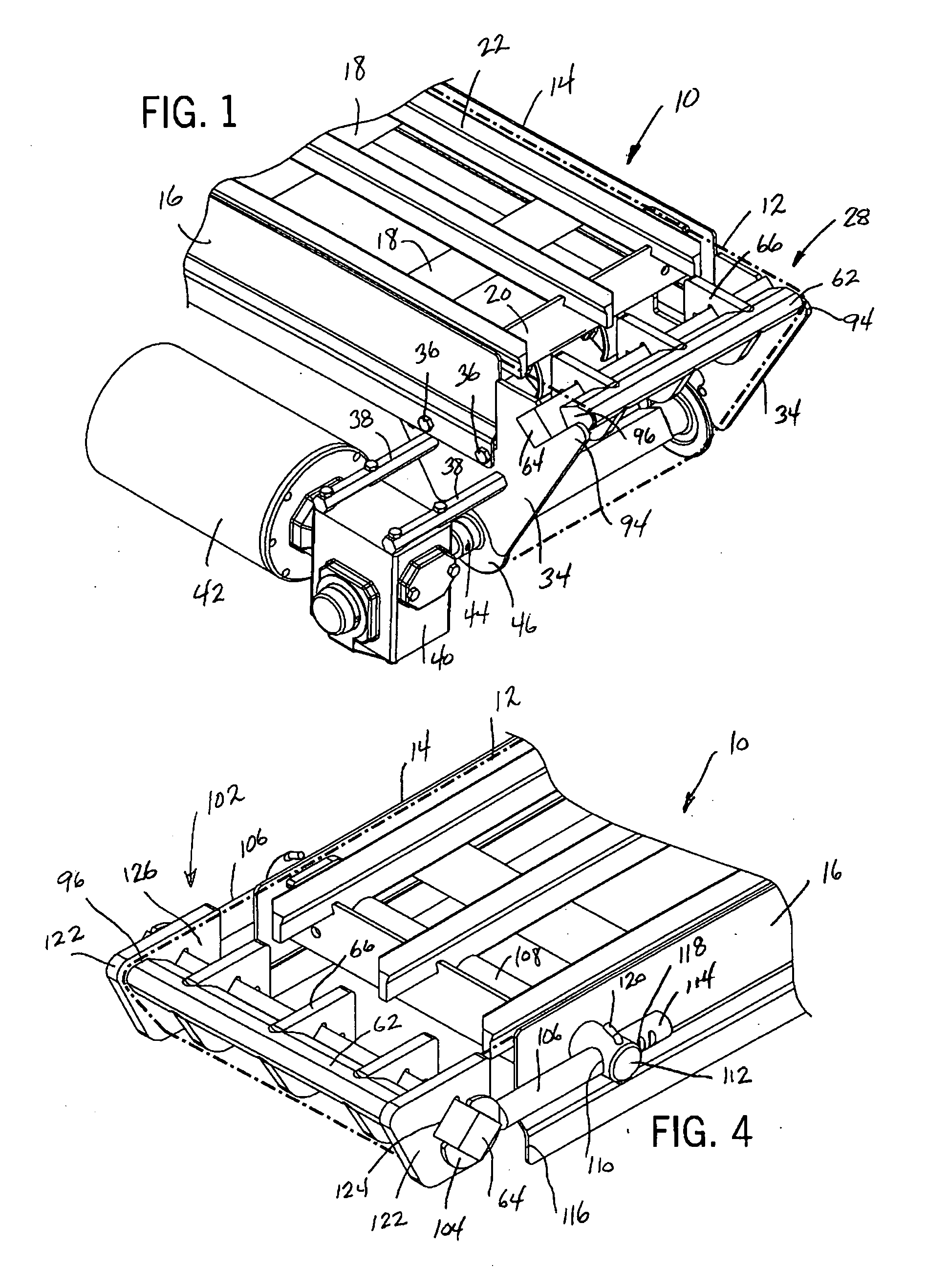
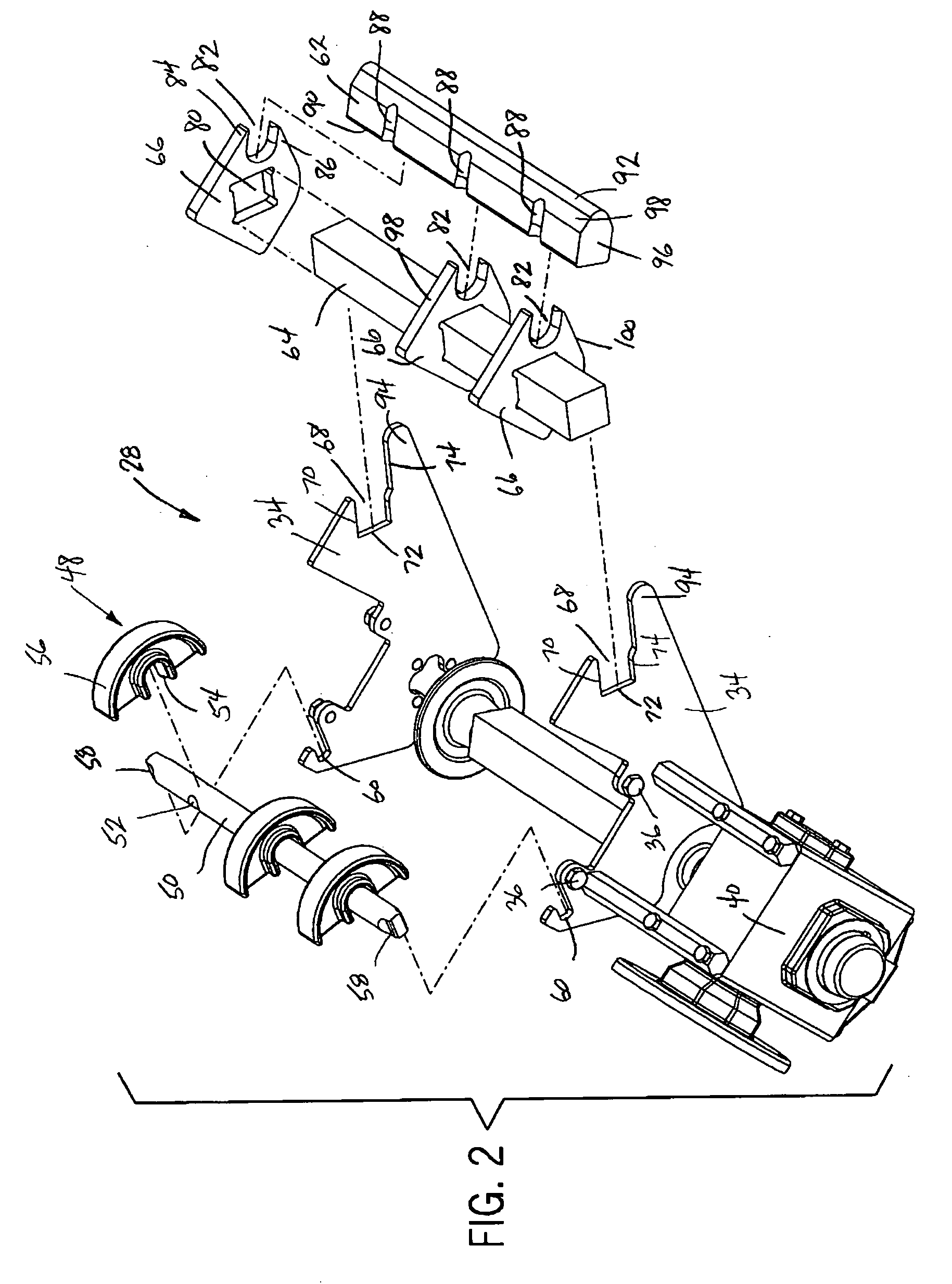
Sanitary conveyor transfer tail assembly
ActiveUS20070017786A1Prevent lateral movementPrevent rotationConveyorsSupporting framesWear resistantEngineering
A transfer tail assembly for use with a conveyor assembly that creates a reduced radius transition from the upper run to the lower run of a continuous conveyor belt used with the conveyor assembly. The transfer tail assembly includes a stationary nose bar over which the continuous conveyor belt passes at the end of the conveyor assembly. The nose bar is supported at the end of the conveyor assembly by a series of support brackets mounted to a cross support. Each of the support brackets is formed from a wear resistant material and contacts the conveyor belt as the conveyor belt passes around the transfer tail assembly. The nose bar, support brackets and cross support are mounted within the tail assembly without the use of any external connectors and thus require no tooling to assemble and disassemble.
Owner:DORNER MFG. CORP.
Three-dimensional imaging device and system
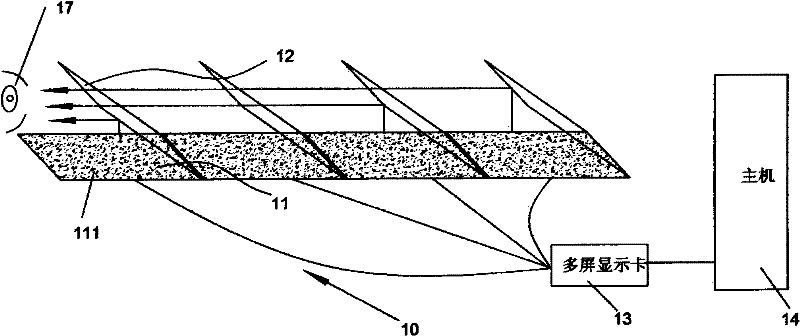
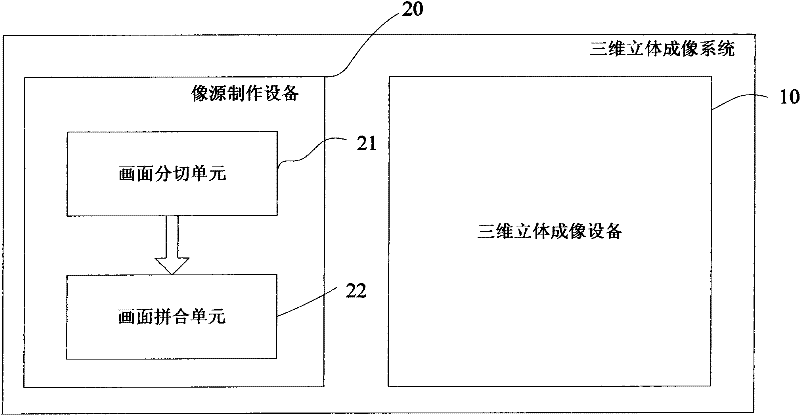
InactiveCN102053377ATrue restorationImprove visual effectsSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsDisplay deviceImaging technique
The invention belongs to the technical field of three-dimensional imaging, in particular relates to a three-dimensional imaging device and system. The three-dimensional imaging device comprises a display unit and a polarizing device, and is characterized in that: the display unit comprises a plurality of two-dimensional displays; each two-dimensional display comprises a display window; display windows of various two-dimensional displays are in the same size and shape; centers of the display windows of the two-dimensional displays are in a straight line; the polarizing device comprises a plurality of semireflecting and semi-transparent optical elements; a semireflecting and semi-transparent optical element is arranged between every two two-dimensional displays; a semireflecting and semi-transparent optical element is respectively arranged on the head and / or the tail of a two-dimensional display row formed by a plurality of the two-dimensional displays; reflecting surfaces of the various semireflecting and semi-transparent optical elements are in parallel to each other; the straight line formed by the connection of the centers of the two-dimensional displays is perpendicular to the reflecting surfaces of the semireflecting and semi-transparent optical elements; and the area of the reflecting surfaces of the semireflecting and semi-transparent optical elements is 1.414 to 2 times that of the display windows of the two-dimensional displays.
Owner:刘武强
Fishing lure and kit
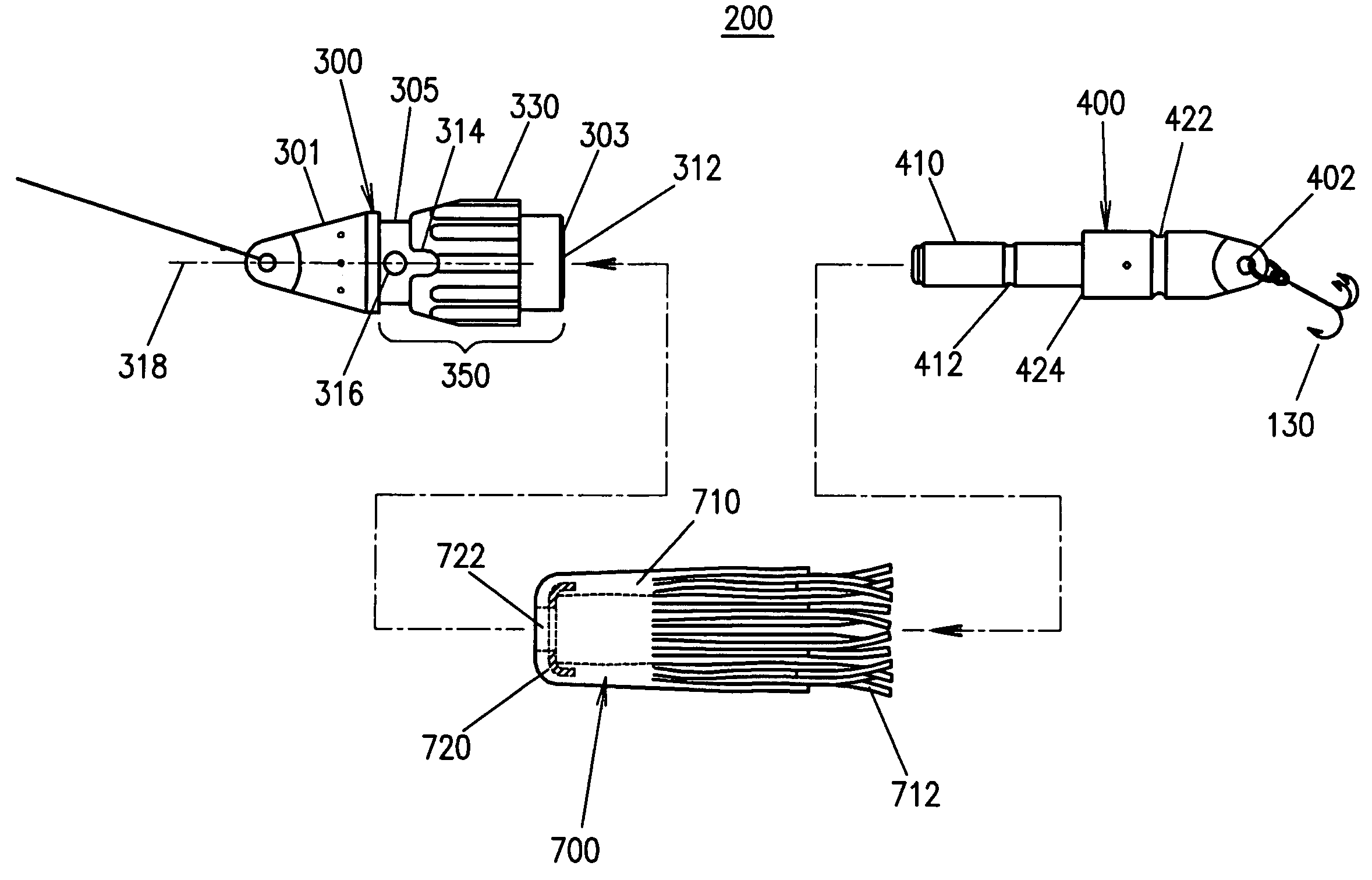
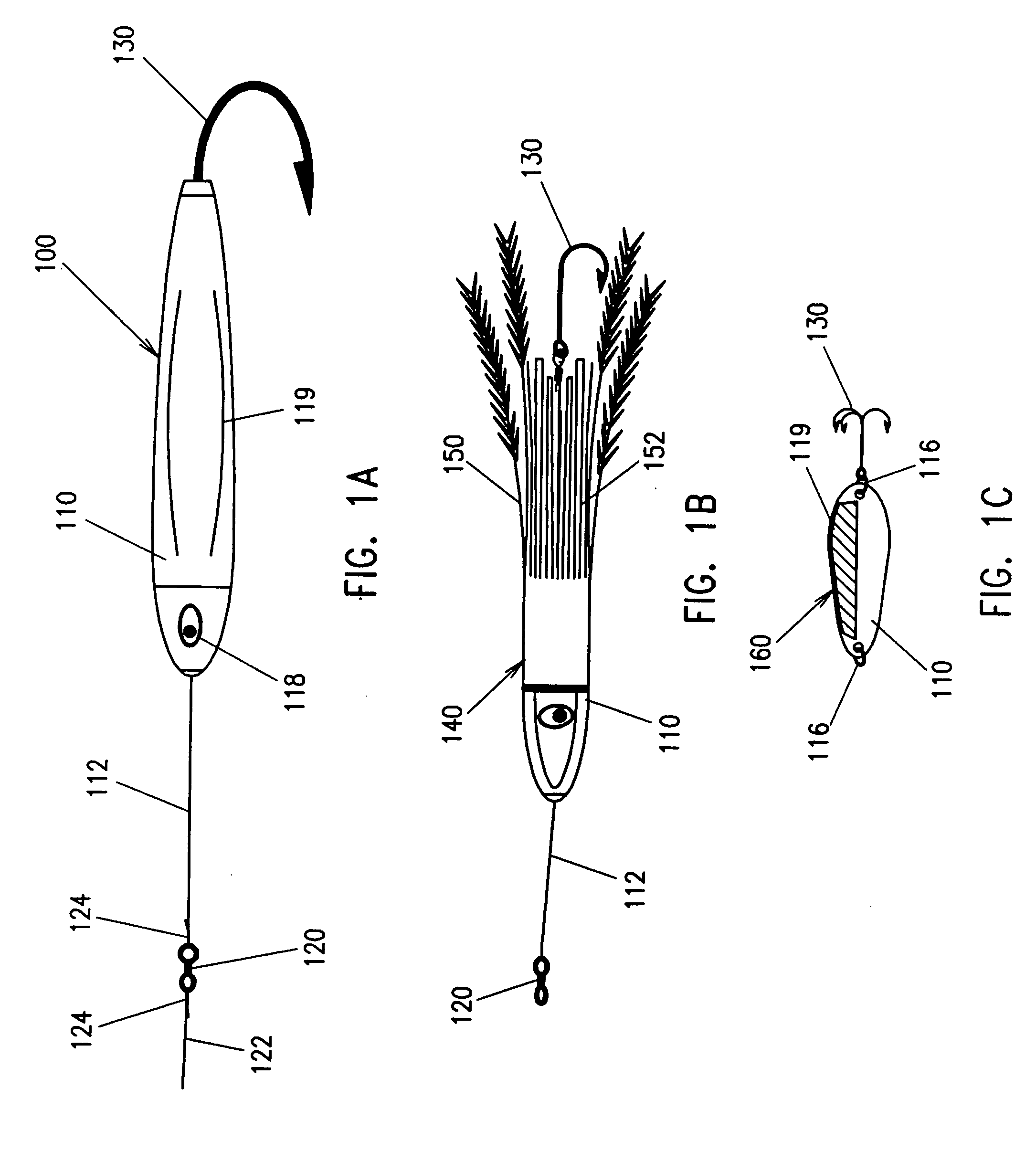
A fishing lure is described, having a head with a release mechanism and a removable tail. Because the tail can be released, fish caught on hooks can be released quickly, and new tails with new hooks rapidly attached to the same head. Multiple tails may be equipped with different lure skirts, for different fish and / or different conditions, and rapidly changed out in the course of fishing. A tail including a drag chute released by a fish strike, attachable to the same head, is also disclosed. A dive wing, attachable to the removable tails, is also disclosed. Tails can include bait scent chambers and release holes and water jets to attract fish. A kit with combinations of heads, tails, dive wings, and other parts and accessories is also disclosed.
Owner:ZUK ANDREW
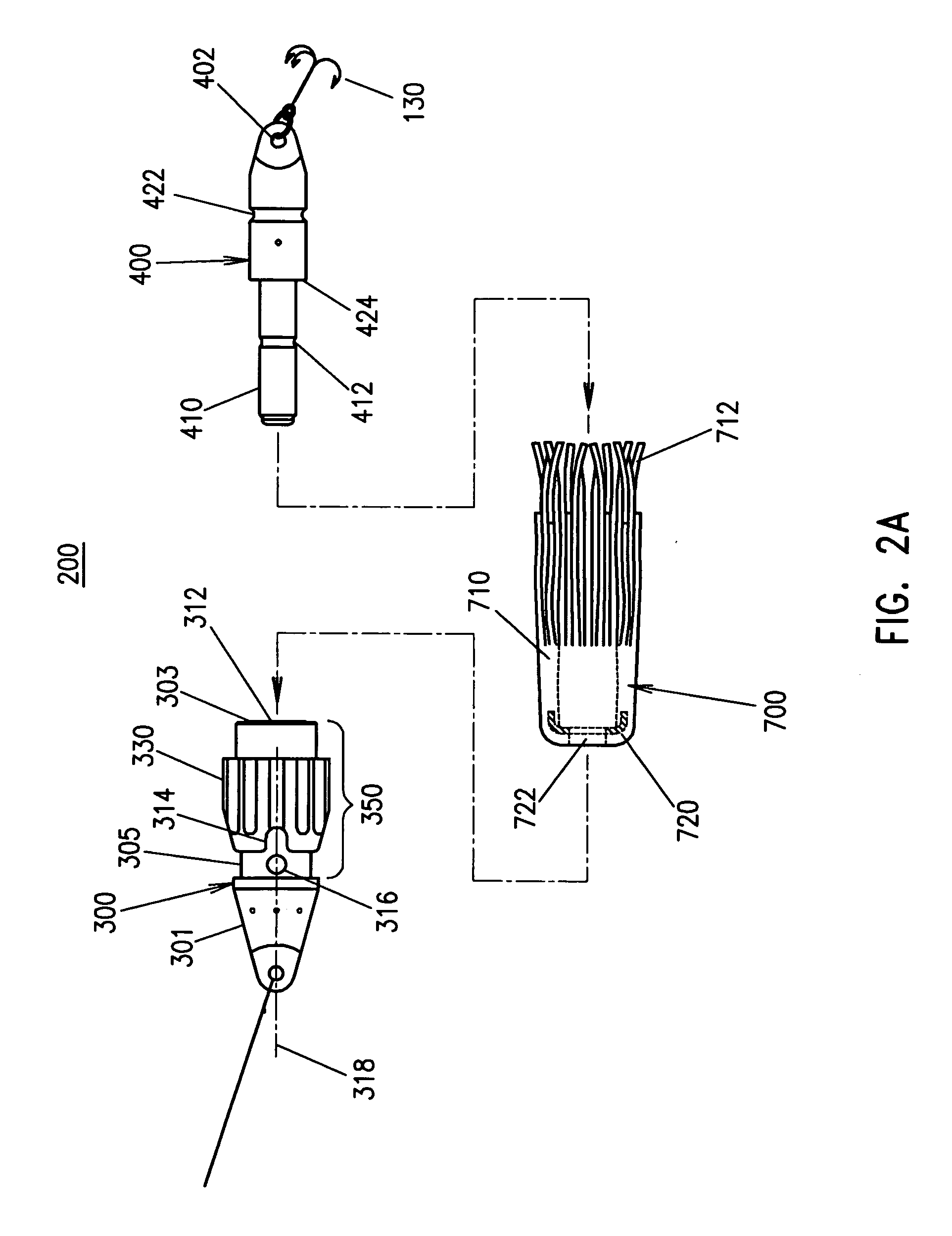
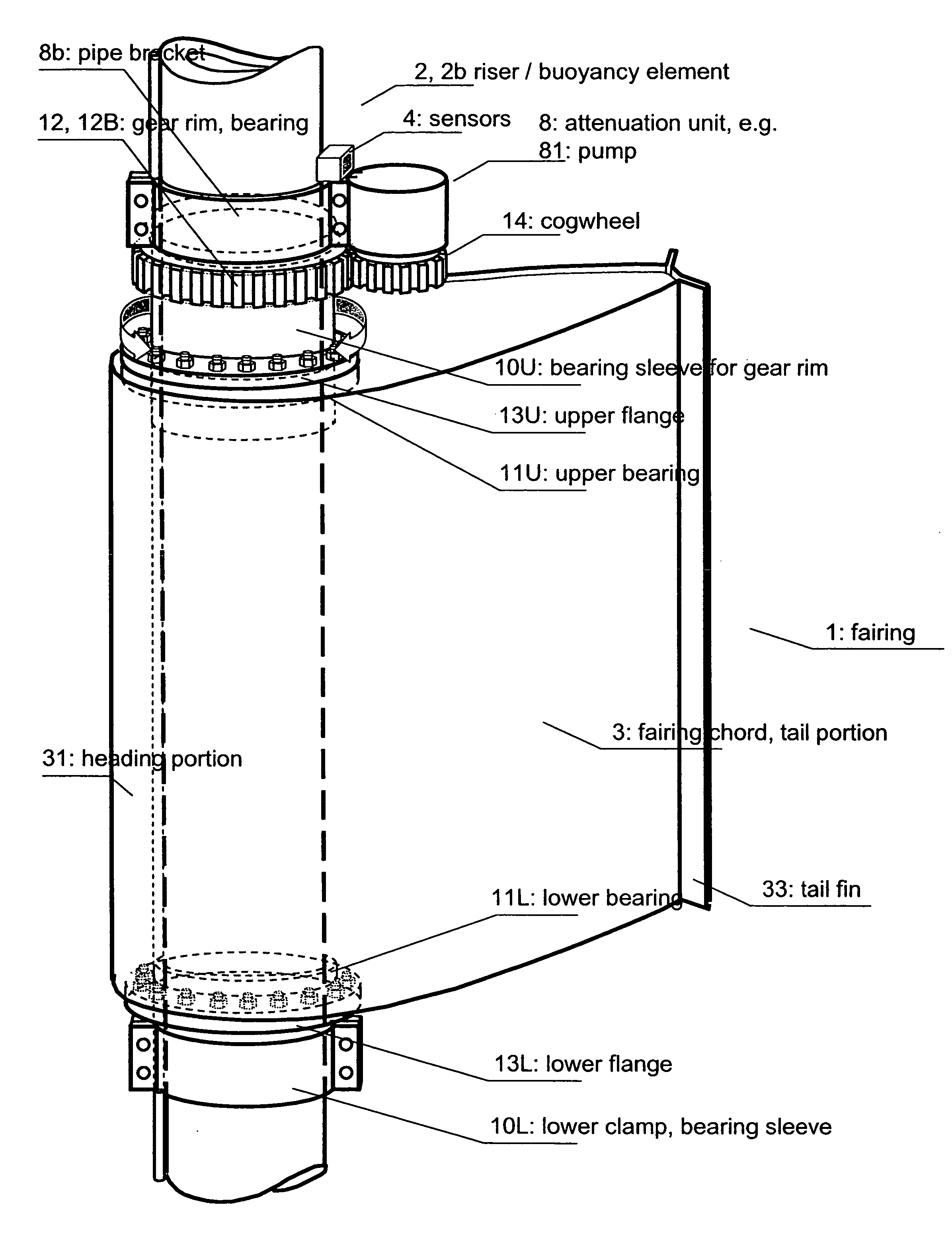
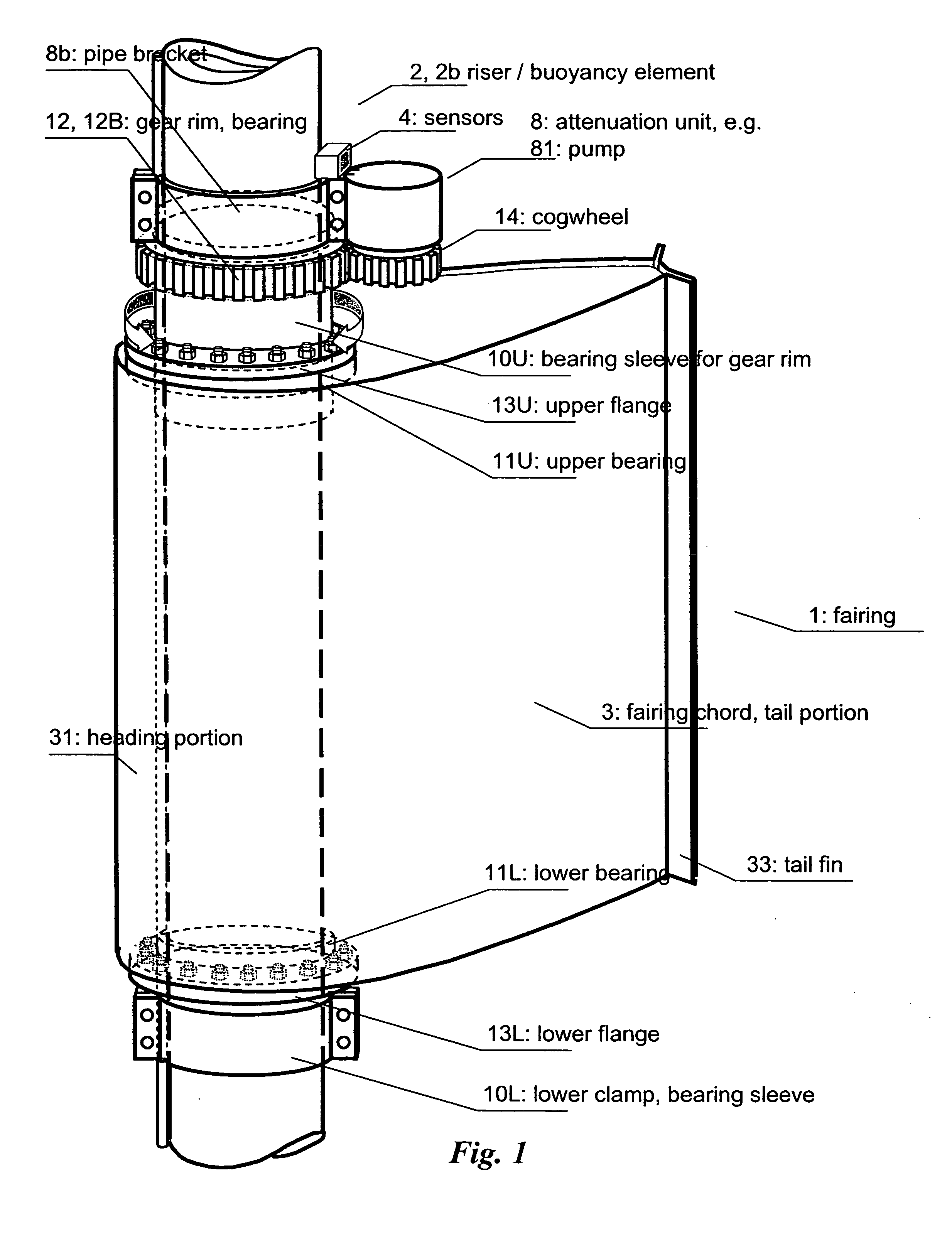
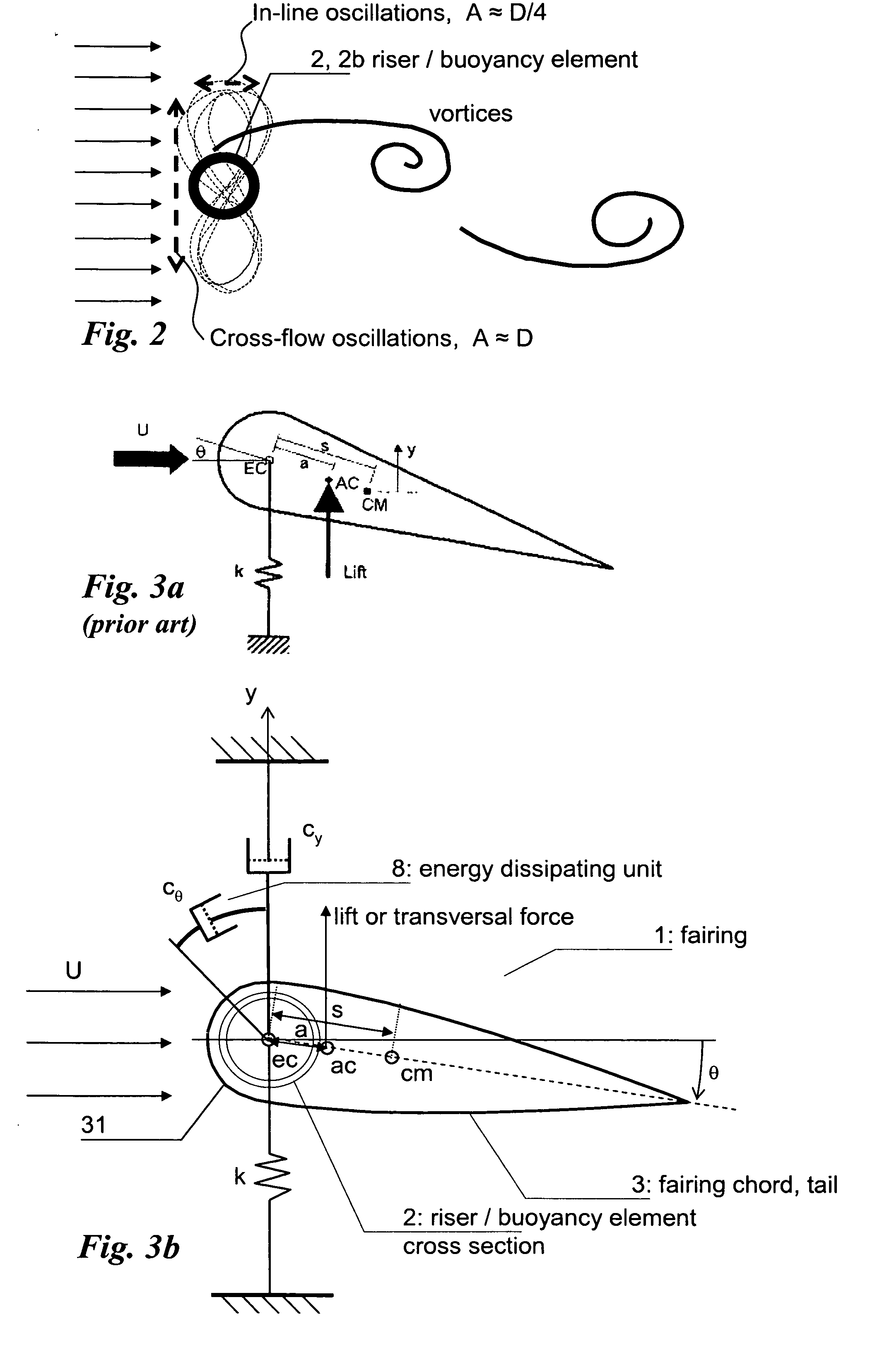
Fairing for reducing watercurrent-induced stresses on a marine riser
InactiveUS20070215028A1Reduce frictionAvoid vibrationDrilling rodsOffensive equipmentUltrasound attenuationWater flow
The invention relates to a rotatable fairing (1) for a marine riser (2) or other slender marine structure. The fairing (1) is arranged on the riser for reducing watercurrent-induced stresses on said riser (2), said fairing (1) having a tail portion (3) for trailing generally in the downstream direction behind said riser. The fairing (1) is provided with an attenuation unit (8) for counteracting the unstable rotation of said fairing (2) relative to said riser (2), in order to prevent undesired vibrations of said riser (2). The fairing is provided with one or more clamps (10) for attachment to and around a periphery of said riser (2), said clamps (10) arranged with a gear rim (12) for engagement with an actuating cogged wheel (14) of said attenuation unit (8).
Owner:SINTEF TTO AS
Remote sensing electric field exploration system
InactiveUS20050285598A1Low costMaintenance requirement is minimalAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAcoustic wave reradiationAviationMotion detector
An airborne exploration system used with an aircraft for shallow and deep exploration for oil and gas, mineral deposits and aquifers. The survey system uses natural electromagnetic EM fields as an energy source. The exploration system includes a pair of aerodynamic housing pods adapted for mounting on wing tips of the aircraft. The housing pods include electric field sensors with three orthogonal electric dipoles oriented along an X, Y and Z axis. An optional third set of orthogonal electric dipoles can be mounted in the tail of the aircraft. The field sensors are electrically attached to angular motion detectors mounted inside housing pods. The motion detectors are used for compensating for errors caused by angular motion of the aircraft when in the presence of strong electric field gradients. The system also includes a total field magnetometer mounted in the aircraft. The various filtered outputs of the magnetometer are used to provide phase and amplitude references for the similarly filtered and angular motion corrected outputs of the electric field sensors. The electric field data when normalized and phase referenced against the magnetic field data provides valuable geological and geophysical information related to the subsurface flow of telluric currents.
Owner:TELLURIC EXPLORATION
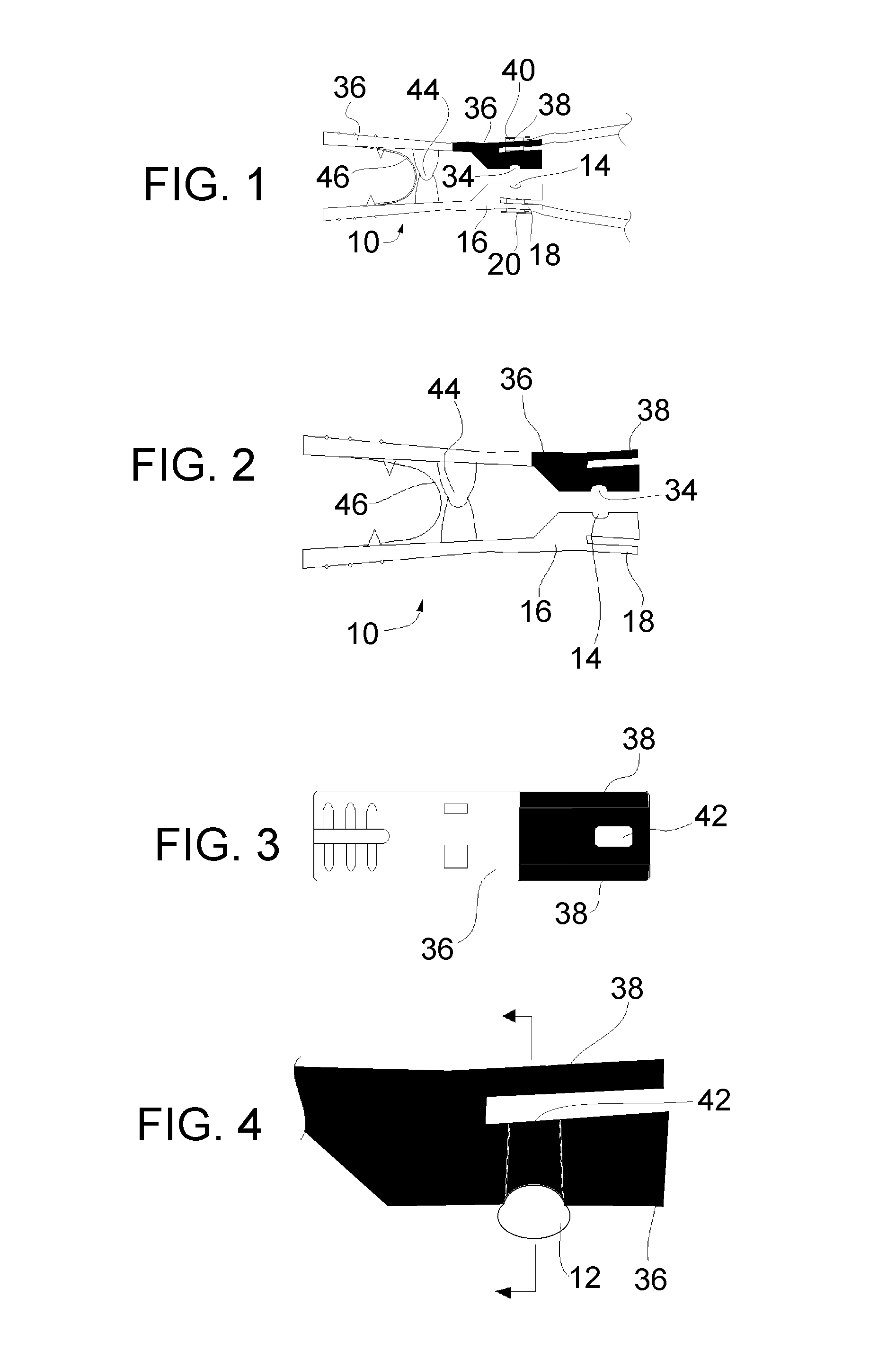
Tail Mounting Clip for Securely Mounting Sensor to Tail and a Tail Mounted Pulse Oximetry Sensor System Using Same
InactiveUS20080076989A1Guaranteed to workKeep properlySnap fastenersClothes buttonsOxygen Saturation MeasurementTail
A tail mounted clip adapted to receive one or more sensors thereon that incorporate at least one circular groove on a tail engaging face thereof for locating the clip on the tail of a subject and retaining clip and associated sensor(s) properly in place. This configuration allows the clip to be securely located in any circumferential orientation around the tail of the subject. The present invention will have the sensors properly positioned adjacent the tail and will prevent relative movement between the sensors and the tail. The tail mounting clip is used to hold an LED sensor and photodiode for making pulse-oximetry measurements, also called a photoplethysmographs.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
Aircraft gas turbine engine counter-rotatable generator
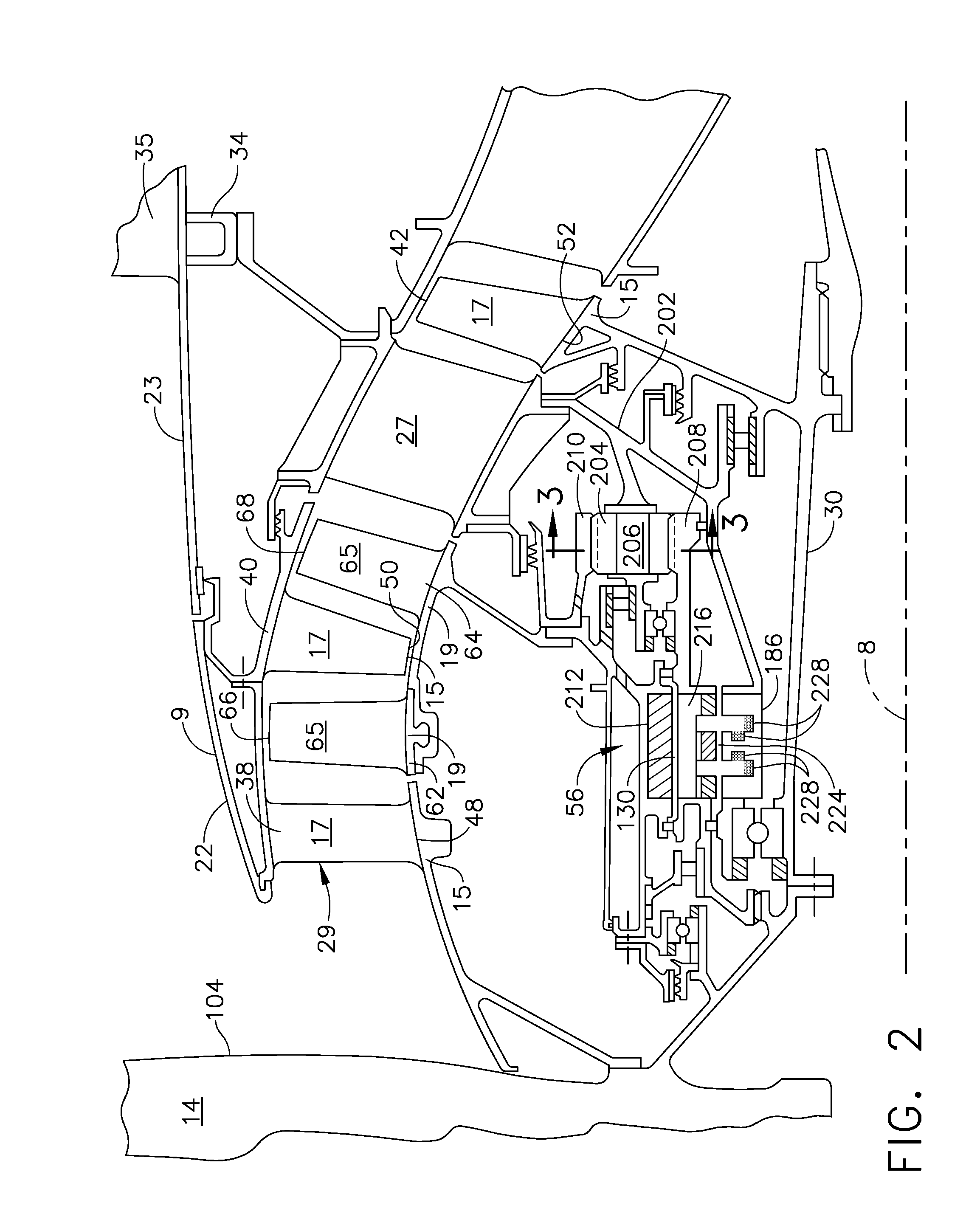
An aircraft gas turbine engine includes a counter-rotatable generator driven by a turbine includes a generator stator and counter-rotatable radially inner pole and outer magnet rotors. A gearbox may be used for counter-rotating the pole and magnet rotors. Counter-rotatable first and second sets of booster stages may be co-rotatable with corresponding ones of the pole and magnet rotors. The generator and the gearbox may be disposed within a booster cavity or a tail cone of the engine. The magnet rotor, the pole rotor, and the stator may be concentric. A particular embodiment of generator includes the magnet rotor encircling the pole rotor, the pole rotor encircling the stator, a rotor air gap between the magnet and pole rotors, and a transformer air gap between the pole rotor and the stator. The counter-rotatable generator may be driven directly by a counter-rotatable turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com