Patents
Literature
350results about How to "Avoid discontinuities" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
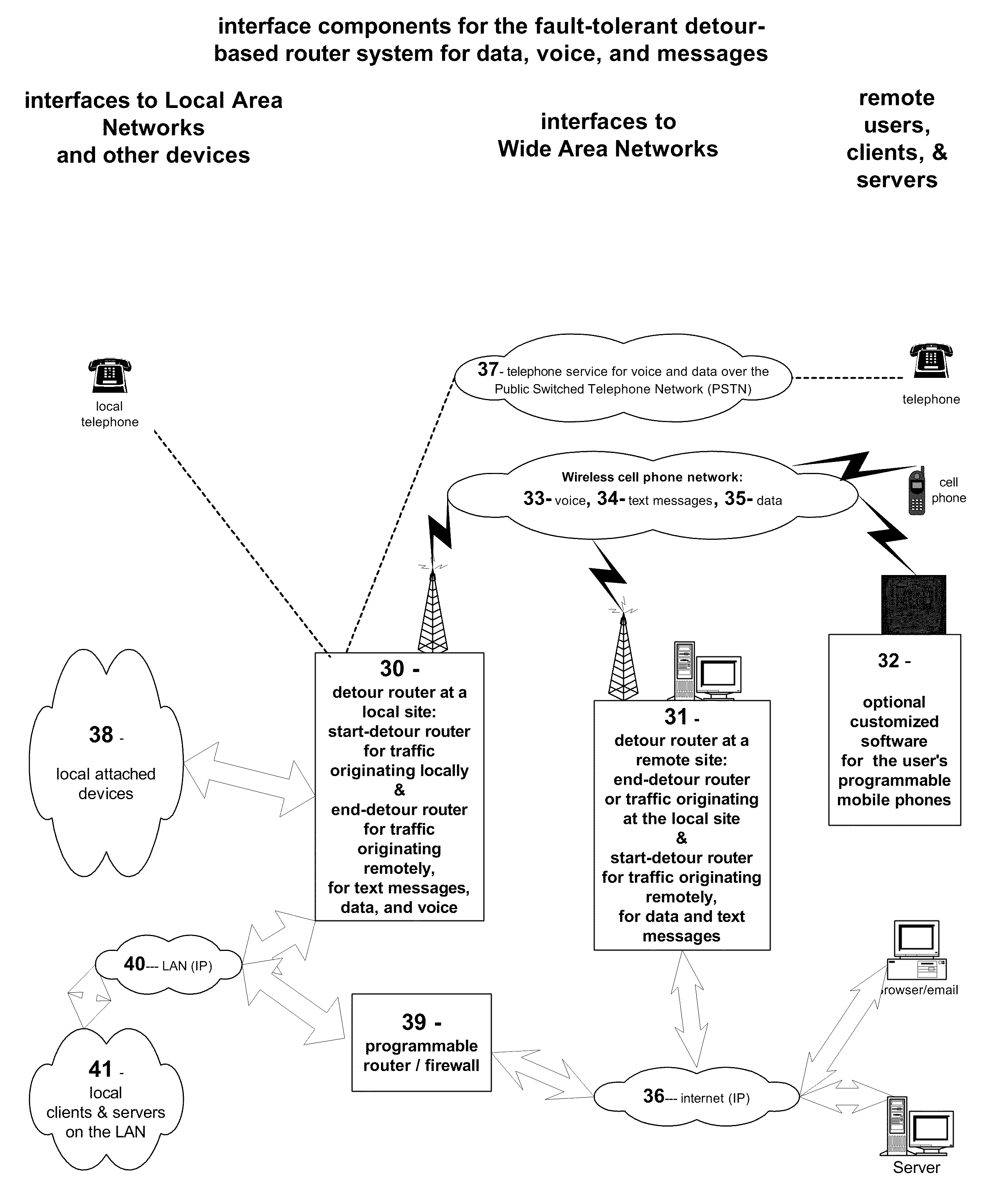
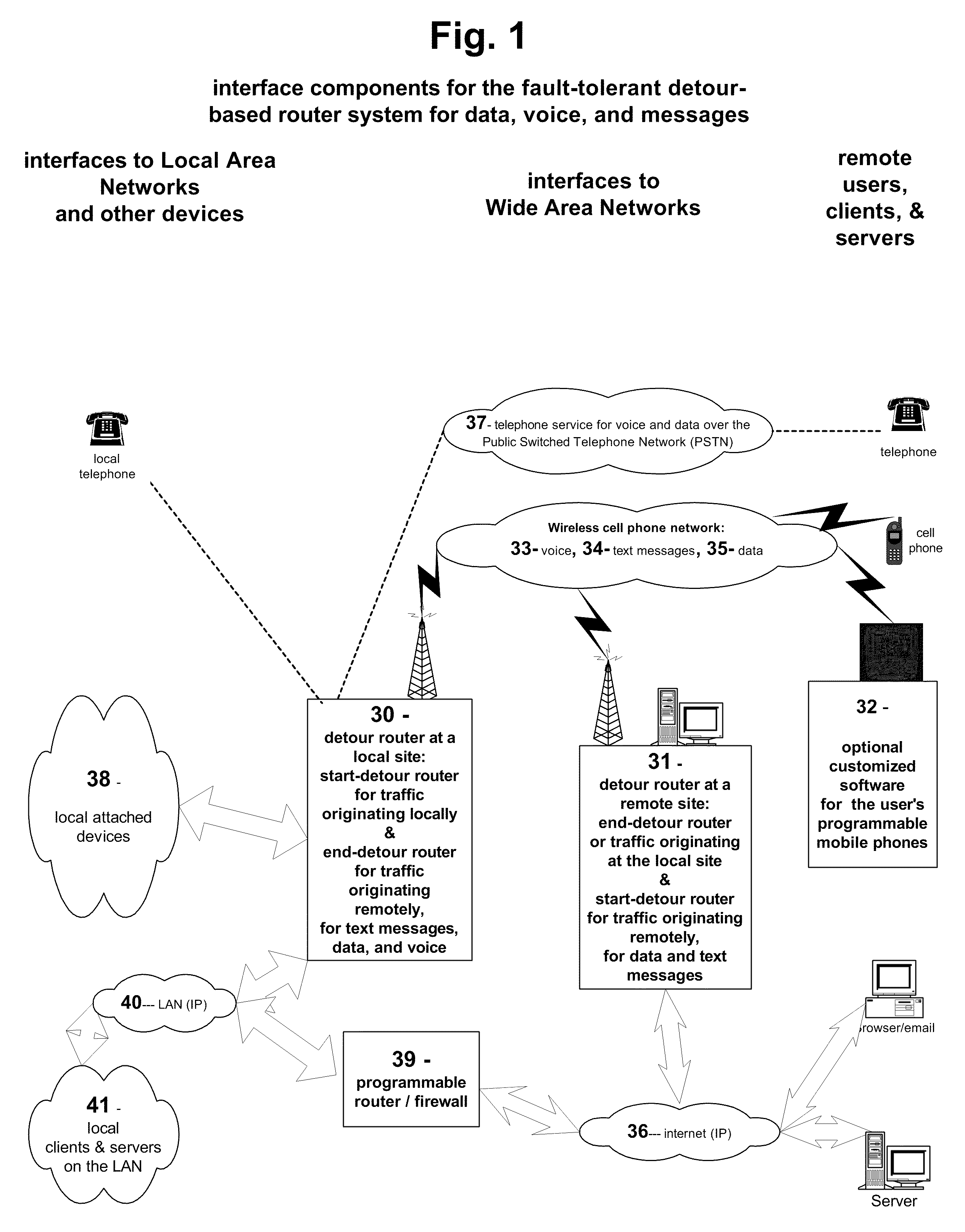
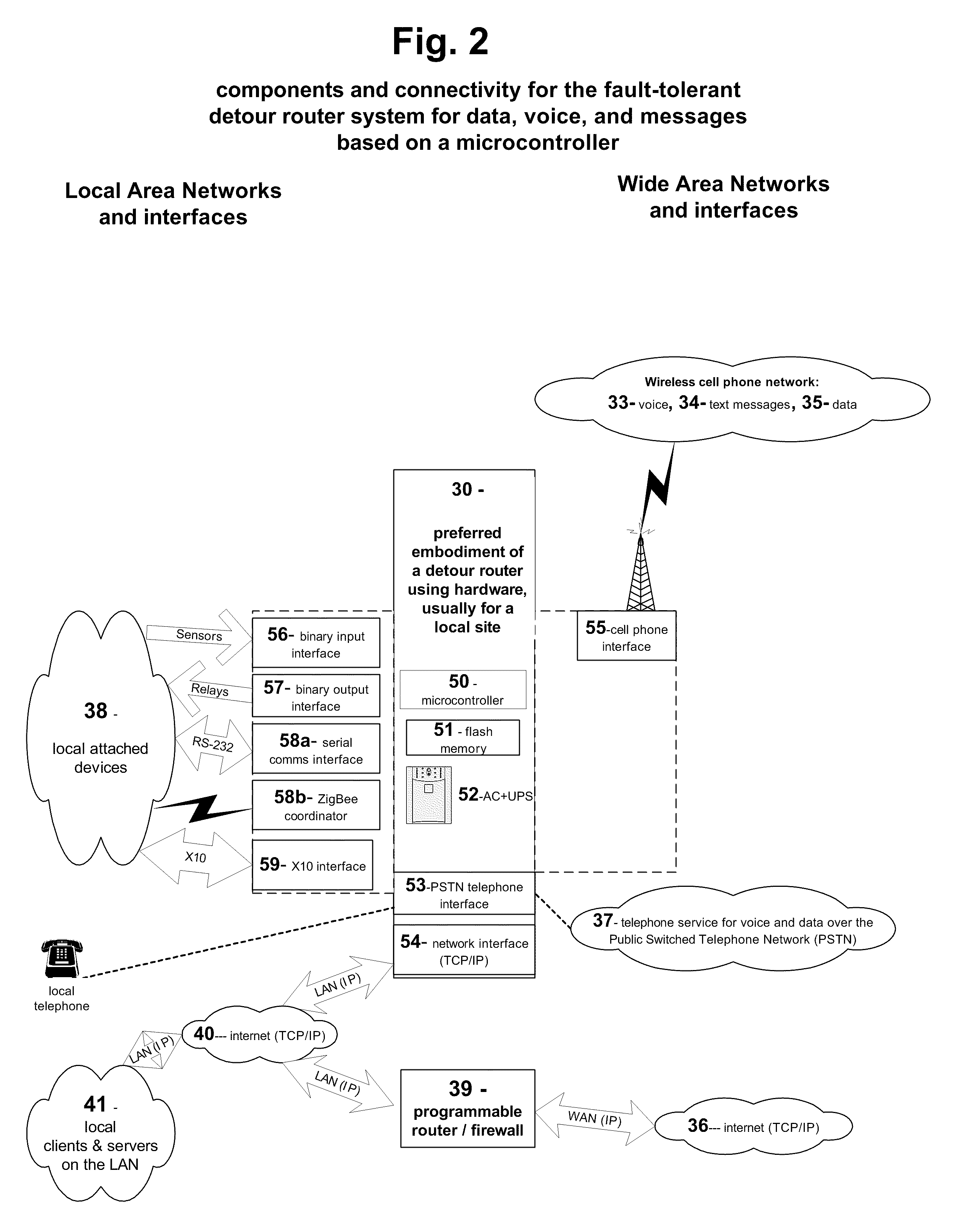
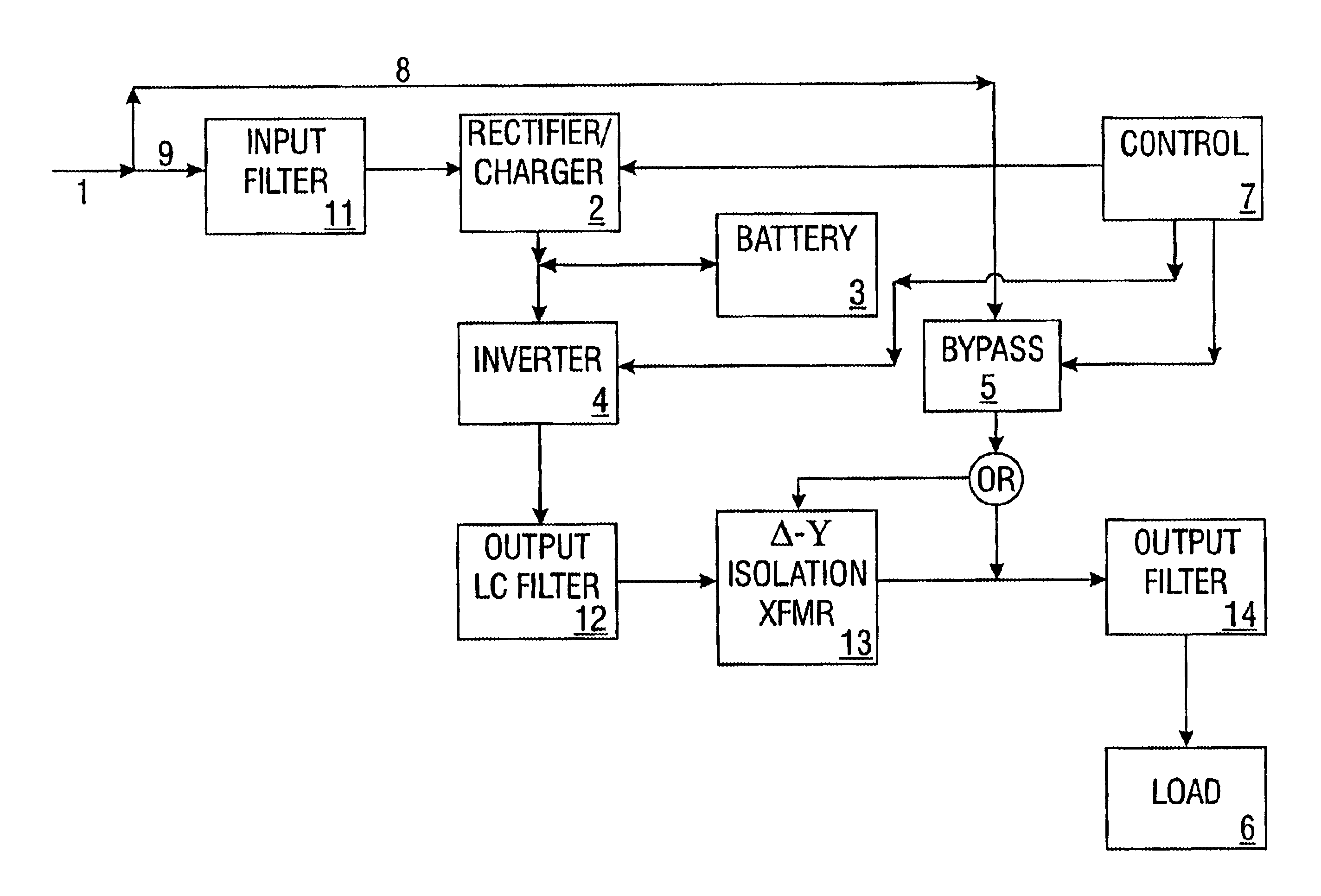
Fault-tolerant, multi-network detour router system for text messages, data, and voice
InactiveUS20100267390A1Avoid discontinuitiesReduce loss rateMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsWireless commuication servicesWide areaThe Internet
The invention provides a method and system for fault-tolerant communication. It utilizes three wide area networks, including the cell phone network, the internet and the telephone network (PSTN). The method and system monitors the wide-area networks and sends warning messages if they cannot be accessed from a local site. Primary failure conditions relate to the access and use of the three wide-area networks. Secondary failure conditions include power outages. The possible fault conditions include: ‘telephone out’, ‘internet out’, ‘wireless radio out’, ‘power out’. If these failure conditions are detected, the method and system alerts the user and redirects voice, text message, and data traffic via a detour over a different wide-area network in order to avoid that failure.A method and system has been disclosed that routs information over one of multiple networks in a fault-tolerant manner. In case of network failure, detour routers allow the start-detour routers to switch the information flow over another network to an end-detour router, where the information flow is switched back to the originally-intended network. Cell radios are utilized, as well as telephones and the internet to provide redundancy and fail-over under ‘telephone out’, ‘internet out’, ‘cell phone out’ conditions. The method has particular strengths in supporting communication even with dynamically assigned addresses, thus assuring that remote users receive monitoring and alarm information in a timely manner.
Owner:LIN GAO +2
Flat panel lens
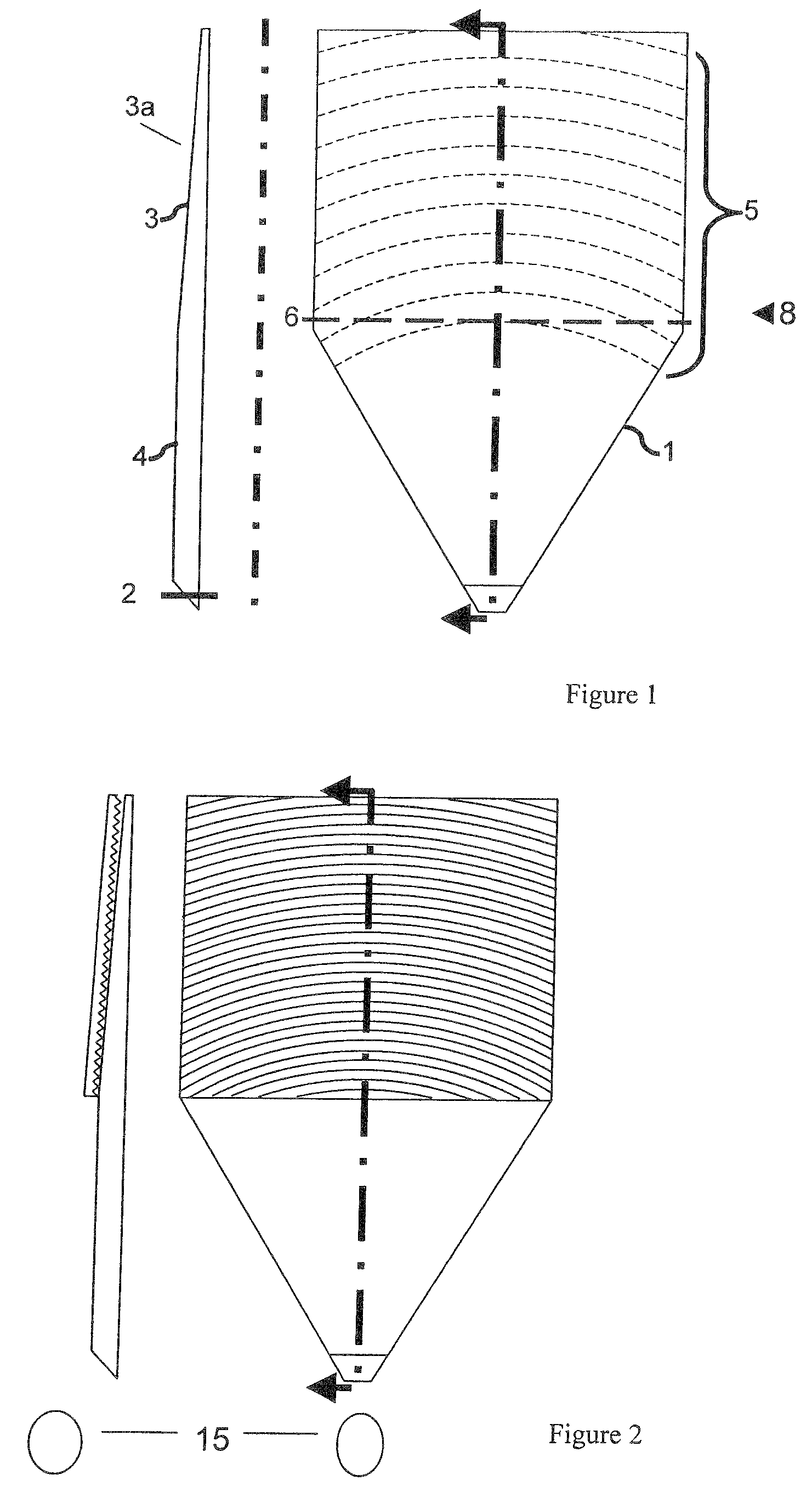
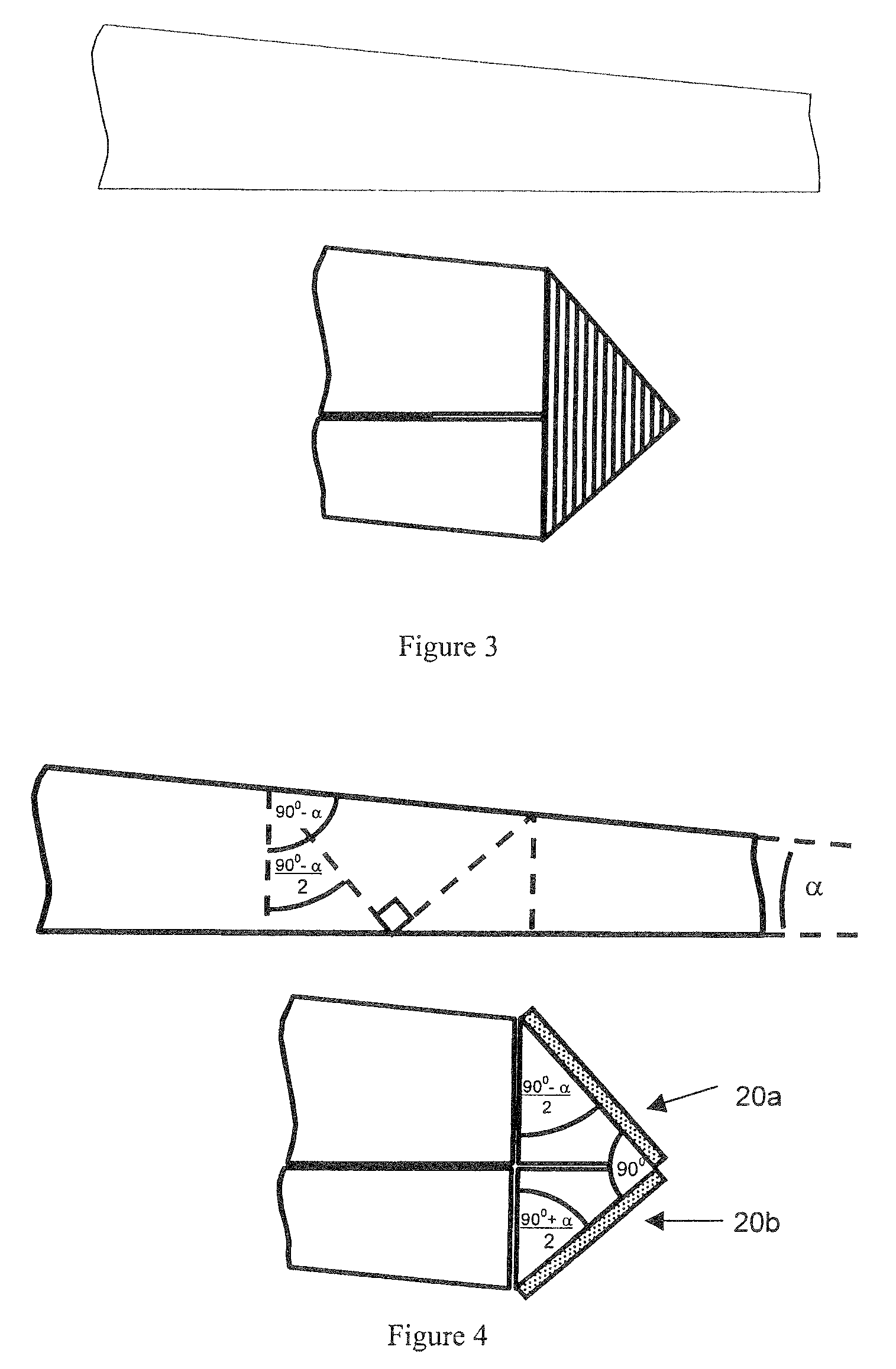
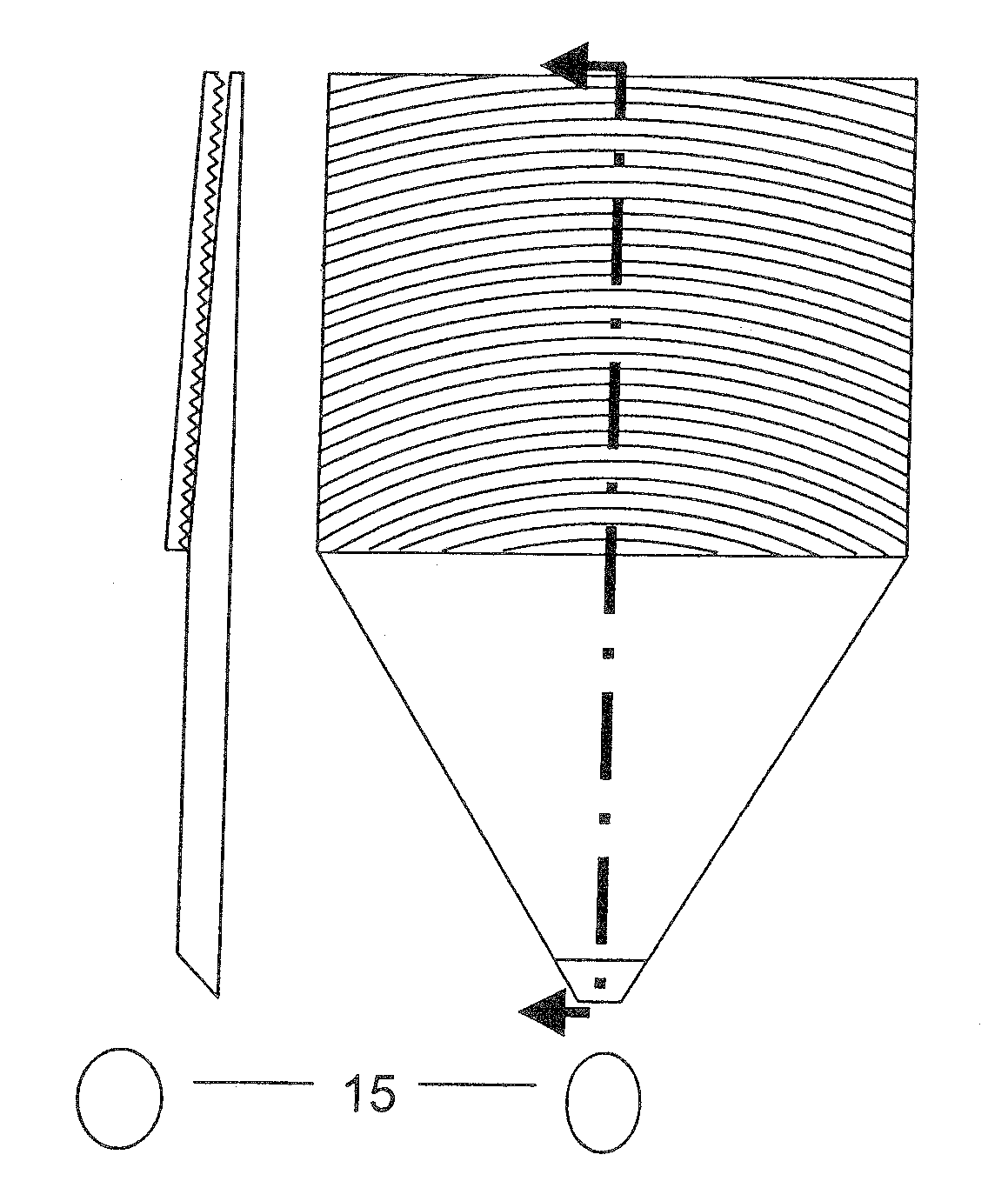
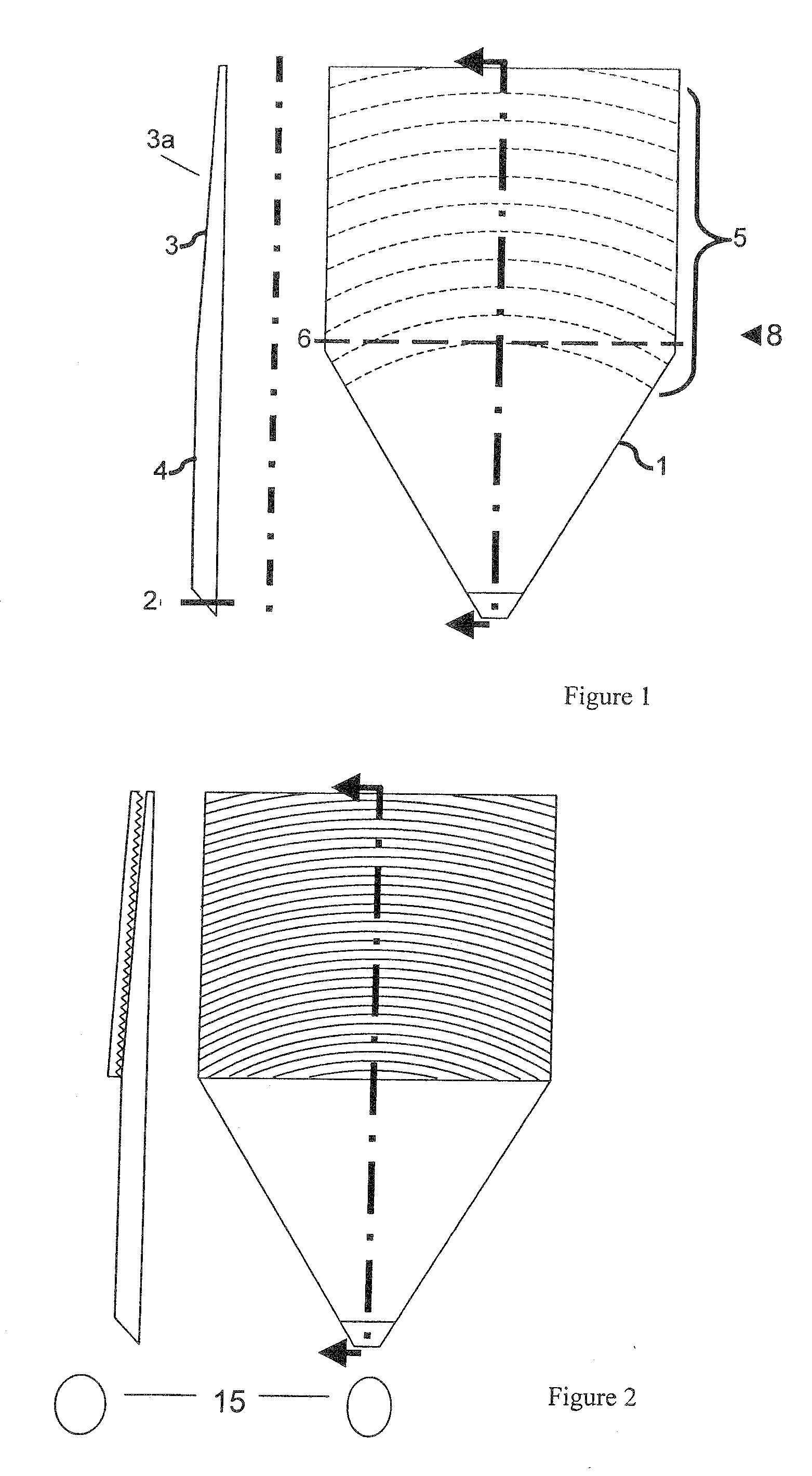
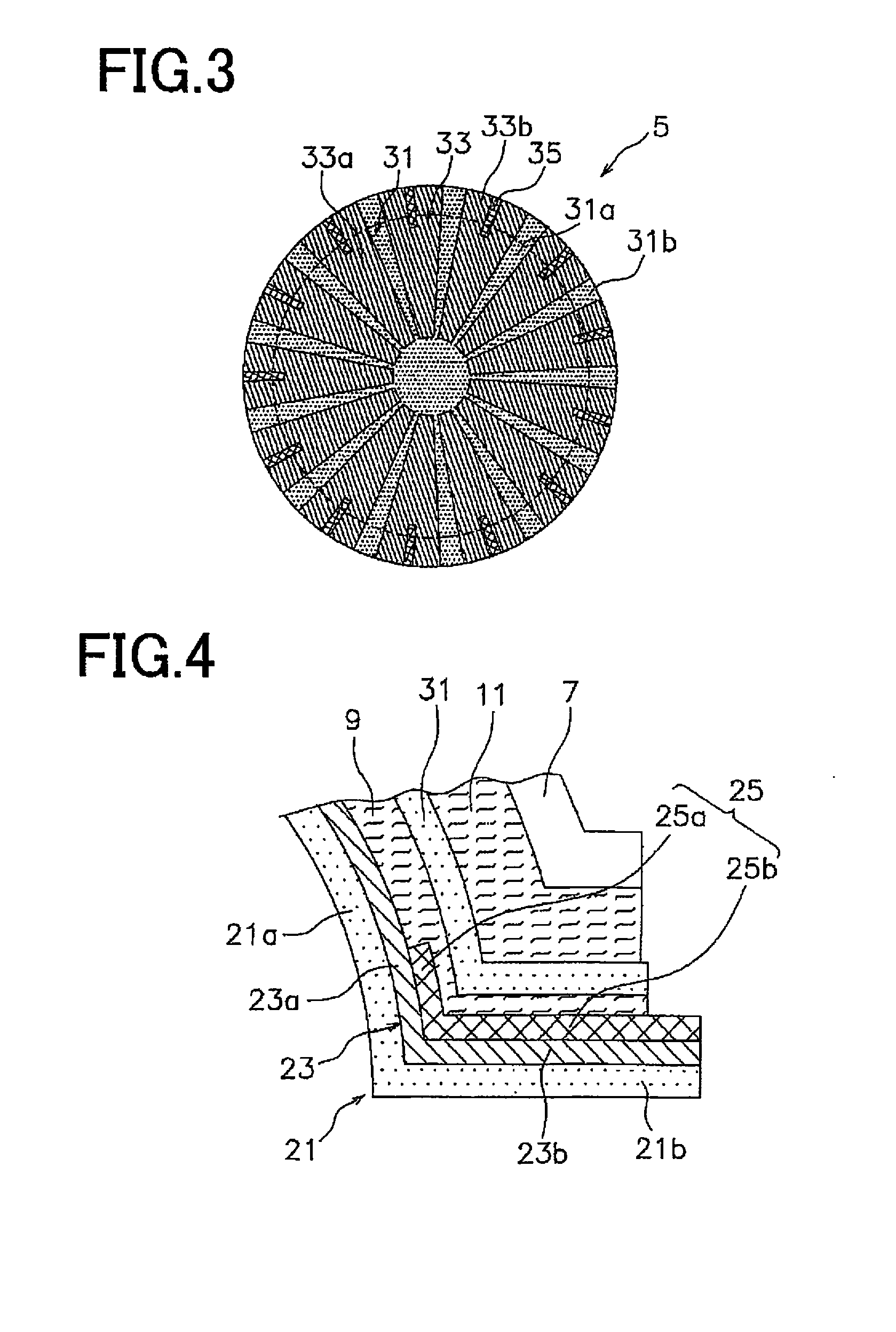
ActiveUS7976208B2Avoid discontinuitiesMore compactPrismsMechanical apparatusOptical propertyLight guide
A light guide with input and output faces 2, 3a is polar-symmetric about the first face 2 and has optical properties such that the angle at which a ray is injected into the first face determines the position at which it leaves the second face 3a, or, if operated in the reverse direction, the position at which the ray enters the second face determines the angle at which the ray leaves the second face. The light guide includes a tapered transparent sheet 3, light from the first face entering at the thick end of this sheet, and the second face forming one face of the tapered sheet. An input / output slab 4 adjoins the tapered sheet 3 for fan-out of light from the first face 2 to the tapered sheet, and a transition region 8 is located between flat and tapered sheets. The polar symmetry means that light rays always travel in line with the taper direction, which suppresses banding. Preferably the light guide further includes a prism device 20 for folding the light so that the flat and tapered sheets can be folded over each other. A method of making such a prism is also disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Flat Panel Lens
ActiveUS20080316768A1Avoid discontinuitiesMore compactPrismsMechanical apparatusOptical propertyLight guide
A light guide with input and output faces 2, 3a is polar-symmetric about the first face 2 and has optical properties such that the angle at which a ray is injected into the first face determines the position at which it leaves the second face 3a, or, if operated in the reverse direction, the position at which the ray enters the second face determines the angle at which the ray leaves the second face. The light guide includes a tapered transparent sheet 3, light from the first face entering at the thick end of this sheet, and the second face forming one face of the tapered sheet. An input / output slab 4 adjoins the tapered sheet 3 for fan-out of light from the first face 2 to the tapered sheet, and a transition region 8 is located between flat and tapered sheets. The polar symmetry means that light rays always travel in line with the taper direction, which suppresses banding. Preferably the light guide further includes a prism device 20 for folding the light so that the flat and tapered sheets can be folded over each other. A method of making such a prism is also disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
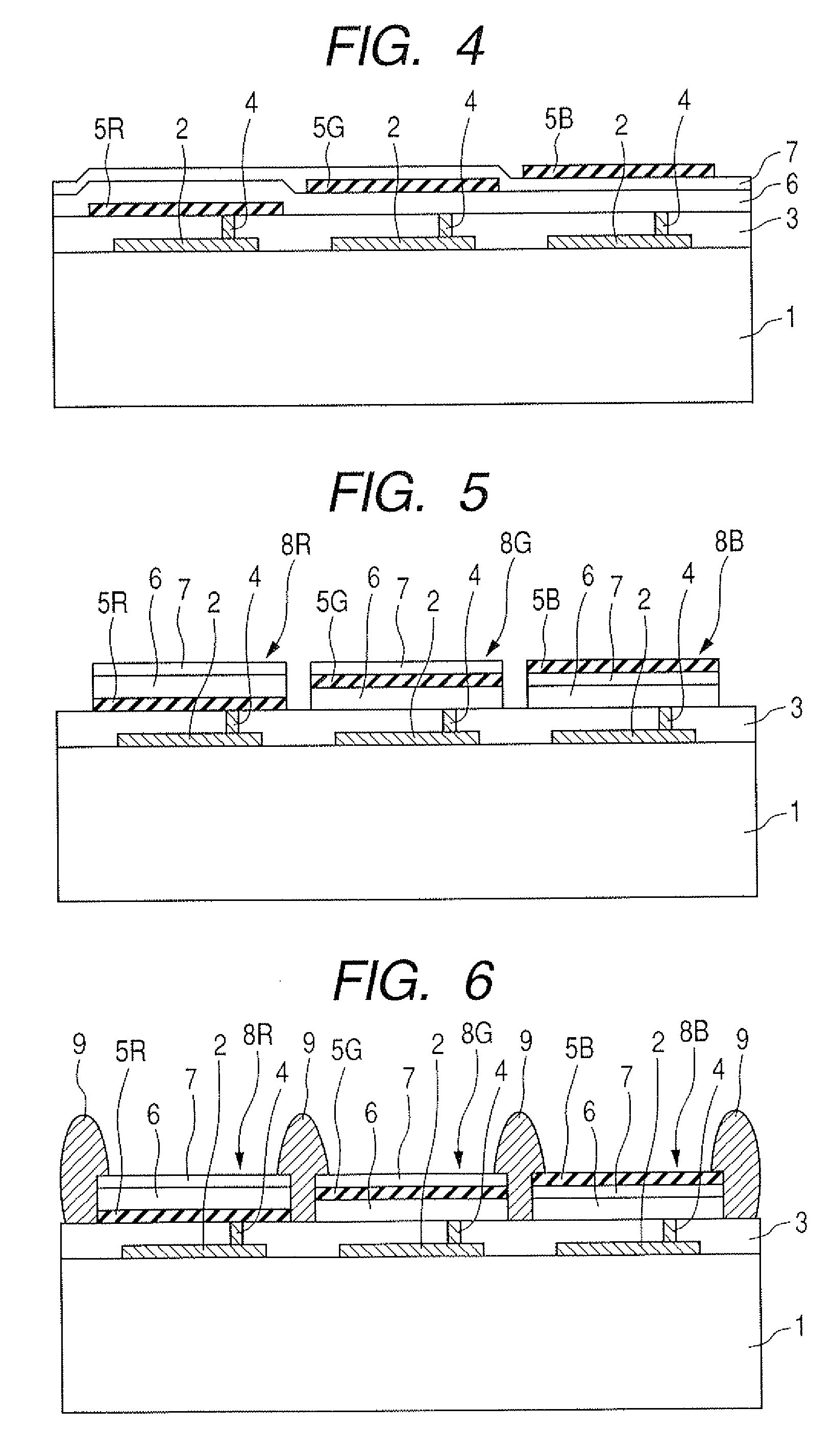
Display device and method of fabricating the display device
InactiveUS6995511B2Form evenlyAvoid discontinuitiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
In an EL element having an anode, an insulating film (bump) formed on the anode, and an EL film and a cathode formed on the insulating film, each of a bottom end portion and a top end portion of the insulating film is formed so as to have a curved surface. The taper angle of a central portion of the insulating film is set within the range from 35° to 70°, thereby preventing the gradient of the film forming surface on which the EL film and the cathode are to be formed from being abruptly changed. On the thus-formed film forming surface, the EL film and the cathode can be formed so as to be uniform in thickness, so that occurrence of discontinuity in each of EL film and the cathode is prevented.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
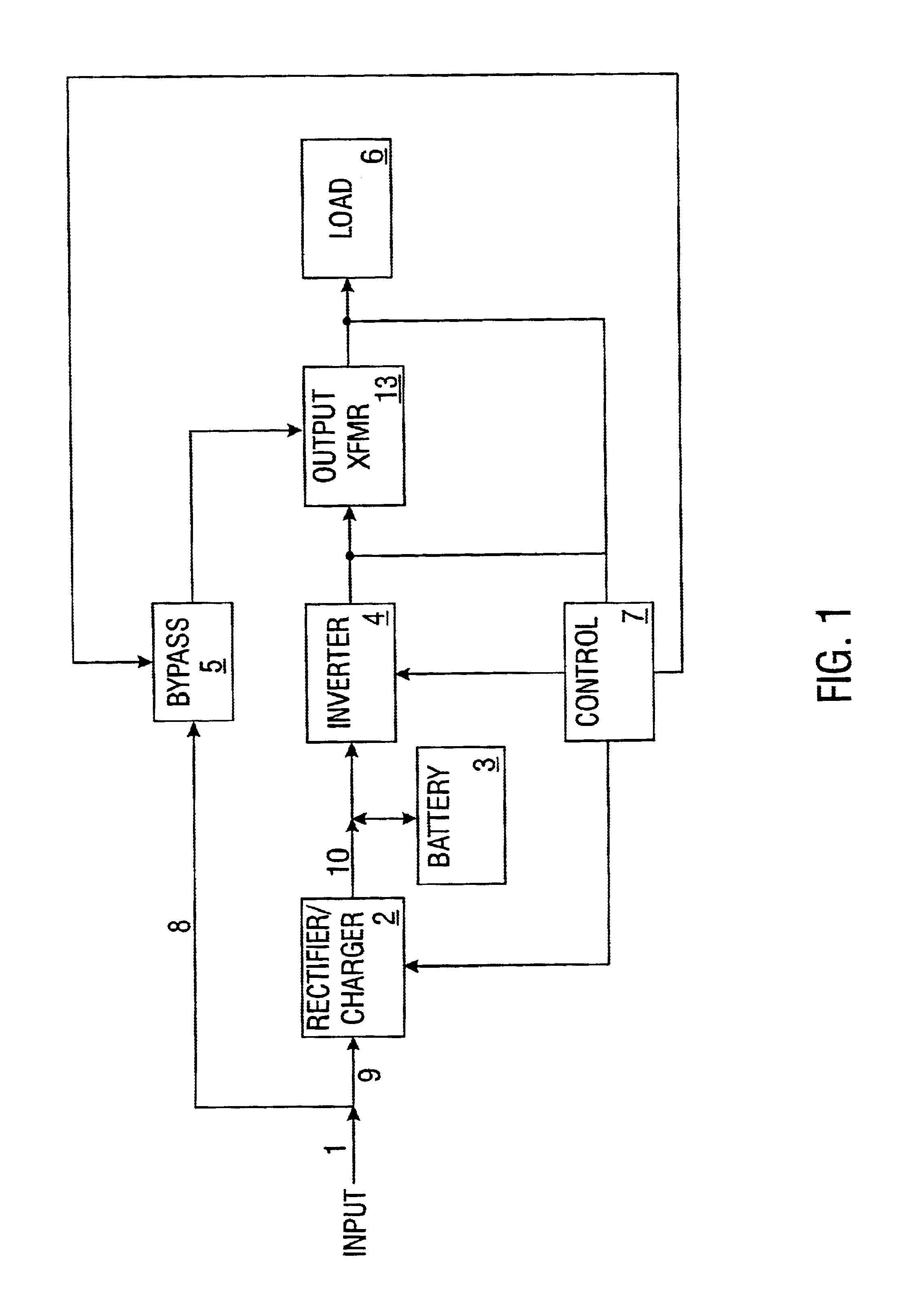
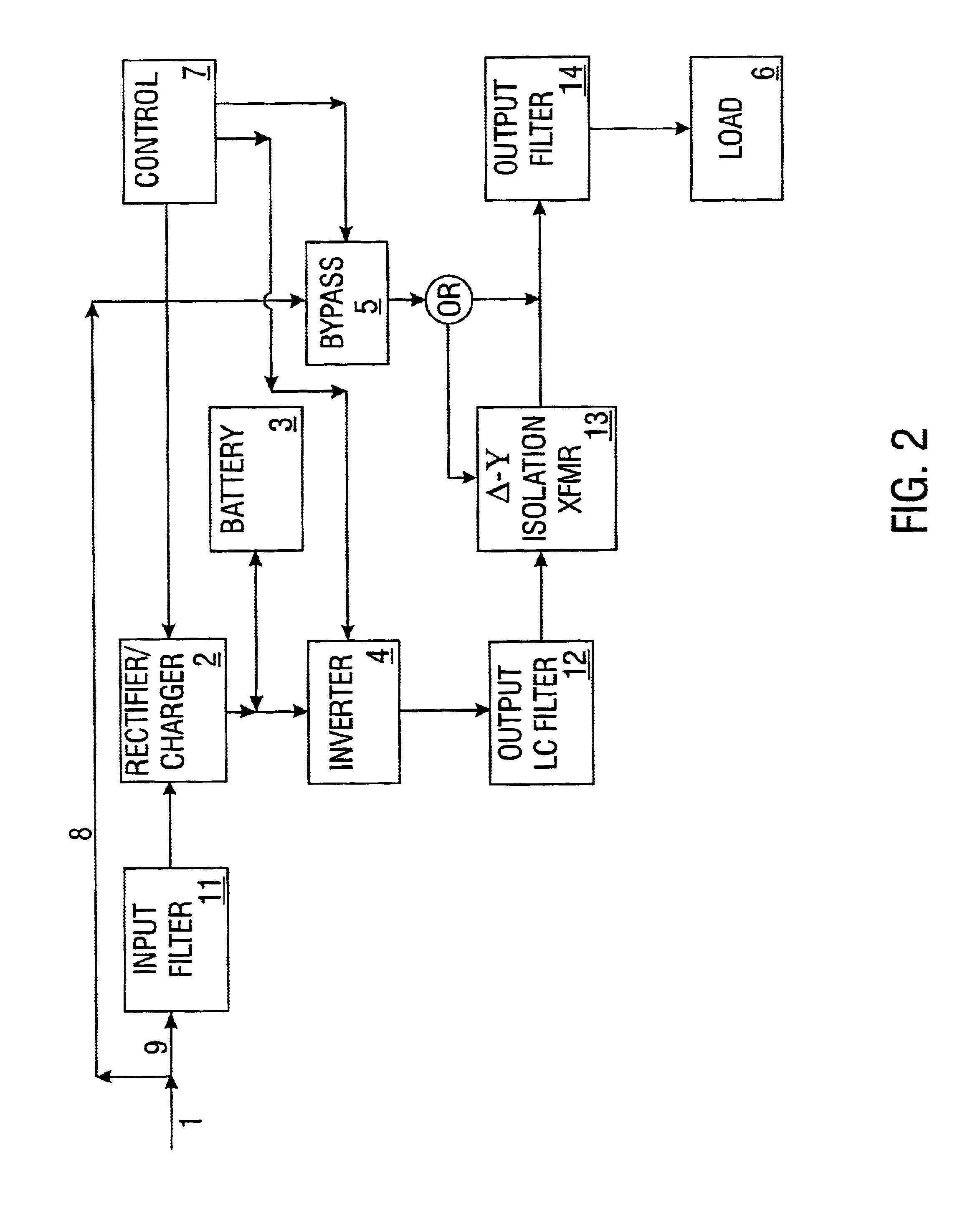
Uninterruptible power supply
InactiveUS6917124B2Prevent any discontinuityIncrease voltageBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerUninterruptible power supplyAnalog controller
An uninterruptible power supply is disclosed that includes a digital controller comprising a plurality of microprocessors. These microprocessors are programmed and arranged to provide various control features heretofore unavailable using analog controllers of the prior art.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
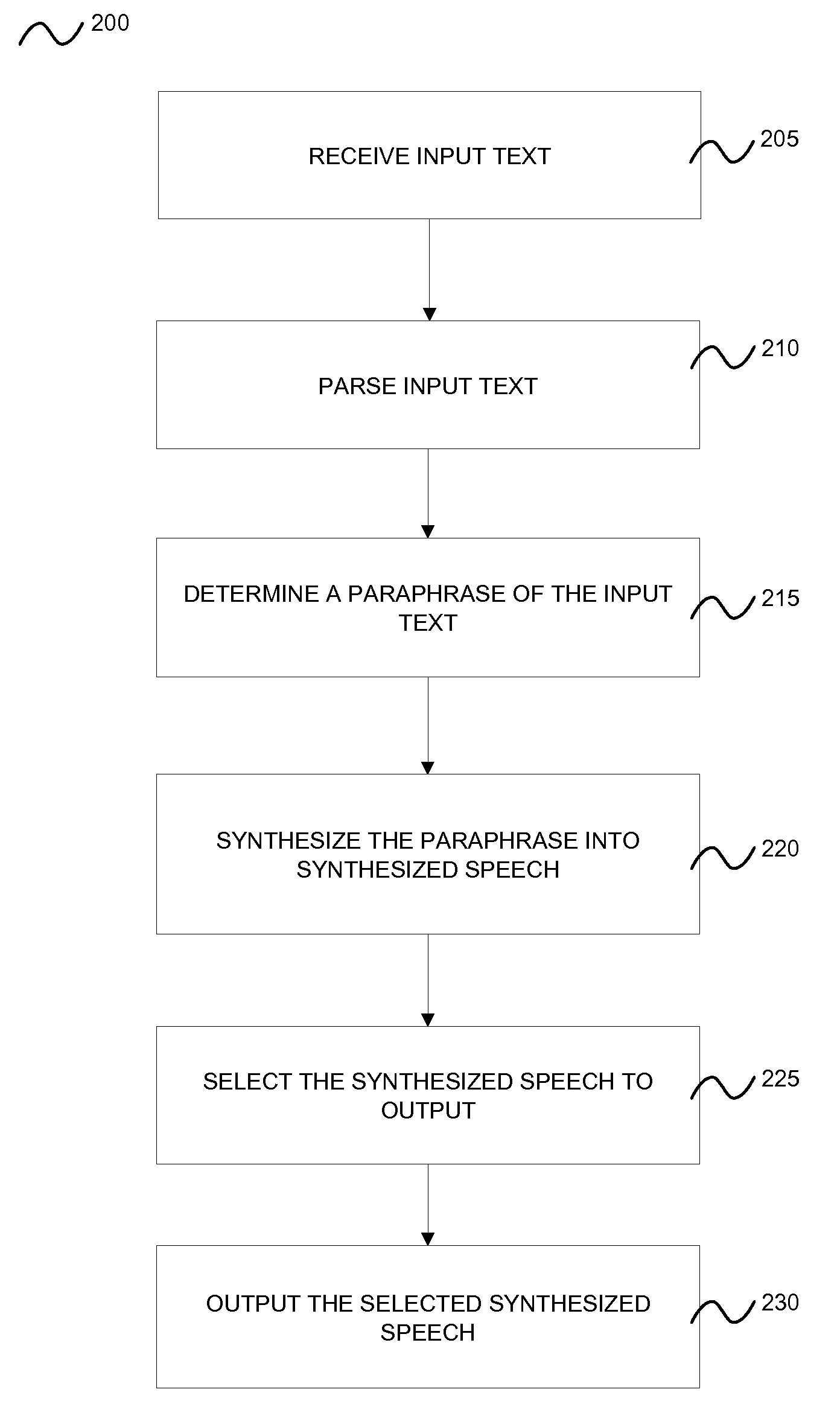
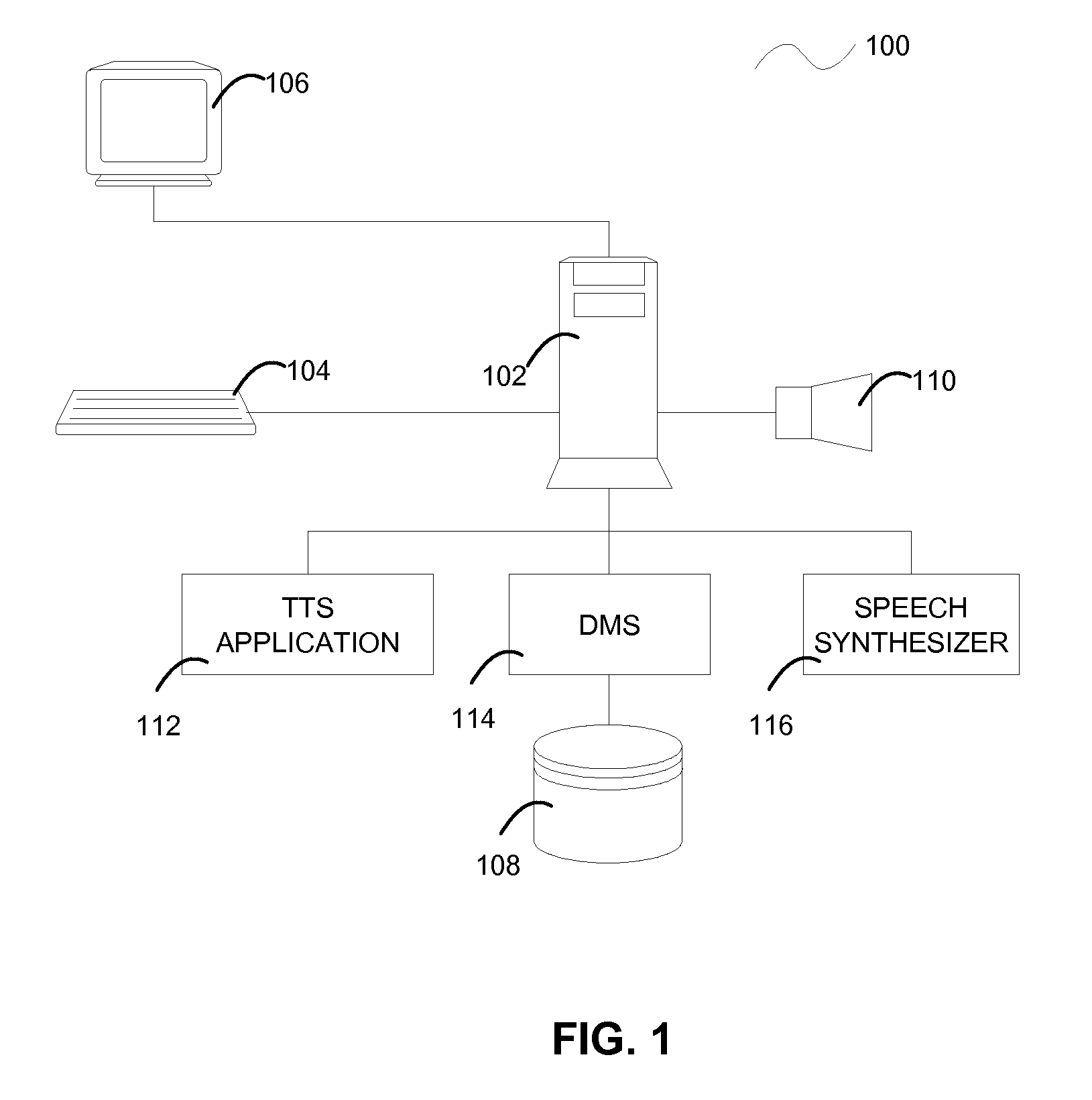
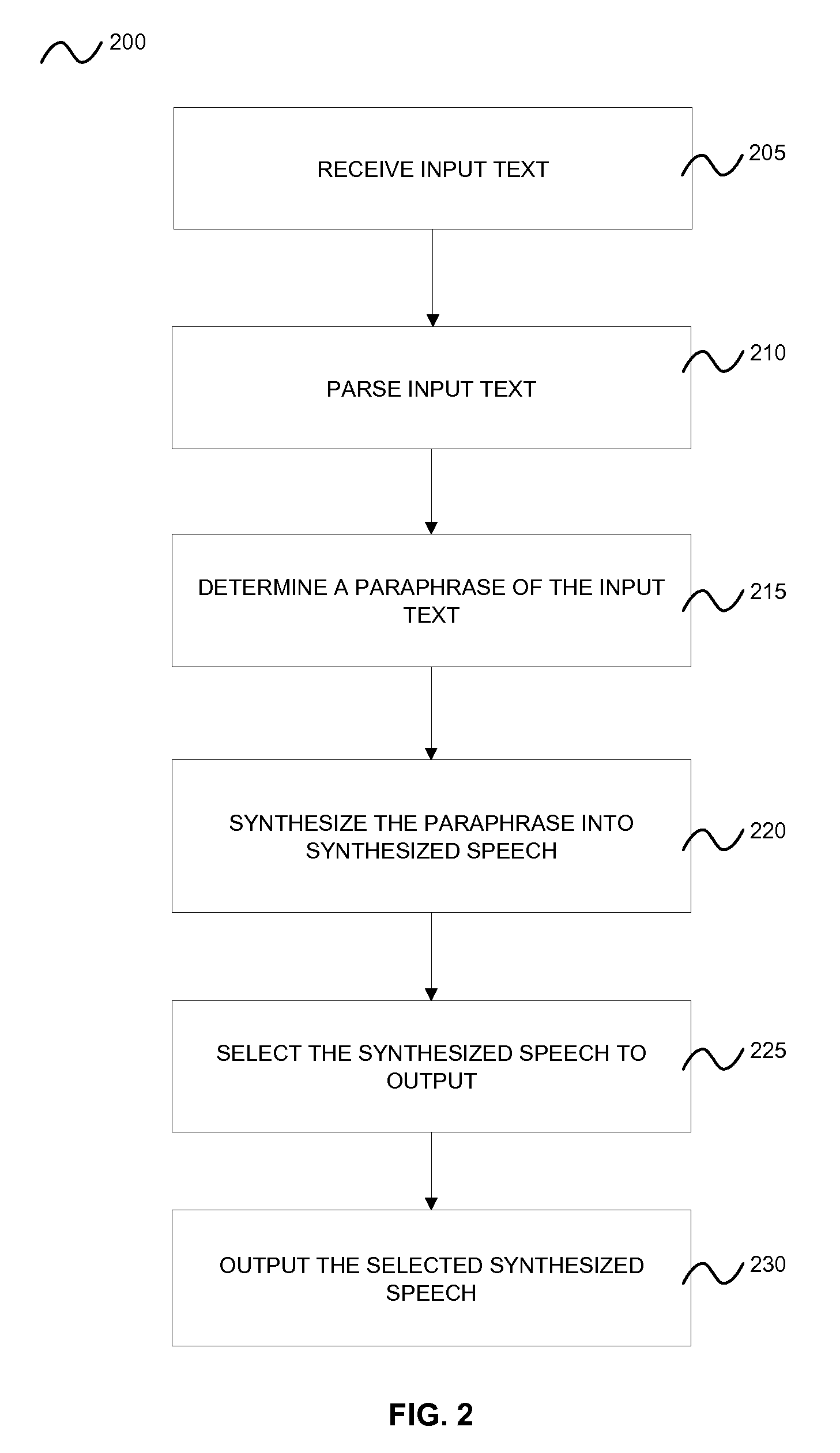
Methods and computer program products for providing paraphrasing in a text-to-speech system
InactiveUS20080167876A1Quality improvementAvoid discontinuitiesSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsParaphraseSpeech sound
A method and computer program product for providing paraphrasing in a text-to-speech (TTS) system is provided. The method includes receiving an input text, parsing the input text, and determining a paraphrase of the input text. The method also includes synthesizing the paraphrase into synthesized speech. The method further includes selecting synthesized speech to output, which includes: assigning a score to each synthesized speech associated with each paraphrase, comparing the score of each synthesized speech associated with each paraphrase, and selecting the top-scoring synthesized speech to output. Furthermore, the method includes outputting the selected synthesized speech.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
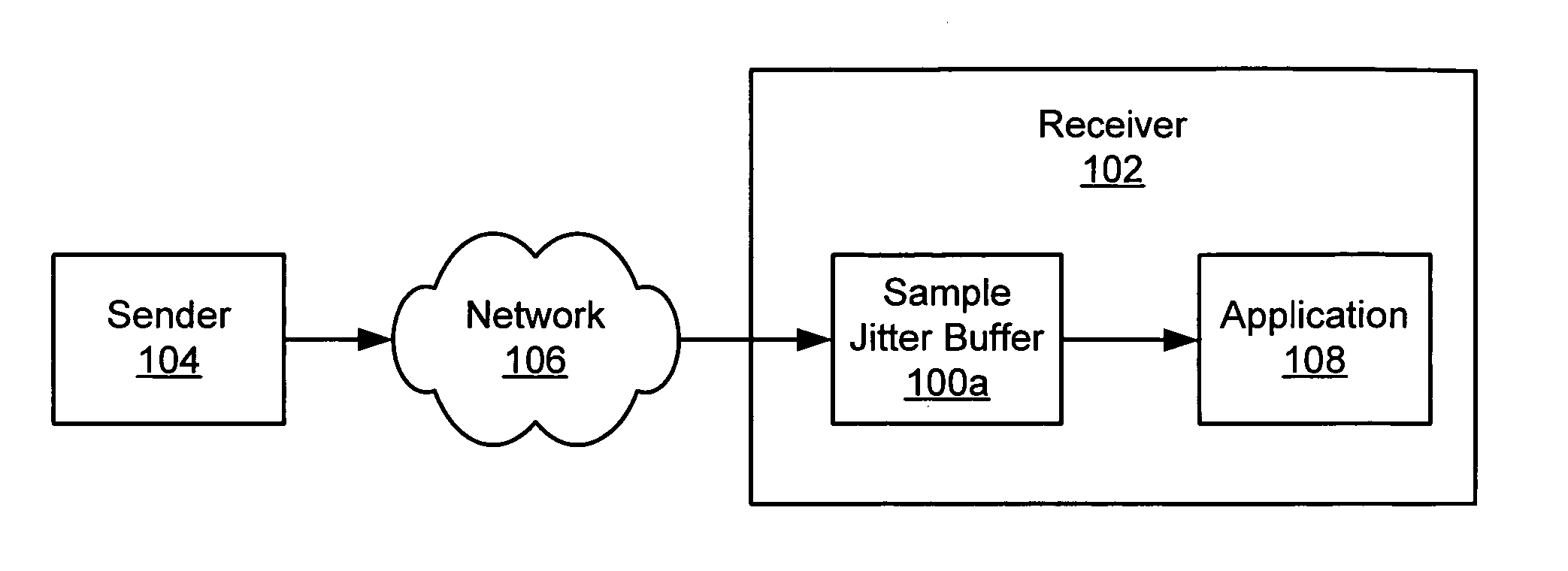
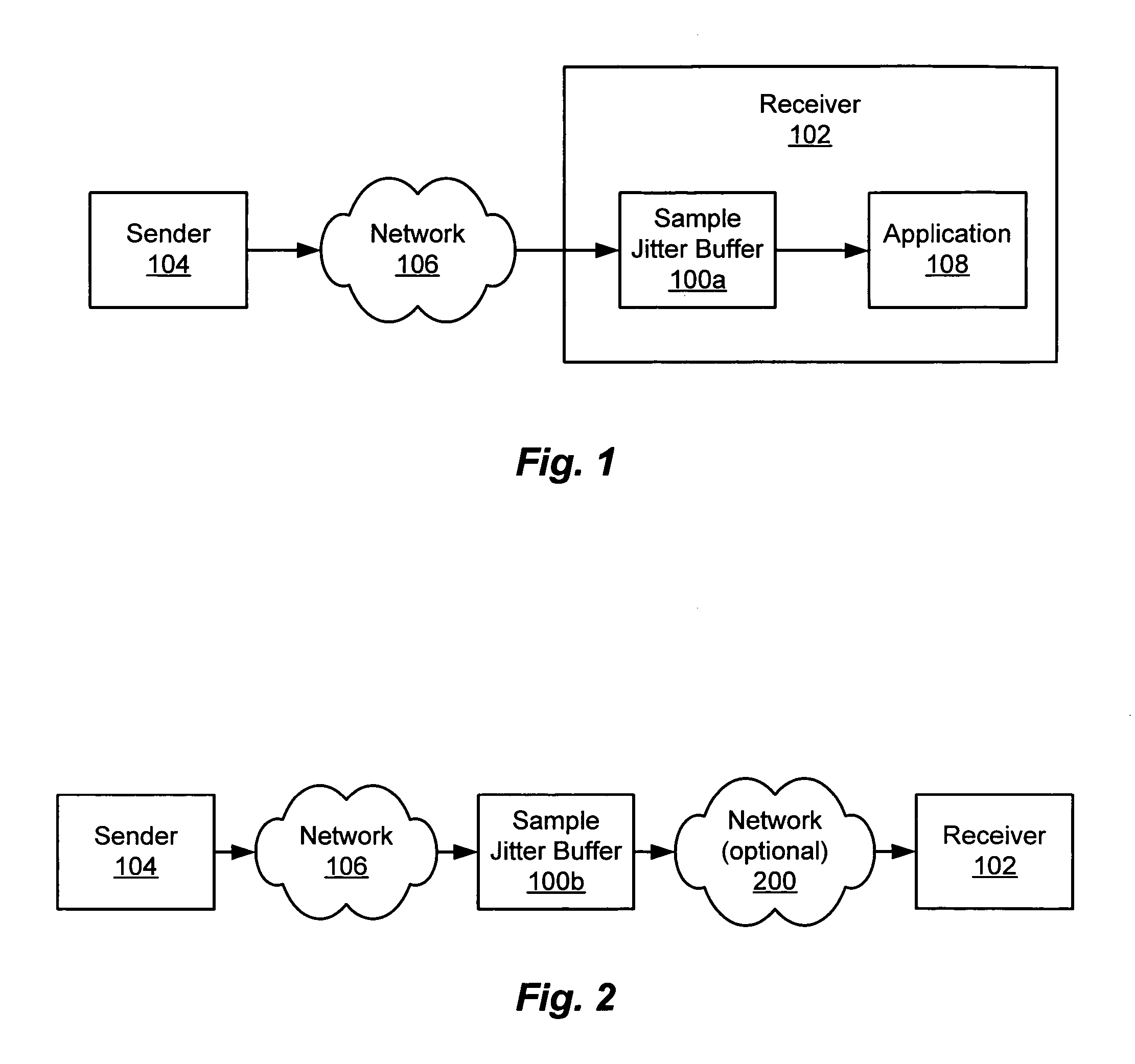
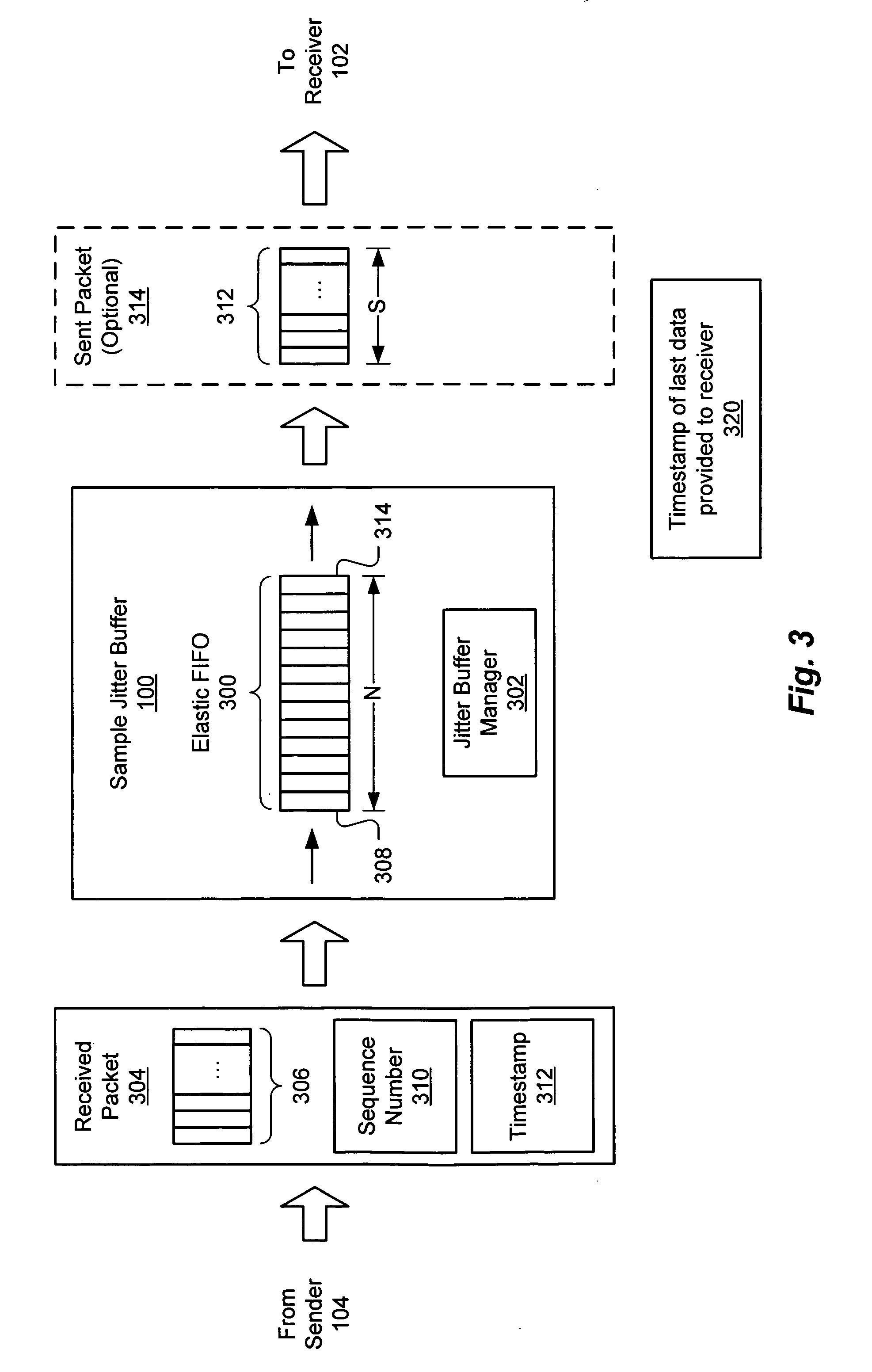
Jitter buffer management
ActiveUS20050207437A1Extension of timeAvoids large discontinuityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationArrival timeSnubber
A sample jitter buffer manager more or less aggressively conserves (rations) or discards data in a jitter buffer, based on the fluctuating amount of data in the jitter buffer. The jitter buffer manager counts, provides, discards and / or otherwise manages individual sample data units, rather than entire packets. Normally, enough data is removed from the jitter buffer to fill a data packet for a receiver. However, if the amount of data in the jitter buffer is low, less data is removed from the jitter buffer and placed into the packet, and the remainder of the packet is filled with duplicates of some of the data in the packet or in the jitter buffer. As the jitter buffer fills beyond a useful level, the jitter buffer discards progressively larger amounts of data, without necessarily discarding one or more entire packets. This fine-grained management of the amount of data in the jitter buffer maintains a buffer size that can provide a steady stream of packets to the receiver, without significantly impacting the fidelity of a signal represented by the data, and it mitigates the impact of fluctuations in packet inter-arrival times.
Owner:DIALOGIC INC +1
Display device and method of fabricating the display device
InactiveUS20060082300A1Form evenlyAvoid discontinuitiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceCathode
In an EL element having an anode, an insulating film (bump) formed on the anode, and an EL film and a cathode formed on the insulating film, each of a bottom end portion and a top end portion of the insulating film is formed so as to have a curved surface. The taper angle of a central portion of the insulating film is set within the range from 35° to 70°, thereby preventing the gradient of the film forming surface on which the EL film and the cathode are to be formed from being abruptly changed. On the thus-formed film forming surface, the EL film and the cathode can be formed so as to be uniform in thickness, so that occurrence of discontinuity in each of EL film and the cathode is prevented.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
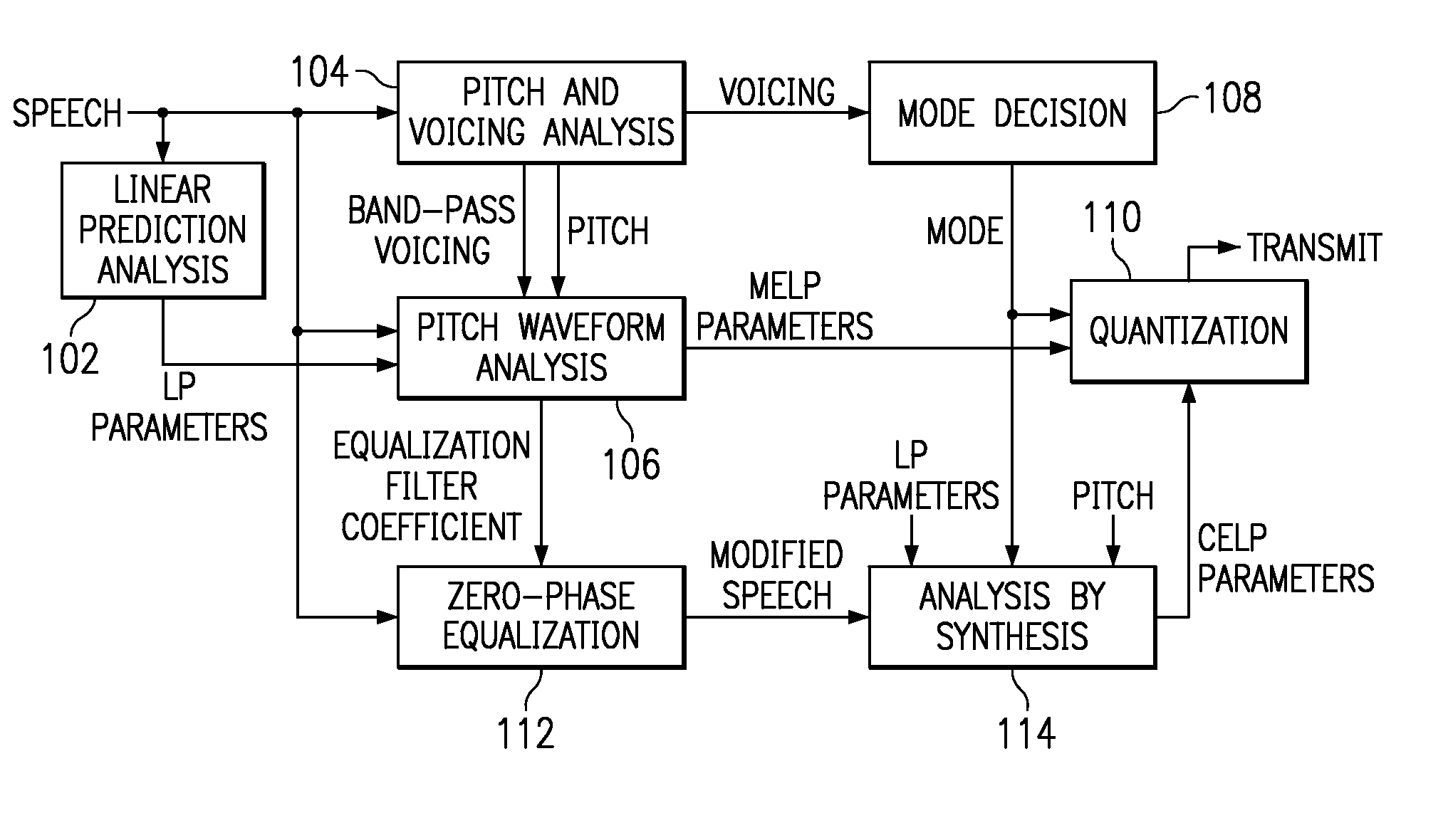
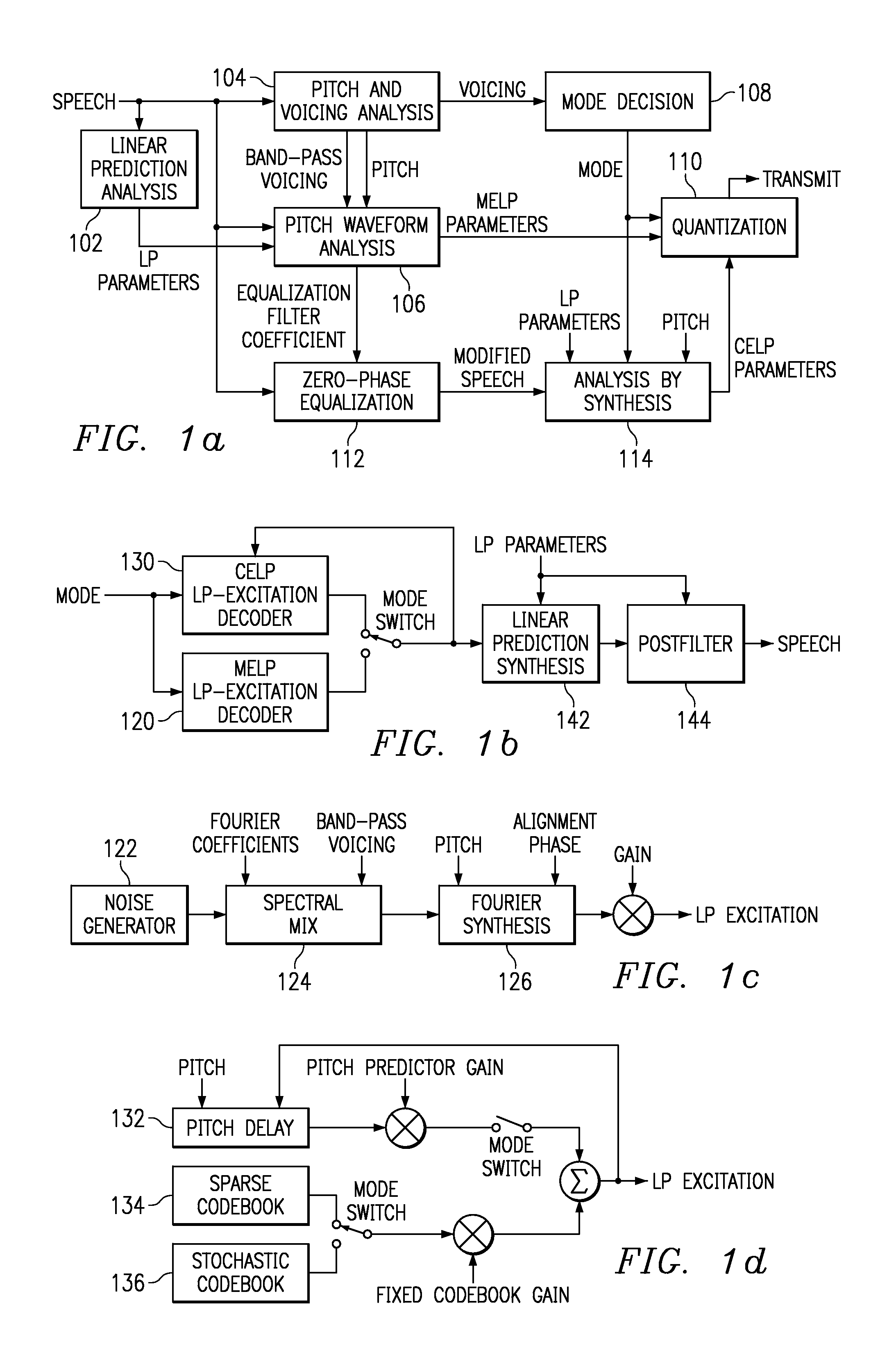
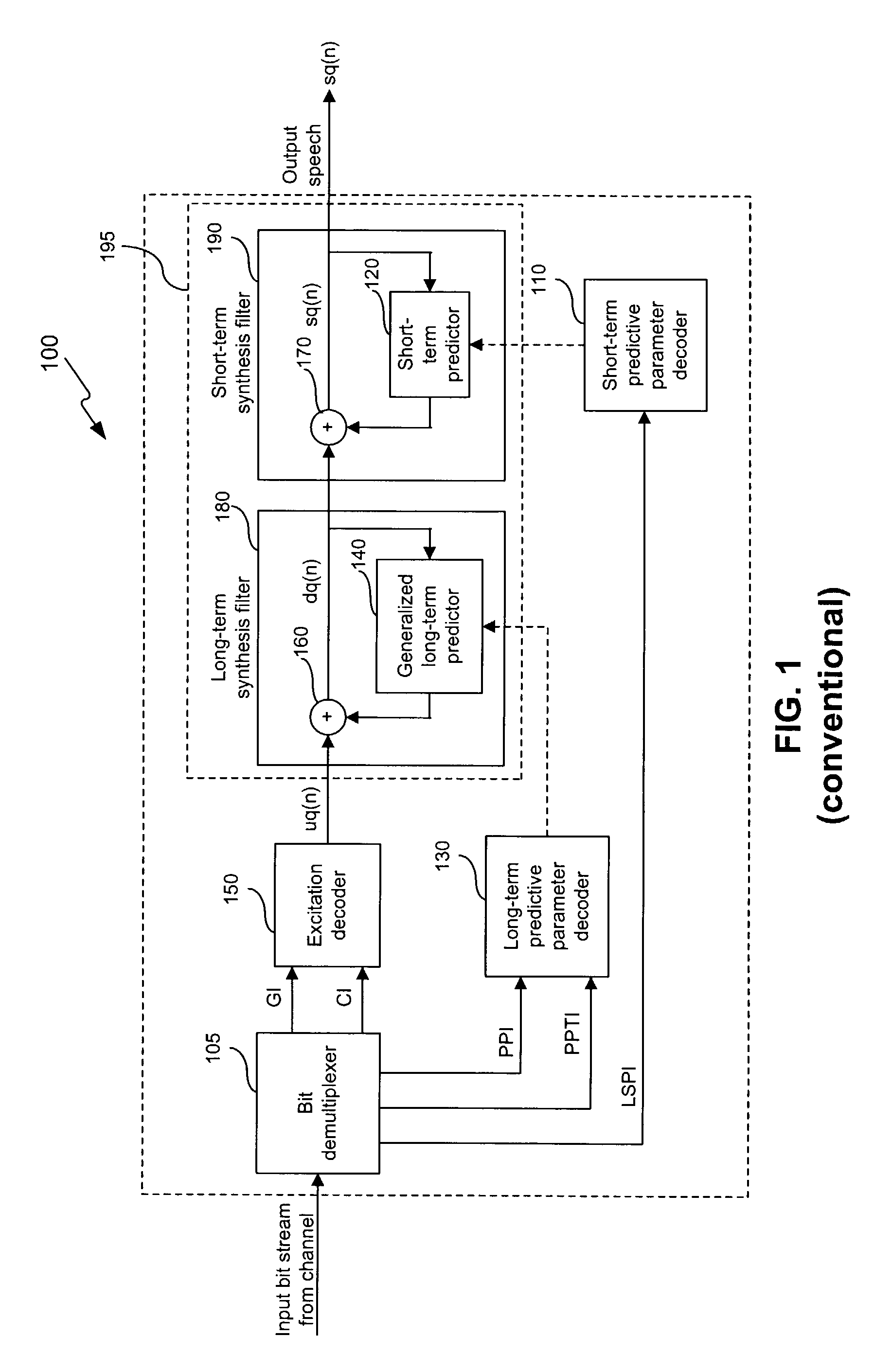
Hybrid speech coding and system
InactiveUS7222070B1Improve performanceEnhance the waveform coderSpeech analysisWaveform codingZero phase
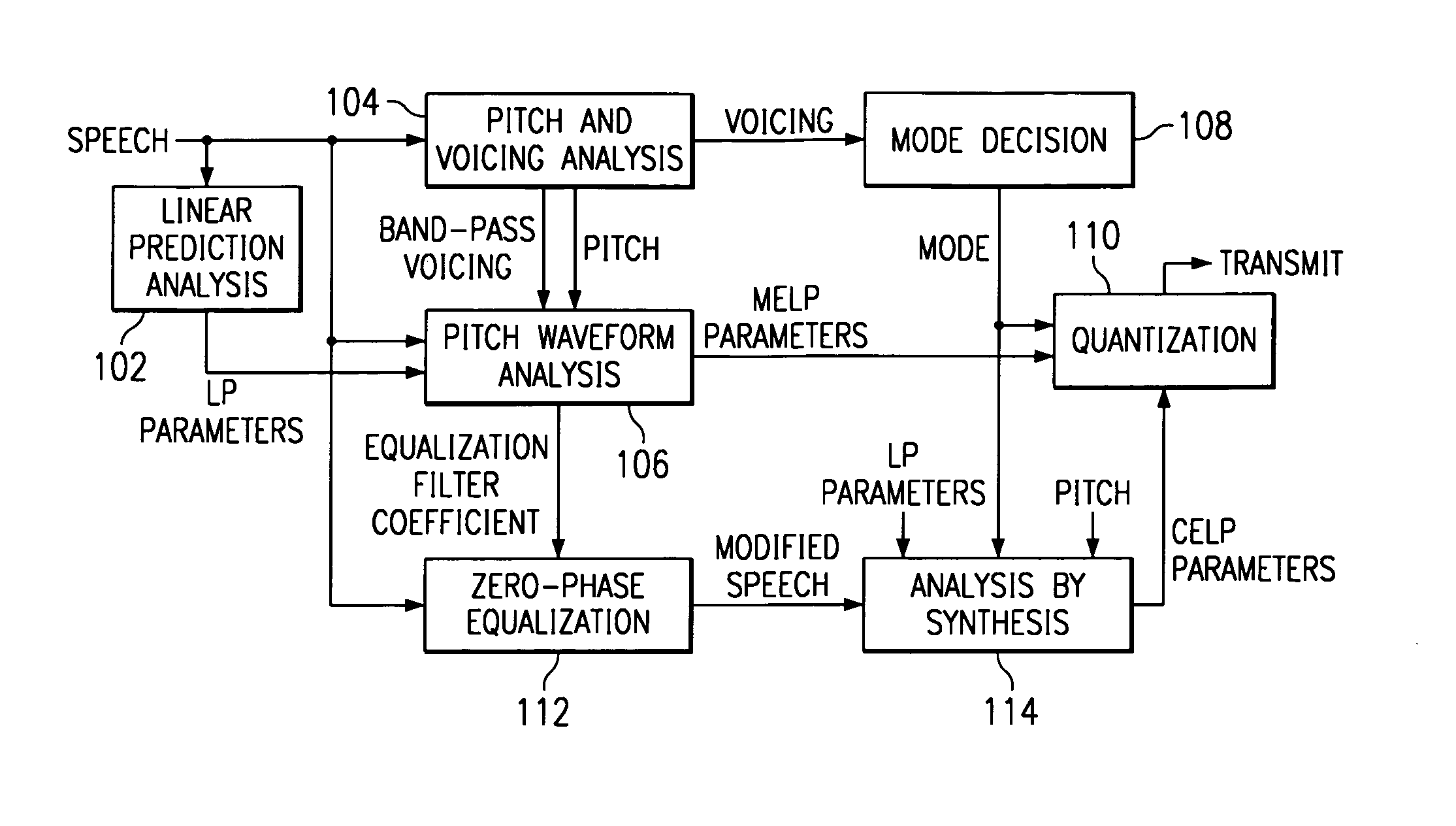
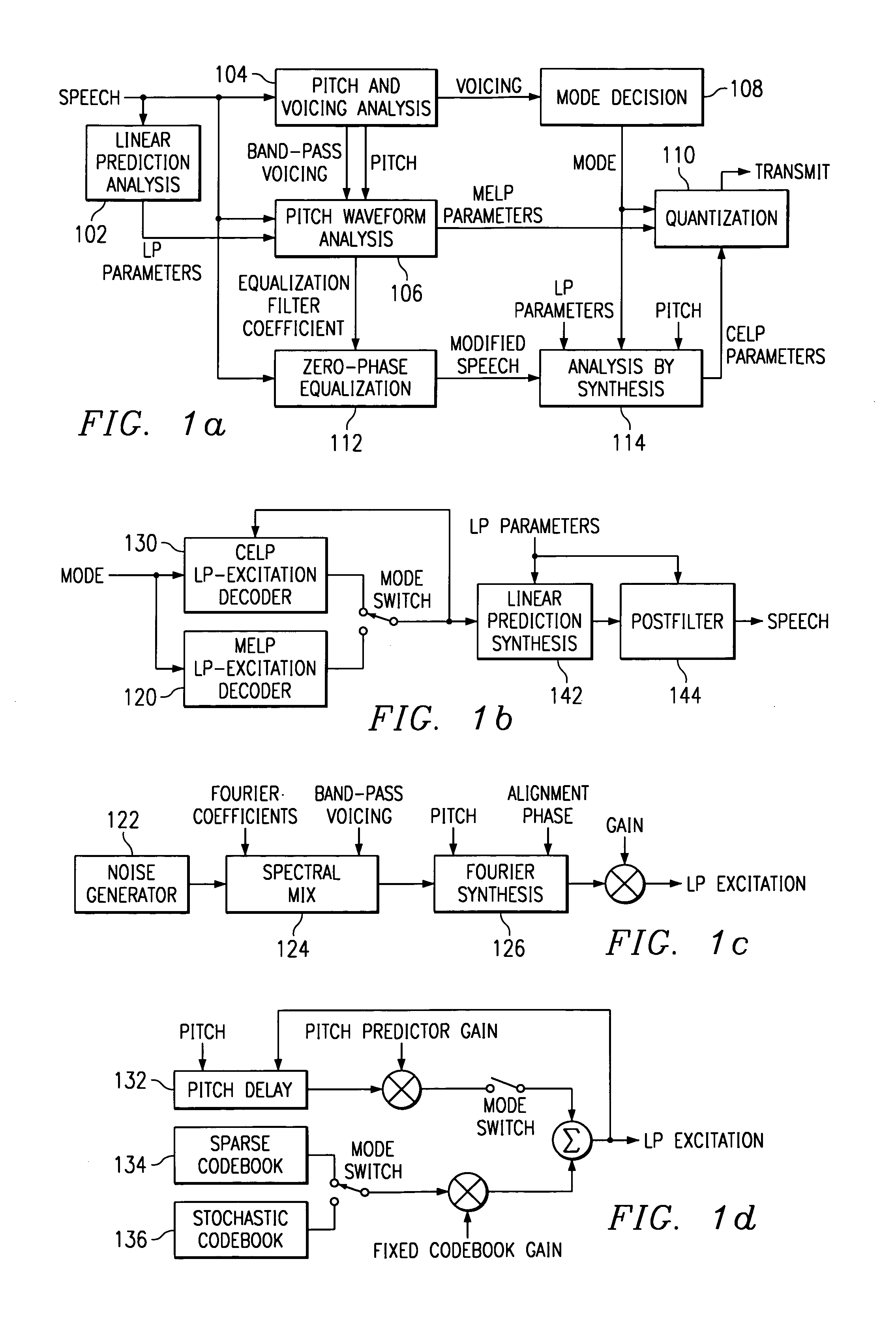
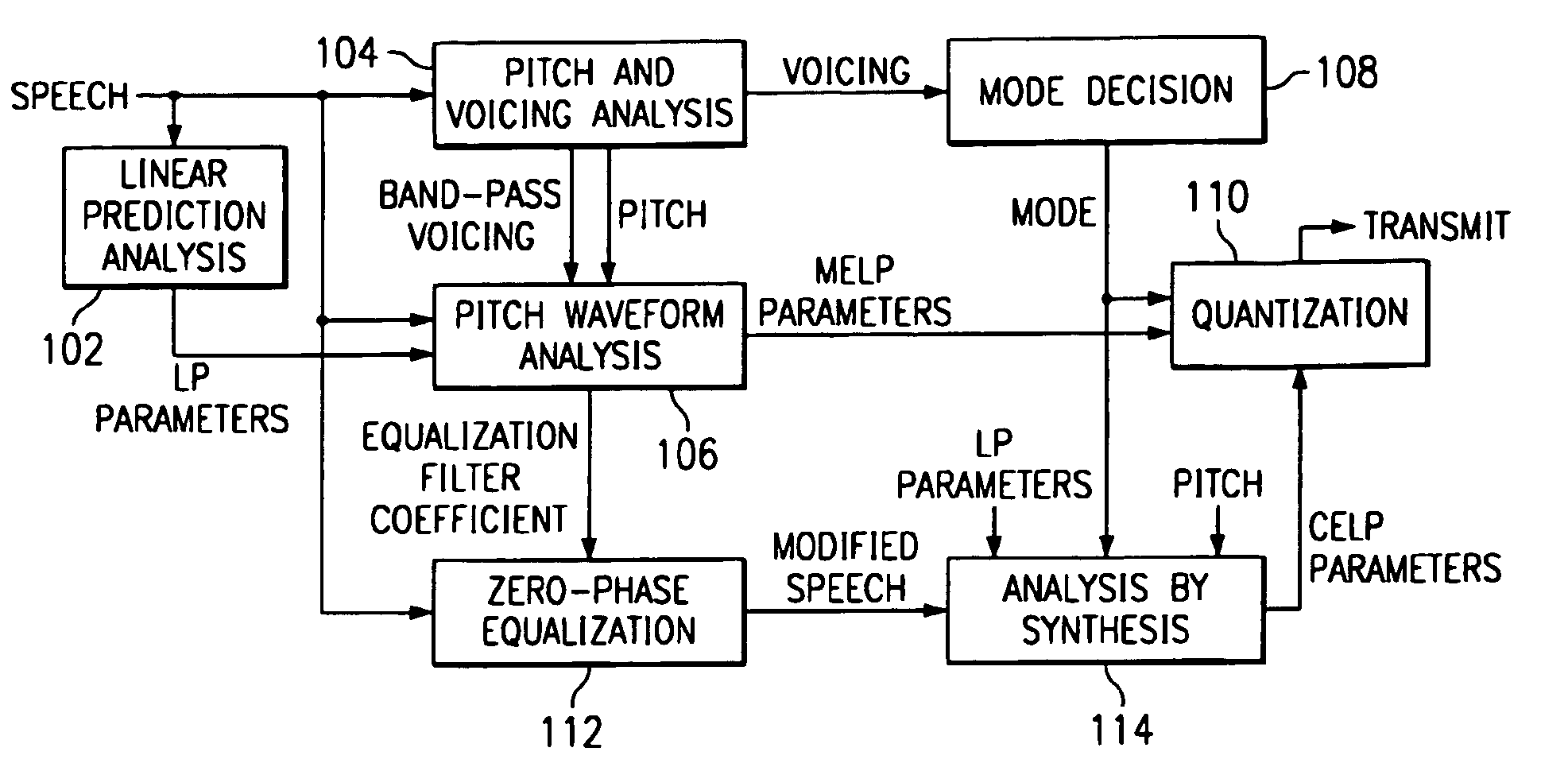
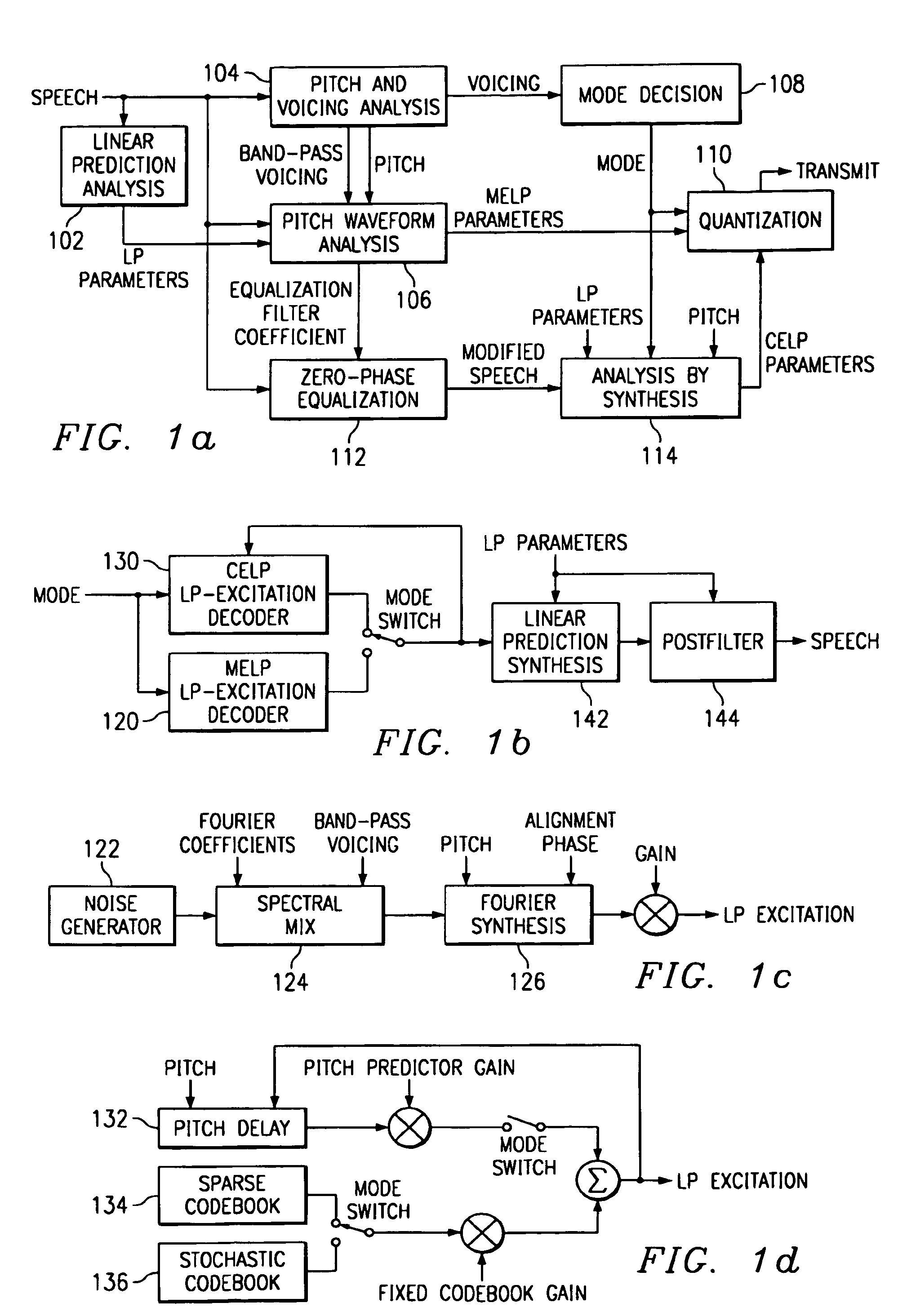
Linear predictive speech coding system with classification of frames and a hybrid coder using both waveform coding and parametric coding for different classes of frames. Phase alignment for a parametric coder aligns synthesized speech frames with adjacent waveform coder synthesized frames. Zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Generation of voice messages
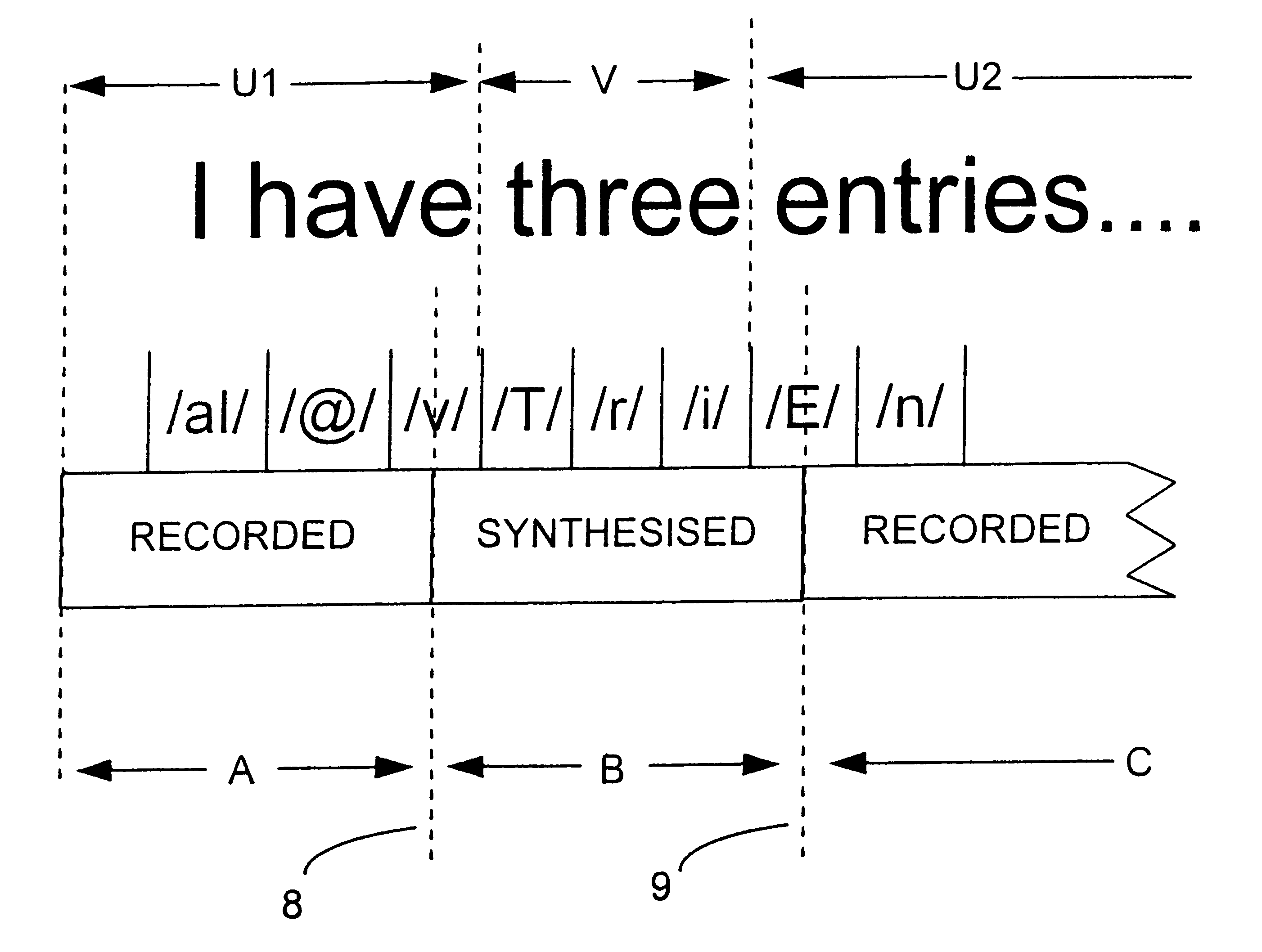
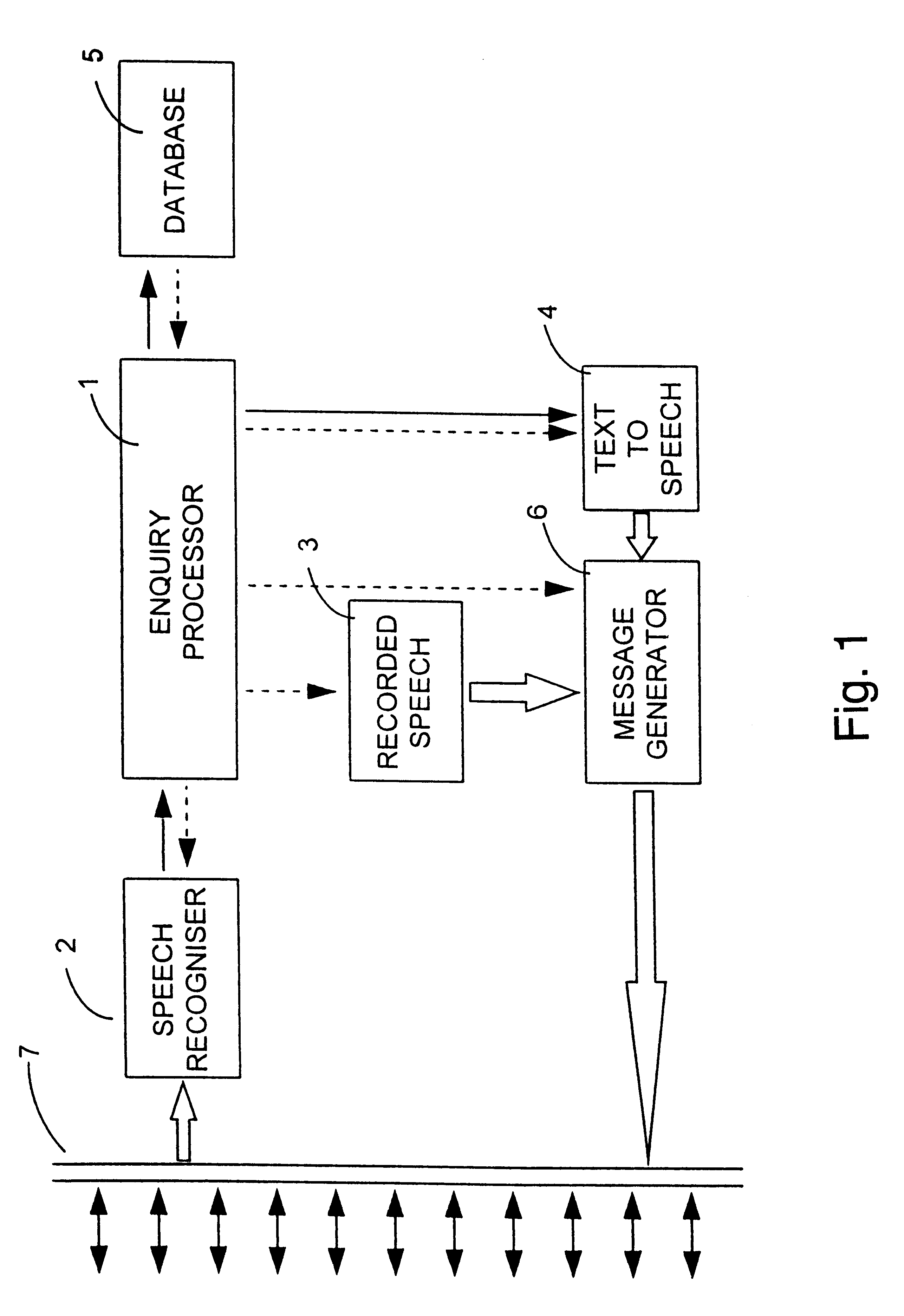
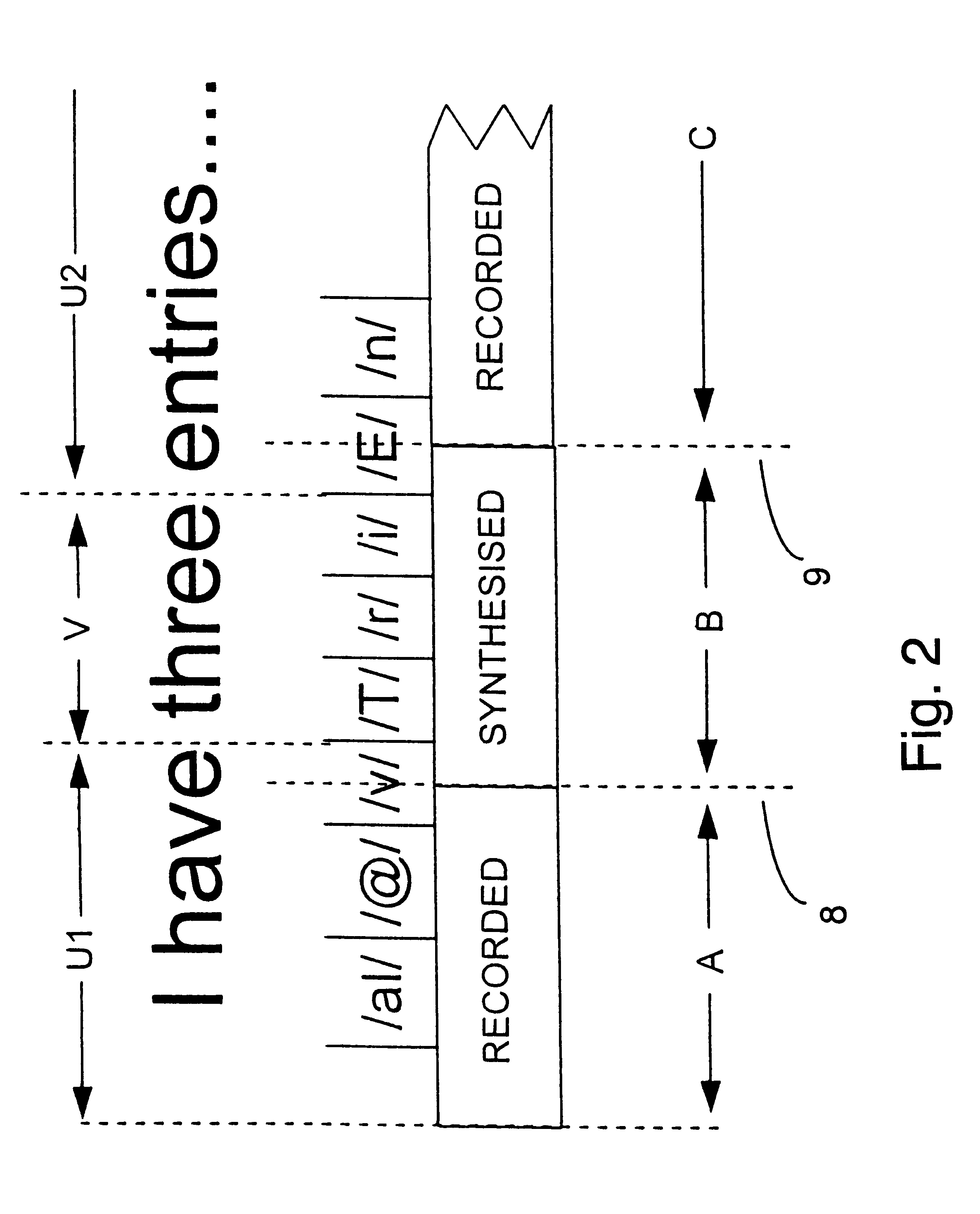
InactiveUS6175821B1Avoid discontinuitiesLow costSpecial service for subscribersSpeech synthesisWave shapeSpeech sound
A voice message is generated having an invariable portion and a variable portion. Most of the invariable portion is provided in the form of recorded speech whereas the variable portion is provided in the form of synthesized speech. The synthesized speech also extends by half a phoneme into the invariable portion of the message. The synthesized speech and the recorded speech are then concatenated, with a transition signal being formed on the basis of a boundary portion of each of the recorded and synthesized signals about any join. In forming the transition signal, a set of transition signal pitchmarks is created and an overlap-add technique is used to copy the waveform within the boundary portions of the speech signals around the transition signal pitchmarks. The signal around the penultimate pitchmark in the leading boundary portion is copied to the trailing half of the transition signal and the signal around the second pitchmark in the trailing boundary portion is copied to the leading half of the transition signal. In this way, the characteristics of the generated message around the join change gradually between the characteristics of the recorded speech and the characteristics of the synthesized speech.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Frame erasure concealment for predictive speech coding based on extrapolation of speech waveform
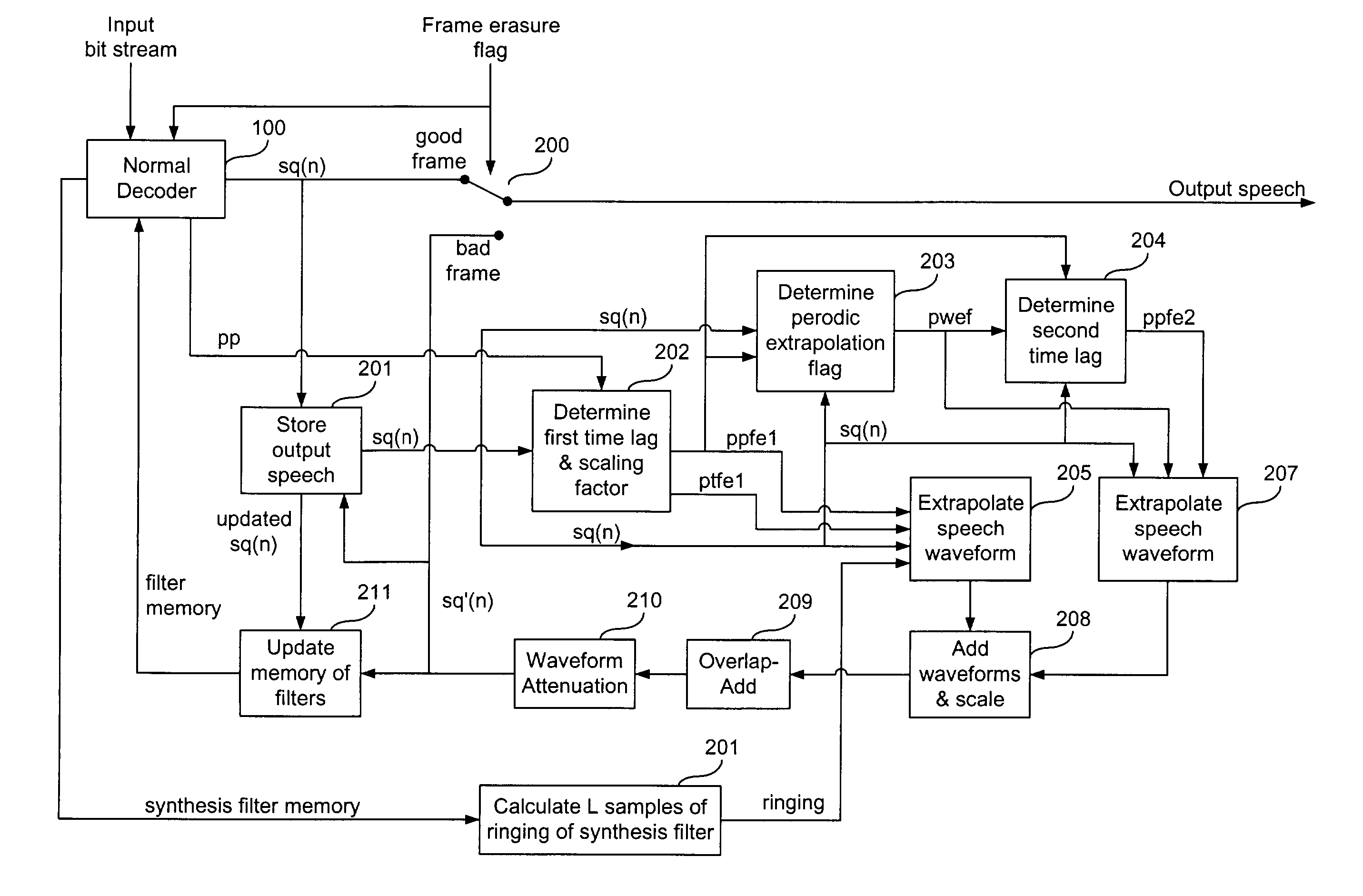
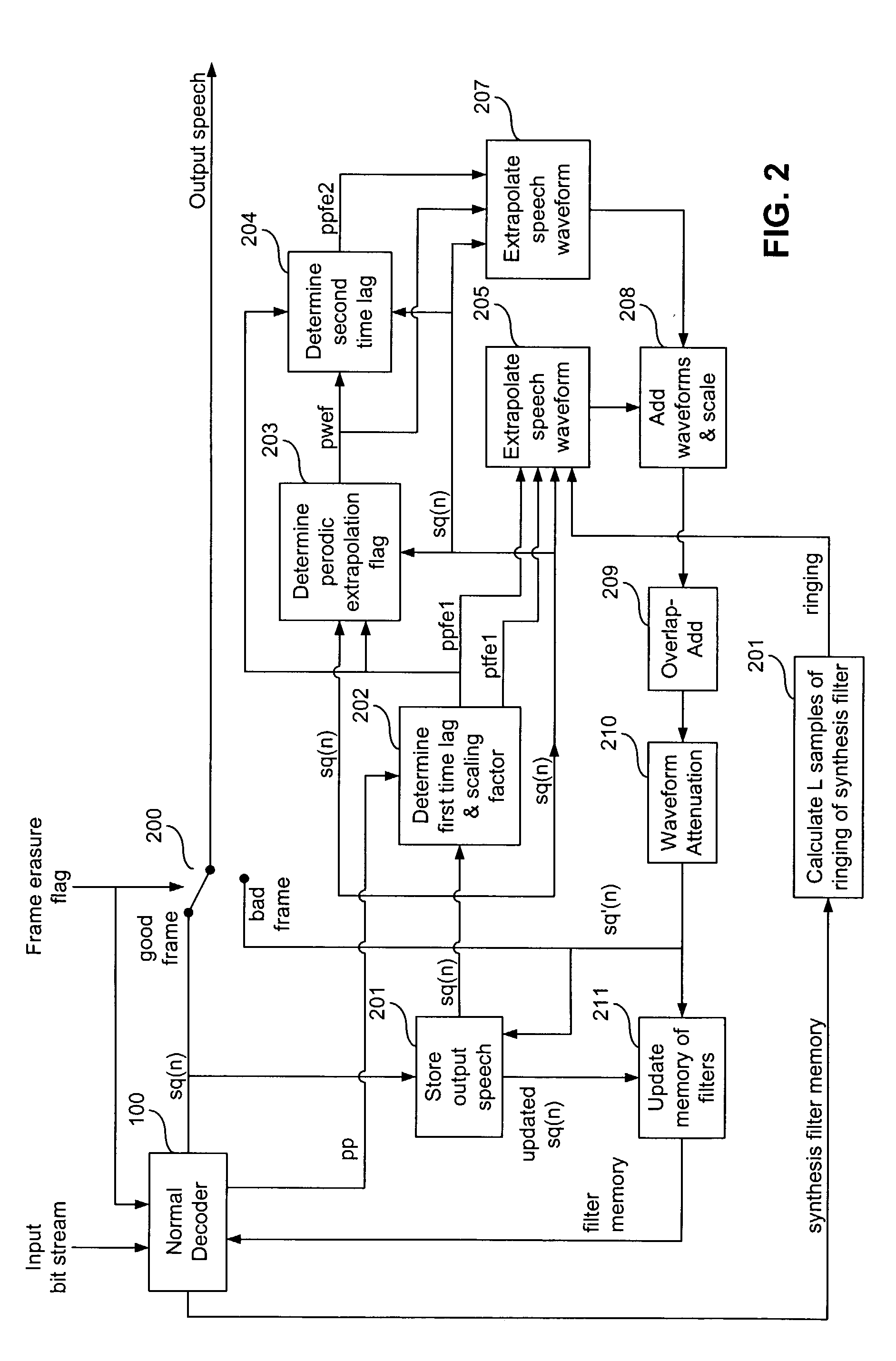
InactiveUS20030078769A1Avoid discontinuitiesEliminate the problemSpeech analysisFrame basedSpeech code
A method and system are provided for synthesizing a number of corrupted frames output from a decoder including one or more predictive filters. The corrupted frames are representative of one segment of a decoded signal (sq(n)) output from the decoder. The method comprises determining a first preliminary time lag (ppfe1) based upon examining a predetermined number (K) of samples of another segment of the decoded signal and determining a scaling factor (ptfe) associated with the examined number (K) of samples when the first preliminary time lag (ppfe1) is determined. The method also comprises extrapolating one or more replacement frames based upon the first preliminary time lag (ppfe1) and the scaling factor (ptfe).
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Fully integrated low noise multi-loop synthesizer with fine frequency resolution for HDD read channel and RF wireless local oscillator applications
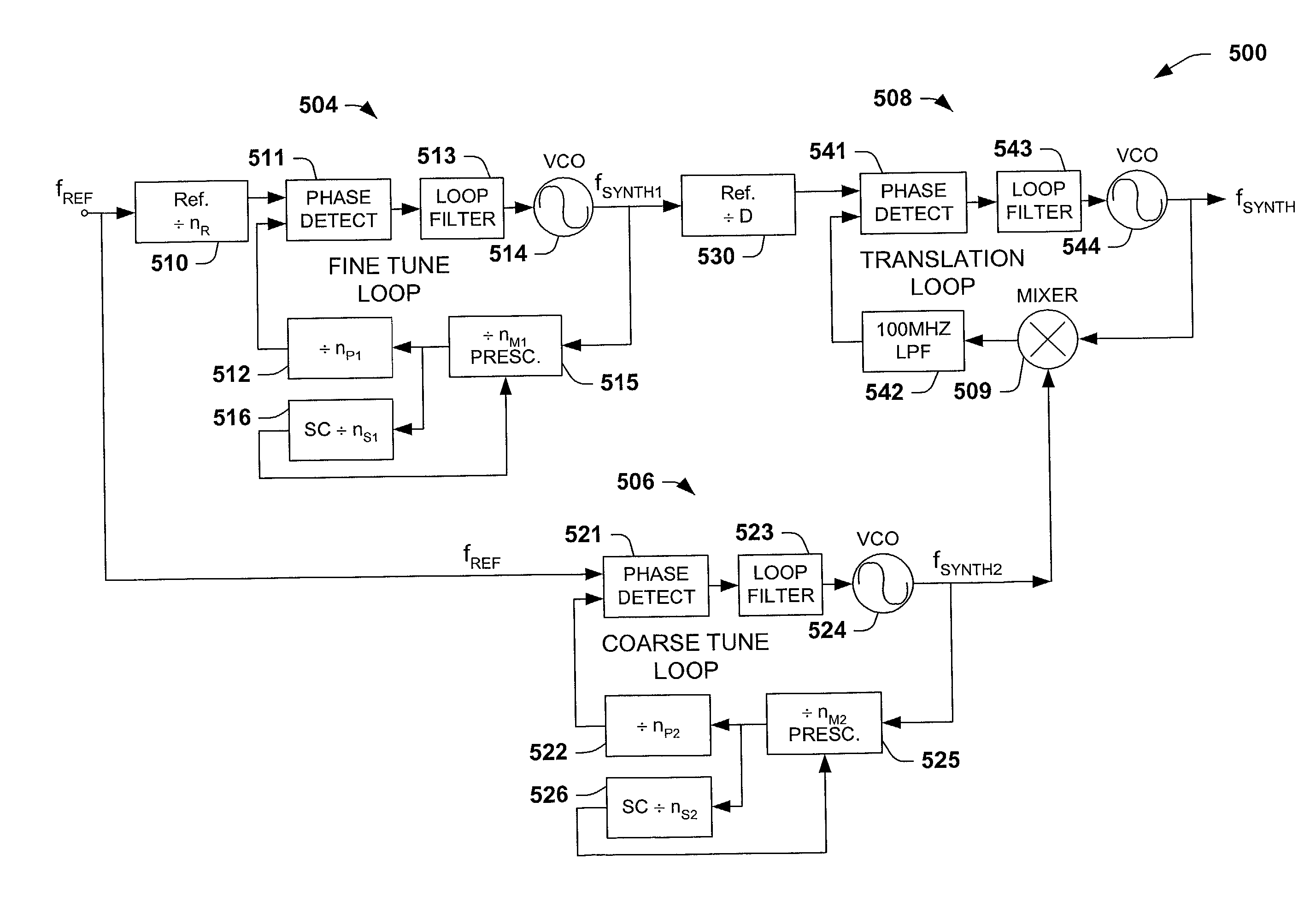
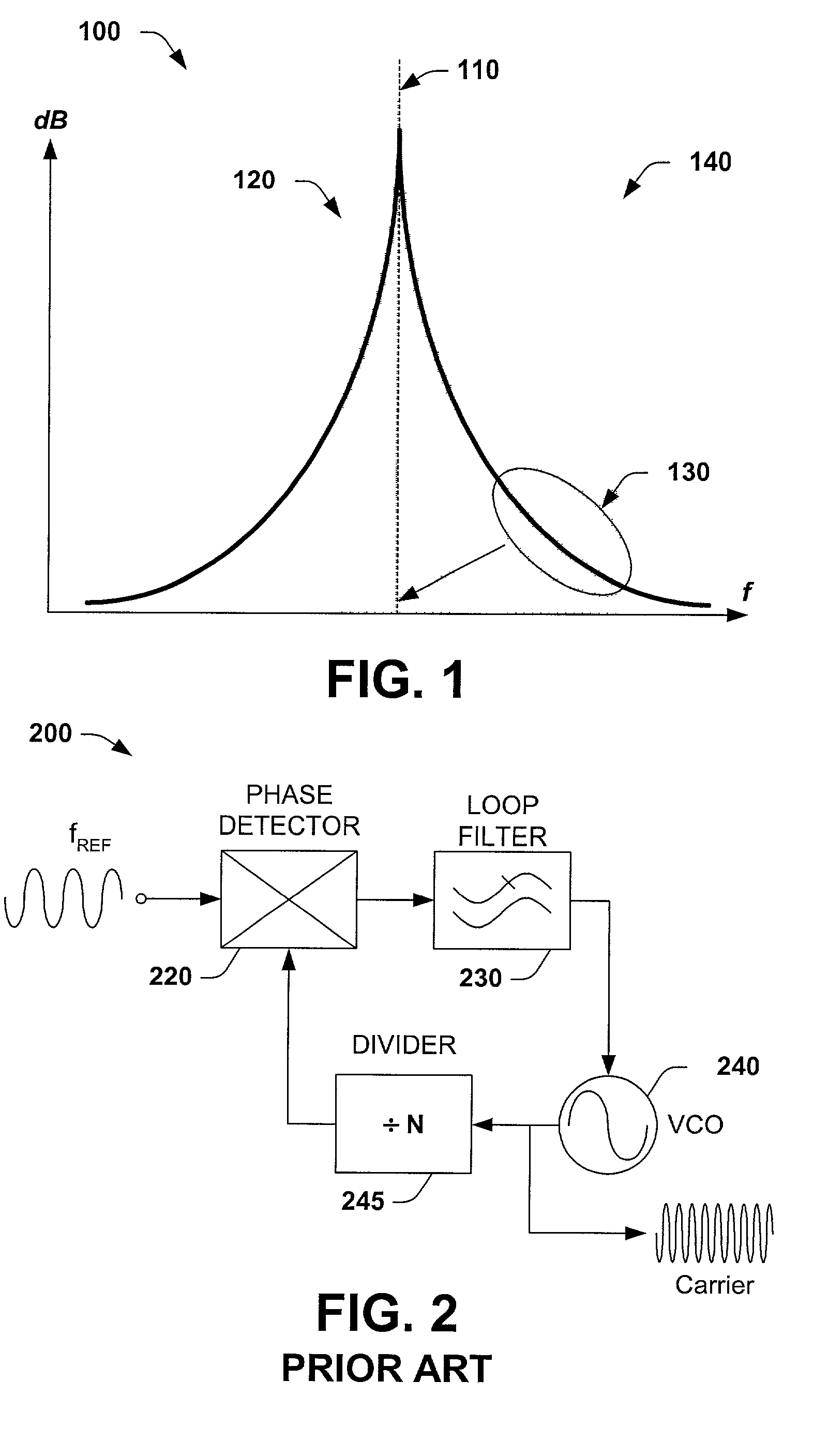
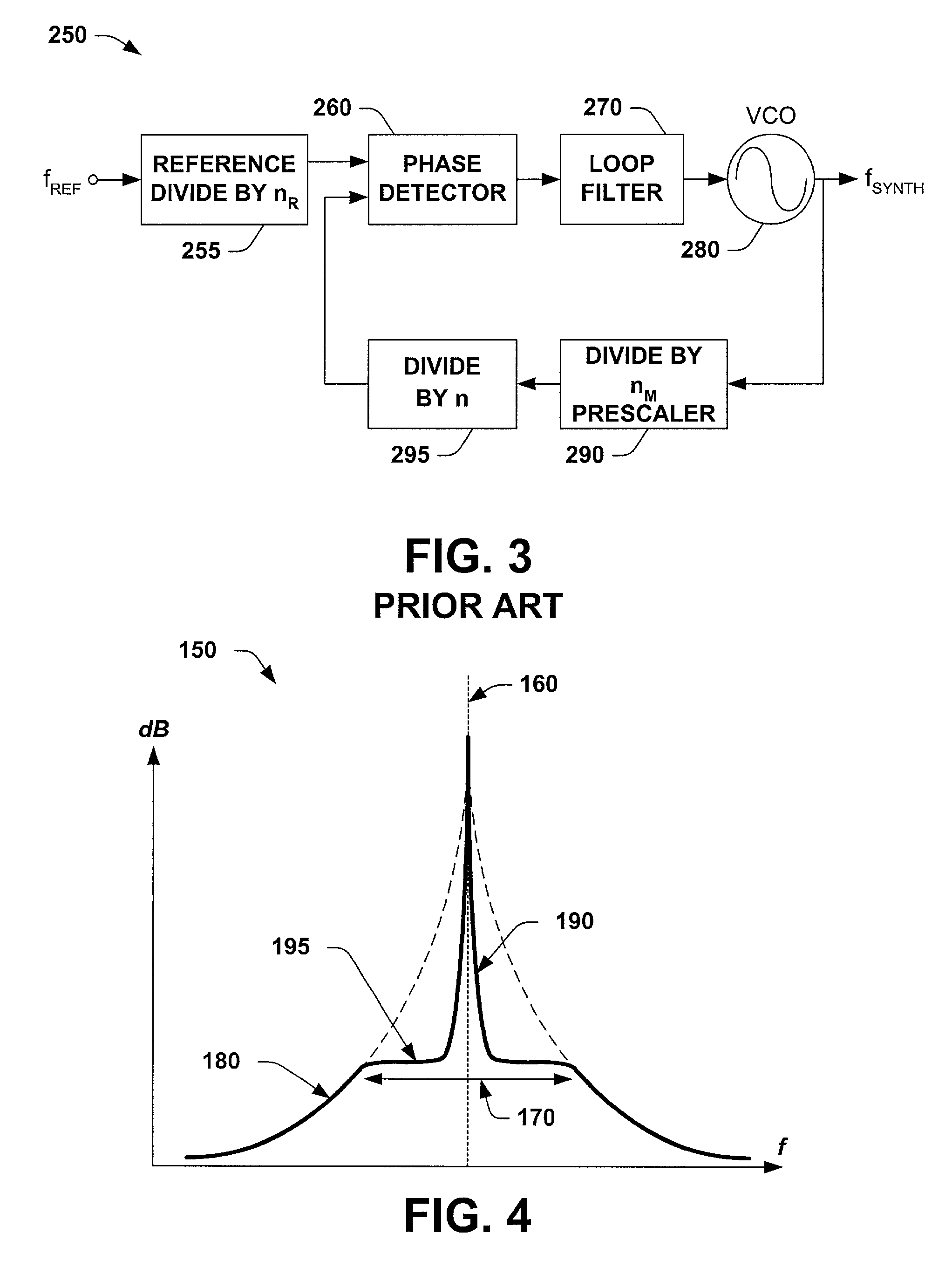
InactiveUS20030119466A1Avoid discontinuitiesLower performance requirementsPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionLow noiseHard disc drive
A low noise multi-loop radio frequency synthesizer is disclosed for the read channel in a hard disk drive, and for RF wireless communications local oscillator applications. The frequency synthesizer receives an input reference signal having a frequency fR, into a fine tune phase locked loop and into a coarse tune phase locked loop. Driven by the input reference signal, the fine tune PLL outputs a fine tune signal with a frequency fR.P, where P is an integer, while the coarse tune PLL, also driven by the same input reference signal, outputs a coarse tune signal with a frequency fR.A, where A is an integer. A translation phase locked loop has a unity multiplication factor and is driven by the fine tune signal output. The frequency synthesizer finally has a Gilbert cell double balanced mixer coupled between the coarse tune and the translation phase locked loops, wherein the Gilbert cell mixer combines the coarse tune signal and the output signal of the translation phase locked loop and couples the mixed signal into the translation phase locked loop. The translation loop outputs a signal with a frequency which is proportional to the linear sum of the coarse tune signal and the fine tune signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Wearable image display device
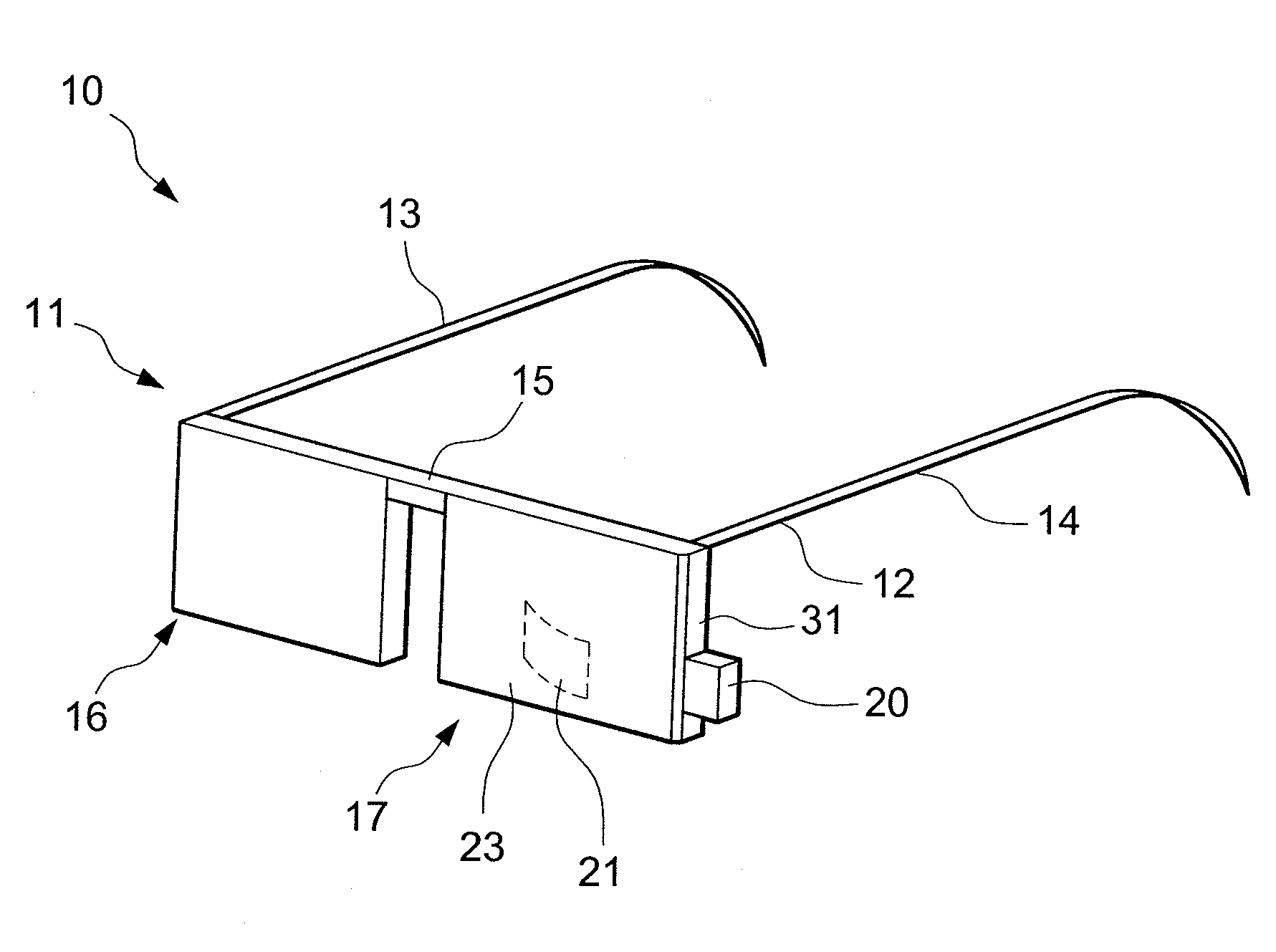
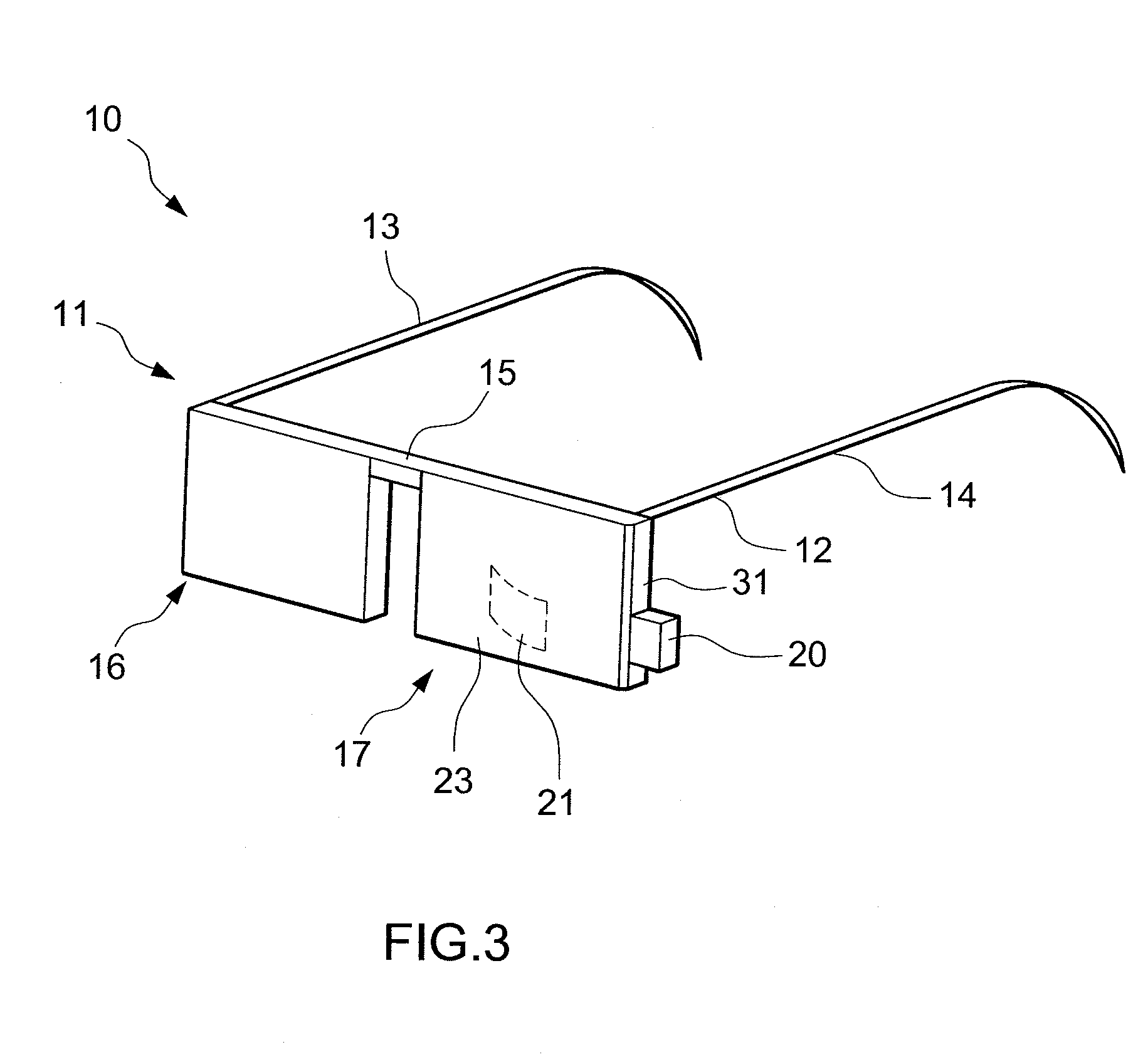
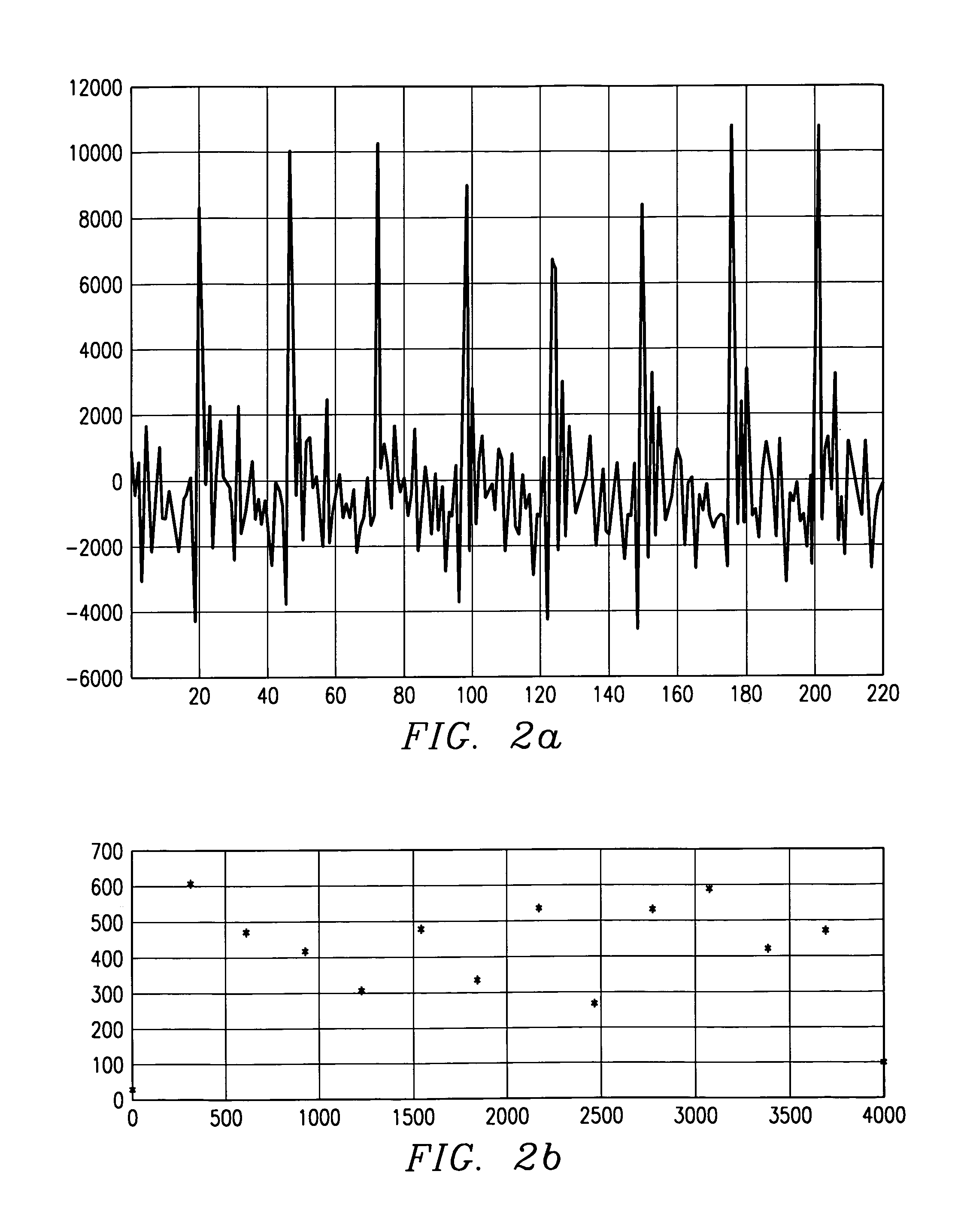
InactiveUS20100033830A1Efficient and effective useAvoid discontinuitiesLensDisplay deviceOptical surface
A wearable image display device for superimposing a virtual image into the wearer's field of vision includes a lens, for spectacles or the like, which includes inner and outer lens portions bonded together at complementary boundary surfaces of the lens portions. One of two opposing optical surfaces of the lens is located on each lens portion. Each boundary surface is disposed between the optical surfaces of the inner and outer lens portions to avoid discontinuities on the optical surfaces. A partially transmissive reflector is located on one of the boundary surfaces and a microdisplay radiates light internally through the lens between the optical surfaces of the inner and outer lens portions to strike the partially transmissive reflector and reflect the light out of the lens to a user's eye.
Owner:YUNG MAN FAT
Multi-primary conversion
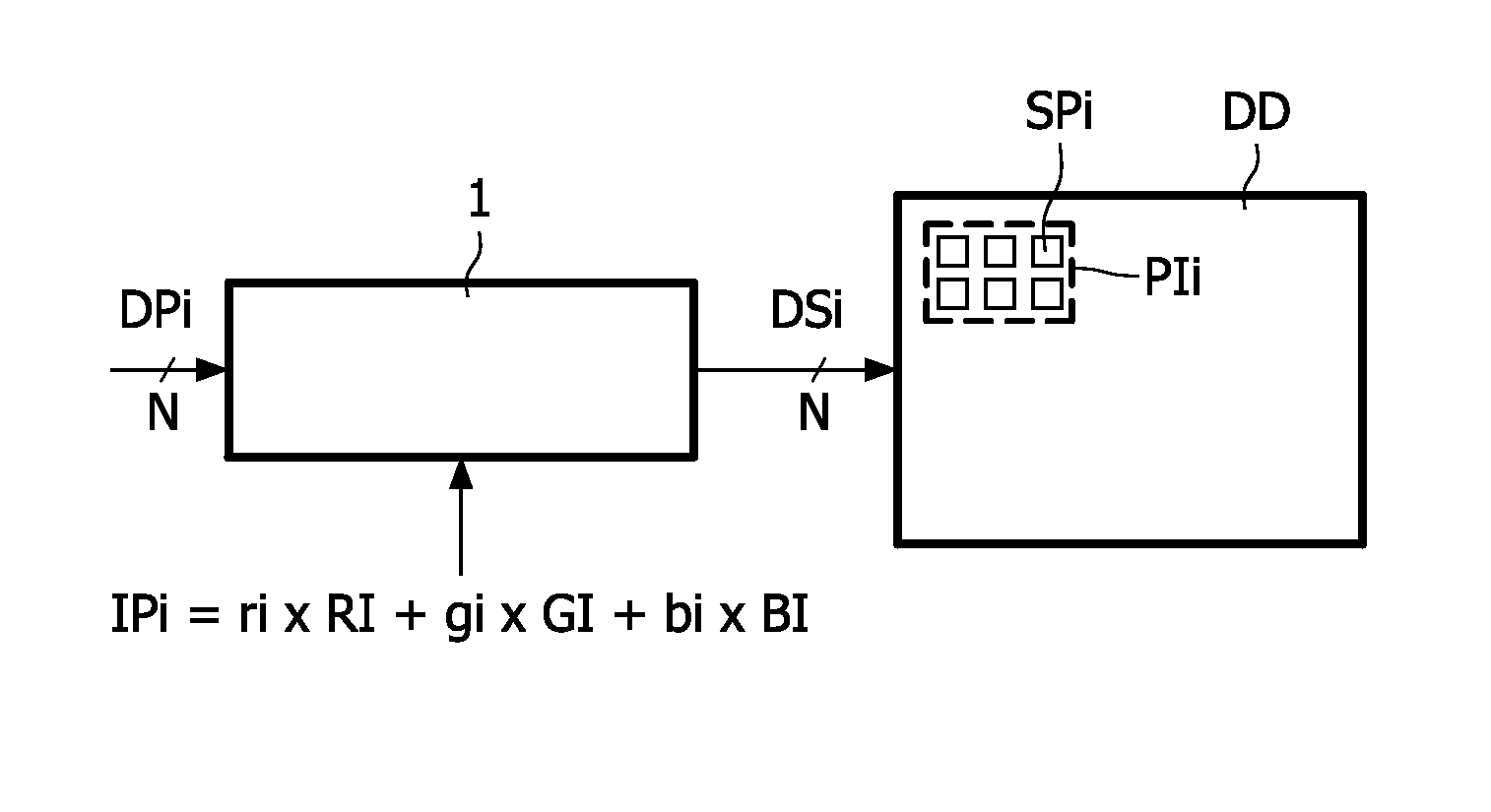
InactiveUS8237751B2Efficient executionAvoid discontinuitiesColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceComputer science
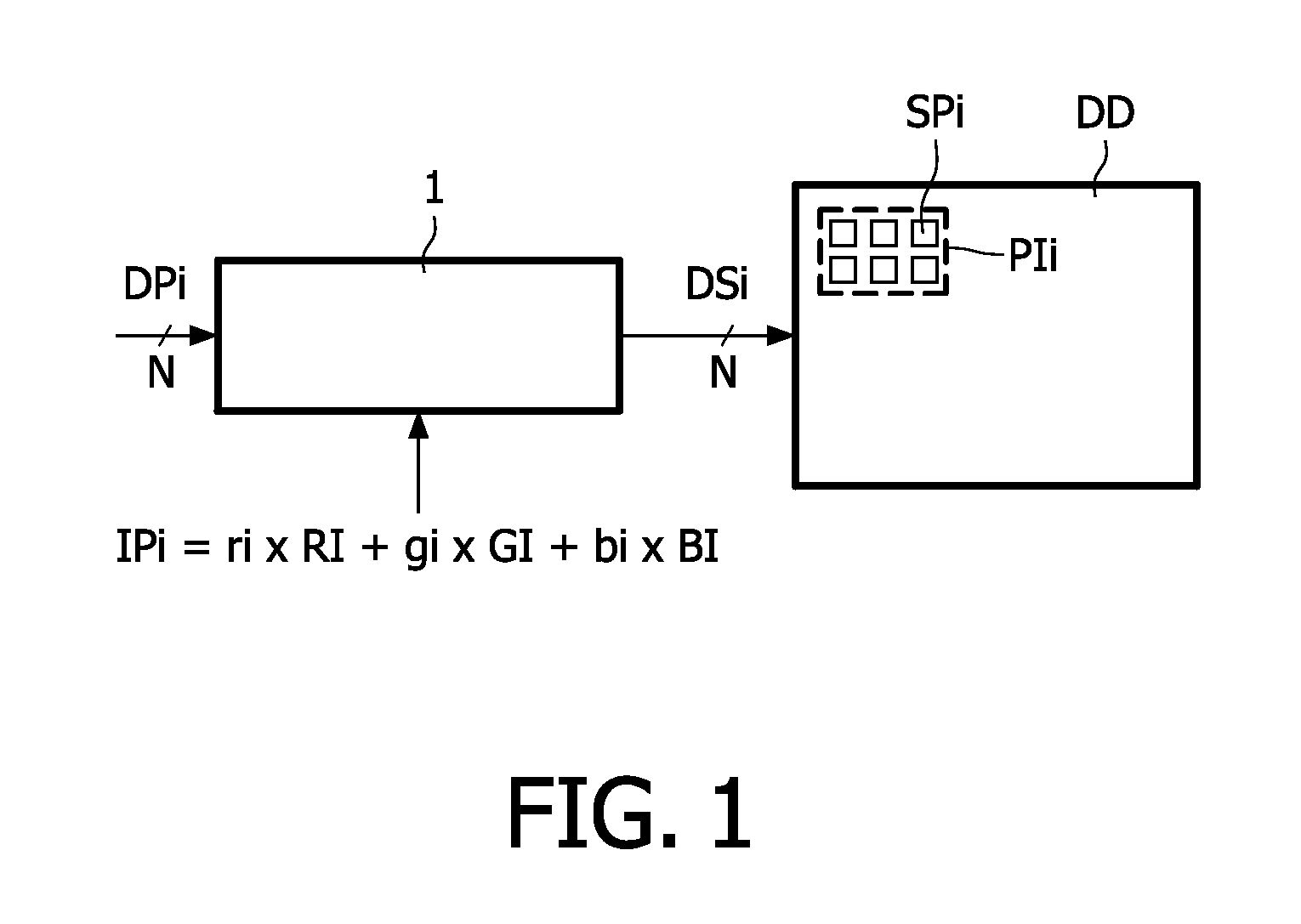
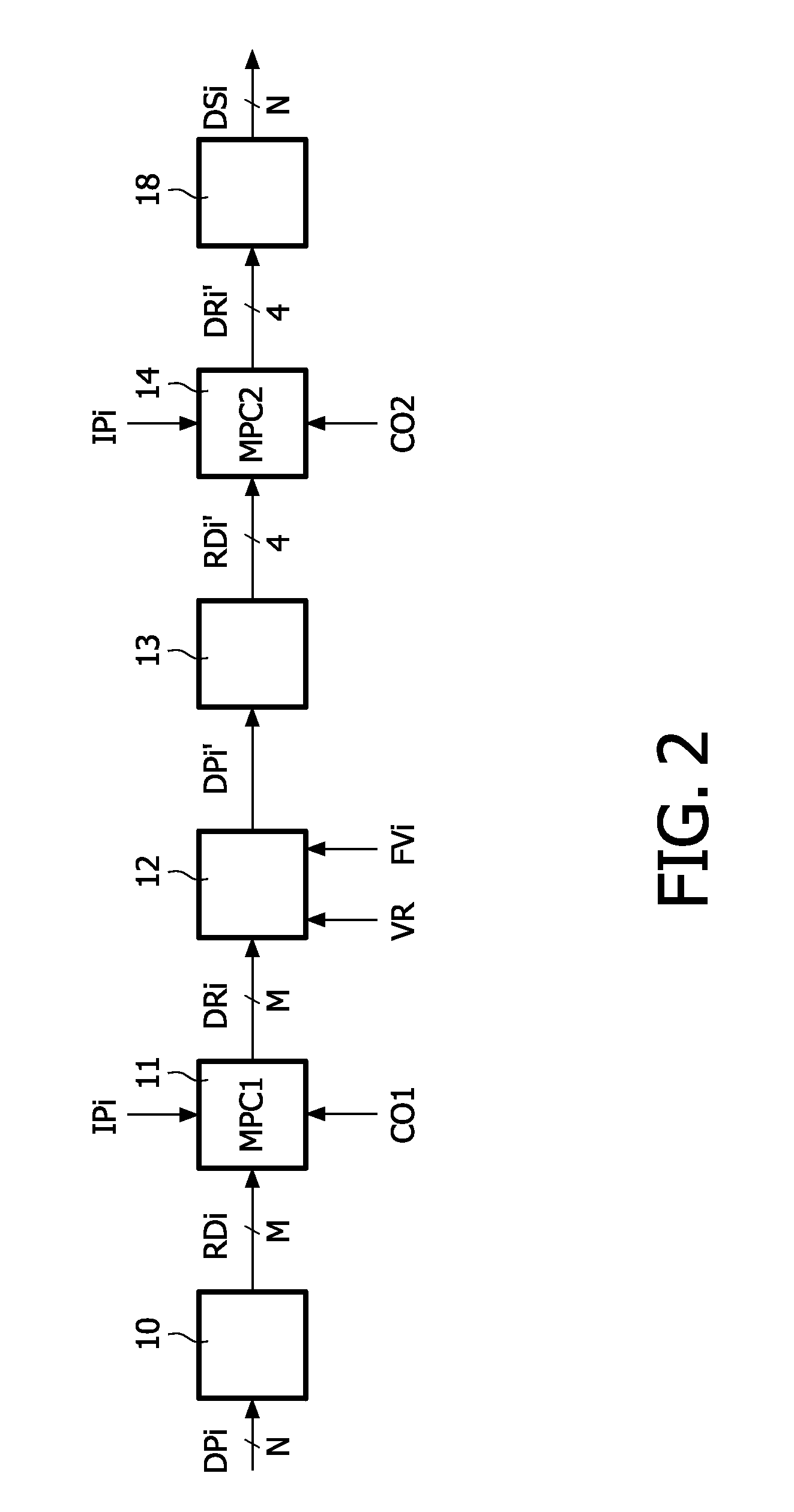
A method converts an input pixel (IPi) defined by three values (ri, gi, bi) of input primaries (RI, GI, BI) into N drive values (DSi) for driving N sub-pixels (SPi) of a pixel (PIi) of a display device (DD). The N drive values (DSi) have a valid range (VR) wherein their values occur. The N sub-pixels (SPi) emit light defined by N display primaries (DPi) of which at least four are independent. M resulting display primaries (RDi) are used (10) wherein a group of ones of the N display primaries (DPi) which are combined into a combined display primary (CDi) are replaced by the combined display primary (CDi). A first multi-primary conversion (MPC1) is performed (11) on the input pixel (IPi) to obtain resulting drive values (DRi) for the M resulting display primaries (RDi). It is checked (12) whether the M resulting drive values (DRi) have values in the valid range (VR). If the resulting drive value (DRi) of at least one of the M resulting display primaries (RDi) has a value outside the valid range (VR) the method allocates (12) a fixed value (FVi) to the resulting drive value (DRi) outside the valid range (VR), and selects (13) K out of the N display primaries (DPi). The selection includes the ones of the N display primaries (DPi) which were combined into a combined display primary (CDi) but not the display primaries (DPi) associated with the resulting drive value (DRi) outside the valid range (VR). The integer K is larger than 3. Finally the method performs (14) a second multi-primary conversion under a constraint (CO2) for the ones of the N display primaries (DPi) being combined into a combined display primary (CDi) in the first multi-primary conversion (MPC1).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Hybrid speed coding and system
Linear predictive speech coding system with classification of frames and a hybrid coder using both waveform coding and parametric coding for different classes of frames. Phase alignment for a parametric coder aligns synthesized speech frames with adjacent waveform coder synthesized frames. Zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Methods and Apparatus for Vision Enhancement
ActiveUS20160156850A1Enhance the imageEasy to storeInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsMagnificationVisual perception
A system and methods for the enhancement of a user's vision using a head-mounted and user-controllable device including a magnification bubble having variable attributes wherein a portion of the scene is magnified within the complete scene, wherein the user is able to modify, in real-time, how the images are processed including the attributes of the magnification bubble.
Owner:IRISVISION INC
System and method for synchronizing channel handoff as among a plurality of devices
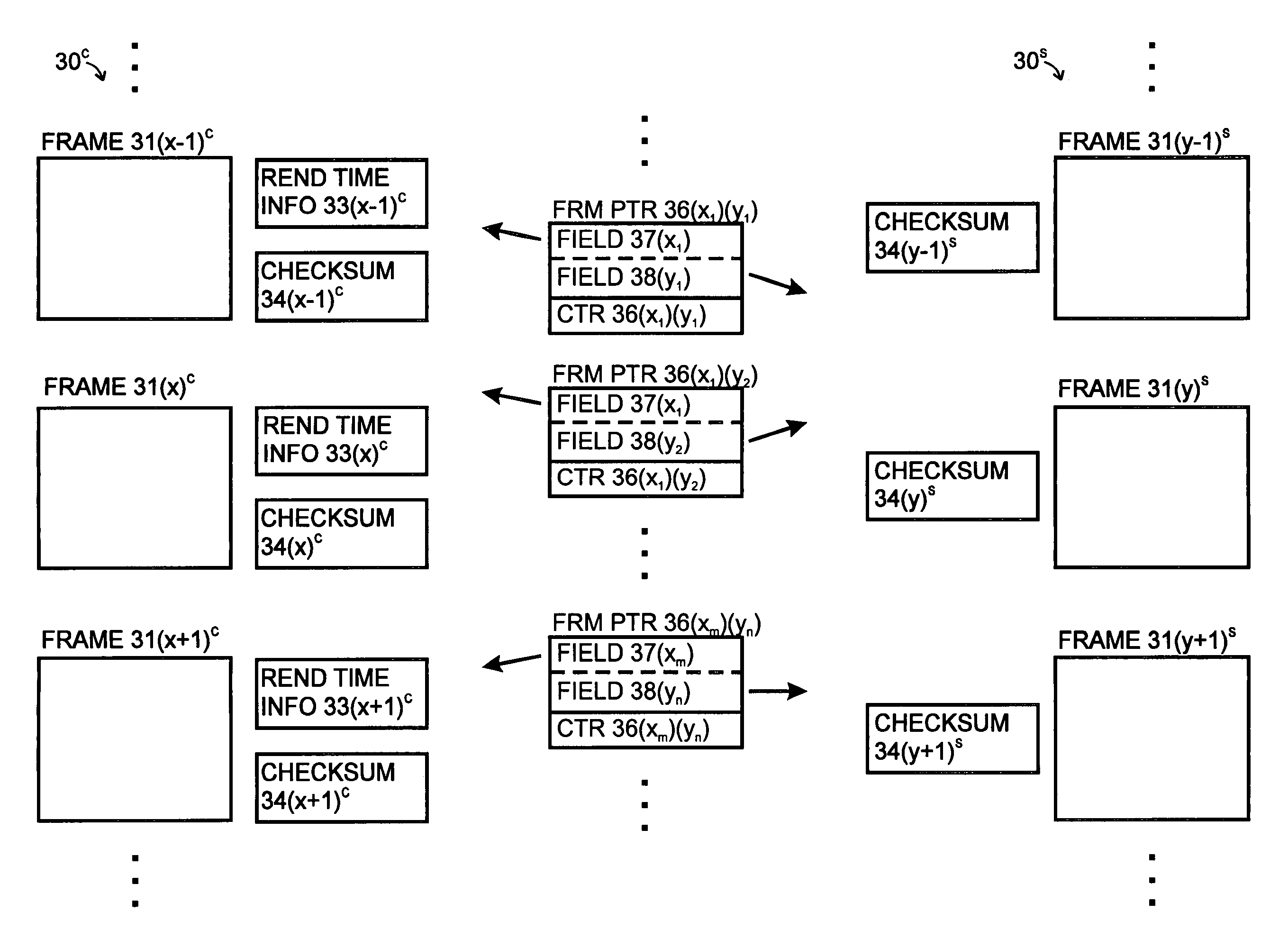
ActiveUS7668964B2Avoid discontinuitiesMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputer networkSynchronization Channel
A system constructed comprises a plurality of devices interconnected to a network. At least two of the devices in the system can access streaming audio information over the network, and are capable of providing audio and rendering timing information to other devices in the system. One device, as the handed-off device, is configured to determine correspondences in connection with two information streams received from two information sources. That device comprises an information receiver module, a position identifier module, and a corresponding position utilization module. The information receiver module is configured to receive the two information streams. The position identifier module is configured to identify corresponding positions regarding corresponding sequences in the two information streams. The corresponding position utilization module is configured to utilize the identification of the corresponding positions in the two information streams.
Owner:SONOS
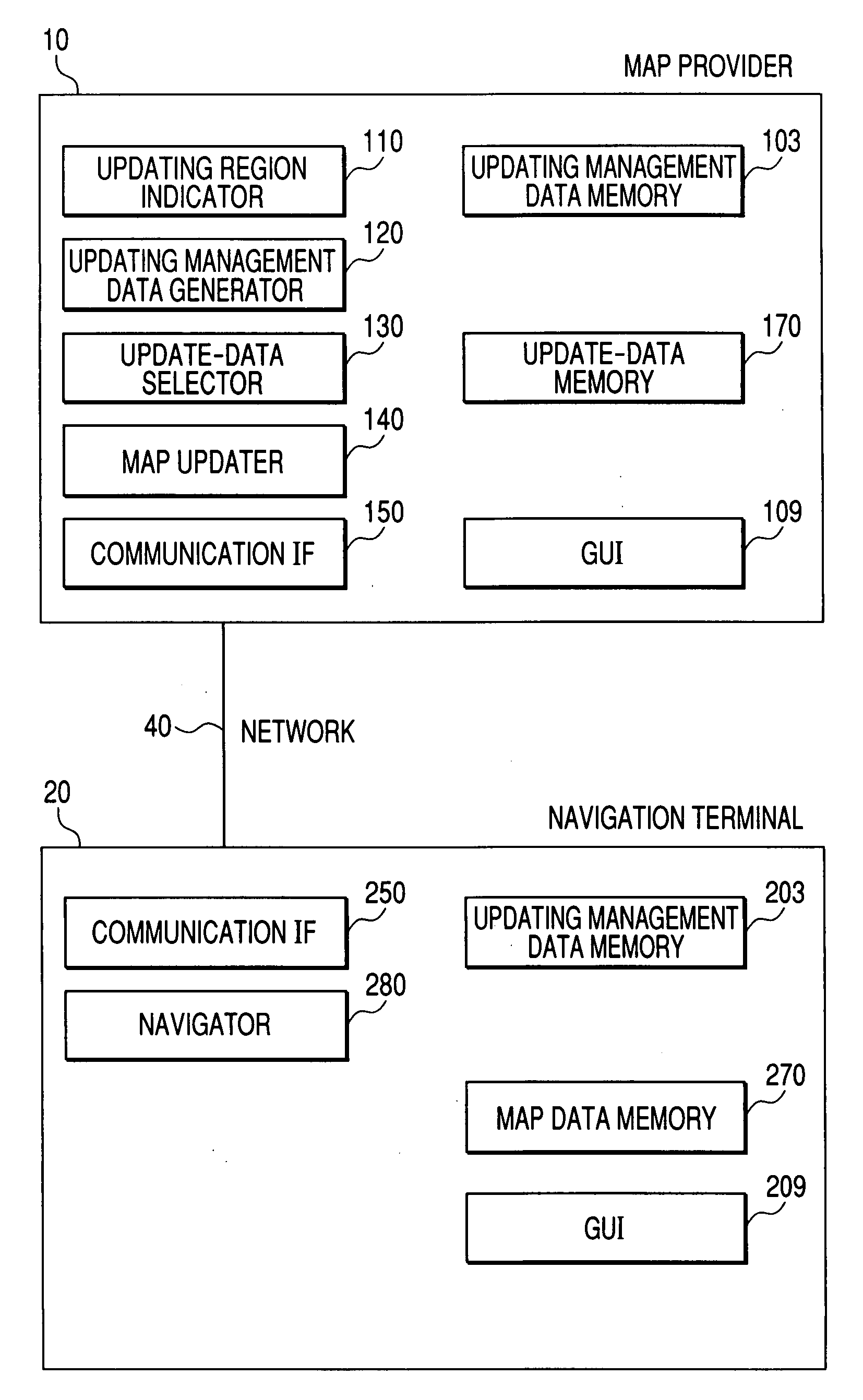
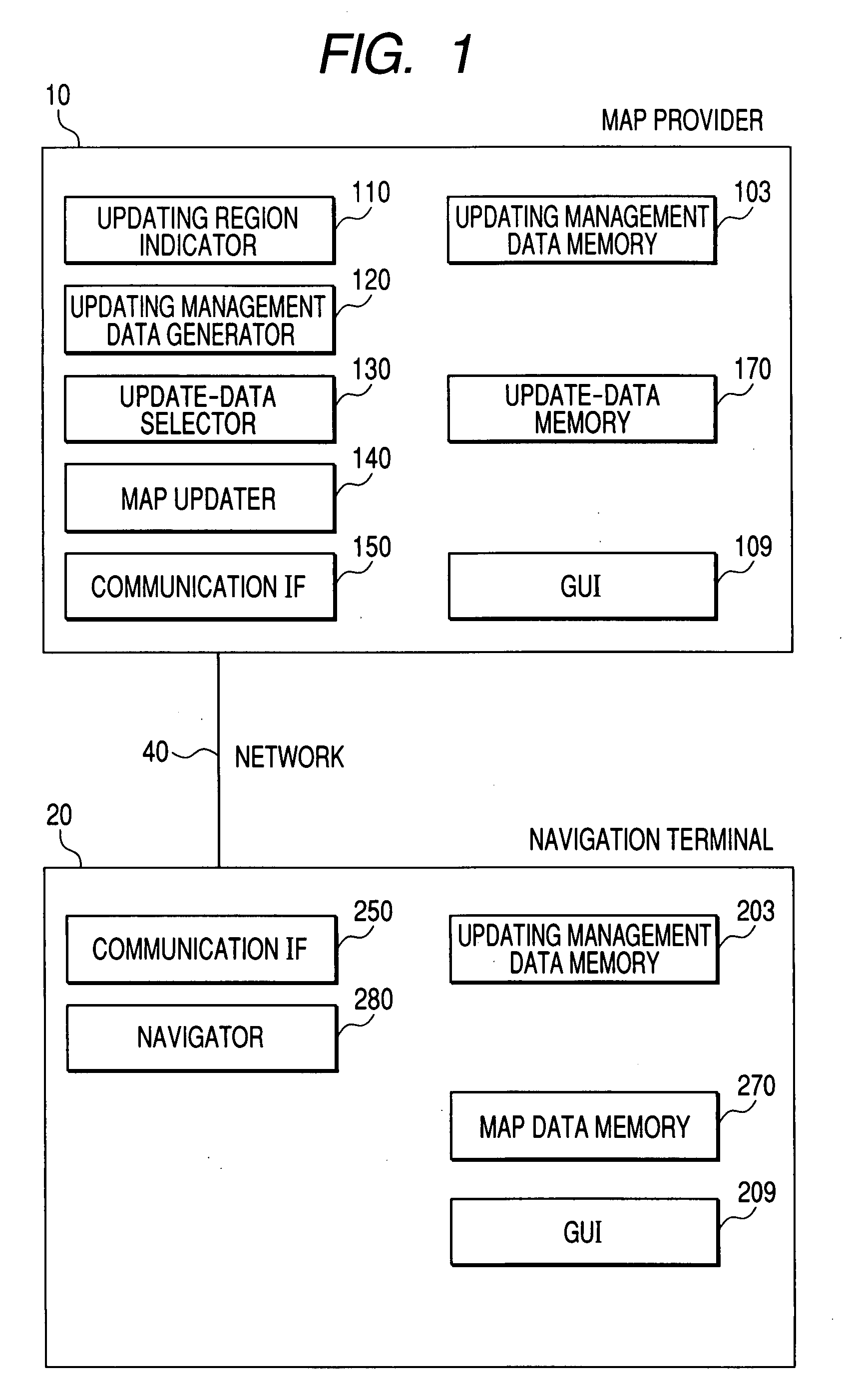
Computer readable medium storing a map data updating program and map data updating terminal
ActiveUS20070213929A1Improve convenienceQuick updateInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer terminalData application
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Organic light-emitting device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20080258609A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedSimple processDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsOrganic compoundSimple Organic Compounds
The present invention provides an organic light-emitting device including a substrate and a plurality of organic light-emitting elements formed on the substrate, wherein the plurality of the organic light-emitting elements include a first organic light-emitting element which emits a light of a first emission color, and a second organic light-emitting element which emits a light of a second emission color different from the first emission color; each of the organic light-emitting elements has a first electrode having a light reflection layer and a transparent conductive layer, an organic compound layer containing a light-emitting layer, and a second electrode as a light extraction electrode, in mentioned order on the substrate; the light reflection layer of the first organic light-emitting element is formed between the substrate and the transparent conductive layer; the light reflection layer of the second organic light-emitting element is formed between the transparent conductive layer and the organic compound layer; and a thickness of the transparent conductive layer of the first organic light-emitting element is the same a thickness of the transparent conductive layer of the second organic light-emitting element.
Owner:CANON KK
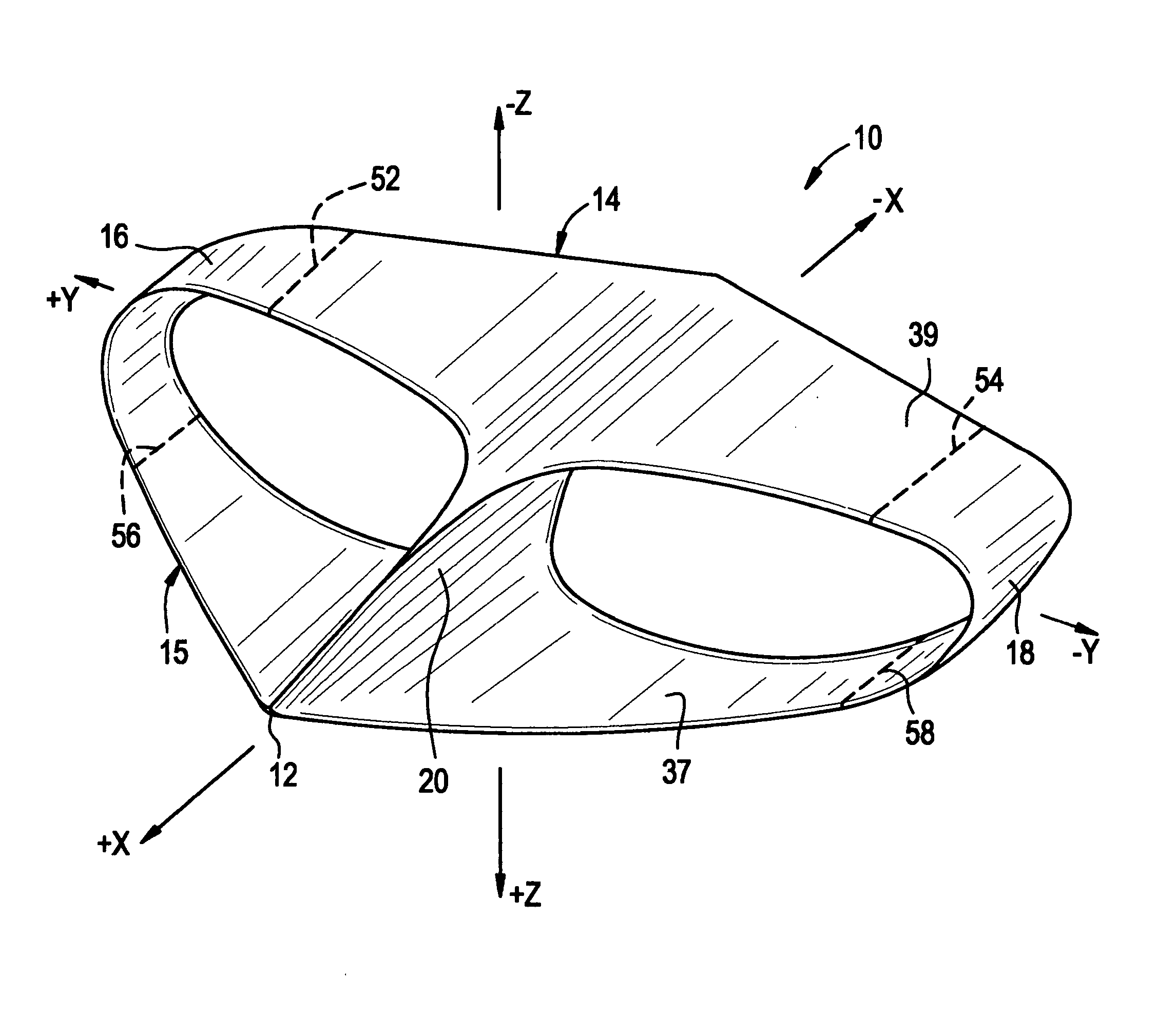
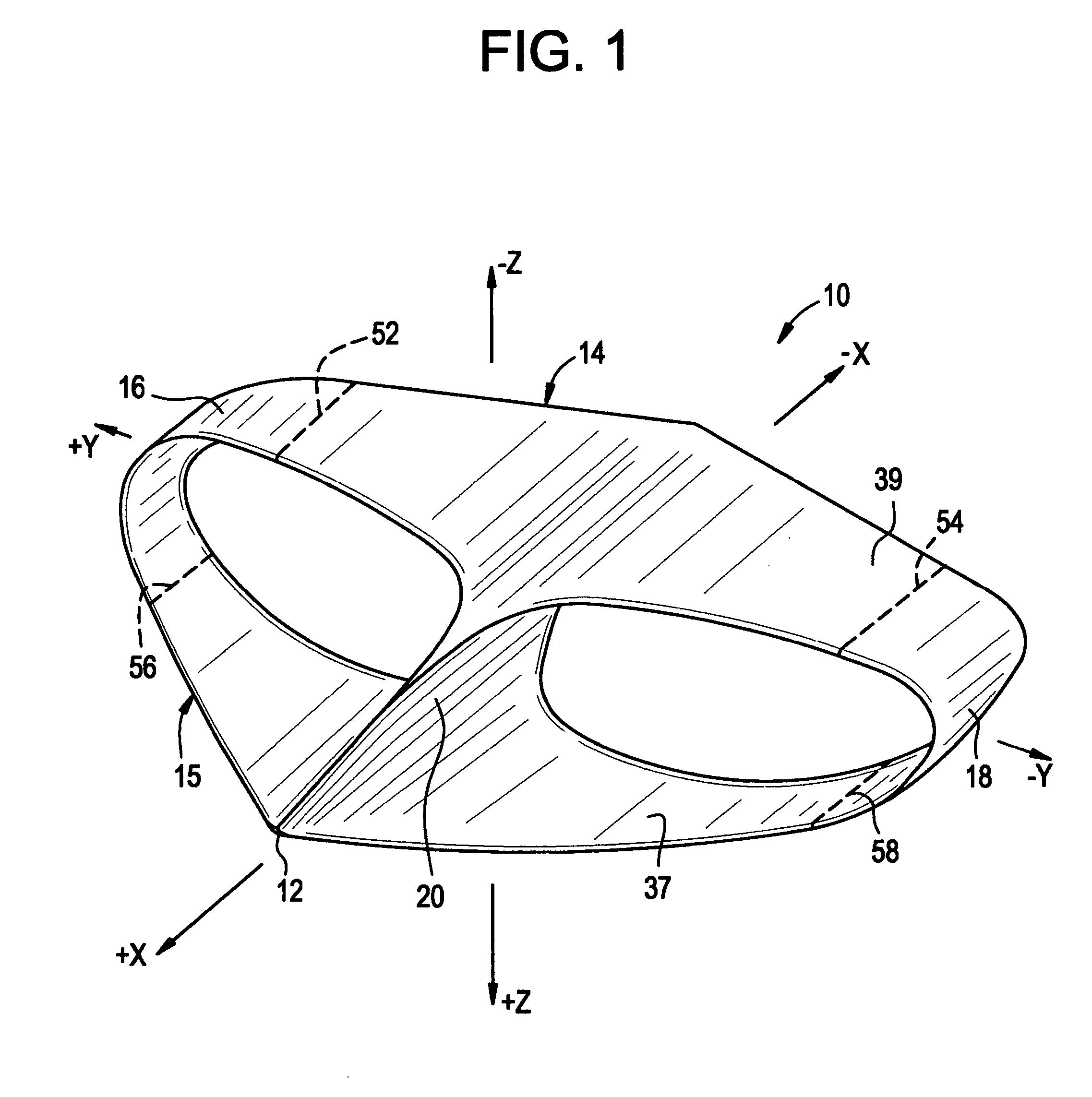
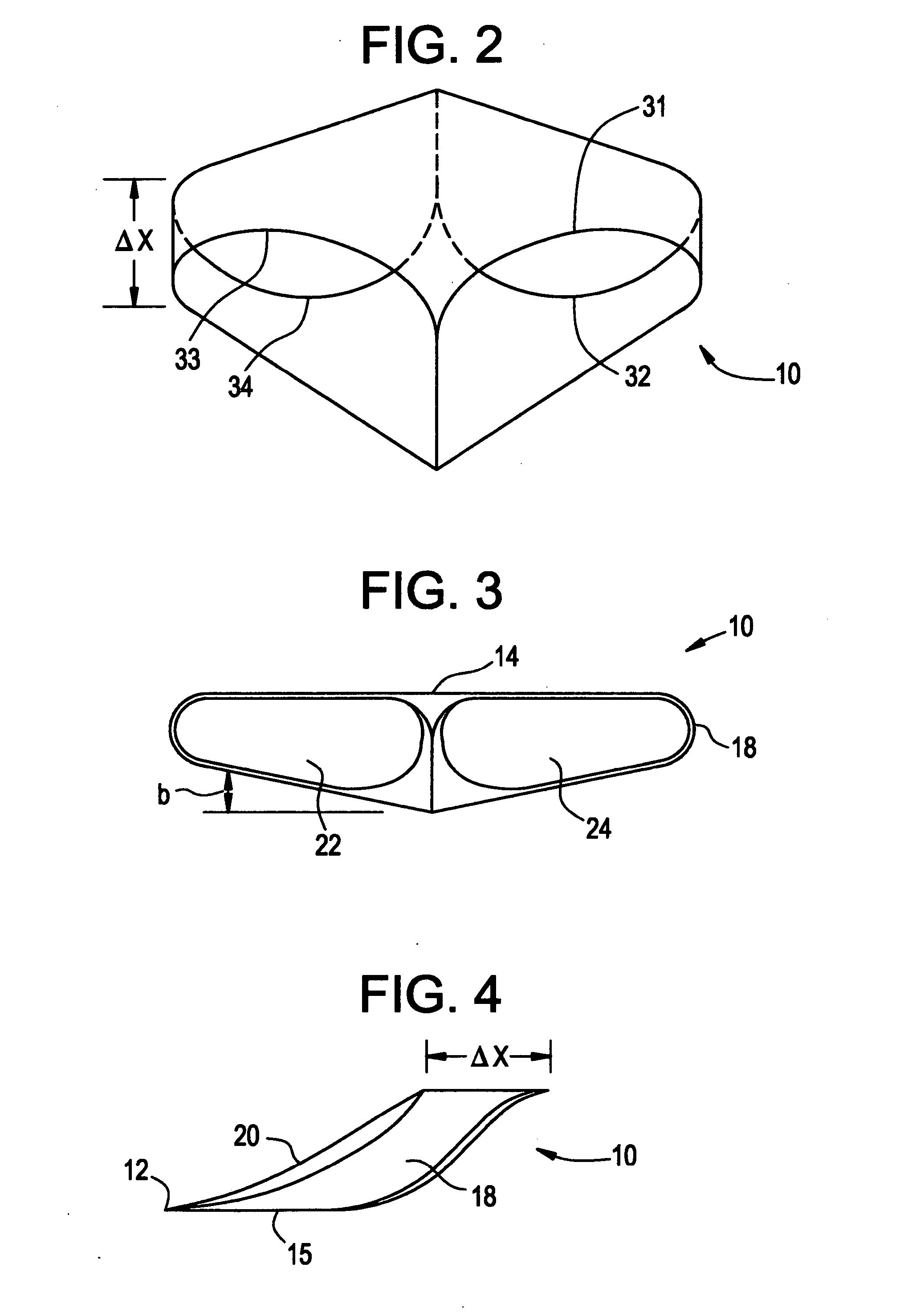
Lifting foil
ActiveUS20050173592A1Easy to liftNo substantial drag penaltyInfluencers by generating vorticesWing shapesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A lifting foil for an aircraft, a hydrofoil or the like having a pair of courses or wings. Vortex losses due to spanwise fluid flow are substantially reduced by joining the tips of the courses with flow guides configured for jointly terminating the undesired flows. Termination is effected by providing the flow guides with crossections cambered for reducing the dynamic pressure of fluid flowing in a spanwise direction across flow guide surfaces.
Owner:HOUCK II RONALD G
Driver apparatus and method
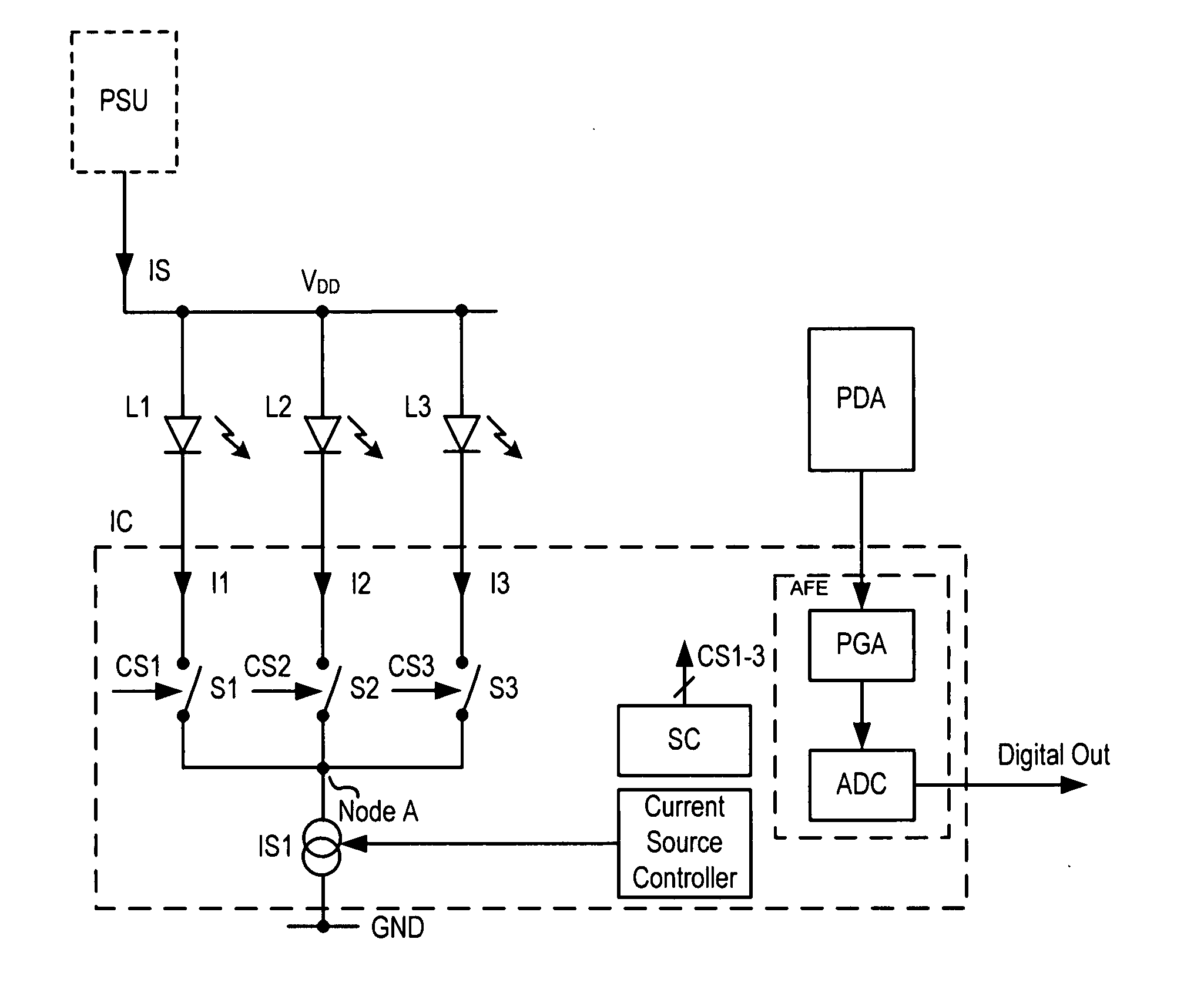
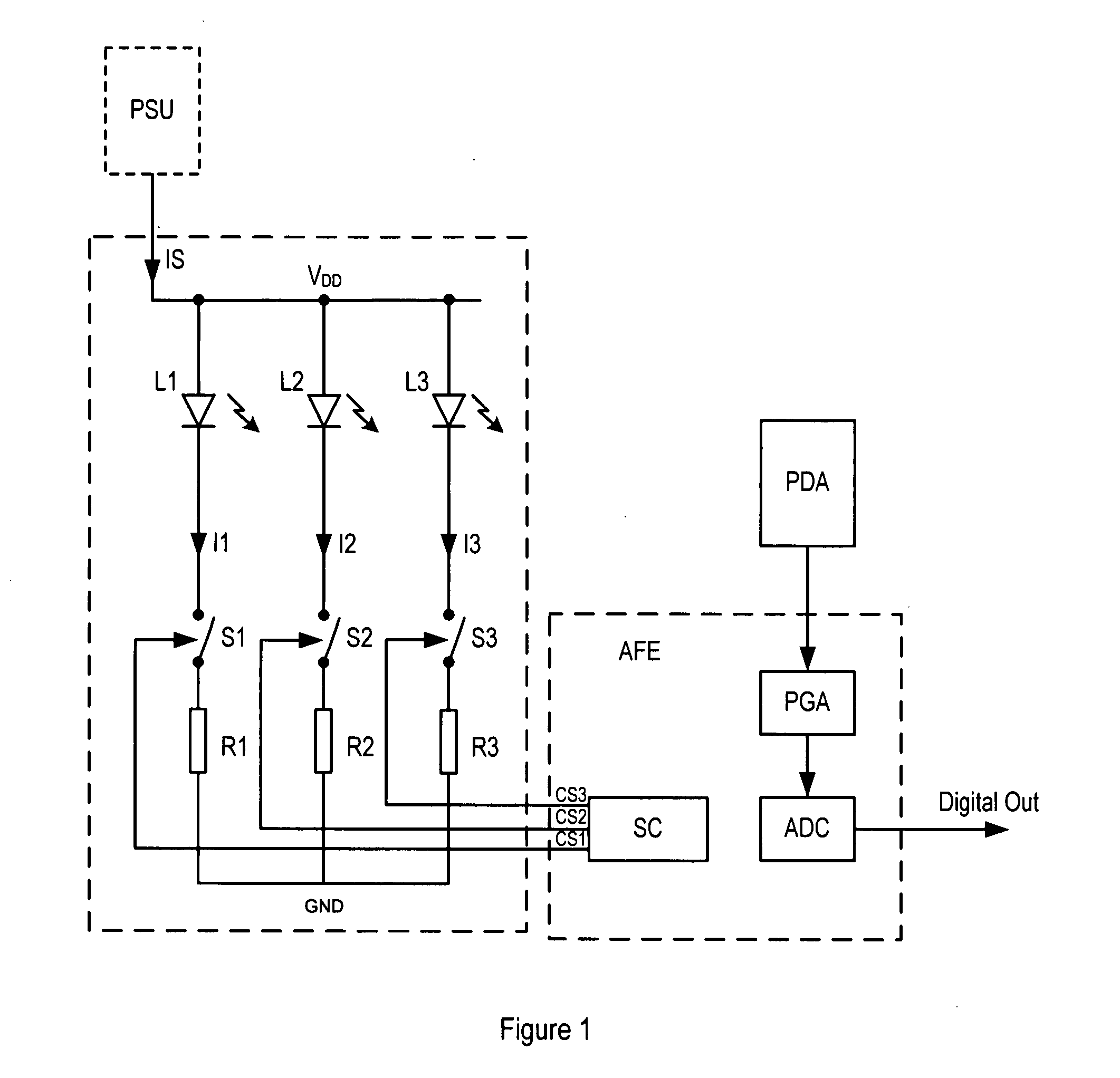
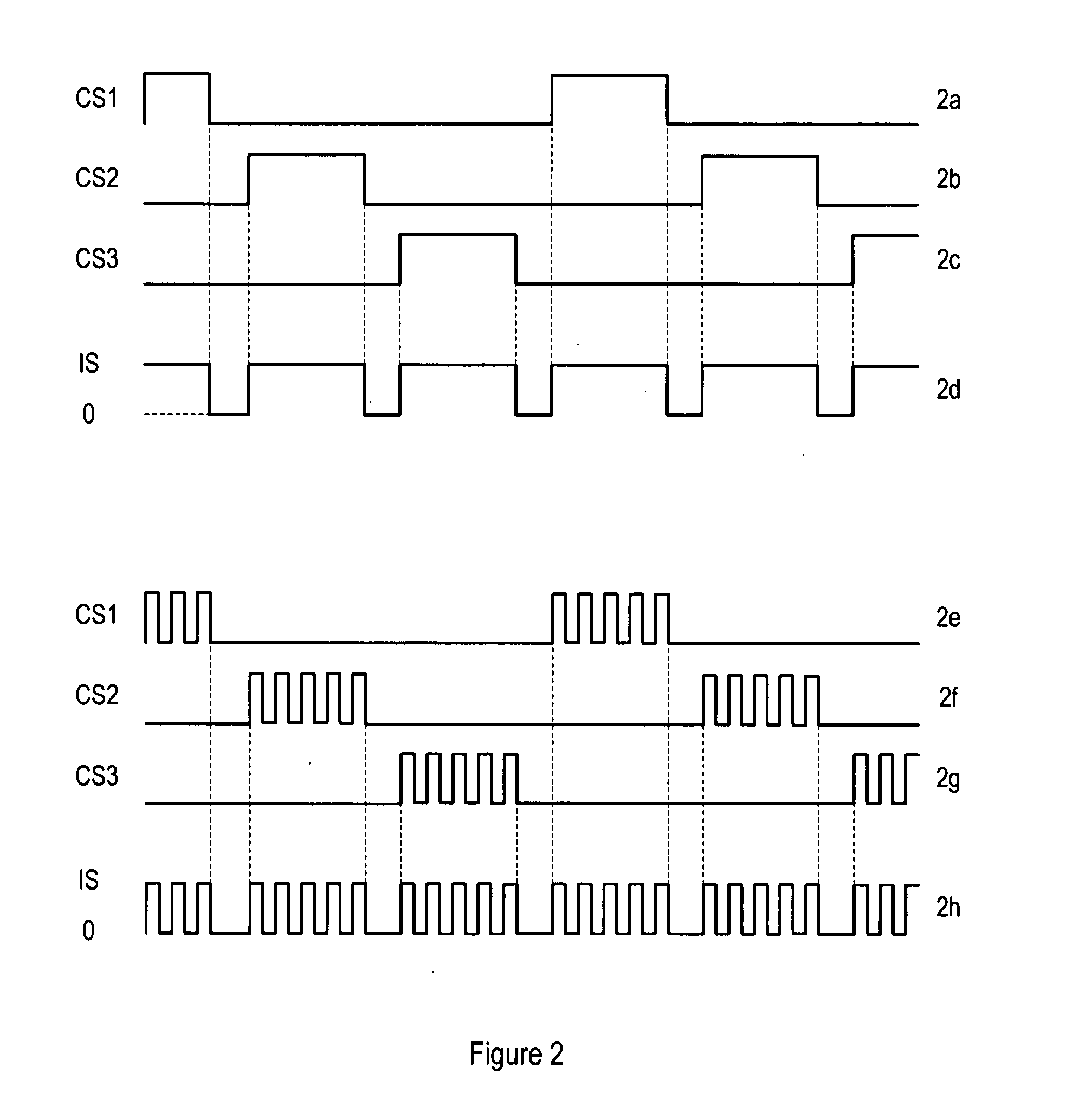
ActiveUS20080048567A1High currentAvoid changeElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageLed arrayAnalog processing circuits
A driver apparatus is provided for controlling a light source array comprising at least first and second light sources, the light source array used for illuminating a scan region on a target object, wherein light reflected from said target object is captured by a detector. The driver apparatus comprises a single integrated circuit comprising processing means for processing image data received from the detector, a switching array comprising at least first and second switches for switching the respective first and second light sources, and a current source for controlling the flow of current through the light sources. In this way the LED switching circuitry that controls an LED array is placed on the same integrated circuit (i.e. monolithic circuit) as the analogue processing circuitry that processes the image data, with the current source controlling the flow of current through the LEDs in the LED array. The current source has the advantage of avoiding rapid changes or slope discontinuities in the current flowing through the LEDs, which would otherwise cause unwanted transient signals. A shunt path comprising a switching device may be provided in parallel with the LED array and switching array. The shunt path has the advantage of enabling the switching sequence from one LED to another to be controlled such that a substantially constant current is drained from the supply (subject to any differences in the inherent current drawn by the Red, Green and Blue LEDs, respectively).
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Video editing apparatus and video editing method
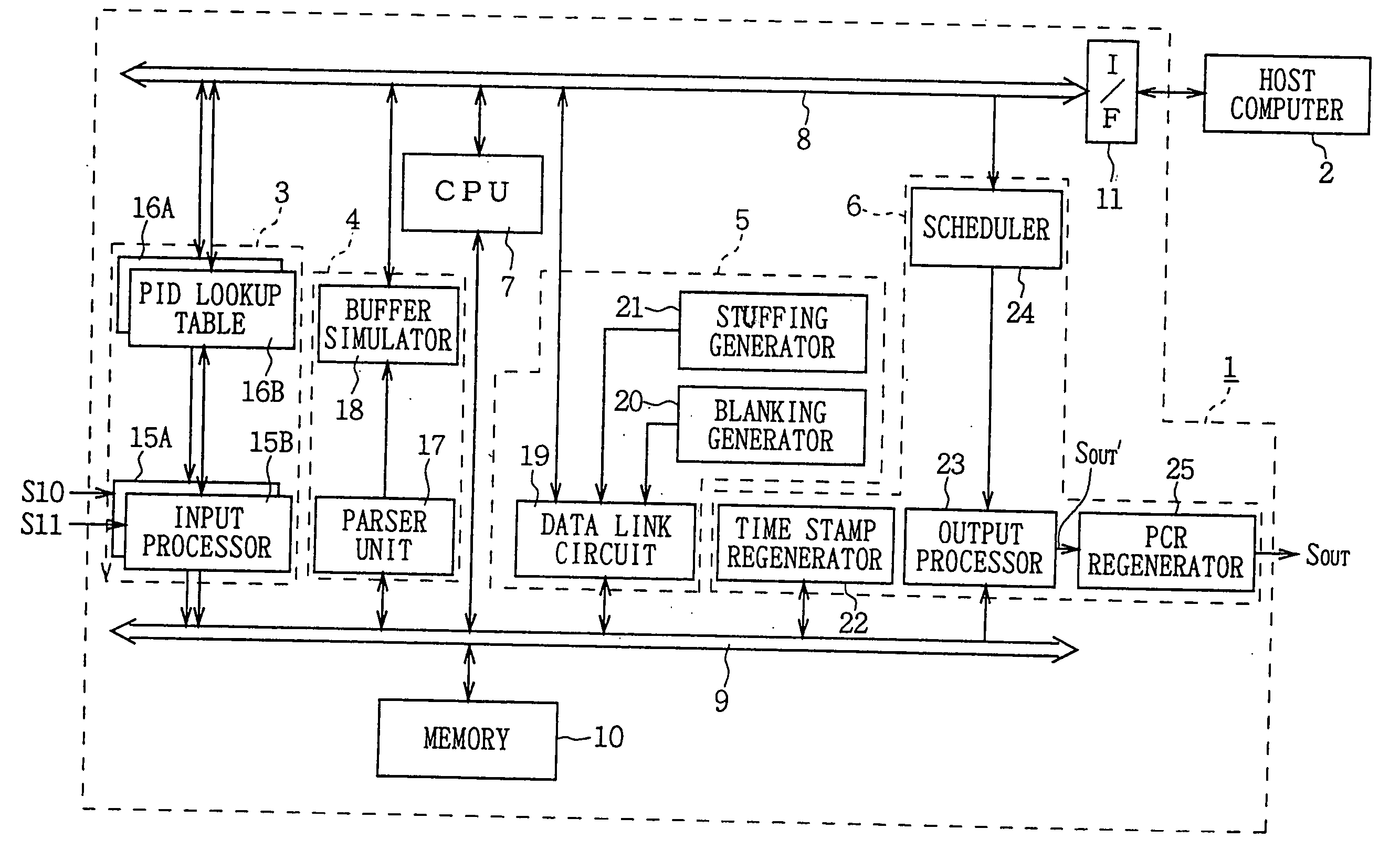
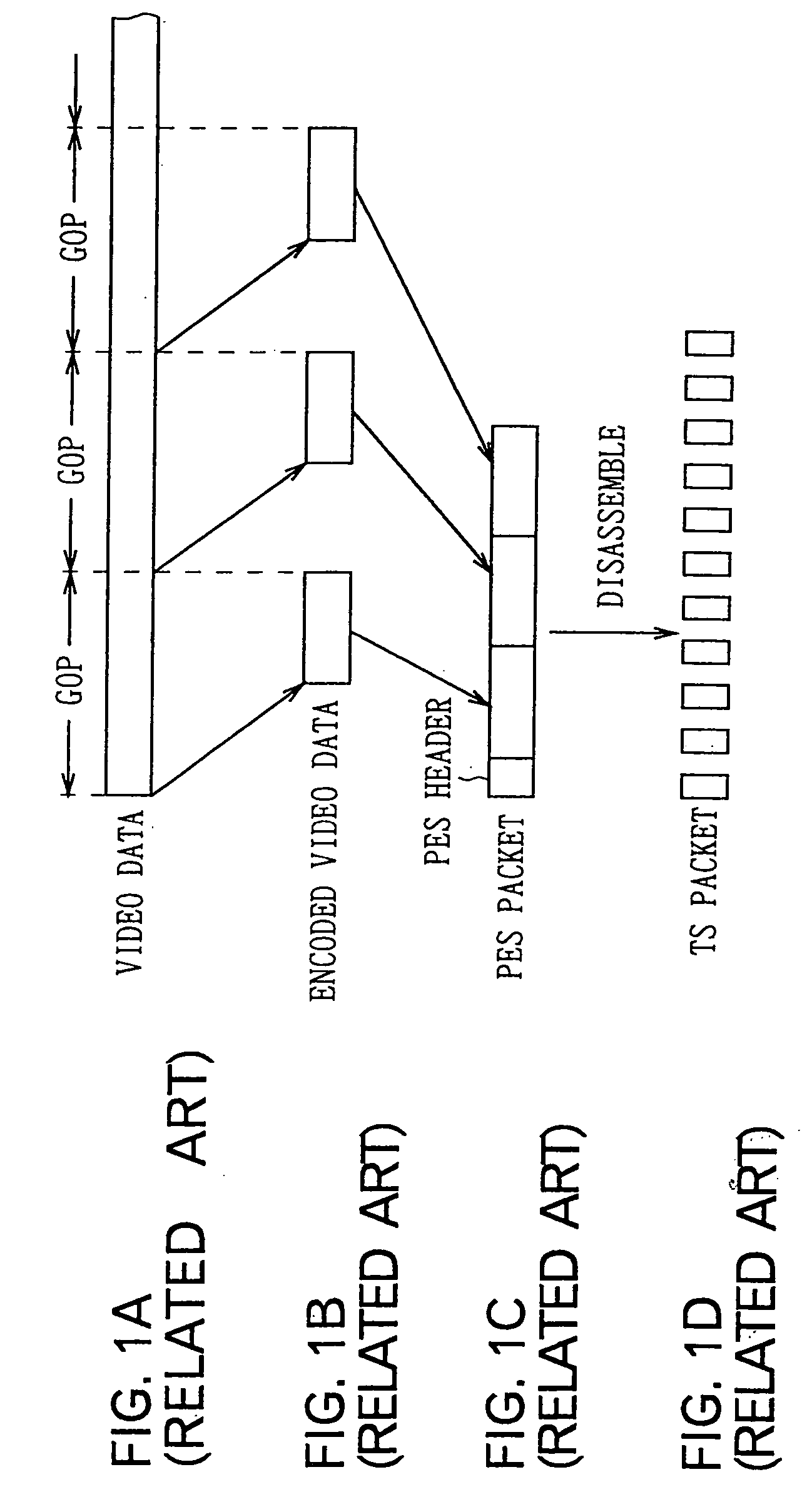
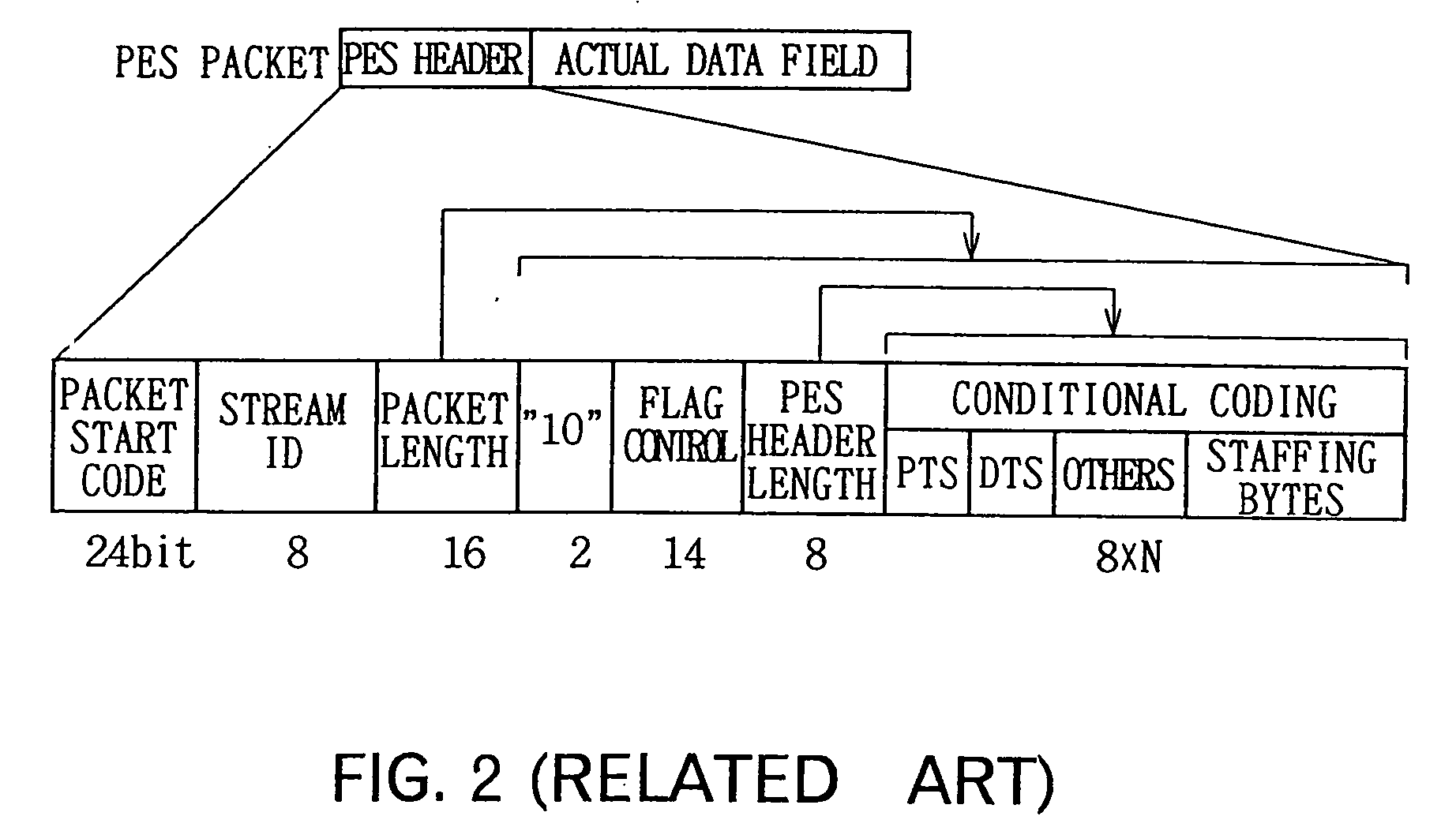
InactiveUS20050259946A1Easy to implementAvoid discontinuitiesTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsComputer hardwareData stream
A video splicing apparatus for receiving a transport stream including a plurality of packetized encoded video data streams, and for splicing the encoded video data streams to generate a spliced video data stream. The video splicing apparatus includes an input processor for disassembling each of the plurality of packetized encoded video data streams in the transport stream into a pseudo-elementary stream before packetization, and for storing the disassembled pseudo-elementary streams in predetermined storage. An analyzer is also provided for analyzing the amount of coded bits of two data streams of the pseudo-elementary streams stored in the storage that will be generated upon decoding upon receipt of the two data streams to be subjected to a splicing operation. A data processor is provided for reading the data streams to be subjected to the splicing operation from the storage, splicing the streams, and inserting a desired amount of additional data at a splice point based on the result of the analysis by said analysis to produce a spliced video data stream and storing the spliced video data stream in the storage. An output processor is provided for determining output timing for the spliced video data stream based on the determined amount of coded bits, and outputting the spliced video data stream read from the storage based on the output timing.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method For Handling Service Failures
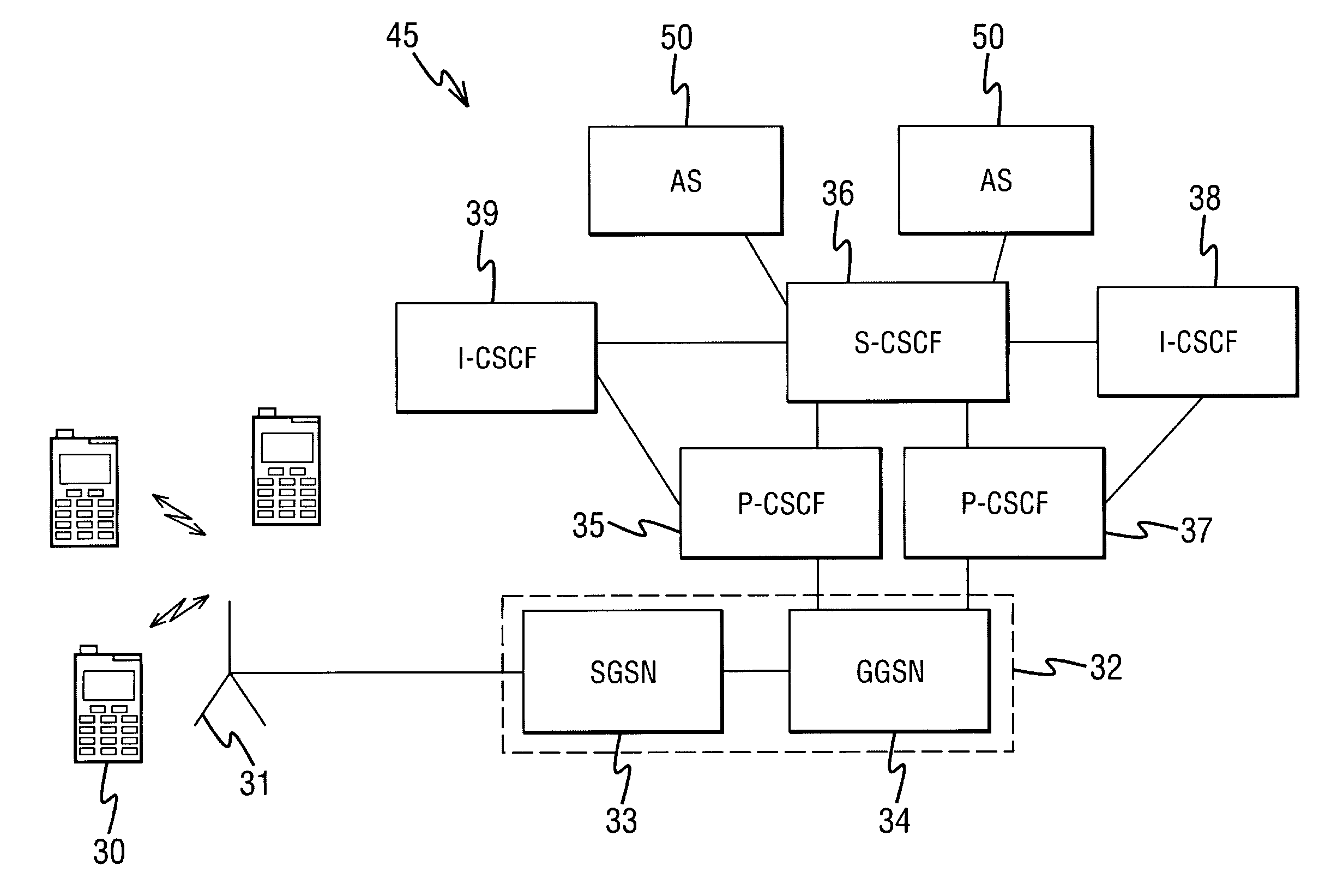
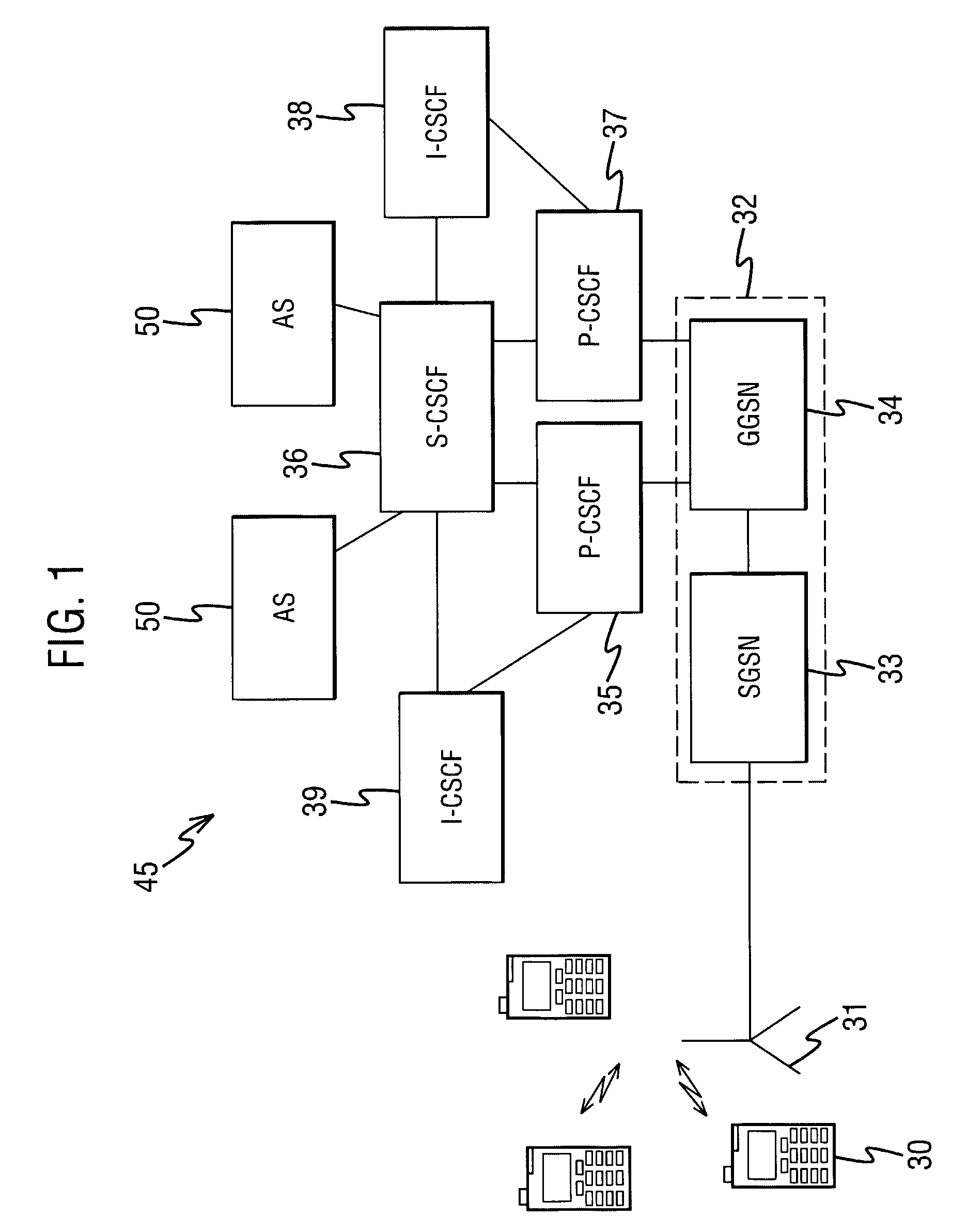
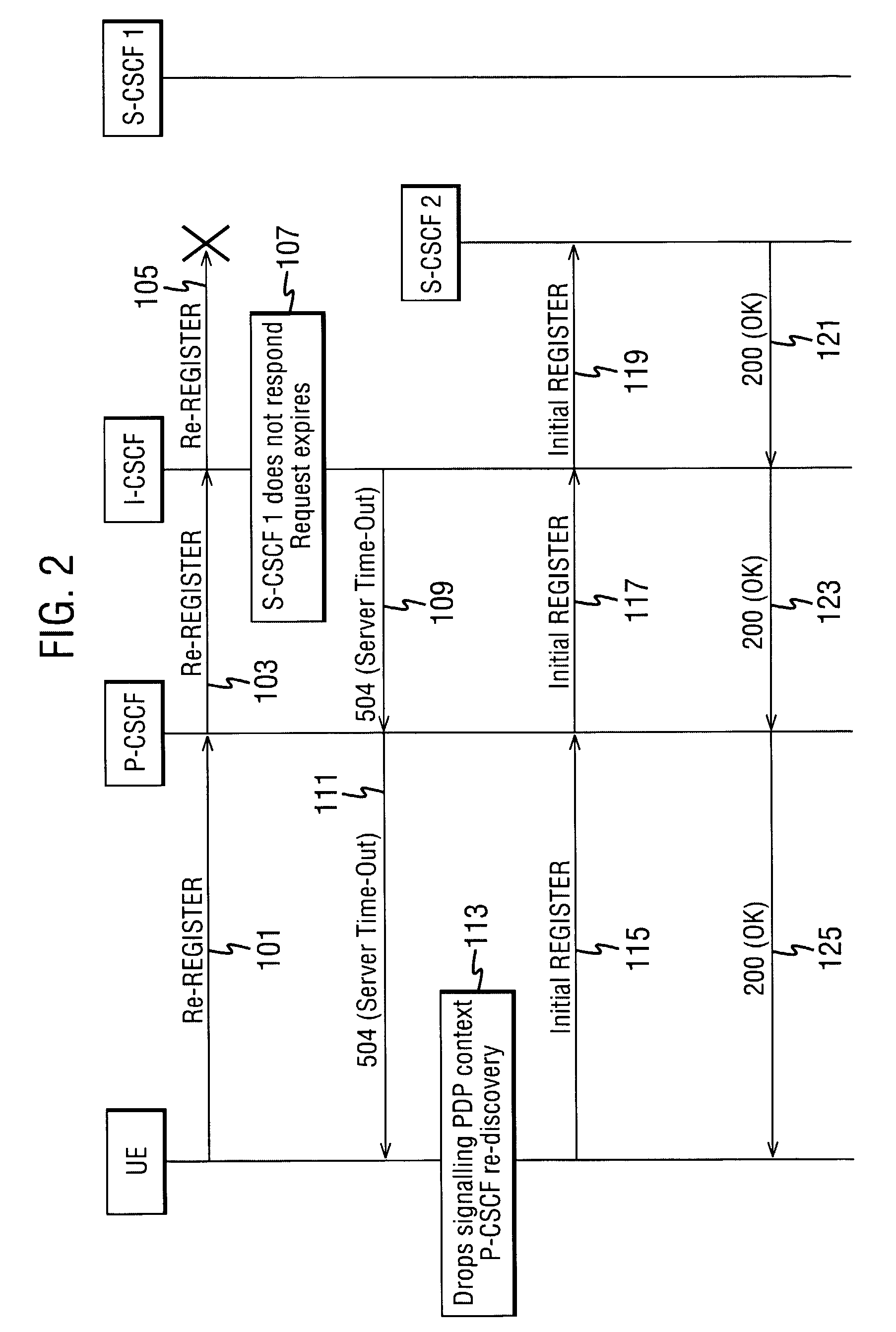
ActiveUS20070275710A1Avoid discontinuitiesImprove user perceptionUser identity/authority verificationAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsUser equipmentService networks
A method for handling service failures for in a communications network comprising a user equipment, a first network element and a serving network element, the method comprising the following steps. Receiving at the first network element a first message from the user equipment. Transmitting the first message from the first network element to the serving network element. Detecting at the first network element that the serving network element is out of service. Determining at the first network element the type of the first message, and in dependence on the type of the first message sending from the first network element to the user equipment an error message including an indication that the serving network element is out of service.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Hybrid speech coding and system
ActiveUS7139700B1Enhance performanceAvoid phase discontinuitySpeech analysisWaveform codingSpeech code
Linear predictive speech coding system with classification of frames and a hybrid coder using both waveform coding and parametric coding for different classes of frames. Phase alignment for a parametric coder aligns synthesized speech frames with adjacent waveform coder synthesized frames. Zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and device for canceling echo
ActiveCN103391381AAvoid discontinuitiesImprove voice qualityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisSelf adaptiveElimination method
Provided are an echo elimination method and device. The method includes: estimating an echo path characteristic parameter of an echo signal; taking a source signal of the echo signal as a reference signal, generating an echo estimation signal according to the echo path characteristic parameter; and subtracting the echo estimation signal from a to-be-processed speech signal. The present invention solves the problem in the related art that self-adaptation cannot be achieved when a returned near-end audio is suppressed, thus facilitating the enhancement of the speech quality of a conference and the improvement of user experience.
Owner:ZTE CORP
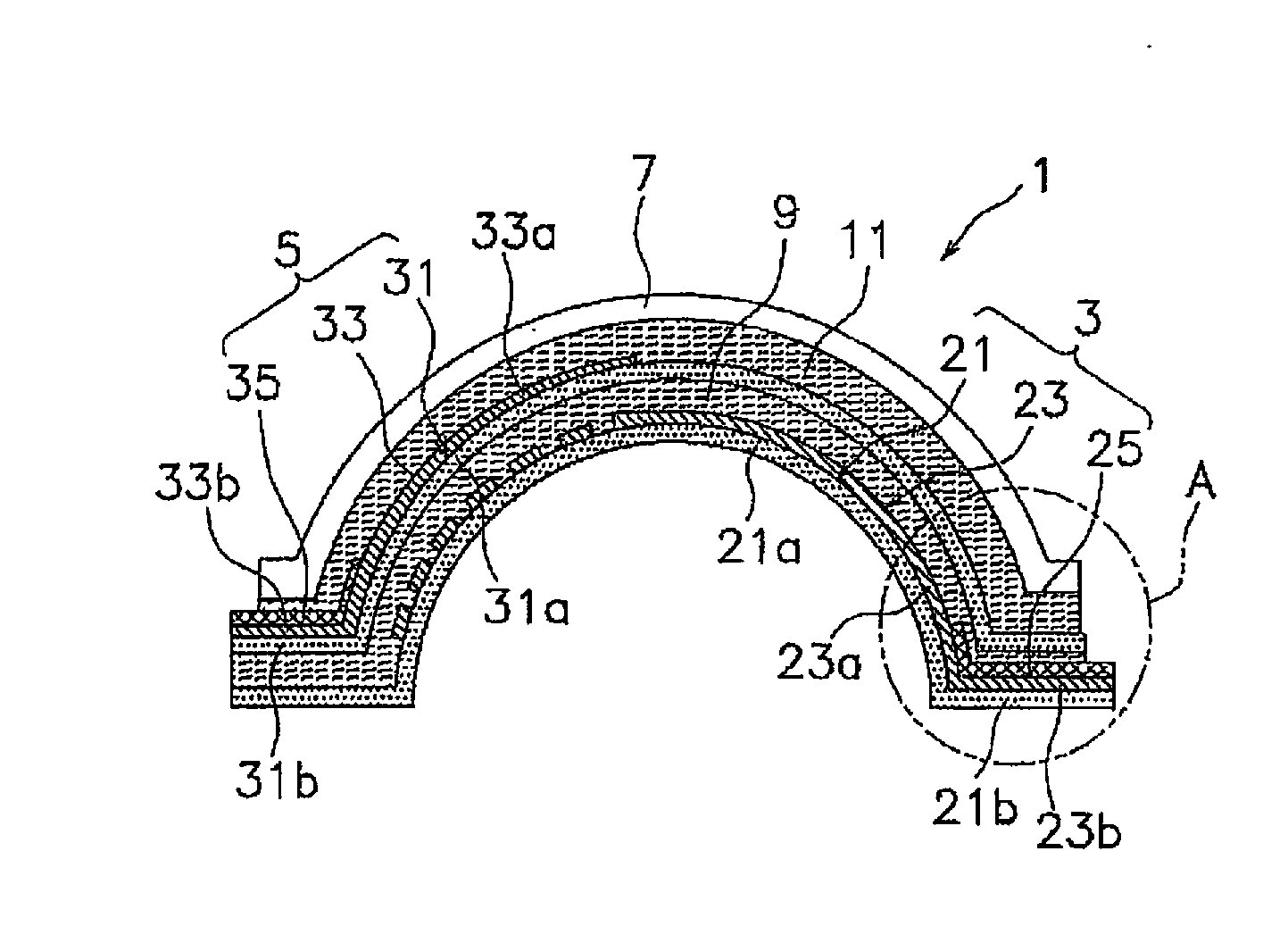
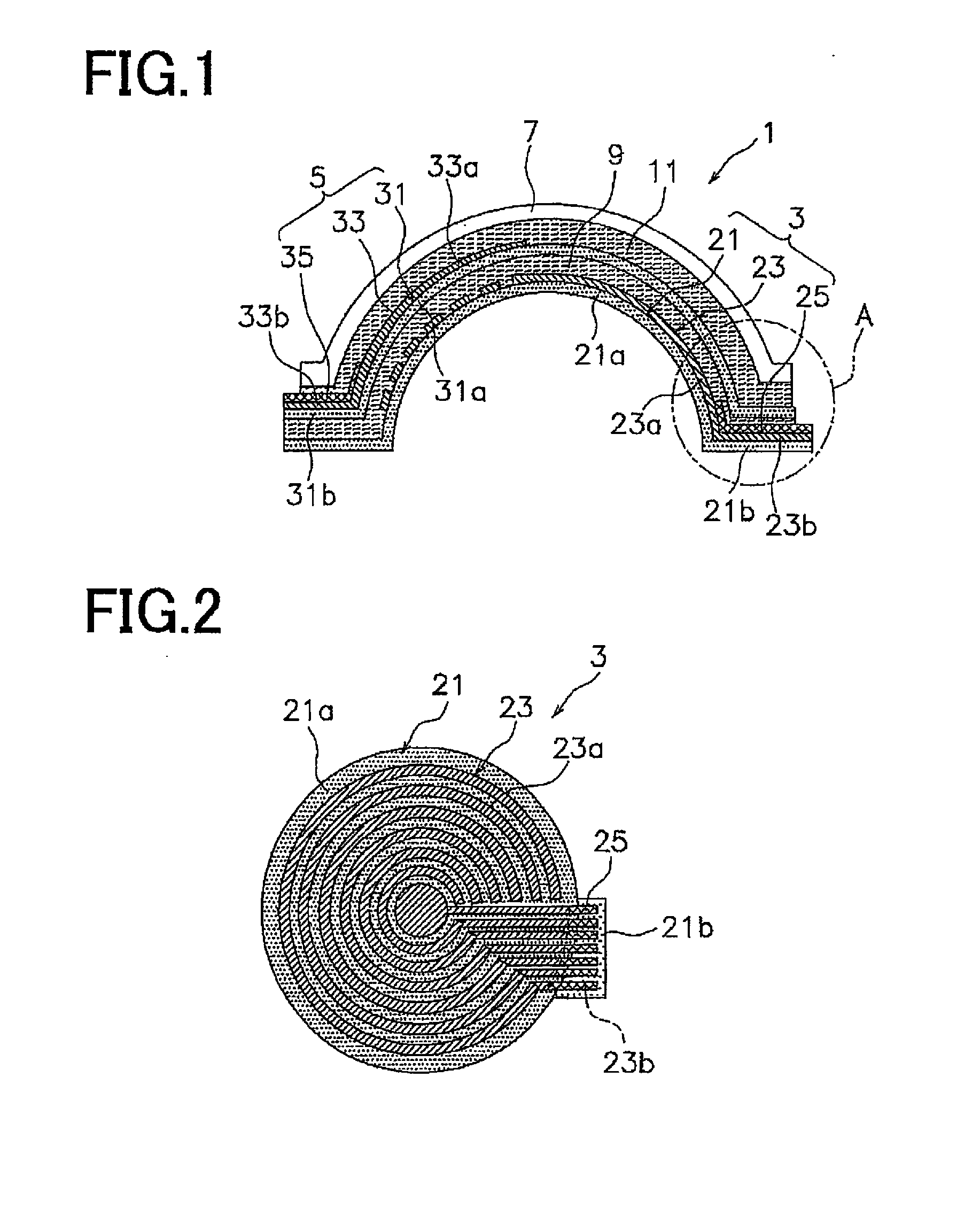
Touch panel and method of manufacturing the touch panel
InactiveUS20150185889A1Avoid discontinuitiesSynthetic resin layered productsWood veneer joiningThree dimensional shapeEngineering
To prevent disconnection of a touch panel to which a three-dimensional shape has been imparted, the touch panel includes a first electrode layer that is formed upon a first base material sheet and includes material having flexibility. The first electrode layer has a first electrode part and a first mount part extending from the first electrode part. A first routing circuit layer is formed upon the first mount part. A second electrode layer is formed upon a second base material sheet and includes material which has flexibility. The second electrode layer has a second electrode part and a second mount part extending from the second electrode part. A second routing circuit layer is formed upon the second mount part. A first bonding layer bonds the first base material sheet to the second base material sheet. A second bonding layer bonds the second base material sheet to a protective layer.
Owner:NISSHA PRINTING COMPANY
Information processing apparatus, media player and method for controlling a storage device
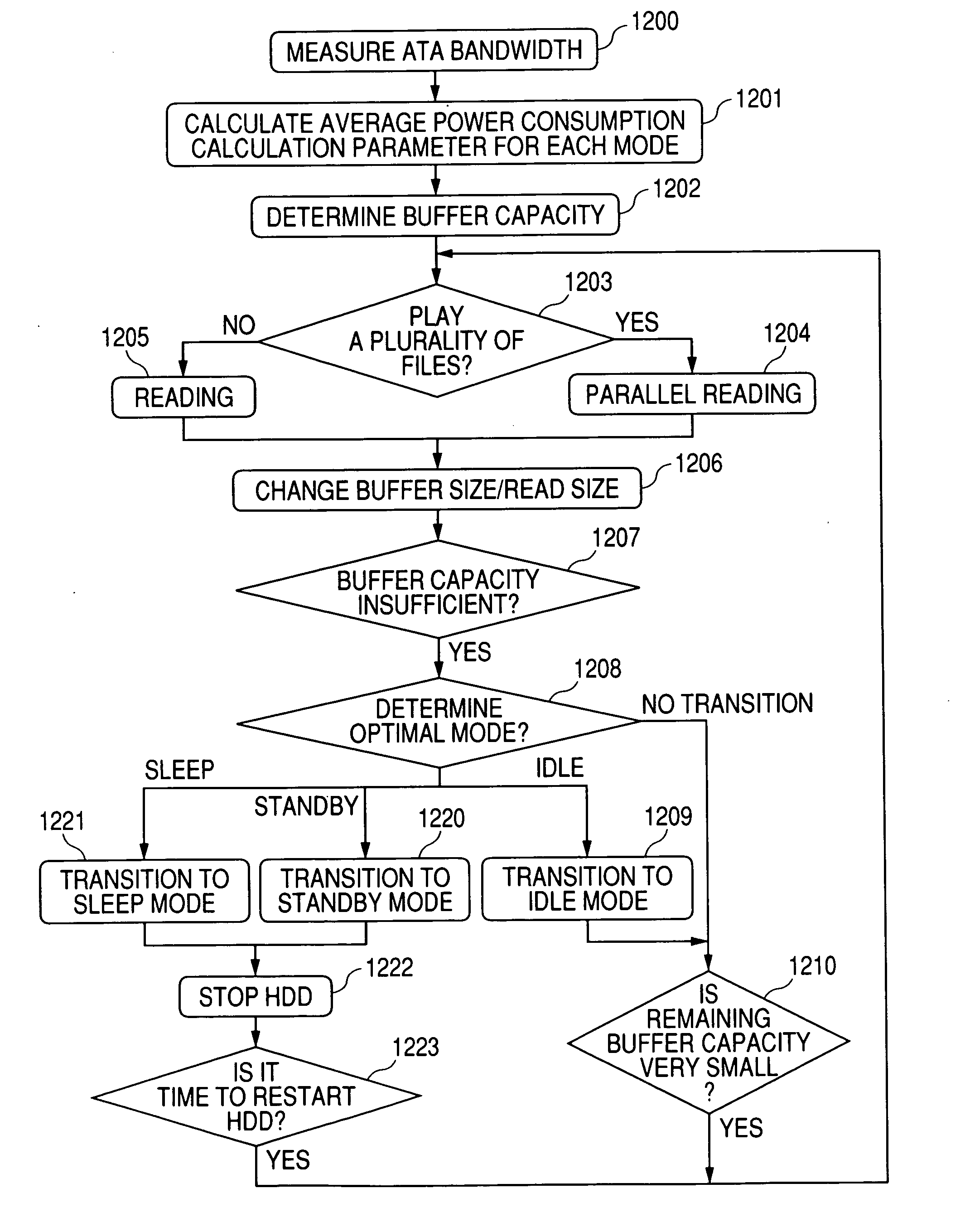
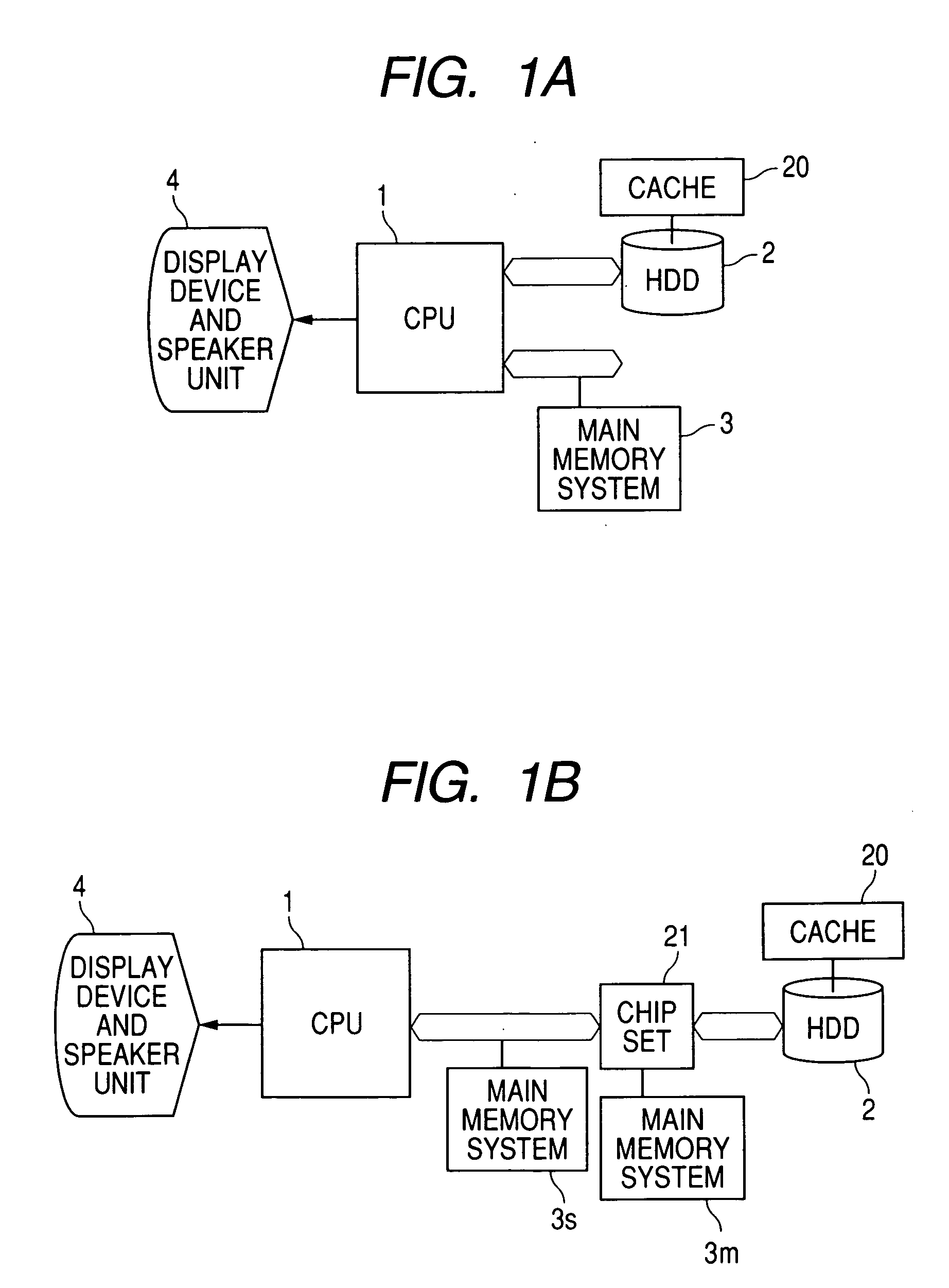
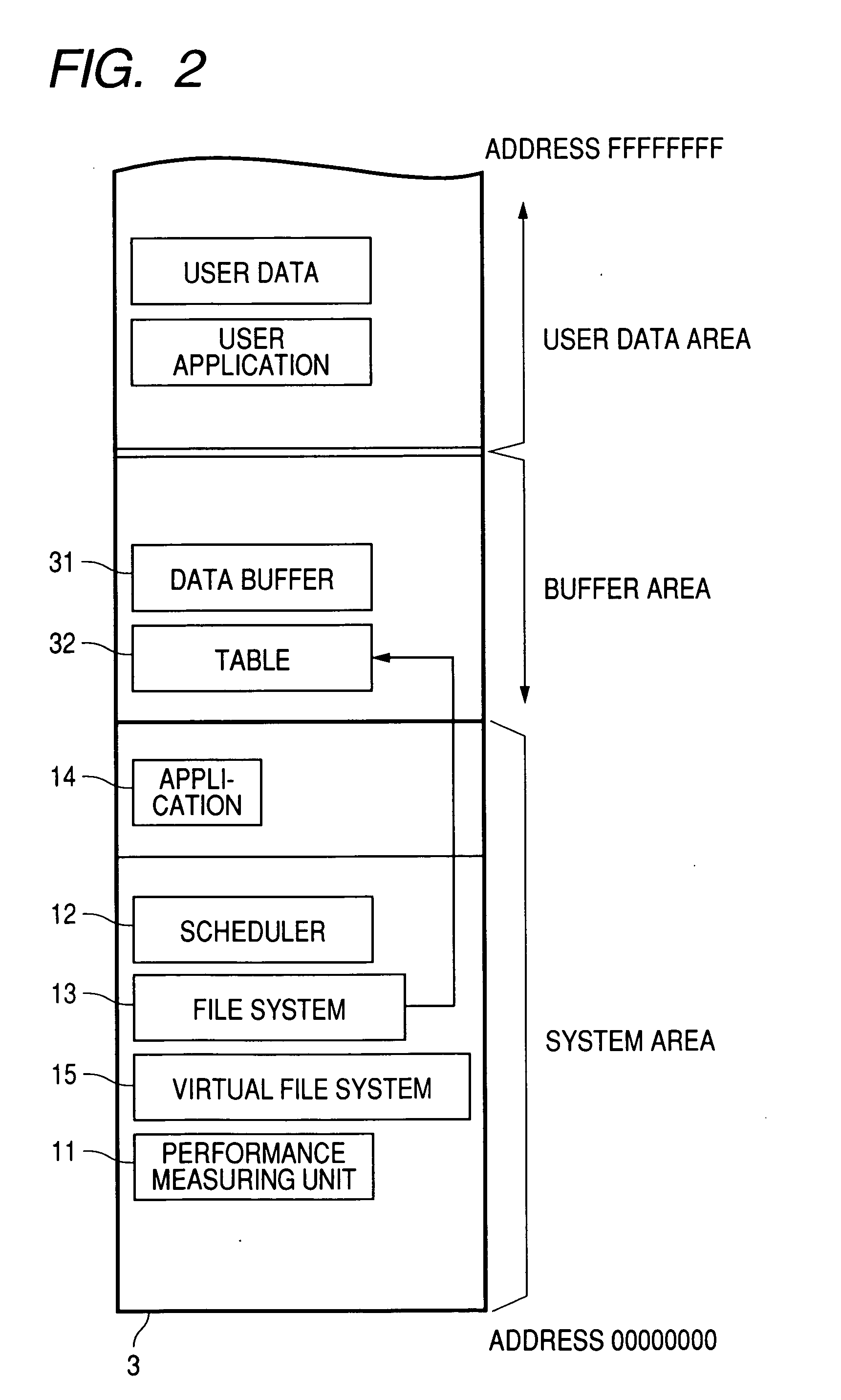
InactiveUS20070136522A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid discontinuitiesTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersComputer hardwarePower consumption
An information processing apparatus is provided with a performance measuring unit of a storage device, a look-ahead buffer whose capacity can be varied and a power profile which is a power consumption value for each operation mode of the storage device, thereby determining the buffer capacity based on performance measured by the performance measuring unit, the power profile and a playback bit rate and playback time of a video, and, after reading data to the buffer, switching the operation mode to an optimal mode (sleep, standby or idle) in the idle period, which can reduce power consumption.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Selectively receiving media content
InactiveUS20120143994A1Prevent visual discontinuityAvoid discontinuitiesMetadata video data retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsImage resolutionEnd user
Disclosed are methods that associate “importance” information with chunks of a media presentation. An end-user device uses this information to intelligently manage resources when downloading or rendering the media presentation. An editor tags a chunk as important based on the contents of the chunk. The importance information includes a recommendation that this chunk be rendered at a higher-than-usual resolution and that the end-user device start downloading this chunk out of order. An advertiser recommends that an advertisement be rendered at a resolution high enough for the end user to view it appropriately. The importance information can include a recommended point at which to display the advertisement (e.g., between scenes in the media presentation). The end-user device can download advertisements before they are needed. Later, when the user requests a media presentation, an already downloaded advertisement is rendered while the initial chunks of the media presentation are downloaded.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Traffic sensing and monitoring apparatus
ActiveUS7652245B2Easy signal processingGreat signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryDetection of traffic movementPhotodetectorPhysics
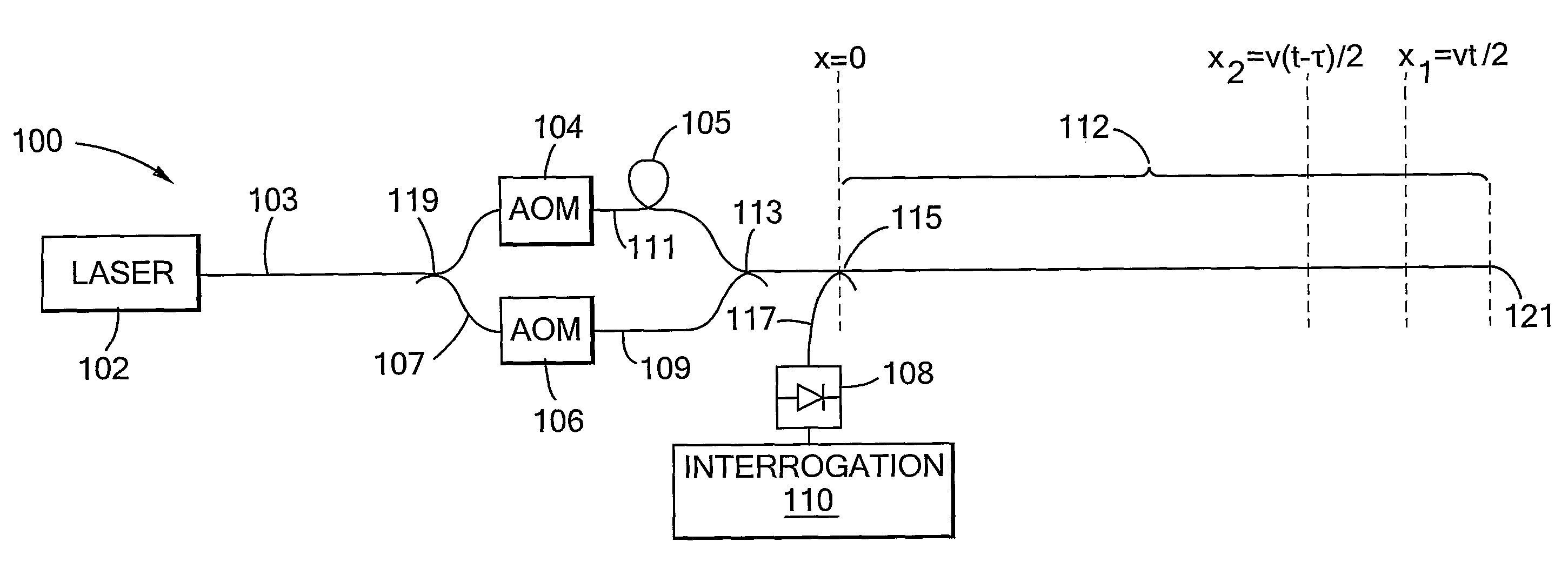
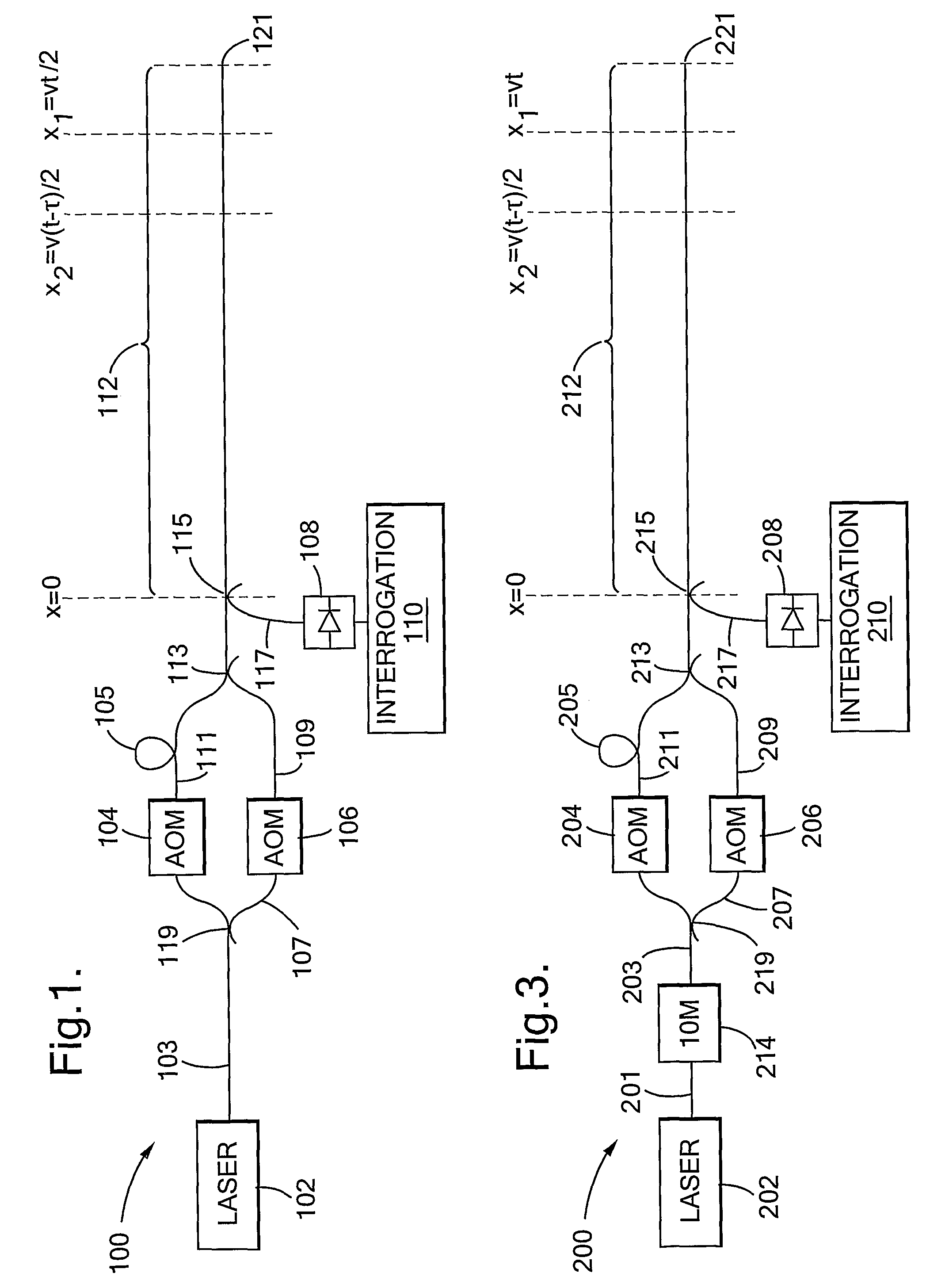
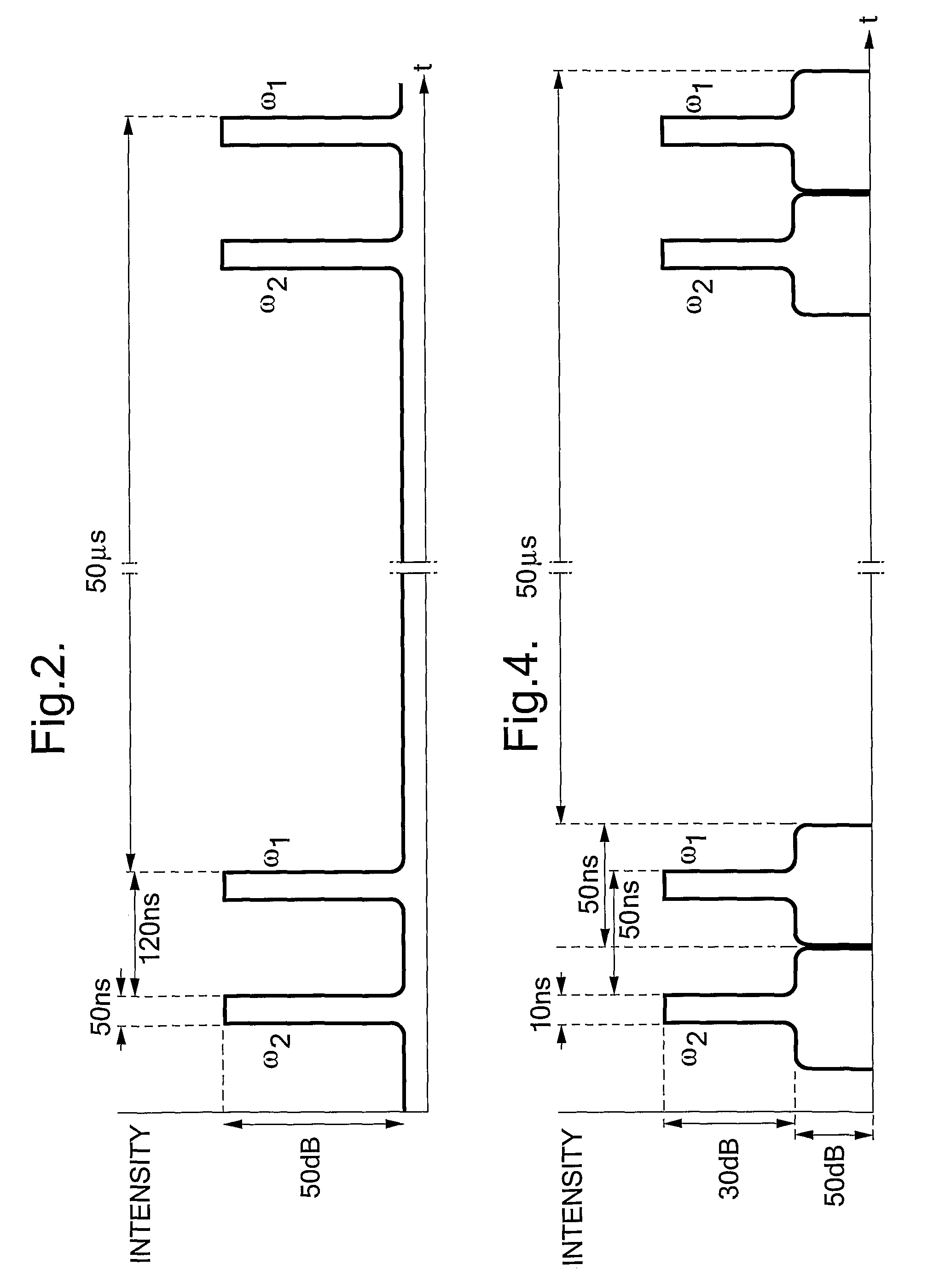
Traffic sensing and monitoring apparatus (100) comprises a length of optical fiber (112), means (102, 103, 104, 106, 107, 109, 119) arranged to introduce a series of pulse pairs into an input end of the length, each of the pulse pairs comprising first and second pulses of radiation having a frequency difference Ω and the second pulse being delayed with respect to the first by a delay τ, and the apparatus further comprising a photodetector arranged to detect radiation which is Rayleigh-backscattered within the length of fiber towards the input end to generate an output signal in response thereto. Apparatus of the invention allows sensing and monitoring of traffic at any position along a long length of road (e.g. 5 km) with lower installation and maintenance costs per unit length compared to prior art systems providing the same spatial resolution.
Owner:OPTASENSE HLDG LTD
Modulation control scheme for power converters in photovoltaic system charge controllers
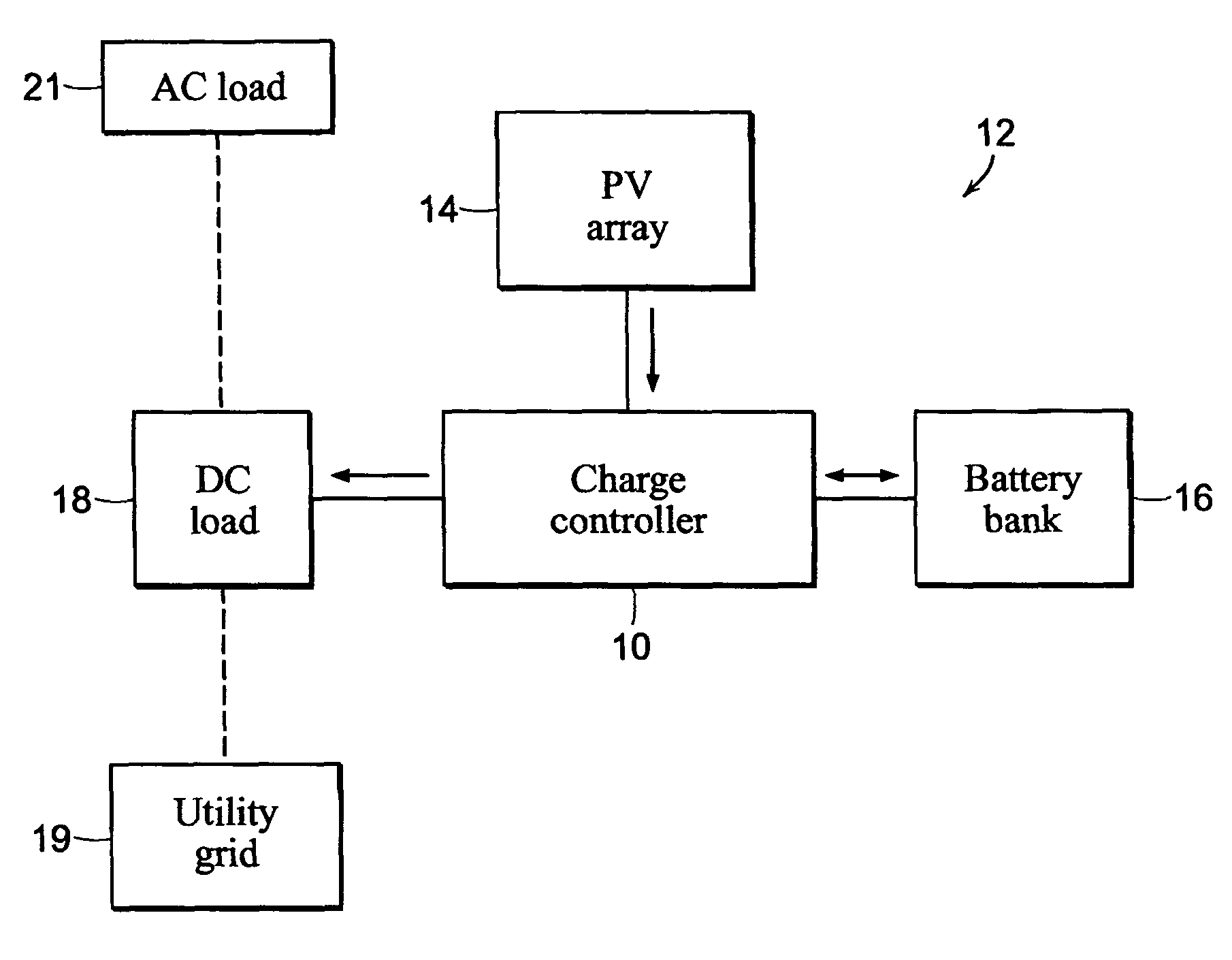
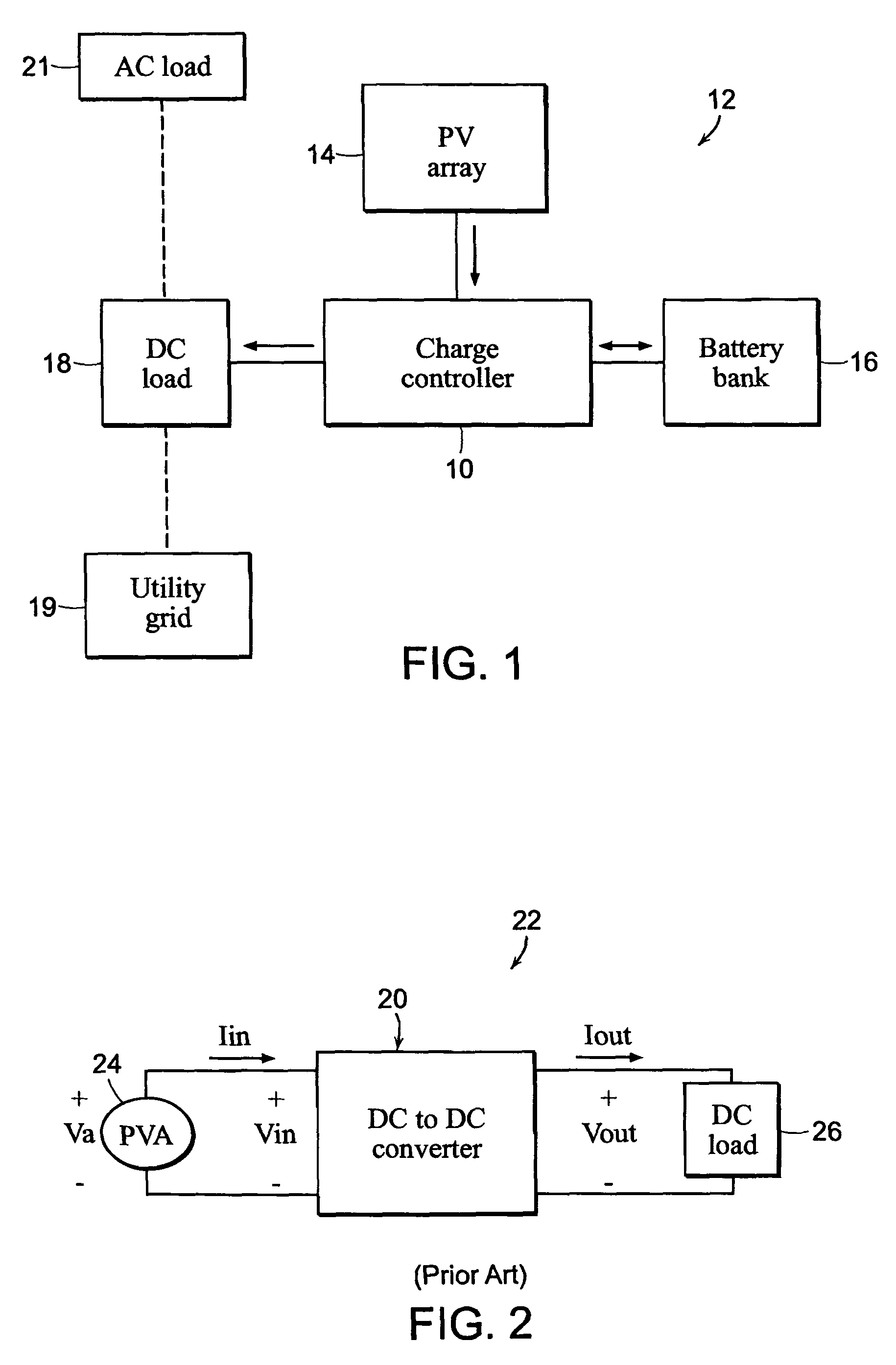
ActiveUS8970161B1Maximize efficiencyConduction loss can be minimizedEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringMaximum power point tracking
A modulation control scheme for a series-connected dual active bridge (DAB) DC to DC converter in a maximum power point tracking charge controller used in a photovoltaic system controls operation of the converter in a forward direction power flow mode to control charging of a battery bank with electricity produced by the photovoltaic array. The modulation control scheme is also capable of operating the converter in a reverse direction power flow mode to control the flow of electricity from the battery bank to a DC load. The modulation control scheme divides the converter's operating range in each mode into five main cases of minimum root mean square (M-RMS) operating regions and seven main cases of full zero-voltage switching (F-ZVS) operating regions, as well as transition operating regions between adjacent main cases, based on applicable power level and value of voltage differential.
Owner:CUADROS CARLOS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com