Patents
Literature
252 results about "Phase alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
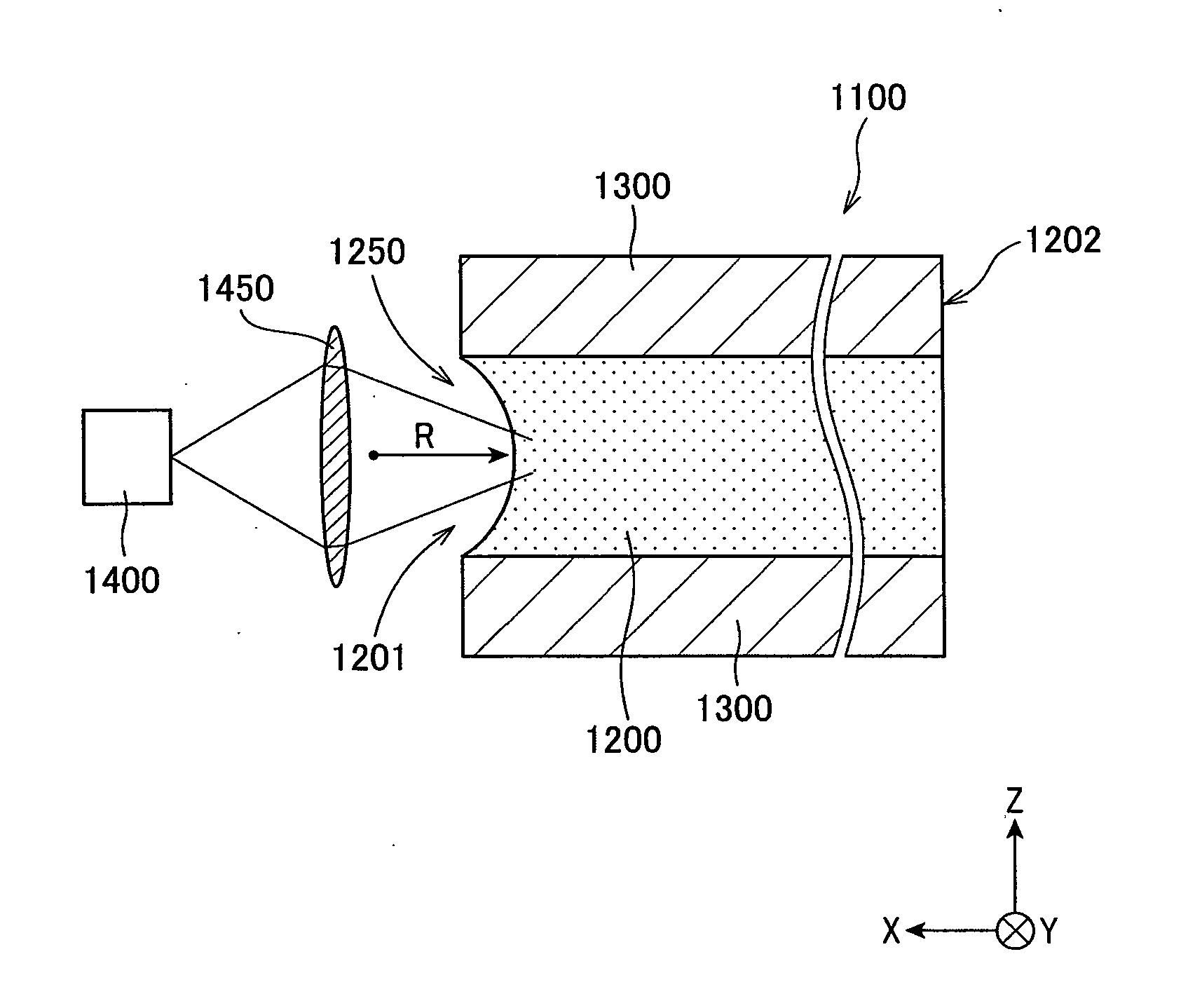
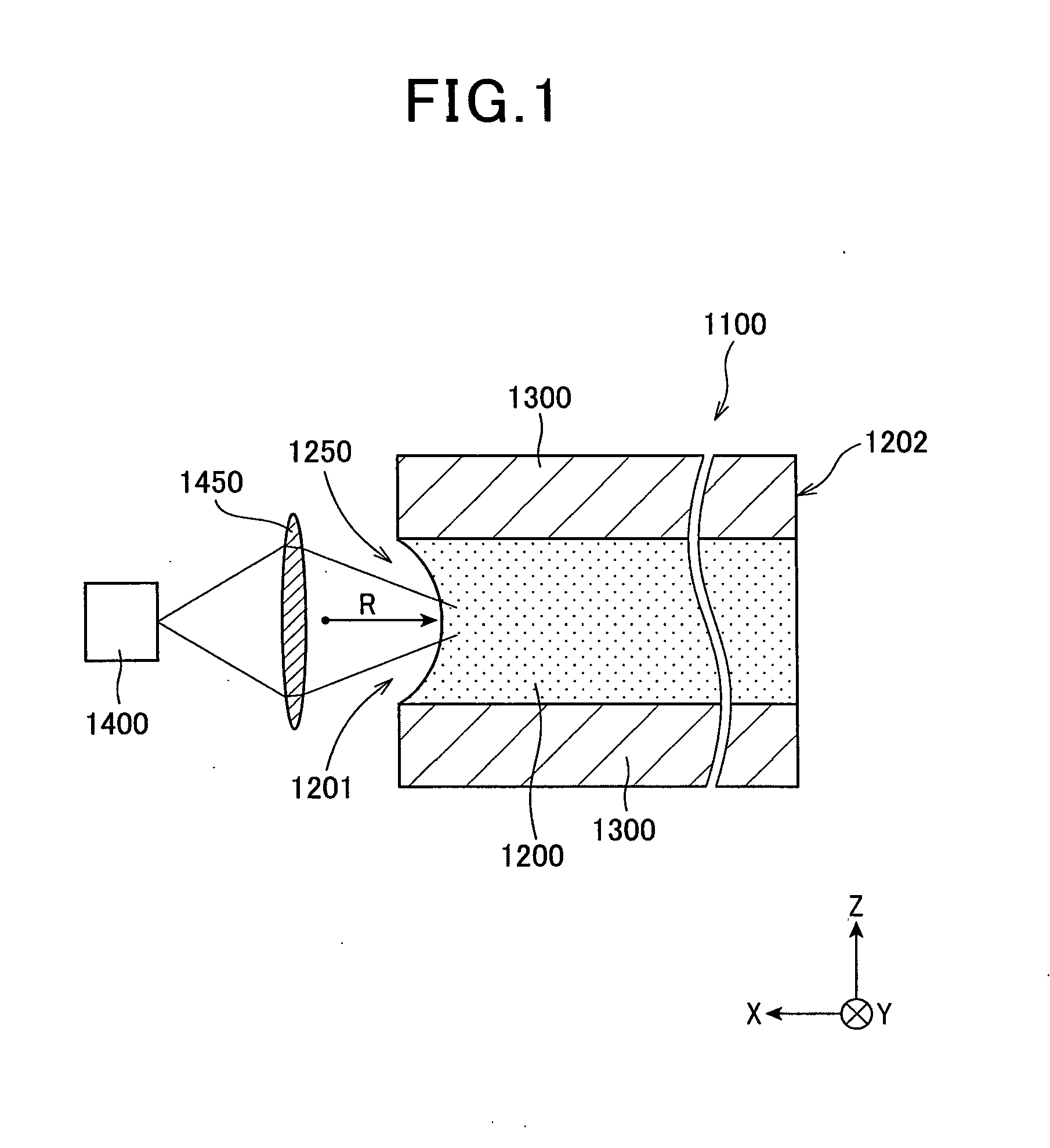
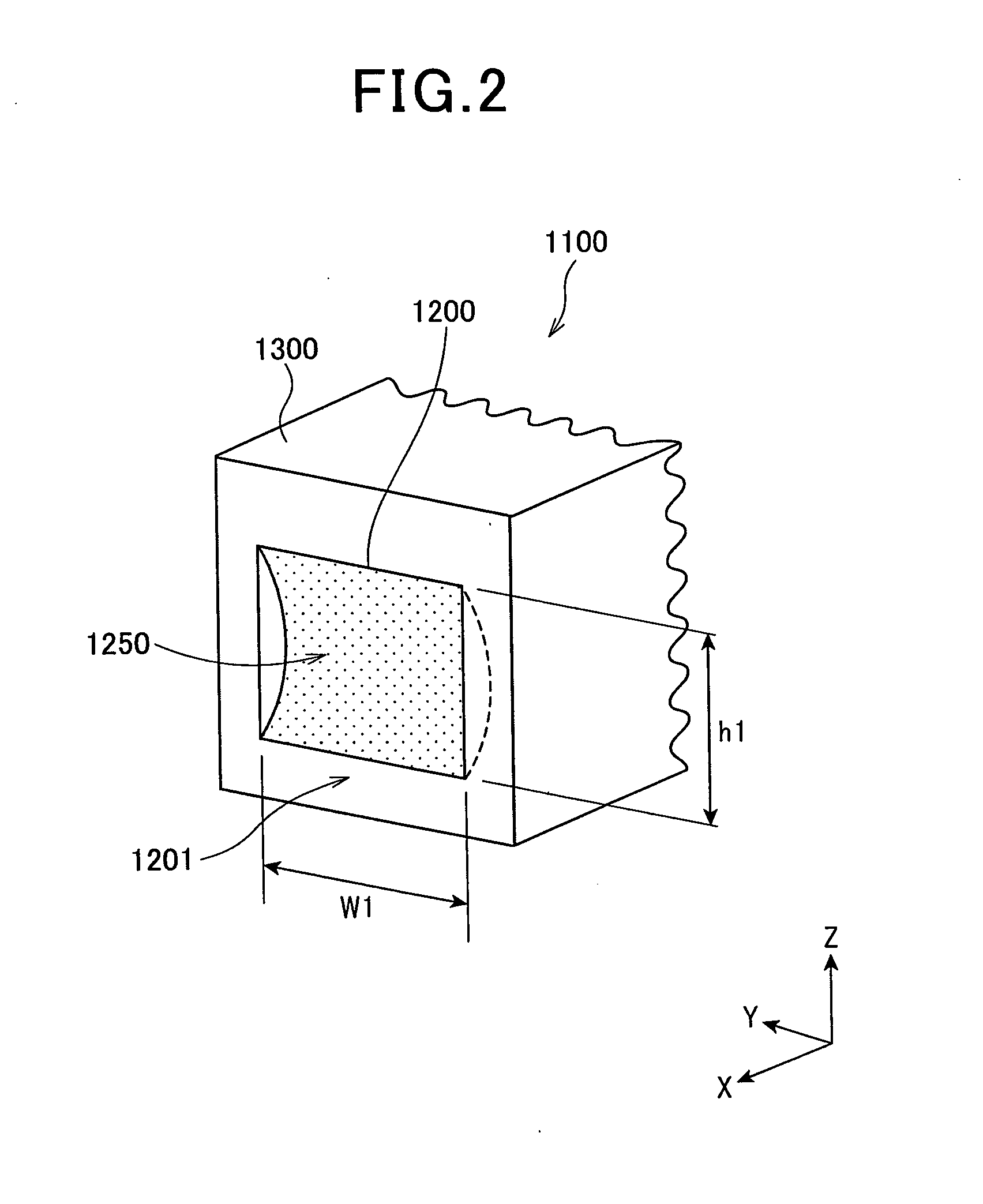
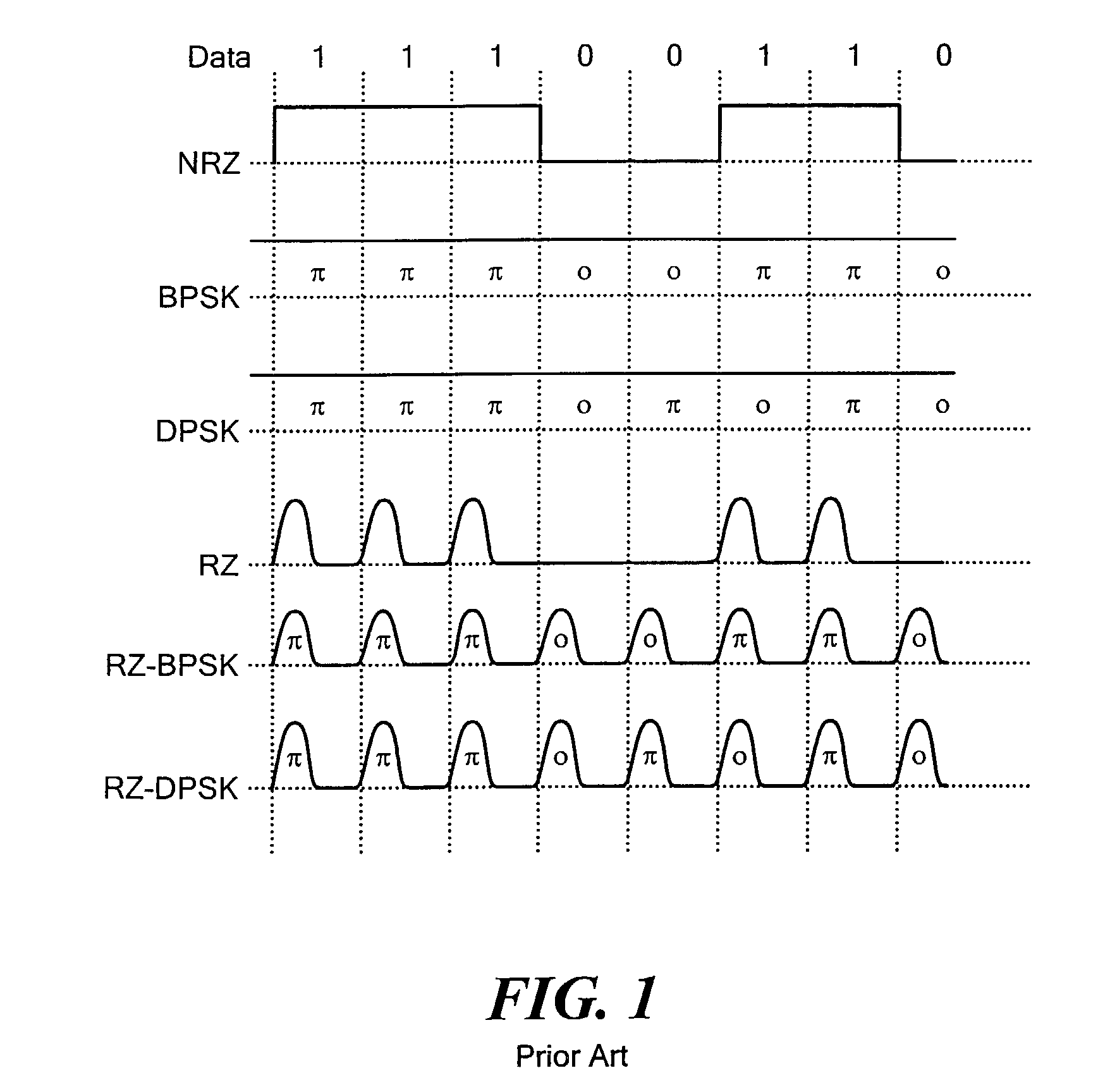
Phase alignment is called upon when sources cover different frequency ranges, e.g., mains and subs. Both time and phase alignment together may be required when unmatched sources cover matched frequency ranges, e.g., Papa Bear mains, Mama Bear side fills and Baby Bear delays.
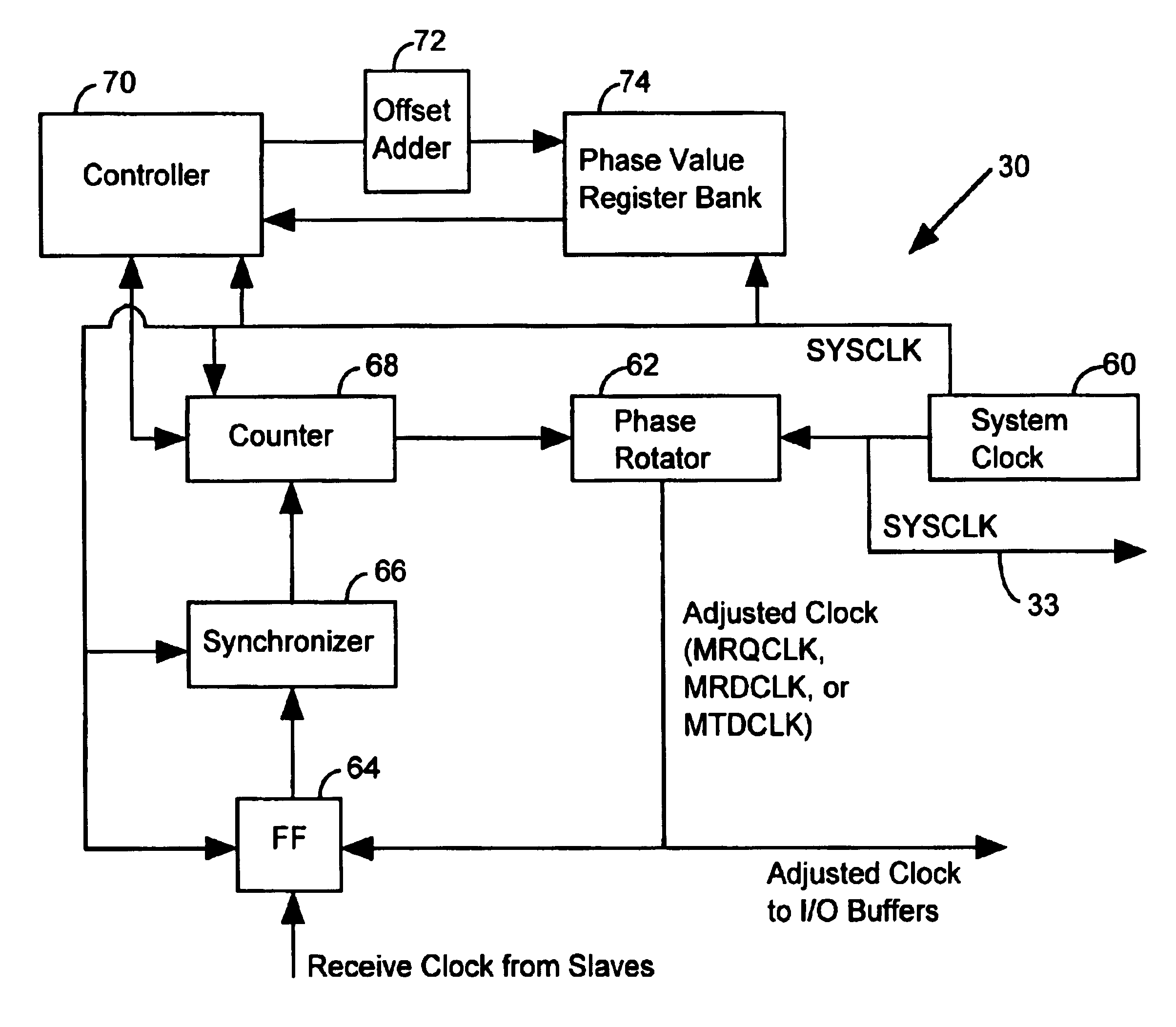
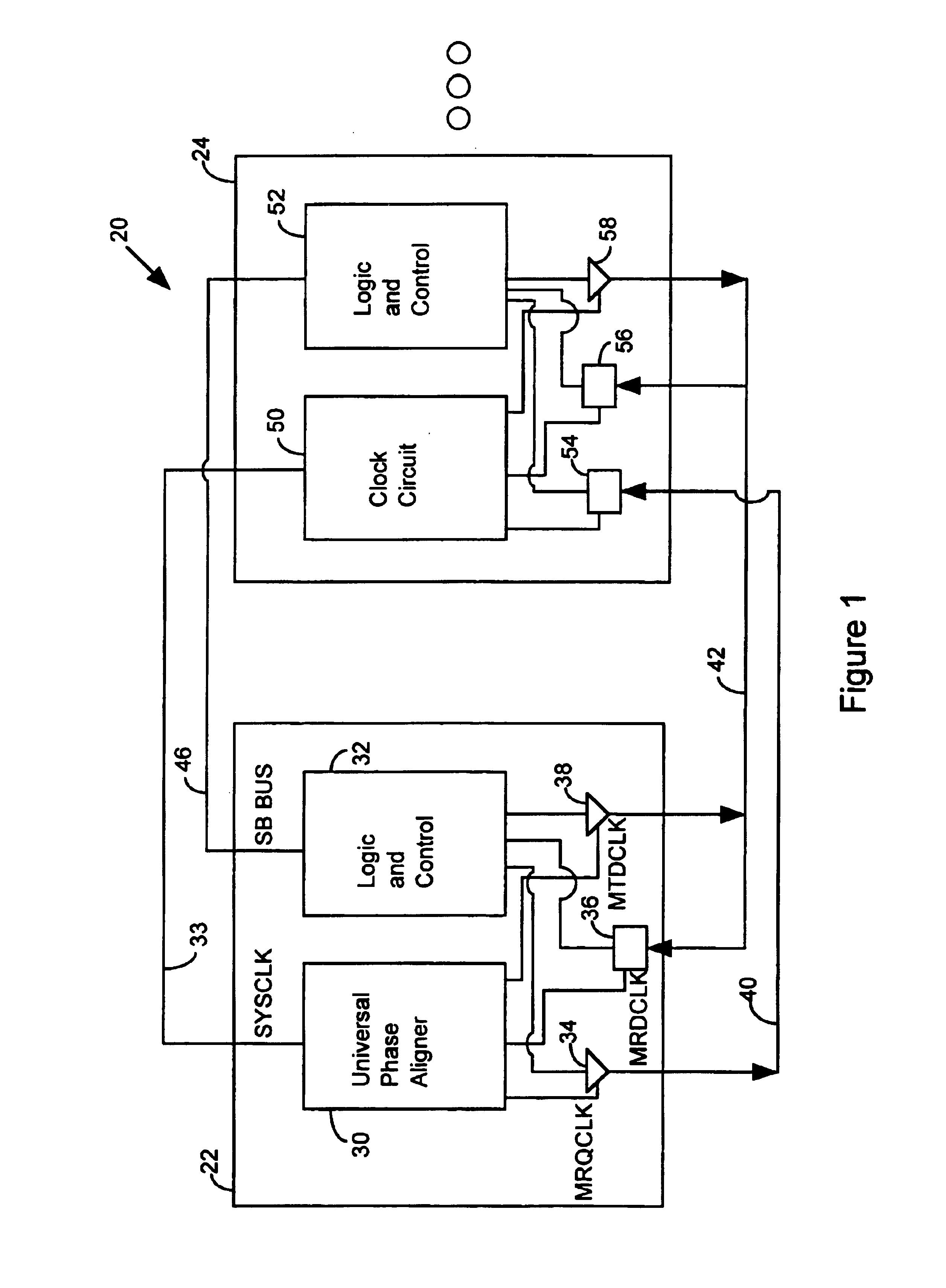
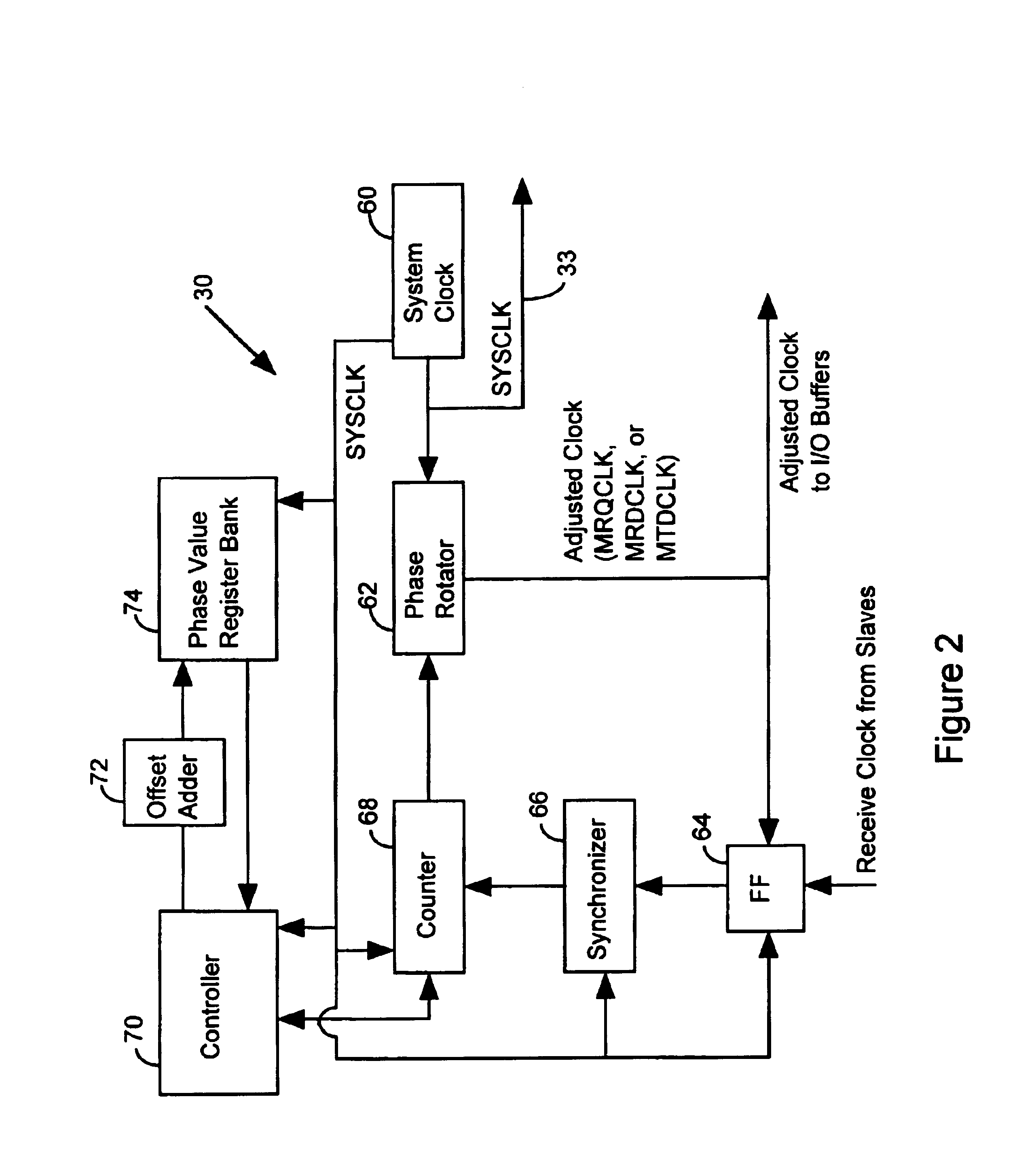
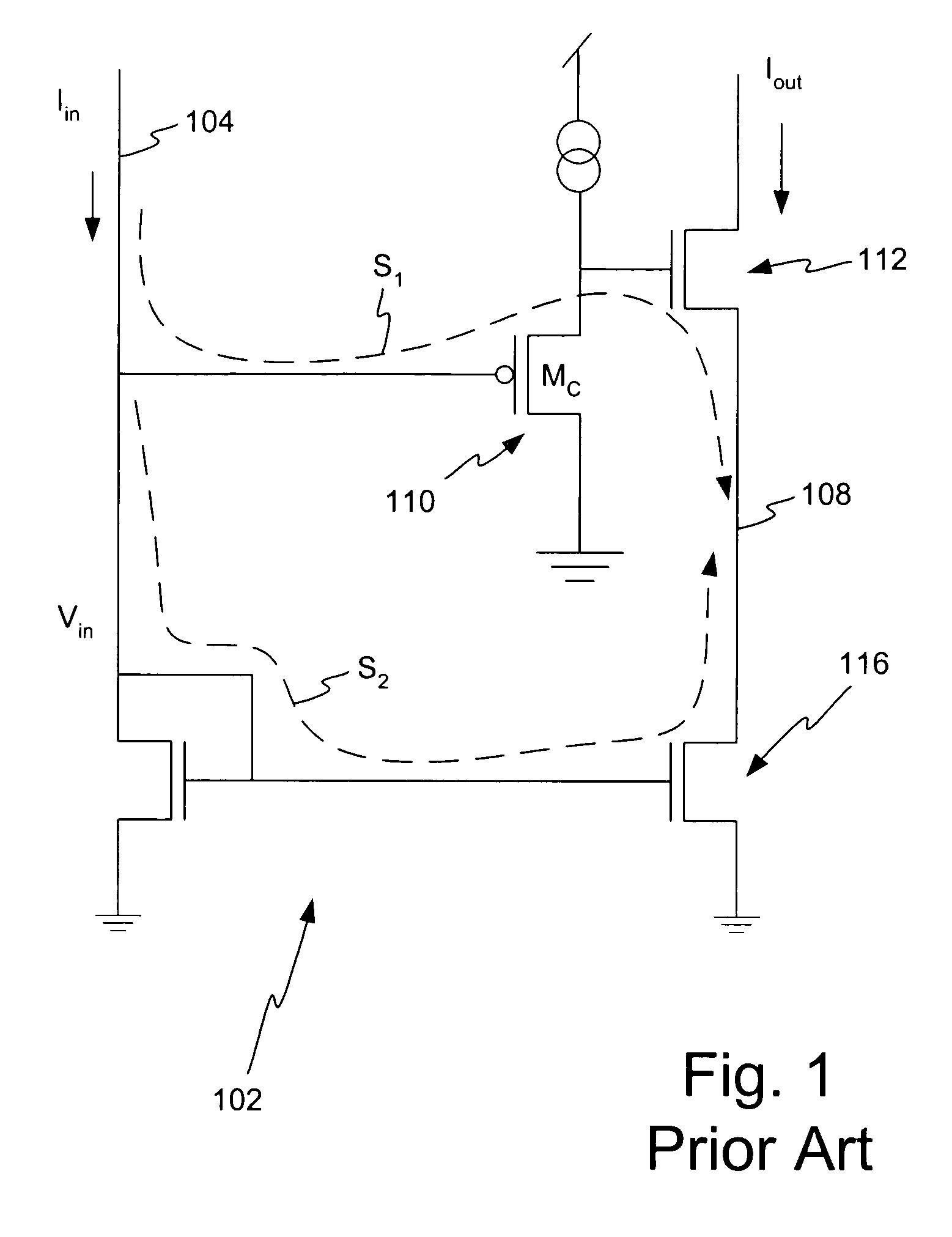
Apparatus and method for controlling a master/slave system via master device synchronization
InactiveUS6839393B1Reduce power consumptionImprove throughputEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlComputer hardwareData shipping
A method of operating a master / slave system includes the step of identifying a master receive data phase value to coordinate the transfer of data from a slave device without phase alignment circuitry to a master device with a universal phase aligner. Data is transferred from the slave device to the master device in accordance with the master receive data phase value. The master device characterizes a master transmit data phase value to coordinate the transfer of data from the master device to the slave device. Subsequently, the master device routes data to the slave device in accordance with the master transmit data phase value.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
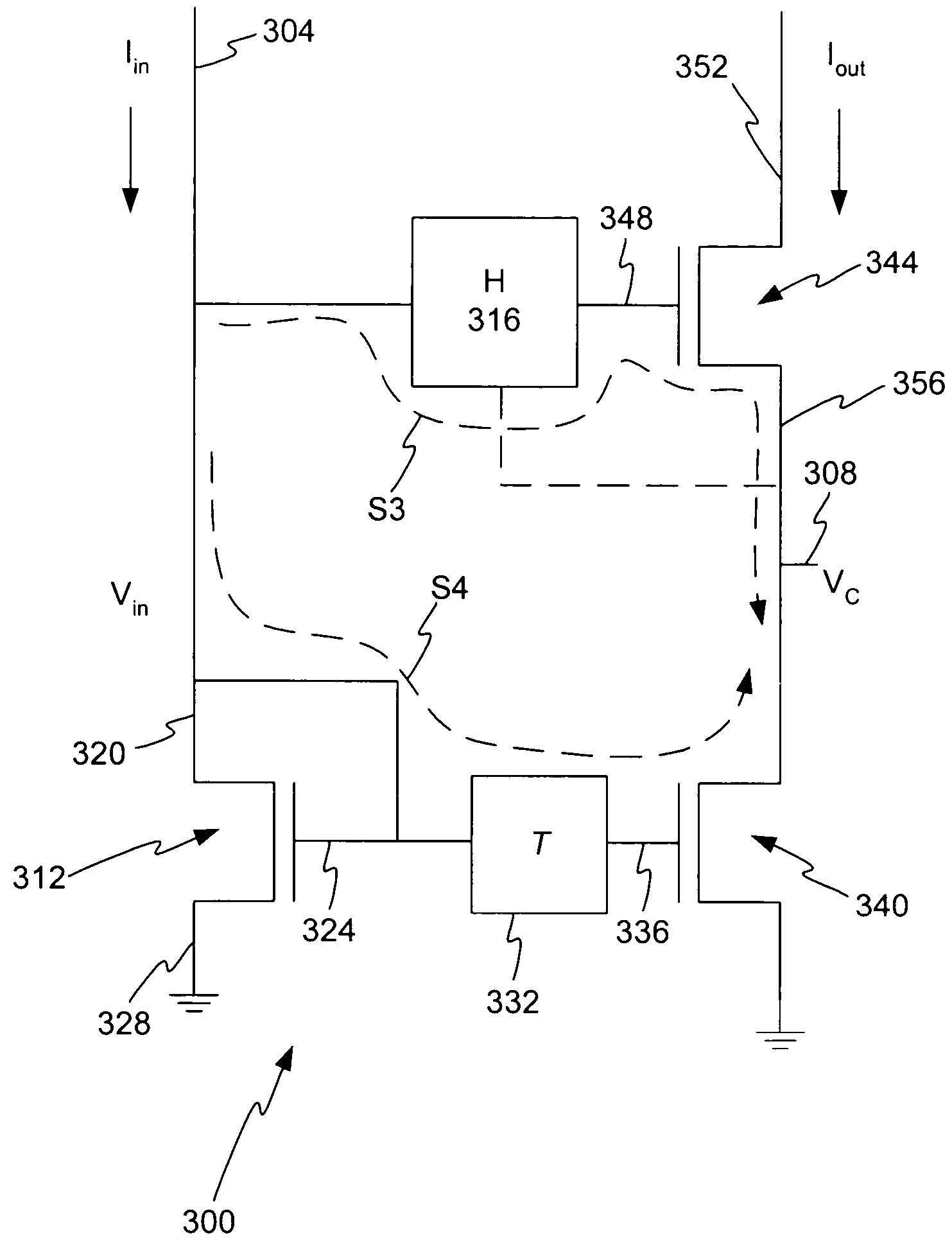
Method and apparatus for increasing the linearity and bandwidth of an amplifier
ActiveUS20050083130A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric variable regulationCascodeEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for improving high frequency performance of an amplifier, such as for example, a current mirror. In one embodiment, a delay element is introduced in a current mirror signal path to account for signal propagation delay that may exist in one or more alternative signal paths. The delay element maintains desired phase alignment at a cascade node of the current mirror thereby establishing, in one embodiment, the cascode node (Vc) in an AC ground state. To extend current mirror high frequency capability an embodiment is disclosed having cross-coupled capacitors, active elements, or one or more other devices configured to provide positive feedback to one or more current mirror inputs. The positive feedback may be selectively configured to increase the operational bandwidth of the current mirror.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
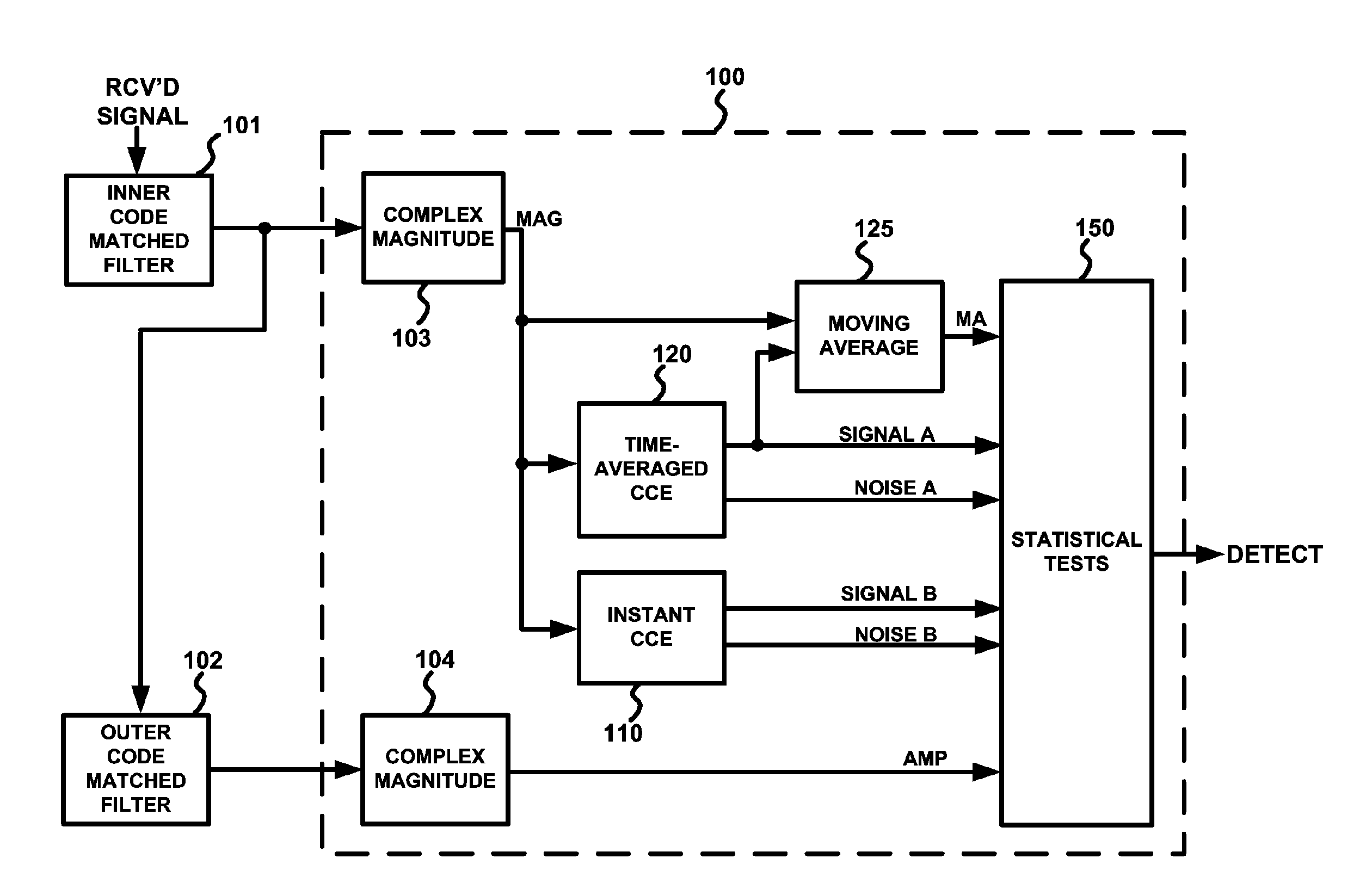
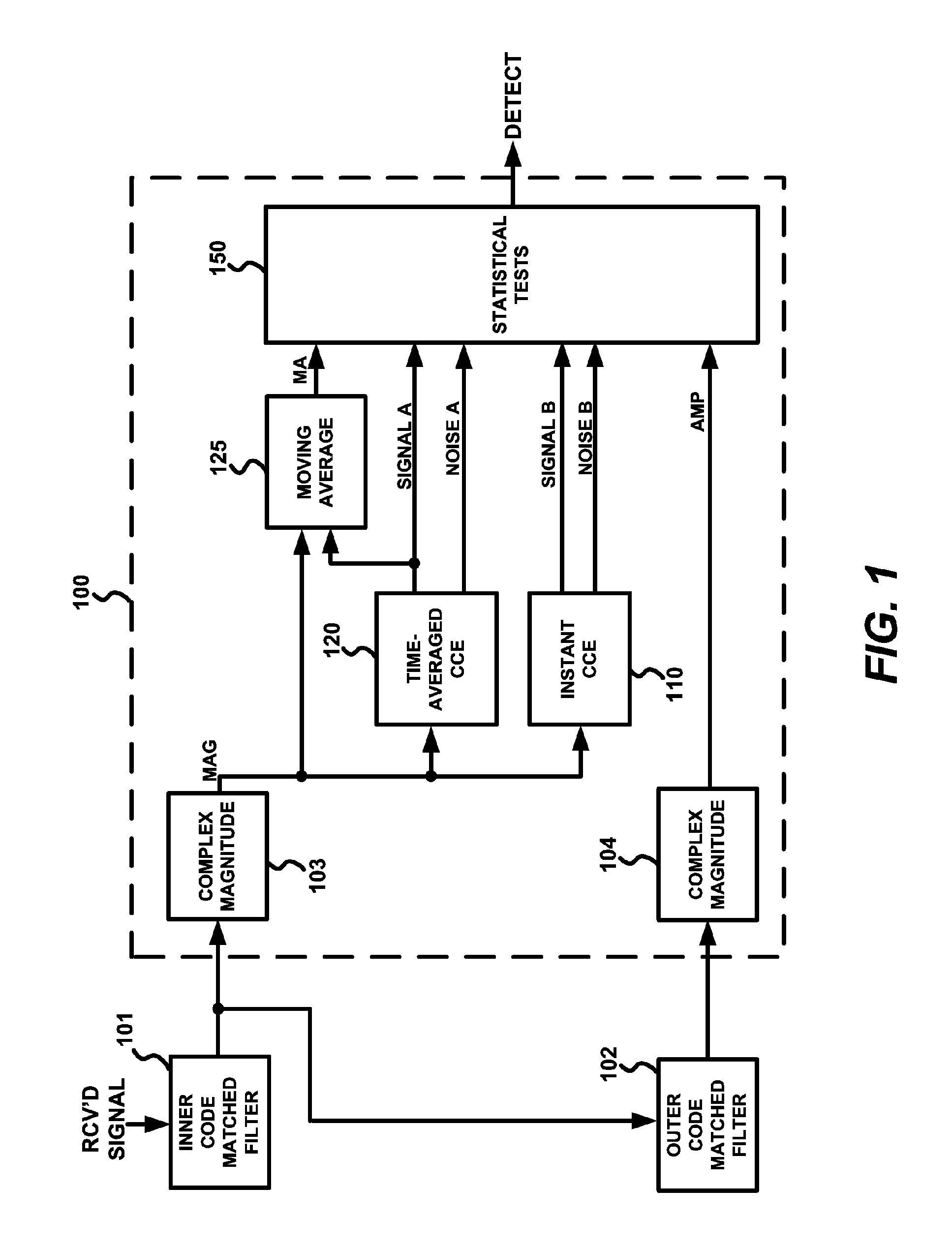
Method and device of peak detection in preamble synchronization for direct sequence spread spectrum communication
ActiveUS20090323766A1Accurate estimateSpecial service for subscribersTime-division multiplexMultipath interferenceNoise level
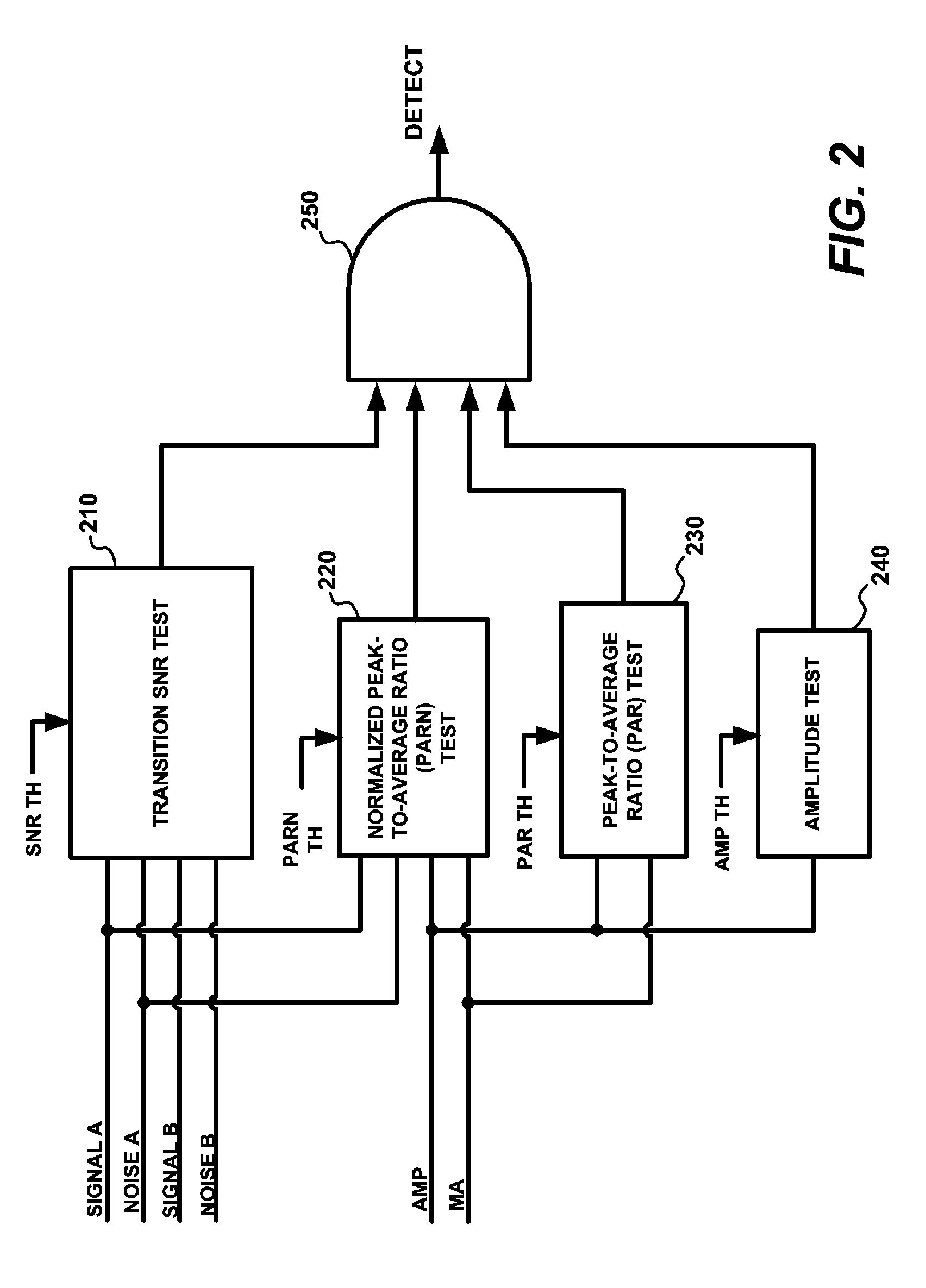
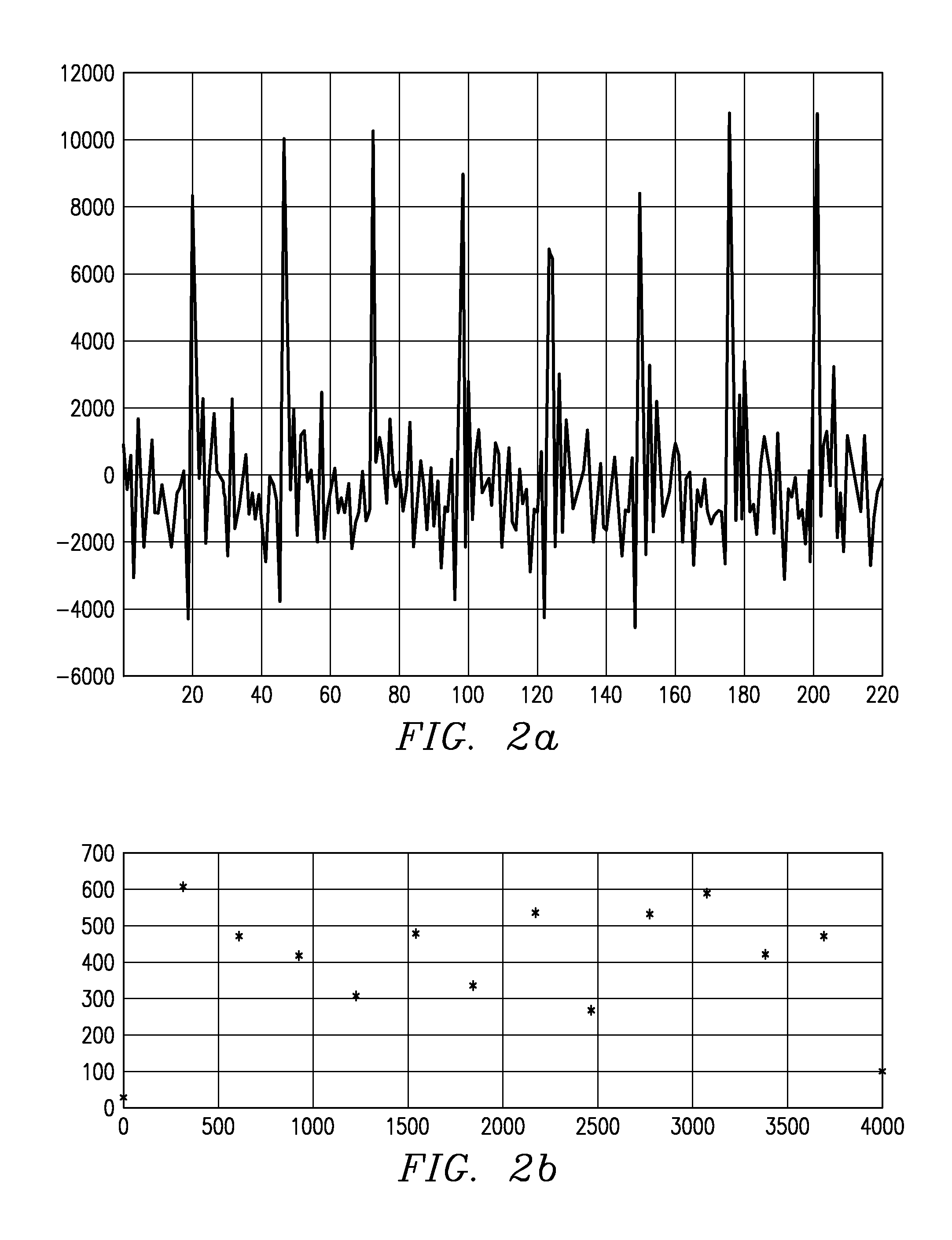
A spread-spectrum preamble synchronization peak detection system performs multiple statistical tests based on instant and time-averaged channel condition measurements to identify the synchronization peak. In a normalized peak-to-average test, a peak-to-average ratio measurement is normalized by a signal-to-noise ratio measurement to form a new statistical measure which effectively eliminates the impact of the wide dynamic range of the signal-to-noise ratio of the received samples. A transition SNR test is used to eliminate potential false alarms caused by spurious PARN peaks during the transition period at the onset of preamble arrival. Code-phase aligned time-averaging is used to estimate the signal and noise levels over a sliding window. The code-phase alignment of samples effectively separates signal and noise samples in the averaging process, and resulting in more accurate signal and noise measurements. In estimating noise levels, the system takes multi-path interference into account by excluding both the peak signal and the side-lobe signals caused by multi-path wireless channels, resulting in more accurate estimation of noise level.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
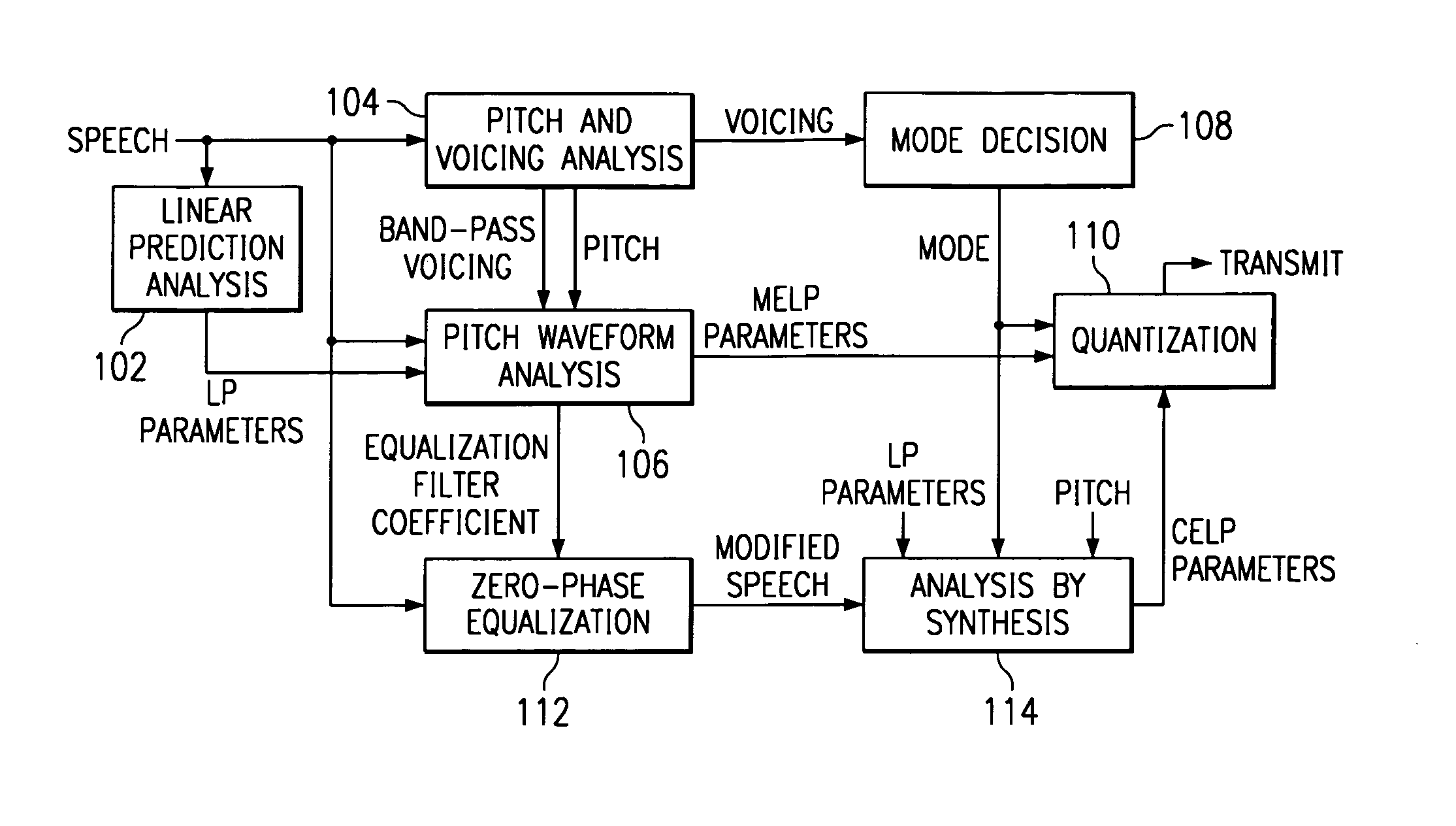
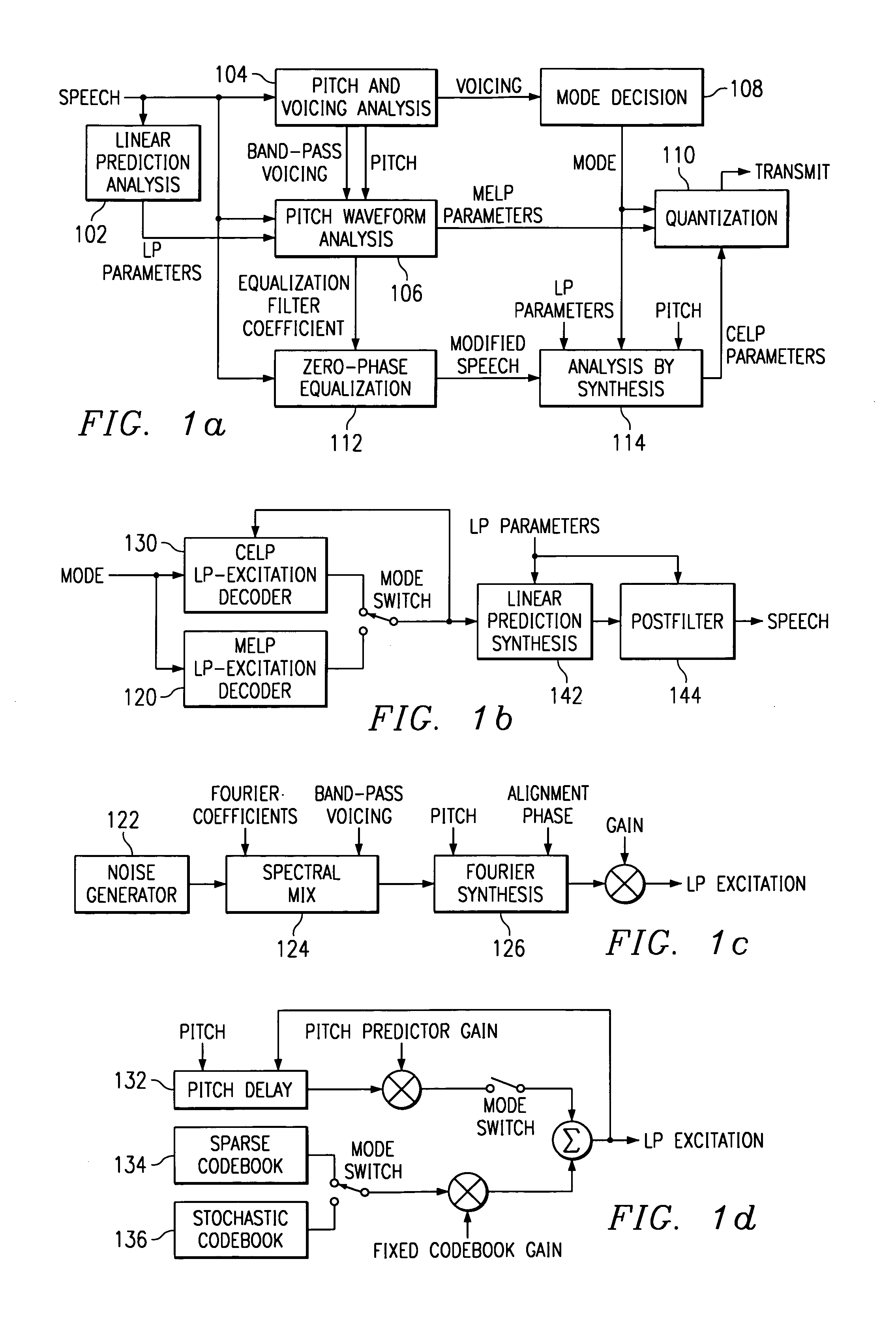
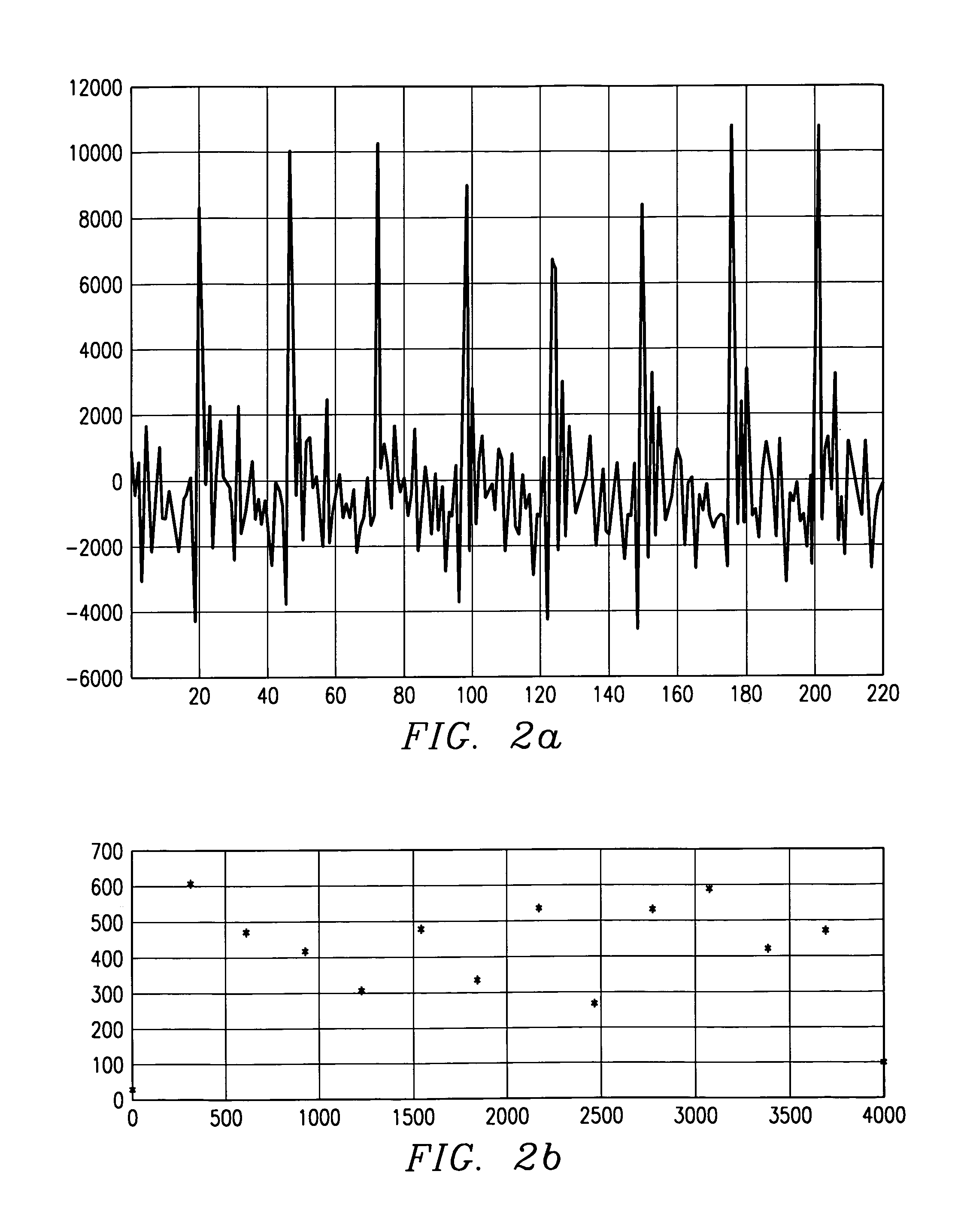
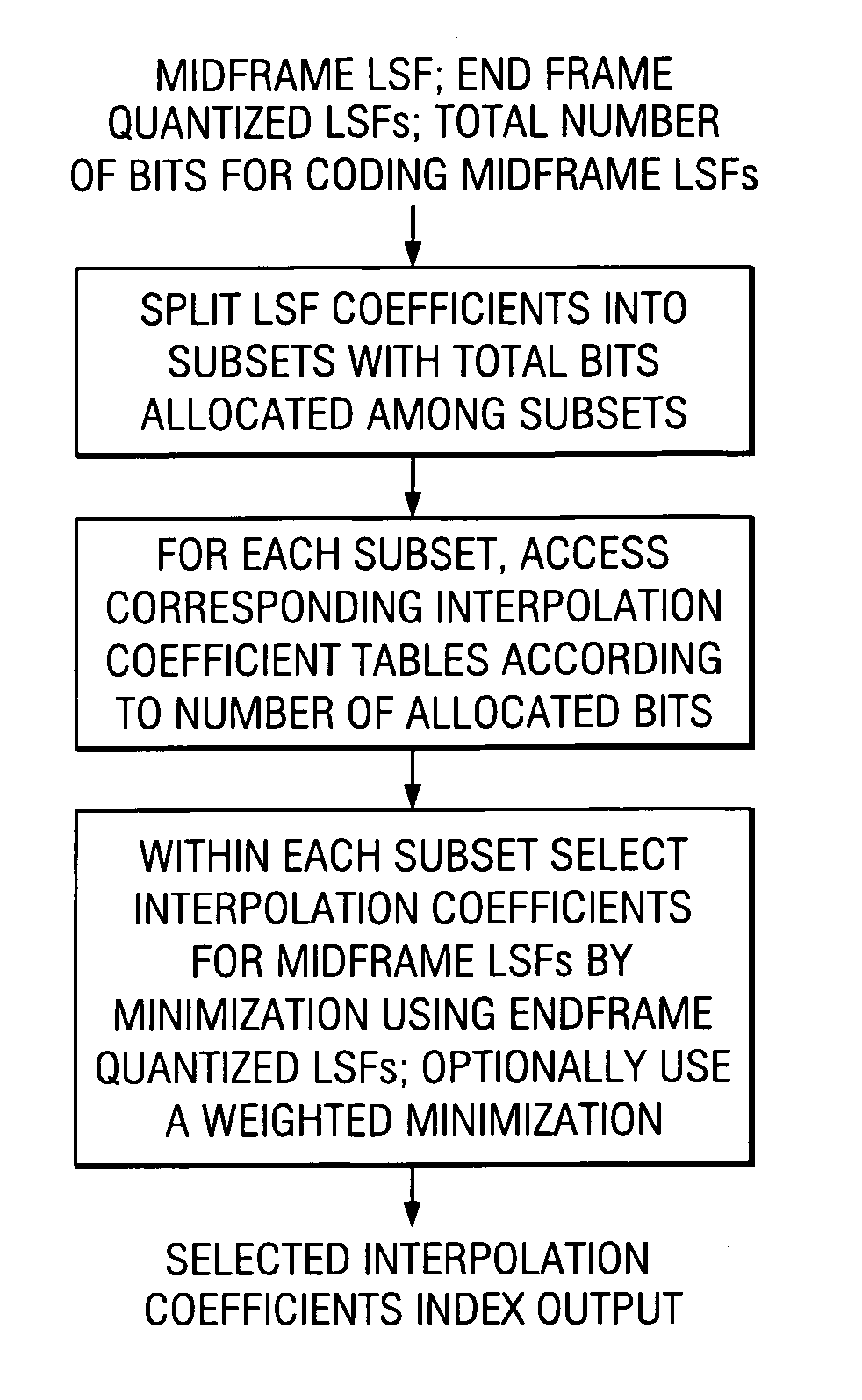
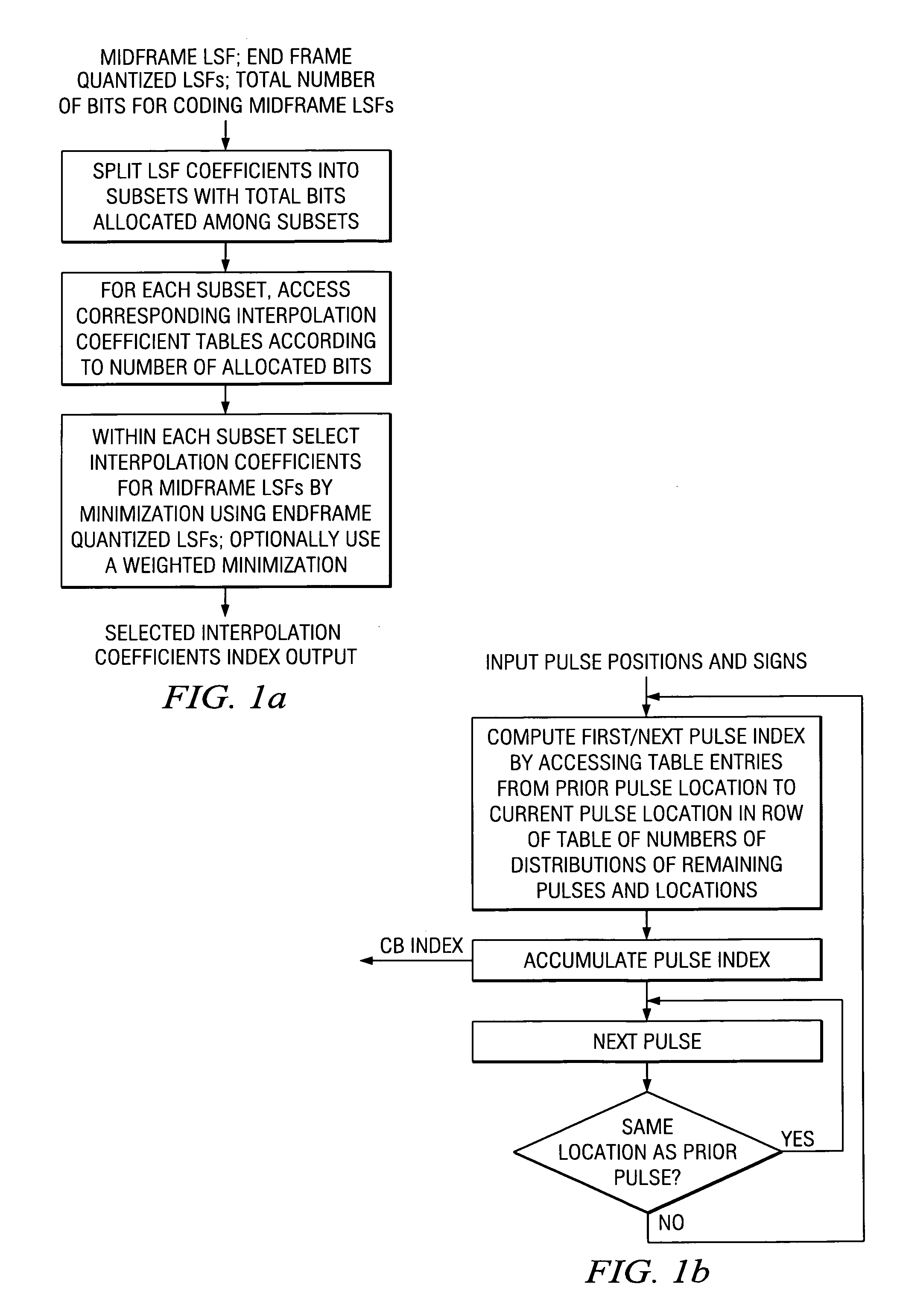
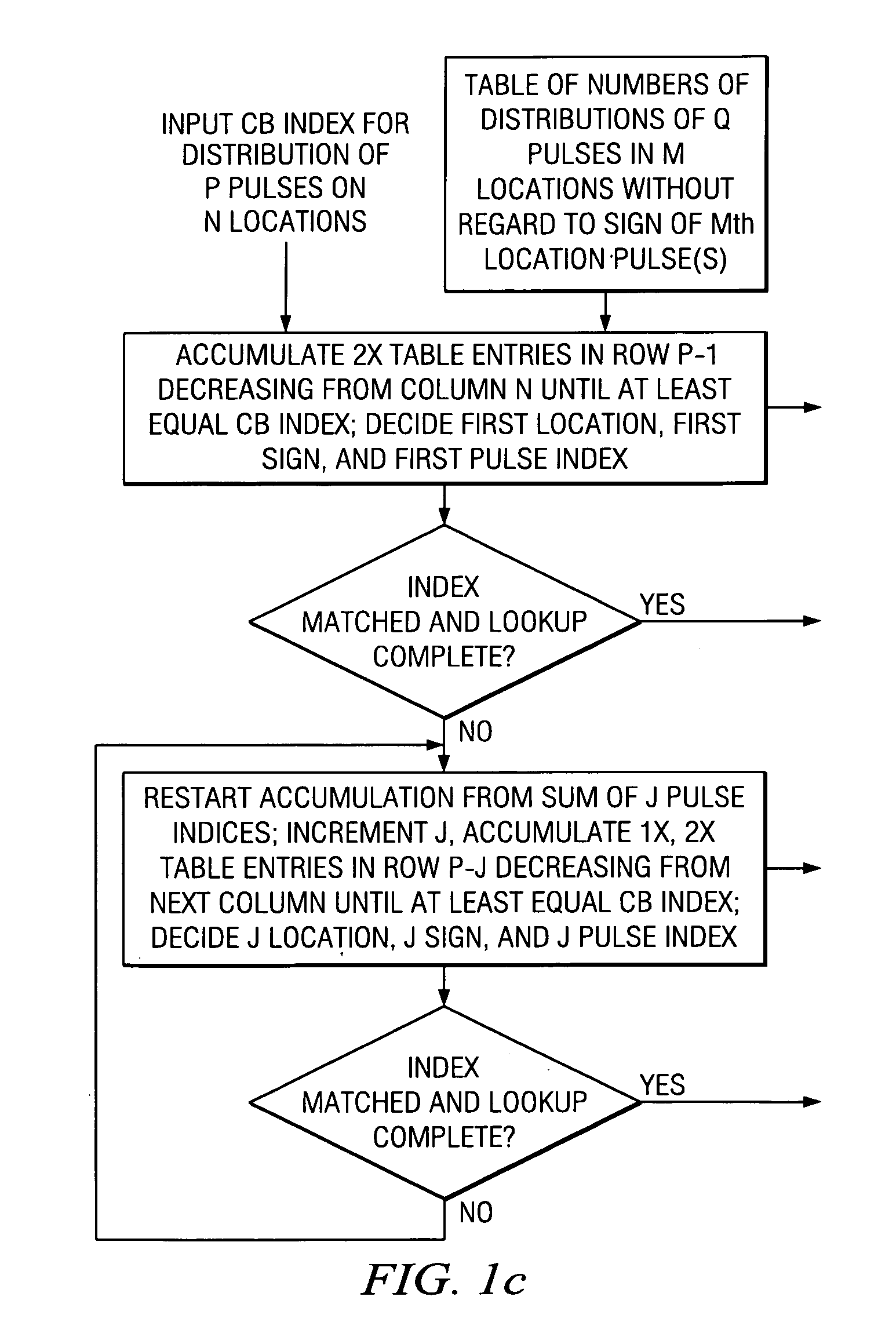
Hybrid speech coding and system
InactiveUS7222070B1Improve performanceEnhance the waveform coderSpeech analysisWaveform codingZero phase
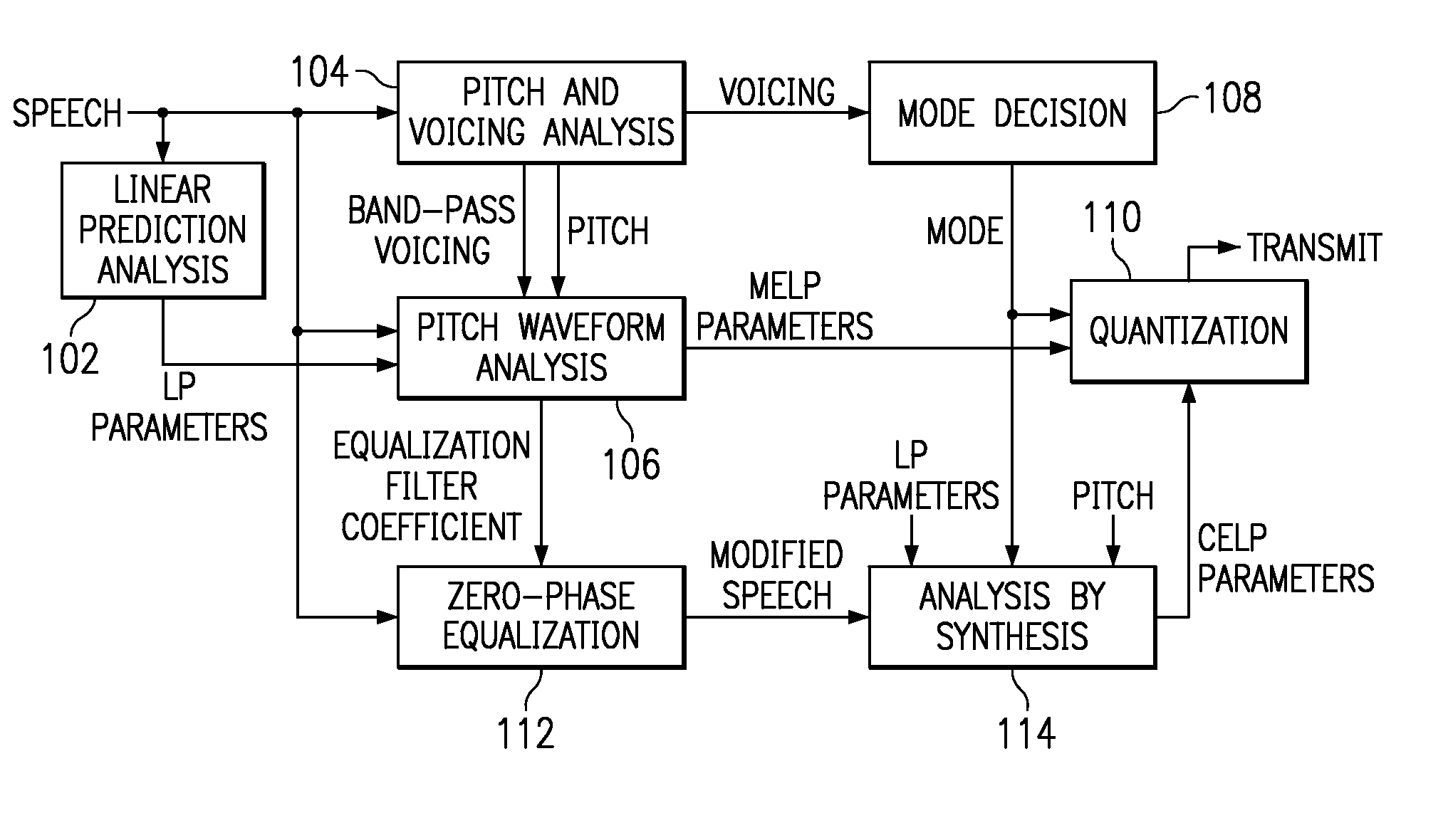
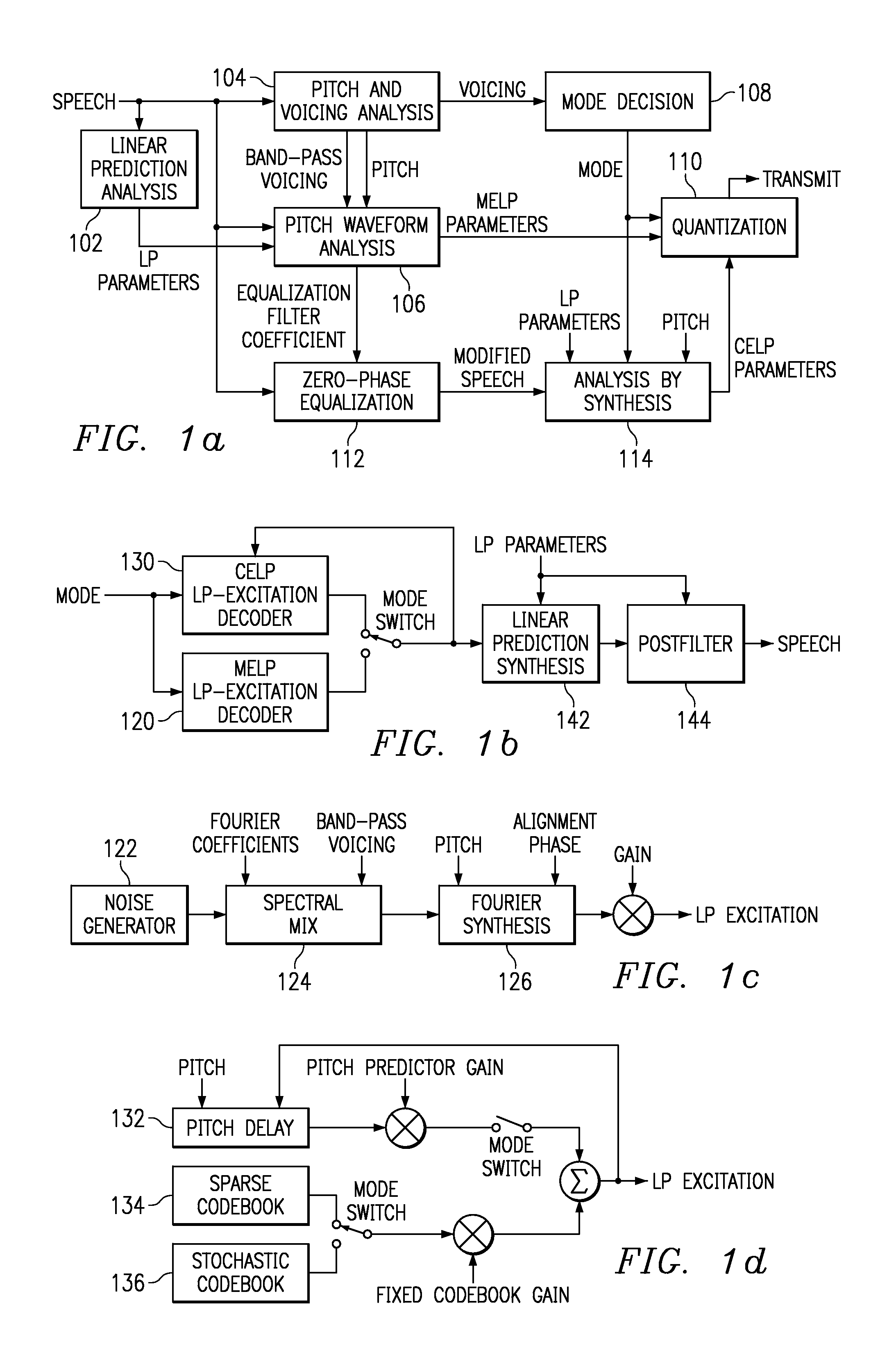
Linear predictive speech coding system with classification of frames and a hybrid coder using both waveform coding and parametric coding for different classes of frames. Phase alignment for a parametric coder aligns synthesized speech frames with adjacent waveform coder synthesized frames. Zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
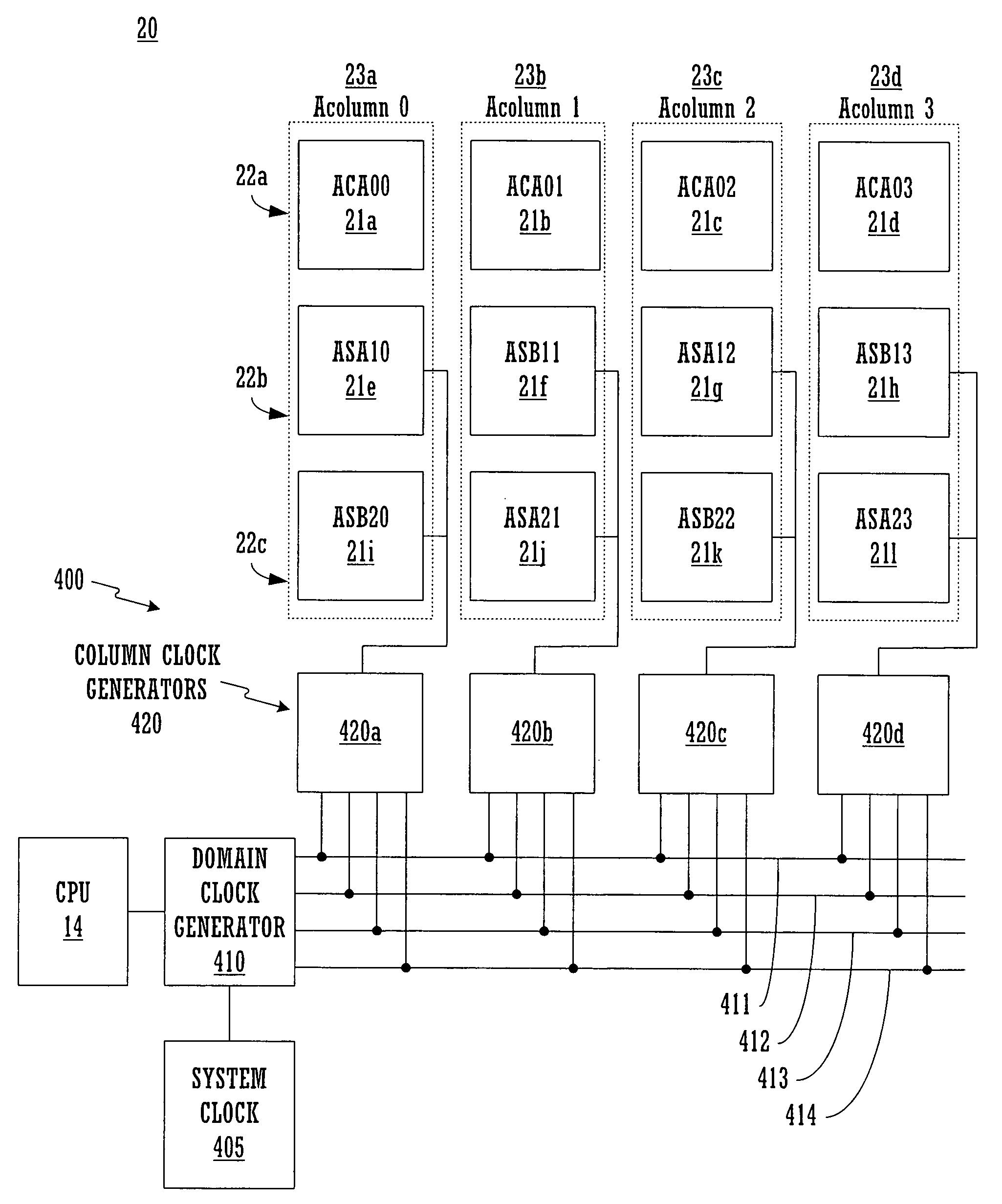
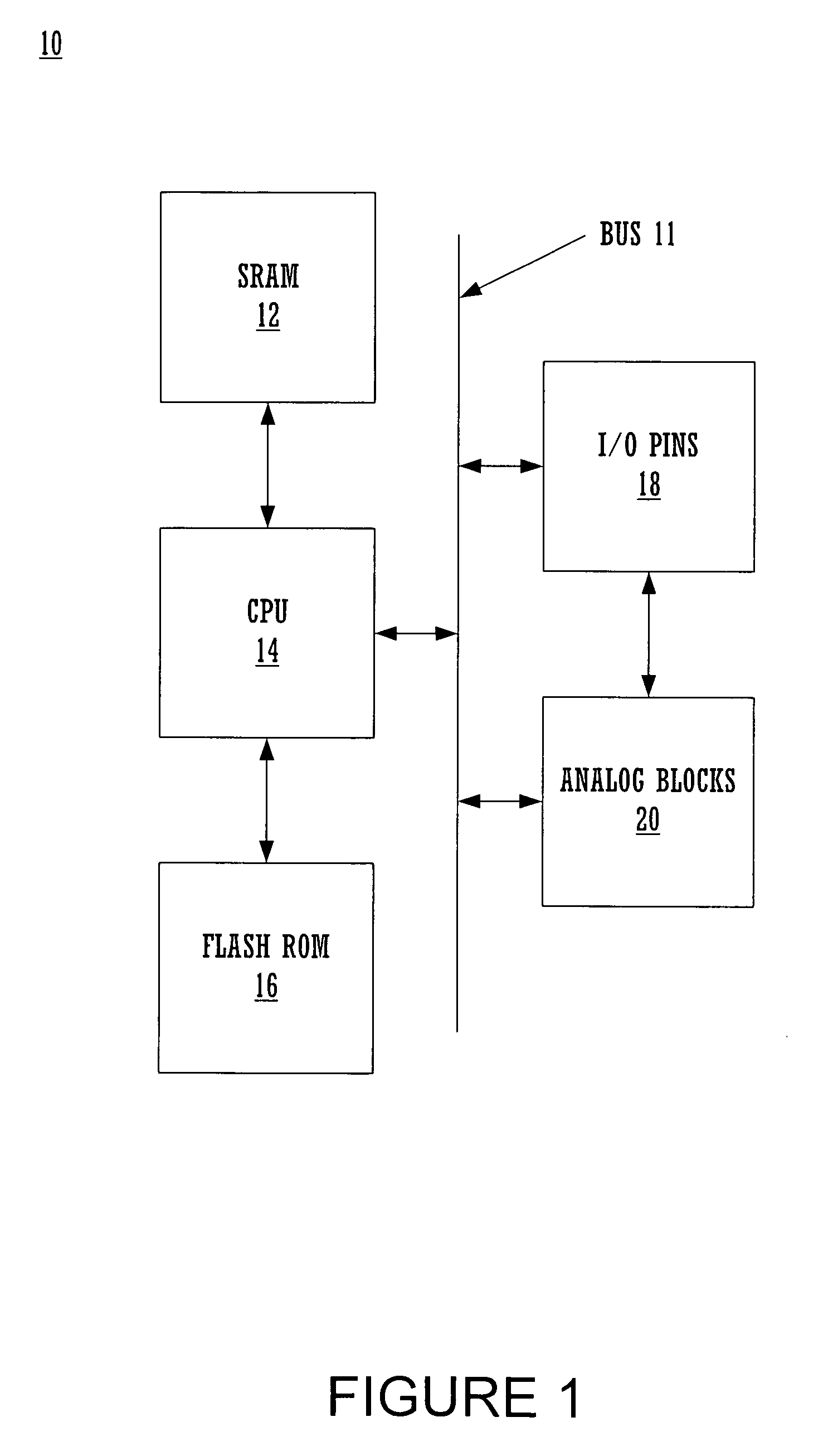
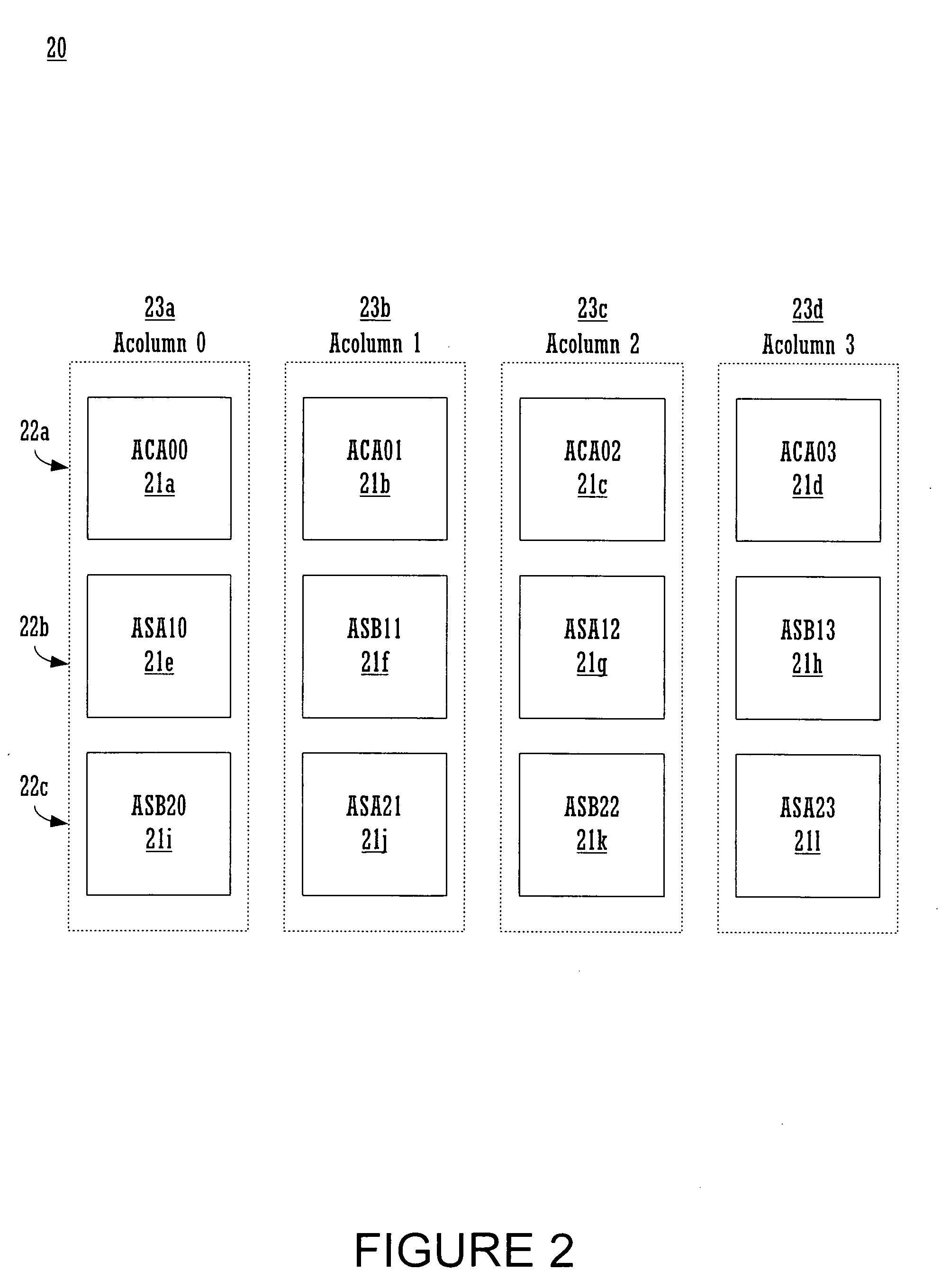
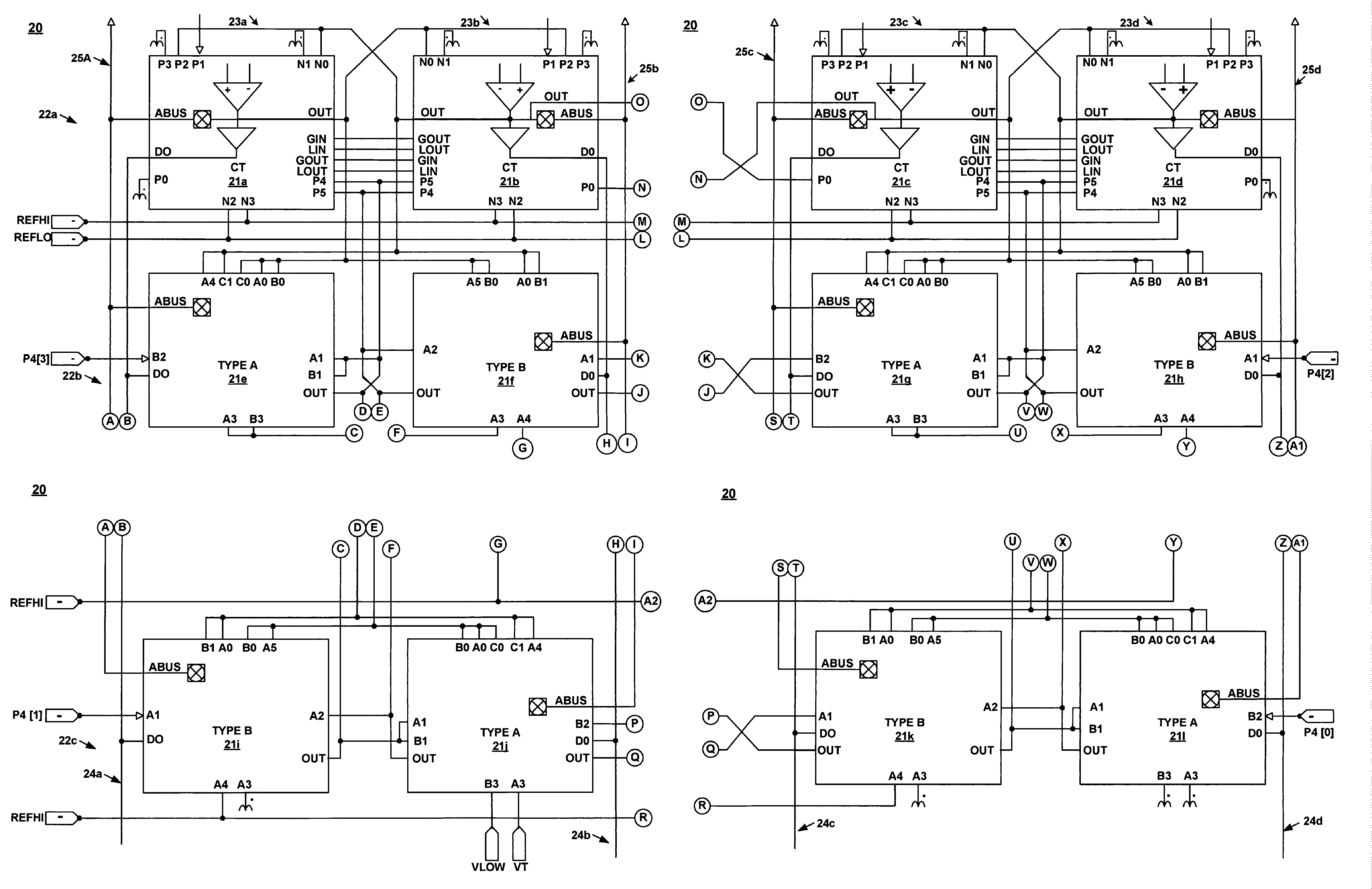
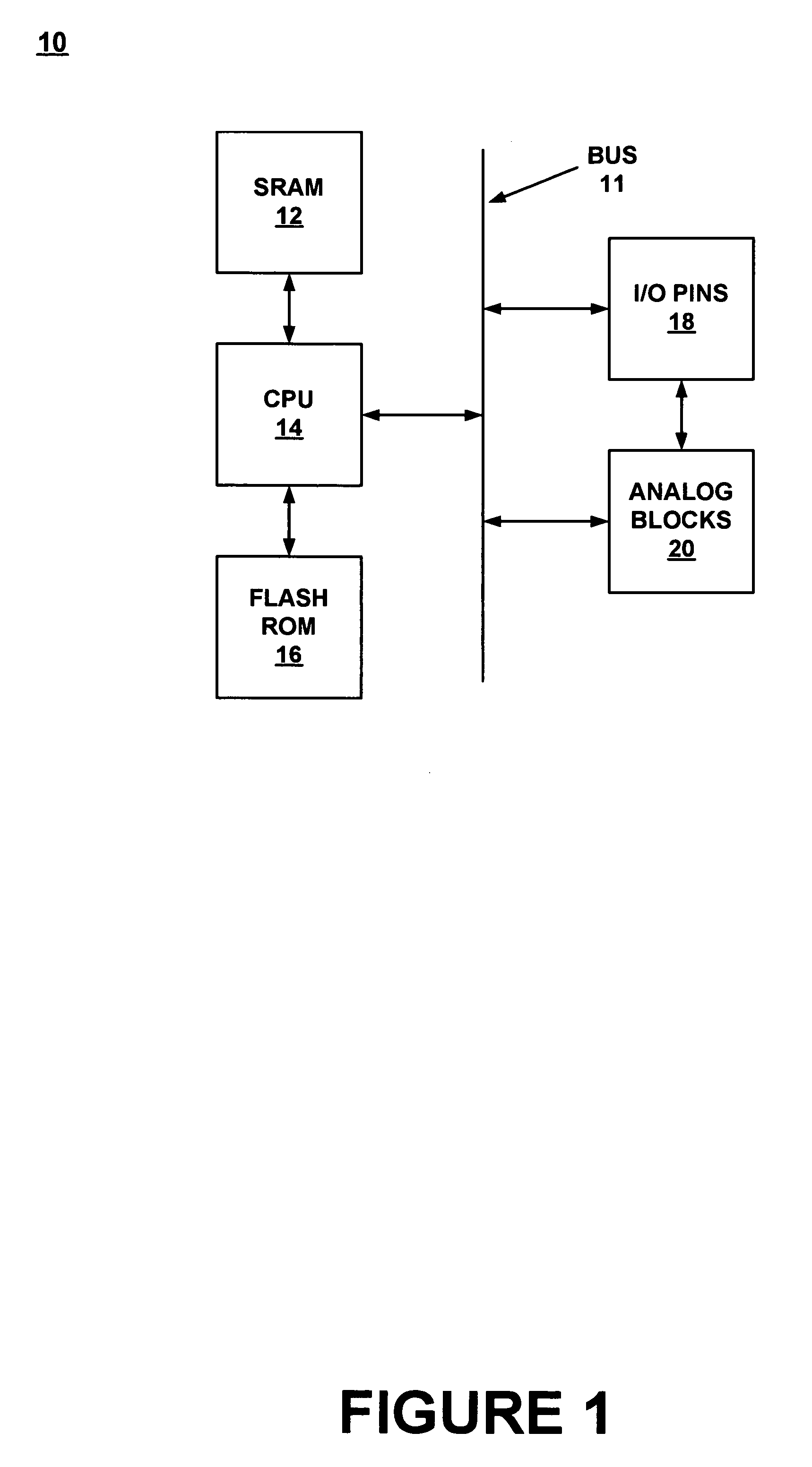
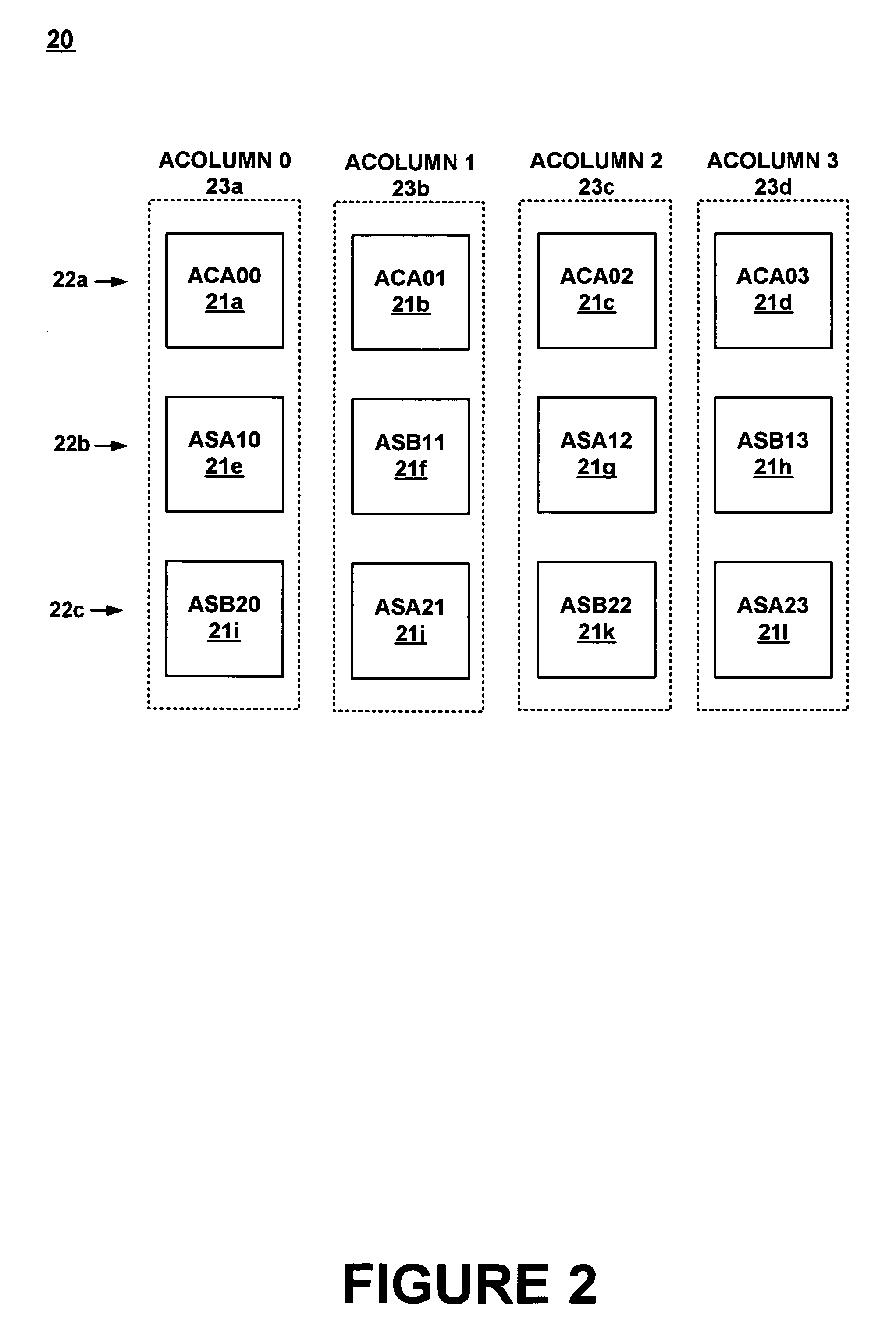
Architecture for synchronizing and resetting clock signals supplied to multiple programmable analog blocks
InactiveUS7023257B1Efficiently usLow costPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorEngineeringA domain
A circuit for establishing frequency and phase alignment of clock signals across a domain of analog blocks coupled in a single integrated circuit. Different analog functions are implemented by selectively and electrically coupling different combinations of analog blocks. The analog blocks may be arrayed in a number of columns. The circuit is coupled to the analog blocks to supply a synchronized clock signal to all of the analog blocks in a combination of blocks, even when the blocks are in different columns. The circuit allows the frequency of the clock signal to be changed dynamically depending on the analog function to be achieved. The circuit also establishes phase alignment when a frequency change occurs.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Method for synchronizing and resetting clock signals supplied to multiple programmable analog blocks
InactiveUS6967511B1Efficiently usLow costComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationA domainComputer science
A method for establishing frequency and phase alignment of clock signals across a domain of analog blocks coupled in a single integrated circuit. Different analog functions are implemented by selectively and electrically coupling different combinations of analog blocks. The analog blocks may be arrayed in a number of columns. A synchronized clock signal is supplied to all of the analog blocks in a combination of blocks, even when the blocks are in different columns. The frequency of the clock signal can be changed dynamically depending on the analog function to be achieved.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
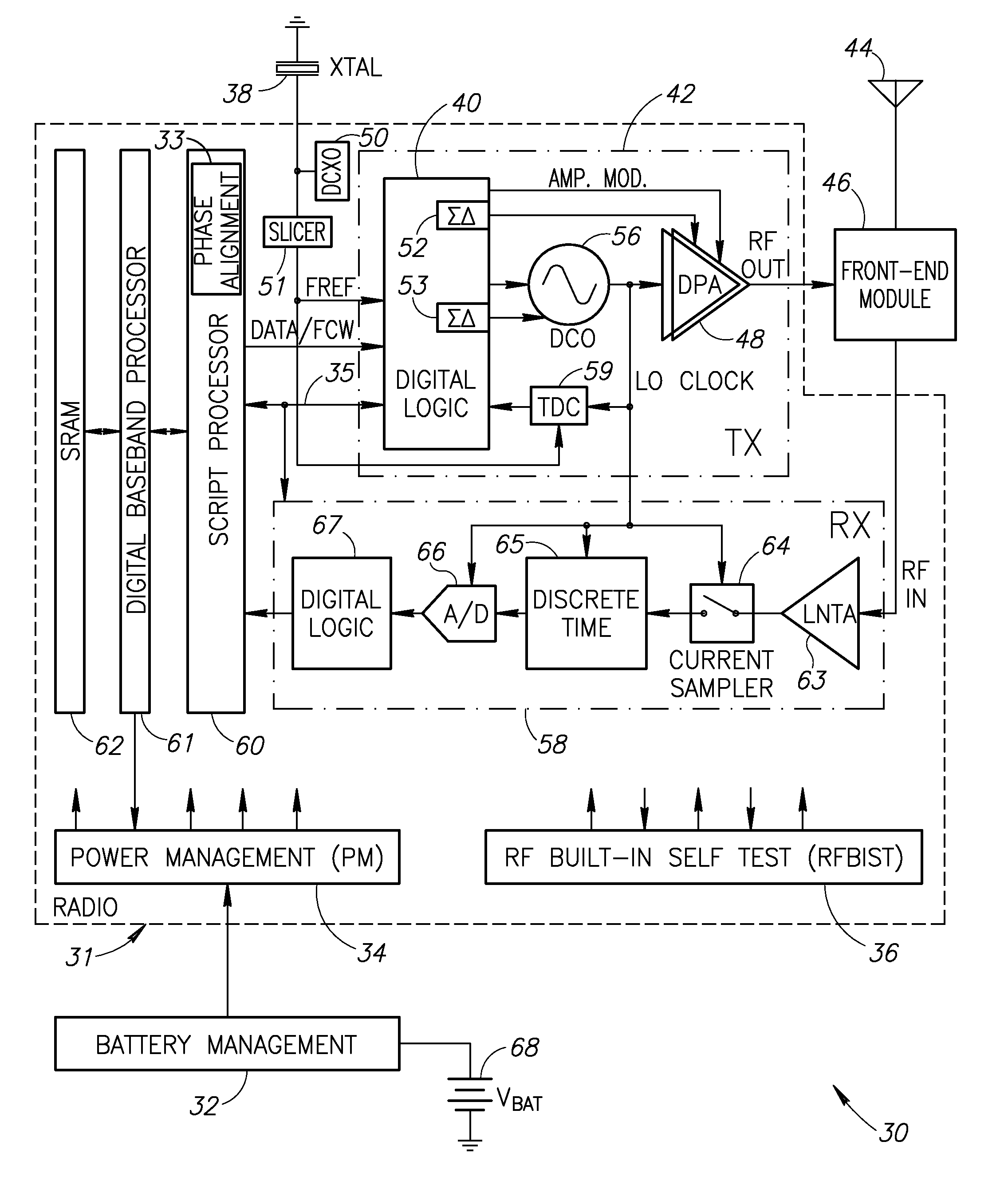
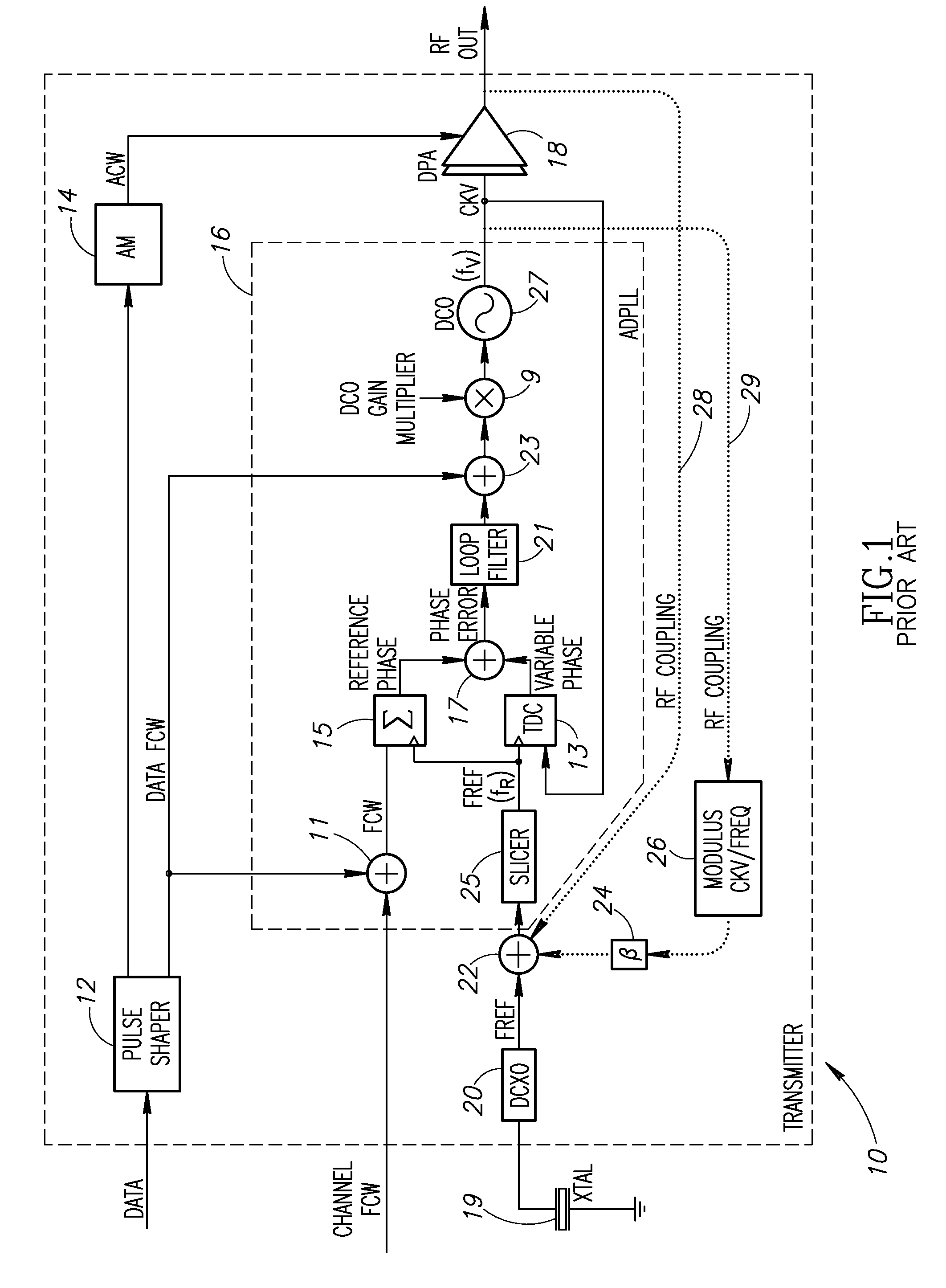
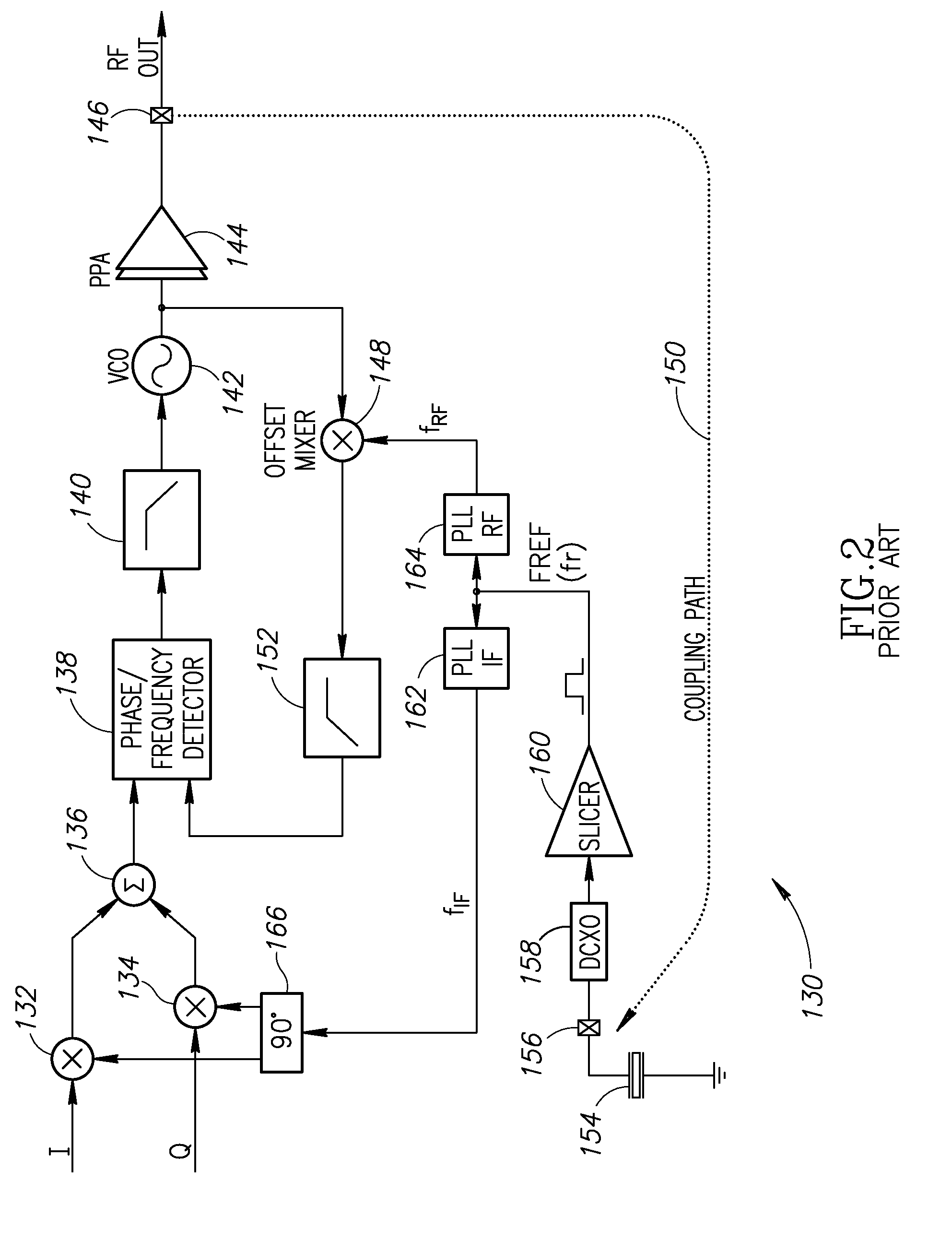
Phase alignment mechanism for minimizing the impact of integer-channel interference in a phase locked loop
InactiveUS20080192877A1Minimize impact of interferenceMinimize jitterPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionEngineeringPhase control
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of minimizing the impact of interference on the phase error performance in a phase locked loop (PLL) at integer channels by adjustment of the phase of the interfering signal such that its impact on the reference signal is minimized. Phase control is achieved by use of the digital architecture of the ADPLL and its insensitivity to an arbitrary phase bias introduced between its digitally represented output and reference phase signals. The optimal phase relationship for each integer channel is determined through a calibration procedure in which the phase is swept and the optimal phase is recorded. Before the transmission of a payload on an integer channel, the phase relationship between the output RF signal and the input reference signal is adjusted to the value found to be optimal for that frequency, based on the values previously recorded during the calibration procedure.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Hybrid speed coding and system
Linear predictive speech coding system with classification of frames and a hybrid coder using both waveform coding and parametric coding for different classes of frames. Phase alignment for a parametric coder aligns synthesized speech frames with adjacent waveform coder synthesized frames. Zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
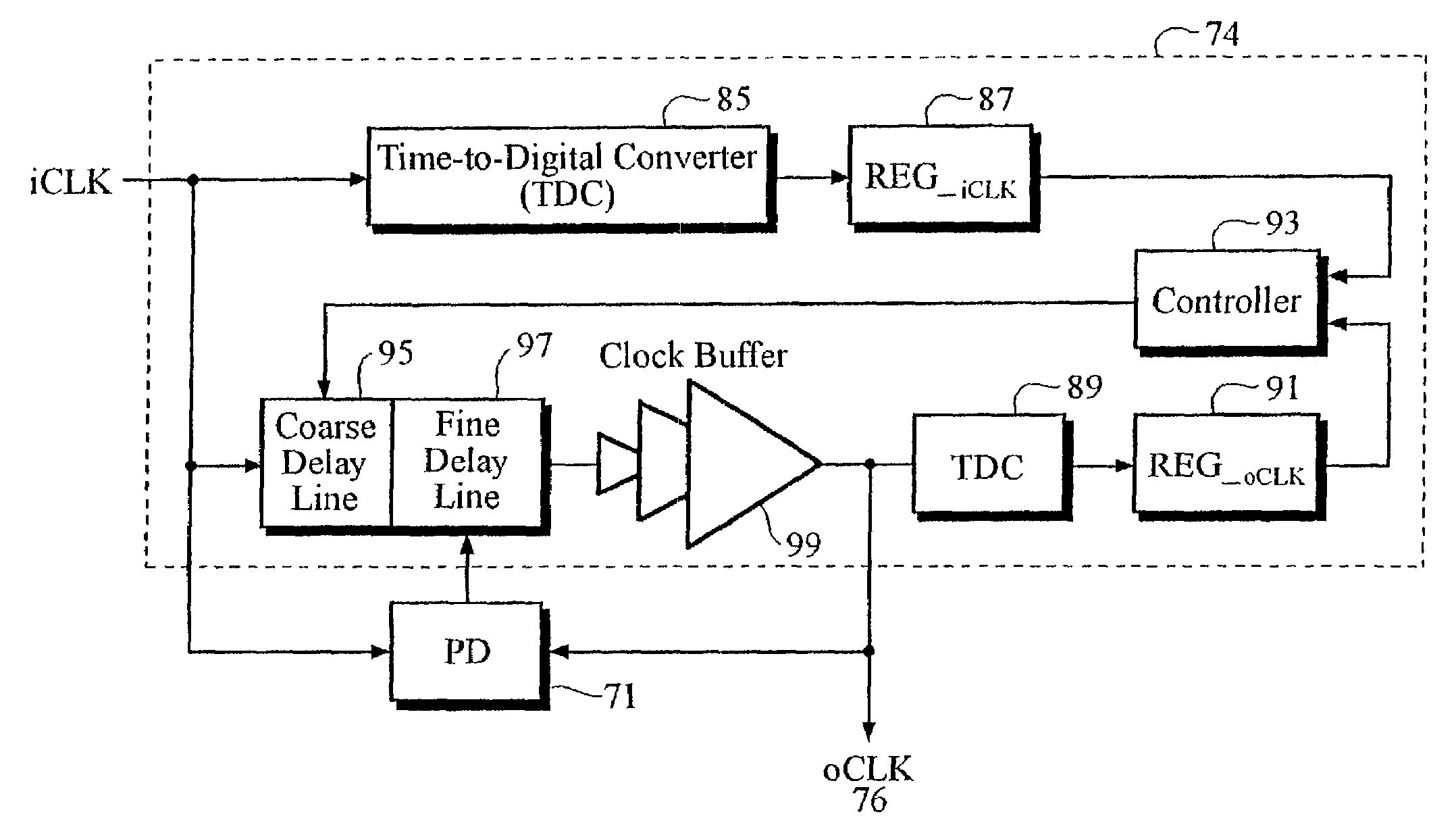
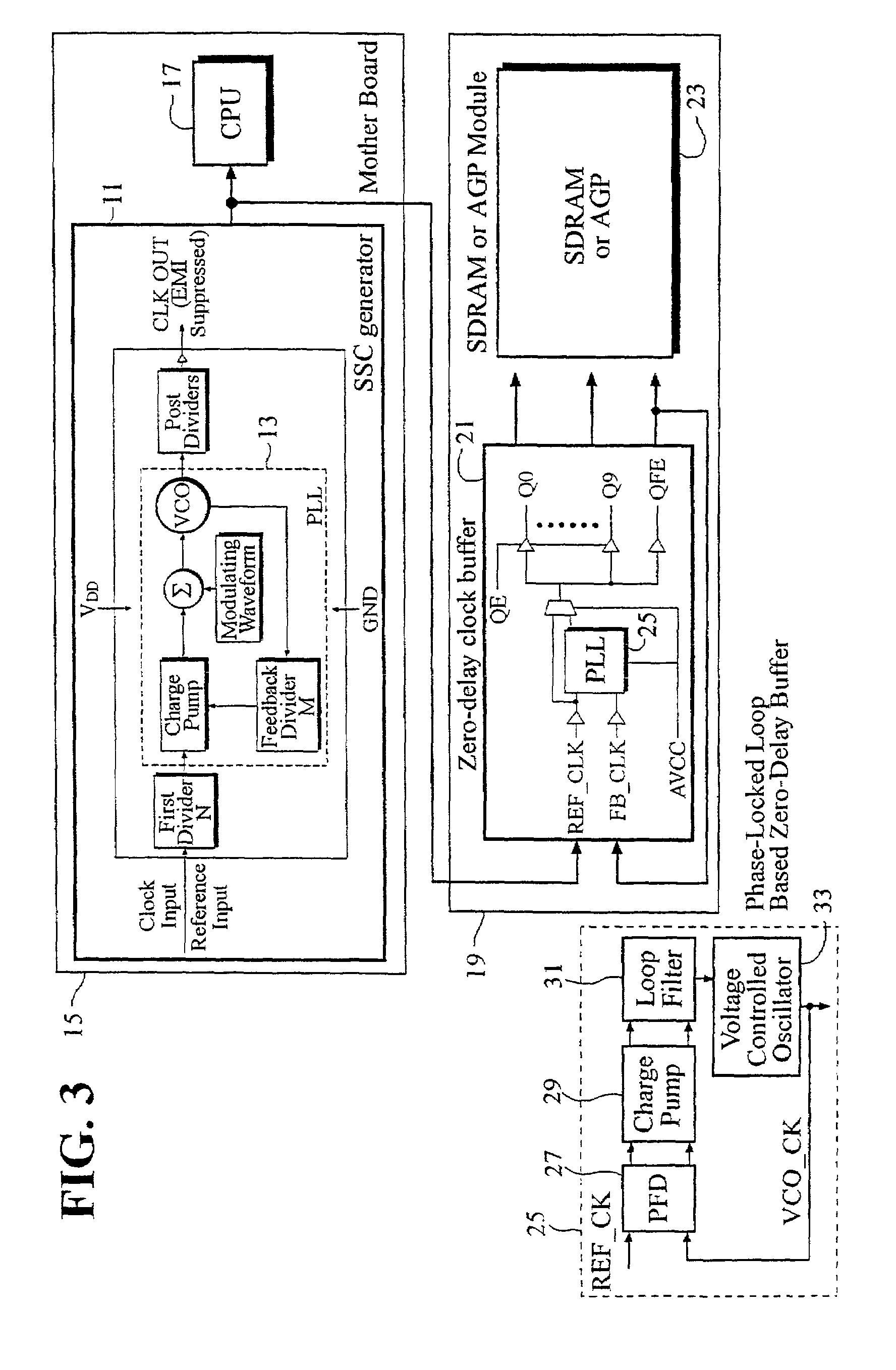
Zero-delay buffer circuit for a spread spectrum clock system and method therefor
InactiveUS6993109B2Improve efficiencyEliminate phase differencePulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsPhase detectorPhase difference
A clock recovery circuit and a method for reducing electromagnetic emission (EMI) and increasing an attainable clock frequency includes a spread spectrum clock (SSC) generator that receives an input clock signal and generates a frequency-modulated clock signal, and a zero-delay buffer circuit that receives and buffers said modulated clock frequency signed to generated an output clock signal. The frequency-modulated clock signal and the output clock signal are phase-aligned such that there is no phase difference between the output clock signal and the modulated frequency clock signal. The clock recovery circuit also includes a delay-locked loop (DLL) circuit that reduces related art jitter and skew characteristics, and a phase detector circuit that eliminates phase ambiguity problems of a related art phase detector.
Owner:ANAPASS
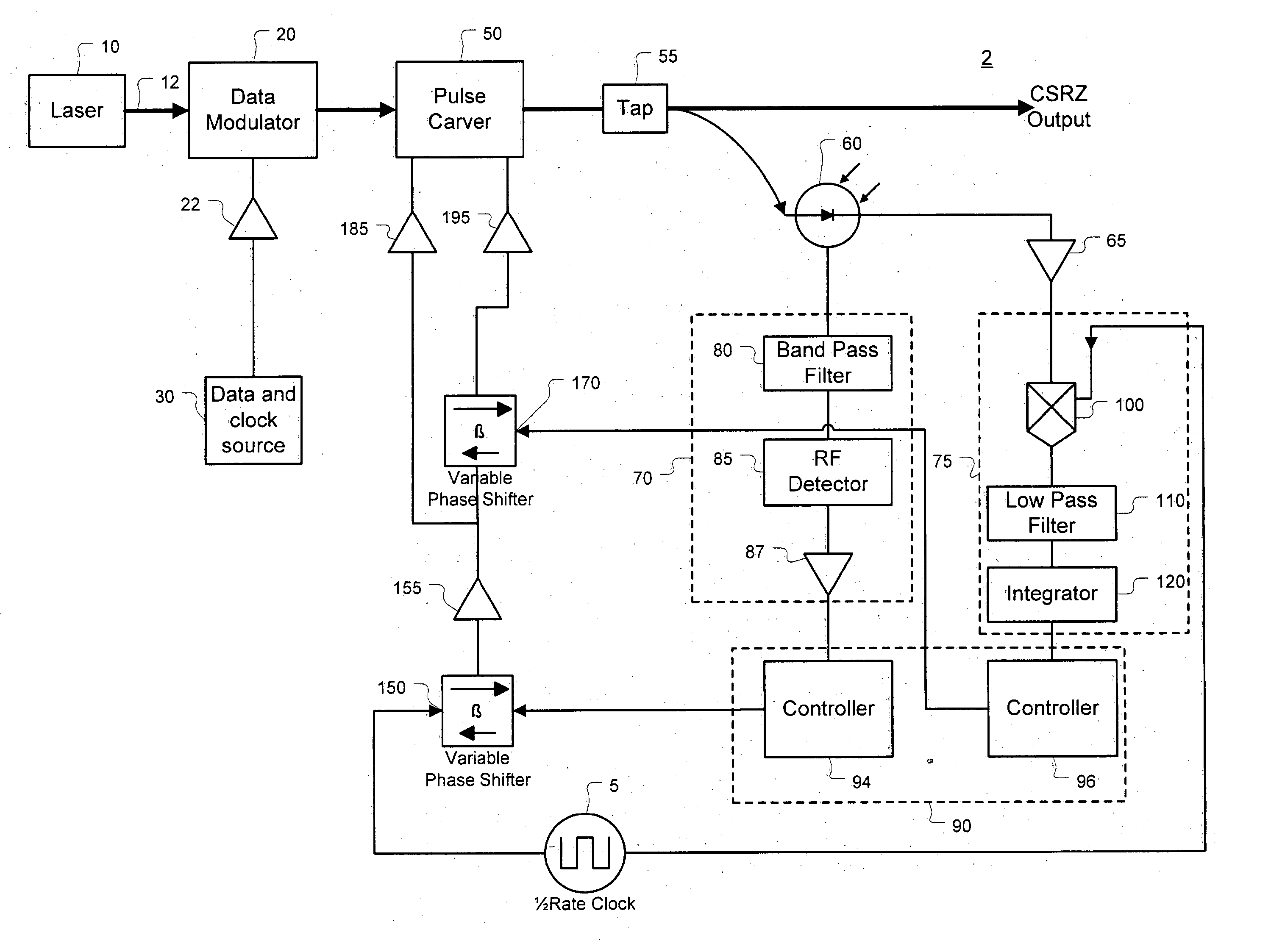
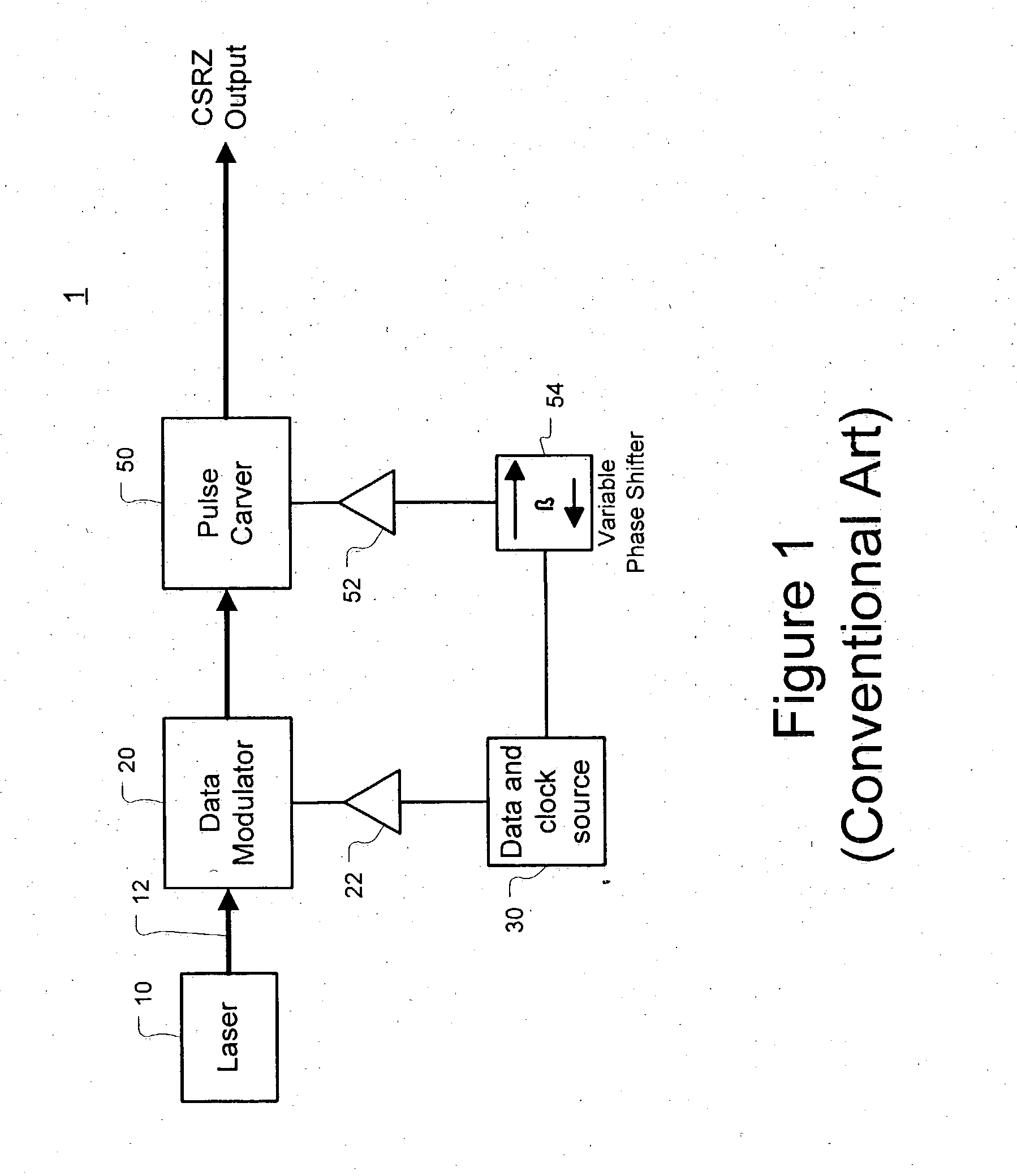
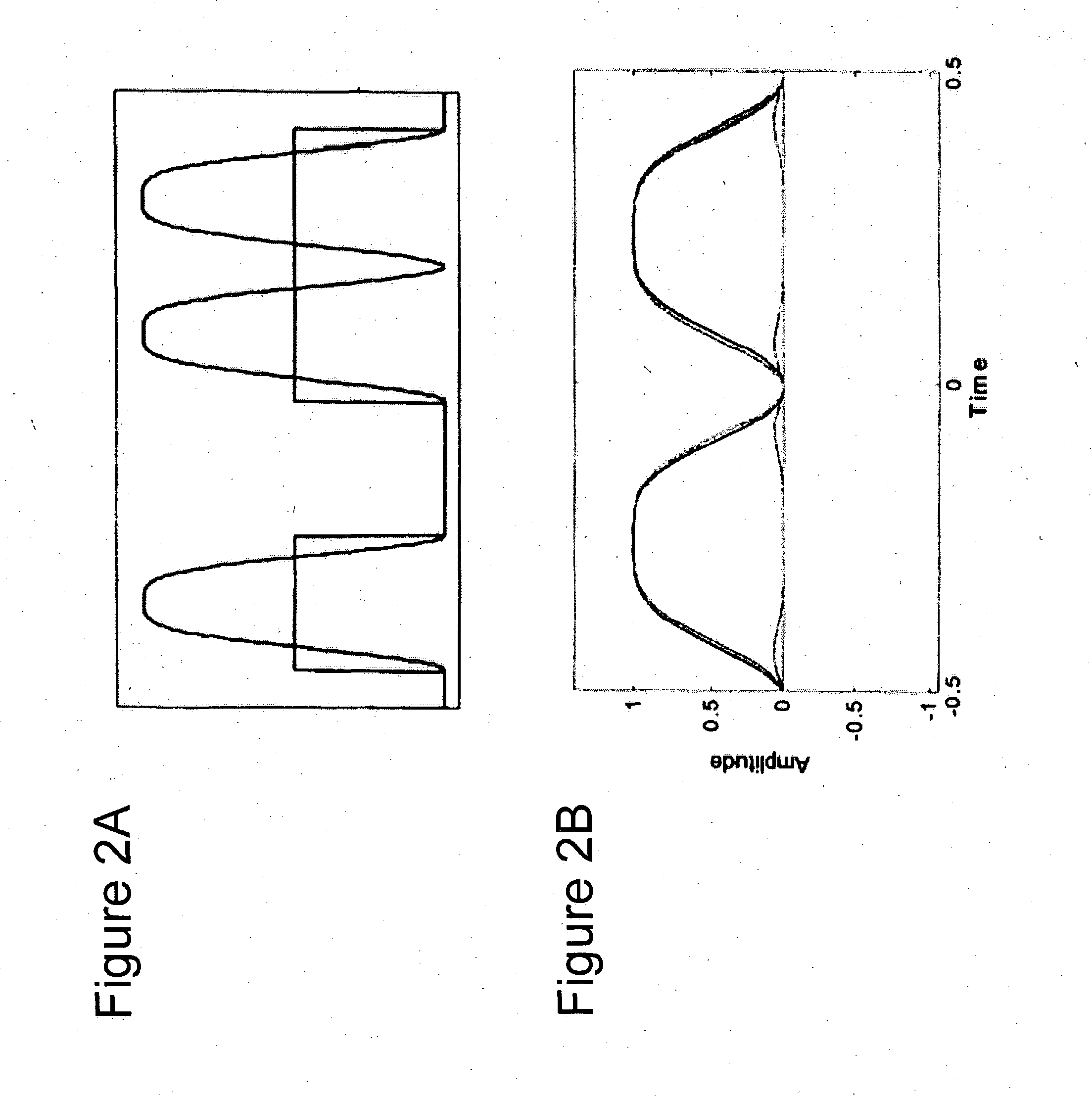
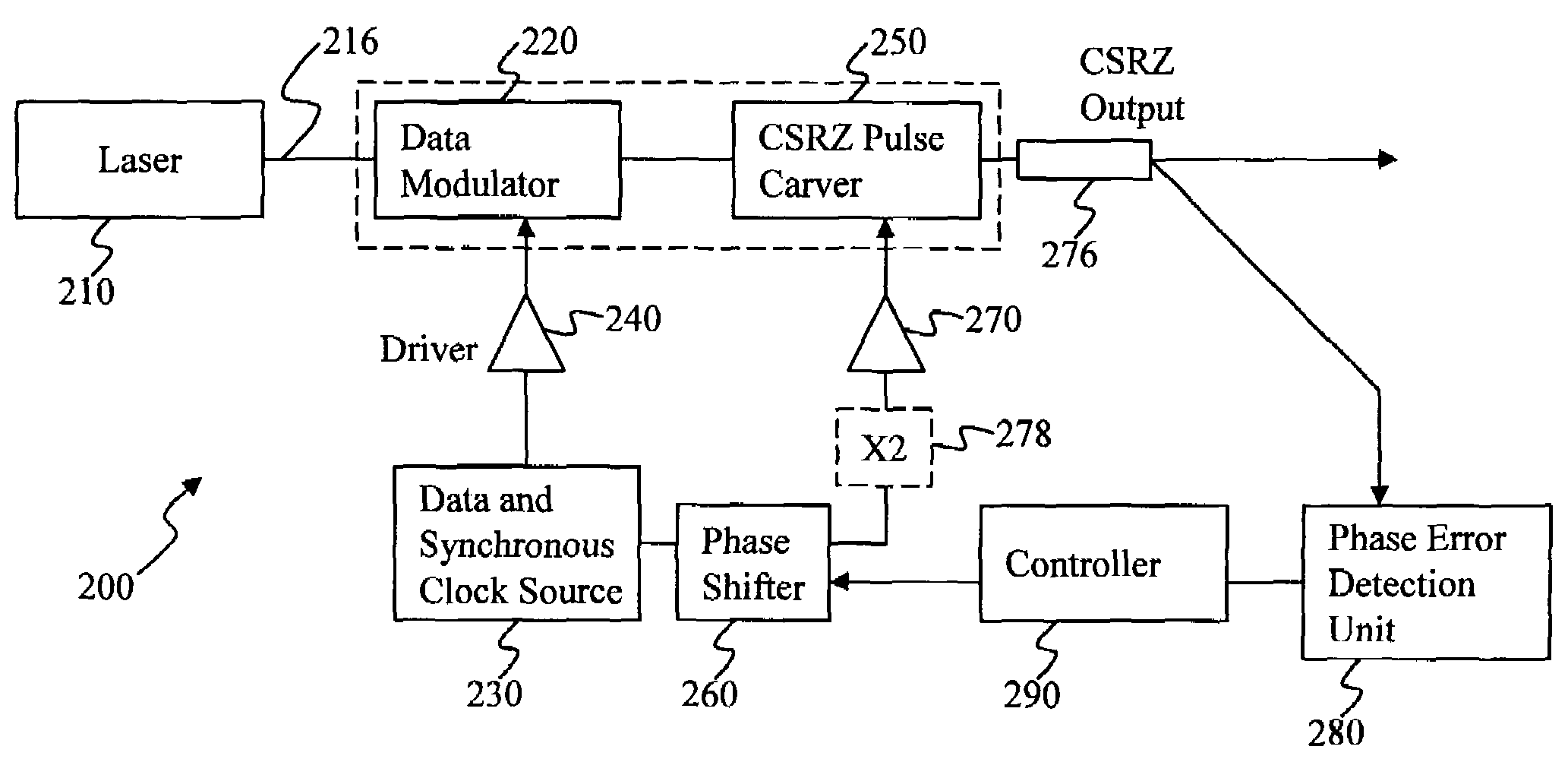
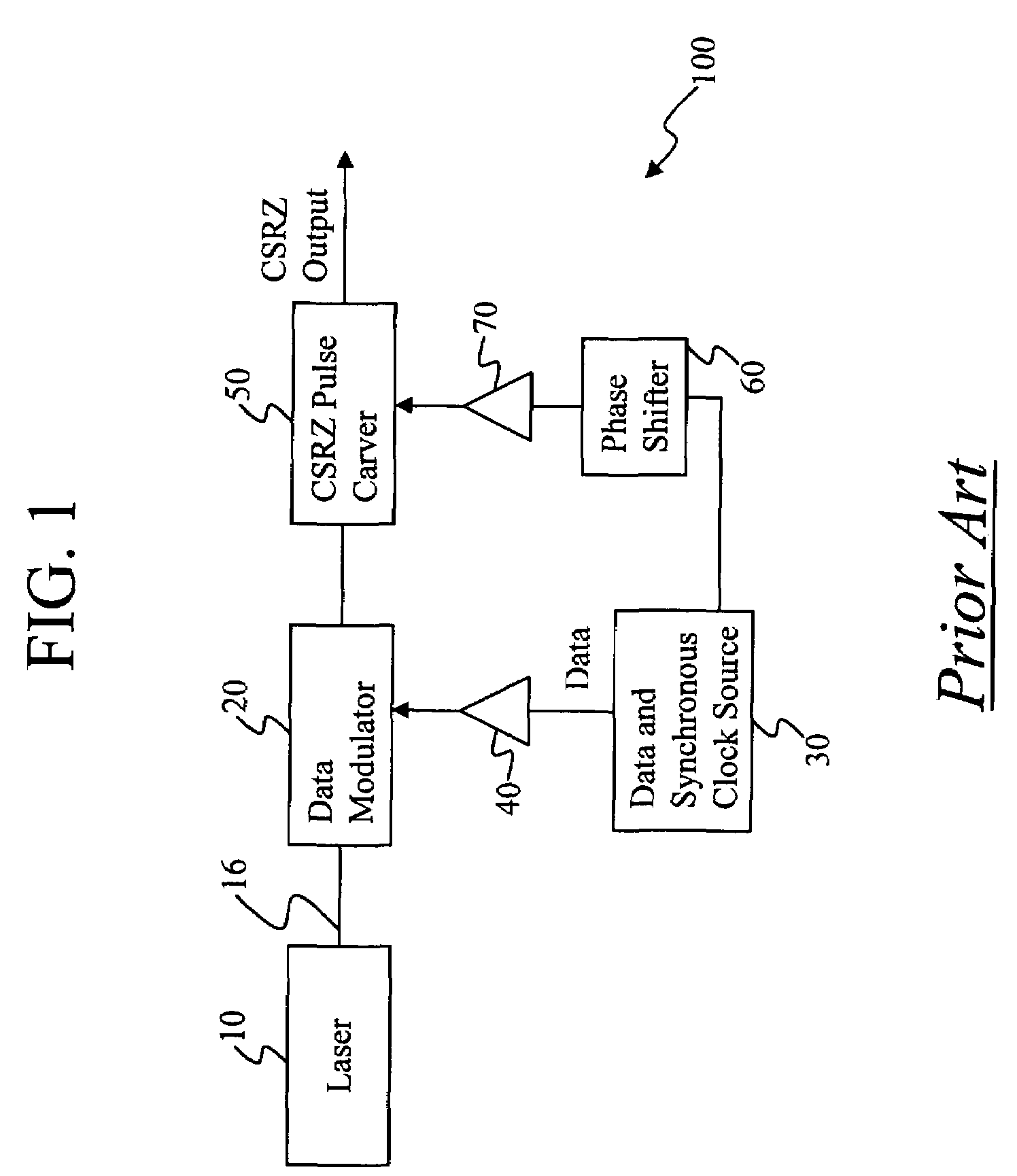
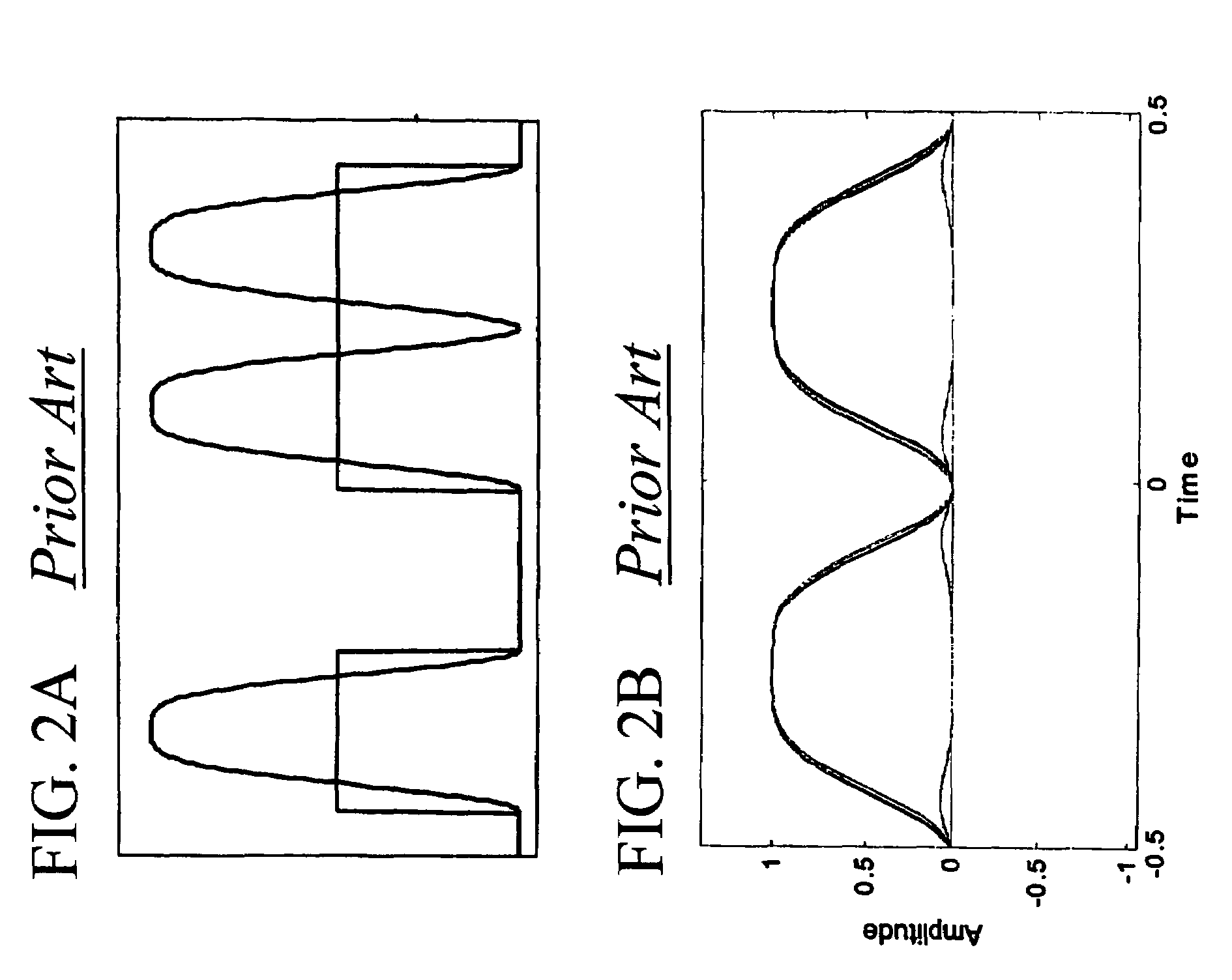
Method and apparatus for controlling modulator phase alignment in a transmitter of an optical communications system
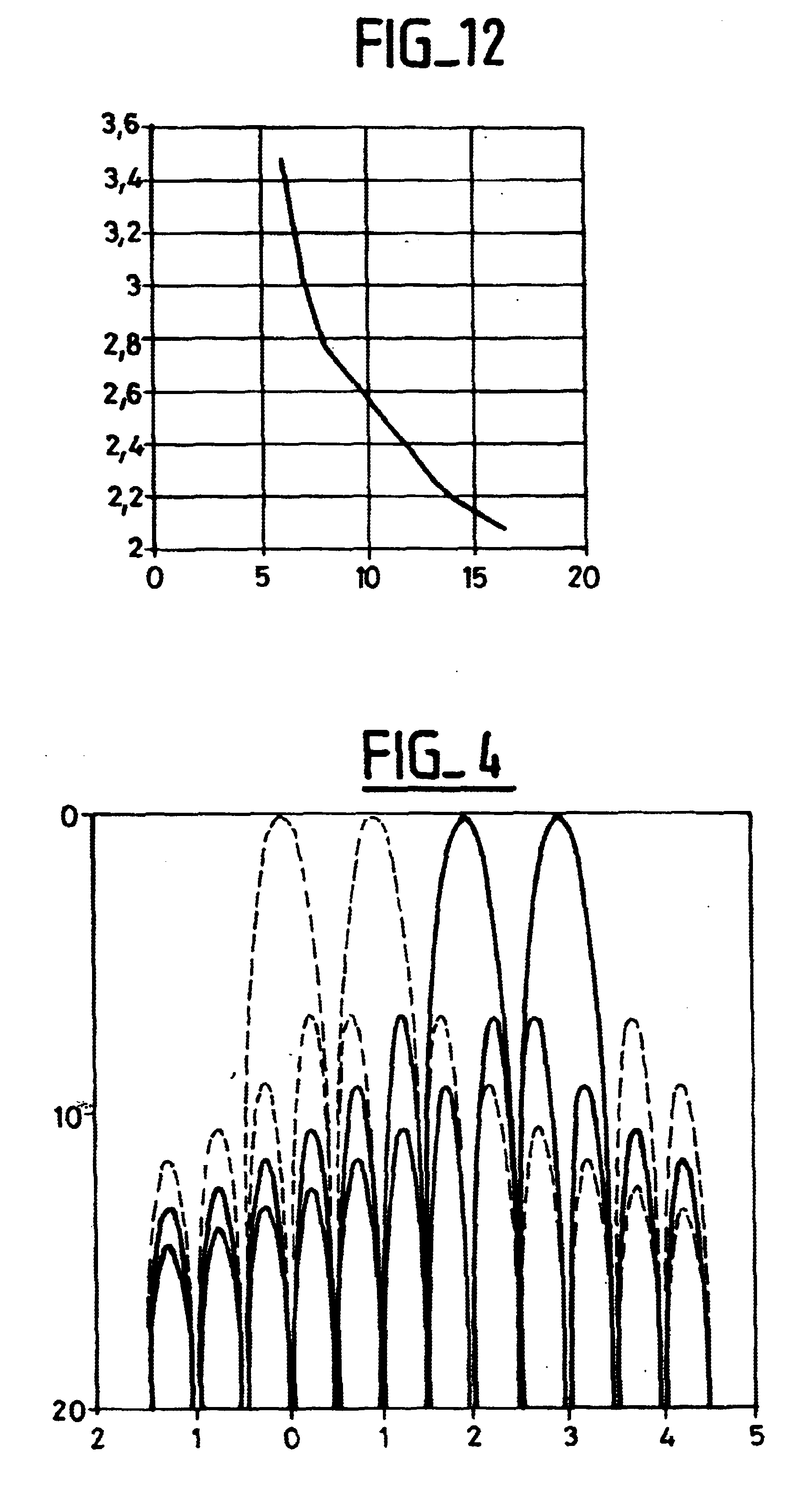
ActiveUS20050002675A1Flexible choiceHigh resolutionElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A method and apparatus for controlling phase alignment in a modulator of a transmitter in an optical communications system utilizes an RF power signature to tune phase alignment. A portion of the optical signal is tapped and converted to an electrical signal. An electrical band-pass filter and RF detector examines a narrow slice of the RF spectrum and utilize the detected RF power to control phase alignment between the data modulator and pulse carver. Another portion of the optical signal is multiplied by the pulse carver clock, filtered and integrated in order to generate a second phase control signal for controlling the relative phase of a dual arm modulator being used as the pulse carver in one embodiment.
Owner:CIENA
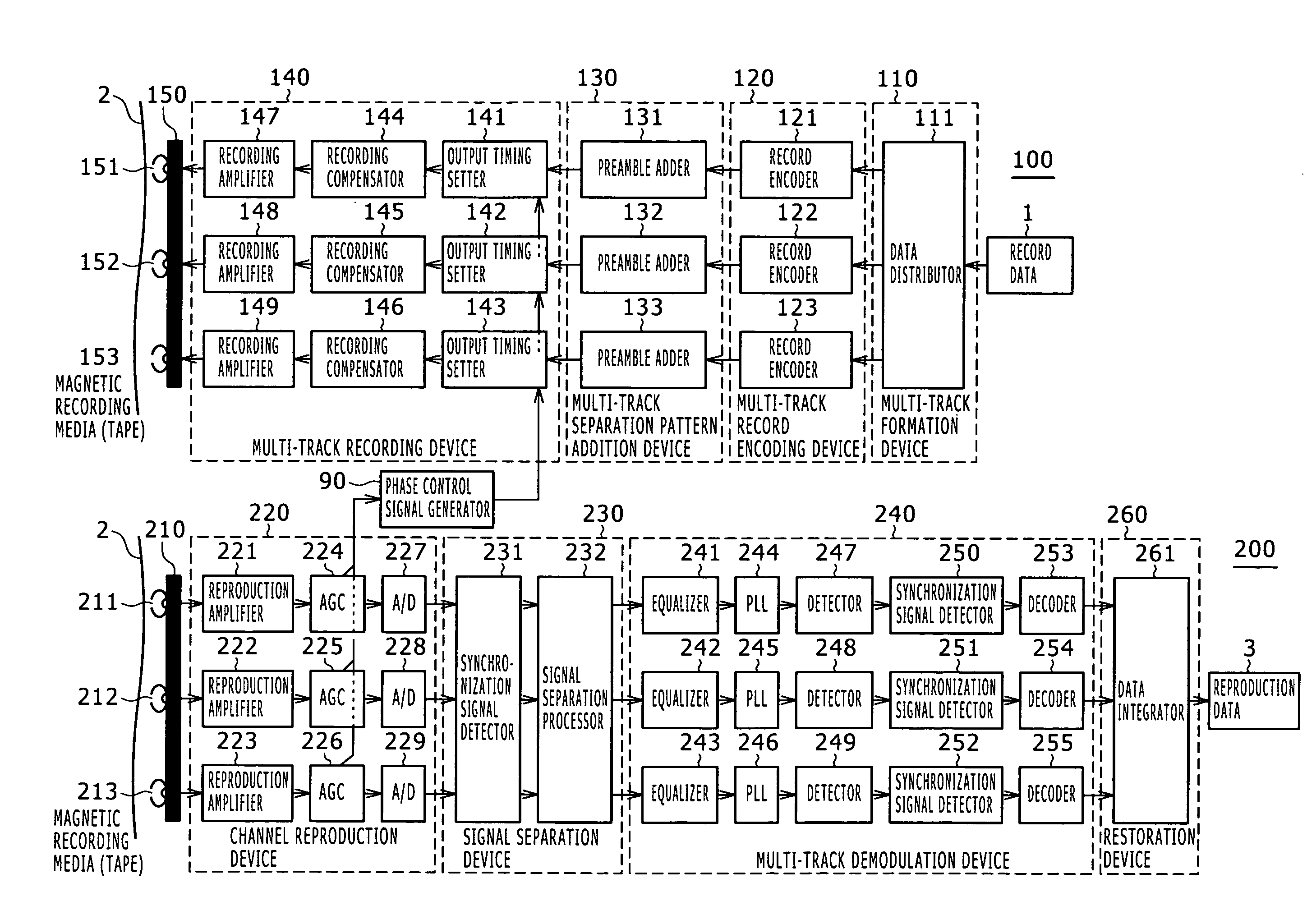
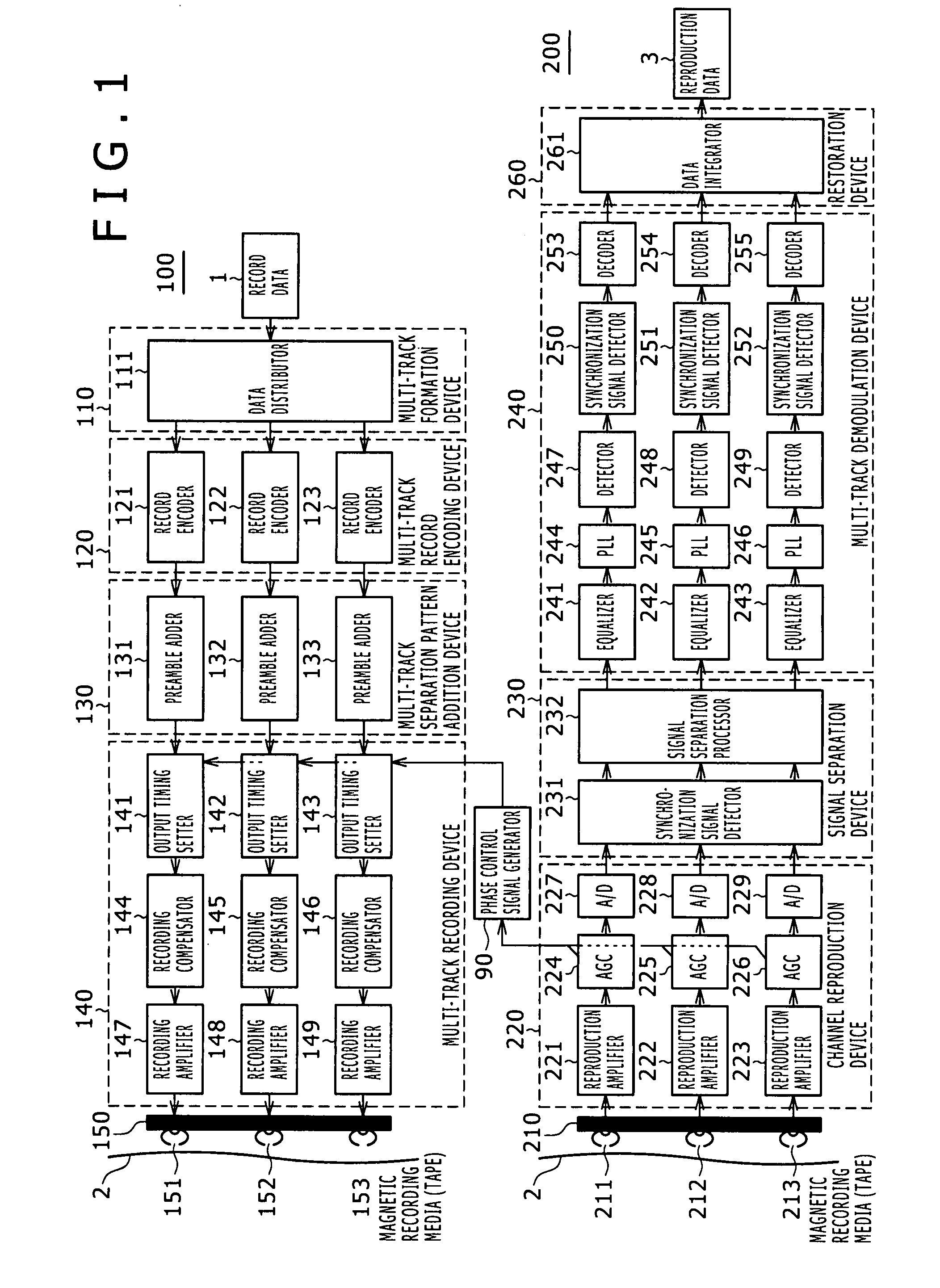
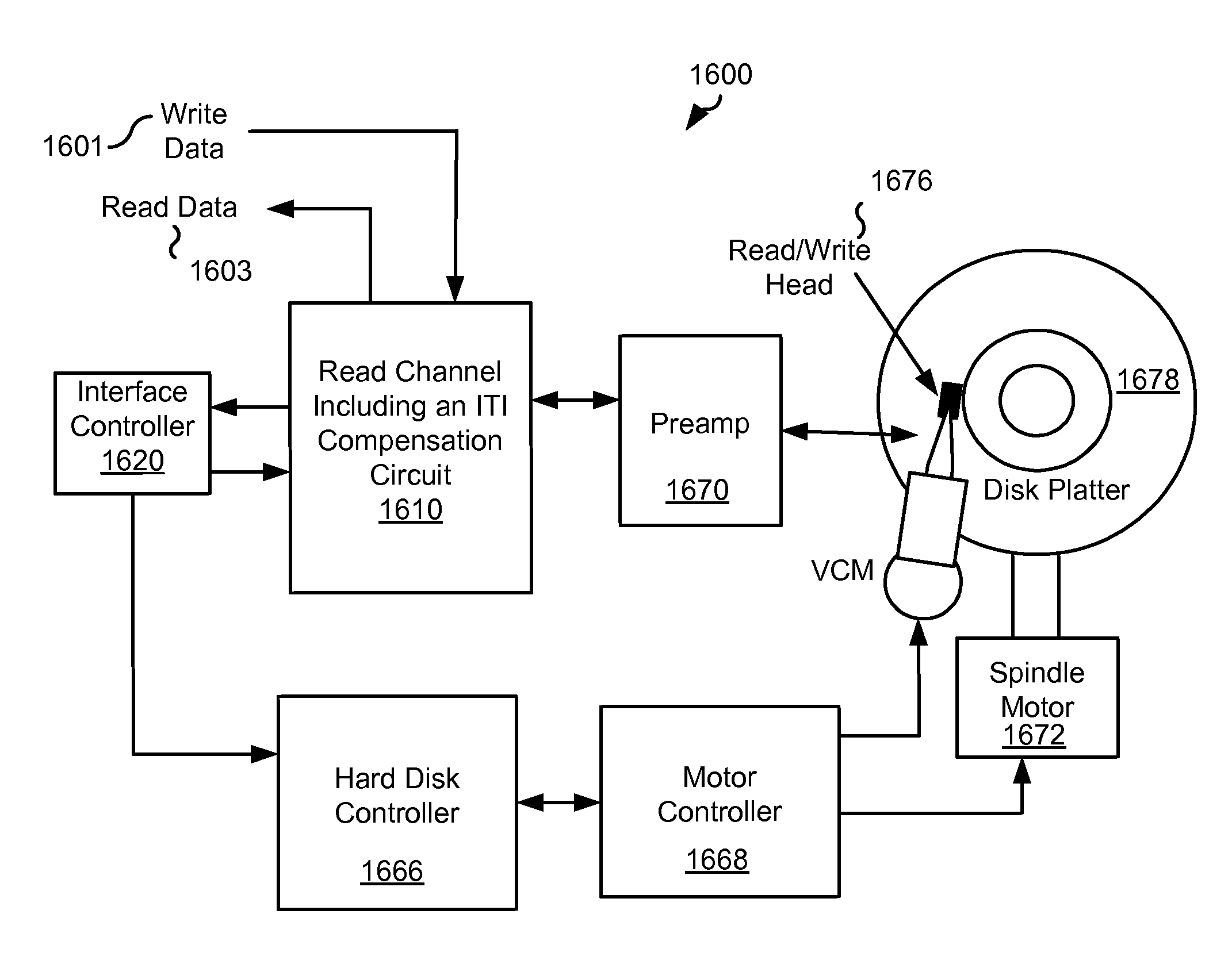
Magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus and magnetic recording and reproducing method
InactiveUS20070242378A1Reduce the amplitudeImprove recording densityModification of read/write signalsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareSignal processing
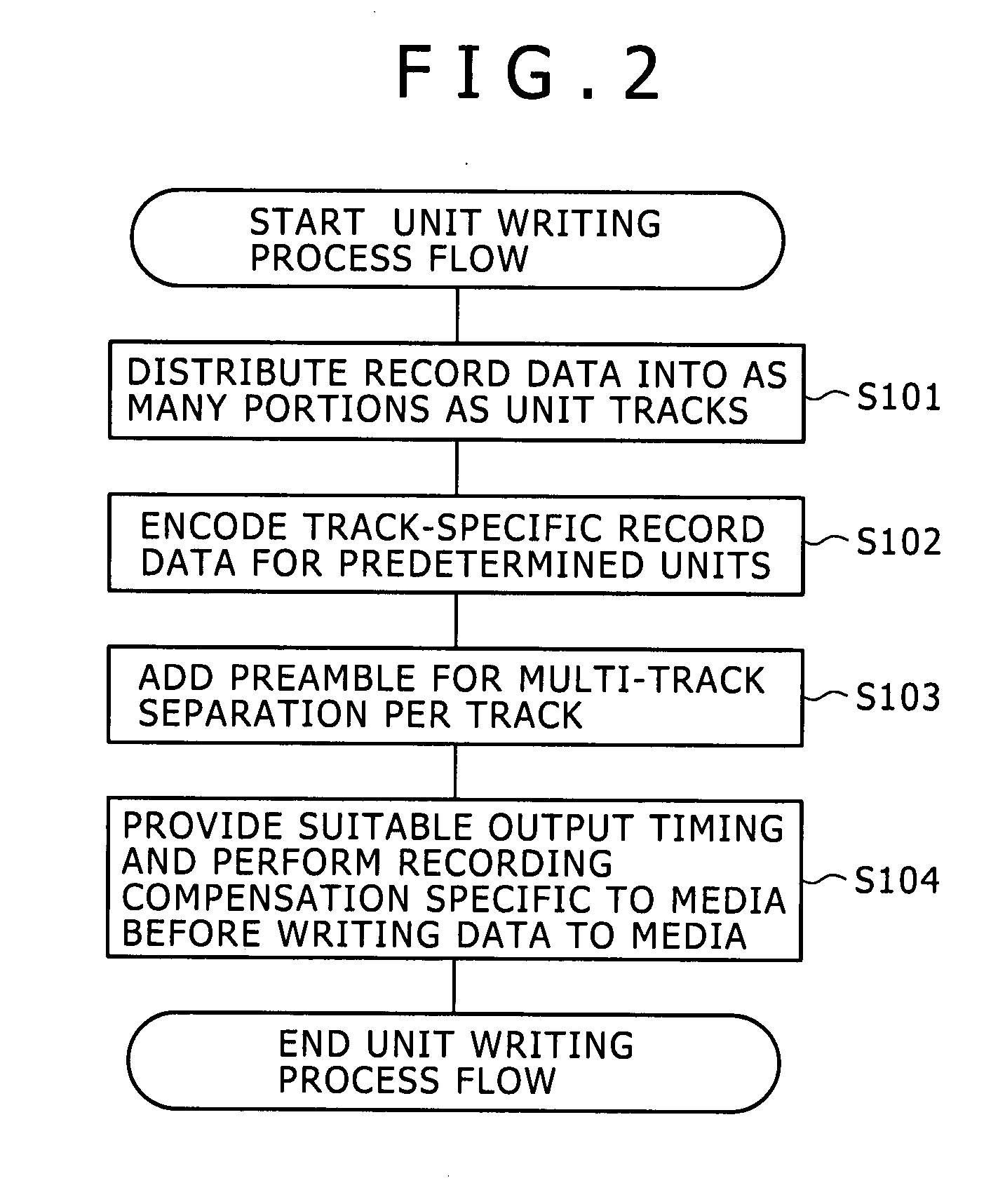
A magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus is disclosed which includes: a recording device configured to record with a write head a plurality of tracks constituting a unit of signal processing for data detection, to magnetic recording media; a reproduction device configured to reproduce with a read head a plurality of reproduction signals concurrently from the plurality of tracks on the magnetic recording media in different positional relations to the tracks, the reproduction signals being arranged into that one unit for signal processing thereby generating the track-specific reproduction signals; and a phase alignment device configured to align phases of record signals between adjacent tracks among the plurality of tracks recorded by the recording device to the magnetic recording media.
Owner:SONY CORP
Hybrid speech coding and system
InactiveUS20050065788A1Improve performanceSpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceWaveform codingSpeech code
Hybrid linear predictive speech coding system with phase alignment predictive quantization zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
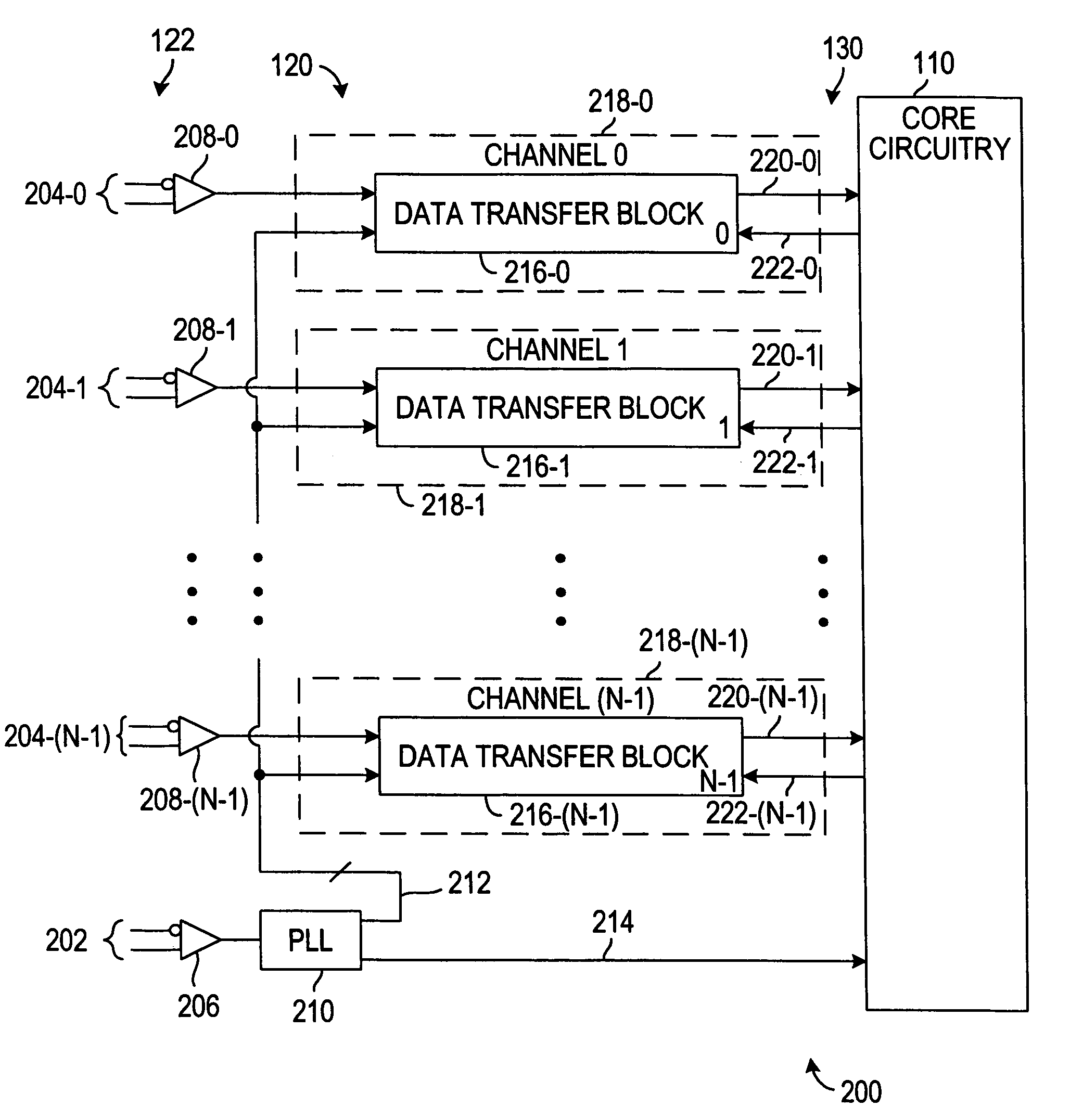
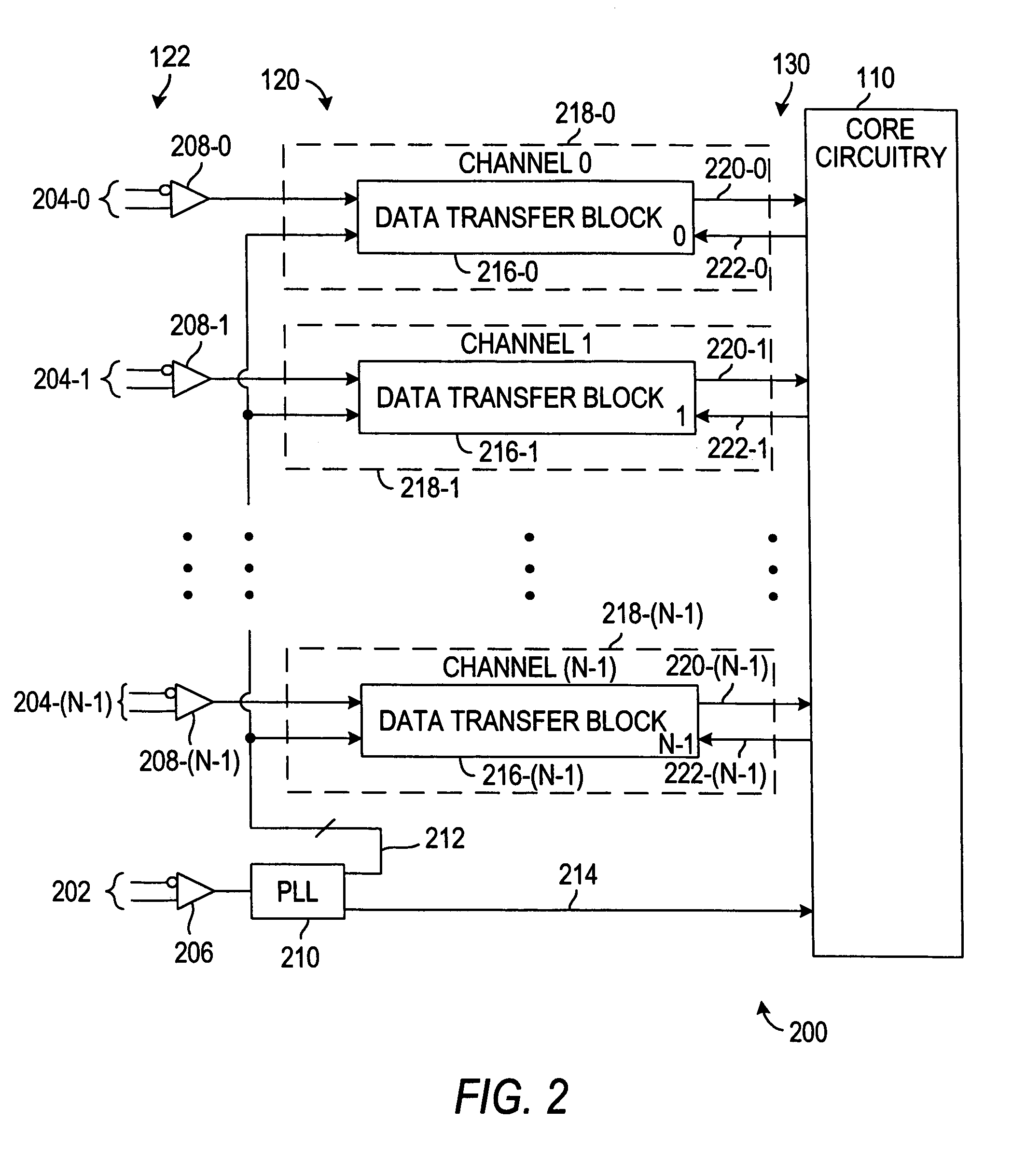
Programmable logic resource with data transfer synchronization
ActiveUS7003423B1Eliminate delaysSimple designResistance/reactance/impedenceStructural/machines measurementData synchronizationTime efficient
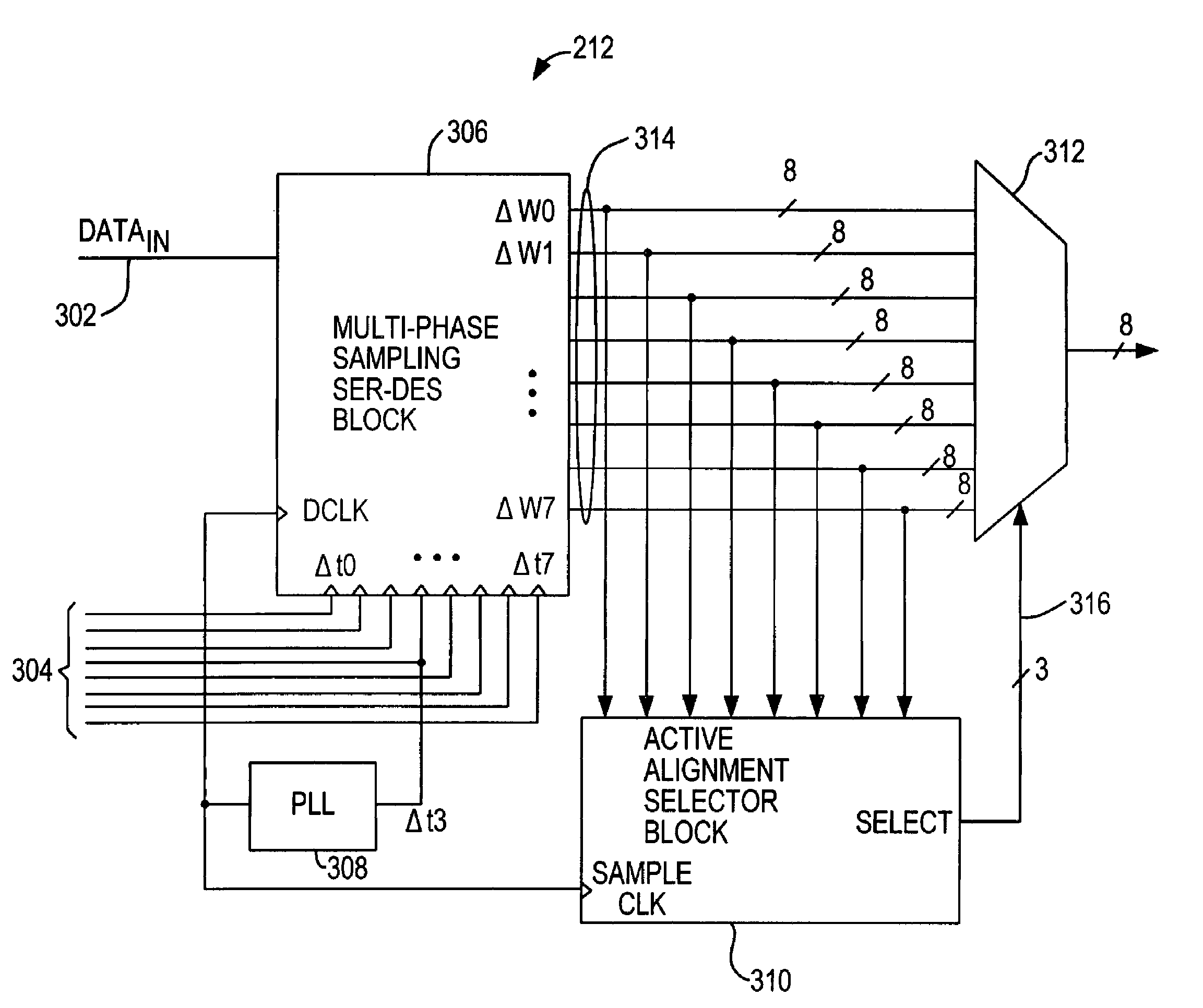
A more time-efficient and area-efficient approach is provided to synchronize the transfer of data into programmable logic resources. A programmable logic resource core clock and a reset signal are routed to a reset register that controls the reset of a dynamic phase alignment circuit and a data realigner. The dynamic phase alignment circuit includes a phase-locked loop circuit, a J counter, and a deserializer. When the output signal of the reset register transitions from logic 1 to logic 0, the J counter begins to count and sets an enable signal accordingly. The enable signal, which controls the output of synchronized parallel data from the deserializer, is therefore phase associated with the programmable logic resource core clock. The synchronized parallel data is input to a data realigner which outputs the data based on the programmable logic resource core clock for input to the programmable logic resource core circuitry.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
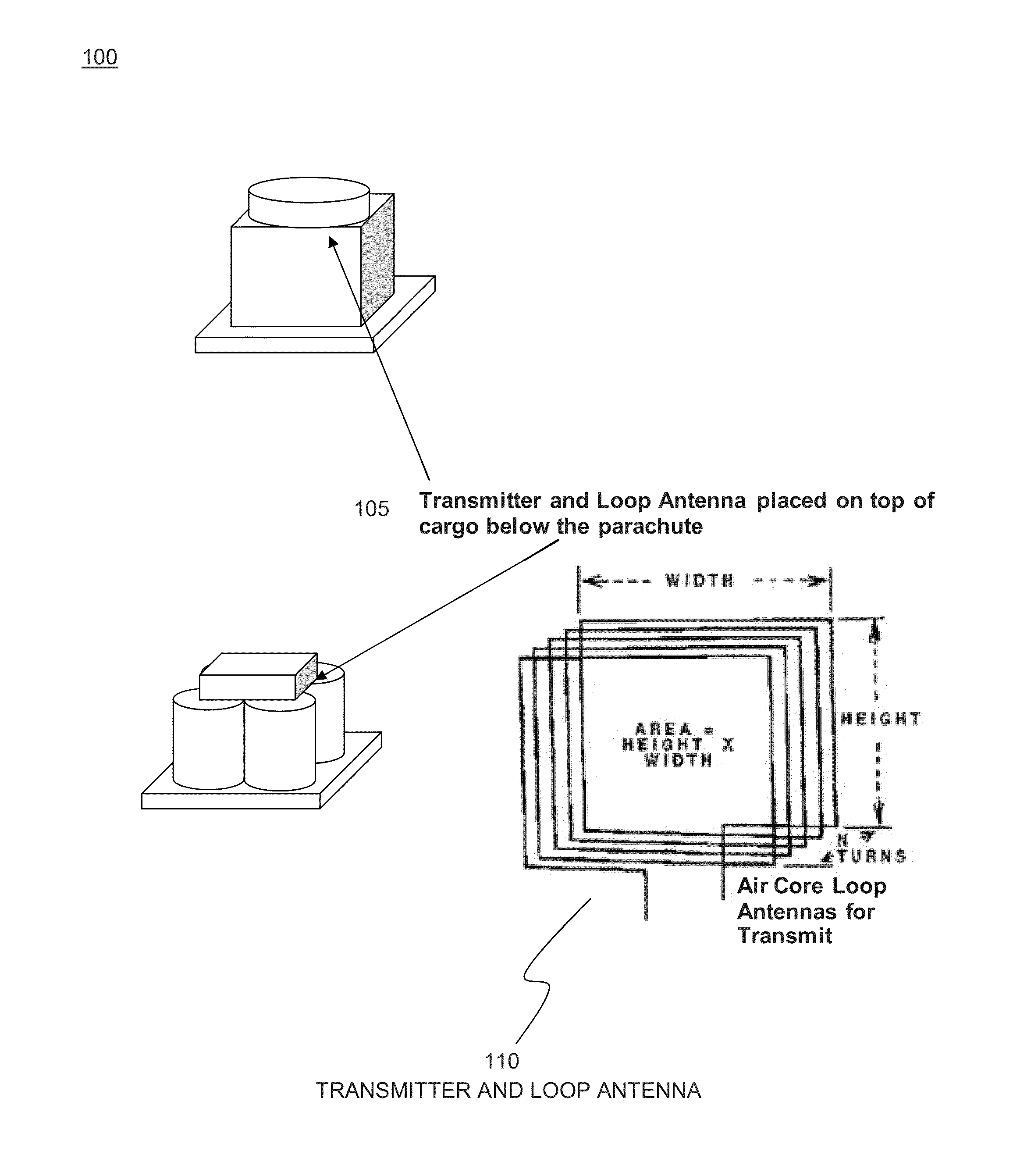
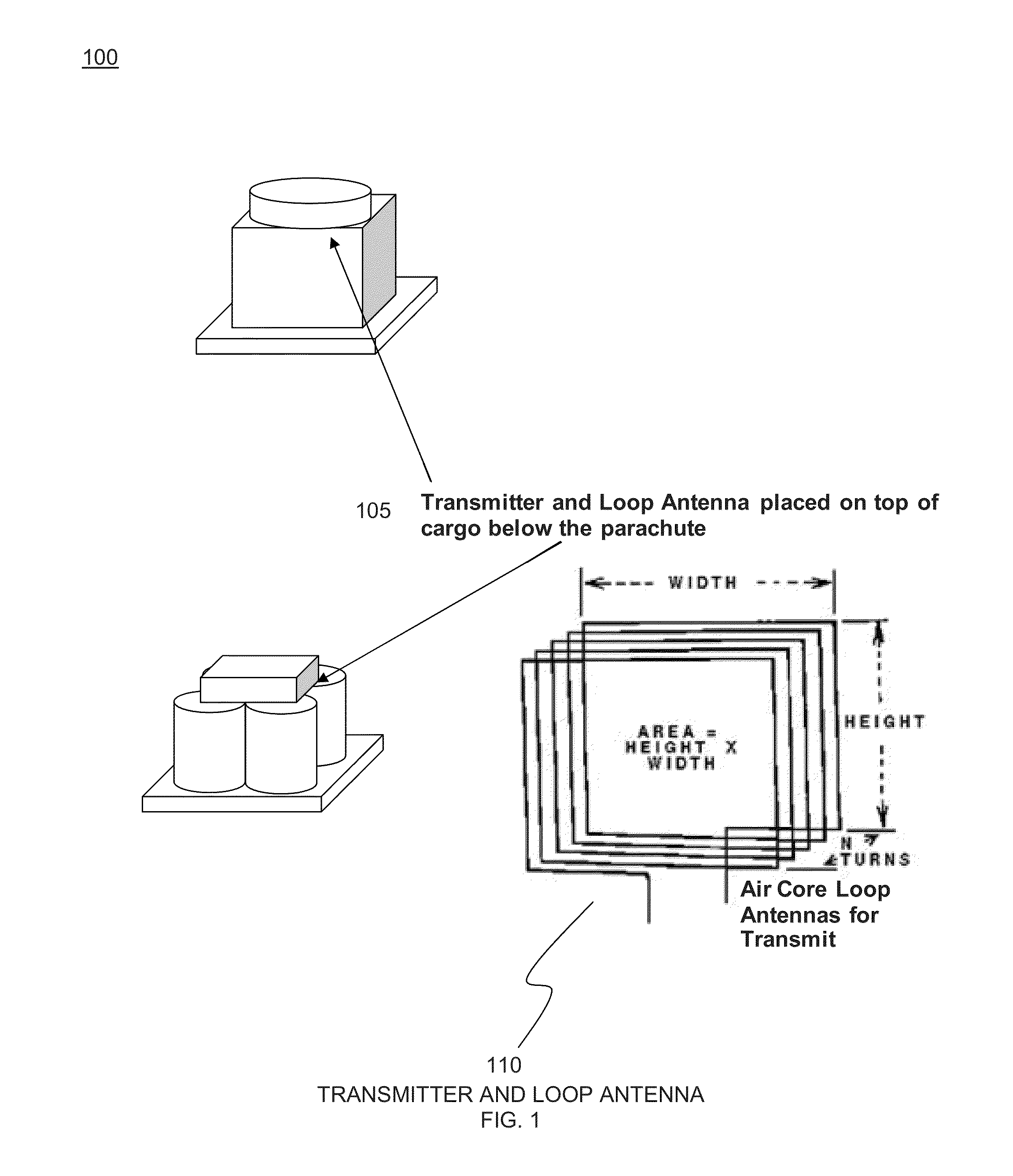
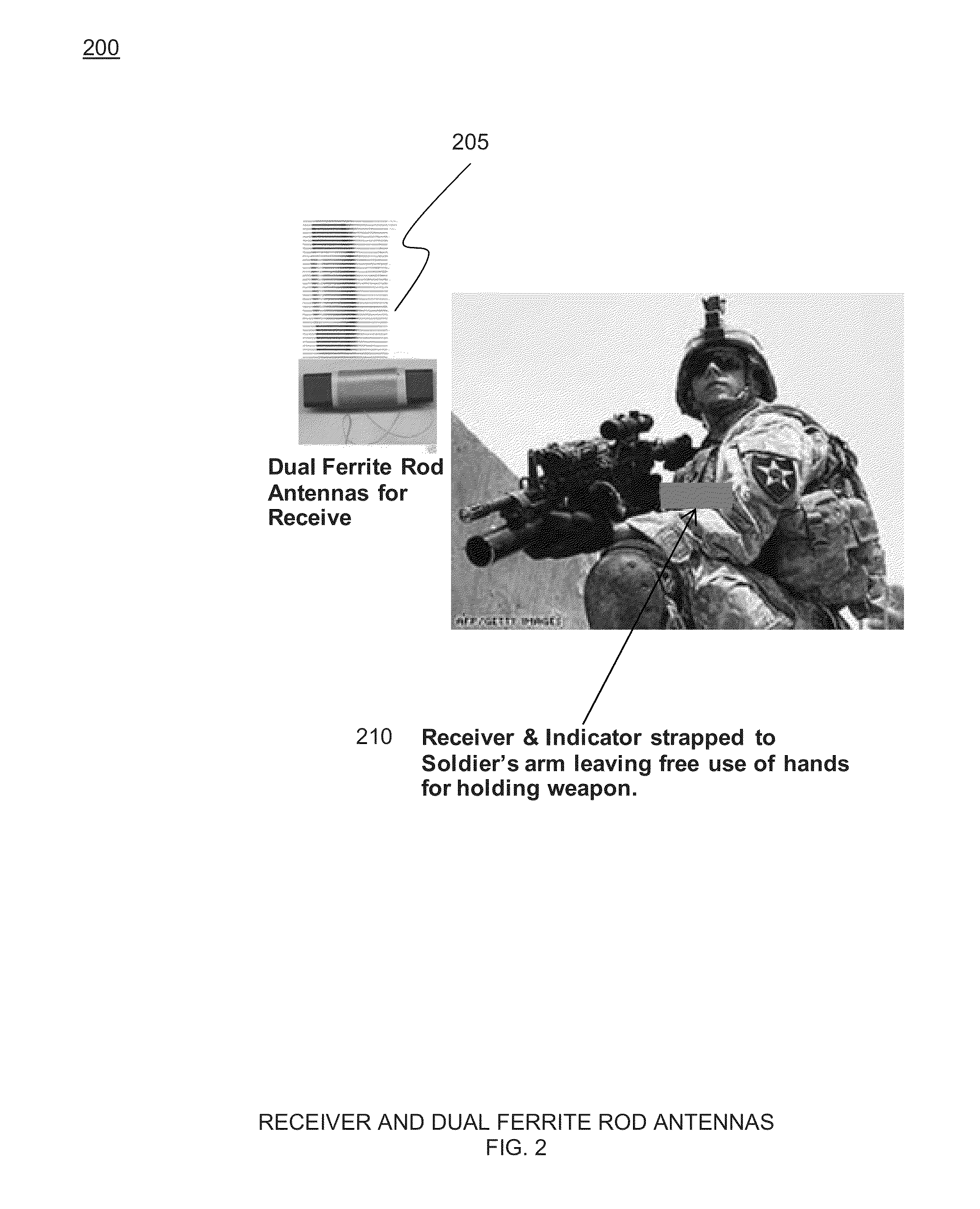
Drop zone rally point beacon
InactiveUS20130149960A1Increase the magnetic field strengthMinimize reflectionNear-field transmissionUltrasound attenuationRF front end
A VLF beacon operates in the near field of the antenna, providing a low impedance (magnetic) wave located by employing simple amplitude gradient and phase alignment direction finding (DF) methods. When rotated, the beacon antenna radiates its signal with little attenuation. Beacon antennas include a loop antenna which has a 1 / r3 B-field amplitude relationship with distance. The antenna radiation range is limited, but the detectable near field signal is strong. The receiver comprises a simple 2-channel RF front end with filtering and an A / D converter. The antenna for each channel is a much smaller ferrite rod loaded loop.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
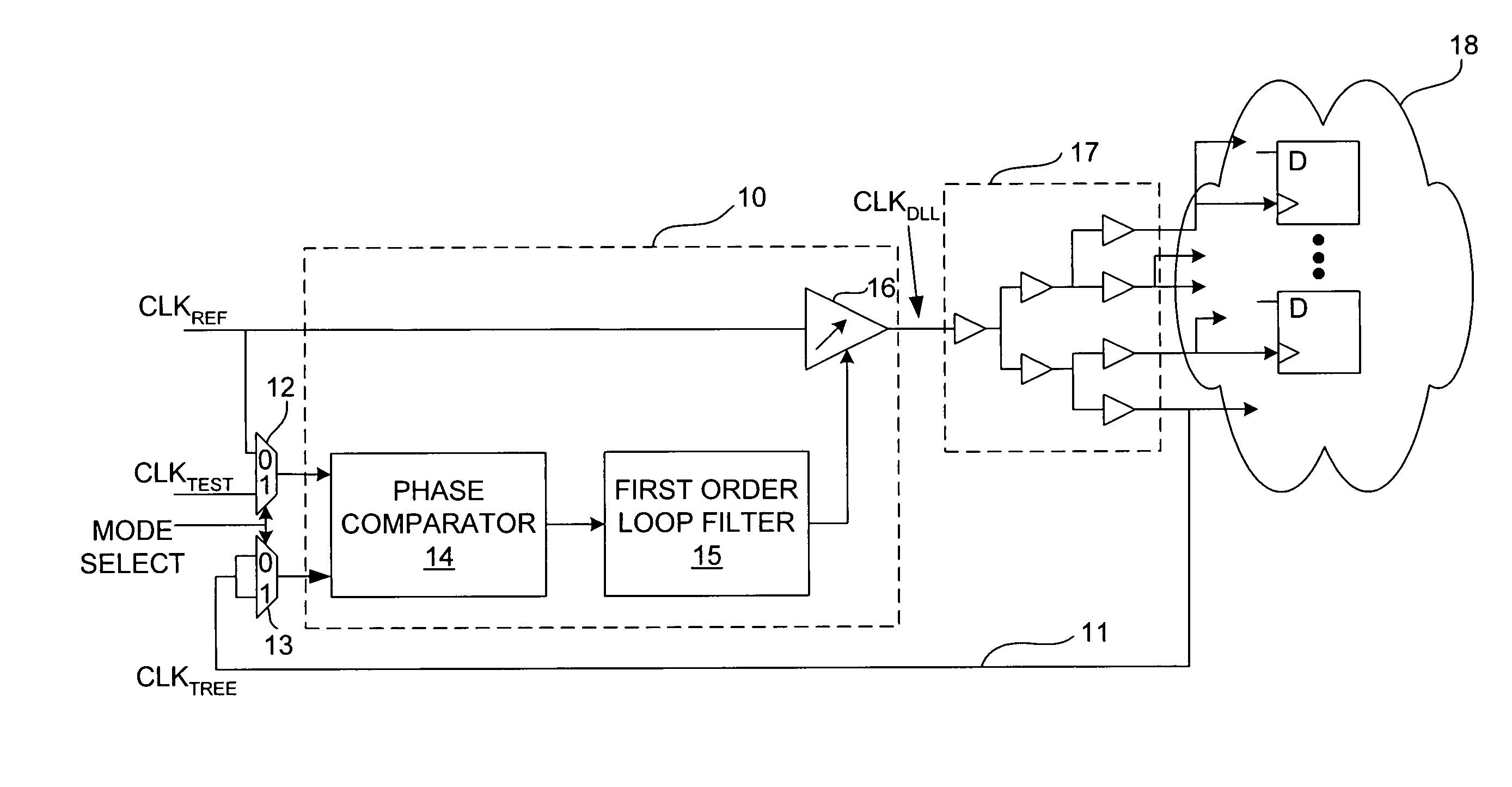
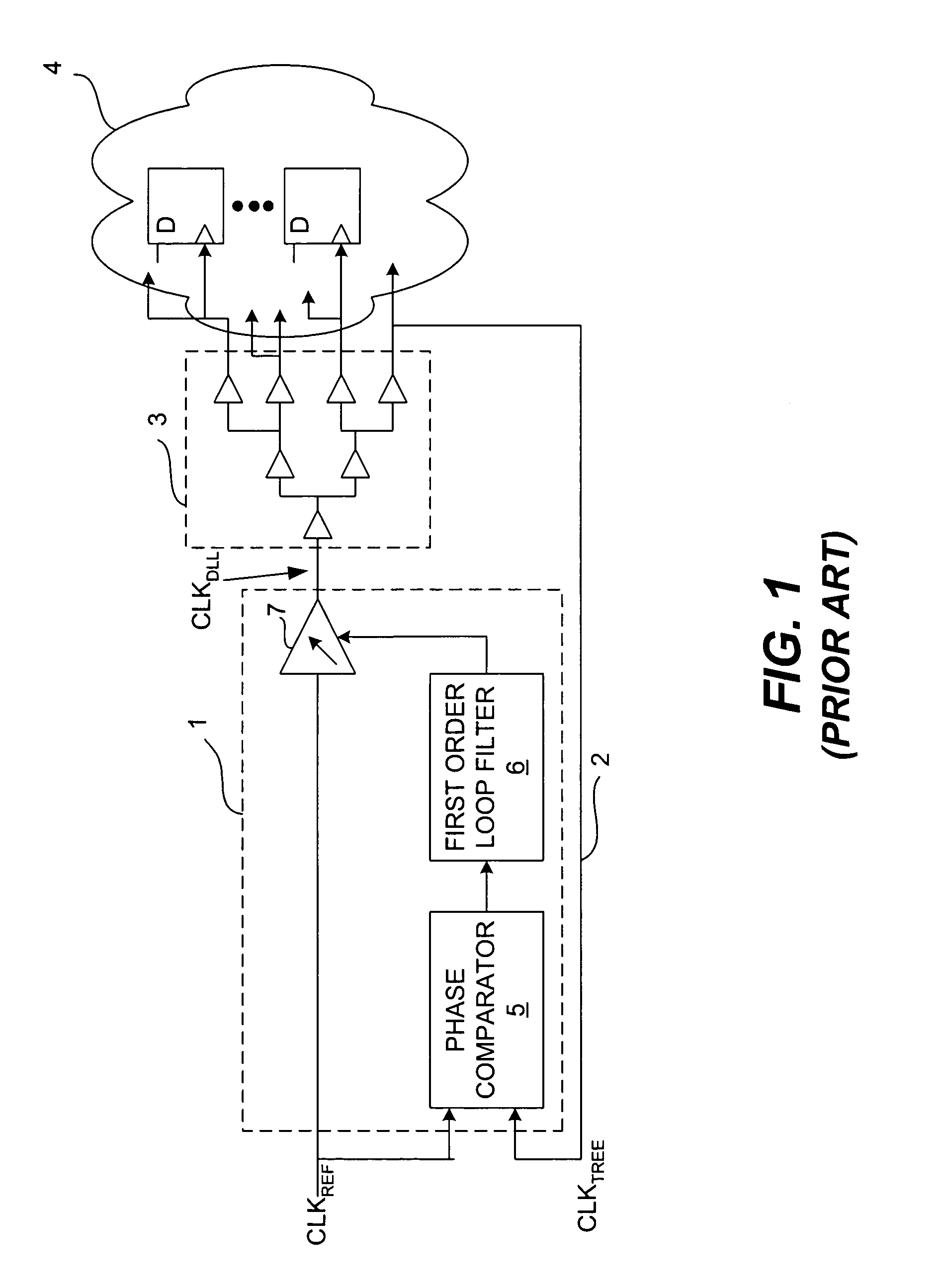
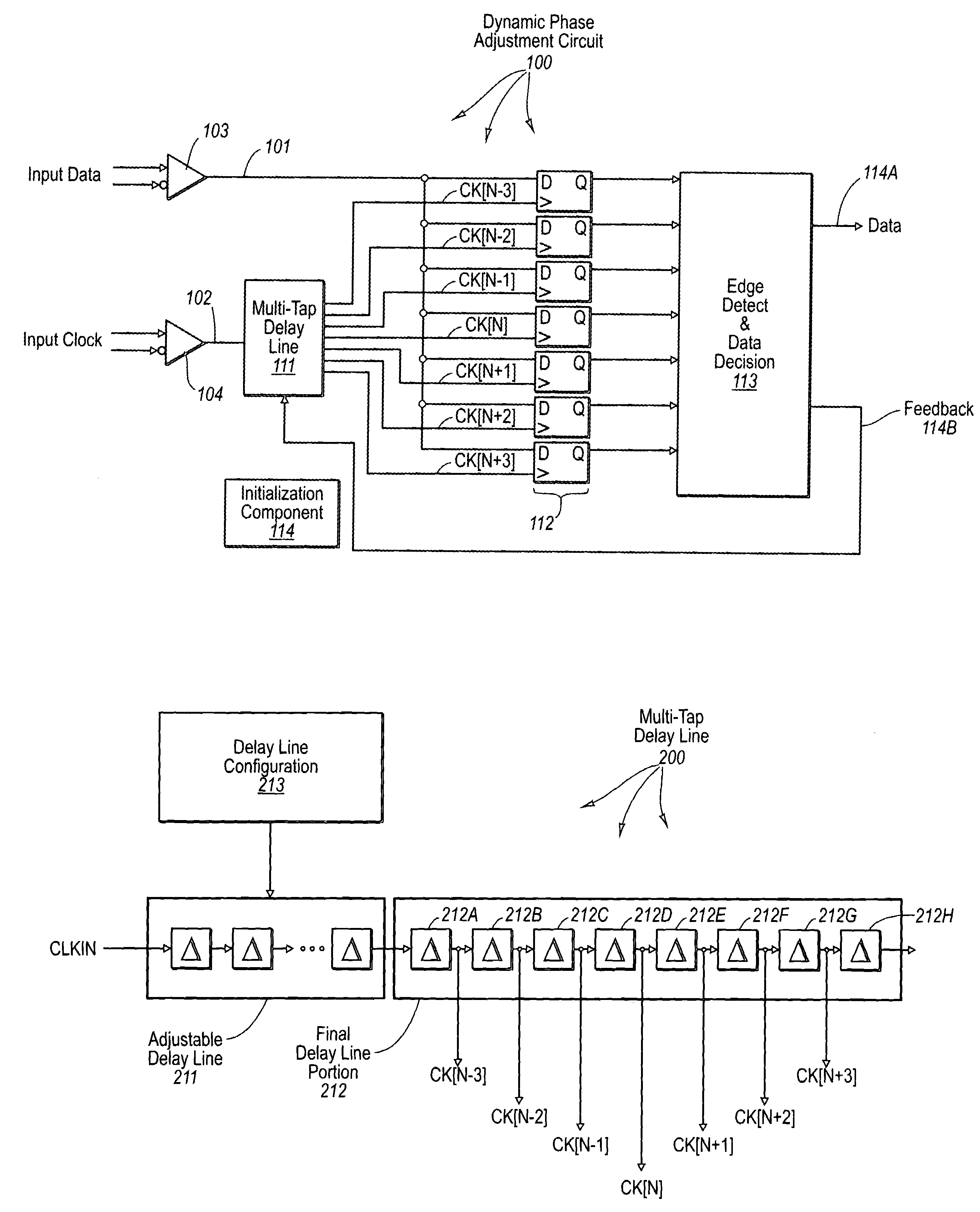
Delay-locked loop and a method of testing a delay-locked loop
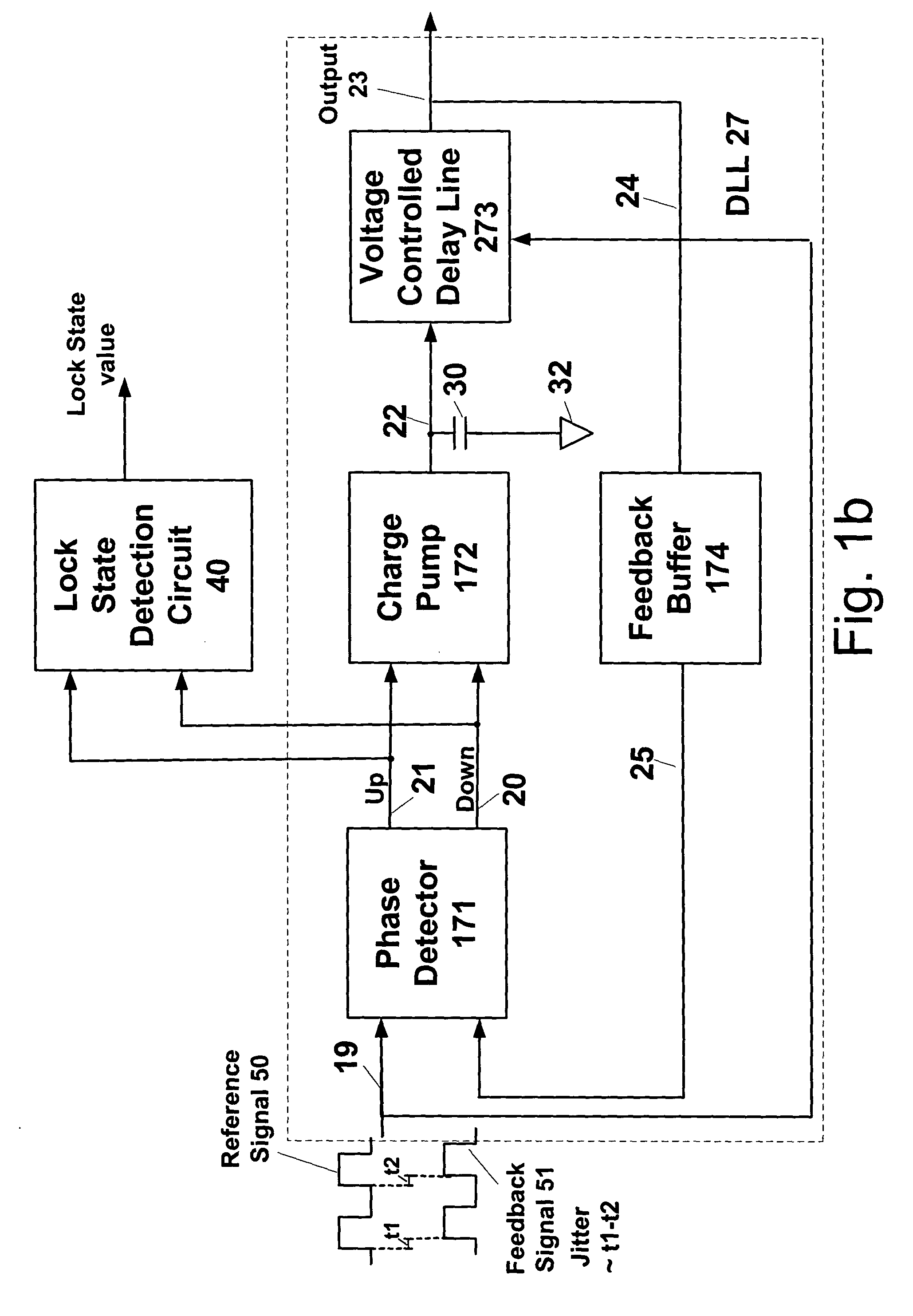
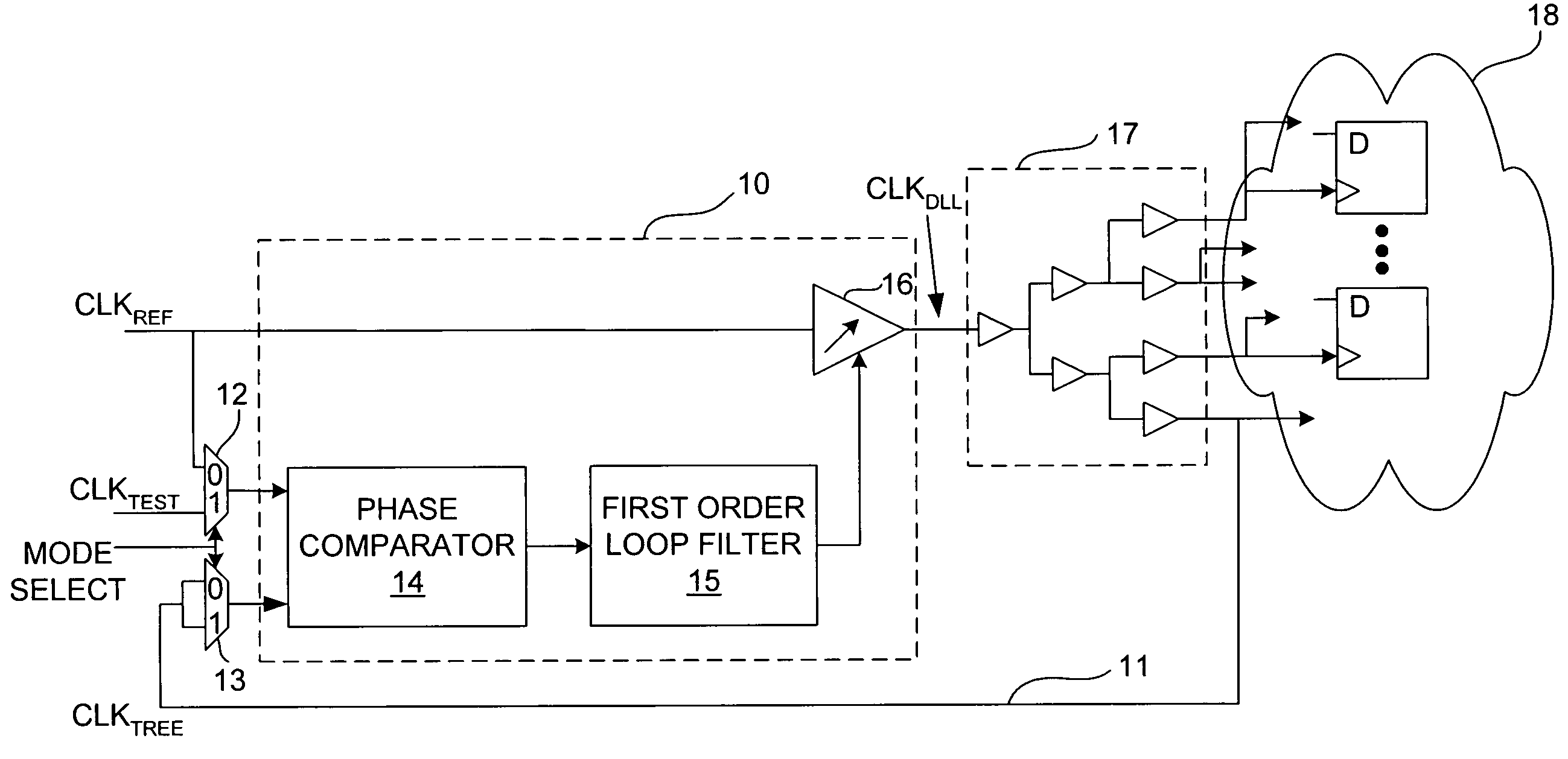
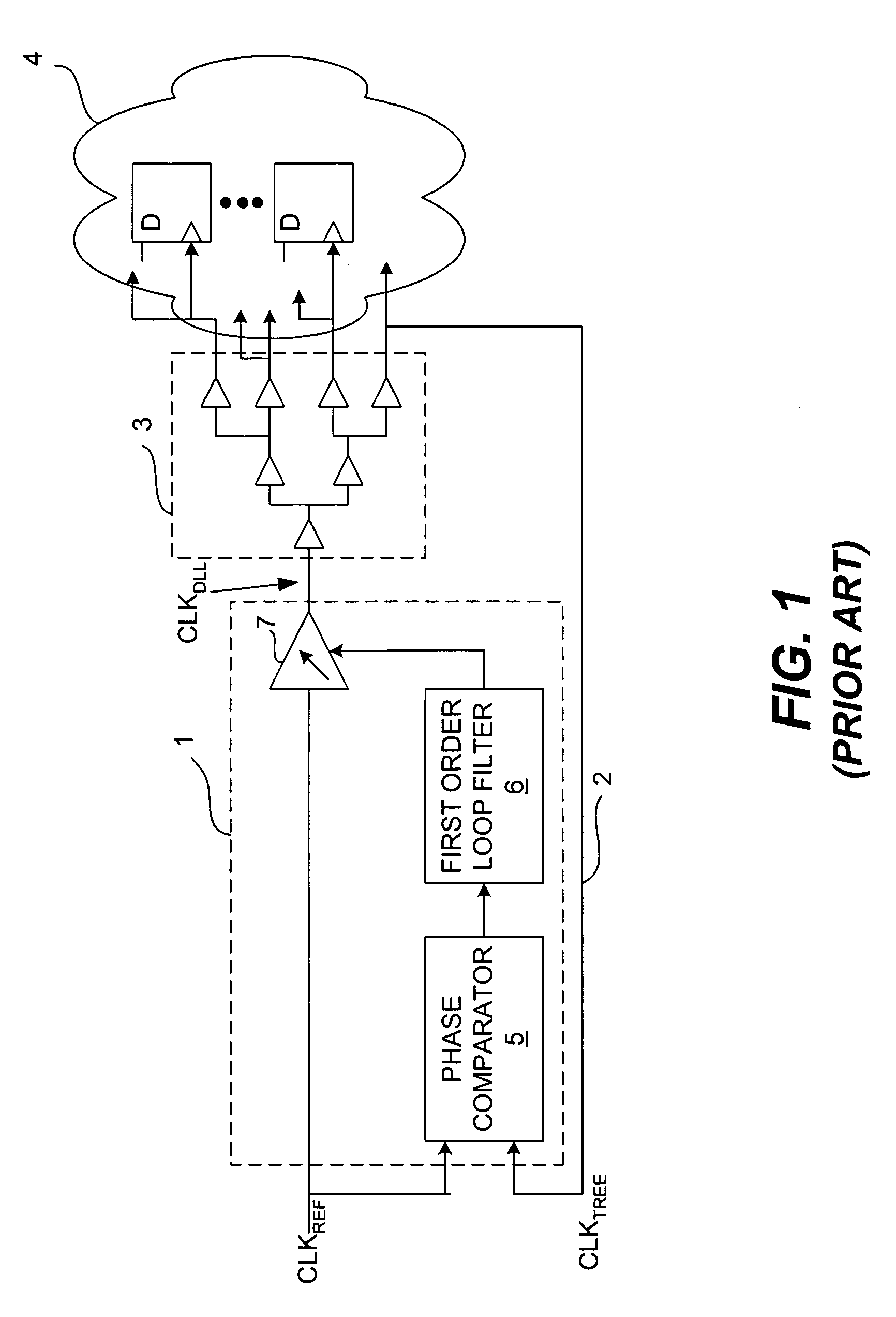
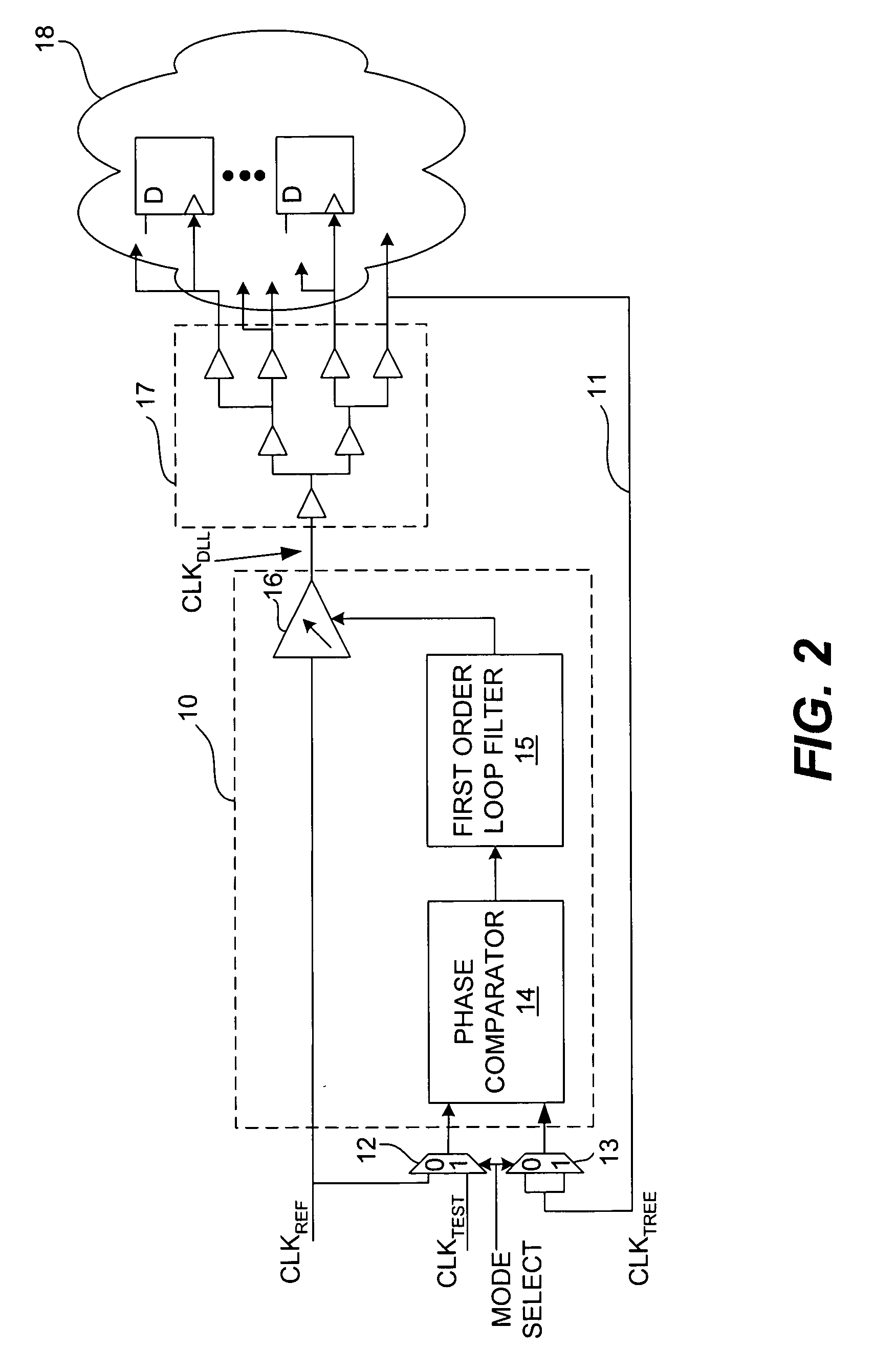
ActiveUS6995554B2Offset errorPulse automatic controlElectronic circuit testingPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
A delay-locked loop (DLL) of an integrated circuit (IC) with testing circuitry and a method for testing a DLL. During test mode, a phase comparator of the DLL receives a test clock in place of the reference clock and determines the phase difference between the test clock and the dock fed back to the DLL from a clock buffer tree. A variable delay element of the DLL then shifts the reference clock in time by an amount that depends on that phase difference. The variable delay element can be exercised by varying the phase of the test clock with respect to the reference clock by a known phase offset to cause the variable delay element to produce a range of delays. Whether the variable delay element is functioning properly can be determined by checking whether the phase of the test clock is aligned with the phase of the feedback clock.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dynamic phase alignment of a clock and data signal using an adjustable clock delay line
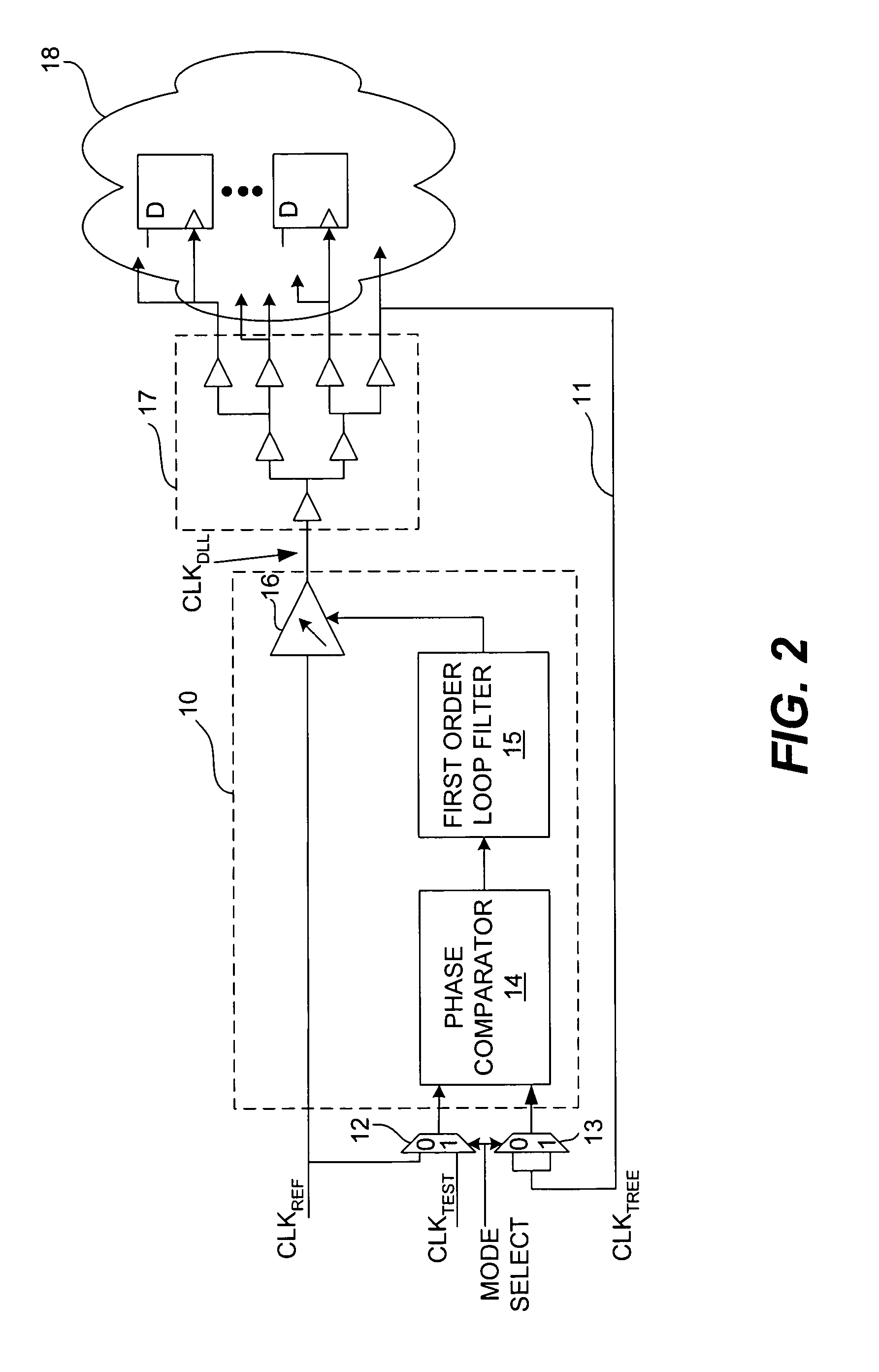
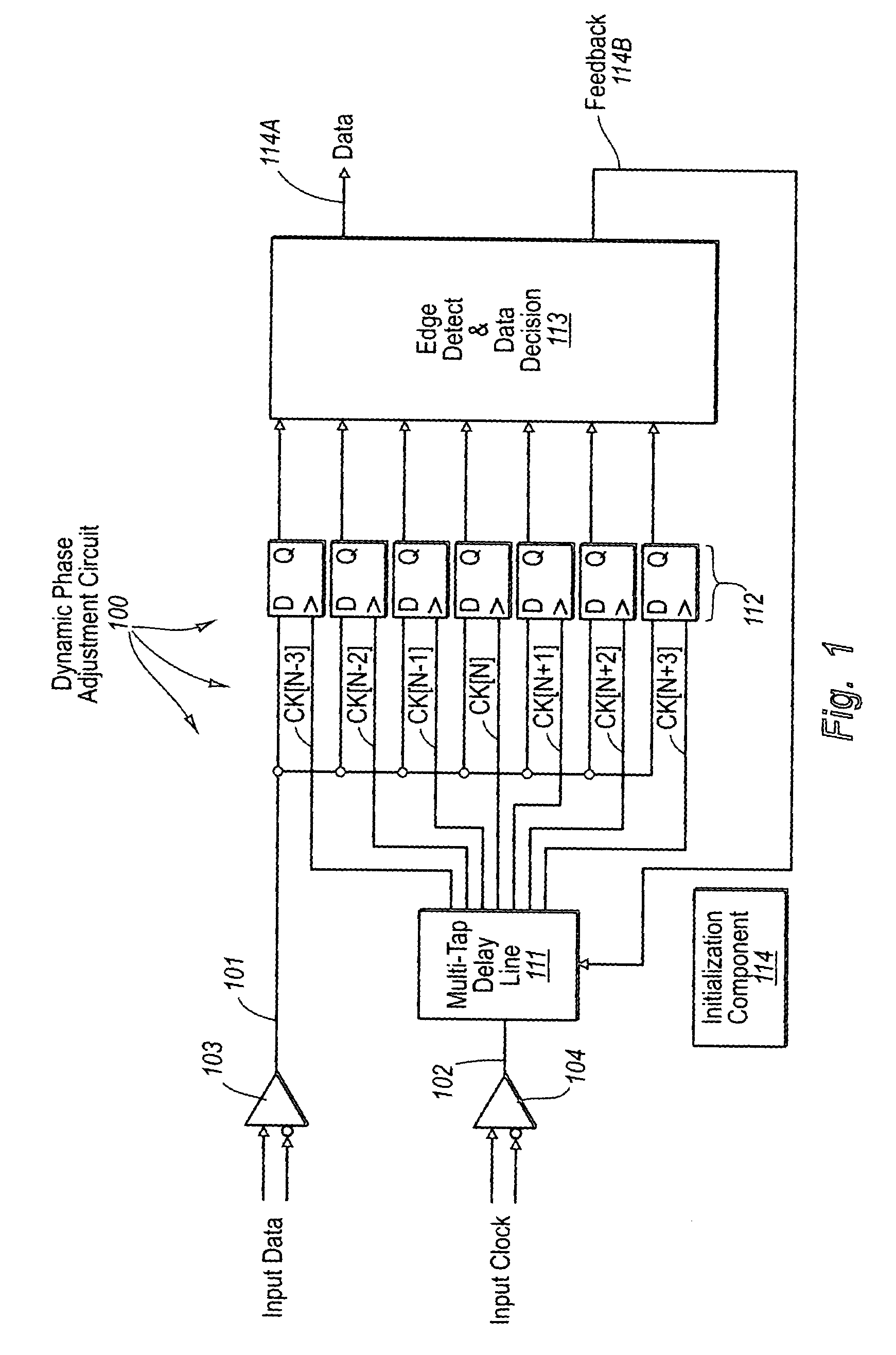
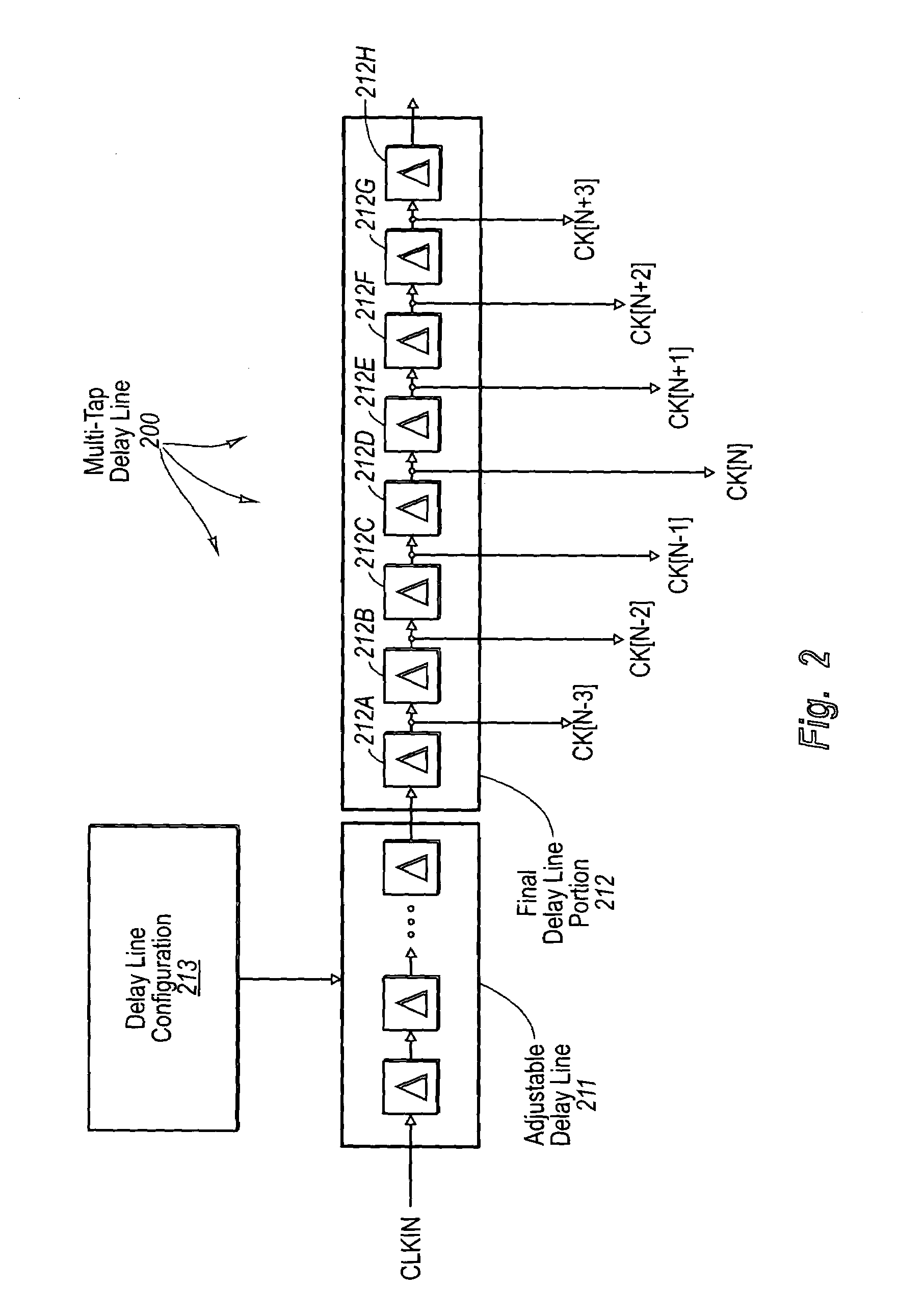
InactiveUS7034597B1High resolutionTo overcome the large delayPulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementDecision circuitImage resolution
A dynamic phase adjustment circuit that includes a multi-tap delay line that receives a clock input signal. The multi-tap delay line includes an initial portion that is adjustable, and final portion after the adjustable portion. A number of registers receive the same data. However, the clock signal that causes the registers to sample is received from a corresponding delay element in the final portion of the multi-tap delay line. An edge detect and data decision circuit receives the sampled data values from each of the registers. Sampling resolution is improved over the PLL-based dynamic phase adjustment circuit since the clock signal is delayed using delay elements, which can be made with relatively small delays. Furthermore, the circuit does not contain excessive circuit elements thereby allowing the dynamic phase adjustment circuit to be contained in a small area.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Optical waveguide and thermal assist magnetic recording head therewith
ActiveUS20110205661A1Maximum couplingCombination recordingNanoopticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight beam
An optical waveguide of the present invention is an optical waveguide in order to directly introduce light beams emitted from a light emitting element. In a core that is a waveguide through which light propagates, a concave part is formed that is a depression in a light incident end surface that is one side where light enters. Therefore, an optical waveguide is realized that can obtain a large optical coupling efficiency is possible by the operation of phase alignment in the concave part.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
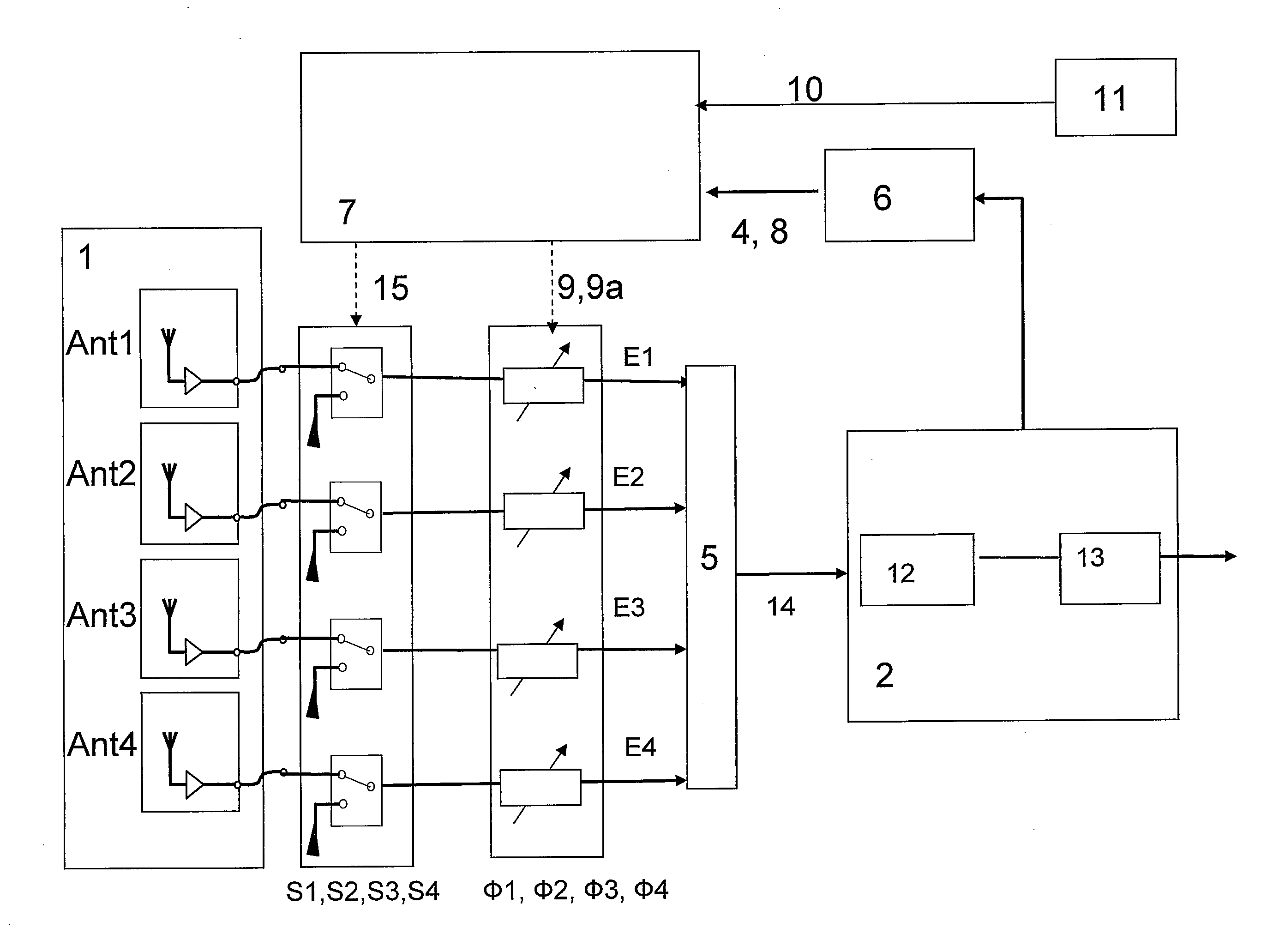
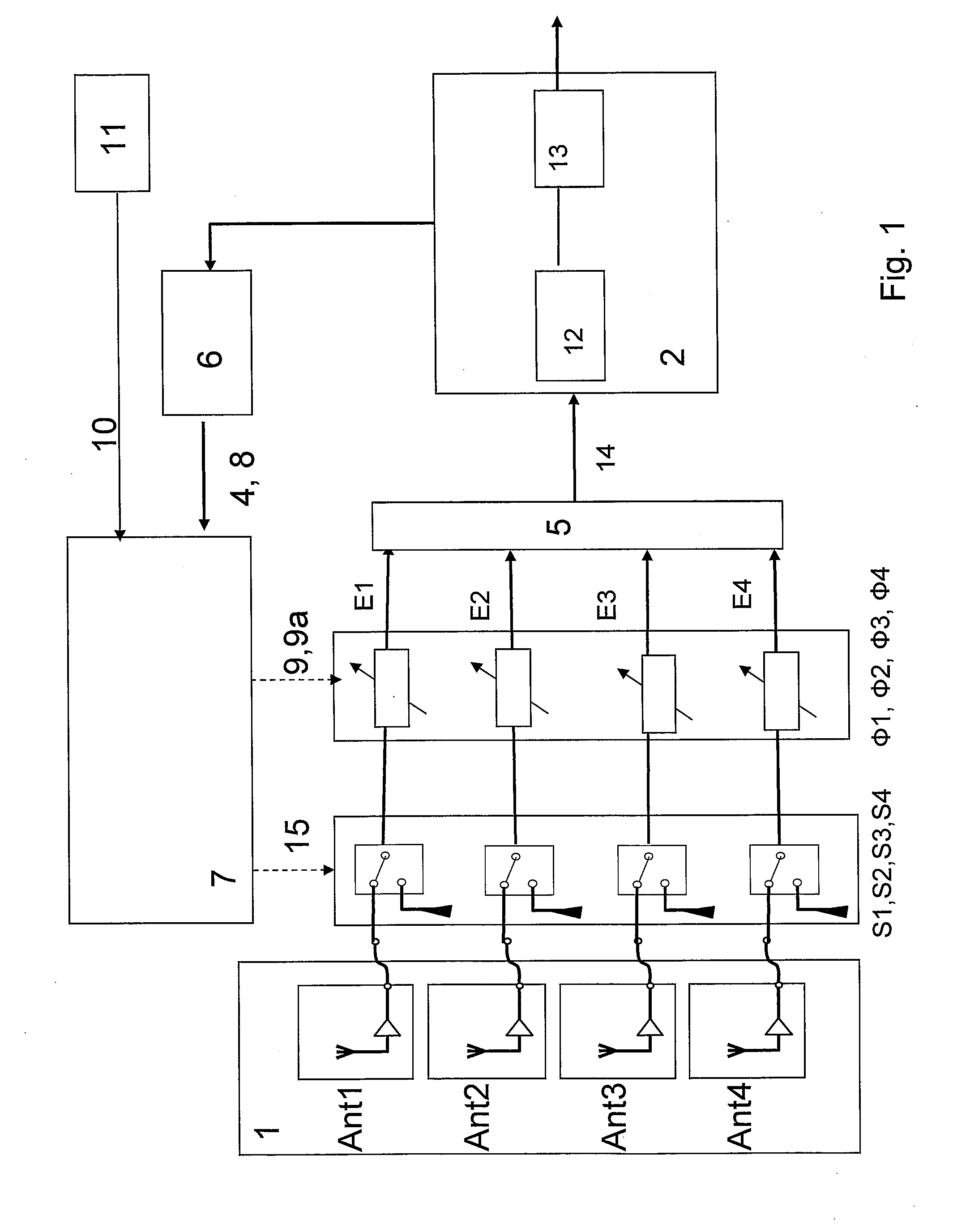
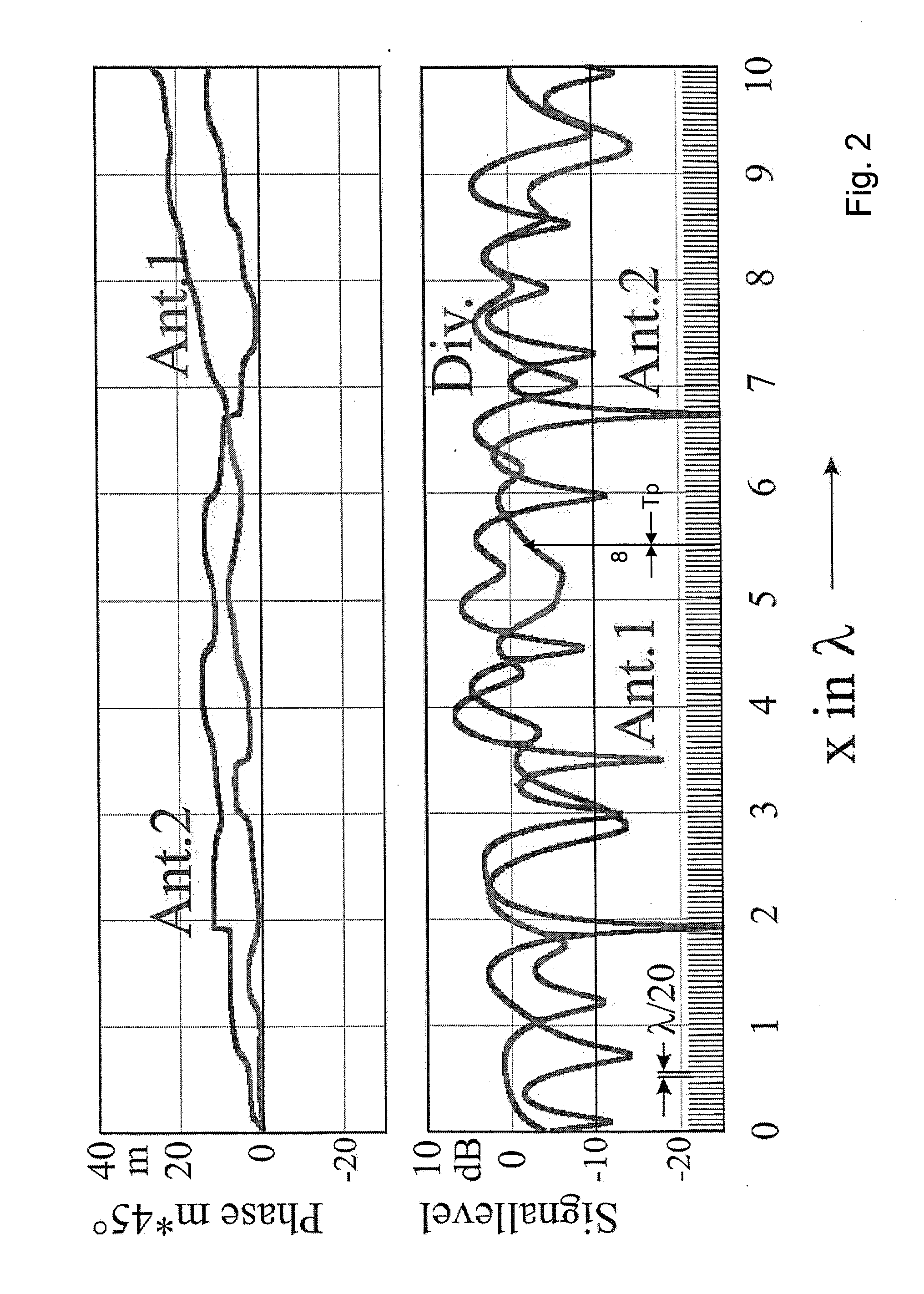
Reception system with phase alignment of antenna signals
InactiveUS20070140389A1Improve efficiencyReduce the possibilityPolarisation/directional diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPhase differenceLevel measurement
A reception system for frequency-modulated, i.e. phase-modulated high-frequency signals, for motor vehicles, having a multi-antenna system having at least two antennas, an individually adjustable phase rotation element, situated in the reception path of the corresponding antenna, in each instance, and a subsequent receiver circuit. There is an individually adjustable switching element for switching through or interrupting the signal flow, respectively, is present in the reception path of every antenna. The reception signals are guided by way of phase rotation elements and the adjustable switching elements which are passed to a linear combination circuit, and wherein the combined signal is passed to the receiver circuit. Furthermore, there can be a level indicator for indicating the level of the combined signal in the form of a level signal and a computer device to which this level signal is passed. An the computer device can include an algorithm for determining the phase differences of the reception signals that are present at the input of the combination circuit at a given setting of the phase rotation elements from their level conditions, by means of calculations. This calculation can occur using level measurement samples of the level signal that are performed one after the other, in terms of time, obtained by way of switch setting signals and phase setting signals brought about by the computer device wherein there are differently defined settings of the switching elements or of the phase rotation elements, respectively. Phase setting signals are generated on the basis of the phase differences determined by calculations, for the subsequent setting of the phase rotation elements for phase alignment of the reception signals that are present at the input of the combination circuit when the adjustable switching elements are switched through.
Owner:DELPHI DELCO ELECTRONICS EUROPE GMBH
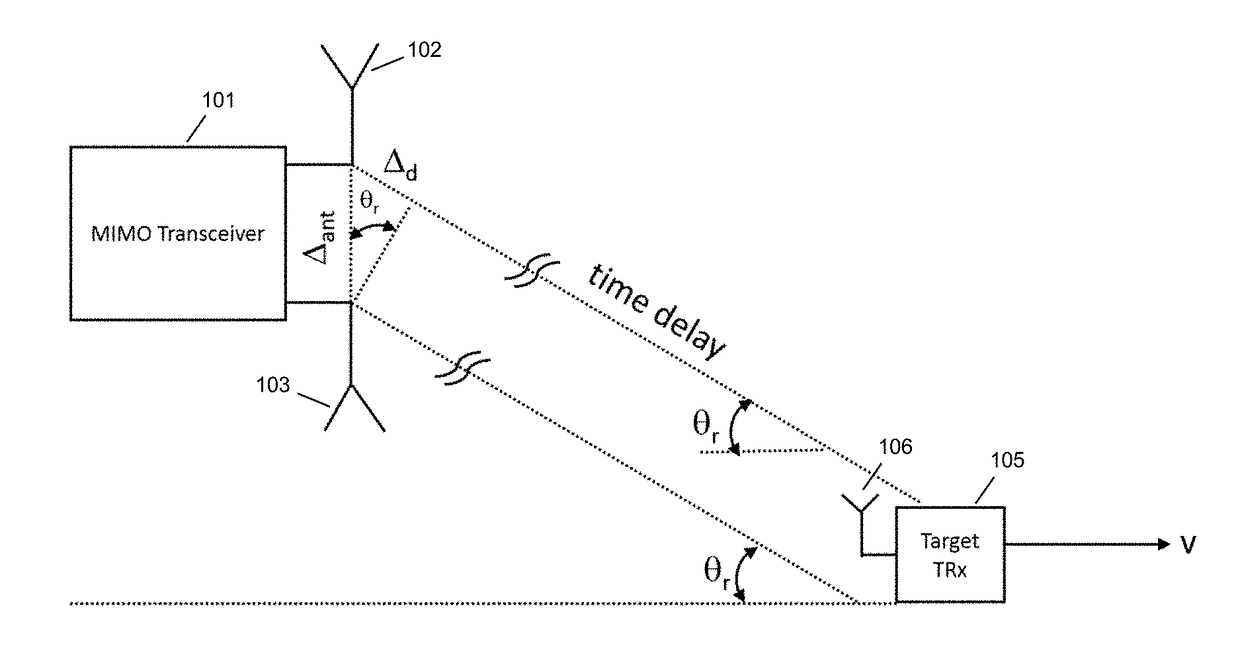
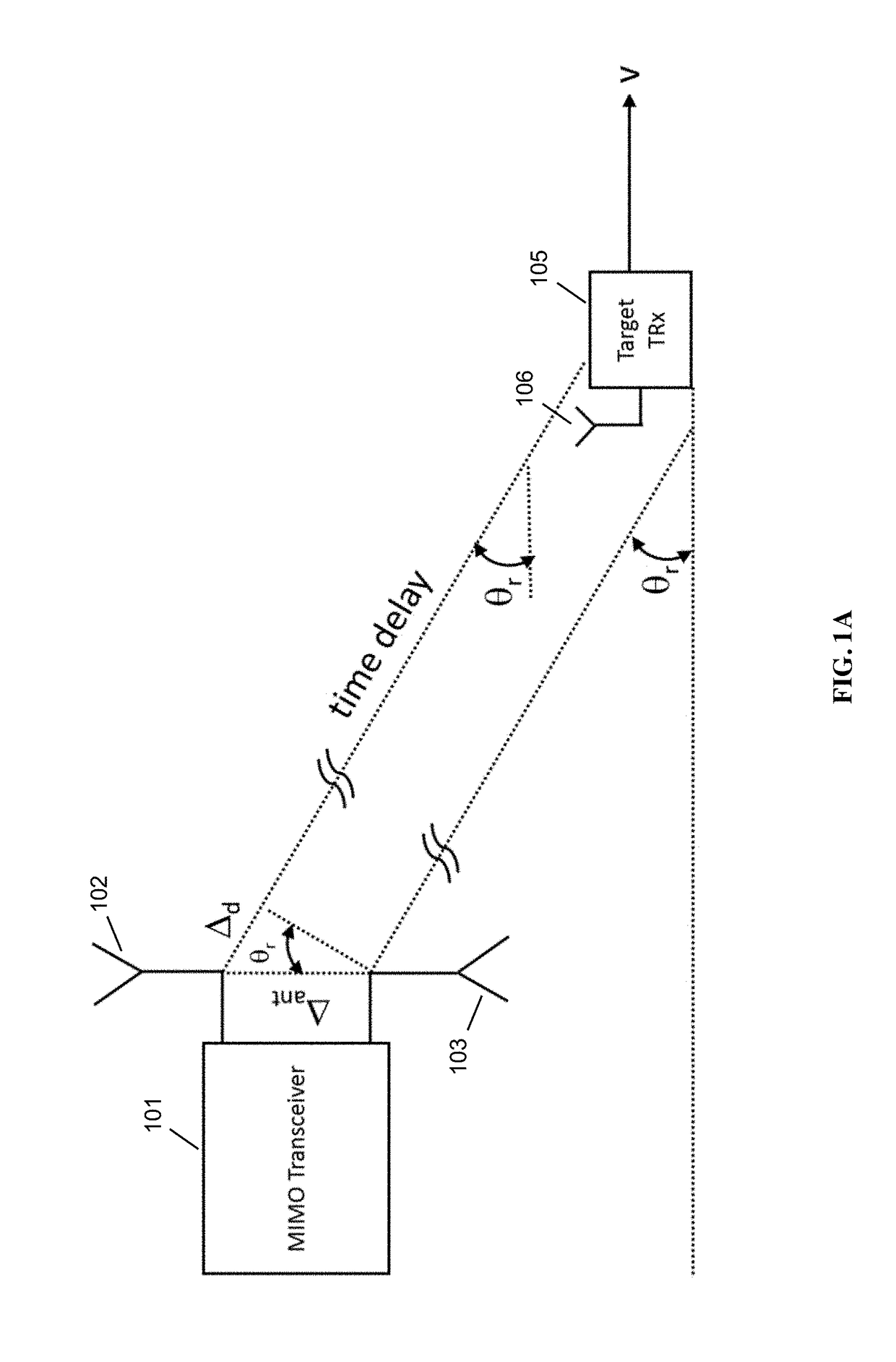
Angle of Arrival Measurements Using RF Carrier Synchronization and Phase Alignment Methods
ActiveUS20170227623A1Synchronisation arrangementRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsLocal oscillatorQuadrature signal
A method for determining an angle of arrival (AOA) of a received signal is disclosed, comprising: generating a baseband information signal by mixing a received signal with a local oscillator (LO) signal, the received signal being an in-phase signal and quadrature signal uncorrelated with each other and derived from different input data sets; obtaining baseband signal samples of the baseband information signal having an in-phase signal sample and a quadrature signal sample; determining a transmitter phase offset based on an estimated correlation between the in-phase signal samples and the quadrature signal samples; performing a plurality of phase measurements using a plurality of antennas to obtain a plurality of phase measurements; correcting the plurality of phase measurements based on the transmitter phase offset to produce a plurality of corrected phase measurement; and calculating an AOA of the received signal based on the difference between the plurality of corrected phase measurements.
Owner:PHASORLAB
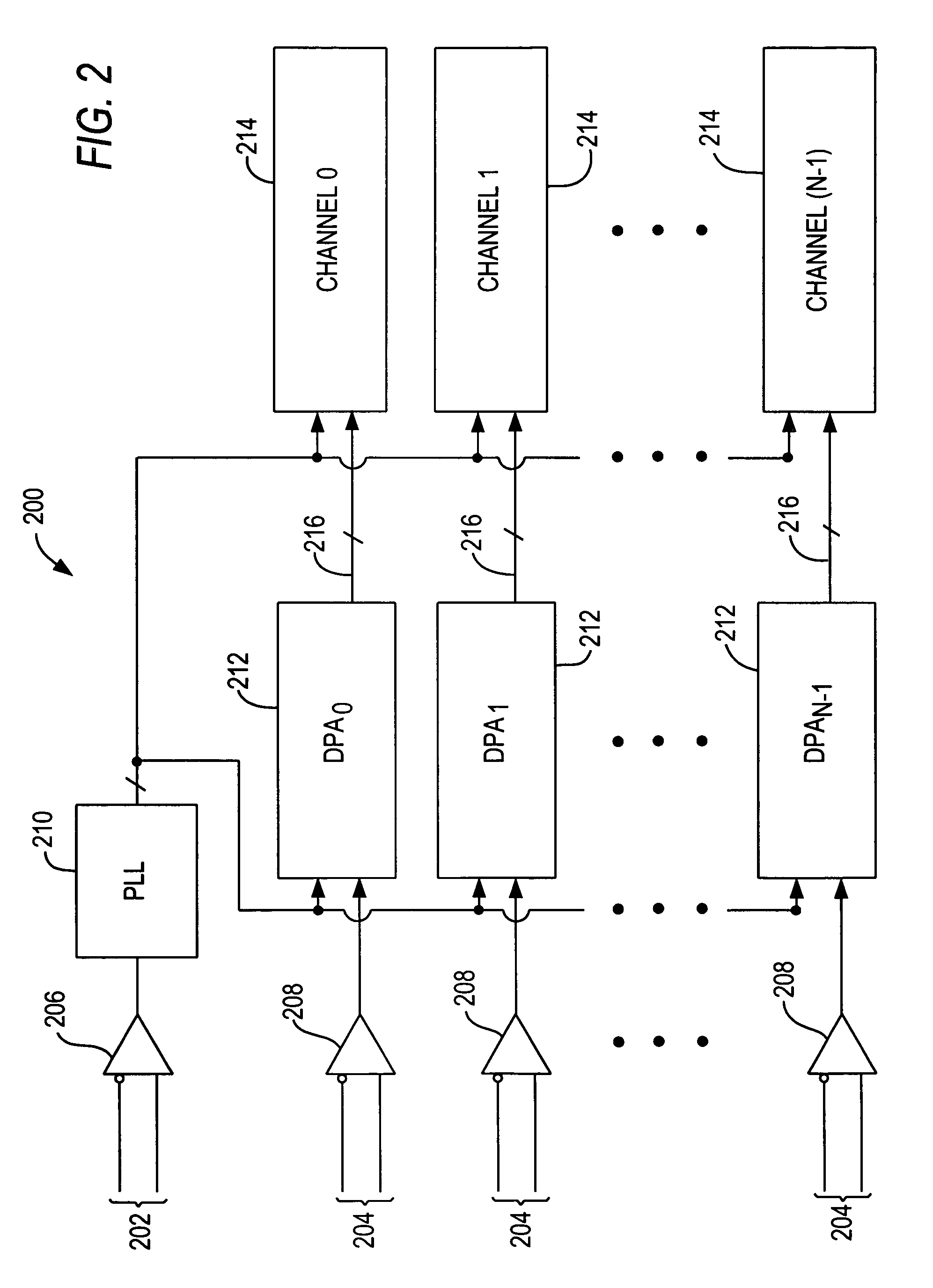
Dynamic phase alignment and clock recovery circuitry
InactiveUS7340021B1Improve reliabilitySynchronisation information channelsModulated-carrier systemsNetwork Communication ProtocolsData signal
A dynamic phase alignment circuit is provided that aligns data signals to a phase of a forwarded clock at each channel in a multi-channel communications protocol. A forwarded clock is sent to a phase locked loop (PLL) circuit that generates multiple clock phases of the forwarded clock. The dynamic phase alignment circuit selects the optimal clock phase with which to align an input data signal for transmission to the corresponding channel. The dynamic phase alignment circuit can also be used for clock recovery.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Control of an optical modulator for desired biasing of data and pulse modulators
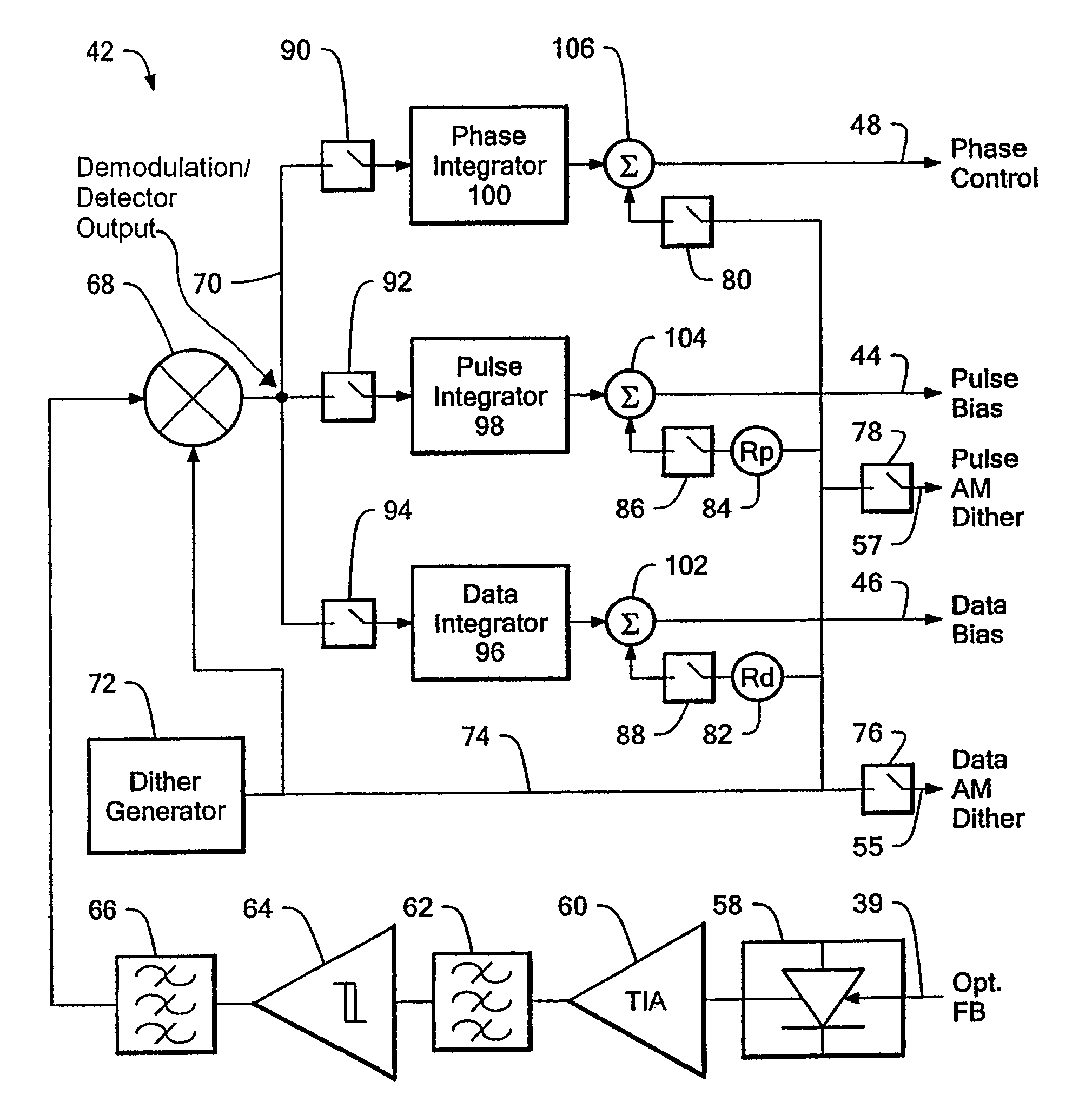
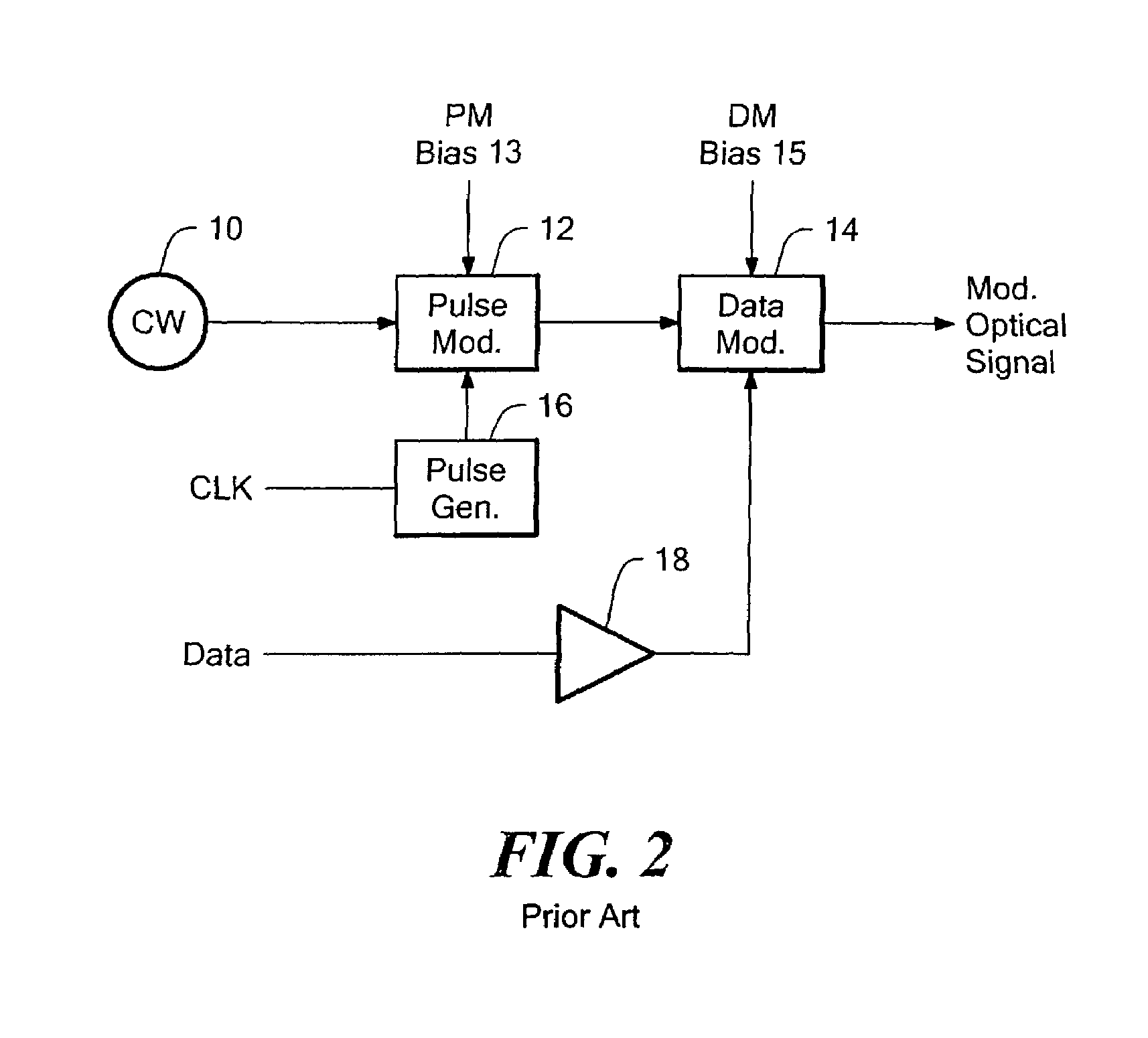
ActiveUS7394992B2Sacrificing performanceStable and accurate operating pointTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmittersData streamPulse modulator
In an optical transmitter, continuous wave light from a laser passes through a data modulator (DM) for non-return-to-zero (NRZ) encoding of a data stream and through a pulse modulator to add return-to-zero encoding to the modulated optical signal. A modulator controller monitors the output optical signal power, optimizes the bias setting for the DM and the PM, and optimizes the phase relationship between the pulse and data components of the modulated optical signal. For each optimization, a low amplitude and low frequency dither signal is injected at appropriate points in the modulator. A single photo detector and electrical receiver are used in a multiplexed fashion to monitor the optical output signal and derive separate feedback signals. Remaining control circuitry forces a null in a respective residual dither component in the optical output signal to maintain the desired bias level or phase alignment.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPTICS INC
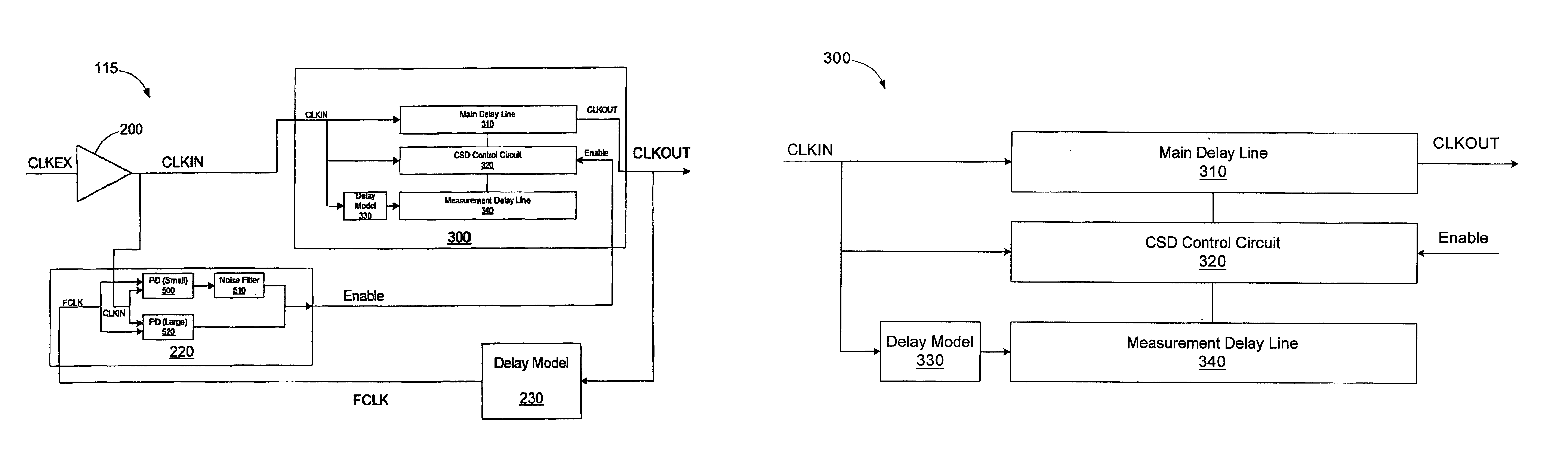
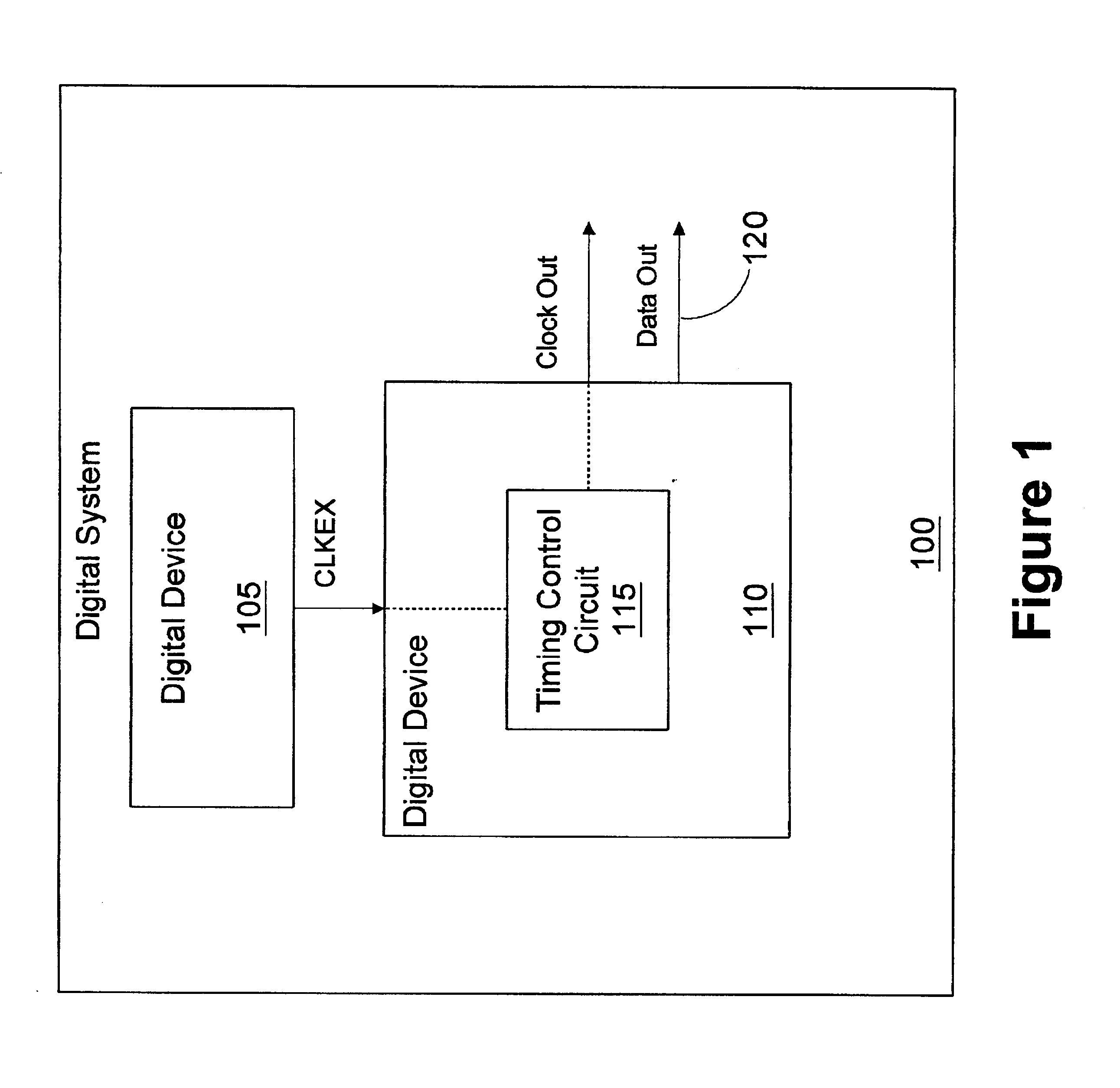
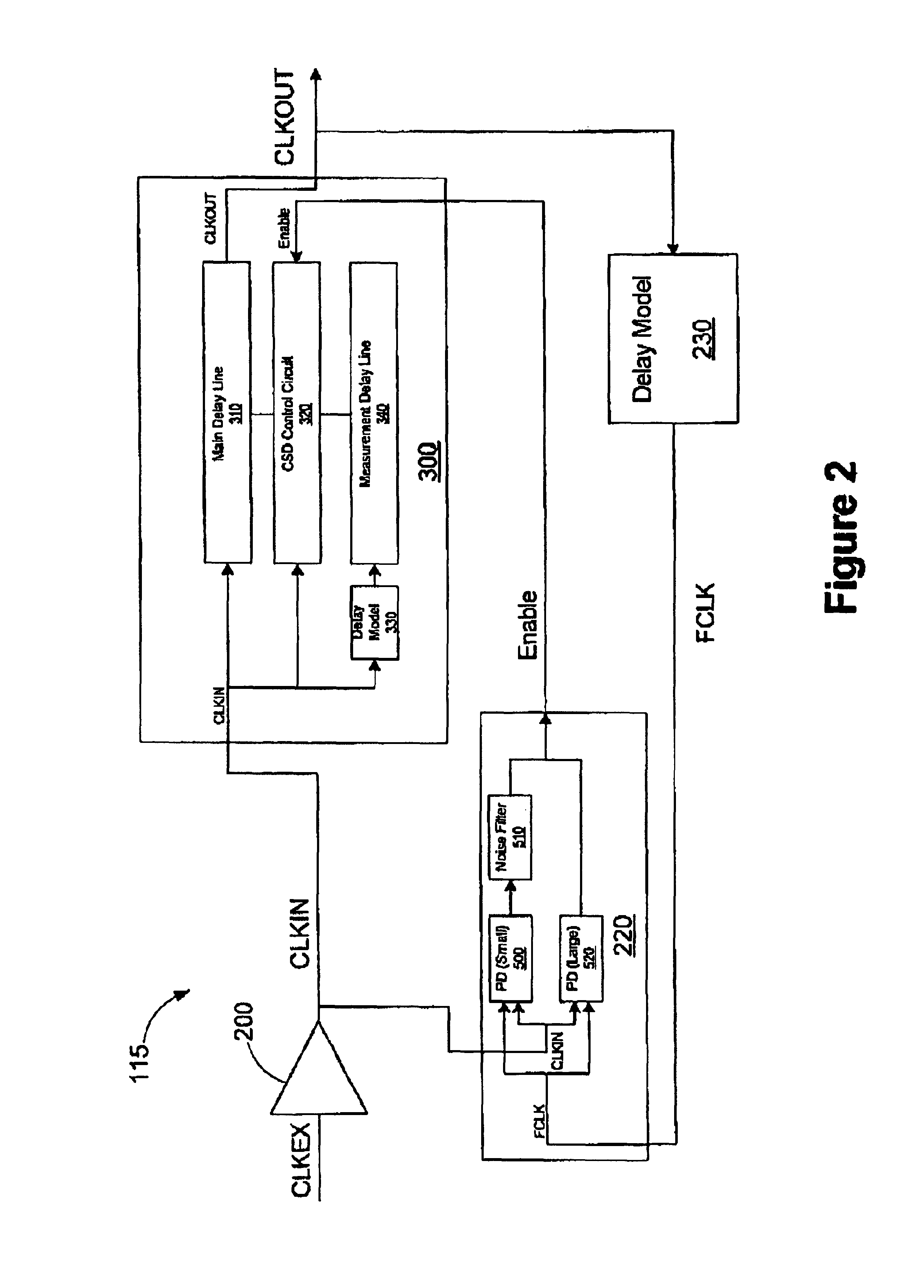
Method and apparatus for enabling a timing synchronization circuit
A timing control circuit includes a synchronization circuit and a detection circuit. The synchronization circuit includes a main delay line configured to receive an input clock signal and delay the input clock signal by a time interval to generate an output clock signal and a control circuit configured to control the main delay line to vary the time interval to synchronize the input clock signal with a feedback clock signal generated from the output clock signal responsive to assertion of an enable signal. The detection circuit is configured to receive the input clock signal and the feedback clock signal, detect a phase alignment error between the input clock signal and the feedback clock signal, and assert the enable signal responsive to the phase alignment error exceeding a predetermined amount. A method for synchronizing clock signals includes receiving an input clock signal; delaying the input signal by a time interval to generate an output clock signal; controlling the time interval to synchronize the input clock signal with a feedback clock signal generated from the output clock signal responsive to assertion of an enable signal; detecting a phase alignment error between the input clock signal and the feedback clock signal; and asserting the enable signal responsive to the phase alignment error exceeding a predetermined amount.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
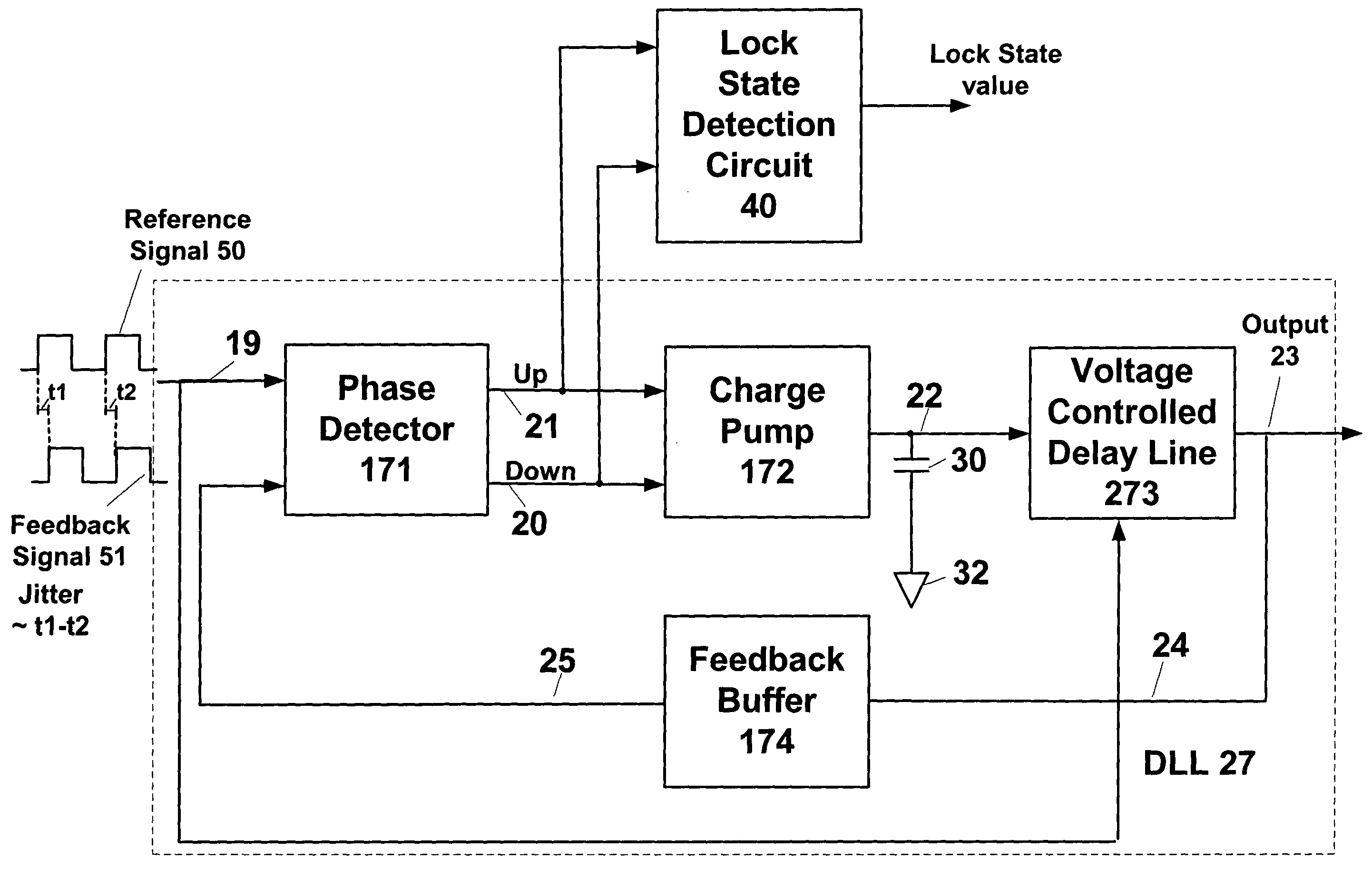
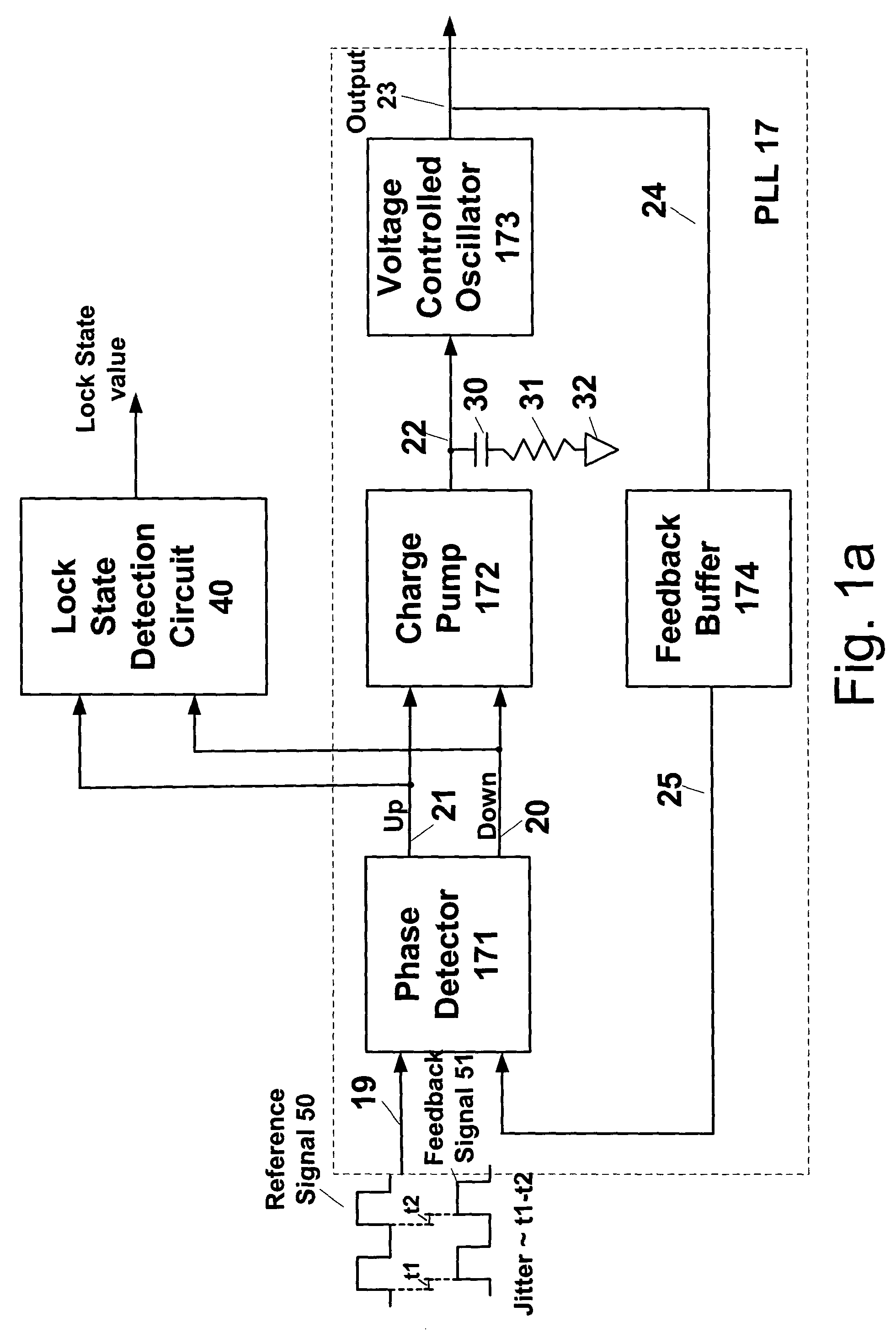
Circuit, apparatus and method for obtaining a lock state value
A circuit, apparatus and method provides a lock state value representing an amount of time a phase alignment circuit (“PAC”), such as a PLL or DLL, is tracking or locked to an incoming reference signal for a predetermined period of time. In an embodiment of the present invention, a lock state detection circuit is coupled to a lock loop circuit and includes a phase detection circuit and a counter circuit. The phase detection circuit includes a phase detector and delay elements that are coupled to the PAC phase detector. The phase detector outputs a lock state sample value of the PAC. In an embodiment of the present invention, the PAC is locked when a stream of alternating lock state sample values, logical 1's and 0's, are output from the phase detector. The counter circuit includes a flip-flop, an XOR gate and counter for obtaining a lock state value for a predetermined period of time.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Delay-locked loop and a method of testing a delay-locked loop
ActiveUS20050280407A1Offset errorPulse automatic controlElectronic circuit testingPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
A delay-locked loop (DLL) of an integrated circuit (IC) with testing circuitry and a method for testing a DLL. During test mode, a phase comparator of the DLL receives a test clock in place of the reference clock and determines the phase difference between the test clock and the clock fed back to the DLL from a clock buffer tree. A variable delay element of the DLL then shifts the reference clock in time by an amount that depends on that phase difference. The variable delay element can be exercised by varying the phase of the test clock with respect to the reference clock by a known phase offset to cause the variable delay element to produce a range of delays. Whether the variable delay element is functioning properly can be determined by checking whether the phase of the test clock is aligned with the phase of the feedback clock.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
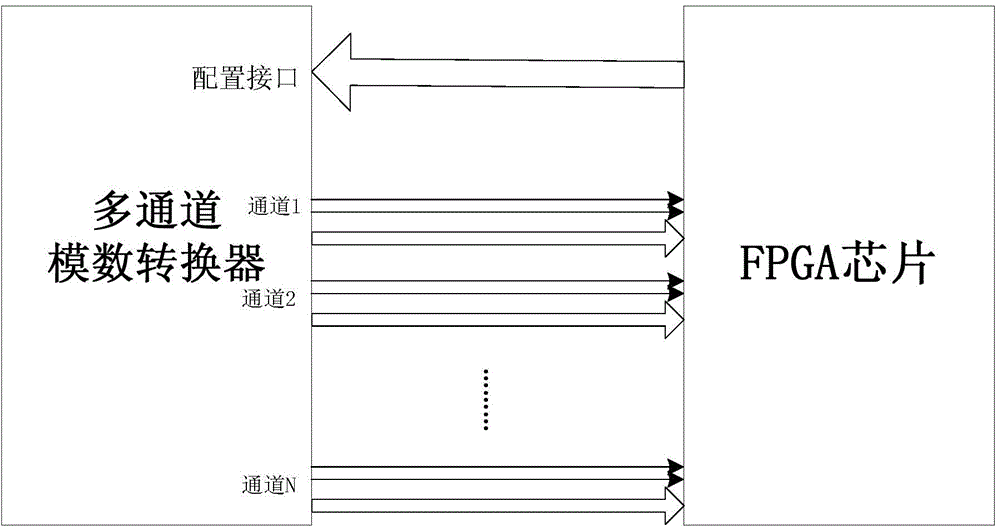
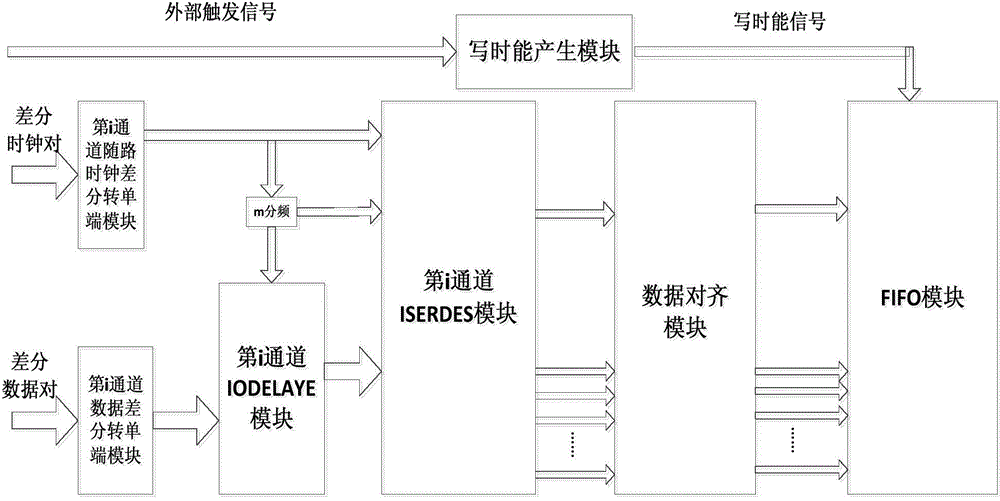
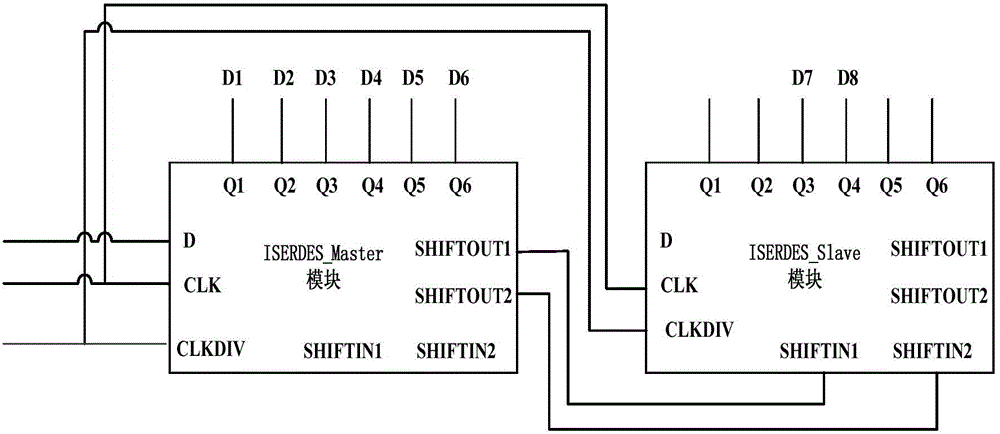
Method for achieving synchronization of multichannel analog-digital converter
ActiveCN104378114AImpact on imaging resultsAvoid glitchesAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterRadar
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar radio-frequency signal collecting technologies and discloses a method for achieving synchronization of a multichannel analog-digital converter. The method comprises the following steps that the multichannel analog-digital converter is configured to work in a multichannel testing mode; the multichannel analog-digital converter generates data differential pairs and channel associated clock differential pairs, and the data differential pair and the channel associated clock differential pair of each channel are sent to an FPGA chip; the FPGA chip obtains corresponding single-ended clock signals and corresponding single-ended data signals; a corresponding delay value is configured to each data bit of the single-ended data signal of each channel, according to the correspondingly delay value configured to each data bit of the singled-ended data signal of each channel, delaying processing is conducted on the signal of each data bit of the singled-ended data signal of each channel; deserializing is conducted on the delayed singled-ended data signal of each channel, and corresponding parallel data are obtained; according to the phase relationship between the parallel data of each channel, phase alignment of the parallel data of each channel is conducted.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
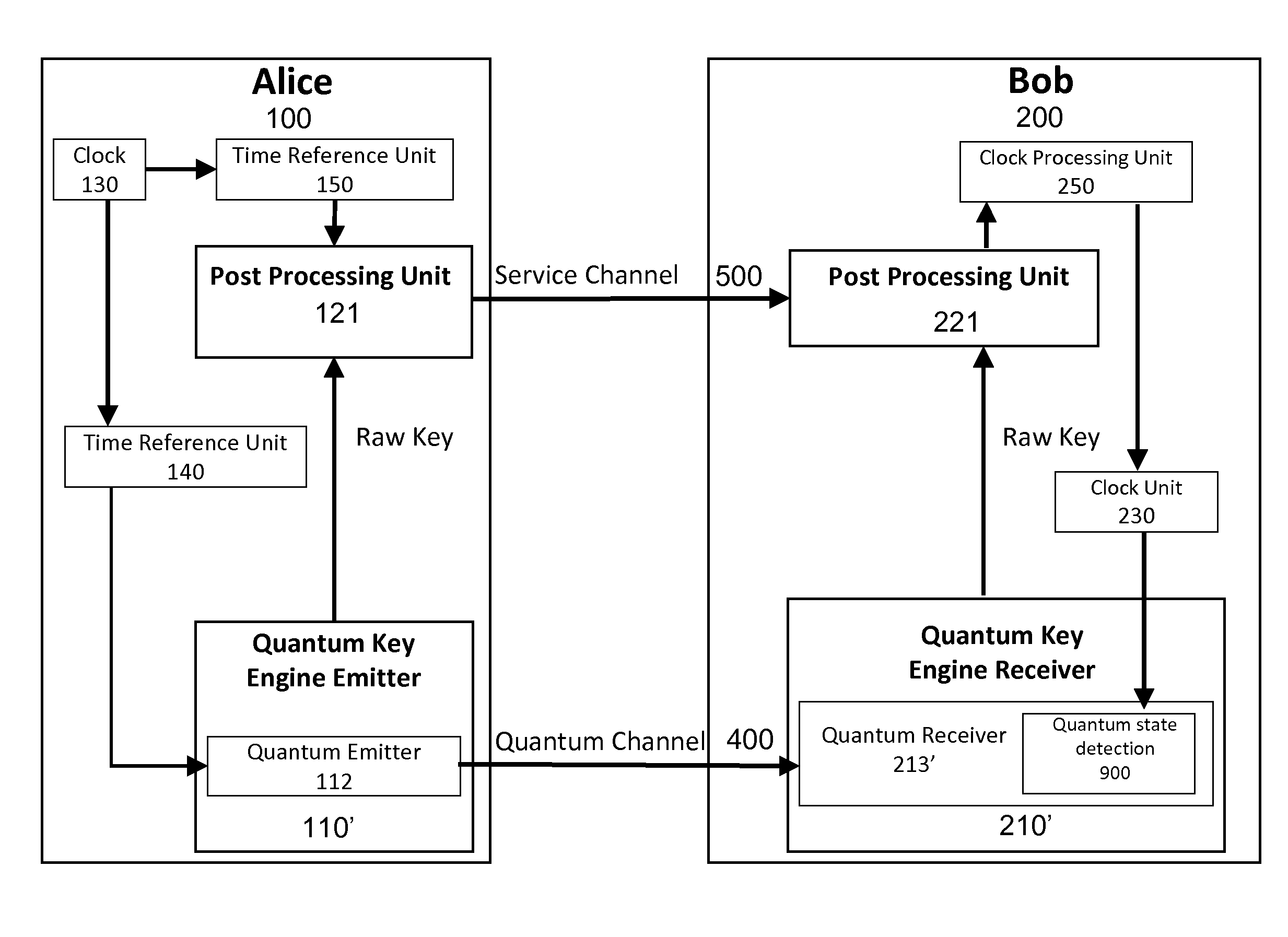
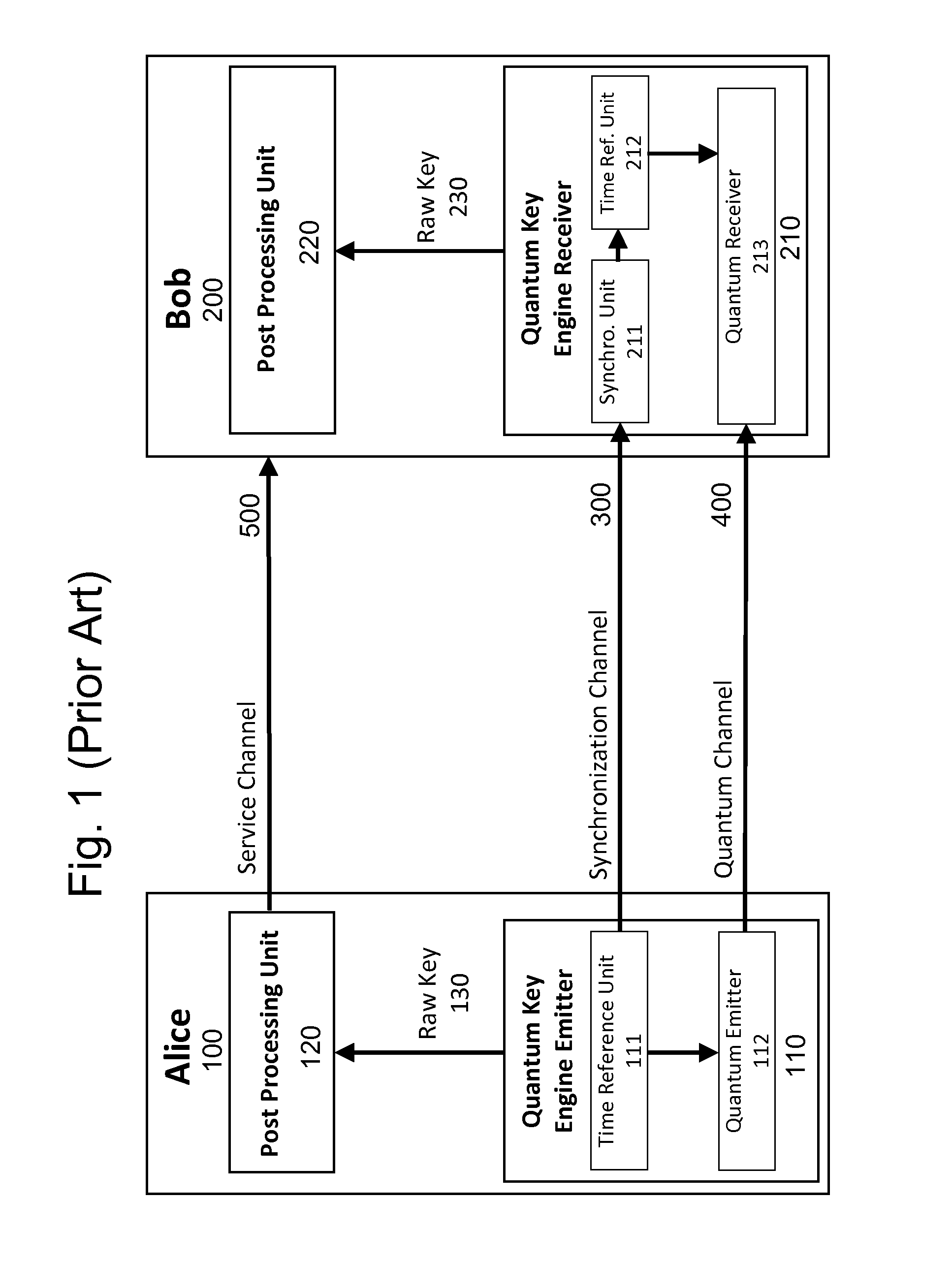
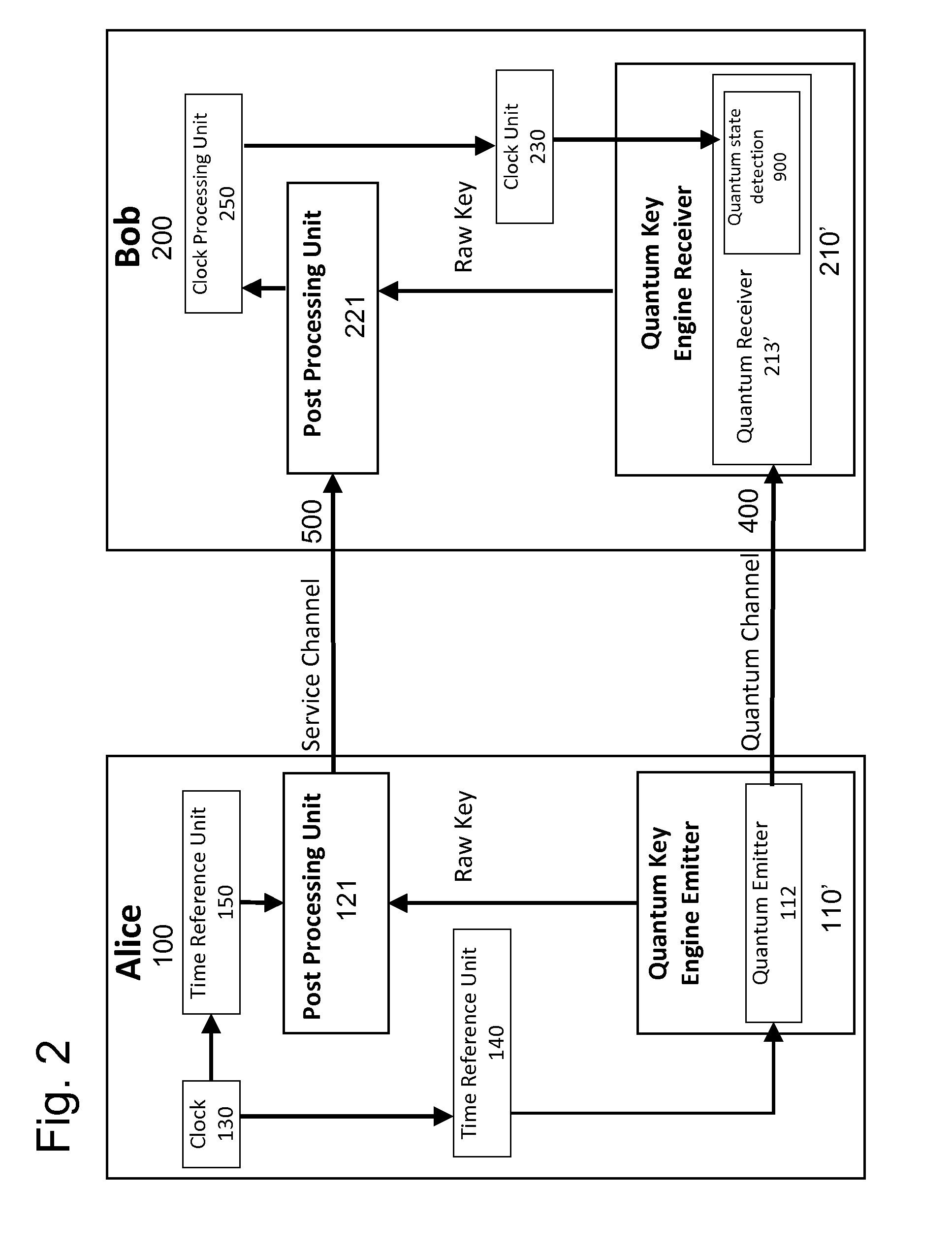
Apparatus and method for qkd quantum communication channel continuous synchronization and alignment
ActiveUS20160134420A1Increase chanceReduce in quantityKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationClock rateQuantum channel
System and methods for synchronizing and aligning quantum channel for Quantum Key Distribution. The primary object of the invention is to allow a Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) apparatus to work continuously with only two communication channels, a quantum communication channel and a service channel. This is achieved by linking the clock frequencies of both channels and completed by an over-sampling method for phase synchronization tracking. Clock signal carry is done through data using a clock data recovery encoding techniques. Having a continuous operating QKD system is not possible without a tracking system that enables phase alignment. This synchronization and alignment system and method for QKD has multiple benefits as it allows real-time synchronization with continuous data flow and is not dedicated to a specific quantum protocol.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
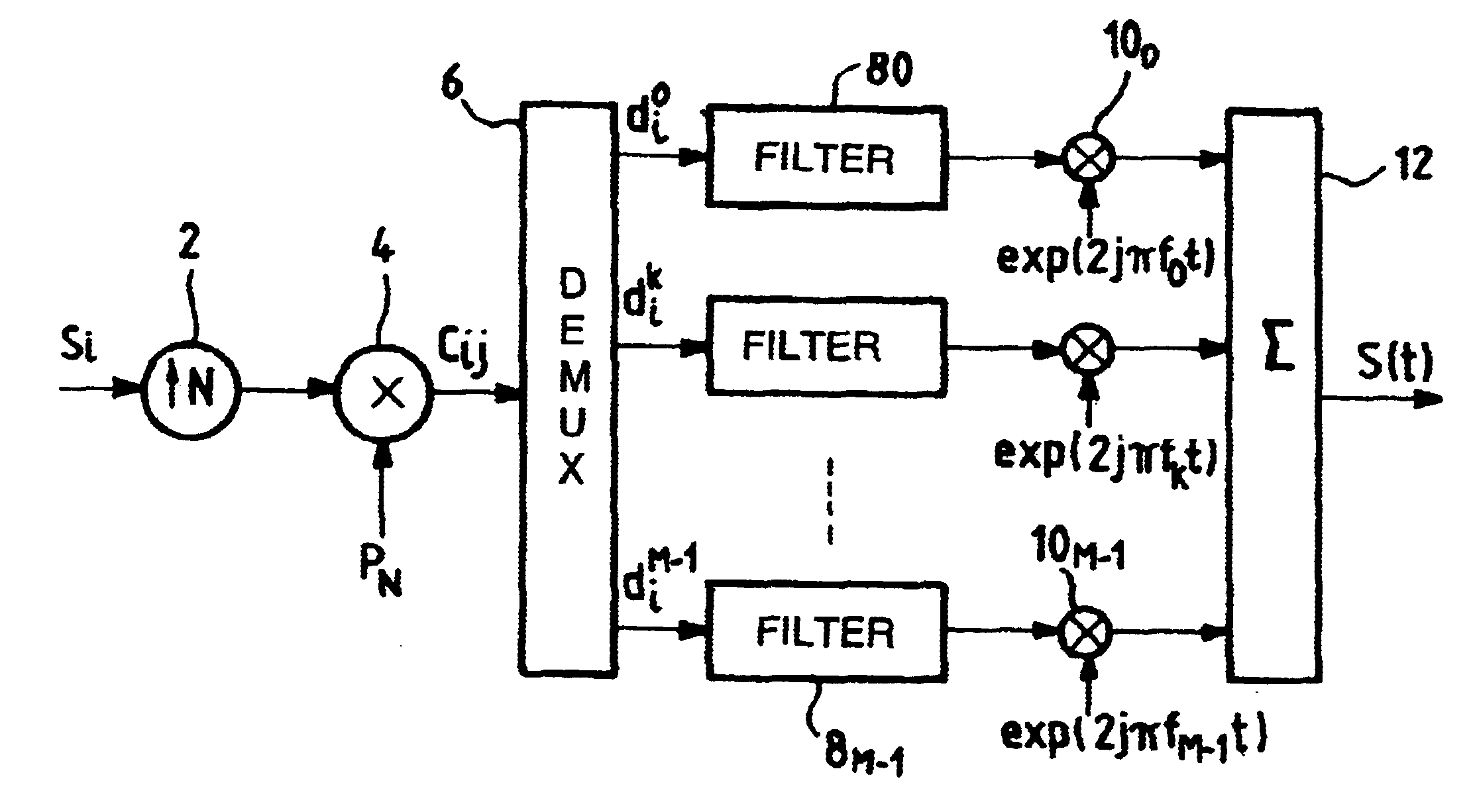
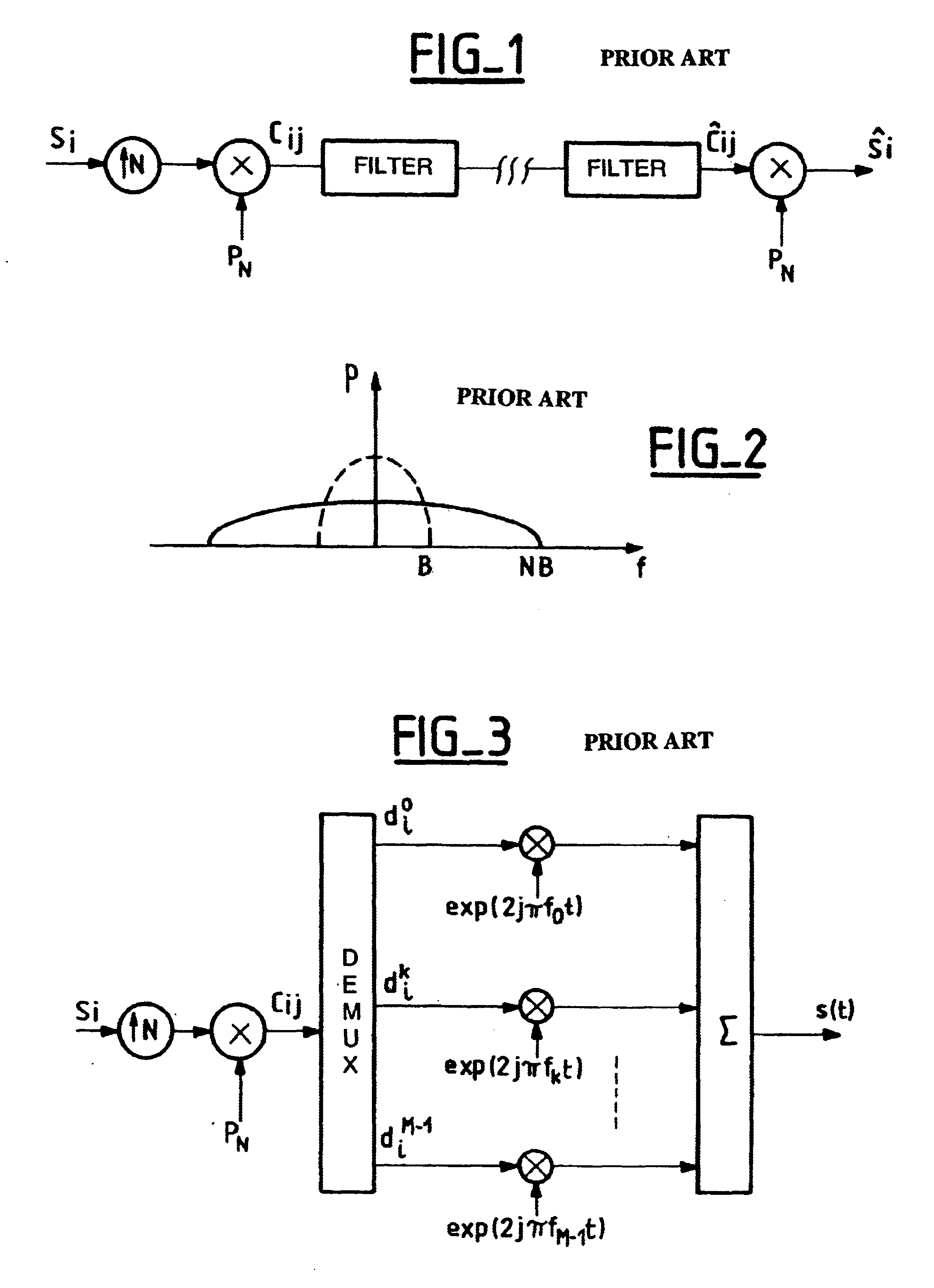
Spread-spectrum transmission system with filtered multi-carrier modulation
InactiveUS6680966B2Conserving adequate resistanceLimit recombination lossMulti-frequency code systemsSignal channelsCarrier signalCarrier modulation
The invention provides a spread-spectrum transmission system with multiple carrier modulation in which the signals for transmission over each of the subcarriers are filtered prior to being transmitted over the subcarrier, thereby making it possible on reception to synchronize the various subcarriers in time, and in which each subcarrier carries a plurality of chips that result from spreading a single symbol. With coherent modulation, the number of chips resulting from spreading a single symbol and transmitted over each subcarrier is selected so as to enable the various subcarriers to be put into phase alignment by recombining the chips coming from the same symbol on each subcarrier. With differential modulation, the transmission over each subcarrier of chips resulting from spreading a single symbol provides resistance to jamming by limiting recombination losses because of the differential modulation.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling modulator phase alignment in a transmitter of an optical communications system
A method of controlling phase alignment in a modulator of a transmitter in an optical communications system uses a narrowband optical filter to monitor changes in power spectral density of a modulated output at and around the optical carrier frequency. In one embodiment, a method controls alignment of a carrier-suppressed-return-to-zero (CSRZ) pulse train in accordance with changes in the power spectral density of the CSRZ modulated optical signal at and around the optical carrier frequency and generates phase adjustment control signals by executing a phase-control loop to maintain the power spectral density of the CSRZ modulated output at the optical carrier frequency at a desired level.
Owner:CIENA
Hybrid speech coding and system
InactiveUS20050065787A1Improve performanceSpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceWaveform codingSpeech code
Hybrid linear predictive speech coding system with phase alignment predictive quantization zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Systems and methods for track to track phase alignment
InactiveUS8379498B2Filamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageData setDetector circuits
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com