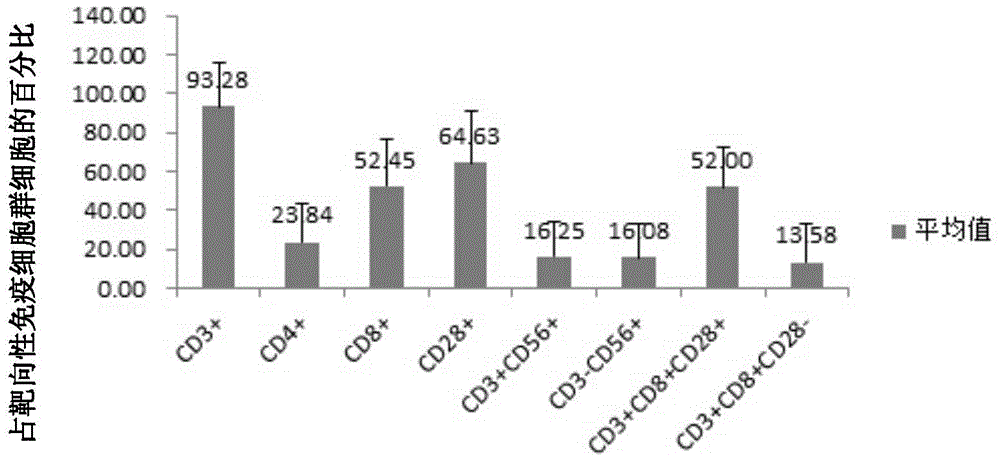
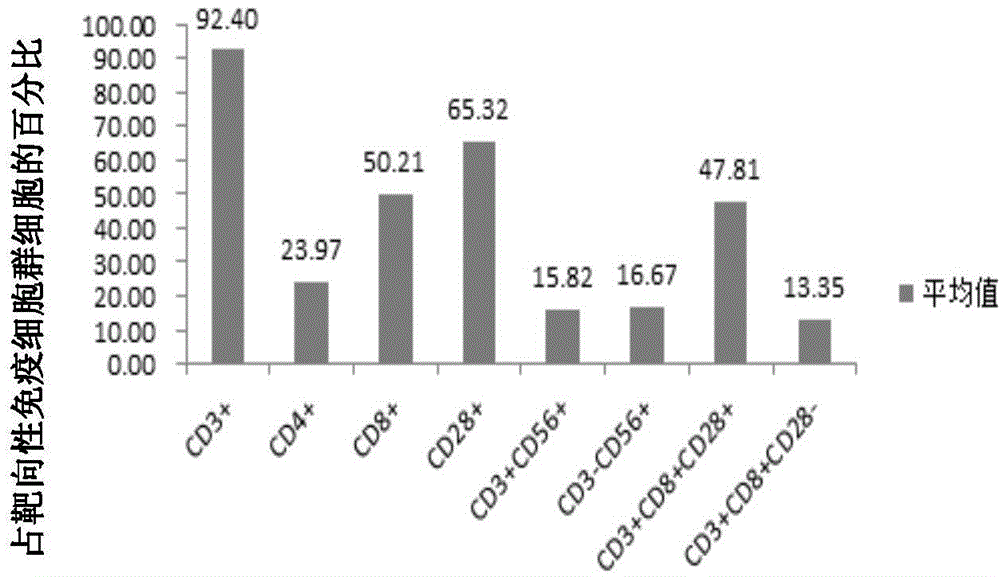
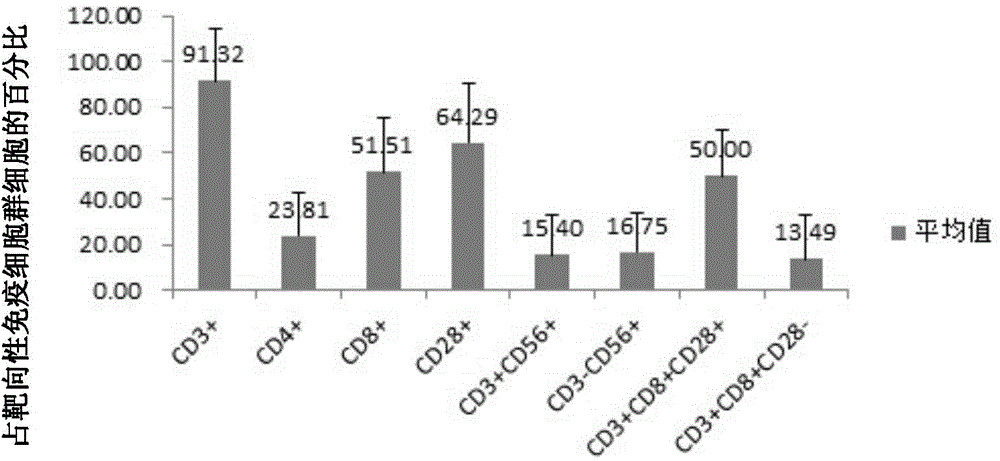
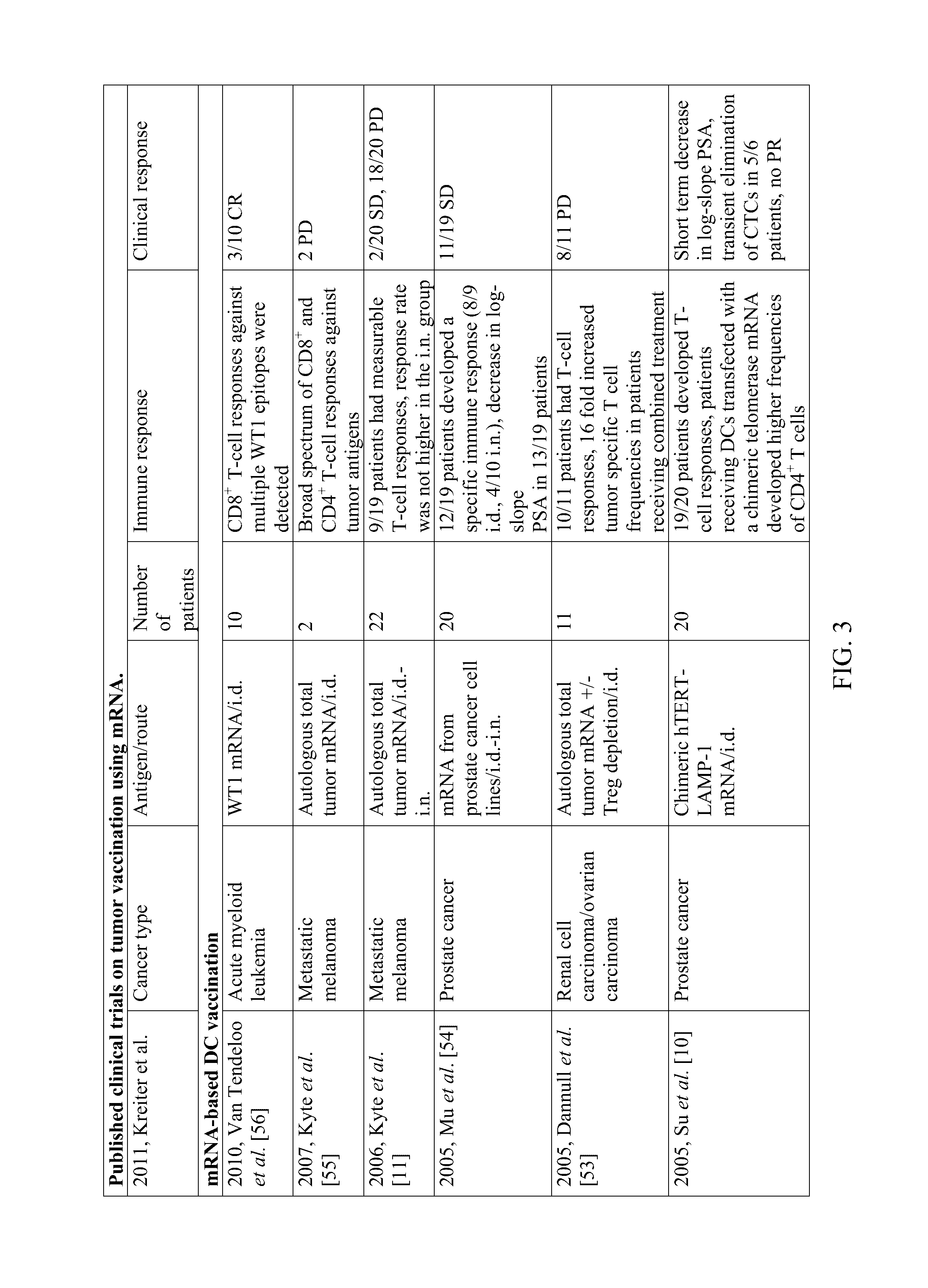
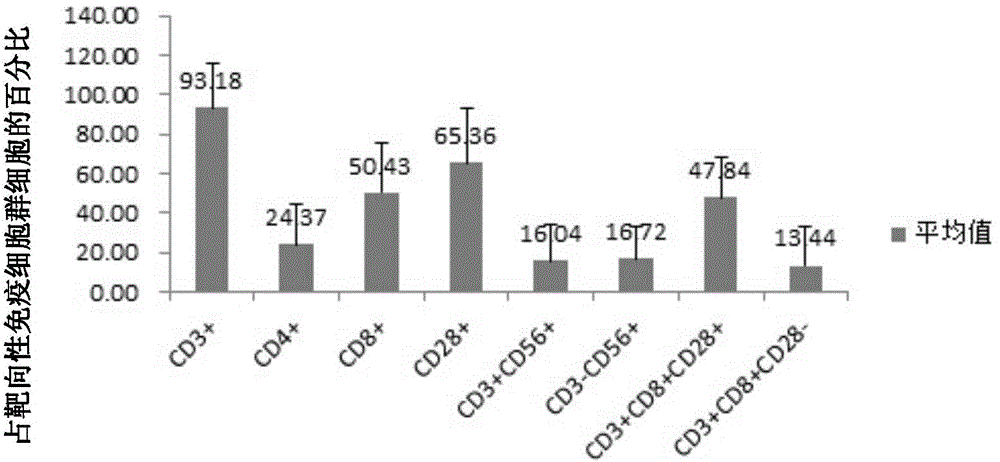
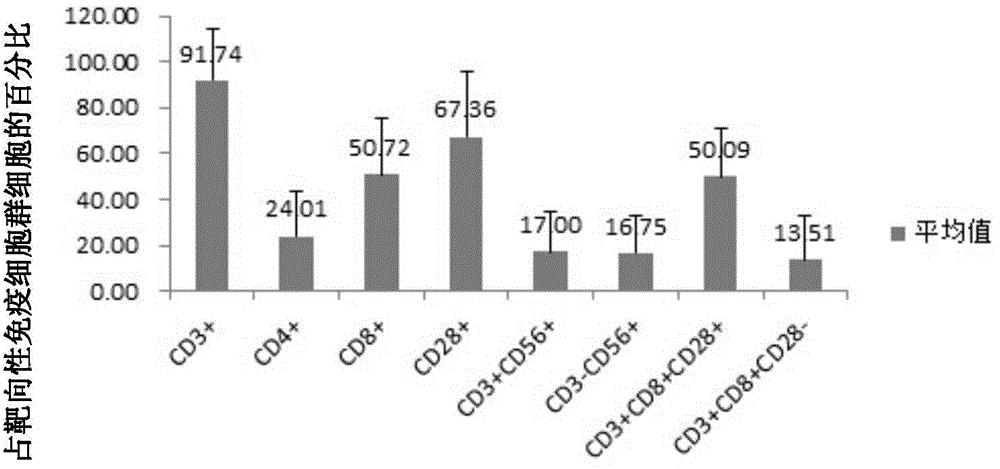
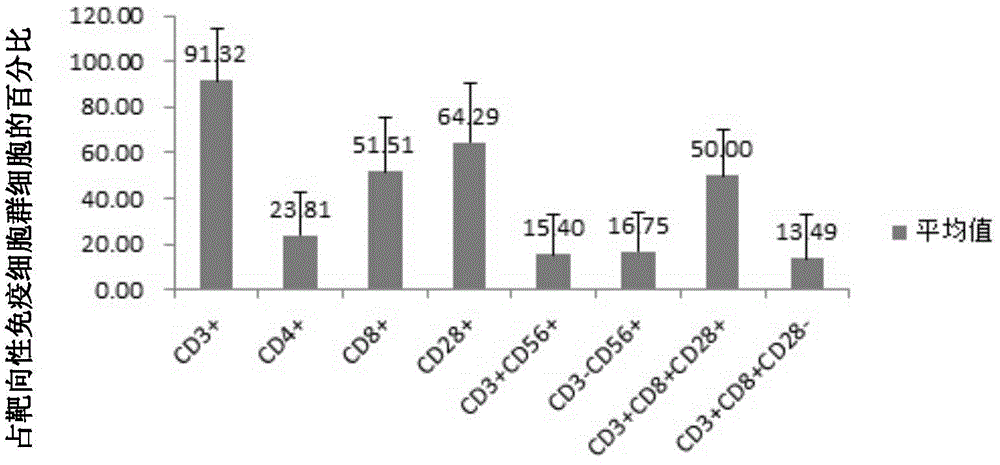
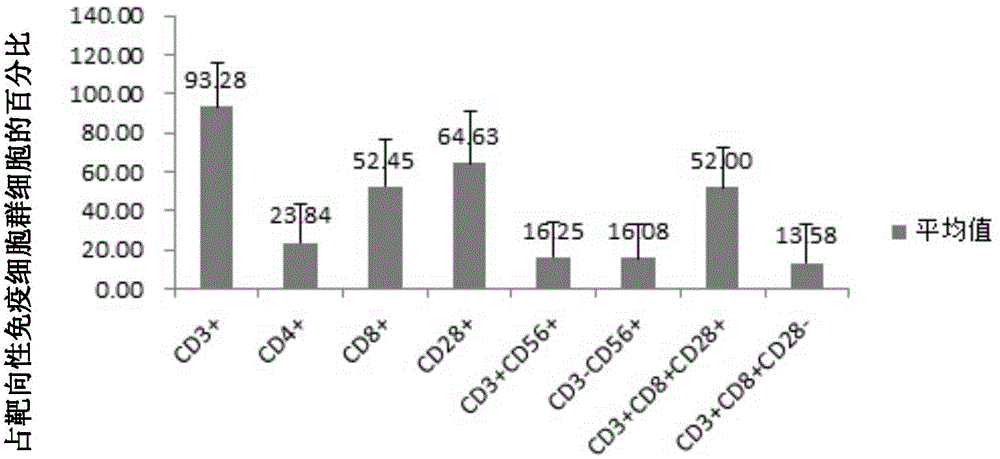
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Mrna transfection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
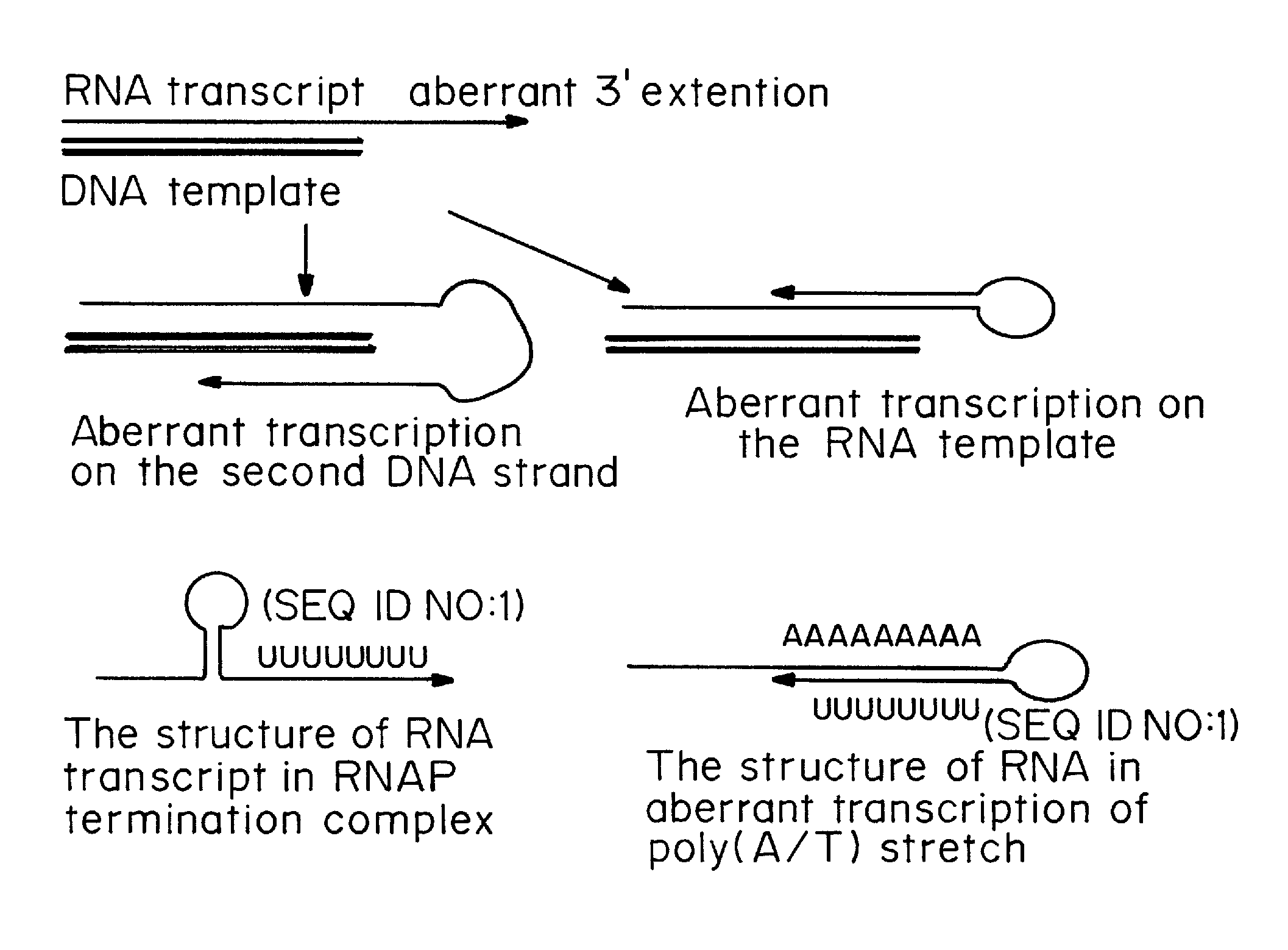
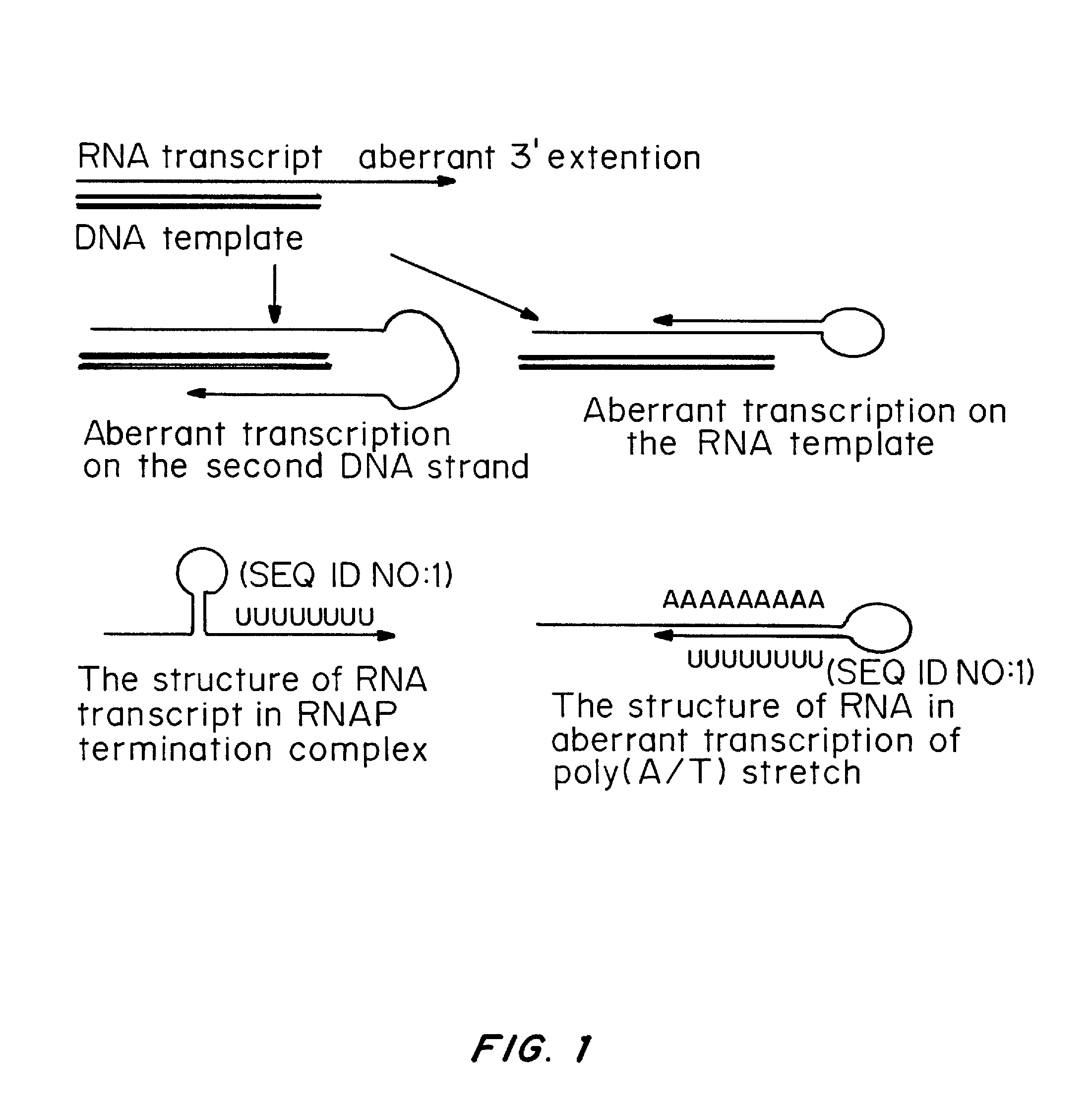
MRNA transfection oversteps limitations of plasmid DNA transfection. Transfection of plasmid DNA is the easiest and the most common method to overexpress proteins in cells grown in culture. When it fails, the transfection reagent is generally recognized as the culprit, or the cells are simply considered as “hard-to-transfect”.
Transient Transfection with RNA
ActiveUS20080260706A1Lymphocyte transfectabilitySimilar efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryDNA construct
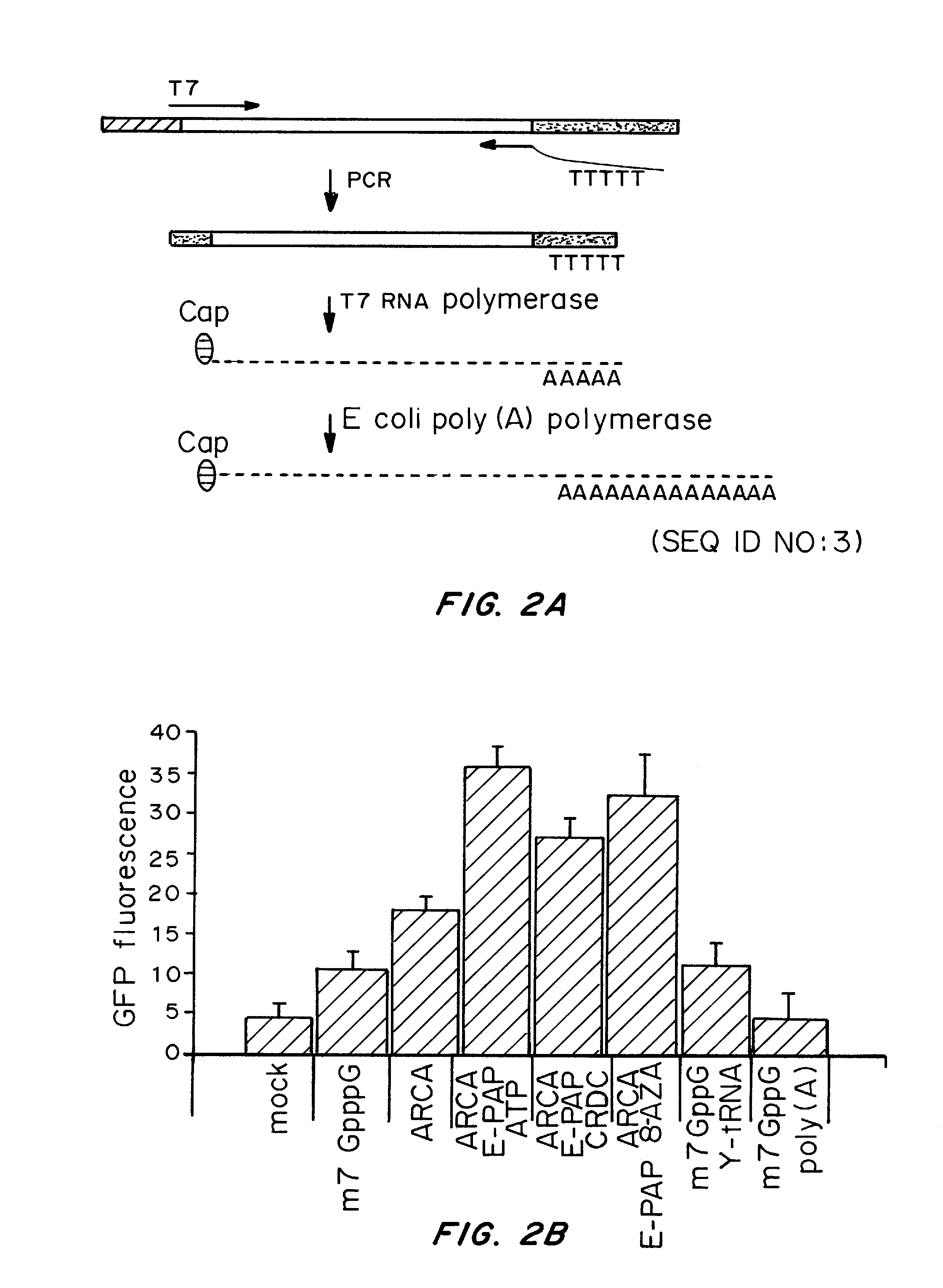
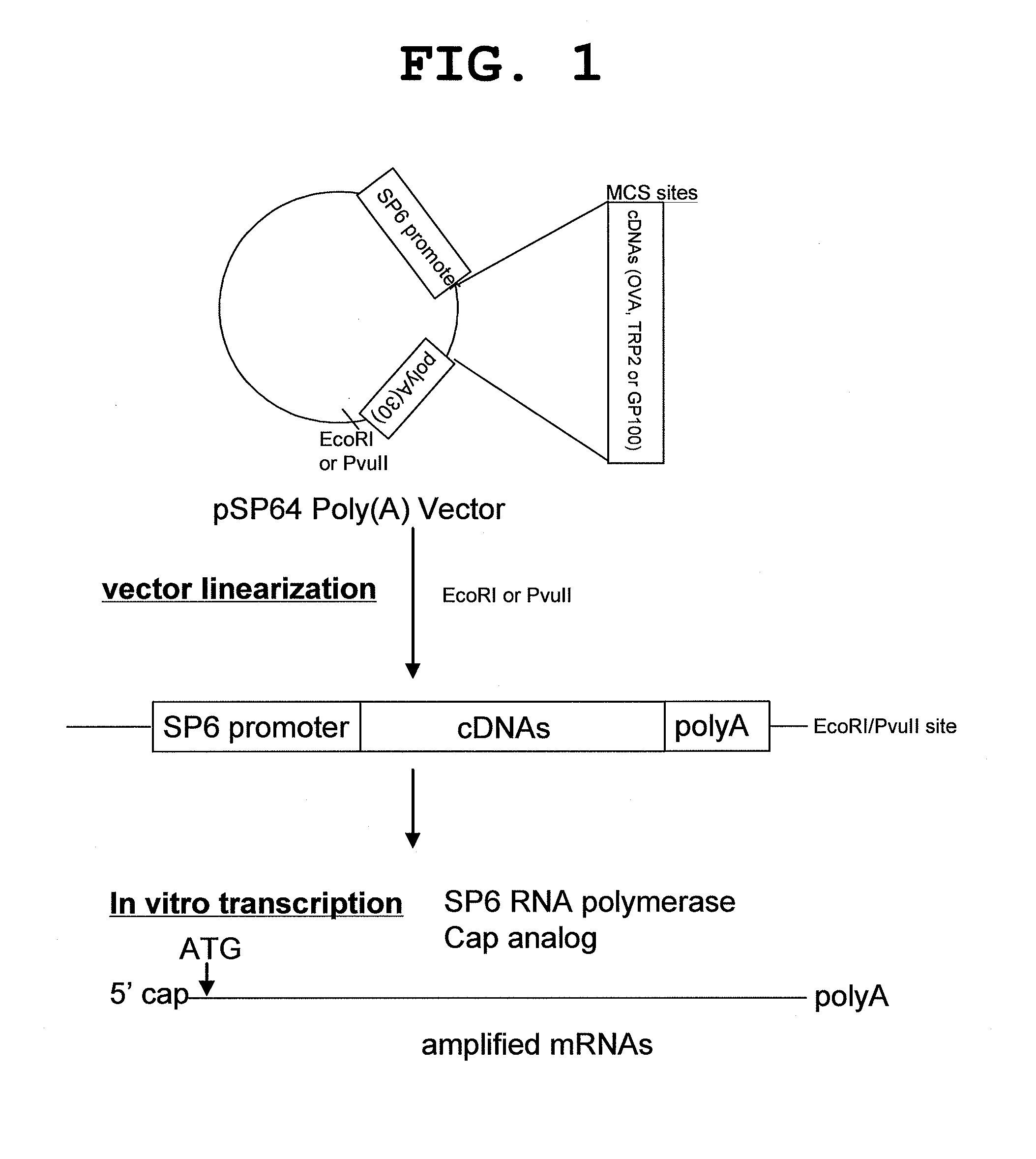
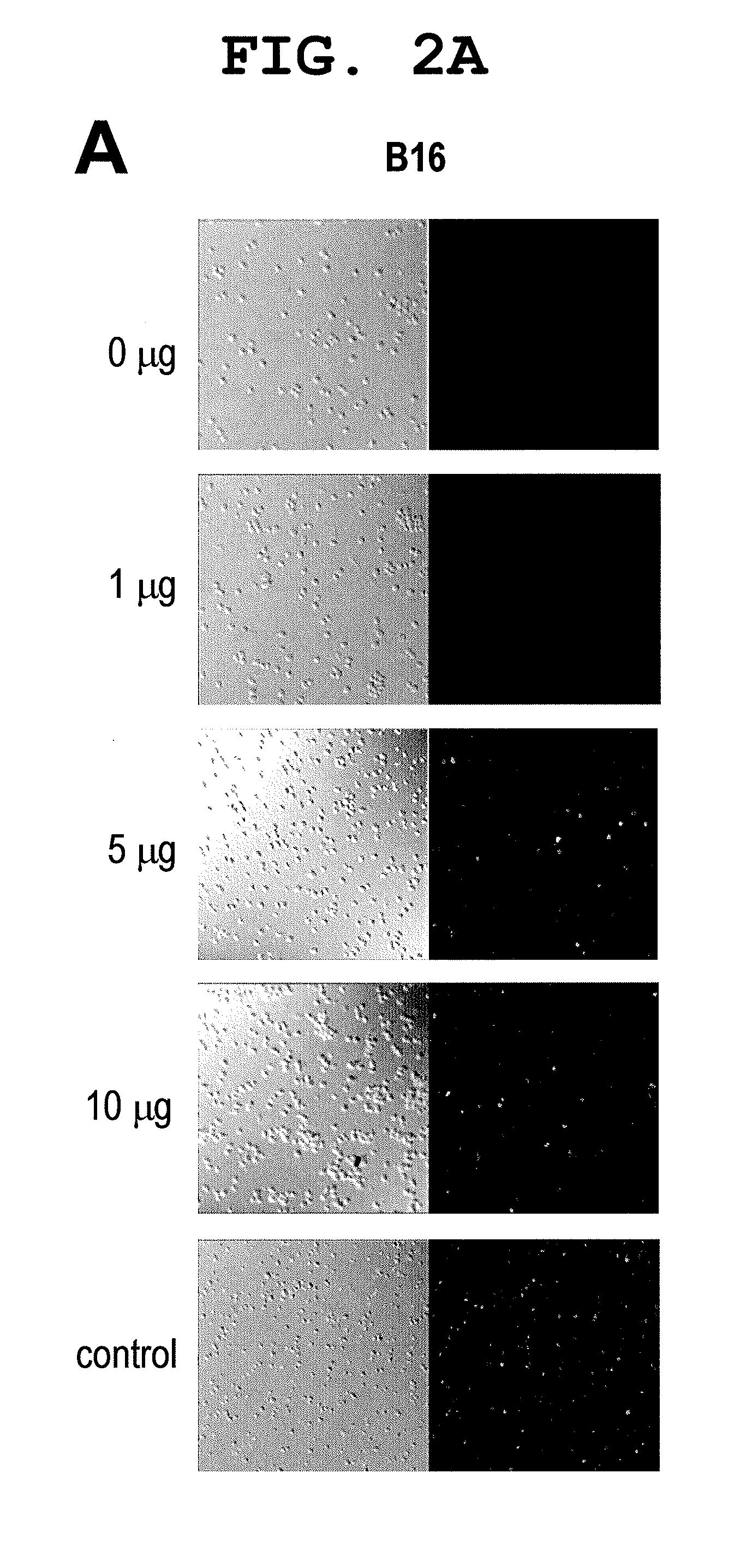
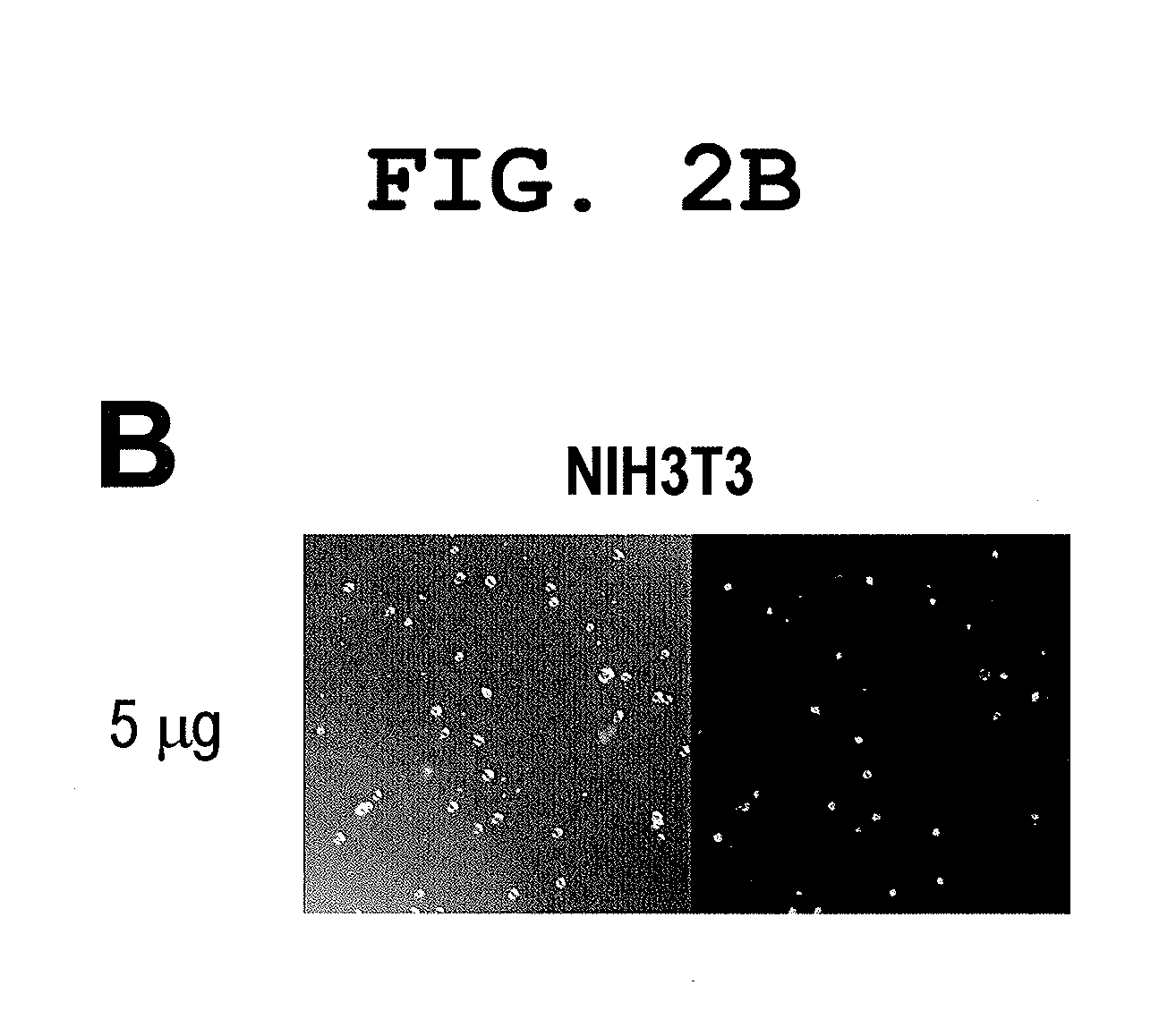
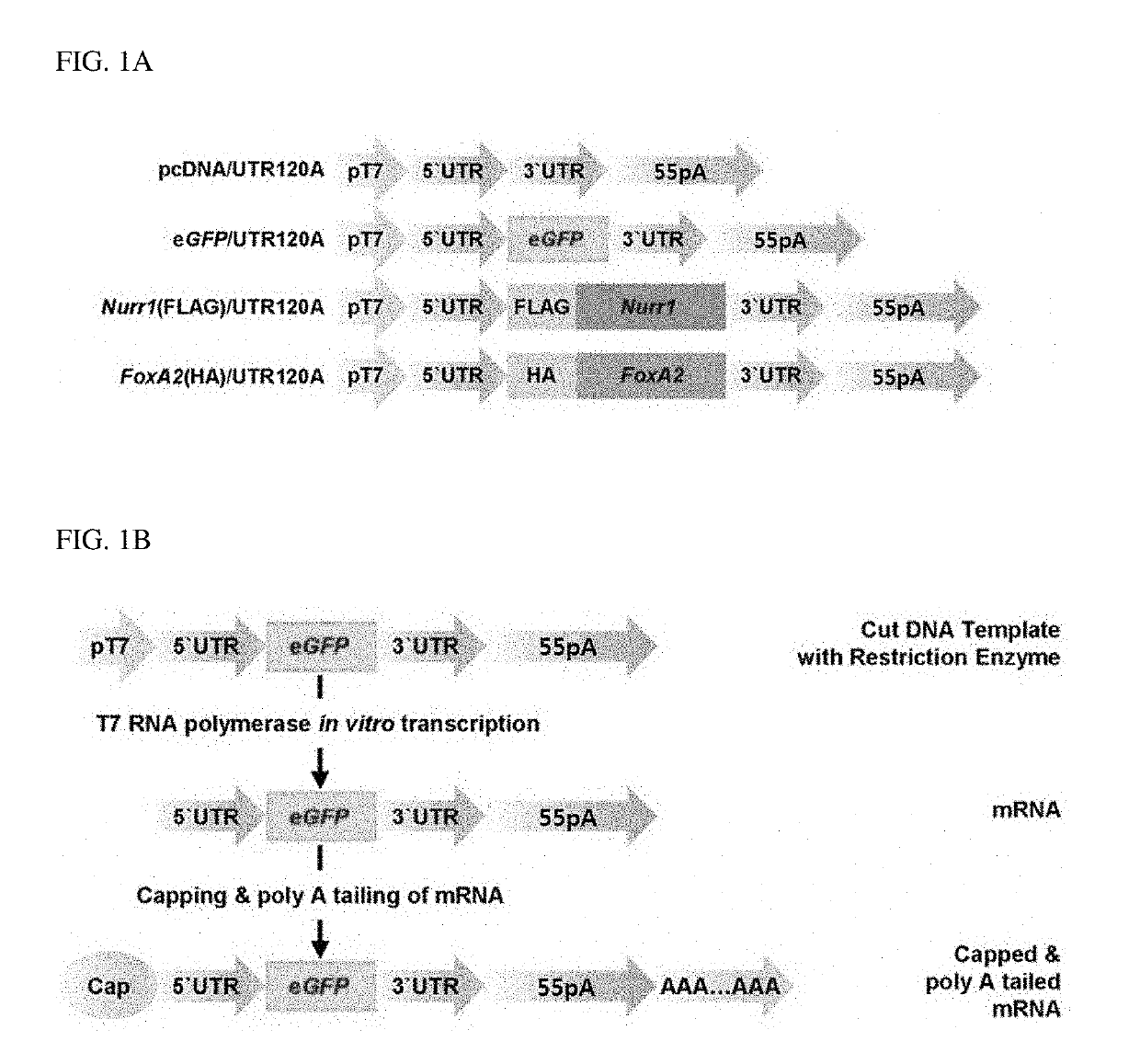
A method of mRNA production for use in transfection is provided, that involves in vitro transcription of PCR generated templates with specially designed primers, followed by polyA addition, to produce a construct containing 3′ and 5′ untranslated sequence (“UTR”), a 5′ cap and / or Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES), the gene to be expressed, and a polyA tail, typically 50-2000 bases in length. This RNA can efficiently transfect different kinds of cells. This approach results in increased efficiency (fidelity and productivity) of mRNA synthesis and is less time consuming because it does not require cloning, and also consequently eliminates the unwanted errors and effects related to RNA made on DNA templates obtained with cloning techniques. The results of transfection of RNAs demonstrate that RNA transfection can be very effective in cells that are exceedingly difficult to transfect efficiently with DNA constructs. Further, the levels of gene expression following mRNA transfection are consistent from cell to cell in an experiment and these levels can be controlled over a wide range simply by changing the amount of mRNA that is transfected, and without obvious cytotoxic effects due to the levels of RNA per se. Due to high efficiency the cells can be simultaneously transfected with multiple genetic constructs. The method can be used to deliver genes into cells not- or only poorly transfectable for DNA, in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:YALE UNIV
MRNA nucleic acid drug intracellular delivery system, preparation method and application
InactiveCN111467321AImprove stabilityHigh transfection efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCholesterolPolyethylene glycol
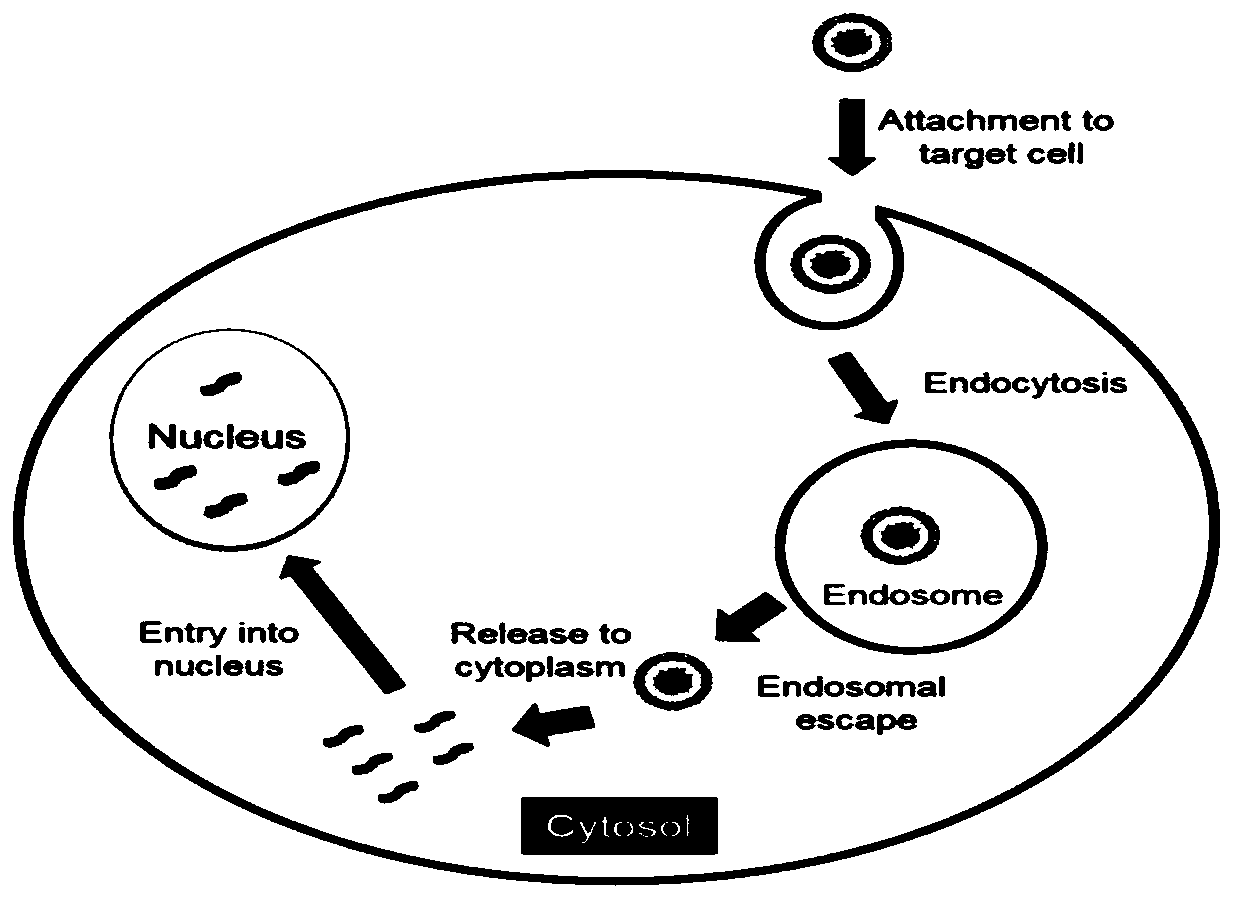
The invention discloses an mRNA nucleic acid drug delivery system, a preparation method and application. The system comprises lipid nanoparticles used for loading one or more mRNAs, and the lipid nanoparticles are prepared from raw materials including ionizable cationic lipid, phospholipid auxiliary lipid, cholesterol and phospholipid polyethylene glycol derivatives. According to the non-viral-vector mRNA nucleic acid drug targeting intracellular delivery system, mRNA is concentrated and loaded through the electrostatic interaction of ionizable cationic lipid and the mRNA, the phospholipid auxiliary lipid component-mediated pH sensitivity and advanced inclusion escape can enable an mRNA nucleic acid drug to be efficiently delivered to target cells, and the mRNA nucleic acid drug is released to cytoplasm of the target cells to play a pharmacodynamic role. The phospholipid auxiliary lipid increases the advanced inclusion escape ability of the mRNA / lipid nanoparticles, and increases the stability of the mRNA / lipid nanoparticles and the mRNA transfection efficiency. The system has efficient and stable mRNA drug intracellular delivery efficiency, and significantly improves the prevention and treatment effects of mRNA nucleic acid drugs.
Owner:深圳市新合生物医疗科技有限公司
Mrna Transfected Antigen Presenting Cells
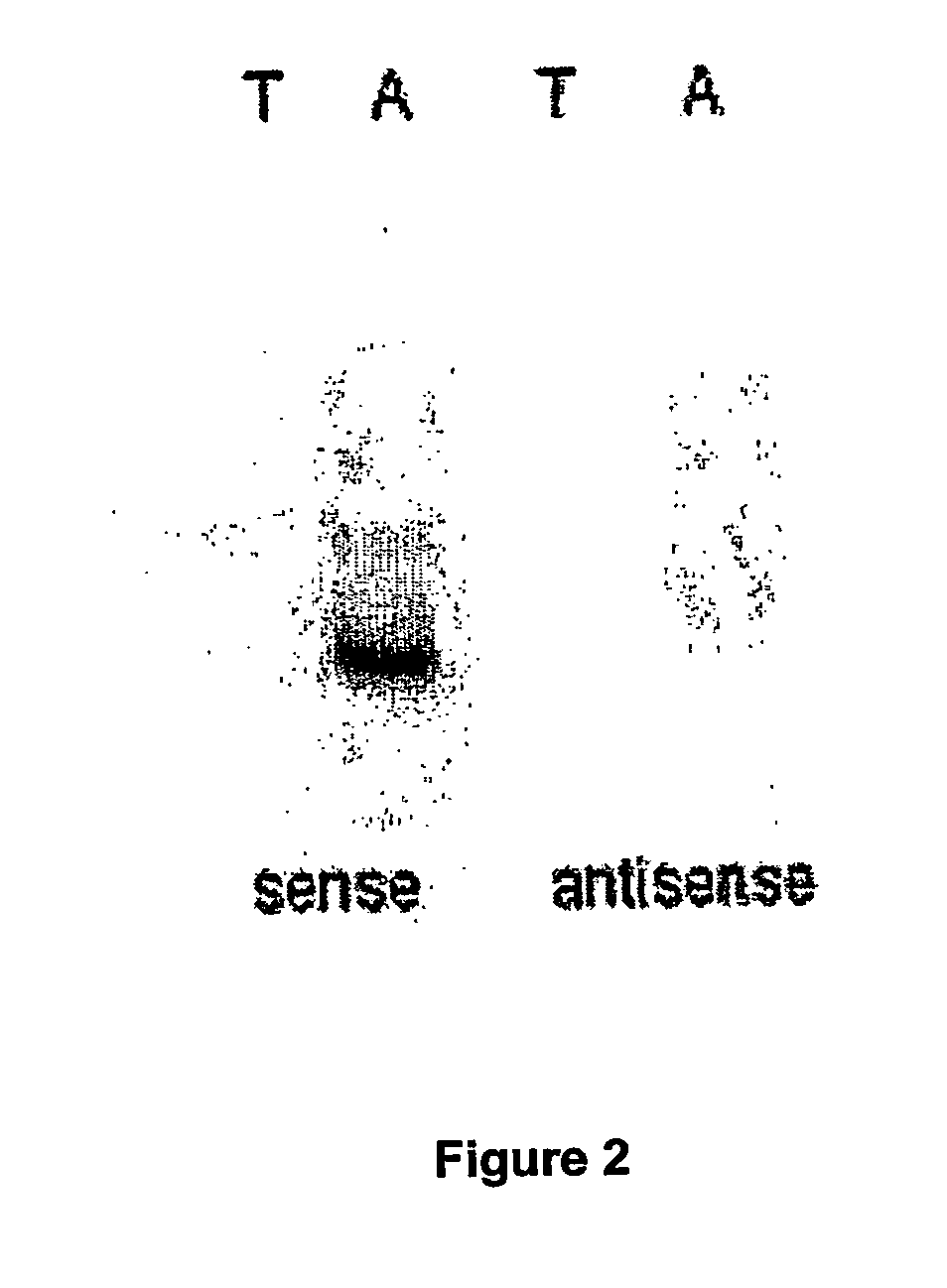
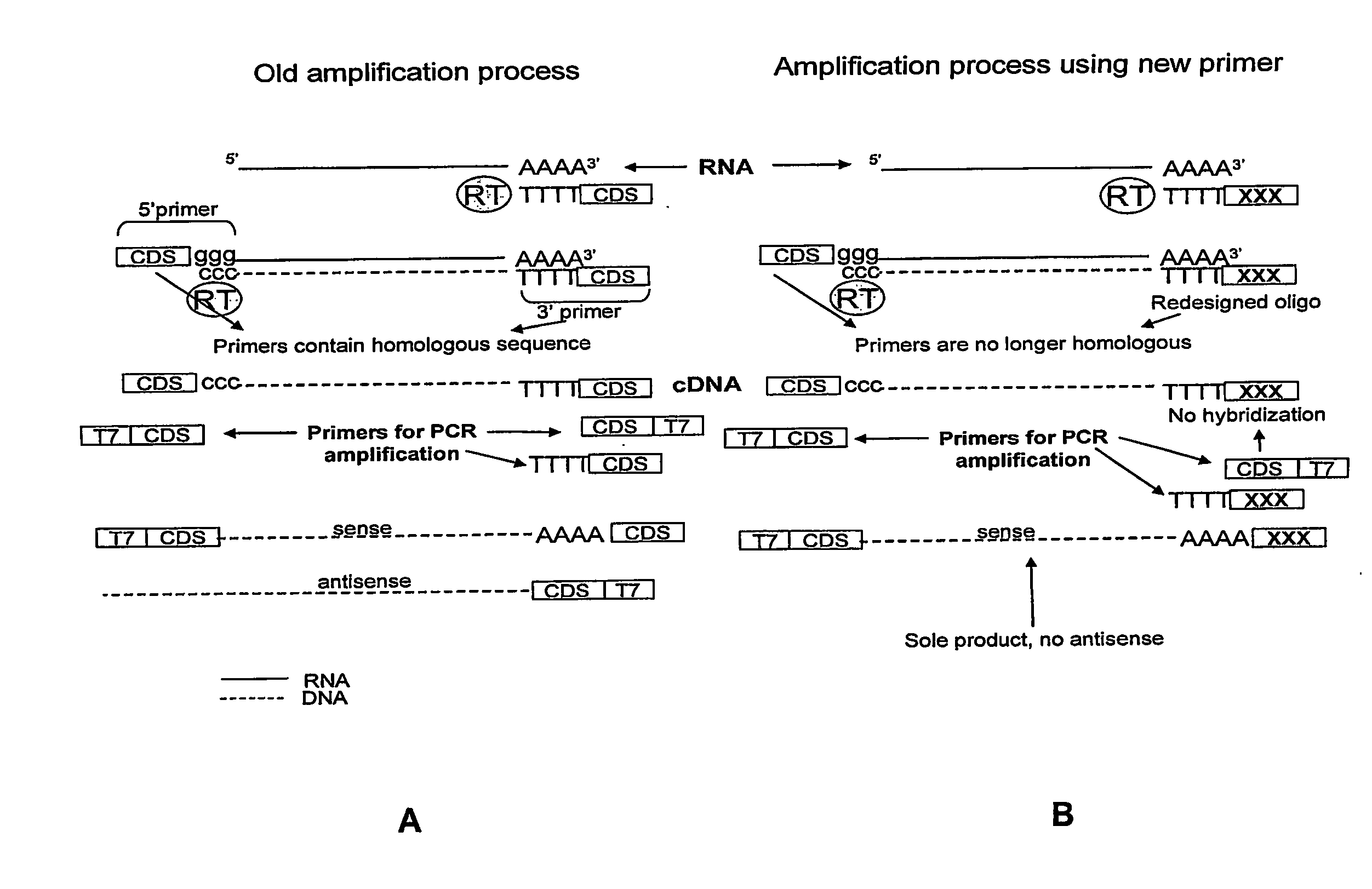
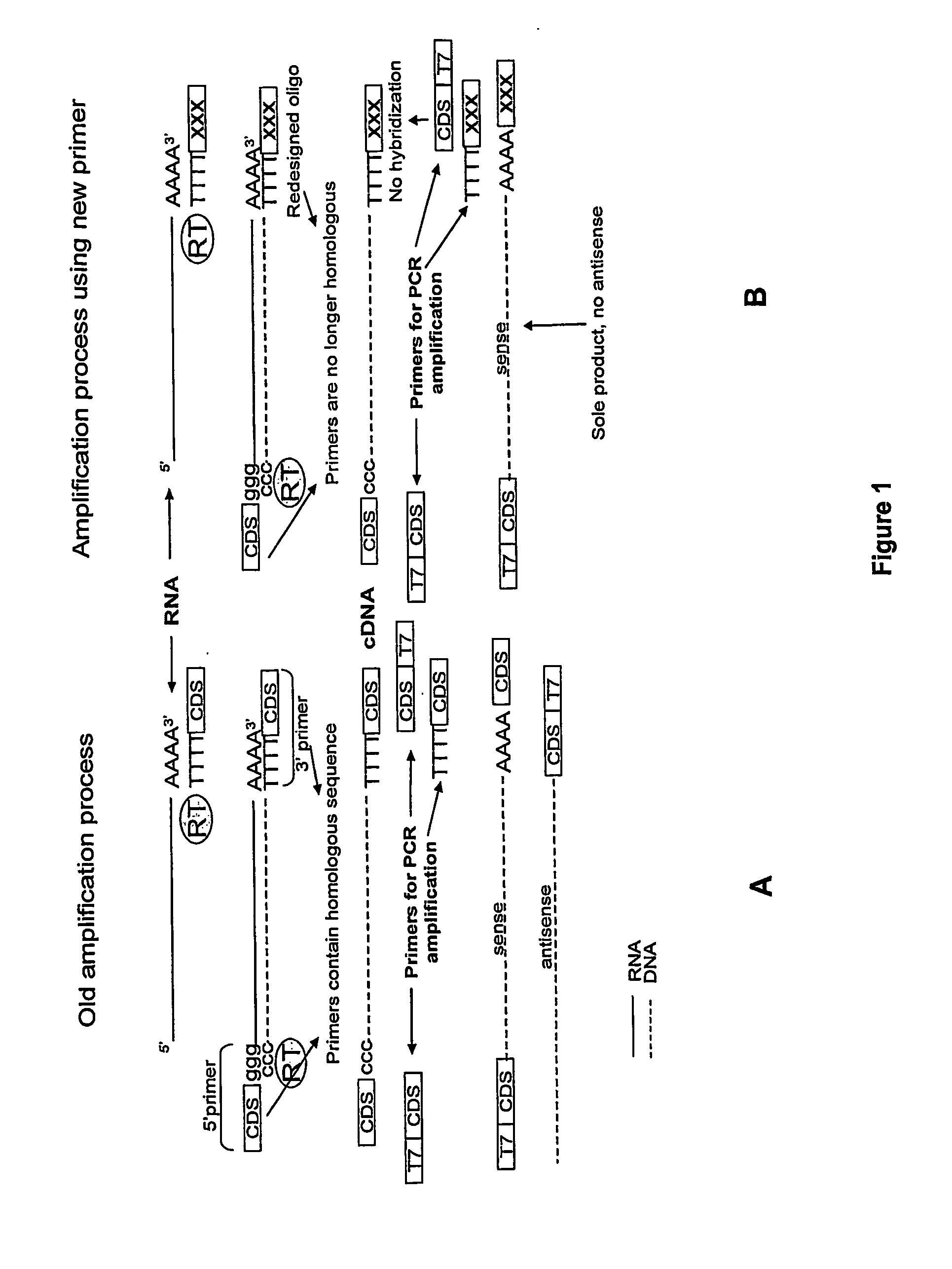
A method of amplifying RNA to obtain RNA molecules that are predominantly in the sense orientation and essentially devoid of RNA molecules that are in the anti-sense orientation. A method of transfecting antigen presenting cells with a composition comprising sense RNA encoding immunogenic antigens and essentially devoid of antisense RNA and dsRNA is also provided as well as dendritic cells prepared according to the method.
Owner:ARGOS THERAPEUTICS INC
Method used for inducing differentiation of stem cells into neurone, neurone, and applications
ActiveCN109385404AMicroencapsulation basedGenetically modified cellsDirected differentiationLiposome
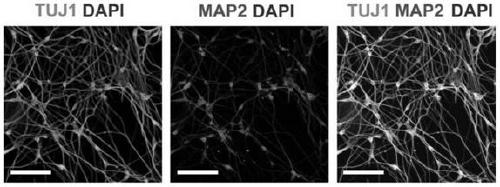
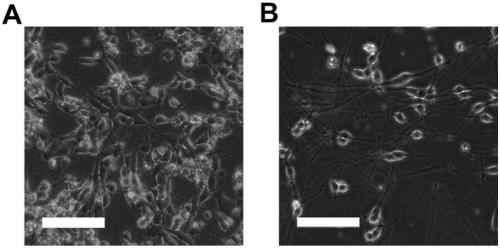
The invention discloses a method used for inducing differentiation of stem cells into neurone, neurone, and applications. According to the method, target gene mRNA is adopted for transfection of stemcells, and induction of stem cell differentiation so as to obtain neurone which is called as mRNA induced neurone. According to the method, utilization of the biological characteristics of human induced multifunctional stem cell iPSCs is adopted, liposome transfected mRNA is adopted in expression of transcription factors capable of promoting neurone differentiation, so that orientation differentiation of stem cells into neuron in vitro is realized. The method is capable of providing guarantee for supplement of neurone damage deflection, and providing foundation for applications of replacing ofclinical treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson disease, Alzheimer's disease, and cerebral ischemic injury with stem cell transplantation. The method is of great effect in the field of medical science, and the application prospect is promising.
Owner:GUIDON PHARM INC
HSV-2 antigen based DC cell and targeting immune cell population, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104830781ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityAntiviralsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell and a targeting immune cell population, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of DC cells includes the steps of: conducting first induced differentiation culture on mononuclear cells in order to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by using HSV-2 antigen mRNA, so as to obtain transfected immature DC cells; and conducting second induced differentiation culture on the transfected immature DC cells, so as to obtain mature DC cells, wherein the mononuclear cells are isolated from mononuclear cells of peripheral blood of a sample. The method can prepare DC cells safely and efficiently, has a low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cytotoxicity. The method can be effectively used for immune cell treatment or stimulation of lymphocytes derived from a same patient to produce a targeting cell population containing a large amount of CTL cells, and then the cell population can be used for virus infection immunotherapy to reach better effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on AFP antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830787ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on AFP antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of the DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by AFP antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, the DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC METHOD USING ALLO-CELLS WHICH CO-EXPRESS CD1d AND TARGET ANTIGEN
InactiveUS20110280895A1Sufficient treatment effectEfficient expressionAntibacterial agentsSnake antigen ingredientsCD1DDendritic cell
The present invention provides a means to be used for a new immunotherapy of cancer or infection utilizing activation of dendritic cell (DC) by innate immunity, namely, a method of preparing a cell co-expressing a target antigen and CD1d and having an ability to activate immunity against the target antigen, comprising the following steps (a) and (b):(a) a step of transfecting an mRNA encoding the target antigen into a CD1d-expressing cell to give a cell co-expressing the target antigen and CD1d; and (b) a step of treating the cell obtained in step (a) with a CD1d ligand in a culture medium.
Owner:RIKEN
DC cell based on SP17 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830797APowerful killImprove immunityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on SP17 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by SP17 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
CEA antigen based DC cell and targeting immune cell population, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104830779ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenAbnormal tissue growth
The invention discloses a DC cell and a targeting immune cell population, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of DC cells includes the steps of: conducting first induced differentiation culture on mononuclear cells in order to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by using CEA antigen mRNA, so as to obtain transfected immature DC cells; and conducting second induced differentiation culture on the transfected immature DC cells, so as to obtain mature DC cells, wherein the mononuclear cells are isolated from mononuclear cells of peripheral blood of a sample. The method can prepare DC cells safely and efficiently, has a low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cytotoxicity. The method can be effectively used for immune cell treatment or stimulation of lymphocytes derived from a same patient to produce a targeting cell population containing a large amount of CTL cells, and then the cell population can be used for tumor immunotherapy to reach better effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
Transient expression of immunomodulatory polypeptides for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune disease, allergy and transplant rejection
ActiveUS8513208B2Reduce incidenceReduced responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsIl 4 receptorAutoimmune responses
A method is provided for treating or preventing an undesired immune response in a patient, comprising: administering to said patient, cells that transiently express, and / or that are transfected with mRNA encoding, one or more polypeptides selected from the group consisting of an IL-4 receptor agonist, an IFN-γ receptor antagonist, an IFN-α receptor antagonist, an IL-12 receptor antagonist, an IL-23 receptor antagonist, and a TNF antagonist. Preferably, the cells selectively accumulate in one or more secondary lymphoid tissues at or proximate to the site of the undesired immune response. Related compositions are provided. The methods and compositions are useful for the treatment or prevention of undesired immune responses including, but not limited to, transplant rejection, autoimmune disease, allergy and immune responses directed against therapeutic compositions.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
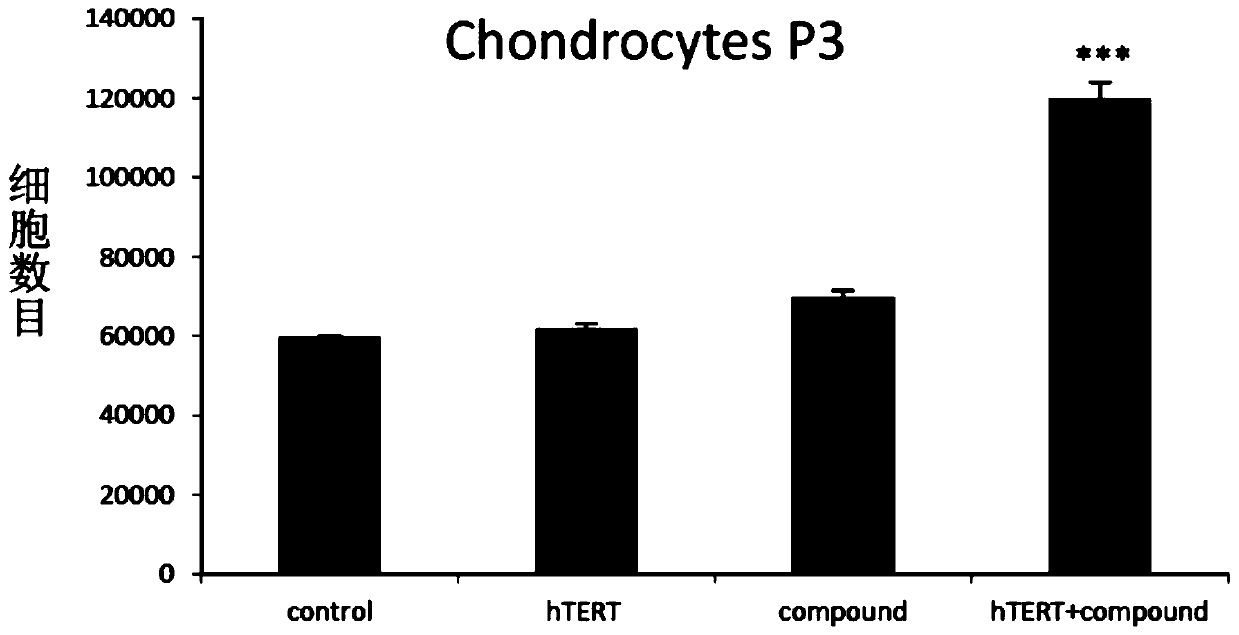
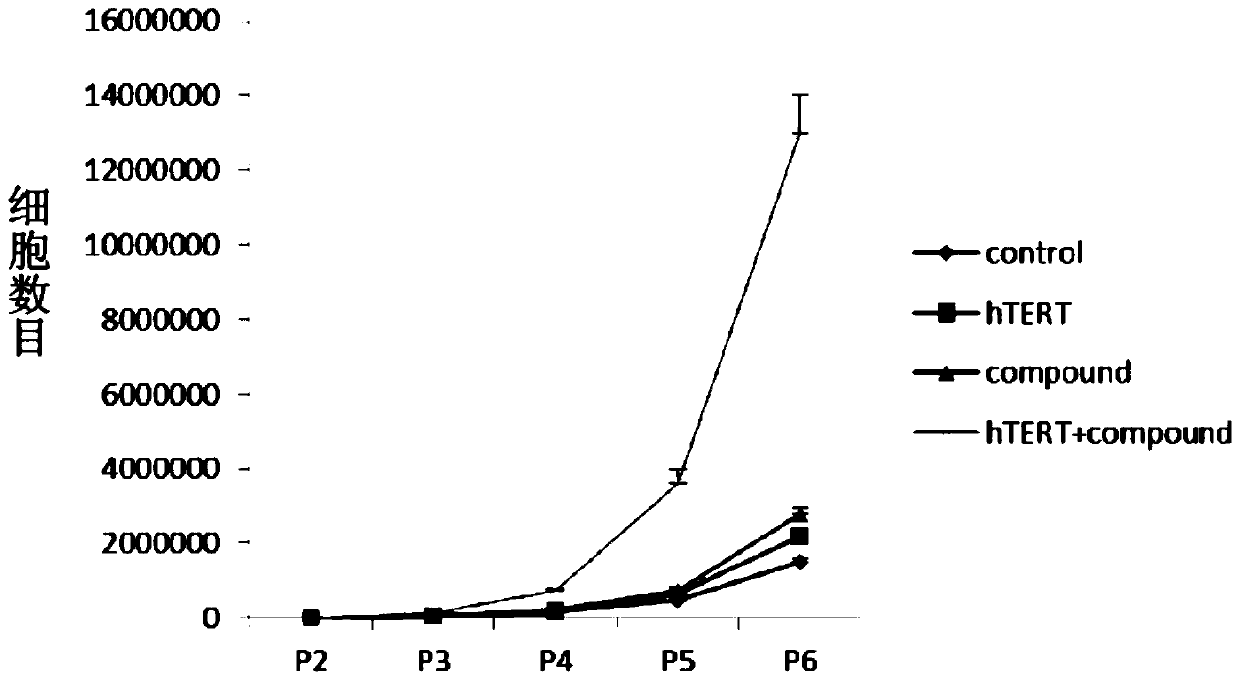
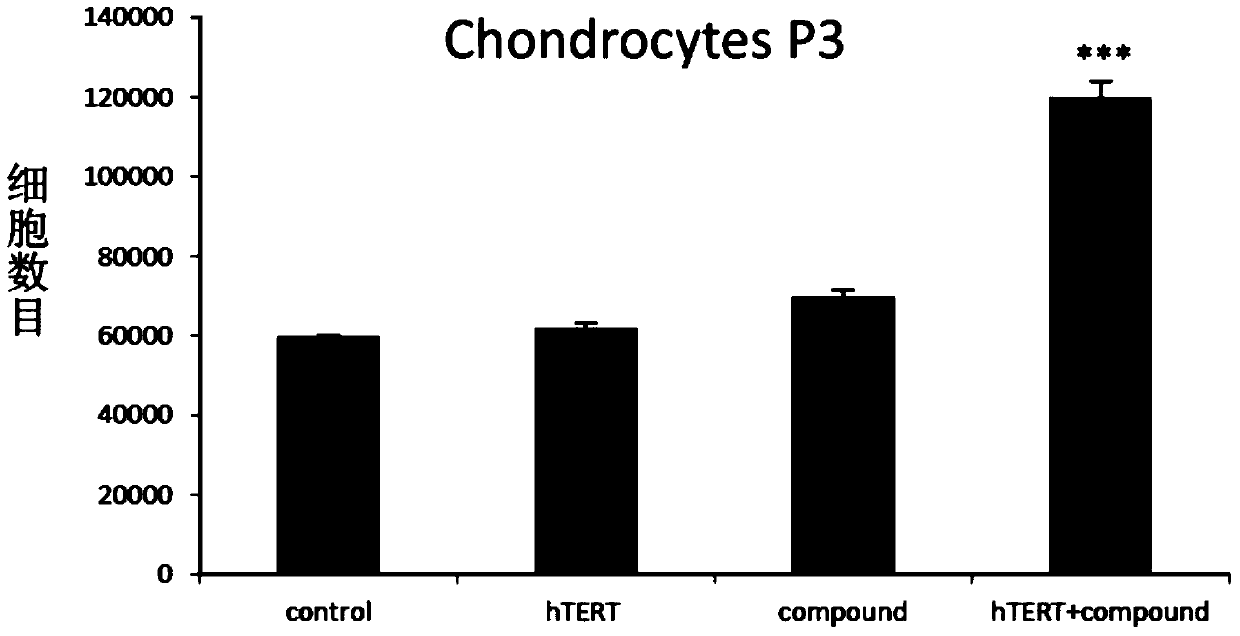
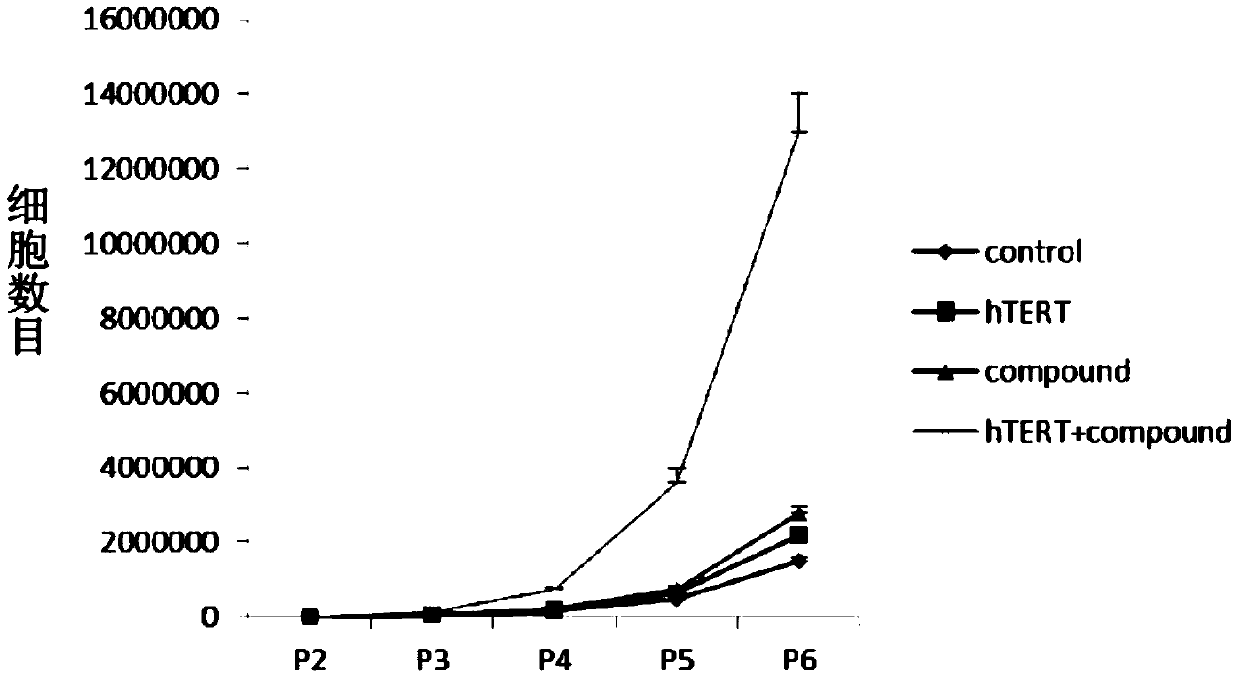
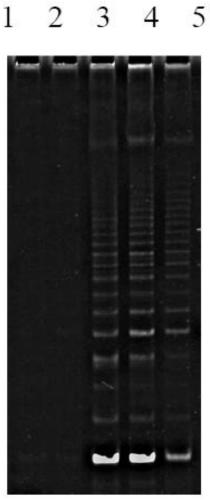
Culture medium, kit and application for in-vitro chondrocyte telomere lengthening multiplication culture
ActiveCN106957820AIncreased proliferationHigh activityGenetically modified cellsCulture processTelomeraseVitamin C
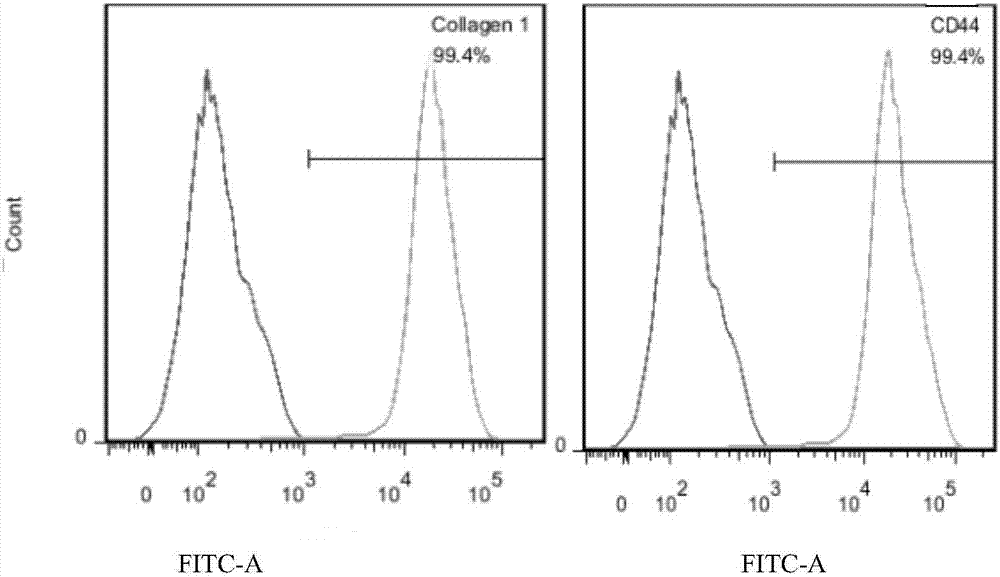
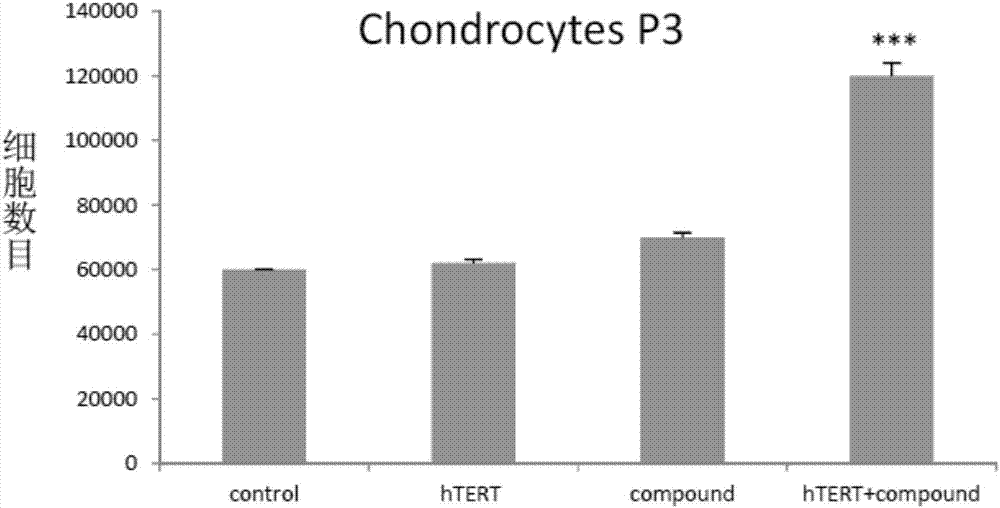
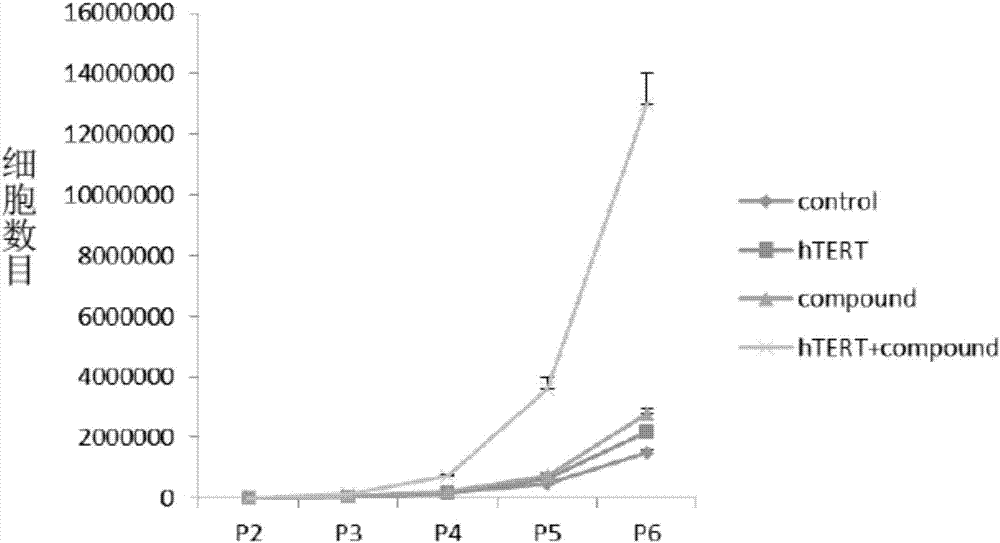
The invention discloses a culture medium, a kit and application for in-vitro chondrocyte telomere multiplication culture. The culture medium is prepared by adding serum, vitamin C having a final concentration of 5-50mu g / ml, B18R or p65i having a final concentration of 0.01-2mu g / ml, rapamycin having a final concentration of 0.1-50ng / ml and resveratrol having a final concentration of 0.1-50mu M into a DMEM / F12 or RPMI1640 basic culture medium, wherein the serum is human AB serum having a volume final concentration of 1-20 percent or fetal calf serum having a volume final concentration of 1-20 percent. By using the culture medium or kit for in-vitro chondrocyte telomere multiplication culture, chondrocyte can be subjected to telomerase mRNA transfection in vitro, so that telomere of chondrocyte is lengthened in subsequent culturing, and multiplication and vitality of chondrocyte, especially senile patients, can be remarkably improved. The culture medium or kit can be used for improving or treating cell function decline caused by senescence, and can be practically applied to regenerative medicine treatment.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV +2
DC cell based on SPANXA1 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830796ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on SPANXA1 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by SPANXA1 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
Multi-indication mRNA cancer immunotherapy
ActiveUS20170042993A1Promote degradationInduce immunogenic responseCancer antigen ingredientsWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsCancer cellIn vivo
Synthetic bacterial messenger RNA can be used to prepare autologous, allogenic or direct nucleic acid cancer vaccines. Cancer cells are transfected either in vitro or in vivo with mRNA obtained from DNA that encodes an immunogenic bacterial protein. An immune response to the cancer is generated from direct administration of the mRNA in vivo or administration of vaccines prepared from cancer cells in vitro.
Owner:MORPHOGENESIS
DC cell based on BCG1 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830792APowerful killImprove immunityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on BCG1 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by BCG1 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on HBV1 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830783ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on HBV1 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of the DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by HBV1 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, the DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on PSA antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830799ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesPeripheral blood mononuclear cellPsa antigen
The invention discloses a DC cell based on PSA antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by PSA antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on P53 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830803APowerful killImprove immunityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on P53 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by P53 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
Method of differentiating neural stem cells or neural precursor cells into dopamine neurons
InactiveUS20190185812A1Efficiently stably differentiatingNervous system cellsUnknown materialsDopaminePrecursor cell
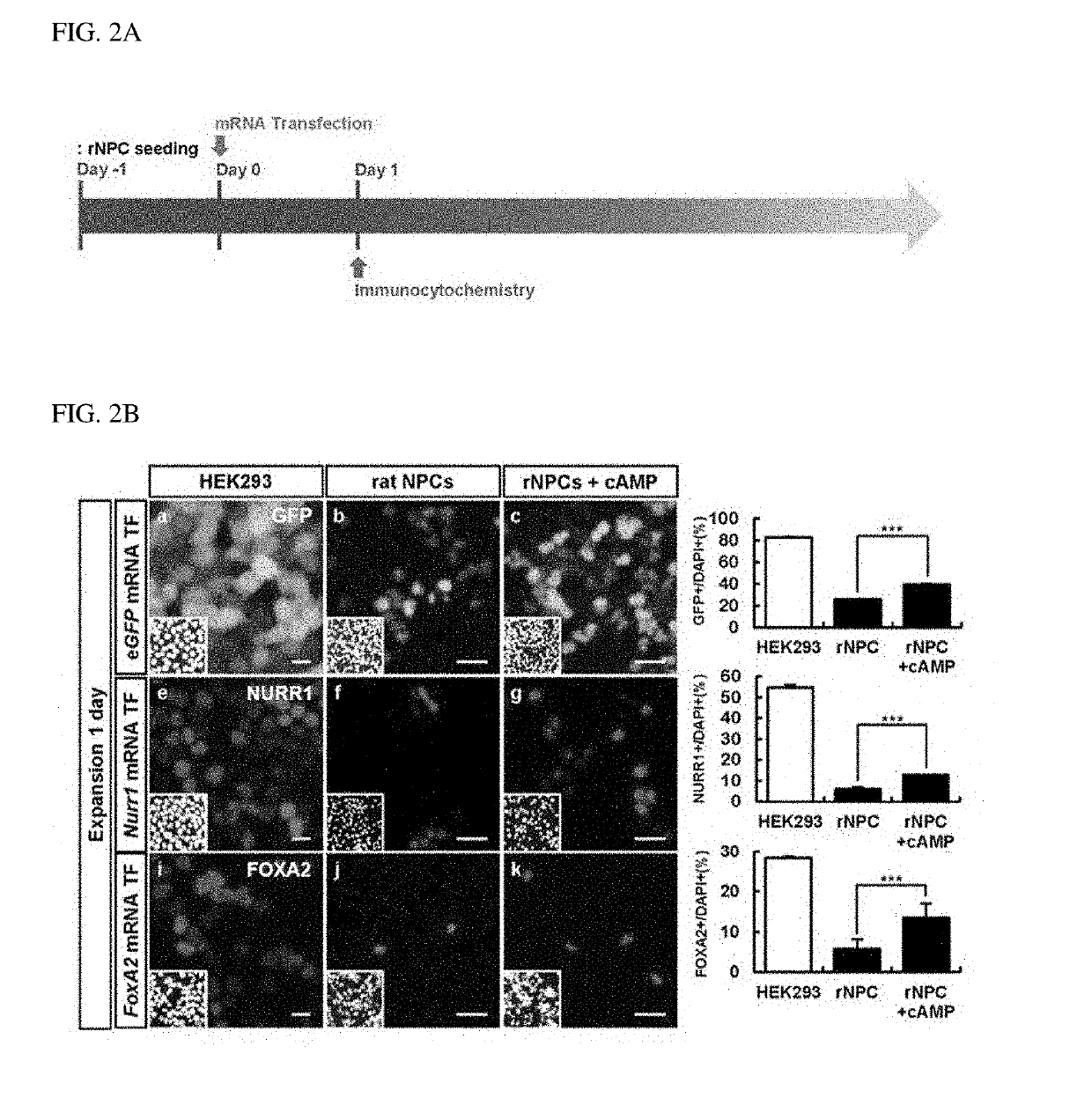
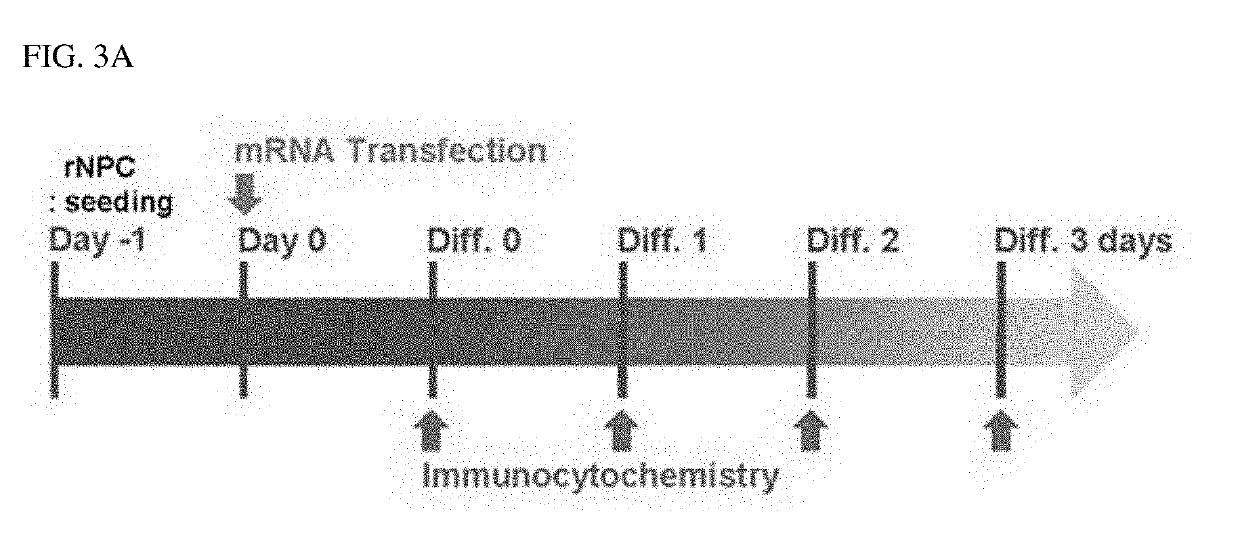
The present invention relates to a method of differentiating neural stem cells or neural precursor cells into dopamine neurons and more particularly, a method of differentiating into dopamine neurons, in which chromosomal stability is maintained by transfecting neural stem cells or neural precursor cells with mRNA of a dopamine neuron-inducing transcription factor under time-based control. The method of differentiating into dopamine neurons, according to the present invention, may enable preparation of mature and functional dopamine neurons having chromosomal stability by synthesizing a dopamine neuron-inducing transcription factor into a mRNA form, which has no risk of genetic modification, and transfecting the synthetic mRNA, unlike existing methods using retroviral vectors, and thus may be usefully used in the clinical field for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
In vitro chondrocyte telomere extension and proliferation culture medium, kit and application
ActiveCN106957820BIncreased proliferationHigh activityGenetically modified cellsCulture processTelomeraseVitamin C
The invention discloses a culture medium, a kit and application for in-vitro chondrocyte telomere multiplication culture. The culture medium is prepared by adding serum, vitamin C having a final concentration of 5-50mu g / ml, B18R or p65i having a final concentration of 0.01-2mu g / ml, rapamycin having a final concentration of 0.1-50ng / ml and resveratrol having a final concentration of 0.1-50mu M into a DMEM / F12 or RPMI1640 basic culture medium, wherein the serum is human AB serum having a volume final concentration of 1-20 percent or fetal calf serum having a volume final concentration of 1-20 percent. By using the culture medium or kit for in-vitro chondrocyte telomere multiplication culture, chondrocyte can be subjected to telomerase mRNA transfection in vitro, so that telomere of chondrocyte is lengthened in subsequent culturing, and multiplication and vitality of chondrocyte, especially senile patients, can be remarkably improved. The culture medium or kit can be used for improving or treating cell function decline caused by senescence, and can be practically applied to regenerative medicine treatment.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV +2
DC cell based on SURVIVIN antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830801ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAbnormal tissue growthPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on SURVIVIN antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by SURVIVIN antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on SCC antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830798APowerful killImprove immunityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesPeripheral blood mononuclear cellMonocyte
The invention discloses a DC cell based on SCC antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by SCC antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on HPVE6 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830785ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on HPVE6 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by HPVE6 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, the DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on HM1.24 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830790ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenAbnormal tissue growth
The invention discloses a DC cell based on HM1.24 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by HM1.24 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on BA46 antigen and targeting immune cell population, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104830780ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenAbnormal tissue growth
The invention discloses a DC cell and a targeting immune cell population, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of DC cells includes the steps of: conducting first induced differentiation culture on mononuclear cells in order to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by using BA46 antigen mRNA, so as to obtain transfected immature DC cells; and conducting second induced differentiation culture on the transfected immature DC cells, so as to obtain mature DC cells, wherein the mononuclear cells are isolated from mononuclear cells of peripheral blood of a sample. The method can prepare DC cells safely and efficiently, has a low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cytotoxicity. The method can be effectively used for immune cell treatment or stimulation of lymphocytes derived from a same patient to produce a targeting cell population containing a large amount of CTL cells, and then the cell population can be used for tumor immunotherapy to reach better effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on HCV1 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830789ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on HCV1 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by HCV1 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on HBV-HCV antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830788ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on HBV-HCV antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of the DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by HBV-HCV antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, the DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on HER-2/NEU antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830786ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention discloses a DC cell based on HER-2 / NEU antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of the DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by HER-2 / NEU antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, the DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
DC cell based on LMP-1 antigen, targeting immune cell population, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104830793ASafe and efficient preparationAddress toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAntigenAbnormal tissue growth
The invention discloses a DC cell based on LMP-1 antigen, a targeting immune cell population, a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of DC cell comprises the following steps: subjecting mononuclear cells to first induced differentiation culture to obtain immature DC cells; transfecting the immature DC cells by LMP-1 antigen mRNA to obtain transfected immature DC cells; subjecting the transfected immature DC cell to second induced differentiation culture to obtain mature DC cells; wherein the mononuclear cells are separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a sample. Through the provided preparation method, DC cells can be obtained efficiently and safely. Moreover, the provided preparation method has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem of cell toxicity. The DC cells can be applied to cell immunotherapy or used to trigger the lymph cells from the same patient to generate targeting immune cell population rich in CTL cells so as to achieve a better effect in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELEBIO BIOMEDICAL
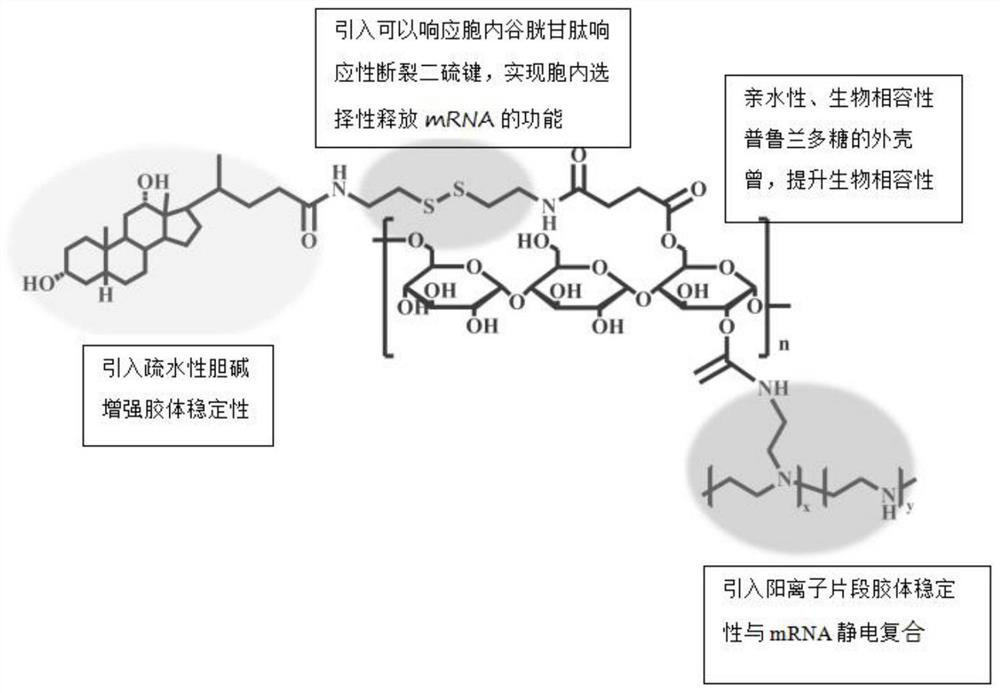
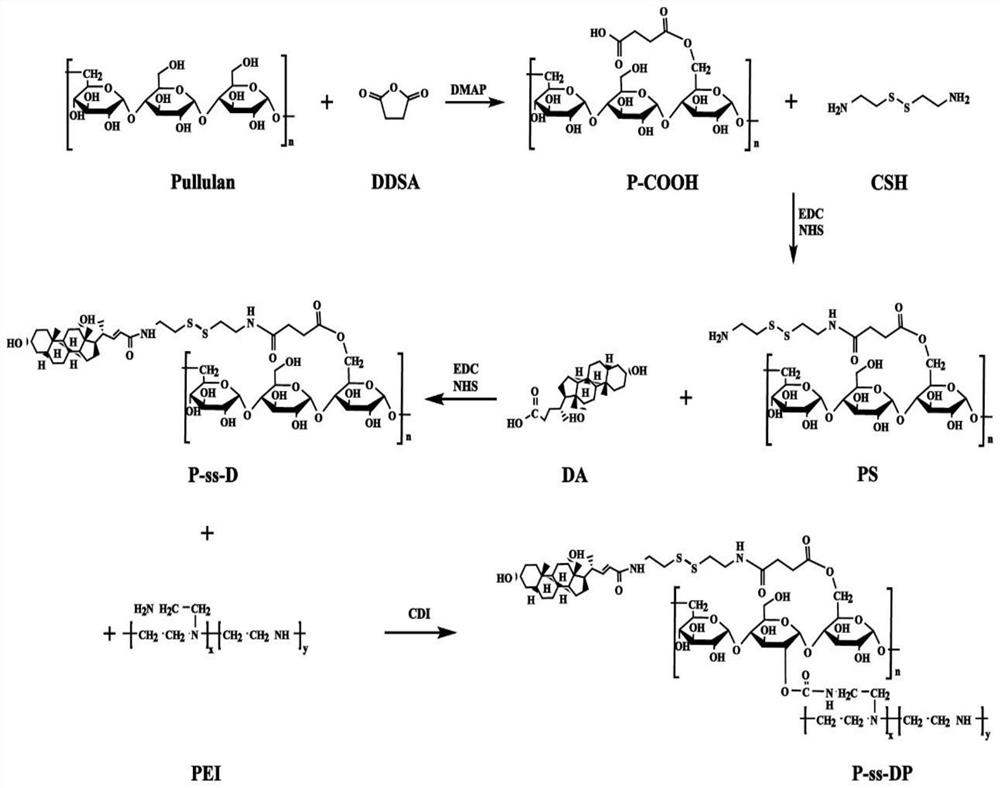
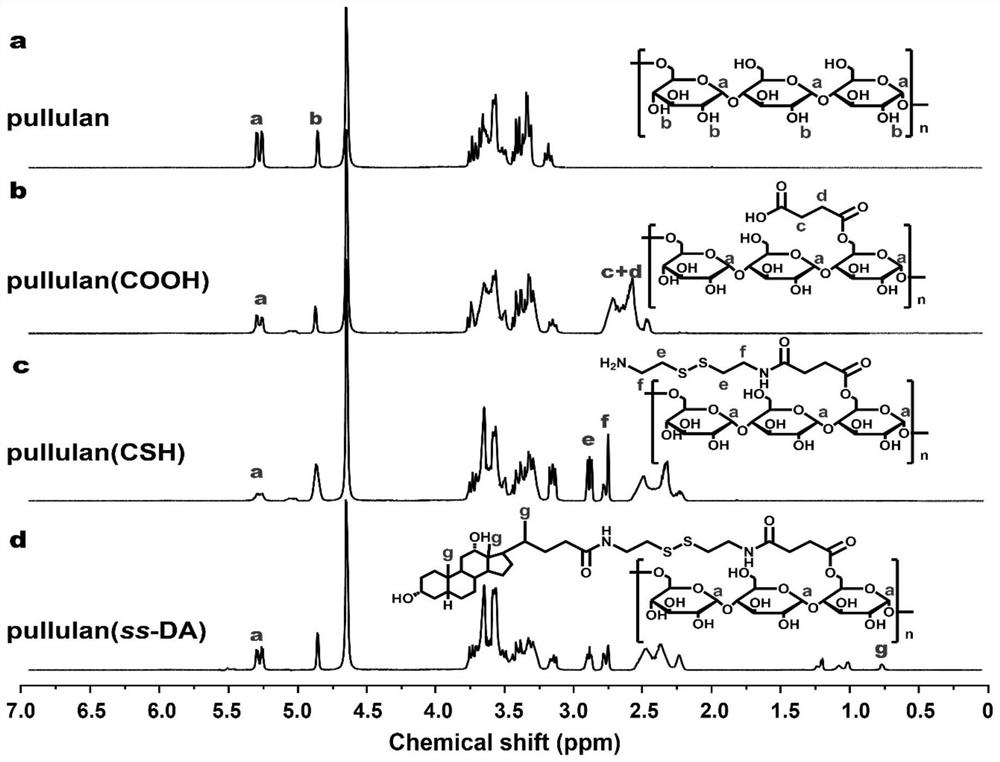
MRNA transfection material, mRNA transfection system and application
PendingCN114540423AImprove stabilityReduced stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesDisulfide bondingExtracellular
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicine, in particular to an mRNA transfection material, an mRNA transfection system and application. The mRNA transfection material is prepared by grafting a cationic polymer on a pulullan framework, and the pulullan framework comprises pulullan with good hydrophilicity and biocompatibility, hydrophobic choline capable of keeping colloidal stability and disulfide bonds capable of responding to intracellular glucose and responding to intracellular glutathione responsive breakage. The cationic polymer fragment can realize the function of selectively releasing mRNA in cells. Experiments show that the stability of the mRNA transfection material provided by the invention is obviously improved, the mRNA transfection material can resist the competition of polyanions and inhibit the degradation of mRNA outside cells, and the colloid stability is obviously reduced in a reducing environment, so that the mRNA can be quickly released in reducing cells.
Owner:深圳近邻生物科技有限公司
In vitro telomere extension and proliferation culture method of chondrocytes and human tissue engineered regeneration of cartilage
ActiveCN106967686BIncreased proliferationHigh activityGenetically modified cellsTransferasesCartilage cellsVitamin C
The invention discloses a method for lengthening, proliferating and culturing in-vitro telomeres of cartilage cells and human tissue engineering regenerated cartilage. The method and the human tissue engineering regenerated cartilage have the advantages that telomerase mRNA [(messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid)) transfection is carried out on the cartilage cells in an in-vitro manner, accordingly, the telomeres in cartilage cells obtained by means of culturing in follow-up procedures can be lengthened, proliferation and the viability of the cartilage cells and cartilage cells of elderly patients in particular can be obviously improved by the aid of synergistic effects of the telomerase mRNA transfection and small molecule compounds such as vitamin C, B18R or p65i, rapamycin and resveratrol in complete media, and the method and the human tissue engineering regenerated cartilage have important significance in improving or treating cell function decline due to senescence when the actually applied to regeneration medical treatment; the telomeres of the cartilage cells are not continuously or even frequently lengthened by the aid of the method for lengthening, proliferating and culturing the in-vitro telomeres of the cartilage cells, accordingly, genome insertion mutation risks or cell immortalization tumor formation risks can be prevented, the safety and the applicability can be greatly improved, and the method and the human tissue engineering regenerated cartilage can be effectively applied to the regeneration medical treatment.
Owner:BEIHAO STEM CELL & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com