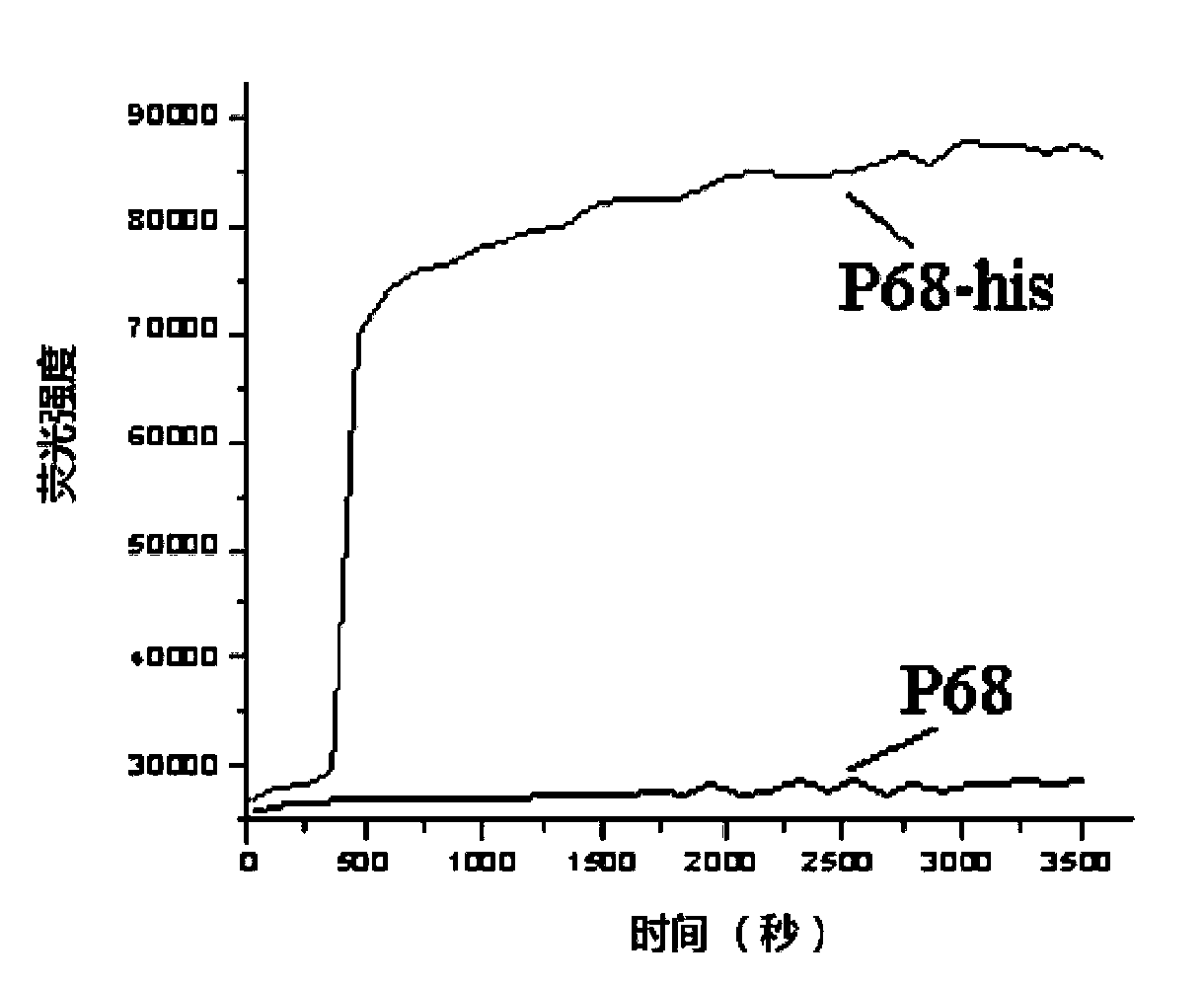
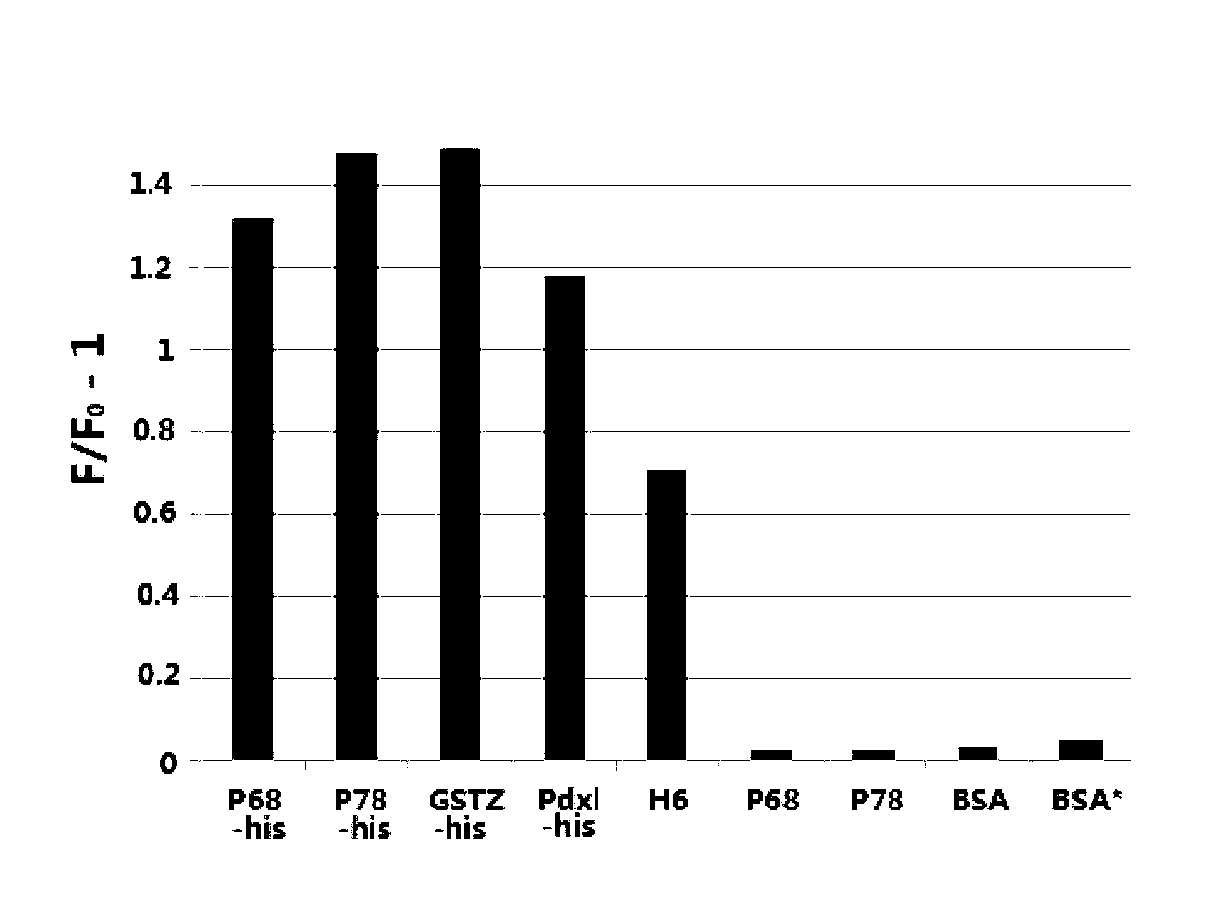
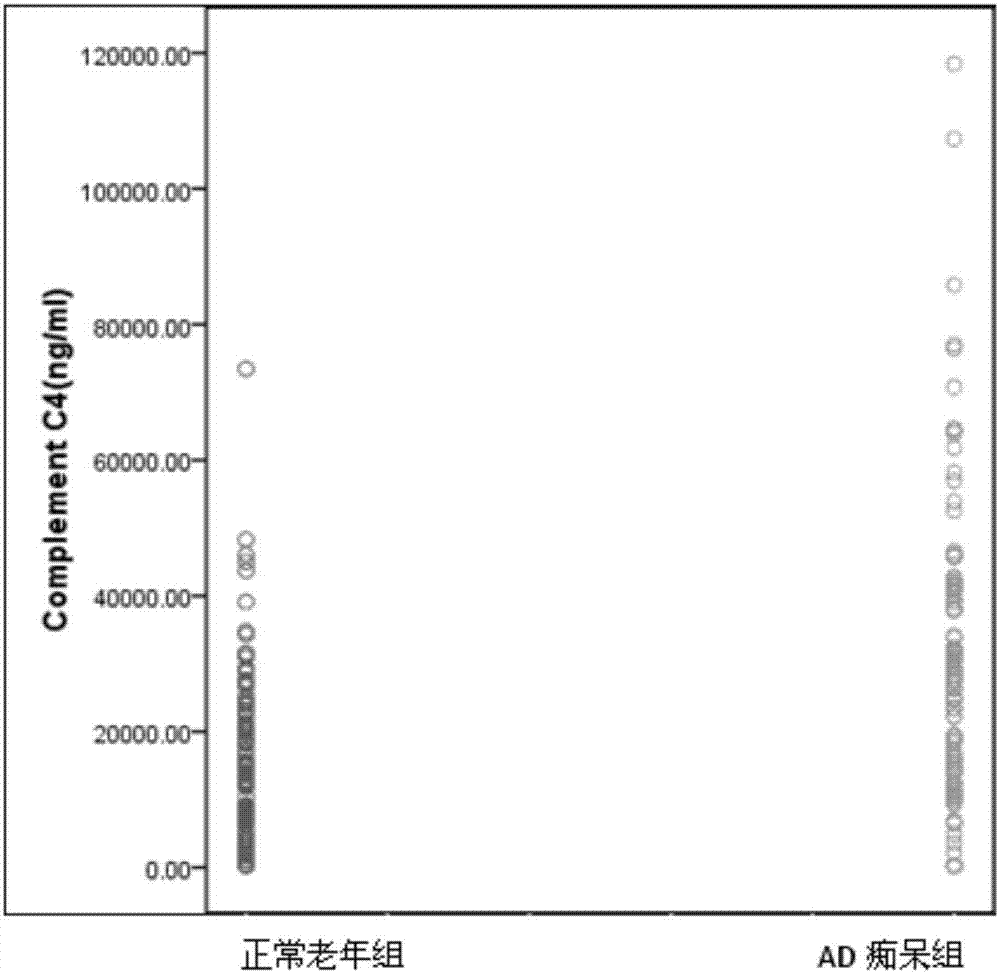
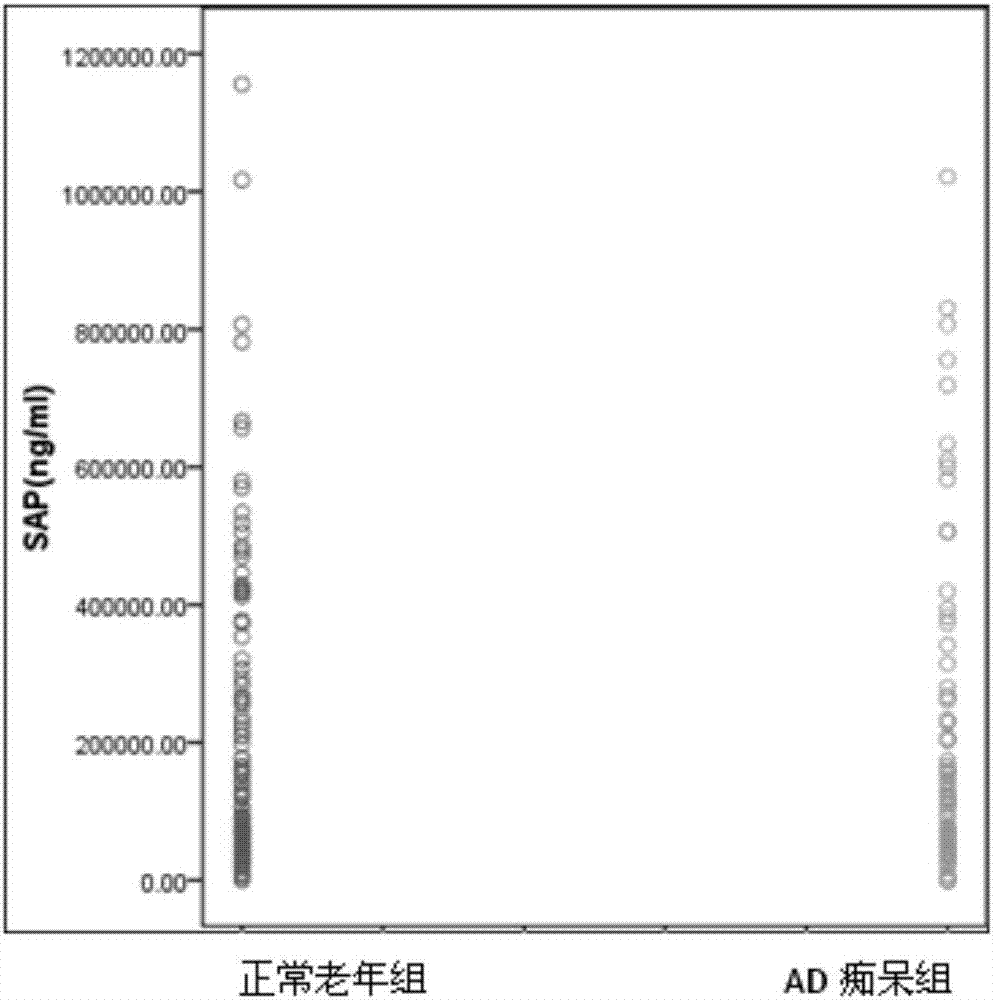
Patents
Literature
217 results about "Protein markers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A protein marker (also called a protein molecular weight marker, a protein MW marker, or a protein ladder) is used to estimate the size of proteins resolved by gel electrophoresis.
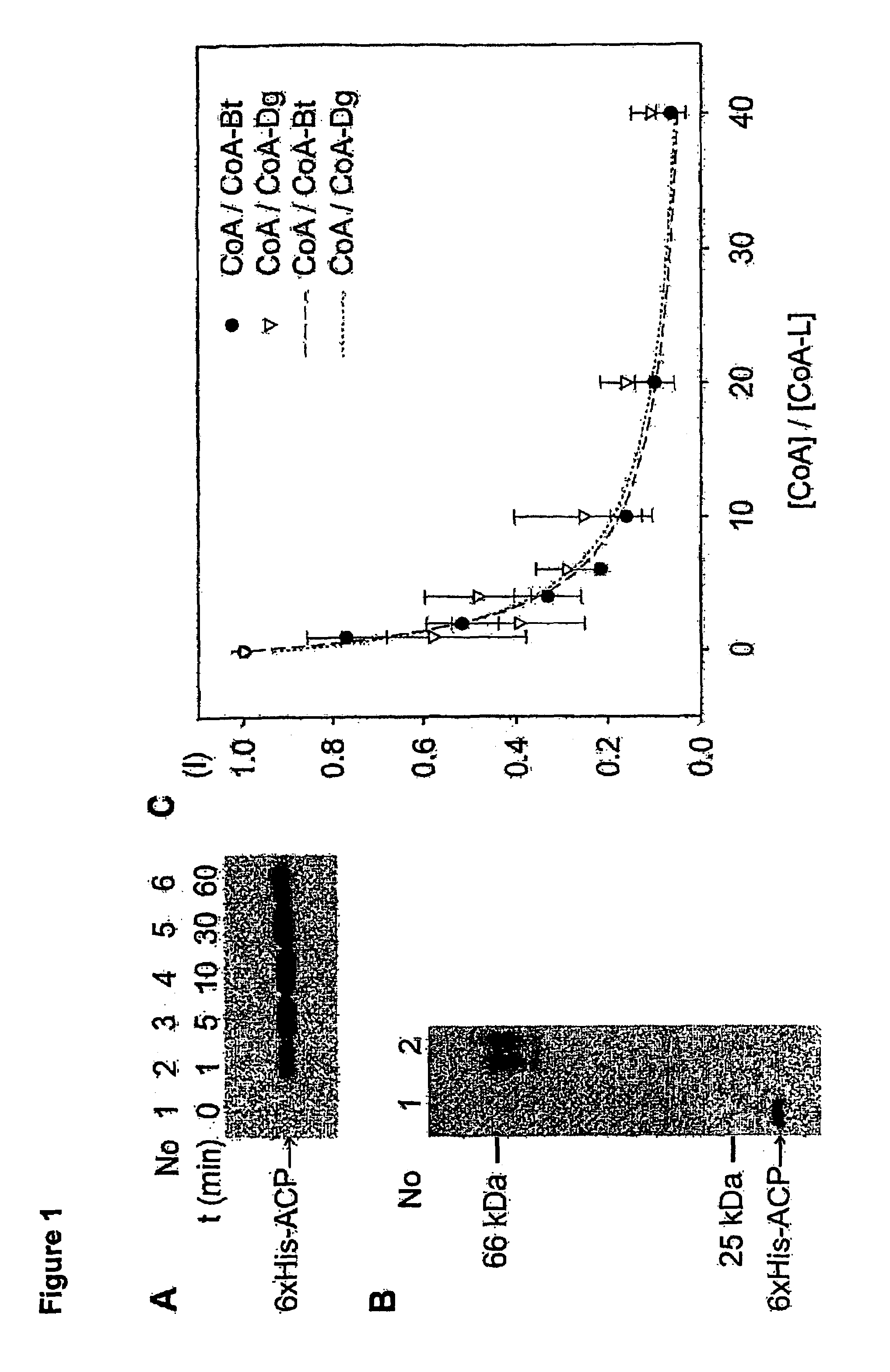
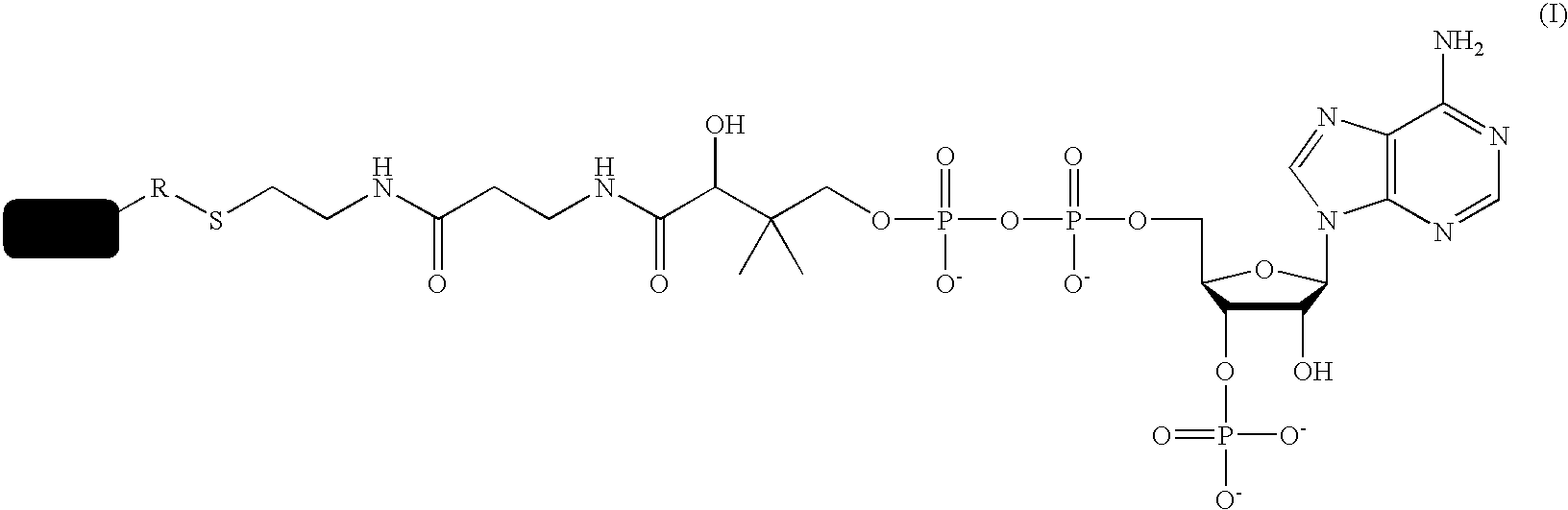
Methods for protein labeling based on acyl carrier protein
InactiveUS7666612B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCoenzyme A biosynthesisCarrier protein
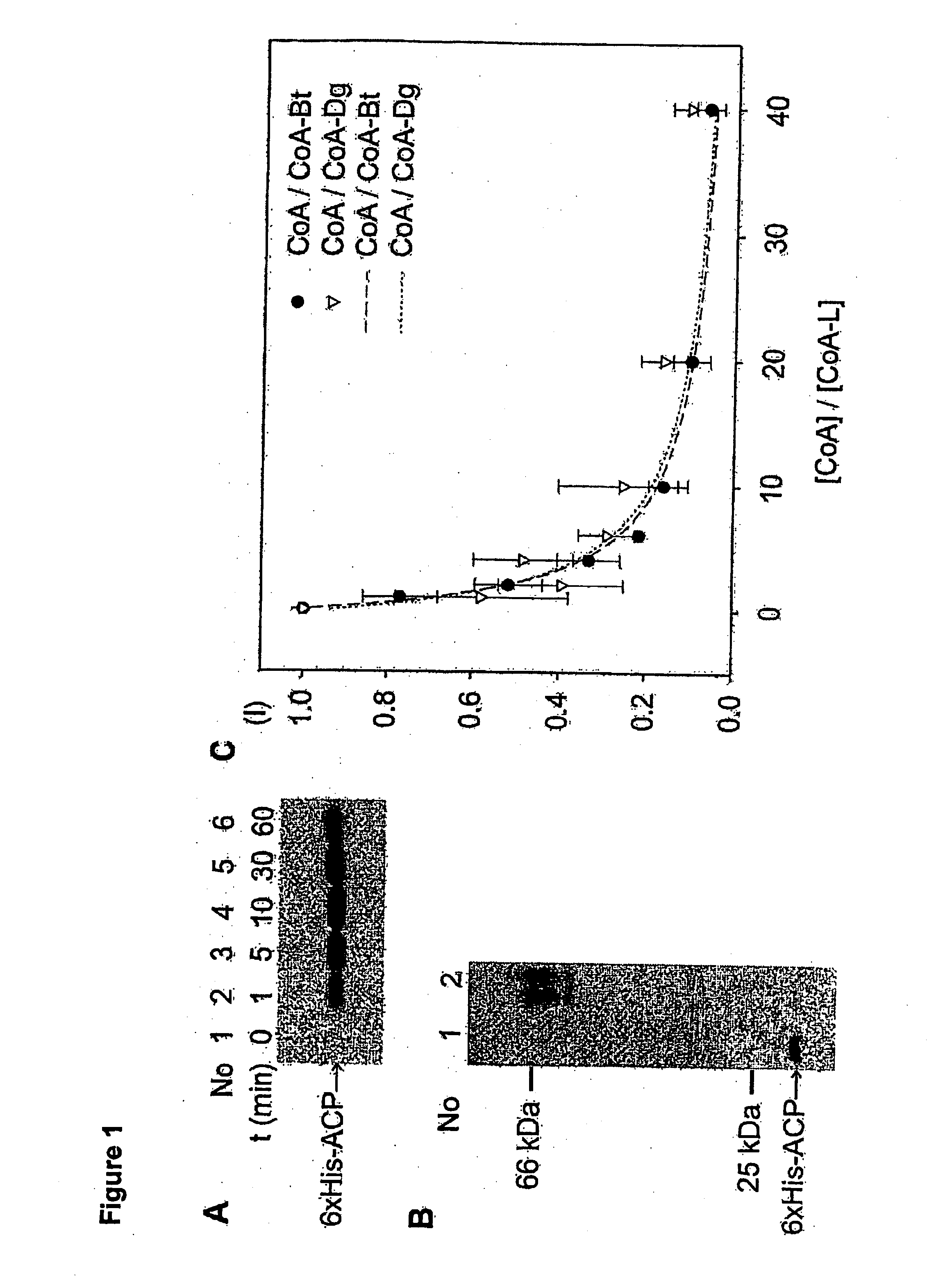
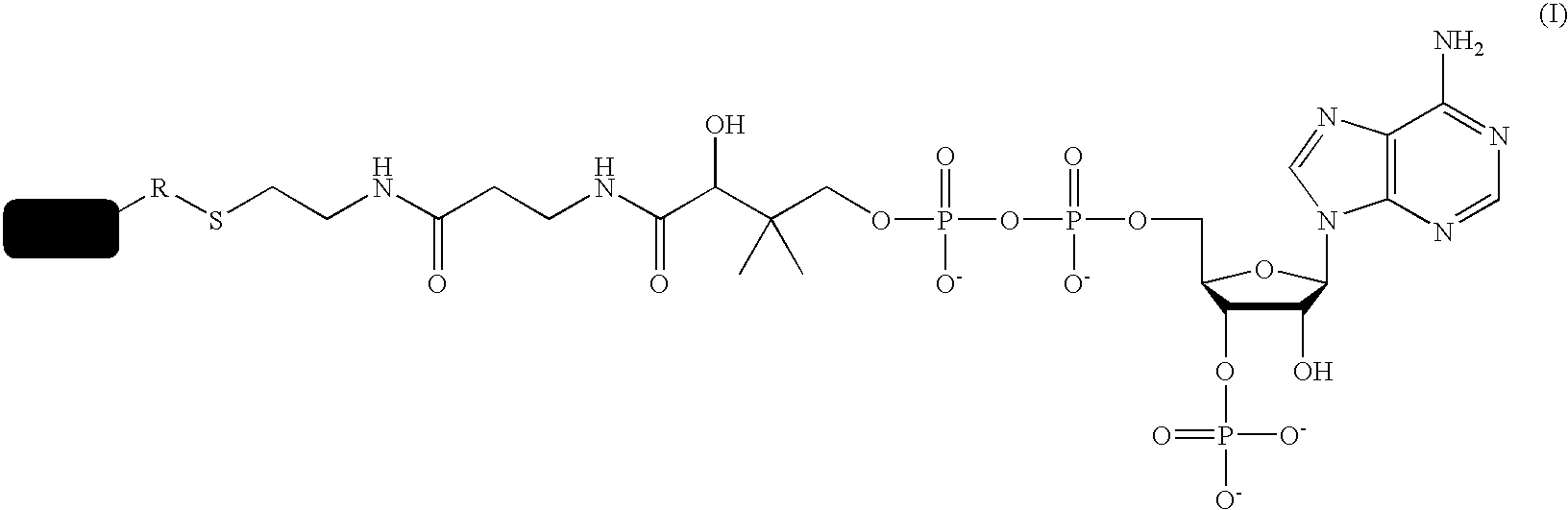
A method for labeling acyl carrier protein (ACP) fusion proteins with a wide variety of different labels is disclosed. The method relies on the transfer of a label from a coenzyme A type substrate to an ACP fusion protein using a holo-acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS) or a homologue thereof. The method allows detecting and manipulating the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such labels are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilization of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Markers of Renal Transplant Rejection and Renal Damage
InactiveUS20080153092A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisProtein markersRenal transplant rejection
The present invention relates to methods of detecting renal transplant rejection and other forms of renal damage. Protein markers or renal damage are provided, along with assays for detecting said markers. Also provided are methods for identifying markers of renal damage.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
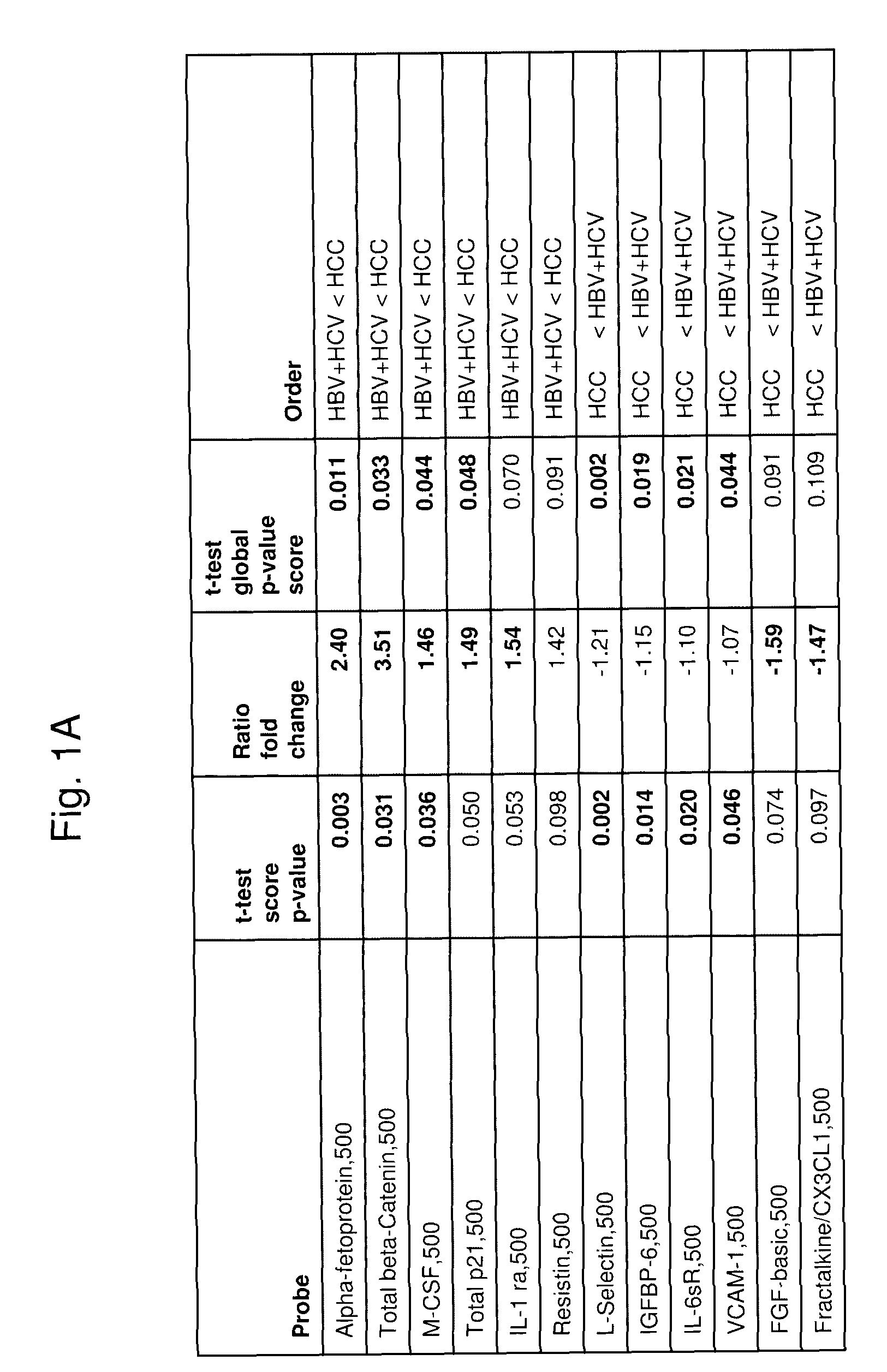
Methods for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma
InactiveUS8357489B2Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHepatocellular carcinomaMedicine
A method for evaluating hepatocellular carcinoma in a subject is provided. In certain embodiments, the method comprises: a) obtaining a hepatocellular carcinoma protein marker profile for a sample obtained from the subject; and b) comparing the protein marker profile to a control profile.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Micro-RNA, autoantibody and protein markers for diagnosis of neuronal injury
InactiveUS20130022982A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtein markersInjury brain
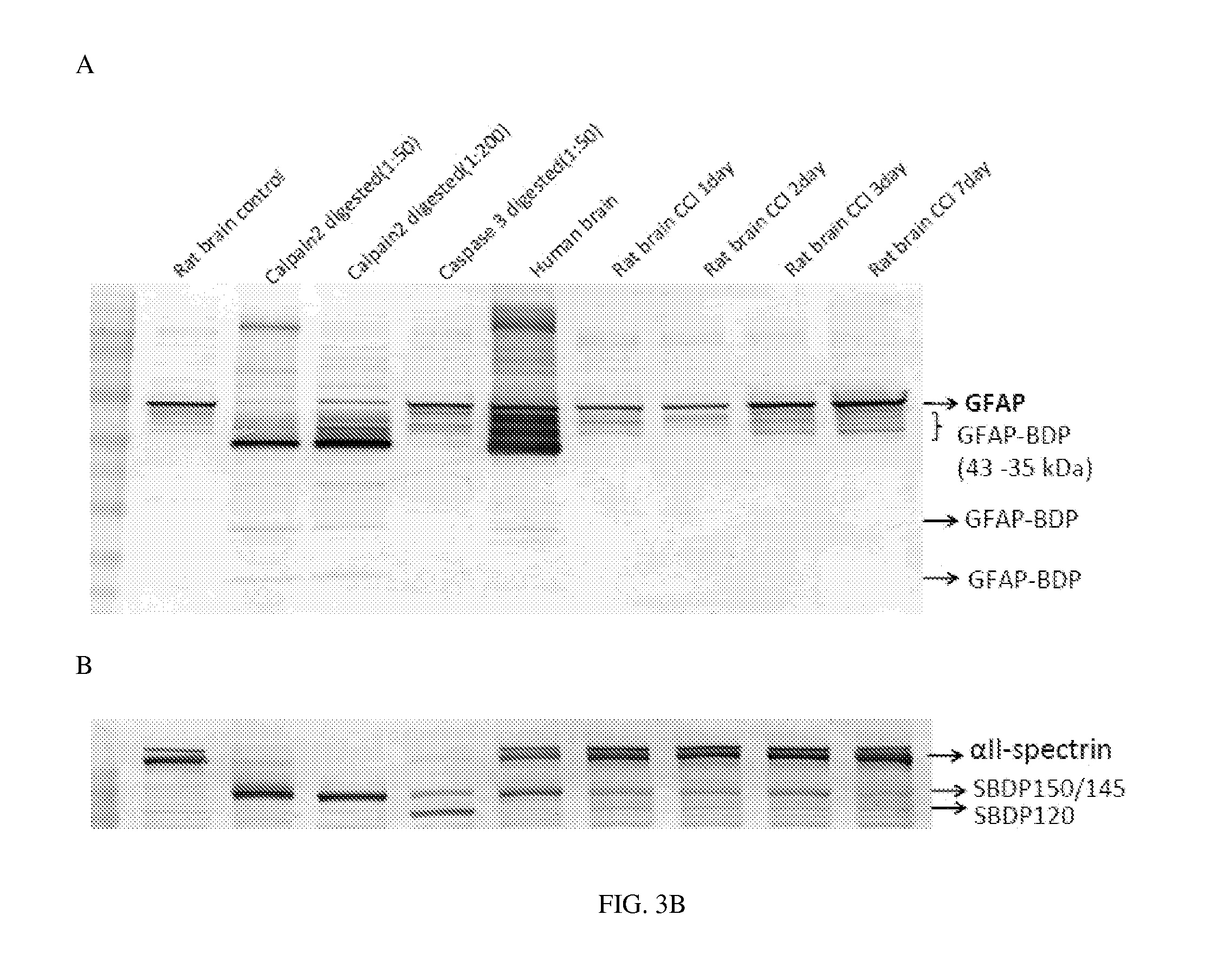
Processes and materials are provided for the detection, diagnosis, or determination of the severity of a neurological injury or condition, including traumatic brain injury, multiple-organ injury, stroke, Alzeimer's disease, Pakinson disease and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE). The processes and materials include biomarkers detected or measured in a biological sample such as whole blood, serum, plasma, or CSF. Such biomarkers include Tau and GFAP proteins, their proteolytic breakdown products, brain specific or enriched micro-RNA, and brain specific or enriched protein directed autoantibodies. The processes and materials are operable to detect the presence of absence of acute, subacute or chronic brain injuries and predict outcome for the brain injury.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
Biochemical method for specific protein labeling
InactiveUS20080305519A1Easy to operatePeptide sourcesTripeptide ingredientsProtein targetProtein insertion
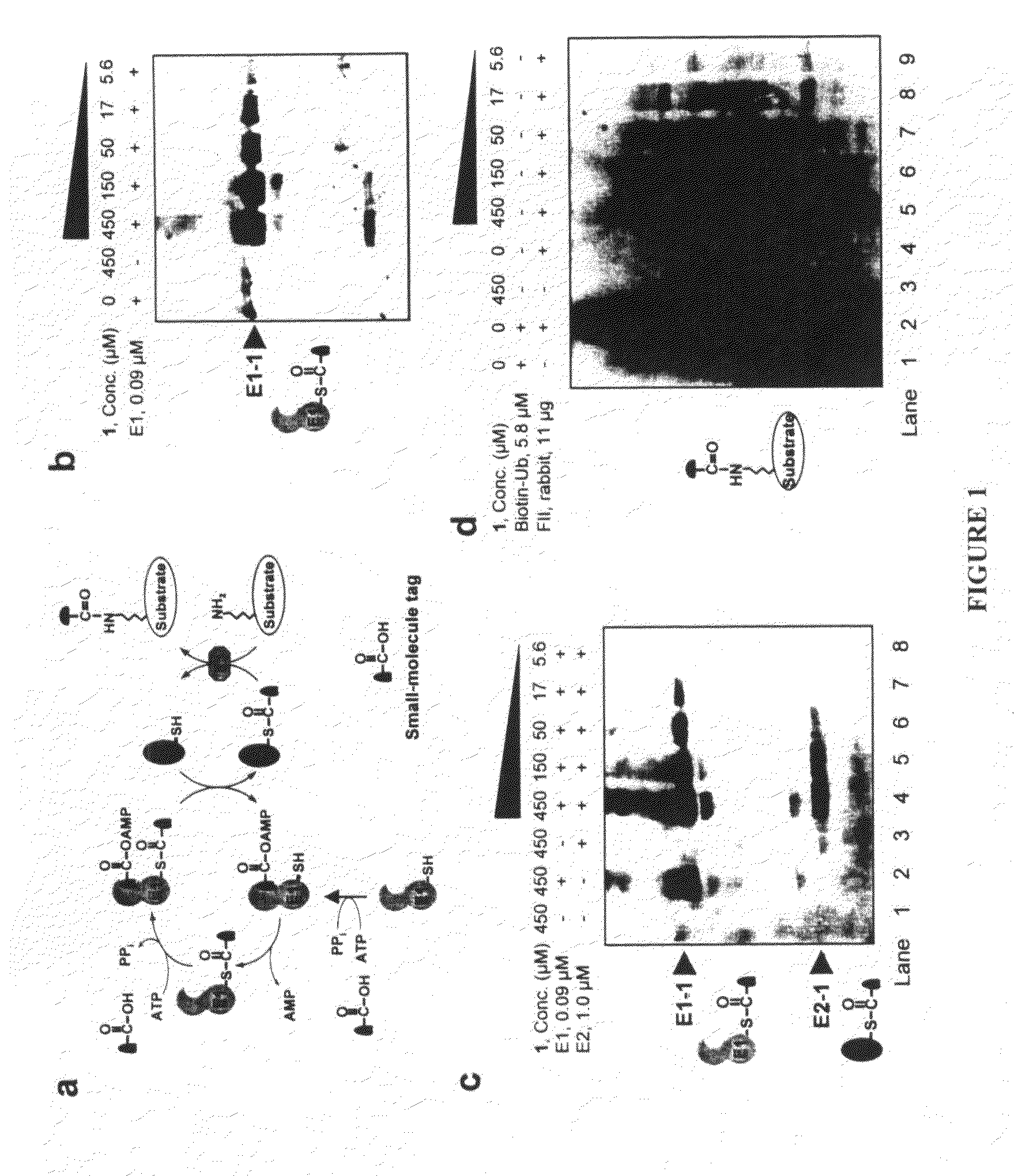
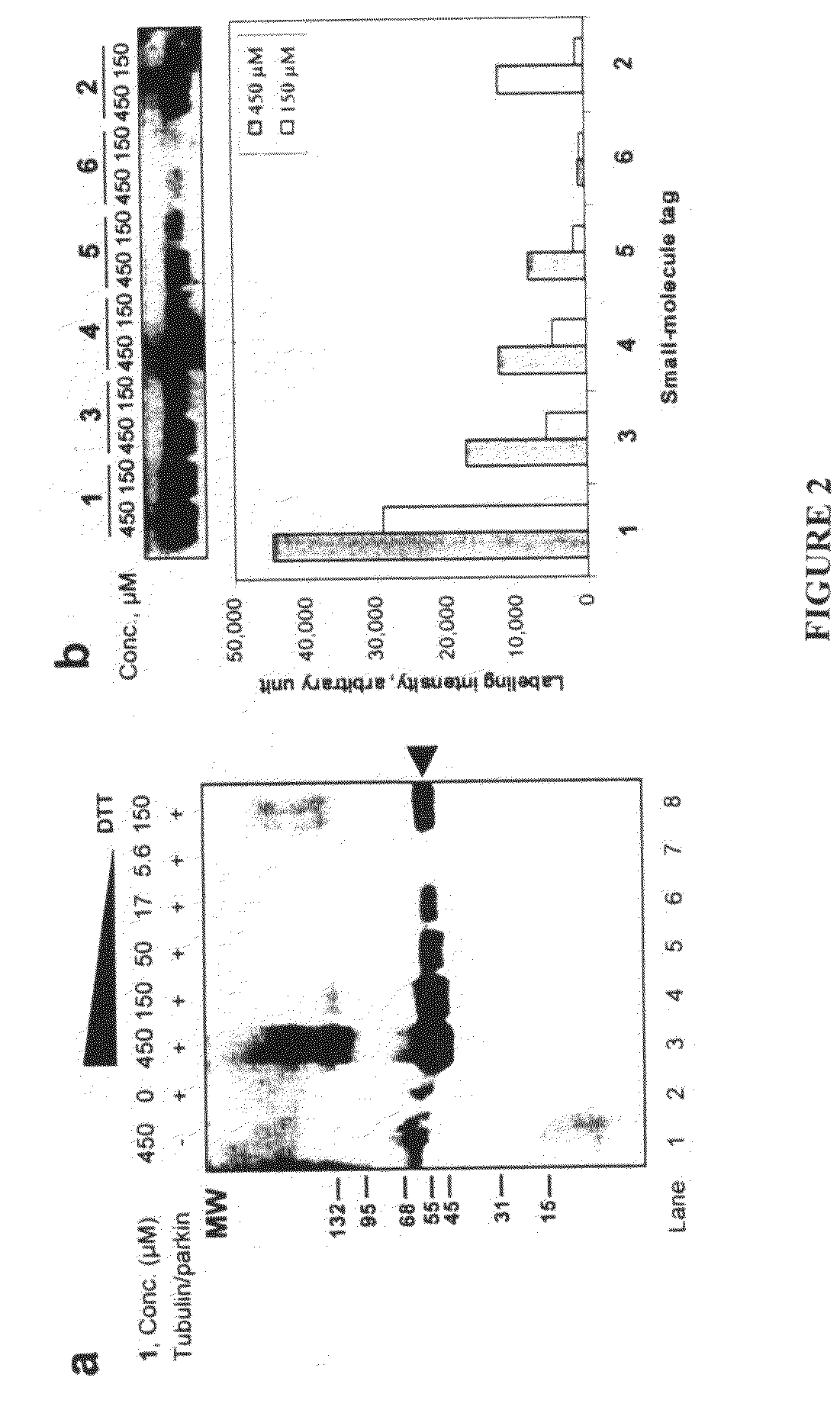
An improved method for protein labeling comprising the steps of providing a synthetic small molecule tag, providing a target protein to be tagged, providing at least two enzymes for catalyzing a conjugation reaction between the tag and the target protein, incubating the tag, the protein and the enzyme, and allowing the tag to conjugate to the target protein. The tag may embody at least one structural feature of an ubiquitin C-terminus, and the structural feature may comprise a recognition sequence that is recognizable by an ubiquitin activating enzyme.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
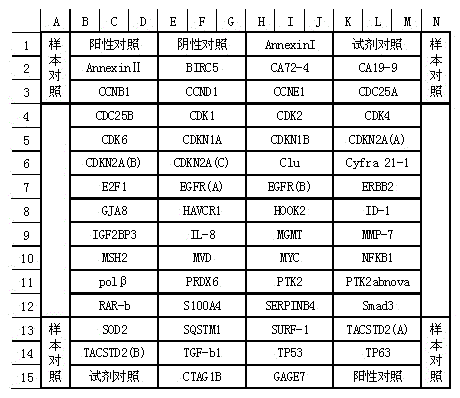
Male multi-tumor marker detection protein chip and kit thereof
InactiveCN101603966AChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingProtein markersProstate cancer
The invention discloses a male multi-tumor marker detection protein chip and a kit thereof. The chip comprises a substrate, protein markers distributed in an array type and point coatings of contrasts, wherein the substrate is a glass substrate or a film substrate; and the tumor markers and the point coatings of the contrasts are seven protein markers of AFP, CEA, NSE, CYFRA21-1, CA19-9, tPSA and SCC-ag, a positive contrast and a negative contrast which are uniformly distributed and latticed on the substrate. A reaction result of various indexes can be obtained only through one reaction by utilizing the protein chip, and the following tumors can be simultaneously screened: primary liver cancer, prostatic cancer, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. The invention is particularly suitable for the general examination of malignant tumors of male asymptomatic groups and high risk groups.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
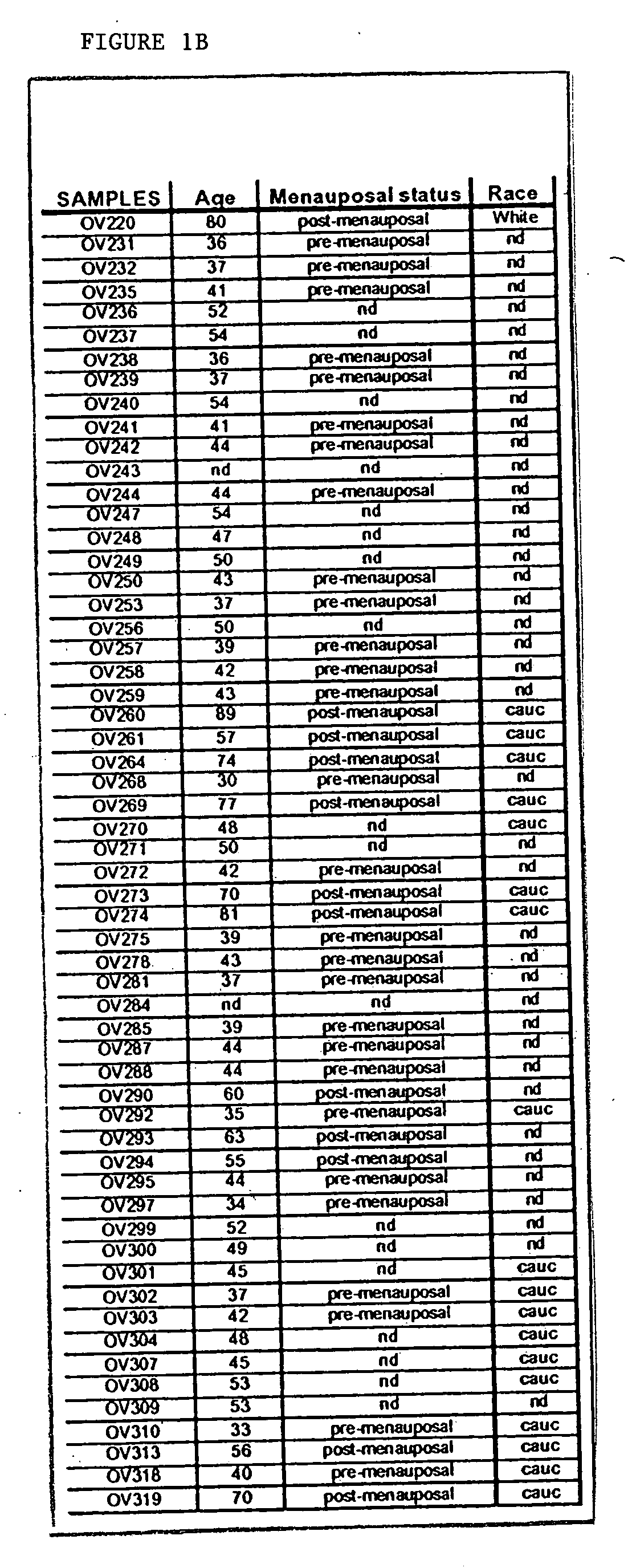
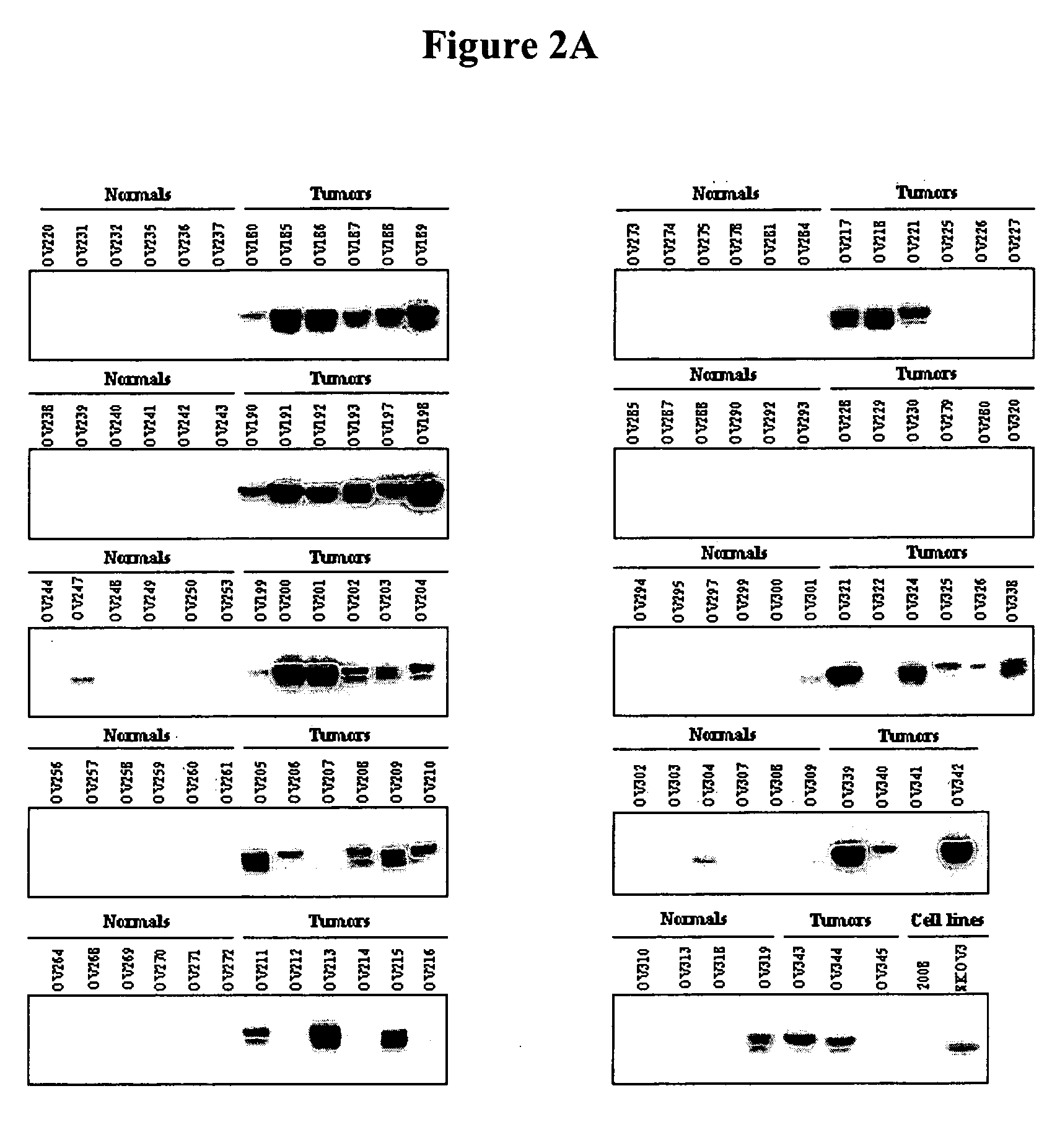
Tissue diagnostics for ovarian cancer
Disclosed are methods for diagnosing ovarian cancer in a cell sample by detecting an increase in the levels of expression of protein markers in the cell sample as compared to the levels of expression of the same protein markers in a normal, nonneoplastic ovarian cell sample. Also disclosed is a device for diagnosis of cancer in a cell sample.
Owner:AURELIUM BIOPHARMA
Protein chip for detecting esophageal squamous carcinoma marker and kit box of protein chip
The invention discloses a high-throughput multi-index protein chip for screening esophageal squamous carcinoma specific protein markers, and discloses a kit supporting the use. 55 types of esophageal squamous carcinoma differential proteins in the serum or blood plasma are selected and used as the esophageal squamous carcinoma protein markers and protein contrast prepare the protein chip; and the protein chip comprises a substrate, protein detection indicators and a contrast detection indicator coating, wherein the protein detection indicators are distributed as arrays on the substrate. Detection liquid of a supplementary experiment reagent is filled in the kit. By adopting the protein chip, the protein profiles of three types of people, namely, normal people, people subjected to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma precancerous lesions, and people subjected to the esophageal squamous carcinoma, can be determined; and means are provided for screening the esophageal squamous carcinoma in the early stage, diagnosing in mid stage and late stage, as well as monitoring the state of illness.
Owner:JIANGSU YUANHUA BIO TECH
Self-immunity hepatitis detection protein chip and kit thereof
InactiveCN101750492AStrong specificityImprove detection accuracyMaterial analysisProtein markersHepatitis
The invention discloses a self-immunity hepatitis detection protein chip and a kit thereof. The chip and the kit can be used for simultaneously detecting 12 immunity protein markers: ANA (dsDNA, RNP, Sm, SS-A / Ro, SS-B / La, Sc1-70, Jo-1), SMA, LKM-1, SLA / LP, F-actin and AMA. The invention overcomes the shortcomings of the current products that the detection index is single and incomplete. The invention provides a detection method which has a complete diction result and a simpler process.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
Methods for protein labeling based on acyl carrier protein
InactiveUS20070082336A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesProtein markersProtein labeling
A method for labeling acyl carrier protein (ACP) fusion proteins with a wide variety of different labels is disclosed. The method relies on the transfer of a label from a coenzyme A type substrate to an ACP fusion protein using a holo-acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS) or a homologue thereof. The method allows detecting and manipulating the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such labels are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilization of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Approach to molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus-related diseases
ActiveUS7361460B2Accurate sensitive toolReduce in quantitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein markersSequential method
The present invention relates to an accurate, sensitive, and efficient sequential or concurrently sequential method for molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus (HPV)-based disease, where the method improves the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic and prognostic assessments of HPV-based disease. The method of the invention comprises a primary screen of a sample for HPV nucleic acids, followed by a secondary screen for molecular markers, such as proliferation and cell cycle control group protein markers. The sequential or concurrently sequential method significantly reduces the number of false positive results.
Owner:DIGENE CORP
Protein markers for diagnosing stomach cancer and the diagnostic kit using them
InactiveUS20090018026A1Facilitates not diagnosisEasy searchElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementProtein markersStomach cancer
The present invention relates to protein markers for diagnosing stomach cancer and a diagnostic kit using the same, more precisely protein markers screened by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and bioinformatics and a diagnostic kit using the same. The markers of the invention can be effectively used for diagnosing stomach cancer and evaluating the extent of progress of the cancer by confirming the expression levels of those marker proteins whose expressions differ in stomach cancer patients from in normal healthy people.
Owner:BIOINFRA
Protein- protein interaction detection system using fluorescent protein microdomains
ActiveUS7666606B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein markersProtein labeling
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Prediction of response to docetaxel therapy based on the presence of TMPRSSG2:ERG fusion in circulating tumor cells
InactiveUS20110166030A1Promote rapid developmentPromote resultsLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisProtein markersDocetaxel-PNP
A method for predicting with high specificity from RTPCR detected markers if a patent is likely to respond to docetaxel treatment is disclosed. RTPCR detects the presence of absence of certain mutations due to fusion events. Together, with other protein markers, additional stratification is possible to identify patents suited for docetaxel therapy as opposed to for alternative treatments.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Prognosis prediction for melanoma cancer
ActiveUS20100136553A1Effective individual testImprove forecast accuracySugar derivativesHealth-index calculationProtein markersPrognostic signature
The invention relates to prognostic markers and prognostic signatures, and compositions and methods for determining the prognosis of cancer in a patient, particularly for melanoma. Specifically, the invention relates to the use of genetic and protein markers for the prediction of the risk of progression of a cancer, such as melanoma, based on markers and signatures of markers. In various aspects, the invention provides methods, compositions, kits, and devices based on prognostic cancer markers, specifically melanoma prognostic markers, to aid in the prognosis and treatment of cancer.
Owner:PACIFIC EDGE +1
Using plasma proteomic pattern for diagnosis, classification, prediction of response to therapy and clinical behavior, stratification of therapy, and monitoring disease in hematologic malignancies
The present invention demonstrates that the diagnosis and prediction of clinical behavior in patients with hematologic malignancies, such as leukemia, can be accomplished by analysis of proteins present in a plasma sample. Thus, in particular embodiments the present invention uses plasma to create a diagnostic or prognostic protein profile of a hematologic malignancy comprising collecting plasma samples from a population of patients with hematologic malignancies; generating protein spectra from the plasma samples with or without fractionation; comparing the protein spectra with clinical data; and identifying protein markers in the plasma samples that correlate with the clinical data. Protein markers identified by this approach can then be used to create a protein profile that can be used to diagnose the hematologic malignancy or determine the prognosis of the hematologic malignancy. Potentially these specific proteins can be identified and targeted in the therapy of these malignancies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
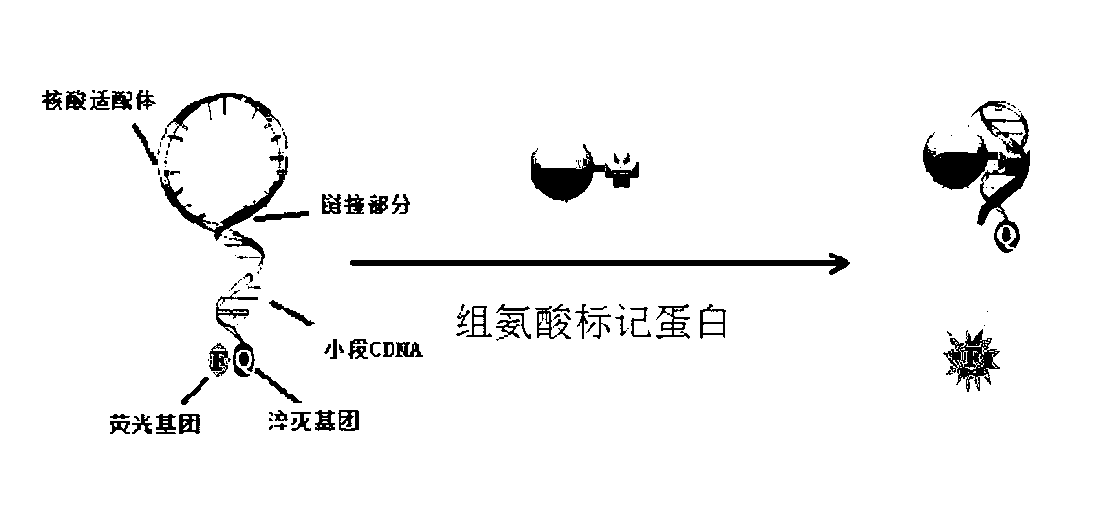
Nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe for detecting histidine-tag recombinant proteins and detection method thereof
ActiveCN102719430ARapid detection and quantitative analysisHigh affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein markersPolyhistidine-tag
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe for detecting histidine-tag recombinant proteins and a direct general method for detecting the histidine-tag recombinant proteins in cell lysates by the probe. The nucleic acid aptamer probe comprises sequences shown in SEQIDNO.1 and SEQIDNO.2; the end 3' of the sequence shown in the SEQIDNO.1 is bridged with the end 5' of the sequence shown in the SEQIDNO.2 through PEG36; the end 5' of the sequence shown in the SEQIDNO.1 is modified with fluorescein FAM; and the end 3' of the sequence shown in the SEQIDNO.2 is modified with a quenching group Dabcy1. According to the nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe, the expression of the histidine-tag recombinant proteins in the cell lysates can be quickly and quantificationally analyzed without protein tagging, and the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of universality and low cost, and the advantage that the histidine-tag recombinant proteins can be simply, quickly and quantificationally analyzed.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
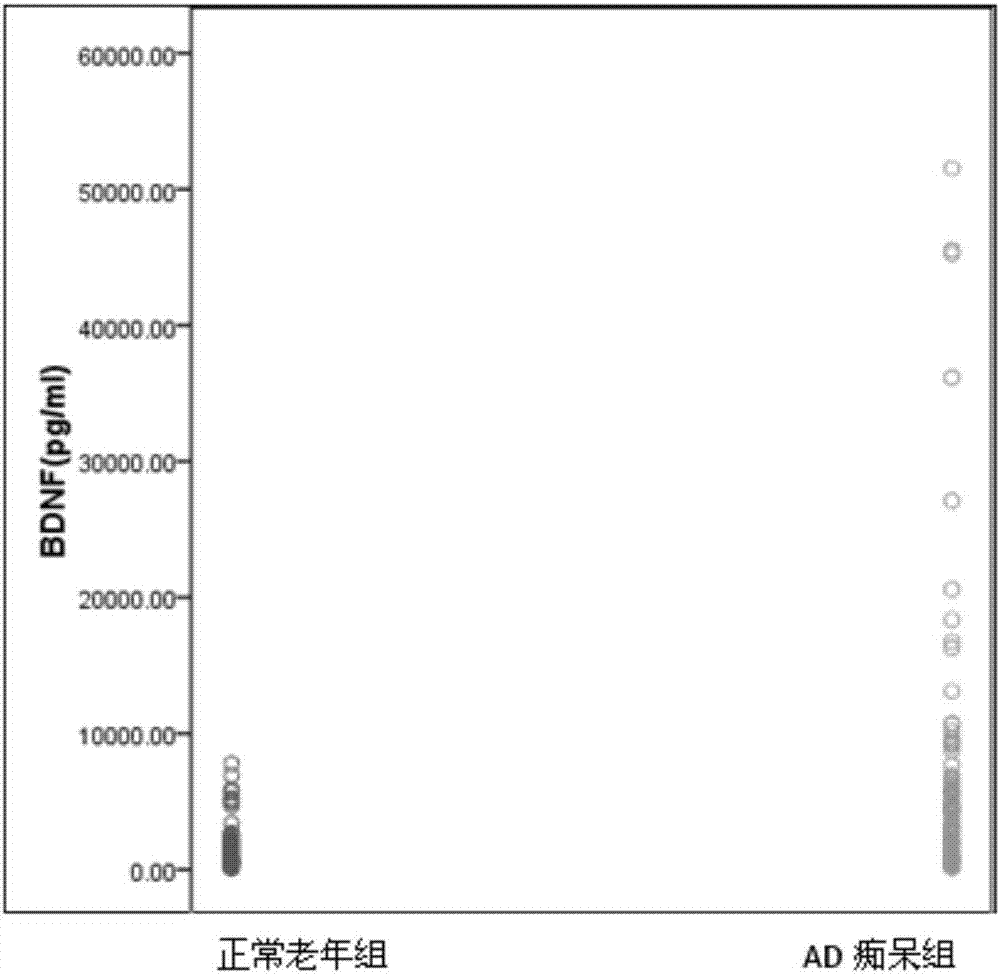
Diagnostic kit for detecting peripheral blood protein marker of Alzheimer disease and detection method using diagnostic kit
ActiveCN107238711AQuick checkAccurate detectionDisease diagnosisBiological testingProtein markersFluorescence
The invention relates to a diagnostic kit for detecting a peripheral blood protein marker of an Alzheimer disease and a detection method using the diagnostic kit and belongs to the technical field of in vitro diagnosis detection. The detection method is characterized in that various protein markers in a same sample can be detected at one time, namely, a tetrad compound 'biotin-labeled detection antibody-Alzheimer disease protein marker-capture antibody-microsphere' is formed in the manner of preparation of a liquid chip, and fluorescence signals of different microspheres can be detected after the tetrad compound is combined with streptavidin-phycoerythrin, so that the existence and content of various protein markers related to the Alzheimer disease in a to-be-detected sample can be confirmed. The invention also discloses the components forming the diagnostic kit. The method and the kit provided by the invention have the advantages of high sensitivity, high throughput, high detection speed, accuracy, and the like, and can be used for simultaneously performing qualitative and quantitative detection on various protein markers related to the Alzheimer disease.
Owner:WUXI MENTAL HEALTH CENT
Novel approach to molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus-related diseases
ActiveUS20070243552A1Accurate sensitive toolReduce in quantitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein markersHuman papillomavirus
The present invention relates to an accurate, sensitive, and efficient sequential or concurrently sequential method for molecular diagnosis of human papillomavirus (HPV)-based disease, where the method improves the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic and prognostic assessments of HPV-based disease. The method of the invention comprises a primary screen of a sample for HPV nucleic acids, followed by a secondary screen for molecular markers, such as proliferation and cell cycle control group protein markers. The sequential or concurrently sequential method significantly reduces the number of false positive results.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG
Application of protein and proteome in preparation of liver cirrhosis diagnostic reagent
InactiveCN102183661AHigh sensitivityBiological testingPIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTORProtein markers
The invention relates to application of protein and proteome in preparation of a liver cirrhosis diagnostic reagent. The protein comprises Lumican, Tetranectin, Pro-platelet basic protein (PBP), Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFbp-3), Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), Thioredoxin and composition of parts in the liver cirrhosis diagnostic reagent. Multiple proteins related with health and disease states are identified and evaluated in large range by adopting a proteome technology, the screened biomarkers for identifying hepatitis and liver fibrosis are used for predicting the degree of hepatitis and liver fibrosis and can be used for preparing a kit for diagnosing liver cirrhosis and liver cirrhosis level, and the protein markers identify the sensitivity of liver cirrhosis and degree thereof; and by combining the optimal conditions of various protein markers, the sensitivity can reach 89 percent, the specificity reaches over 90 percent, and the sensitivity and the specificity are higher than those of any known detection method.
Owner:天津宝瑞生物技术有限公司
Lupus erythematosus detection protein chip and kit thereof
InactiveCN101726586AThe detection indicators are comprehensive and appropriateImprove detection efficiencyBiological testingDiseaseProtein markers
The invention discloses lupus erythematosus detection protein chip and kit thereof. The chip comprises a substrate, protein markers distributed in an array type and control point coatings, wherein the markers and the control point coatings are seven antigen markers, positive controls and negative controls comprising dsDNA (double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid), ssDNA (single stranded deoxyribonucleic acid), Histon, SS-A(Ro60), SS-B(La), Sm (smith) and RNP (ribonucleoprotein) / Sm which are uniformly distributed on the substrate in a dot matrix mode. The invention has comprehensive and appropriate detection indexes and consistent applied reaction conditions, can detect a plurality of indexes at a time, is convenient and quick, greatly improves the detection efficiency and reduces the detection cost. The invention can be suitable for aided diagnosis of suspected lupus erythematosus disease people.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
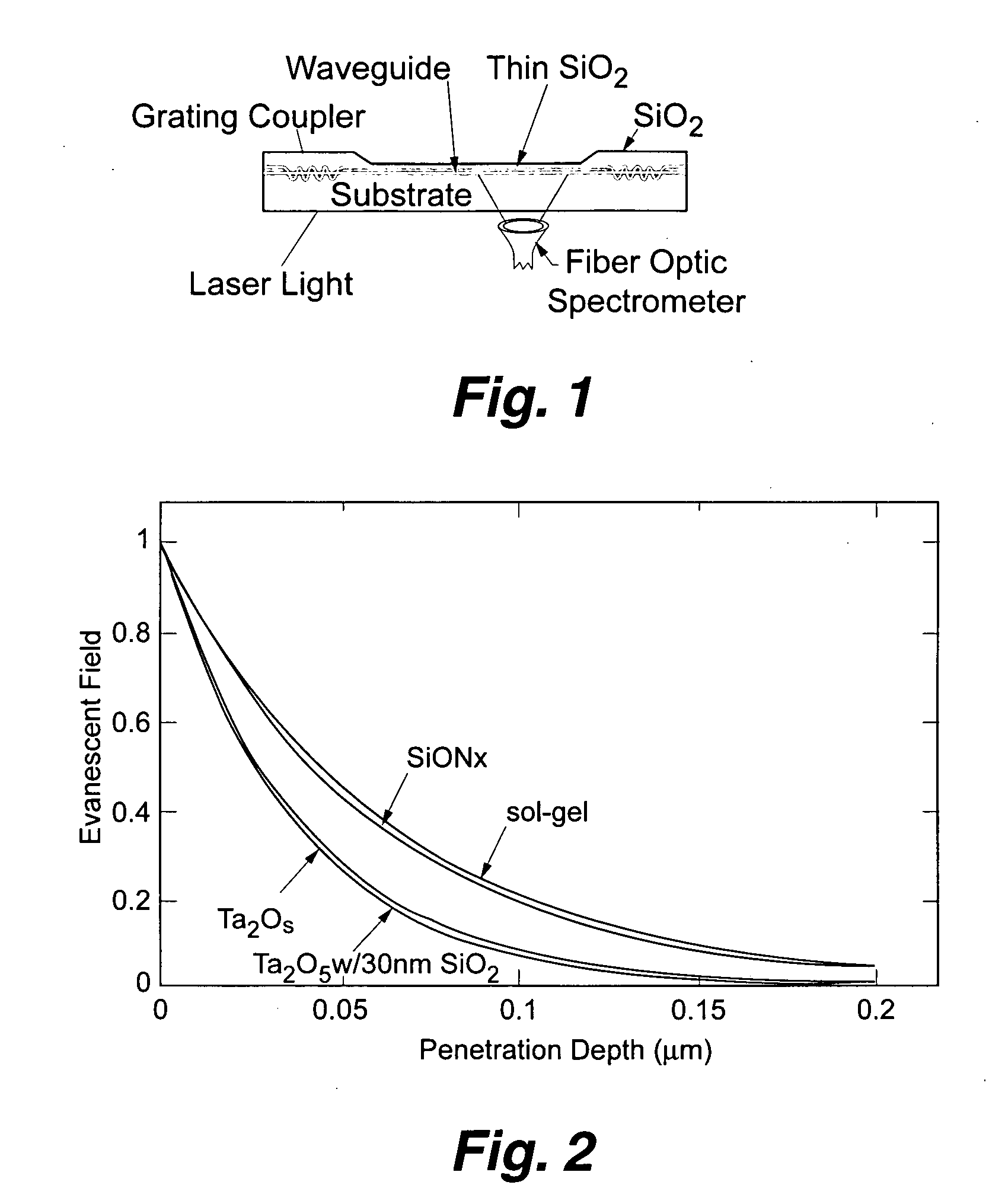
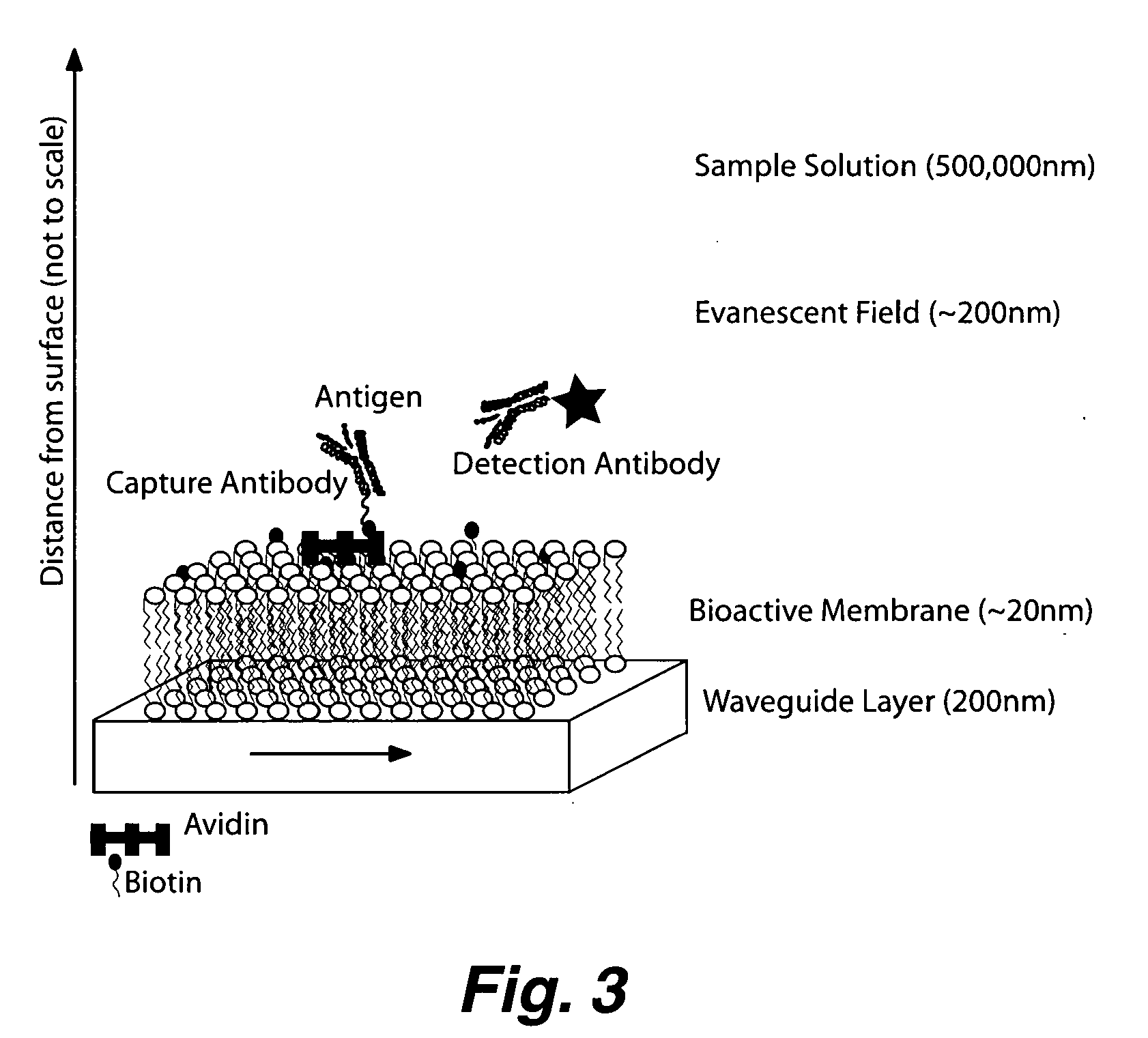
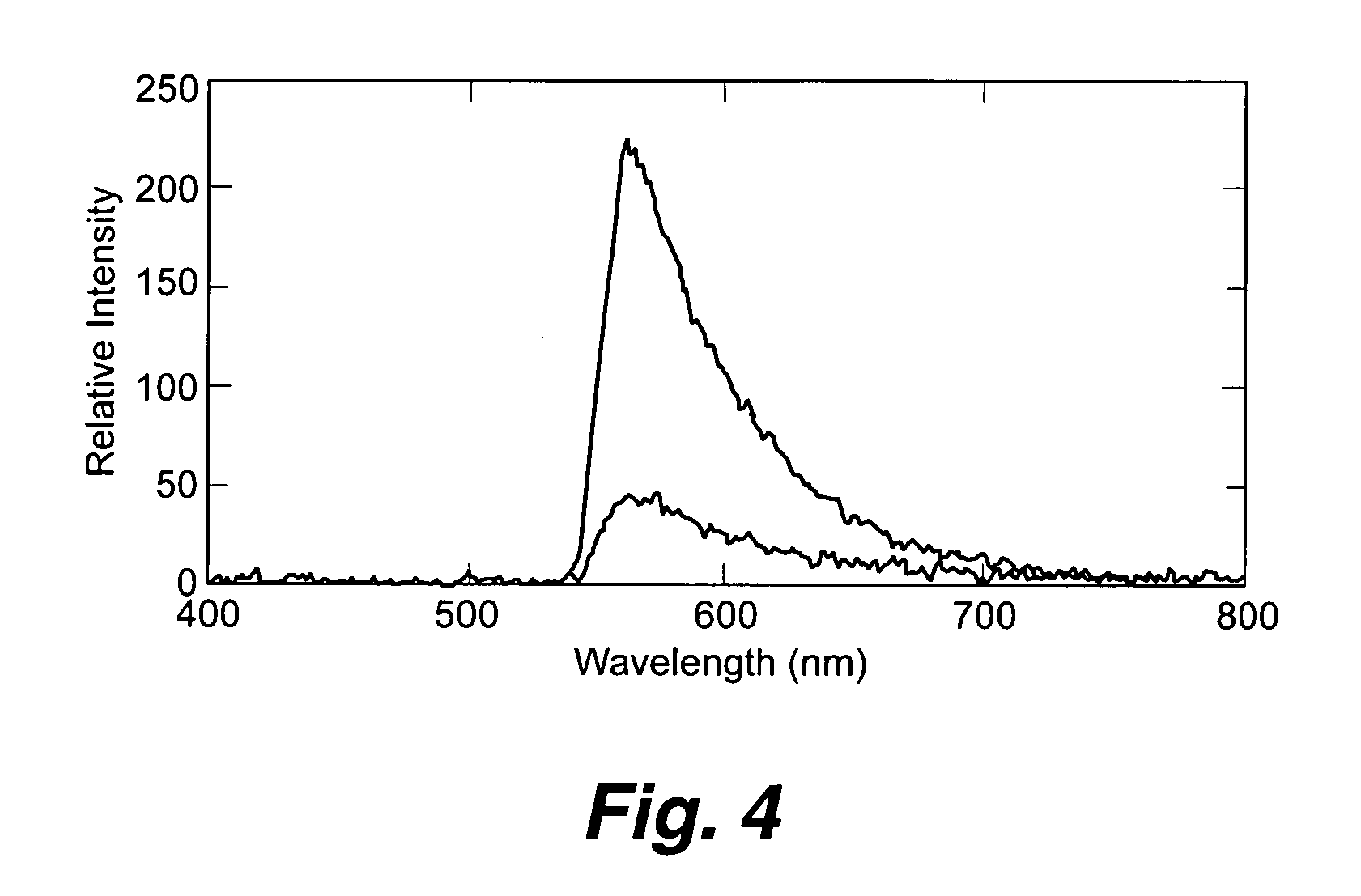
Planar optical waveguide based sandwich assay sensors and processes for the detection of biological targets including protein markers, pathogens and cellular debris
InactiveUS20060019244A1Enough timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyProtein markersSelf-assembled monolayer
An assay element is described including recognition ligands bound to a film on a single mode planar optical waveguide, the film from the group of a membrane, a polymerized bilayer membrane, and a self-assembled monolayer containing polyethylene glycol or polypropylene glycol groups therein and an assay process for detecting the presence of a biological target is described including injecting a biological target-containing sample into a sensor cell including the assay element, with the recognition ligands adapted for binding to selected biological targets, maintaining the sample within the sensor cell for time sufficient for binding to occur between selected biological targets within the sample and the recognition ligands, injecting a solution including a reporter ligand into the sensor cell; and, interrogating the sample within the sensor cell with excitation light from the waveguide, the excitation light provided by an evanescent field of the single mode penetrating into the biological target-containing sample to a distance of less than about 200 nanometers from the waveguide thereby exciting the fluorescent-label in any bound reporter ligand within a distance of less than about 200 nanometers from the waveguide and resulting in a detectable signal.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method and device for detecting free epithelial cell organ sources in blood
ActiveCN105063168ANo lossSolve the bottleneck of detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein markersOrgan Specificity
The invention relates to a method and a device for detecting free epithelial cell organ sources in blood. The method includes the following steps: capturing epithelial cells from a blood sample; cracking the epithelial cells to release protein therein; specifically recognizing at least four protein markers with organ specificity; acquiring the organ sources of the epithelial cells by detecting expression quantity of the protein markers. The device comprises a microgroove chip and an antibody loading glass piece, 100-10000 microgrooves are formed in the microgroove chip and used for containing the cells, the antibody loading glass piece is used for loading an antibody micro-array which comprises at least four mutually-independent antibody strips, and the microgrooves and the antibody micro-array are arranged in a matched manner to enable at least one part of each antibody strip to be contained at corresponding positions of the microgrooves. The problem of detecting the epithelial cell organ sources in blood is solved by quickly and effectively detecting multiple proteins in single cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Use of microRNA in exosomes for diagnosis of cerebral arterial thrombosis
ActiveCN108070650AImprove the level ofAccurately reflectMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein markersIschemic injury
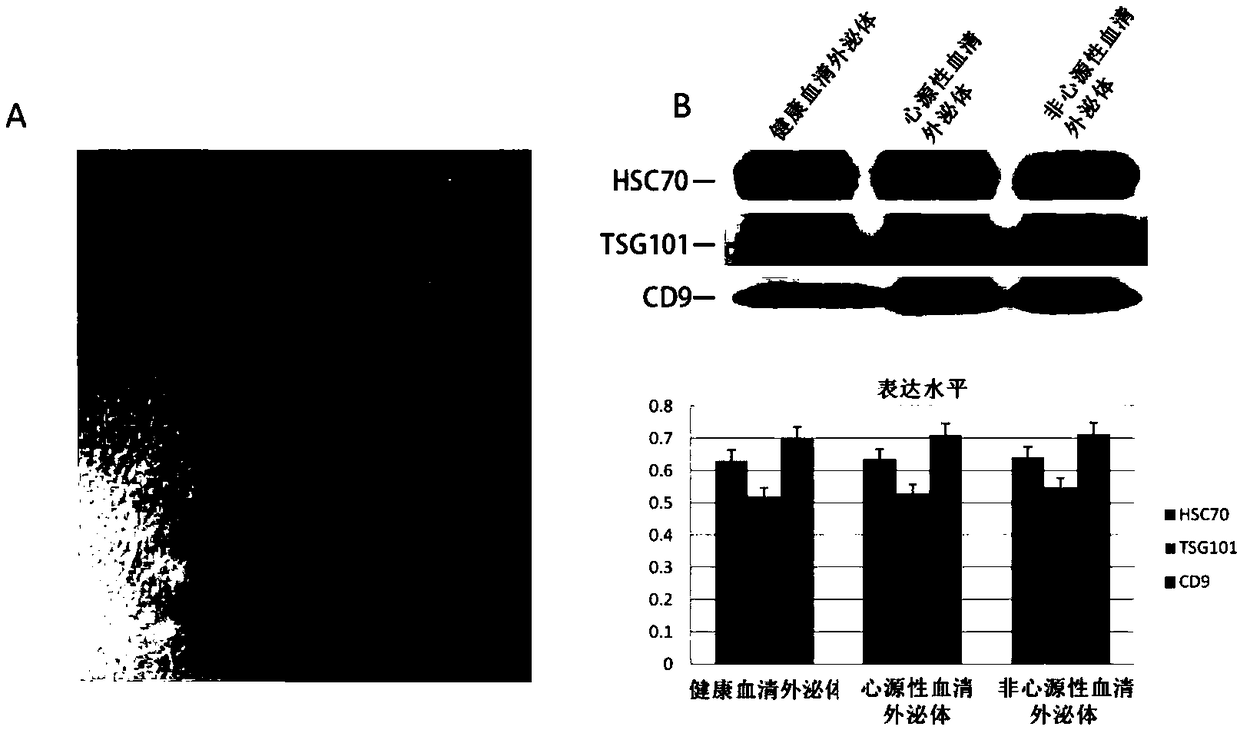
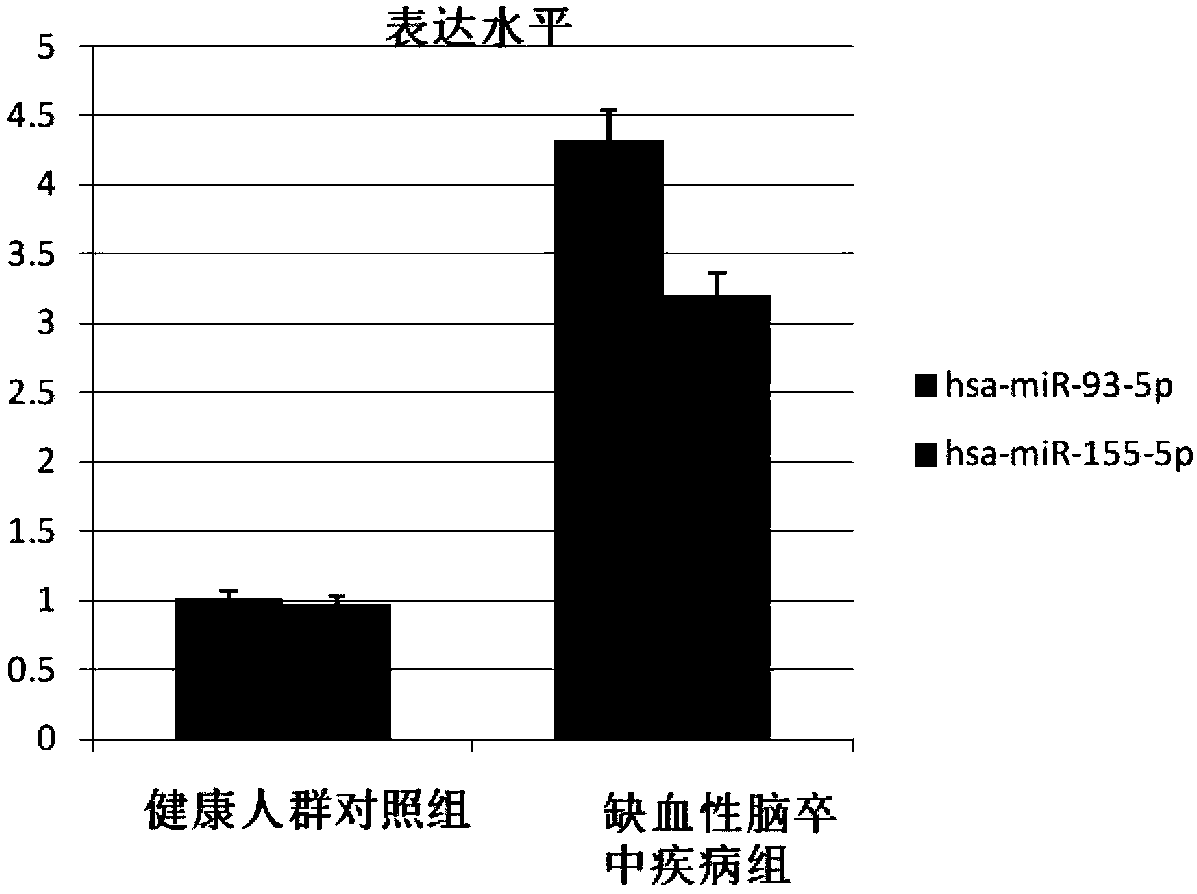
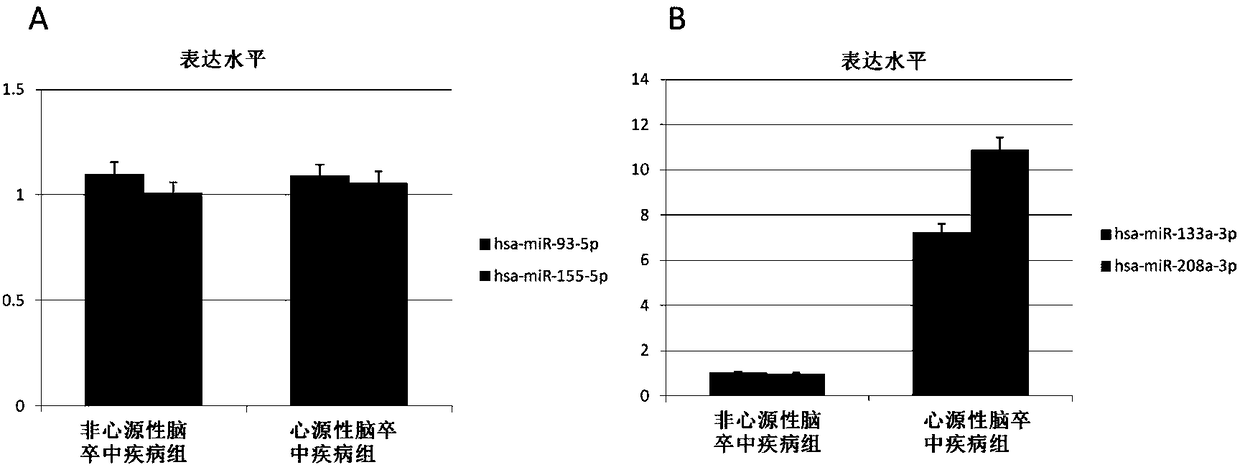
The invention discloses the use of an agent for detecting microRNA in exosomes in the preparation of a product for judging the presence and / or degree of cerebral ischemic injury, and relates to a method for early discrimination of a subject suffering from cardiogenic ischemic stroke and non-cardiogenic ischemic stroke. The method uses the exosomes in high-molecular polymer precipitate serum and areal-time fluorescence quantitative PCR technology, and experimental results show that the specificity and sensitivity of miR-155-5p and miR-93-5p are significantly higher than existing protein markers. Meanwhile, miR-133a-3p and miR-208a-3p expression of the exosomes of patients with cardiogenic ischemic stroke is significantly higher compared with patients with non-cardiogenic ischemic stroke under the condition of no significant changes in the serum miR-133a-3p and miR-208a-3p at the early stage so that the agent can be used as a marker to distinguish the cardiogenic ischemic stroke and thenon-cardiogenic ischemic stroke.
Owner:CHI BIOTECH CO LTD
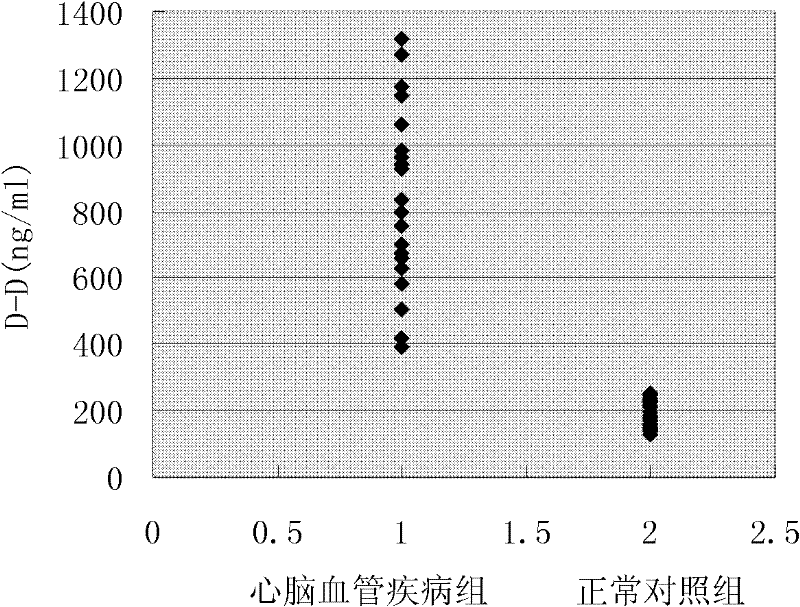
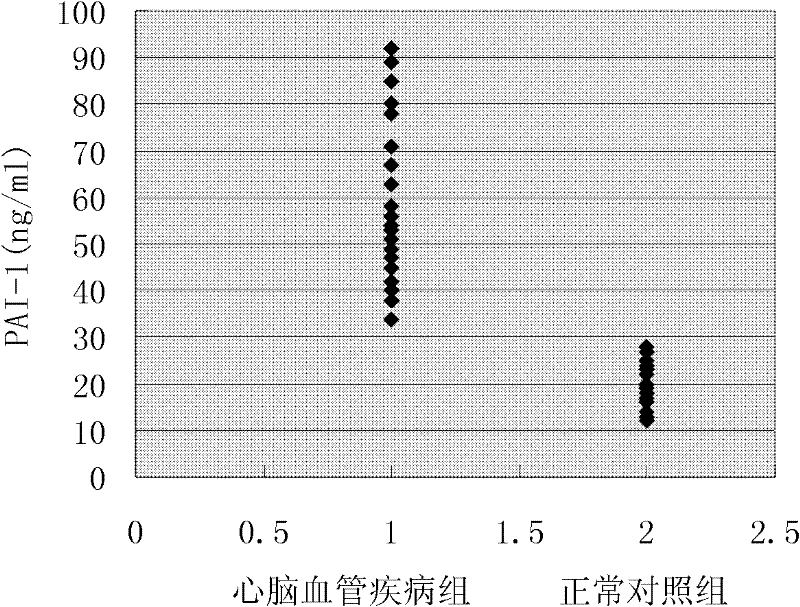
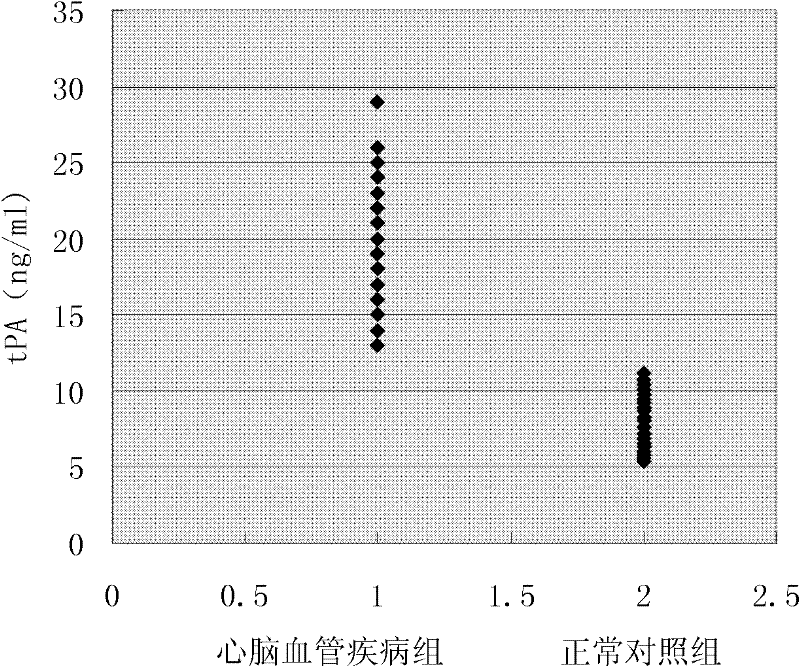
Joint detection method for heart cerebrovascular disease-related protein marker and diagnostic kit thereof
The invention discloses a joint detection method for heart cerebrovascular disease-related protein markers and a diagnostic kit thereof. A joint parallel detection method is characterized in that: a plurality of protein markers of the same sample can be detected at one time, i.e., a quadruple complex consisting of a signal marking detection antibody, a heart cerebrovascular disease-related protein marker, a capture antibody and microspheres is formed by preparing a liquid-phase chip, and the presence and content of various different heart cerebrovascular disease-related protein markers in a sample to be detected are determined by detecting marking signals of different microspheres in the quadruple complex. The invention further discloses constituents of the diagnostic kit and application of the diagnostic kit. The method and the kit provided by the invention have the outstanding advantages of high flux, high sensitivity, high specificity, quick and accurate detection and the like, and can be used for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting a plurality of heart cerebrovascular disease-related protein markers simultaneously.
Owner:MEDI GENETECH
Protein chip, protein chip diagnostic kit, preparation method and using method
ActiveCN105527435AFacilitate early diagnosisConvenient census screeningMaterial analysisProtein markersHigh risk populations
The invention relates to a protein chip, a protein chip diagnostic kit, a preparation method and a using method. The protein chip contains the following protein markers of autologous antigen protein: a P53 antigen fragment, an SOX2 antigen fragment, a COPB1 antigen fragment, an EFHD2 antigen fragment, an EIF4G3 antigen fragment and a PCNA antigen fragment, wherein the characteristic amino acid sequence of the P53 antigen fragment is as shown in ID.1sequence; the characteristic amino acid sequence of the SOX2 antigen fragment is as shown in ID.2sequence; the characteristic amino acid sequence of the COPB1 antigen fragment is as shown in ID.3sequence; the characteristic amino acid sequence of the EFHD2 fragment is as shown in picture 4seeqeunce; the characteristic amino acid sequence of the EIF4G3 antigen fragment is as shown in ID.5seqeunce; the characteristic amino acid sequence of the PCNA antigen fragment is as shown in ID.6sequence. Early diagnosis or general investigation screening for suspected patients of lung cancer or high-risk population of lung cancer can be carried out extremely conveniently, quickly, noninvasively and efficiently.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO BLUE TECH CO LTD
Signal amplification system based on bioluminescence resonance energy transfer and detection method thereof
ActiveCN108796041AAchieve signal amplificationHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesEnergy transferProtein markers
The invention provides a signal amplification system based on bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. The system relates to an energy donor protein capable of being bound to DNA, an energy receptorprotein capable of being bound to DNA and a nucleic acid assembly system composed of three kinds of DNA probes. The energy donor protein and the energy receptor protein can be specifically bound to adouble-stranded DNA product produced by the nucleic acid assembly system to achieve signal amplification of bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. The signal amplification system can be applied to the analysis of different protein markers and improves the sensitivity and the versatility of a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer detection method.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
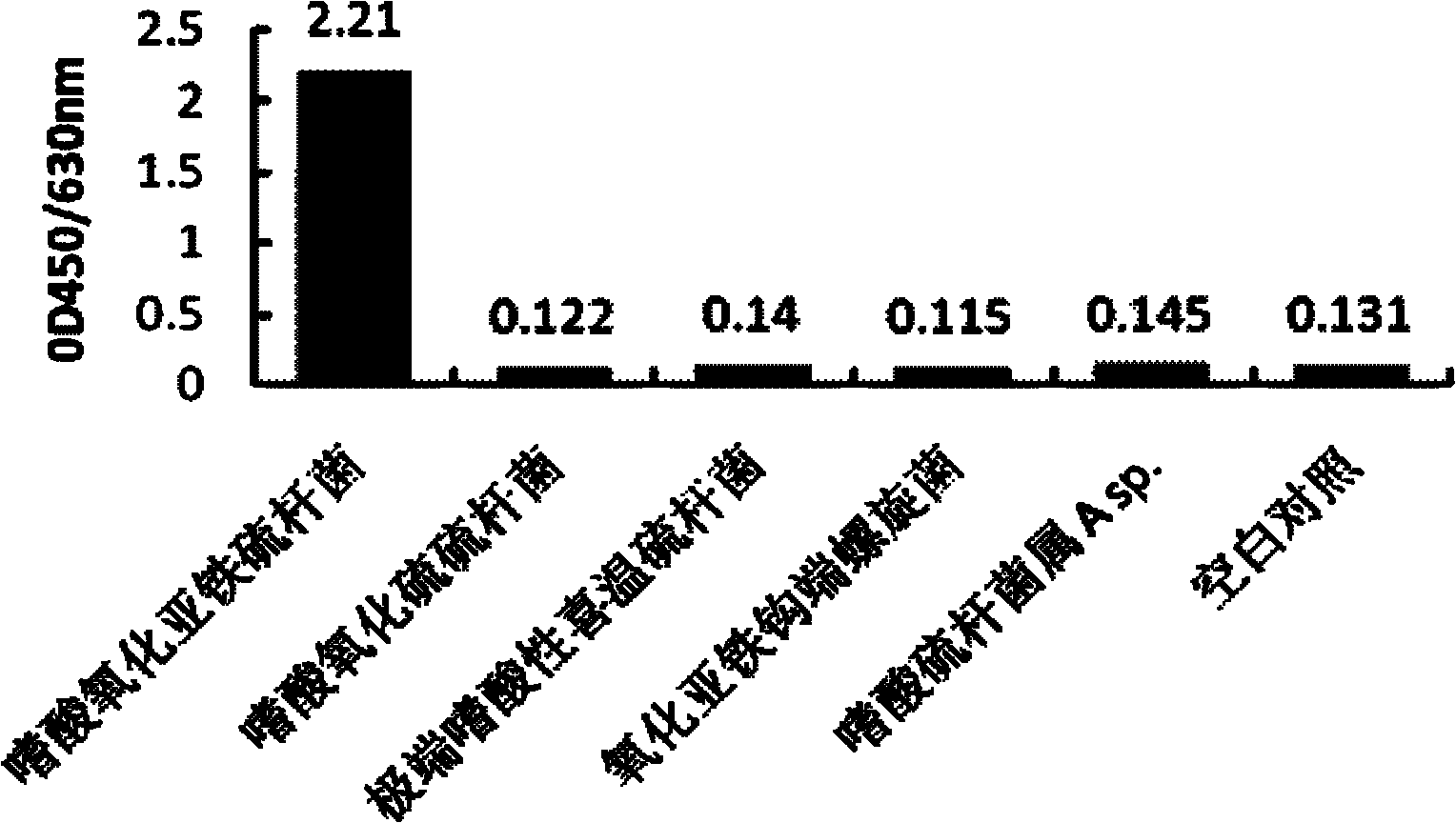
Thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection probe composition and related detection method
ActiveCN102839210AStrong specificityImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationThiobacillus ferrooxidansProtein markers
The invention relates to a thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection probe composition comprising an analysis probe used to be specifically combined with the rRNA of the thiobacillus ferrooxidans, a capturing probe used to be combined on a carrier and is used to be specifically combined with the analysis probe, and a signal probe used to be specifically combined with the analysis probe. The signal probe has protein markers. Preferably, the analysis probe has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 1, the capturing probe has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.2 and has biotin markers, and the signal probe has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 3. The protein markers are fluorescein markers. The invention also provides a thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection method. The thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection probe composition provided by the invention is inelegantly designed. With the detection probe composition, thiobacillus ferrooxidans can be rapidly quantitatively and qualitatively detected. The detection method has the advantages of simple operation and good repeatability. The method is suitable for large-scale popularization.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Evaluation Method for Arteriosclerosis
ActiveUS20130040851A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein markersVon Willebrand factor
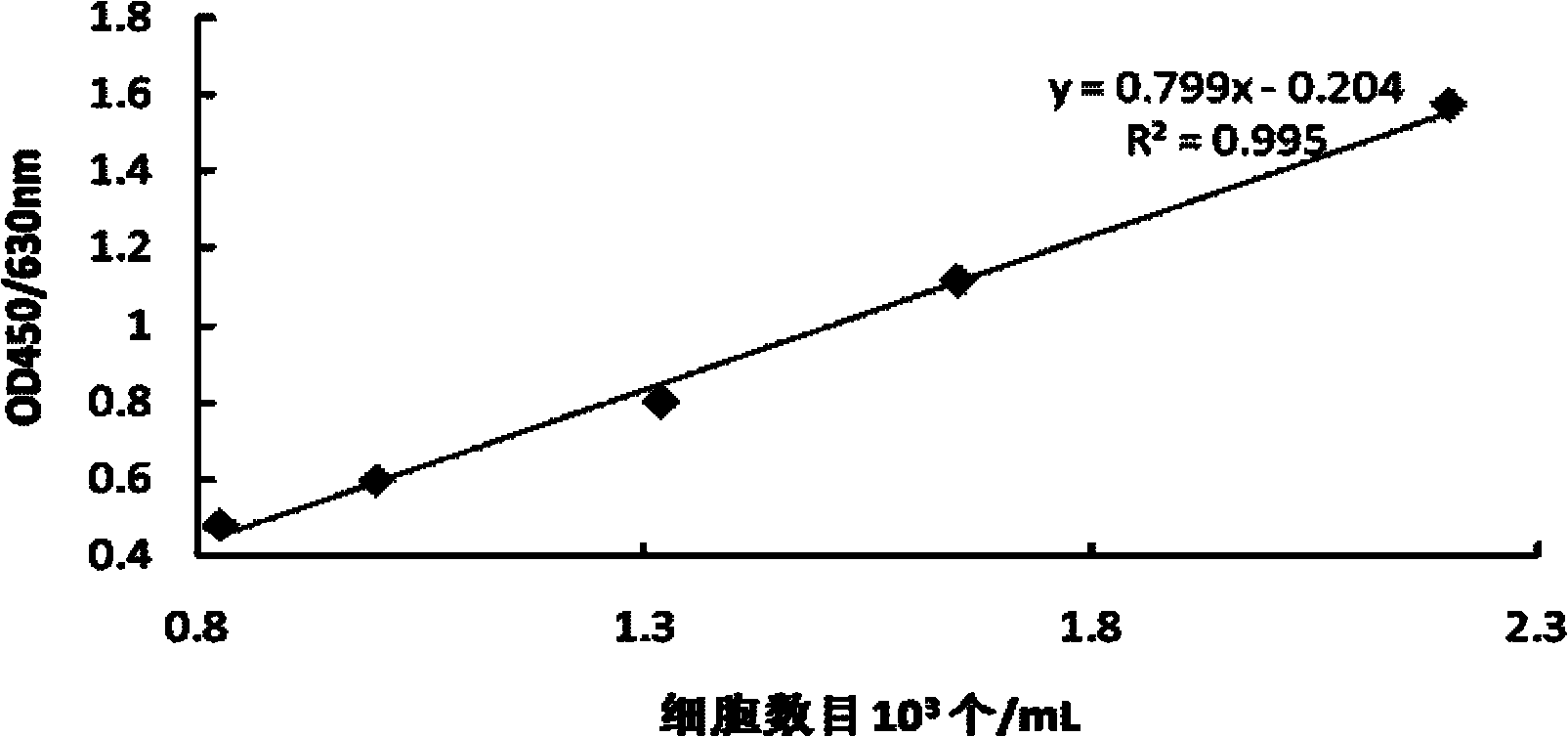
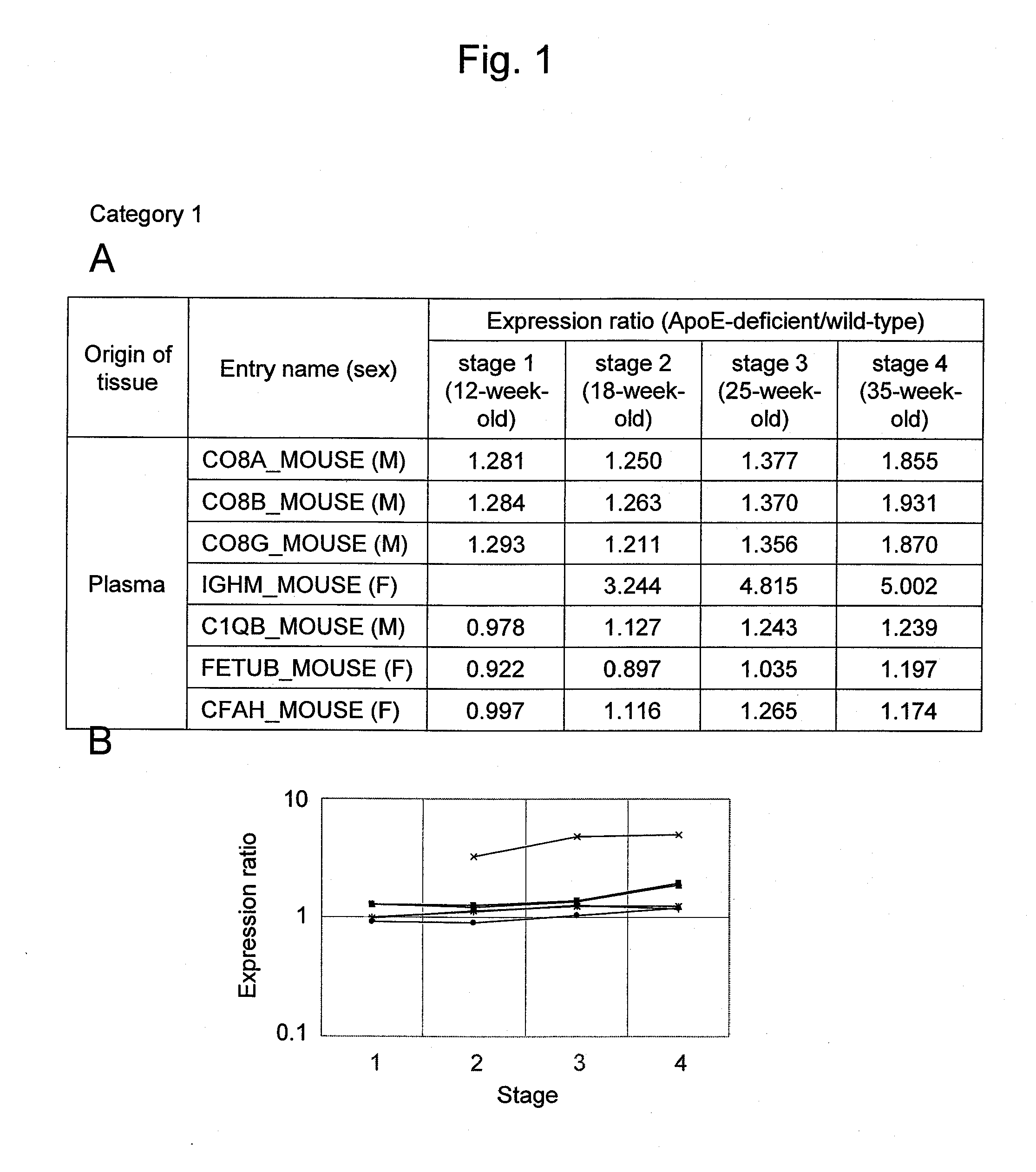
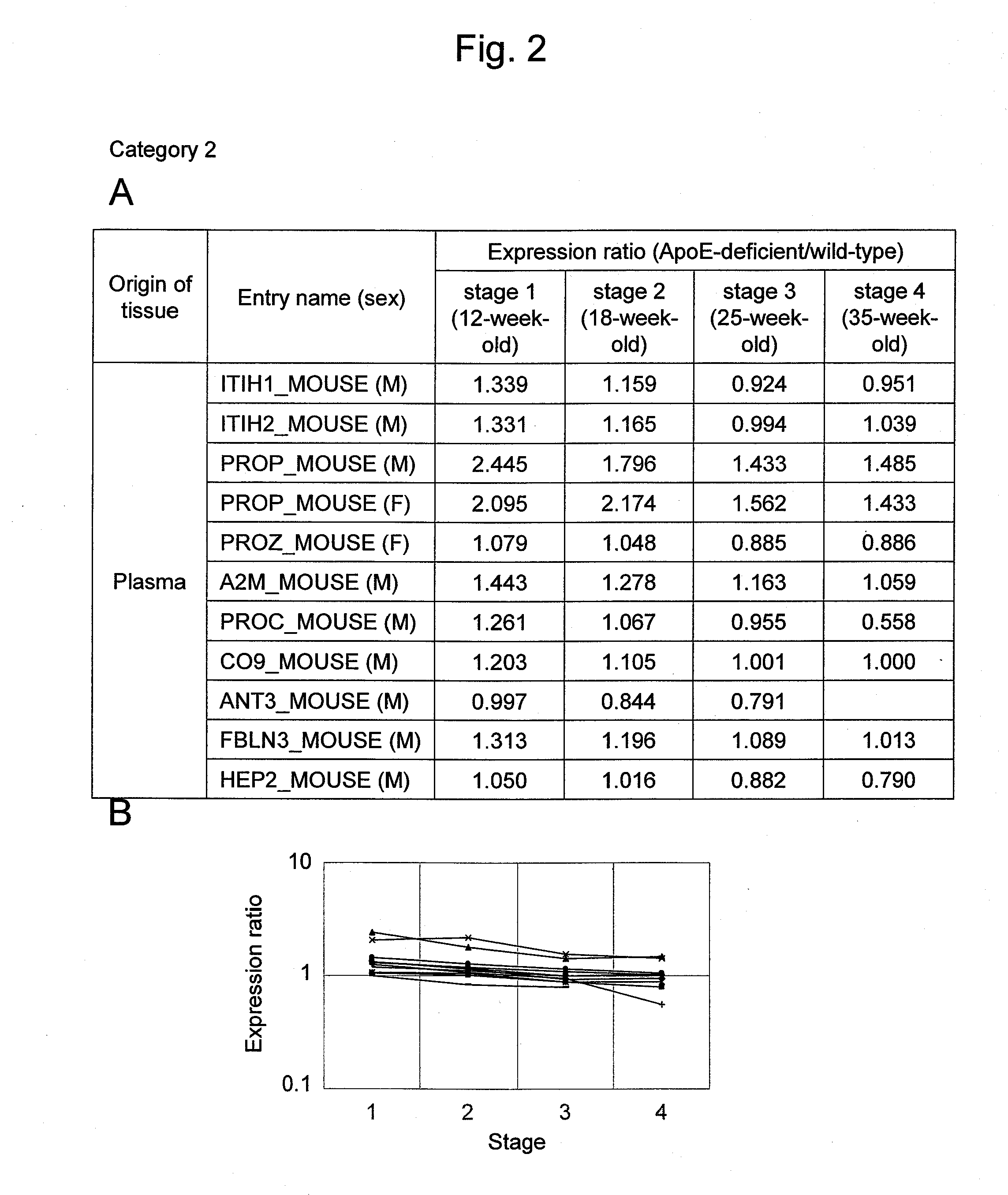
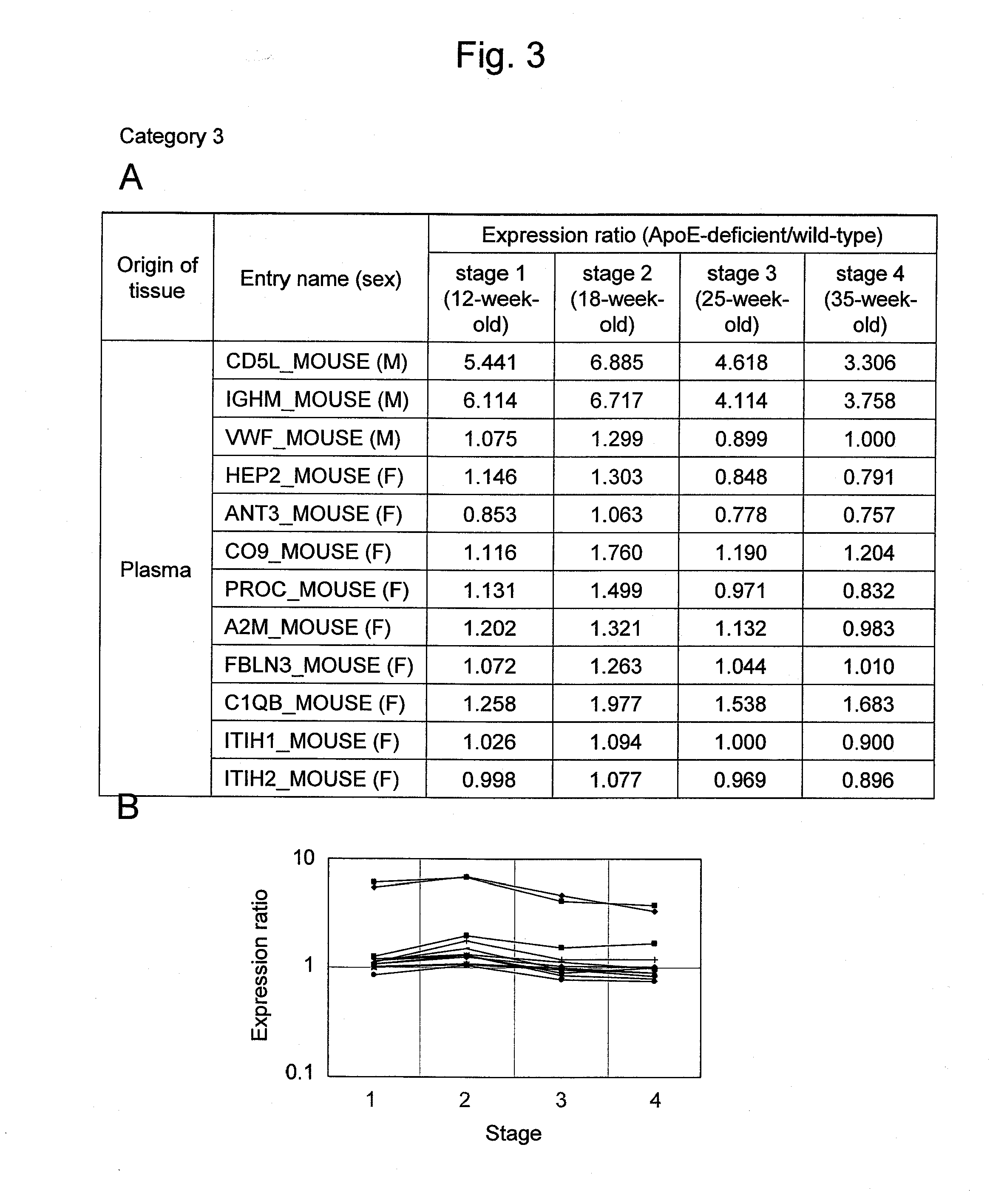
Arteriosclerosis induces cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction. A multi-marker (a group of protein markers) that assesses the accurate pathogenesis of arteriosclerosis and enables the selection of an adequate treatment method for arteriosclerosis and prediction of the progression of arteriosclerosis, and an evaluation method for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of arteriosclerosis that uses said marker group as an indicator have been sought. The present invention relates to A method for evaluation of arteriosclerosis comprising the steps of (a) measuring the expression of von Willebrand factor and / or complement factor D in a sample derived from a subject, (b) measuring the expression of complement component C8 and / or vitamin K-dependent protein Z in the sample derived from the subject, and (c) evaluating arteriosclerosis in the subject on the basis of the results from (a) and (b).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
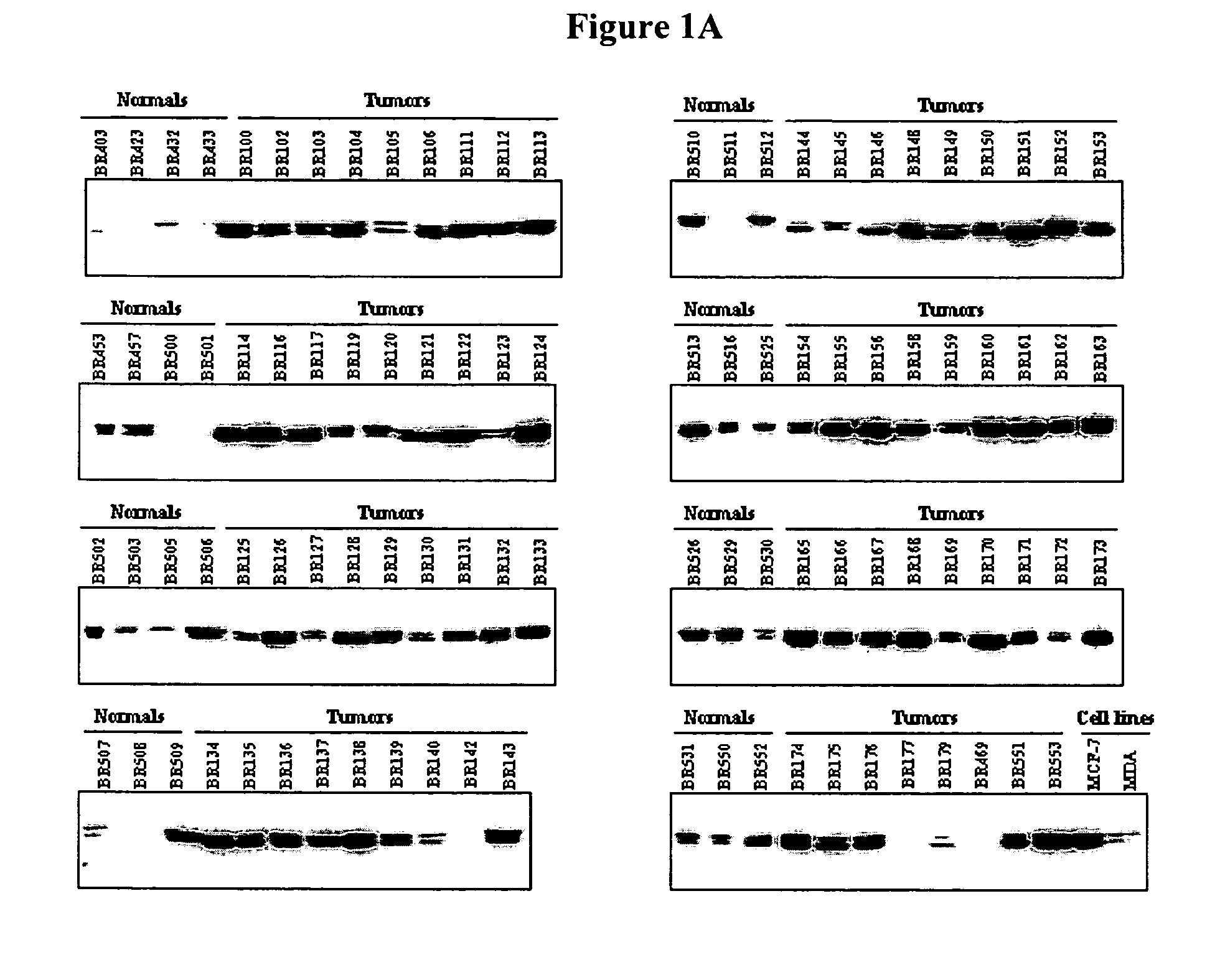
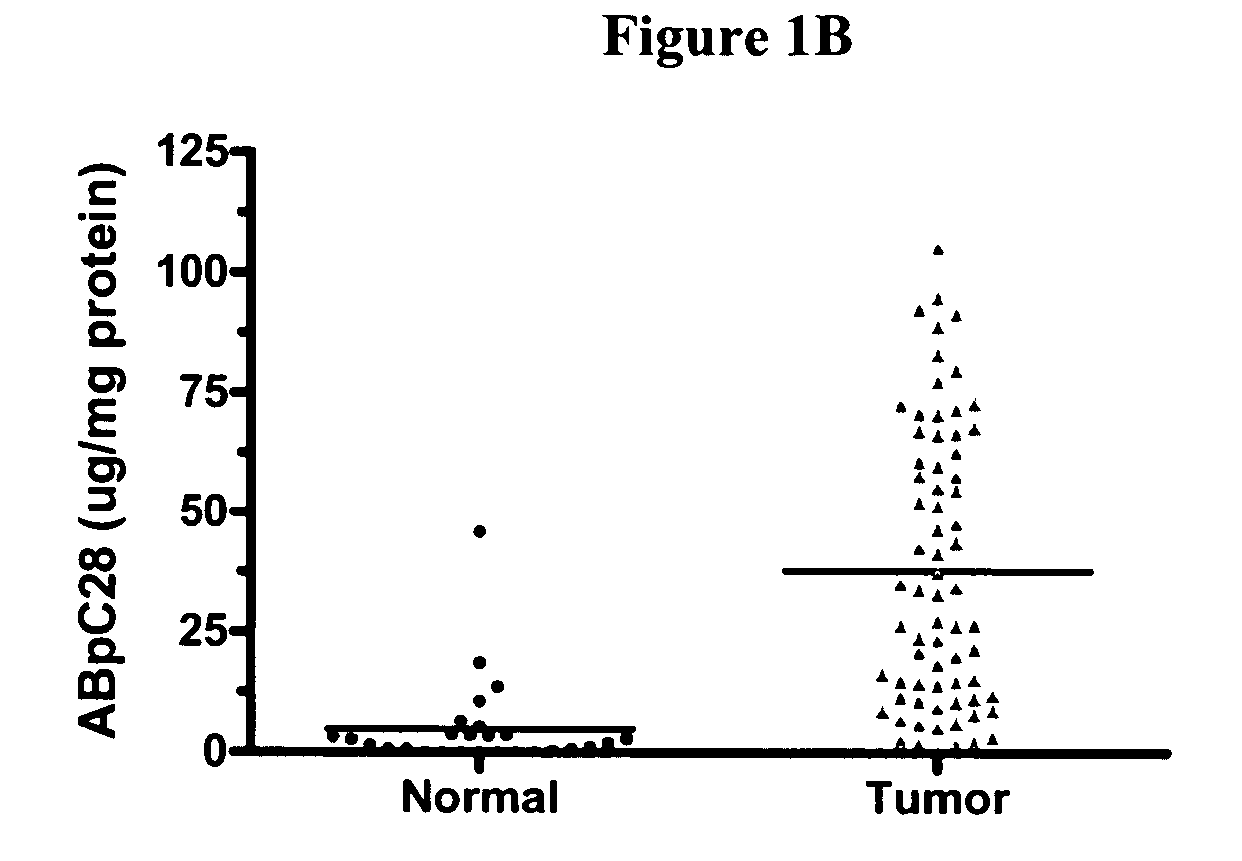
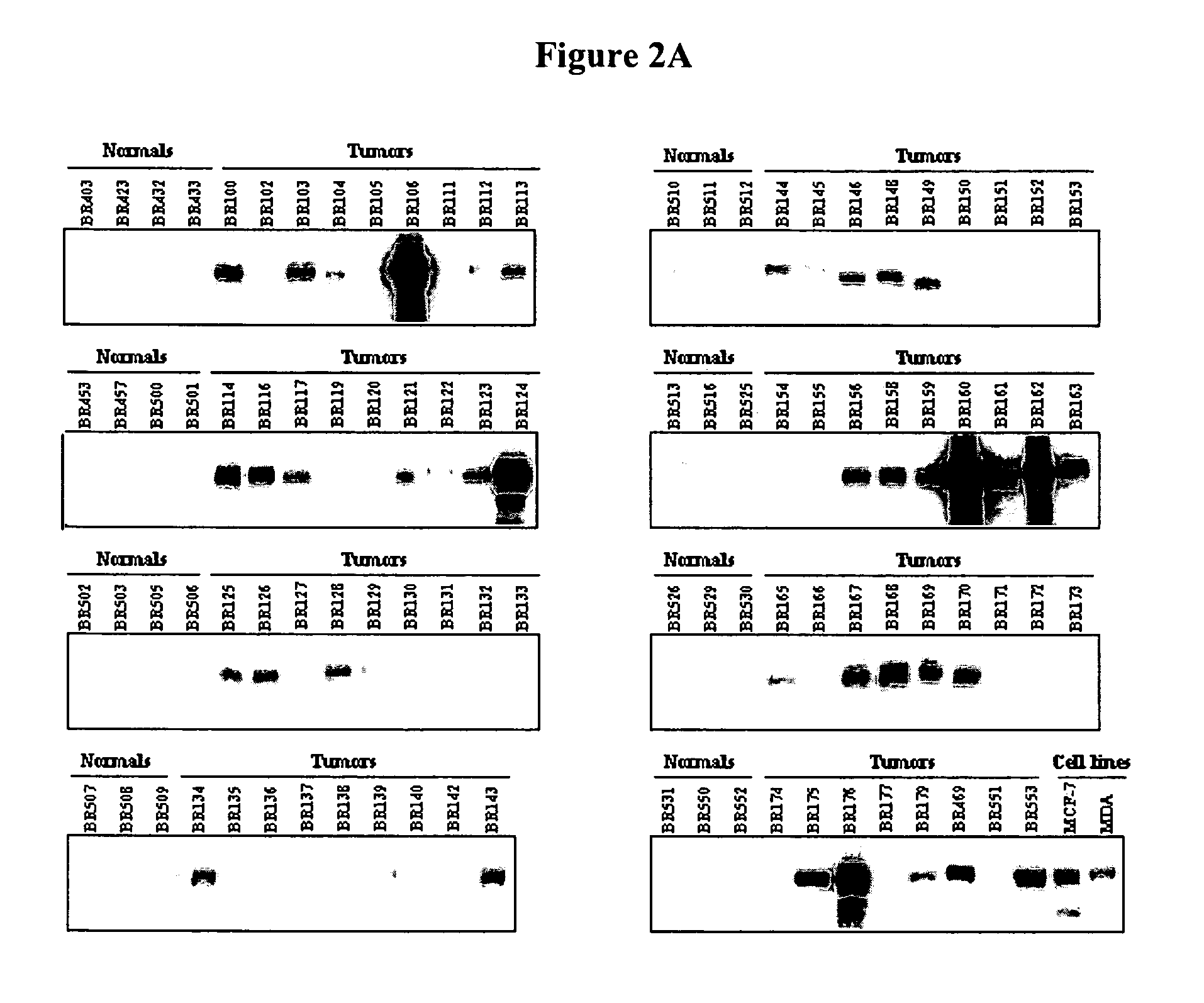
Tissue diagnostics for breast cancer
InactiveUS20070111244A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein markersMammary cells
Disclosed are methods for diagnosing breast cancer in a cell sample by detecting an increase in the levels of expression of protein markers in the cell sample as compared to the levels of expression of the same protein markers in a normal, nonneoplastic breast cell sample. Also disclosed is a device for diagnosis of cancer in a cell sample.
Owner:AURELIUM BIOPHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com