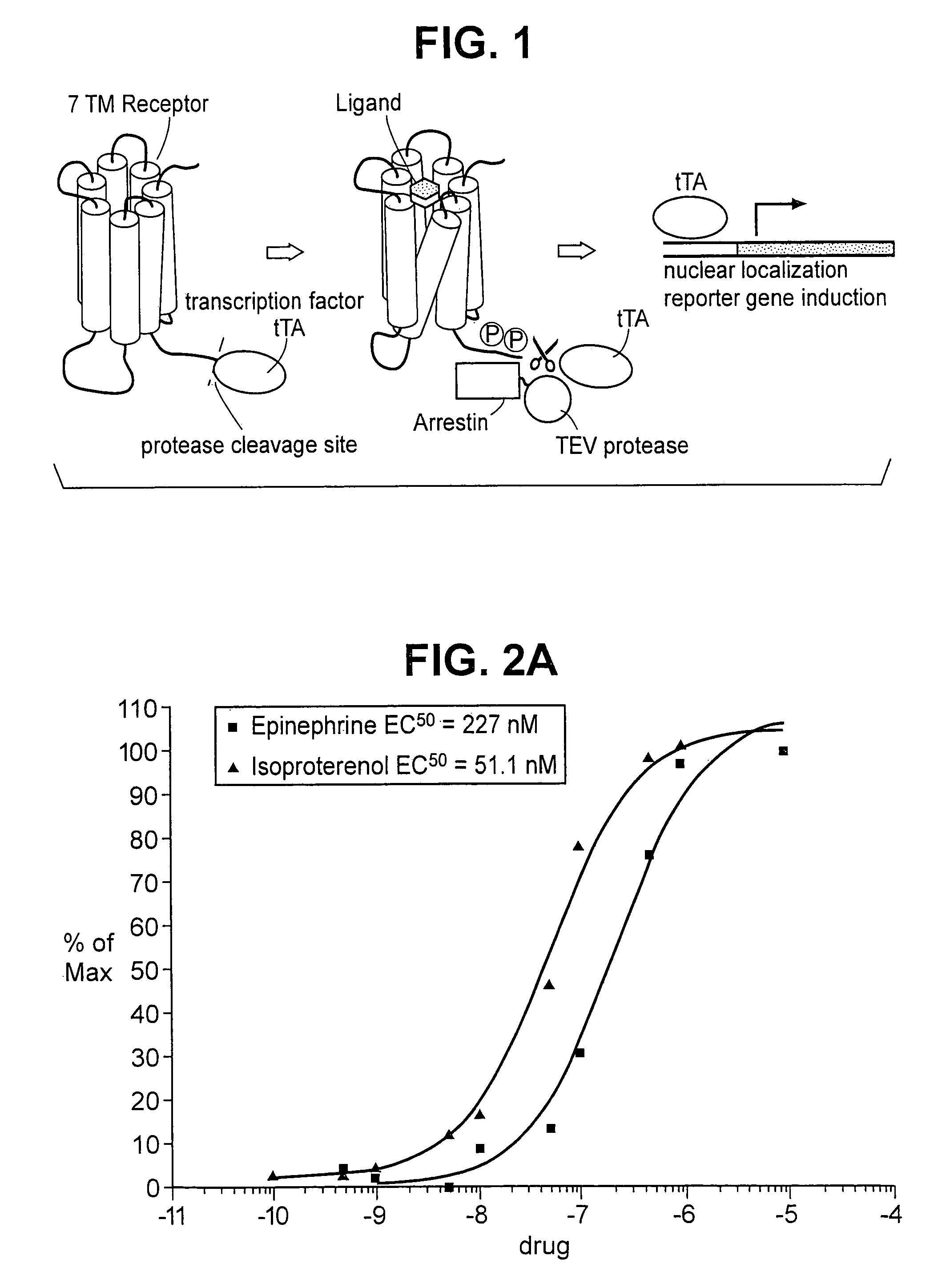
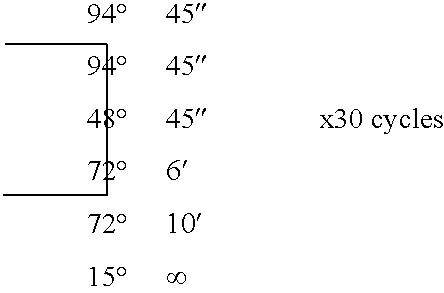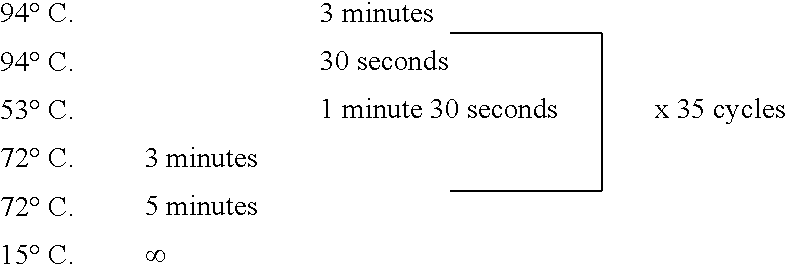Patents
Literature
317 results about "Protein–protein interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) are the physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events steered by electrostatic forces including the hydrophobic effect. Many are physical contacts with molecular associations between chains that occur in a cell or in a living organism in a specific biomolecular context.
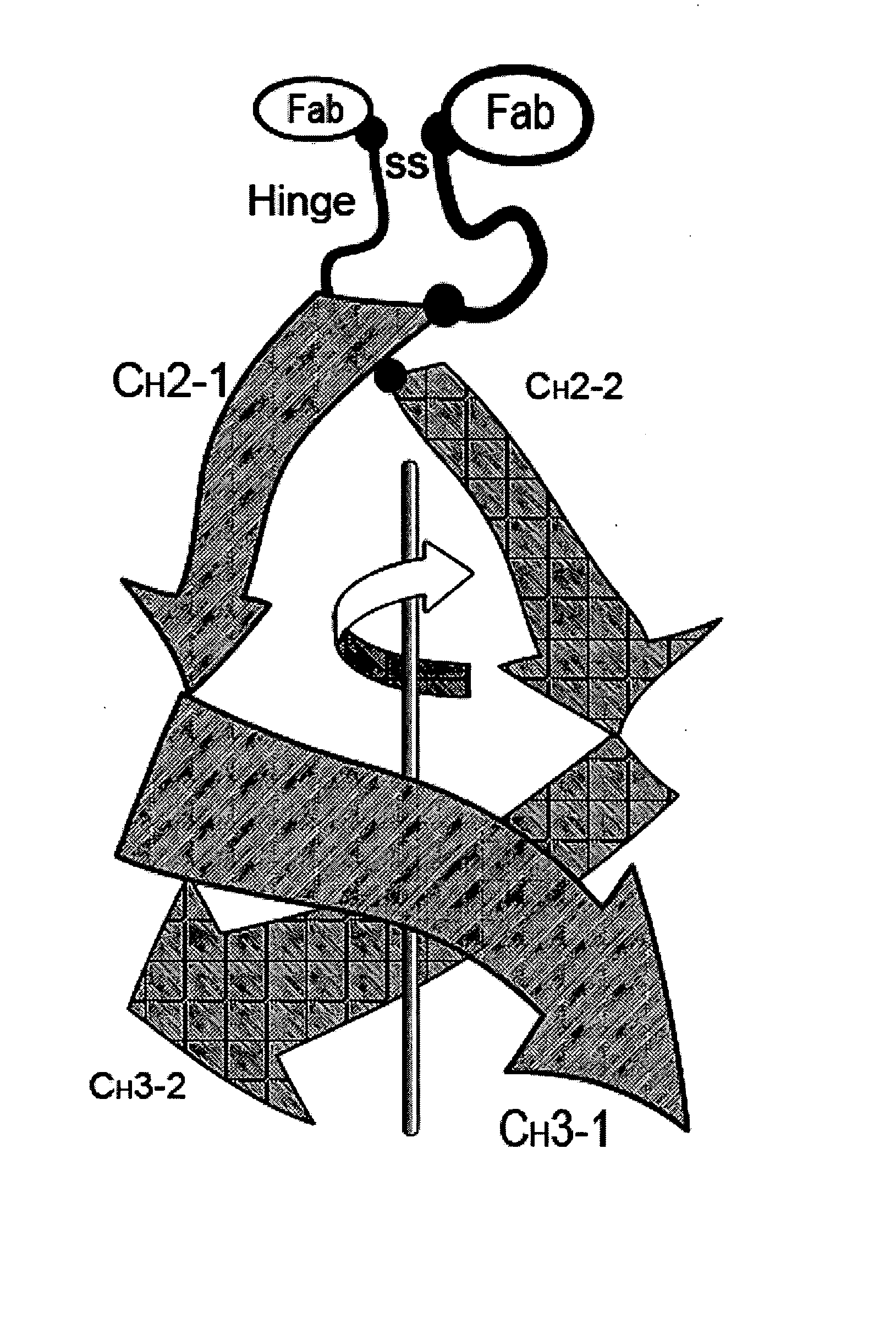
Engineered heterodimeric protein domains
ActiveUS20070287170A1Easy to assembleStrong specificitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyAmino acid
The present invention provides an engineered multidomain protein including at least two nonidentical engineered domains, each of which contains a protein-protein interaction interface containing amino acid sequence segments derived from two or more existing homologous parent domains, thereby conferring on the engineered domains assembly specificities distinct from assembly specificities of the parent domains. In particular, the engineered domains form heterodimers with one another preferentially over forming homodimers. Methods of designing and using the engineered proteins are also included.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
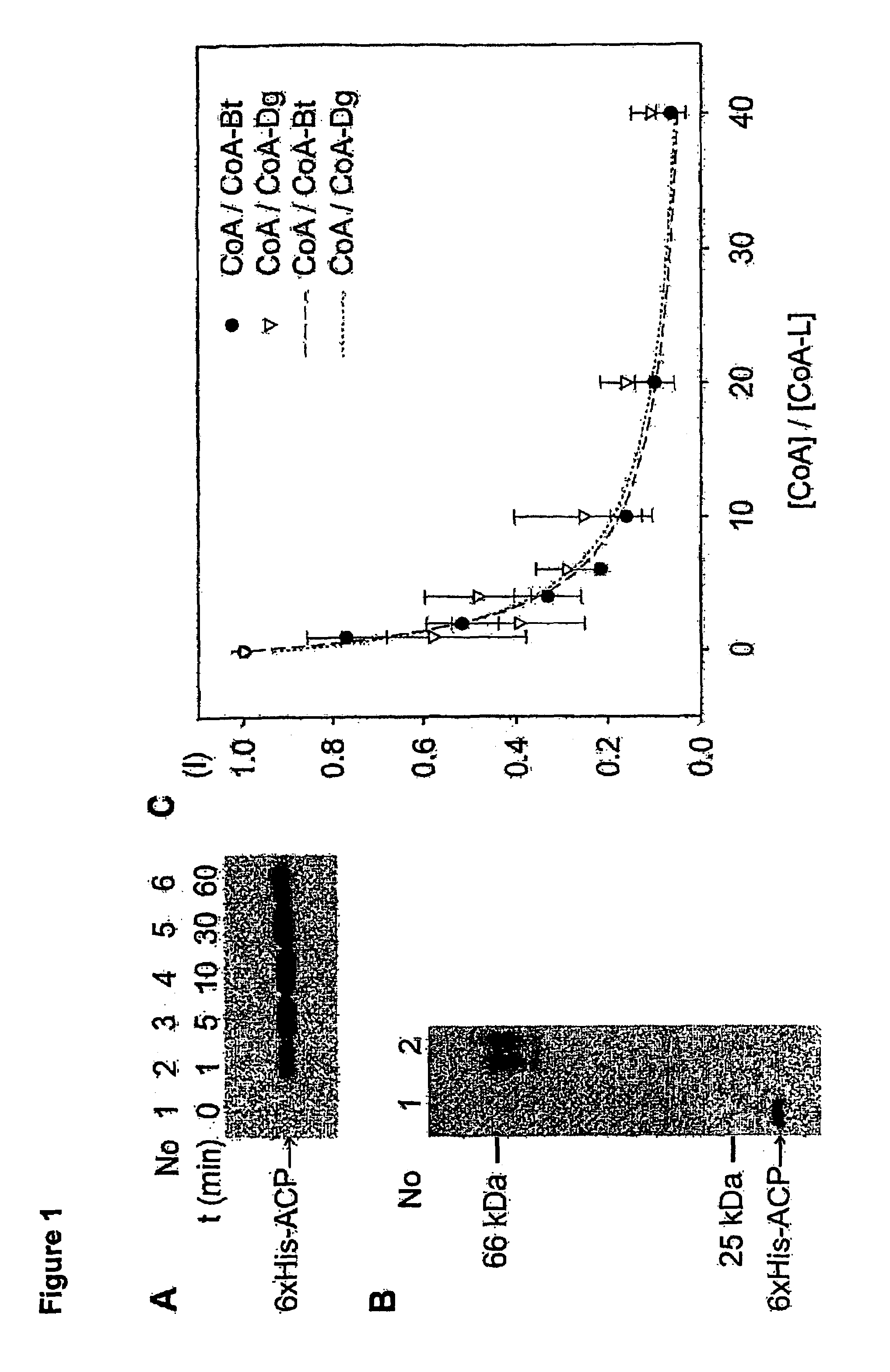
Methods for protein labeling based on acyl carrier protein
InactiveUS7666612B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCoenzyme A biosynthesisCarrier protein
A method for labeling acyl carrier protein (ACP) fusion proteins with a wide variety of different labels is disclosed. The method relies on the transfer of a label from a coenzyme A type substrate to an ACP fusion protein using a holo-acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS) or a homologue thereof. The method allows detecting and manipulating the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such labels are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilization of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Detection of ion channel or receptor activity
InactiveUS20060148104A1Easy accessImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeterologousBiological activation
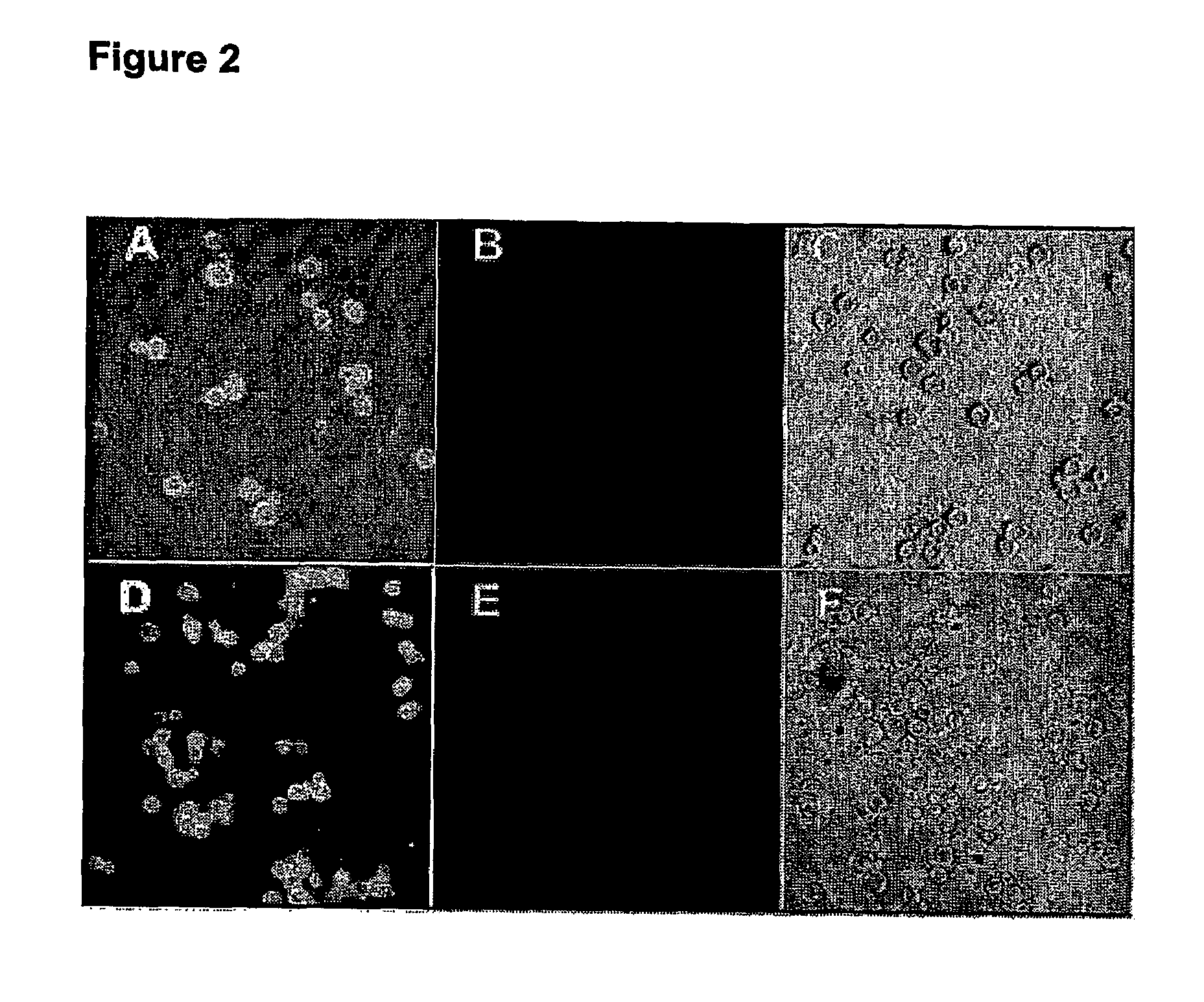
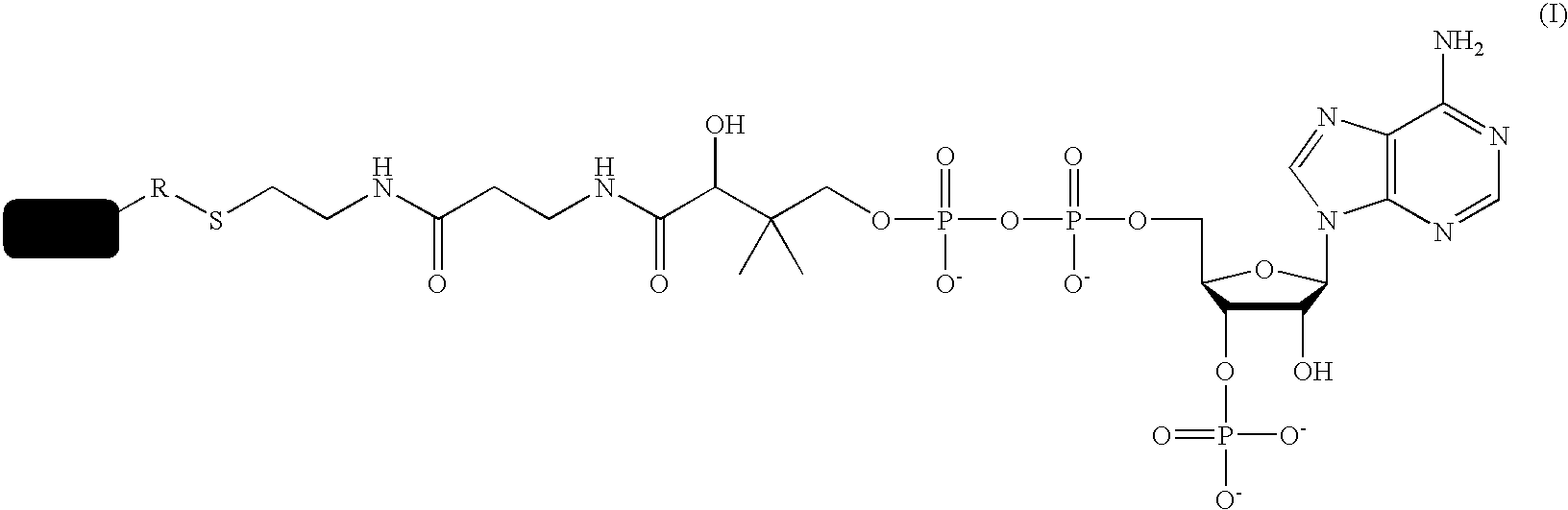
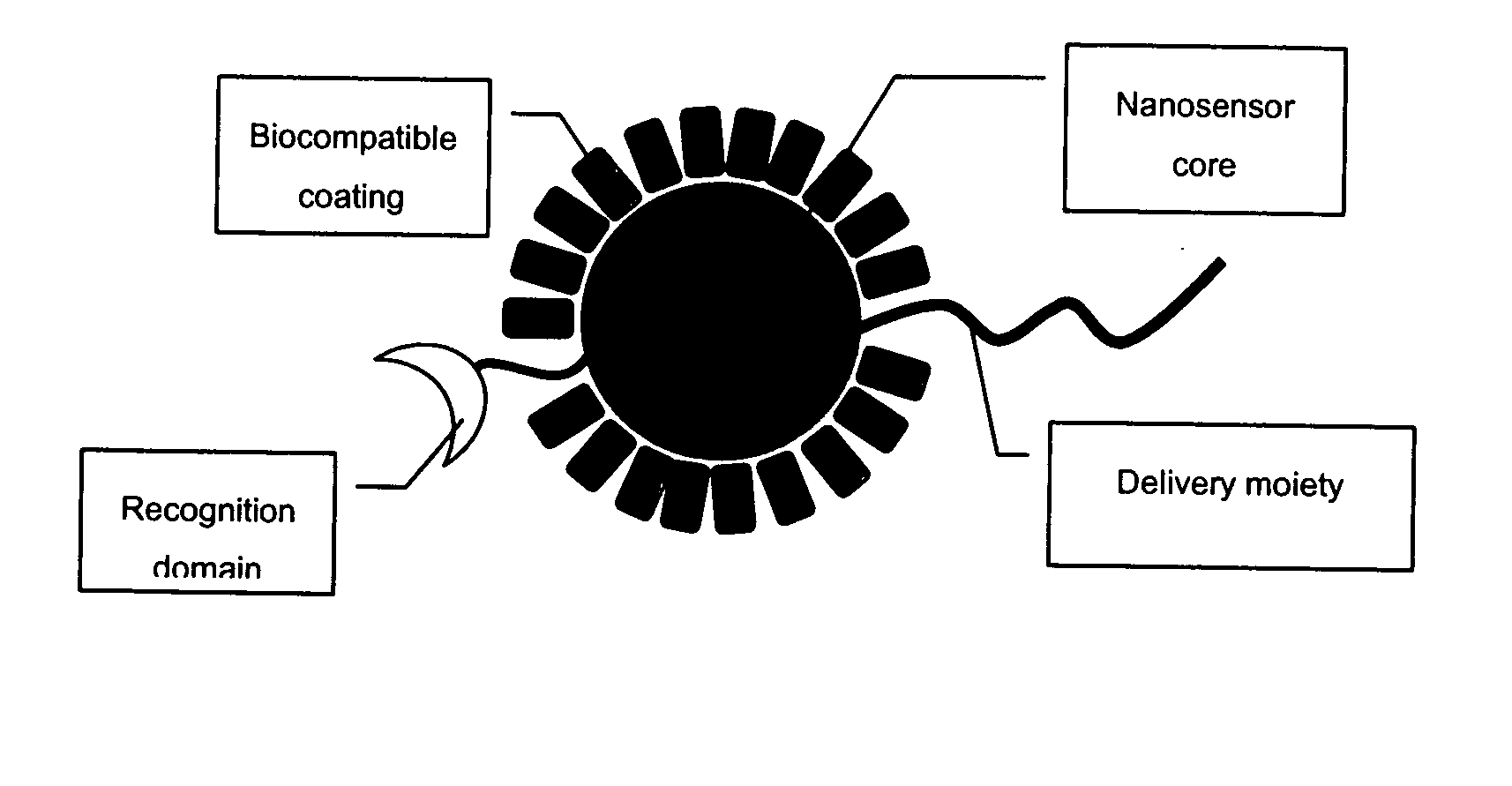
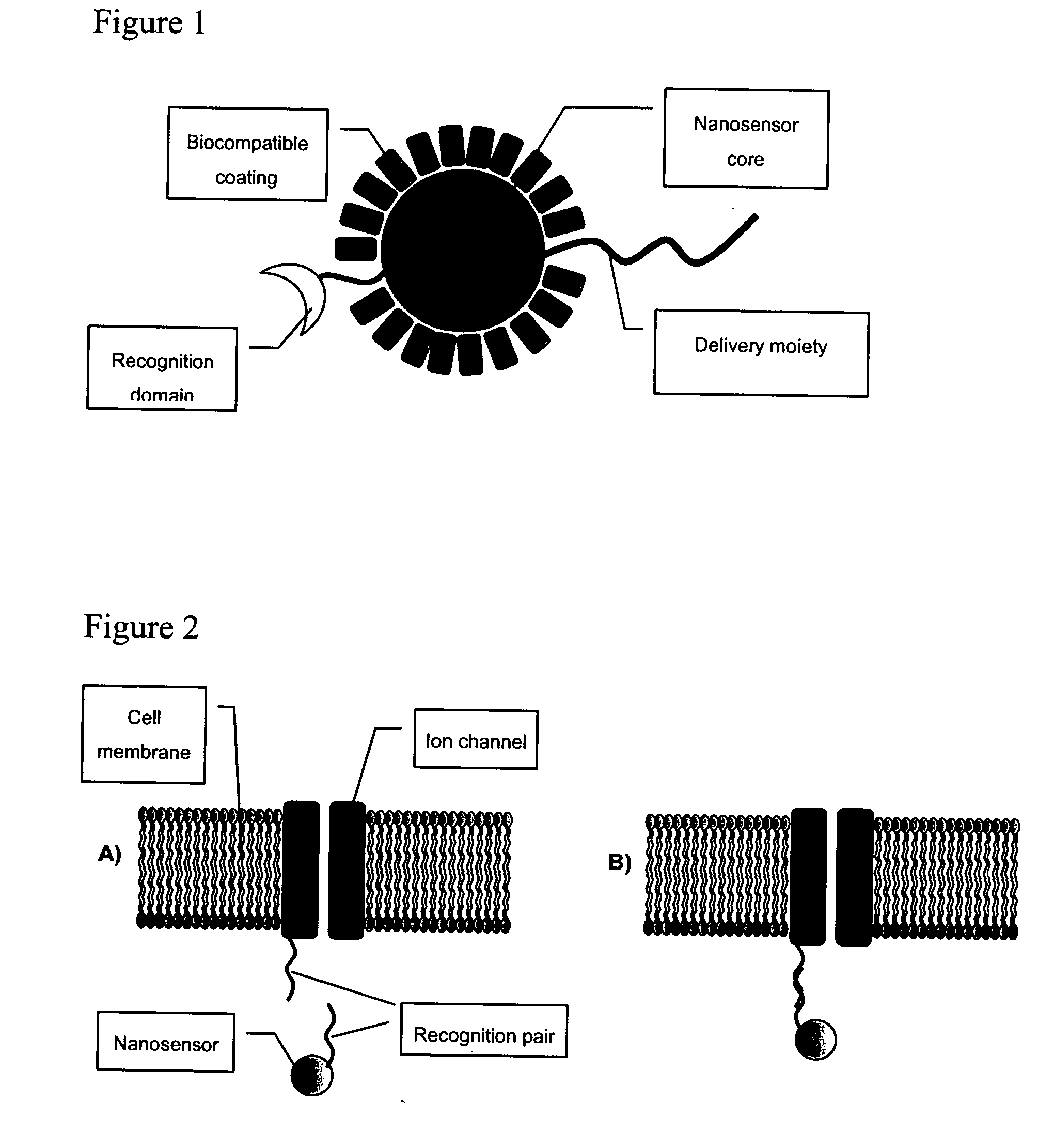
The invention provides nanosensors and nanosensor components for the detection of ion channel activity, receptor activity, or protein protein interactions. Certain of the nanosensor components comprise a nanoparticle and recognition domain. Following contact with cells and, optionally, internalization of the nanosensor component by a cell, the recognition domain binds to a target domain, e.g., a heterologous target domain, of a polypeptide of interest such as an ion channel subunit, G protein coupled receptor (GPCR), or G protein subunit. Ion channel activity, GPCR activity, or altered protein interaction results in a detectable signal. The nanoparticles may be functionalized so that they respond to the presence of an ion by altering their proximity. Certain of the nanosensors utilize the phenomenon of plasmon resonance to produce a signal while others utilize magnetic properties, RET, and / or ion-sensitive moieties. Also provided are polypeptides, e.g., ion channel subunits, comprising a heterologous target domain, and cell lines that express the polypeptides. Further provided are a variety of methods for detecting ion channel activity, receptor activity, or protein interaction and for identifying compounds that modulate one or more of these. In certain embodiments the invention allows the user to detect the activity of specific ion channels even in the presence of other channels that permit passage of the same ion(s) or result in activation of the same downstream targets, thereby achieving improved specificity in high throughput screens while at the same time providing a high signal to noise ratio.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +1
Engineered heterodimeric protein domains
ActiveUS8871912B2Strong specificityEasy to assembleHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesBiotechnologyAmino acid
The present invention provides an engineered multidomain protein including at least two nonidentical engineered domains, each of which contains a protein-protein interaction interface containing amino acid sequence segments derived from two or more existing homologous parent domains, thereby conferring on the engineered domains assembly specificities distinct from assembly specificities of the parent domains. In particular, the engineered domains form heterodimers with one another preferentially over forming homodimers. Methods of designing and using the engineered proteins are also included.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
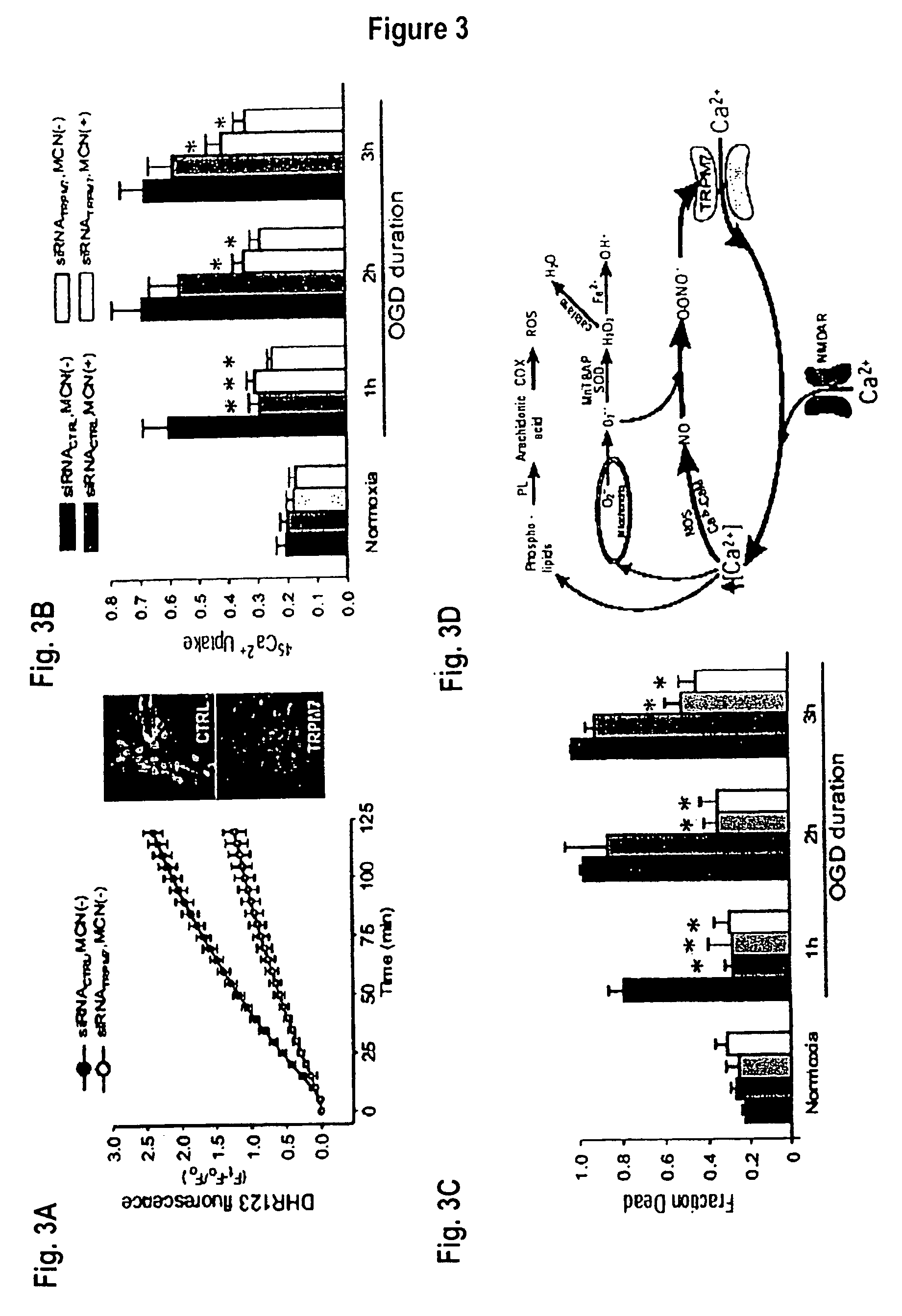
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
This invention relates to methods of reducing the damaging effect of an injury to mammalian cells by treatment with compounds which reduce cell death or dysfunction, including cellular damage following episodes of tissue ischemia, trauma, epilepsy, and acute or chronic degeneration. The invention discloses methods of treating these disorders by administering inhibitors that disrupt protein-protein interactions involved in these disorders, screening methods to identify such inhibitors and specific compositions useful for treating these disorders.
Owner:NONO INC
Direct mass spectrometric analysis of drug candidates targeting protein complexes
ActiveUS20100099200A1Improve throughputEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein targetProtein-protein complex
The invention relates to a method of using high mass matrix assisted laser desorption-ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the effect of drug candidates on protein complexes such as protein-protein interactions in purified samples or complex biological matrices, as well as to the use of this method for lead compound optimization, drug characterization, drug manufacturing processes, and drug quality control processes, including automated high throughput applications.
Owner:COVALX
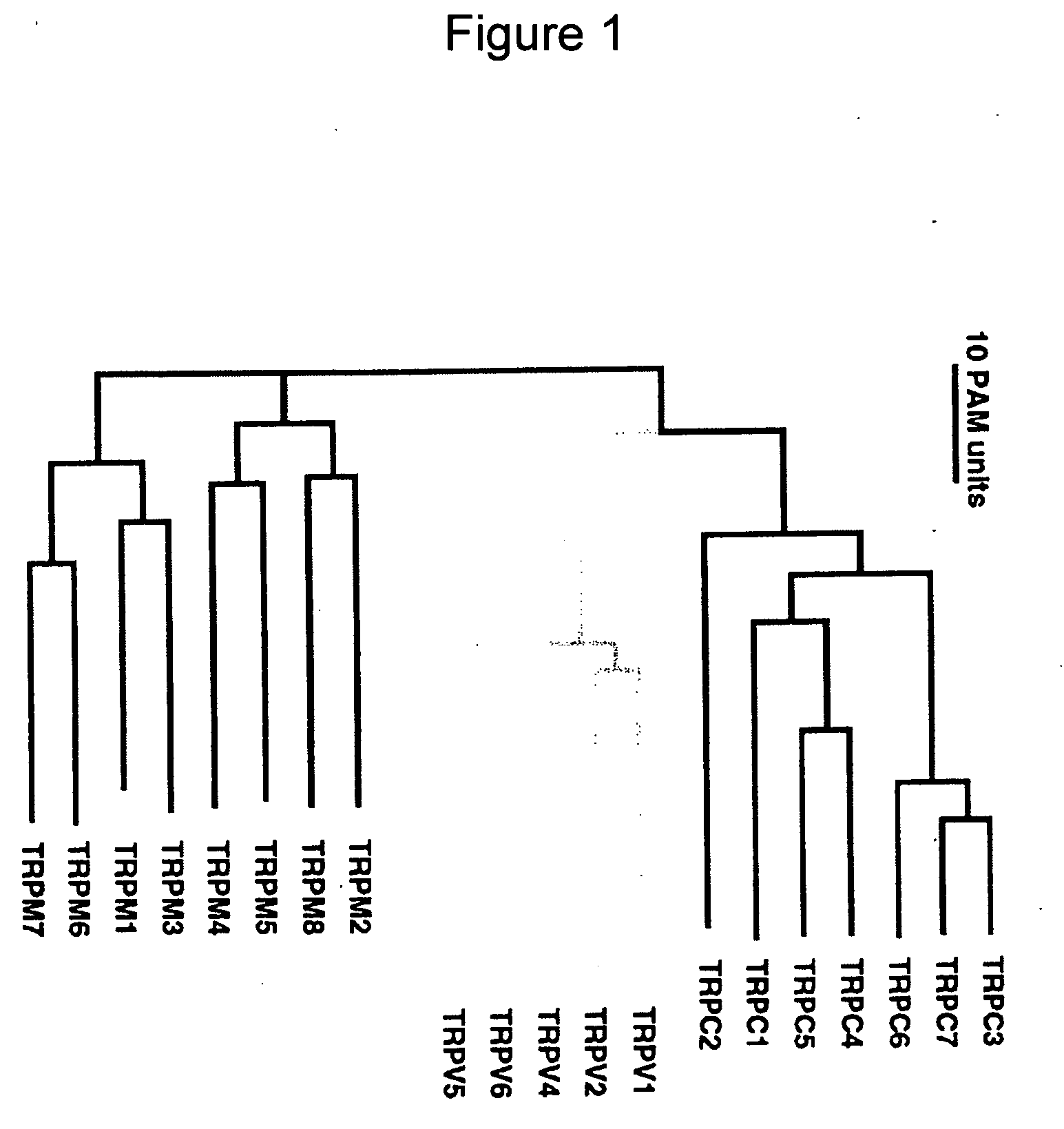
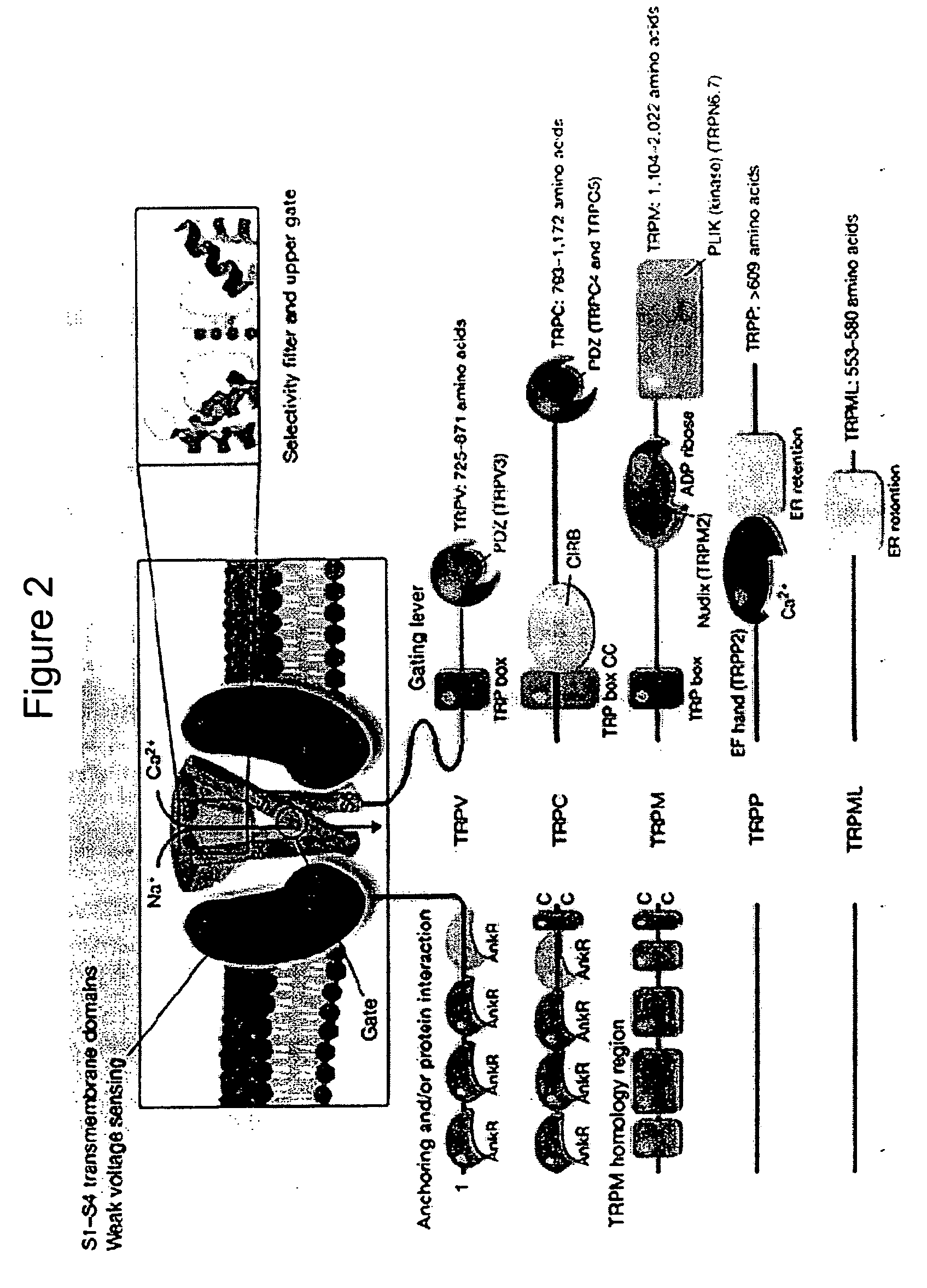
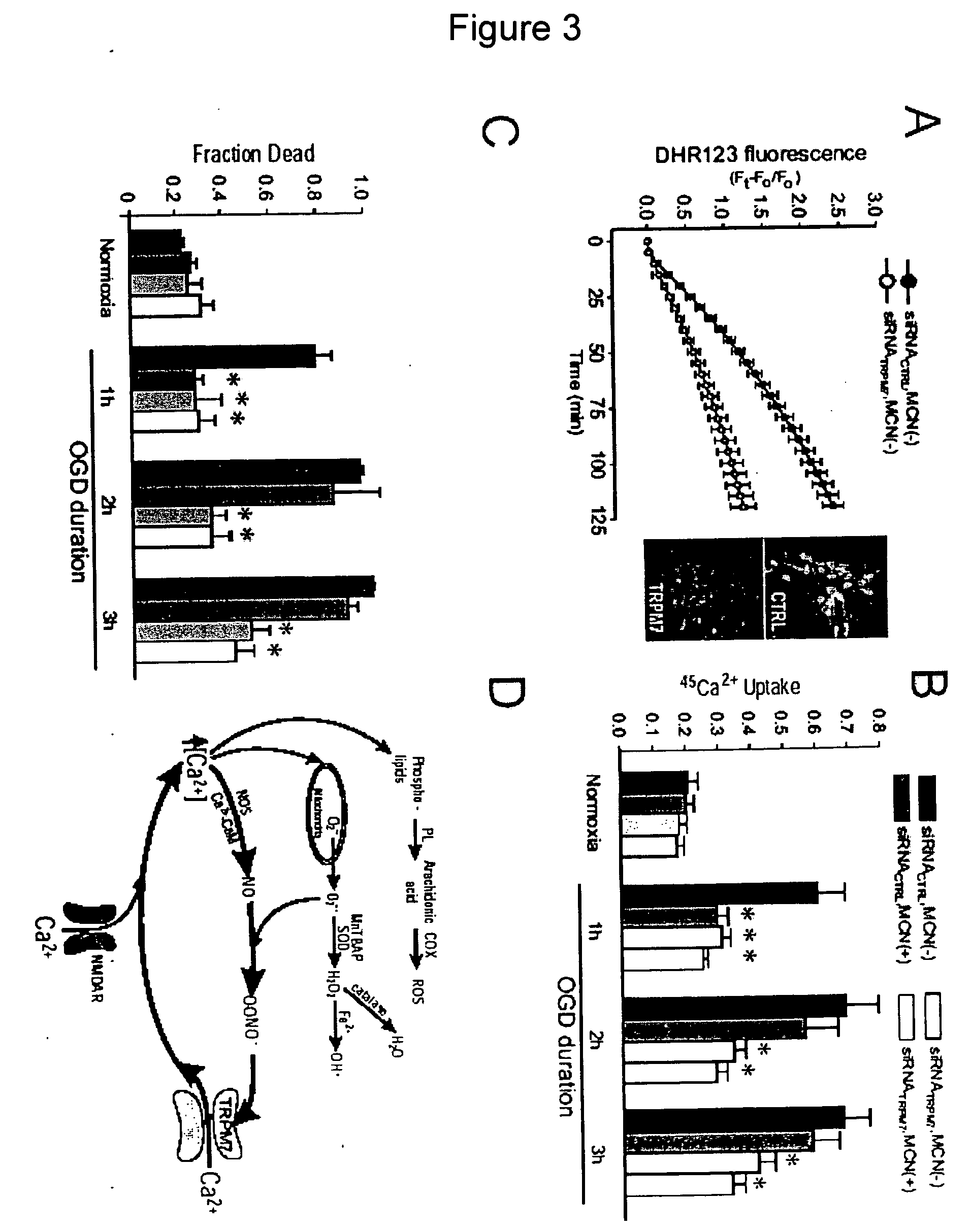
Method of determining inhibition of binding to TRPM7 protein
This invention relates to methods of reducing the damaging effect of an injury to mammalian cells by treatment with compounds which reduce cell death or dysfunction, including cellular damage following episodes of tissue ischemia, trauma, epilepsy, and acute or chronic degeneration. The invention discloses methods of treating these disorders by administering inhibitors that disrupt protein-protein interactions involved in these disorders, screening methods to identify such inhibitors and specific compositions useful for treating these disorders.
Owner:NONO INC
Target sequences for synthetic molecules
The invention is based on the discovery that certain biarsenical molecules react with specified target sequences, thereby providing a facile means for labeling polypeptides containing the target sequence. The invention is useful in creating stable mammalian cell lines expressing a certain tetracysteine tagged polypeptides, thereby overcoming toxicity associated with native tetracysteine. In addition, the invention allows for orthogonal labeling of polypeptides, thereby allowing for the observation of protein-protein interactions and conformational changes in proteins, for example.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
High voltage electrospinning method for preparing multi-fluorescence-encoded micro-beads
InactiveCN101338189AEasy to operateWide applicabilityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the fluorescence-coded technology field and in particular relates to a high voltage electric spinning preparation method of multiplex fluorescence coding microsphere. In the method, fluorescent materials (quantum dots material or fluorescent dyes) with different quantities and different fluorescent characteristics are dispersed in polymer solution (or inorganic matter sol). Then, through the high voltage electric spinning process, the coding microsphere with controllable size and adjustable fluorescent strength and lighting wavelength is obtained. The quantum dots material can be used alone or used in mixing way. The fluorescent material can be used alone or used in mixing way. The flurescent material can also be used together with the quantum dots material. The coding microsphere prepared through the invention can provide fluorescent probes in large quantities for the fields of gene expression, protein-protein interaction, simultaneous detection of various diseases, high throughput screening, combinational chemistry, etc. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, wide application, low cost, stable fluorescence performance, and the like, and is provided with good application and expansion value.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
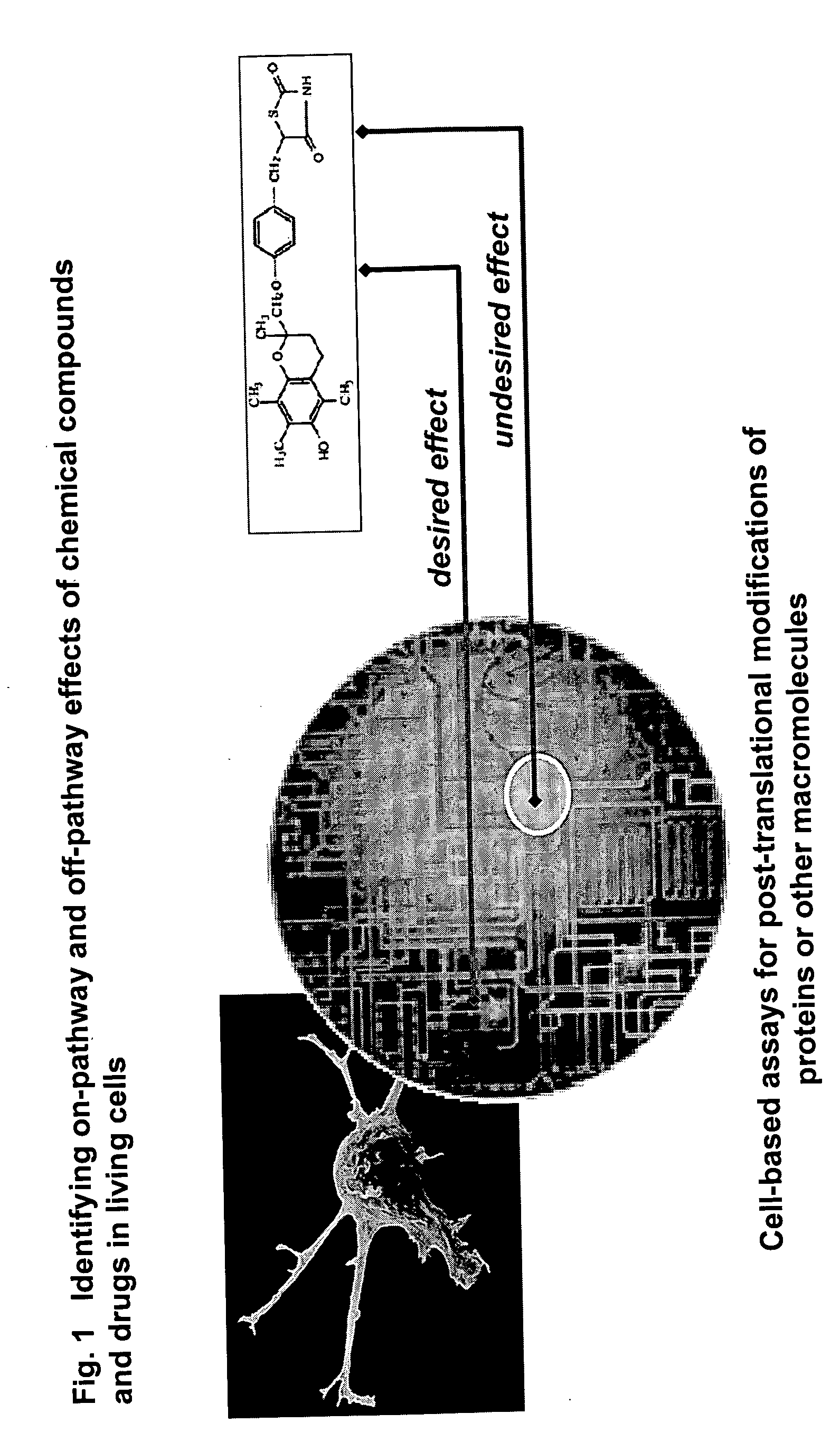
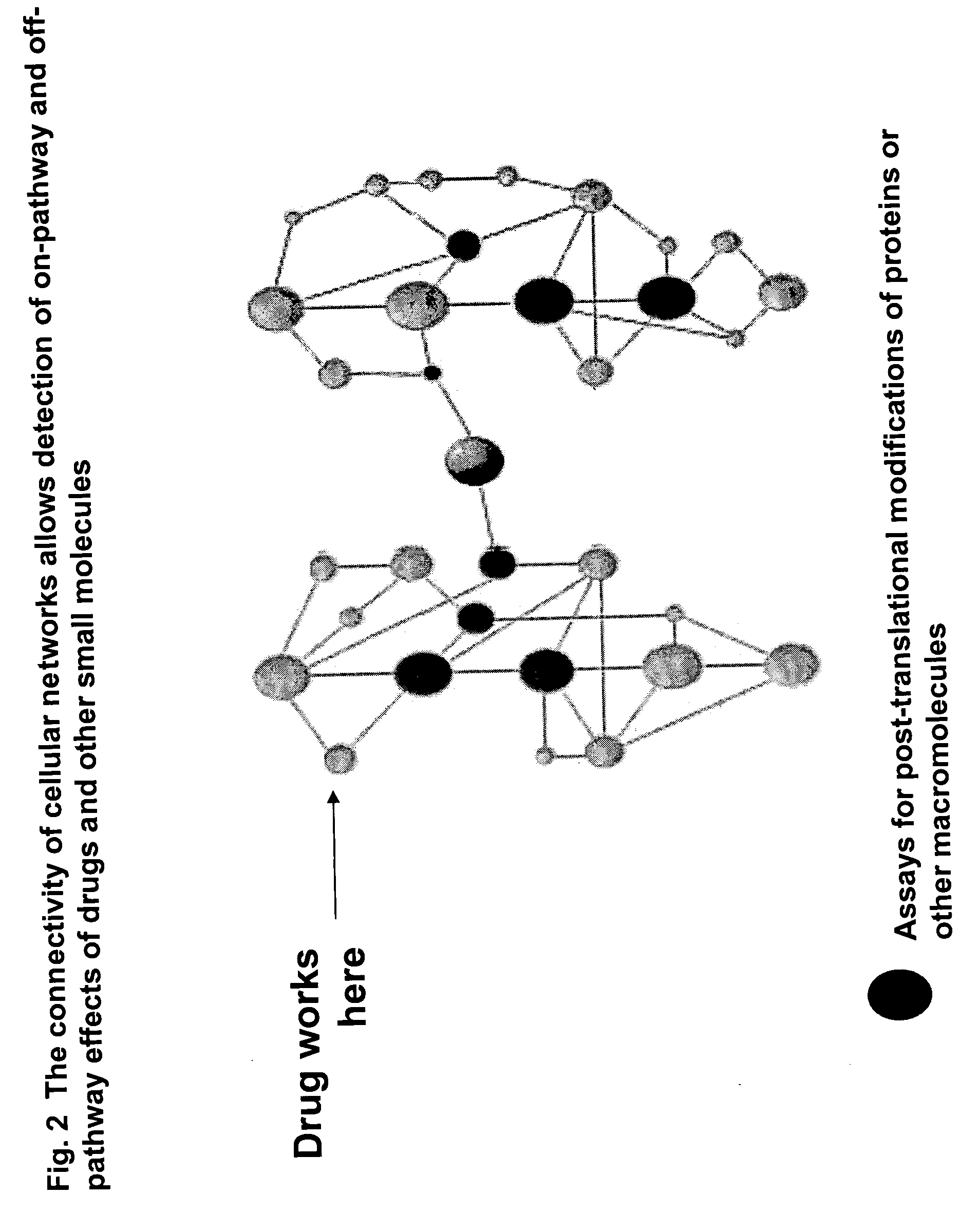
Pharmacological profiling of drugs with cell-based assays
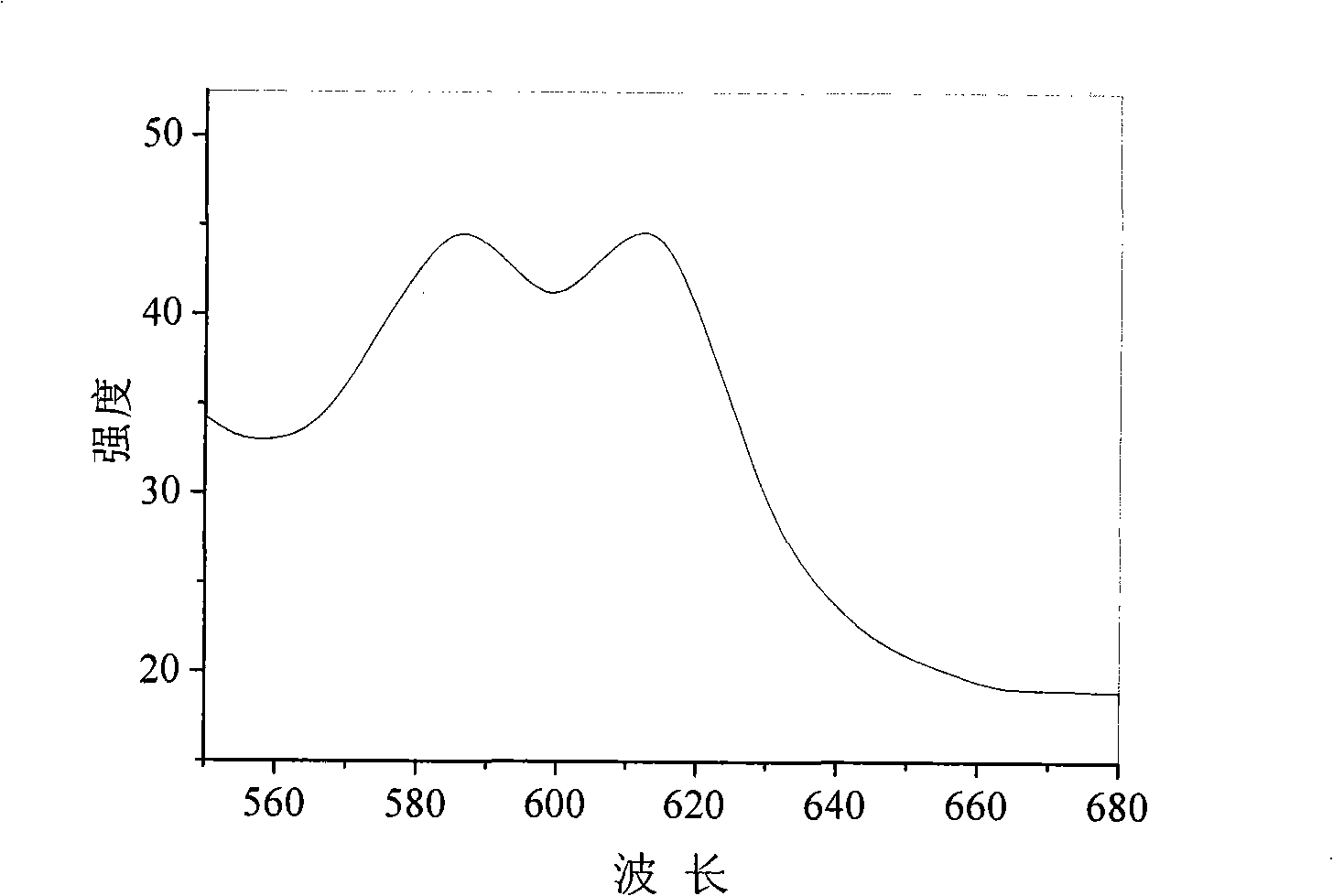
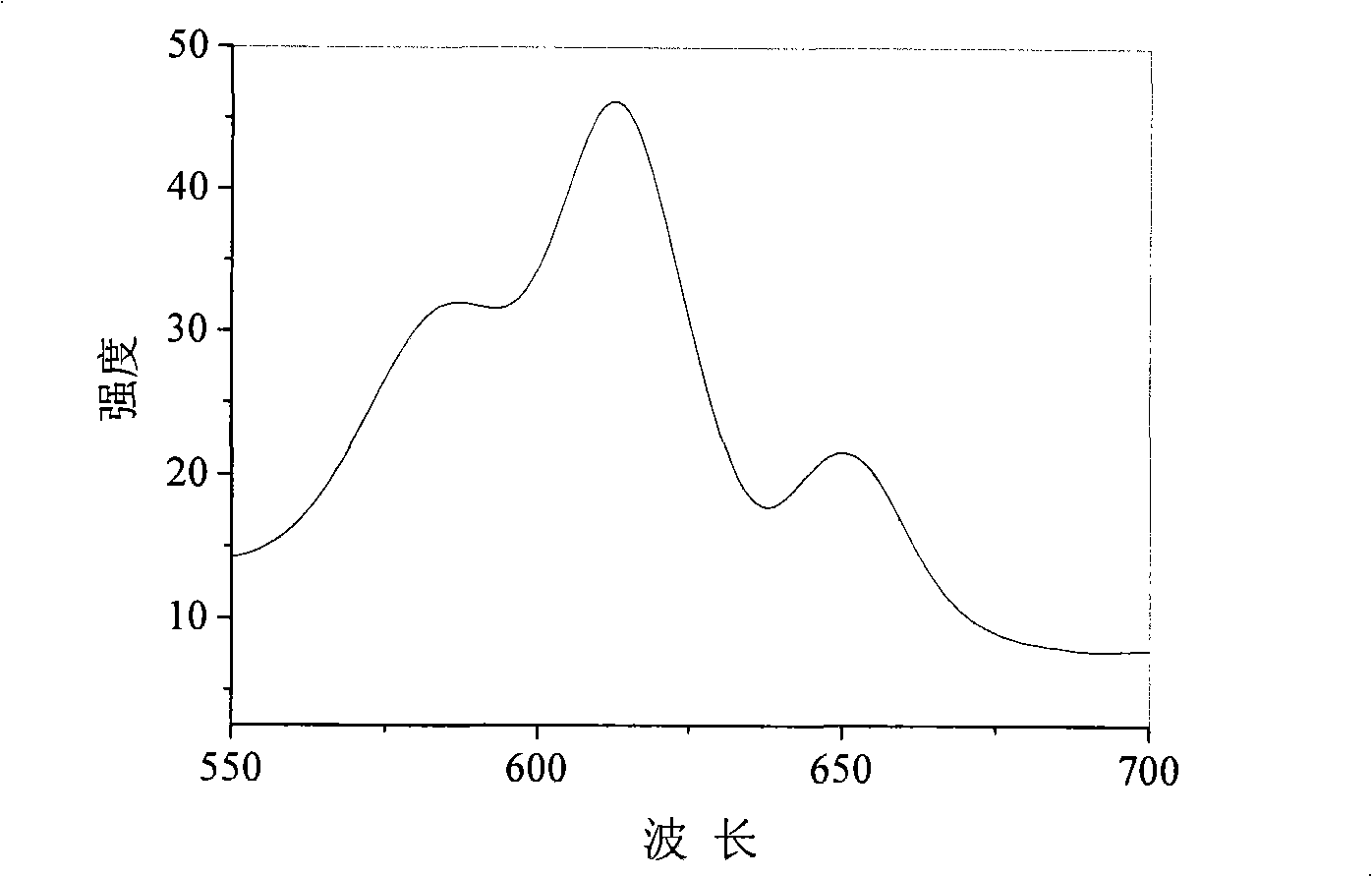
InactiveUS20060040338A1Enable optimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningPost translationalAssay
The instant invention provides a method for establishing safety profiles for chemical compounds, as well as pharmacological profiling said method comprising (A) testing the effects of said chemical compounds on the amount and / or post-translational modifications of two or more macromolecules in intact cells; (B) constructing a pharmacological profile based on the results of said tests; and (C) comparing said profile to the profile(s) of drugs with established safety characteristics. Additionally, the invention is also directed to a composition comprising an assay panel, said panel comprising at least one high-content assay for the amount and / or post-translational modification of a protein and at least one high-content assay for the amount and / or subcellular location of a protein-protein interaction.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Protein-protein interactions between Shigella flexneri polypeptides and mammalian polypeptides
InactiveUS20030055220A1Treat and prevent bacillary dysenteryMore effective and better targeted therapeutic applicationsPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to protein-protein interactions between Shigella polypeptides and mammalian polypeptides. More specifically, the present invention relates to complexes of polypeptides or polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides, fragments of the polypeptides, antibodies to the complexes, Selected Interacting Domains (SID(R)) which are identified due to the protein-protein interactions, methods for screening drugs for agents which modulate the interaction of proteins and pharmaceutical compositions that are capable of modulating the protein-protein interactions.
Owner:HYBRIGENICS SA
Method for assaying protein—protein interaction
The invention relates to a method for determining if a test compound, or a mix of compounds, modulates the interaction between two proteins of interest. The determination is made possible via the use of two recombinant molecules, one of which contains the first protein a cleavage site for a proteolytic molecules, and an activator of a gene. The second recombinant molecule includes the second protein and the proteolytic molecule. If the test compound binds to the first protein, a reaction is initiated whereby the activator is cleaved, and activates a reporter gene.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP +1
Human papillomavirus inhibitors
The present invention provides systems for identifying anti-viral agents. In particular, the invention encompasses reagents and strategies for identifying agents that inhibit or disrupt key protein-protein interactions that are important in the life cycle of papillomaviruses. The invention allows identification, production, and / or use of agents that reduce or inhibit the replication of HPV by inhibiting (e.g., precluding, reversing, or disrupting) the formation of the E1-E2 protein-protein complex. The invention also provides specific inhibitory agents, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of using these inhibitors and pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting viral replication in vitro. Methods are also described for the treatment and prevention of HPV infections and HPV-related diseases in patients.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
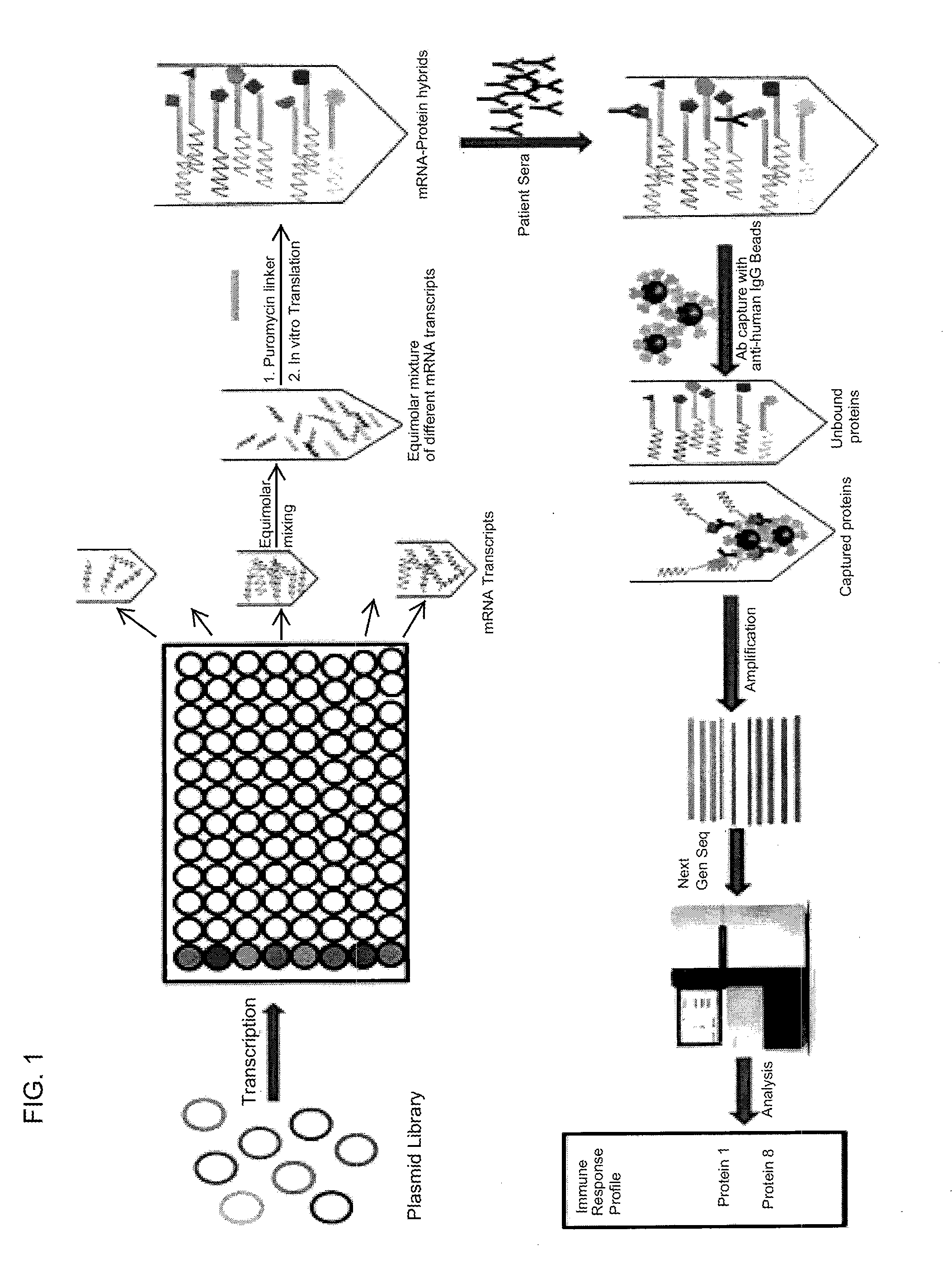
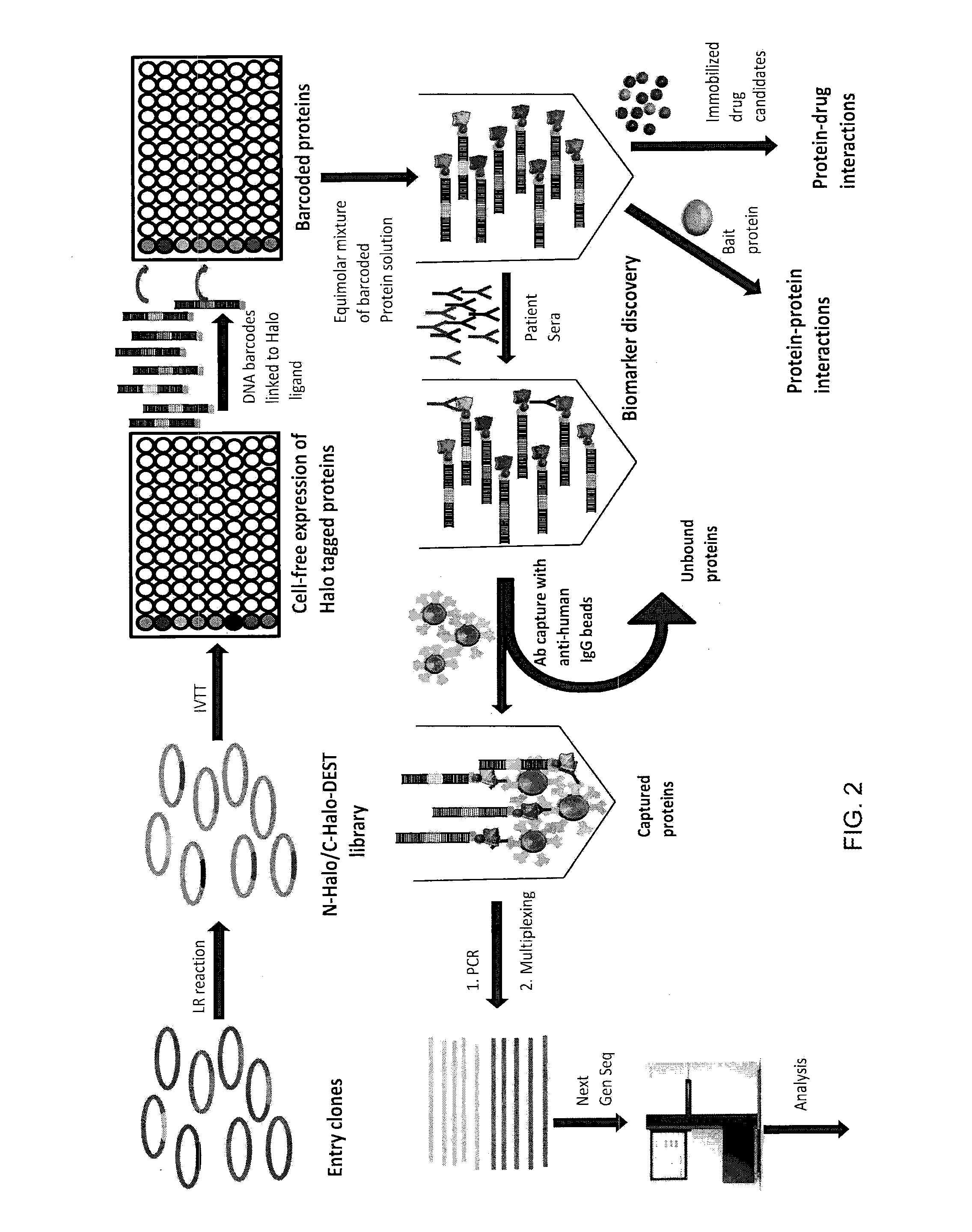
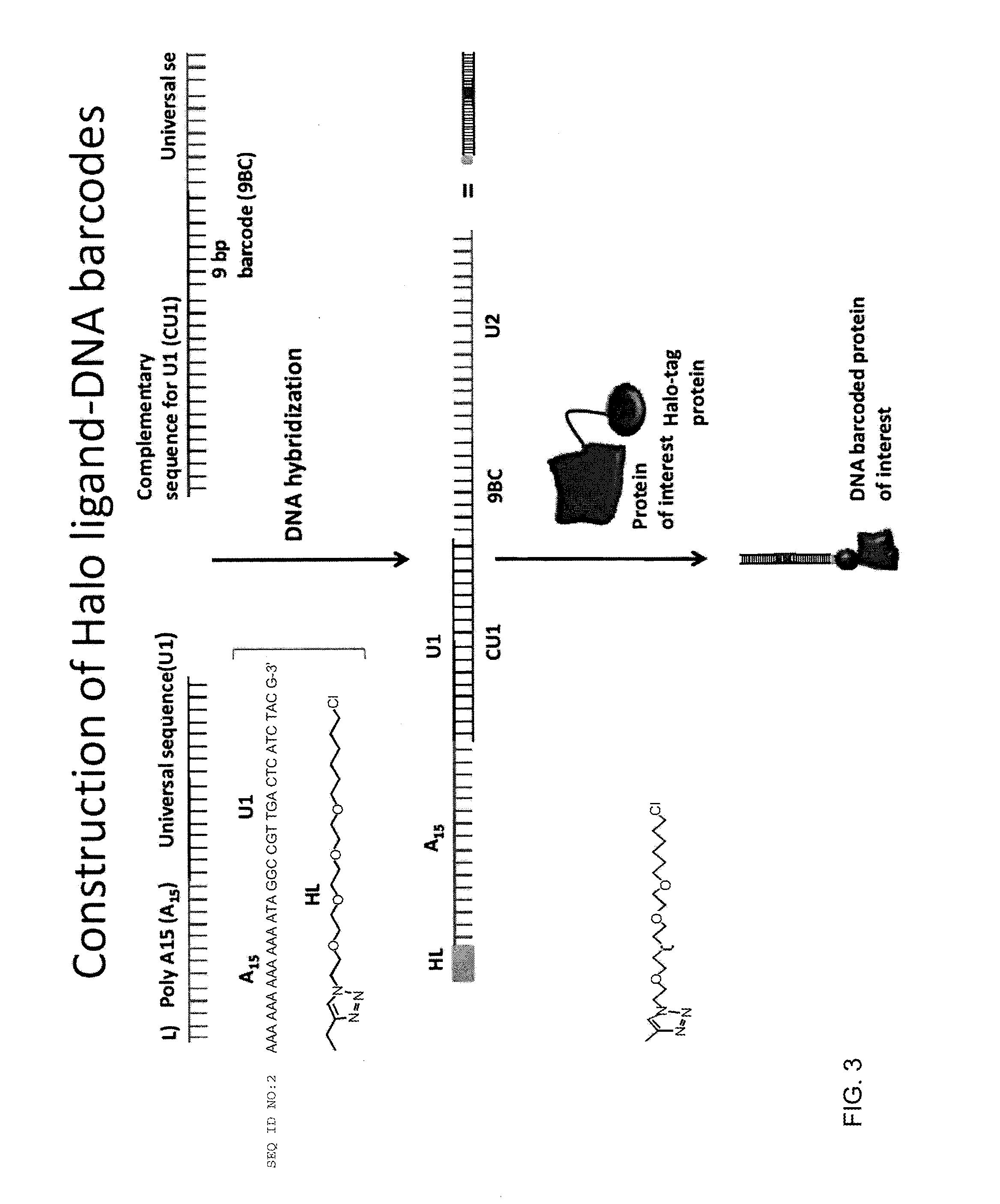
Nucleic acid-tagged compositions and methods for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling
Methods and compositions for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling (e.g., immunoprofiling), based on nucleic acid tagging of polypeptides (e.g., by RNA display) are described. In some embodiments the described compositions and methods utilize a library of prey polypeptide targets linked to prey RNAs encoding them, and a population of bait polypeptides, e.g., a mixture of antibodies, that bind to one or more of the prey polypeptide targets and are used to isolate and identify the bound prey polypeptide targets by amplification of their associated prey RNAs and sequencing of the corresponding cDNAs. In other embodiments the prey polypeptide targets are linked to DNA Bar Codes, which serve as unique identifiers of the tagged polypeptide.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Cancer chemosensitivity prediction technique based on molecular subnet and random forest classifier
InactiveCN104573410ADefine biological functionImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmPredictive methods
The invention discloses a cancer chemosensitivity prediction technique based on a molecular subnet and a random forest classifier. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of fusing data of oncogene expression profile, information of tumor mutation genome information and information of protein-protein interaction group, and excavating carcinogenic and cancer suppressor gene molecular subnets to realize feature extraction; taking the feature extraction as an input feature, designing a training model based on a random forest algorithm, and using the training model to be used for the testing of an independent test set, so as to obtain a chemosensitivity assessment of a patient. If the method provided by the invention is used for screening patients with effective chemotherapy effects before chemotherapy, the method has a significant meaning on cancer therapy.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
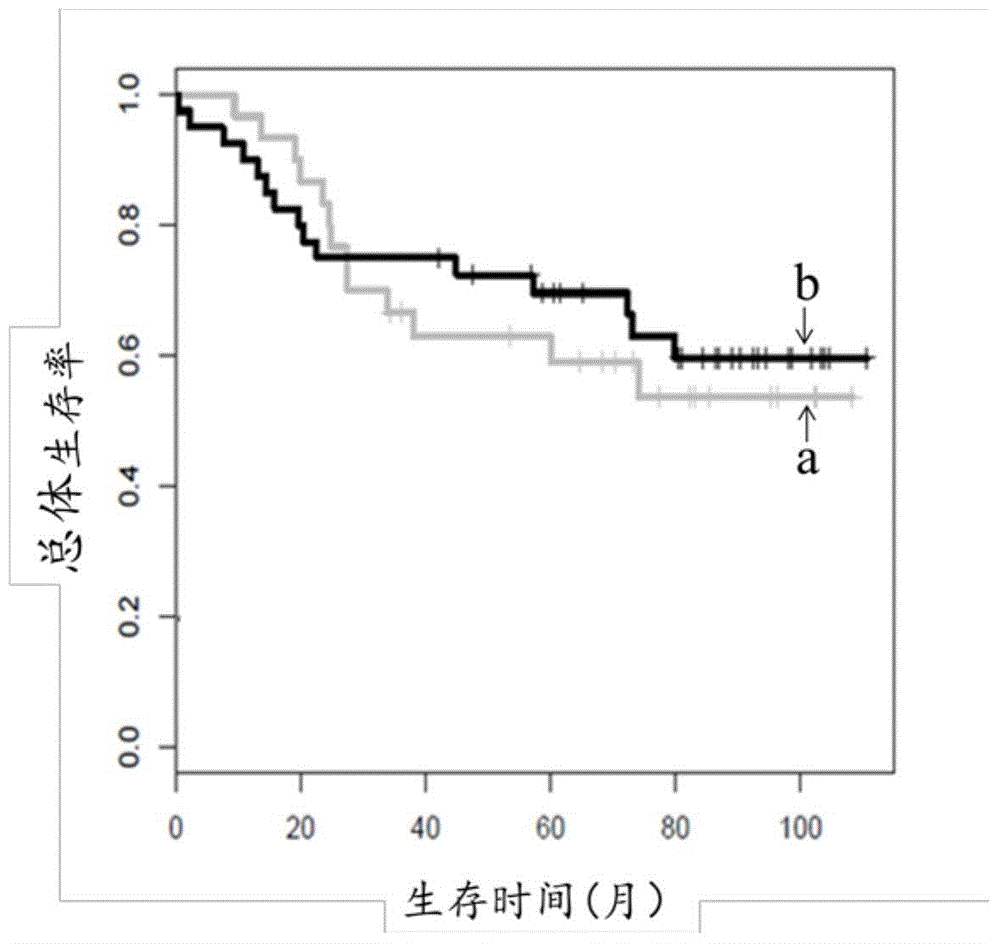
Compounds and assays for controlling Wnt activity
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Nucleic acid-tagged compositions and methods for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling
ActiveUS20160122751A1Nucleotide librariesLibrary member identificationDNA barcodingUnique identifier
Methods and compositions for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling (e.g., immunoprofiling), based on nucleic acid tagging of polypeptides (e.g., by RNA display) are described. In some embodiments the described compositions and methods utilize a library of prey polypeptide targets linked to prey RNAs encoding them, and a population of bait polypeptides, e.g., a mixture of antibodies, that bind to one or more of the prey polypeptide targets and are used to isolate and identify the bound prey polypeptide targets by amplification of their associated prey RNAs and sequencing of the corresponding cDNAs. In other embodiments the prey polypeptide targets are linked to DNA Bar Codes, which serve as unique identifiers of the tagged polypeptide.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Breakpoint fusion fragment complementation system
InactiveUS20040038317A1Peptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousRNA-Protein Interaction
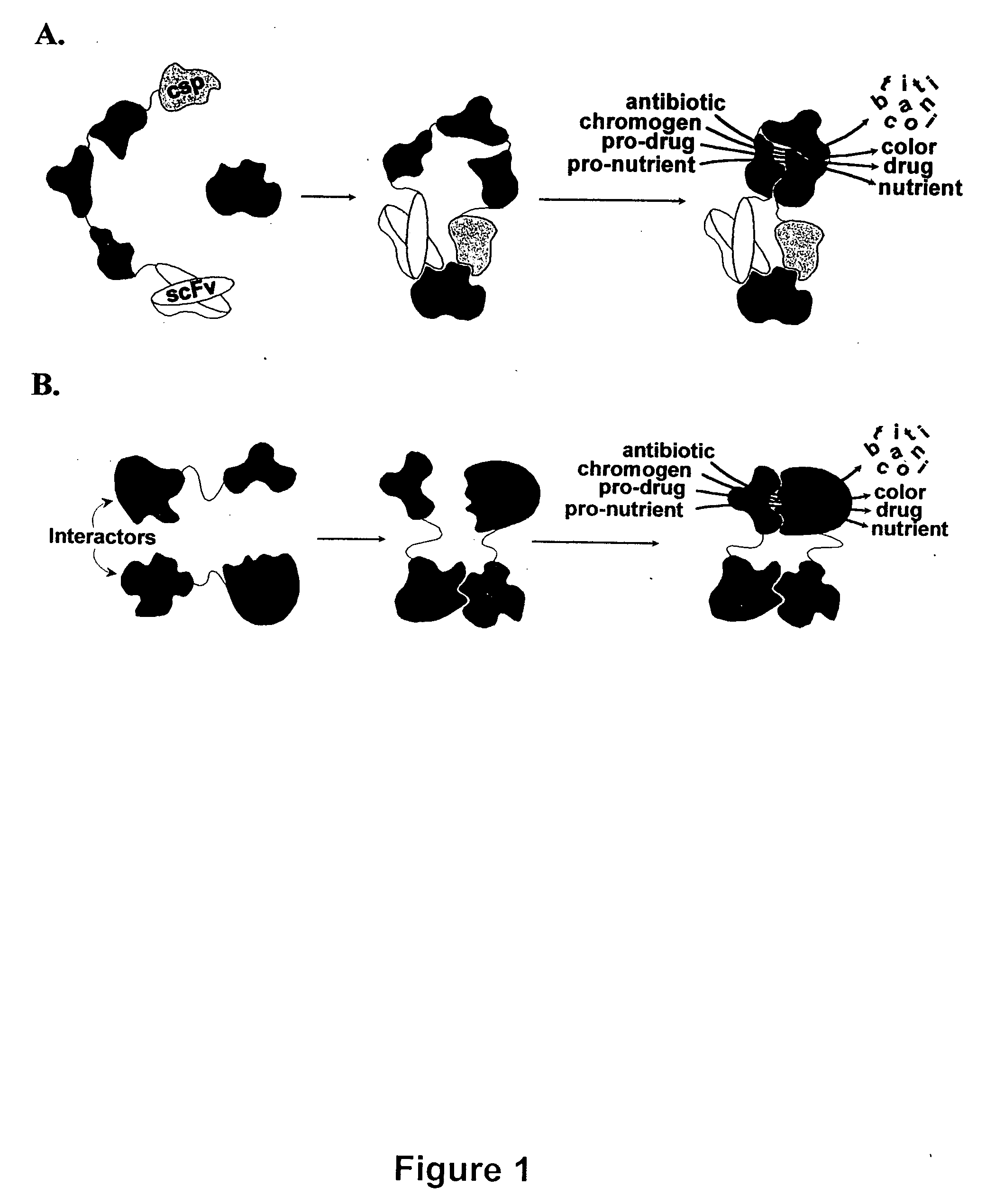
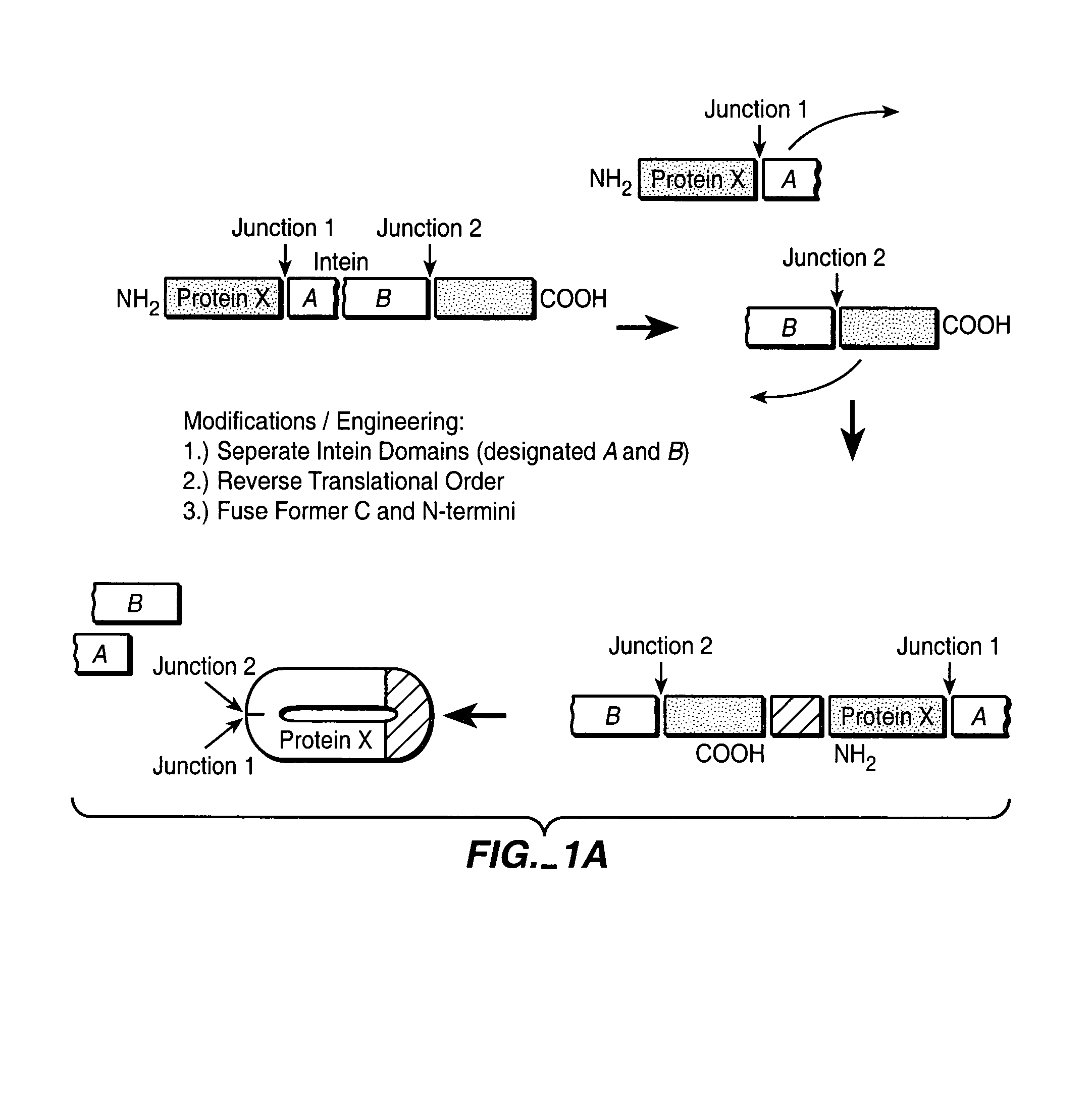
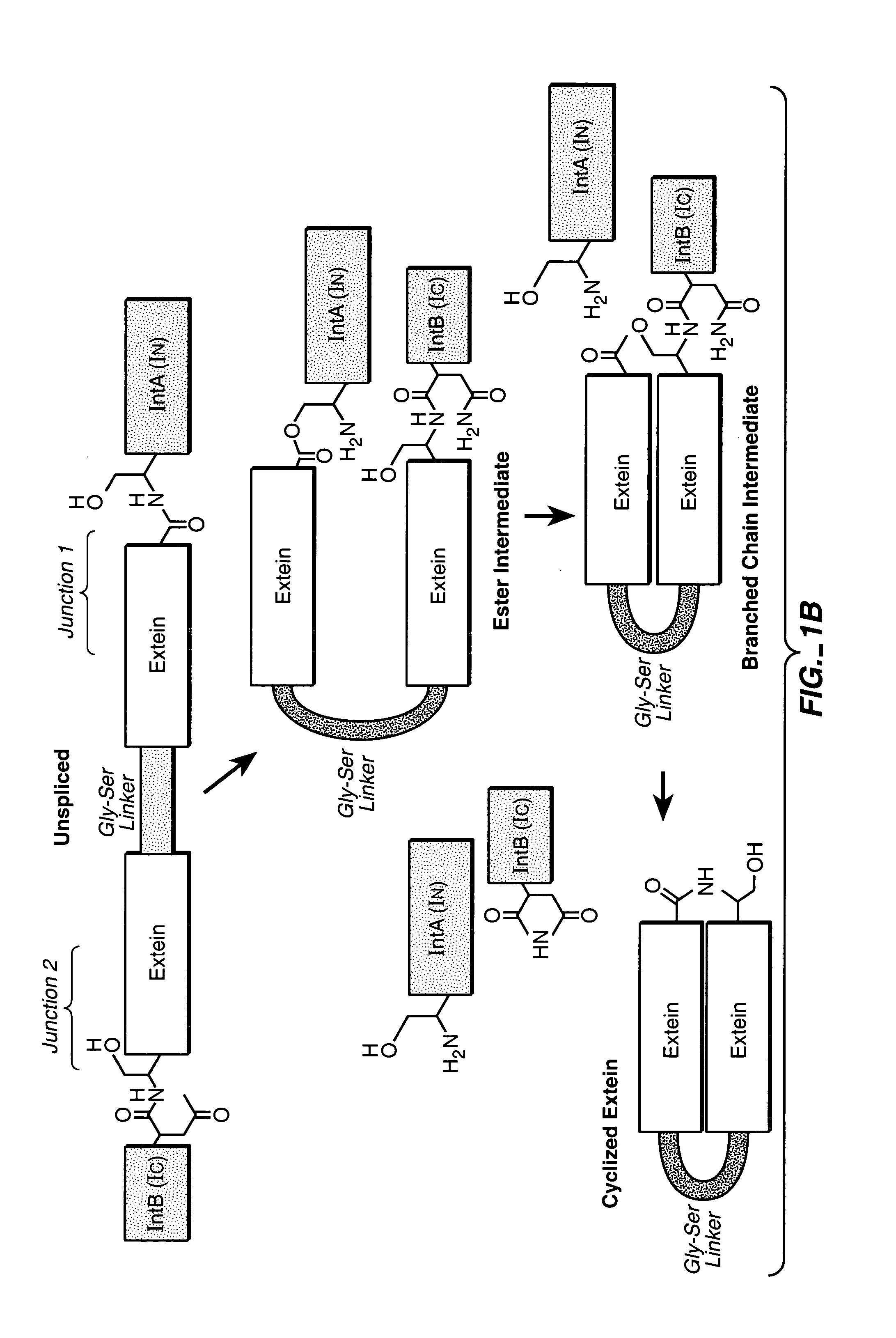
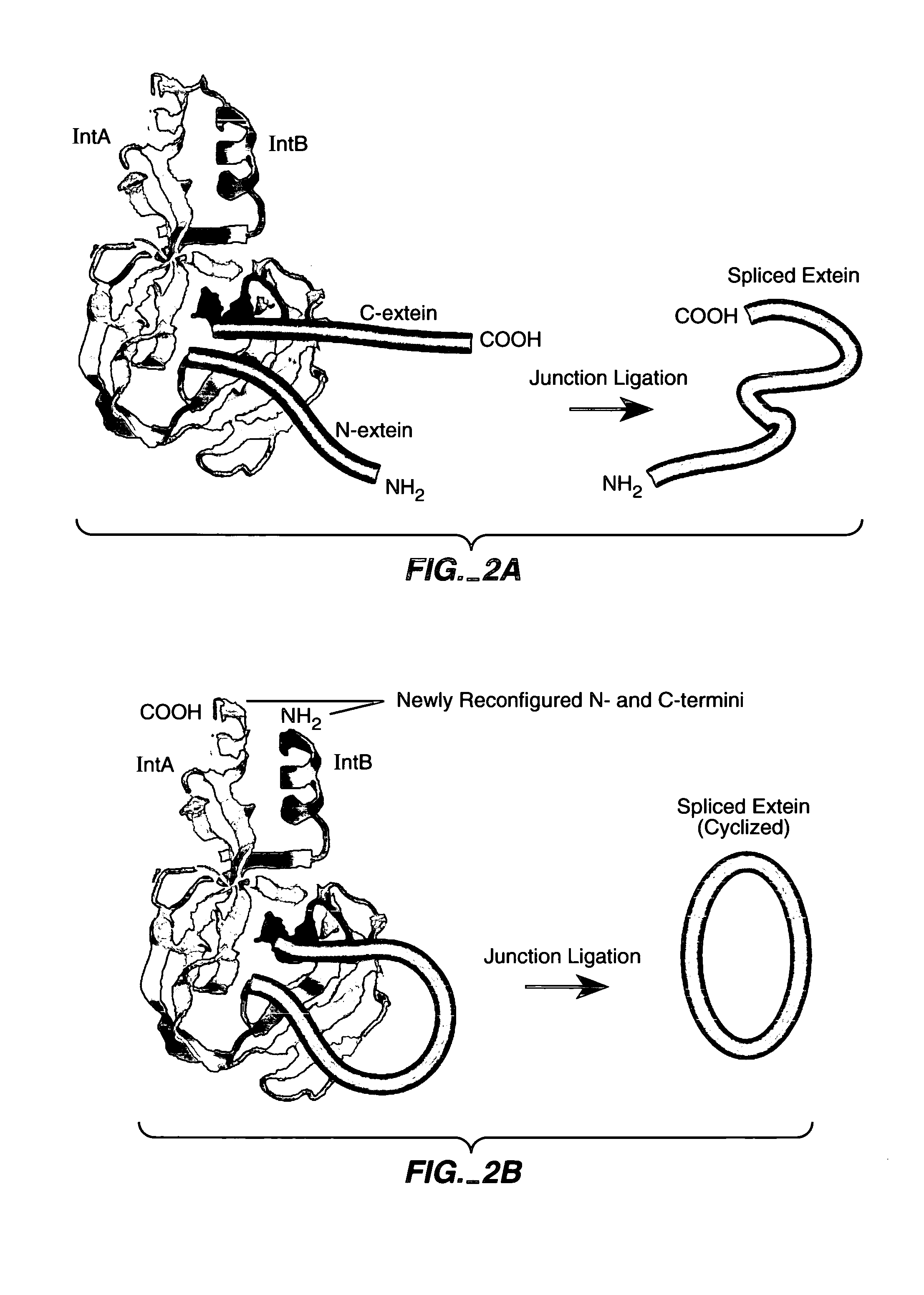
Fragment pairs of a Class A beta-lactamase (TEM-1 of E. coli) are disclosed that depend for their functional reassembly into the parent protein on the interaction of heterologous polypeptides or other molecules which have been genetically or chemically conjugated to the break-point termini of the fragment pairs. In addition, methods are provided for identifying fragment pairs that will optimally reassemble into a functional parent protein. Fragment pairs that comprise molecular interaction-dependent enzymes find use in (1) homogeneous assays and biosensors for any analyte having two or more independent binding sites, (2) tissue-localized activation of therapeutic and imaging reagents in vivo for early detection and treatment of cancer, chronic inflammation, atherosclerosis, amyloidosis, infection, transplant rejection, and other pathologies, (3 cell-based sensors for activation or inhibition of metabolic or signal transduction pathways for high-efficiency, high-throughput screening for agonists / antagonists of the target pathway, (4) high-throughput mapping of pair-wise protein-protein interactions within and between the proteomes of cells, tissues, and pathogenic organisms, (5) rapid selection of antibody fragments or other binding proteins which bind specifically to polypeptides of interest, (6) rapid antigen identification for anti-cell and anti-tissue antibodies, (7) rapid epitope identification for antibodies, (10) cell-based screens for high-throughput selection of inhibitors of any protein-protein interaction.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
Analytical method for researching protein structure or protein-protein interaction
ActiveCN107525842ARich varietySimple and fast operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein containing complexHydrolysate
The invention relates to an analytical method for researching protein structure or protein-protein interaction. The method comprises the following steps: performing crosslinking and enzymolysis on a protein composite in a cell by using a crosslinking agent with reactive groups on two sides and a breakable group, and taking a part of the enzymatic hydrolysate for a derivatization reaction for mass spectrometry; after breaking the crosslinking agent by means of a chemical method for the other part of the enzymatic hydrolysate, enriching peptide sections with an enriching material, and performing mass spectrometry on the enzymatic hydrolysate without the enriched peptide sections; determining the crosslinked peptide sections according to a library searching result so as to establish a peptide section library; finding out a candidate peptide section from the peptide section library according to N-terminal amino acid information of the crosslinked peptide section determined in the mass spectrogram of the crosslinked peptide section; and determining the crosslinked peptide section sequence by combining the mass spectrogram m / z of the crosslinked peptide section and the characteristic ions of the peptide section so as to obtain the protein structure and protein-protein interaction information. The method has the advantage of being simple to operate, and is applied to structural analysis of proteins and analysis of protein-protein composite interaction.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vivo library-versus-library selection of optimized protein-protein interactions
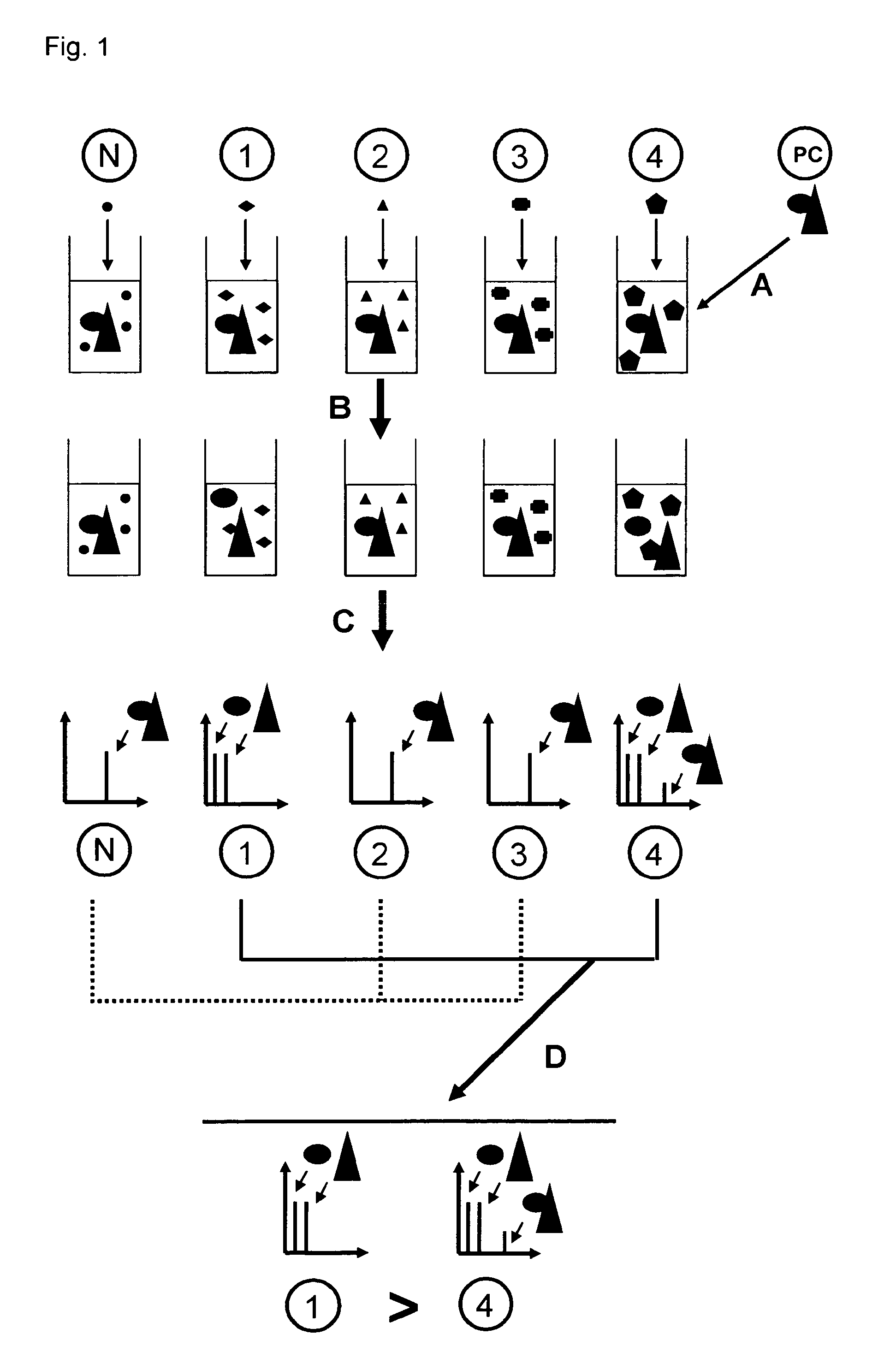
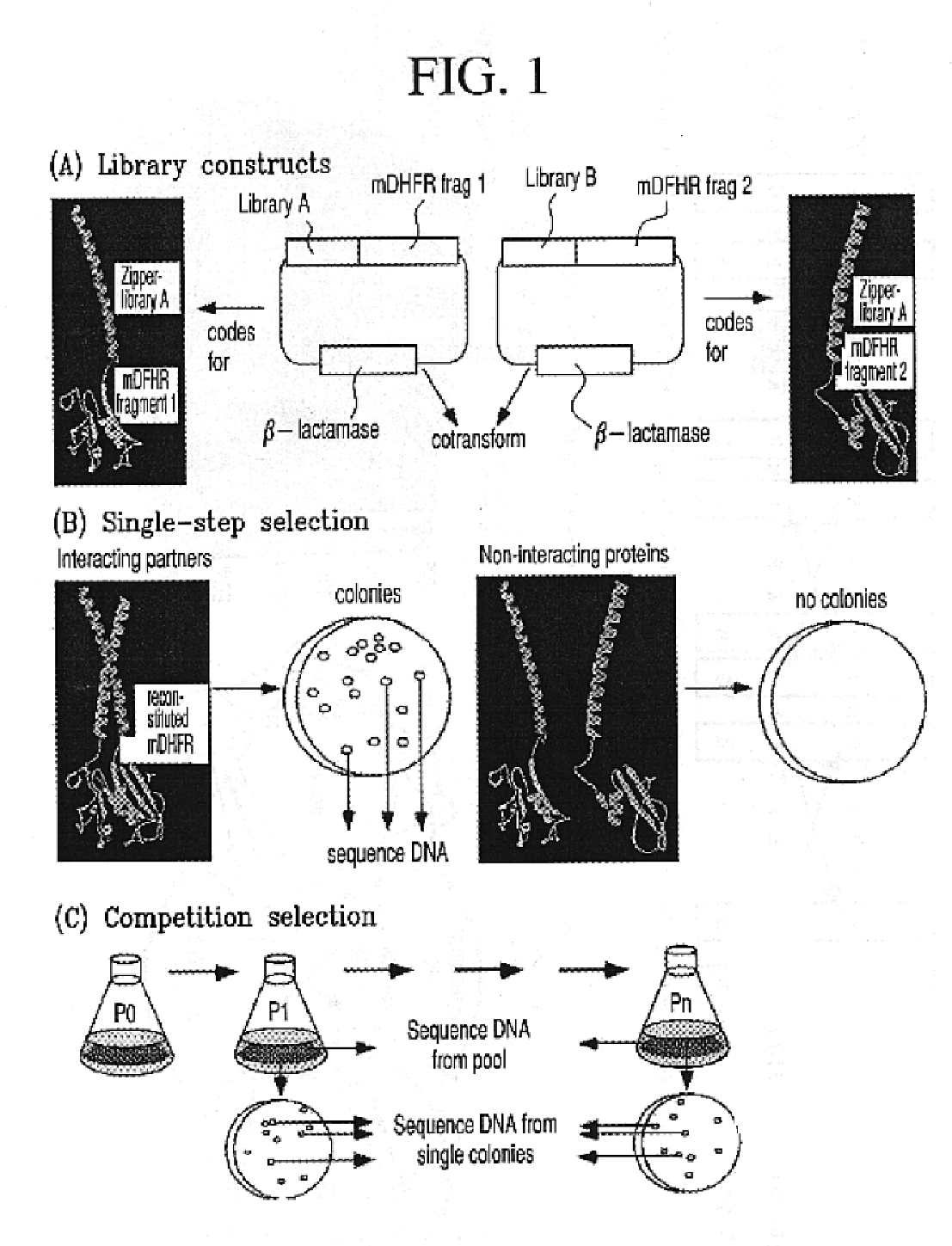
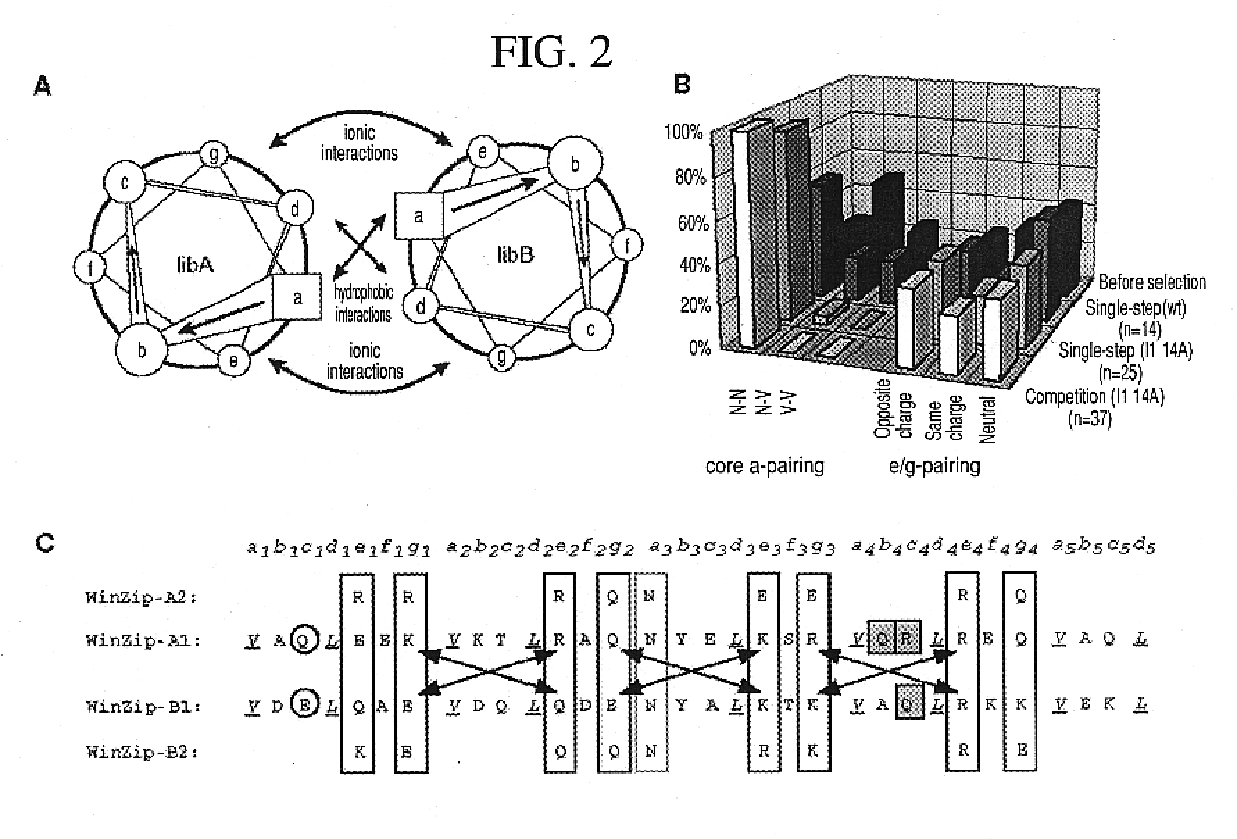
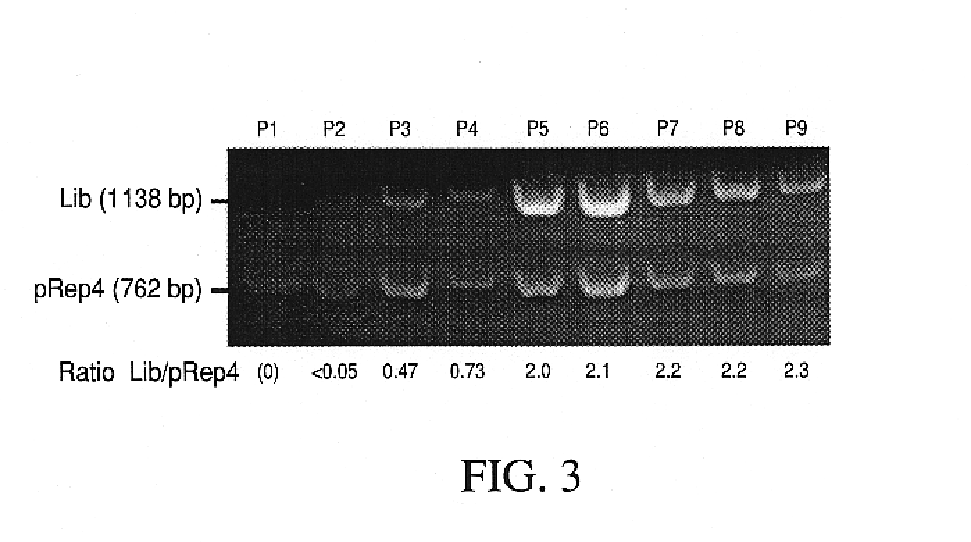
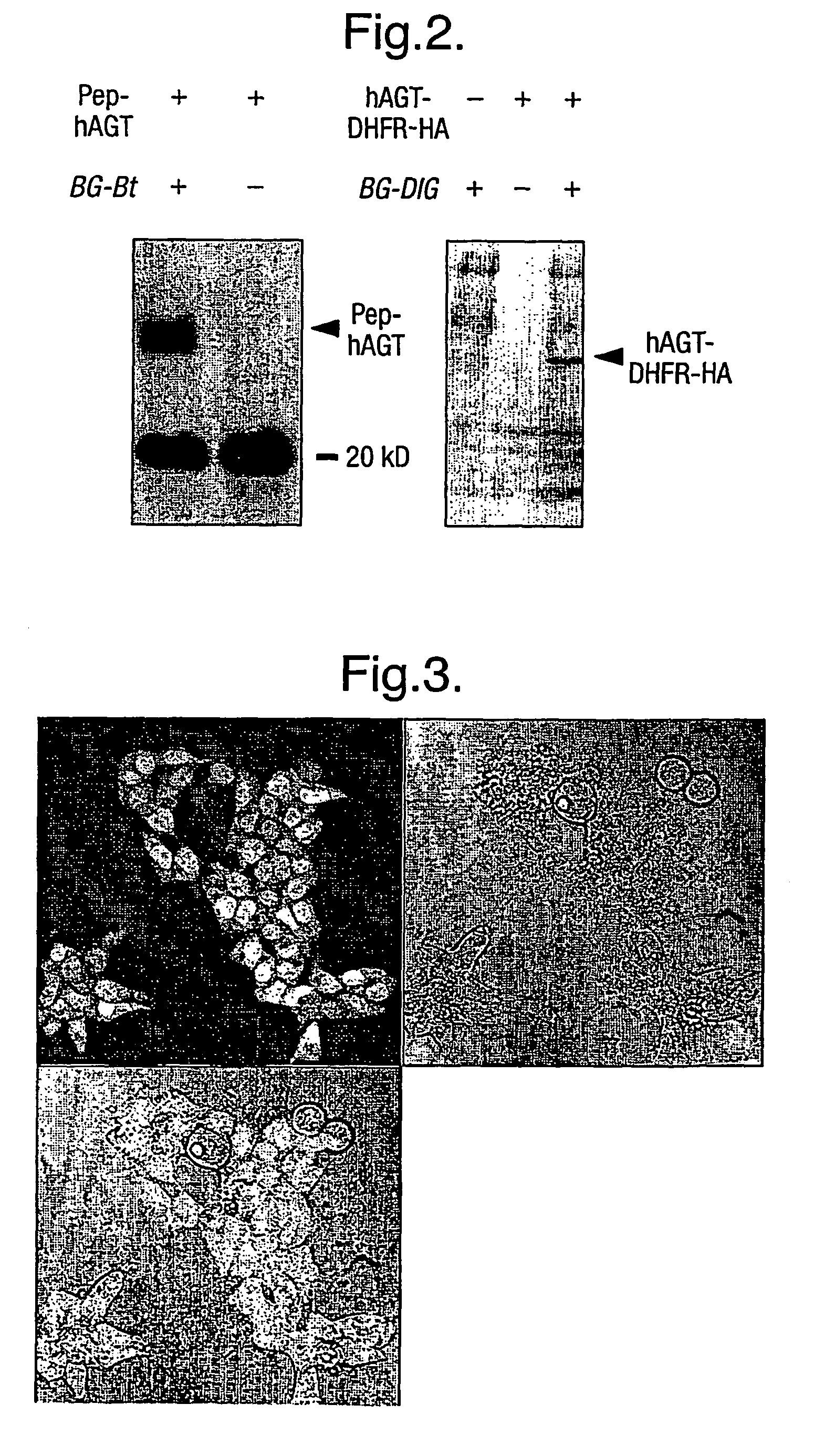
The present invention describes a rapid and efficient in vivo library-versus-library screening strategy for identifying optimally interacting pairs of heterodimerizing polypeptides. It allows for the screening of a protein library against a second protein library, rather than against a single bait protein, and thus has numerous applications in the study of protein-protein interactions. Additionally, it allows for the application of different selection stringencies. Two leucine zipper libraries, semi-randomized at the positions adjacent to the hydrophobic core, were genetically fused to either one of two designed fragments of the enzyme murine dihydrofolate reductase (mDHFR), and cotransformed into E. coli. Interaction between the library polypeptides was required for reconstitution of the enzymatic activity of mDHFR, allowing bacterial growth. Analysis of the resulting colonies revealed important biases in the zipper sequences relative to the original libraries, which are consistent with selection for stable, heterodimerizing pairs. Using more weakly associating mDHFR fragments, we increased the stringency of selection. We enriched the best performing leucine zipper pairs by multiple passaging of the pooled, selected colonies in liquid culture, as the best pairs allowed for better bacterial propagation. This competitive growth allowed small differences among the pairs to be amplified, and different sequence positions were enriched at different rates. We applied these selection processes to a library-versus-library sample of 2.0×106 combinations, and selected a novel leucine zipper pair which may be appropriate for use in further in vivo heterodimerization strategies.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction
InactiveUS20080009068A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLibrary screeningBiologyHigh affinity binding
The invention relates to protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction. Using overlapping hexapeptides that encode for the entire amino acid sequences of the linker domains of human P-glycoprotein gene 1 and 3 (HP-gp1 and HP-gp3), a direct and specific binding between HP-gp1 and 3 linker domains and intracellular proteins was demonstrated. Three different stretches (617EKGIYFKLVTM627, (SEQ ID NO: 1) 658SRSSLIRKRSTRRSVRGSQA677 (SEQ ID NO: 2) and 694PVSFWRIMKLNLT706 (SEQ ID NO: 3) for HP-gp1 and 618LMKKEGVYFKLVNM631 (SEQ ID NO: 4), 648KAATRMAPNGWKSRLFRHSTQKNLKNS674 (SEQ ID NO: 5), and 695PVSFLKVLKLNKT707 (SEQ ID NO: 6) for HP-gp3) in linker domains bound to proteins with apparent molecular masses of ˜80 kDa, 57 kDa and 30 kDa. The binding of the 57 kDa protein was further characterized. Purification and partial N-terminal amino acid sequencing of the 57 kDa protein showed that it encodes the N-terminal amino acids of alpha and beta-tubulins. The method of the present invention was further validated with Annexin. The present invention thus demonstrates a novel concept whereby the interactions between two proteins are mediated by strings of few amino acids with high and repulsive binding energies, enabling the identification of high affinity binding sites between any interacting proteins.
Owner:GEORGES ELIAS
Allosteric protein kinase modulators
The invention provides specific small molecule compounds that allosterically regulate the activity or modulate protein-protein interactions of AGC protein kinases and the Aurora family of protein kinases, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions comprising same, and their use for preparing medicaments for the treatment and prevention of diseases related to abnormal activities of AGC protein kinases or of protein kinases of the Aurora family.
Owner:UNIV DES SAARLANDES
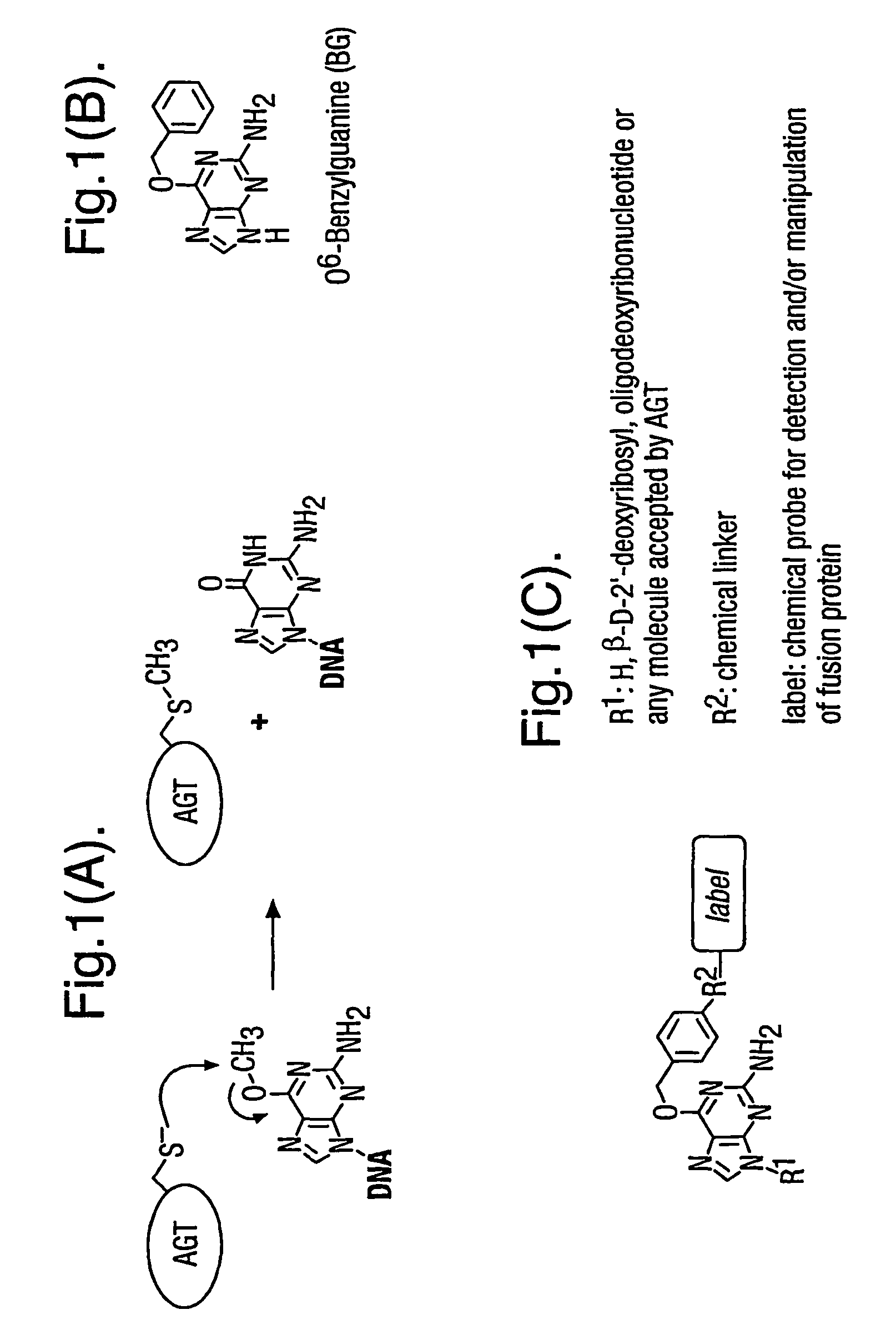
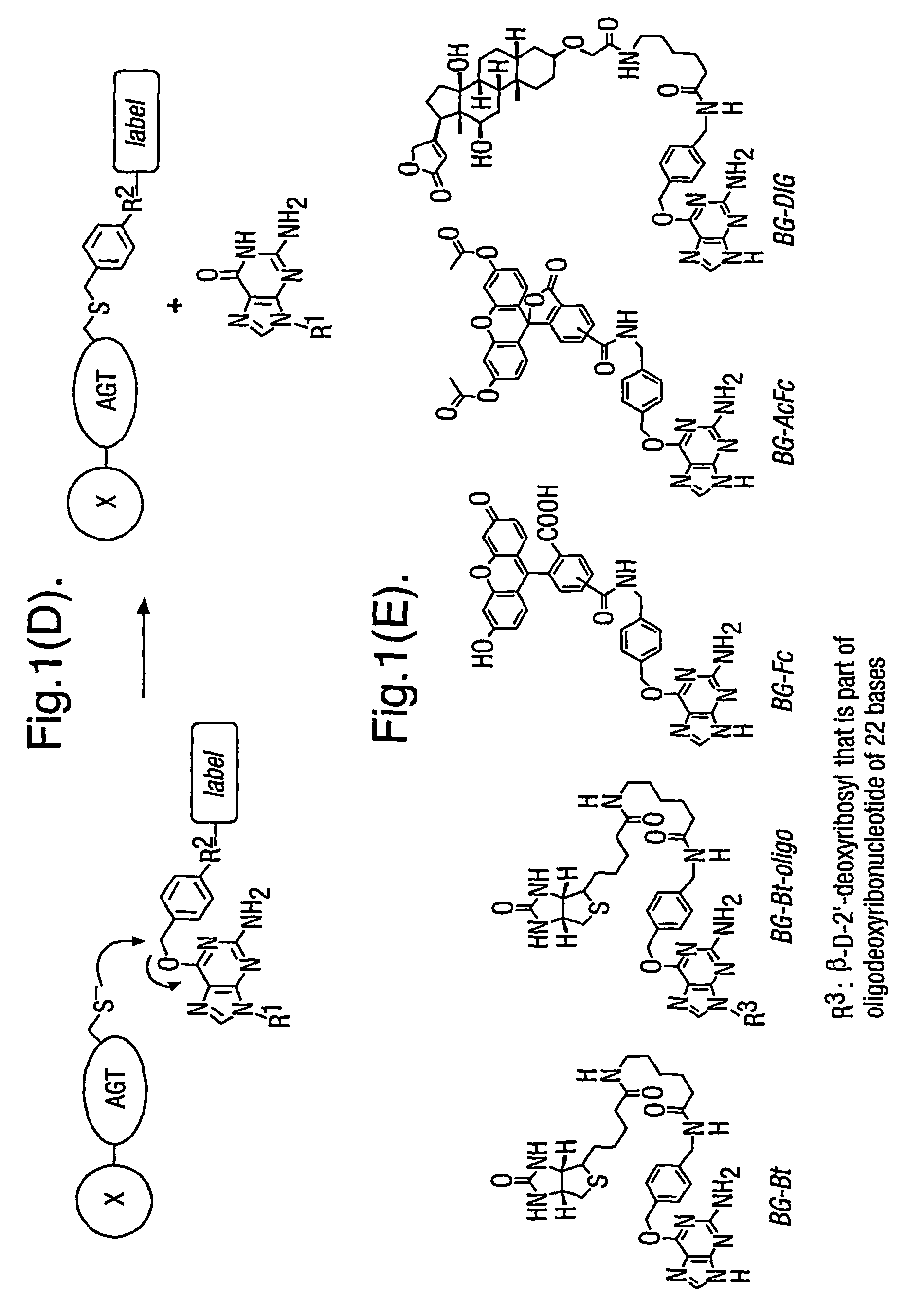
Methods using O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferases
ActiveUS7939284B2Consider flexibilityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPolypeptide with affinity tagCross linkerIn vivo
A method using O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferases (AGT) is disclosed for transferring a label from a substrate to a fusion protein comprising the AGT. This allows the detection and / or manipulating of the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such molecules are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilisation of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
System and methods for electrophoretic separation of proteins on protein binding membranes
ActiveUS7326326B2Increase capacityEasy to separateSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementProteinHeat generation
Proteins can be rapidly separated to a high degree of resolution by electrophoresis on polymeric membranes that have high protein binding capacity. The electrophoretic separation is carried out in a low conductivity, water-miscible organic solvent buffer. The low conductivity of the organic solvent buffer minimizes heat generation, and the water-miscible nature of the organic solvent buffer permits the analysis of hydrophobic and low molecular weight proteins as well as hydrophilic proteins. When electrophoresis is conducted under non-denaturing conditions, it allows the detection of enzymatic activities, protein-protein interactions and protein-ligand interactions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
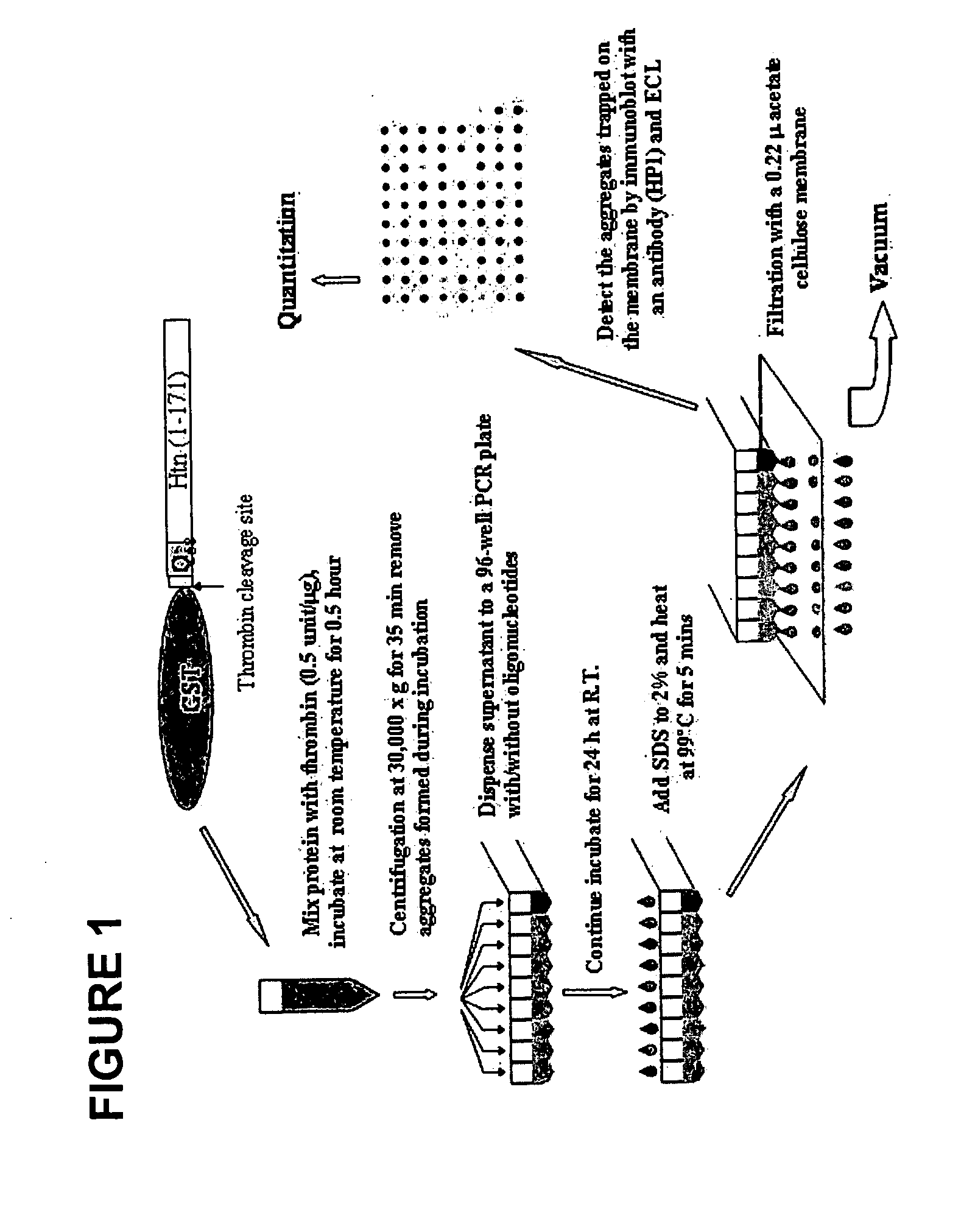
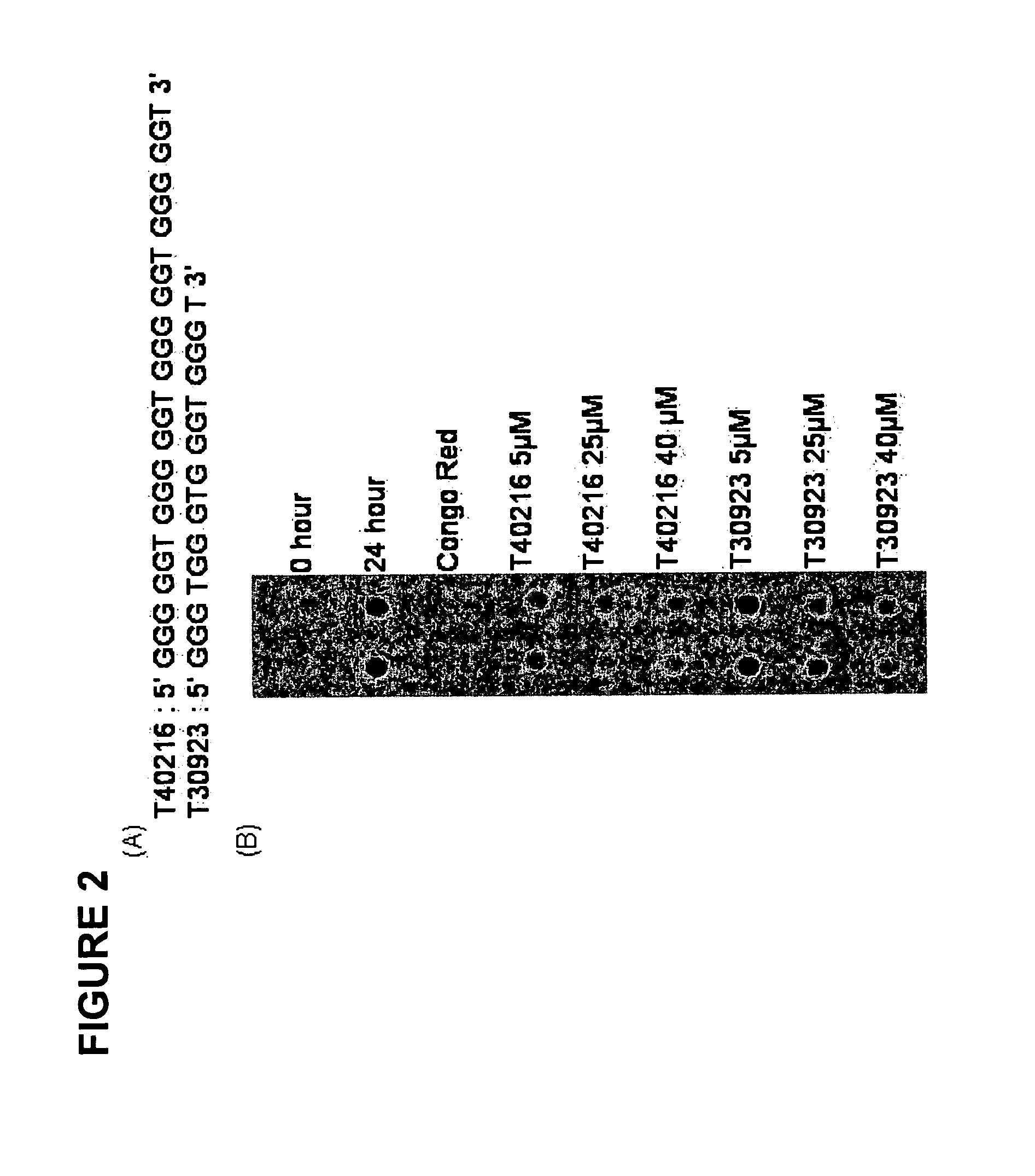
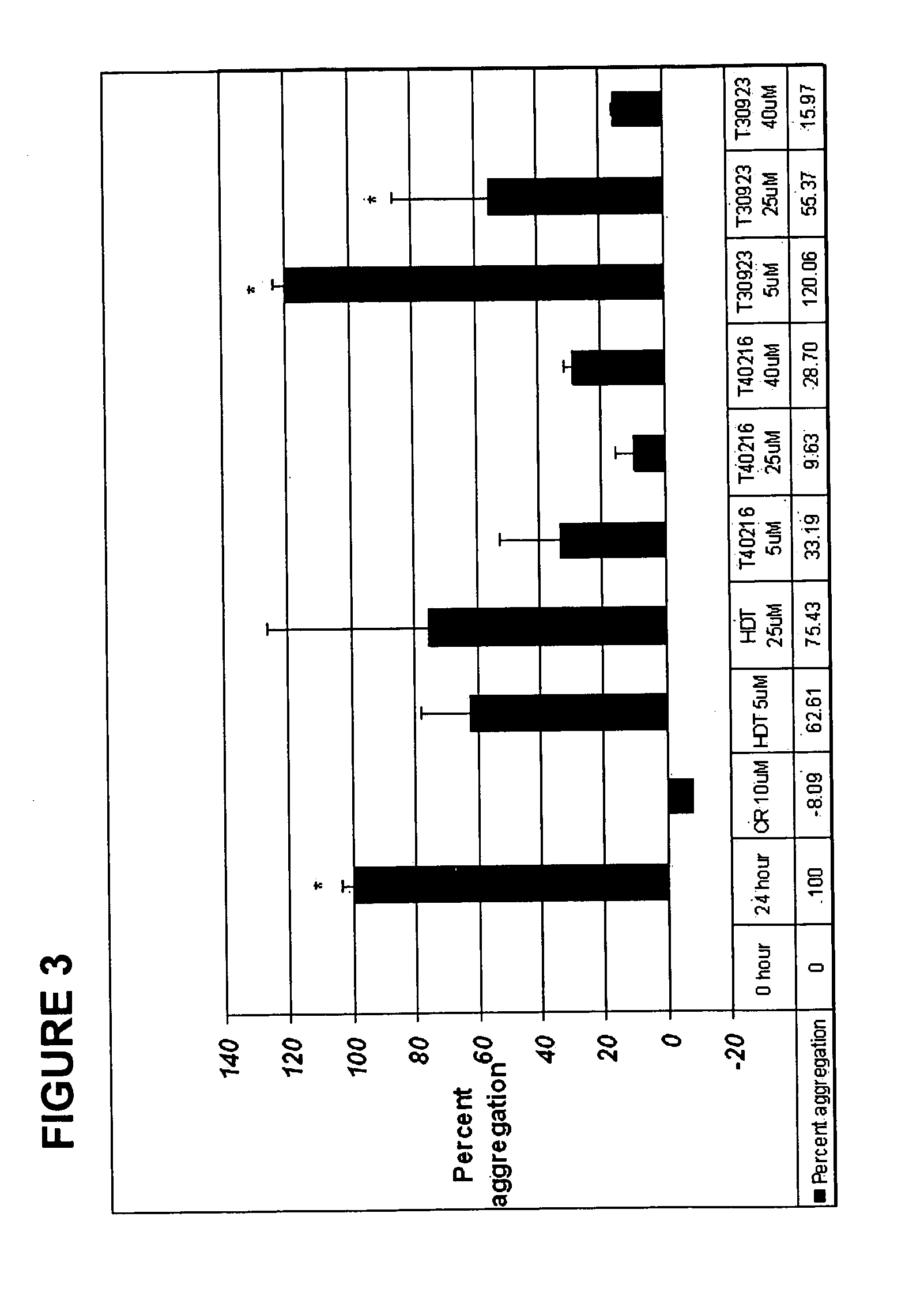
G-rich polynucleotides for the treatment of huntington's disease
The present invention relates to oligonucleotide compositions and therapeutic uses thereof to modify protein-protein interactions. In particular, the invention relates to the use of a guanidine-rich oligonucleotides to disrupt disease-causing protein aggregates, for example, Huntington's Disease (HD) protein aggregates
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
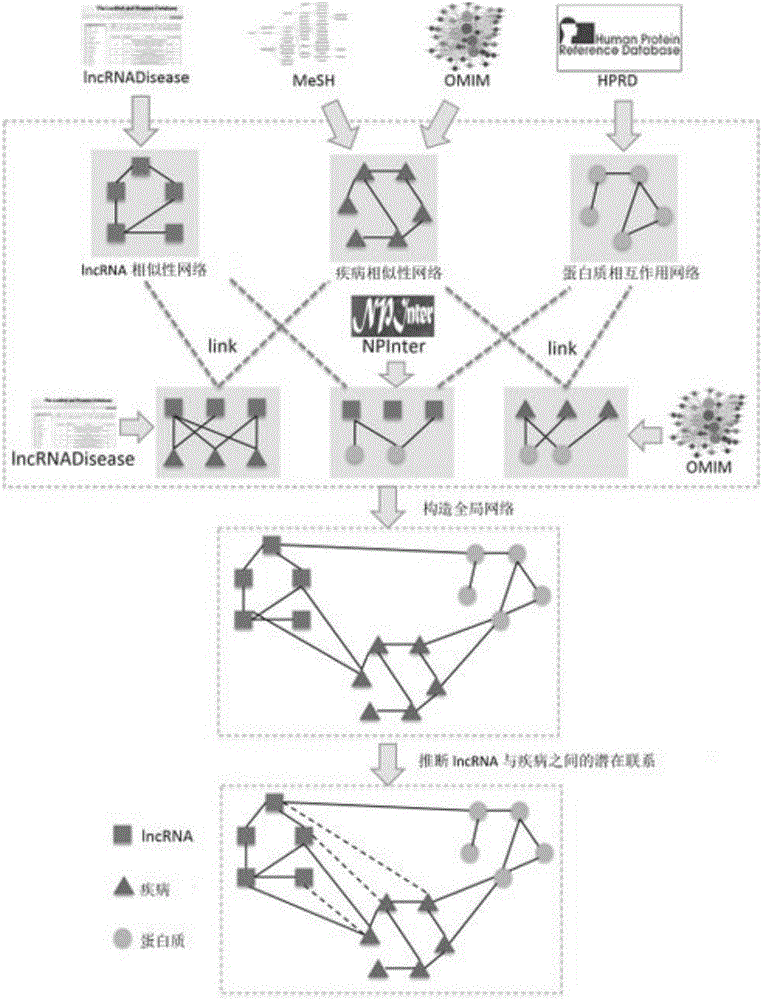
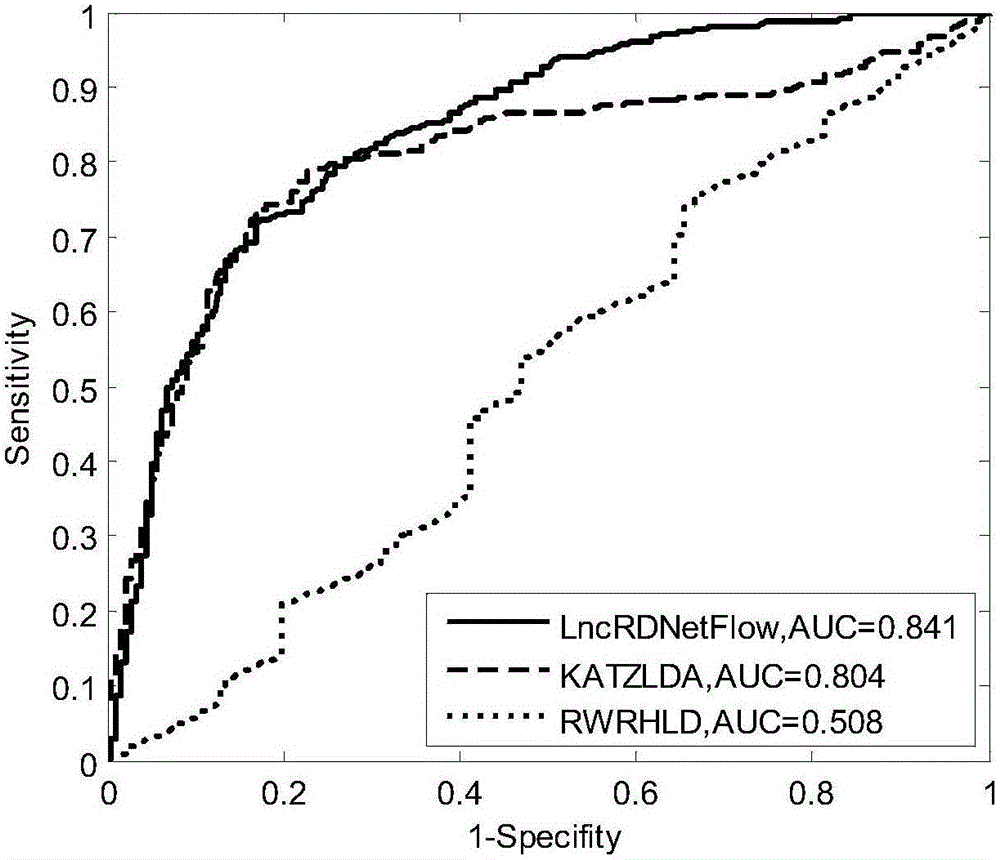
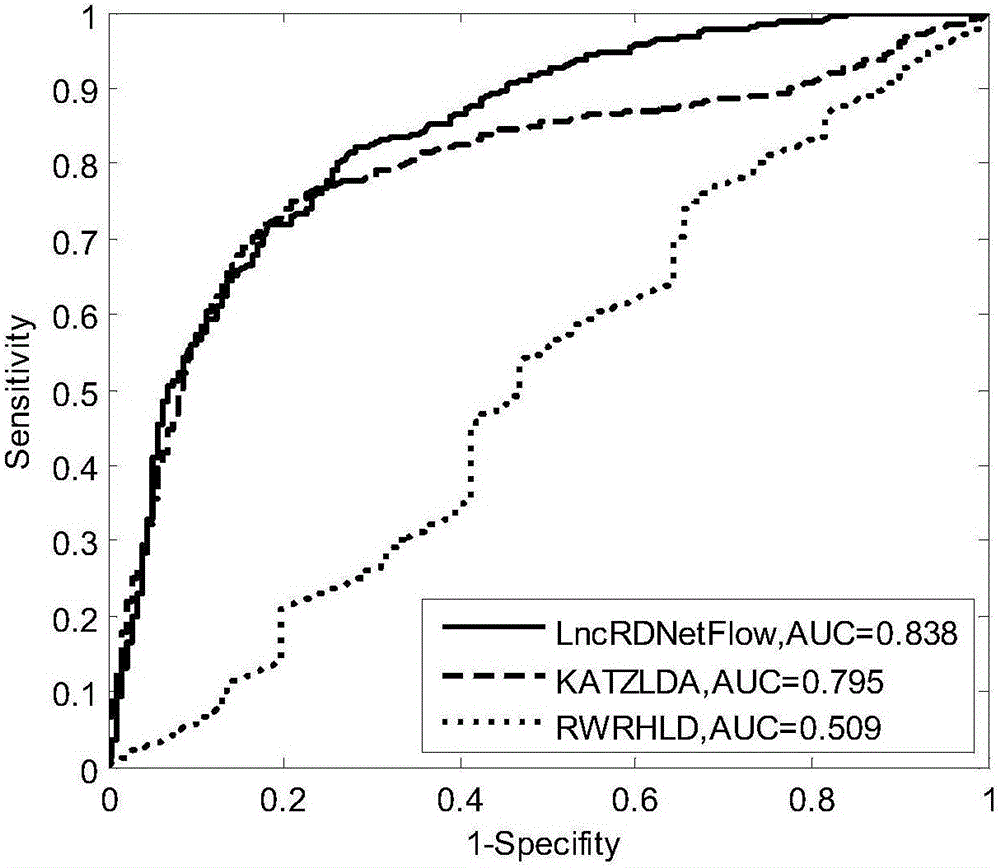
Method for deducing relations between lncRNA and diseases
The invention discloses a method for deducing relations between lncRNA and diseases. The method comprises the steps that a global heterogeneous network is constructed according to multiple kinds of heterogeneous data (lncRNA-disease relational data, protein-protein interaction data, lncRNA-protein interaction data and the like), and then possible relations between lncRNA and diseases are identified through the network communication algorithm. Compared with the prior art, in addition to the relations, provided by experiments, between lncRNA and diseases, more biological data can be integrated, for example, the lncRNA-protein relation, the protein-protein interaction relation, the protein-disease relation and the like are integrated. By fusing more biological data, the relations between lncRNA and diseases can be predicted more accurately compared with the prior art, multiple lncRNA-disease relations can be predicted once on a large scale, and the problems of blindness and high cost of biological experimental methods are effectively solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
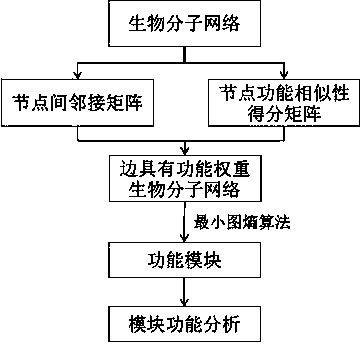
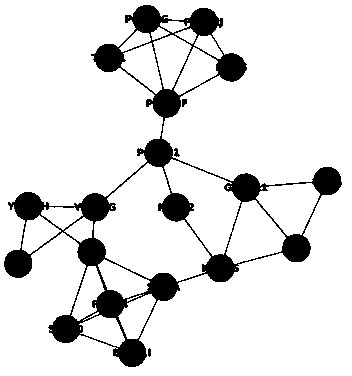
Biomolecular network analysis method based on function module
ActiveCN103778349AHigh functional relevanceEfficient integrationSpecial data processing applicationsRegulation of gene expressionComputer science
The invention belongs to the field of a biotechnology, and provides a comparison method based on a function module and used for biomolecular networks such as a genetic expression regulatory network or protein-protein interaction and the like. The method mainly comprises steps as follows: an adjacency matrix Madj of a biological network is built, a function similarity matrix Msim between network nodes is calculated, a function weight matrix ME of a network side is calculated according to the formula as follows: ME=Madj.*Msim, a network module is mined with a minimum graph entropy algorithm, and finally, function enrichment analysis is performed on the network module, wherein the symbols are defined in the instruction.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
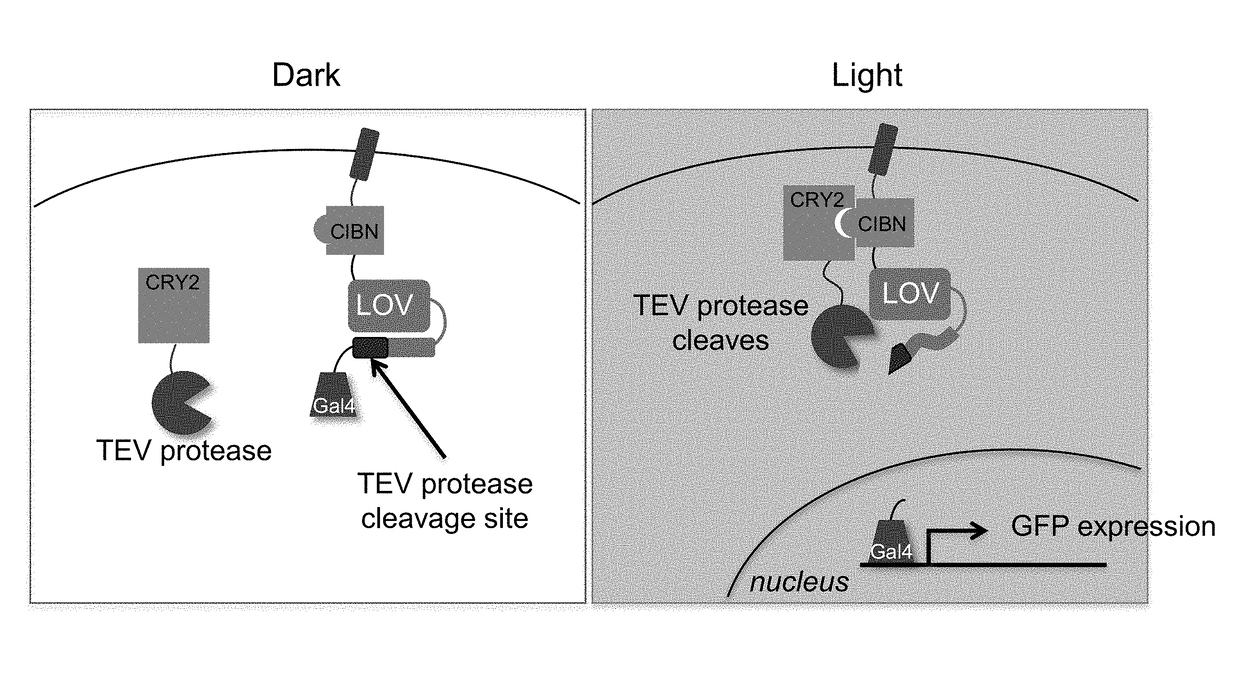
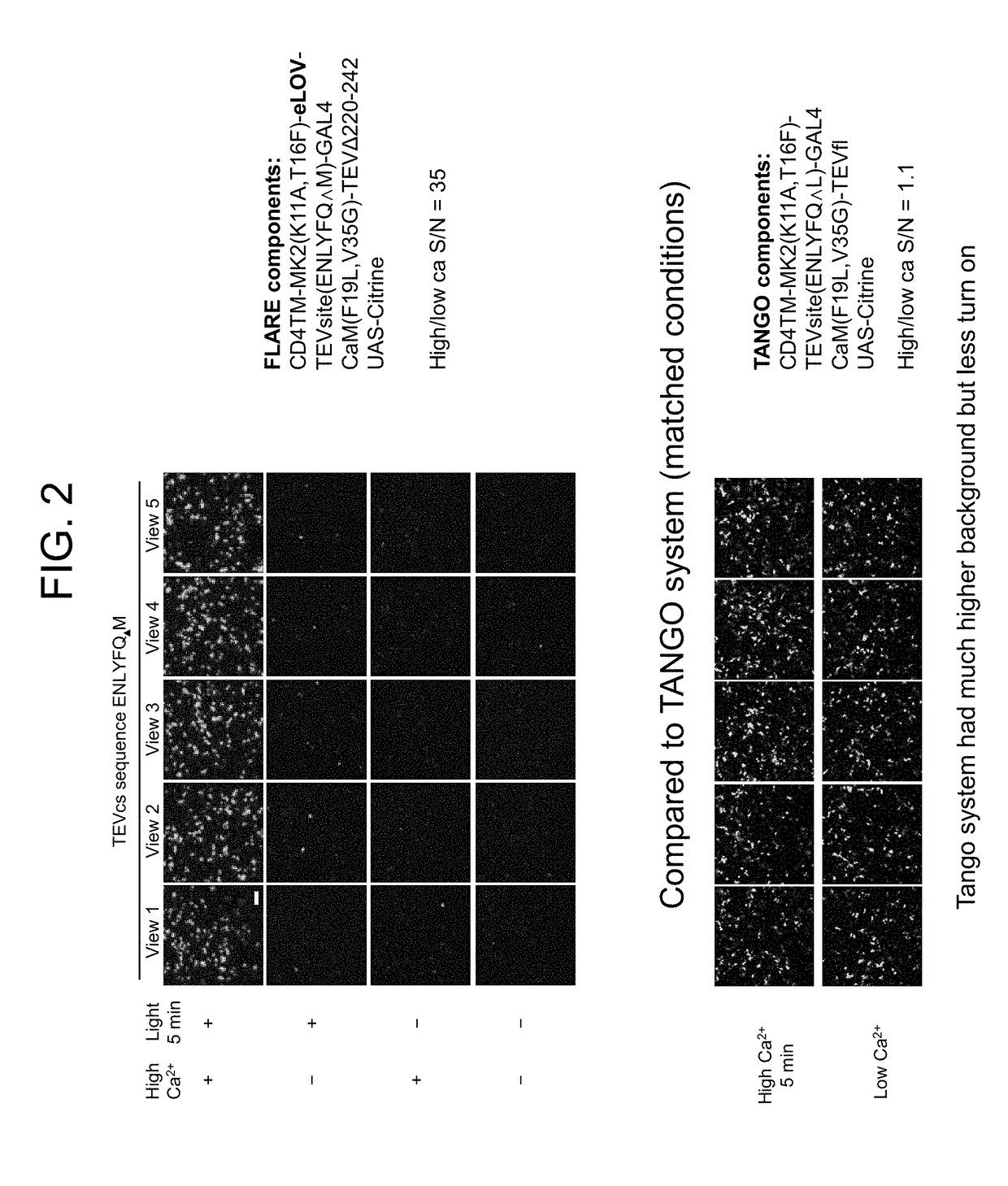
Protein-protein interaction detection systems and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20180203017A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiological testingBioinformaticsProtein
The present disclosure provides polypeptides, nucleic acids, polypeptide systems, and nucleic acid systems for detecting protein-protein interactions. The polypeptides, nucleic acids, and systems are useful for detecting protein-protein interactions. The present disclosure also provides such methods.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Protein microarrays on mirrored surfaces for performing proteomic analyses
InactiveUS7148058B2Enhanced signalFacilitating drug discoveryCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyAntigenStructure analysis
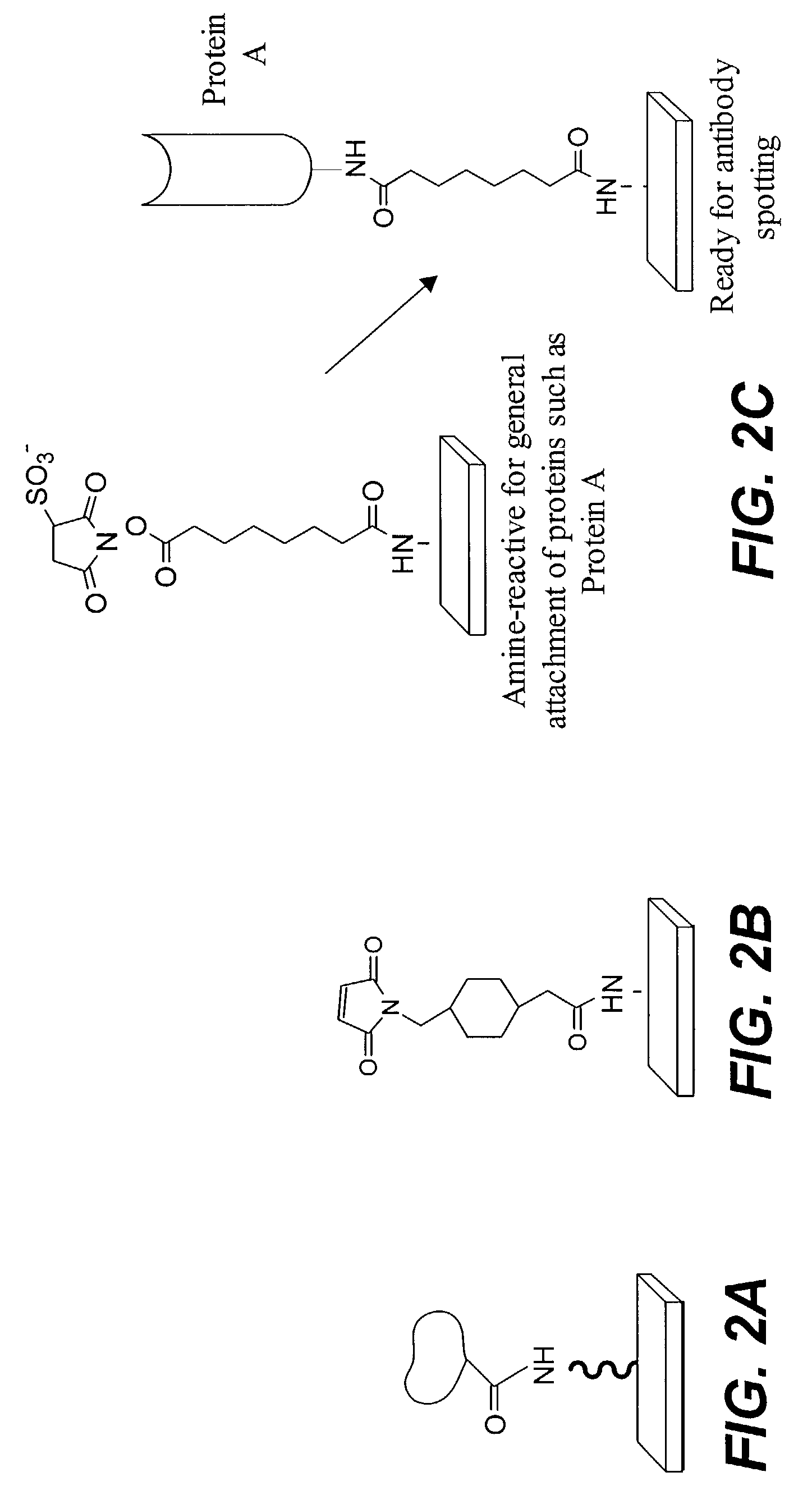
Provided are protein microarrays, their manufacture, use, and application. Protein microarrays in accordance with the present invention are useful in a variety preoteomic analyses. Various protein arrays in accordance with the present invention may immobilize large arrays of proteins that may be useful for studying protein-protein interactions to improve understanding of disease processes, facilitating drug discovery, or for identifying potential antigens for vaccine development. The protein array elements of the invention are native or modified proteins (e.g., antibodies or fusion proteins). The protein array elements may be attached directly to a organic functionalized mirrored substrate by a binding reaction between functional groups on the substrate (e.g., amine) and protein (e.g., activated carboxylic acid). Techniques for chemical blocking of the arrays are also provided. The invention contemplates spotting of array elements onto solid planar substrates, labeling of complex protein mixtures, and the analysis of protein binding to the array. The invention also enables the enrichment or purification, and subsequent sequencing or structural analysis of proteins that are identified as differential by the array screen. Kits including protein-binding microarrays for proteomic analysis in accordance with the present invention are also provided.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com