Method and device for detecting free epithelial cell organ sources in blood
A technology of epithelial cells and detection methods, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, biological testing, material inspection products, etc., to achieve the effects of simple structure, accurate early diagnosis, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Detection device for rare cell proteome in blood
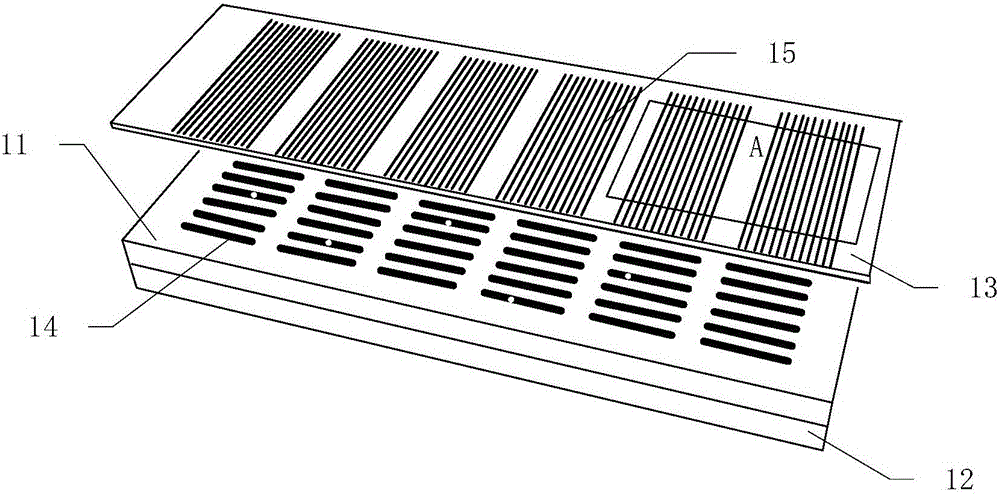
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the device for detecting rare cell protein groups in blood according to the present invention includes a microgroove chip 11 , a magnet 12 and an antibody-loaded glass slide 13 .
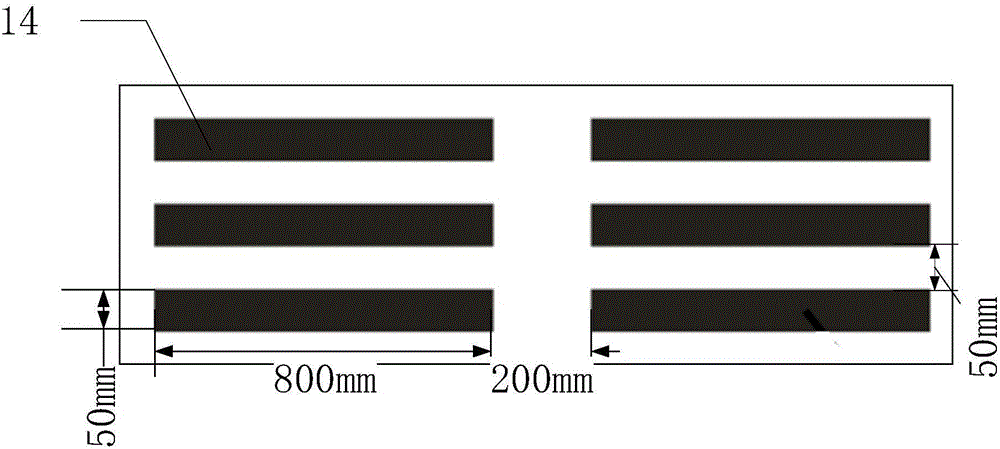
[0044] Such as figure 2 As shown, the microgroove chip 11 is provided with 3220 (35×92) microgrooves 14 with a volume of 1 nanoliter arranged in a matrix. Such as image 3 As shown, the cross-section of a single microgroove 14 is rectangular, with a length of 800 microns, a width of 50 microns, and a depth of 25 microns. During fabrication, a mask is first printed on a film substrate, a photoresist template is obtained through a photolithography process, and then a chip made of PDMS, that is, a microgroove chip 11 , is fabricated by using the photoresist template as a template.
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, the antibody-loaded glass slide 13 is loaded with an antibody microarray 15 , and...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Detection of multiple organ-specific protein markers in circulating epithelial cells in human peripheral blood
[0050] In order to identify the organ source of the epithelial cells isolated from blood, a set of 8 organ-specific protein markers was designed in this example for identification.
[0051] Anti-TTF-1 (thyroid transcription factor 1), anti-GCDFP-15 (grosscystic disease fluid protein 15), anti-CDX2, anti-CK7, anti-CK20, anti-SMAD4, anti-CEA, anti - CD45, anti-CD105 (or anti-CD146) and single-stranded polynucleotide M are passed into different microchannels 19 of the antibody-loaded chip described in Example 1, respectively. Among them, anti-TTF-1 (thyroid transcription factor 1), anti-GCDFP-15 (grosscystic disease fluid protein 15), anti-CDX2, anti-CK7, anti-CK20, anti-SMAD4 and anti-CEA are used to specifically bind protein markers with organ specificity Anti-CD45 is used for specifically binding leukocyte markers, anti-CD105 (or anti-CD146) is use...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Identification of Organ Source of Circulating Epithelial Cells
[0055] Adopt the method for embodiment 2 to have lung (100 examples), stomach (30 examples), colon (30 examples), ovary (10 examples), pancreas (10 examples) and breast ( 20 cases) samples from patients with malignant lesions were detected and organ source identification.
[0056] Cluster analysis was performed on the results of protein marker detection, combined with the existing biological knowledge about organ-specific markers and the location of malignant lesions in patients, the following protein-based identification method for epithelial cell organ localization was obtained.
[0057] First, remove the data of CD45+ cells (leukocytes) and CD105+ (or CD146+) cells (endothelial cells) in the test results;
[0058] Then, according to the rules in Table 1, the results of epithelial cell origin were obtained.
[0059] Table I
[0060]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com