Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Prevent negative consequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
E-Cigarette With Vitamin Infusion
InactiveUS20100200008A1Prevent negative consequenceImprove health benefitsTobacco preparationTobacco devicesInhalationEnvironmental health
Owner:TAIEB ELI
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
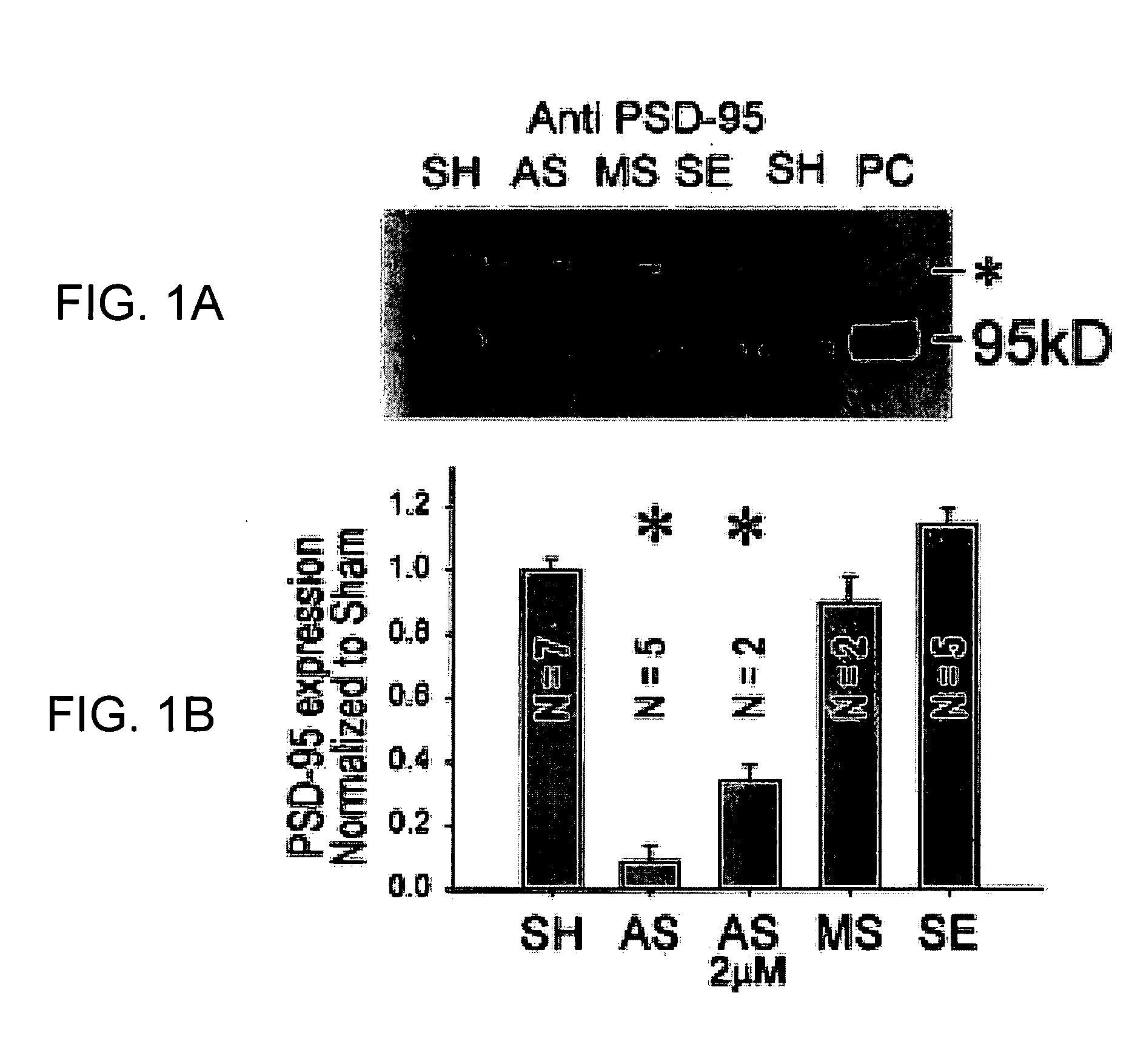
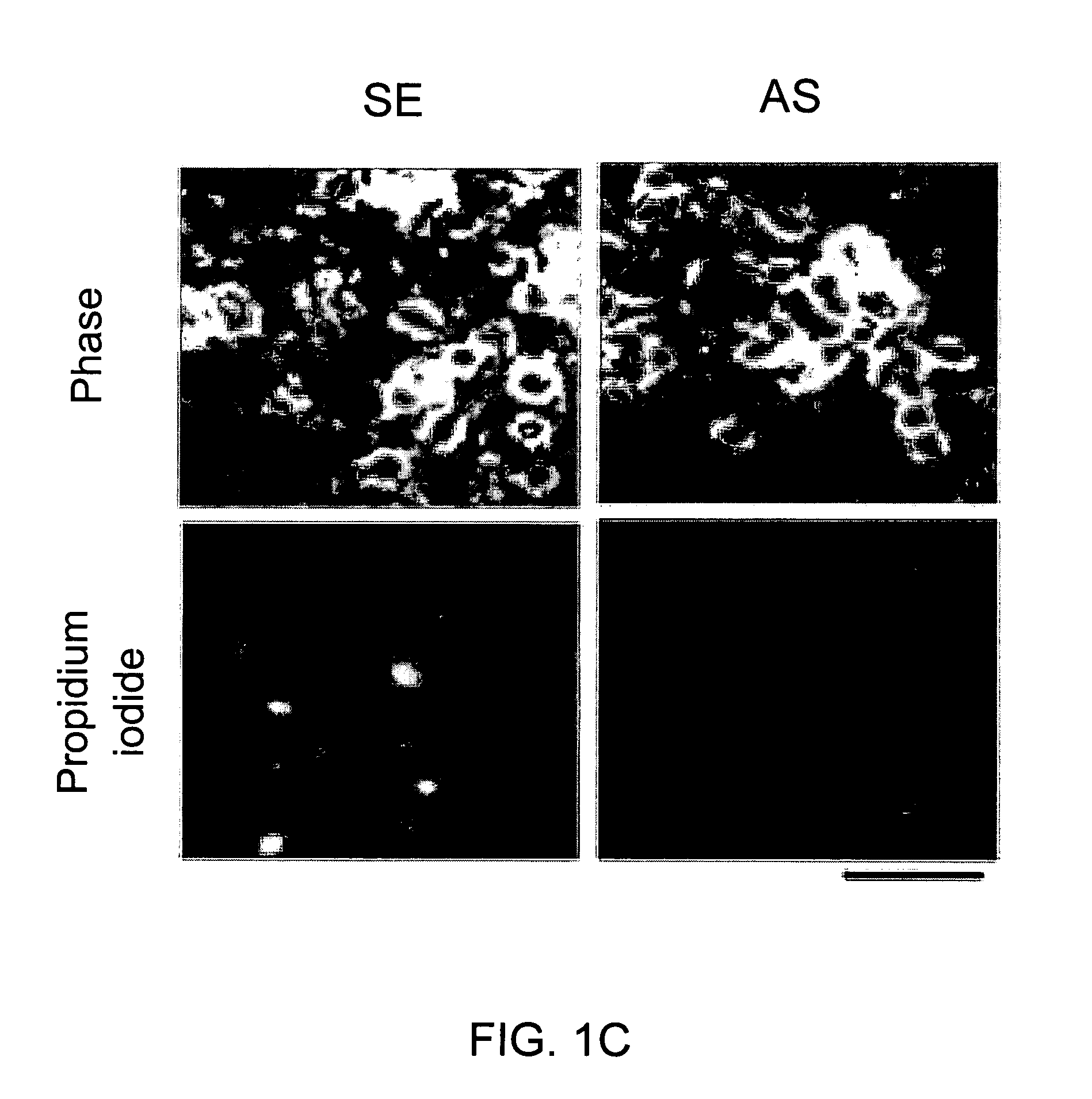
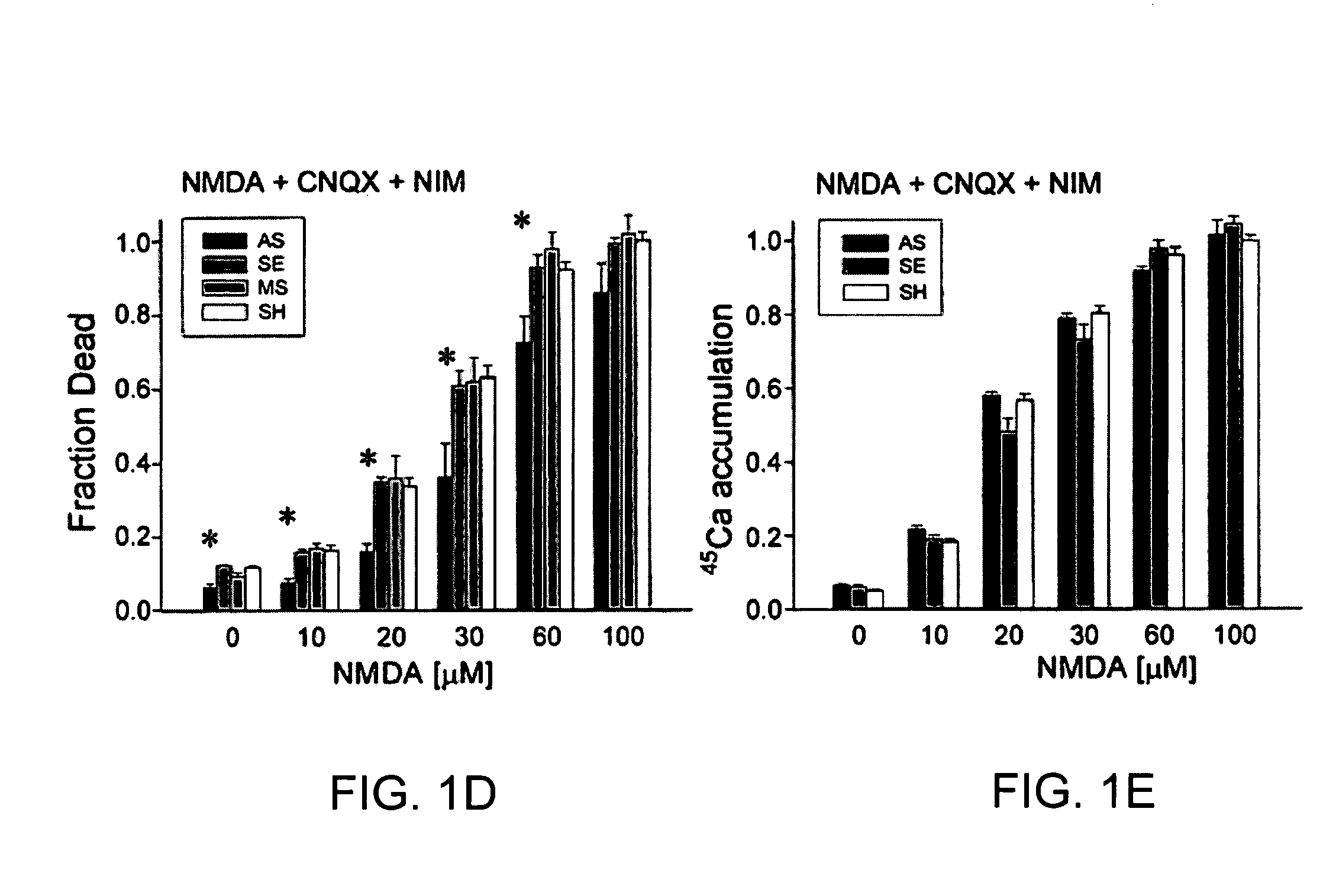
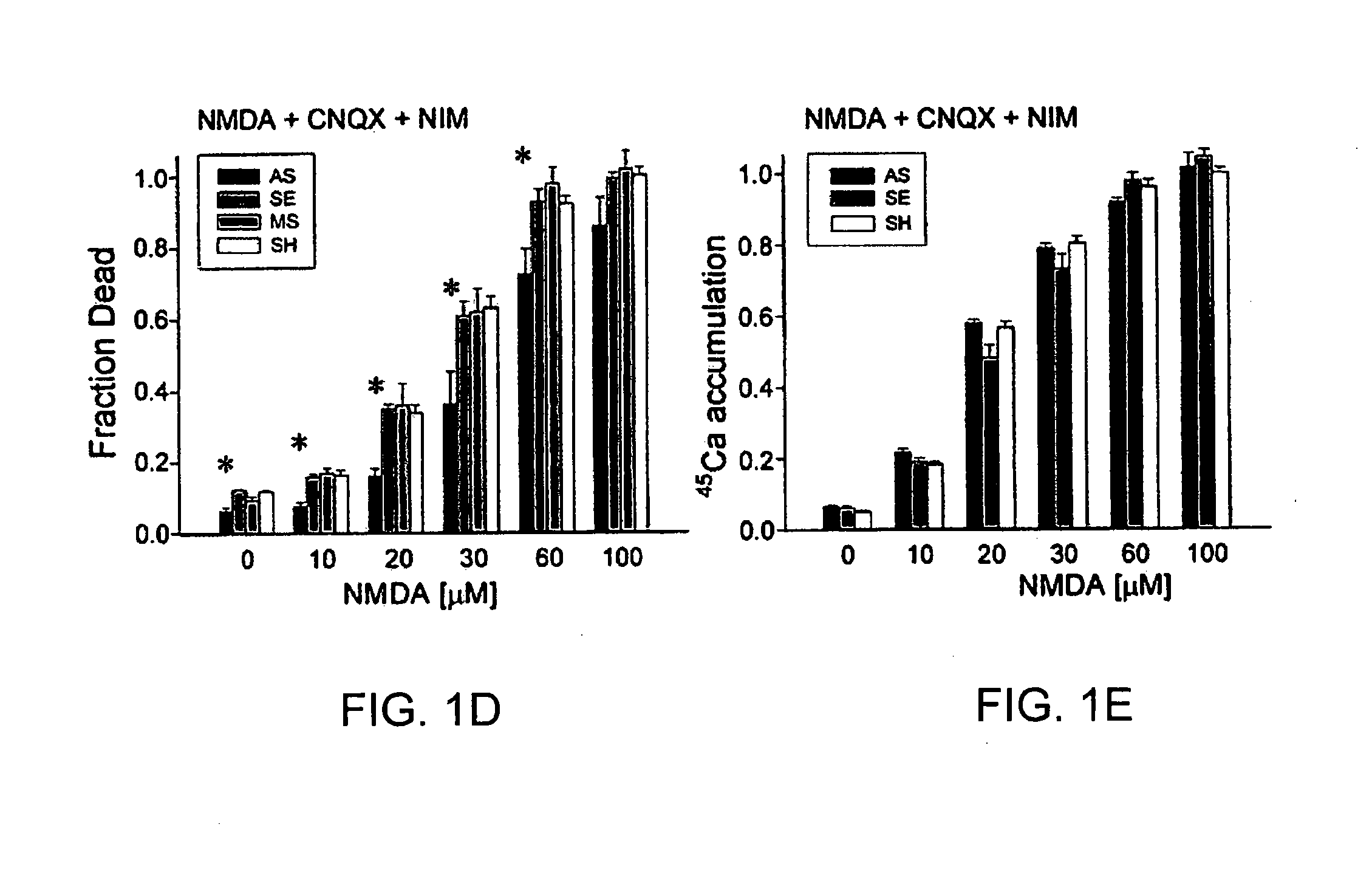
InactiveUS20050059597A1Attenuated downstream NMDAR signalingReduced infarct volumeNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
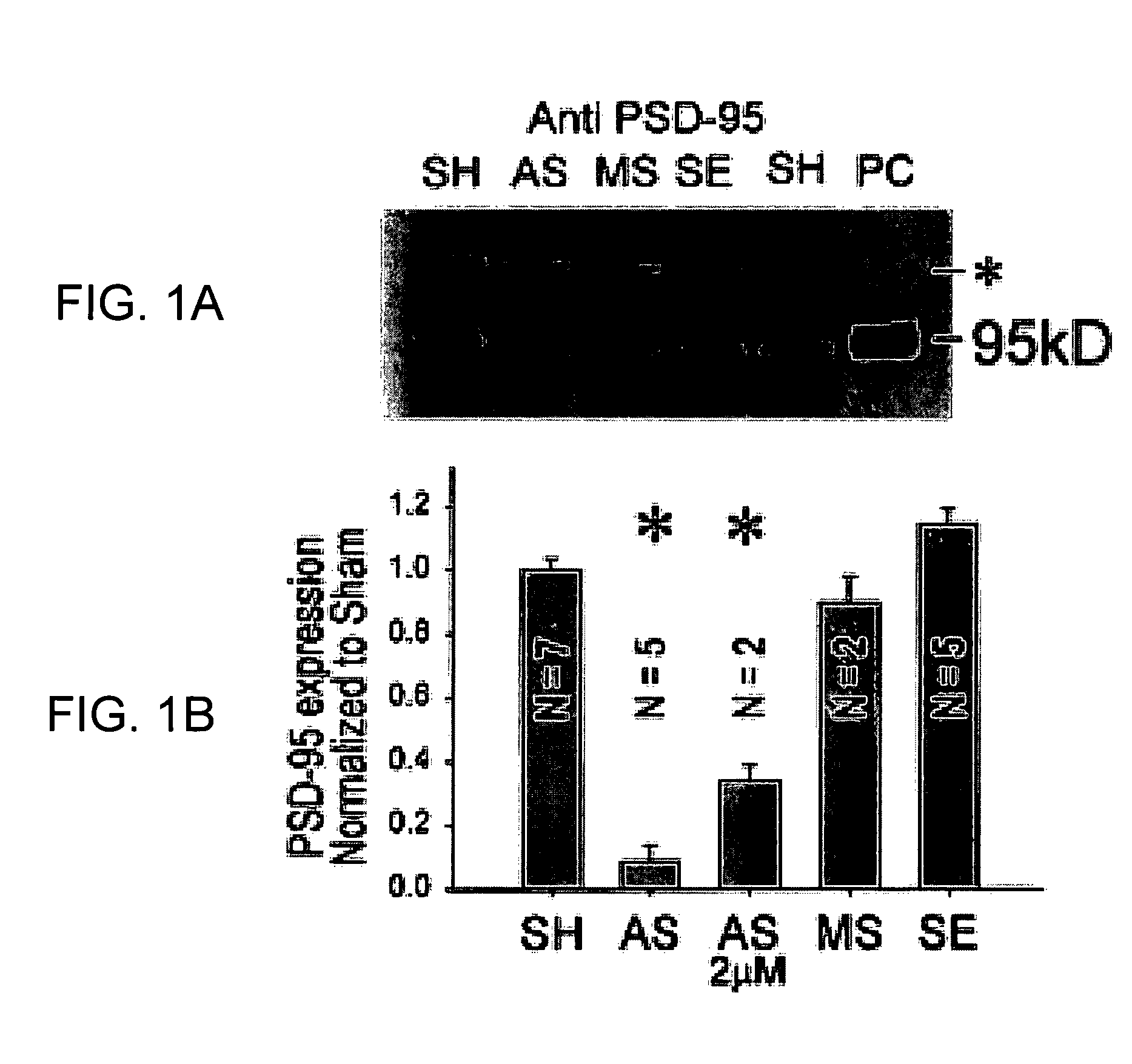
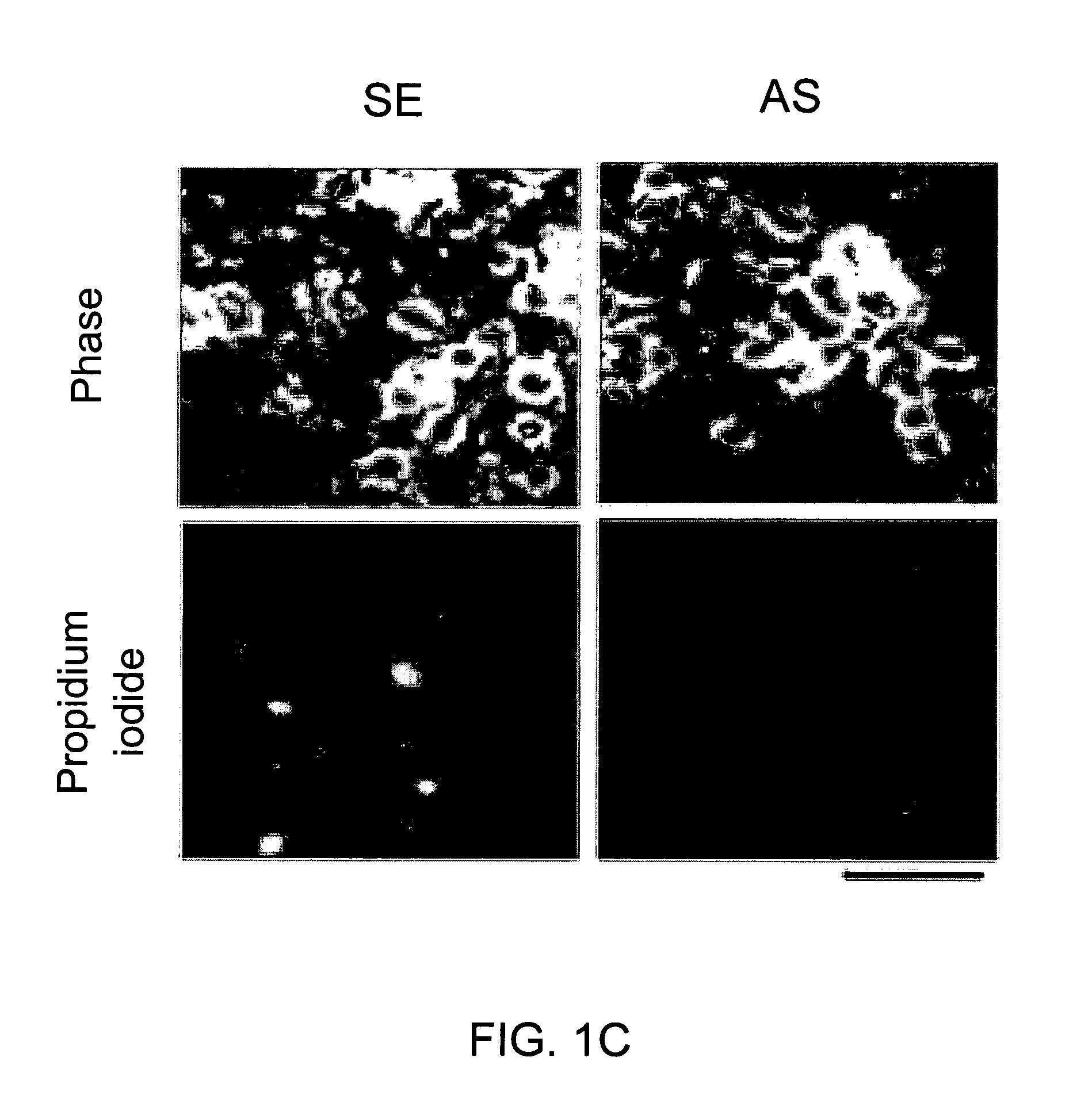
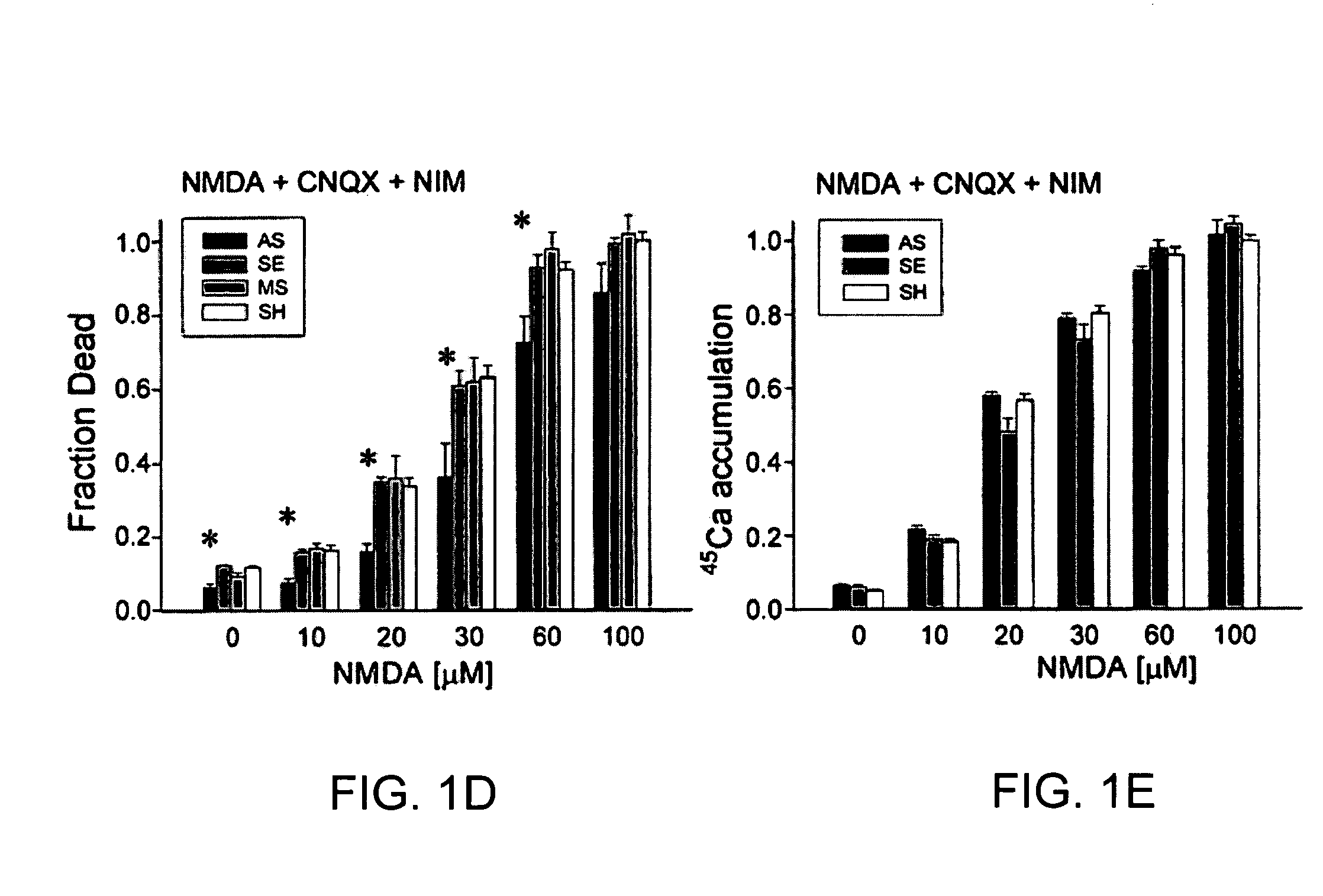
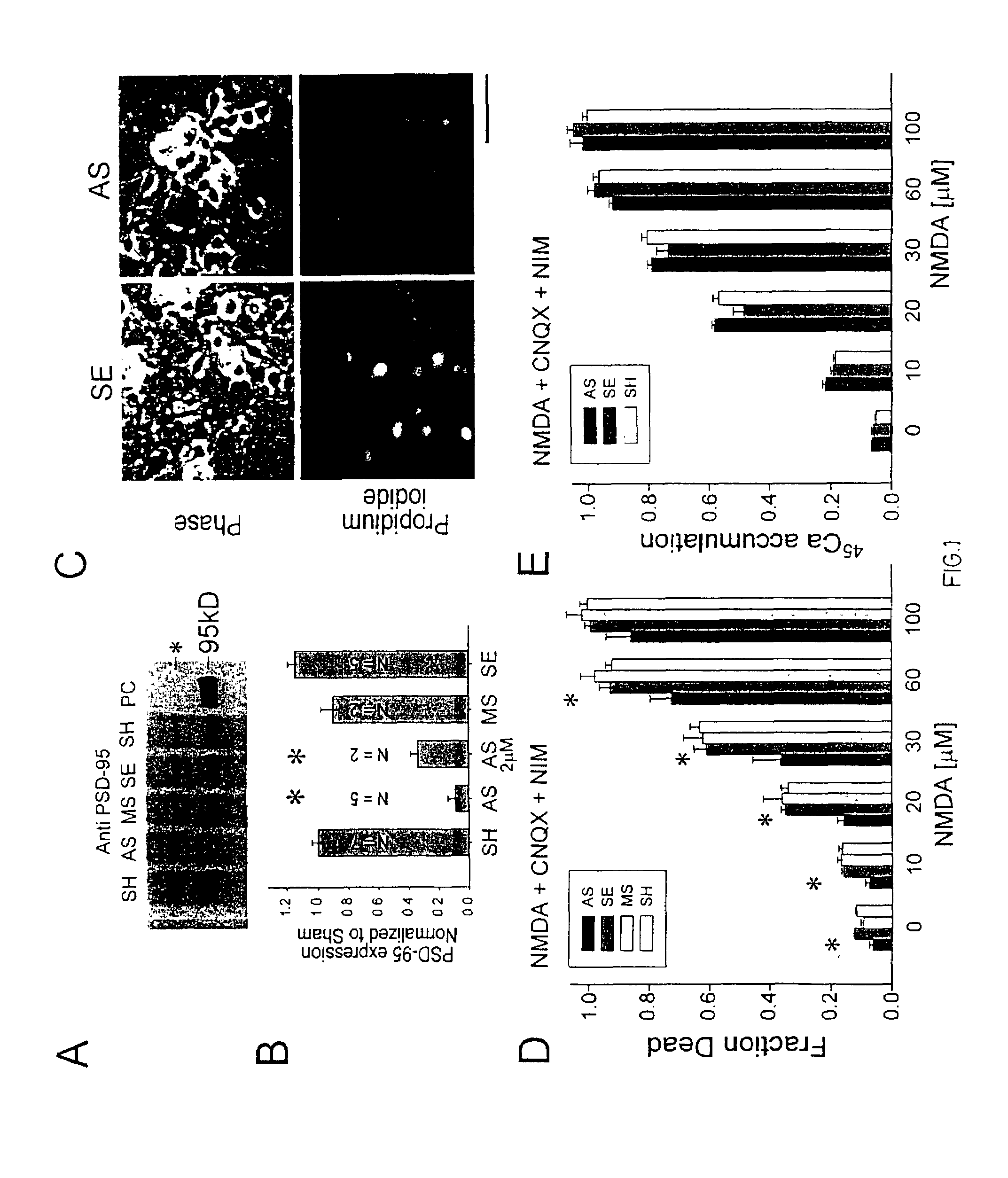
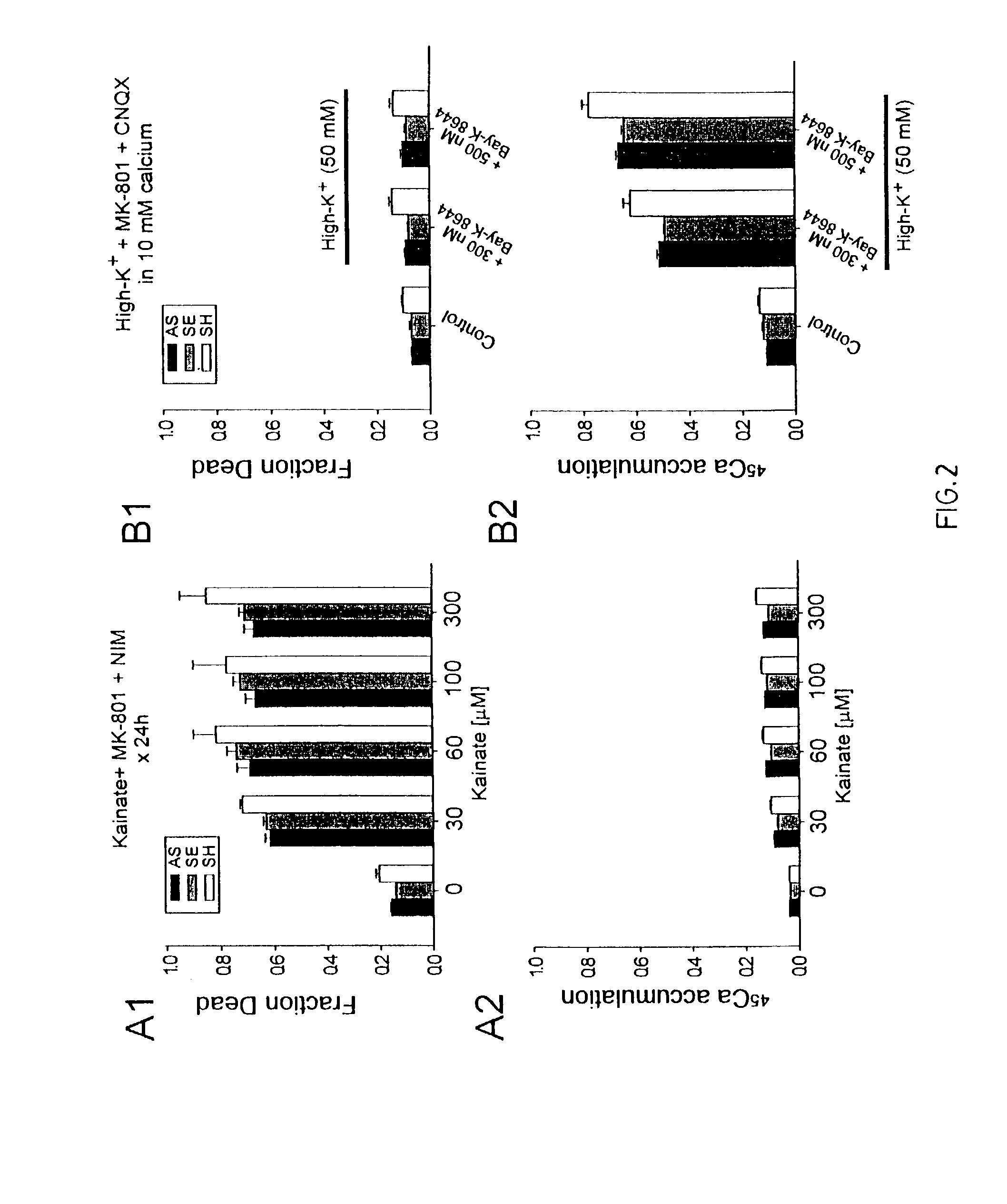
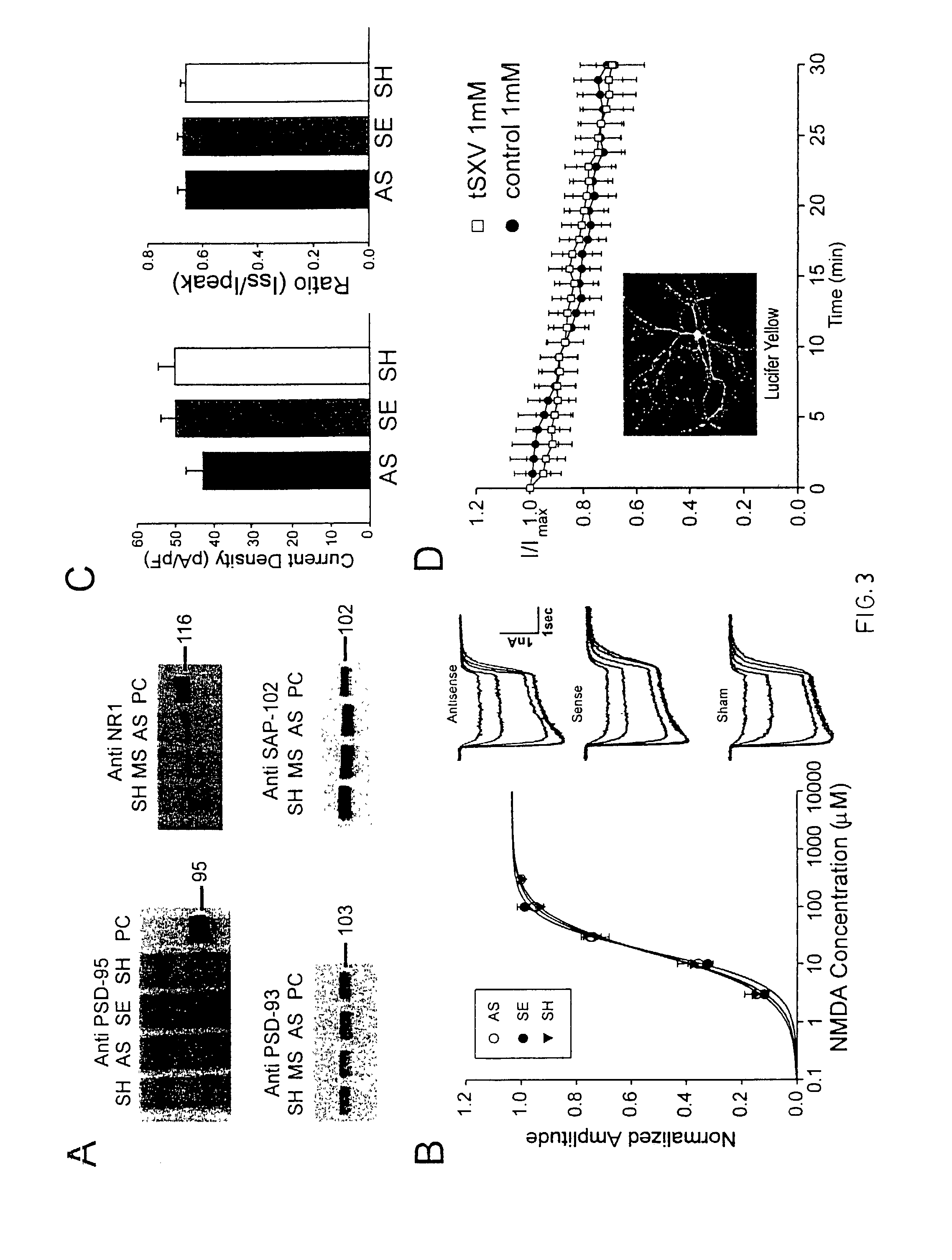
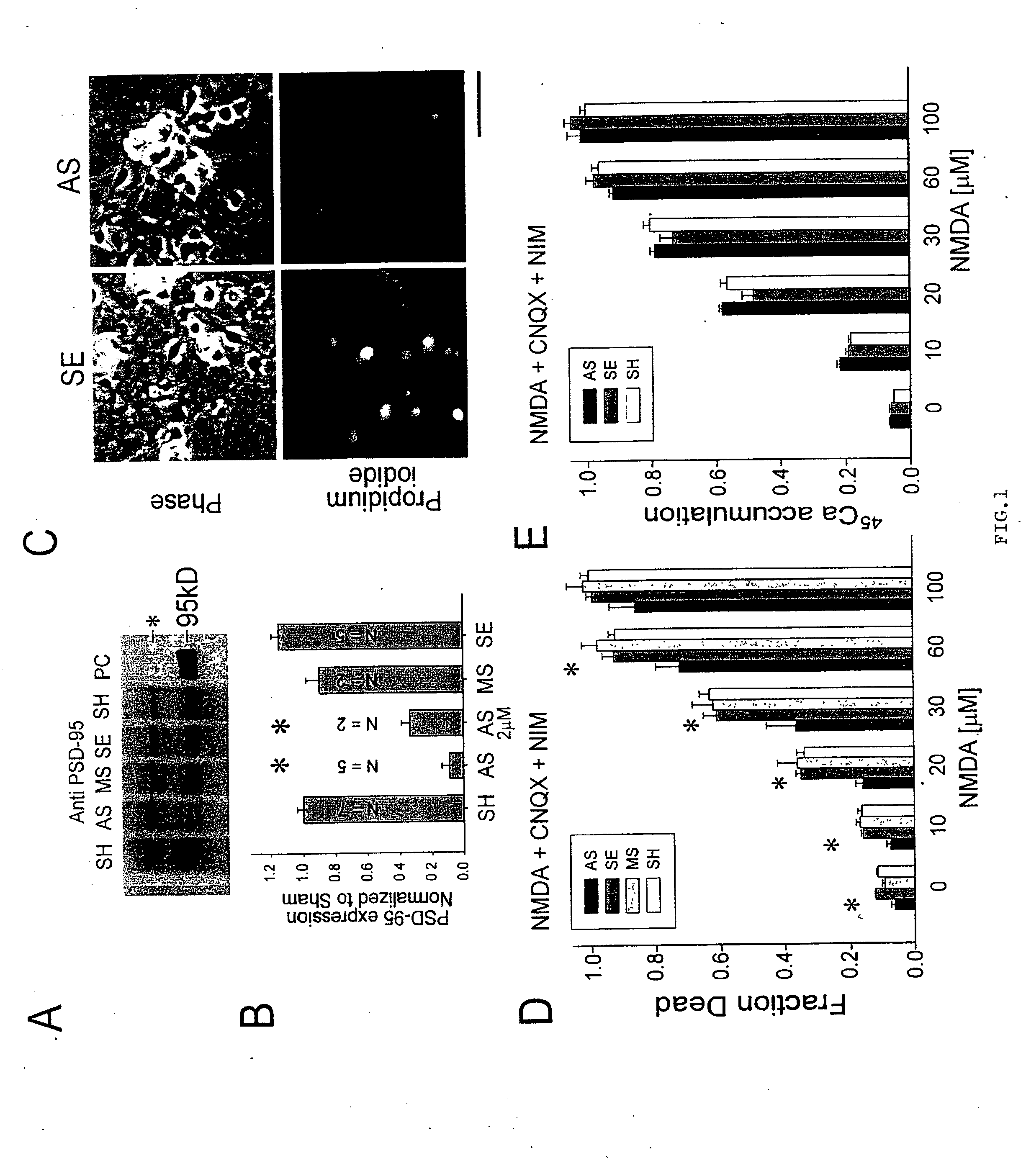
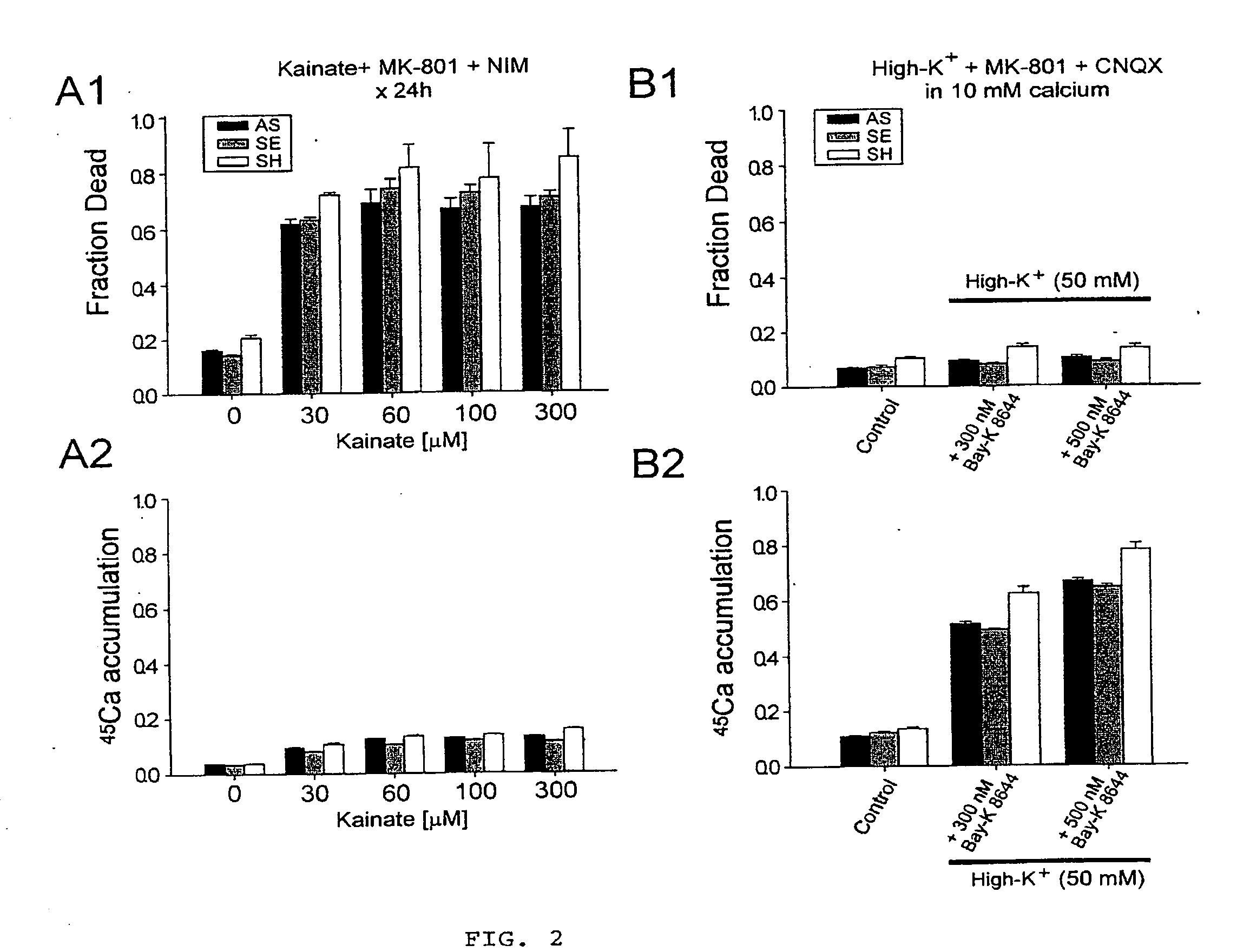
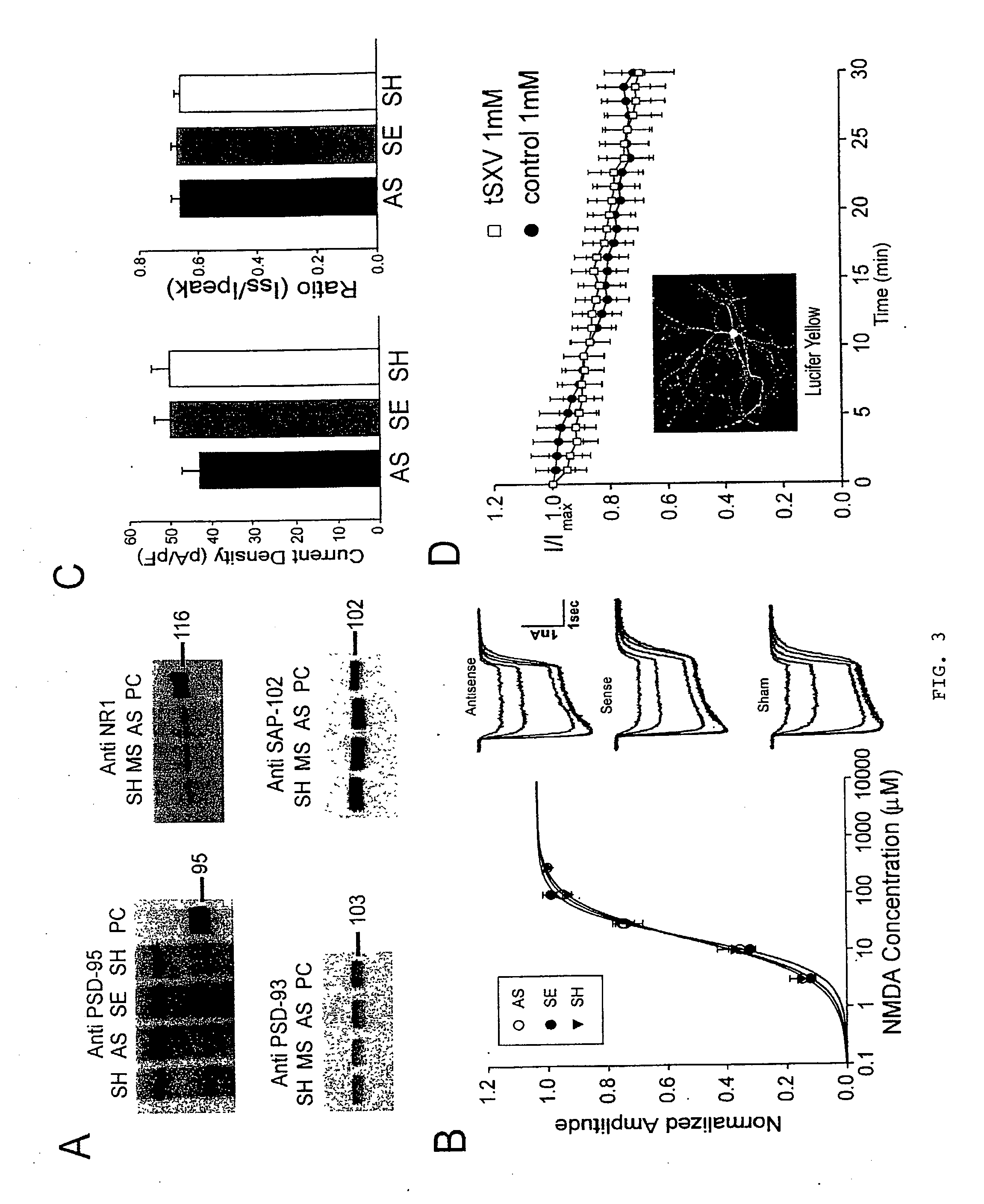
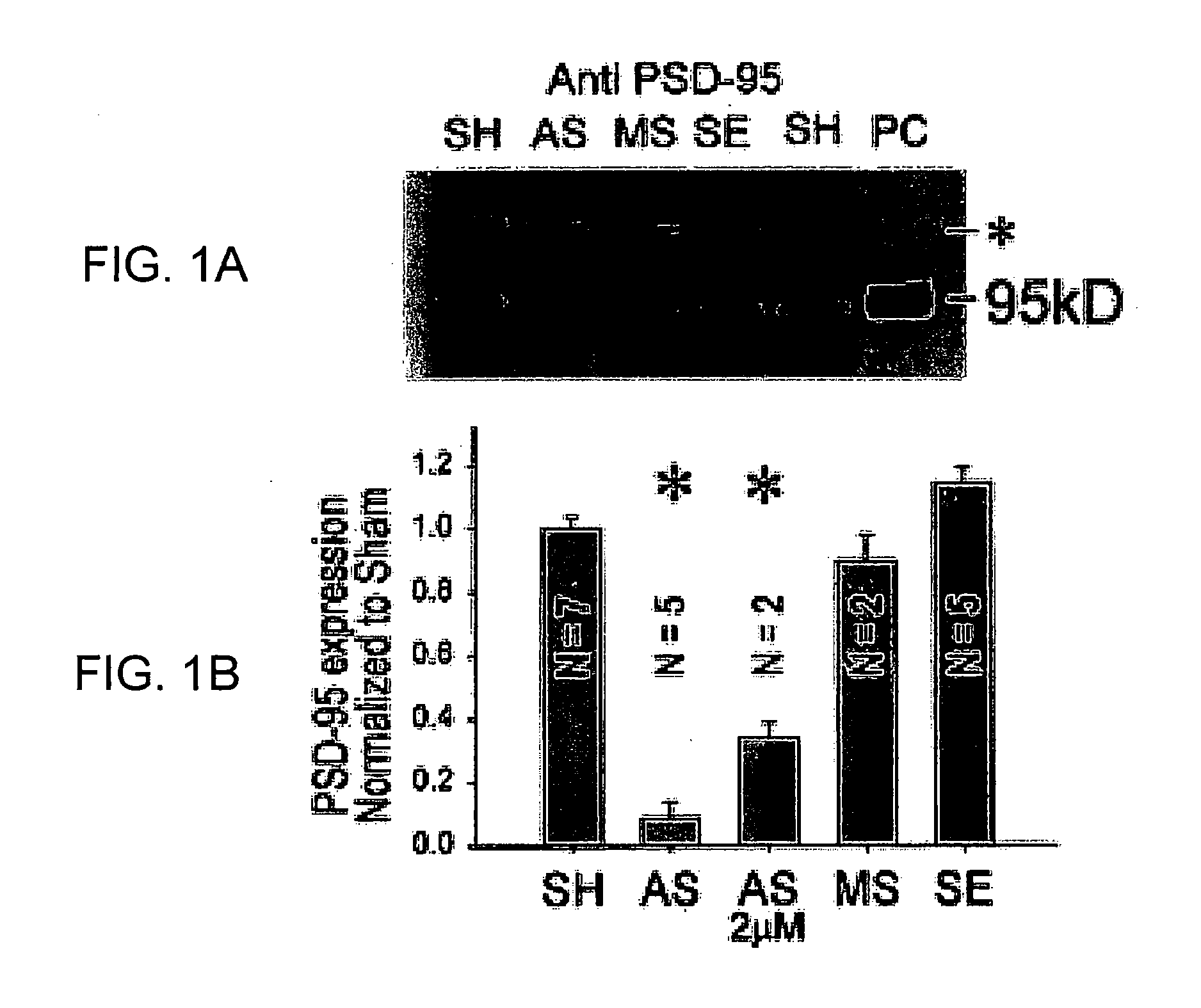
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor—neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
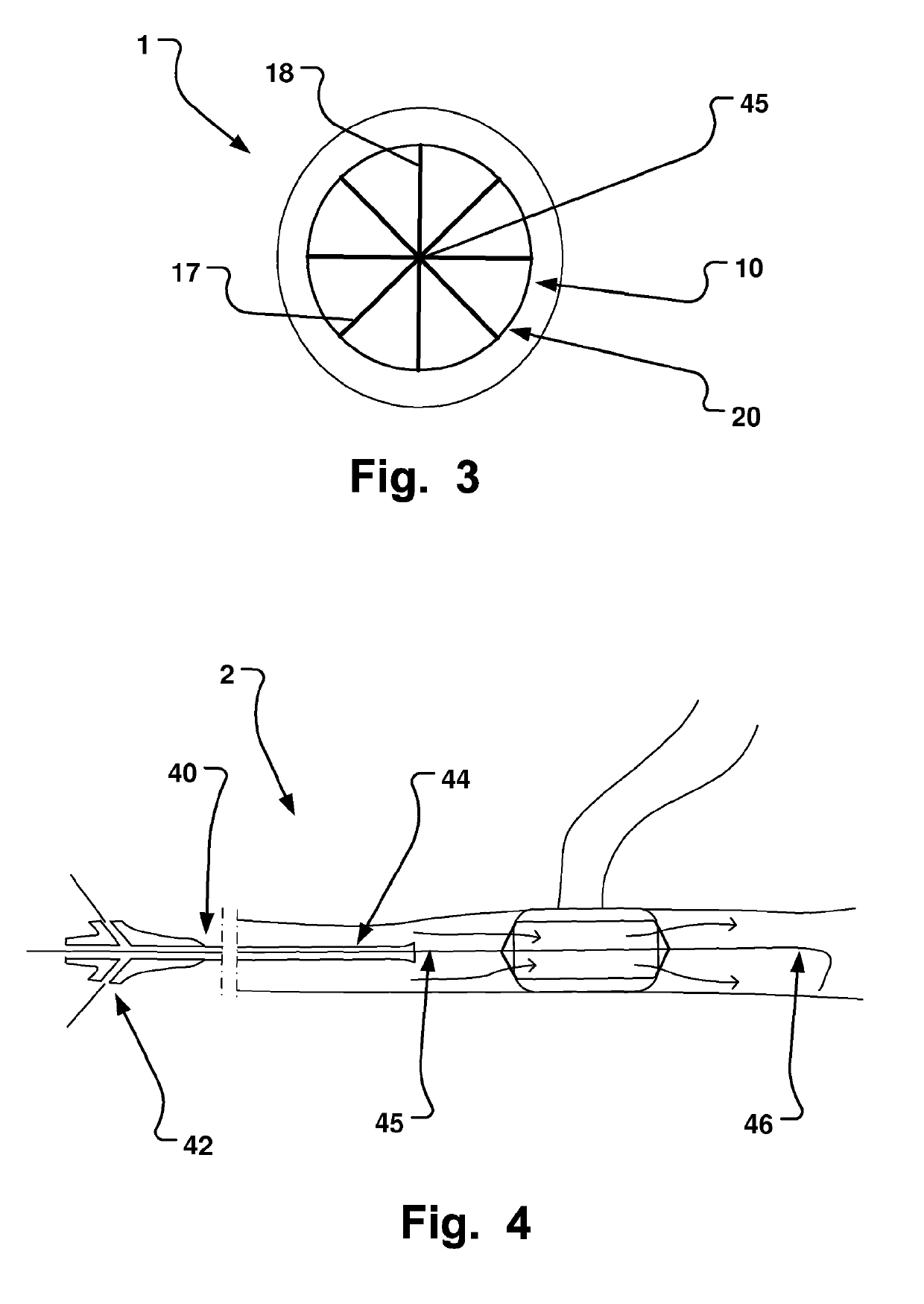
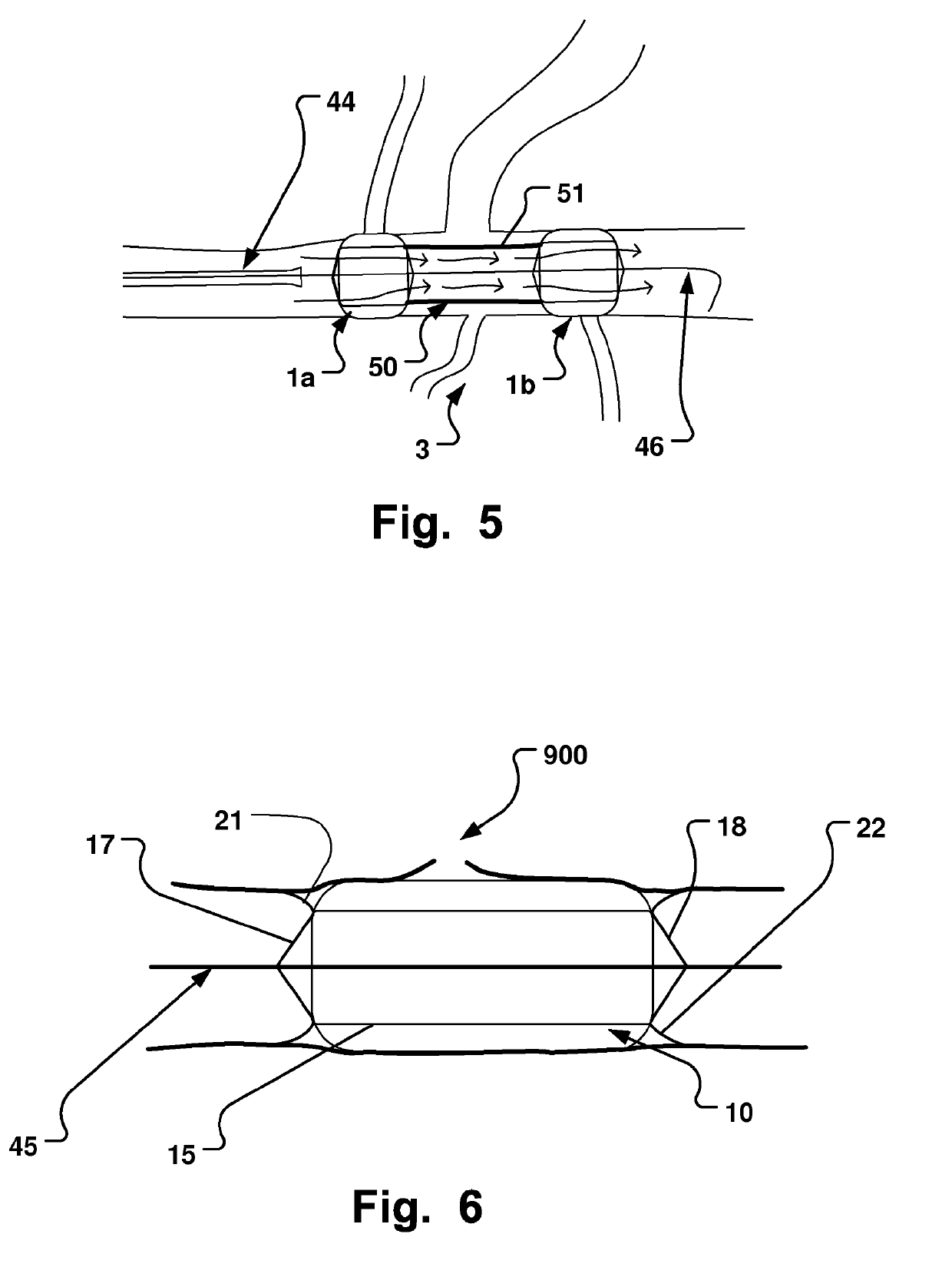
Medical Device, Method And System For Temporary Occlusion Of An Opening In A Lumen Of A Body
InactiveUS20110172697A1Avoid communicationAvoid flowStentsBalloon catheterTemporary occlusionVideo fluoroscopy
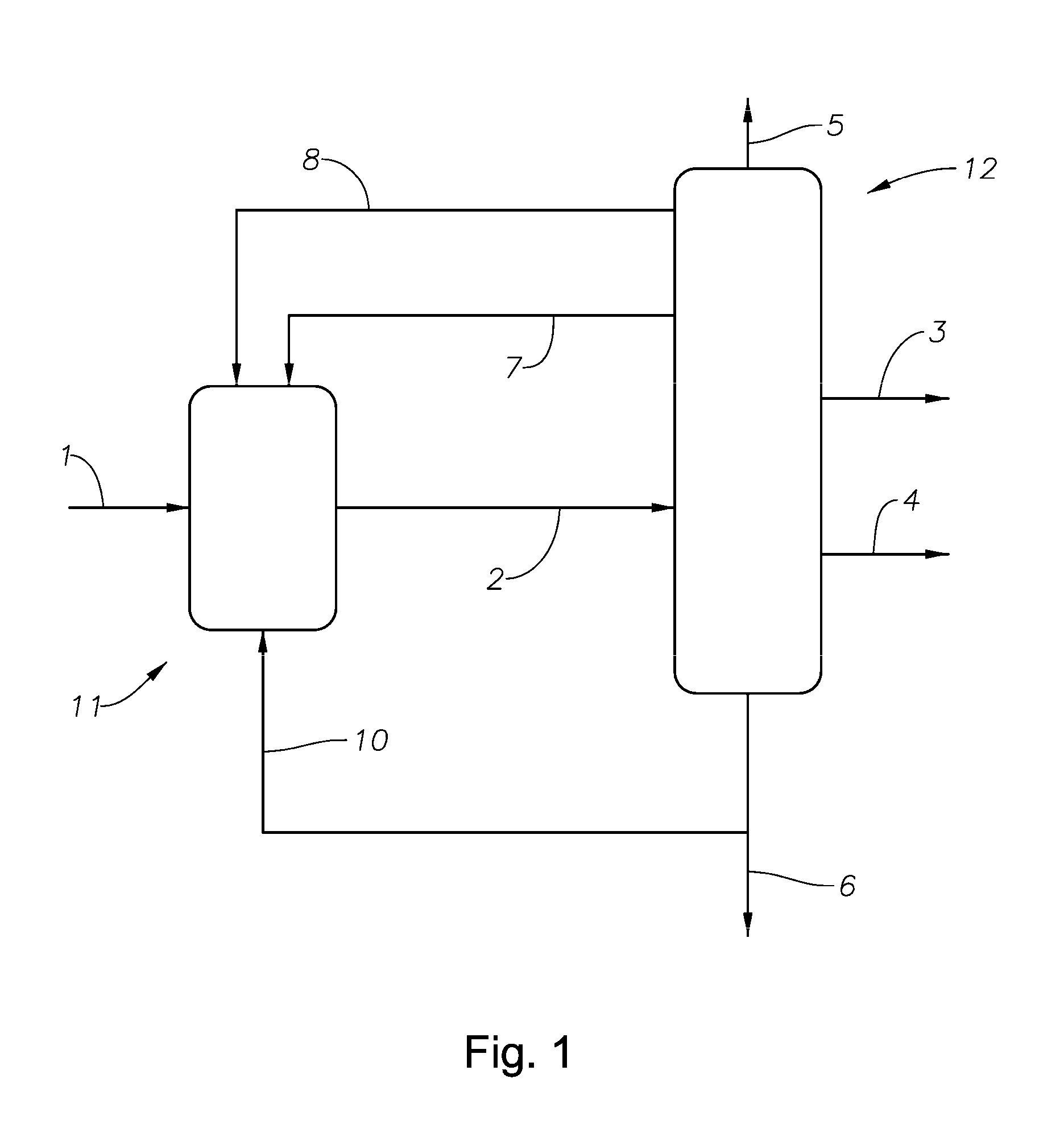
A medical system is disclosed that has three basic components; a retractable sheet, a first balloon that has a centrally arranged hollow, and a collapsible / expandable support structure at the hollow. The first balloon is for instance mounted / molded onto the exterior surface of the support structure. The aggregate of support structure and the first balloon is positioned, and once the sheet has been retracted from the first balloon, the first balloon is inflated. The support structure may be self-expandable or expandable by an expansion unit, such as a further balloon arranged at its inside. The lumen of the support structure is chosen to be smaller than that of a main lumen. The outside diameter of the inflated first balloon is chosen to be larger than the interior diameter of the main lumen. This procedure may be done using standard Seldinger technique and fluoroscopy. This makes the system user friendly and increases patient safety, as a well established clinical method may be used with some modifications according to the invention.
Owner:AEEG
Alkylation Process
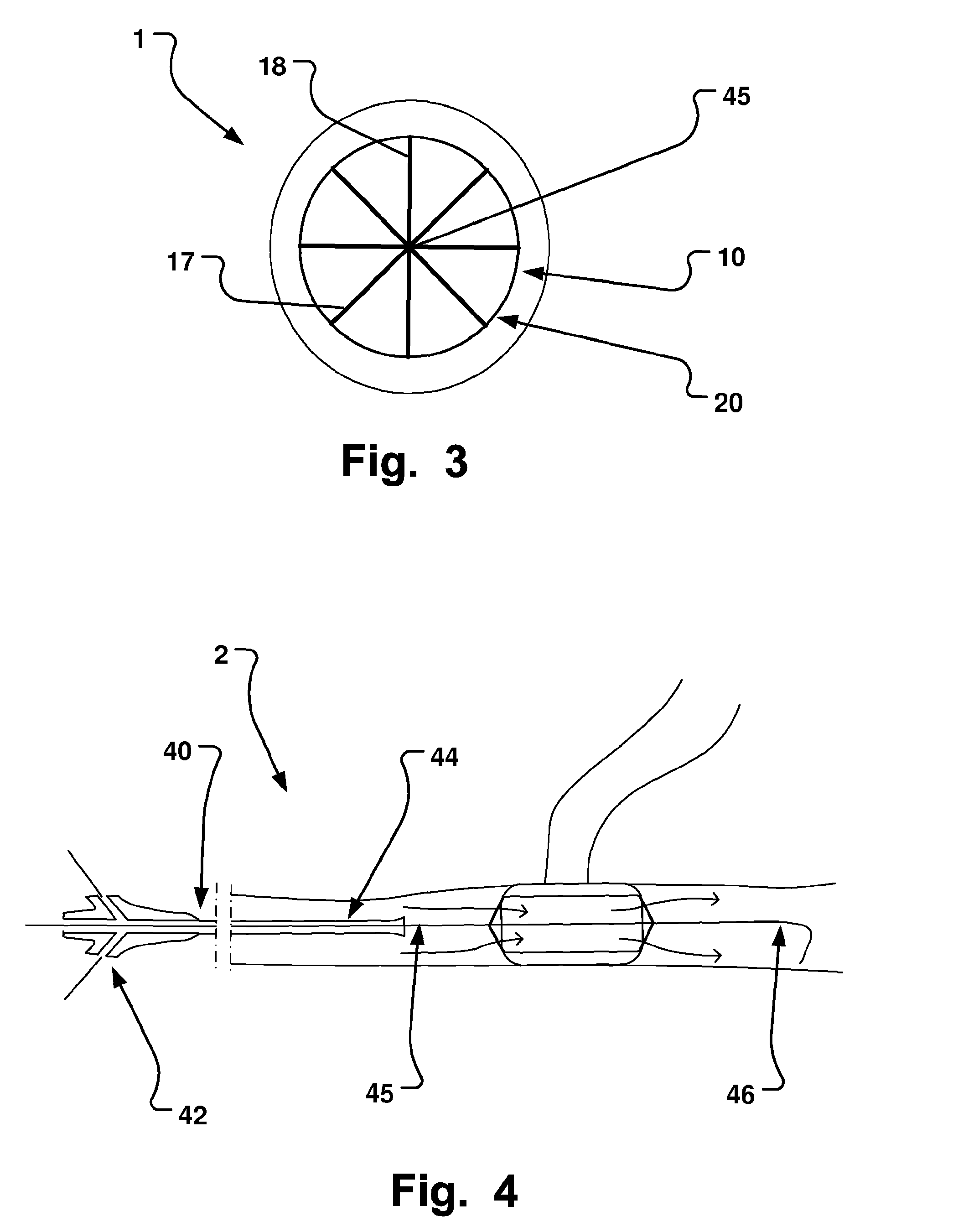
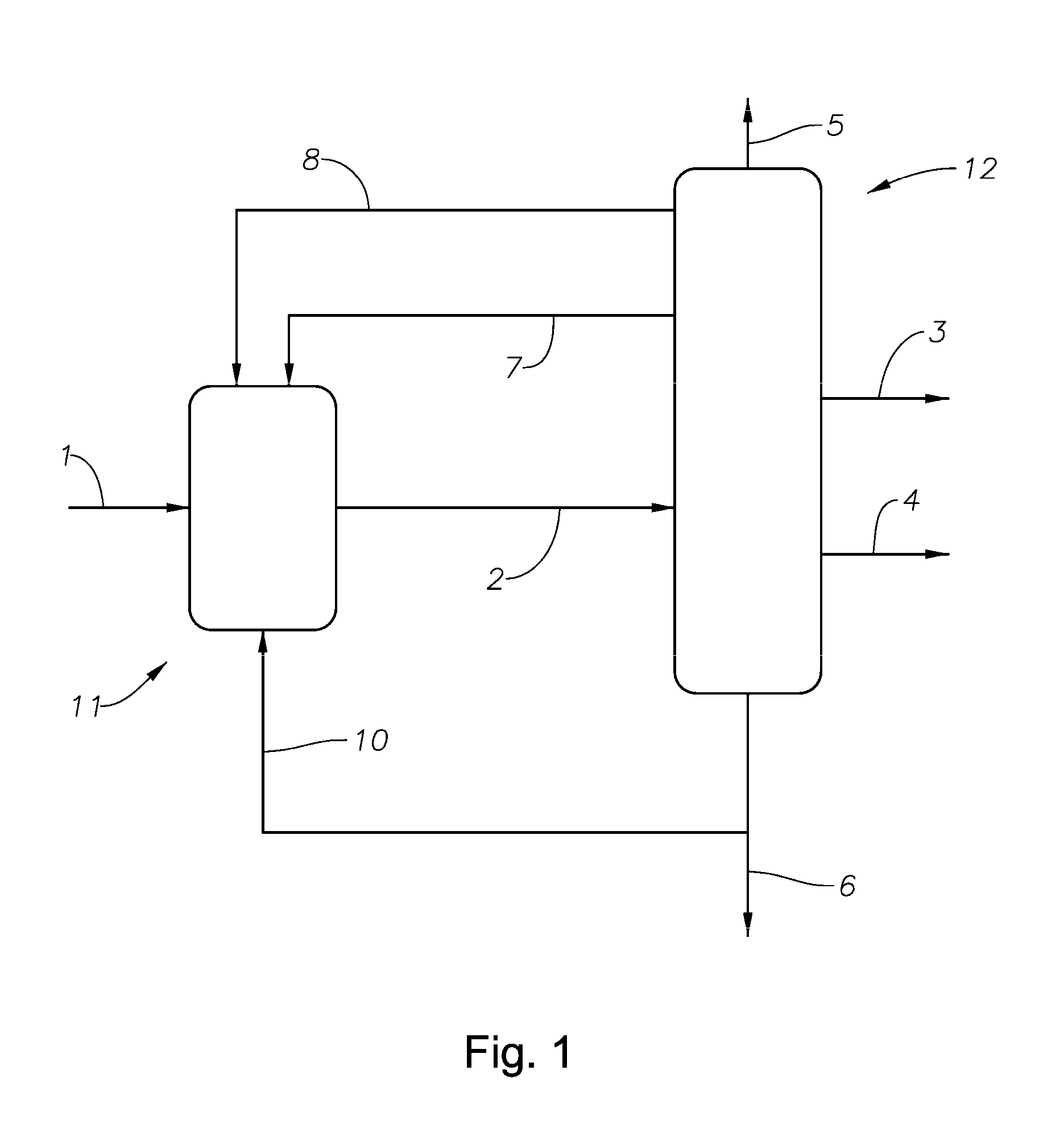
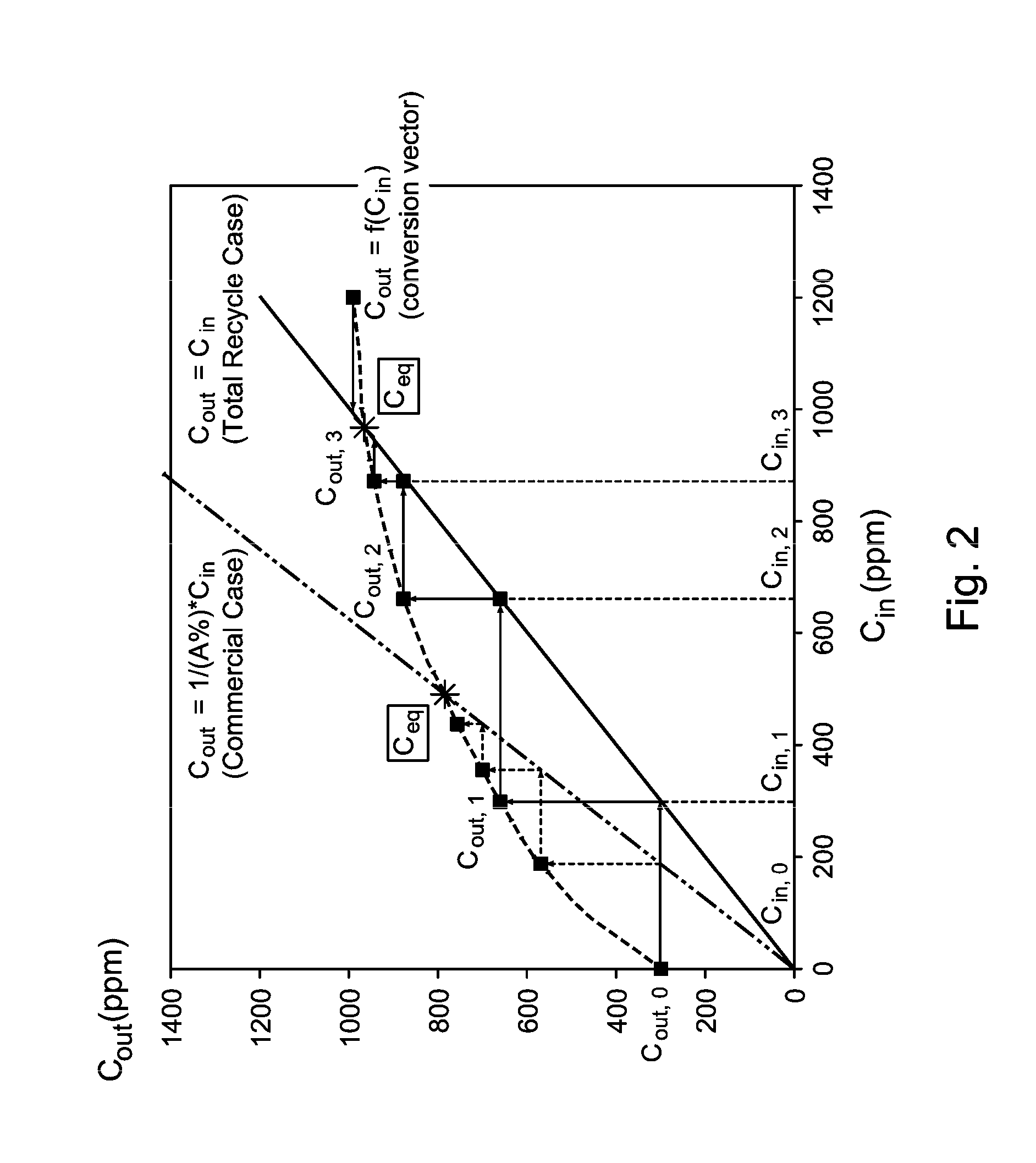
ActiveUS20130253245A1Prevent negative consequenceHydrocarbonsHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationOxygenateAlkylation
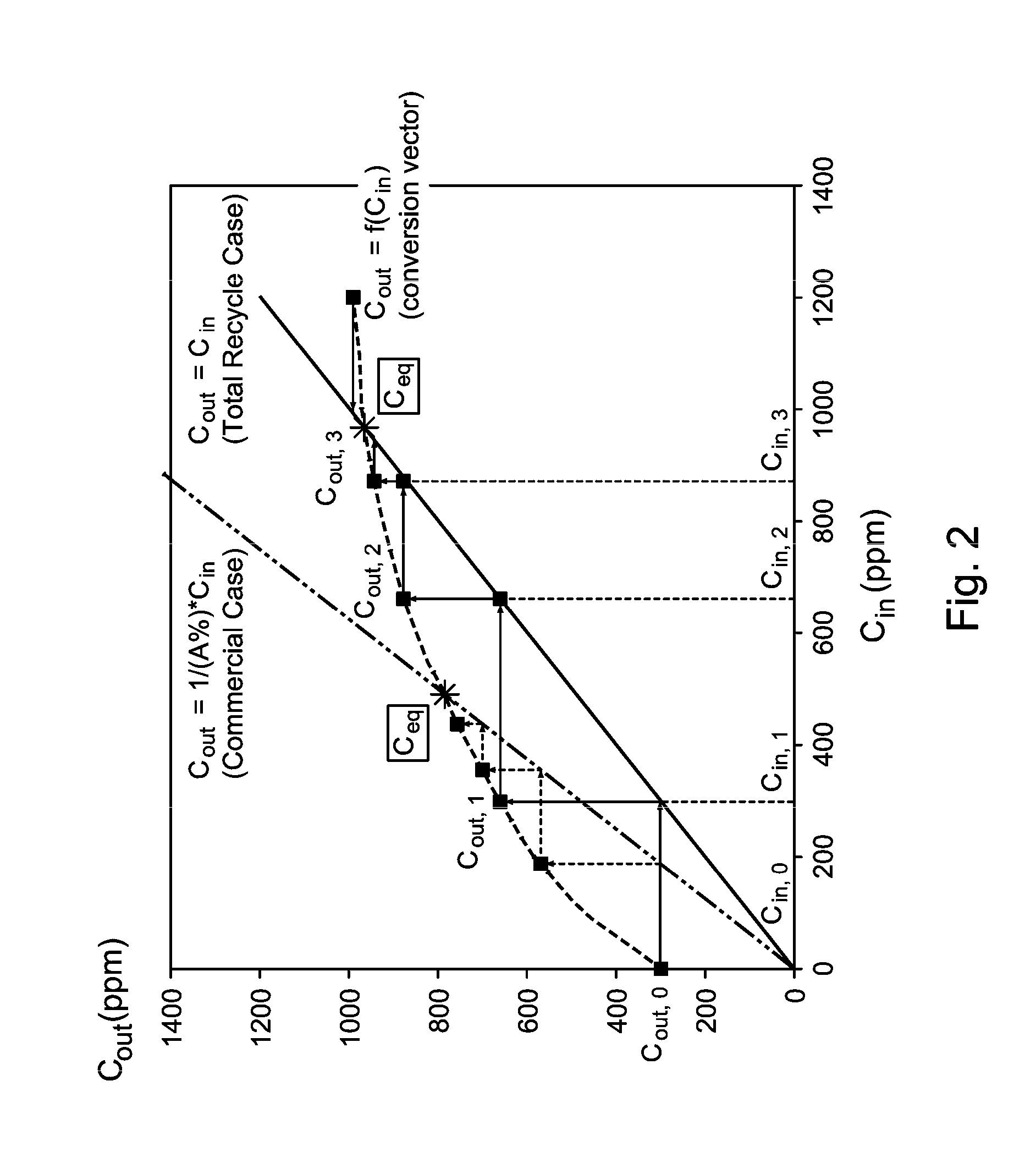
The invention relates to the production of paraxylene by an alkylation process that also produces oxygenates. The process is controlled to utilize recycle to minimize said oxygenates.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Method of screening peptides useful in treating traumatic injury to the brain or spinal cord
InactiveUS7510824B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsInjury causeMedicine
A method of screening peptides which bind to at least one PDZ domain and comprise a cell-membrane transduction domain for use in treating traumatic injury to the brain or spinal cord by deforming neurons on a flexible substrate with sublethal stretch, then inflicting a secondary injury, and determining survival of the stretched neurons in the absence or presence of the peptide which is being screened.
Owner:NONO INC
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS7595297B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron the method comprising administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor neuronal protein. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults and dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. The treatment was effective when applied either before, or one hour after, the onset of excitotoxicity in vitro and cerebral ischemia in vivo. This approach prevents negative consequences associated with blocking NMDAR activity and constitutes practical therapy for stroke.
Owner:NONO INC
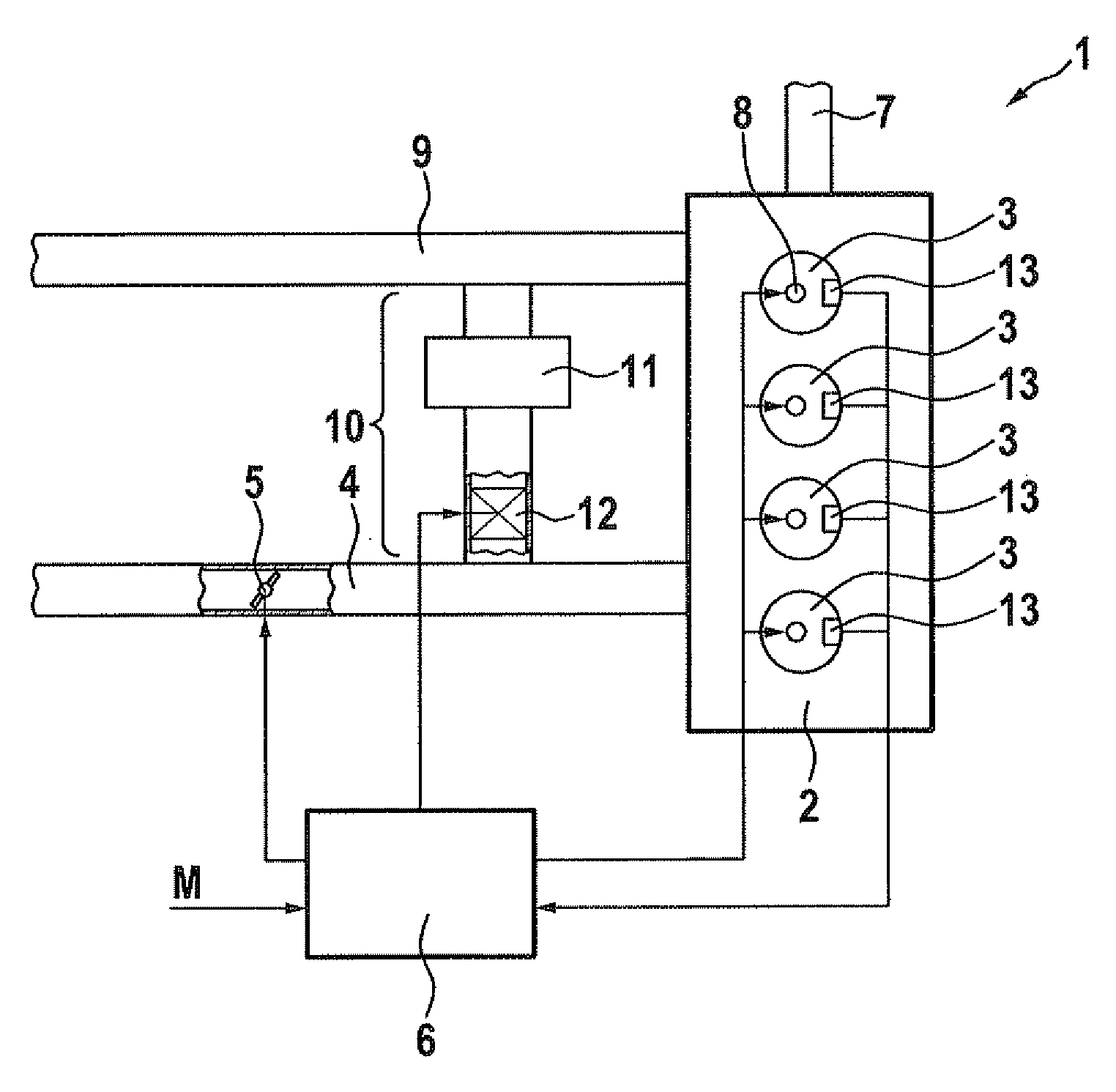
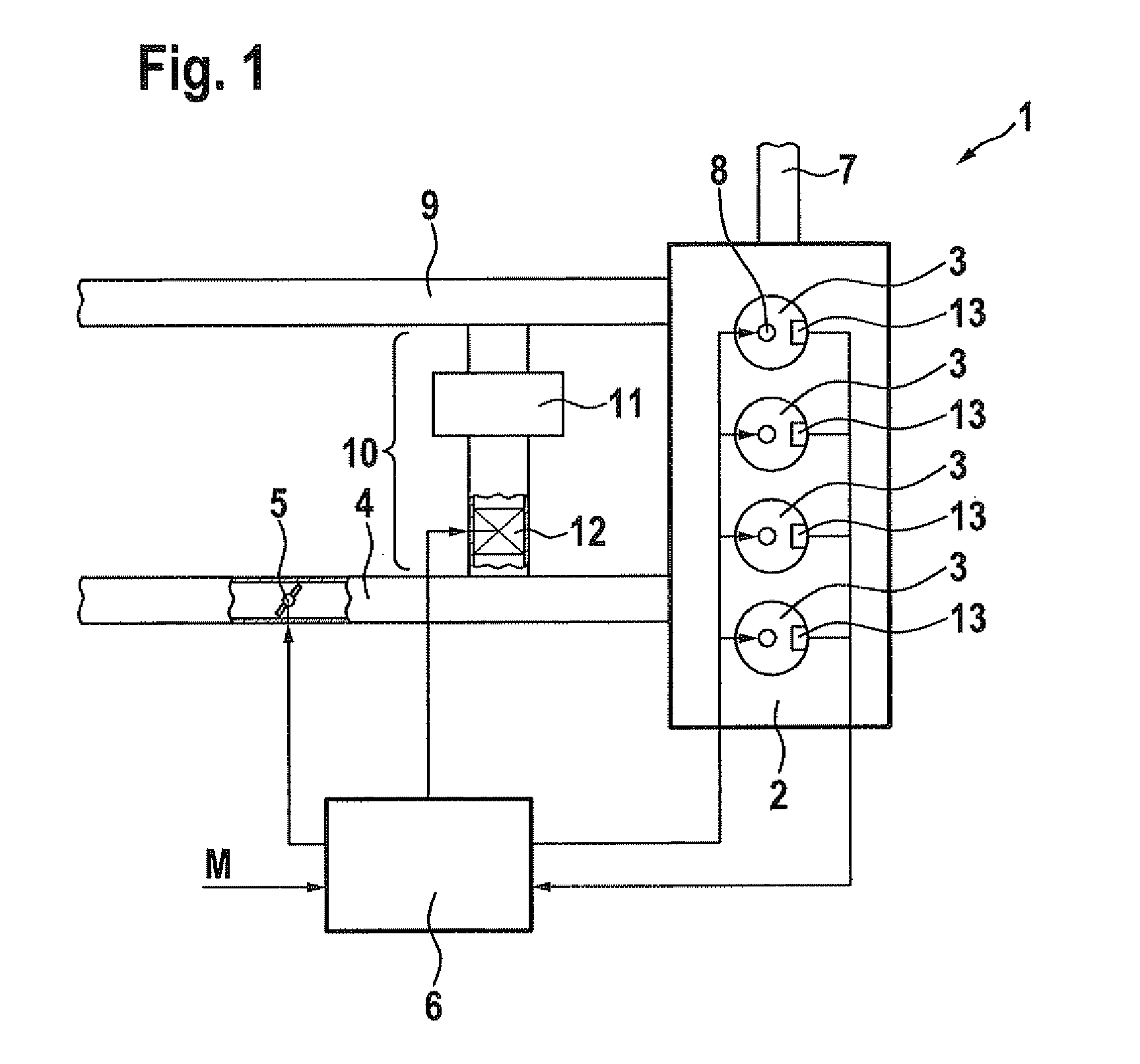
Method for controlling a compression-ignition internal combustion engine and control device for controlling a compression-ignition internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20090187325A1Reduce fuel consumptionGood homogeneous mixture formationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustionInternal combustion engine
A method for controlling a compression-ignition internal combustion engine includes the following steps: predefining a setpoint combustion point for the compression-ignition internal combustion engine, predefining a calculation model for calculating a probable deviation of a future cycle of the internal combustion engine from the predefined setpoint combustion point while taking an ascertained actual combustion point of a completed cycle of the internal combustion engine into consideration, predefining a mean deviation for the internal combustion engine, operating the internal combustion engine for a first cycle and ascertaining an actual combustion point of the first cycle, calculating a probable deviation of a second cycle, which occurs after the first cycle, of the internal combustion engine from the predefined setpoint combustion point, comparing the calculated probable deviation of the second cycle to the predefined mean deviation, and ascertaining at least one operating variable for operating the internal combustion engine at least during the second cycle as a function of the comparison. In addition, a control device for controlling a compression-ignition internal combustion engine is described.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and device for fail-safe erase of flash memory
ActiveUS20170052734A1Prevent negative consequenceAvoid readingInput/output to record carriersRead-only memoriesMemory controllerFlash memory
The present disclosure provides a flash memory device including a flash memory comprising a plurality of nonvolatile memory cells, divided into a plurality of erase units; a memory section dedicated to storing erase status information, the erase status information indicating an erase status of the plurality of erase units; and a memory controller configured to receive an erase request indicating at least one erase unit; store erase status information for the at least one erase unit in the memory section; perform an erase operation on the at least one erase unit; and update the stored erase status information upon completion of the erase operation. In addition, the present disclosure provides a way how incomplete erase commands can be handled transparently in a fail safe way.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
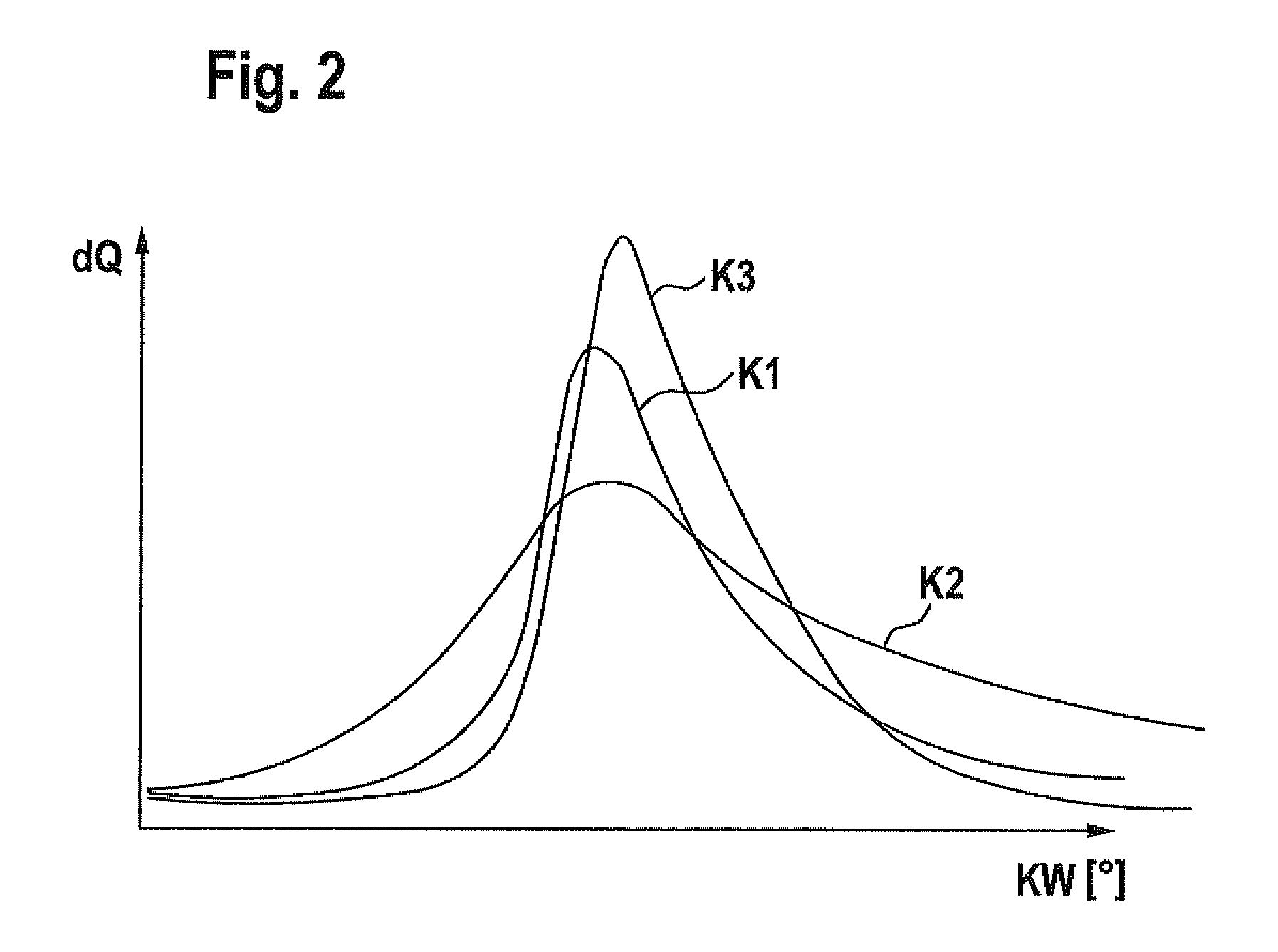
Method and device for operating a combustion engine
ActiveUS8434456B2Prevent negative consequenceAvoid it happening againAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustionEngineering
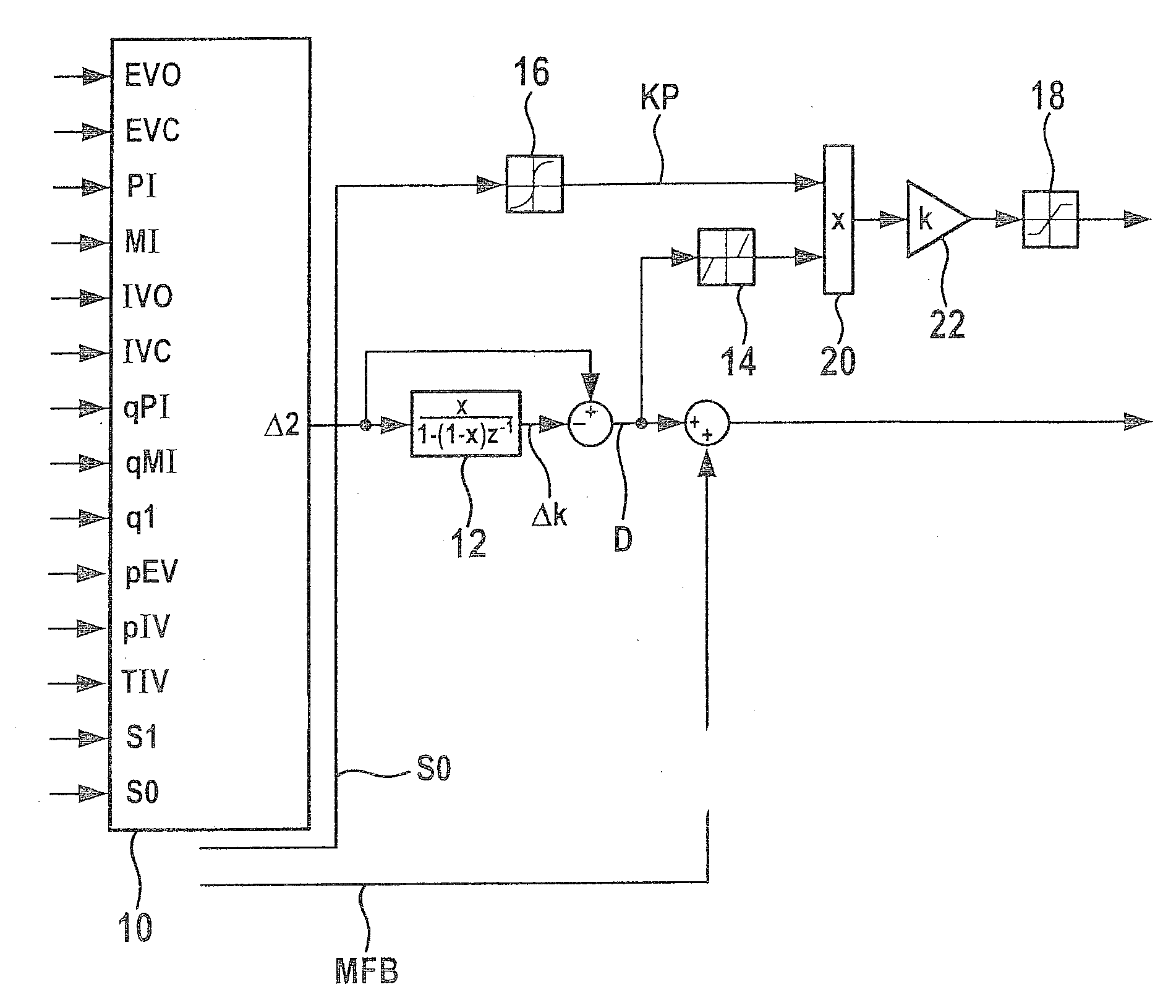
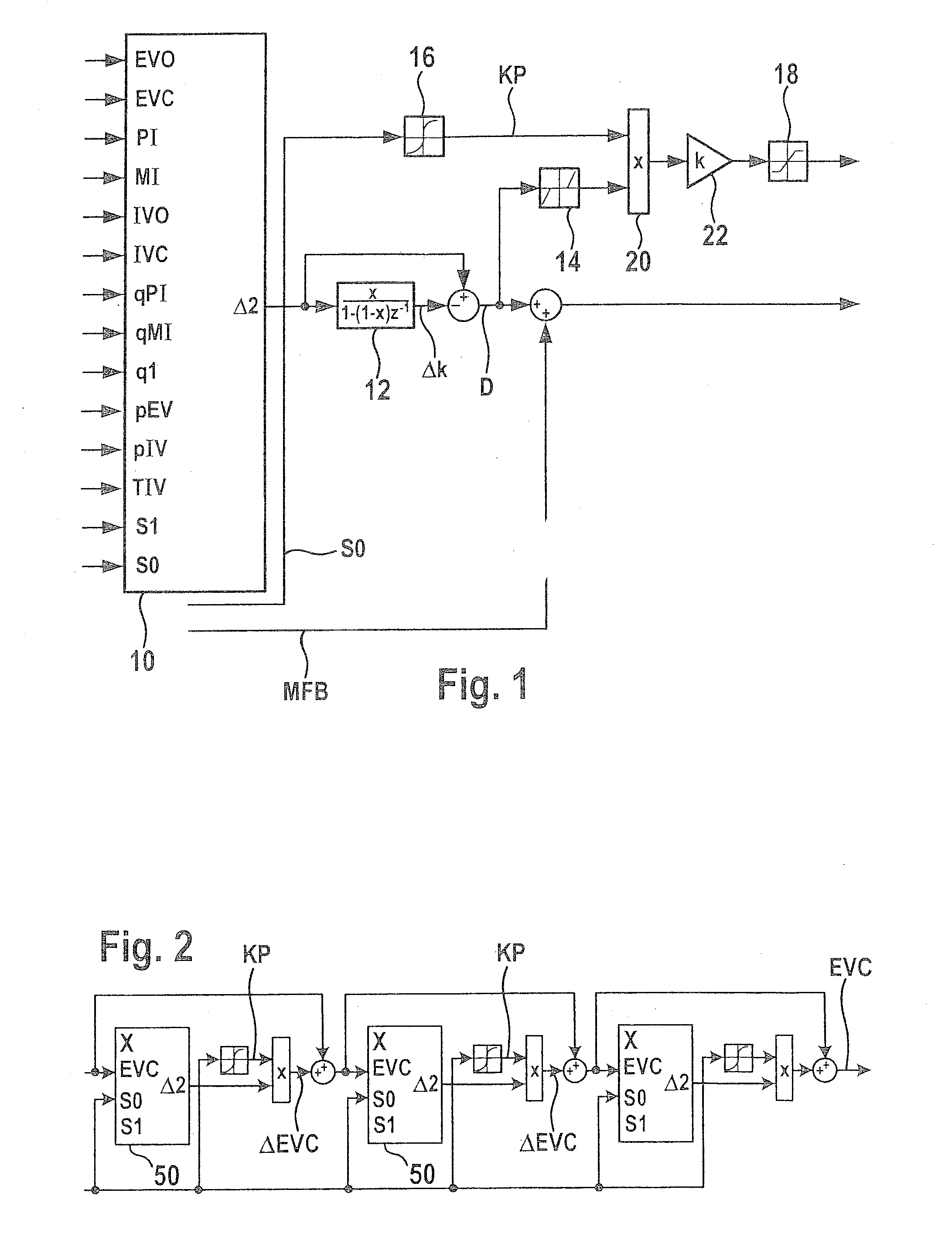
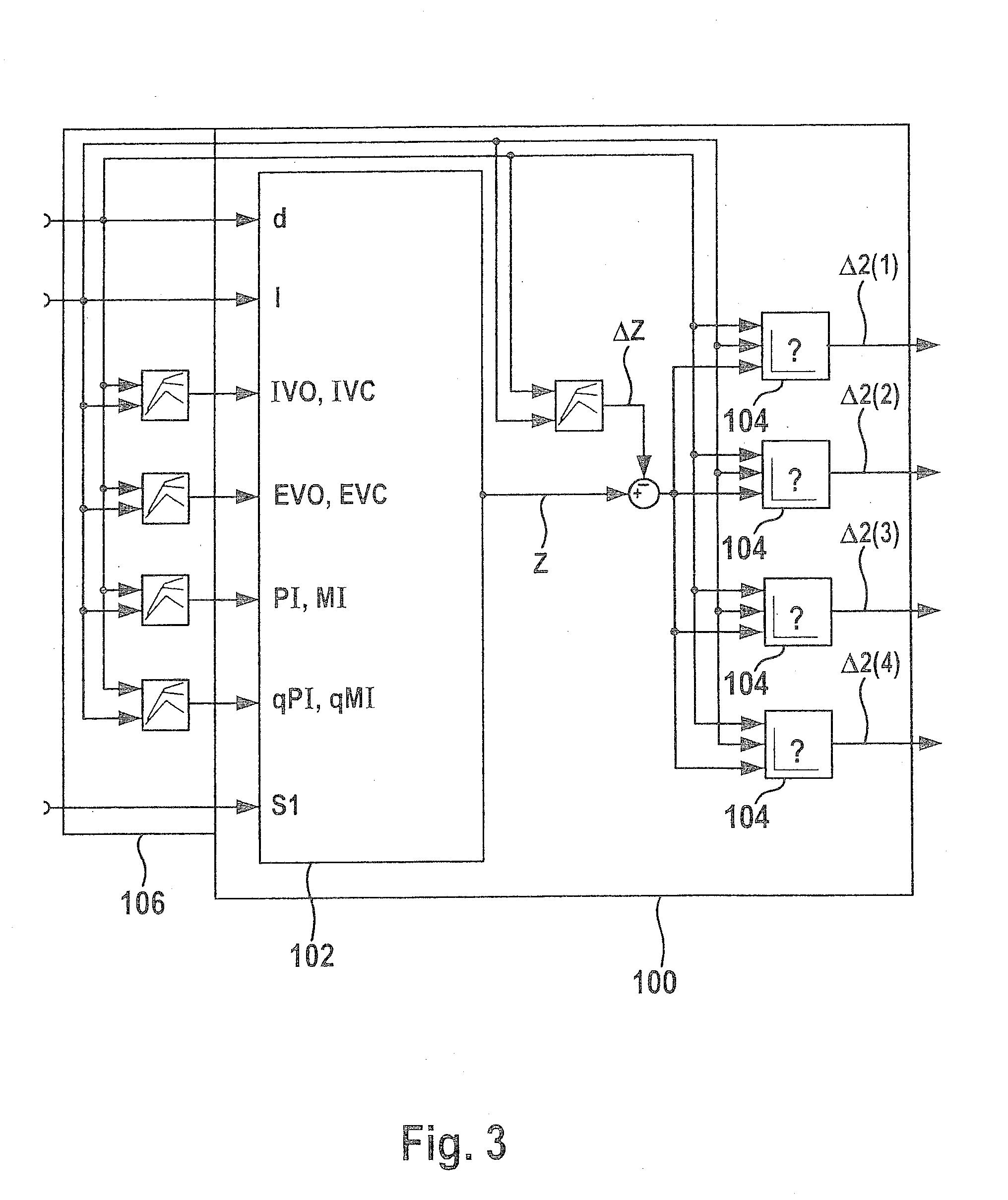
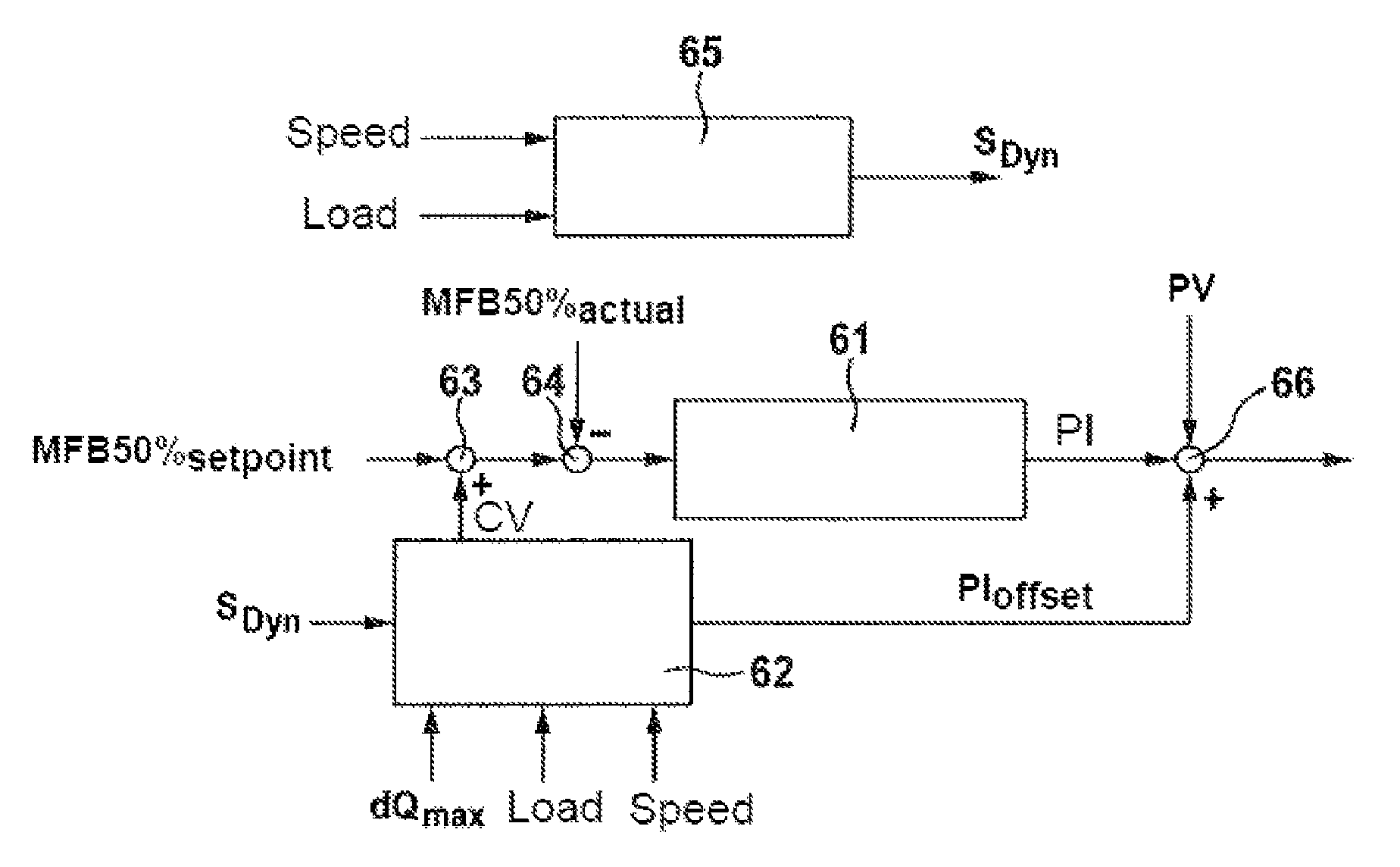
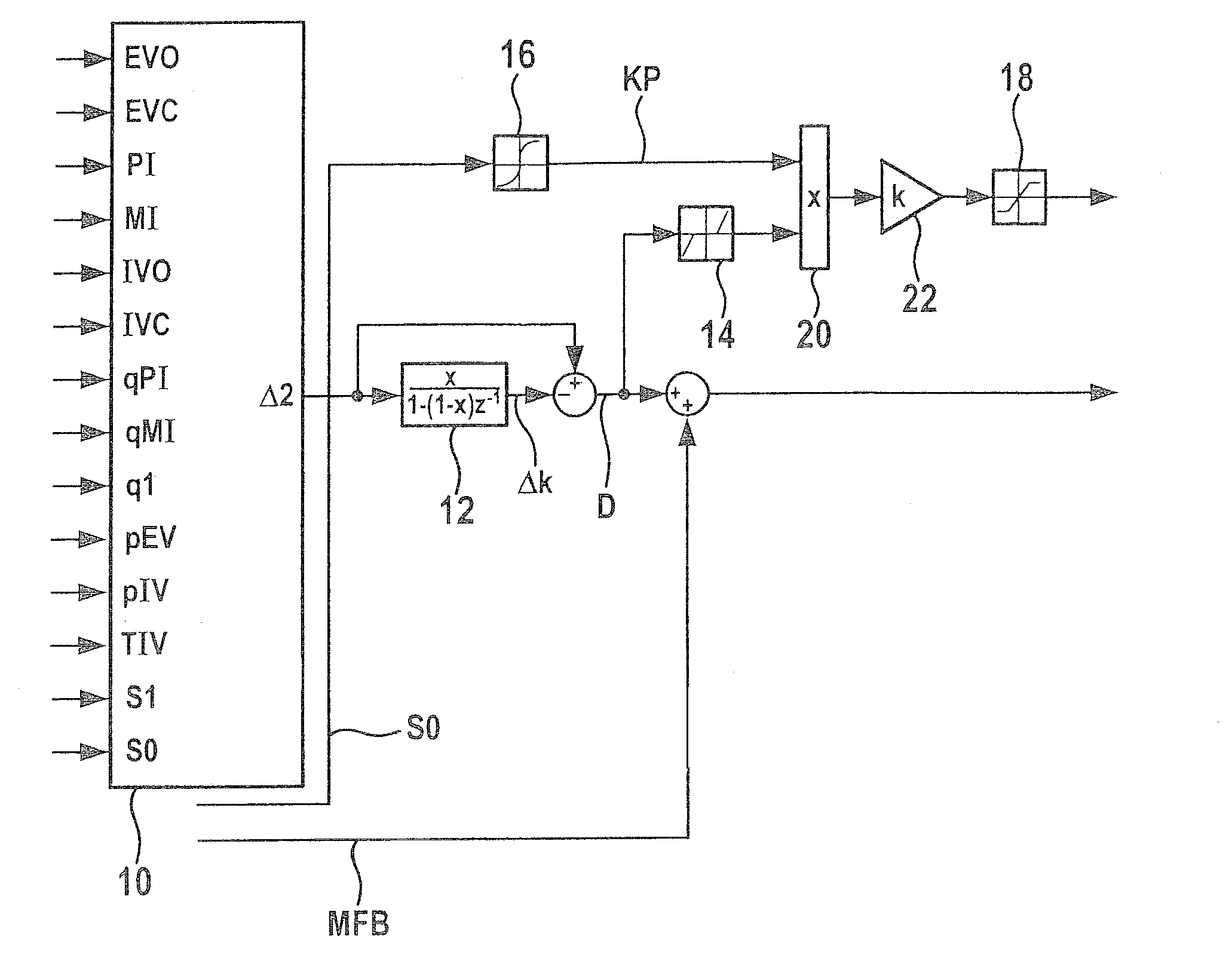
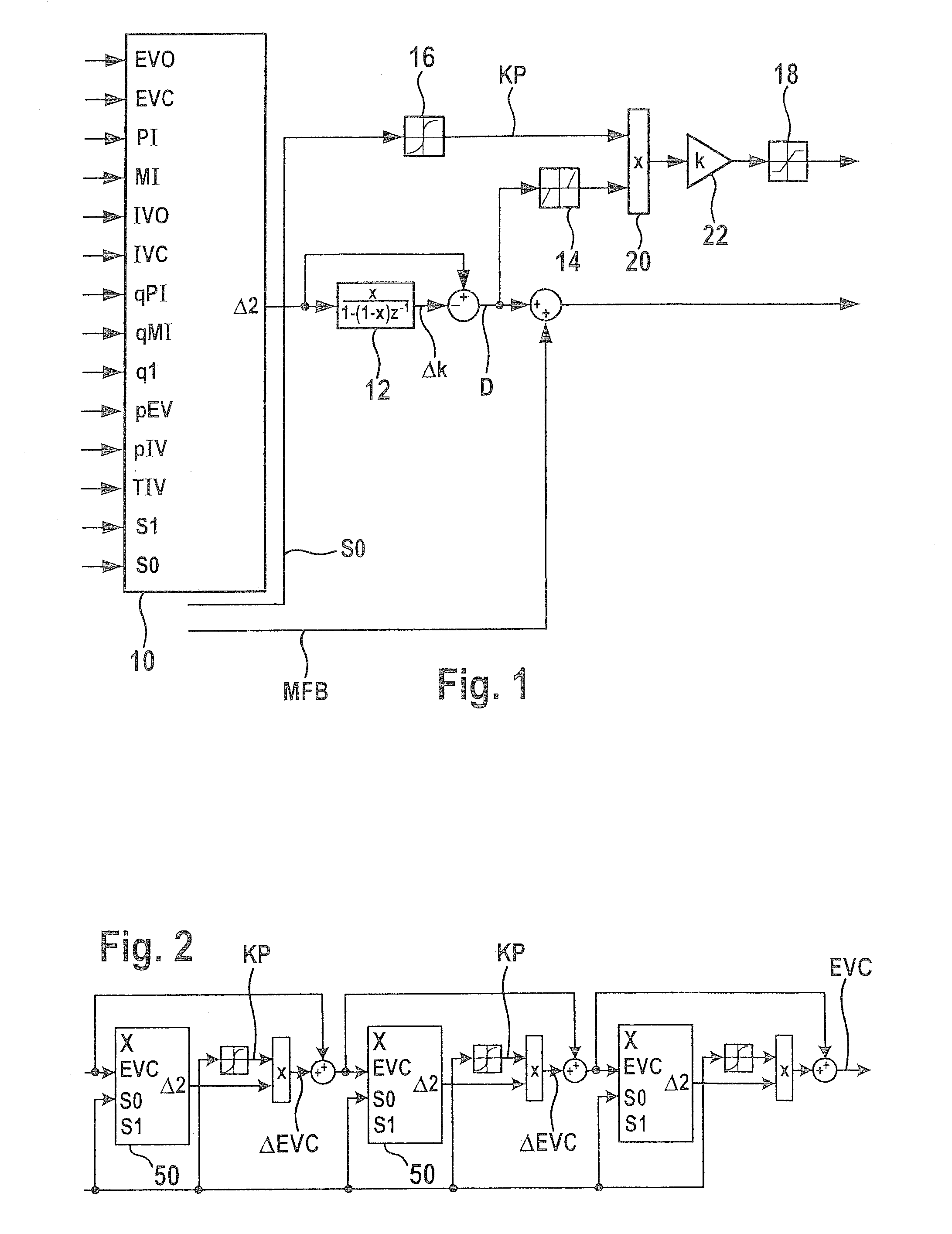
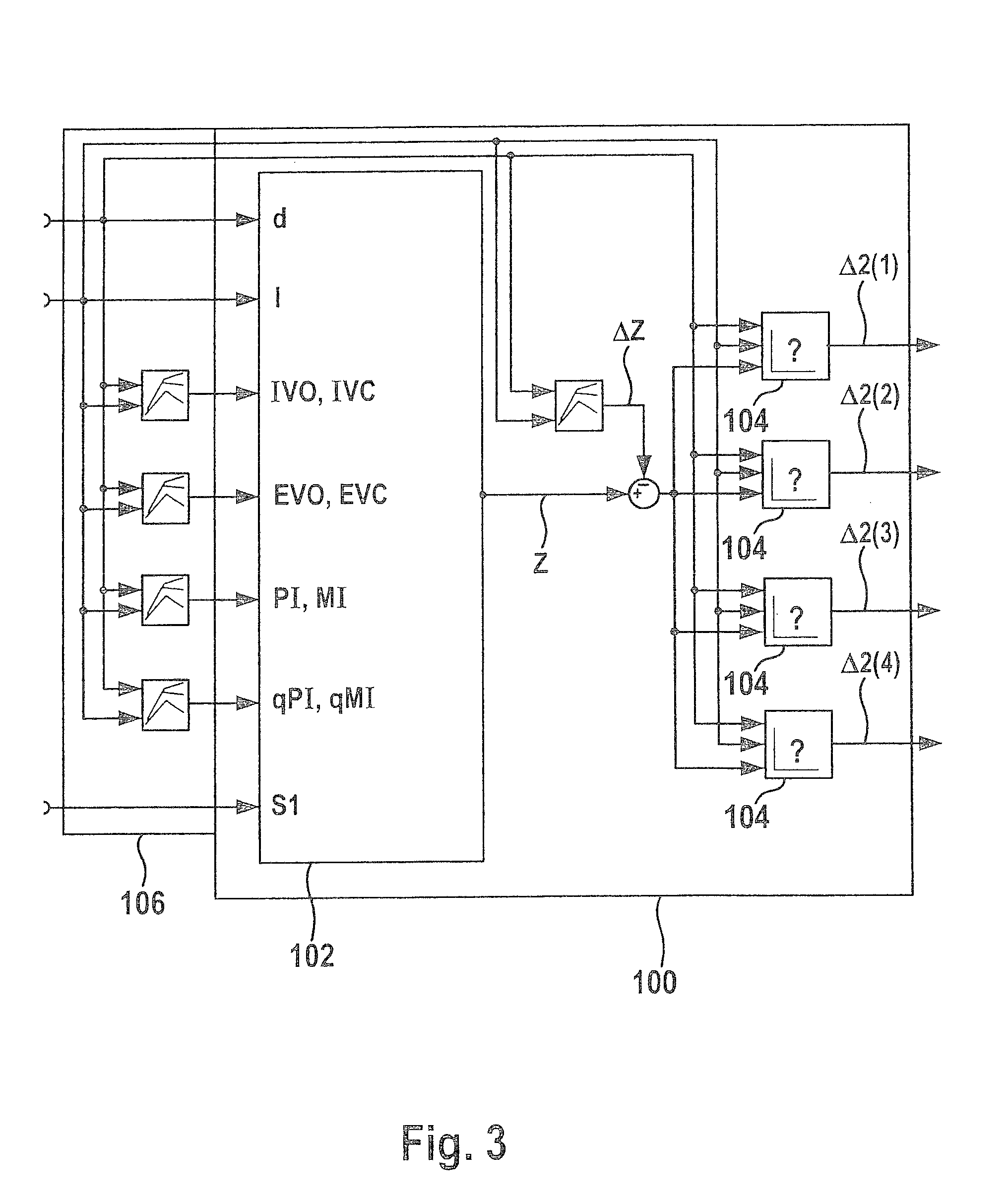
A method for setting a combustion in a combustion engine, particularly in a diesel engine, having the following steps of generating a manipulated variable, particularly a point of injection (PI), as a function of a combustion feature (MFB50%), the combustion feature (MFB50%) representing a condition in cylinder, especially a pressure characteristic in the cylinder, and setting the combustion in cylinders of the combustion engine with the aid of the manipulated variable, the manipulated variable further being generated as a function of a correction value (CV), which is determined as a function of combustion information (dQmax) that provides an indication about the quality of the combustion.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for high spatial resolution examination of samples
InactiveUS20070206277A1Reduce resolutionReduce intensityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical propertyImage resolution
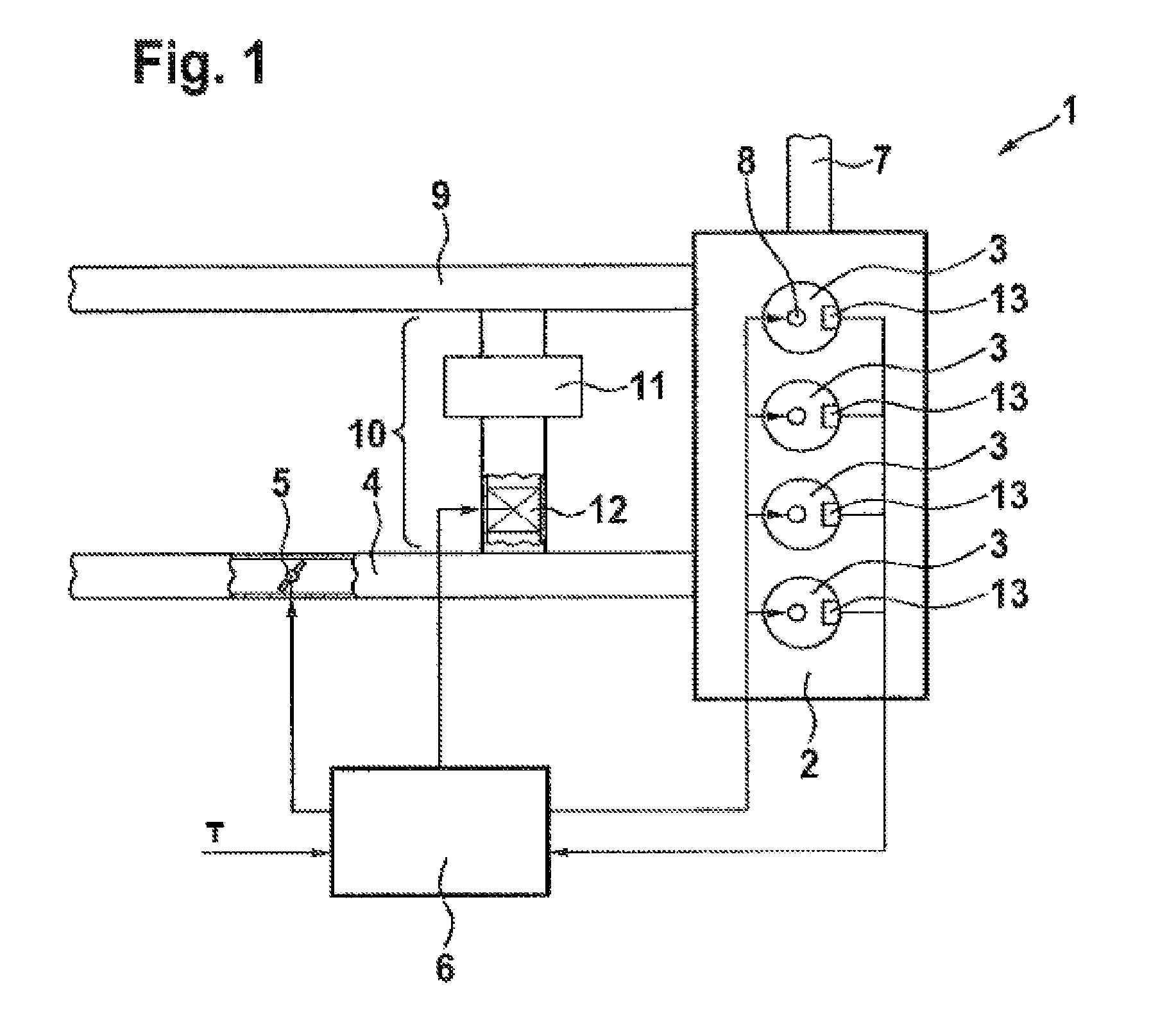
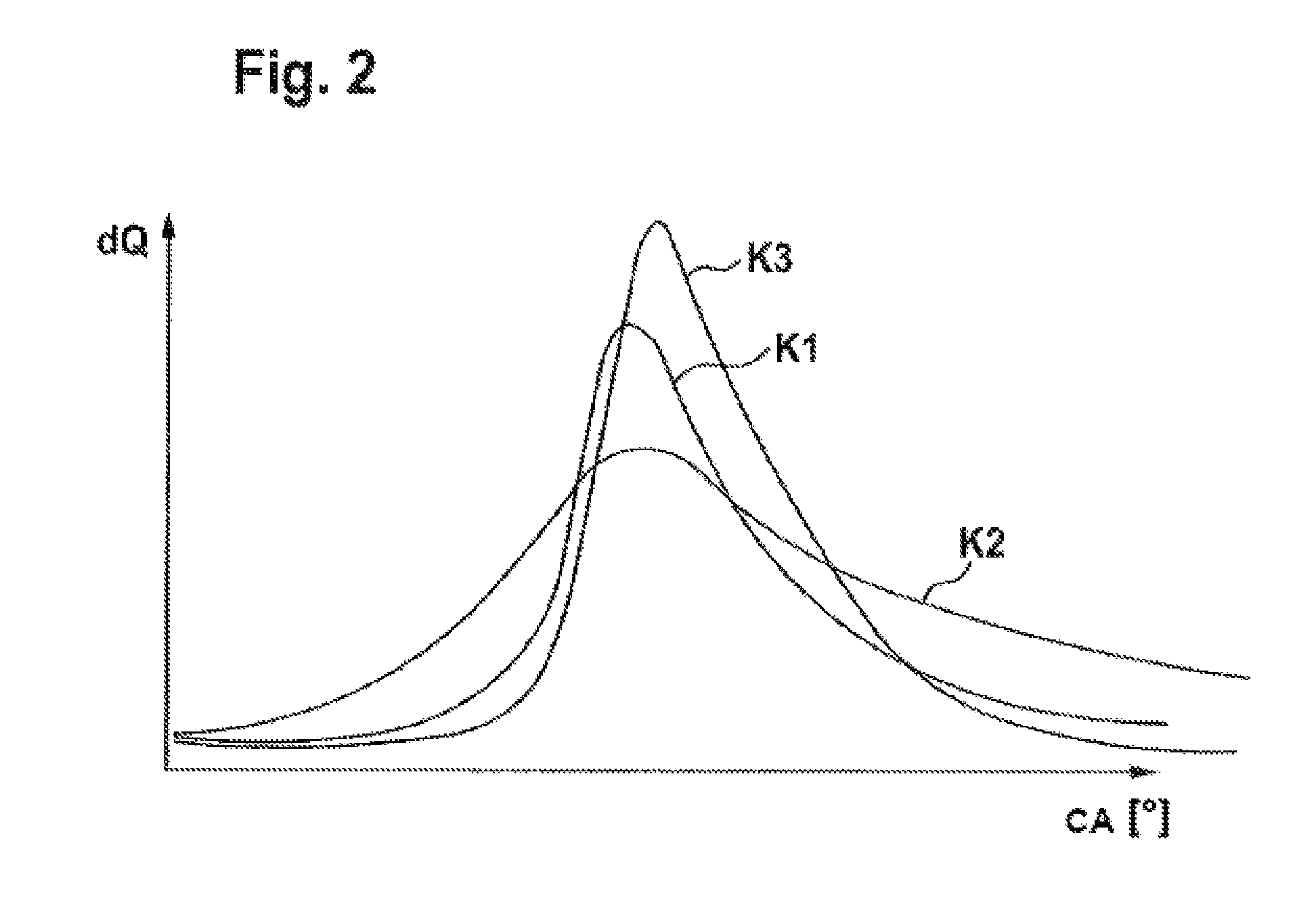
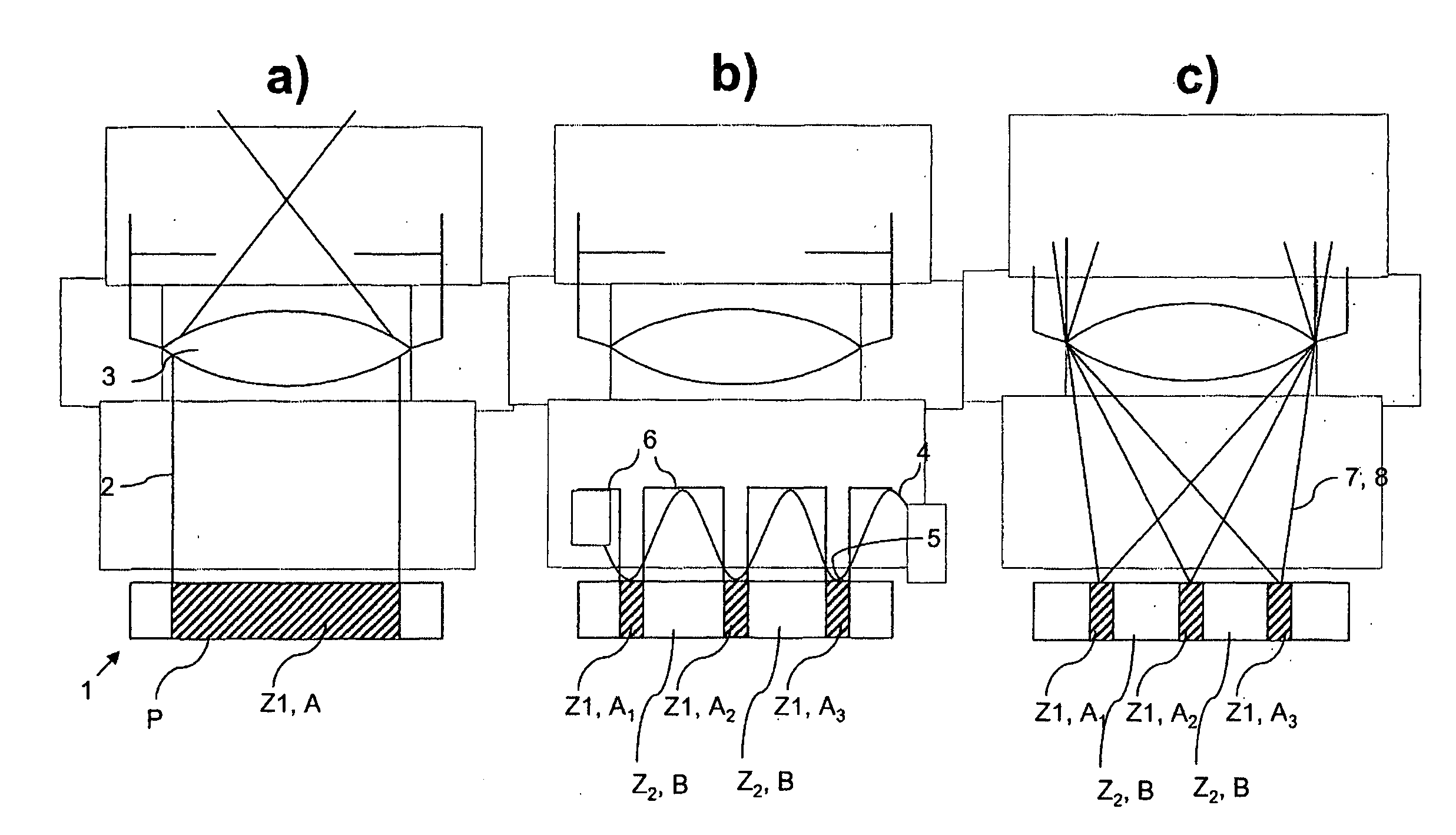
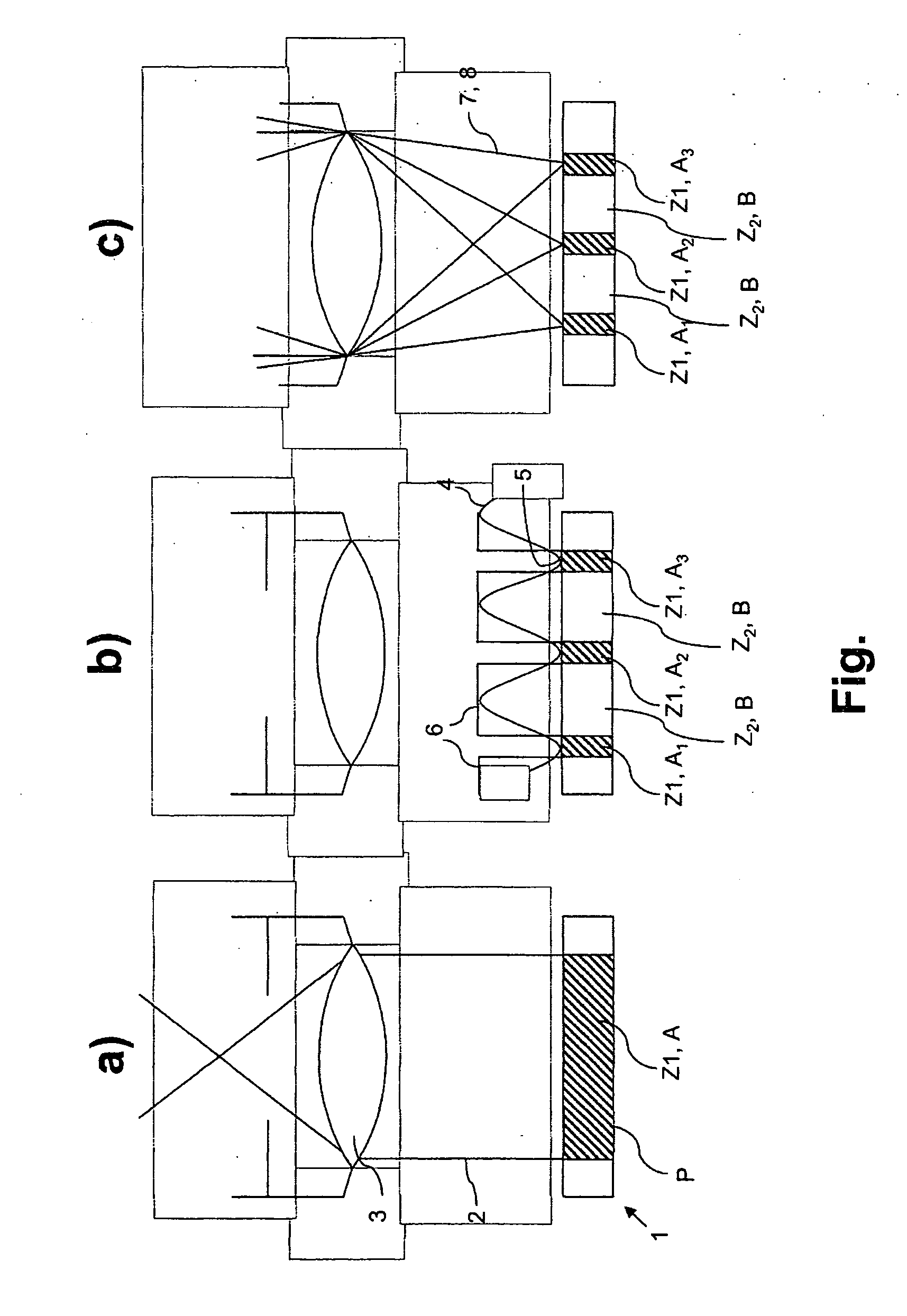
A method for high spatial resolution examination of samples, preferably by using a laser scanning fluorescence microscope, the sample (1) to be examined comprising a substance that can be repeatedly converted from a first state (Z1, A) into a second state (Z2, B), the first and the second states (Z1, A; Z2, B) differing from one another in at least one optical property, comprising the following steps:a) the substance is brought into the first state (Z1, A) by means of a switching signal (2) in a sample region (P) to be recorded,b) the second state (Z2, B) is induced by means of an optical signal (4), spatially delimited subregions being specifically excluded within the sample region (P) to be recorded,c) the remaining first states (Z1, A1, A2, A3) are read out by means of a test signal (7), andd) steps a) to c) are repeated, the optical signal (4) being displaced upon each repetition in order to scan the sample (1),is defined in that the individual steps a) to d) are carried out in a sequence adapted to the respective measuring situation.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS20090131321A1Signal attenuationPrevent negative consequenceHormone peptidesNervous disorderN-Methyl-D-aspartic acidNeuron
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron the method comprising administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor neuronal protein. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults and dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. The treatment was effective when applied either before, or one hour after, the onset of excitotoxicity in vitro and cerebral ischemia in vivo. This approach prevents negative consequences associated with blocking NMDAR activity and constitutes practical therapy for stroke.
Owner:TYMIANSKI MICHAEL
Method and device for operating a combustion engine
ActiveUS20100121555A1Prevent negative consequenceAvoid it happening againAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustionInternal combustion engine
A method for setting a combustion in a combustion engine, particularly in a diesel engine, having the following steps of generating a manipulated variable, particularly a point of injection (PI), as a function of a combustion feature (MFB50%), the combustion feature (MFB50%) representing a condition in cylinder, especially a pressure characteristic in the cylinder, and setting the combustion in cylinders of the combustion engine with the aid of the manipulated variable, the manipulated variable further being generated as a function of a correction value (CV), which is determined as a function of combustion information (dQmax) that provides an indication about the quality of the combustion.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Aloe vera based vaping compositions
ActiveUS9364512B1Exhibits antioxidant activityImprove bioavailabilityHydroxy compound active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsOxidative stressAntioxidant
An aloe vera based liquid composition comprising at least one antioxidant agent that reduces oxidative stress in the lungs and delivers various antioxidants and nutrients when absorbed upon vaping by the user.
Owner:DRUMMOND III HALISTER JOSEPH
Alkylation process
ActiveUS9006506B2Prevent negative consequenceHydrocarbonsHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationAlkyl transferOxygenate
The invention relates to the production of paraxylene by an alkylation process that also produces oxygenates. The process is controlled to utilize recycle to minimize said oxygenates.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Method of Reducing Injury to Mammalian Cells
InactiveUS20090281037A1Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor-neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARS) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
Production of paraxylene
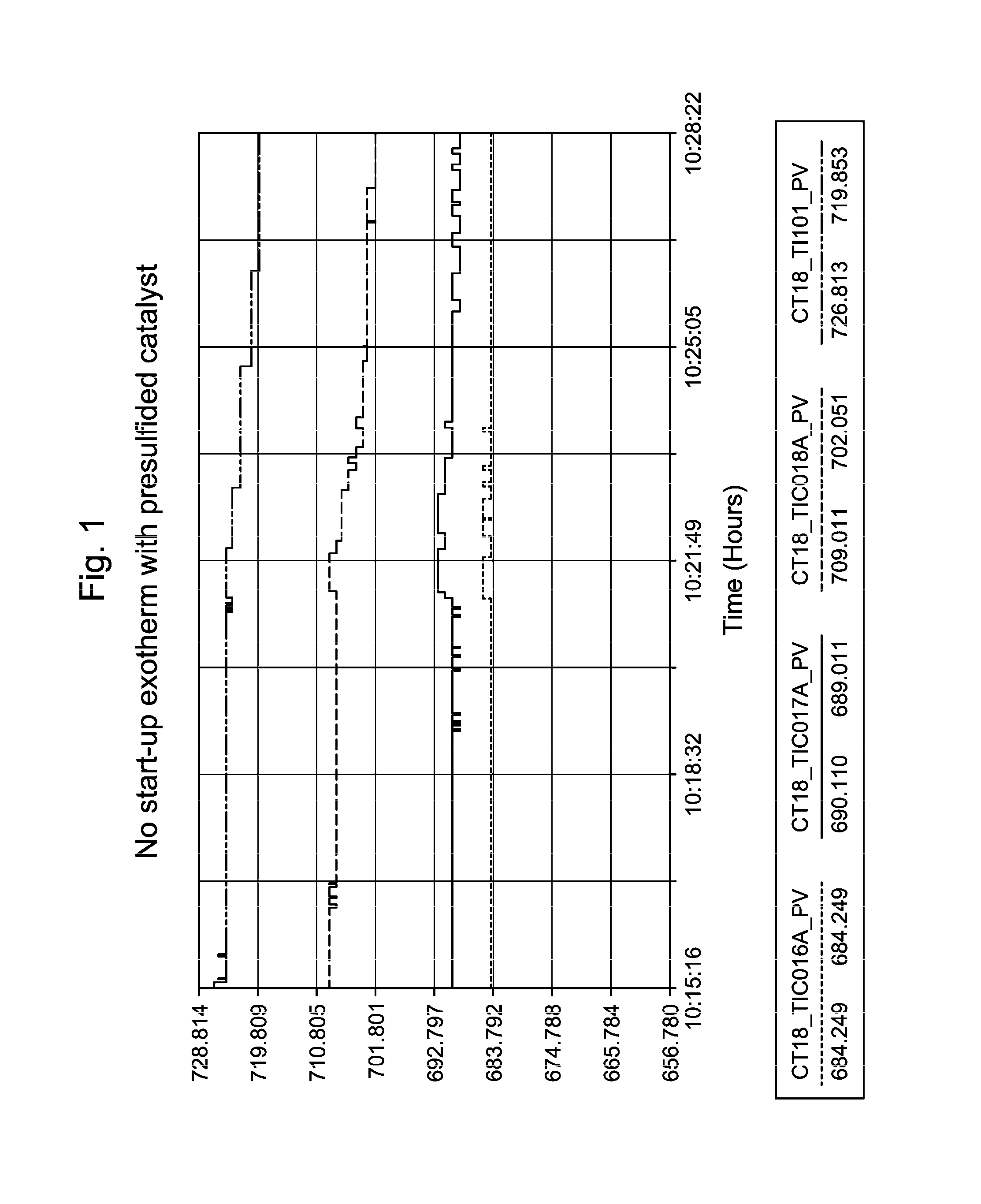
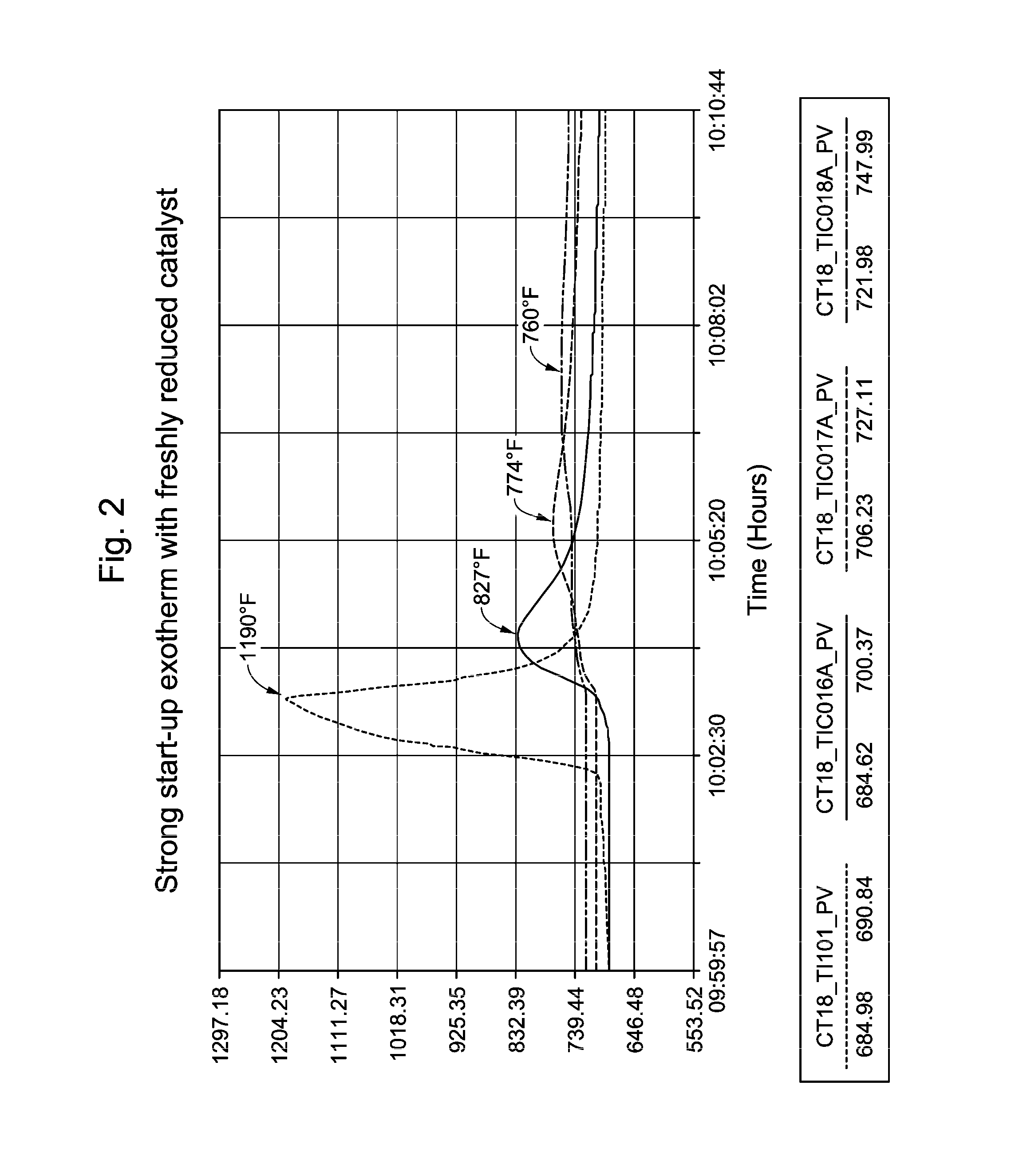
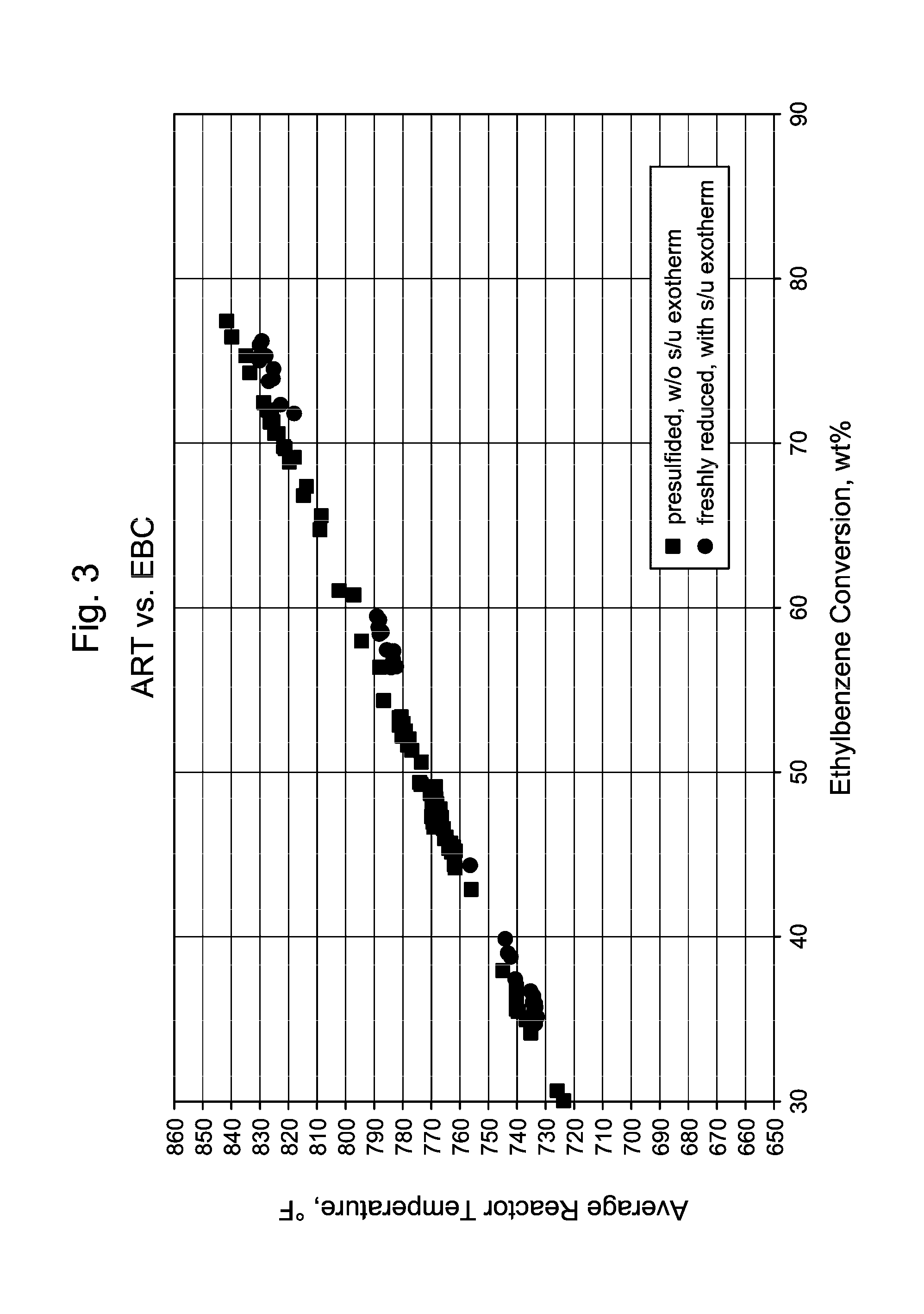
InactiveUS8835705B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce lossesHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsIsomerizationChemistry
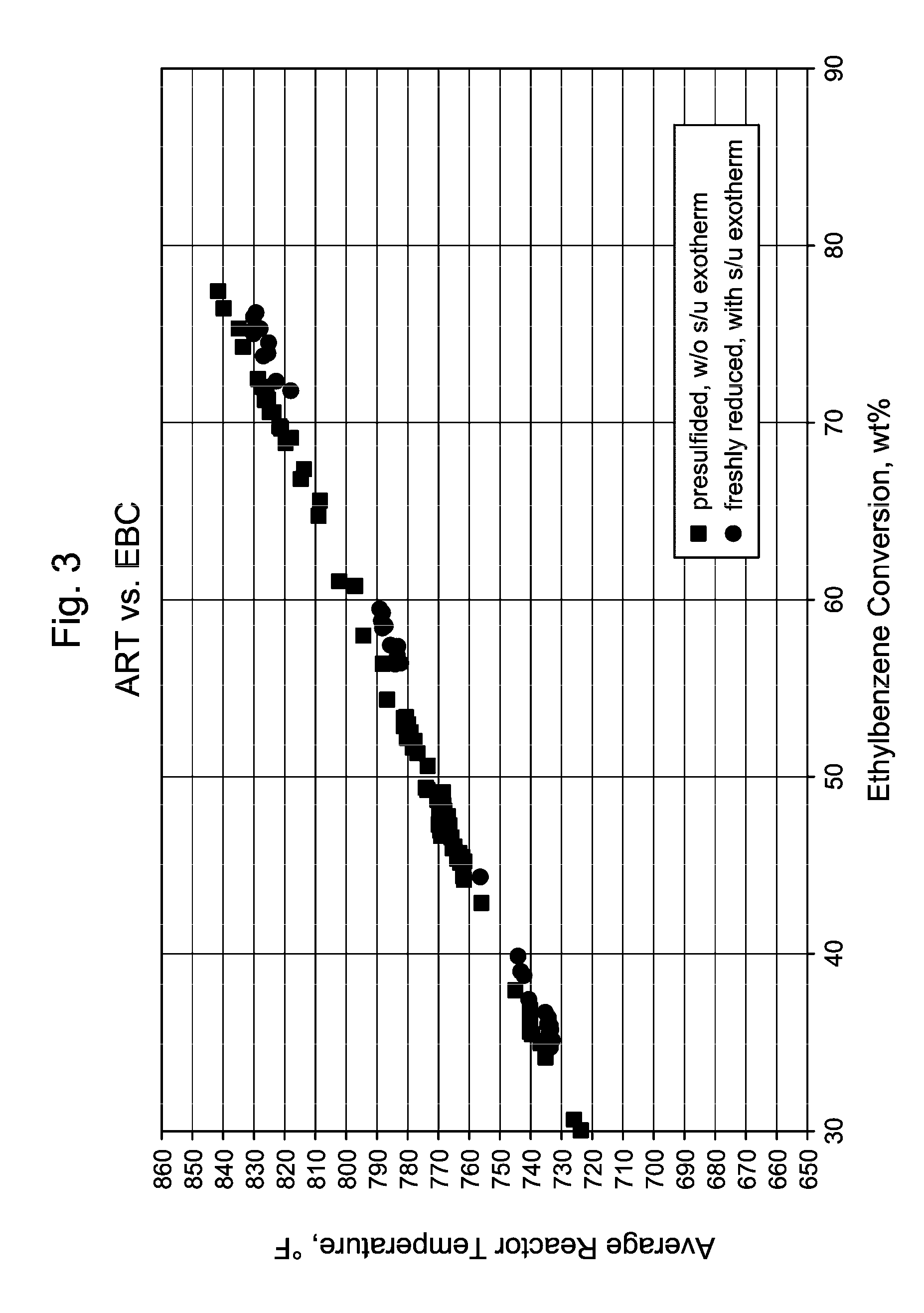
The process concerns ethylbenzene conversion and xylene isomerization with a catalyst pretreated by sulfiding.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
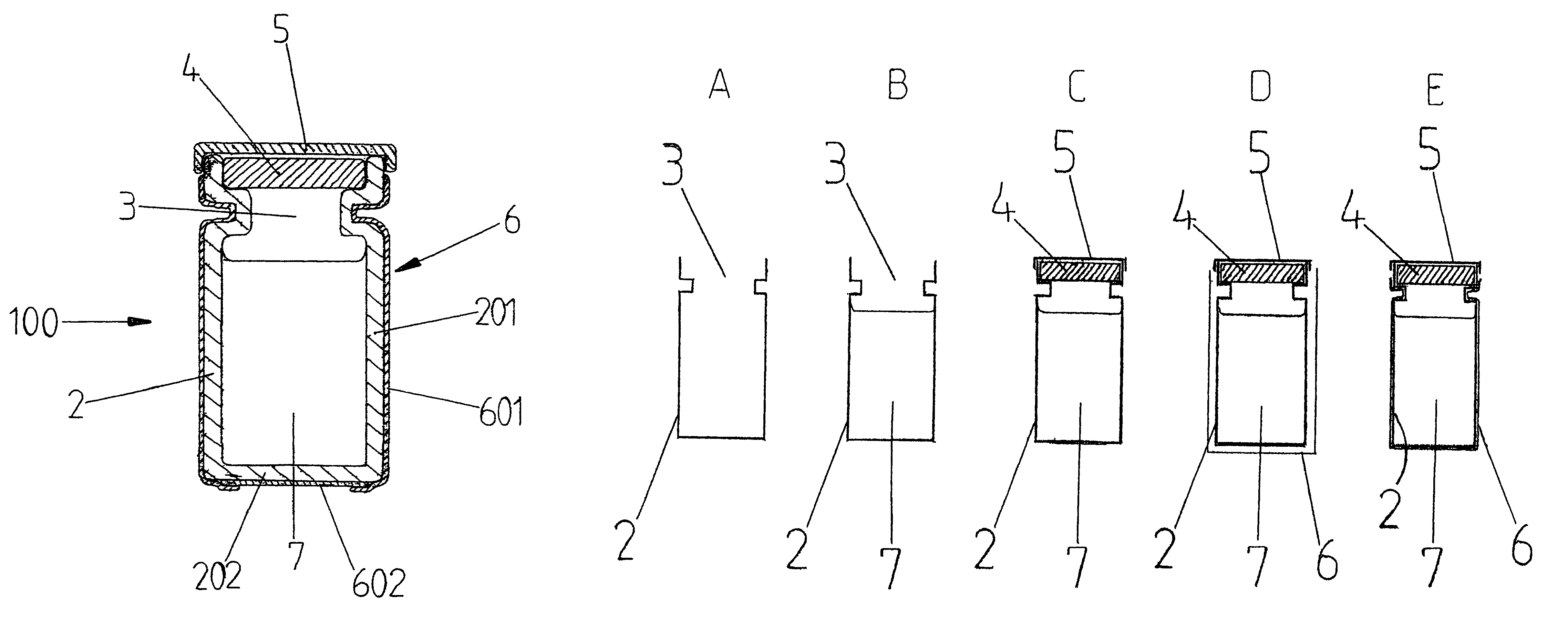
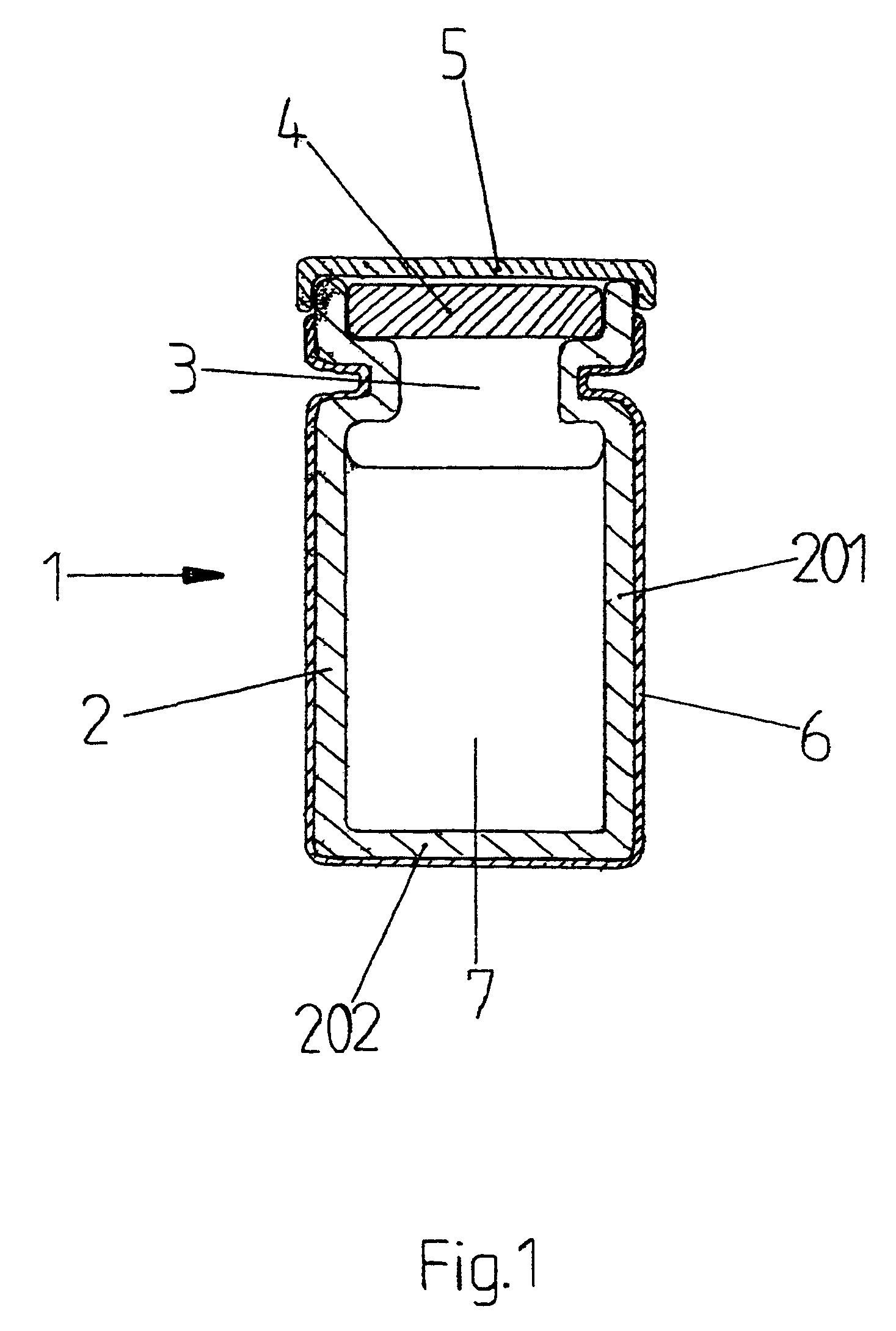
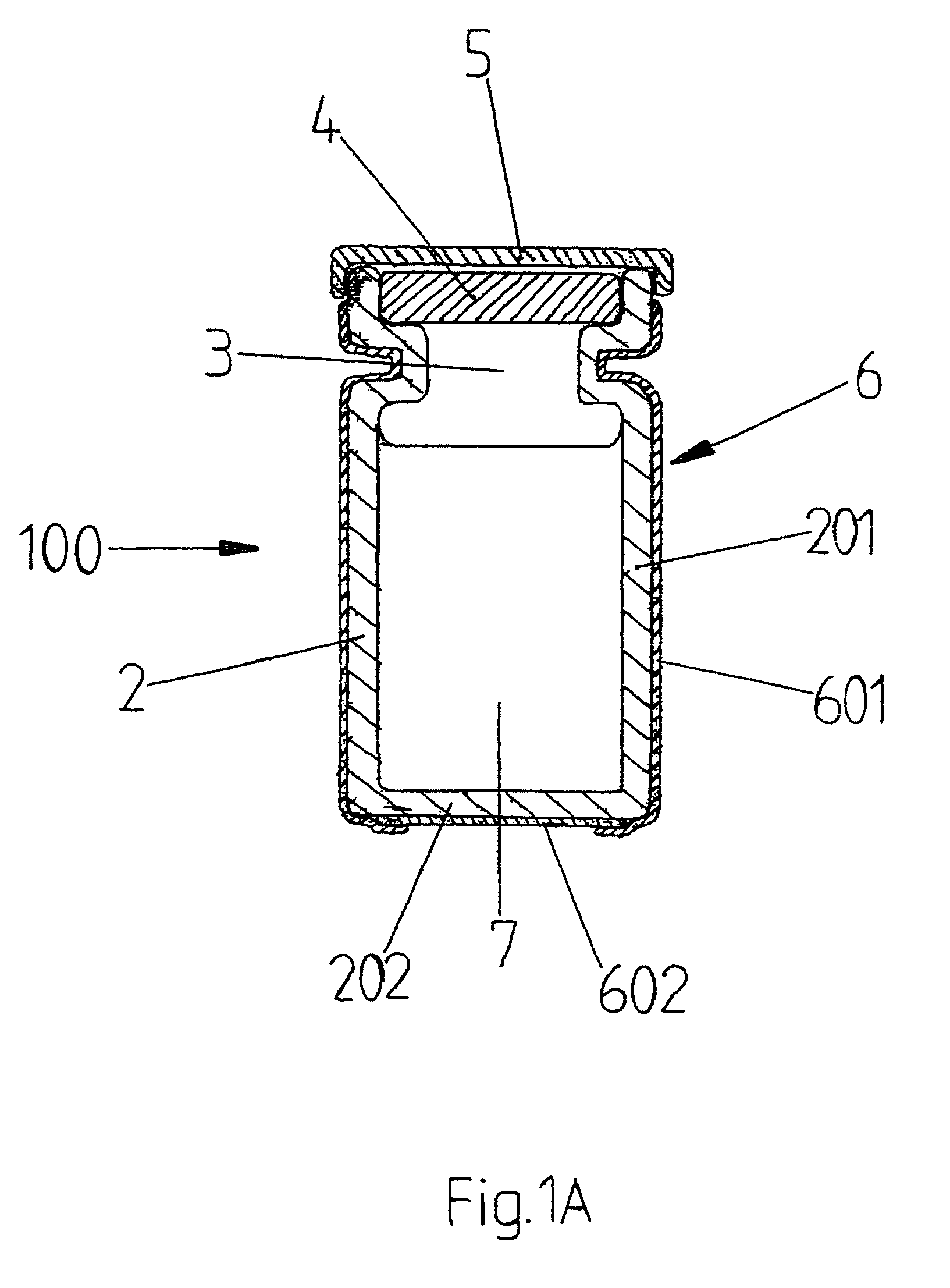
Protected vial, and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS7430842B2Prevent negative consequencePrevent liquid leakageWrappers shrinkageClosuresSynthetic materialsMedicine
For the prevention of contamination of a vial with traces of medicinal fluids, for example cytostatics and antibiotics, which may be spilt on the outside of the vial while filling, the vial is provided with a tight-fitting protective envelope, preferably made of a transparent synthetic material, as a last step in the production process. Because of this, a possible contamination which remains on the outside of the vial is encapsulated between the vial and the envelope. Hereby, a user is no longer exposed to toxic substances, because the user will not touch the vial itself, but will touch the envelope. An additional advantage of the provision of the envelope is that if breaking of the vial occurs, the envelope will keep the pieces of broken glass together and will possibly prevent the medicinal fluid from leaking away.
Owner:PHARMACHEMIE BV
Medical Device, Method And System For Temporary Occlusion Of An Opening In A Lumen Of A Body
A medical system is disclosed that has three basic components; a retractable sheet, a first balloon that has a centrally arranged hollow, and a collapsible / expandable support structure at the hollow. The first balloon is for instance mounted / molded onto the exterior surface of the support structure. The aggregate of support structure and the first balloon is positioned, and once the sheet has been retracted from the first balloon, the first balloon is inflated. The support structure may be self-expandable or expandable by an expansion unit, such as a further balloon arranged at its inside. The lumen of the support structure is chosen to be smaller than that of a main lumen. The outside diameter of the inflated first balloon is chosen to be larger than the interior diameter of the main lumen.
Owner:AEEG
Non-spreading pestivirus
InactiveUS20050220813A1Prevent negative consequenceSafely vaccinatedSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsPestivirusWild type
The invention relates to vaccines used in the eradication or control of pestivirus infections, particularly those used in pigs or ruminants. The invention provides nucleic acid, pestivirus-like particles and a pestivirus vaccine, comprising the nucleic acid or particles, which is capable of eliciting a proper immune response without having the ability to spread throughout the vaccinated animal, thereby avoiding the negative consequences of viral spread. Preferably, the immune response allows for serological discrimination between vaccinated animals and wild-type pestivirus infected animals.
Owner:INTERVET INT BV
Method for controlling a compression-ignition internal combustion engine and control device for controlling a compression-ignition internal combustion engine
InactiveUS8073611B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce fuel consumptionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustionInternal combustion engine
A method is described for controlling a compression-ignition internal combustion engine, including predefining a setpoint combustion point for a compression-ignition internal combustion engine, predefining a calculation model for calculating a probable deviation of a future cycle of the engine from the predefined setpoint combustion point while taking an ascertained actual combustion point of a completed cycle engine into consideration, predefining a mean deviation for the engine, operating the engine for a first cycle and ascertaining an actual combustion point of the first cycle, calculating a probable deviation of a second cycle, which occurs after the first cycle, of the engine from the predefined setpoint combustion point, comparing the calculated probable deviation of the second cycle to the predefined mean deviation, and ascertaining at least one operating variable for operating the engine at least during the second cycle as a function of the comparison. Also described is a related method.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Burner for a thermal post-combustion device
InactiveUS9194580B2Good combustion valueSimple structureIncandescent ignitionSolid fuel combustionCombustorMechanical engineering
The invention describes a burner for a thermal post-combustion device, which has a burner jet arranged in a housing. Arranged on the end region of the housing is a swirl apparatus, through which the exhaust gas to be purified can be made to flow. The burner jet comprises an outer tube and an inner tube, wherein it is possible for combustion gas to be made to flow through the interspace between said two tubes as far as an annular outlet gap in the end region thereof. The flow path for the combustion gas has a bottleneck in the vicinity of the outlet gap. In this way, a compact flame can be achieved, the form of which can be designated “bell-shaped” and which, for a given volume, has a relatively small surface. Although, such a flame has poor CO2 values, the swirl apparatus ensures that the exhaust gas burns in the flame with very low NOx and CO values.
Owner:EISENMANN AG
Gate for a tablet discharge of a tablet press and method for actuating a gate
ActiveUS20200009057A1Reduce movement speedEnsure reliableControl devices for conveyorsPill deliveryEngineeringPhysics
A tablet press comprises a gate that defines a first switching position that feeds tablets into a first tablet outlet and at least a second switching position that feeds tablets into at least one second tablet outlet. The table press further comprises a control apparatus and a drive apparatus. The drive apparatus is configured to be actuated by the control apparatus to move the gate from a home position defined as one of the first switching position and the at least a second switching position into a target position defined as a switching position that is not the home position. The gate is moved from the home switching position at a speed of movement toward the target position such that the speed of movement of the gate is reduced before the target position is reached.
Owner:FETTE COMPACTING GMBH
Gate for a tablet discharge of a tablet press, and method for actuating a gate
PendingUS20200009058A1Increase widthAvoid interferenceControl devices for conveyorsPill deliverySwitching signalControl theory
A tablet press comprises a gate and a control apparatus configured to generate a switching signal. A drive apparatus is configured to move the gate in response to the switching signal received from the control apparatus between a first switching position and at least a second switching position. At least one sensor is configured to generate a detection signal when the gate reaches one of the switching positions. The control apparatus receives the detection signal and is configured to output a switching signal to the drive apparatus to at least partially move the gate back into a home position when there is a switching signal to move the gate out of the home position and there is no detection signal received from the at least one sensor. The control apparatus subsequently outputs a switching signal to again move the gate out of the home position to a target position.
Owner:FETTE COMPACTING GMBH
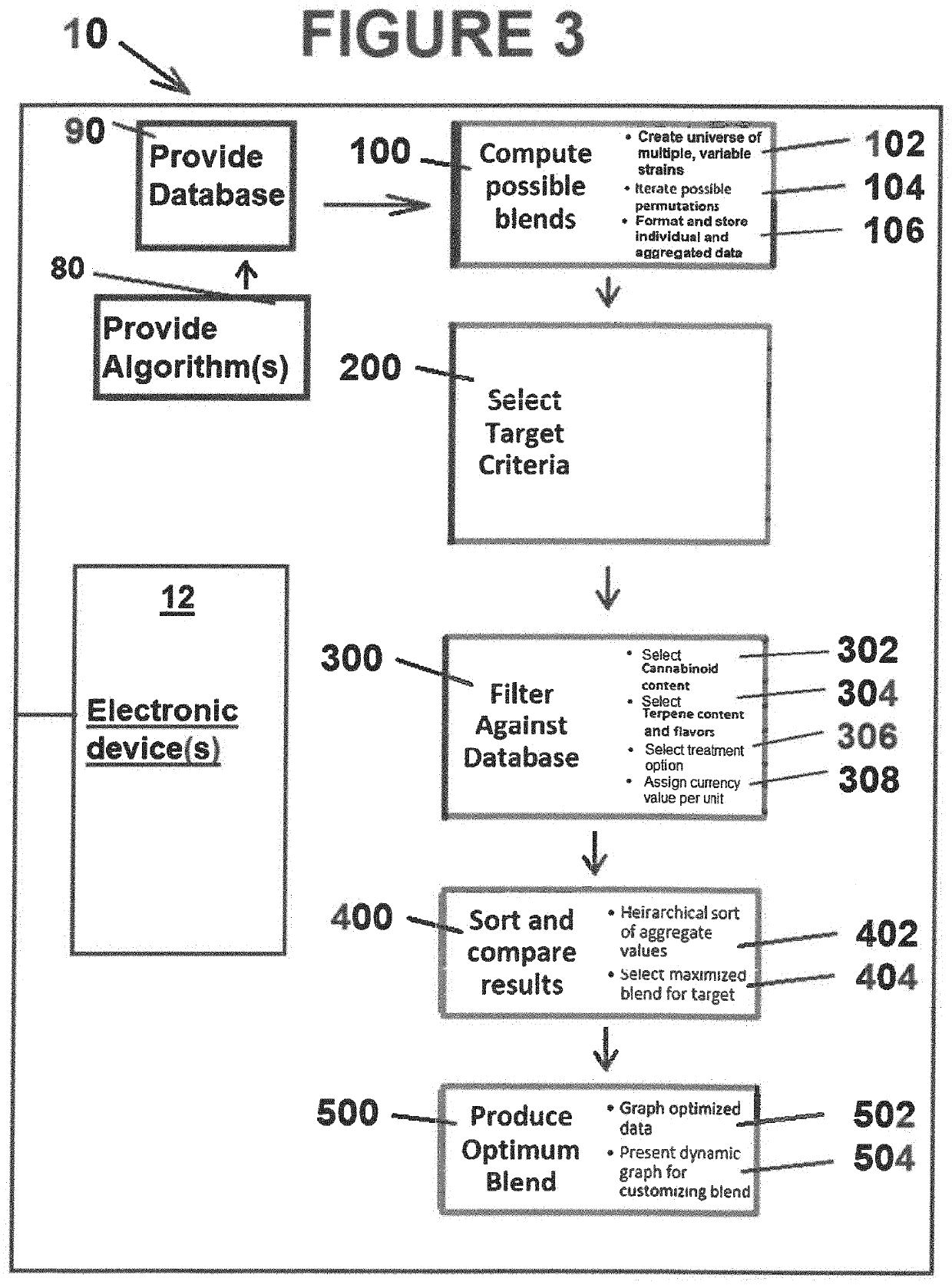
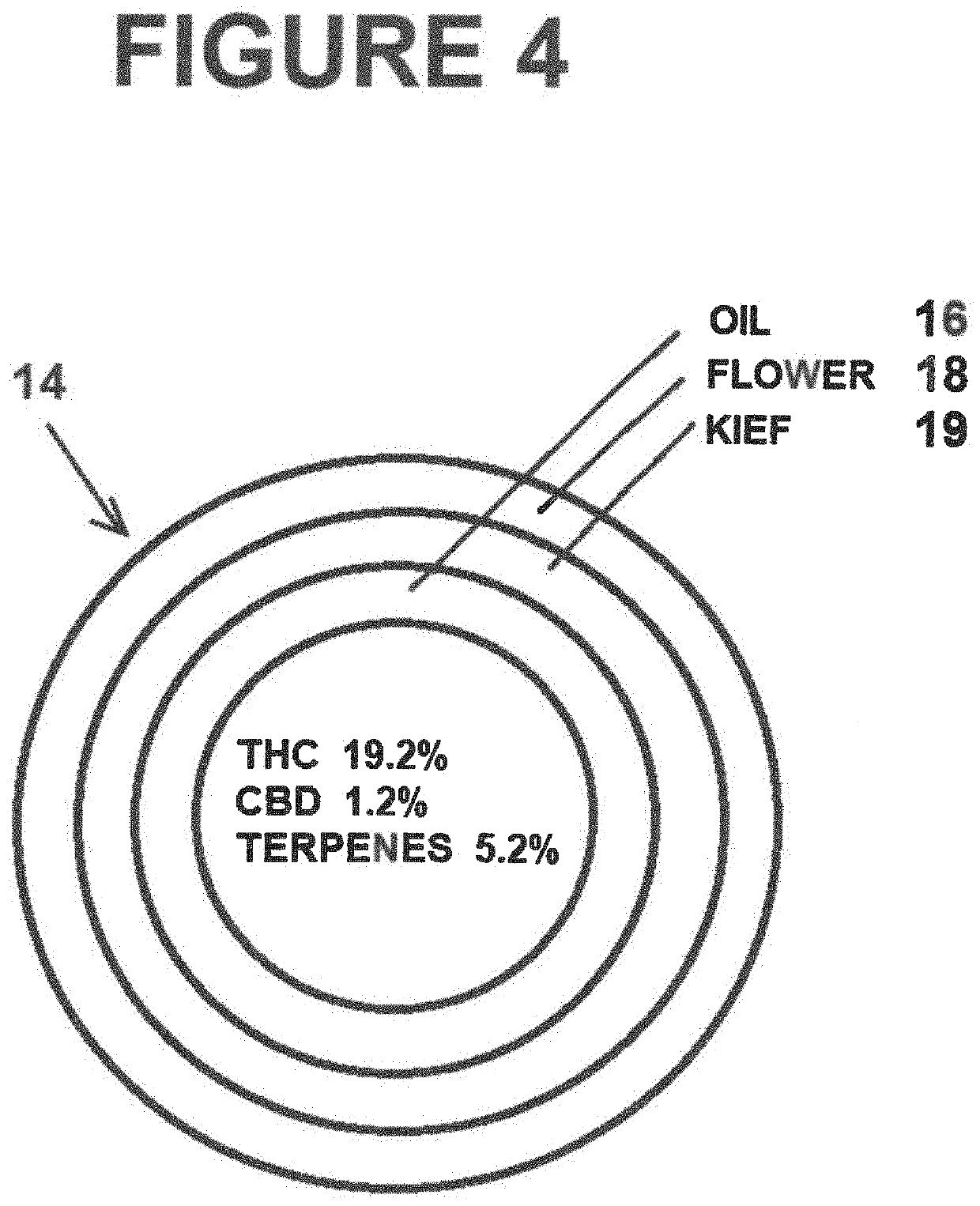
Cannabis calibration system and method of use
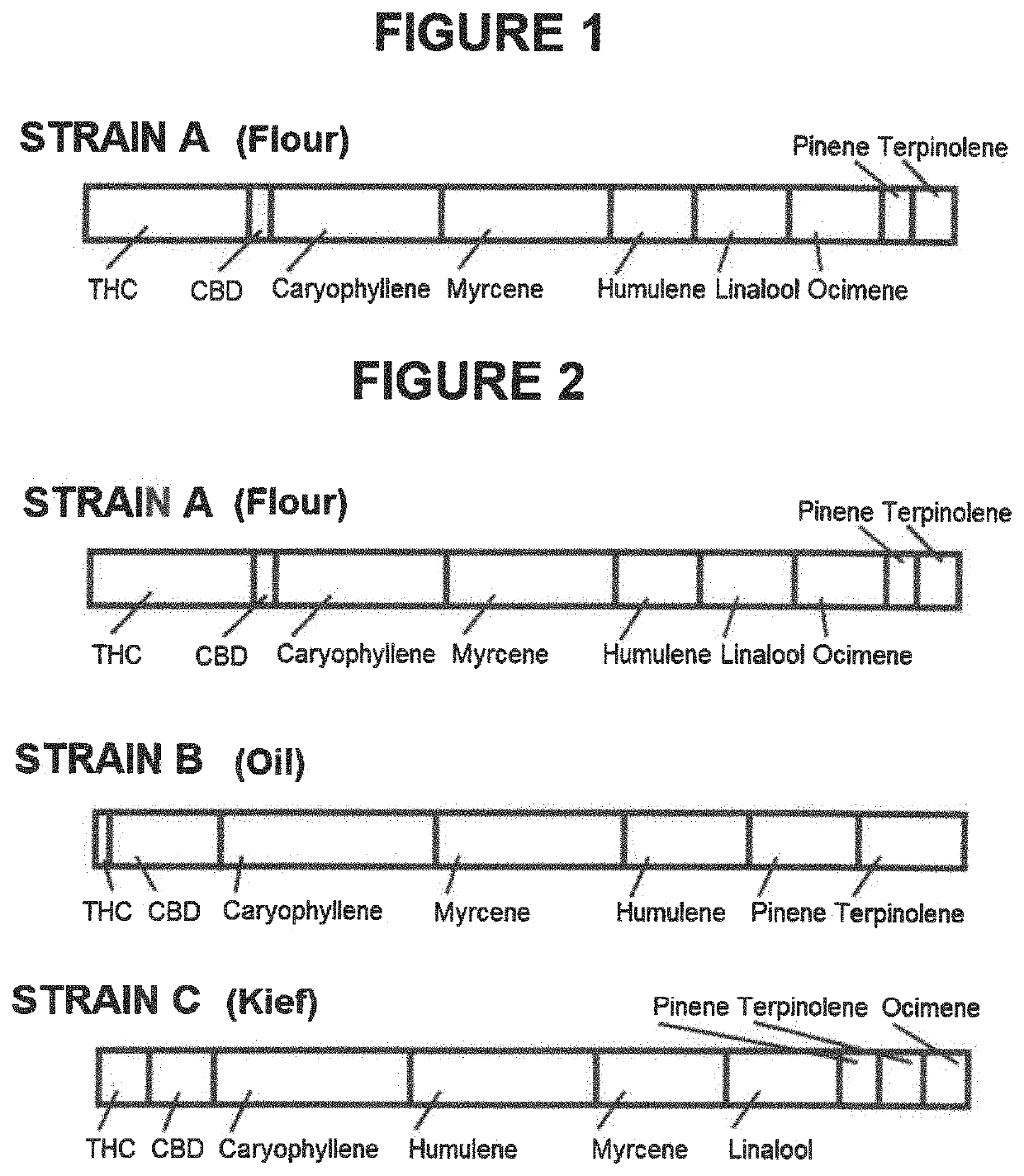
PendingUS20220012782A1Raises number of potentialProfit maximizationHydroxy compound active ingredientsOther databases queryingData miningCannabis substance
A method and system for creating a combined cannabis profile blend. Generally, a universe of possible blends of strain profiles is provided within a database, at least one target criteria selected, the selected at least one target criteria is filtered against the database, the results are sorted and compared to each other: and an optimized formulation target blend of strain profiles is selected.
Owner:BYRN BRANDS LLC
Cell culture substrate for cultivating adherent cells
PendingUS20220195381A1Prevent negative consequenceCell culture supports/coatingChemical recyclingCell culture mediaPolymer
A cell culture substrate for cultivating adherent cells, including:a substrate (S),a polymer (P) comprising amino groups, which is bonded to the substrate, anda saccharide (Z) having at least two monosaccharide units for attaching the adherent cells,wherein the saccharide (Z) is covalently bonded to the polymer (P) via the amino groups.Such a cell culture substrate is suitable for cultivating adherent cells and allows the cells to be detached from the cell culture substrate in a gentle manner by adding a saccharide.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Gate for a tablet discharge of a tablet press and method for actuating a gate
ActiveUS11464743B2Reduce movement speedPrevent negative consequenceControl devices for conveyorsPill deliveryEngineeringPhysics
A tablet press comprises a gate that defines a first switching position that feeds tablets into a first tablet outlet and at least a second switching position that feeds tablets into at least one second tablet outlet. The table press further comprises a control apparatus and a drive apparatus. The drive apparatus is configured to be actuated by the control apparatus to move the gate from a home position defined as one of the first switching position and the at least a second switching position into a target position defined as a switching position that is not the home position. The gate is moved from the home switching position at a speed of movement toward the target position such that the speed of movement of the gate is reduced before the target position is reached.
Owner:FETTE COMPACTING GMBH
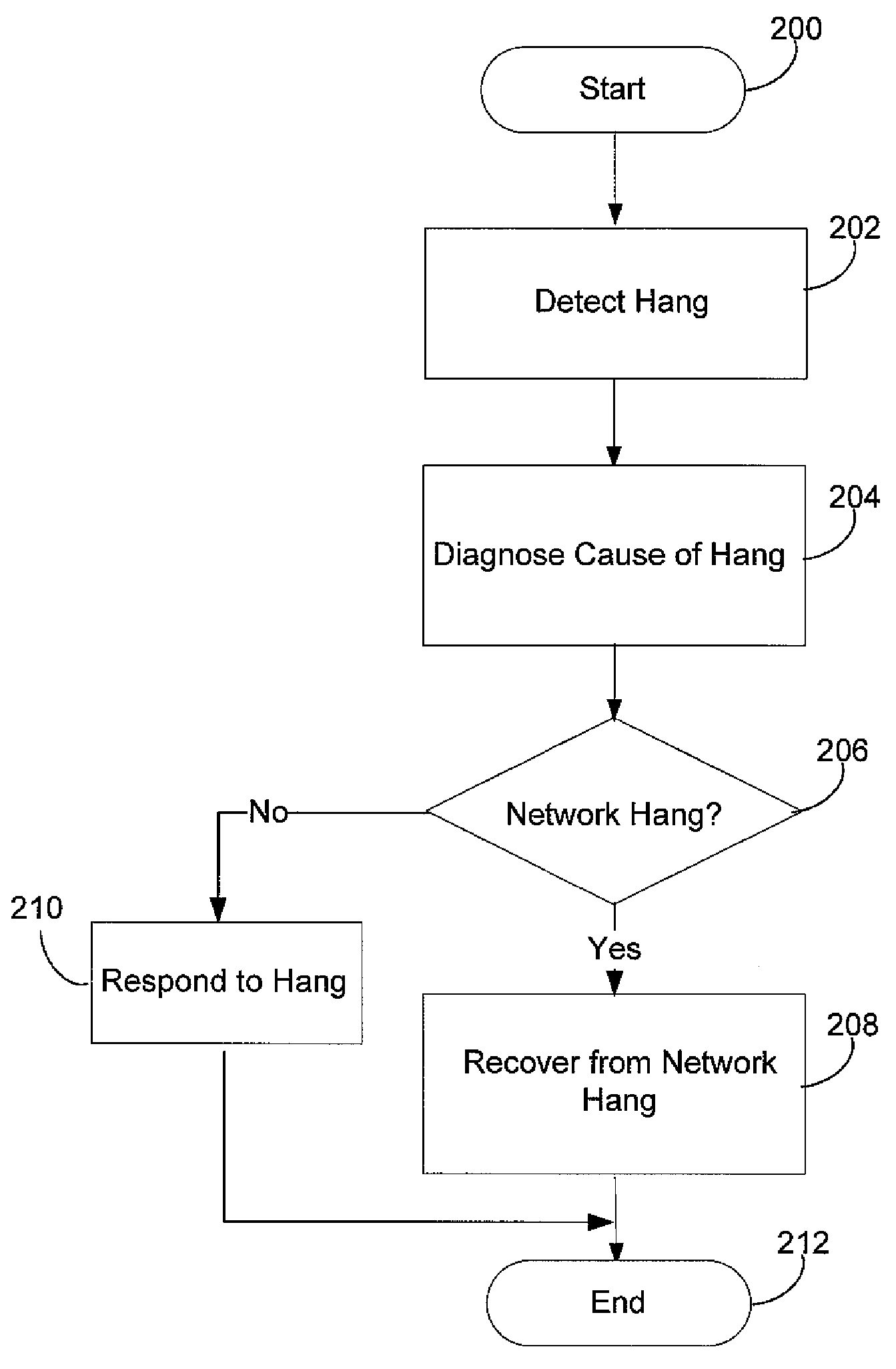
Network hang recovery
ActiveUS7934129B2Improve user experienceData can be lostError detection/correctionNetwork connectionApplication software
A method of detecting a network hang and restoring an application that communicates on a connection giving rise to the network hang. A user experience may be improved by providing the user with an option to restore the hung application without losing unsaved data or state information. The network hang may be detected when the user tries to terminate the application. The method may include determining whether the network hang is recoverable, which may involve diagnosing a type of the hang. If recoverable, a network connection reset mechanism may be triggered by instructing a network stack of the computer to terminate the network connection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Production of Paraxylene
InactiveUS20130197286A1Prevent negative consequenceReduce lossesHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsIsomerizationOrganic chemistry
The process concerns ethylbenzene conversion and xylene isomerization with a catalyst pretreated by sulfiding.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Isolated nucleic acids encoding autoactivated resistance proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS8080706B2Negatively influencingReliably activatedBryophytesSugar derivativesCoding regionBiology
The invention relates to nucleic acid, which codes for an autoactivated resistance protein for creating a resistance to pathogens in plants, characterized in that the nucleic acid has a limited portion of an NBS-LRR resistance gene, which extends from the 5′-end of the coded region of the NBS-LRR resistance downstream to the beginning of the NBS domain of the NBS-LRR resistance gene, the NBS-LRR resistance gene not being a TIR-NBS-LRR resistance gene.
Owner:KWS SAAT SE
Method to control a road vehicle with a microslip of the clutch
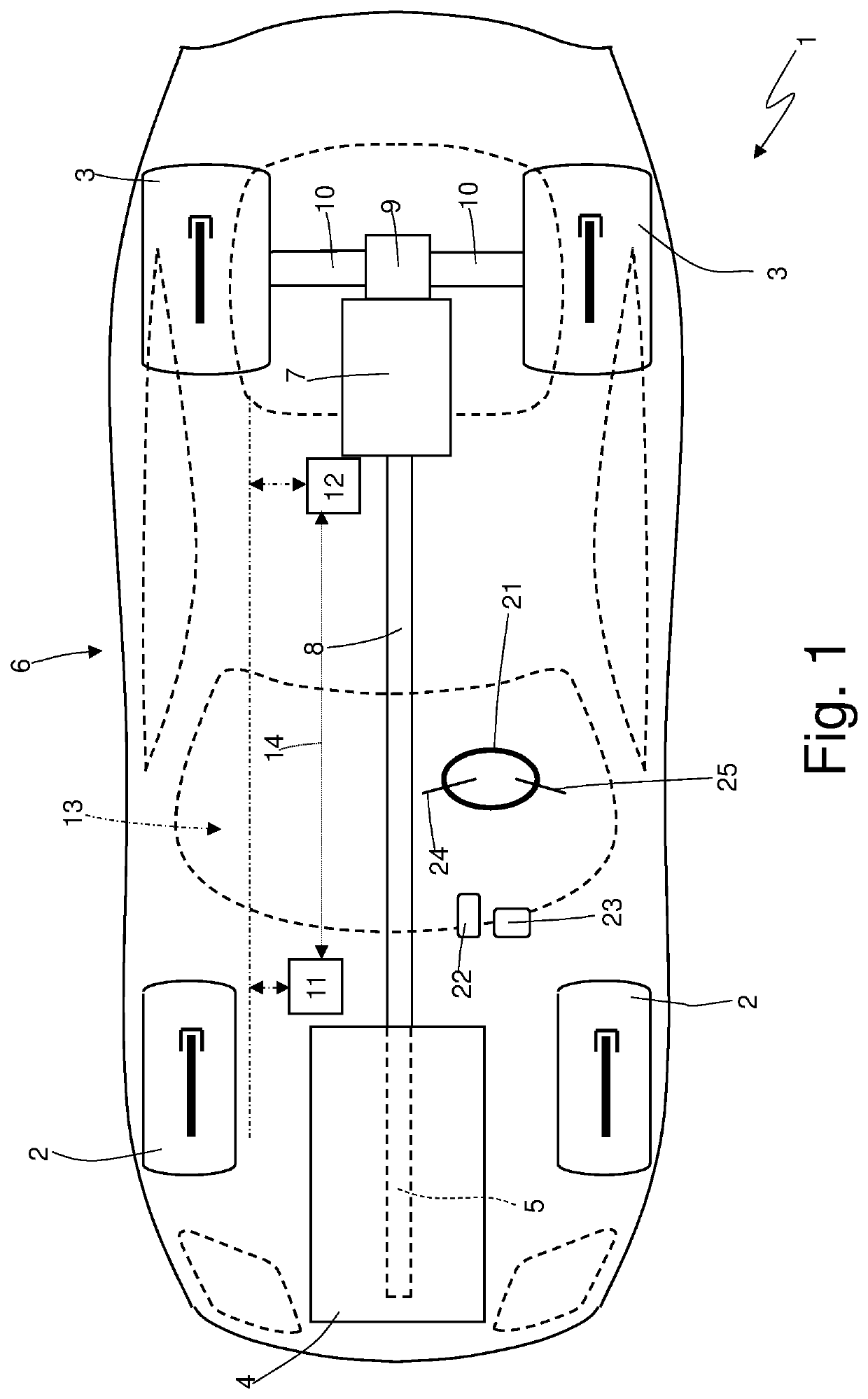
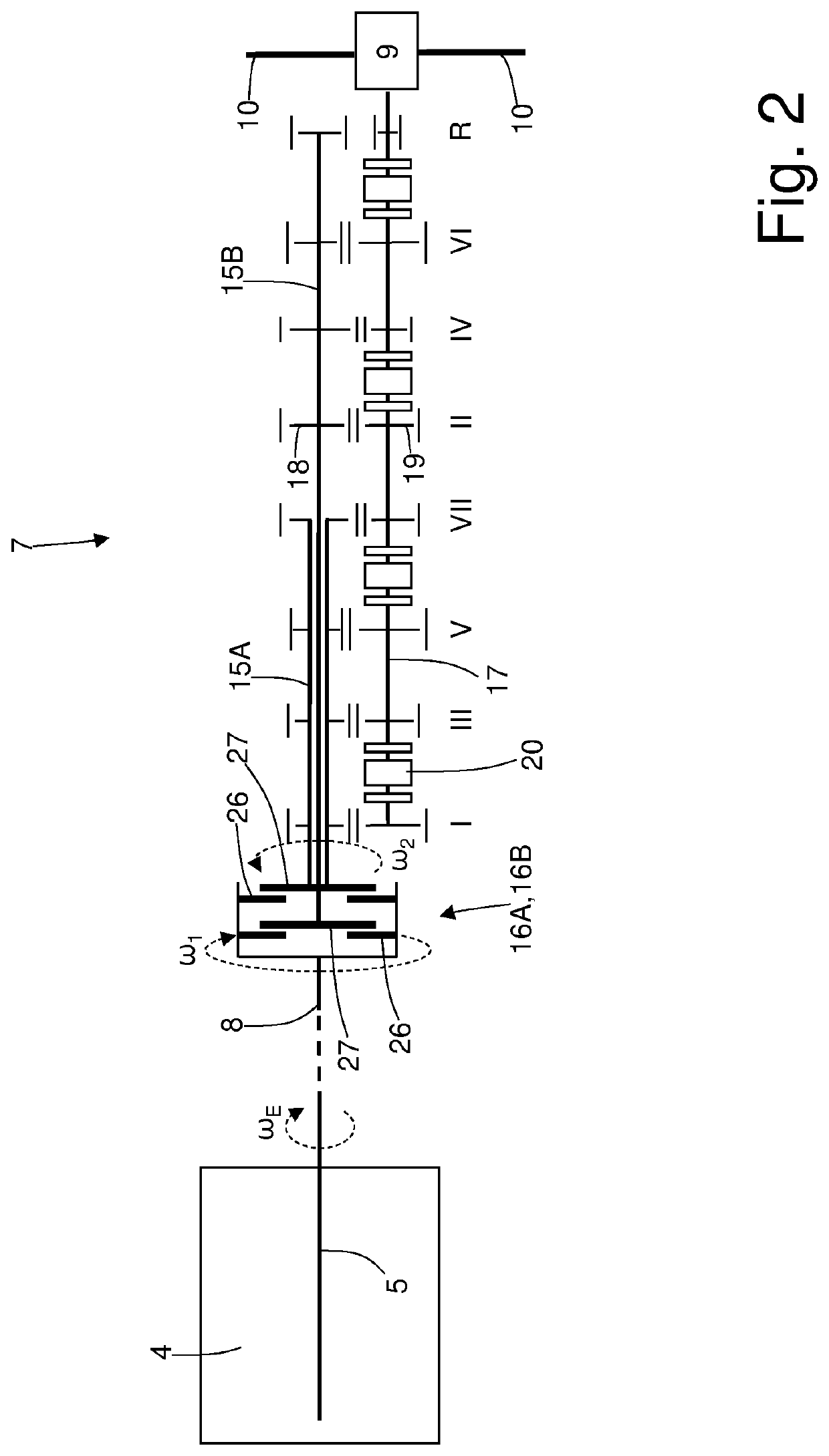
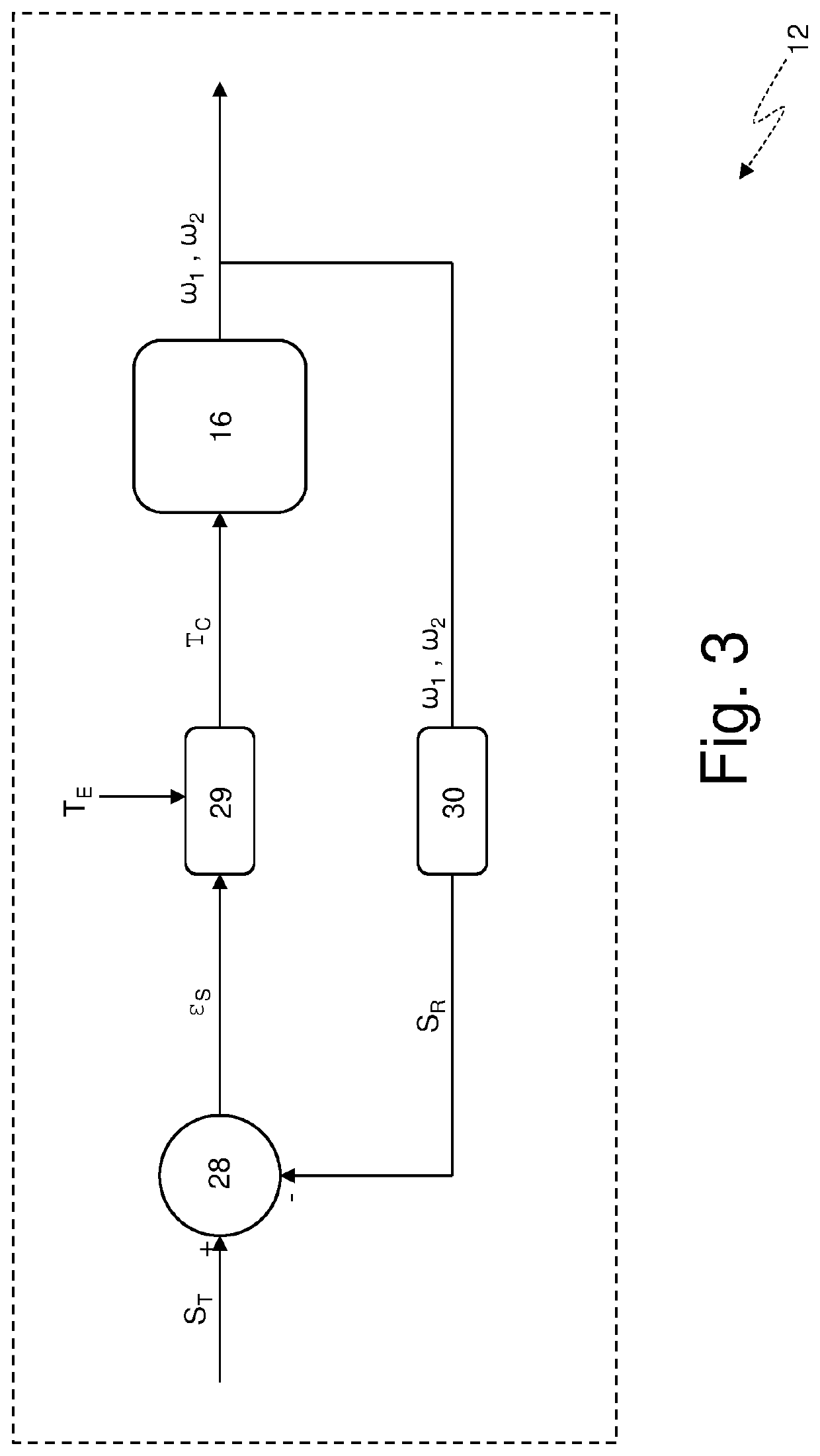
ActiveUS20210095726A1Economical and simplePrevent negative consequenceClutchesGear vibration/noise dampingDrive wheelTorque transmission
A method to control a road vehicle provided with a clutch, which connects an internal combustion engine to drive wheels and is arranged upstream of a servo-assisted transmission; the control method comprises the steps of: checking whether the tyres of the drive wheels are close to a grip limit; and opening the clutch so that the clutch transmits a torque to the drive wheels with a slip of the clutch that is constant and other than zero when the tyres of the drive wheels are close to the grip limit.
Owner:SPAN FERRARI SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com