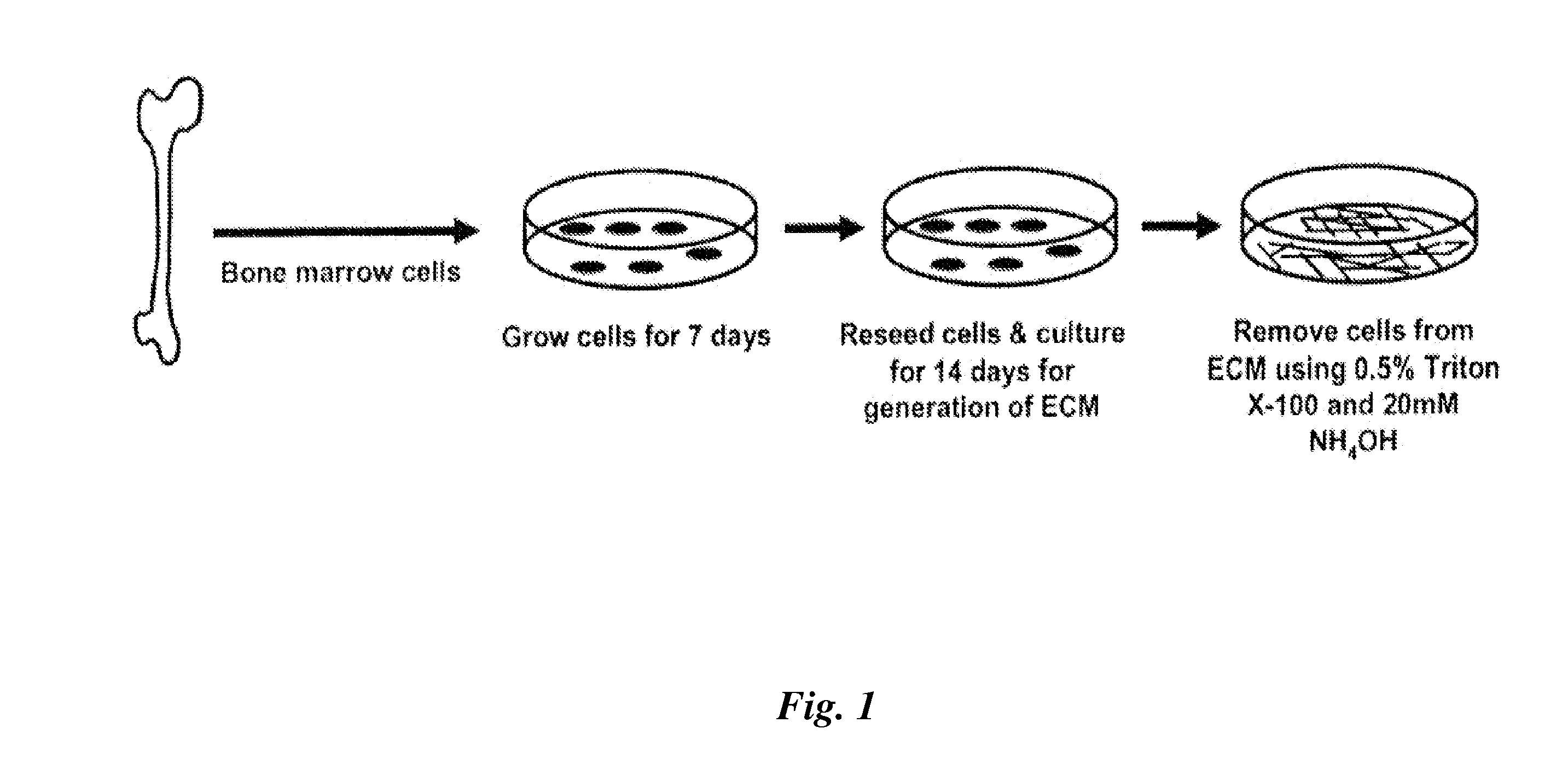
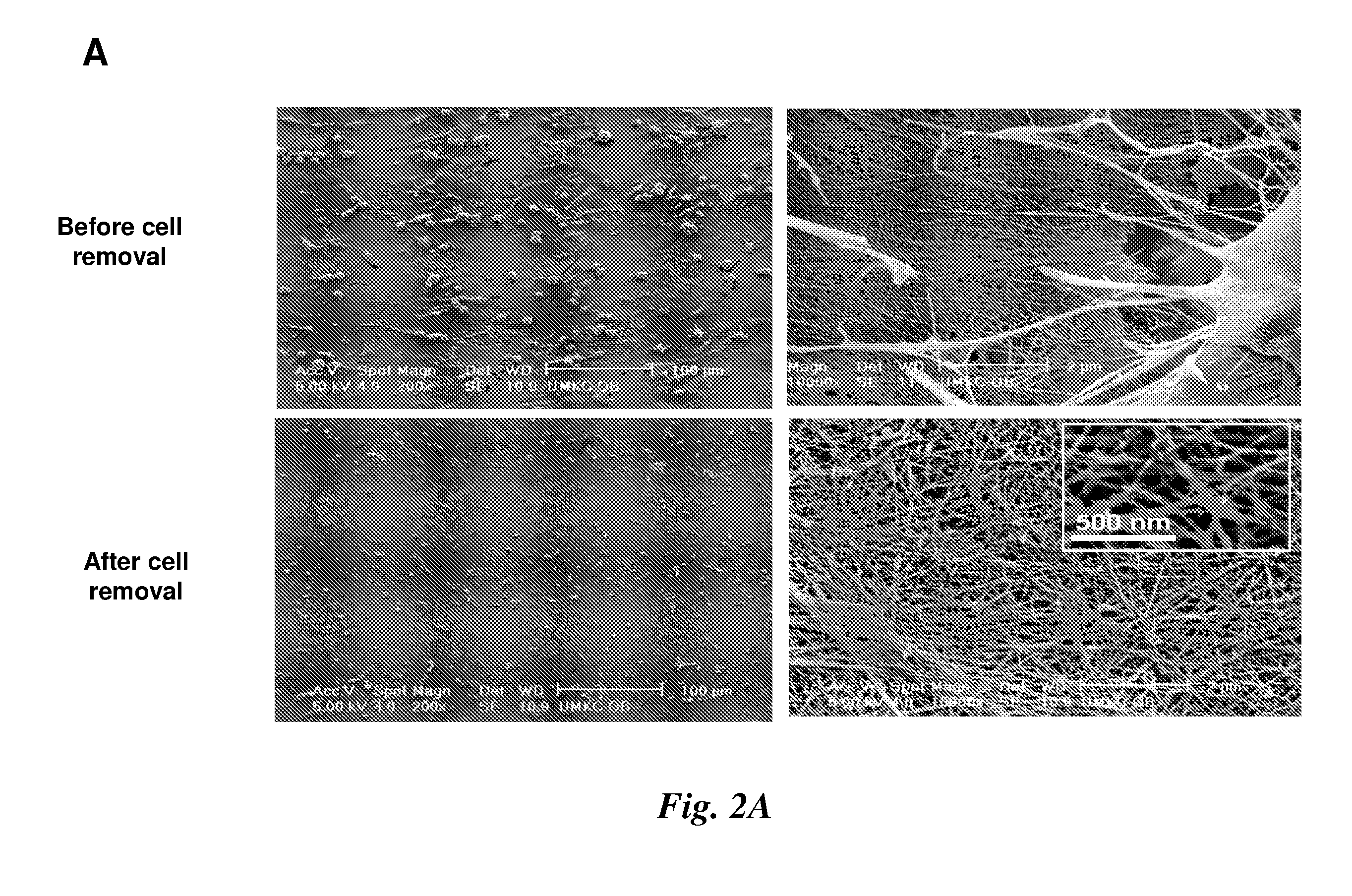
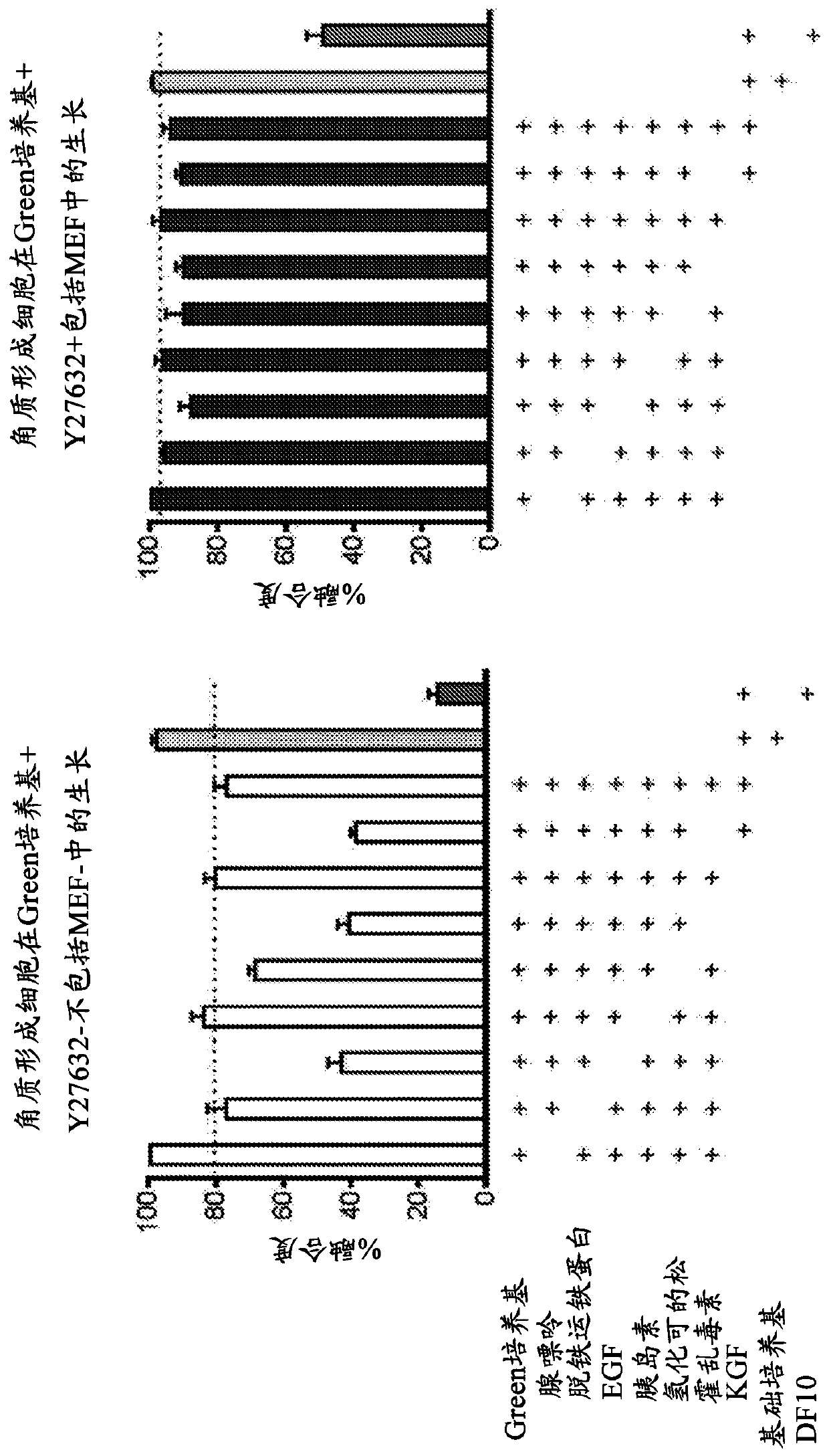
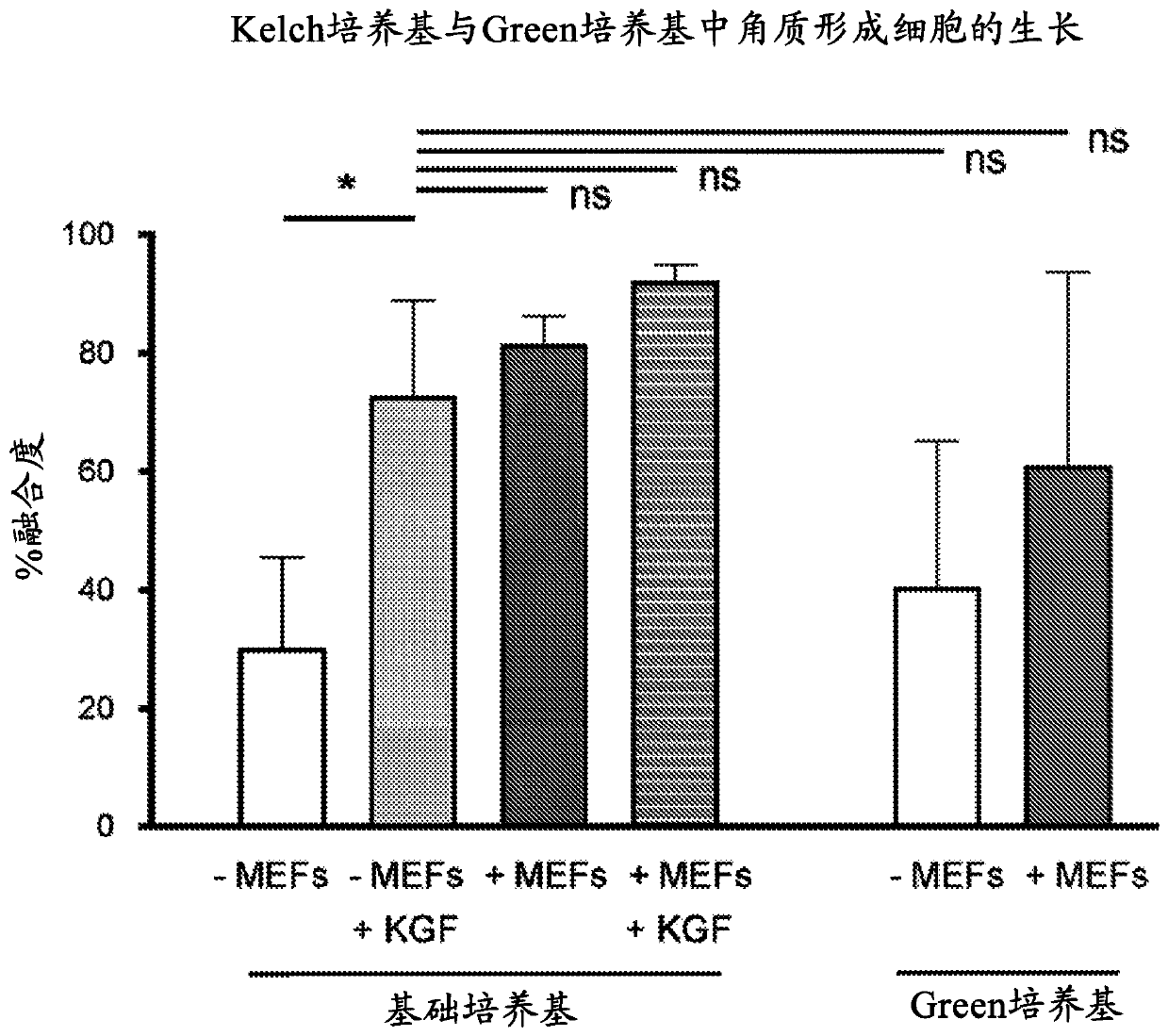
Patents
Literature
115 results about "Feeder Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Organisms Feeder cattle Feeder cell, a fibroblast, a type of cell used in human embryonic stem cell research Feeder fish, certain types of inexpensive fish commonly fed as live prey to captive animals Fluid feeder (disambiguation), organisms that feed on the fluid of other organisms
Methods and materials for the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells in feeder-free culture
Methods and materials for culturing primate-derived primordial stem cells are described. In one embodiment, a cell culture medium for growing primate-derived primordial stem cells in a substantially undifferentiated state is provided which includes a low osmotic pressure, low endotoxin basic medium that is effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells. The basic medium is combined with a nutrient serum effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells and a substrate selected from the group consisting of feeder cells and an extracellular matrix component derived from feeder cells. The medium further includes non-essential amino acids, an anti-oxidant, and a first growth factor selected from the group consisting of nucleosides and a pyruvate salt.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for the culture of human embryonic stem cells on human feeder cells
InactiveUS7432104B2Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050158852A1Improve breeding conditionsImprove survival rateGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsCell-Extracellular MatrixIn vitro growth
The present invention discloses a method for improving growth and survival of single human embryonic stem cells. The method includes the step of obtaining a single undifferentiated HES cell; mixing the single undifferentiated cell with an extracellular matrix (ECM) to encompass the cell; and inoculating the mixture onto feeder cells with a nutrient medium in a growth environment. Therefore the single cells can survive, proliferate and grow in vitro.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Methods and compositions for the differentiation of stem cells
ActiveUS20100216181A1Overcome limitationsPromote cell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of hematopoietic progenitor cells or endothelial progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells using a defined cell culture medium without the need to utilize feeder cells or serum. In some embodiments, differentiation is accomplished using hypoxic atmospheric conditions. The defined medium of the present invention may contain growth factors and a matrix component. The hematopoietic progenitor cells may be further differentiated into cell lineages including red blood cells, macrophages, granulocytes, and megakaryocytes. The endothelial progenitor cells may be further differentiated into endothelial cells. Also disclosed are screening assays for identification of candidate substances that affect differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into progenitor cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Pancreatic and liver endoderm cells and tissue by differentiation of definitive endoderm cells obtained from human embryonic stems
The invention relates to methods that allow for the efficient differentiation to form pancreatic endoderm cells from pluripotent stem cells such as human embryonic stem cells and definitive endoderm cells. The invention is directly applicable to the ultimate generation of pancreatic beta cells that could be used as part of a therapy to treat or even cure diabetes. Additionally, the present invention may be used to generate liver endoderm cells from human embryonic stem cells and definite endoderm cells as well. This invention relates to a method for generating definitive endoderm and pancreatic endoderm cells from stem cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells using defined media in the absence of feeder cells. A simply two step procedure to provide pancreatic endoderm cells from embryonic stem cells represents further embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
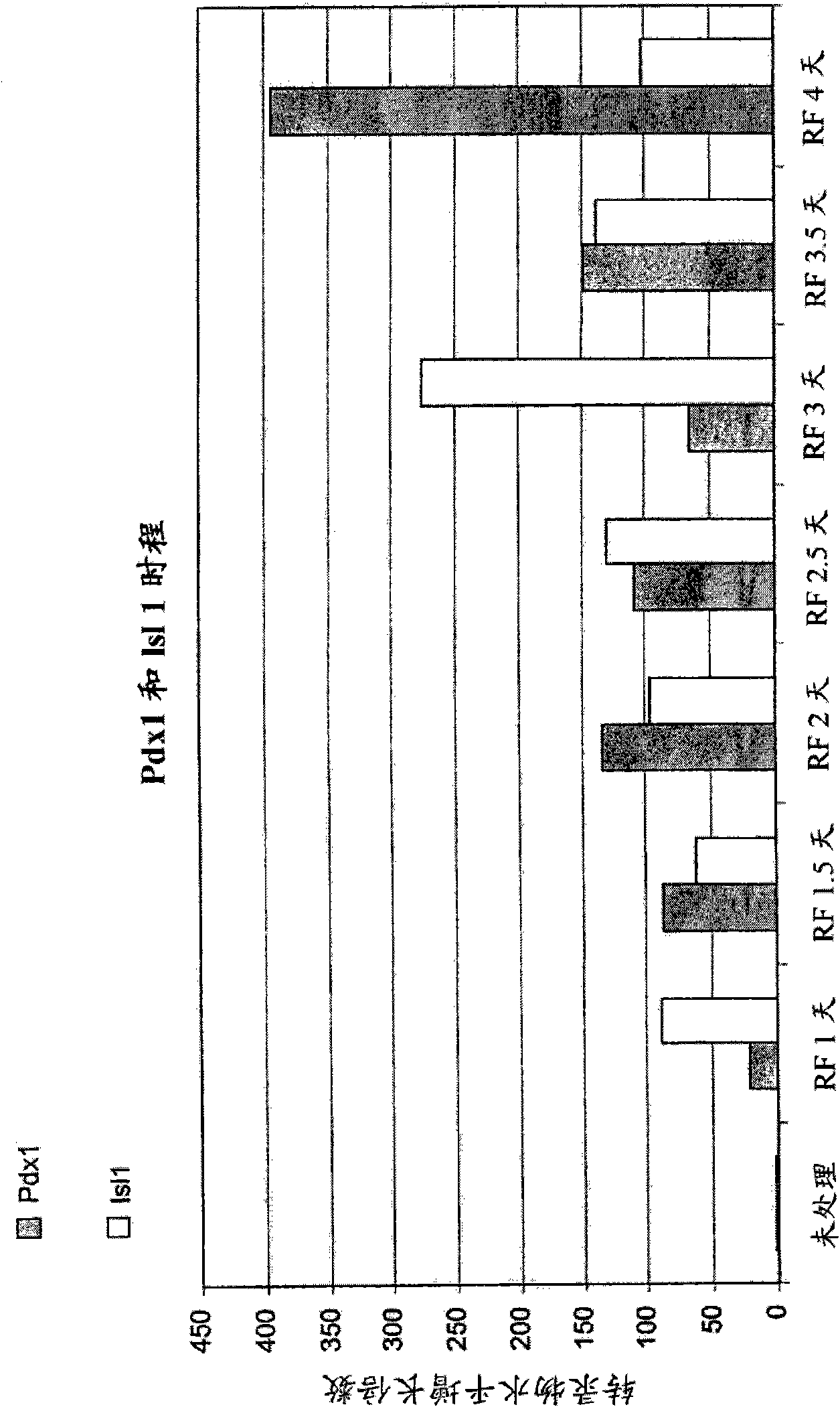
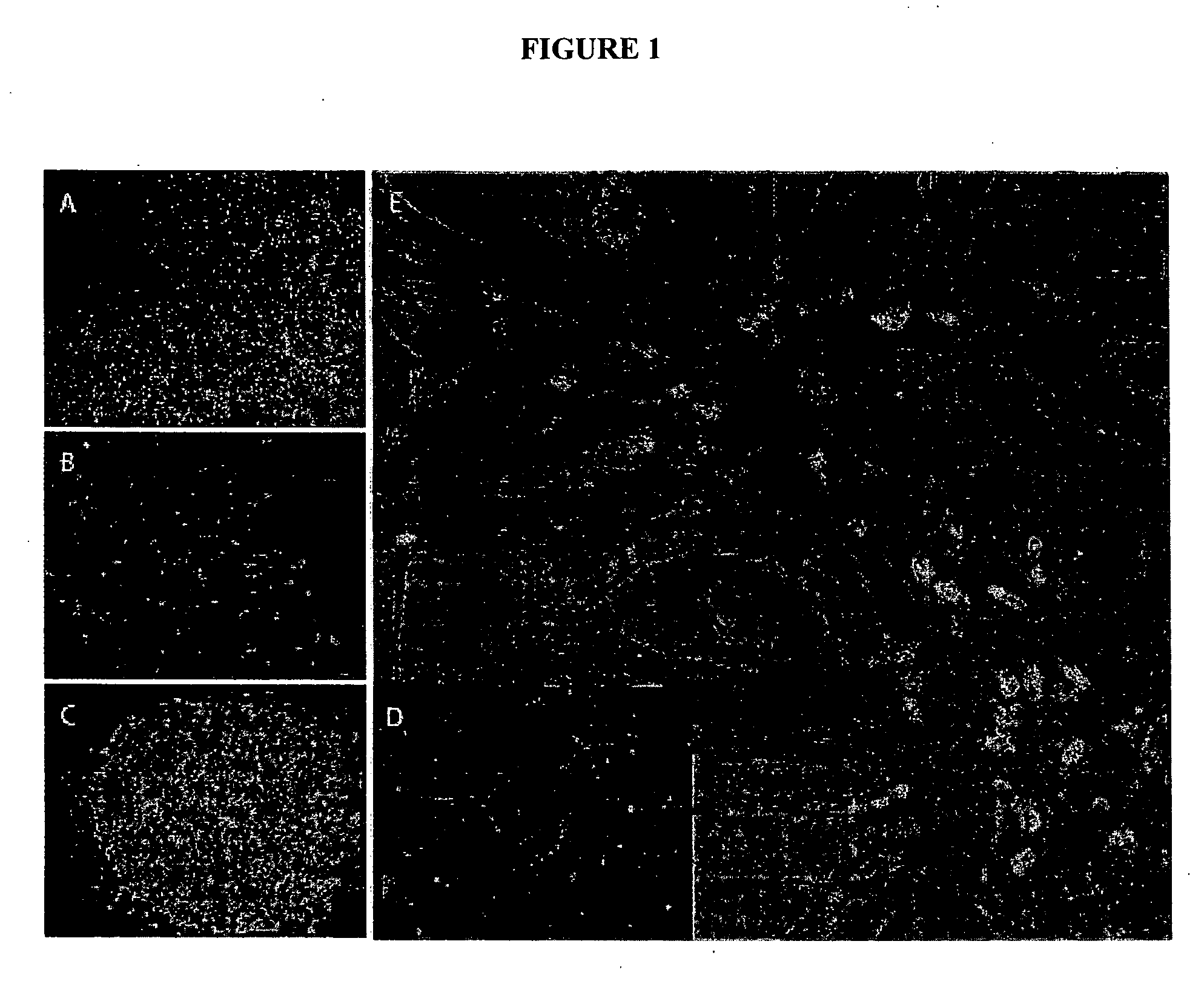
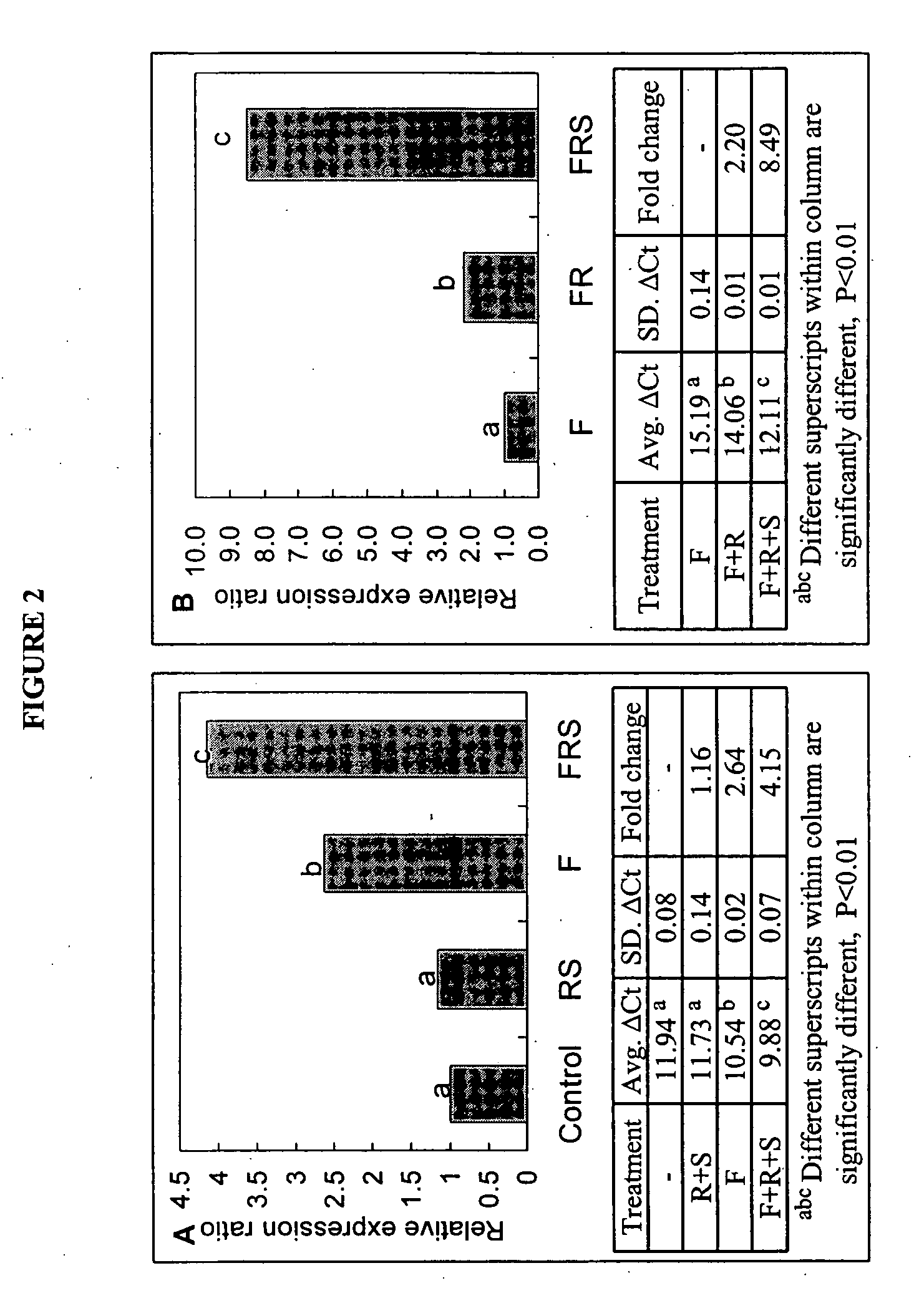
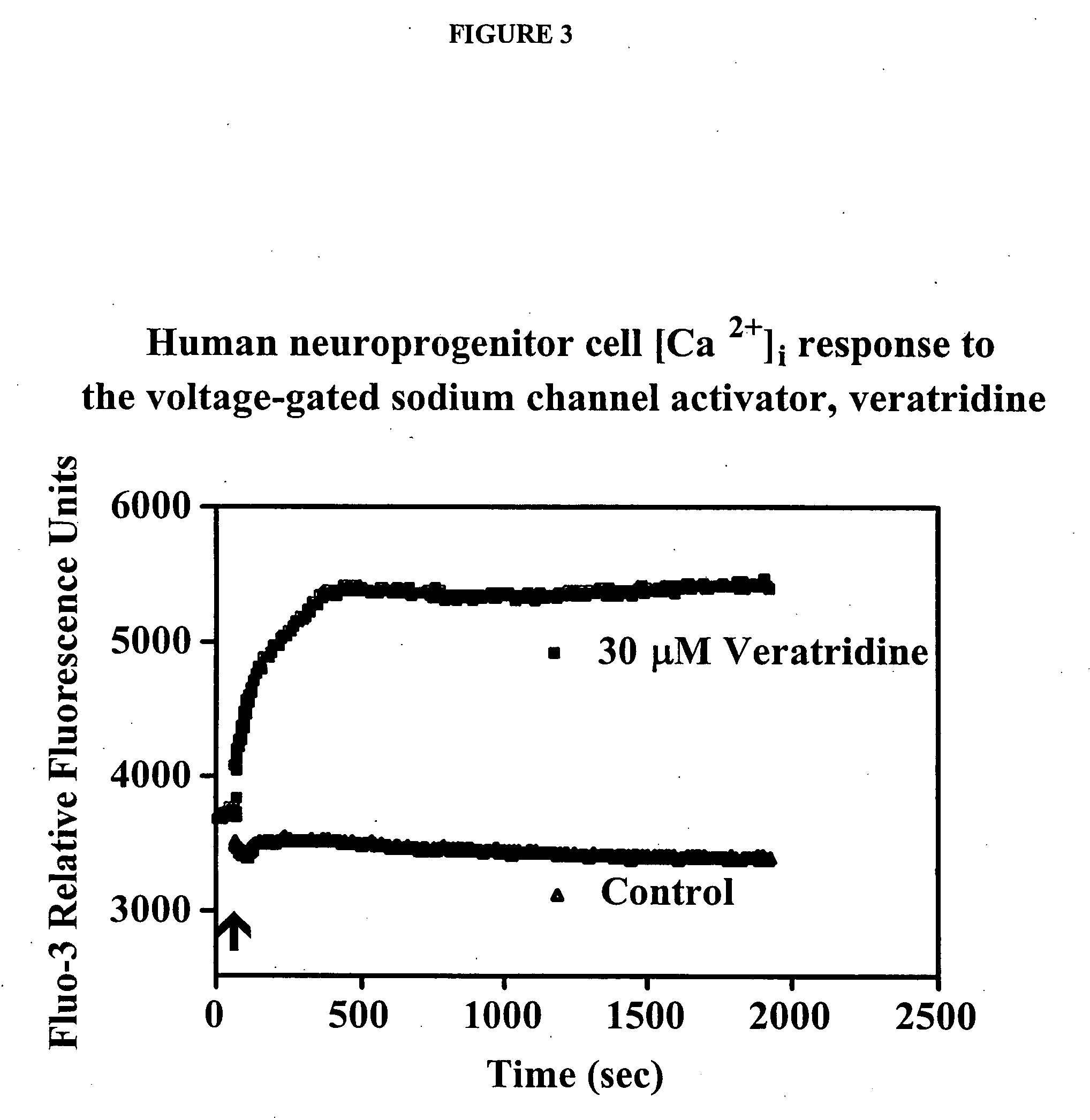
Neuronal progenitors from feeder-free human embryonic stem cell culture
The present invention relates to methods for producing feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells (preferably adherent) from embryonic stems cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells, the feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells, preferably human cells themselves, as well as methods for producing feeder cell-free samples of neuronal cells, preferably adherent human neuronal cells and the feeder cell-free neuronal cells themselves. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating neurodegenerative diseases as well as the use of the described cells in assay systems is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Compositions Comprising Human Embryonic Stem Cells and their Derivatives, Methods of Use, and Methods of Preparation
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising of preparations of human embryonic stem (hES) cells and their derivatives and methods for their transplantation into the human body, wherein transplantation results in the clinical reversal of symptoms, cure, stabilization or arrest of degeneration of a wide variety of presently incurable and terminal medical conditions, diseases and disorders. The invention further relates to novel processes of preparing novel stem cell lines which are free of animal products, feeder cells, growth factors, leukaemia inhibitory factor, supplementary mineral combinations, amino acid supplements, vitamin supplements, fibroblast growth factor, membrane associated steel factor, soluble steel factor and conditioned media. This invention further relates to the isolation, culture, maintenance, expansion, differentiation, storage, and preservation of such stem cells.
Owner:SHROFF GEETA
Method for the induction and expansion of natural killer cells derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells
ActiveUS20150152387A1Improve efficiencyImprove efficacyBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsNatural Killer Cell FunctionNatural killer cell
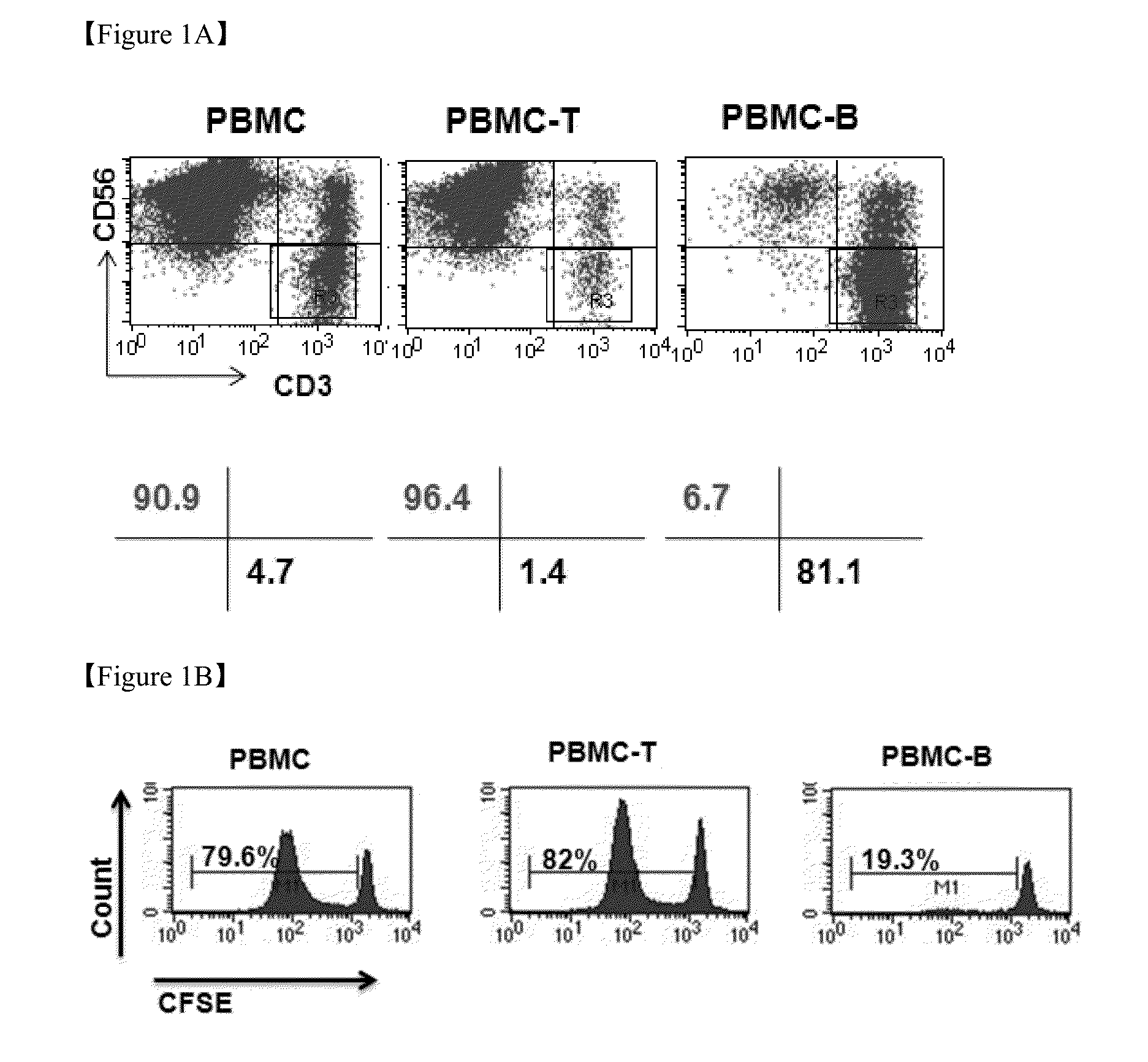
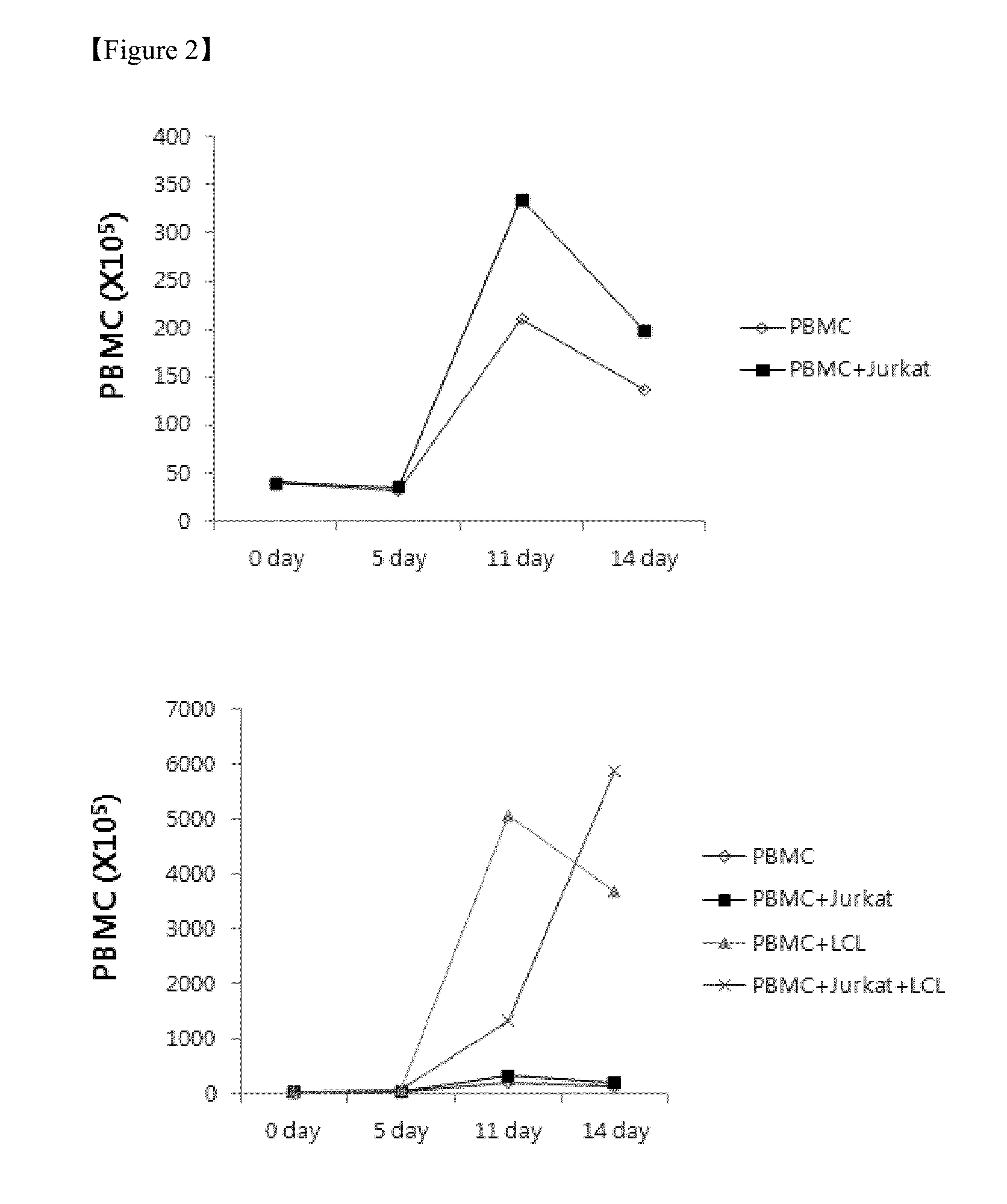
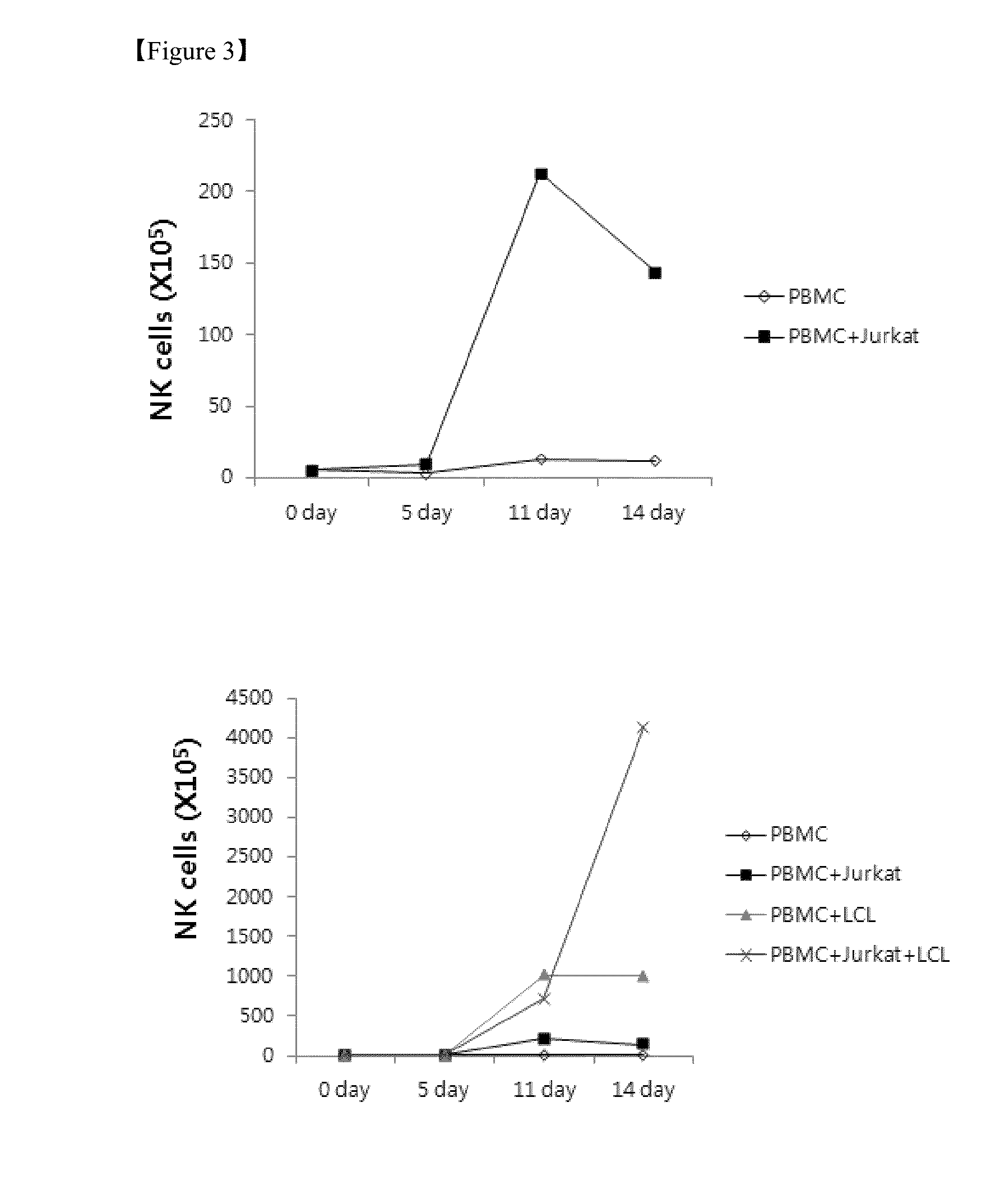
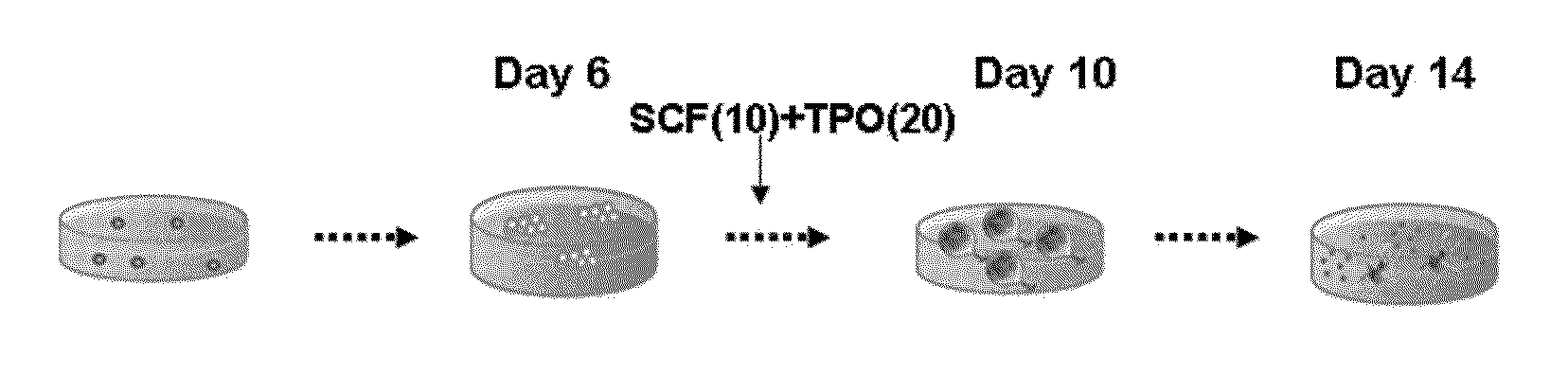
The present invention relates to a method for inducing and expanding natural killer cells derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells, which comprises co-culturing, as feeder cells, irradiated Jurkat cells and irradiated Epstein-Barr virus transformed lymphocyte continuous line (EBV-LCL) cells in the presence of cytokines, along with peripheral blood mononuclear cells. According to the present invention, a large quantity of natural killer cells can be induced and proliferated from a small quantity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells even without the use of high-cost equipment or various kinds of expensive cytokines, thereby making it possible to significantly improve the efficiency and efficacy of the prevention and treatment of cancer using the natural killer cells.
Owner:NKMAX CO LTD
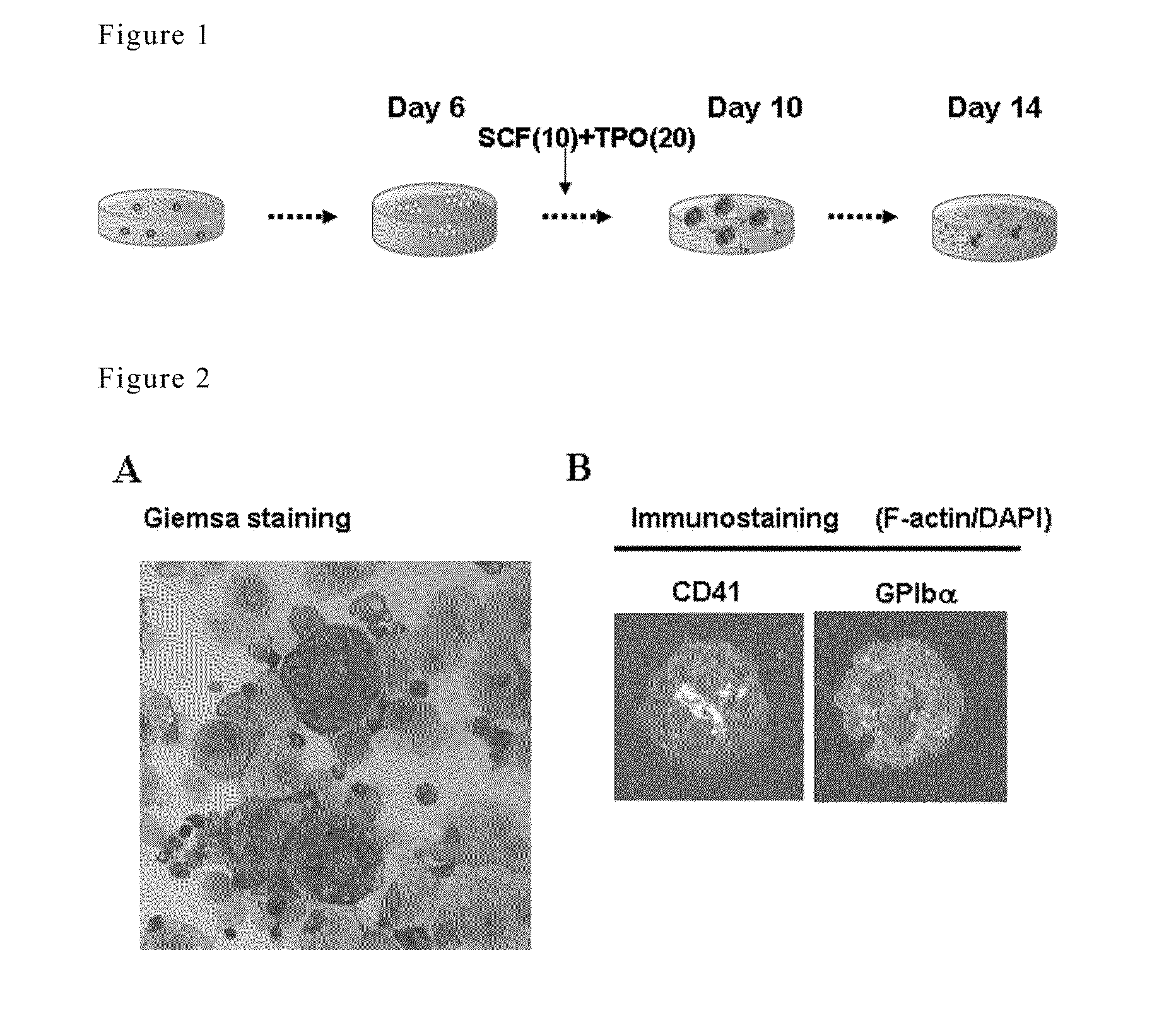
METHOD FOR PREPARATION OF PLATELET FROM iPS CELL
ActiveUS20110053267A1Avoid generationEfficiently obtainMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHematopoietic progenitor cell differentiationMolecular biology
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for efficiently preparing blood cells, such as mature megakaryocytes and platelets, from iPS cells in an in vitro culture system.The present invention provides a sac-like structure enclosing hematopoietic progenitor cells, which is obtained by inoculating iPS cells onto feeder cells and then culturing the iPS cells under conditions suitable for inducing the differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Moreover, the present invention also provides a method for producing various types of blood cells, which comprises culturing hematopoietic progenitor cells enclosed in the sac-like structure under conditions suitable for inducing the differentiation of blood cells. Furthermore, the present invention also provides a method for producing various types of blood cells, particularly megakaryocytes and platelets, without involving the sac-like structure.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Non-Embryonic Totipotent Blastomere-Like Stem Cells And Methods Therefor
Human non-embryonic adult totipotent and pluripotent stem cells are isolated in a simplified serum-free and feeder cell-free process. Most remarkably, certain stem cells, and especially BLSCs, are extremely small, fail to exclude trypan blue, but are nevertheless able to proliferate from even high dilutions. Therefore, so obtained stem cells can be used to prepare true monoclonal stem cell populations, which are useful in numerous uses, including therapeutic, prophylactic, diagnostic, and research uses.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
Screening method for hybrid tumor cell monoclonal preparation
ActiveCN101270380ANo training workloadReduce training workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationScreening methodBiology
The invention relates to a method of realizing the screening and the monoclone preparation of hybridoma cell in one step. The method comprises that the semisolid medium of the monoclone of hybridoma cell is firstly prepared, the basic fibroblast growth factor of human is added into the fusion cell, then hydridoma fusion factor and clone factor are added and well-mixed, then the mixed material and the semisolid medium are gently well-mixed and packaged into plates and cultivated in the condition of 35 DEG C and CO2 with concentration of 5 percent; when visible clone colony grows in the plates, the clone is aspirated from the culture medium by a micropipettor and moved onto a cell culture plate for liquid scale-up culture, and one clone is moved in one hole; till the cell grows to half to two-third of the hole bottom, the culture supernatant is aspirated to do positive detection, and the positive hole is chosen to directly scale-up frozen and stored for further carrying out the characteristic identification of antibody or ascites production. The method of realizing the screening and the monoclone preparation of hybridoma cell in one step has the advantages of the simple operation, the short culture period, not requiring feeder cells and easily achieving the screening and the monoclone preparation of hybridoma cell after cell fusion in one step.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Defined Culture Conditions of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for culturing stem cells, particularly embryonic stem cells. Specifically, the invention relates to a culture medium that supports proliferation of substantially undifferentiated stem cells, while maintaining potency of the cells. An an embodiment, the culture medium is defined and supports proliferation of substantially undifferentiated embryonic stem cells in essentially serum free and feeder cell free conditions. Compositions for making the medium and methods using the culture medium are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for culturing and subculturing primate embryonic stem cell, as well as method for inducing differentiation thereof
InactiveUS20110151554A1Safely culturedLow costCell dissociation methodsCulture processCell-Extracellular MatrixVascular endothelium
The present invention provides a method for subculturing primate embryonic stem cells, and a method for inducing differentiation of the same cell into a vascular endothelial cell and a blood cell. The present invention provides a method comprising culturing primate embryonic stem cells in a medium containing a protein component without using feeder cells and cytokines in a container coated with an extracellular matrix, detaching colonies of the resulting embryonic stem cells in the presence of a cytodetachment agent, and plating the colonies in the similar medium, and a method comprising culturing primate embryonic stem cells in a serum-containing or not containing medium in the presence of cytokine, adhesion-culturing the resulting embryoid body or embroyid body-analogous cellular aggregate in the presence of a cytokine to obtain specific precursor cells, and separating non-adherent cells and adherent cells from the specific precursor cells to obtain blood cells and vascular endothelial precursor cells.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR GLOBAL HEALTH & MEDICINE +2
Alternative Compositions and Methods for the Culture of Stem Cells
InactiveUS20090186407A1Mammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation and maintenance of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human feeder cell conditioned medium, and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors.
Owner:BRESAGEN
Serum-free medium of embryonic stem cells, and its application
InactiveCN103555660AMaintain normal stateMaintain totipotencyEmbryonic cellsGerm cellsChemical synthesisCell culture media
The invention relates to a serum-free medium of embryonic stem cells, and its application. The medium comprises a micro-molecular inhibitor CHIR99021, a micro-molecular inhibitor XAV939, an additive B27 / N2 and a basic medium DMEM / F12. The serum-free medium of embryonic stem cells, which contains no animal source substances and has a determined composition, is obtained by using the micro-molecular inhibitor CHIR99021, the micro-molecular inhibitor XAV939 and the B27 / N2 additive having a clear composition to substitute serum and feeder cells in a traditional embryo hepatocyte medium. Experiments prove that the medium can maintain the self updating of human embryonic stem cells, and maintains the undifferentiated state and totipotency of the embryonic stem cells; and the medium has a clear composition, and proteins and other components contained in the medium are from human recombinant proteins or are obtained through chemical synthesis, so there is no embryonic stem cell pollution, thereby no corresponding immune response is excited, and no immune immunological rejection is initiated.
Owner:苏州依科赛生物科技股份有限公司
Compositions Comprising Human Embryonic Stem Cells and Their Derivatives, Methods of Use, and Methods of Preparation
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising of preparations of human embryonic stem (hES) cells and their derivatives and methods for their transplantation into the human body, wherein transplantation results in the clinical reversal of symptoms, cure, stabilization or arrest of degeneration of a wide variety of presently incurable and terminal medical conditions, diseases and disorders. The invention further relates to novel processes of preparing novel stem cell lines which are free of animal products, feeder cells, growth factors, leukaemia inhibitory factor, supplementary mineral combinations, amino acid supplements, vitamin supplements, fibroblast growth factor, membrane associated steel factor, soluble steel factor and conditioned media. This invention further relates to the isolation, culture, maintenance, expansion, differentiation, storage, and preservation of such stem cells.
Owner:SHROFF GEETA
Culture system and method for propagation of human blastocyst-derived stem cells
InactiveCN101443445AFix stability issuesSolve quality problemsCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSingle cell suspensionExtended time
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
A feeder cell-free culture medium and system
A cell culture medium and system are provided which eliminates or at least reduces the need for feeder cells. The cell culture medium comprises one or more factors that are normally secreted and / or produced by a feeder cell and a synthetic chimeric protein comprising IGF-I and a portion of vitronectin. The cell culture medium is particularly suitable for propagating human embryonic stem cells and keratinocytes. This invention also relates to compositions and methods which utilize the cells cultured in the cell culture medium of the invention.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIVERSITY OF TECH
Hepatocyte lineage cells derived from pluripotent stem cells
InactiveCN1439049AMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemSurface markerPluripotential stem cell
It has been found that when pluripotent stem cells are cultured in the presence of hepatocyte differentiating agents, a population of cells is derived that has a remarkably high proportion of cells with a stem cell phenotype. In one example, human embryonic stem cells are allowed to form embryoid bodies and then mixed with the differentiation agent n-butyrate, optionally supplemented with maturation factors. In another example, n-butyrate is added to human embryonic stem cells in feeder-free culture. A remarkably homogeneous population of cells was obtained in both methods, consisting primarily of cells with morphological characteristics of hepatocytes, expressing characteristic surface markers of hepatocytes, and also possessing enzymatic and biosynthetic roles important for liver function. Since hepatocytes readily proliferate in culture, this system provides a rich source of hepatocyte lineage cells for various uses, such as drug screening and supplementation of liver function in clinical therapy.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Method for preparing induced pluripotent stem cells using synthetic peptide
ActiveUS20170275594A1Peptide-nucleic acidsGenetically modified cellsHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsPeptide
Provided is a method of preparing induced pluripotent stem cells using a synthetic peptide, and more particularly, to a method of preparing induced pluripotent stem cells using a peptide capable of inhibiting the activity of NF-κB and promoting mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET). Since undifferentiated multipotent stem cells may be efficiently prepared under xenopathogen-free or feeder cell-free conditions without requiring co-culture with animal serum or xenogeneic cells, the method for preparing the induced pluripotent stem cells using the synthetic peptide according to the present disclosure is very useful for developing stem cell therapeutic agents that are clinically applicable.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
Compositions Comprising Human Embryonic Stem Cells and Their Derivatives, Methods of Use, and Methods of Preparation
Owner:SHROFF GEETA
Non-tumorigenic expansion of pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20120270314A1Artificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
A method for expansion of human embryonic stem (hES) cells in a medium including human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSCs) as a feeder is provided. The human embryonic stem cells (hES) maintain the features of embryonic stem cells in the medium, such as pluripotency, unlimited undifferentiated proliferation and normal karyotypes. Also provided is a method for non-tumorigenic expansion of the human embryonic stem cells (hES) that is free from forming teratoma.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP +1
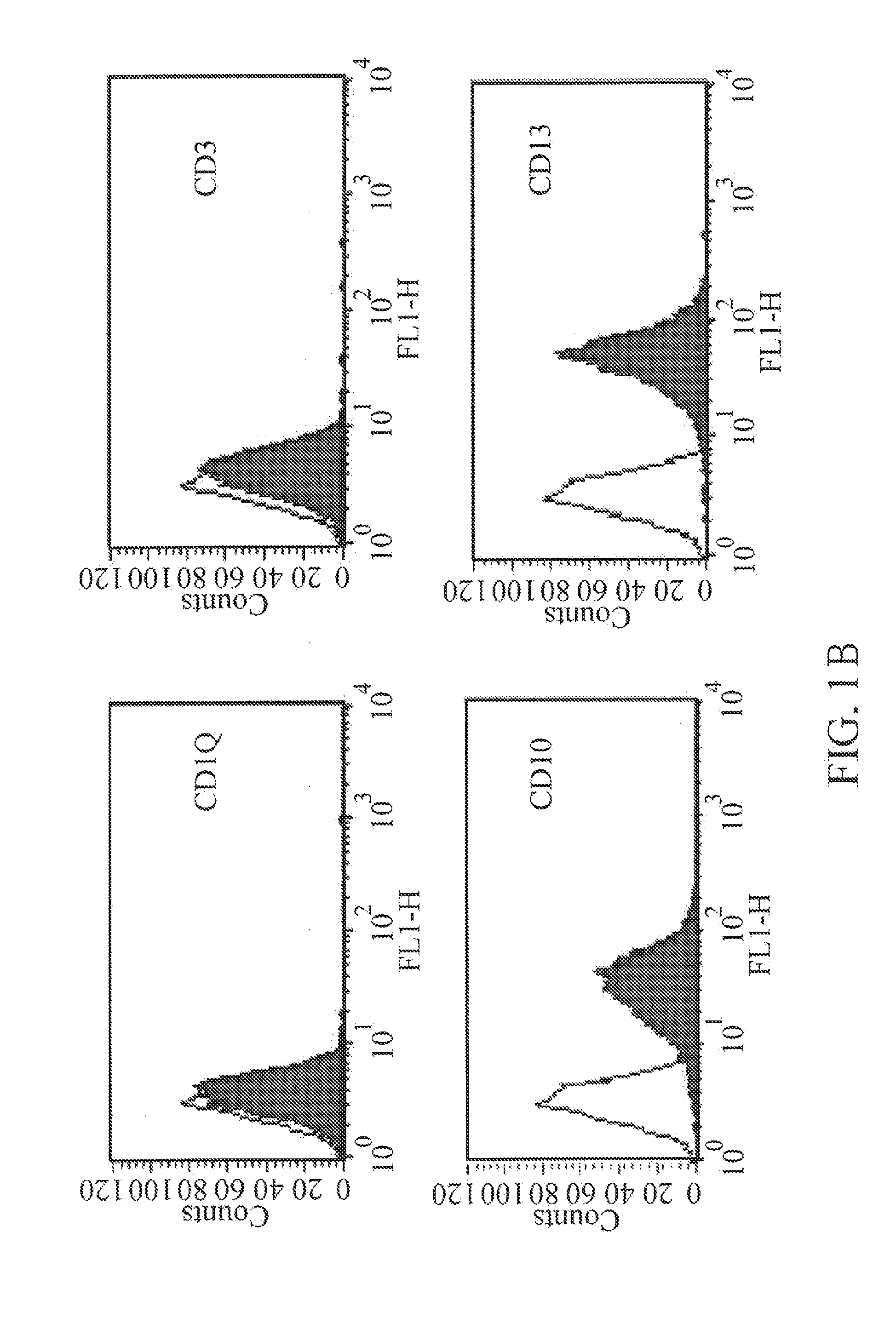
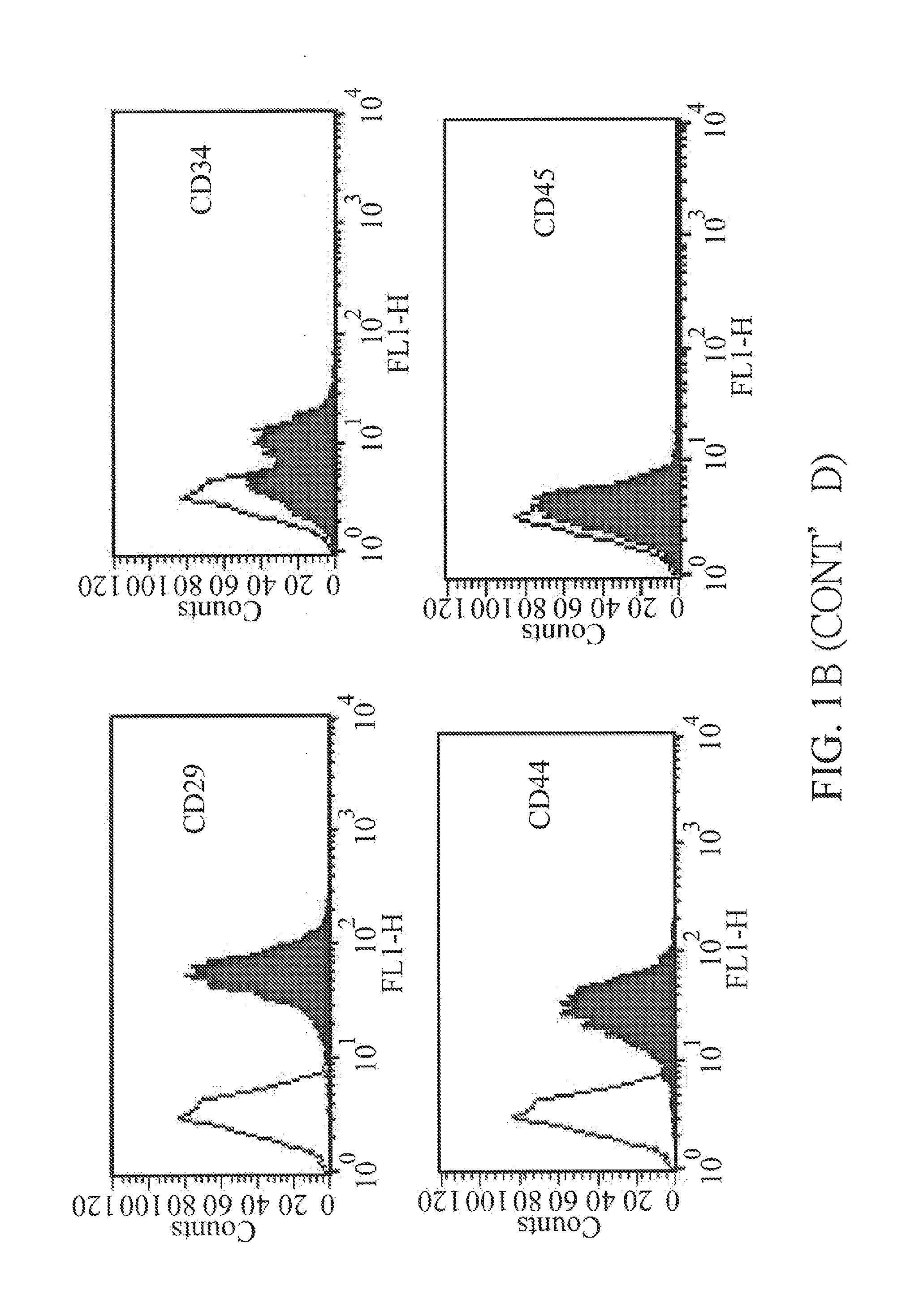
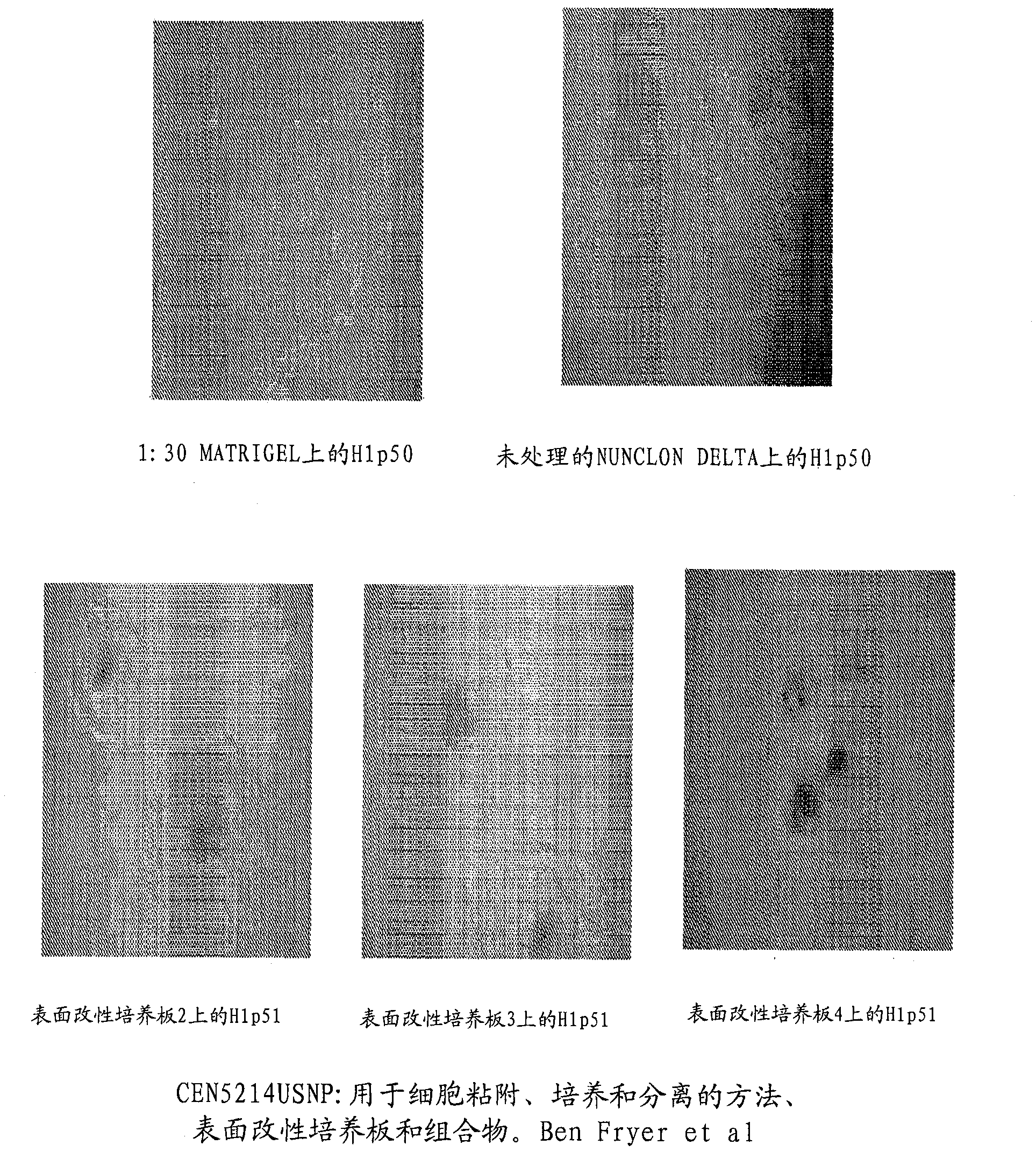
Methods, surface modified plates and compositions for cell attachment, cultivation and detachment
InactiveCN102046779ACell dissociation methodsCell culture supports/coatingKinase activityCell adhesion
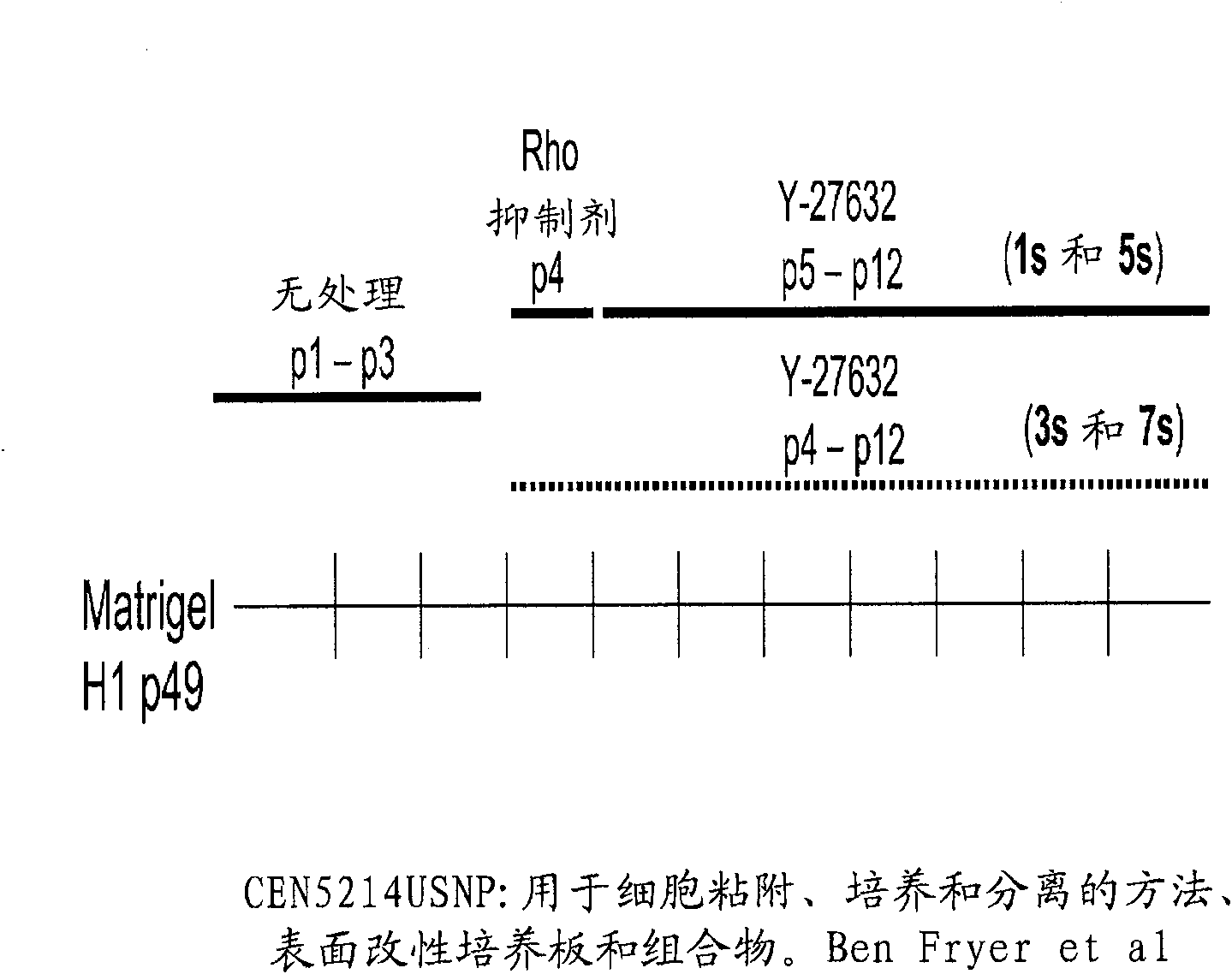
The present invention relates to the field of mammalian cell culture, and provides methods and compositions for cell attachment to, cultivation on and detachment from a solid substrate surface containing from at least about 0.5% N, a sum of O and N of greater than or equal to 17.2% and a contact angle of at least about 13.9 degrees, lacking a feeder cell layer and lacking an adlayer. In one embodiment of the present invention, the cells are treated with a compound capable of inhibiting Rho kinase activity. In another embodiment, the cells are treated with a compound capable of inhibiting Rho activity.
Owner:CENTOCOR ORTHO BIOTECH
Method for producing dopamine-producing neural precursor cells
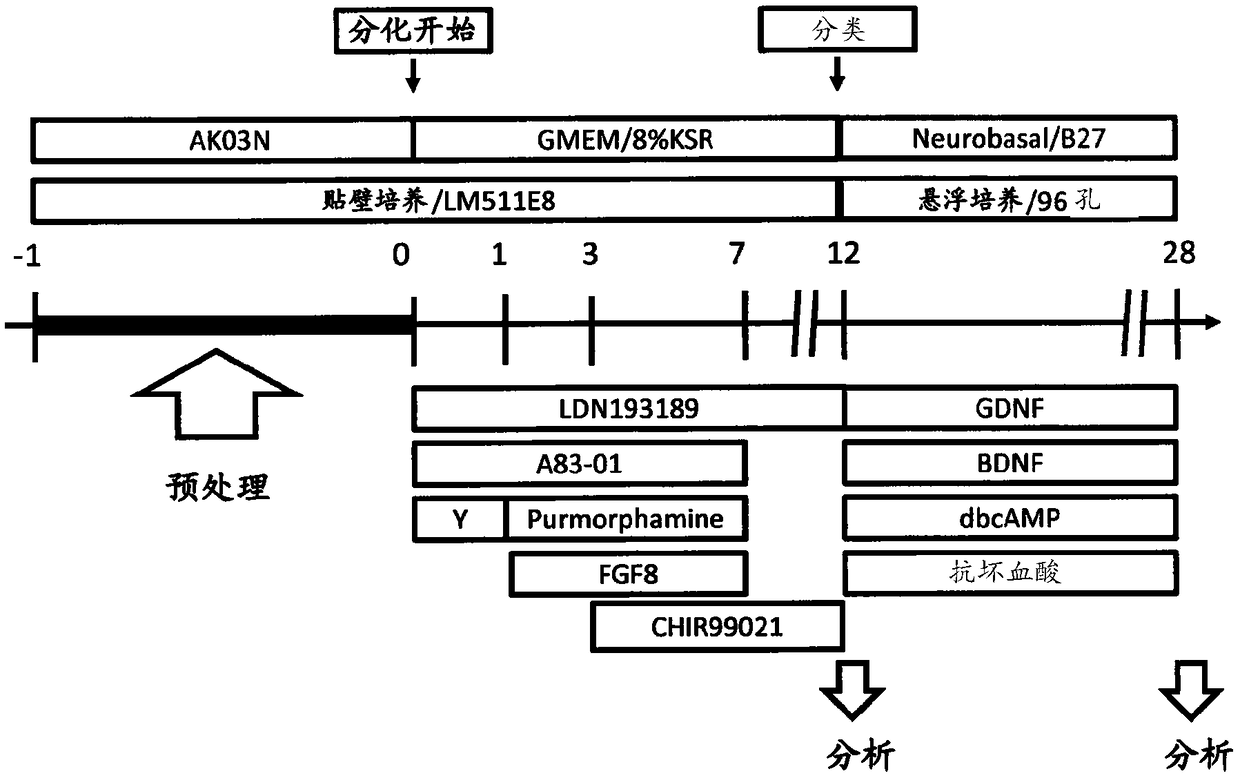
ActiveCN109072198AGet efficientlyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCell-Extracellular MatrixCulture fluid
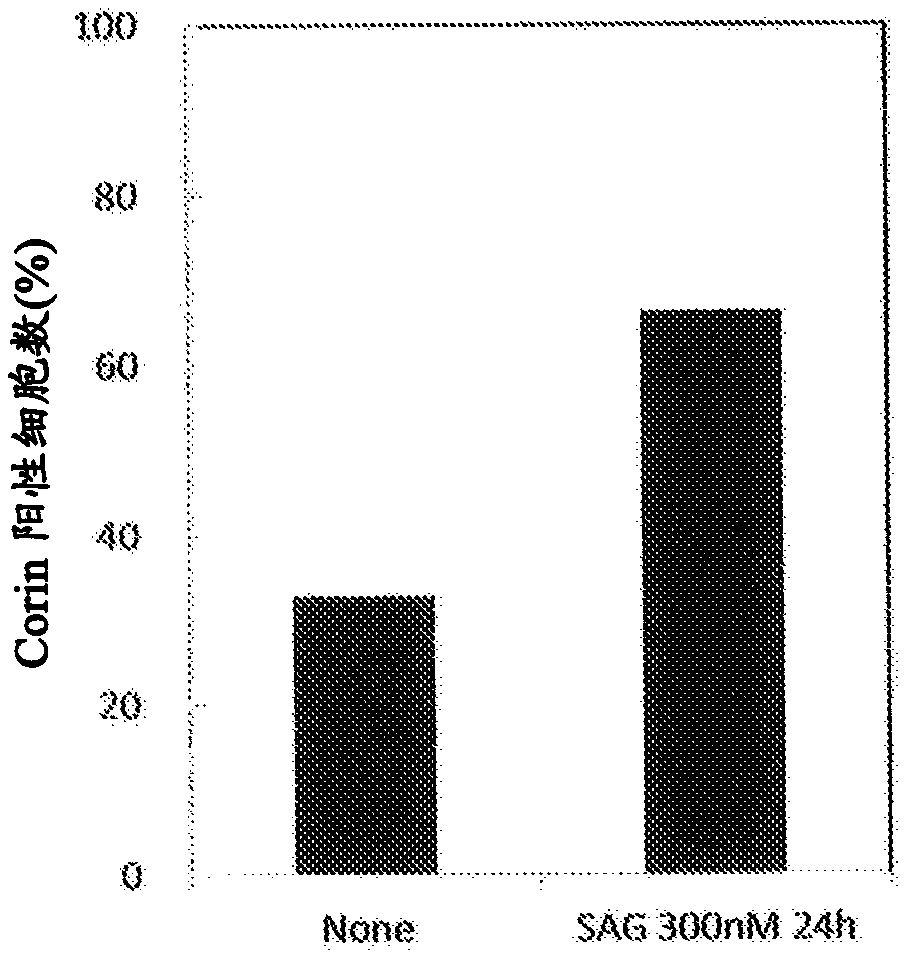
Dopamine-producing neural precursor cells are produced by: producing a cell population containing Corin and / or Lrtm1 positive cells via steps (1) and (2) as will be shown below; collecting the Corin and / or Lrtm1 positive cells from the cell population thus obtained by using a substance that binds to Corin and / or a substance that binds to Lrtm1; and suspension-culturing the Corin and / or Lrtm1 positive cells in a liquid culture medium that contains one or more neurotrophic factors: (1) a step for adhesion-culturing pluripotent stem cells in the absence of any feeder cells in an undifferentiatedstate-maintaining culture medium that contains a sonic hedgehog (SHH) signal stimulant and an undifferentiated state-maintaining factor in the presence of an extracellular matrix; and (2) a step for culturing the cell population obtained in step (1) in a liquid culture medium that contains one or more differentiation inducing factors.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Skin regeneration system
InactiveUS20060233764A1Enhanced growthLarge responseBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsVitronectinCell culture media
A cell culture medium and system are provided which eliminate or at least reduce the requirement for exogenous components such as serum and feeder cells. The cell culture medium comprises an IGF and vitronectin or fibronectin and, optionally an IGFBP, and is particularly suitable for propagating keratinocytes for subsequent use in skin growth and regeneration. This invention also relates to compositions and methods for skin growth and regeneration in situ, which utilize aerosol delivery of cultured keratinocytes.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIVERSITY OF TECH
Maintenance and Propagation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
ActiveUS20080175816A1Promote self-renewalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideMolecular biologyMesenchymal stem cell
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
Cell culture medium
Owner:UPSIDE BIOTECH LTD
Composition for culturing multipotent stem cells and utilization of the same
The invention aims to proliferate or establish undifferentiated pluripotent stem cells that retain their differentiation potency by culturing pluripotent stem cells in a medium free of a feeder cell, or a serum. The aim is attained by using a culture medium for pluripotent stem cells comprising the known ingredients, which is supplemented with an inhibitor of an adenylate cyclase activity.
Owner:RIKEN
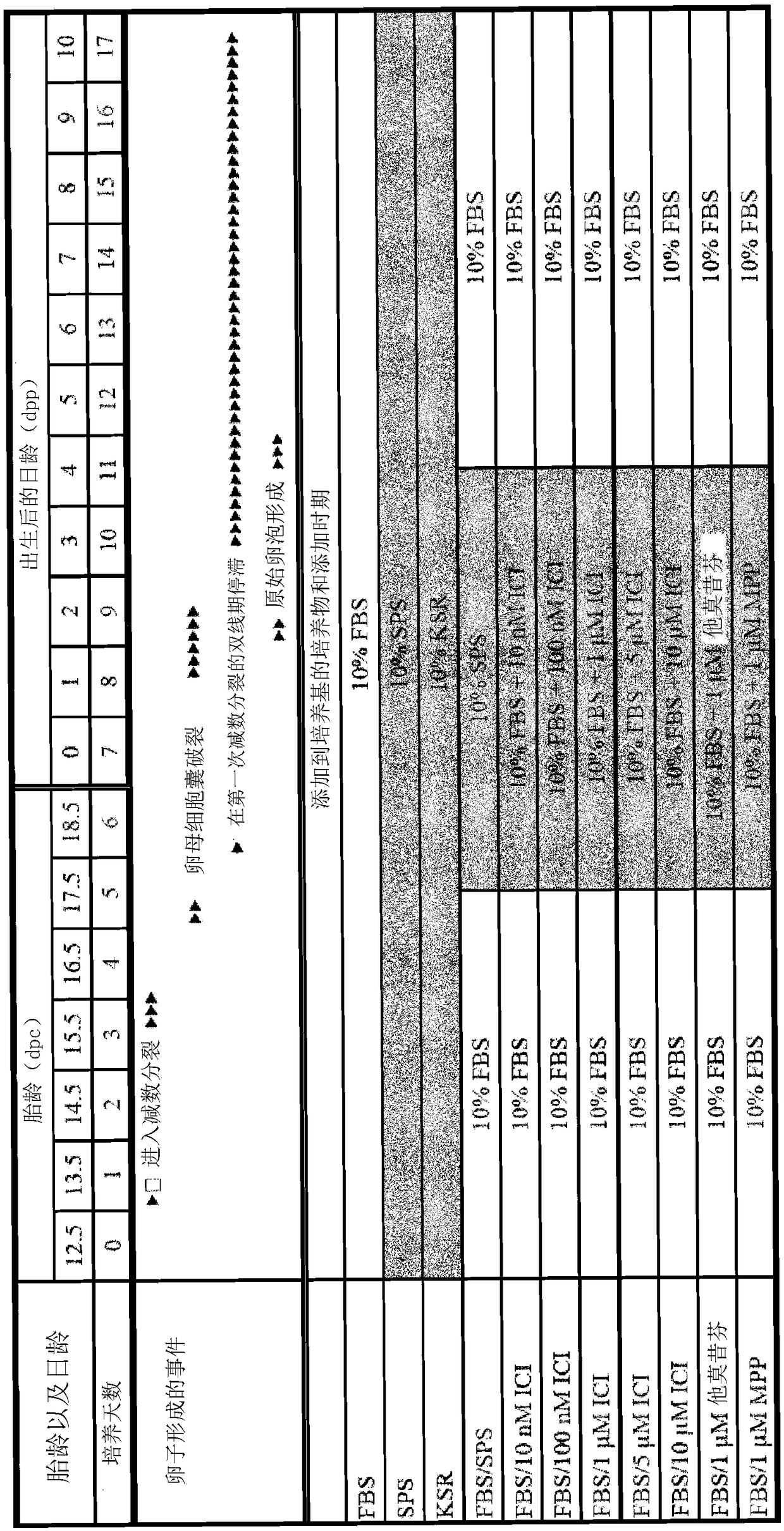
Culture method for differentiating primordial germ cells into functionally mature oocytes
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a method for differentiating primordial germ cells into functionally mature GV stage oocytes by in vitro culture. The present invention pertains to a method for differentiating primordial germ cells into functional GV stage oocytes in vitro including (a) a step for forming secondary follicles by culturing primordial germ cells and feeder cells adjacent to the primordial germ cells under conditions that eliminate the effects of estrogen or factors having a similar function to estrogen, (b) a step for partially cleaving the bonds between the granulosa cell layer and the thecal cell layer among the oocyte, granulosa cell layer, and thecal cell layer that constitute the formed secondary follicles, and (c) a step for differentiating the oocytes into functional GV stage oocytes by culturing the oocytes and granulosa cell layer that constitute the secondary follicles and the thecal cell layer in medium including a polymer compound.
Owner:TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE +2
Medium for ES culturing
Owner:FUJIFILM WAKO PURE CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com