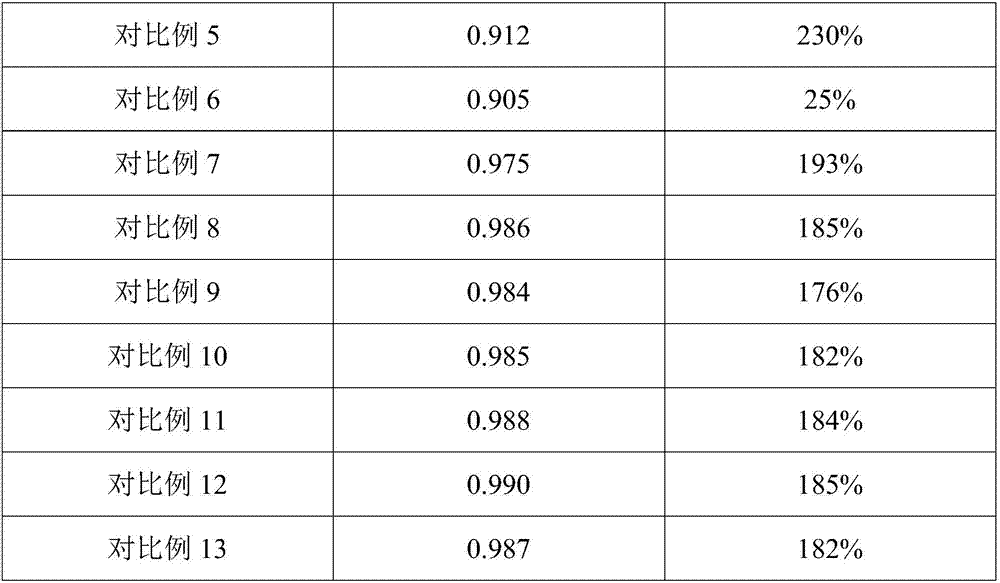
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Trypan blue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
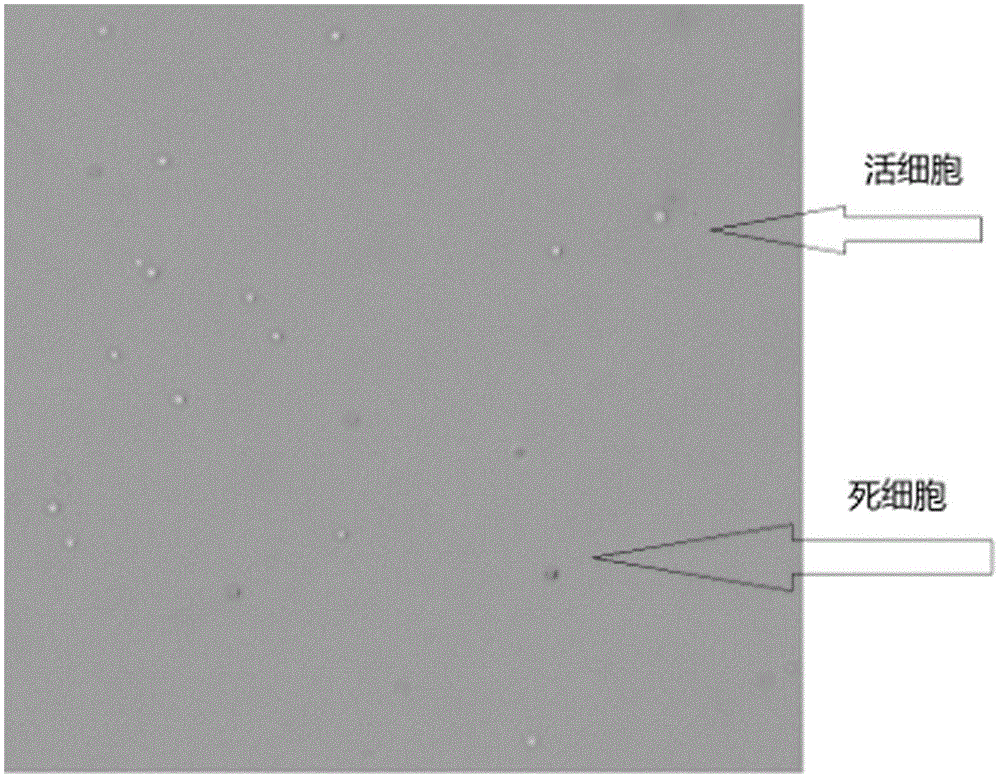
Trypan blue is an azo dye that is used as a dye-stuff. It is a direct dye for cotton textiles. In biosciences, it is used as vital stain to selectively colour dead tissues or cells blue. Live cells or tissues with intact cell membranes are not coloured. Since cells are very selective in the compounds that pass through the membrane, in a viable cell trypan blue is not absorbed; however, it traverses the membrane in a dead cell. Hence, dead cells appear as a distinctive blue colour under a microscope. Since live cells are excluded from staining, this staining method is also described as a dye exclusion method.
Non-Embryonic Totipotent Blastomere-Like Stem Cells And Methods Therefor
Human non-embryonic adult totipotent and pluripotent stem cells are isolated in a simplified serum-free and feeder cell-free process. Most remarkably, certain stem cells, and especially BLSCs, are extremely small, fail to exclude trypan blue, but are nevertheless able to proliferate from even high dilutions. Therefore, so obtained stem cells can be used to prepare true monoclonal stem cell populations, which are useful in numerous uses, including therapeutic, prophylactic, diagnostic, and research uses.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
Full-automatic cell non-staining image recognizing and counting method
ActiveCN103146800AAvoid Potential ToxicityRealize non-staining real-time online cell countingMicrobiological testing/measurementDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention discloses a full-automatic cell non-staining image recognizing and counting method. The full-automatic cell non-staining image recognizing and counting method comprises the following steps of: selecting a full-automatic cell counting meter through an image recognition method, adding a cell suspension to be detected into a counting sheet directly, and inserting the cell suspension to be detected into a counting meter; lowering the receiving capability of a light sensing chip to the light intensity of a red light R and a green light G, intensifying the receiving capability of the light sensing chip to the light intensity of a blue light B, and regulating the aeration time and gain manually so as to change the background of a display to be light blue, and take round hot spots as images of active cells, and take the round blue spots darker than the background color as images of dead cells; and analyzing through cell image recognition software, thereby obtaining accurate large-small cell activity analysis data. According to the full-automatic cell non-staining image recognizing and counting method, dyes are not required to be used for counting cell activities; latent toxicity brought to cells to be detected by trypan blue is prevented; detected cells can continue to live, and the activities of the cells are counted during the culturing process; and meanwhile, according to the full-automatic cell non-staining image recognizing and counting method provided by the invention, non-staining real-time on-line cell counting can be achieved, and the method can be widely applied to the field of life science research.
Owner:广州博大博聚科技有限公司
Squaliobarbus curriculus fin cell line as well as establishing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105925523AEasy accessReduce the impactCell dissociation methodsMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceSqualiobarbus curriculus
The invention discloses a squaliobarbus curriculus fin cell line as well as an establishing method and an application thereof. The preservation number of the squaliobarbus curriculus fin cell line is CCTCC NO: C201642; the squaliobarbus curriculus fin cell line is obtained from the tail fin of squaliobarbus curriculus through primary culture and subculture; and an adopted culture medium is obtained by cultivating through Leibovitz' sl-15. The squaliobarbus curriculus fin cell line has the biological characteristics as follows: cells are fibroblast-like cells, and the cells are cultivated to an optimal state by the Leibovitz' sl-15 culture medium which contains 20% of fetal calf serum by volume in a constant-temperature incubator at 25 degrees. The cells, which are resuscitated under the growth conditions, are dyed with trypan blue, so that a cell survival rate reaches 82.5% or above; and the cells are fibroblast-like cells which are vigorous in growth, and the cells include 48 characteristic chromosomes. In addition, a plasmid pEGFP-N1 is transferred to the cell line for expressing and displaying fluorescence. The cell line disclosed by the invention is used for supporting growth and replication of grass carp hemorrhage viruses; and the cell line is not only applicable to expression of exogenous genes but also suitable for toxicology.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Fluorescence digital imaging microscopy system
InactiveUS20020191824A1High degreeIncrease rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationDigital imagingEosin
A method of preparing cell samples for viable cell number quantification with a fluorescence digital imaging microscopy system employing digital thresholding technique. The cell sample is stained with a first, fluorescent dye and treated with a second dye that is able to quench the fluorescence of the first dye. The fluorescent dye accumulates in viable cells only and is used to stain the viable cells. The second dye is excluded from viable cells but enters non-viable cells, thereby quenching the background fluorescence in non-viable cells and the medium. Two examples of dye combinations are described: fluorescein diacetate used as the fluorescent dye with eosin Y as the quenching dye; and calcein-AM used as the fluorescent dye with trypan blue as the quenching dye. By reducing the background fluorescence, the dynamic range and accuracy of viable cell number measurements are enhanced. In low viability cultures treated with fluorescein diacetate, background fluorescence completely masked viable cells, but digital thresholding and eosin treatment dramatically reduced background fluorescence, producing a linear response over 4 logs of viable cell density.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
Convenient observation method of orchid mycorrhiza microstructure
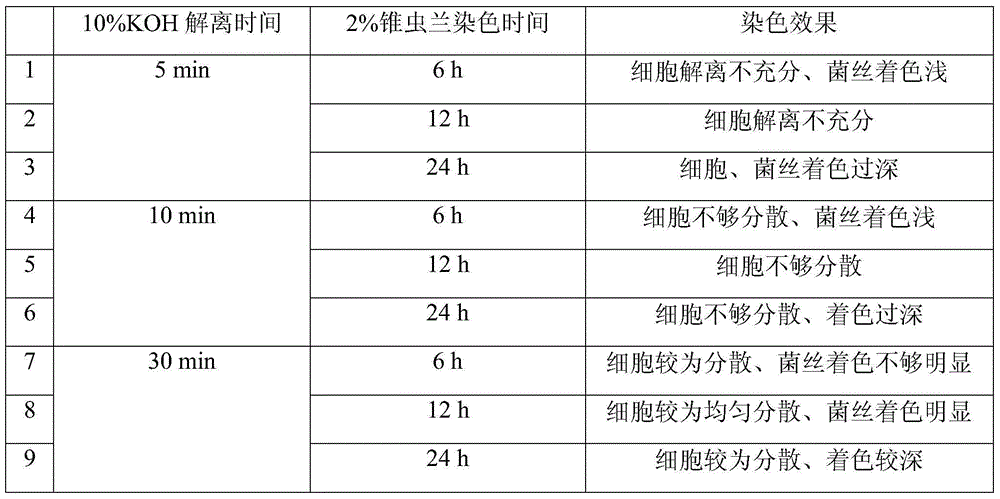
InactiveCN104132940APromote growthEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansInfected cellTrypan blue
A convenient observation method of an orchid mycorrhiza microstructure comprises the following steps: Step 1, preparing a root segment material, a stationary liquid, a dissociation buffer and a staining solution; Step 2, fixing the root segment, and completely immersing the orchid root segment in the stationary liquid; Step 3, slicing the root segment, and shifting the sliced root segment into a clear water-containing container for later use; Step 4, a step of dissociation of the root material: immersing the root material into a KOH solution for dissociation; Step 5, a staining step of the root material: the dissociated root material is placed into a trypan blue solution for staining; and Step 6, carrying out preforming and mounting on the root material, and carrying out microscopic examination with an optical microscope. According to the invention, whether cells in sight are infected by mycorrhiza fungi can be observed clearly, and whether orchid root is infected and the infection degree are detected by statistics of the proportion of the infected cells in sight in total cells in sight. Thus, essential data is provided for the research on coupled growth of orchid.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE SCI & PLANNING
Method for rapidly and efficiently dyeing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
InactiveCN103411813AEfficient DyeingAdaptablePreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention relates to a method for rapidly and efficiently dyeing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, belonging to the field of application microbiology, and being capable of rapidly and efficiently dyeing and observing the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at the root of a plant. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out transparency treatment on a root tissue by using a KOH (Potassium Hydroxide) solution with the concentration being 20% at high temperature, whitening the root tissue by using H2O2, subsequently dyeing by using trypan blue with the concentration being 0.1%, and observing the structure of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi after decoloration by using a decoloration liquid. The method has the characteristics of convenience, rapidness and efficiency, and has the characteristics that the decoloration is thorough, the dyeing effect is clear, the arbuscular structure and the vesicle structure are clear and discernable, and the coloring is long-lasting. The roots of most plants can be dyed by using the method, the arbuscule and the vesicle of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are clearly observed, and the method has good application prospects as the mycorrhiza research is gradually taken seriously.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Human primary colon cancer cell separation and culture method
InactiveCN108070561AHigh purityA large amountCell dissociation methodsCell culture supports/coatingTissue ProcessorColon cancer cell
The invention provides a human primary colon cancer cell separation and culture method. The method comprises the following steps of (1) cutting a fresh colon cancer tissue under an aseptic condition,sealing at 4 DEG C and then carrying back to a lab; (2) disinfecting a tissue processing device; (3) using a pair of operating scissors for separating the colon cancer tissue, placing the tissue intoa precooled sterile PBS liquid containing double antibodies, and washing multiple times to remove blood vessels, fat and necrotic tissues; (4) cutting up the tissues, and using preheated pancreatin and IV type collagenase for digesting respectively; (5) terminating digestion, centrifuging, and removing a supernatant; (6) using trypan-blue for dyeing a cell filter liquor to detect cell activity; (7) after carrying out cell counting, inoculating into a coated culture flask; (8) culturing at 37 DEG C in an environment with 5 percent of CO2; (9) purifying the cells; (10) subculturing the tissues;(11) observing cell morphology; (12) determining cell survival rate; (13) carrying out immunological identification. The invention provides the human primary colon cancer cell separation and culture method which is simple to operate, the number of the obtained cells is large, the survival rate is high, the method is the ideal human primary colon cancer cell primary separation and culture method, and a reliable cell resource is provided for experiments.
Owner:JIANGYIN CHI SCI
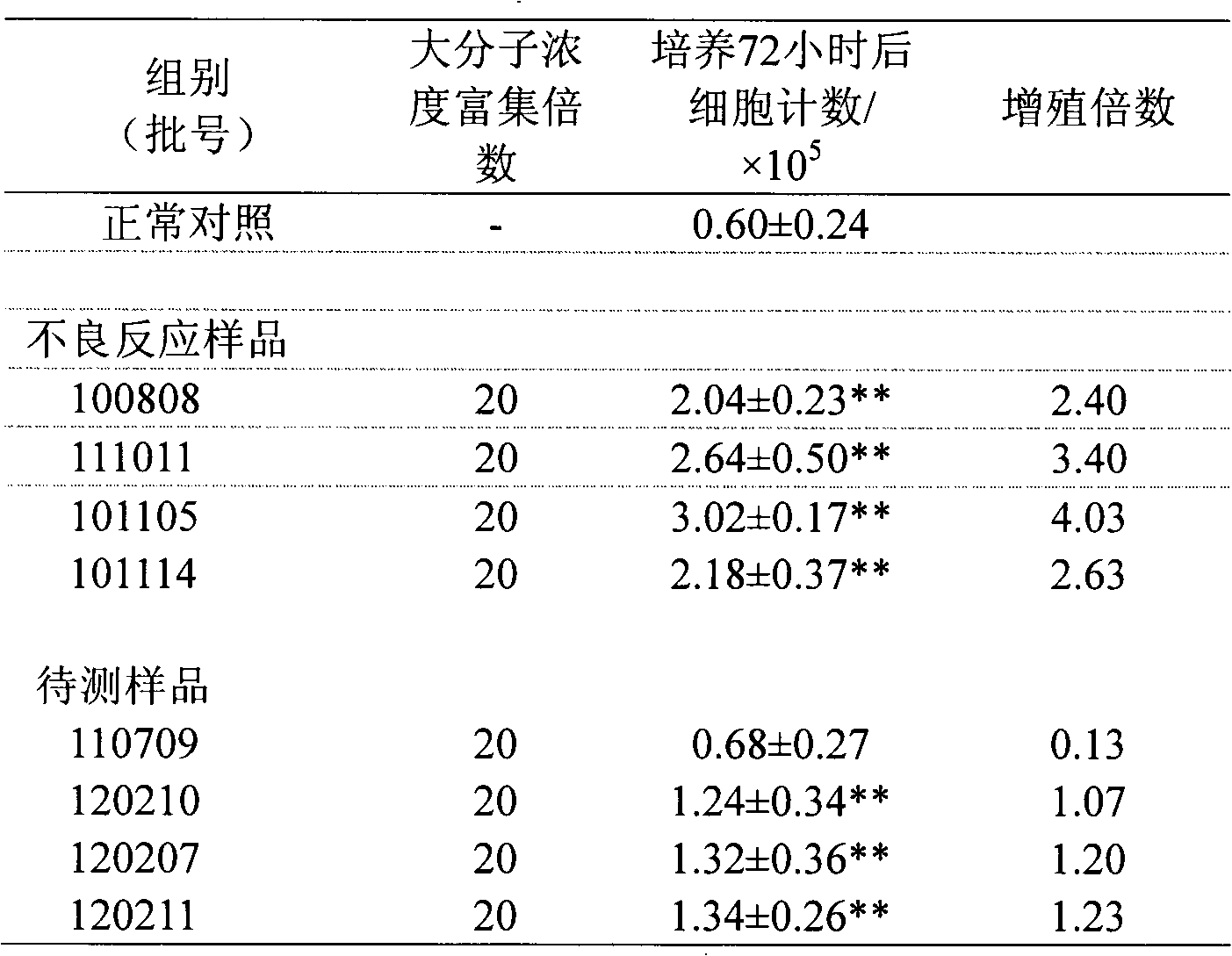
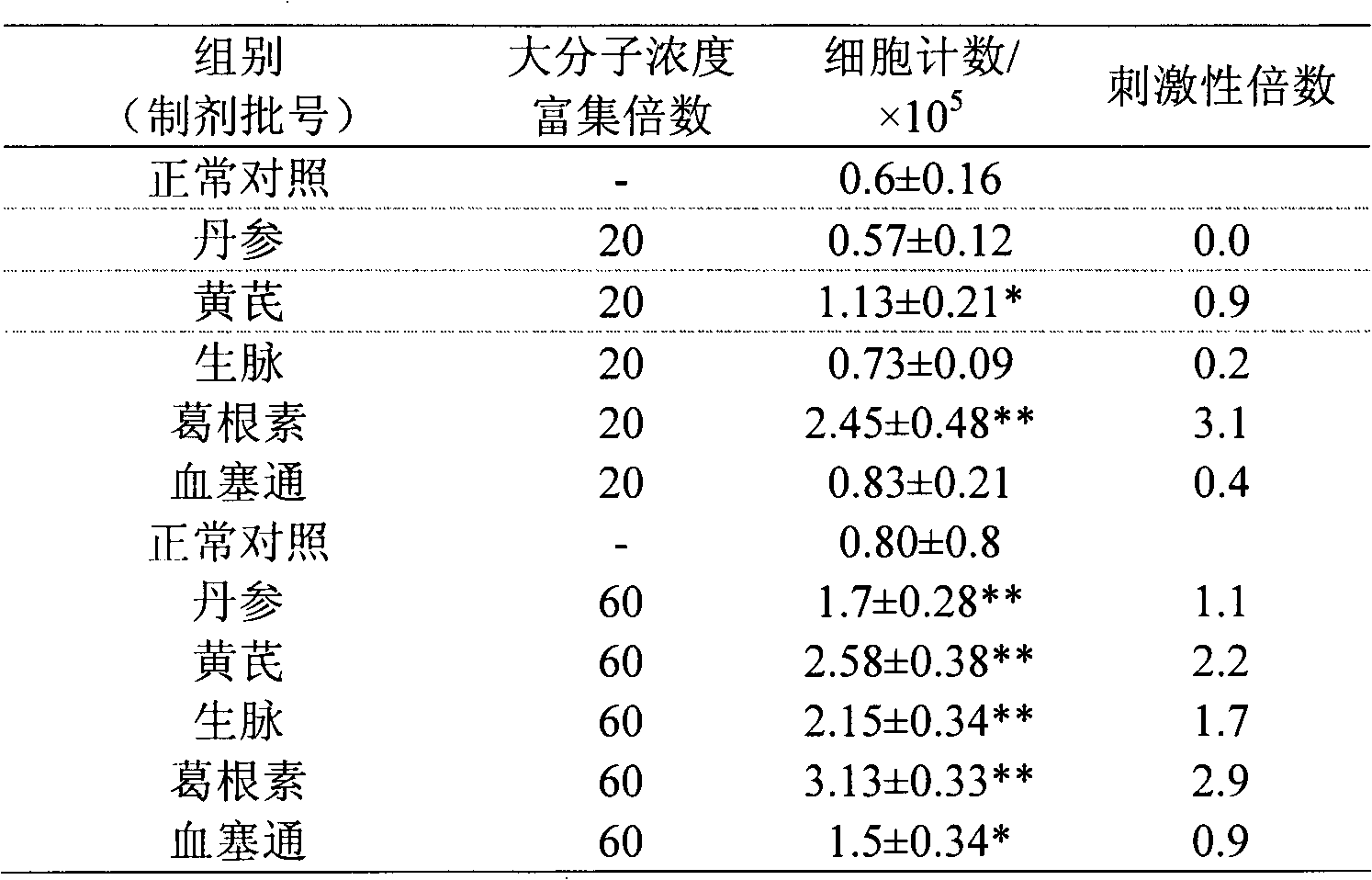
Test evaluation method for sensitization of traditional Chinese medicine injection
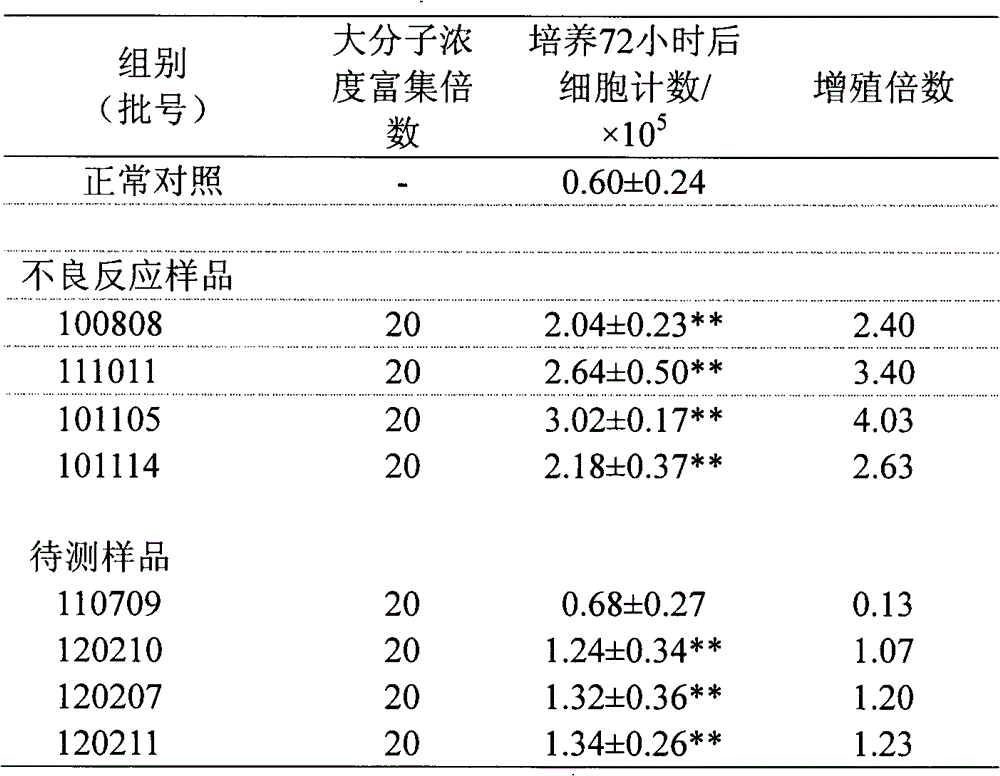
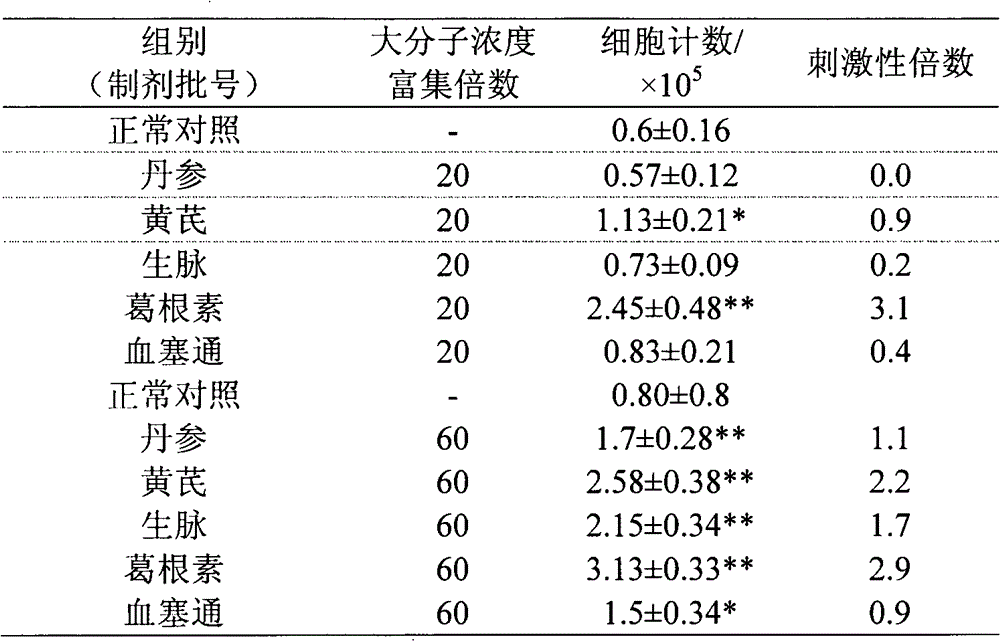
InactiveCN102747130AHigh operational reliabilityGood experimental stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementTrypan bluePeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention provides a test evaluation method for sensitization of a traditional Chinese medicine injection. The method comprises the steps of: treating a traditional Chinese medicine injection by ultrafiltration enrichment with 1-3KD to prepare a sensitized large molecular part; then adding the large molecular part into a peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) solution; carrying out co-culture for 1-3 days; and employing optimized trypan blue or fluorescent dye to dye living cell numbers, in order to calculate and evaluate sensitization strength of the traditional Chinese medicine injection. The method has advantages of convenience, rapidness and sensitivity, can be widely used in test and evaluation on sensitization and irritation of various traditional Chinese medicine injections, and provides scientific basis for safety evaluation and quality control of traditional Chinese medicine injections, and safety of clinical medication.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
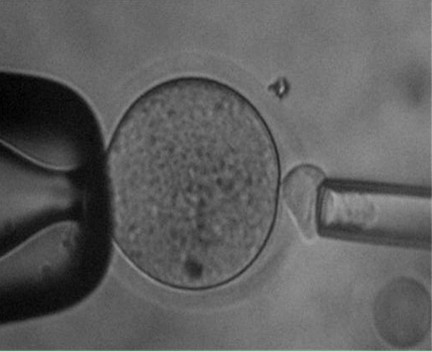
Method for removing mouse oocyte nuclei by adopting zona pellucida solution cavity method
The invention discloses a method for removing mouse oocyte nuclei by adopting a zona pellucida solution cavity method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing central slight dripping and peripheral slight dripping in a plastic utensil; making an acid Tyrode's solution react with a zona pellucida under a microscope; forming a pore on the zona pellucida 1-6 seconds later by dissolving till the zona pellucida becomes thin and soft and cytoplasm protrudes outwards; absorbing a first polar body and surrounding cytoplasm out; releasing an oocyte; and denucleating and observing integrality by adopting trypan blue dyeing, wherein the denucleation success rate is over 99.1 percent. In the preparation method, used equipment is simple and the denucleation operation can be completed under a micromanipulator; a reagent has the advantages of simple components, easiness of preparation, low cost, low difficulty of operation, easiness of comprehension, soft denucleation operation, small mechanical damage, quick denucleation and high efficiency; the average denucleation time of each oocyte is 1-6 seconds, the survival rate of each denucleated oocyte is over 97 percent and the success rate of denucleation is over 99 percent; and the method is suitable for researching mouse nucleus transplantation in a Piezo-free laboratory and early events relevant to embryonic development.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
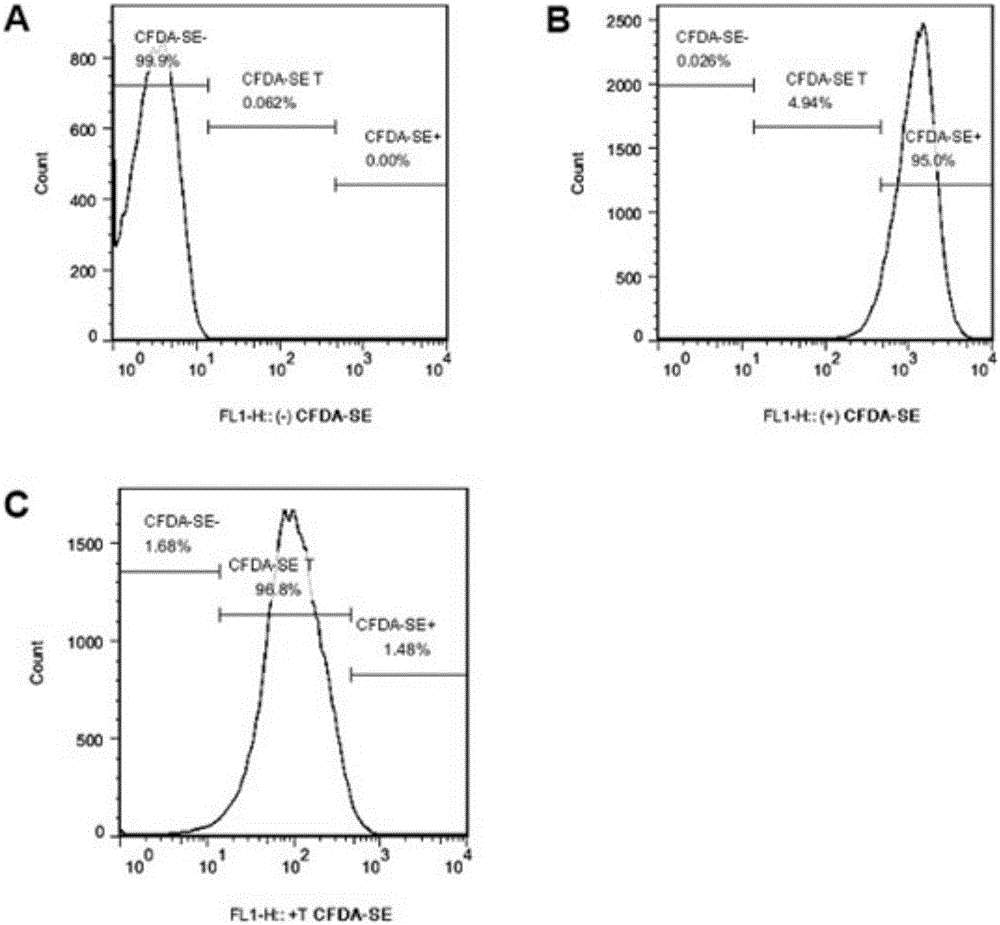
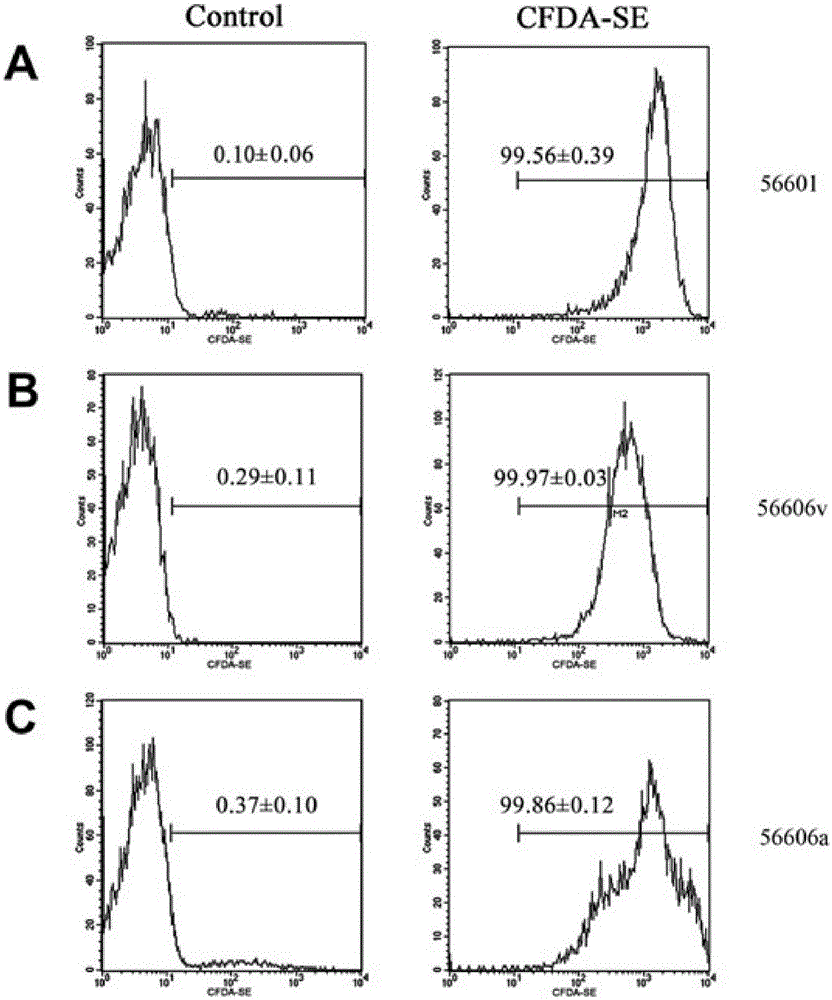
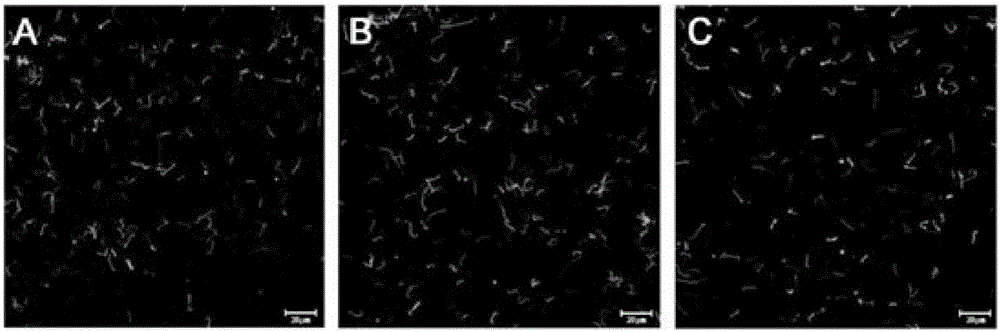
Detection method for adhesion rate and phagocytosis rate of phagocytes on baterial
InactiveCN106442277AAccurate AdhesionAccurate phagocytosis rateIndividual particle analysisTrypan blueMicrobiology
The invention discloses a detection method for the adhesion rate and the phagocytosis rate of phagocytes on bacterial. According to the detection method, phagocytes are divided into a control group, a treatment group and a untreated group, the control group cells are treated with trypan blue and cytochalasin D, the treatment group cells are treated with trypan blue or cytochalasin D, the untreated group cells are not treated, bacteria are labeled with CFDA-SE, and after the bacterial and cells interact, the adhesion rate and the phagocytosis rate of the phagocytes are detected through flow cytometry. According to the present invention, the adhesion rate and the phagocytosis rate of the phagocytes on pathogenic bacteria can be rapidly and accurately detected, and the whole experimental process does not exceed 3 h; the required operation steps after the interaction of the pathogenic bacteria and the phagocytes are less, such that the detection of the large batch sample can be performed; the required reagent is less and the price is economical so as to substantially reduce the scientific research cost; and the detection method is suitable for the adherently growing phagocytes and the difficult-detected phagocytes having the suspending growing state, and broaden the research idea to a certain extent.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of quickly measuring titer of ascovirus
InactiveCN106048090ALower requirementEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMortality rateBiology
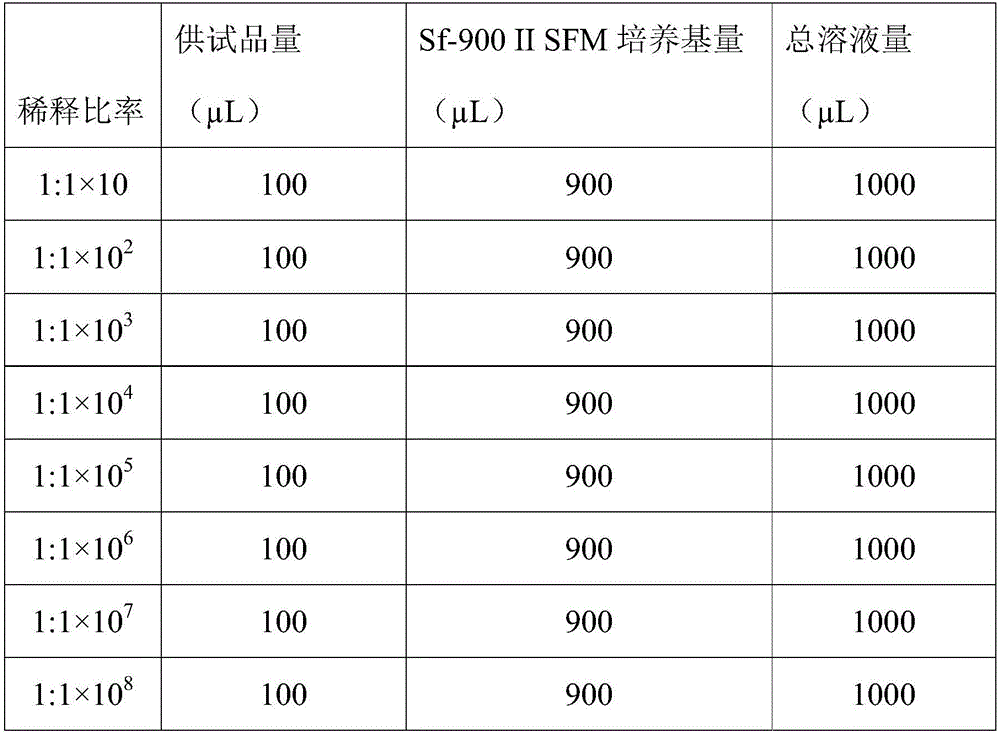
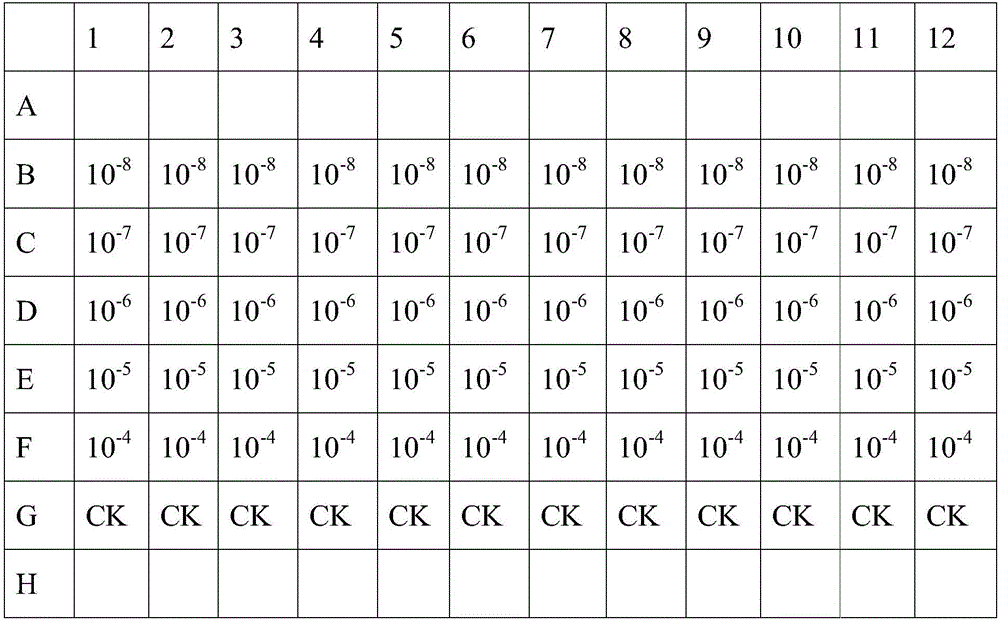
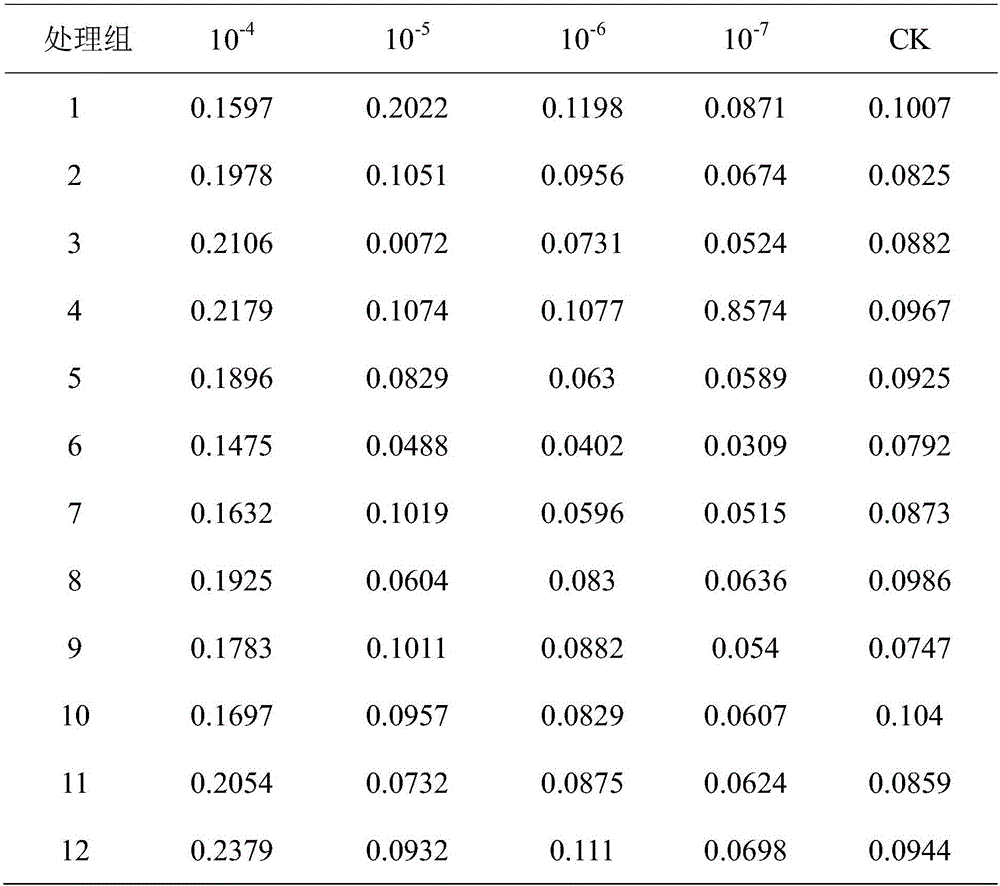
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a method of quickly measuring titer of ascovirus. The method includes: resuspending logarithmic phase Sf9 insect cells; placing into an incubator, standing for culture for 30 min until the cells are attached to walls, abandoning a supernatant culture medium, and replacing with a new Sf-900IISFM culture medium; utilizing a blood ball counting plate to measure cell concentration; taking and well mixing Sf9 insect cell suspension with ascovirus diluent, and inoculating to a 96-hole cell culture tray; disposing in the incubator for culture for 24 h, adding trypan blue dyeing liquid into each hole, and recording dyed cell number and total cell number of each hole; calculating Sf9 insect cell death rate of each hole, determining that the corresponding hole is infected with ascovirus if cell death rate of each hole is lower than that of a control group, determining that the corresponding hole is not infected with ascovirus if not, and calculating TCID50 of ascovirus according to a formula. The method combines cell dyeing, can be used for quick measuring of titer of ascovirus and is more accurate in measuring result.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
Non-integrative reprogramming method of peripheral blood mononuclear cell for MERRF patient
InactiveCN106636206ASuitable for every needSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetically modified cellsDiseaseInfected cell
The invention discloses a non-integrative reprogramming method of the peripheral blood mononuclear cell for an MERRF patient. The non-integrative reprogramming method comprises the following steps: resuscitating the cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC), inoculating the resuscitated peripheral blood mononuclear cell to a 24-hole cell culture plate, and carrying out continuous culture for 4 days under the saturated humidity condition with the temperature of 37 DEG C and with 5% CO2, wherein liquid is exchanged each day; carrying out vital cell staining counting by adopting trypan blue, adjusting the cell density, abandoning a culture solution containing viruses, carrying out further culture for three days by adopting PBMC complete culture solution, and transferring the infected cell to a 6-hole cell culture plate covered by Matrigel basement-membrane matrix; carrying out median liquid exchanging by adopting StemPro-34 containing no cell factors, after three days, taking the PSC culture solution, and after cloning with suitable size is obtained, carrying out passage, carrying out enlarged culture, and carrying out cryopreservation. The detection experiment proves that the obtained cell line has totipotency and normal karyotype, and completely contains no exogenous genes, meanwhile, the mutation existing in the mitochondria genetic material of the MERRF patient can be simulated, and various demands for MERRF disease research can be adapted.
Owner:NANJING MATERNITY & CHILD HEALTH CARE HOSPITAL
Bacillus subtilis heterologous protein expression quantity improving method
InactiveCN104862299AReduce filter rangeIncreased foreign protein expressionMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh-throughput screening
The present invention provides a bacillus subtilis heterologous protein expression quantity improving method. Recombinant plasmid-contained B.s ubtilis is directly induced for mutation by ARTP and starch-trypan blue panel prescreening, 96 orifice plate high-throughput screening and shaking flask fermentation test to obtain a high enzyme activity mutant strain, and the enzyme activity is increased by 31.4%. The ARTP technology used in the method is a biological mutagenesis technology very wide in application range; during induced mutation, the recombinant plasmid-contained B.s ubtilis strain is directly induced for mutation, the recombinant plasmid conversion step can be eliminated after the induced mutation, efficiency is high; at the same time, and by combination with a 96 orifice plate for high-throughput screening, the efficiency for screening of direct mutation strains can be greatly improved, so that the method can rapidly screen a heterologous protein high yield B.s ubtilis strain, and has important economic value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for rapidly identifying disease resistance by inoculating grape powdery mildew to detached grape leaf
InactiveCN104313117AHigh sporulationStrong pathogenicityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHighly pathogenicSpore germination
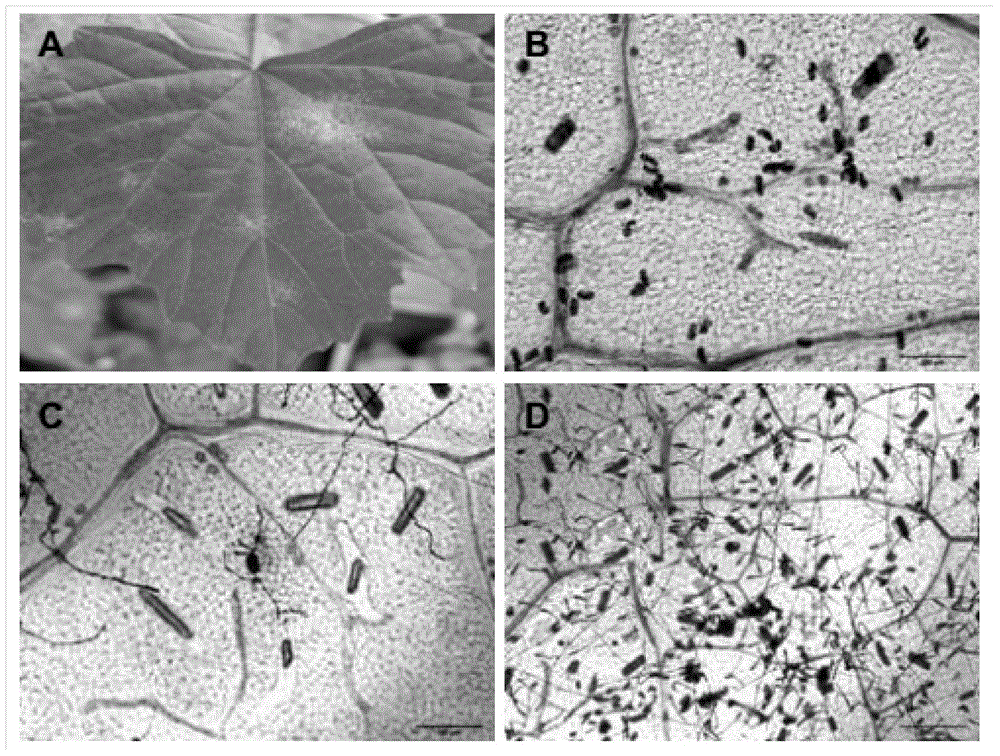
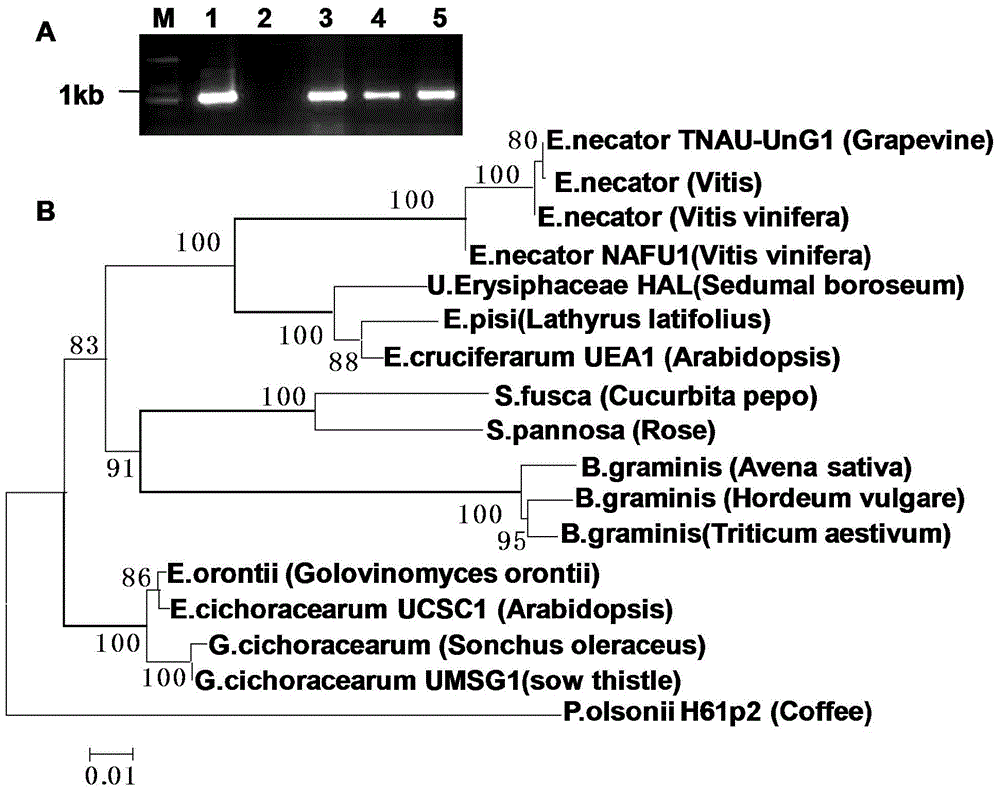
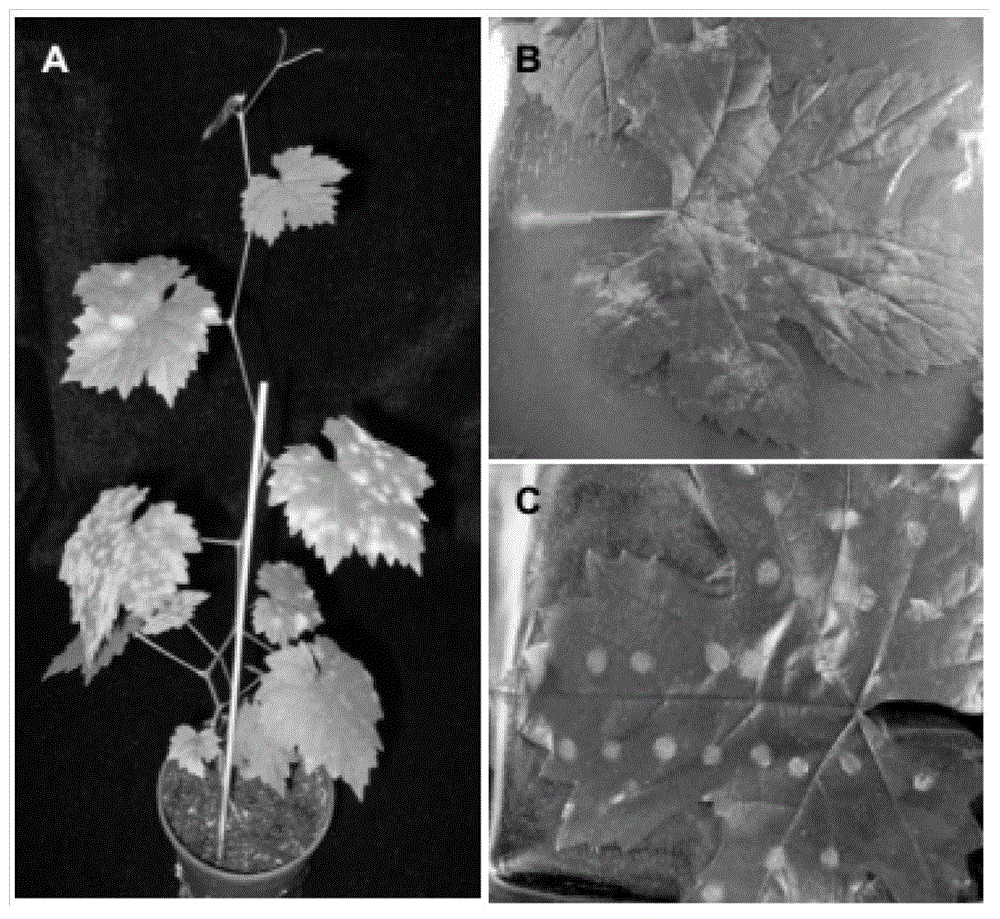
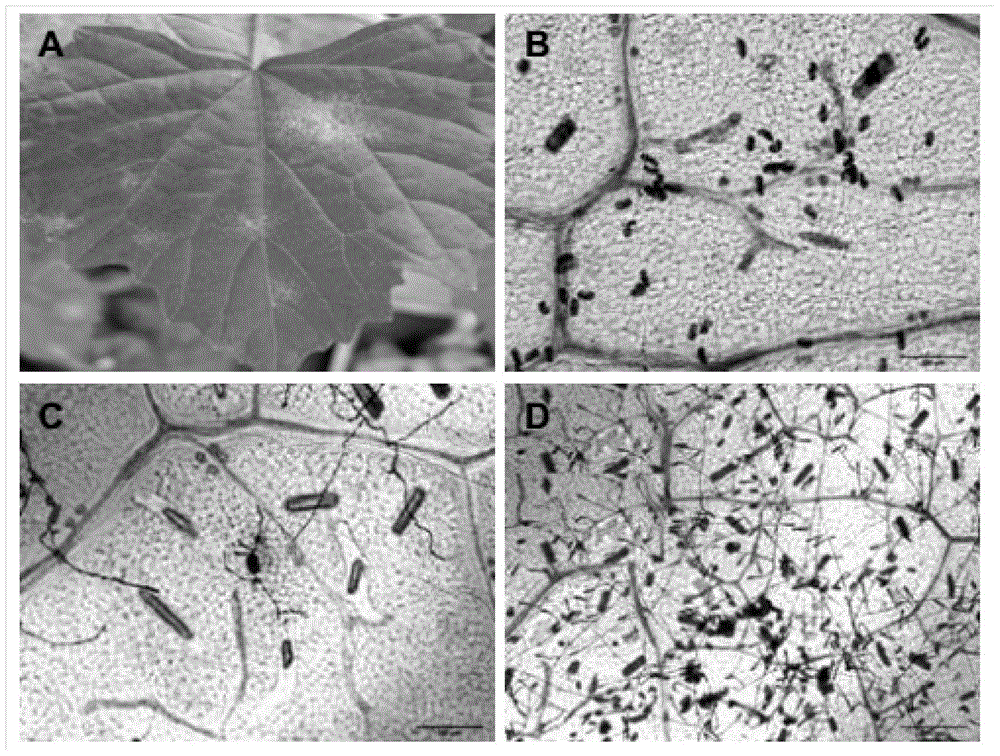
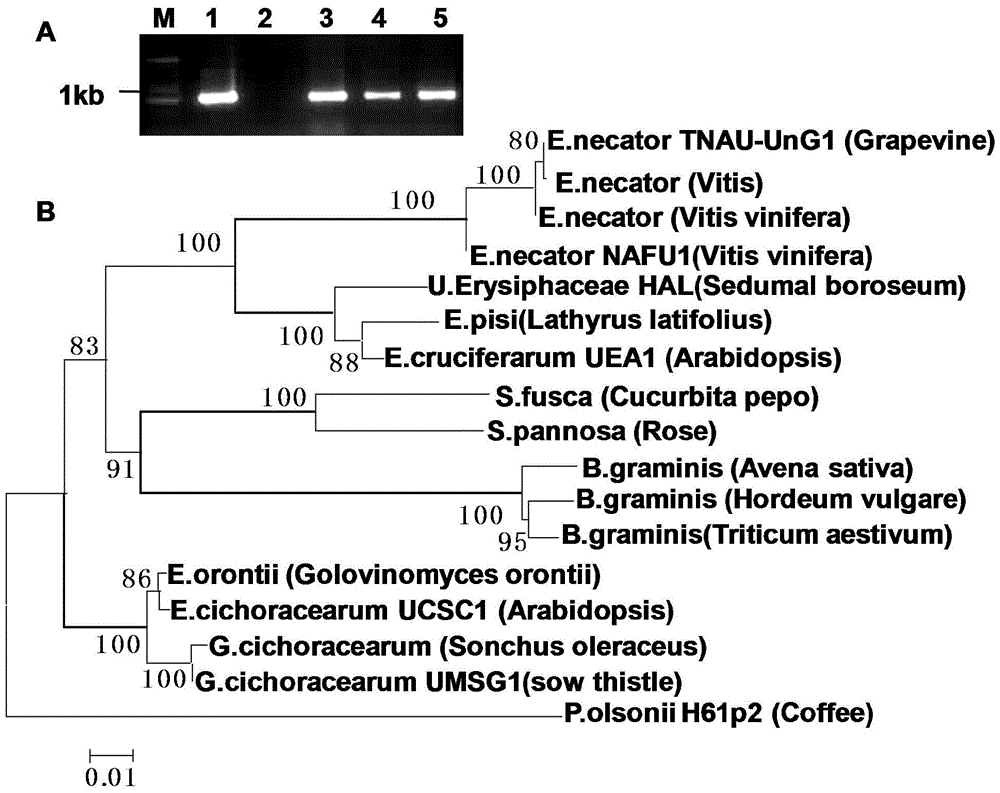
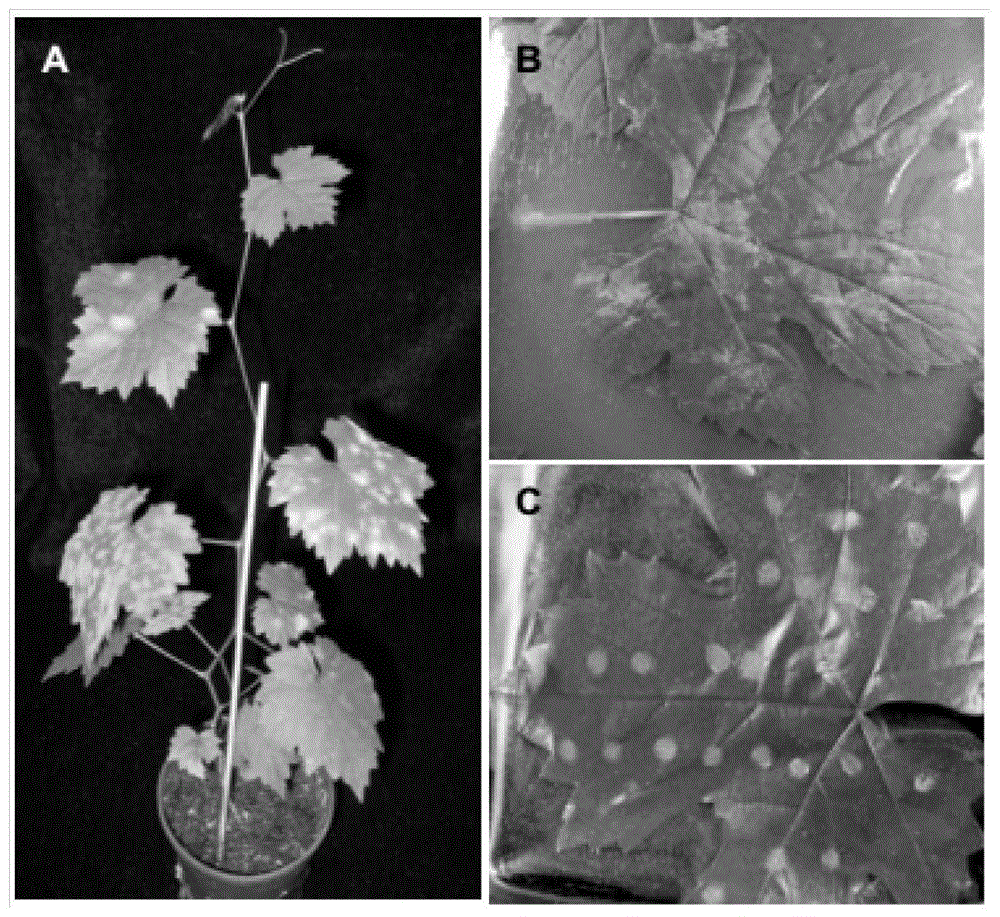
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying disease resistance by inoculating grape powdery mildew to detached grape leaves. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: separating grape powdery mildew strain microspecies, purifying and infecting; performing rDNA sequence amplification and evolution analysis so as to obtain a grape powdery midew NAFU1 with high pathogenicity; analyzing the preservation and the expanding propagation of the strain; inoculating the strain with the detached grape leaves, dyeing by using trypan blue, inoculating to sick leaves in different periods, and observing indexes such as the time of spore germination, growth velocity, hypha length and necrocytosis, thereby rapidly and accurately detecting the disease resistance of grape. The grape powdery mildew preserved and amplified by using the method is high in sporulation quantity, the spore is fresh and high in pathogenicity, the defects that the conventional field identification period is long, the repeatability is poor and the weather influence can be caused are overcome, not only is the efficiency in detecting the disease resistance of a grape germplasm resource in large scale improved, but also direct reference values in rapidly identifying the disease resistance of the grape germplasm resource as well as hybrid progeny and transgenosis plants of the grape germplasm resource in large scale are achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
FISH pretreatment method and pretreatment fluid for FFPE sample
ActiveCN105018598AReduce fluorescenceLow backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementPretreatment methodTrypan blue
The invention discloses a FISH pretreatment method and pretreatment fluid for an FFPE sample. The pretreatment fluid comprises a pretreatment fluid I, a pretreatment fluid II and a pretreatment fluid III, wherein, the pretreatment fluid I is at least one selected from the group consisting of an EDTA solution, a citric acid buffer and a sodium sulfocyanate solution, the pretreatment fluid II is at least one selected from the group consisting of pontamine sky blue with a concentration of 0.01 to 0.5% and trypan blue with a concentration of 0.025 to 1%, the pretreatment fluid III is sodium borohydride with a concentration of 0.1 to 5%, and the above-mentioned substances are weighed according to a mass volume ratio. The pretreatment method is composed of a plurality of steps. The FISH pretreatment method and pretreatment fluid provided by the invention can substantially reduce FISH autofluorescence and background of liver cancer FFPE.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Separation and culture method of human skin keratinization layer cells
InactiveCN110387348AHigh purityA large amountCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementFiberCutin
The invention provides a separation and culture method of human skin keratinization layer cells. The separation and culture method comprises the following steps of (1) cutting and obtaining fresh skintissue, and transporting the obtained fresh skin tissue back to a laboratory at 4 DEG C; (2) performing cleaning with PBS for 3 times; (3) cutting up the cleaned tissue, and performing digestion withneutral protease at 4 DEG C; (4) separating derma from cuticle; (5) continuing to digest cuticle tissue with preheated trypsin; (6) finishing digestion, performing centrifuging, and discarding supernatant; (7) detecting cell activity through an trypan blue dyeing experiment; (8) after the cells are counted, performing re-suspending with complete culture mediums, performing inoculation to a coatedculture flask, and placing the culture flask in 5% CO2 environment of 37 DEG C for culture; (9) removing fiber forming cells by a differential wall-adherence method; and (10) performing cell identification. The separation and culture method of human skin keratinization layer cells provided by the invention is simple to operate, the obtained cells are high in quantity and high in survival rate, the separation and culture method of human skin keratinization layer cells is ideal, and reliable cell resources are provided for the experiment.
Owner:JIANGYIN CHI SCI
Test evaluation method for sensitization of traditional Chinese medicine injection
InactiveCN102747130BAllergenicity GuaranteeEnsure safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementTrypan bluePeripheral blood mononuclear cell
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
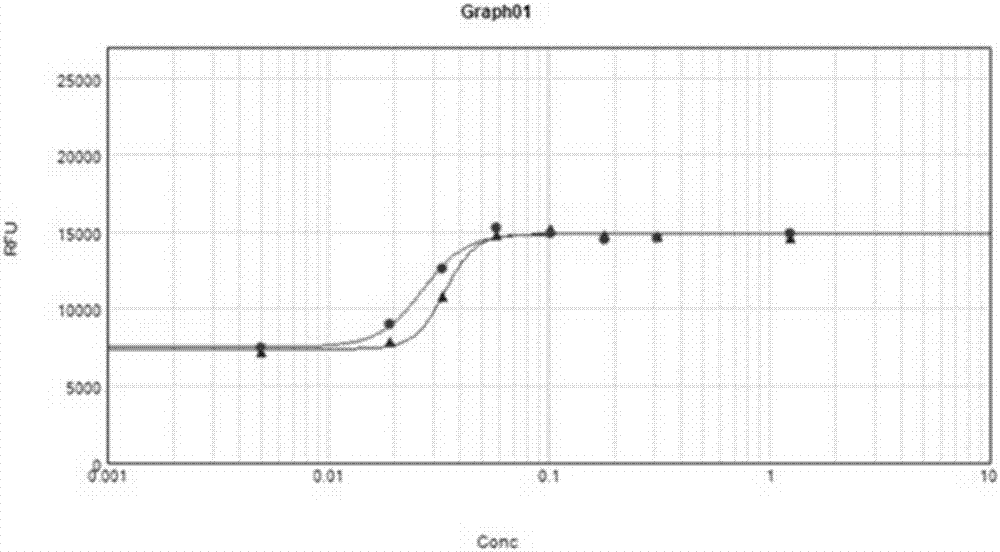
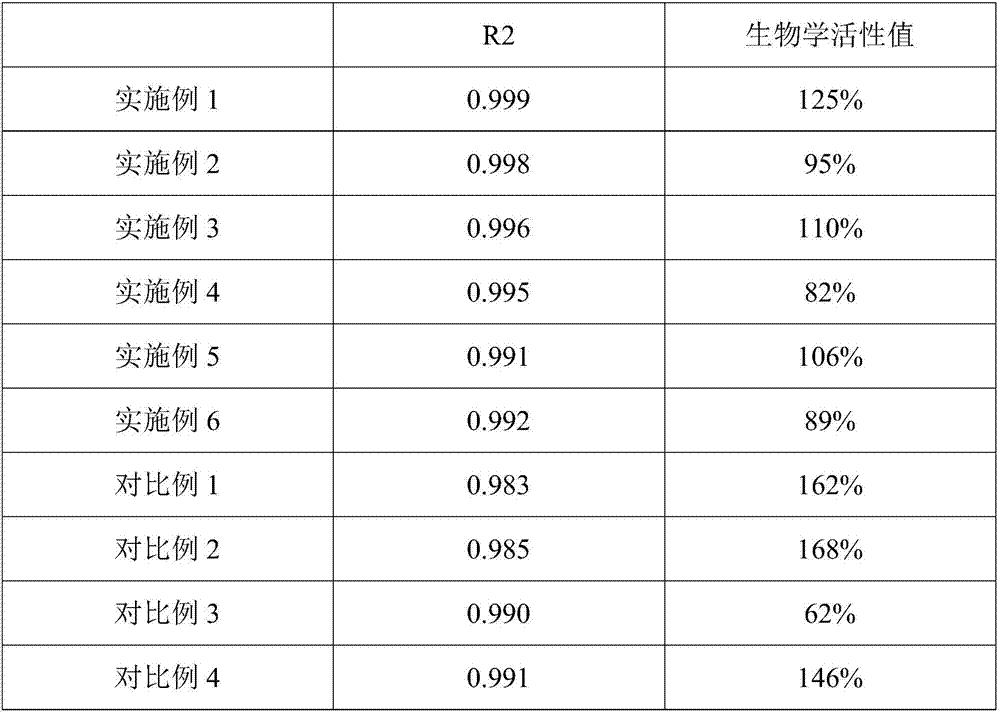
Detection method of biological activity of vascular endothelial growth factors and application
ActiveCN107328943AGuaranteed stabilityConducive to the establishment of activity evaluation criteriaBiological material analysisBiological testingConcentration gradientDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a detection method of the biological activity of vascular endothelial growth factors. The method comprises the following steps of (1) adding trypan blue into collected human umbilical vein endothelial cells; performing counting after the uniform mixing; regulating the cell concentration to (2 to 10)*10<4>mL according to the counting result; (2) culturing the regulated cells for 3 to 10h in a CO2 culture box; (3) performing concentration gradient dilution on the endothelial growth factors; adding all gradient dilution endothelial growth factor solutions into cells cultured in the step (2); after the uniform mixing, performing culture for 80 to 100h in the CO2 culture box; (4) adding Alma blue color developing liquid into a mixed solution of the vascular endothelial growth factors and the cells cultured in the step (3); after uniform mixing, performing culturing for 1 to 10h in the CO2 culture box; (5) performing fluorescence intensity detection on the sample cultured in the step (4). Through the activity detection on the vascular endothelial growth factors, the use quantity of the vascular endothelial growth factors in different batches is regulated, so that the activity detection result is stable and more accurate.
Owner:TOT BIOPHARM CO LTD
Full-automatic cell viability analysis system
PendingCN109825427AMachine processing is fastNot easy to make mistakesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsData acquisitionFlat panel display
The invention discloses a full-automatic cell viability analysis system which comprises the following steps: adding a trypan blue dye on a cell slide, inserting the slide into the whole system, triggering the whole system, calculating the cell concentration and the survival rate through an algorithm after imaging, withdrawing the slide from the device, completing the imaging process, and insertingthe slide into a system device, wherein the system device comprises a flat panel display screen, an operation keyboard, supporting legs, a slot, a box body, a control main board, a fixed rod, a CCD imager, a microscope barrel, a supporting rod, a fixing block, an anti-slip pad, a supporting plate, a connecting rod, a sliding groove, a sliding block, a supporting frame and a toothed belt. The trypan blue dye is added to cells on the cell slide, CCD imaging is controlled, five visual fields are photographed at one time, data is transmitted to a computer, cell concentration, survival rate and the like are calculated through the algorithm, intelligent imaging is achieved, machine processing is fast, errors are not easy to occur, full automation is achieved, a result can be directly obtained as long as the slide is inserted, and data acquisition and cell viability analysis can be directly and conveniently executed.
Owner:广州牛顿光学研究院有限公司
Mouse skeletal muscle satellite cell separation and culture method
InactiveCN109423475AHigh purityHigh activityCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTrypsinIcr mice
The invention provides a mouse skeletal muscle satellite cell separation and culture method. The mouse skeletal muscle satellite cell separation and culture method comprises following steps: 1, mice are killed through intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium, and are immersed in 75% alcohol for disinfection; 2, the mice are fixed on plates with the venter posterior surfaces upward, hind limb skin is peeled under aseptic conditions, and thighbone muscle tissues are collected; 3, in an aseptic operation bench, PBS washing is carried out for three times, surface blood vessels, tendons, and connective tissues are removed; 4, the processed tissues are cut into pieces, and are subjected to digestion with preheated trypsin and IV type collagenase respectively; 5, digestion is stopped, centrifugation is carried out, and an obtained supernatant is removed; 6, a cell filtrate is collected, and trypan-blue drying detection is adopted to detect cell activity; 7, after cell counting, a complete medium is adopted for resuspension inoculation into a coated culture flask for culture at 37 DEG C at 5% CO2 environment; 8, differential attachment method is adopted to remove fibrocytes; 9, cell morphology is carried out; 10, ELISA method detection is carried out; and 11, RT-PCR detection is carried out. The mouse skeletal muscle satellite cell separation and culture method is simple in operation, and is high in survival rate; the number of obtained cells is large; the mouse skeletal muscle satellite cell separation and culture method is an ideal method, and is capable of providing experiments with reliable cell resources.
Owner:JIANGYIN CHI SCI
Submucosal injection solution composition for endoscope and preparation method
ActiveCN111991620ADone successfullyGuaranteed performanceSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEndoscopic ProcedureMethyl palmoxirate
The invention relates to the technical field of injection reagent, in particular to a submucosal injection solution composition for an endoscope and a preparation method. The composition is prepared from 0.01 w / v% to 0.5 w / v% of hyaluronic acid, 0.005 w / v% to 0.5 w / v% of carboxymethyl chitosan, 0.001 w / v% to 0.1 w / v% of coloring agent and the balance of phosphate buffer solution, wherein the hyaluronic acid is selected from sodium hyaluronate, magnesium hyaluronate, calcium hyaluronate or zinc hyaluronate; the substitution degree of the carboxymethyl chitosan is greater than 0.85, and the dynamic viscosity of the carboxymethyl chitosan is 500-5000 mPa*s; and the coloring agent is selected from trypan blue, methylene blue, indigo blue, gentian violet or indocyanine green. The hyaluronic acid, the carboxymethyl chitosan and the coloring agent are combined for use, relatively long mucous membrane lifting time is kept, the lesion boundary is clearly displayed, postoperative bleeding and infection are reduced, and the submucosal injection solution can serve as an endoscopic submucosal injection solution to be applied to endoscopic surgery.
Owner:上海建华精细生物制品有限公司
System for characterizing macrophage phagocytosis microorganisms of pompanos
ActiveCN106771110APreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisAbnormal macrophageCell survival
The invention discloses a system for characterizing macrophage phagocytosis microorganisms of pompanos. The pompanos are dissected and separated through a surgical knife and tweezers to obtain heads and kidneys; the heads and the kidneys are abraded through a cell sieve to obtain cell suspension containing macrophages, and the macrophages of the heads and the kidneys are obtained through a Percoll solution density gradient centrifugal tube. The survival amount of cells cultured in vitro through a trypan blue dyeing manner is counted, and the survival condition in one week is detected. The system is used for carrying out a phagocytosis experiment, and phagocytosis conditions of nocardia, yeast and the like of the pompanos by the head and kidney macrophages of trachinotus ovatus are determined, and a phagocytosis function is observed. An experiment result of the system shows that the macrophages of the pompanos can be extracted very well, and the survival condition and the phagocytosis condition of the macrophages of the pompanos can be observed very well. The system disclosed by the invention lays a foundation for further researches on physiology, pathology and toxicology of the macrophages of the pompanos.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIV +2
Non-embryonic totipotent blastomere-like stem cells and methods therefor
Human non-embryonic adult totipotent and pluripotent stem cells are isolated in a simplified serum-free and feeder cell-free process. Most remarkably, certain stem cells, and especially BLSCs, are extremely small, fail to exclude trypan blue, but are nevertheless able to proliferate from even high dilutions. Therefore, so obtained stem cells can be used to prepare true monoclonal stem cell populations, which are useful in numerous uses, including therapeutic, prophylactic, diagnostic, and research uses.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
Method for detecting CHO cell proliferation by using optical analysis and application thereof
InactiveCN104561091AAvoid toxicityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliNon toxicity
The invention discloses a method for detecting CHO cell proliferation by using optical analysis and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) converting pEGFP-N2 into Escherichia coli DH5alpha, shaking the bacteria, and extracting endotoxin-free plasmids; (2) inoculating CHO cells into a pore plate, performing transient transfection on the plasmids in the step (1) into the CHO cells by adopting a lipofection transfection method when the cell growth density is 70 percent; (3) screening the transfection cells by adopting geneticin G418, performing resistance screening of over 30 generations at least, thereby obtaining a cell strain which can stably express the GFP; and (4) performing multiplication culture on the cell strain which can stably express the GFP, digesting the cells, performing cell counting by adopting trypan blue, detecting the fluorescent intensity by adopting an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay detector, and judging the CHO cell proliferation conditions based on a linear relation between GFP fluorescent intensity in the cells and the cell number. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of operability, detection result accuracy, high repeatability, high sensitivity, non-toxicity and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A method for rapid identification of disease resistance by using powdery mildew of grapes to inoculate detached leaves of grapes
InactiveCN104313117BHigh sporulationStrong pathogenicityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseHighly pathogenic
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying disease resistance by inoculating grape powdery mildew to detached grape leaves. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: separating grape powdery mildew strain microspecies, purifying and infecting; performing rDNA sequence amplification and evolution analysis so as to obtain a grape powdery midew NAFU1 with high pathogenicity; analyzing the preservation and the expanding propagation of the strain; inoculating the strain with the detached grape leaves, dyeing by using trypan blue, inoculating to sick leaves in different periods, and observing indexes such as the time of spore germination, growth velocity, hypha length and necrocytosis, thereby rapidly and accurately detecting the disease resistance of grape. The grape powdery mildew preserved and amplified by using the method is high in sporulation quantity, the spore is fresh and high in pathogenicity, the defects that the conventional field identification period is long, the repeatability is poor and the weather influence can be caused are overcome, not only is the efficiency in detecting the disease resistance of a grape germplasm resource in large scale improved, but also direct reference values in rapidly identifying the disease resistance of the grape germplasm resource as well as hybrid progeny and transgenosis plants of the grape germplasm resource in large scale are achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
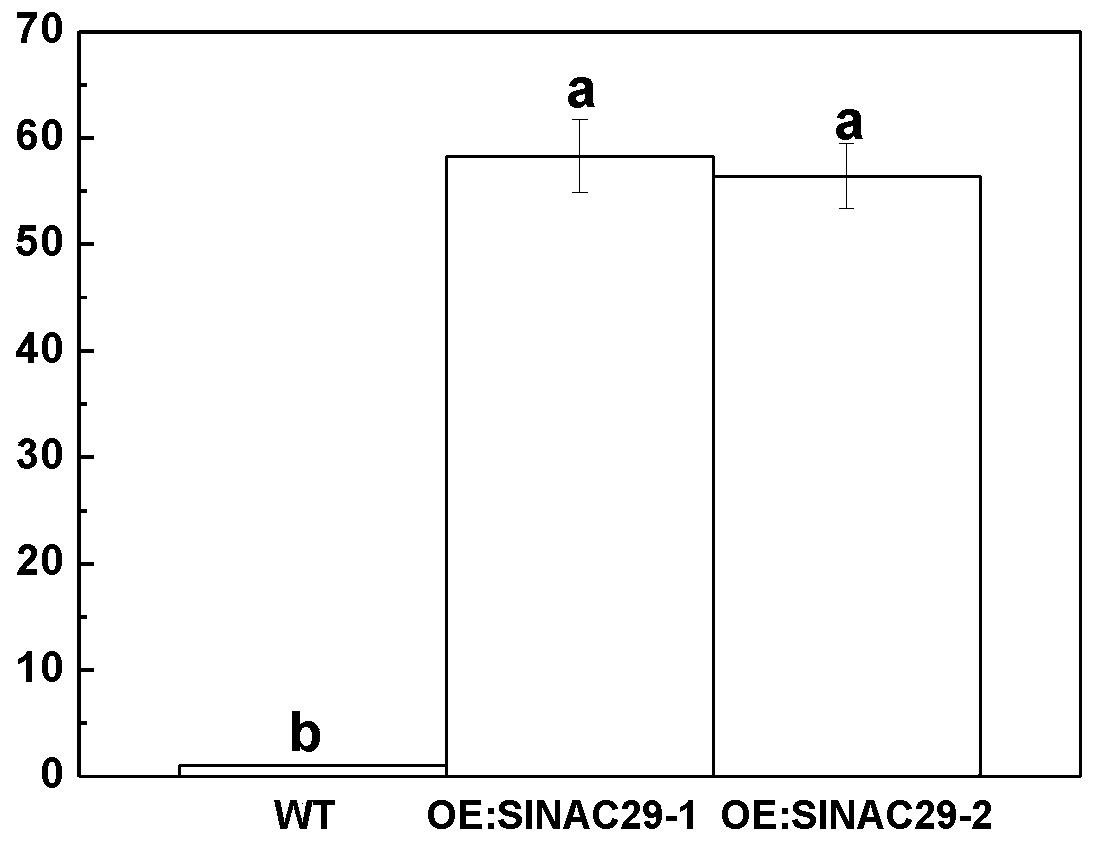
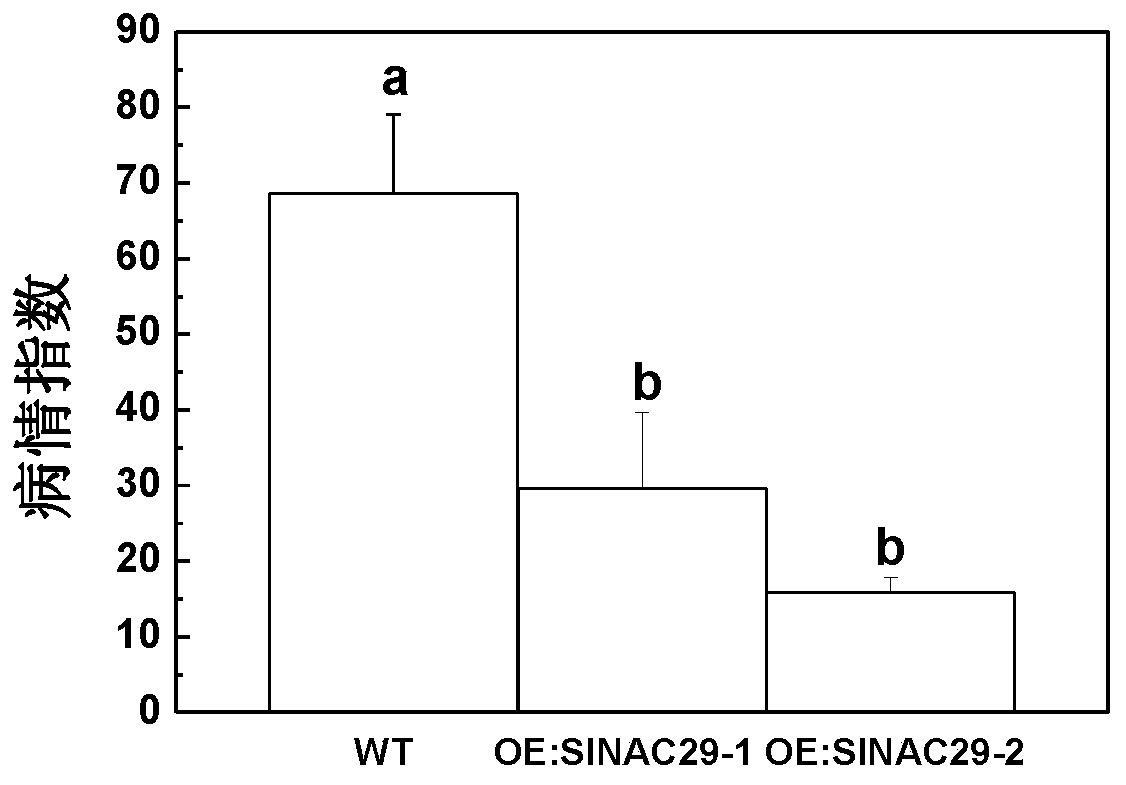
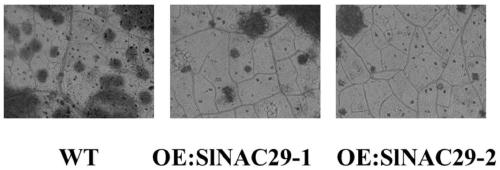
Application of slnac29 Gene in Improving Tomato Bacterial Leaf Spot Resistance and Drought Tolerance
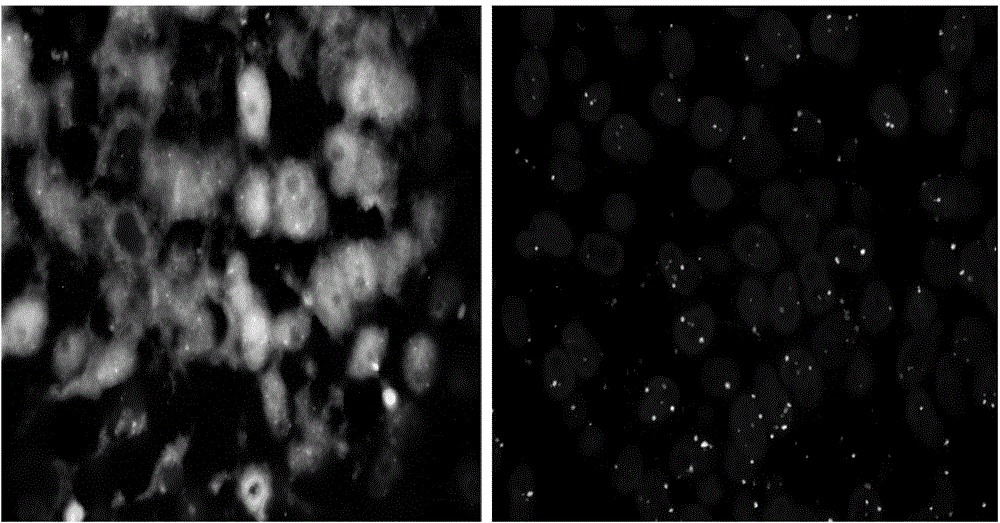
The invention discloses application of a SlNAC29 gene to improving theresistance and the drought resistance of tomatoes to bacterial leaf spot. The nucleotide sequence of the SlNAC29 gene is shown asSEQ ID NO.1. Through the transgenic technology, an overexpression vector of the SlNAC29 gene is established; through the tissue culture technology, an SlNAC29 overexpressionhomozygous line OE of SlNAC29-1 and an SlNAC29 overexpressionhomozygous line OE of SlNAC29-2 are obtained through screening; then a tomato bacterial leaf spot germ is inoculated, the incidence rate is counted, trypan blue dyeing is carried out to detect whether cells are died or not, and it is proved that the resistance of plants to the bacterial leaf spot can be improved through the overexpressed SlNAC29 gene. Meanwhile, overexpressed plants are subjected to droughttreatment, drought-resistant phenotypes of the plants are shot, and it is proved that the overexpressed SlNAC29 gene can improve the tolerance of the plantsto draught.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for promoting proliferation of intestinal cancer cells based on CCL20 and CXCL8
PendingCN112877289AEasy to calculate percent survivalDetermine expression positionGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementIntestinal CancerStaining
The invention discloses a method for promoting proliferation of intestinal cancer cells based on CCL20 and CXCL8. The method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting a proper experimental material; 2, preparing a main reagent and storing the prepared reagent; 3, proliferating the cells, and carrying out different experimental tests on the proliferated cells; 4, carrying out trypan blue discharge dyeing experiment on the cells, and calculating the survival rate of the cells; 5, carrying out immunohistochemical staining on the cells. Compared with the prior art, multiple groups of experiments are adopted for comparison, the CCL20 stock solution and the CXCL8 stock solution with different concentrations can be respectively arranged for proliferation culture of the intestinal cancer cells; on one hand, the influence of the chemotactic factor concentration on the proliferation rate of the intestinal cancer cells under the condition of the same chemotactic factor is determined; on the other hand, the influence of a single chemotactic factor and two chemotactic factors on the proliferation rate of the intestinal cancer cells under the same chemotactic factor concentration condition can be determined, and the influence of the chemotactic factor concentration and the chemotactic factor number on the proliferation rate of the intestinal cancer cells can be known.
Owner:云南省肿瘤医院
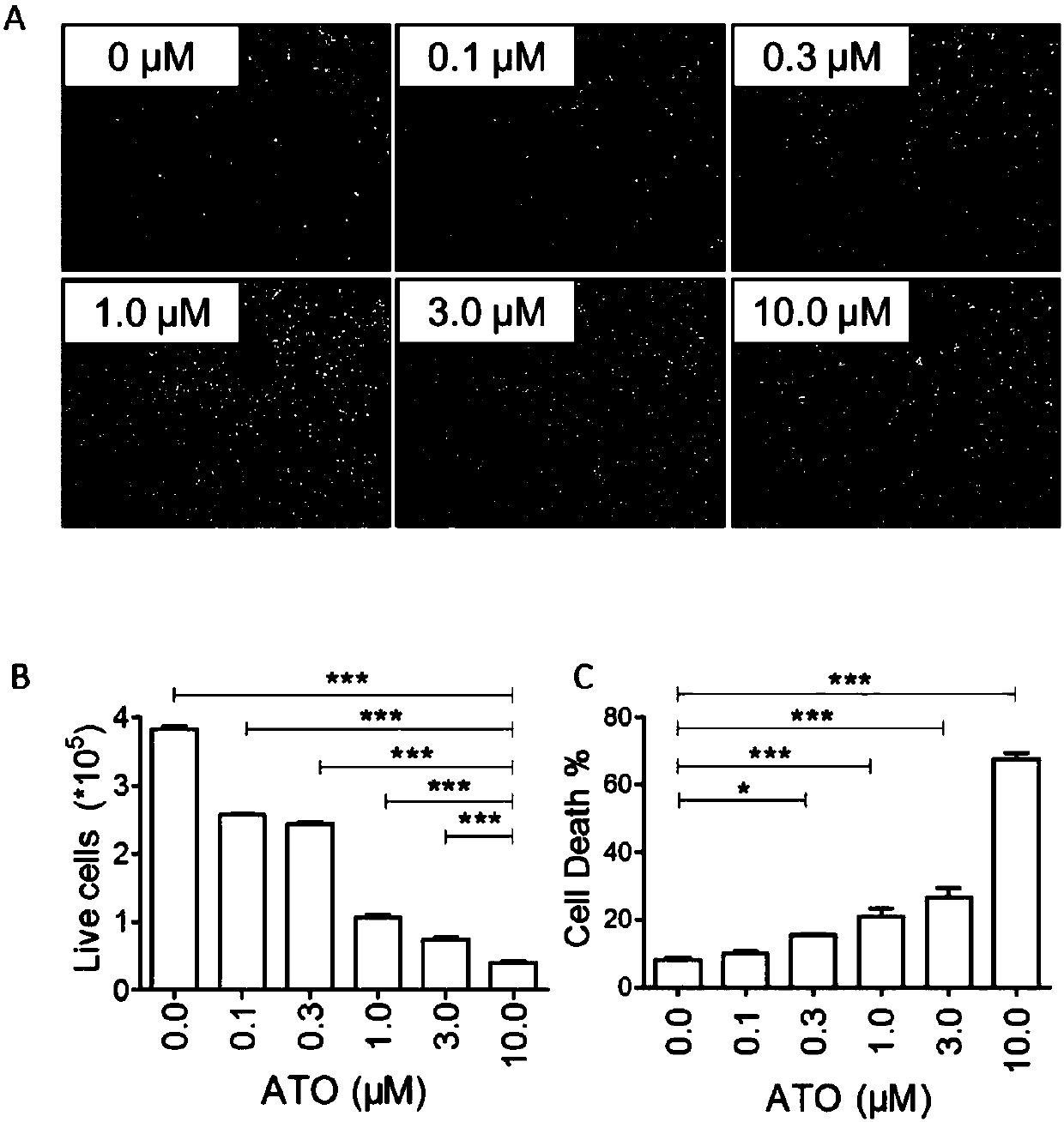
Application of 450-490 nm LED-blue-light combined with arsenic trioxide in osteosarcoma treatment
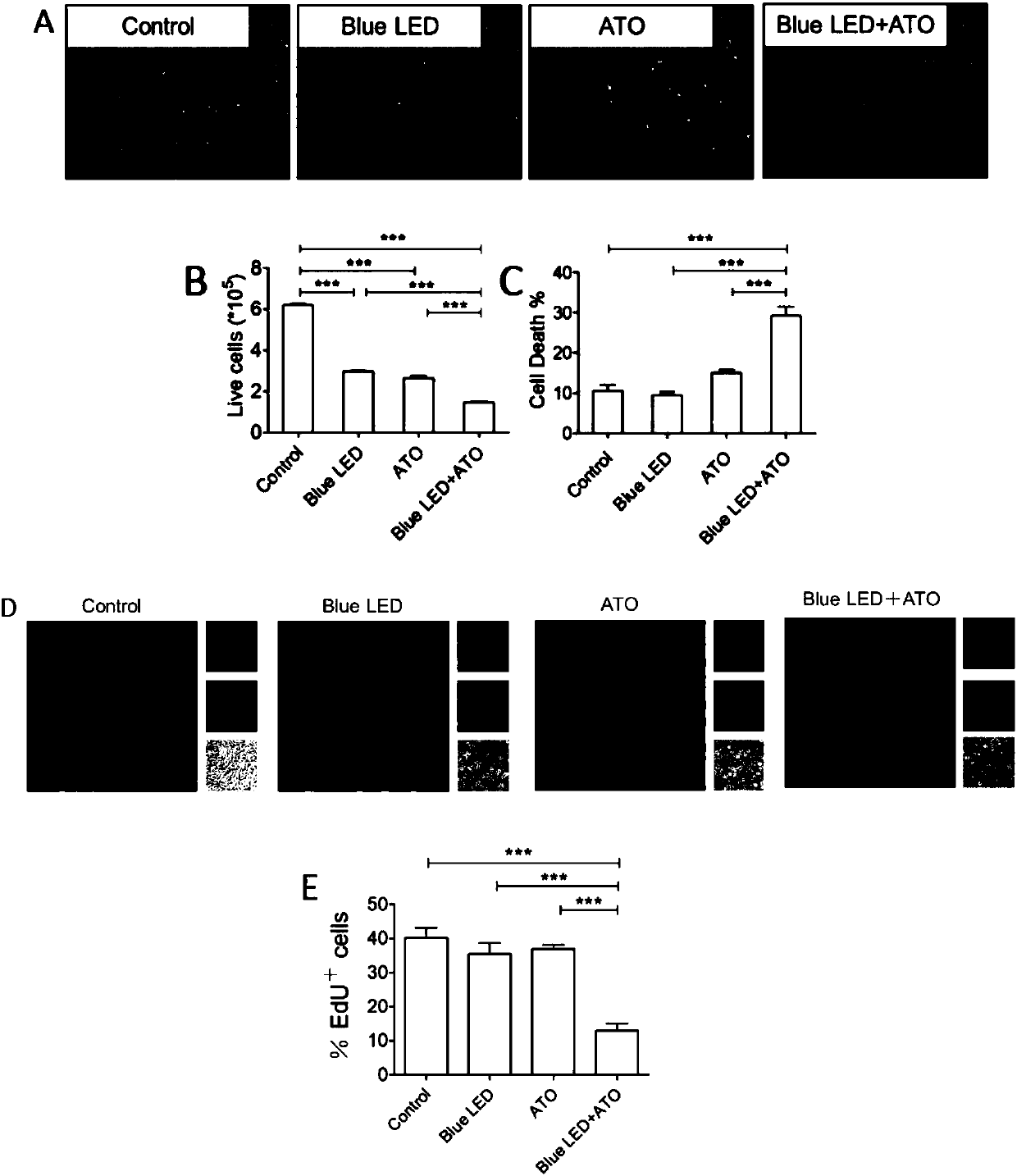
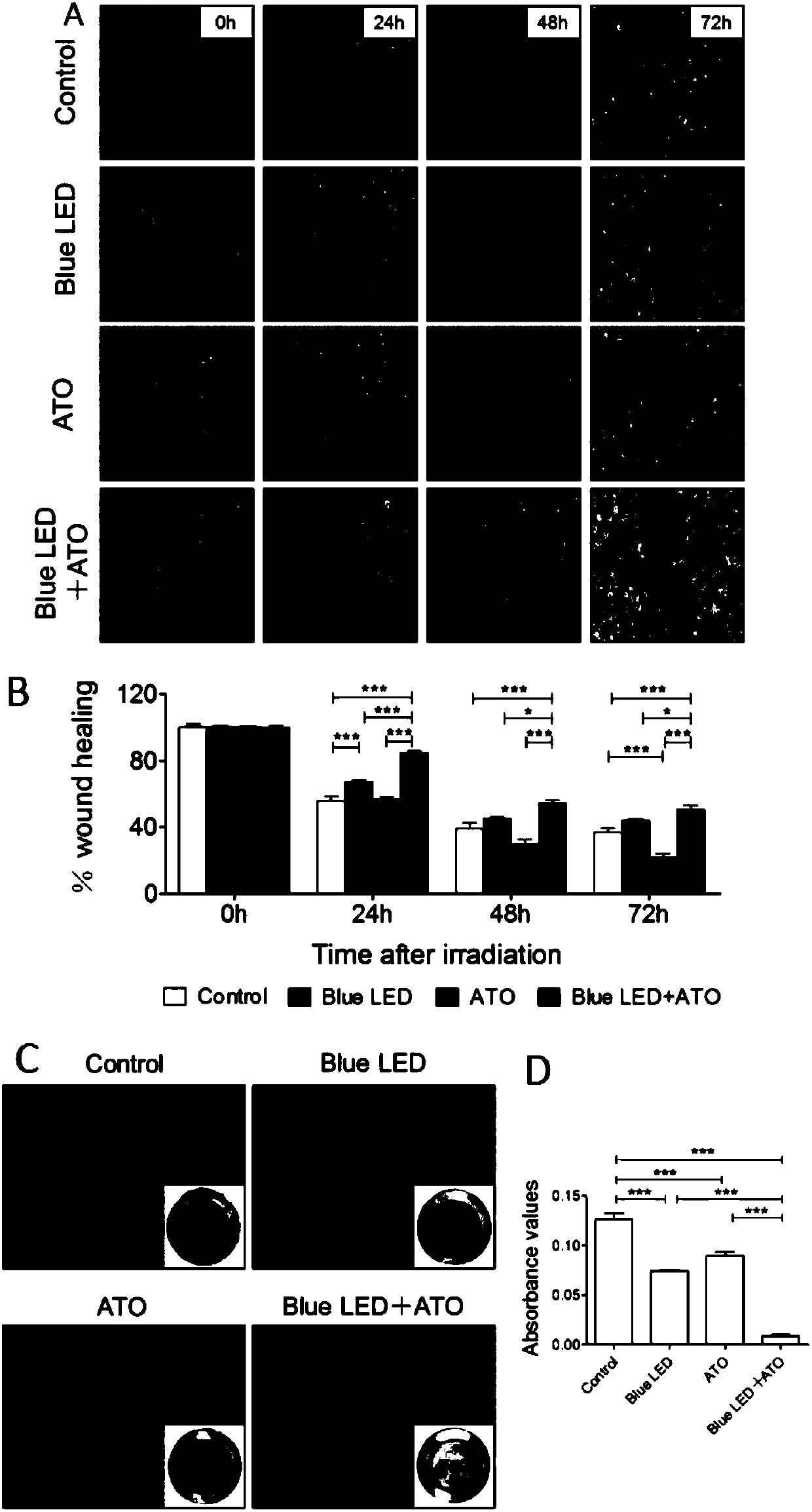
InactiveCN107737409ALittle side effectsLighten the bodyInorganic active ingredientsLight therapyStainingCell migration
The invention discloses application of 450-490 nm LED-blue-light combined with arsenic trioxide in osteosarcoma treatment. Trypan-blue dyeing, cell counting and the EdU dyeing method are adopted to detect the influence of the 450-490 nm LED-blue-light combined with the arsenic trioxide on osteosarcoma cell growth and proliferation, scratch tests and Transwell tests are applied to detecting the influence on cell migration and invasion capabilities, and gamma-H2AX immunofluorescent staining is applied to detecting the influence on cell nucleus damage. Test results show that through combination of the 450-490 nm LED-blue-light and As2O3, curative effects of independently used small-dosage As2O3 can be improved, the toxicity is reduced, the growth, proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells can be effectively inhibited, the cell nucleus damage is induced, and then the purposes of relieving and treating osteosarcoma are achieved. The clinical application of the 450-490 nm LED-blue-light combined with arsenic trioxide is simple and low in medical treatment cost, pain of treated patients is reduced at the same time, and a new technological means is provided for the osteosarcoma treatment.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
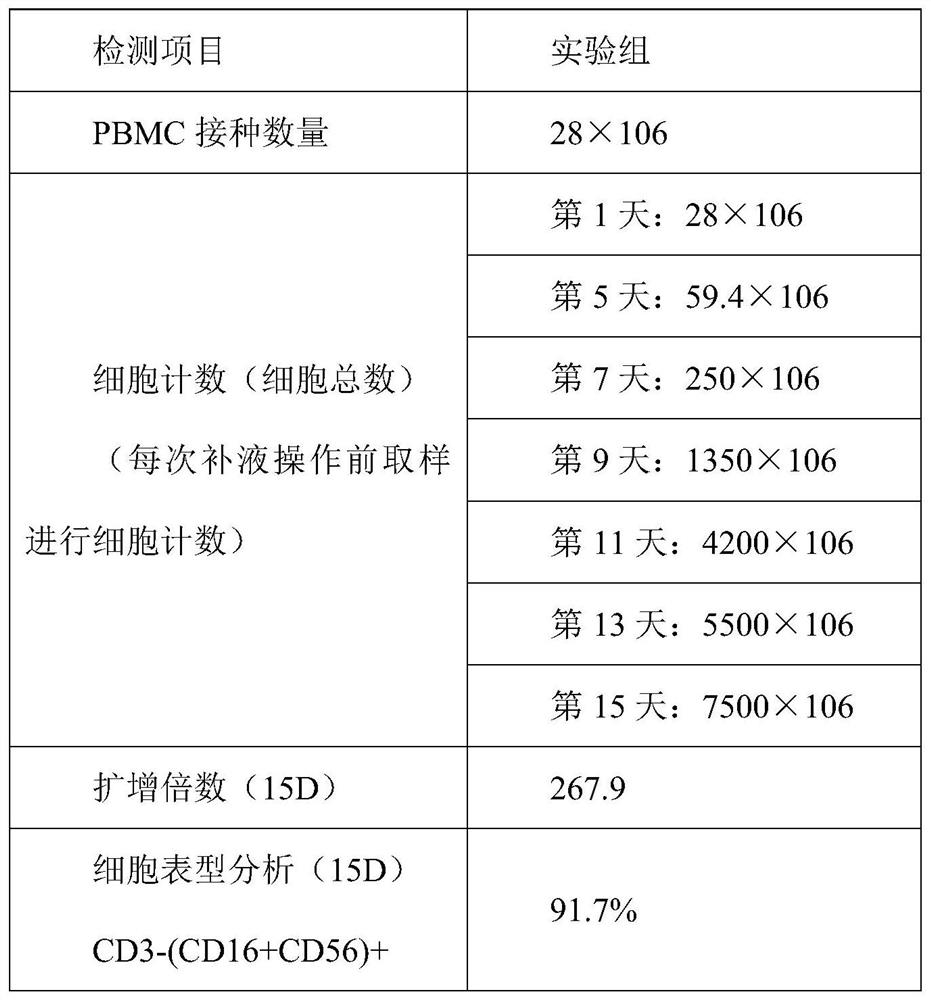
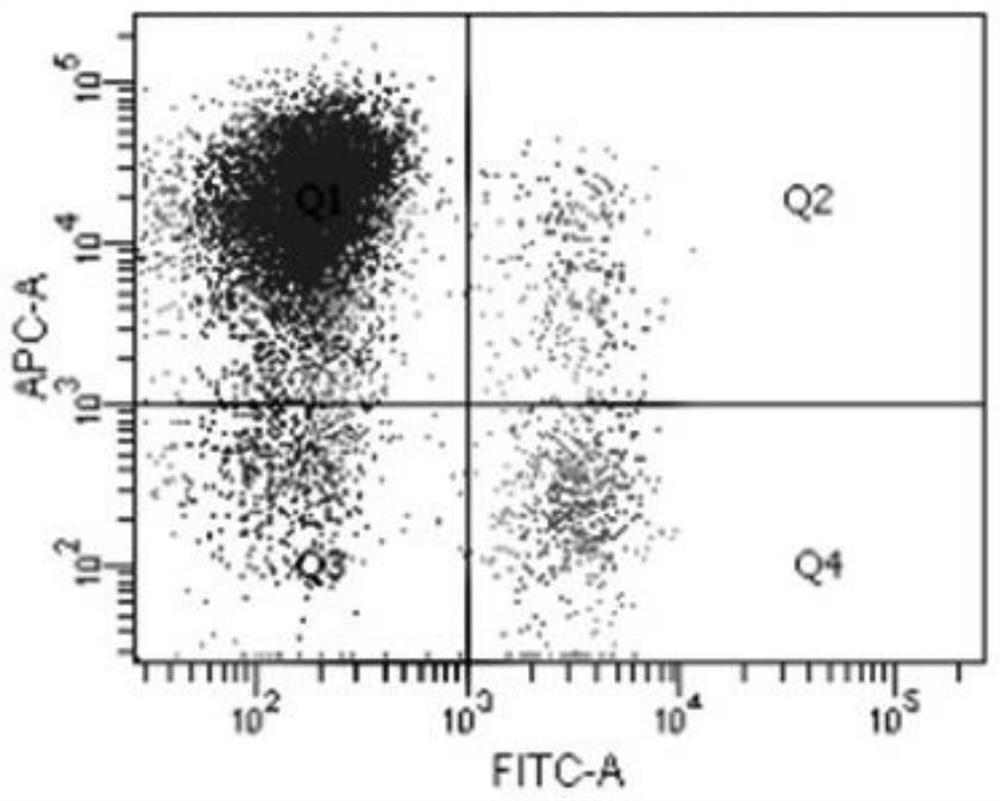
In-vitro culture method for improving activity of umbilical cord blood derived NK cells
PendingCN111826350ALow costHigh value-added multipleBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsCell phenotypeWhite blood cell
The invention discloses an in-vitro culture method for improving the activity of umbilical cord blood derived NK cells. The method adopts the following raw materials: a biosafety cabinet, a flow cytometer, a horizontal temperature control centrifuge, a sterilization pot, a CO2 incubator, an inverted microscope, a three-classification blood analyzer, a cell counter, a pipettor, refrigerators with the temperatures of -20 DEG C and 4 DEG C, a 75cm<2> culture bottle, a 225cm<2> culture bottle, a 2L culture bag, a 10ml transfer pipette, a 50ml efficient centrifuge tube, 15ml and 50ml centrifuge tubes, a 250ml centrifuge tube, medical sterile gloves, disposable sterile cap and sterile gloves, a serum-free culture medium LonzaX-VIVO15, recombinant interleukin 2, recombinant interleukin 15, a 0.4%trypan blue solution, physiological saline, human lymphocyte separation liquid, gamma interferon and recombinant interleukin 1[alpha]. According to the method, lentinan is added into related cytokines to culture the umbilical cord blood NK cells, so that the cost of culturing the NK cells by the method is not high, the proliferation speed is increased by 13-15 days, the proliferation multiple isincreased by about 270 times, the cell activity is high, and the cell phenotype is 91%.
Owner:深圳国科靶点药物有限公司
Ophthalmic composition of indigo carmine and ophthalmic application thereof
PendingCN114173724ATreatment helpsAids in diagnosisLaser surgeryLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical operationSurgical treatment
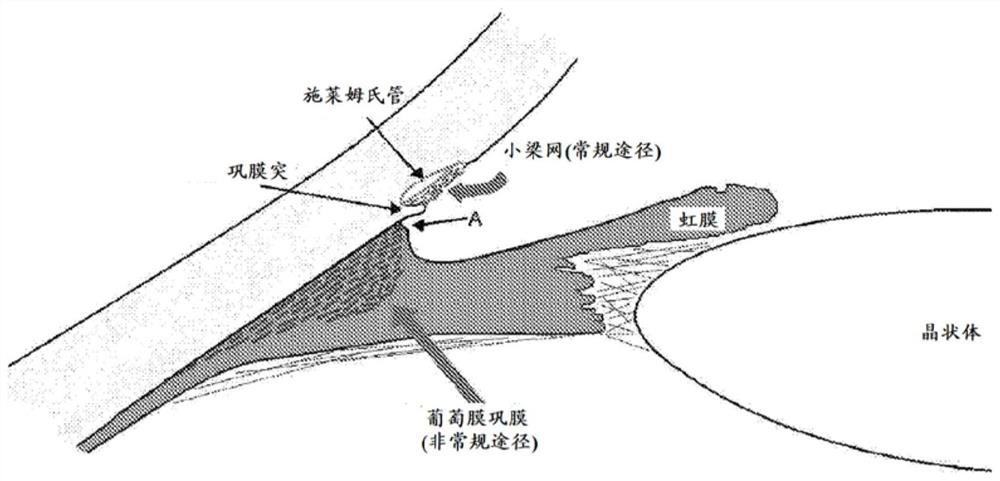
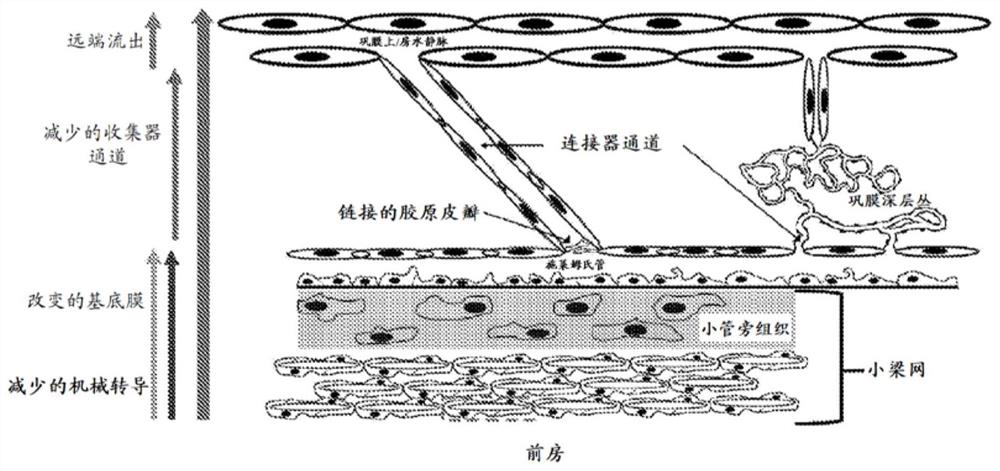
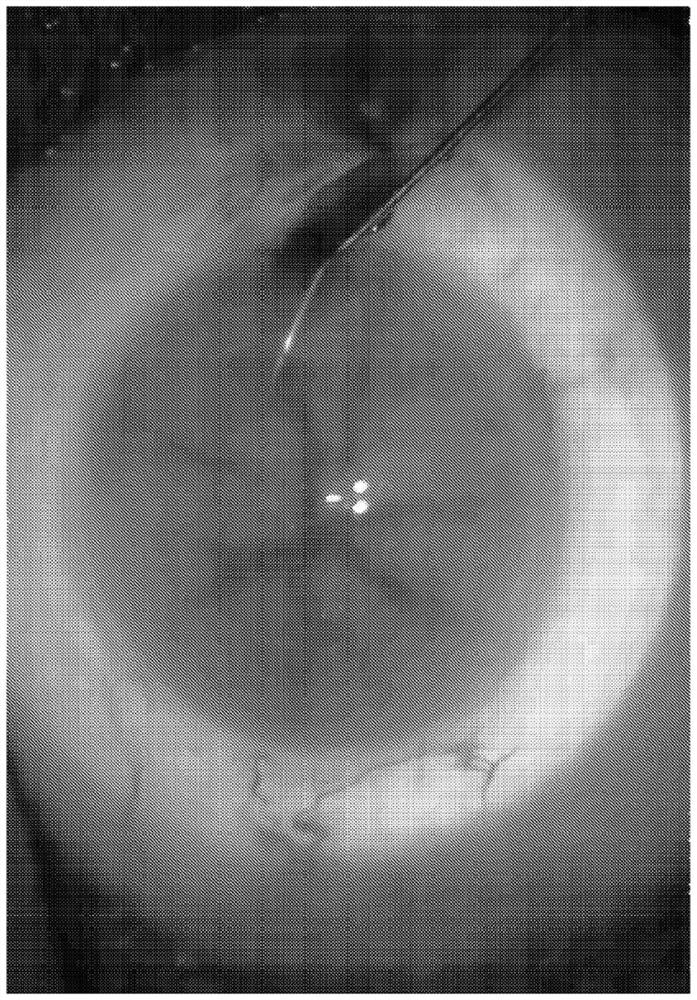
An ophthalmic composition comprising indigo carmine or indigo carmine and trypan blue for identifying intraocular structures and membranes within the eye, and methods of delivering and using the ophthalmic composition for surgical treatment of the eye, including glaucoma and cataract surgery.
Owner:米纳斯希欧多尔科罗内奥
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com