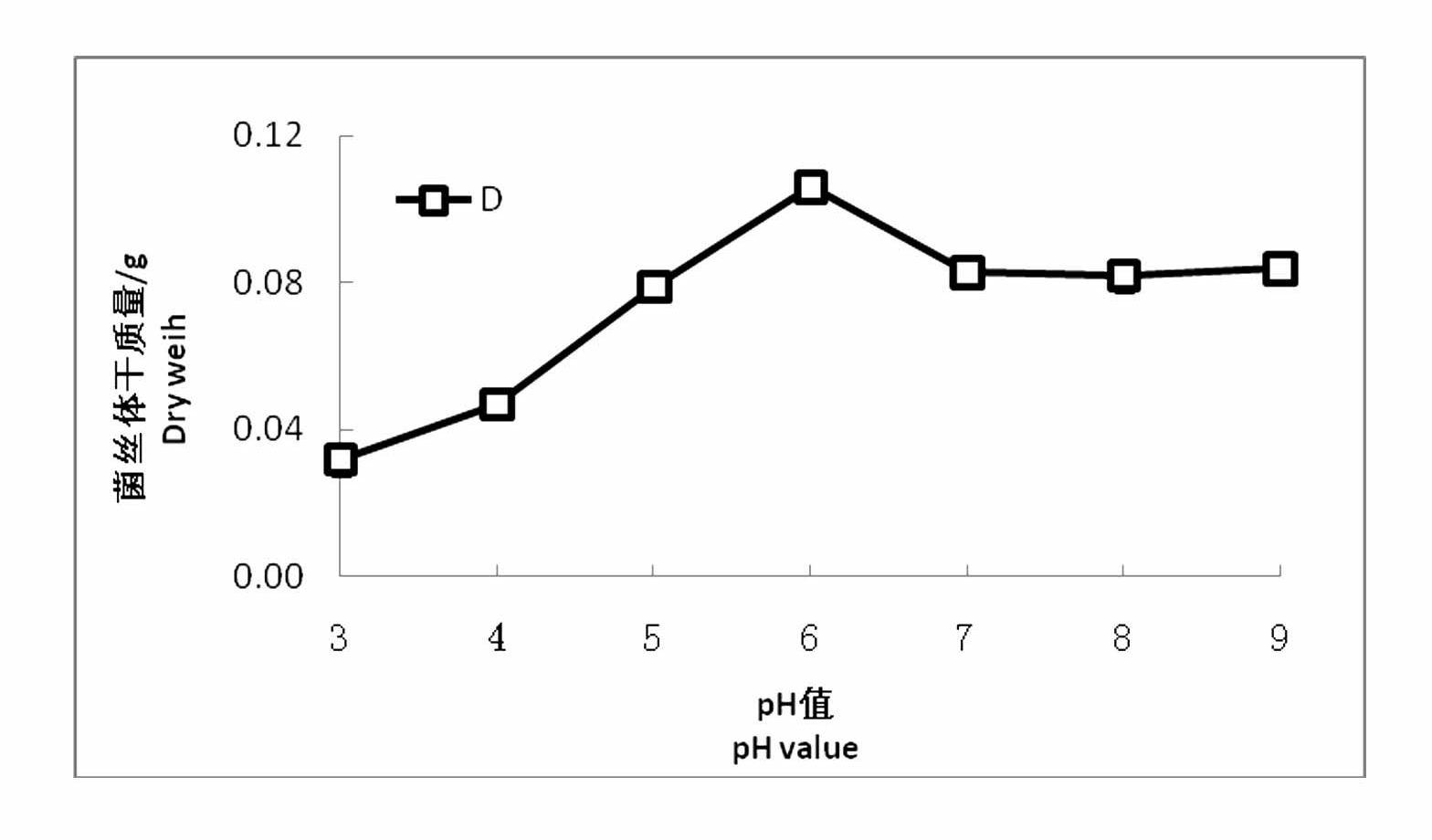
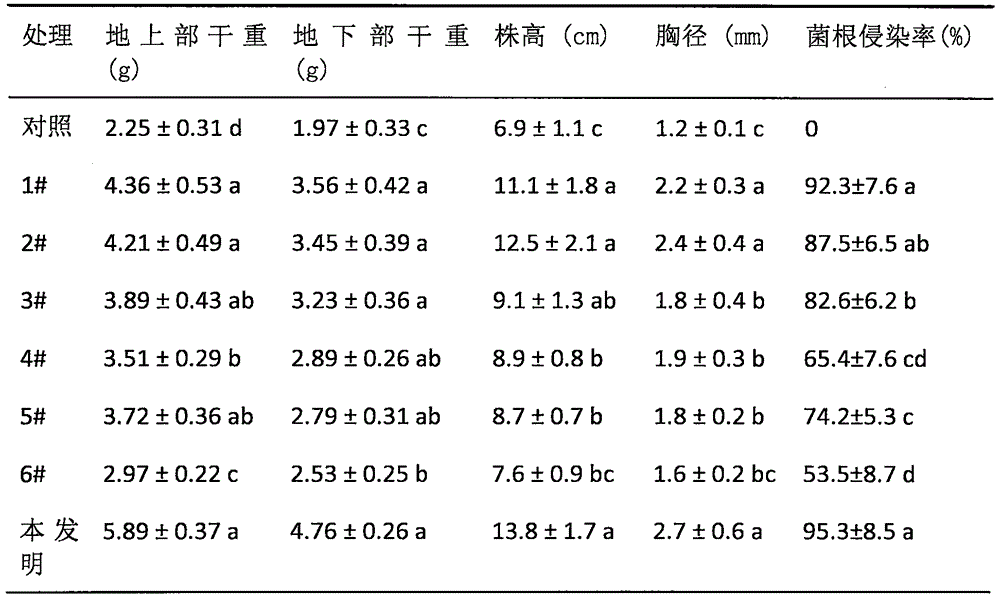
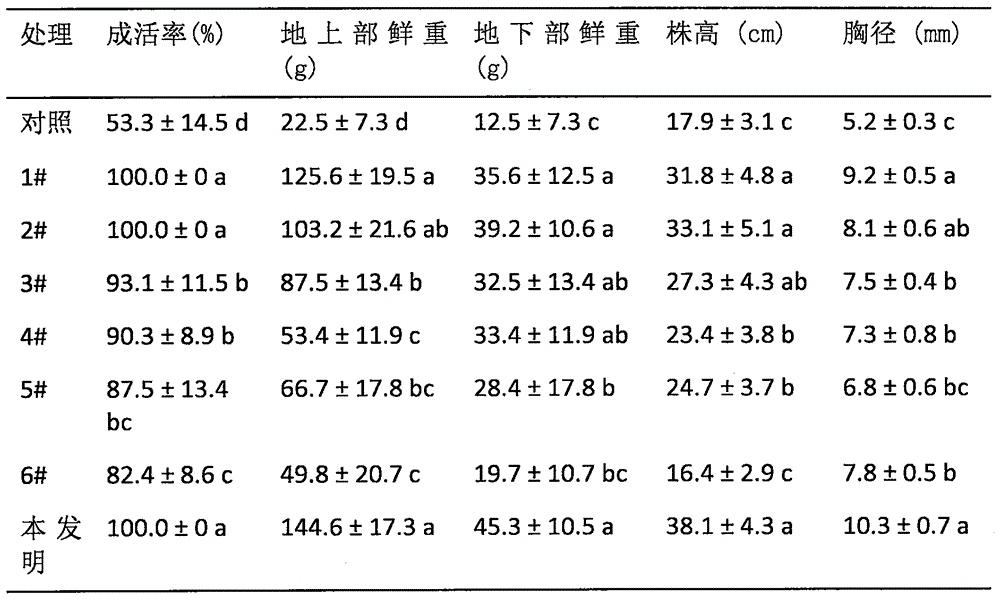
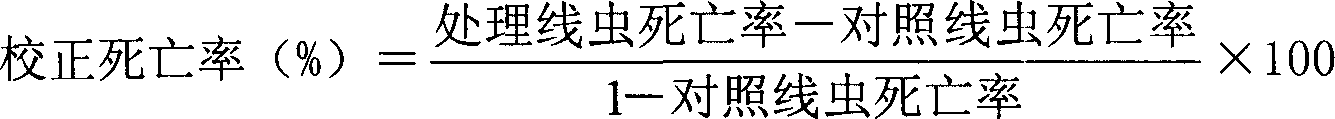Patents
Literature
524 results about "Mycorrhiza" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A mycorrhiza (from Greek μύκης mýkēs, "fungus", and ῥίζα rhiza, "root"; pl. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology and soil chemistry.
Living systems from cardboard packaging materials
InactiveUS20080046277A1Increase valueEffect shipping rateBiocideSustainable waste treatmentCardboardLiving systems
Compositions, methods and business applications of using new and recycled cardboard infused with a plurality of saprophytic (including endophytic) and mycorrhizal fungi matched with seeds of plants (including trees, vegetables, herbs and grasses) whereby the cardboard can be sprouted by end-users to start ecosystems. Such containers may have carbon-credit value for companies and consumers when planted and grown as a carbon sink or carbon offset for the photosynthetic and mycelial sequestration of carbon dioxide. The relative weight of the Life Box's added seeds and spores does not significantly affect the total weight of the infused cardboard, thus not increasing transportation costs.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
Combined restoring method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
InactiveCN101972772AIncrease the number ofHigh activityContaminated soil reclamationArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPlant roots
The invention relates to a combined restoring method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil, comprising the following restoring steps of: planting lucerne as perennial leguminous plants in the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil; inoculating a mixed bacterial inoculum comprising arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, bacillus and flavobacterium; and meanwhile, adding rhamnolipid as a biosurfactant. By rhizosphere effect generated by plant root exudates, the number and the metabolic activity of soil microorganisms are increased; and by inoculating the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, the plant growth is promoted, and the root exudates are increased, thereby increasing the root accumulation of organic pollutants and the number of root soil microorganisms. The inoculated high-efficiency polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacteria use plant root secretions as a carbon source and an energy source and can quickly grow and propagate. The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is stripped from soil grains by the biosurfactant, and the bioavailability and the degradability of the organic pollutants are increased.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of synergistic microorganisms and nutrients to produce signals that facilitate the germination and plant root colonization of mycorrhizal fungi in phosphorus rich environments
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Coal gangue-fly ash-sludge substrate and mycorrhiza technology for restoring ecology of mining area
InactiveCN101920261AOvercome poor water holding capacityOvercoming low fertilityContaminated soil reclamationBiological sludge treatmentSurface layerSludge
The invention relates to a coal gangue-fly ash-sludge substrate and a mycorrhiza technology for restoring ecology of a mining area. The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection, and relates to an ecology restoring technology, in particular to a method for restoring the ecology of an abandoned coal mine area. The method for restoring the abandoned coal mine area by the mycorrhiza technology of the invention adopts a composite substrate prepared by mixing fly ash, coal gangue and sludge, and comprises the following steps: a, preparing an inoculant; b, preparing a basic plant material; c, carrying out inoculating mycorrhiza treatment on the plant by the inoculant obtained in the step a; d, analyzing the physicochemical property of the abandoned coal mine area, and carrying out mixed treatment to form the composite substrate; and e, sowing seeds on the composite substrate surface layer of the treated abandoned coal mine area. The method of the invention can improve the adaptability of plants to the complex adverse environment of the abandoned coal mine area, wherein the adaptability comprises stronger nutrient acquisition capability and cold resistance, thereby fully utilizing waste and sludge in the mining area, and solving the source problem of other soil for melioration in the mining area.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of biogas residue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103848698AWon't burnDecompose thoroughlyBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelMicrobial agentPseudomonas
The invention provides a biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of a biogas residue and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing the biogas residue and a swelling agent to form a fermentation raw material, inoculating a compound microbial agent in the fermentation raw material, uniformly mixing for fermenting, and adding urea, diammonium phosphate, a potassium chloride inorganic salt, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhiza fungi, silicate bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria acetic bacteria, bifidobacterium, and saccharomycetes after the fermentation is completed to prepare the biological organic fertilizer, wherein the compound microbial agent comprises strains of bacillus, pseudomonas, staphylococcus, streptomyces, penicillium, aspergillus and trichoderma. The compound microbial agent prepared by using the biological organic fertilizer has a pertinence to aerobic fermentation of the biogas residue, and is capable of effectively increasing the fermentation rate of the biogas residue, shortening the fermentation time and realizing high-additional value production, innocent treatment and recycling of the biogas residue; and the problem of resources and environment of villages and small towns is solved, and the rapid development of construction of new countryside and towns and cities can be promoted.
Owner:青岛福瑞斯生物能源科技开发有限公司
Liquid mycorrhiza compositions
The present invention relates to liquid mycorrhiza compositions and to methods for colonizing a plant, grass, tree or shrub with one or more mycorrhizas.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes and application of flora
InactiveCN105859339AImprove the current situation of serious hardeningHigh nutritional valueFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisBacillus thuringiensis
The invention is suitable for the technical field of recycling organic wastes, and discloses a flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes. The flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes is efficiently compounded from a variety of bacteria such as bacillus subtilis, aspergillus niger, saccharomycete and soil flora, wherein the soil flora is extracted from the natural world and comprises three or more of bacillus megatherium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus thuringiensis, bacillus laterosporus, bacillus mucilaginosus, streptomyces jingyangensis, mycorrhiza fungi, azotobacter vinelandii, photosynthetic bacteria, bacillus coagulans, aspergillus oryzae, and paecilomyces lilacinus. According to the flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes, disclosed by the invention, by virtue of mutual promotion, mutual coordination and combined action of a variety of beneficial microorganisms, the organic wastes are recycled, environmental pollution is reduced, and wastes are changed into valuables; and the flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes can be used for producing industrial fermentation products and improving the health and growth conditions of animals, and can also improve the current situation of serious soil hardening at present and improve soil quality, thereby promoting the rapid development of agricultural economics.
Owner:王云飞
Soil improver
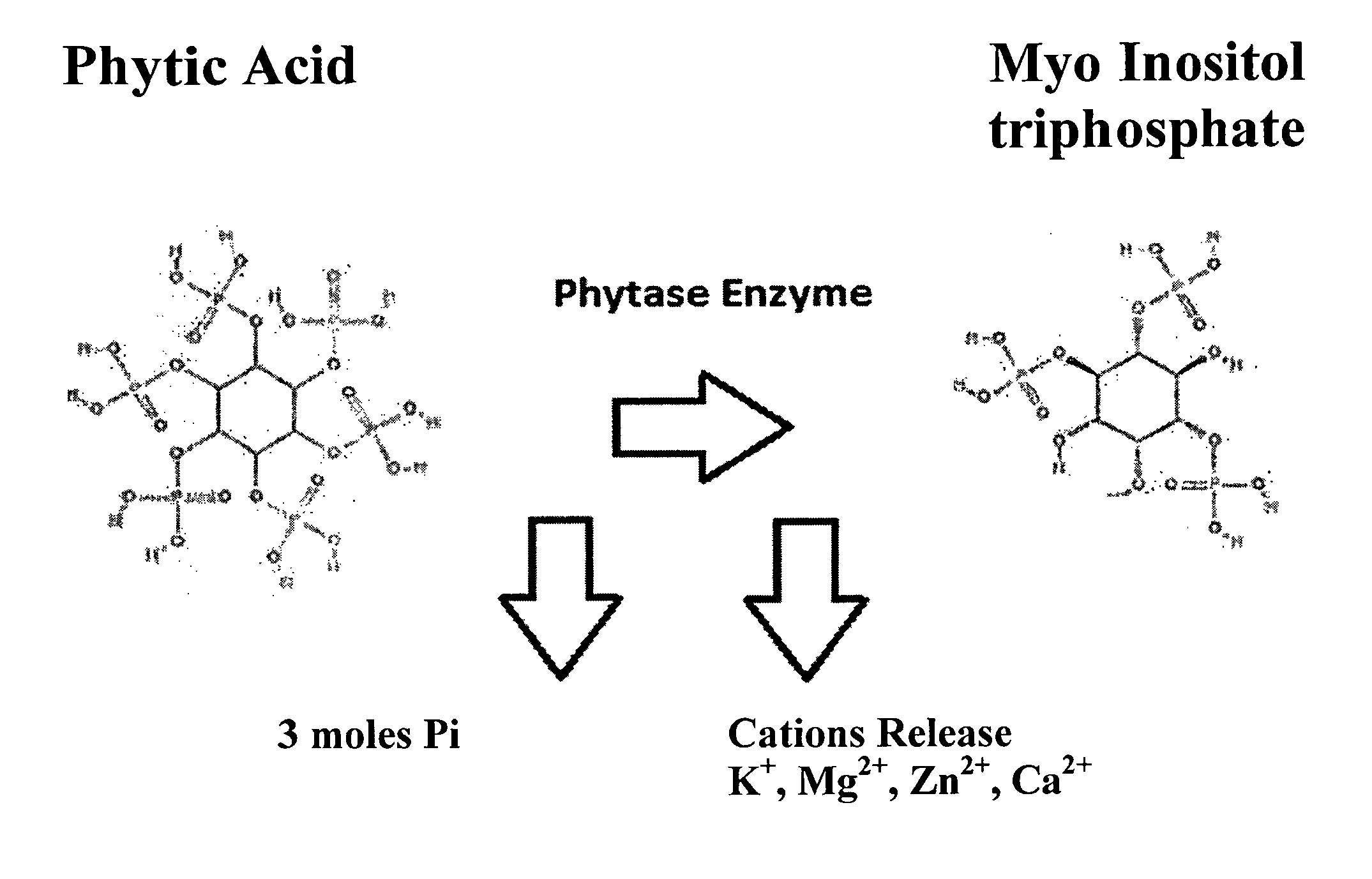
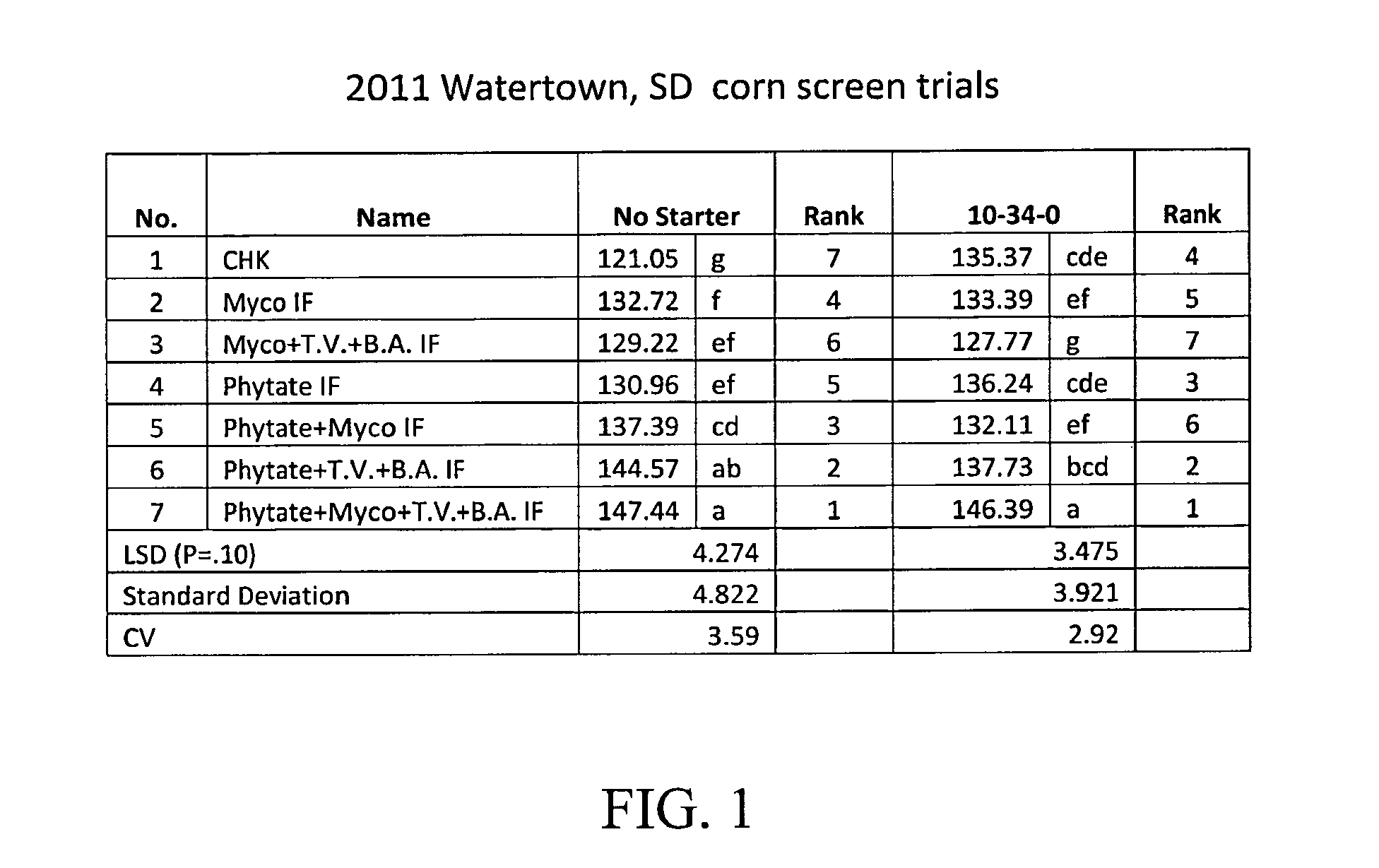
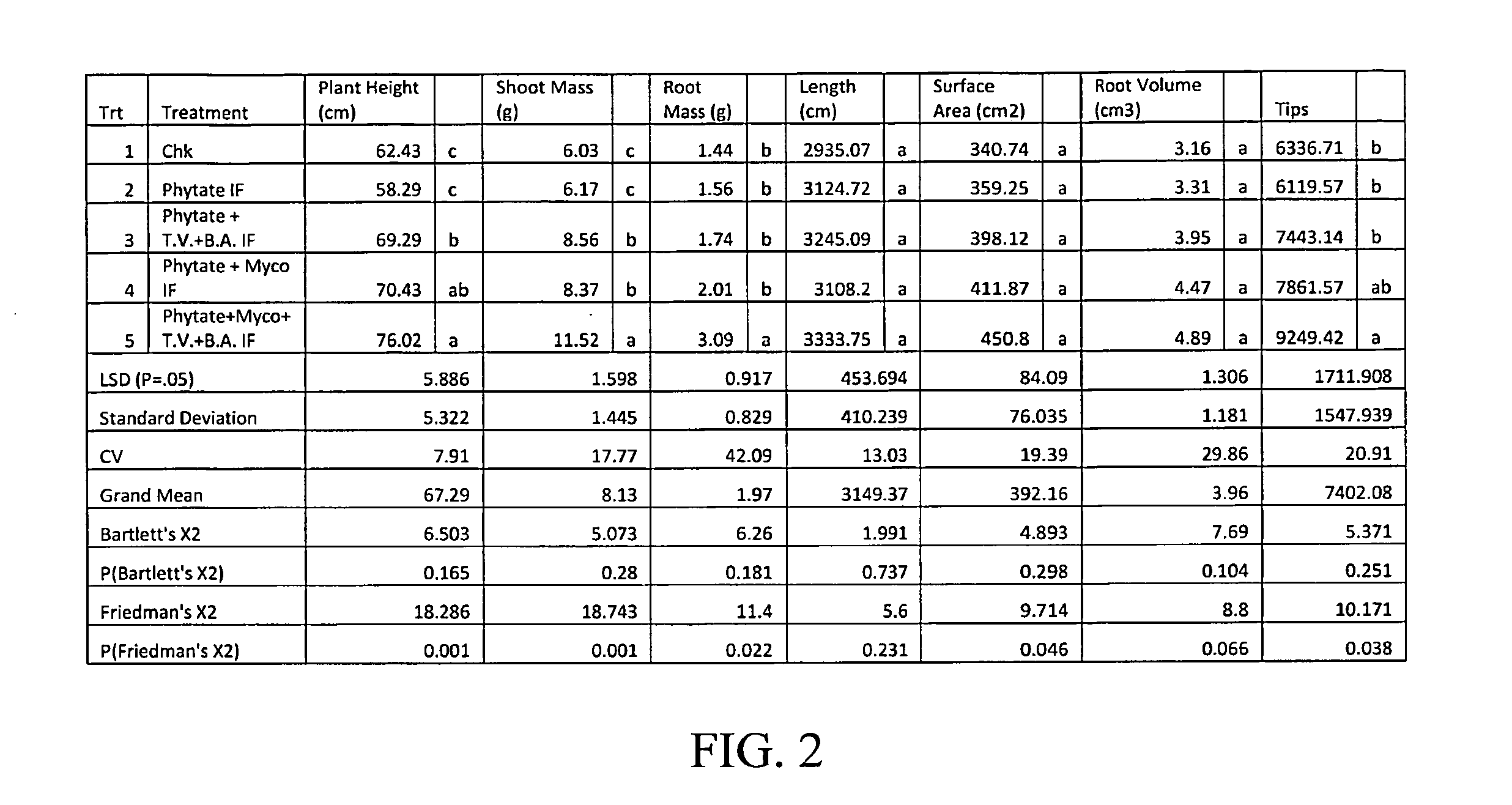
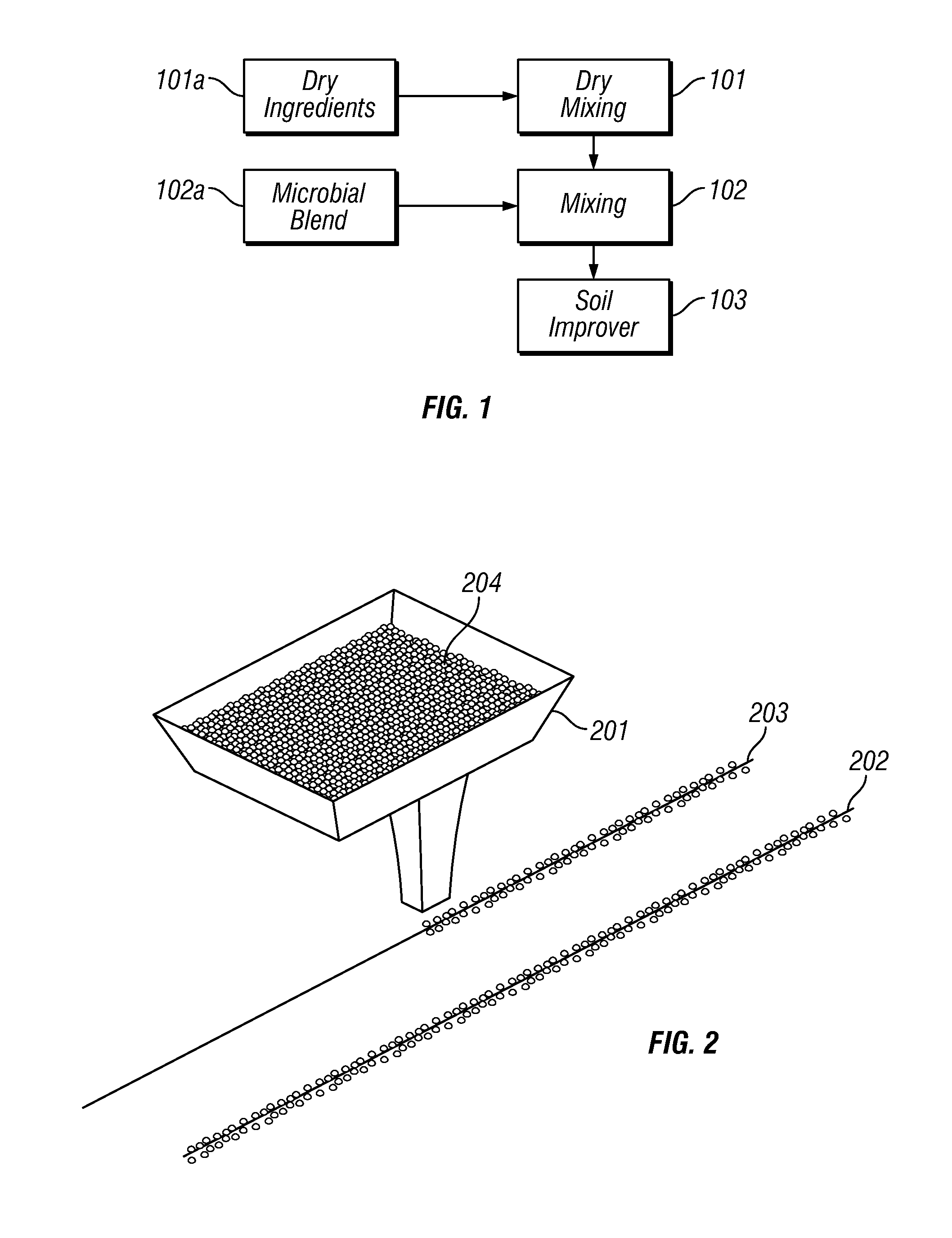
A soil improver and method for making the same. The soil improver, in one example, comprises a nitrogen source, a surfactant, a multi-mineral, and a microbial blend. The microbial blend comprises at least one bacterium, at least one fungus, and at least one mycorrhiza. The mycorrhizae mine water and nutrients for plant roots in exchange for food. Further the mycorrhizae greatly expands the effective root zone of the host plant. The soil improver is made by mixing the dry ingredients. Thereafter the microbial blend is mixed with the dry ingredients.
Owner:STET ACQUISITION INC
Biological phosphatic fertilizer as well as preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104016795AAvoid fixationImprove phosphorus dissolution rateFertilizer mixturesSoil sciencePhosphate solubilizing bacteria
The invention discloses a biological phosphatic fertilizer. The preparation method of the phosphatic fertilizer comprises the following steps: culturing AM mycorrhiza, phosphate solubilizing bacteria and rhizobium respectively, mixing with a phosphatic fertilizer to react, then adding various nutritional elements required for plants, and mixing and granulating to obtain porous fertilizer particles, so that the contact area between the fertilizer and water is increased, and the dissolving velocity of the fertilizer in water is accelerated. The biological phosphatic fertilizer can activate the phosphatic fertilizer, and can improve the absorption of the phosphatic fertilizer by plants, increase the utilization ratio of the phosphatic fertilizer, reduce the using quantity of the fertilizer and reduce the pollution to the environment; the fertilizer can be rapidly dissolved in water for irrigation and fertilization together with water, and is suitable for modern agricultural water and fertilization integration.
Owner:内蒙古和盛生态科技研究院有限公司
Synthetic method of truffle and bacteriorhiza
The invention provides a method for synthesizing Chinese truffles and mycorhiza of China pinus montana. The steps related are as follows: filtration of China pinus montana seeds and truffle seed entities; culture of aseptic seedlings; preparation of microbial inoculum; arrangement, optimal selection and inoculation of culture substrates; culture of mycorrhizal seedlings; anatomization of mycorhiza forms; detection and confirmation of molecules and transplanting culture, and finally, the culture of truffles is realized.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reproduction method of Chinese cymbidium seedlings
InactiveCN101983554AShort reproductive cycleSpeed up breedingSymbiotic/parasitic combinationsHorticulture methodsMycorrhizaSeedling
The invention discloses a reproduction method of Chinese cymbidium seedlings, belonging to an orchid seedling reproduction technology, in particular to a reproduction technology for raising seedlings by tissue culture and mycorrhizal fungi intergrowth culture. In the reproduction method of the Chinese cymbidium seedlings, seedling acquisition mainly comprises the steps of seed germination, protocorm successive proliferation and rhizogenesis culture. The reproduction method of the Chinese cymbidium seedlings is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out hardening on rooted seedlings and the process of mycorhiza on mycorhiza fungi after the seedlings are obtained. By adopting the mycorhiza culture technology of sterile germination and mycorhiza fungi intergrowth of Chinese cymbidium seeds, the invention has the advantages that excellent variety can be bred, excellent Chinese cymbidium plants can be selected from the seedlings, the Chinese cymbidium breeding speed can be rapidly improved and the defects that pure tissue culture seedlings grow slowly, have long period and even do not bloom can be overcome, thus the invention has an important utilization value on large-area industrial reproduction for the Chinese cymbidium.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Delivery systems for mycotechnologies, mycofiltration and mycoremediation
InactiveUS20050176583A1Promote decompositionEnhancing habitat recoveryBiocideFungiBiospherePlanting seed
The present invention utilizes fungal spore mass or hyphal fragments in landscaping cloths, fiber substrates, paper products, hydroseeders and agricultural equipment. The fungi may include saprophytic fungi, including gourmet and medicinal mushrooms, mycorrhizal fungi, entomopathogenic fungi, parasitic fungi and fungi imperfecti. The fungi function as keystone species, delivering benefits to both the microsphere and biosphere. Such fungal delivery systems are useful for purposes including ecological rehabilitation and restoration, preservation and improvement of habitats, bioremediation of toxic wastes and polluted sites, filtration of agricultural, mine and urban runoff, improvement of agricultural yields and control of biological organisms. The invention allow for a variety of methods and products including the use of cardboard boxes as a delivery system for fungi with or without the combination with plant seeds for starting gardens, for controlling insects, or for the process of ecological recovery.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Application of mycorrhizal fungi in large-scale plantation of gold thread lotus
The invention relates to a method for using fungus root fungi in the large cultivation of gold thread lotus, wherein used four fungus root fungis are small mushroom pieces, as Mycena dendrobii, Mycena osmundicol, Mycena orchidicola, and Mycena anoectochila. And the method comprises that first cultivating fungus root fungi and gold thread lotus; when transplating the gold thread lotus into large field, adding fungus root fungi and gold thread lotus to be planted together. The invention can reduce the grow period of gold thread lotus, improve yield and the content of effective component.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Chinese truffle and India truffle mycorrhiza fungi seeding cultivating method
InactiveCN101061781AHigh infection rateRelieve the aftermath of extinctionFungiCultivating equipmentsMycorrhizaMushroom
The invention discloses a mycorrhizomata fostering method of Chinese and Indian mushroom, which comprises the following steps: collecting mushroom bacteria; gathering host plant seed such as Yunnan pine, mountain Hua pine and chestnut; disposing the host plant seed; breeding the host plant; inoculating the bacteria; cultivating the bacteria; detecting. The invention reduces the infectious rate of bacteria, which satisfies the living need with wide market prospect.
Owner:攀枝花市农林科学研究院
Large-scale propagation technology for mycorrhiza fungi inoculum
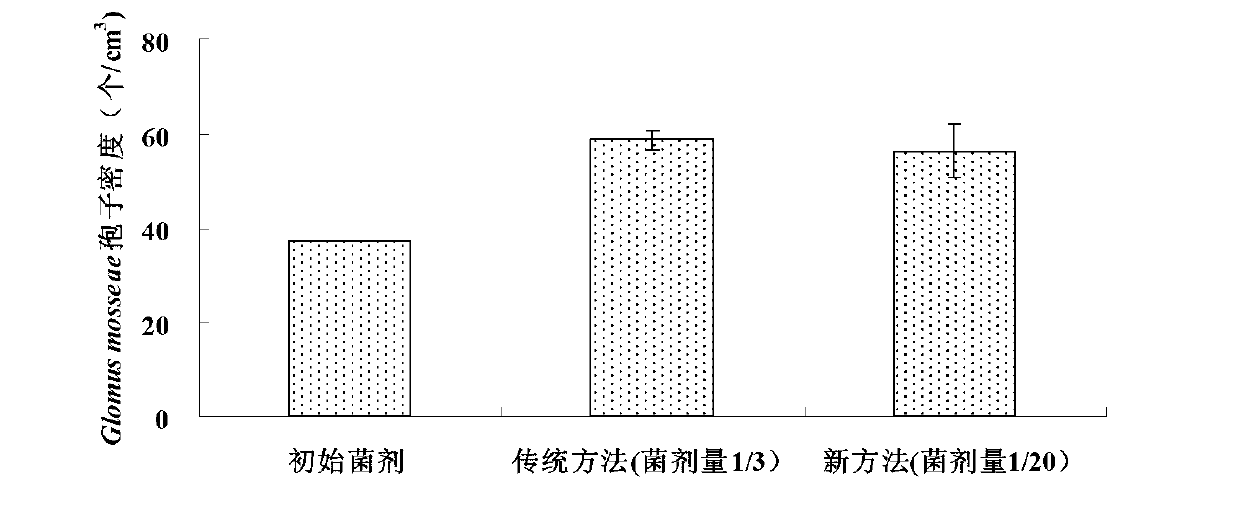
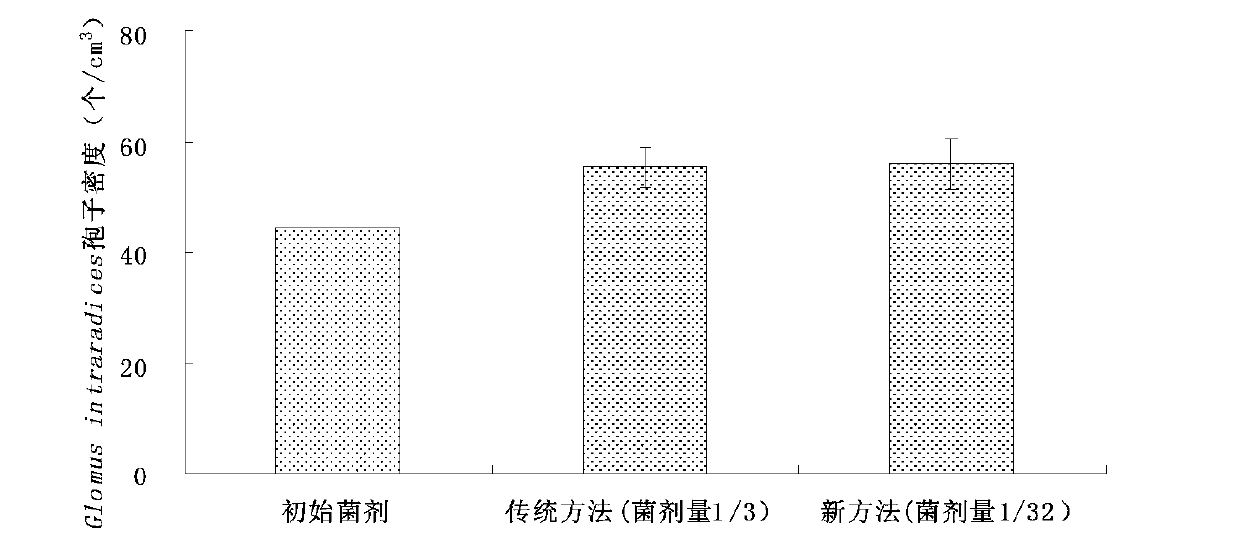
The invention discloses a high-efficient large-scale propagation technology for mycorrhiza fungi inoculum, and belongs to the field of bio-fertilizer productions. The high-efficient large-scale propagation technology suitable for mycorrhiza fungi includes material selection, production process, quality control and product formation. Materials for the technology are easy to obtain, operation is easy and convenient and cost is low. Spore density of the propagated mycorrhiza fungi inoculum can reach more than fifty per cubic centimeter, and can even reach more than one hundred per cubic centimeter, and propagation efficiency is more than four times higher as compared with conventional propagation technology efficiency. The device adopted in the technology is high in flexibility, easy to be regulated in real time and small in occupation. Detection of product quality of the mycorrhiza fungi and large-scale production thereof are facilitated. An AMF (abuscular mycorrhizal fungi) propagation technology, high-efficient and prone to large-scale production, formed in the technology, is beneficial to application of the AMF in agricultural production, and new approaches for sustainable development for agriculture are provided.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Facility vegetable mycorrhiza production method
InactiveCN1843073AImprove utilizationImprove efficiencyCultivating equipmentsChemicalsDiseasePlant disease
The invention relates to a method for producing protective vegetable fungus root sprout, comprising the following steps: 1) planting susceptive crop after inoculating the bush AMF for sterilized organic soil or soil, taking the strand roots of plant or fungus root spore as inoculating bacteria; 2) sterilizing seedling soil or medium; 3) loading the sterilized soil into dish, spraying the inoculating bacteria onto soil, 4) sowing on the dish, then covering with sterilized soil for seedling in greenhouse. The invention is characterized by the low cost, good popularity and simple operation. The bacteria can on one side increase the usage of nutrient and water and fertilizer under organic cultivating condition, which results in productivity and quality improvement of vegetable; on the other side can strengthen the disease and drought resistance, reduce disease spread through soil and improve vegetable root condition.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of mycorrhizal fungi in large-sclae plantation of dendrobium stem
The invention relates to a method for using fungus root fungi in the large cultivation of gold thread lotus, wherein used four fungus root fungis are small mushroom pieces, as Mycena dendrobii, Mycena osmundicol, Mycena orchidicola, and Mycena anoectochila. And the method comprises that first cultivating fungus root fungi and gold thread lotus; when transplanting the gold thread lotus into large field, adding fungus root fungi and gold thread lotus to be planted together. The invention can reduce the grow period of gold thread lotus, improve yield and the content of effective component.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Blueberry mycorrhizal fungi (coprinus micaceus) and separation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102220246AHarm reductionReduced low pH requirementsBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismFruit set
The invention relates to a blueberry mycorrhizal fungi (coprinus micaceus) and a separation method and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of microbiology, and mainly relates to a mycorrhizal fungi which separated from a Changbai Mountain wild cowberry root system for blueberry inoculation and application of the mycorrhizal fungi at promoting the growth of blueberry and improving the yield of the blueberry. The blueberry mycorrhizal fungi is preserved in the Chinese General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the classification name is Coprinus micaceus. By the application of the mycorrhizal fungi, the growth of the blueberry root system can be promoted. The invention has the advantages that the yield, fruit setting rate and insect damage prevention function can be improved, and the like.
Owner:LIAONING ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A novel method for controlling soybean root disease by using rhizobia
The invention relates to a method for using soybean root nodule and endotrophic mycorrhiza to prevent soybean root disease. Wherein, the inventive bacteria seed has been stored in national microbe storage manager center, whose storage number is sinorhizobium sp; the seed L396 storage number is CGMCC No. 1851; the bacillus subtilis seed Snb2 storage number is CGMCC No.1850. And the invention uses general liquid to ferment and cultivate, uses itself or metabolite as effective active component; mixing the ferment solutions at different ratios, with effective restrain function on soybean cyst nematization and root pathogenic fungi; the density ratio between Snb2 and L392 is 8:3, and the dead ratio of young bacteria can reach 98.92%, and the relative restrain rate on cyst cultivation can reach 99.66%; the invention prepares the metabolite into water agent, to reach 78.6% prevent rate on the soybean cyst nematization. The inventive nodule bacteria can fix nitrogen and accelerate growth.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Method for optimizing nursery-grown plant cultivation by using ectomycorrhizal fungi
ActiveCN105861315AIncrease the number ofPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant cultivationMycorrhiza
The invention discloses a method for optimizing nursery-grown plant cultivation by using ectomycorrhizal fungi. The method comprises the main process including the following steps: production of an ectomycorrhizal fungi agent, cultivation of tree seedlings, inoculation with the ectomycorrhizal fungi, and nutrition management of the tree seedlings after inoculation. In actual use, a pre-experiment can be performed according to different tree species, and a best ectomycorrhizal fungi strain is selected. 6 kinds of ectomycorrhizal fungi are adopted as materials to inoculate root systems of the tree seedlings, and the growth amount and the transplanting survival rate of the tree seedlings are significantly improved.
Owner:NANJING JINPU LANDSCAPE
Application technology of mycorrhizal fungi in Anoectochilus blume cultivation
InactiveCN1433670AShorten the growth cycleIncrease productionSymbiotic/parasitic combinationsHorticulture methodsMycena dendrobiiMycorrhiza
The present invention relates to an application technique of mycorrhizal fungi in cultivation of anoectochilus formosanus. It is characterized by that the used mycena-generic four fungi respectively are mycena dendrobii, mycena osmundicola, mycena orchidicola and mycena anoectochila. First, the mycorrhizal fungi and seedling of anoectochilus formosanus are respectively cultured, then they are symbiotically cultivated. The adoption of said invented technique can greatly shorten the growth period of anoectochilus formosanus, and can raise its yield and effective component content.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Cottage breeding method of sabina przewalskii
InactiveCN101702978AImprove survival rateGood conditionCultivating equipmentsHorticultureGreenhouseJuniperus przewalskii
The invention discloses a cottage breeding method of sabina przewalskii, comprising the following steps: manufacture of a cottage seedling bed: manufacturing a seedling bed on the seedling culturing ground in a greenhouse in the spring of the current year; and covering fine sand and mycorrhiza soil as cottage matrix; strip picking: in the middle of May to June, selecting healthy, strong, pest and disease-and-damage-free sabina przewalskiiseedlings at the age of 3-5 with good growth and development for picking strips; and cutting processing: placing the cutting into clear water for soaking, drying rapidly, respectively placing into ABT1 rooting powder and potassium permanganate solution for respectively soaking for one time and then carrying out cottage; digging holes on the cottage seedling bed and obliquely cutting, and compacting the cutting hole; leading the cutting bed and the cutting to be fully contacted; spraying with carbendazim or Tuzet and copper abietate for once every half a month, thus preventing root rot of sabina przewalskii seedlings. The method of the invention greatly improves propagation coefficient, can shorten seeding culturing period, has high cottage seedling culturing survival rate, and can enable the cultured nursery stock to keep excellent characters of parent trees.
Owner:GANSU PROVINCE ACAD OF QILIAN WATER RESOURCE CONSERVATION FORESTS RES INST
Method for recovering gangue vegetation using mycorrhiza technology
InactiveCN1633833AImprove adaptabilityMaintain ecological balanceFungiSymbiotic/parasitic combinationsVegetationMycorrhiza
Disclosed is a process for comprehensive treatment of discarded metal tailings, wherein fungus root technology is employed to recover the metal tailing vegetation, the process comprises the steps of, (1) preparing the seeding agent, (2) preparing the basic plant material, (3) carrying out seeding bacteriorhiza treatment to plants by using the seeding agent obtained in (1), (4) conducting physical and chemical analysis to the metal tailing and related treatment, (5) sowing seeds or replanting young sprouts on the skin layer of the treated metal tailing, (6) curing the young sprouts.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing edible fungus mycorrhizal seedling of mycorhiza
InactiveCN101595803AEasy to operateImprove efficiencyHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for producing the edible fungus mycorrhizal seedling of a mycorhiza. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: the mycelium of a target mycorrhizal fungus and the mycorhiza of a non-competitive mixed fungus are synthesized into a culture medium, are uniformly mixed, are spread in a container and are cultured under a condition which is suitable for the growth of hypha, wherein the surface of the container is disinfected by a potassium permanganate solution or sterilized under high temperature and high pressure, and the lower part of the container is spread with a layer of non-competitive mixed fungi or media sterilized under high temperature and high pressure; and a sterile germinated host plant seed of which the surface is disinfected and the culture medium culturing the target hypha are mixed and cultured under a proper ecological condition until the mycorhiza of a tree seedling root is formed. The synthesis experiment of the edible fungus mycorrhizal seedlings of various mycorhiza shows that the method has simple and effective operation and high efficiency, is very suitable for popularization and application in mass production, can be used for producing mycorrhizal seedlings at any time in one year and has obvious economic benefits.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
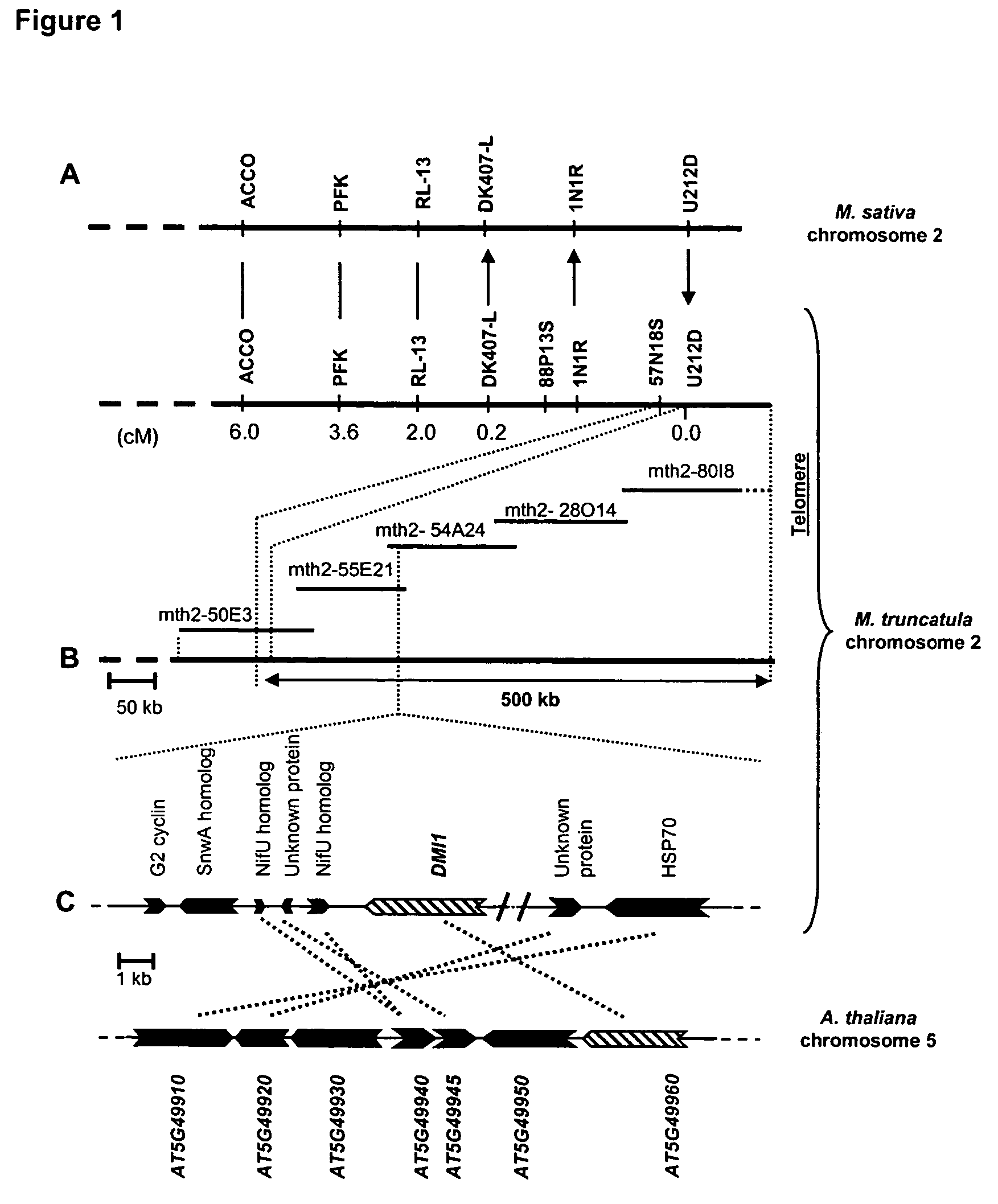
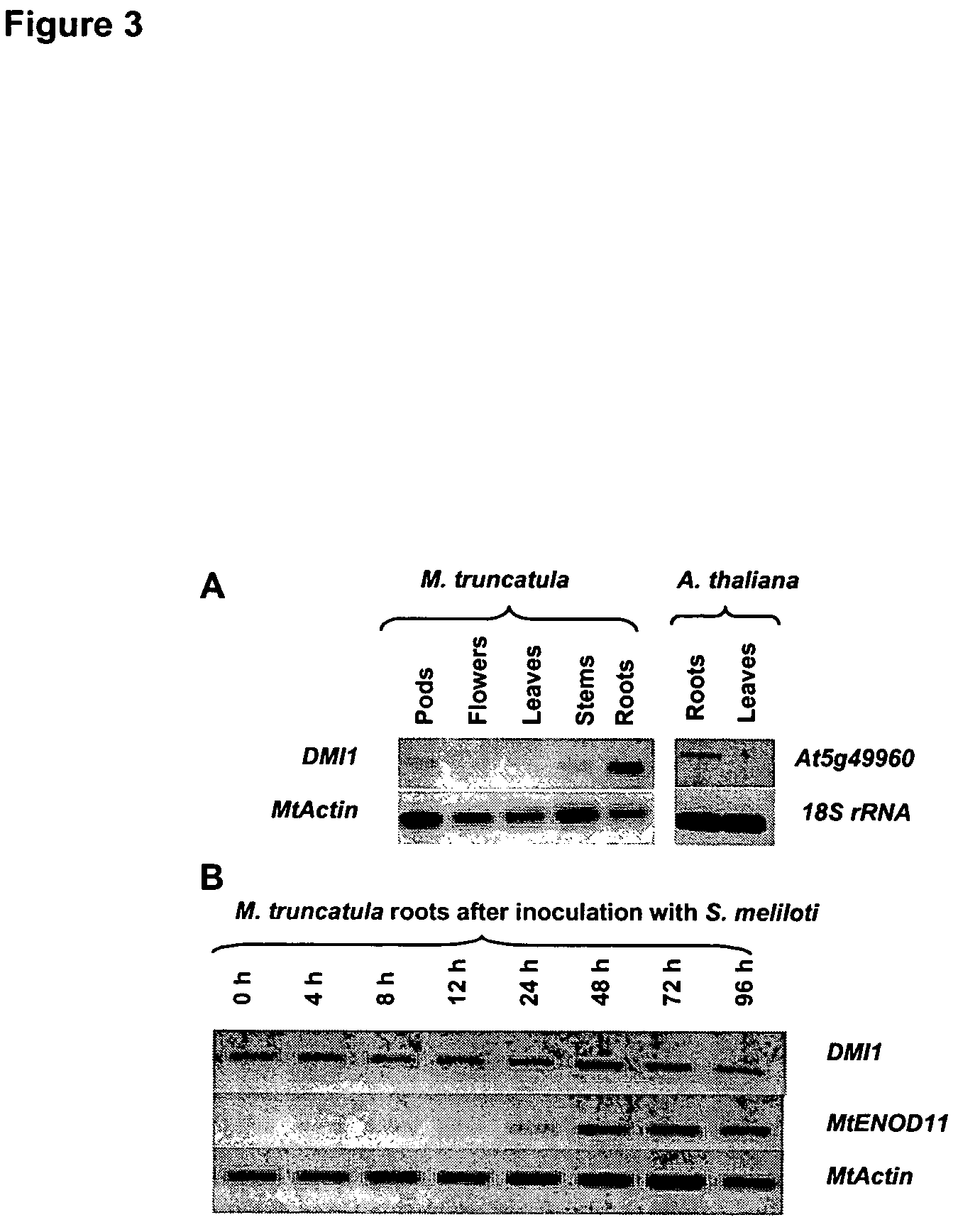
DMI1 gene encodes a protein that is required for the early steps of bacterial and fungal symbioses
InactiveUS7205450B2Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorous acquisitionBryophytesSugar derivativesPlant cellNodulations
The invention relates to isolated DMI11 genes from Medicago truncatula which play a major role both in the early steps of Nod factor signaling that trigger several key developmental responses in the host plant and in the establishment of mycorrhizal symbiosis. The invention also relates to transgenic plants and plant cells expressing the DMI1 protein for increased root nodulation, and methods for transforming plants with a M. truncatula DMI1 gene.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
Application of method for smearing and transforming agrobacterium rhizogene-mediated hypocotyl to soybean transformation
InactiveCN101705243AEstablish and optimize smear conversion methodsPrecise determination of germination timeMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionHypocotylRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention discloses application of a method for smearing and transforming agrobacterium rhizogene-mediated hypocotyl to soybean transformation. The method for smearing and transforming agrobacterium rhizogen-mediated hypocotyl to is applied to soybeans for the first time, and hairy root transformation of soybean roots is successfully carried out. In this invention, the sprouting time of seeds and the concentration of screening agents are optimized, therefore not only increasing the quantity of transgenic hairy roots induced by each soybean explant, but also obviously enhancing the transformation frequency and growth conditions of hairy roots. A screening marker weed killer usually used for soybean transformation is successfully used for obtaining soybean compound plants in aseptic conditions, wherein each soybean compound plant has a transgenic root and a non-transgenic over-ground part and can be used as the ideal material for studying genes relative to the form of root systems, the symbiotic nitrogen fixation of roots and the formation of fungus roots.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Living systems from cardboard packaging materials
InactiveUS20080005046A1Effect shipping rateCost-effectiveData processing applicationsPackagingCardboardLiving systems
Compositions, methods and business applications of using new and recycled cardboard infused with a plurality of saprophytic (including endophytic) and mycorrhizal fungi matched with seeds of plants (including trees, vegetables, herbs and grasses) whereby the cardboard can be sprouted by end-users to start ecosystems. Such containers may have carbon-credit value for companies and consumers when planted and grown as a carbon sink or carbon offset for the photosynthetic and mycelial sequestration of carbon dioxide. The relative weight of the Life Box's added seeds and spores does not significantly affect the total weight of the infused cardboard, thus not increasing transportation costs.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
Method of increasing gesarex polluted soil phyto remediation efficiency
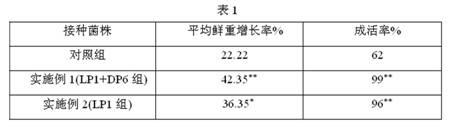
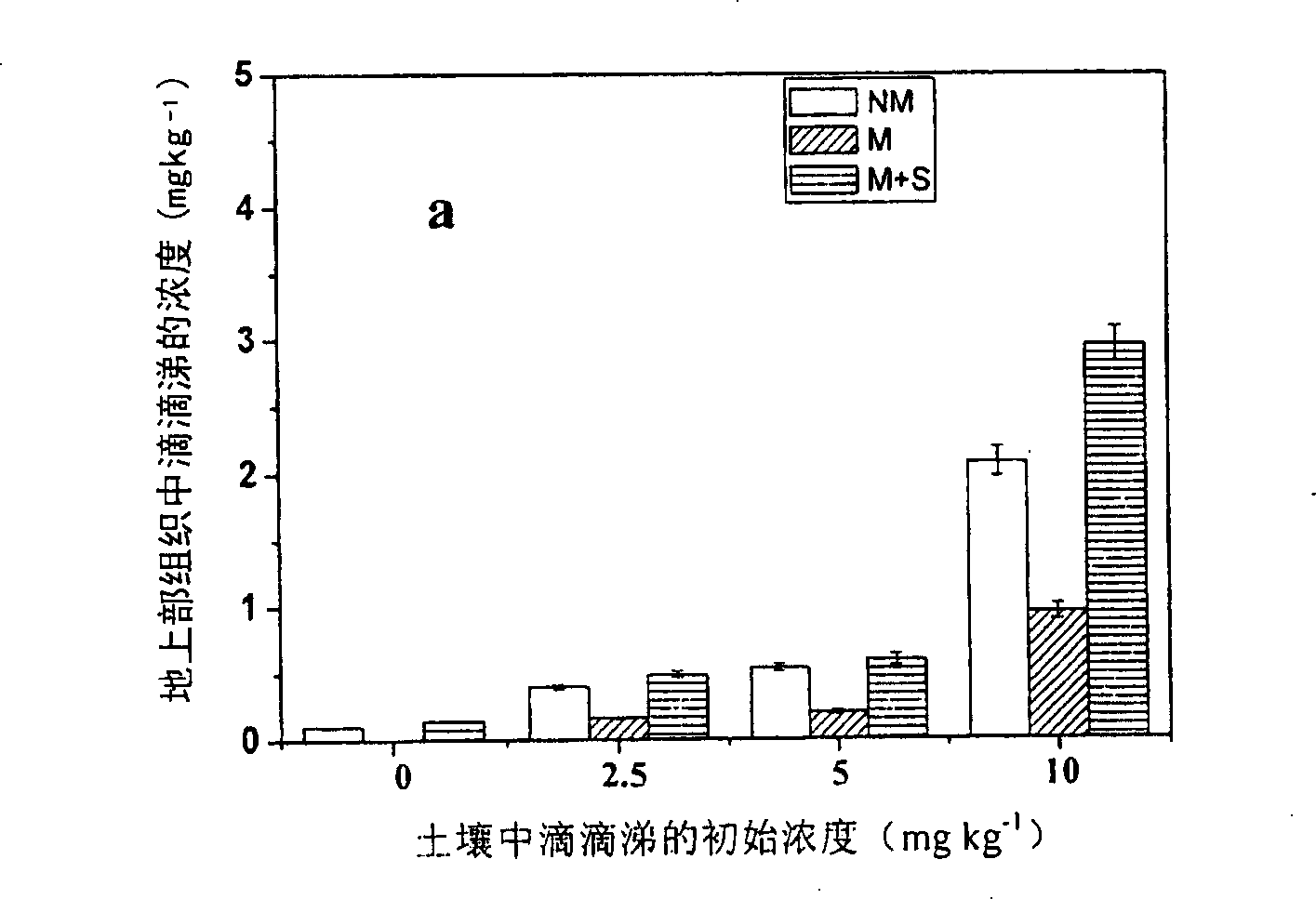
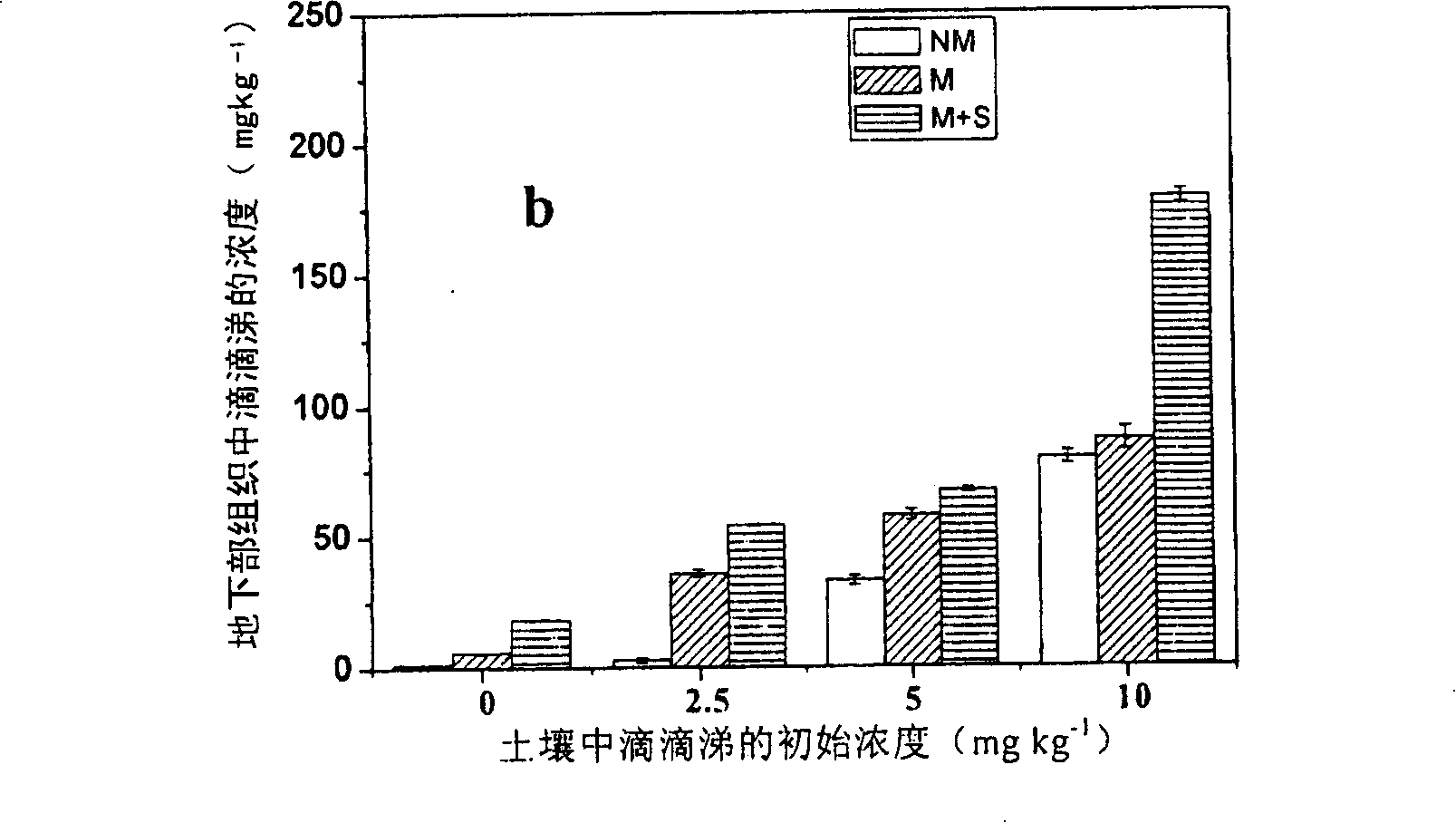
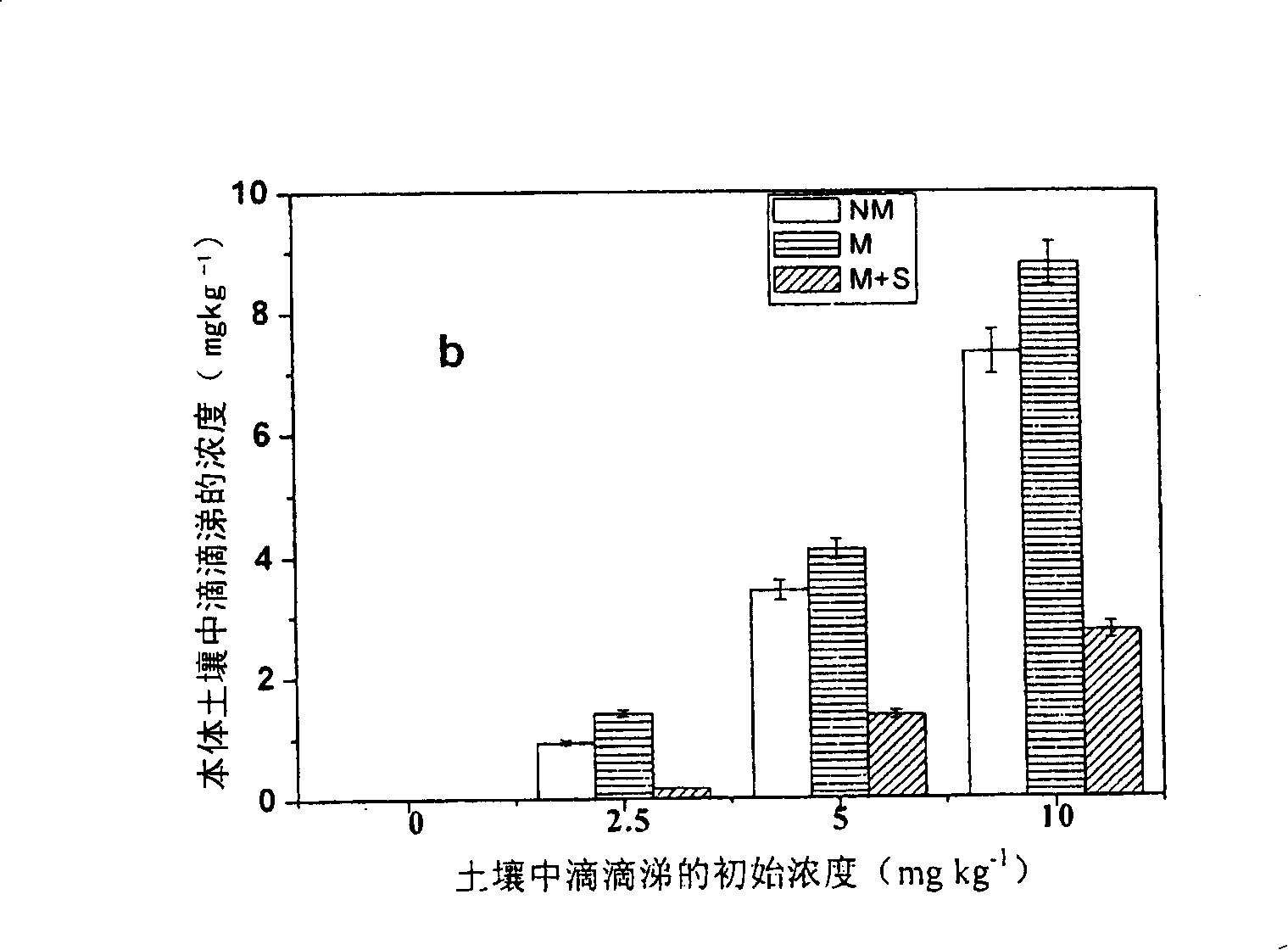
InactiveCN101229550APromote absorptionReduce DDT contentFungiContaminated soil reclamationBioremediationPhytoremediation
The invention provides a method for improving the plant-based recovery efficiency of dichlorodiphenyl trichloroethane (DDT)-polluted soil. The method is to promote mycorrhiza of clover and add chemical surfactant to recover the DDT-polluted soil with the joint function of uromyces striatus schroter and the surfactant. The steps of the method include that an inoculant layer is inoculated in a culture medium; mycorrhiza is carried out to the clover and that the sprouted clover is planted in the DDT-polluted soil and the surfactant TritonX-100 is added to the soil. The joint effect of the mycorrhiza and the surfactant can remarkably improve the resistance of plants to the DDT, reduce the concentration of the DDT in the soil and have evident plant-based recovery efficiency of the DDT-polluted soil. The method of the invention can be used for reference for the recovery of the soil polluted by other organic matters.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Planting method for interplanting rhizoma polygonate under pear trees
InactiveCN108040724AAvoid sun exposureImprove survival rateCultivating equipmentsRoot crop cultivationPlant nodulePear tree
The invention discloses a planting method for interplanting rhizoma polygonate under pear trees and relates to the technical filed of planting. The method comprises the steps of land selection, soil loosening, pear tree transplantation, rhizoma polygonate treatment and planting, weeding, fertilization and the like. By adopting the planting method, rhizoma polygonate can be prevented from being insolated, the survival rate of rhizoma polygonate is increased, and accordingly the yield of rhizoma polygonate is increased; the root systems of the pear trees are developed and have root nodule or mycorrhiza, the soil fertility is improved, and the appropriate growth environment can be provided for rhizoma polygonate for a long time; overground parts of pear leaves and rhizoma polygonate plants are treated and can be applied to organic fertilizer for improving the soil quality, waste is sufficiently used, and the yield of the pear trees and rhizoma polygonate is increased; through interplanting of the pear trees and rhizoma polygonate, weed infestation is avoided, the use amount of the weed killer is effectively reduced, and the labor cost is saved.
Owner:渠县新市贡和中草药农民专业合作社
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com