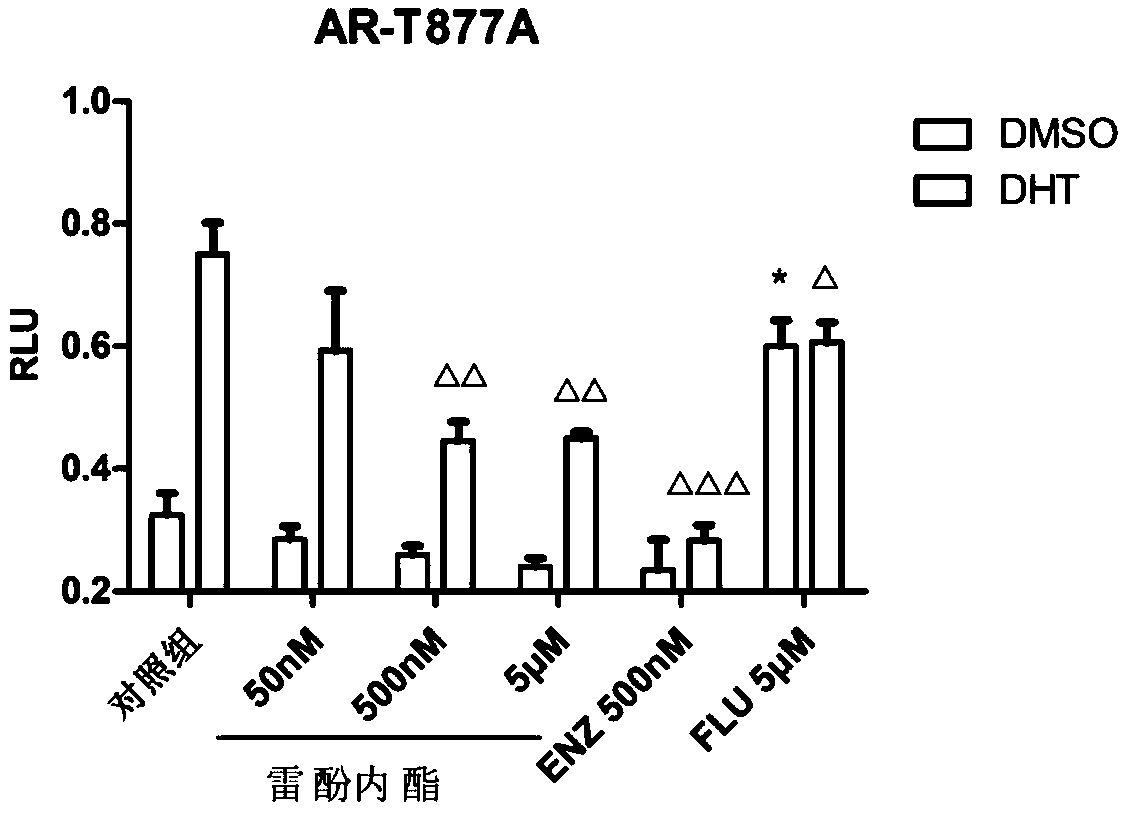
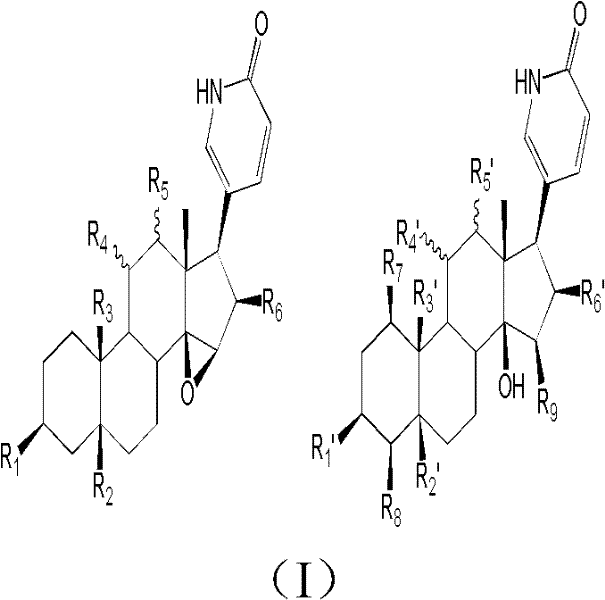
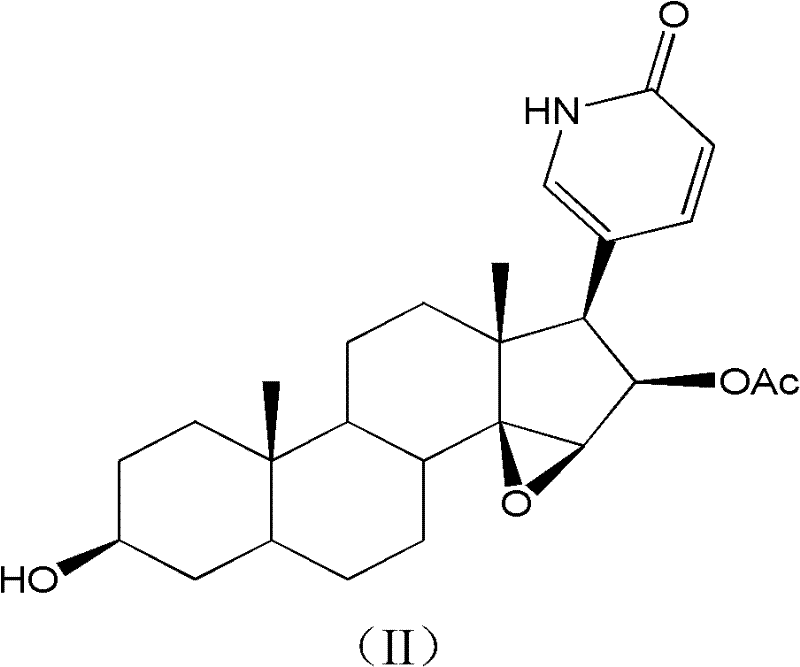
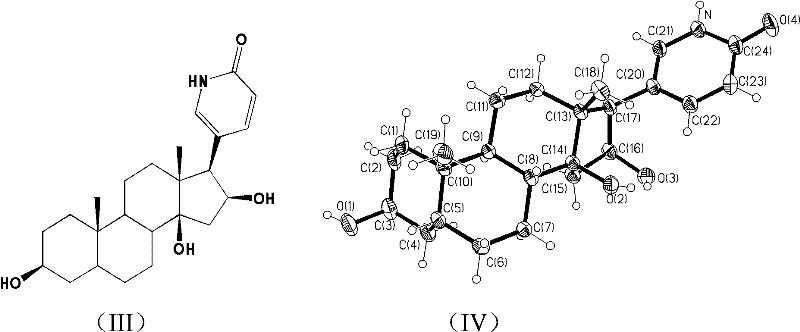
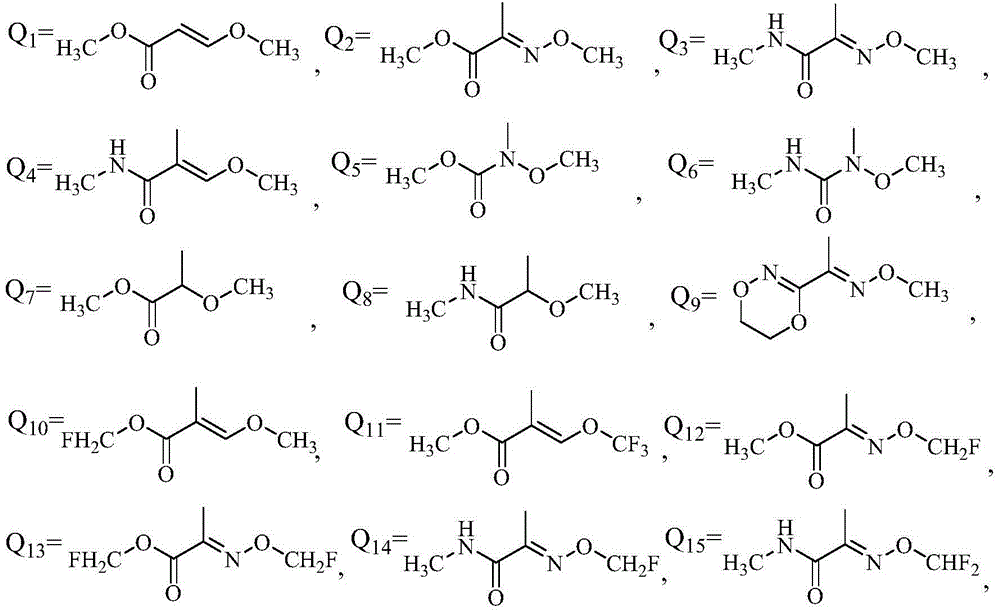
Patents
Literature
67 results about "LNCaP" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
LNCaP cells are a cell line of human cells commonly used in the field of oncology. LNCaP cells are androgen-sensitive human prostate adenocarcinoma cells derived from the left supraclavicular lymph node metastasis from a 50-year-old caucasian male in 1977. They are adherent epithelial cells growing in aggregates and as single cells.
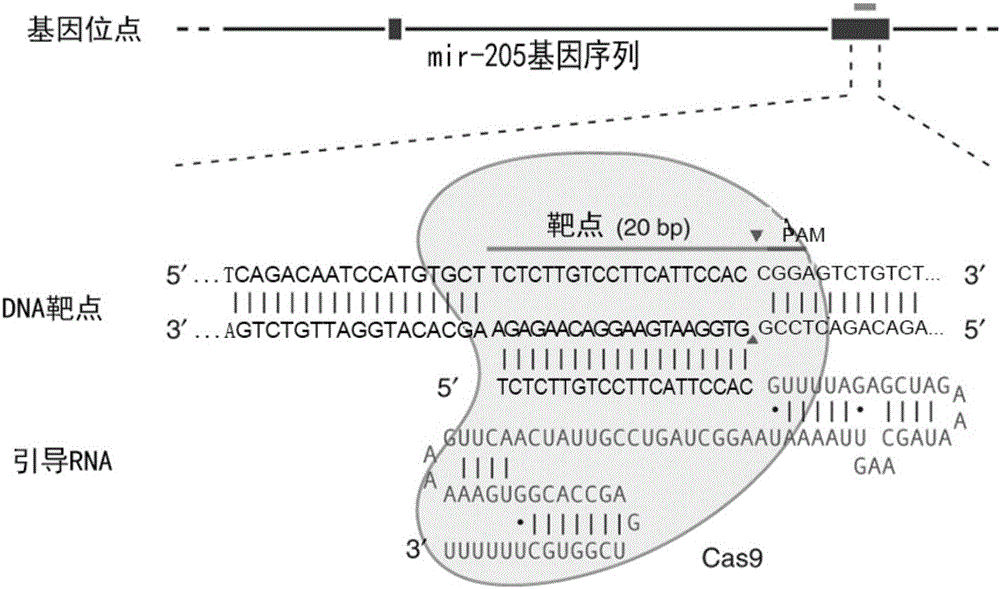
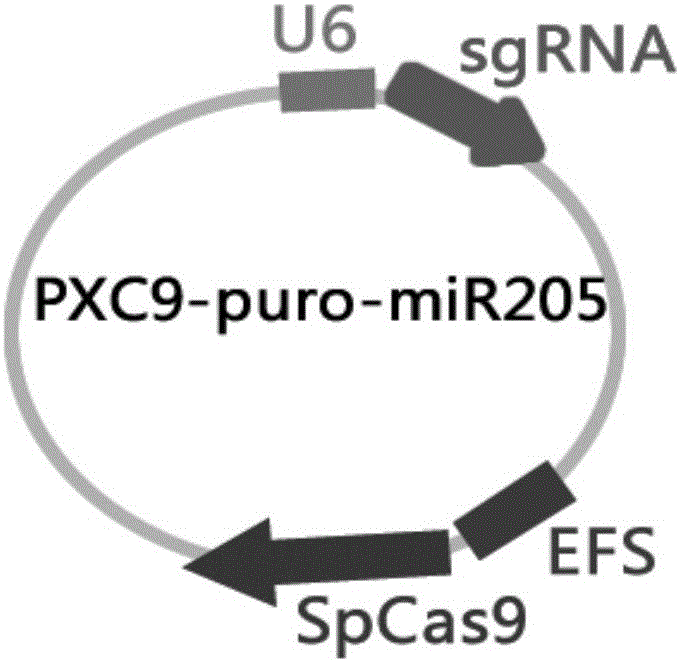
MiR-205 gene knockout kit based on CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout technology
ActiveCN105112445AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionFluorescence
The invention discloses a miR-205 gene knockout kit based on CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout technology. According to the invention, an optimal CRISPR-Cas9 target sequence of a certain amount of miR-205 is obtained through target design software and an sgRNA single chain is synthesized in vitro; an insertion fragment is obtained through processing; then sgRNA is inoculated into a plasmid vector by using T4 ligase; and a miR-205 gene knockout cell strain is obtained through transfection of an LNCap cell strain, continuous drug screening and fluorescence detection. Heterogenous hybridization double strands are obtained by extracting DNAs of a cell, PCR amplification of miR-205, purification, denaturation of a PCR product and annealing; T7E1 enzyme digestion test is employed to determining shearing efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas9 system on miR-205; a verified optimized a miR-205 gene knockout CRISPR-Cas9 target sequence is obtained; and the kit is constructed on the basis of the target sequence and can be used for directional knockout of miR-205 genes. The kit has the characteristics of high gene knockout efficiency, fast speed, easiness and economic performance and has wide prospects in the aspects of construction of animal models and clinical research of medical science.
Owner:广州辉园苑医药科技有限公司
3-methoxylflavonoid compound, preparation method and application thereof
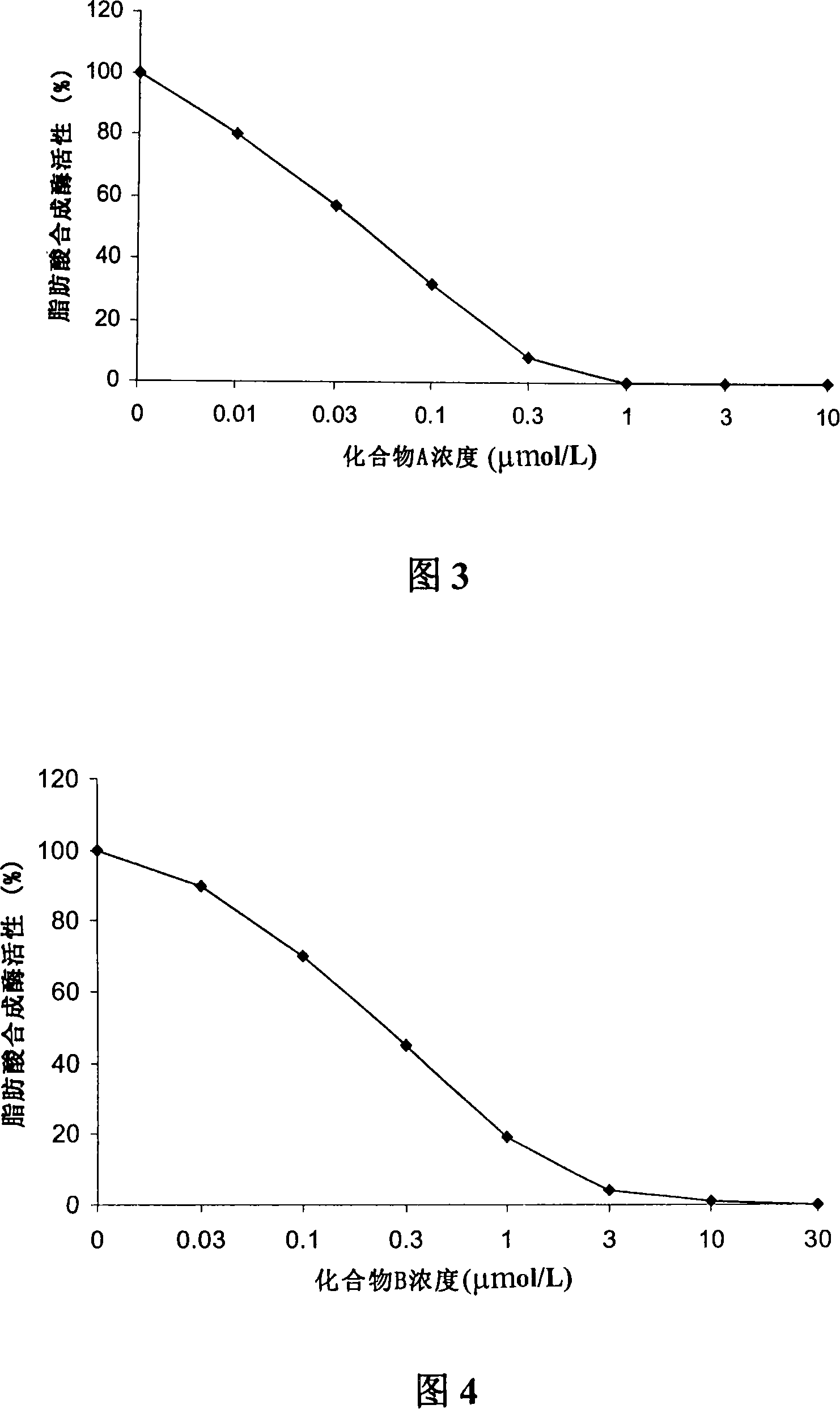
A 3-methoxy-flavone compound comprises 5,7-dihydroxy-8-(3,3-dimethyl diallyl)-3,3', 4'-trimethoxy flavone and 5, 7-2 dihydroxy-8- (3,3-dimethyl allyl)-3,4'-dimethoxy flavonoe. harmacological test results prove that: the 3-methoxy-flavone compound is an effective fatty acid synthase inhibitor, which shows the broad-spectrum anti-tumor effect in the cytotoxicity tests of various tumor cell lines and has strong tumor growth inhibiting effect on human prostate cancer cell LnCAP, human breast cancer cell ZR-75-1, human lung cancer cell NCI-H23 or human colon cancer cell HCT-116 when applied to human tumor transplant nude mice model tests. In addition, the 3-methoxy-flavone compound reveals no toxicity in mice acute toxicity tests, which then can be used as anti-tumor drug and is a new broad-spectrum anti-tumor drug with great development prospects.
Owner:殷正丰 +2
PI3K-Akt Pathway Inhibitors
InactiveUS20070238745A1Increase Bim abundanceBiocideAnimal repellantsProstate cancer cellMitochondrial pathway
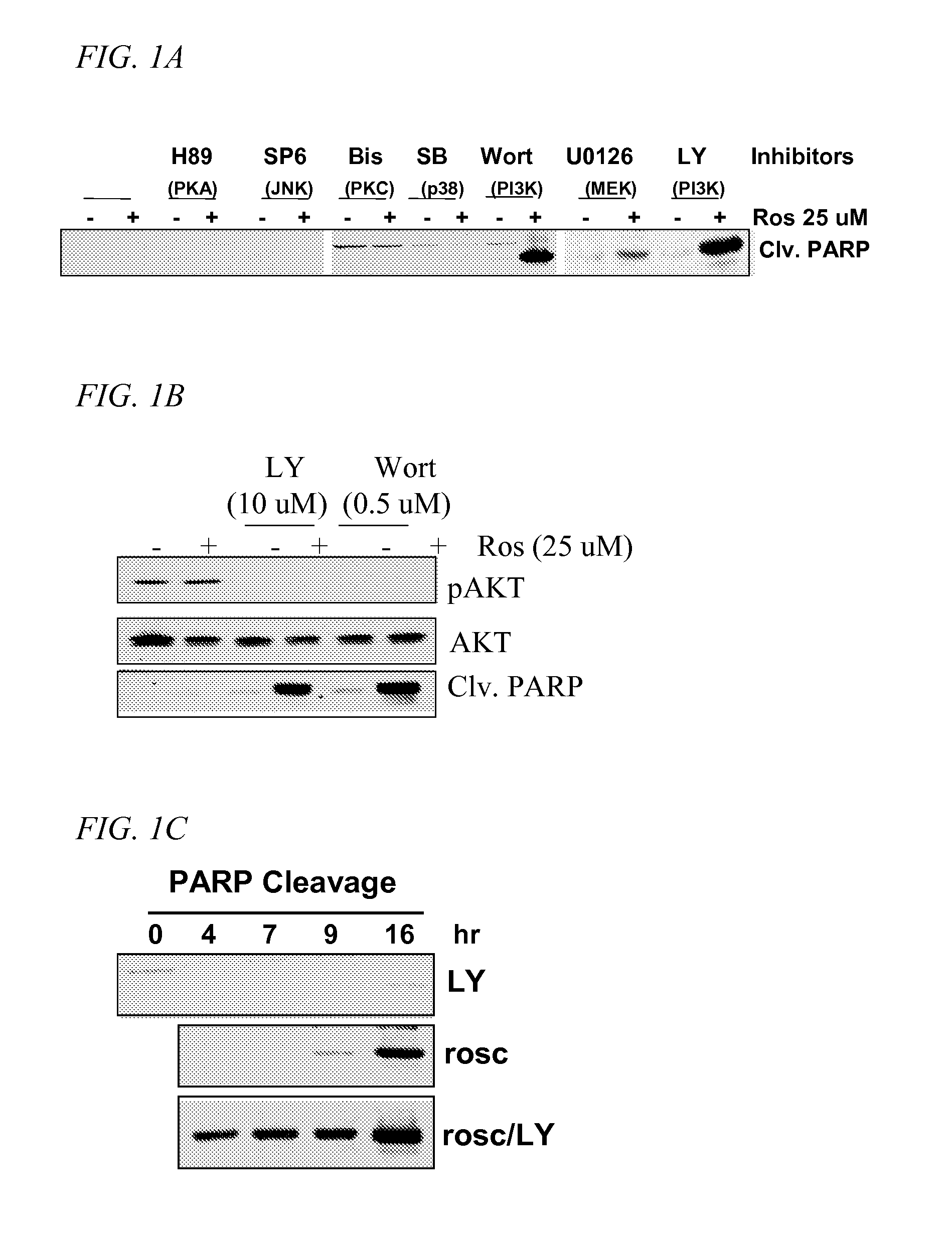
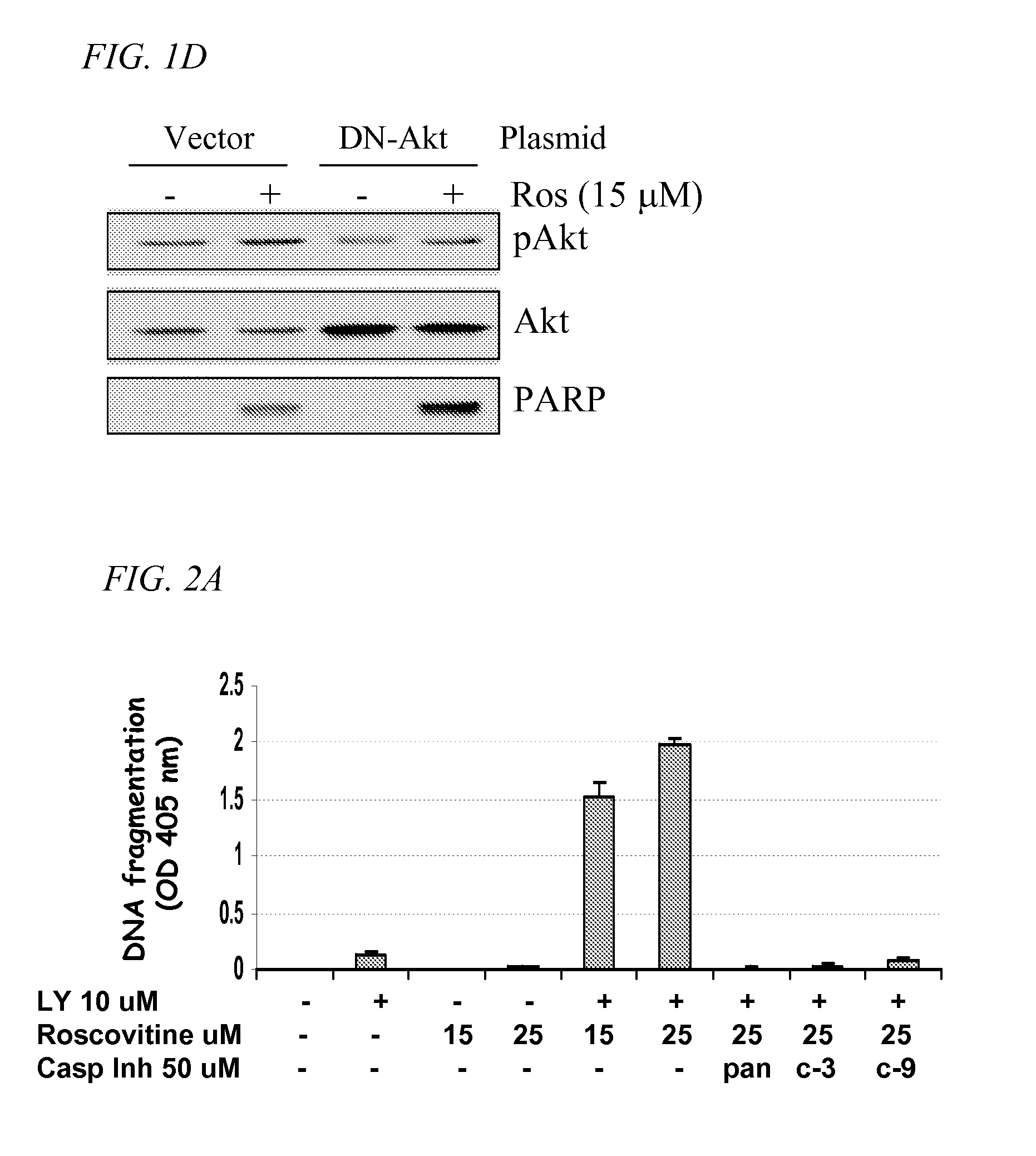
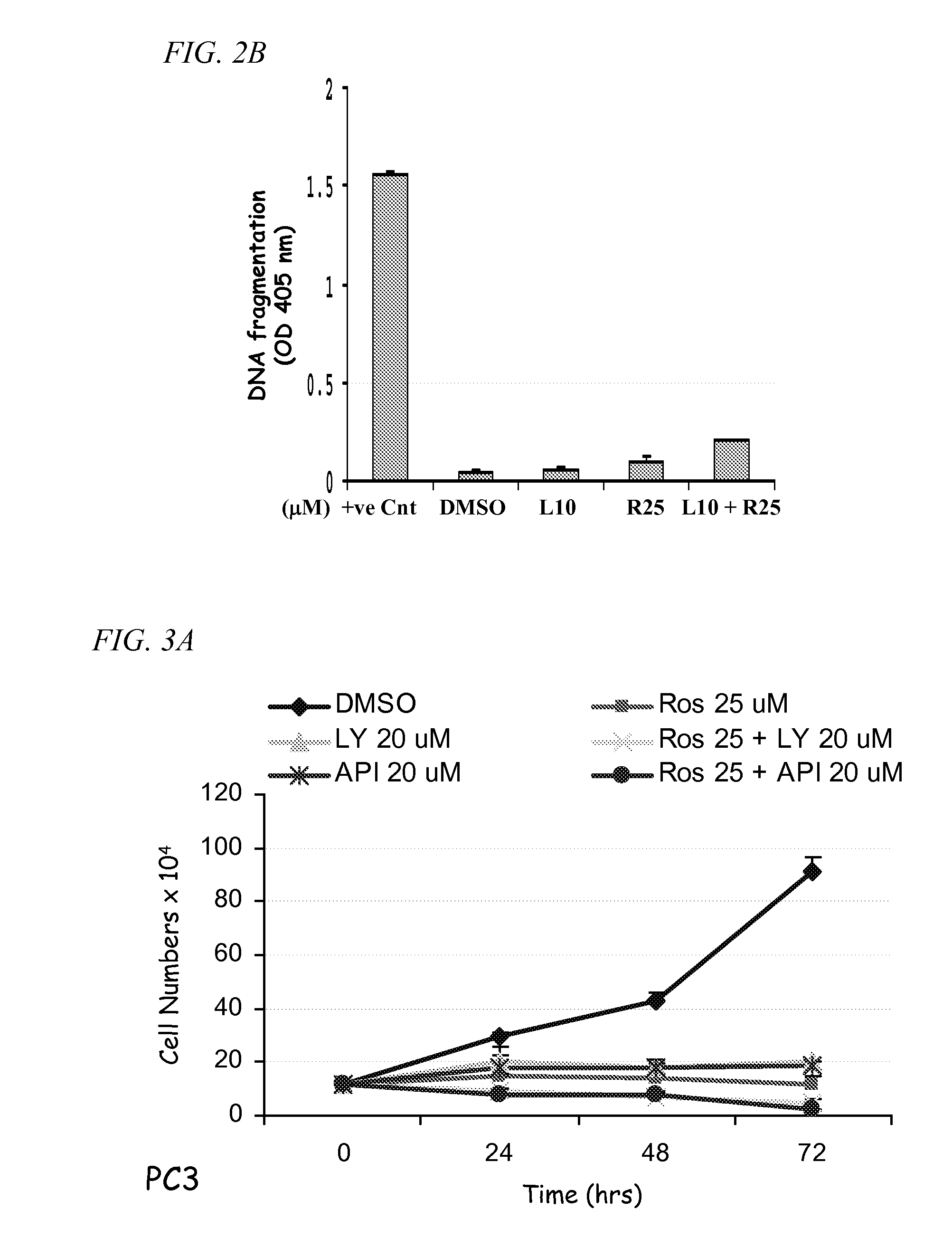
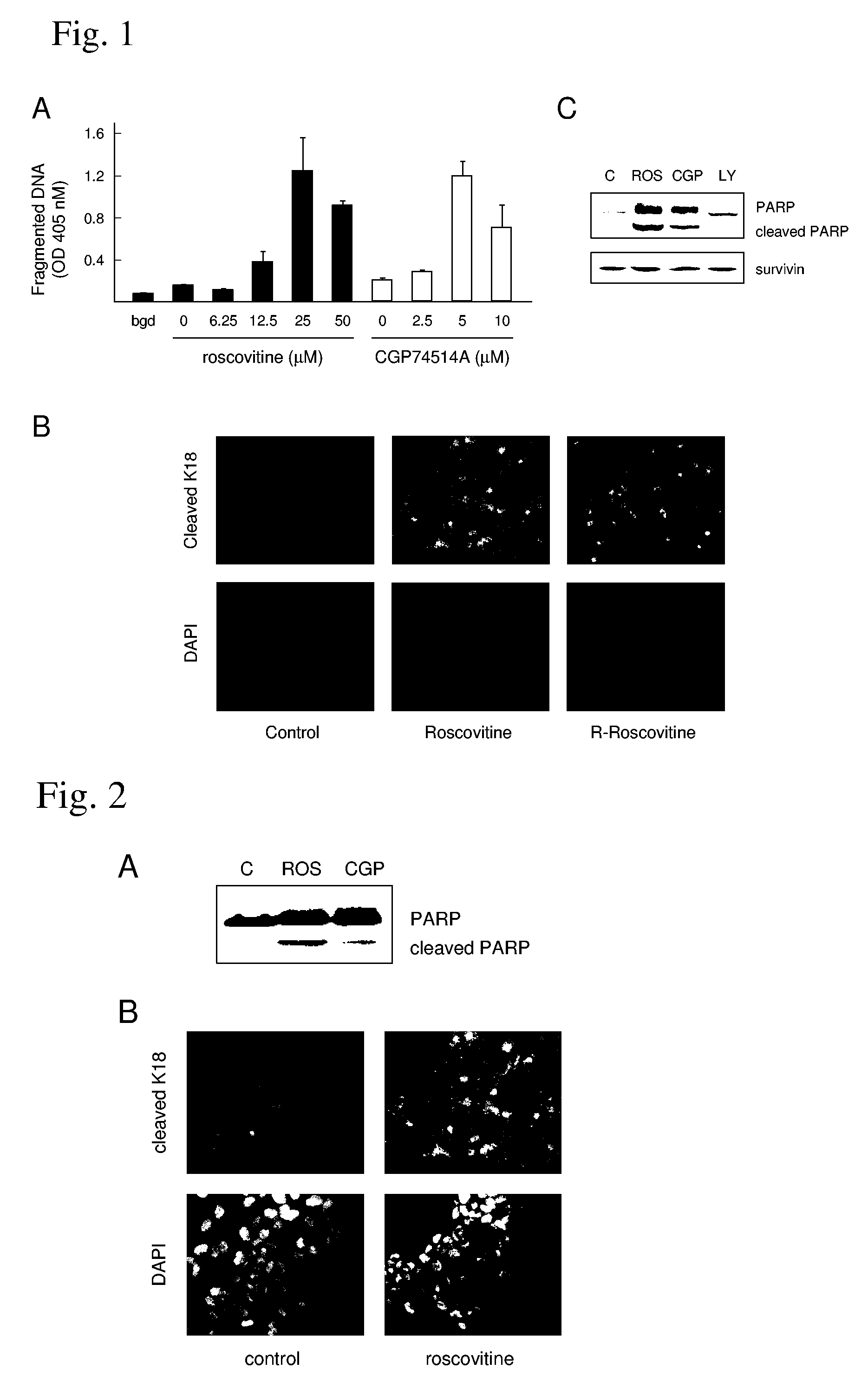
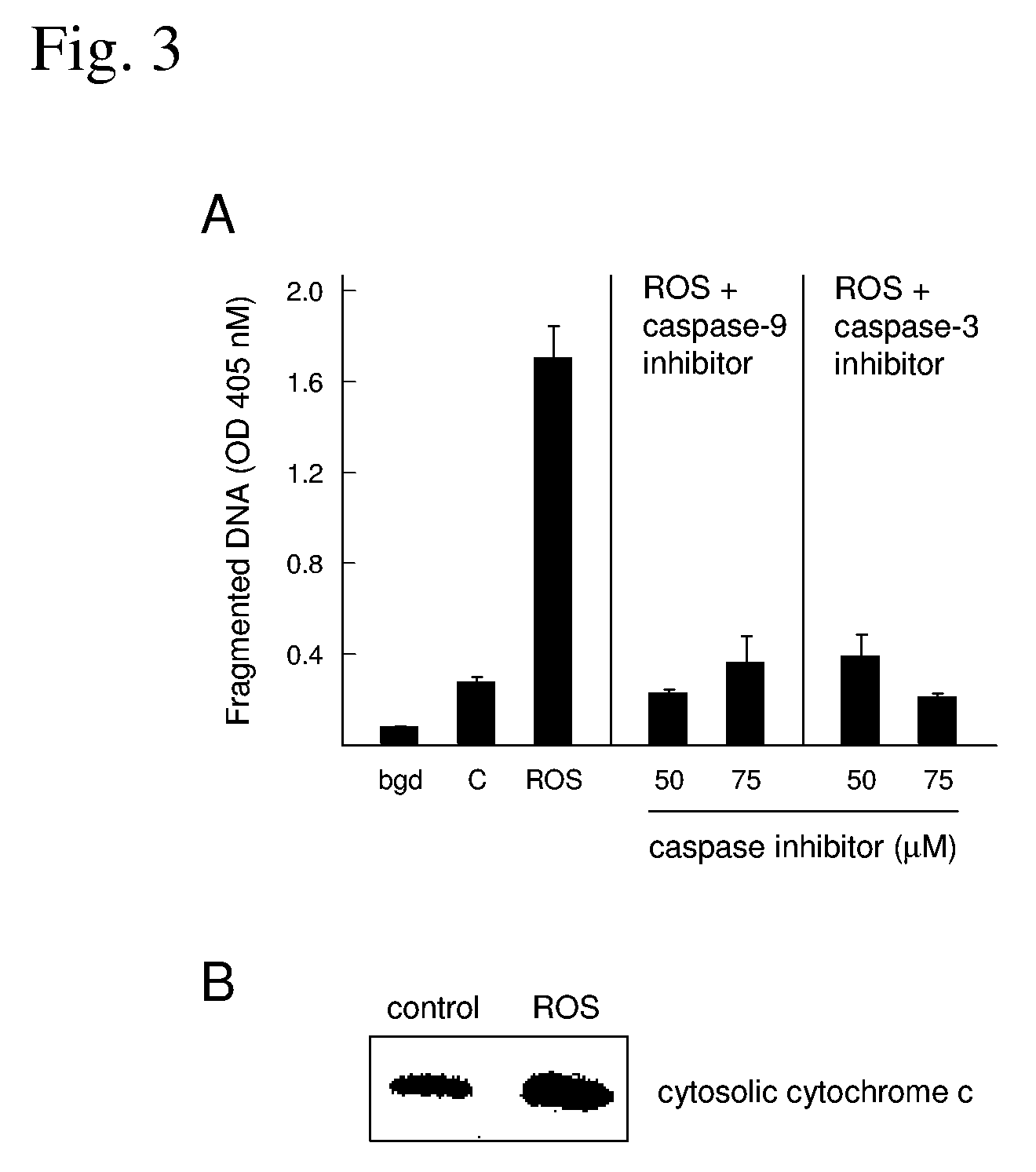
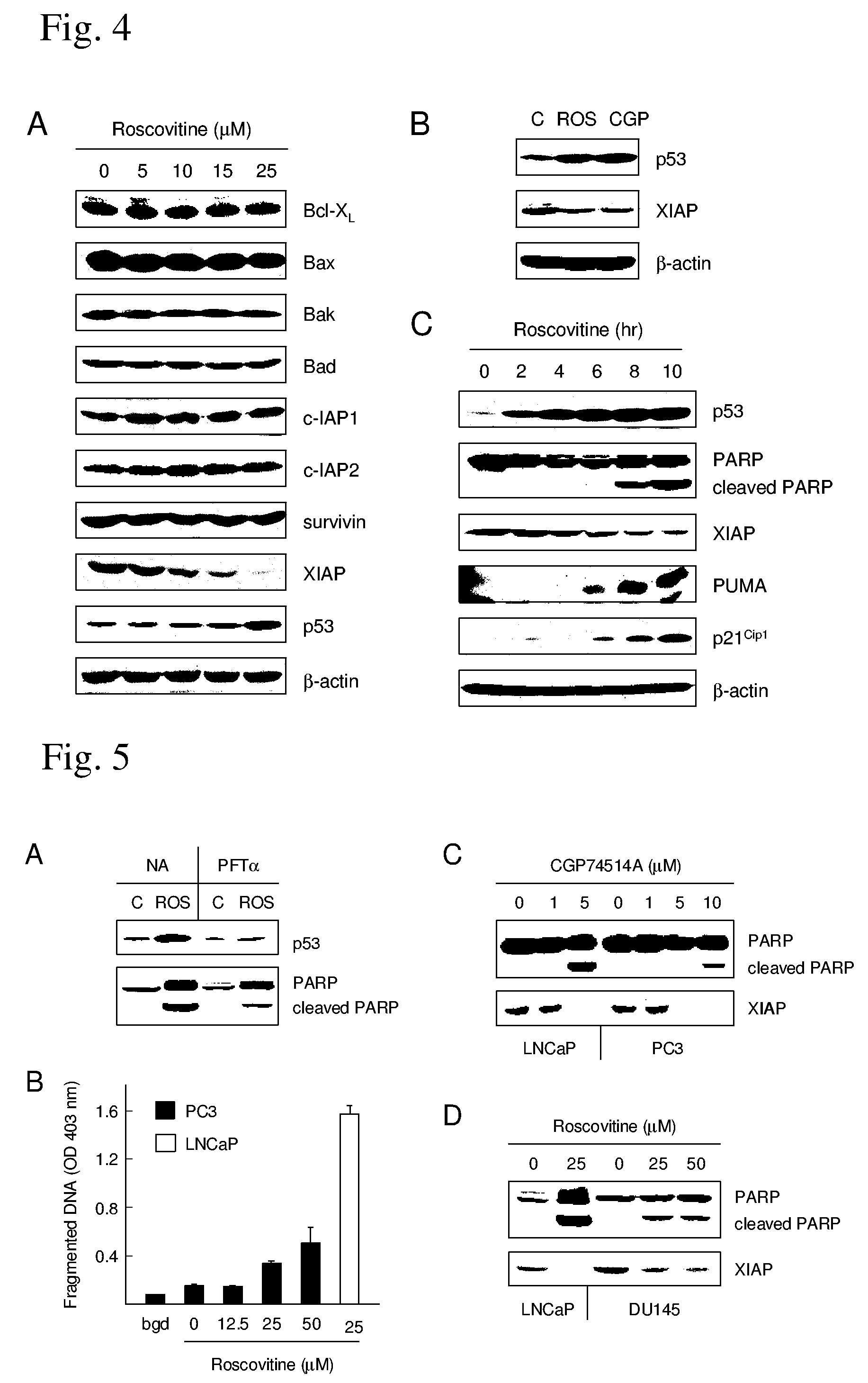
A treatment for cancer using a combination therapy including an inhibitor of the PI3K / Akt pathway in combination with roscovitine. It is shown that the combination of roscovitine and API-2 (Triciribine) or roscovitine and LY294002 induce the apoptosis of androgen-dependent (LNCaP) and androgen-independent (PC3) prostate cancer cells. Two important results have been observed. First, cells that respond to roscovitine alone (LNCaP) initiate apoptosis sooner when co-treated. Second, cells that do not respond to roscovitine alone (PC3) apoptose when co-treated, although with delayed kinetics. In the absence of roscovitine, AKT inhibitors had no effect on LNCaP or PC3 survival, and in both cell lines, the combined treatment activated the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Importantly, normal epithelial cells (RPWE) remained viable in the presence of roscovitine and AKT inhibitors. Events elicited by roscovitine (down-regulation of XIAP) and AKT inhibitors (accumulation of Bim) in LNCaP and PC3 cells are identified. Additional data show that PC3 cells apoptose when treated with AKT inhibitors and depleted of either XIAP or Cdk9. Taken together, these important results lead to improved treatments for cancers, such as prostate cancer, through the combination therapies taught herein.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Method of identifying and treating invasive carcinomas
InactiveUS6864093B1Reduce intrusionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProstate cancer cellMda mb 231
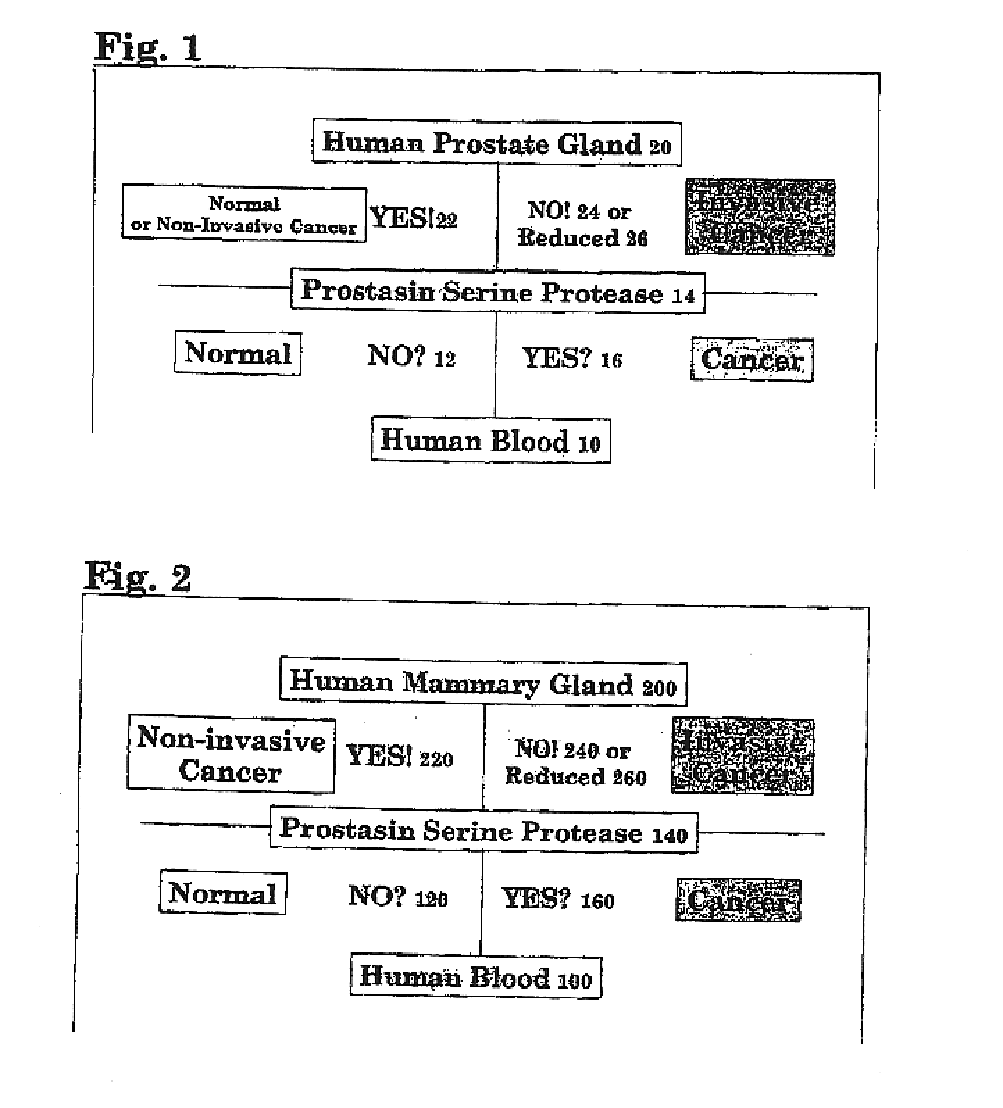
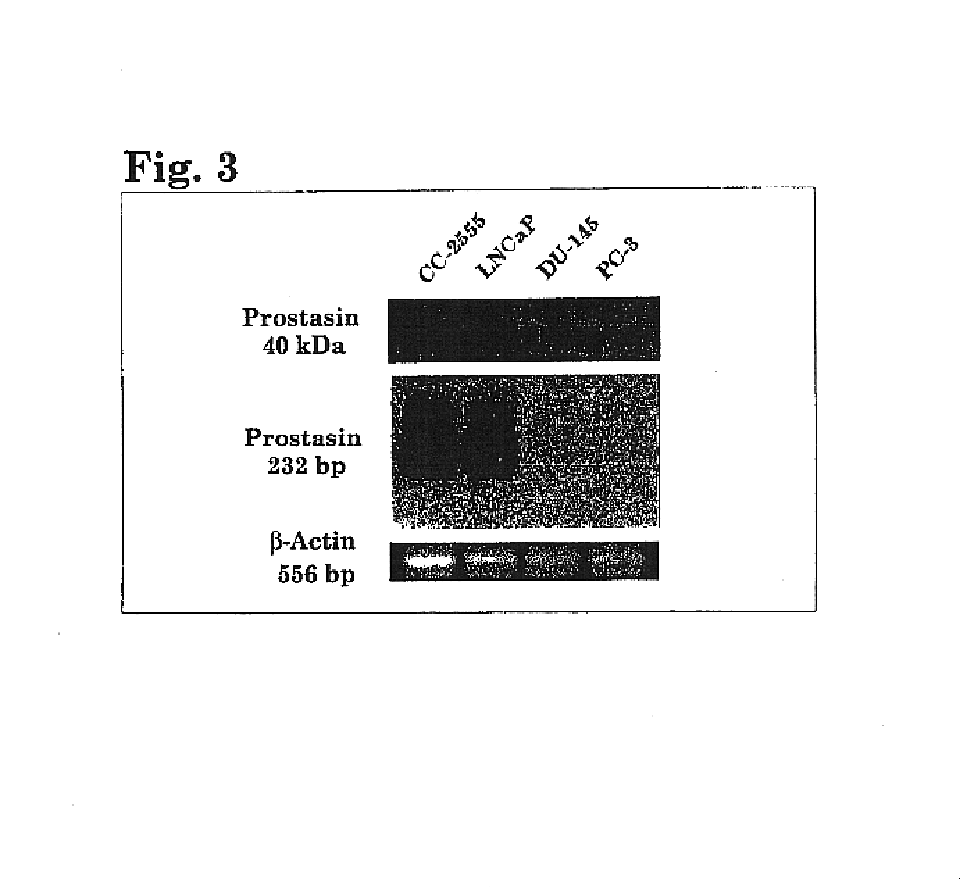
Prostasin protein has been found to be a useful marker for determination of the invasiveness of and as a means to treat human carcinomas. Using RT-PCR and western blot analyses, prostasin protein and mRNA expression were found in normal human prostate epithelial cells and the human prostate cancer cell line LNCaP, but not in the highly invasive human prostate cancer cell lines DU-145 and PC-3. Imunohistochemistry studies of human prostate cancer specimens revealed a down-regulation of prostasin in high-grade tumors. Using RT-PCR and western blot analyses, prostasin protein and mRNA expression were found in a non-invasive human breast cancer cell line, MCF-7, while invasive human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435s were found not to express either the prostasin protein or the mRNA. A non-invasive human breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-453, was shown to express prostasin mRNA but not prostasin protein. Transfection of DU-145 and PC-3 cells with a full-length human prostasin cDNA restored prostasin expression and reduced the in vitro invasiveness by 68% and 42%, respectively. Transfection of MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435s cells with a full-length human prostasin cDNA restored prostasin expression and reduced the in vitro invasiveness by 50% for either cell line. The prostasin gene promoter region was found to be hypermethylated at specific sites in invasive cancer cells.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
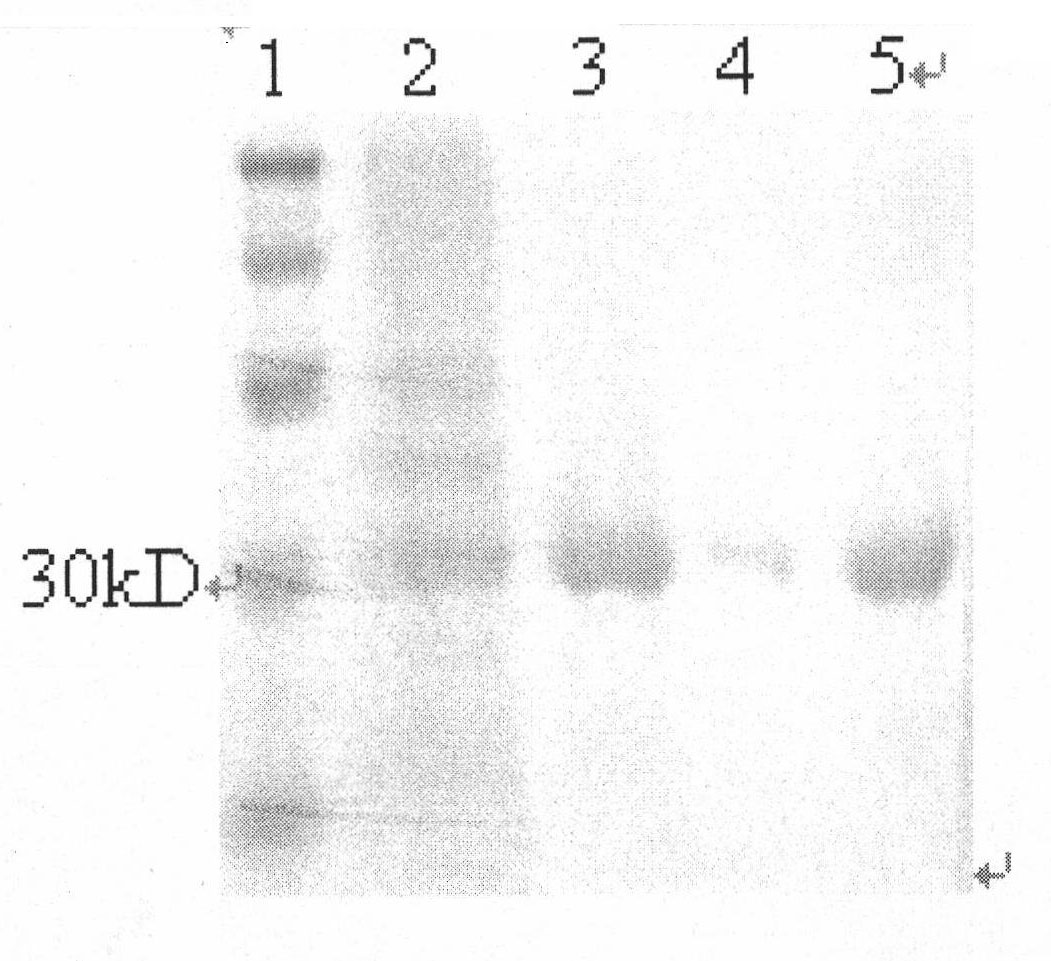
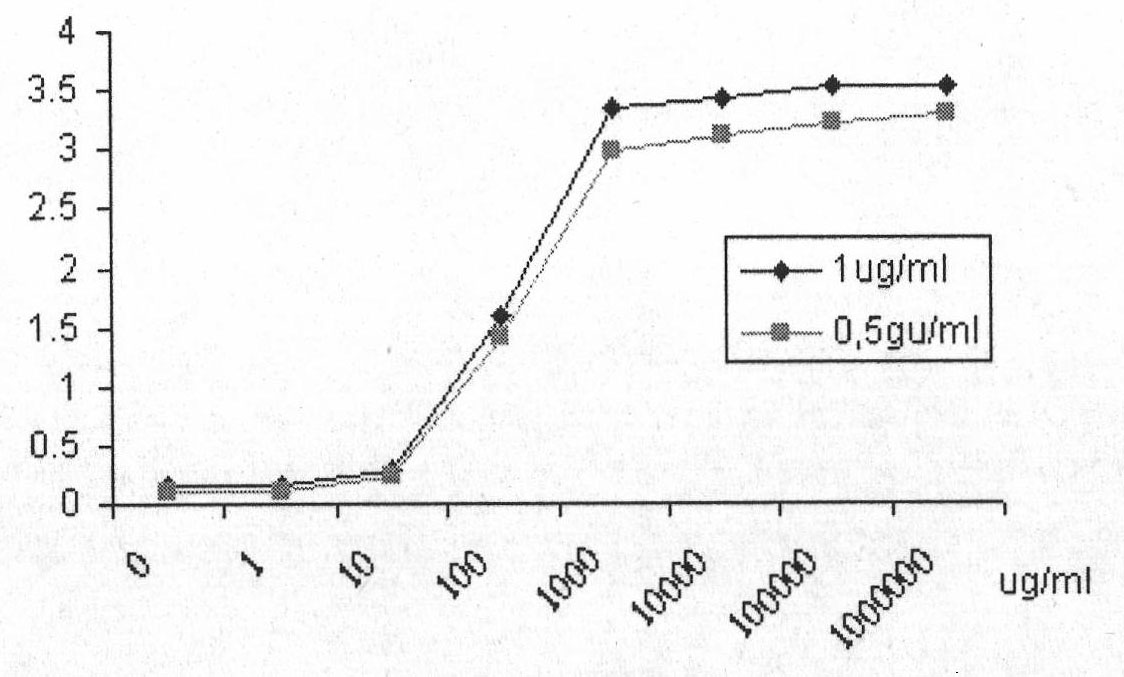
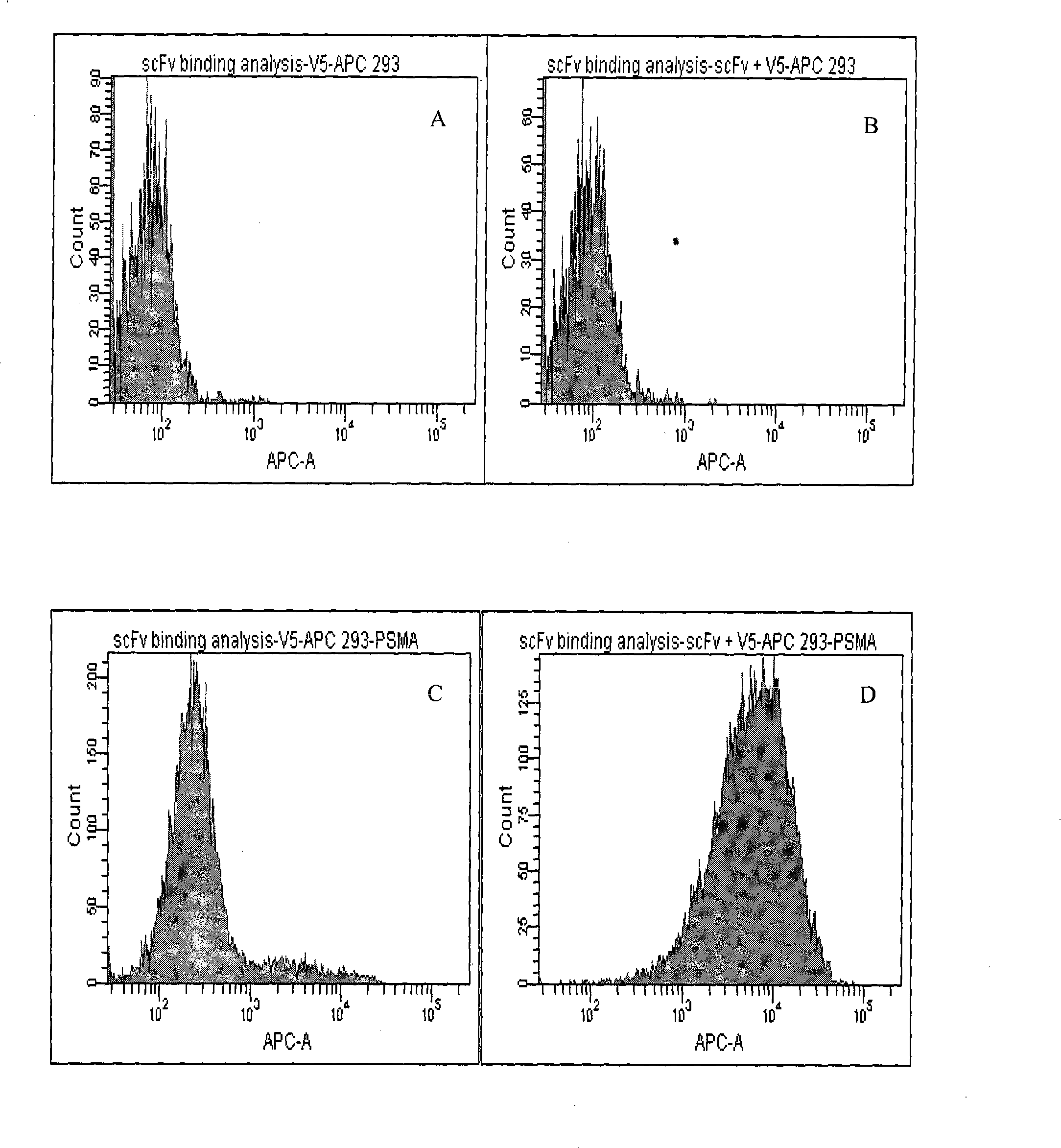
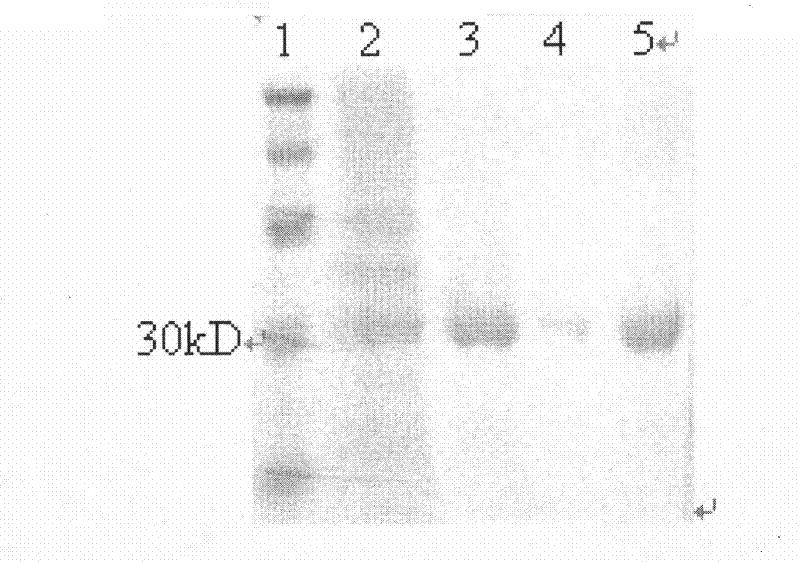
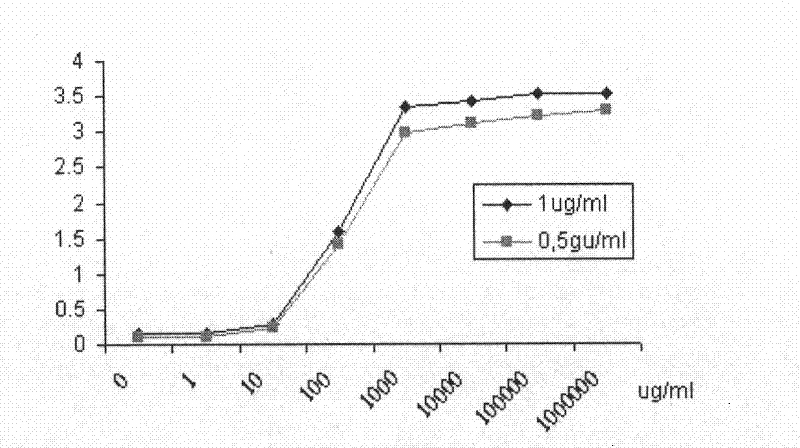
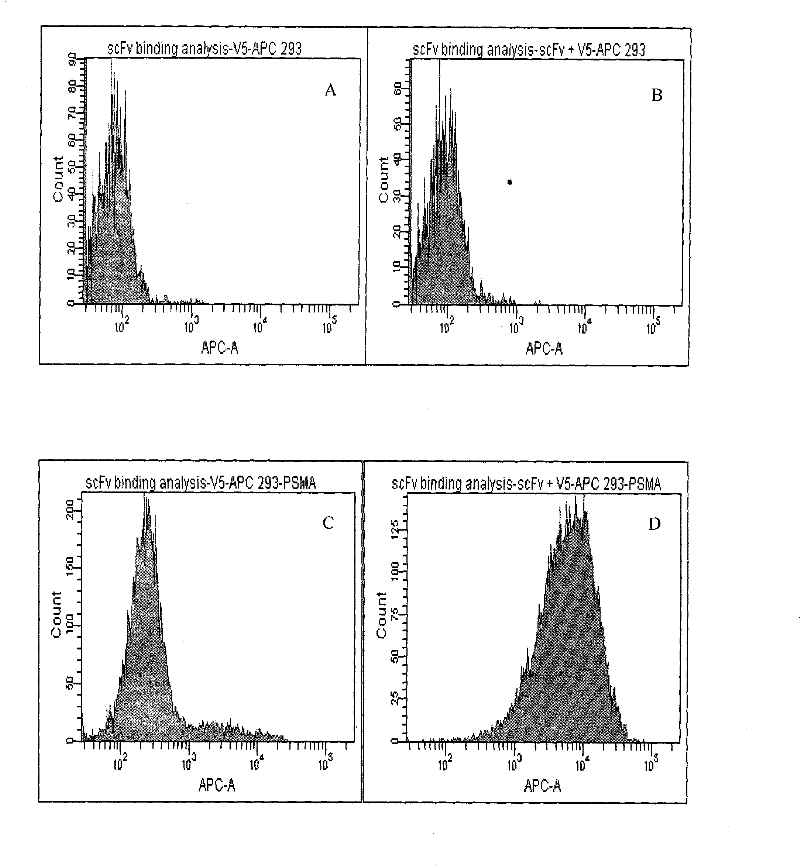
Single-chain antibody in anti-human prostate-specific membrane antigen extracellular region and application thereof
InactiveCN101891818AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsProstate cancer cellEscherichia coli
The invention provides a single-chain antibody in an anti-human prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) extracellular region, which adopts the phage display technology. The antibody is obtained by screening and enriching a large-storage capacity single-chain antibody library which is established by using peripheral blood mono-nuclear cells of a prostatic cancer patient through successive relaxation and rigorousness. The antibody can be solubly expressed in colon bacillus, and the affinity of the antibody with the prostate-specific membrane antigen extracellular region reaches Kd of 0.2nM. The antibody not only can be combined with the recombinant PSMA extracellular region, but also can be combined with NEK 293 cells with PSMA expressed on surface thereof and a prostate adenocarcinoma cell LNCaP, thus laying a foundation for adopting the antibody to perform prostate adenocarcinoma image diagnosis and guiding treatment.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
XIAP-Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapy
InactiveUS20070027169A1BiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProstate cancer cellMitochondria mediated apoptosis
A treatment for prostate cancer using cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors is provided. The effects of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors on the survival of prostate cancer cells was examined. Roscovitine, R-roscovitine, and CGP74514A were shown to induce the apoptosis of LNCaP and LNCaP-Rf cells, both of which express wild-type p53. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors of the present invention induce the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by a dual mechanism: p53 accumulation and XIAP depletion.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Application of triptophenolide as androgen receptor antagonist
ActiveCN105497045AAchieve contraceptive effectPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderProstate cancer cellDisease
The invention relates to the field of traditional Chinese medicine extract, and particularly discloses application of tripterygium wilfordii root extract triptophenolide (CAS number:74285-86-2) as an androgen receptor antagonist and application of triptophenolide to preparation of drugs for treating androgen disorders and drugs for male contraception. A reliable androgen activity screening method is constructed, the inhibiting effect of various kinds of traditional Chinese medicine extract on androgen receptor activity is tested, and finally it is found that the tripterygium wilfordii root extract triptophenolide is a novel androgen receptor antagonist and can inhibit activity of wild type and mutability androgen receptors. Further, anti-prostrate-cancer activity of triptophenolide is tested, and it is found that triptophenolide has good activity for AR (androgen receptor) positive prostrate cancer cells such as LNCaP and 22 RV1.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Toad lactam compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102382164AGood preventionGood therapeuticOrganic active ingredientsSteroidsHormoneHplc mass spectrometry
The invention discloses a toad lactam compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: mixing a toad lactone compound and ammonium acetate according to molar ratio of 1: (3-8); dissolving by utilizing organic solvent; reacting at a temperature of 100-160 DEG C for 0.5-3h under the protection of inert gas; decompressing, concentrating, removing the organic solvent; separating and purifying by utilizing a preparative high performance liquid chromatography method; and obtaining the toad lactam compound. The preparation method is simple, easy to carry out, safe, reliable and higher in yield. Proved by experiments, the toad lactam compound obtained in the invention has the advantages of good antitumor effect, very strong inhibitory action on various cancer cells such as PC3, DU145, LNCaP, MCF-7 and Hela, especially much better selective inhibitory action to hormone-dependent cancer cells such as the LNCaP and the MCF-7 than the toad lactone compound and remarkably lower toxicity to normal cells than the toad lactone compound. The toad lactam compound applied in preparing antitumor drugs has the advantages of being high in efficiency and low in toxicity and meeting the requirements of drug development.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
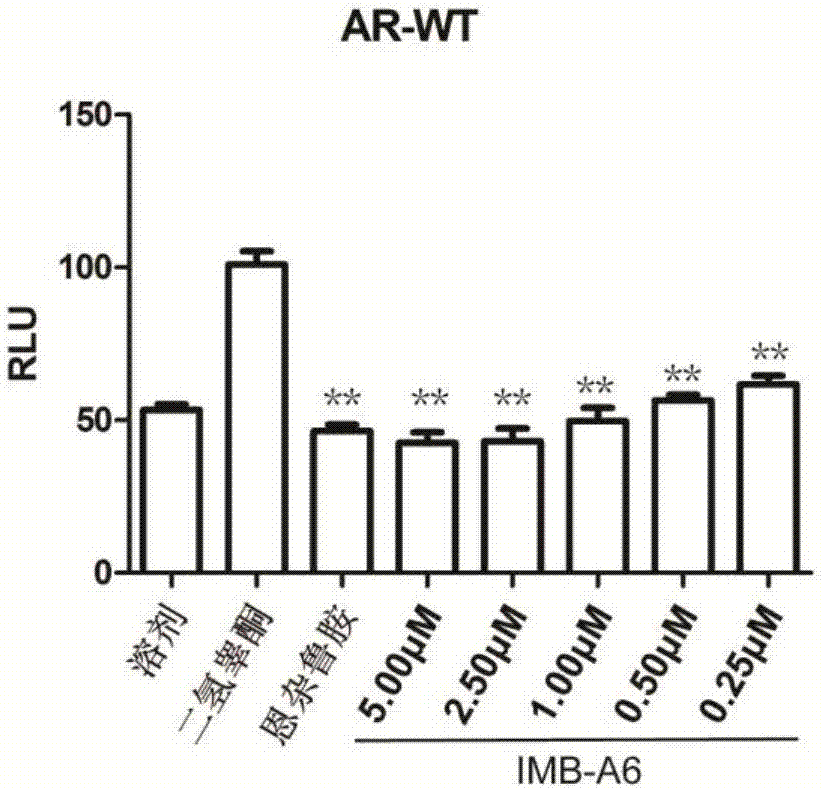
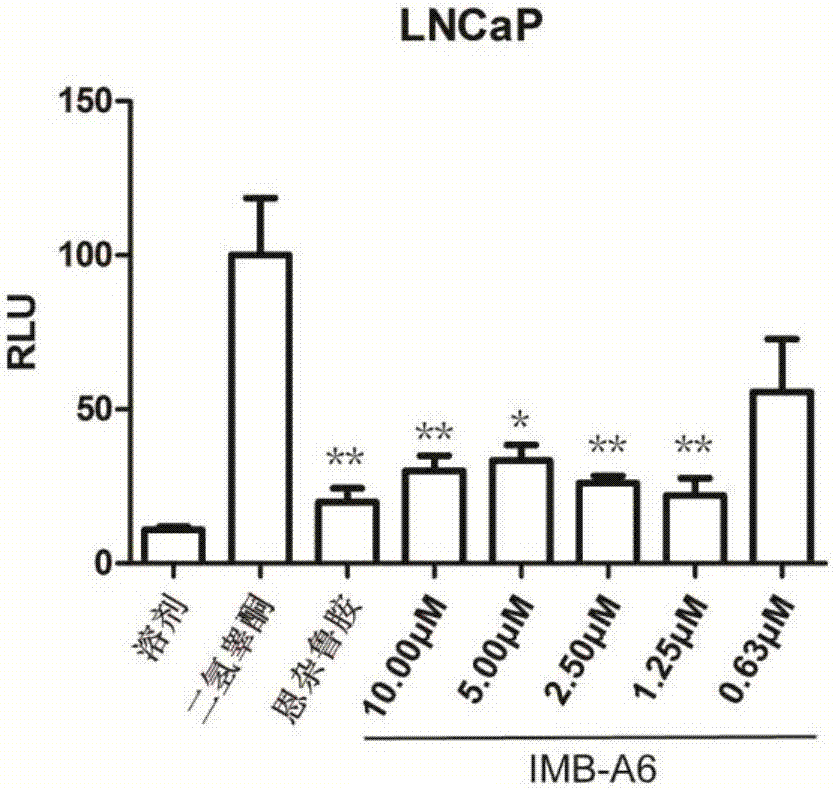
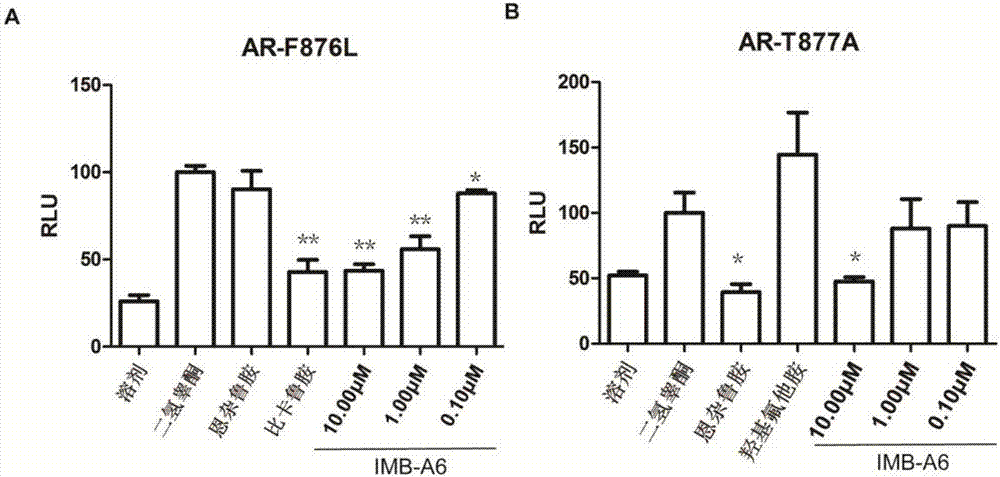
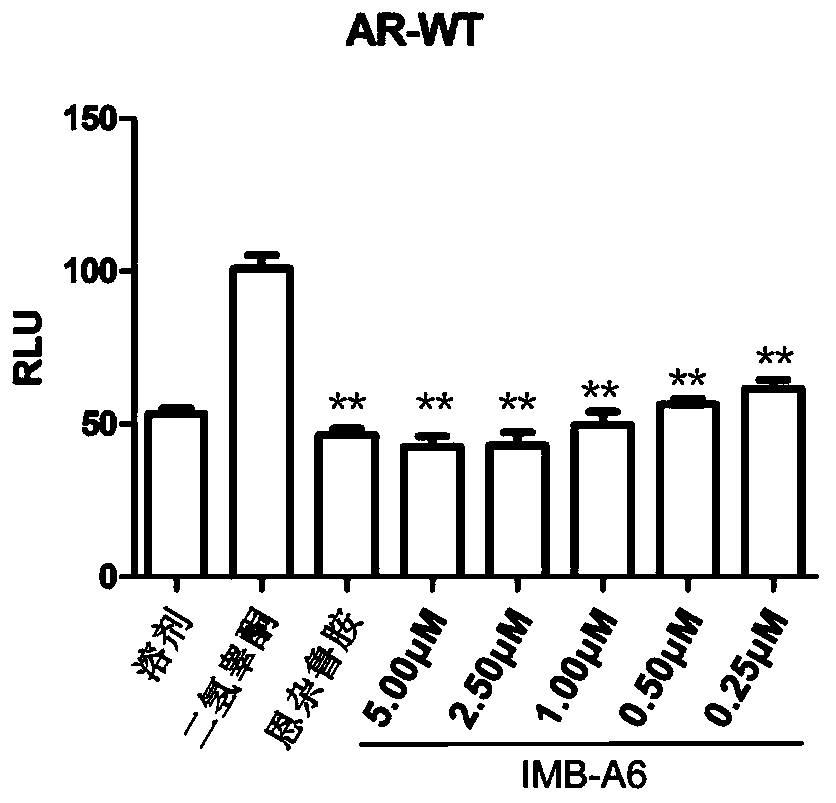
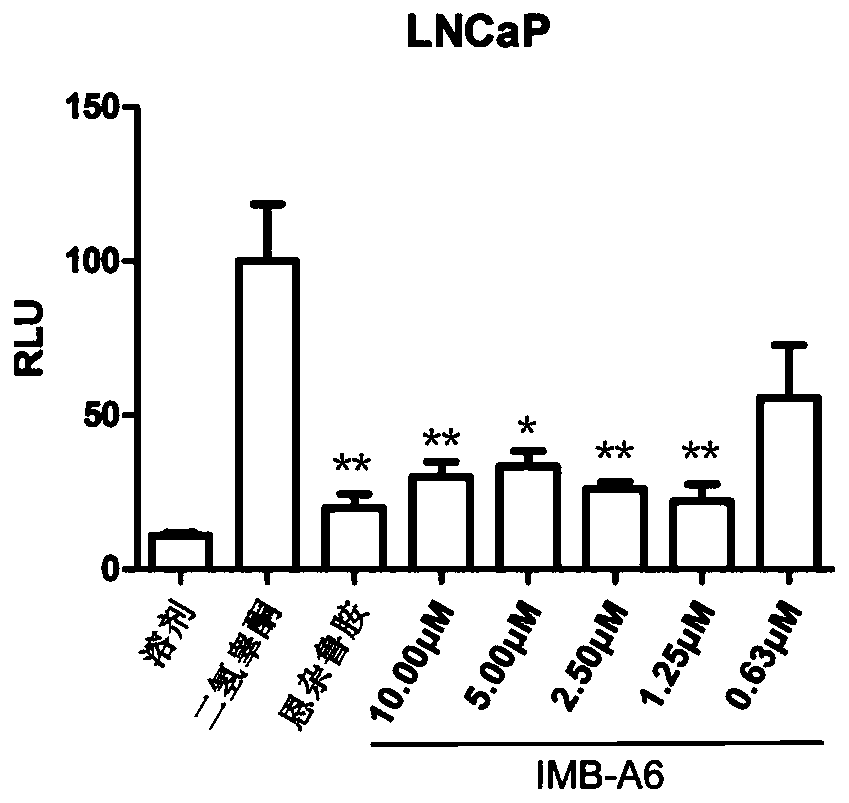
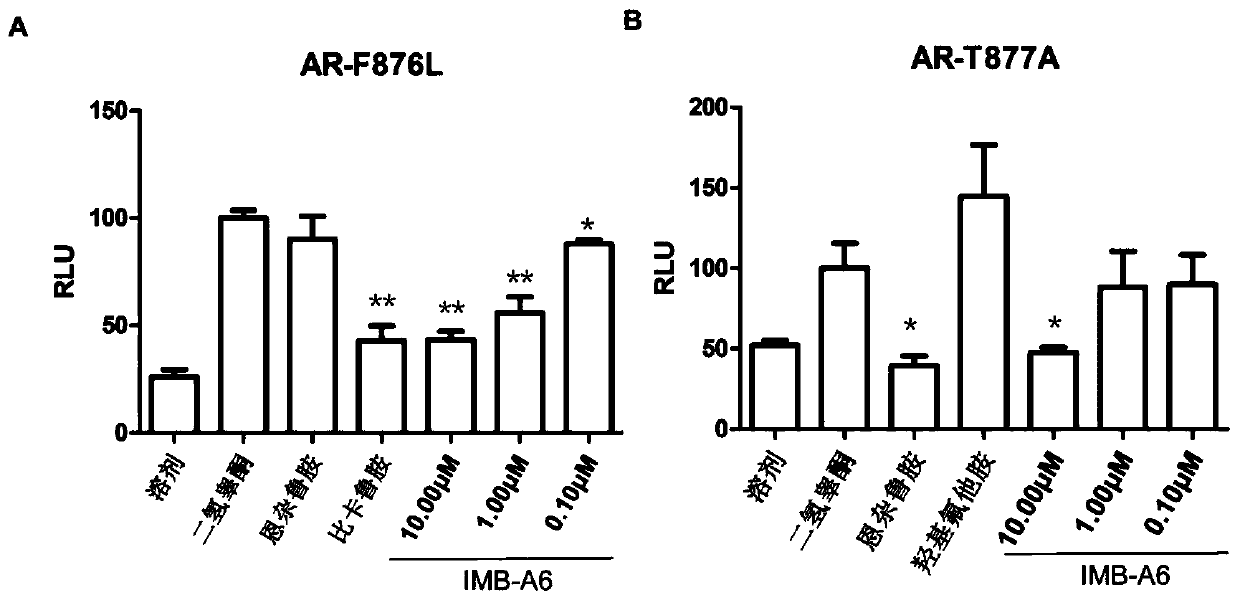
Application of IMB-A6 serving as androgen receptor antagonist
ActiveCN106902112AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh activityUrinary disorderDermatological disorderDiseaseProstate cancer cell
The invention relates to the field of medicine primers, and particularly discloses an application of IMB-A6 serving as an androgen receptor antagonist and an application of the IMB-A6 to preparation of androgen imbalance disease treating medicines and male contraception pills. By building a reliable androgen activity screening method, the inhibiting effect of a plurality of medicine primers on androgen receptor activity is tested to finally find that the IMB-A6 is a novel androgen receptor antagonist, and activity of wild and mutagenic androgen receptors can be inhibited. Further, activity of the prostate cancer resistance of the IMB-A6 is tested to find that the IMB-A6 has good activity for AR positive prostate cancer cells such as LNCaP and has no activity for AR negative prostate cancer cells, the expression activity of the androgen receptors can be inhibited, and the IMB-A6 is similar to positive medicines such as enzalutamide.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
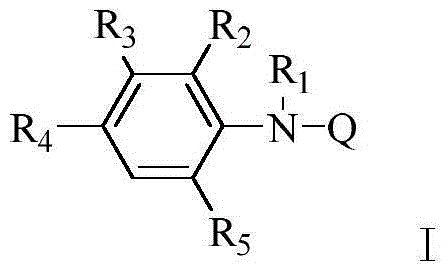
Application of N-heteroaryl phenylamine compounds for preparation of antitumor drugs
ActiveCN105267214AAntineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsBladder cancerProstatic Cancers
The invention discloses an application of N-heteroaryl phenylamine compounds for preparation of antitumor drugs; the N-heteroaryl phenylamine compounds are represented by the general formula I, wherein in the formula, definitions of all substituents are shown in the description. The compounds represented by the general formula (I) have good antitumor activity, and especially have excellent activity on lung cancer A549 and H460, bladder cancer T24 and J82, prostatic cancer LNCap and PC-3 and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF CHEM IND
Application of bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 or its medicinal salt in preparing anticancer medicaments
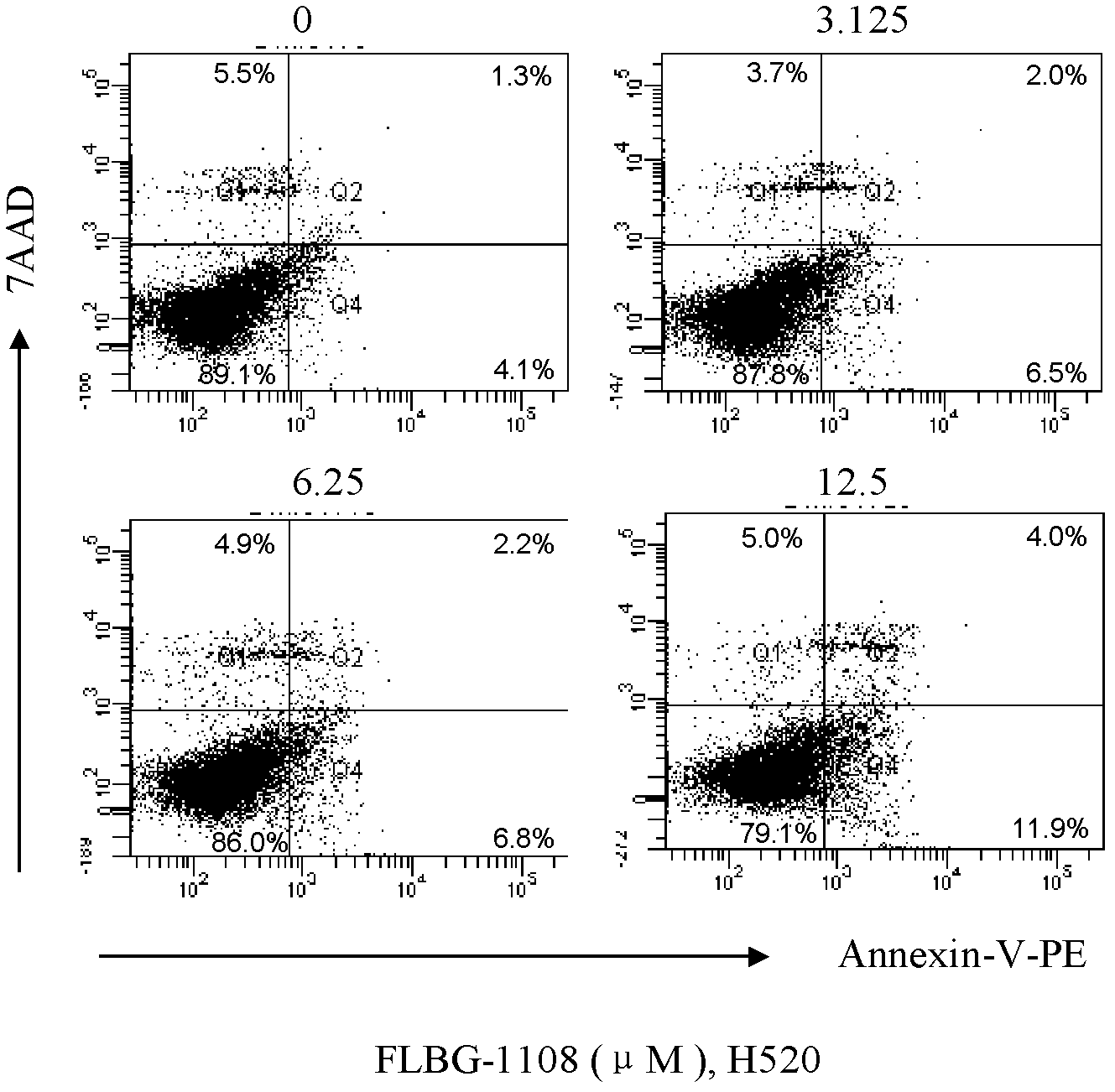
InactiveCN102440985APrevent proliferationHas anticancer effectOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderCytotoxicityOncology
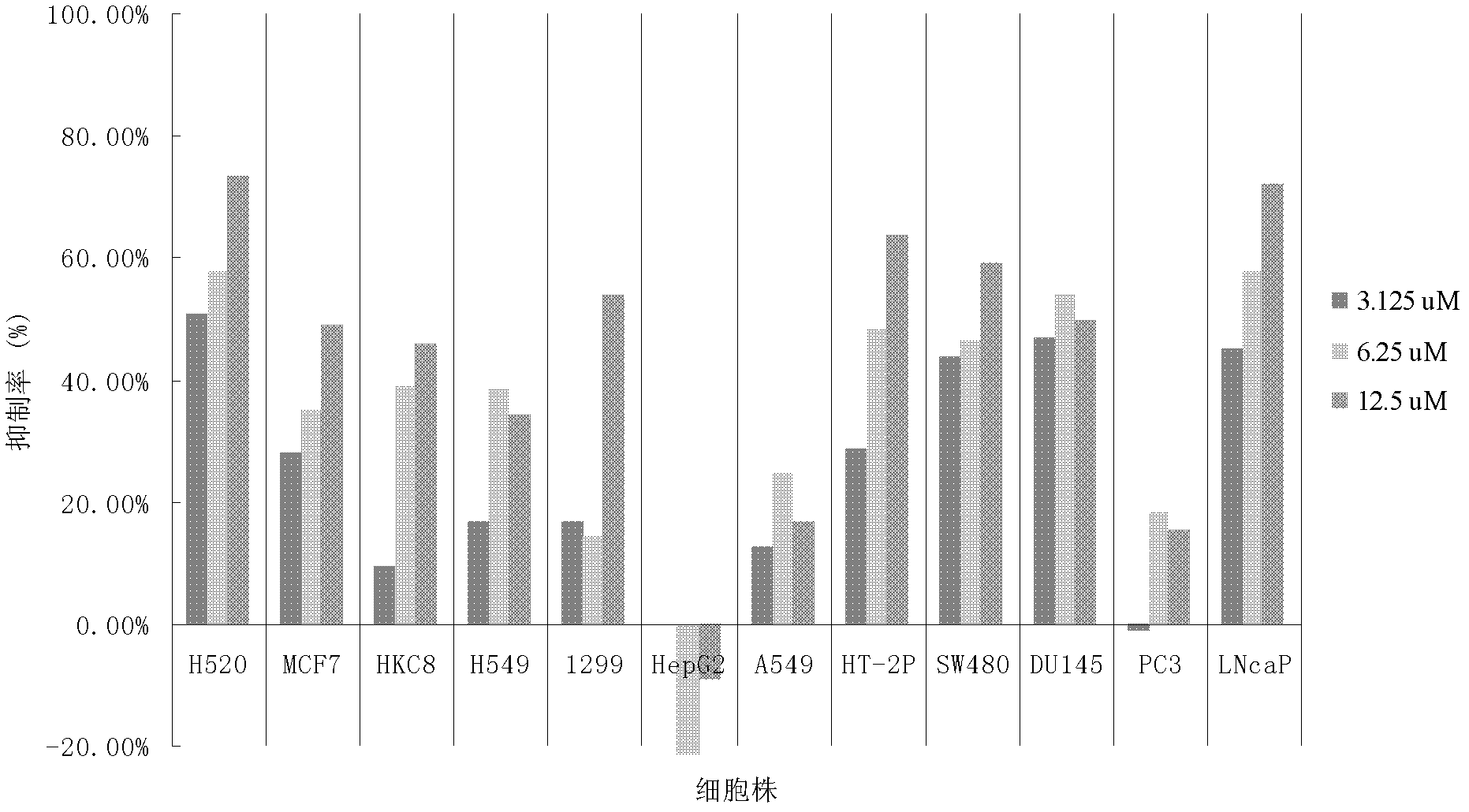
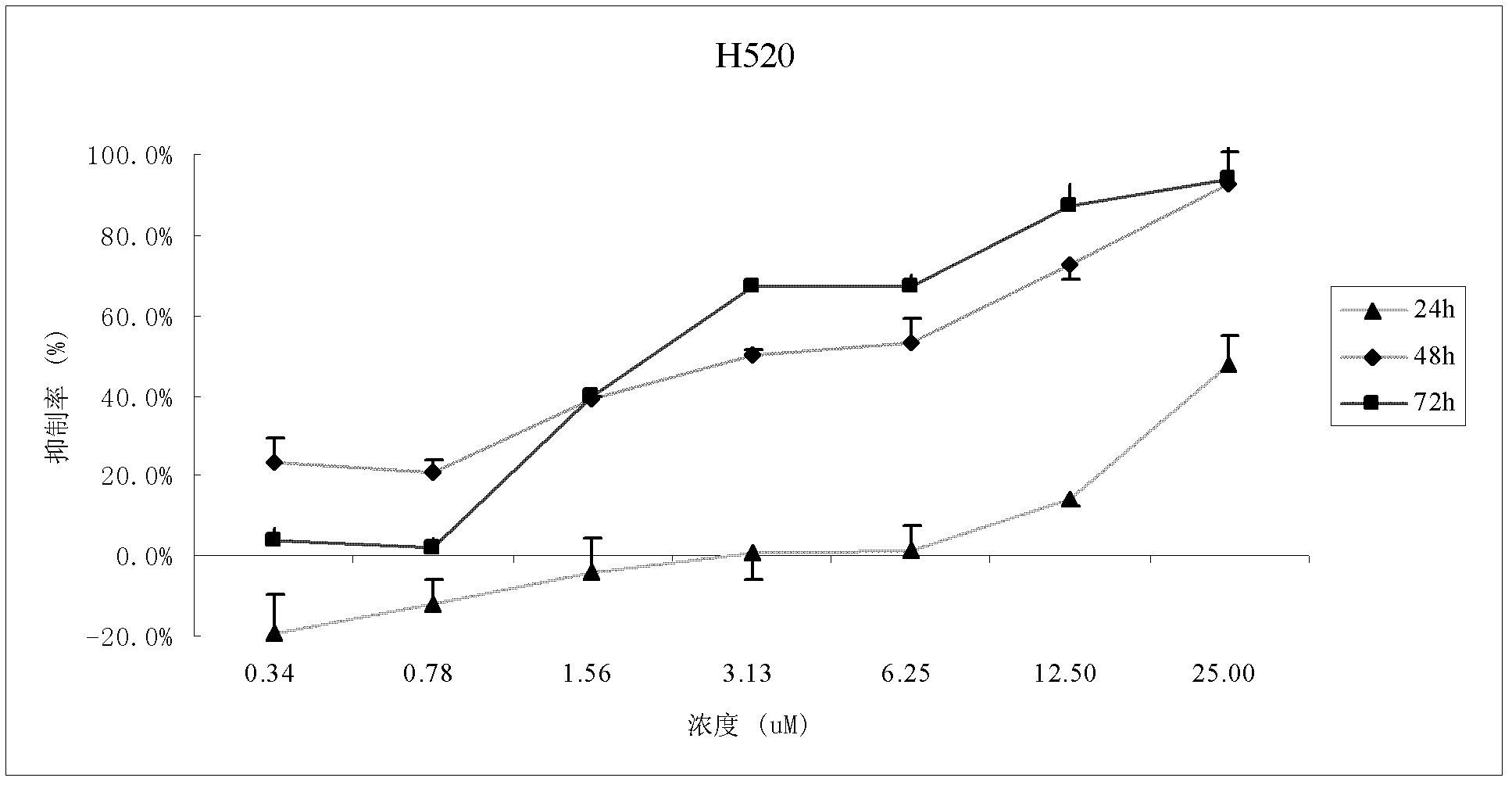
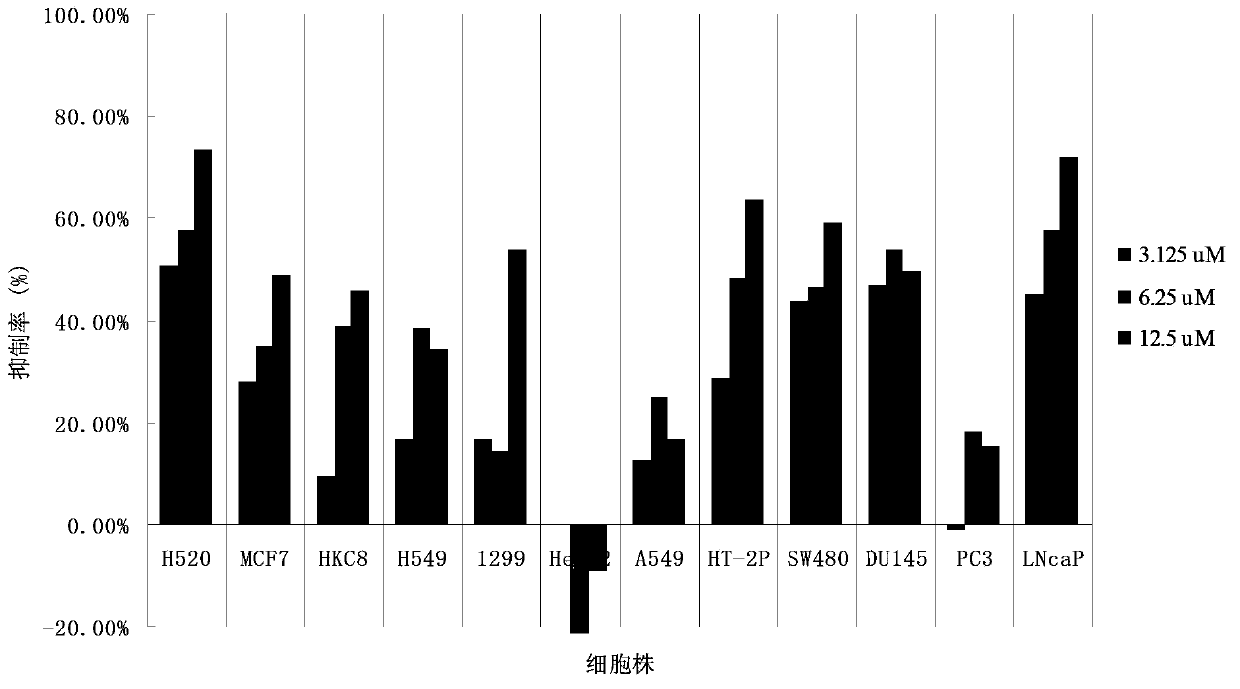
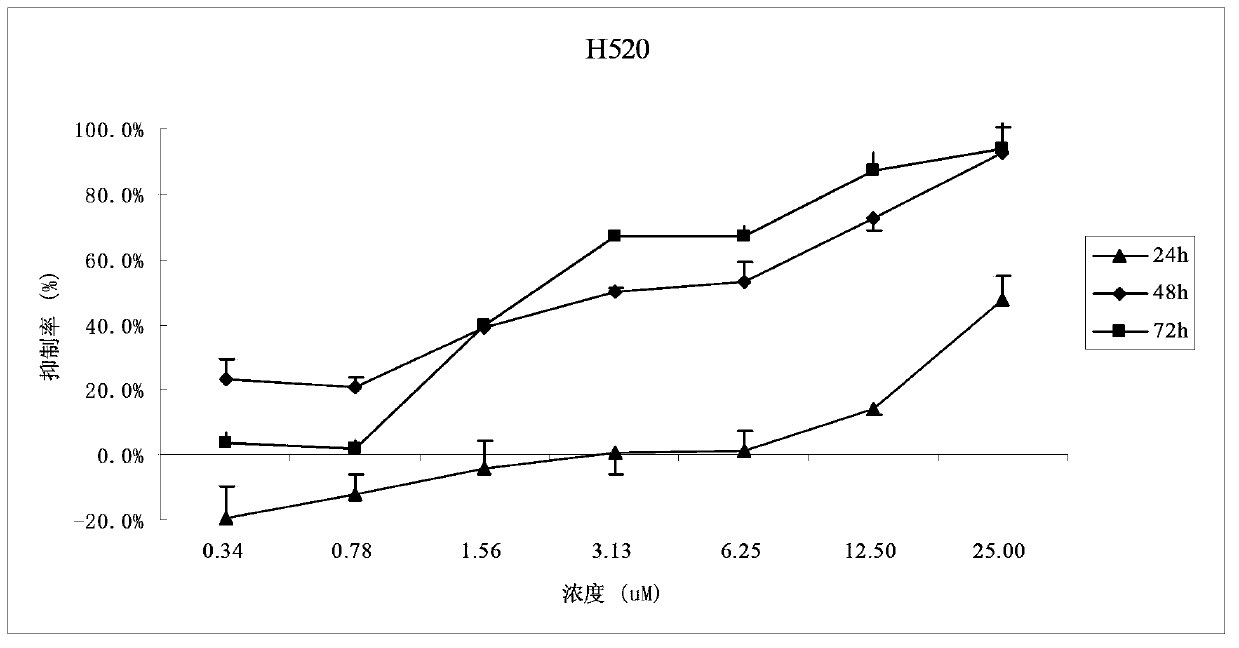
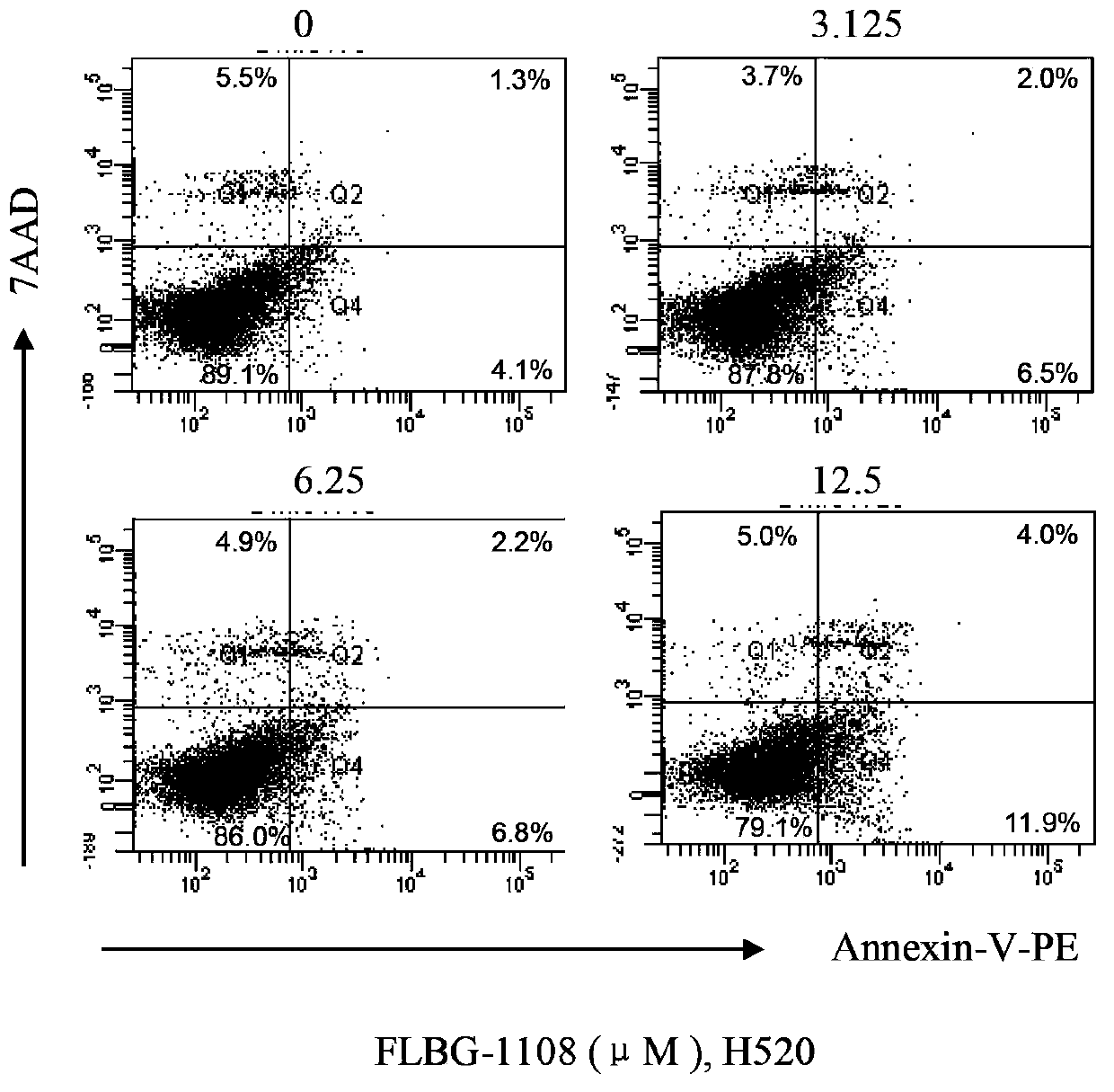
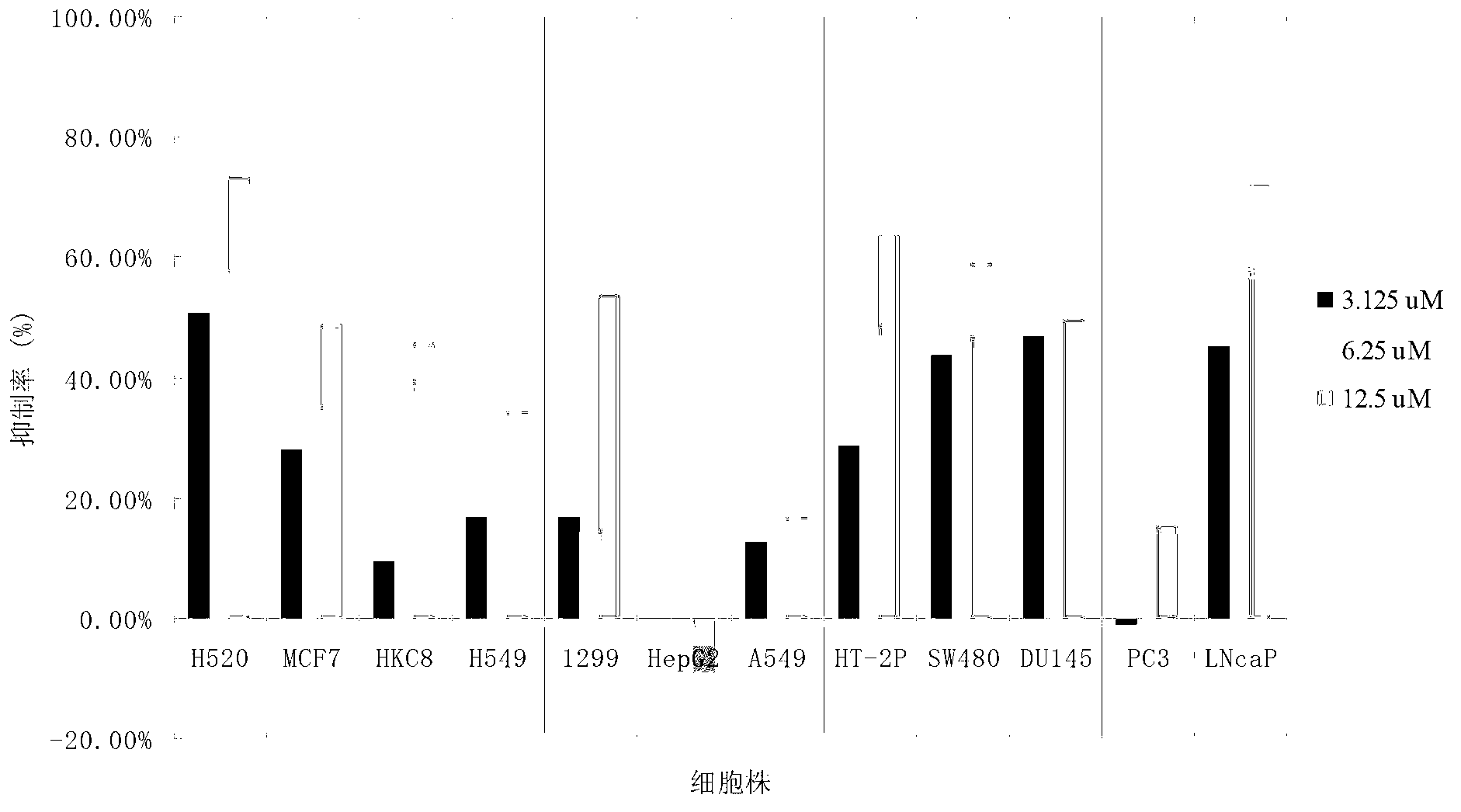
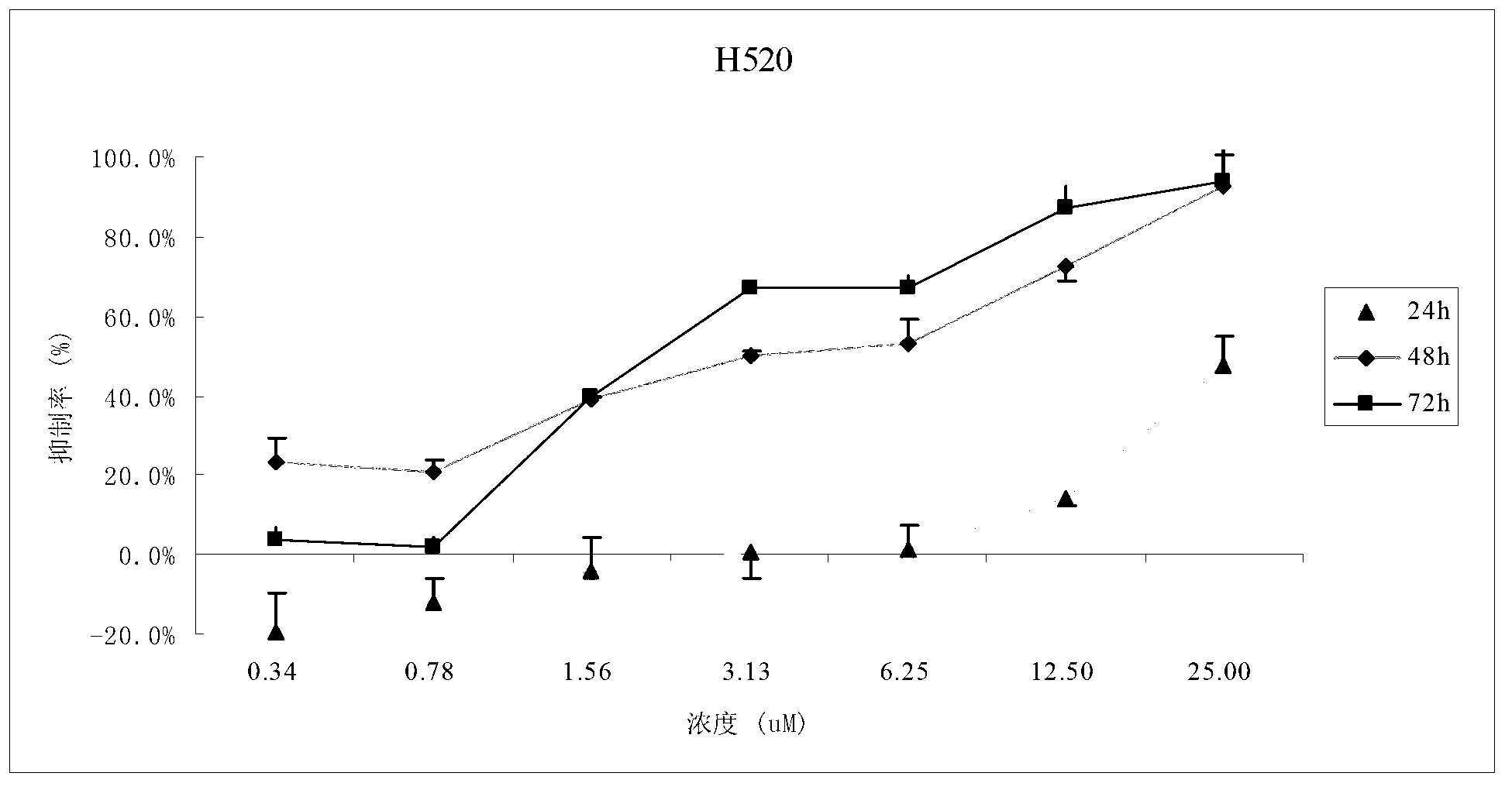
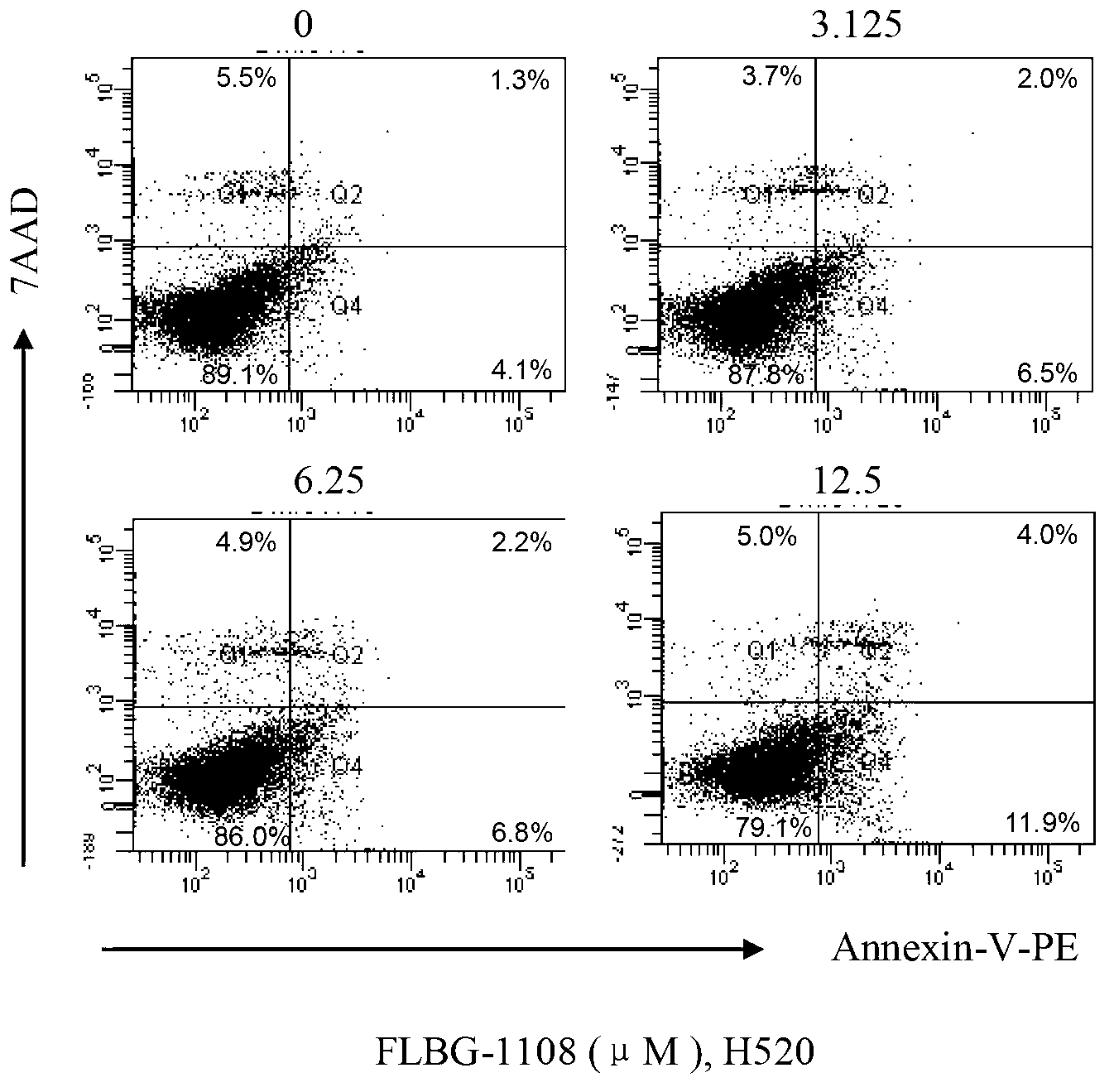
The invention discloses application of a bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 or its medicinal salt in preparing anticancer medicaments. The invention, by means of experiments, finds that the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 has an obvious inhibition effect on propagation of human non-small cell lung cancer H520, A549, H549, 1299, human breast cancer cell MCF7, human prostatic cancer cell PC3, LNcaP, DU145, as well as human intestinal cancer cell SW480 and HT-2P, can selectively inhibit the propagation of the human lung cancer cell H520, and presents good time and concentration dependence. After 48h of action, the IC50 value is 2.90 micrometers, which shows no cytotoxicity to a normal kidney epidermal cell. Further, the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 is found to play an effective role in inducing apoptosis of the lung cancer cell H520, preventing propagation of cancer cells but showing no toxicity, and can specifically block the cell cycle of the lung cancer cell H520 in S stage, thus inhibiting the propagation of cancer cells. Therefore, the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 can be developed into novel candidate medicaments with an anticancer effect, especially an anti-lung cancer effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN XIANHU BOTANICAL GARDEN ADMINISTRATION
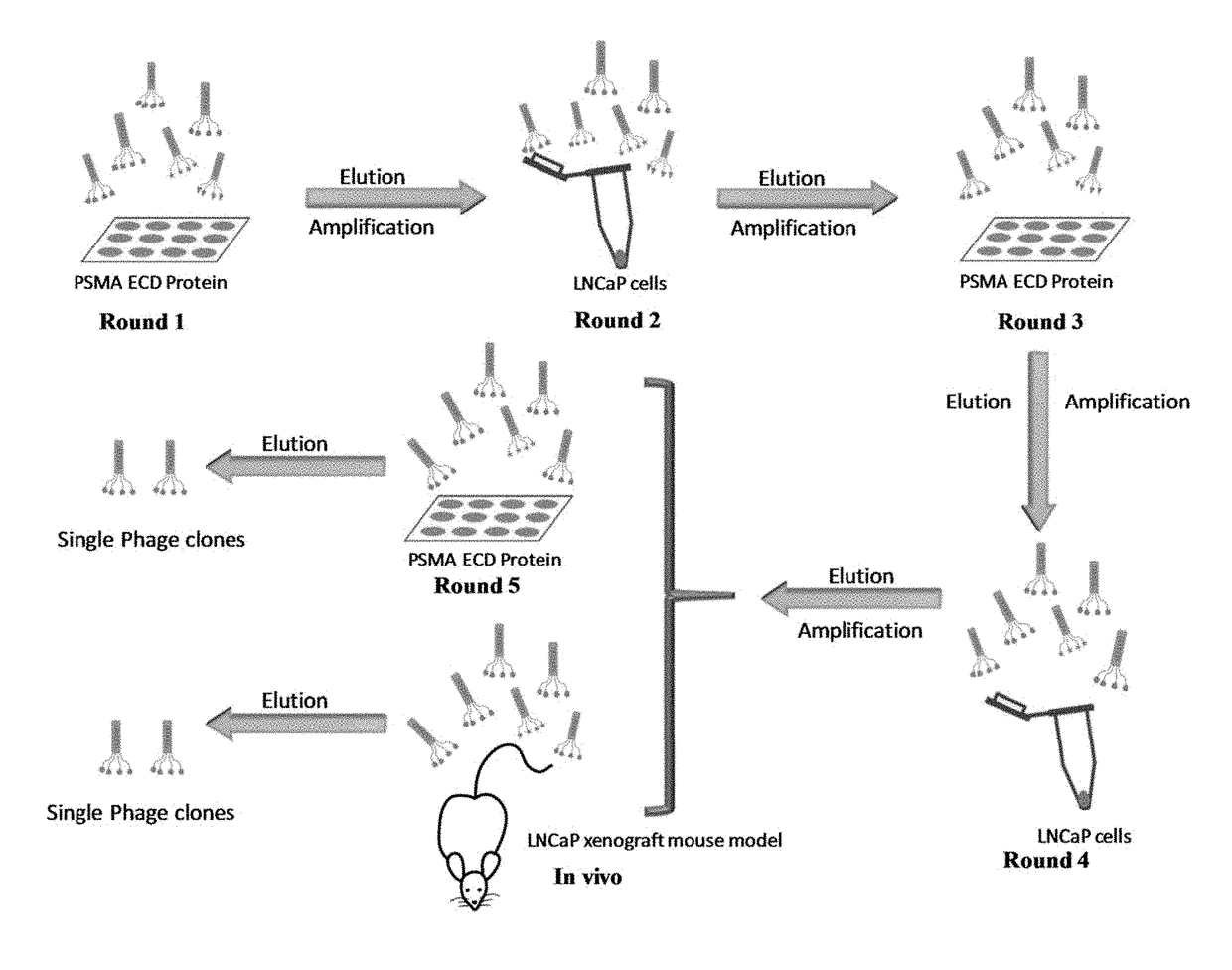
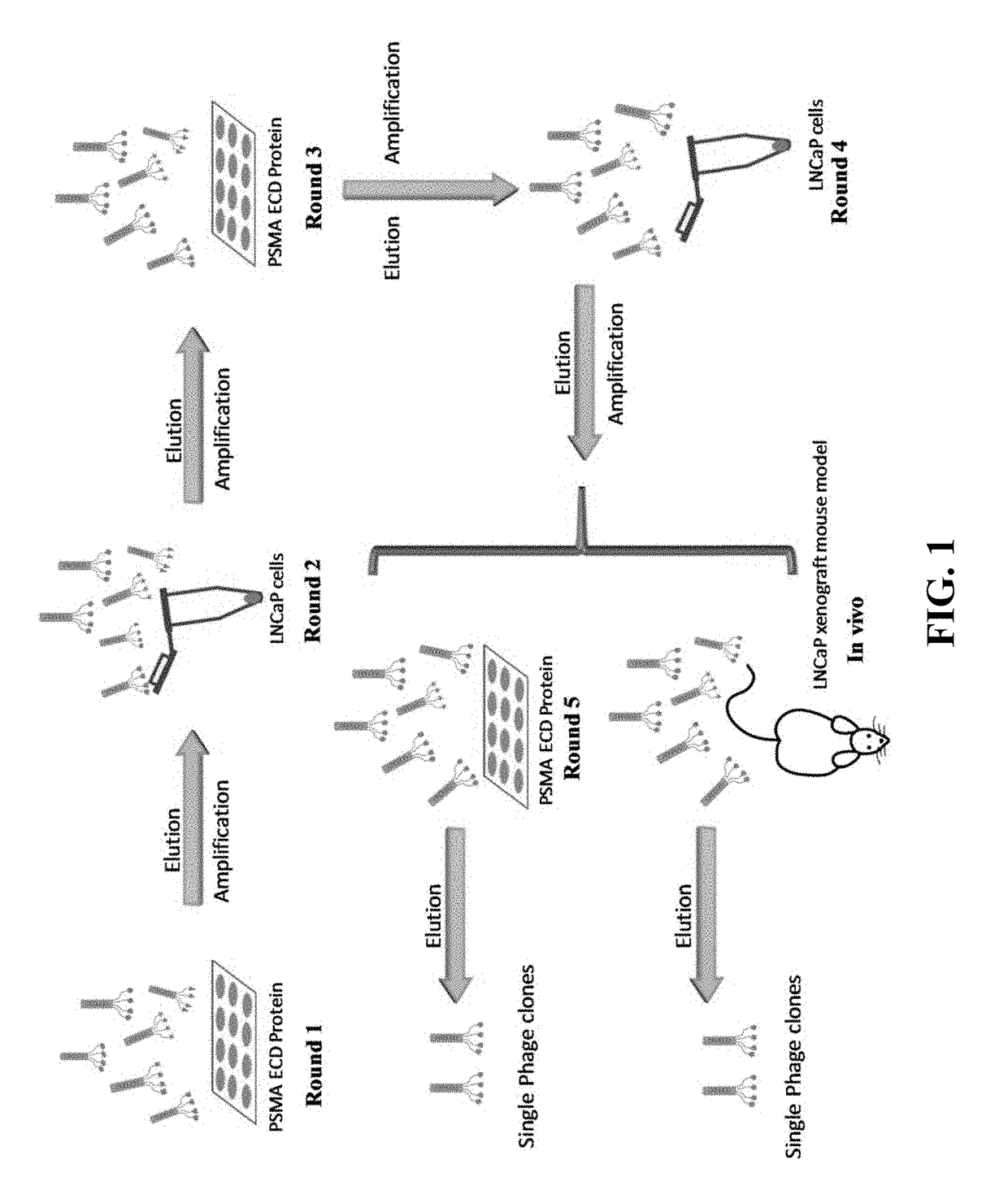
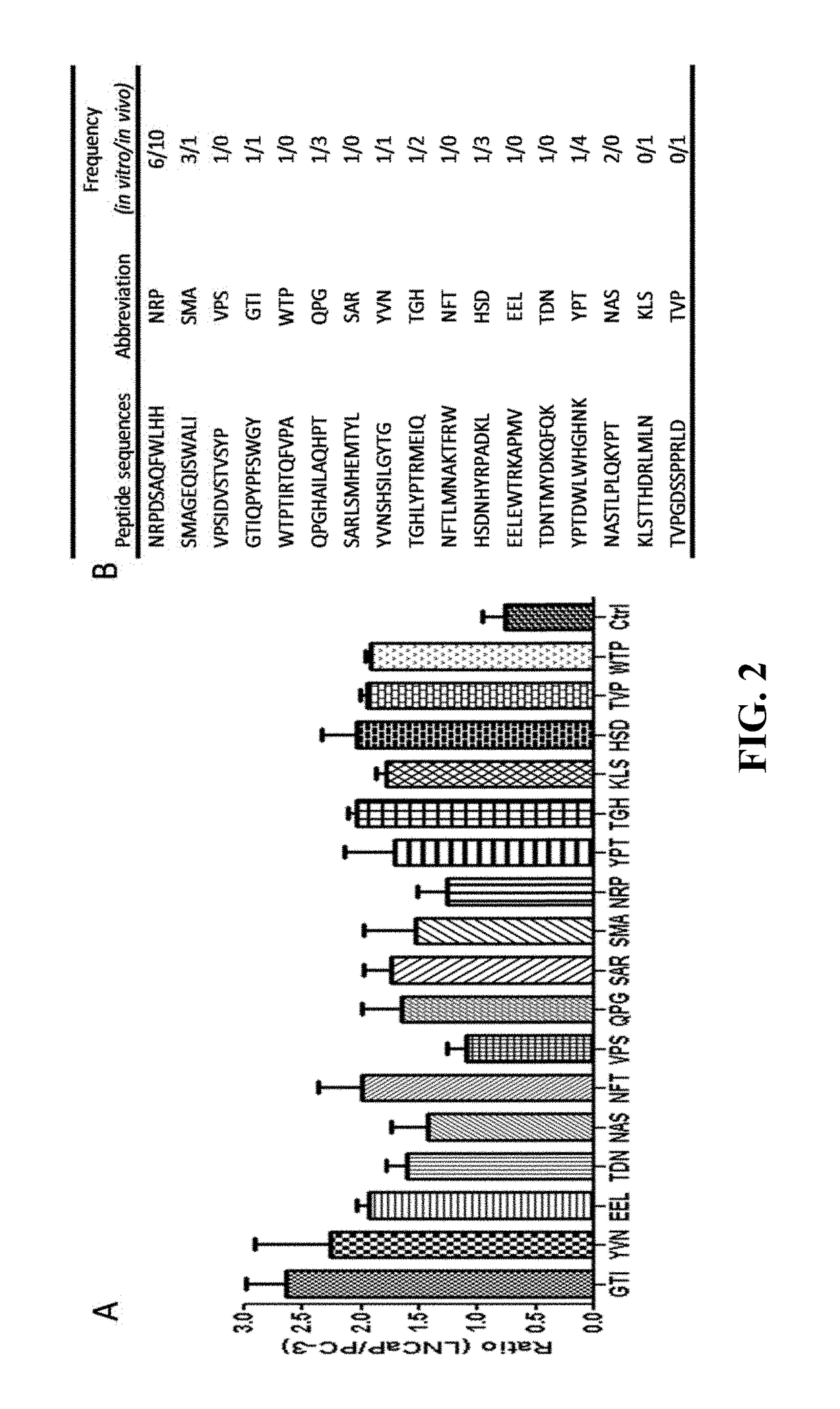
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeting peptides
ActiveUS20170240596A1High binding affinityImproves its apparent affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProstate cancer cellAntigen
Described herein is the discovery of novel PSMA-specific peptides, which were identified through a novel combinatorial biopanning method. One of the novel PSMA-specific peptides discovered, GTIQPYPFSWGY (or GTI) (SEQ ID NO: 2), exhibits high binding affinity and selectivity to PSMA and PSMA-positive prostate cancer cells. It was found that GTI can mediate internalization of the apoptotic KLA peptide to PSMA-positive LNCaP cells and induce cell death. Moreover, a FAM-labeled GTI peptide shows a high and specific tumor uptake in nude mice bearing human prostate cancer xenografts. It was demonstrated that the GTI peptide can be employed as a PSMA-specific ligand for prostate cancer diagnosis and / or for targeted drug delivery to prostate cancer cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
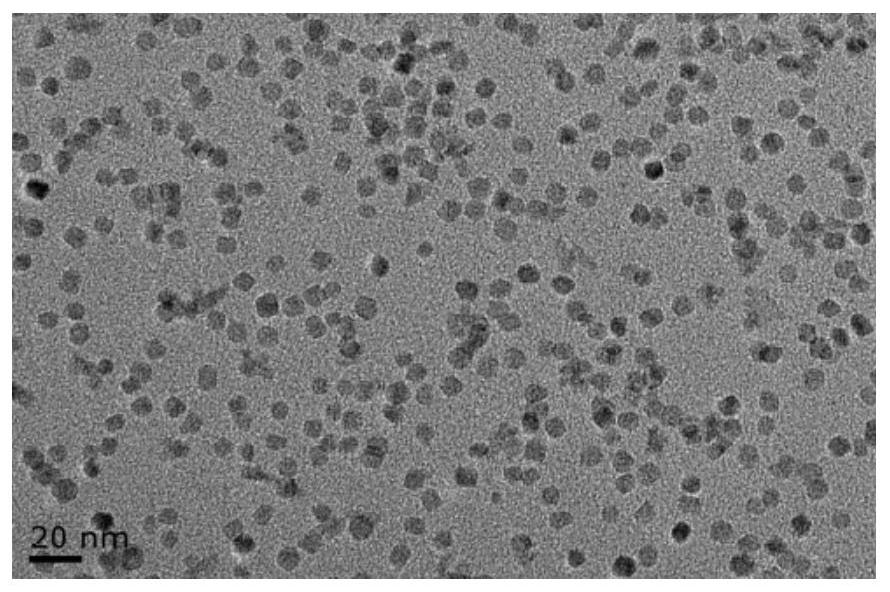
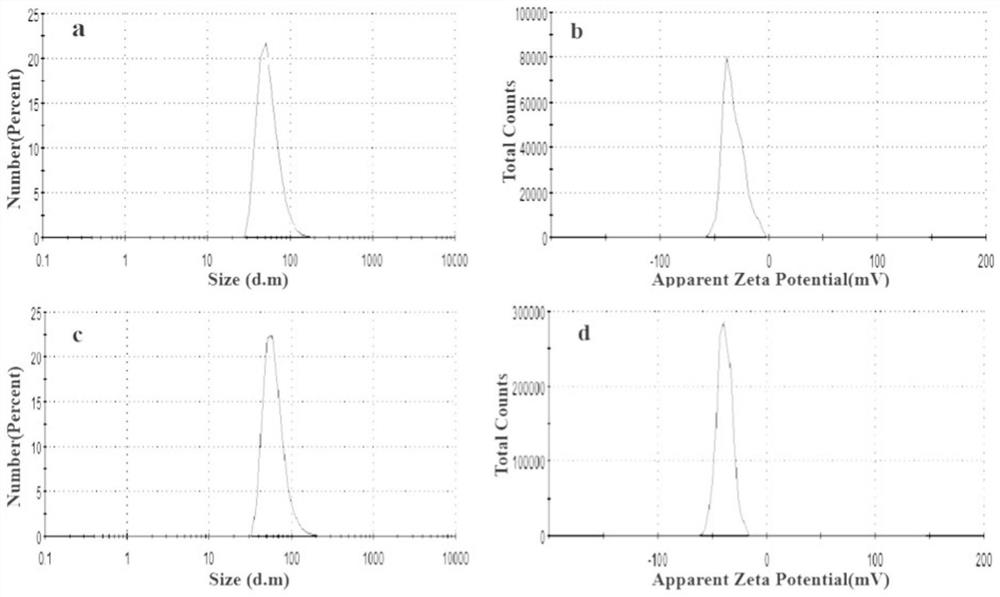
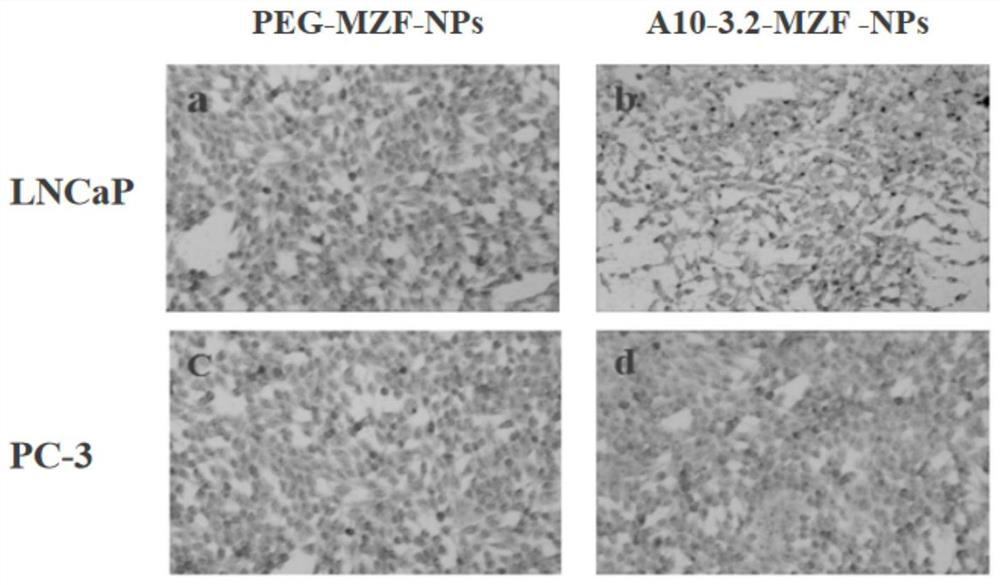
Molecular probe APT10-3.2-MZF-NPs for diagnosing prostatic cancer and preparation method of molecular probe APT10-3.2-MZF-NPs
InactiveCN111658786AHas a specific targeting effectIn-vivo testing preparationsProstate cancer cellOncology
The invention belongs to the field of medical care detection, and particularly relates to a molecular probe APT10-3.2-MZF-NPs for diagnosing prostatic cancer and a preparation method of the molecularprobe APT10-3.2-MZF-NPs. The probe is prepared by coupling an aptamer A10-3.2 with manganese-zinc ferrite nanoparticles. The APT10-3.2-MZF-NPs molecular probe has specificity targeting on prostatic cancer LNCaP cells, can pass MR detection, and is hopeful to become a novel targetting contrast to be used for MR molecular imaging.
Owner:JIANGSU TAIZHOU PEOPLES HOSPITAL
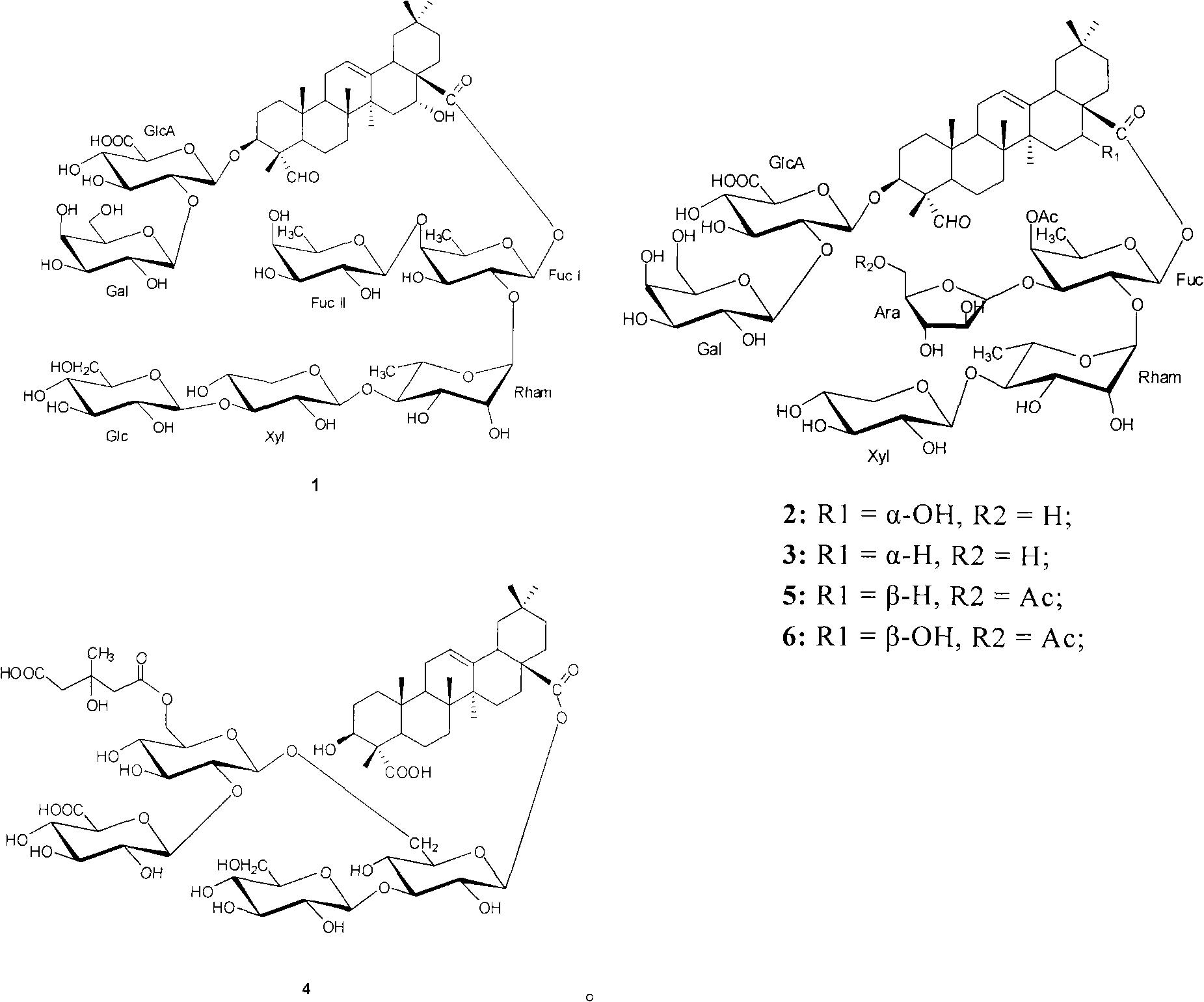
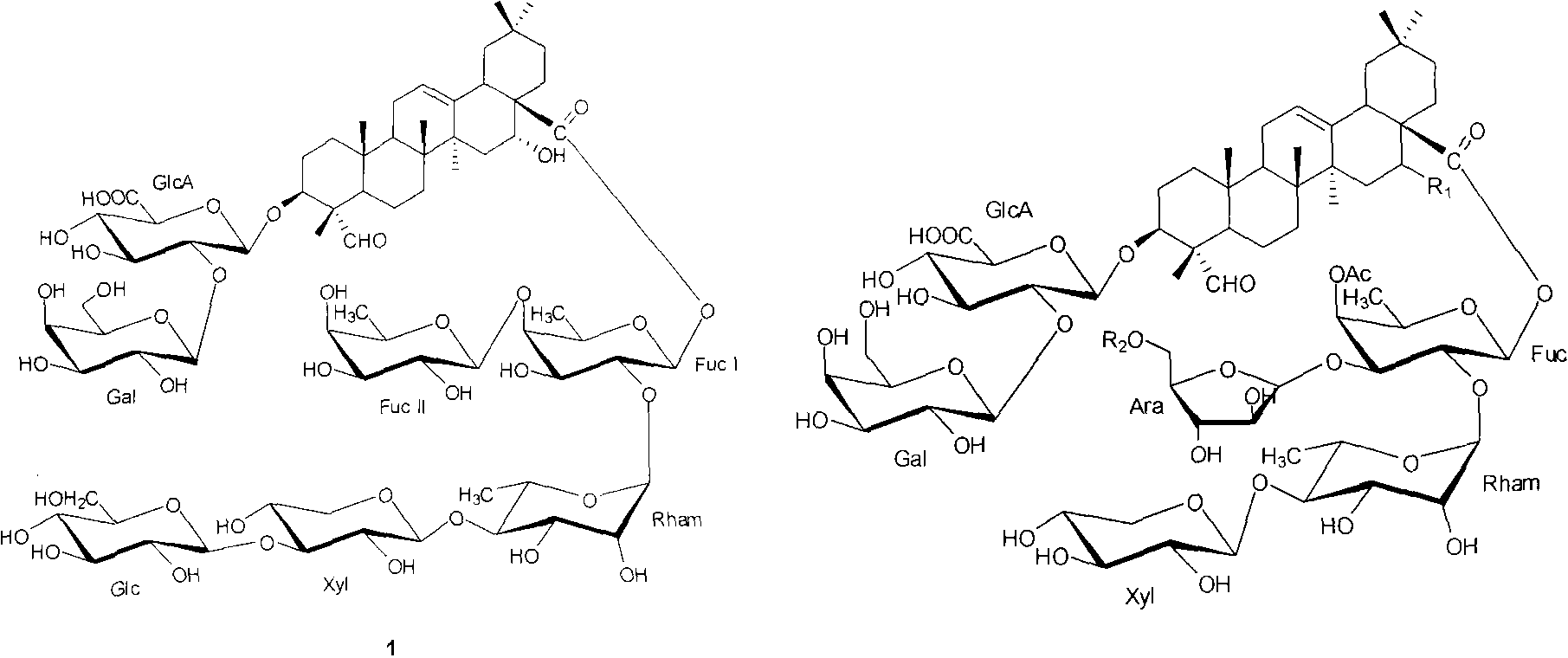
Triterpene compounds separated from seed of cowherb of Chinese traditional medicine and uses thereof
The invention discloses six triterpenoid compounds separated from the vaccaroside, namely, vaccaroside I, vaccaroside E, vaccaroside G, vaccaroside B, segetoside H and segetoside I. The in-vitro antitumor tests show that the compounds have obvious inhibitory effect on LNcap, P-388 and A-549 cell lines and provide a new ides on the development of new anti-cancer drugs and have great value on the deep development of traditional Chinese medicine resources.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
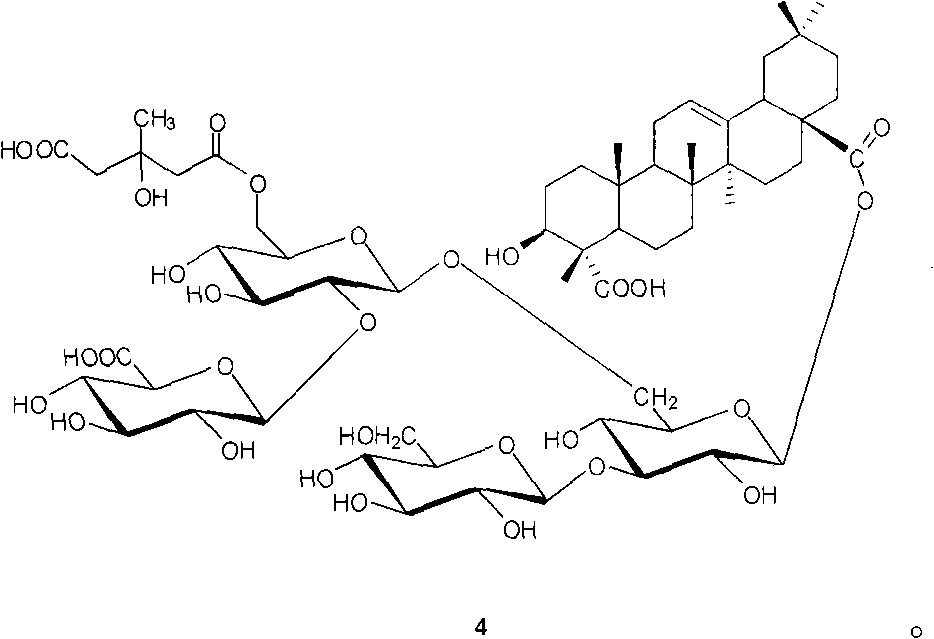
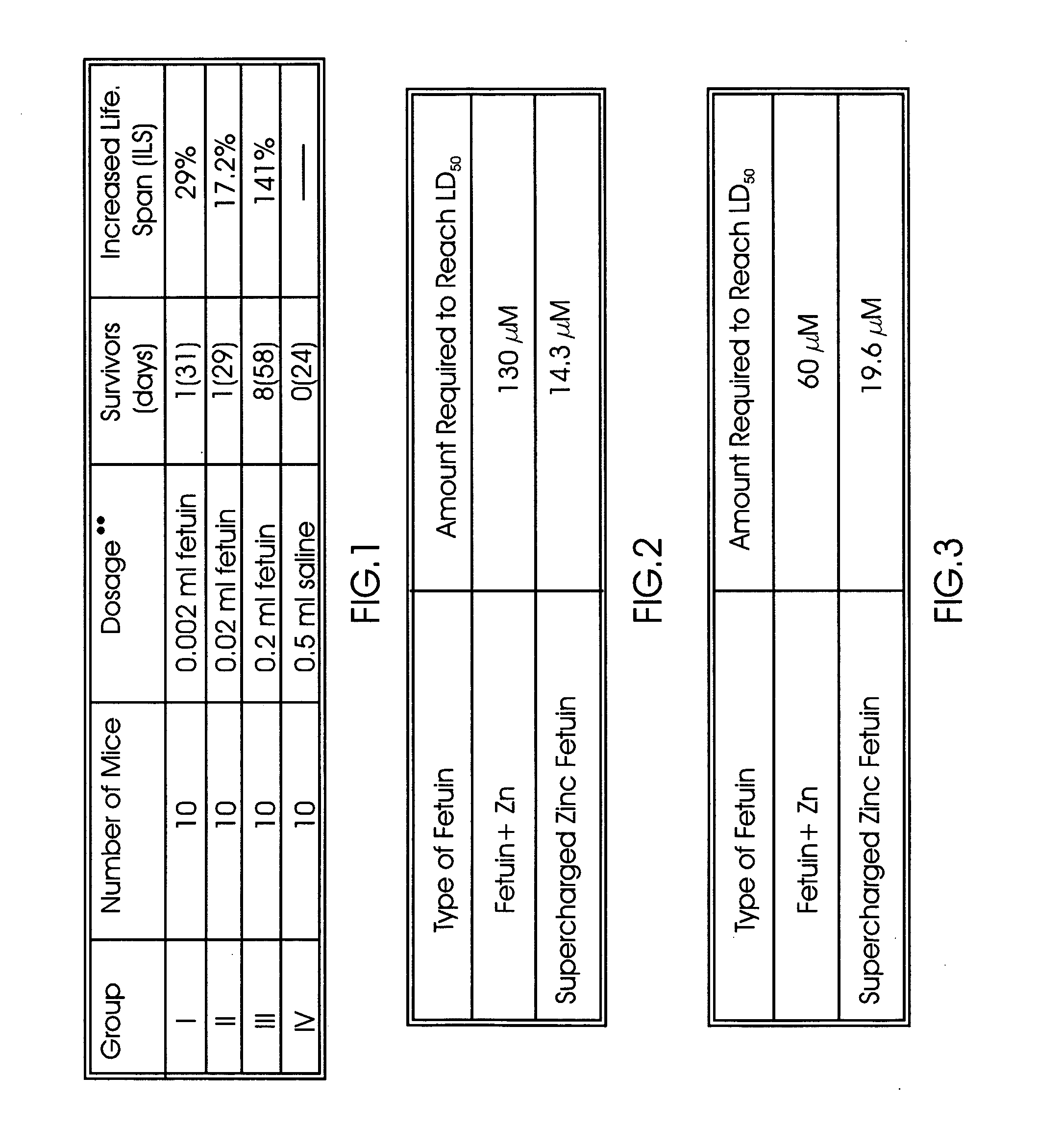
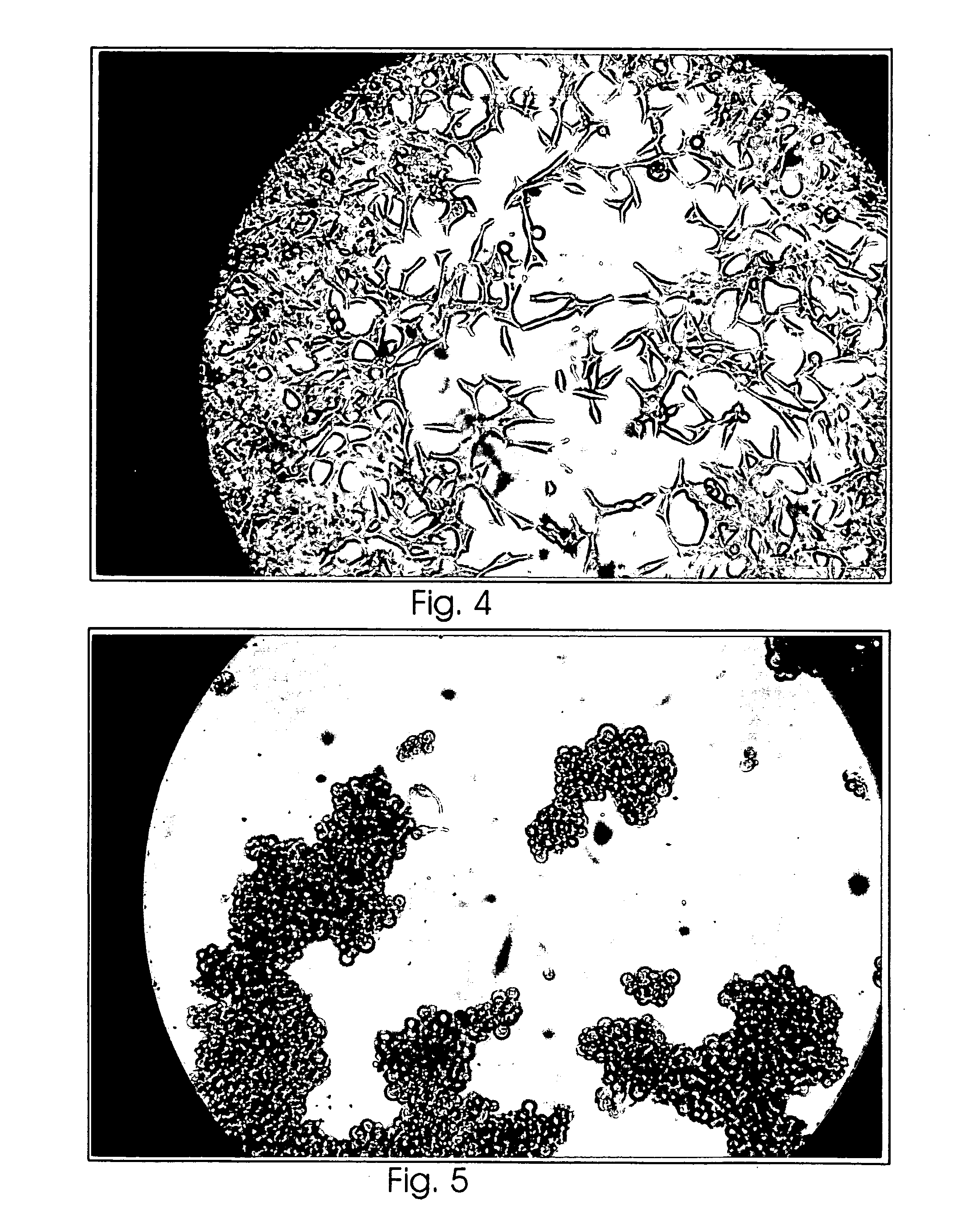
Polypeptide for the treatment of cancer and a method for preparation thereof
This invention characterizes the specific peptide fragment derived from specially prepared zinc charged fetuin and a method of preparation thereof, wherein the fragment was found to contain an apoptosis-inducing activity. Specifically, the amino acid sequence of this peptide is His Thr Phe Ser Gly Val Ala Ser Val Glu and correlates to amino acid no. 300-309 of fetuin, referred to herein as Fetuin Peptide Fragment (FPF 300-09). FPF 300-09 strongly induced apoptosis in LNCaP (prostate cancer) and HT-29 (colon cancer) cells without affecting CCD 18 Co (normal colon) cells. The in vitro tissue culture study demonstrated that the FPF 300-09 is more potent than the parent molecule (full-length zinc charged fetuin) in inducing apoptosis. FPF 300-09 has a LD50 of 0.3-0.4 μM, while the LD50 for zinc-charged fetuin is 3-10 μM.
Owner:AMBRYX BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
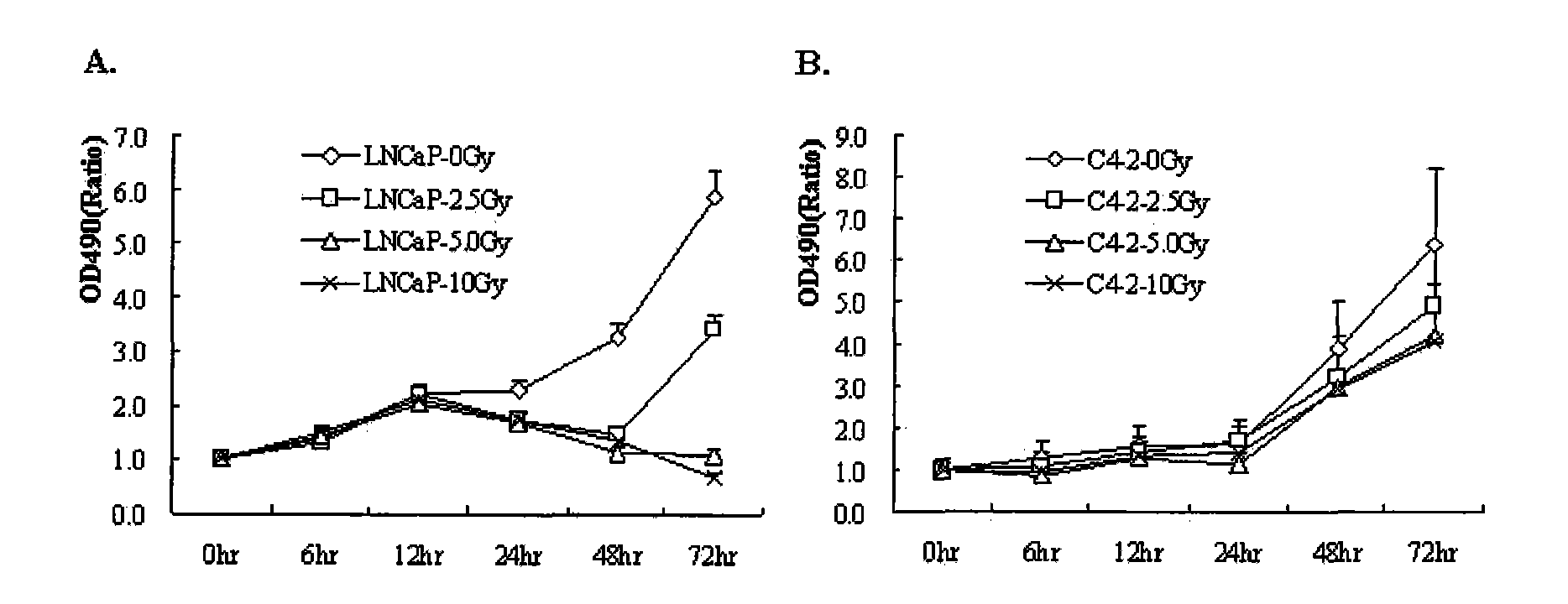
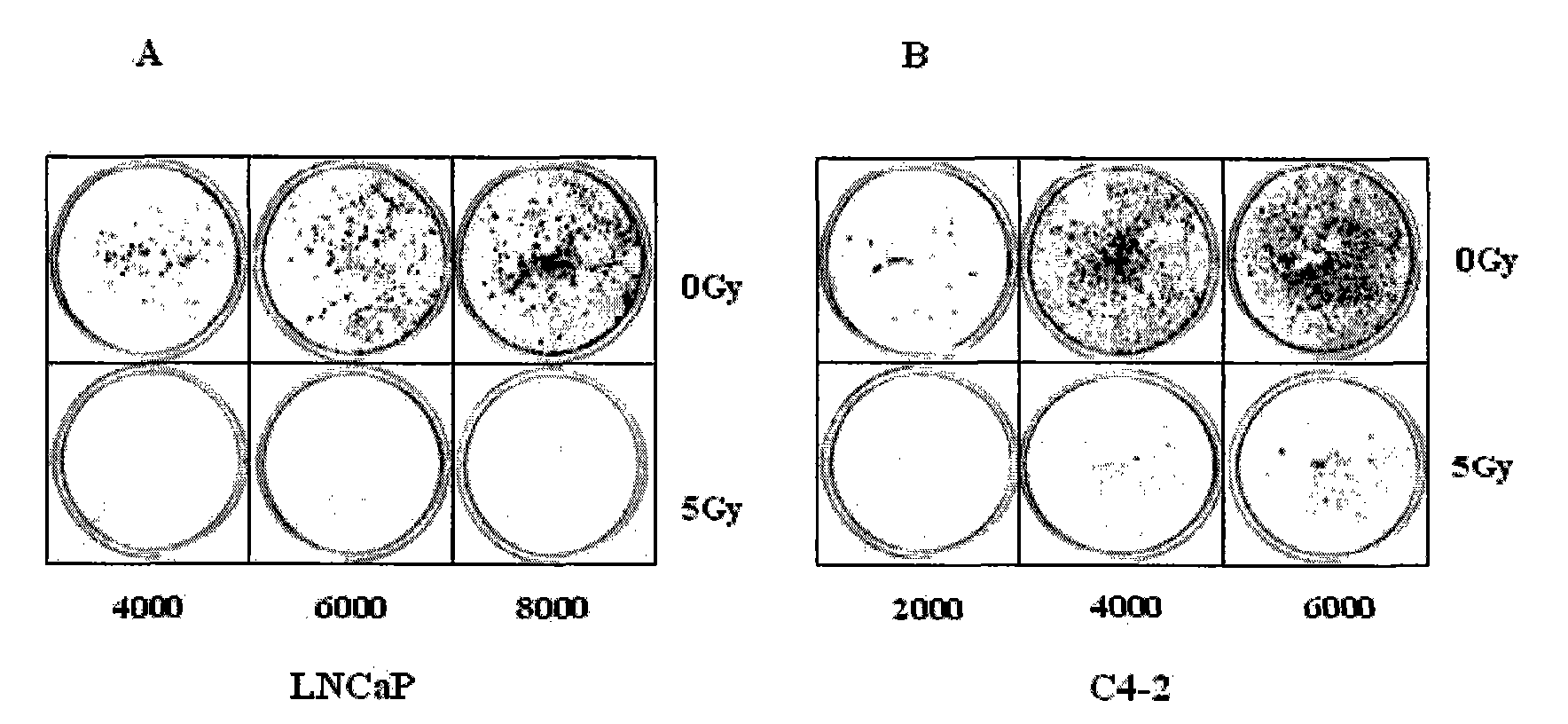
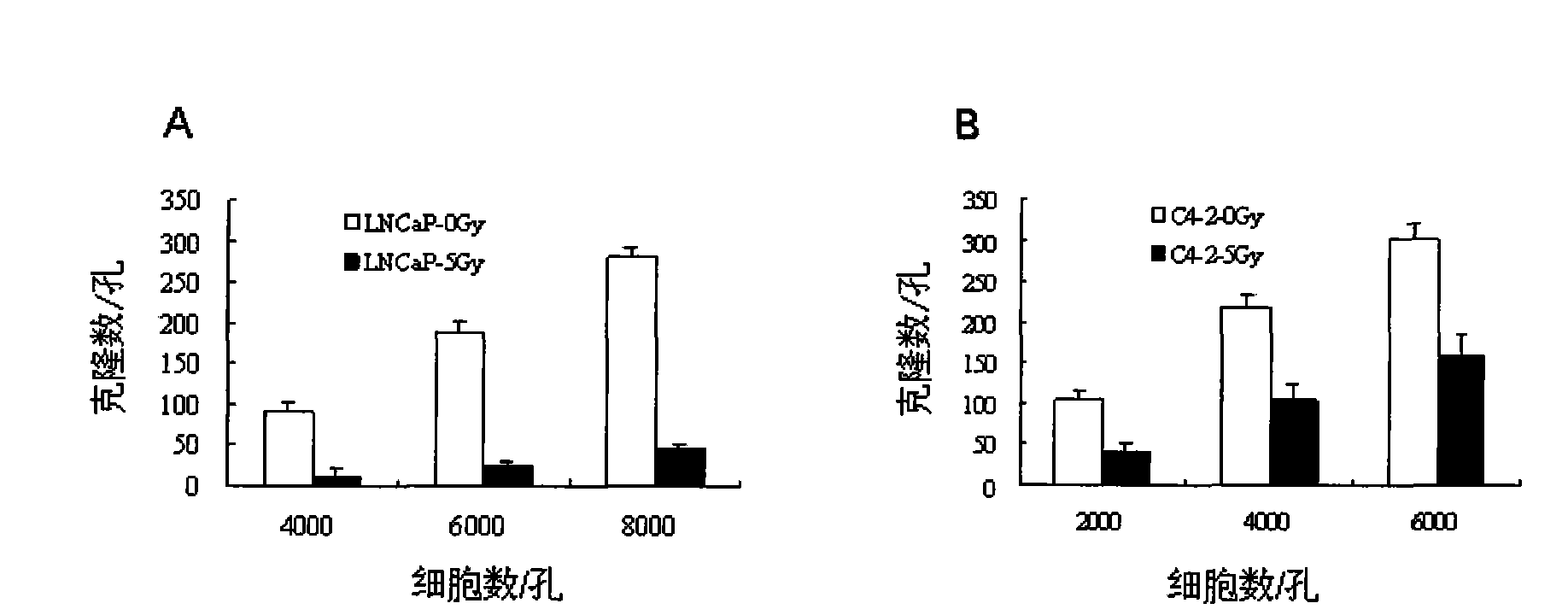
New use of cell line LNCaP and cell line C4-2
InactiveCN101831406AElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentTumor/cancer cellsProstate cancer cellRadiation sensitivity
The invention discloses new use of a cell line LNCaP and a cell line C4-2. The new use is the use of the cell line LNCaP and the cell line C4-2 in the preparation of a prostate cancer cell model which is sensitive to radiation and generates resistance to the radiation. The new use of the cell line LNCaP and the cell line C4-2 demonstrates a new characteristic, namely the resistance of theC4-2 cells to ionizing radiation, of the LNCaP / C4-2 cell model first, and the LNCaP / C4-2 may be the cell model which represents the prostate cancer cells developing from IR sensitivity into IR resistance. The new use of the cell line LNCaP and the cell line C4-2 can be used for selecting an ionizing radiation induced gene which determines that the prostate cancer cells developing from the radiation sensitivity into the radiation resistance so as to select relative genes which take part in and determine the progression of the prostatic cancer, and thus, the first stone for discovering more effective clinic therapeutic target with hormone resistance and radiation resistance is laid.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
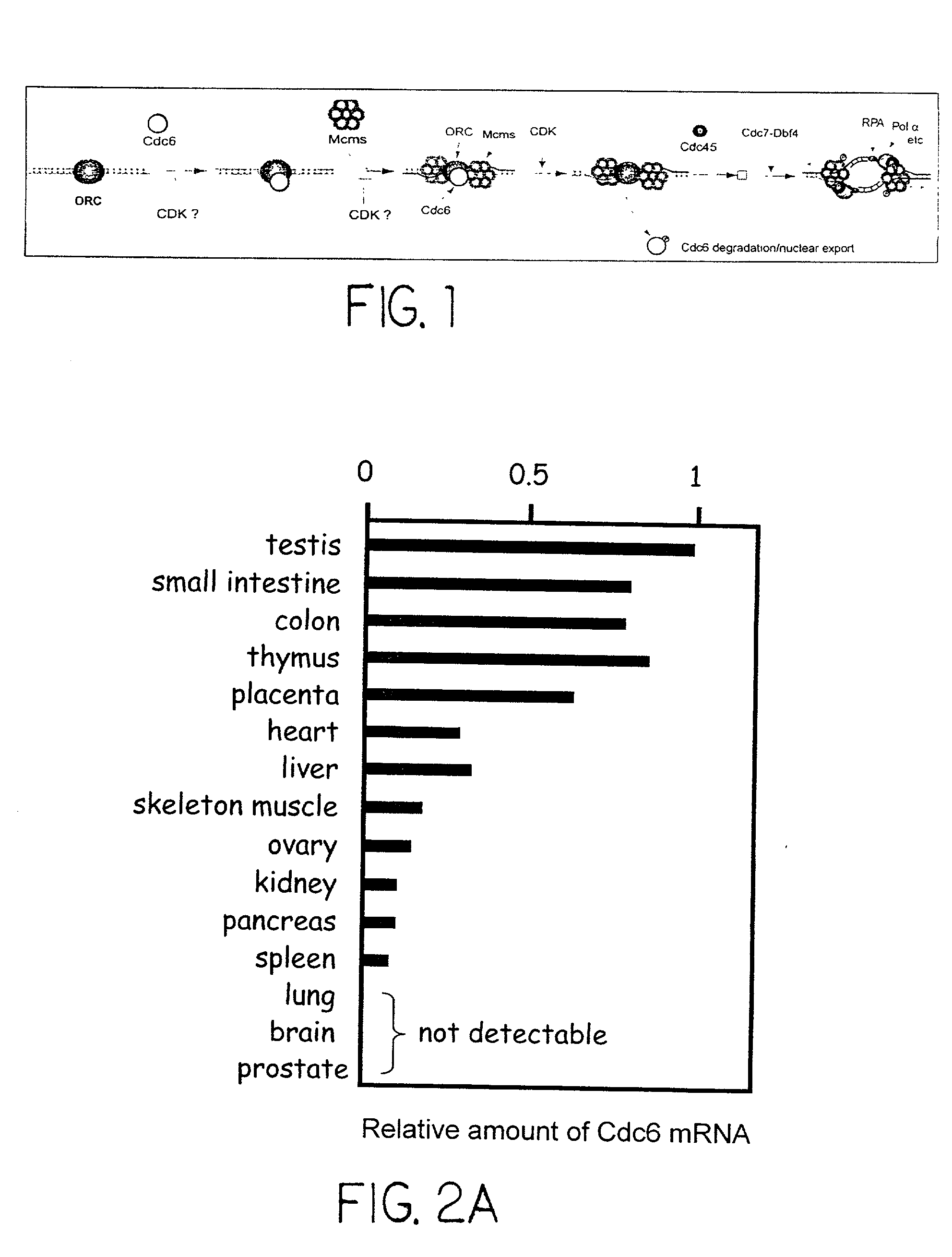
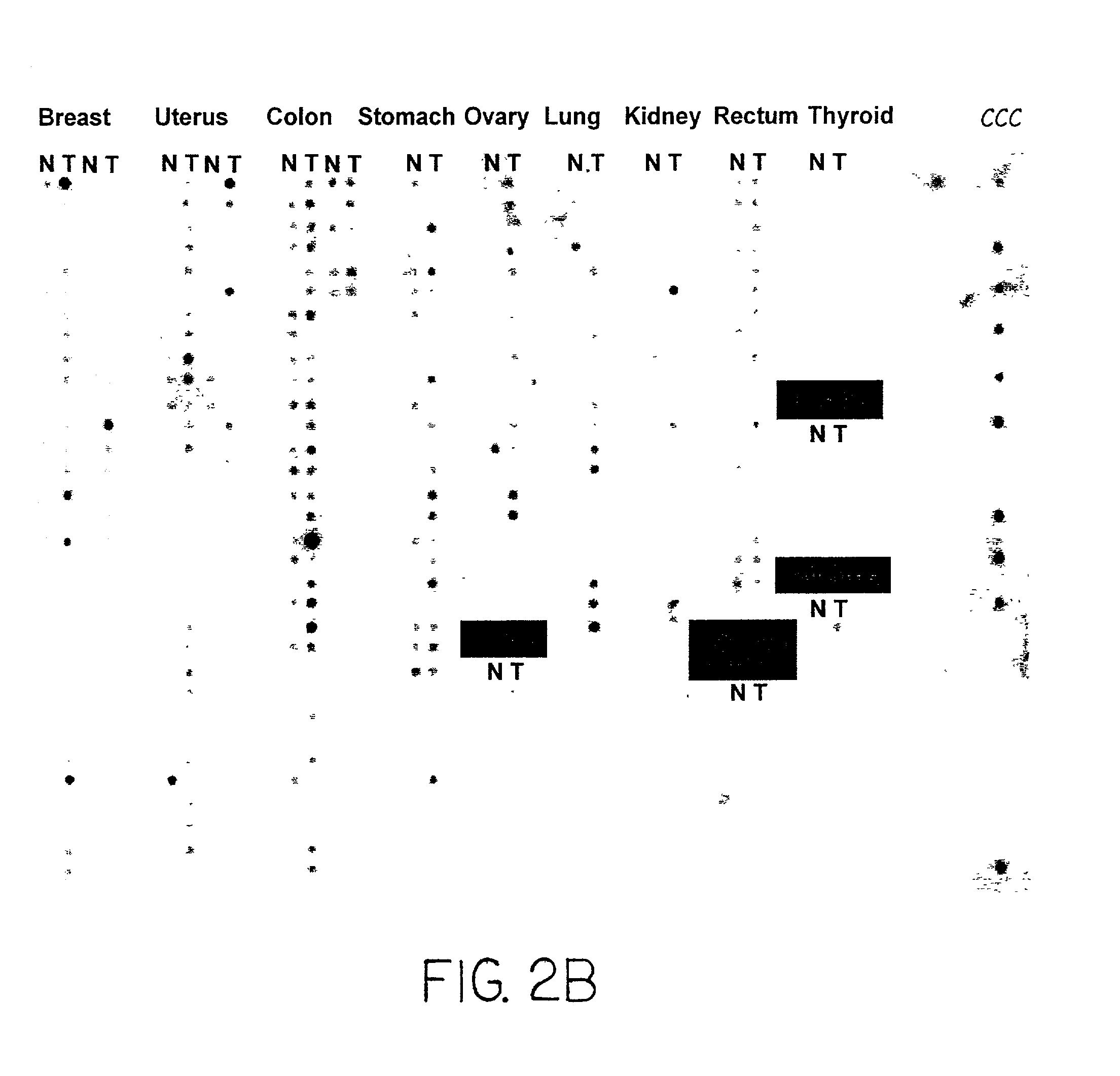
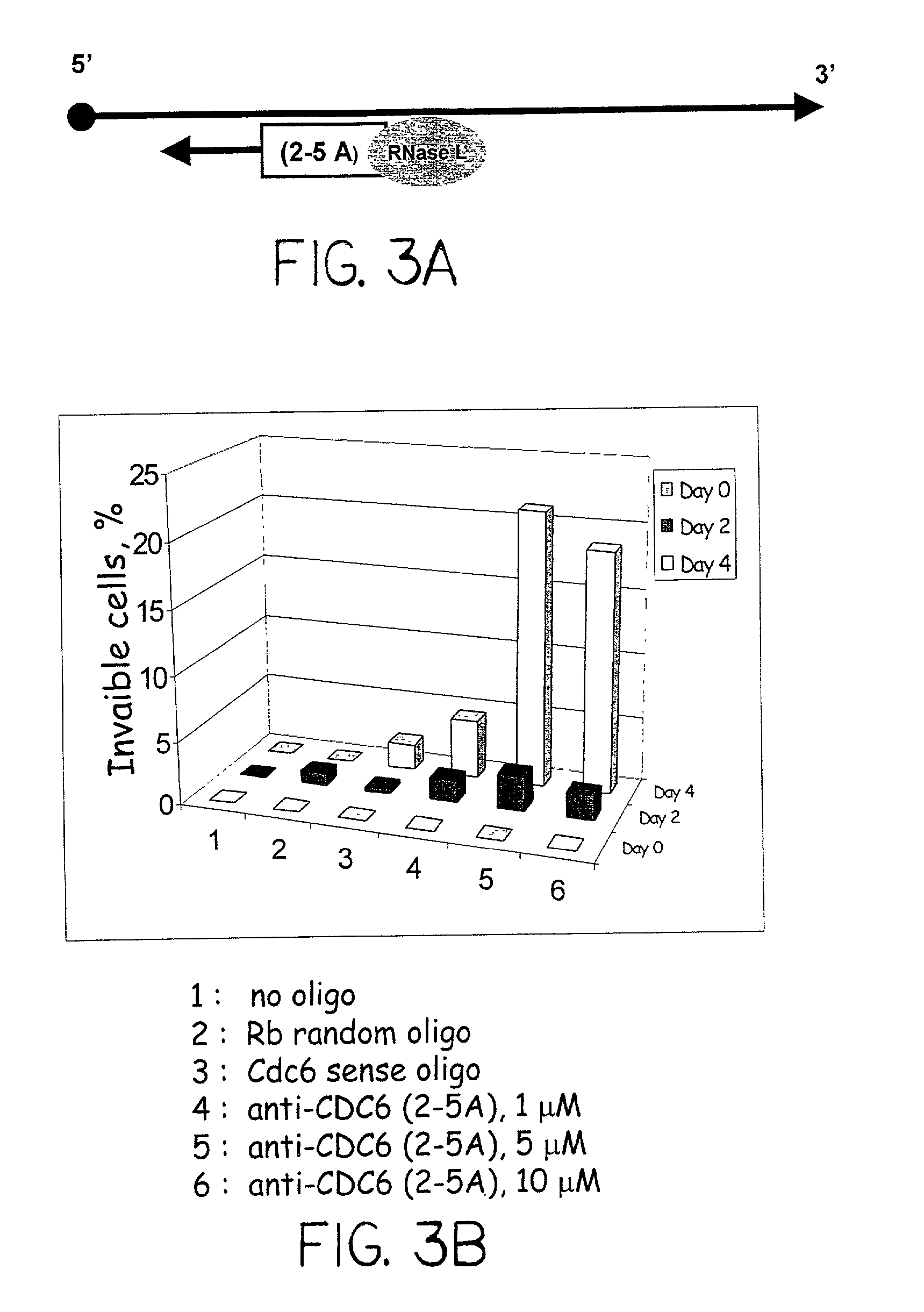
Using Cdc6 as therapeutic, prognostic and diagnostic targets for cell growth/proliferation
Using Cdc6 as therapeutic, prognostic and diagnostic targets for cell growth / proliferation. The unique features of Cdc6 allow anti-Cdc6 treatments to have affect on cancer cells, not on normal cells. Antisense anti-Cdc6 DNA technology is used to test Cdc6 as a target for growth inhibition and shows that the abrogation of Cdc6 mRNA in rapid cell results in death of prostate PC-3, DU145 and LNCaP cancer cells. The study demonstrated the abrogation of Cdc6 mRNA functions in prostate cancer cells could be an extremely effective way to block the cancer cell proliferation. Anti-Cdc6 treatment can be used alone, in combination, or in synergy with currently used therapeutic drugs or radiation therapies. Thus, the Cdc6 gene, mRNA and protein can also be a useful marker for diagnosis, prognosis, or therapy of cell proliferation.
Owner:JONG AMBROSE Y
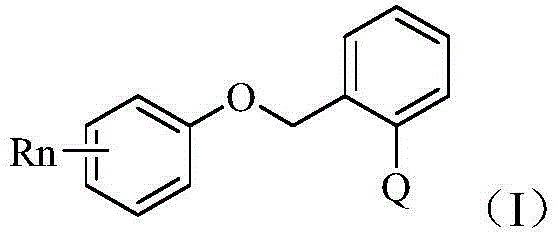
Application of phenyl ether compound with antitumor activity
InactiveCN104415038AAntineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsHuman bladderPhenyl Ethers
The invention discloses an application of a phenyl ether compound as shown in general formula I in preparation of antitumor drugs. The compound of the general formula I has very good antitumor activity, and especially has excellent activity for human bladder cancer LNCap, T24, J82 and human prostate cancer PC-3.
Owner:中国中化股份有限公司 +1
hTERT gene antisense oligodeoxynucleotide, drug composition and application
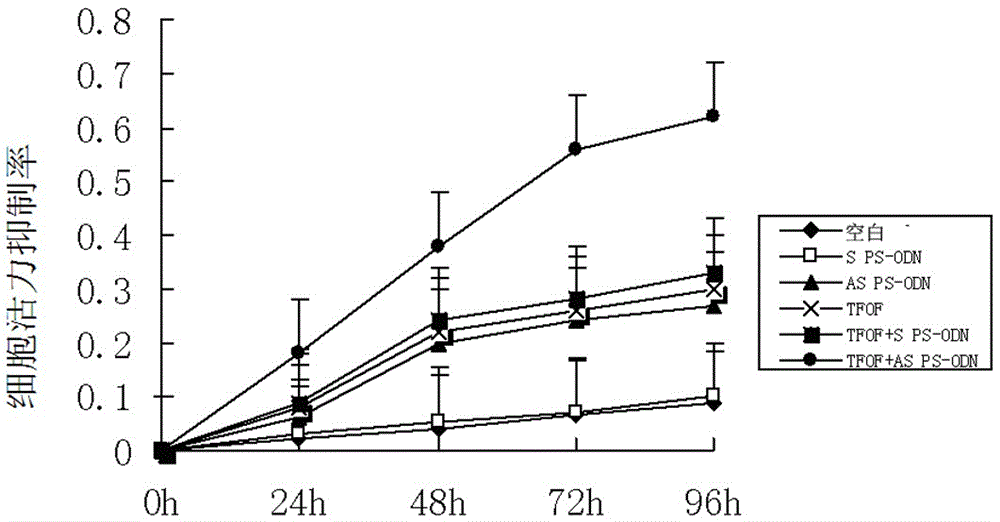
The invention provides hTERT gene antisense oligodeoxynucleotide, a drug composition and application, belonging to the technical field of gene drugs. The sequence of the antisense oligodeoxynucleotide is 5minute-GGAGCGCGCGGCATCGCGGG-3minute. After hTERT gene total phosphorothioate modified antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (AS PS-ODN) inhibits flutamide tolerance type prostate cancer cell LNCaP-flu telomerase activity, a Tibetan drug, i.e., dry whole grass of O. Falcata Bunge has a sensibilization effect on LNCaP-flu cell apoptosis.
Owner:甘肃省中医院
Application of bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 or its pharmaceutical salts in preparation of anti-cancer drugs
ActiveCN103263409BPrevent proliferationHas anticancer effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCytotoxicityHuman breast
The invention discloses an application of bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 or its pharmaceutical salts in the preparation of anti-cancer drugs. It is found in the invention through experiments that the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 has an obvious inhibitory effect on the multiplication of human non-small cells lung cancer cells H520, A549, H549, 1299, a human breast cancer cell MCF7, human prostatic cancer cells PC3, LNcaP, and DU145 and human intestinal cancer cells SW480 and HT-2P. The multiplication of human lung cancer cells H520 can be inhibited selectively by the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108. The good time and the concentration dependence can be presented. The value of IC50 after 48 h action is 2.90 muM. The cytotoxicity is not expressed at this concentration on normal renal epidermal cells. Further, the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 can effectively induce the apoptosis of lung cancer cells H520 and prevent the multiplication of cancer cells. Meanwhile, no toxicity will be presented. The bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 can specifically interdict the cell cycle of lung cancer cells H520 in S phase and can therefore inhibit the multiplication of cancer cells. Therefore, the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 can be developed into a new candidate drug with an anti-cancer effect especially an anti-lung cancer effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN XIANHU BOTANICAL GARDEN ADMINISTRATION
Cell culture plate coated with Matrigel as well as preparation method and application of cell culture plate
InactiveCN103087916AFully stretchedLong storage timeNervous system cellsTissue/virus culture apparatusMatrigelPolystyrene
The invention discloses a cell culture plate coated with Matrigel as well as a preparation method and an application of the cell culture plate. A carboxy surface is formed on the surface of a cell culture plate by adopting a plasma spraying technology, the Matrigel is connected to the surface of the polystyrene cell culture plate or culture dish in a form of a covalent bond by adopting a chemical riveting technology, and the cell culture plate or culture dish coated with the Matrigel is formed. Because a chemical combined surface treatment mode is adopted on the surface of a base material of the culture plate, the Matrigel on the surface is not dissolved. Compared with a physically coated cell culture plate, the cell culture plate has the advantage of long preservation time. The culture plate (dish) is applicable to culture of primary cells and a few cells which are difficult in attaching to walls, easily cluster, easily drop and are slow in growth such as neurons, LNCaP and PC-12; and by adopting the culture plate (dish), the cells attach to the walls firmly and extend fully, and a stable growth state is obtained.
Owner:黑龙江省重生生物科技有限公司
Application of bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 or its pharmaceutical salts in preparation of anti-cancer drugs
ActiveCN103263409APrevent proliferationHas anticancer effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCytotoxicityHuman breast
The invention discloses an application of bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 or its pharmaceutical salts in the preparation of anti-cancer drugs. It is found in the invention through experiments that the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 has an obvious inhibitory effect on the multiplication of human non-small cells lung cancer cells H520, A549, H549, 1299, a human breast cancer cell MCF7, human prostatic cancer cells PC3, LNcaP, and DU145 and human intestinal cancer cells SW480 and HT-2P. The multiplication of human lung cancer cells H520 can be inhibited selectively by the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108. The good time and the concentration dependence can be presented. The value of IC50 after 48 h action is 2.90 muM. The cytotoxicity is not expressed at this concentration on normal renal epidermal cells. Further, the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 can effectively induce the apoptosis of lung cancer cells H520 and prevent the multiplication of cancer cells. Meanwhile, no toxicity will be presented. The bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 can specifically interdict the cell cycle of lung cancer cells H520 in S phase and can therefore inhibit the multiplication of cancer cells. Therefore, the bixanthone compound FLBG-1108 can be developed into a new candidate drug with an anti-cancer effect especially an anti-lung cancer effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN XIANHU BOTANICAL GARDEN ADMINISTRATION
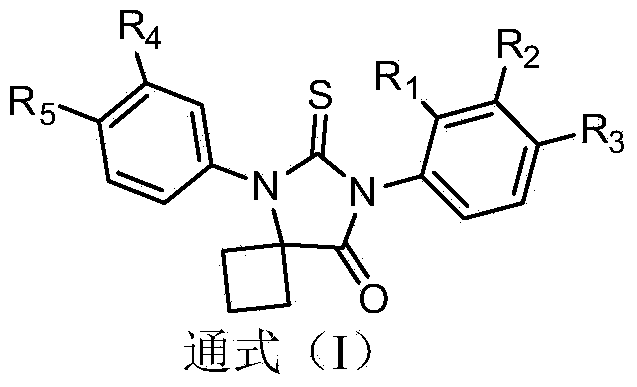
Diaryl substituted glycolythiourea compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses diaryl substituted glycolythiourea compounds, the structure of which are shown in a formula (I), wherein R1 is hydrogen, halogen or trifluoromethyl; R2 is hydrogen, halogen, trifluoromethyl, nitrile or alkoxyl; R3 is hydrogen, halogen or nitrile; R4 is hydrogen or halogen; R5 is hydrogen, halogen, methyl, N-methylamine formyl, N-ethylamine formyl, N-isopropylamine formyl and N-cyclopropylamine formyl. The diaryl substituted glycolythiourea compounds disclosed by the invention, particularly 7b-7g, 7i-7k, 7m-7p and 7r-7t, have strong growth inhibiting activity to a hormone-dependent prostate cancer cell LNCaP and can be used for preparing anti-tumor medicines.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Use of imb-a6 as an androgen receptor antagonist
ActiveCN106902112BEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh activityUrinary disorderDermatological disorderProstate cancer cellDisease
The invention relates to the field of medicine primers, and particularly discloses an application of IMB-A6 serving as an androgen receptor antagonist and an application of the IMB-A6 to preparation of androgen imbalance disease treating medicines and male contraception pills. By building a reliable androgen activity screening method, the inhibiting effect of a plurality of medicine primers on androgen receptor activity is tested to finally find that the IMB-A6 is a novel androgen receptor antagonist, and activity of wild and mutagenic androgen receptors can be inhibited. Further, activity of the prostate cancer resistance of the IMB-A6 is tested to find that the IMB-A6 has good activity for AR positive prostate cancer cells such as LNCaP and has no activity for AR negative prostate cancer cells, the expression activity of the androgen receptors can be inhibited, and the IMB-A6 is similar to positive medicines such as enzalutamide.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
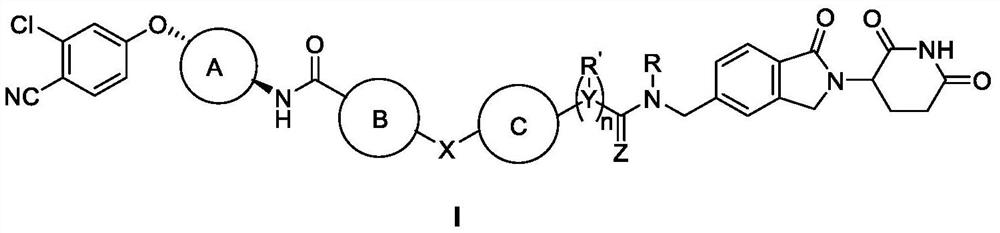
Bifunctional molecule as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114262319APrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryMedicineChemical compound
The invention discloses a bifunctional molecule as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The bifunctional molecule provided by the invention can inhibit proliferation of LNCap cells, and part of the compounds also have an effect of inhibiting proliferation of PC-3 cells, so that the bifunctional molecule provided by the invention has the potential of treating cancers, especially prostatic cancers. In addition, the preparation method of the bifunctional molecule is mild in condition, simple to operate, free of high-temperature and low-temperature extreme reaction conditions, free of high-risk and highly toxic substances, suitable for laboratory synthesis and industrial production and wide in industrial application prospect.
Owner:AUBRAK THERAPEUTICS
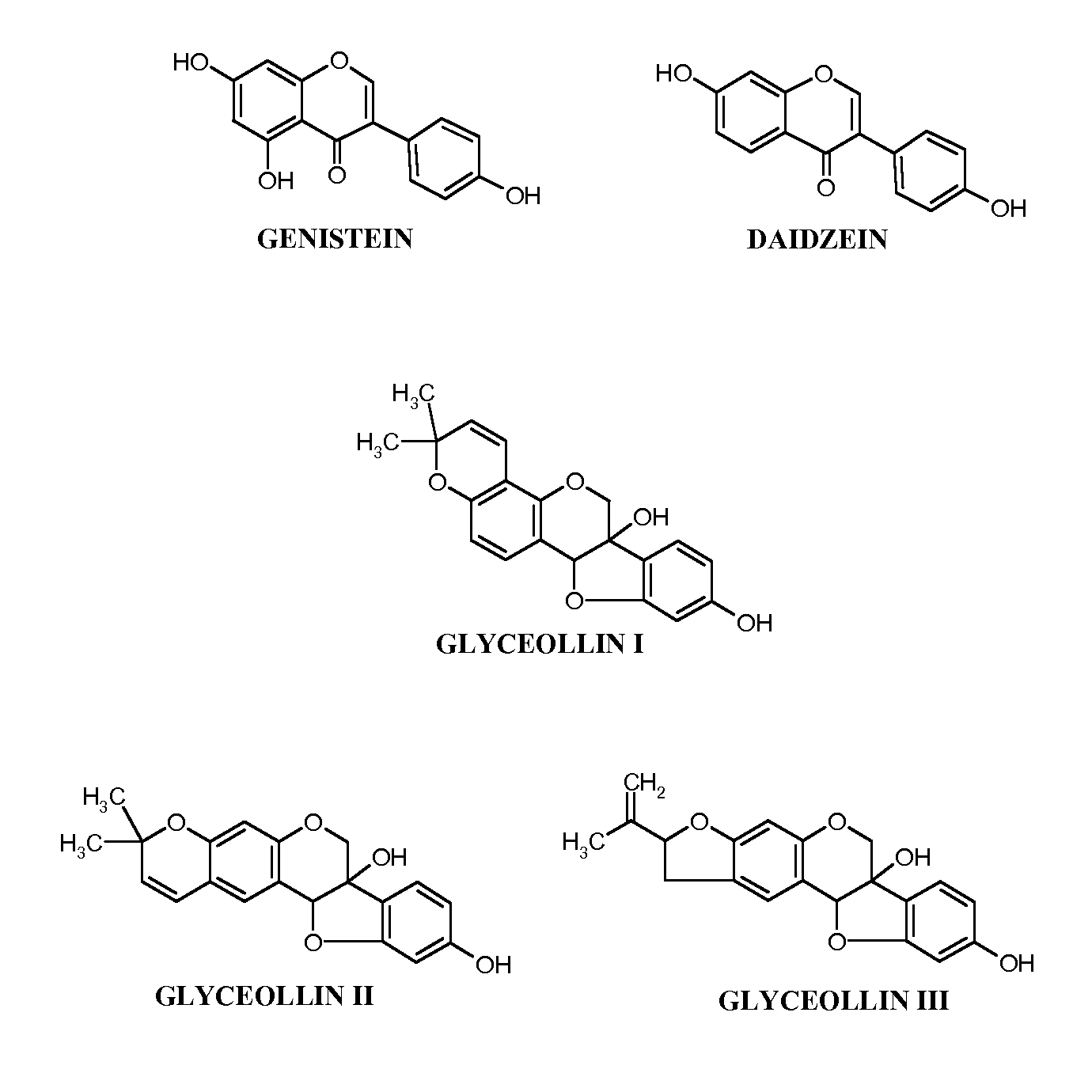
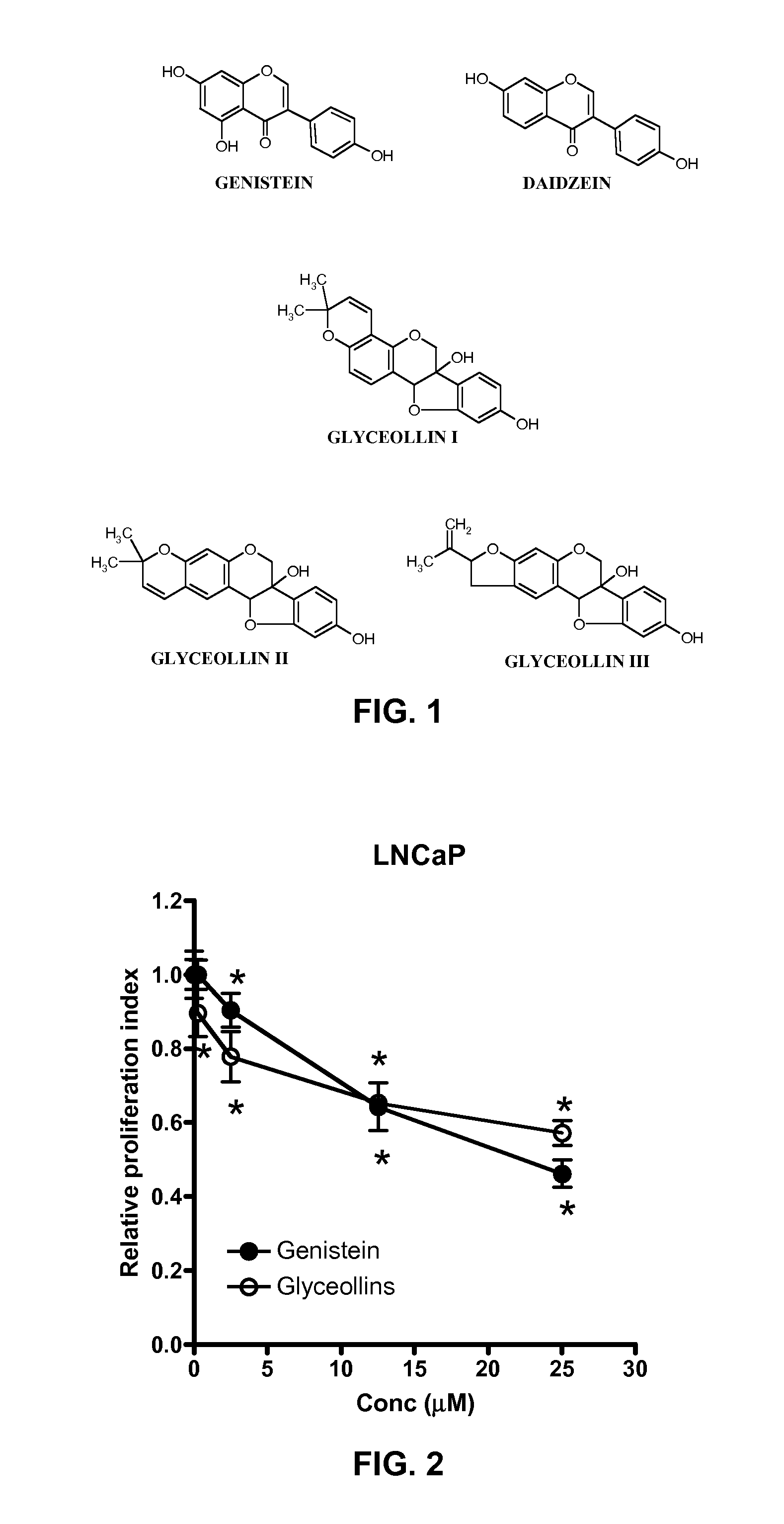
Glyceollins Suppress Androgen-Responsive Prostate Cancer
InactiveUS20130041022A1Preventing and minimizing developmentPreventing and minimizing and growthBiocideOrganic chemistryADAMTS ProteinsPotential effect
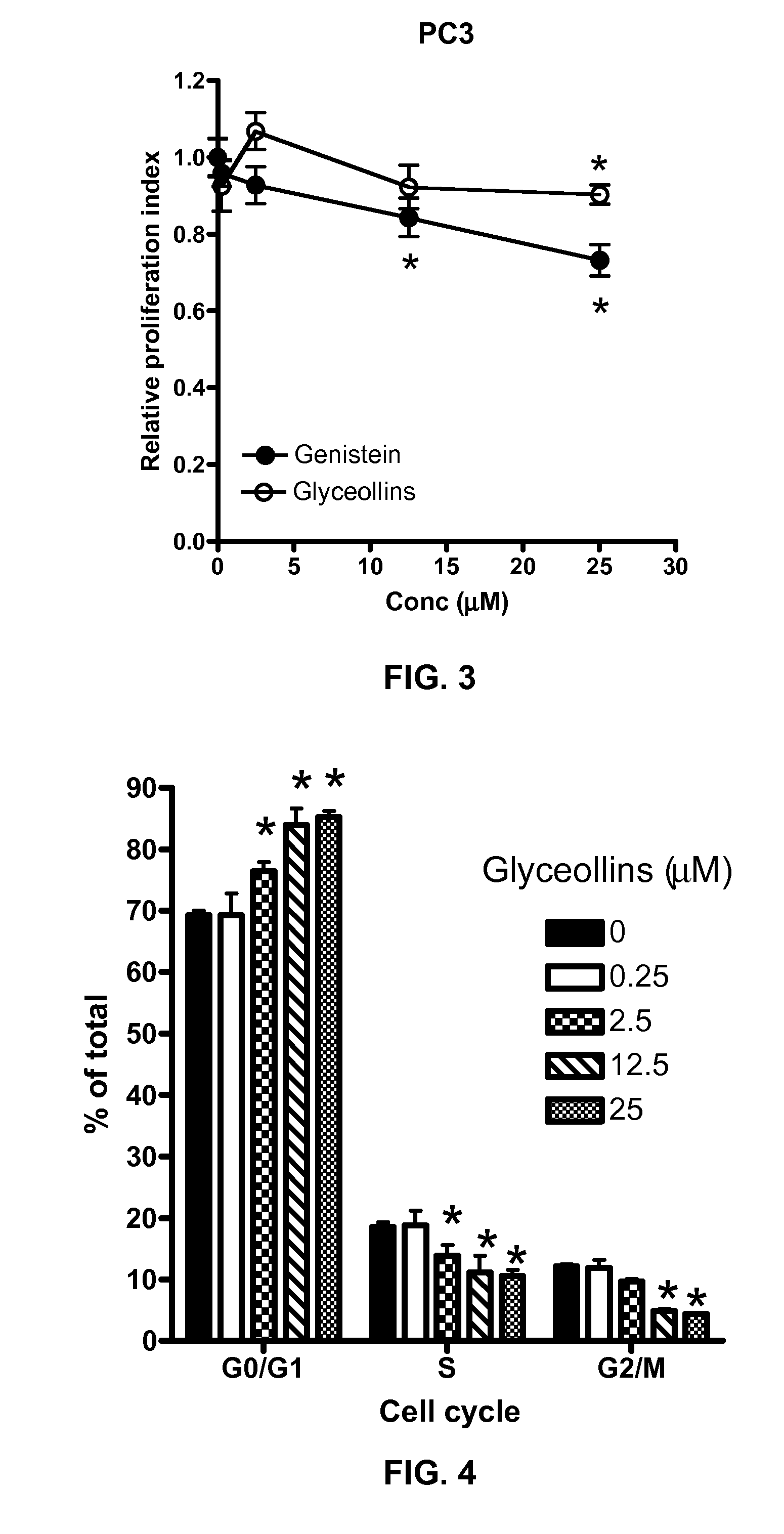
The present disclosure demonstrates the molecular effects of glyceollins on human prostate cancer cell LNCaP to further elucidate its potential effects on prostate cancer prevention. The glyceollins inhibited LNCaP cell growth similar to that of the soy isoflavone genistein. The growth inhibitory effects of the glyceollins appeared to be due to an inhibition on G1 / S progression and correlated with an up-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor A1 and B1 mRNA and protein levels. By contrast, genistein only up-regulates cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor A1. In addition, glyceollin treatments led to down-regulated mRNA levels for androgen responsive genes. In contrast to genistein, this effect of glyceollins on androgen responsive genes appeared to be mediated through modulation of an estrogen- but not androgen-mediated pathway. Hence, the glyceollins exerted multiple effects on LNCaP cells that may be considered cancer preventive and the mechanisms of action appeared to be different from other soy-derived phytochemicals.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Drug target and applications thereof related to castration-resistant prostate cancer
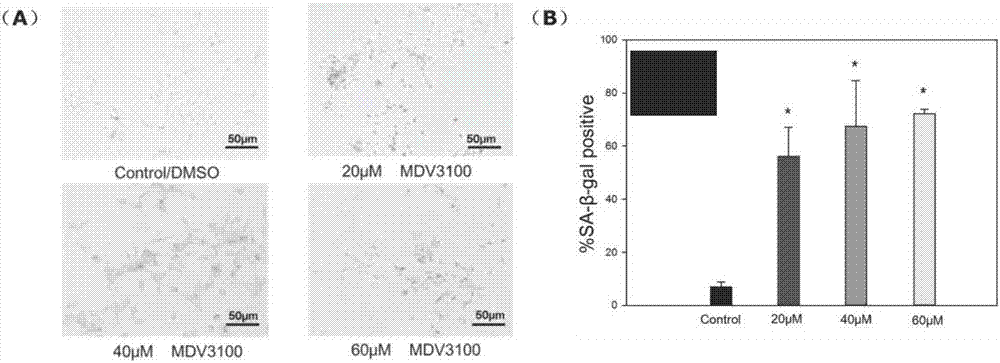
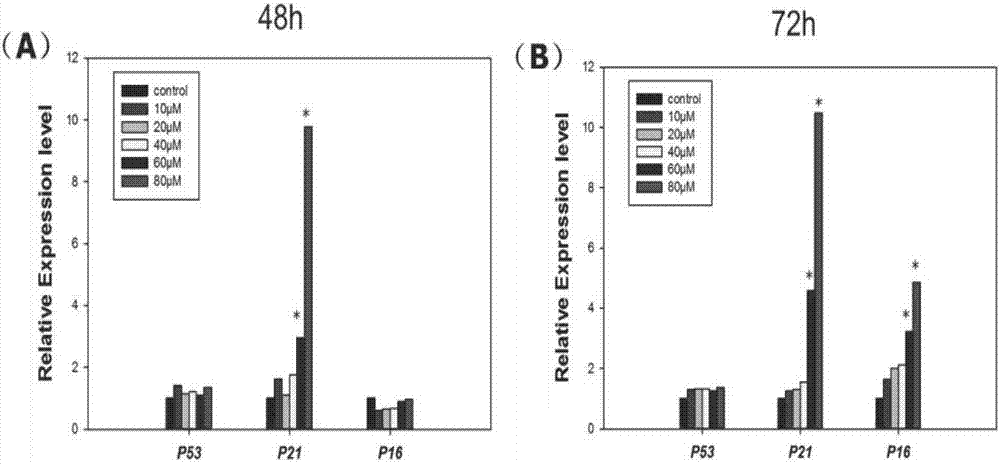
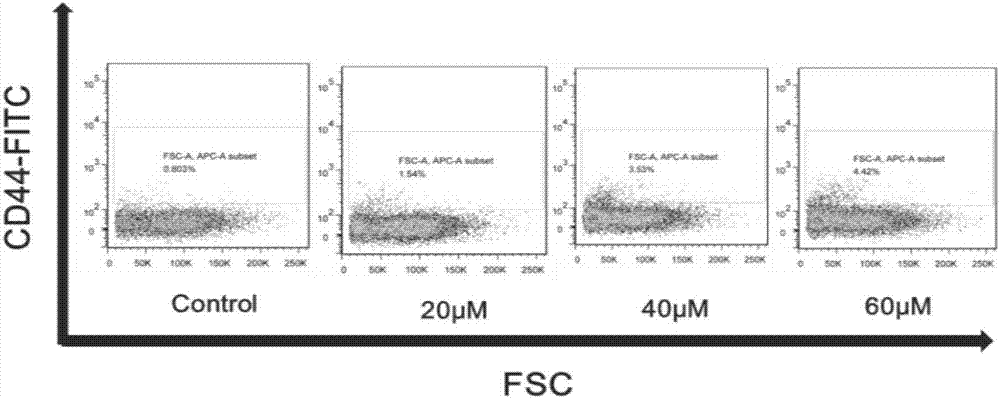
The invention relates to applications of antagonist of aging related secreted factors, and a pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting castration-resistant prostate cancer. The aging related secreted factors are selected from MIP-3-alpha, RANTES, MCP-2 factors. The invention also provides applications of the aging related secreted factors to preparation of products for predicting prostate cancer prognosis, and the aging related secreted factors are selected from MIP-3-alpha, RANTES, and MCP-2 factors. The composition is advantageous in that based on discovery that MDV3100 can induce LNCaP FGC cells to generate cell aging, protein chips are employed to discover that MDV3100 can induce the LNCaP FGC cells to secrete a lot of chemotactic factors, such as MIP-3-alpha, RANTES, MCP-2 factors and the like, as well as SASP proteins, such as cytokine and the like, and a base is provided for subsequent researches, such as SASP and CRPC, prostate carcinoma with bone metastasis and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
Single-chain antibody in anti-human prostate-specific membrane antigen extracellular region and application thereof
InactiveCN101891818BImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntigenProstate cancer cell
The invention provides a single-chain antibody in an anti-human prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) extracellular region, which adopts the phage display technology. The antibody is obtained by screening and enriching a large-storage capacity single-chain antibody library which is established by using peripheral blood mono-nuclear cells of a prostatic cancer patient through successive relaxation and rigorousness. The antibody can be solubly expressed in colon bacillus, and the affinity of the antibody with the prostate-specific membrane antigen extracellular region reaches Kd of 0.2nM. The antibody not only can be combined with the recombinant PSMA extracellular region, but also can be combined with NEK 293 cells with PSMA expressed on surface thereof and a prostate adenocarcinoma cell LNCaP, thus laying a foundation for adopting the antibody to perform prostate adenocarcinoma image diagnosis and guiding treatment.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
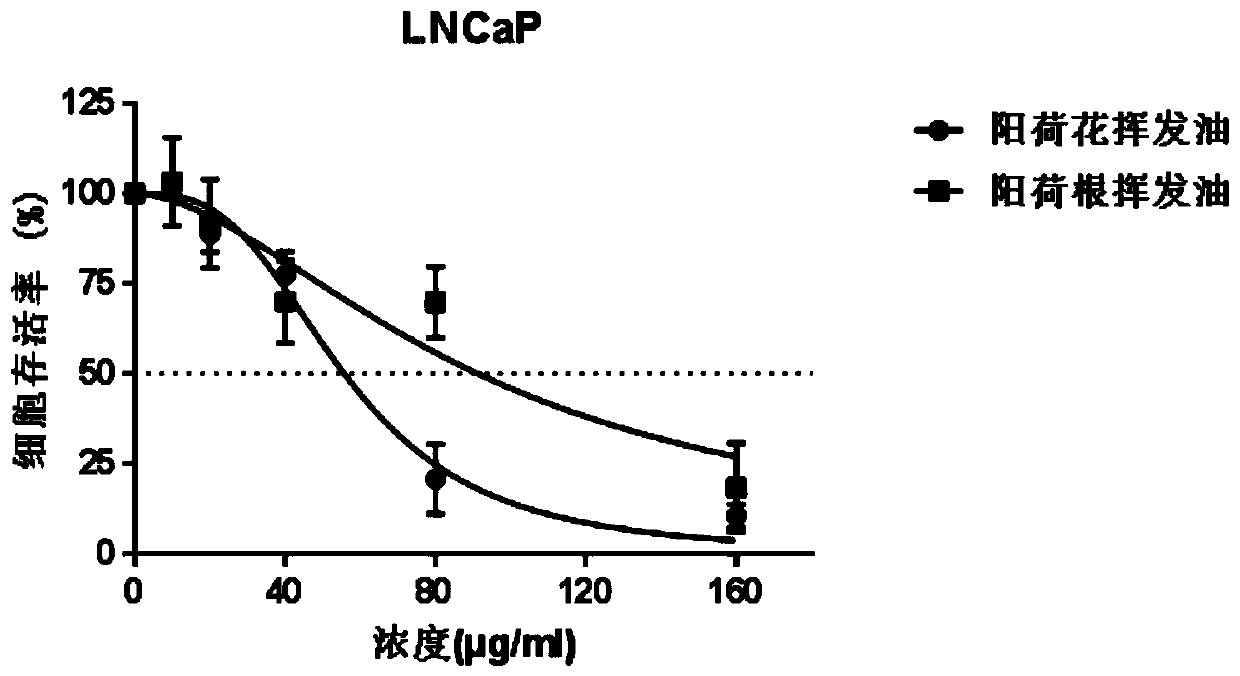
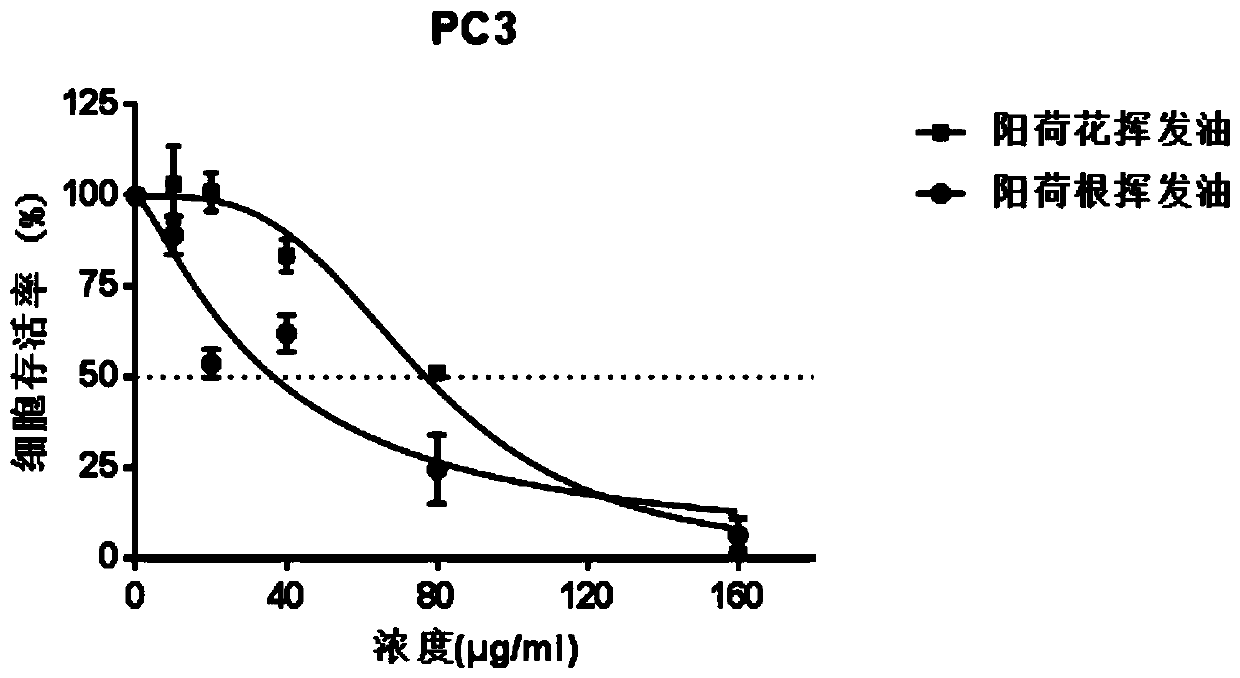
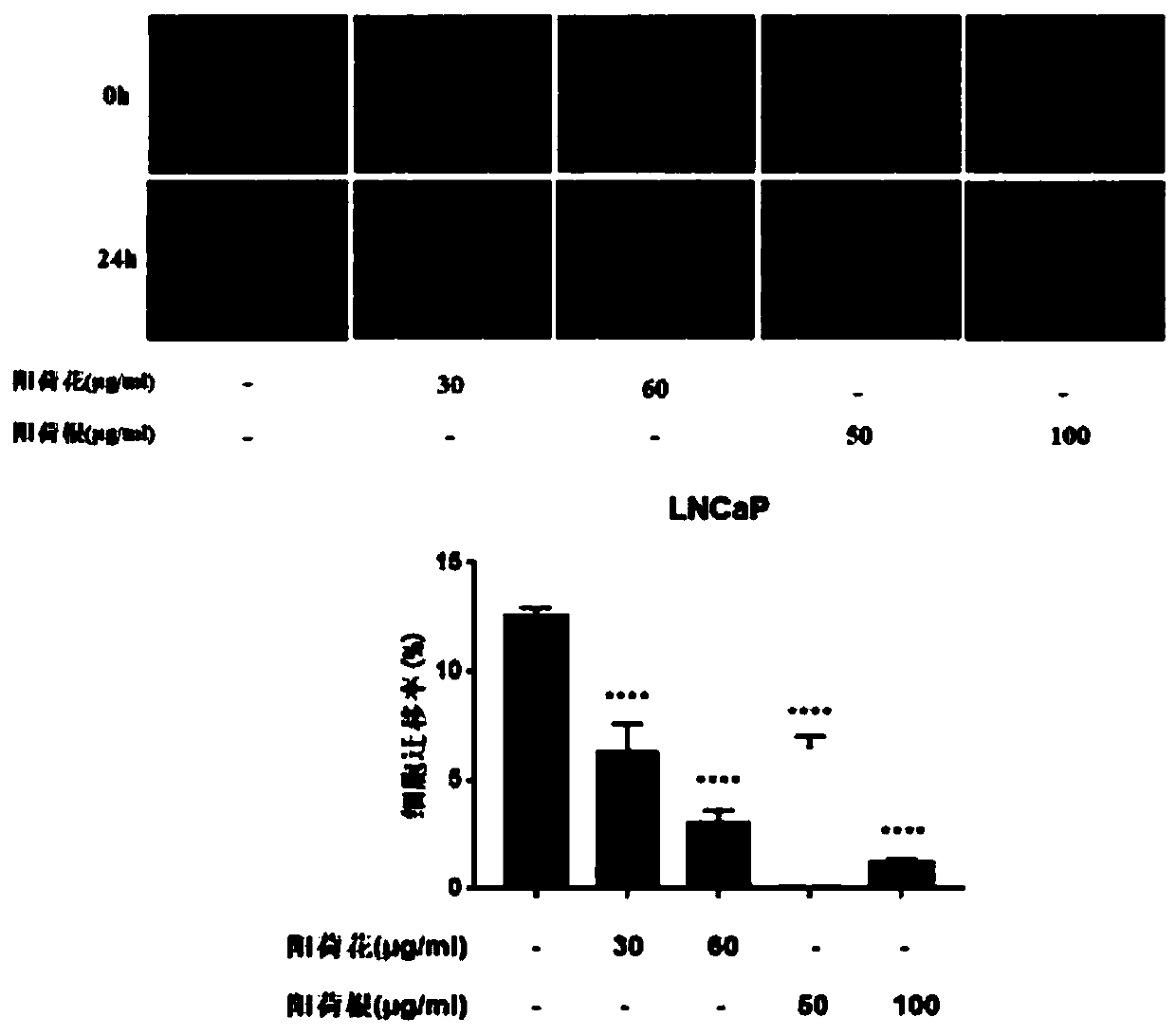
Application of zingiber strioatum volatile oil to preparation of anti-prostatic-cancer products
The invention discloses application of zingiber strioatum volatile oil to preparation of anti-prostatic-cancer products and provides the application of the zingiber strioatum volatile oil to preparation of the anti-prostatic-cancer products. The zingiber strioatum volatile oil is especially suitable for the prostatic cancer caused by LNCaP and / or PC-3 cell pathological change; the IC50 of zingiberstrioatum flour volatile oil to LNCaP is 55.75 ug / mL, and the IC50 of the zingiber strioatum flour volatile oil to the PC-3 is 77.17 ug / mL; and the IC50 of zingiber strioatum root cynomorium songaricum volatile oil to LNCaP is 91.37 ug / mL, and the IC50 of the zingiber strioatum root volatile oil to the PC-3 is 36.68 ug / mL. The zingiber strioatum flour volatile oil comprises the main components ofbeta-phellandrene, beta-pinene, alpha-humulene, alpha-pinene, cryptone, beta-elemene and beta-myrcene. The zingiber strioatum root volatile oil comprises the main components of (E,E)-geranyl linalool, beta-phellandrene, beta-pinene, alpha-humulene, beta-humulene and isolongifolol. The zingiber strioatum volatile oil has a very good inhibition effect on the migration of LNCaP and PC-3 cells.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Prostate-specific tumor antigens and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150202273A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsProstate cancer cellPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
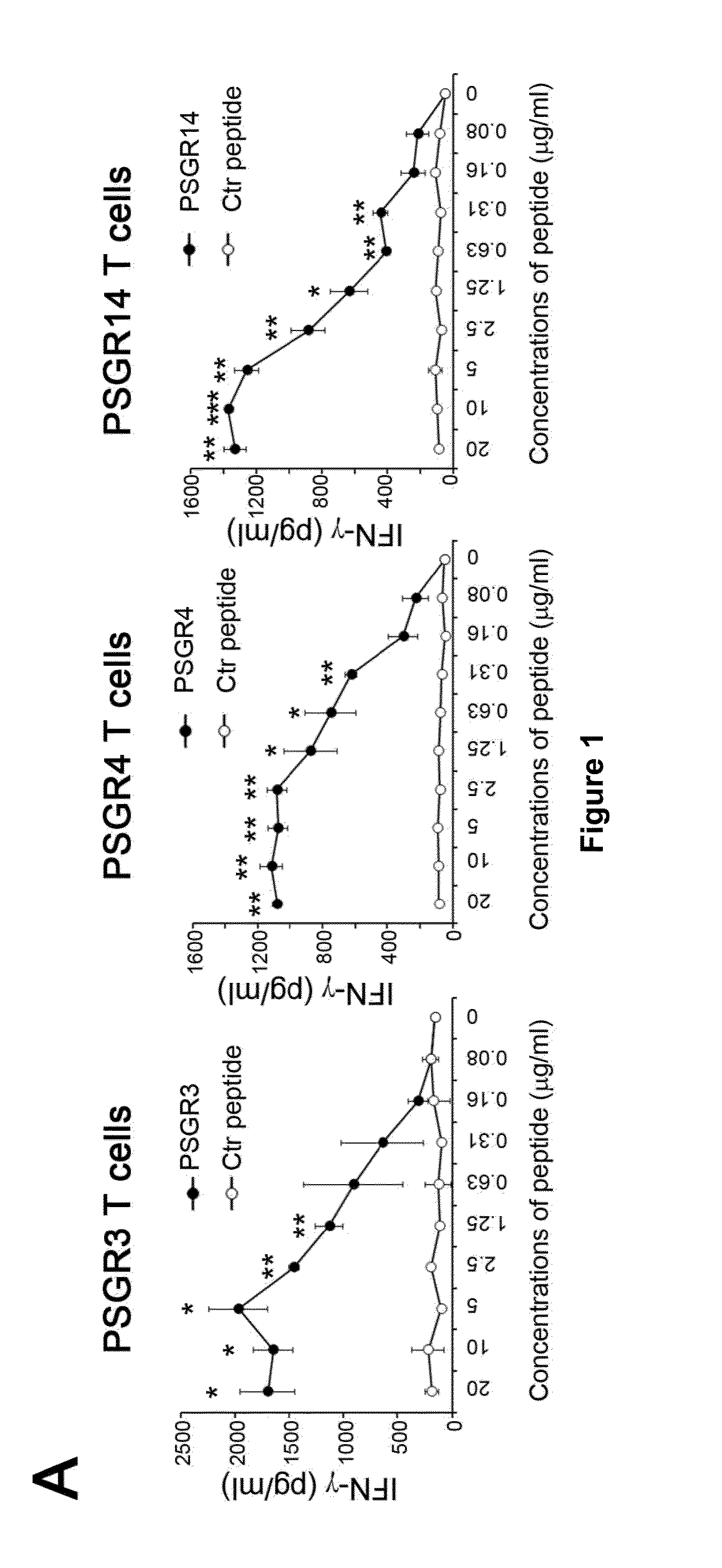
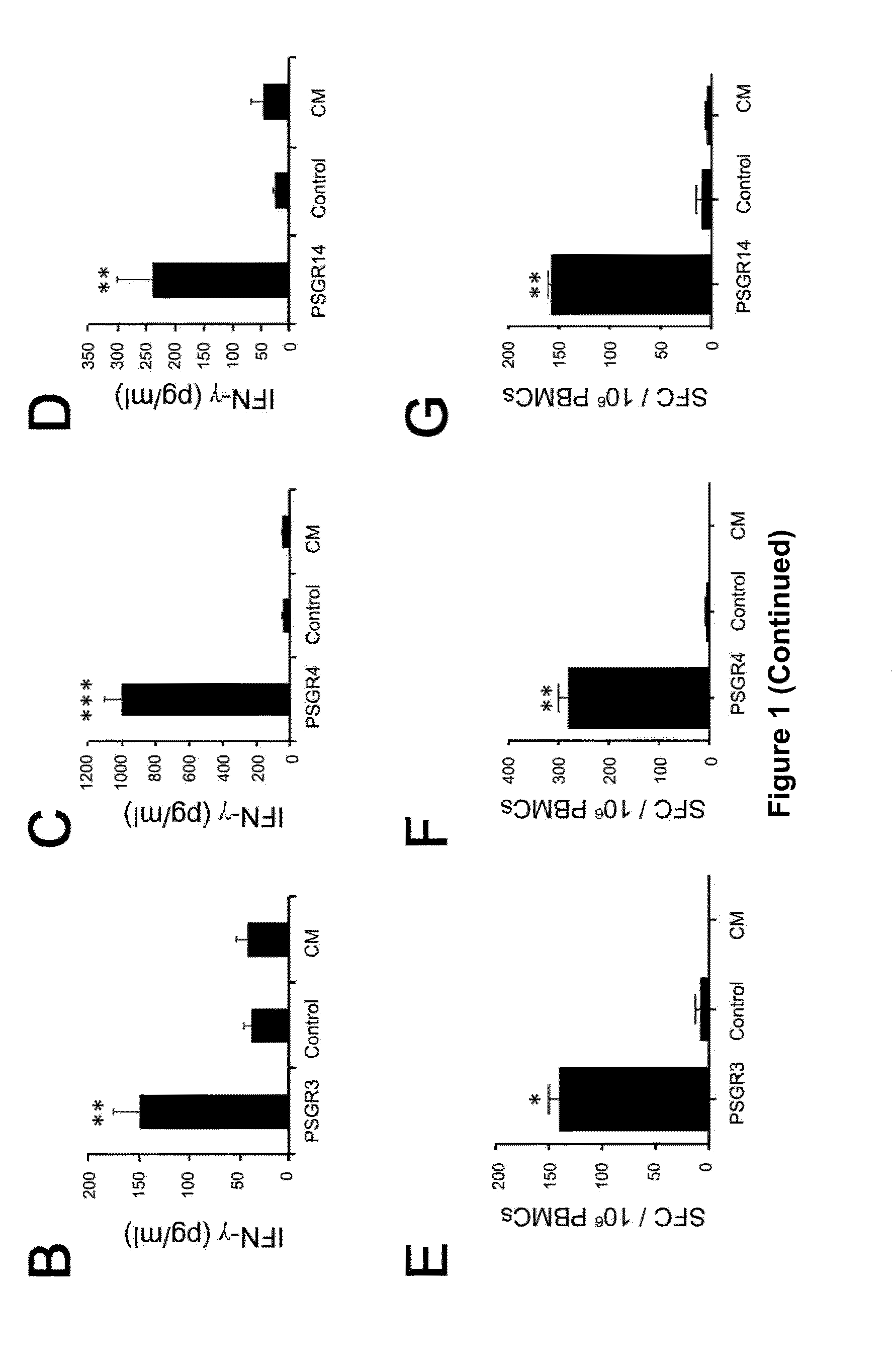
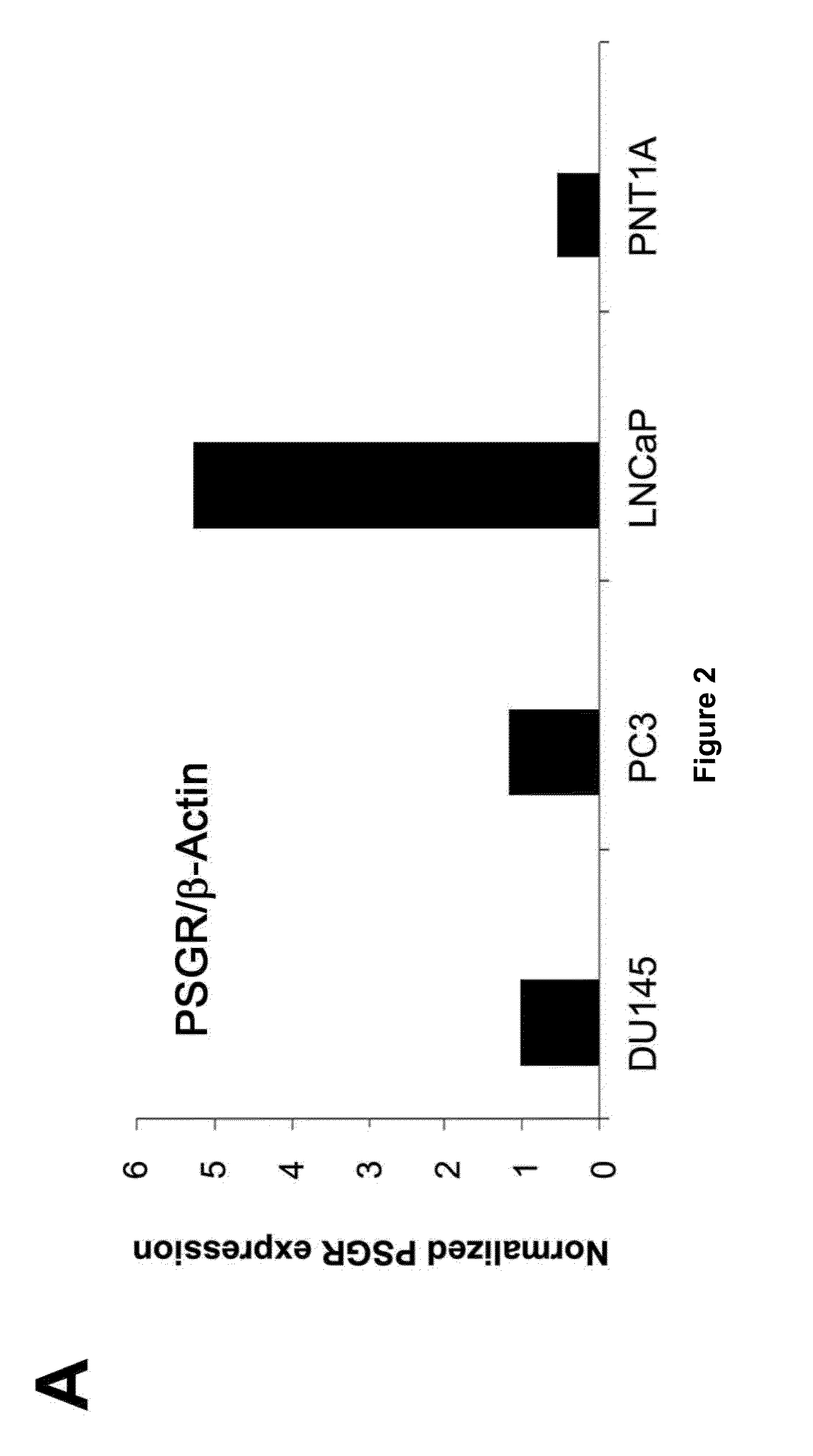
Twenty-one PSGR-derived peptides predicted by an immuno-informatics approach based on the HLA-A2 binding motif were examined for their ability to induce peptide-specific T cell responses in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) obtained from either HLA-A2+ healthy donors or HLA-A2+ prostate cancer patients. The recognition of HLA-A2 positive and PSGR expressing LNCaP cells was also tested. Three peptides, PSGR3, PSGR4 and PSGR14 frequently induced peptide-specific T cell responses in PBMCs from both healthy donors and prostate cancer patients, and are recognized by CD8+ T cells in an HLA-A2 dependent manner. These peptide-specific T cells recognize HLA-A2+ and PSGR+ tumor cells, and killed LNCaP prostate cancer cells in an HLA class I-restricted manner. These PSGR-derived peptides identified are useful as diagnostic markers as well as immune targets for anticancer vaccines.
Owner:SHENZHEN INNOVATION IMMUNOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com