CCN1 compositions and methods
A kind of analog, homologous technology, applied in the field of anti-CCN1 antibody, CCN1 related peptide, its composition, extracellular matrix signal transduction molecule
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
Domain III (TSPI-homology domain) of CCN1 supports α 6 beta 1 dependent cell adhesion
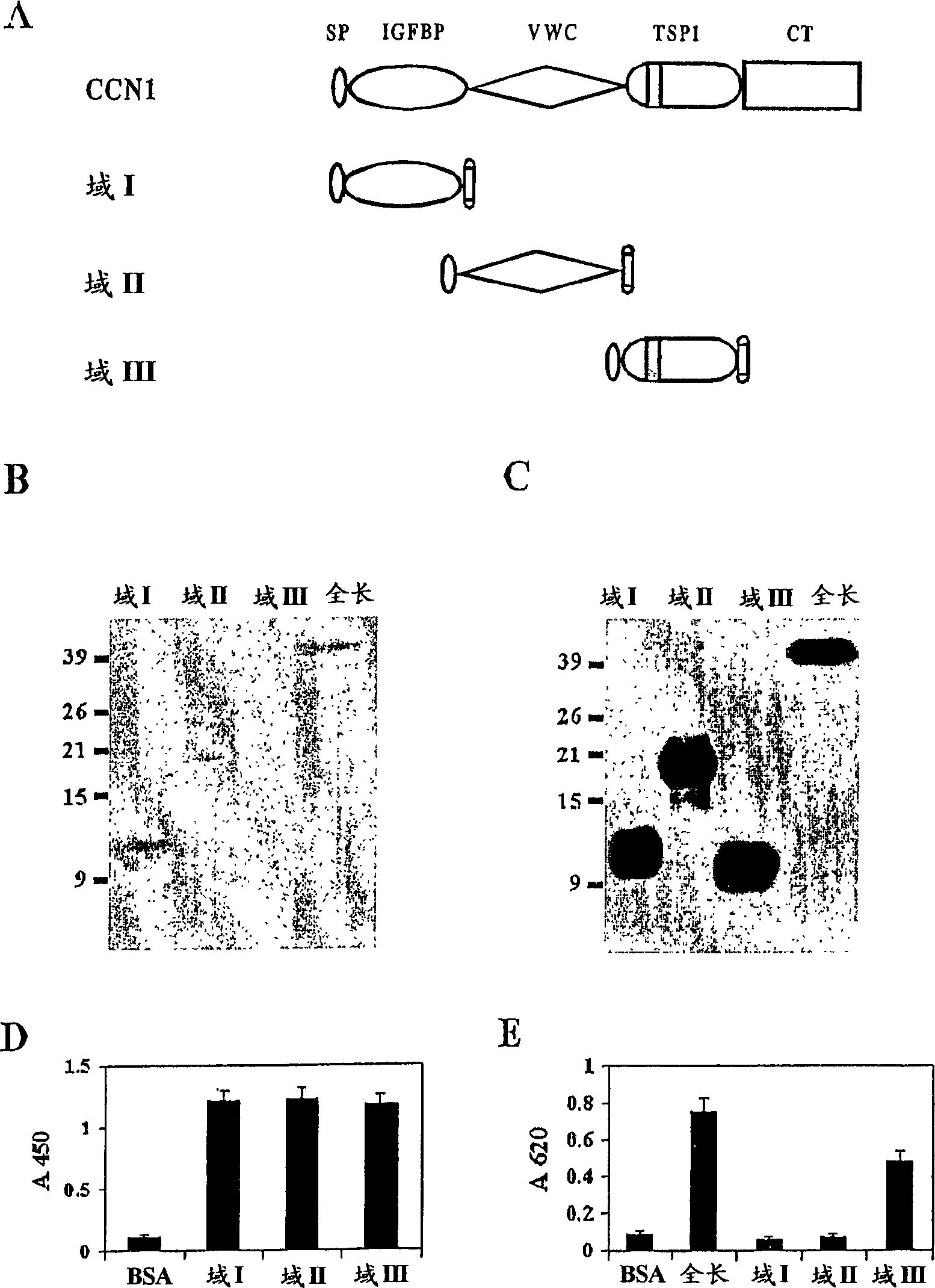
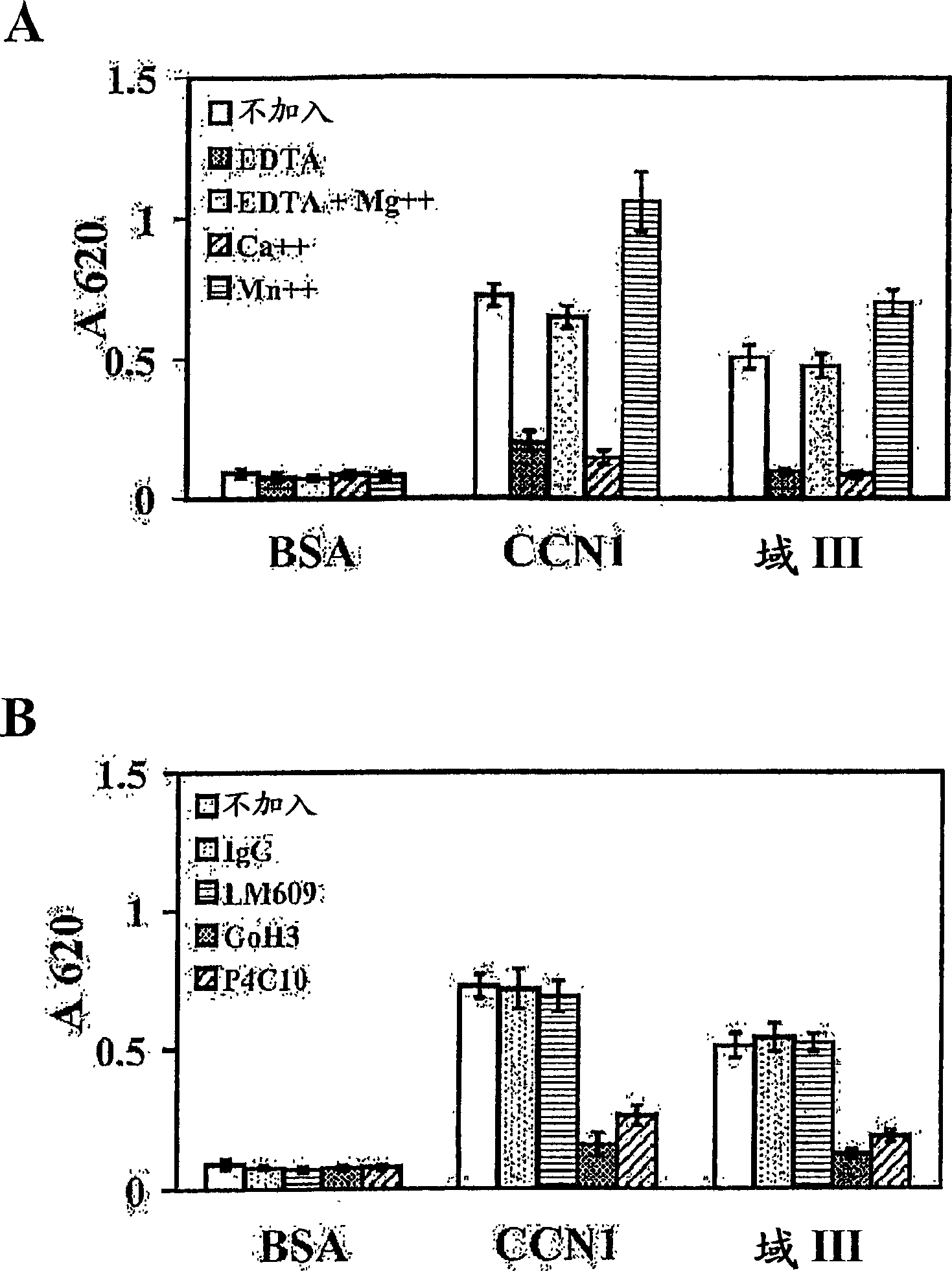
[0064] Previous studies identified primary human dermal fibroblasts through integrin α 6 beta 1 and heparan sulfate proteoglycans adhere to CCN1, inducing the formation of α-containing 6 beta 1 Foci complexes and activation of focal adhesion kinases, paxillin and Rac. See Chen et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 24953-24961; Chen et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 10443-10452. Deletion analysis reveals that a C-terminally truncated CCN1 mutant containing only the first three domains is retained in smooth muscle by integrin α 6 beta 1 Ability to induce chemotaxis, thus positioning integrin binding sites in the first three domains. See Grzeszkiewicz et al (2002) Endocrinology 143, 1441-1450.
[0065] In order to define the relationship with integrin alpha 6 beta 1 interacting CCN1 domains, we expressed each of these three domains in insect cells via a baculovirus vector ( figure 1 A)....
Embodiment 2
T1 sequence in domain III of CCN1 contains integrin α 6 beta 1 binding site
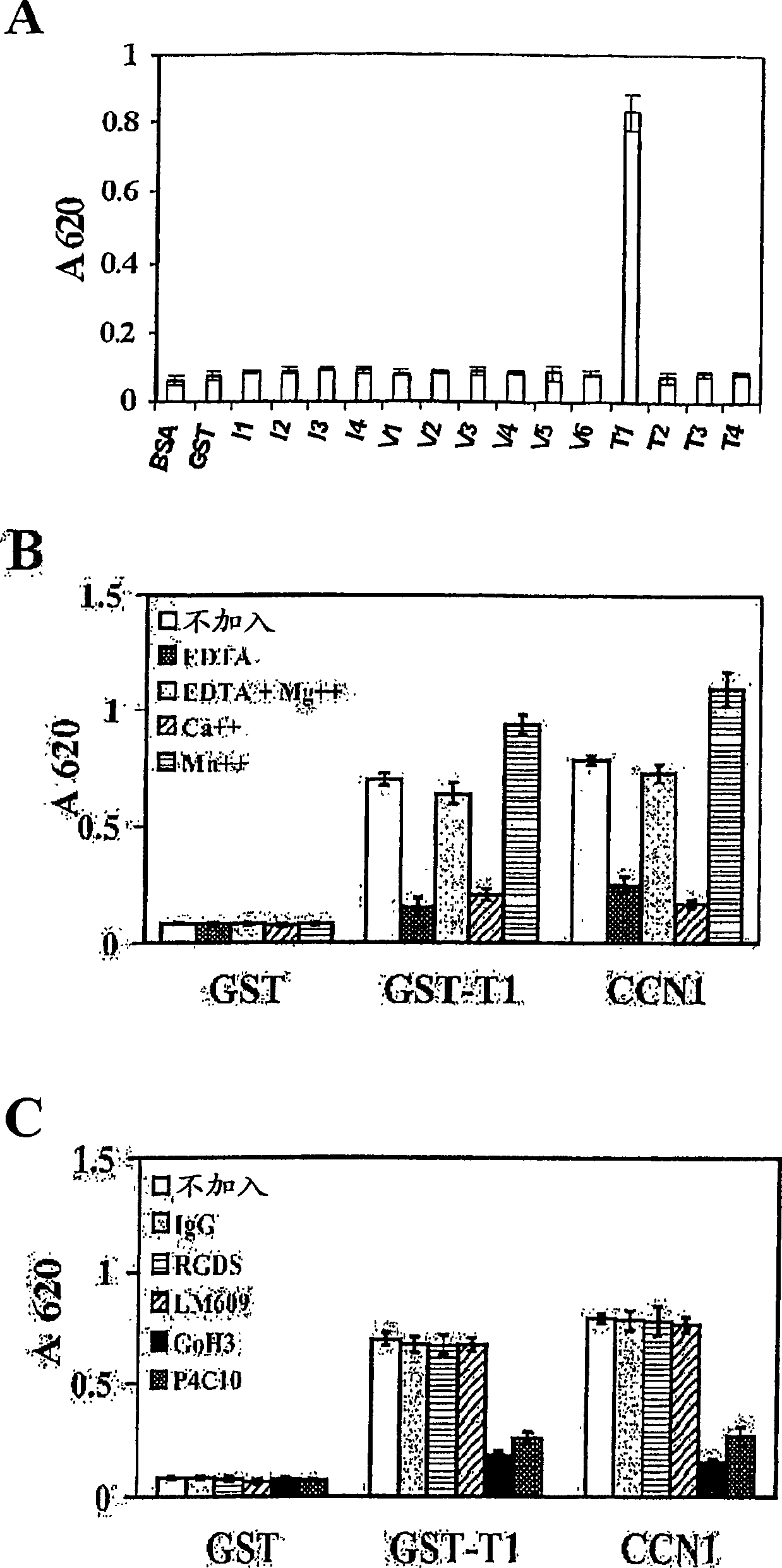
[0071] We used an additional systematic screening strategy to pinpoint integrin α in CCN1 6 beta 1 binding site. A series of overlapping peptides covering the entire first three domains of CCN1 were prepared by expressing the peptides as fusion proteins linked to GST (Table 1). By polymerase chain reaction (PCR), using CCN1 cDNA as a template to amplify various peptides encoding ( image 3 ) coding sequence. The primers used corresponded to the appropriate coding sequences and contained BamHI and EcoRI restriction sites for cloning. For example, the following primers were used to generate the T1 peptide coding sequence:
5'-CGGGATCCGCGGGCCAGAAATGCATCGTT-3' and
5'-CCGGAATTCCGCTCTTGGAGCACTGGGACC-3' The PCR product was purified on a polyacrylamide gel, digested with BamHI and EcoRI, and ligated in pGEX-4T-2 vector (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech). All cloning steps were confirmed by sequence analys...
Embodiment 3
Soluble T1 peptide inhibits alpha 6 beta 1 dependent cell adhesion
[0074] We predict that soluble T1 peptides are capable of blocking cell adhesion to integrins known to bind alpha 6 beta 1 substrate. Such as Figure 5 As shown in A, addition of 0.2 mM T1 to the cell suspension effectively blocked fibroblast adhesion to CCN1 whereas T2, T3 and T4 had no effect. The inhibitory effect of T1 on cell adhesion CCN1 was dose-dependent, and the maximum inhibitory effect was obtained at 100 μM ( Figure 5 C). Other members of the CCN protein family, CCN2 (CTGF) and CCN3 (NOV), have also been shown to act through integrin α 6 beta 1 Supports fibroblast adhesion (see Chen et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 10443-10452; Lin et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. in press), corresponding among these CCN proteins There is a high degree of homology in the T1 sequence of . Figure 5 A shows that T1 also specifically inhibits cell adhesion to CCN2 and CCN3, suggesting a T1 sequence integrin α...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com